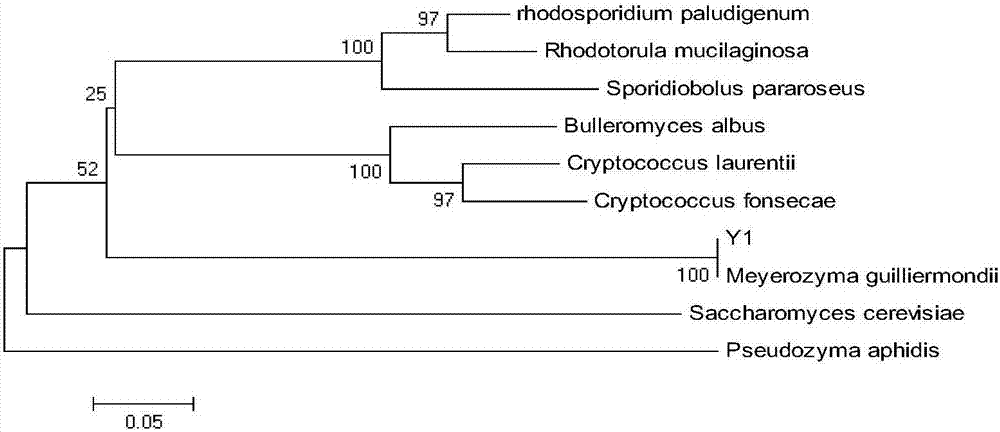
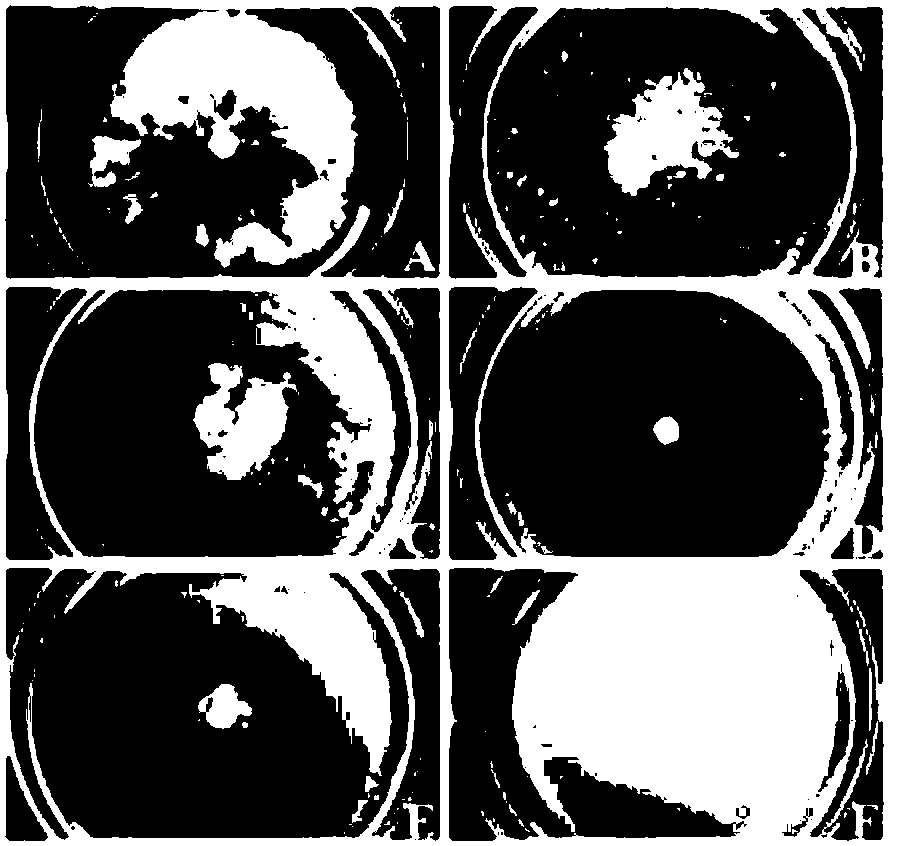
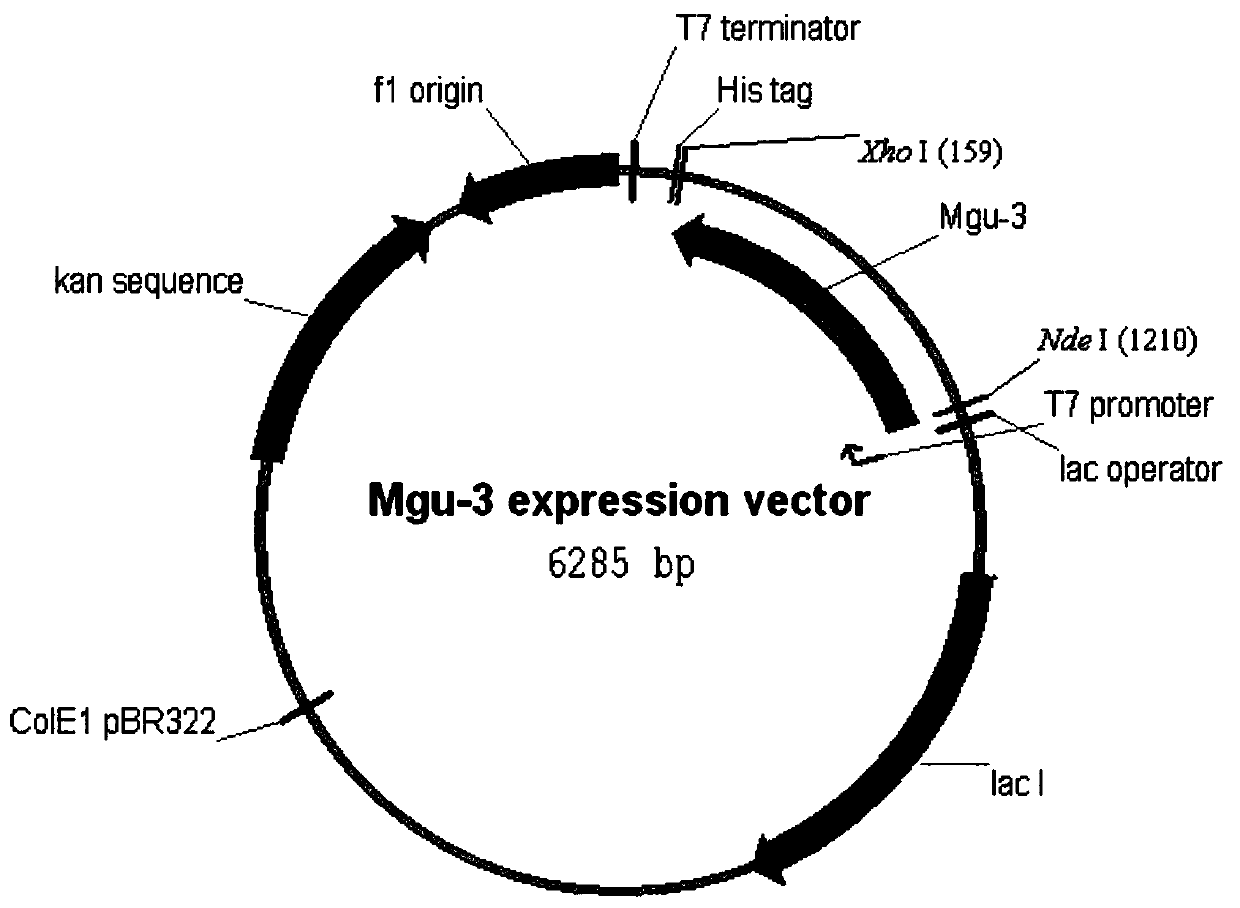
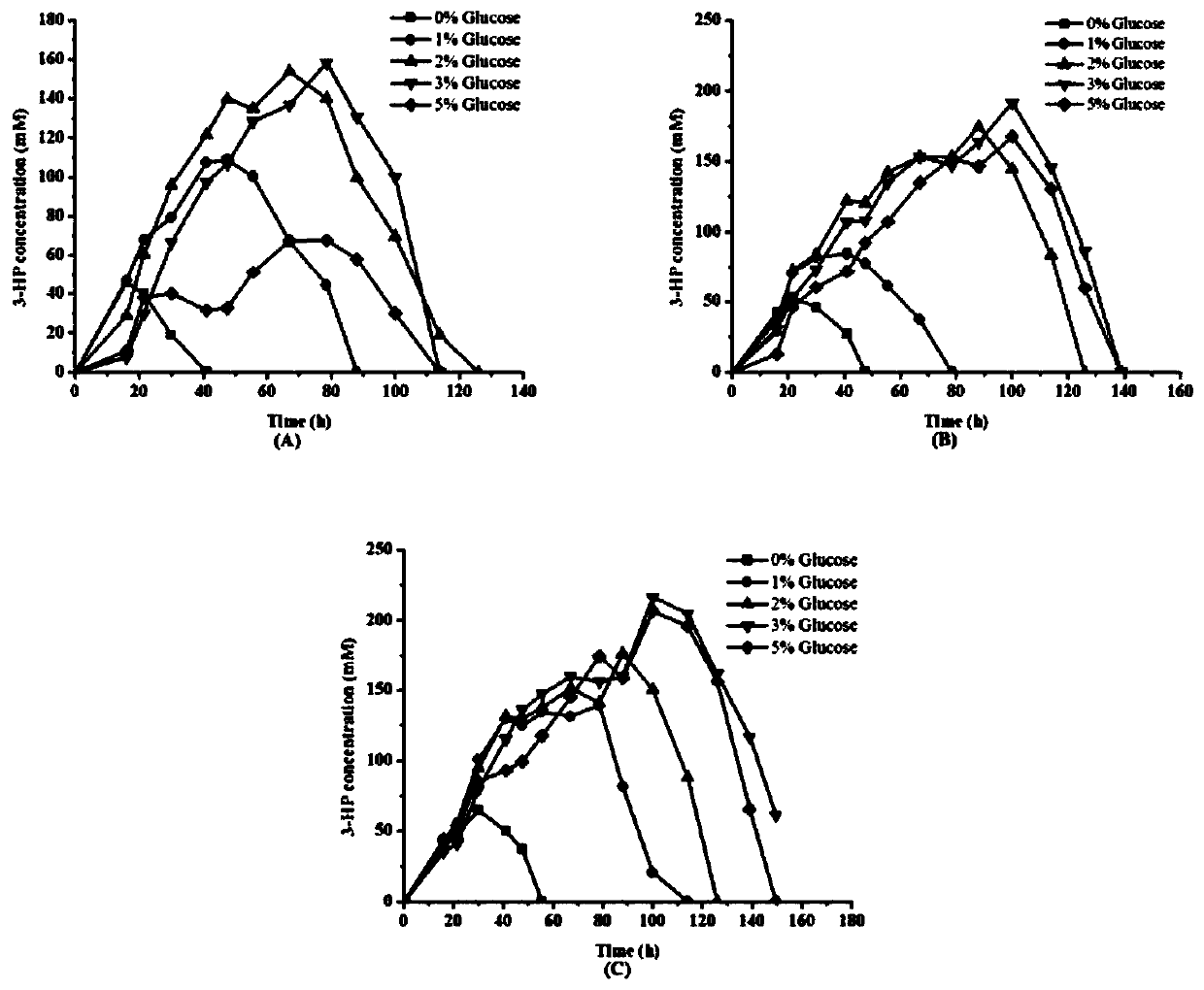
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
40 results about "Meyerozyma guilliermondii" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Meyerozyma guilliermondii for controlling postharvest diseases of pome
ActiveCN107460134ABroad antibacterial spectrumInhibition of PenicilliumFungiFruit and vegetables preservationFungicideSocial benefits
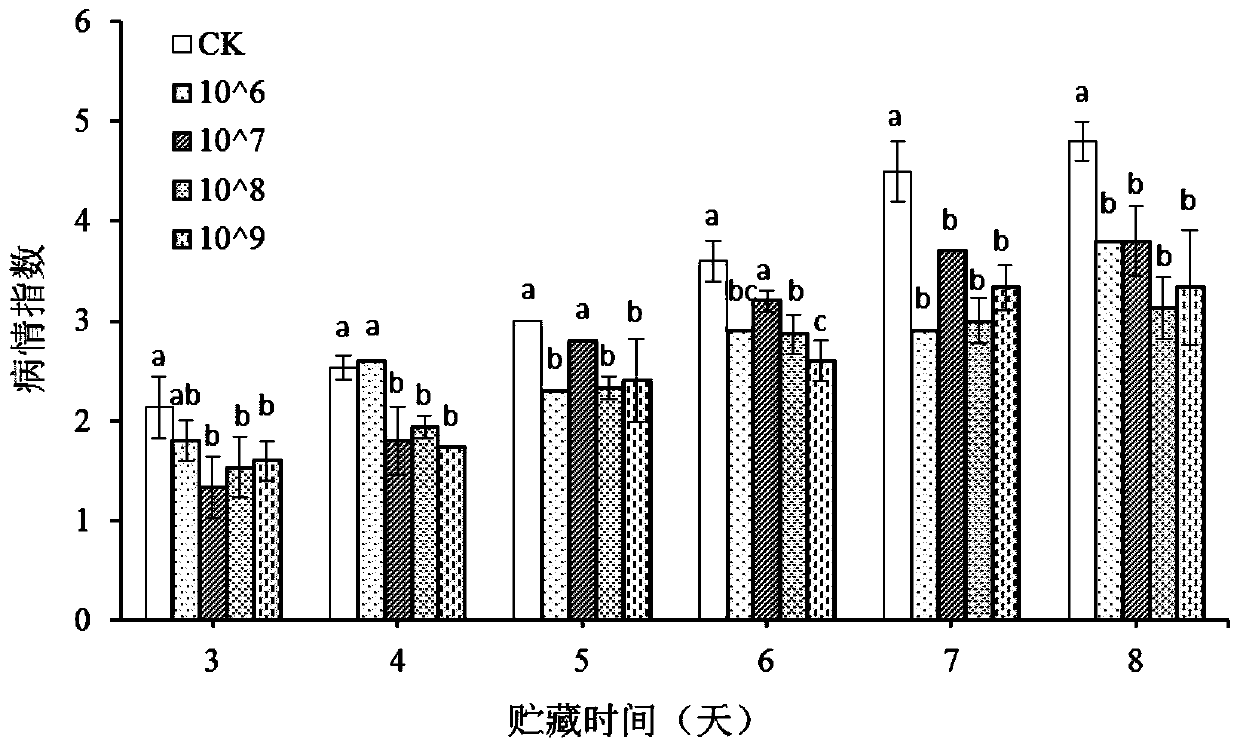
The invention discloses meyerozyma guilliermondii for controlling postharvest diseases of pome, and belongs to the field of biological prevention and treatment for postharvest diseases of fruits. The preservation number of the identified meyerozyma guilliermondii is CCTCC NO:M 2017270. The meyerozyma guilliermondii is activated, cultured and centrifuged to obtain thalli when used, and the thalli are diluted by sterile water to prepare bacterium suspension with the concentration of 1.0*10<8>bacteria / mL. The pome is soaked in the bacterium suspension for approximately 1 min, then is subjected to natural air drying, is placed in plastic baskets and is stored under room-temperature conditions after being sealed by preservative films. The meyerozyma guilliermondii has the advantages that the penicillosis incidence and the natural rotting rate of the pome treated by the meyerozyma guilliermondii are obviously reduced, accordingly, the meyerozyma guilliermondii can be used for preventing and treating the postharvest diseases of the pome instead of chemical fungicides, harm on human due to the chemical fungicides can be prevented, and the meyerozyma guilliermondii has an obvious economic benefit and an obvious social benefit.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Meyerozyma guilliermondii and application thereof
The invention relates to a biocontrol strain Y-1 for preventing and controlling fungal diseases of grapes and application of the biocontrol strain Y-1 in prevention and control of grape diseases and belongs to the technical field of biological prevention and control of plant diseases. The strain is Meyerozyma guilliermondii Y-1 with a preservation number of CCTCC (China Center For Type Culture Collection) NO:M2015814. The Meyerozyma guilliermondii Y-1 is used for preparing a biocontrol preparation for preventing and controlling the grape diseases, and the biocontrol preparation has an obviousprevention and control effect on multiple pathogenic fungi. The Meyerozyma guilliermondii Y-1, provided by the invention, as an active ingredient of the biocontrol preparation, has the characteristicsof stable prevention and control effect, long persistence and wide disease control spectrum as well as has the properties of environment friendliness, safety and low possibility of generating pesticide resistance; the strain has high propagation speed, is cultured under simple culture conditions and is easy for storage and industrial production; defense related enzyme activity in plant bodies canbe improved, and a good development and application prospect is realized.
Owner:QINGDAO AGRI UNIV
High-sugar-tolerant Meyerozyma guilliermondii strain and applications thereof
ActiveCN107354102AImprove nutritional and health benefitsGreat tasteFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyAlcohol
The present invention discloses a high-sugar-tolerant Meyerozyma guilliermondii strain, which is named Meyerozyma guilliermondii ZJUQH, and has the preservation number of CCTCC NO:M 2016755. According to the present invention, the high-sugar-tolerant Meyerozyma guilliermondii strain is separated and screened from the interior of the wild kiwifruit peel, can resist high sugar and a certain concentration of alcohol, can be used for fermenting fruits in a high sugar environment to produce fruit beverages, can reduce the high-temperature sterilization treatment process during a production process, can less damage a variety of heat-sensitive active substances, can greatly improve the nutritional health effects of fruit beverages, can substantially improve the taste of products, and can reduce the production energy consumption cost.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
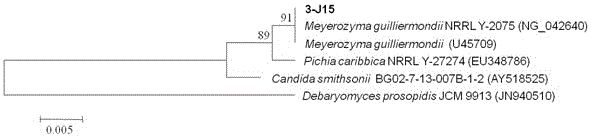
Meyerozyma guilliermondii 3-J15 and application thereof
ActiveCN106085889APromote growthAdd flavorFungiMicroorganism based processesMeyerozyma guilliermondiiSalinity
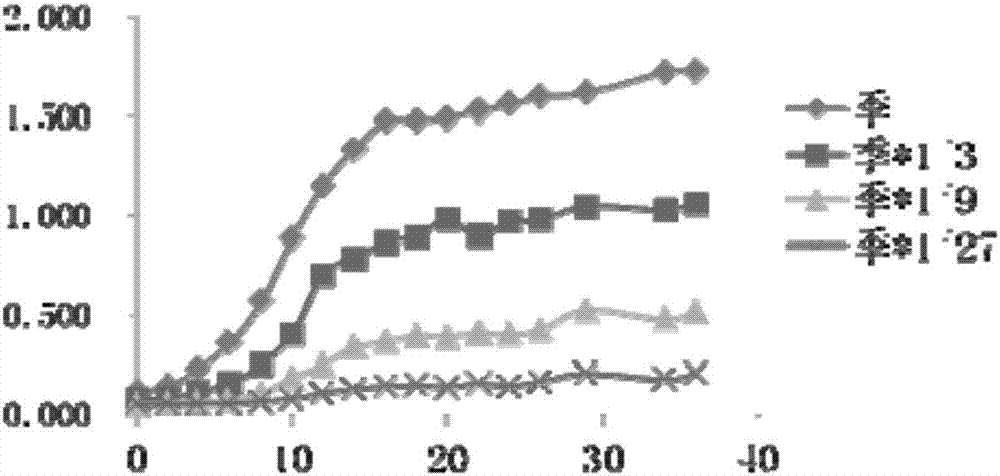
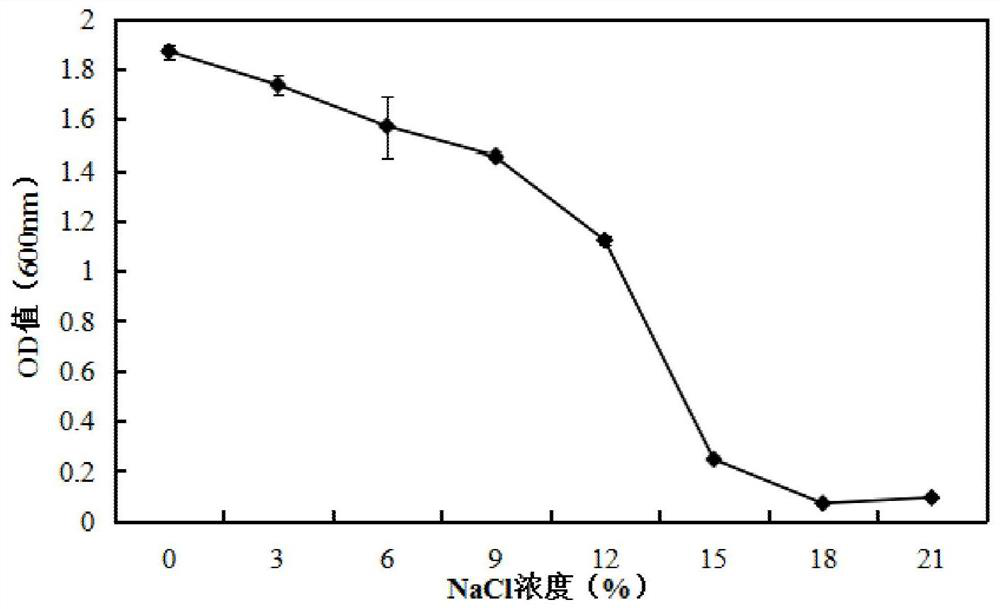
The invention provides a Meyerozyma guilliermondii 3-J15. The Meyerozyma guilliermondii 3-J15 realizes high yield of volatile aroma substances 2-phenylethanol and 3-methyl-1-butanol, can at least tolerate the salinity of 15%, and not only has good soy sauce aroma enhancement fermentation capacity, good adaptive capacity to environment, and great potential of application to practical soy sauce production, but also can be taken as a fermentation strain for fermentation preparation of 3-methyl-1-butanol and 2-phenylethanol in a fluid medium, thereby providing a new effective means for preparation of 3-methyl-1-butanol and 2-phenylethanol.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
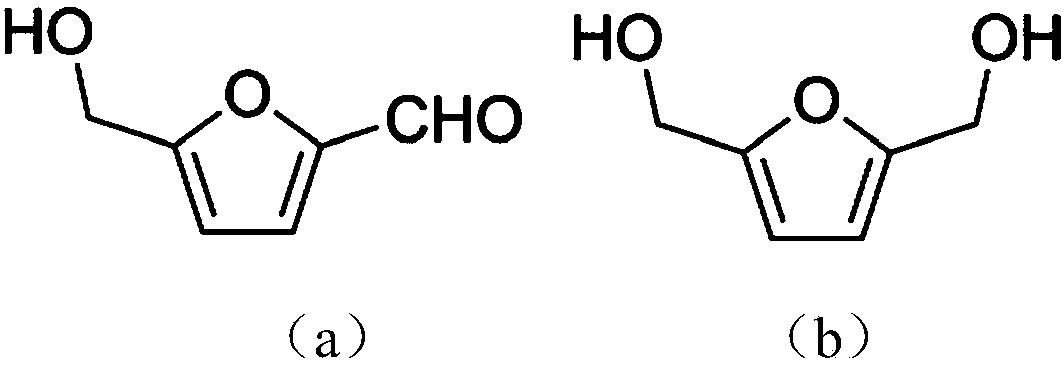
Selective synthesis method for 2, 5-dihydroxymethylfuran
InactiveCN108611380AAchieve reuseOvercome the disadvantage of unfriendlinessFungiMicroorganism based processesHigh concentrationSynthesis methods
The invention discloses a selective synthesis method for 2, 5-dihydroxymethylfuran. The method includes the steps of: (1) conducting domestication, activation and immobilization on meyerozyma guilliermondii SC1103 to obtain immobilized cells; (2) adding the immobilized cells into a buffer solution containing 50-350mM 5-hydroxymethylfurfural and cosubstrates, and carrying out reaction at 10-40DEG Cunder a stirring condition to obtain 2, 5-dihydroxymethylfuran. Specifically, the molar concentration of reducing sugar in the cosubstrates is 0.3-1.0 times that of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural. The immobilized biocatalyst provided by the invention has high tolerance to the substrate, can achieve efficient and high selective catalysis of high concentration substrate reduction to synthesize a target product, achieve a high product space time yield, and is beneficial to simplifying the subsequent separation and purification process of the target product.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Biocontrol bacterium Meyerozyma guilliermondii Y-1 for controlling apple ring rot and biocontrol preparation thereof
The invention relates to a biocontrol strain Y-1 for controlling apple ring rot and application thereof to control of the apple ring rot, and belongs to the technical field of plant disease and pest biocontrol. The strain is Meyerozyma guilliermondii Y-1, and the culture collection number is CCTCC NO: M2015814. The Meyerozyma guilliermondii Y-1 is used for preparing a biocontrol preparation for controlling the apple ring rot, and the biocontrol preparation has a significant effect of controlling a variety of pathogenic fungi. An active component, namely the Meyerozyma guilliermondii Y-1, of the biocontrol preparation provided by the invention has the characteristics of a stable control effect, a long persistent effect, a wide disease control spectrum, environment friendliness and the like.The biocontrol strain Y-1 breeding speed is high, a culture condition is simple, collection and industrial production are easy, and development and application prospects are good.
Owner:QINGDAO AGRI UNIV
Method for preparing bioethanol by taking sodium alginate or algae as active ingredients
InactiveCN103614448AIncrease profitSave foodBiofuelsMicroorganism based processesMeyerozyma guilliermondiiBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENT
The invention discloses a method for preparing bioethanol by taking sodium alginate or algae as active ingredients. Fermentation culture medium taking sodium alginate as a carbon source can be adopted, or the fermentation culture medium taking algae treatment liquor as a carbon source can be adopted, the algae treatment liquor is obtained by adopting the following method: mixing algae powder with water, and sterilizing; mixing algae powder with citric acid-sodium citrate buffer solution, regulating the pH value to be neutral with NaOH solution, adding cellulase which is 10% of the mass of algae powder, performing enzymolysis so that the cellulase is inactivated; mixing algae powder with aqueous sulfuric acid solution, and hydrolyzing. The method for preparing bioethanol comprises the steps of: inoculating 5% Meyerozyma guilliermondii strain seed solution into a sterilized fermentation culture medium, multiplying, then performing airtight anaerobic fermentation for 5-7 days at 28-32DEG C; distilling the fermented liquid to obtain bioethanol. According to the method, the bioethanol can be produced by utilizing marine algae resources; therefore, the commercial crops of grains and the like can be saved, cultivated land cannot be occupied and fresh water resources cannot be consumed; remaining solids after fermentation can serve as organic fertilizers, and the algae utilization rate can be improved; the method is simple and easy, and absolutely capable of carrying out industrial production.
Owner:YANSHAN UNIV
Ketoreductase mutant with enhanced enzyme activity and applications thereof
ActiveCN111454921AIncrease the number of cyclesExpand the range of downstream applicationsBacteriaMicroorganism based processesWild typeMeyerozyma guilliermondii
The invention discloses a ketoreductase mutant with enhanced enzyme activity and applications thereof, and belongs to the technical field of biology. The mutant is derived from the wild-type ketoreductase of Meyerozyma guilliermondii and can convert ethyl 4-chloroacetoacetate to generate ethyl (R)-4-chloro-3-hydroxybutyrate; and compared with wild-type sequences, the mutant has higher alcohol dehydrogenase activity and is more than 90% similar to SEQ ID NO. 8. The mutant has obvious high-specific enzyme activity which is enhanced 2-10 times than the wild-type ketoreductase; the mutant is mildin reaction condition and low in equipment requirement, and high temperature or cooling is not needed during production, so that low energy consumption can be realized; as enzyme catalysis has efficient and exclusive selection, so that convenient purification can be achieved; and in addition, the vast majority of solvents in reaction is water, and the solvents such as butyl acetate are not neededto be added to form a two-phase reaction system, so that the mutant is low in discharging of waste gas, waste water and industrial residues, green and environment-friendly in preparation process.
Owner:NANJING LANGEN BIOLOGICAL SCI & TECH
Meyerozyma guilliermondii and application thereof in biological deodorization
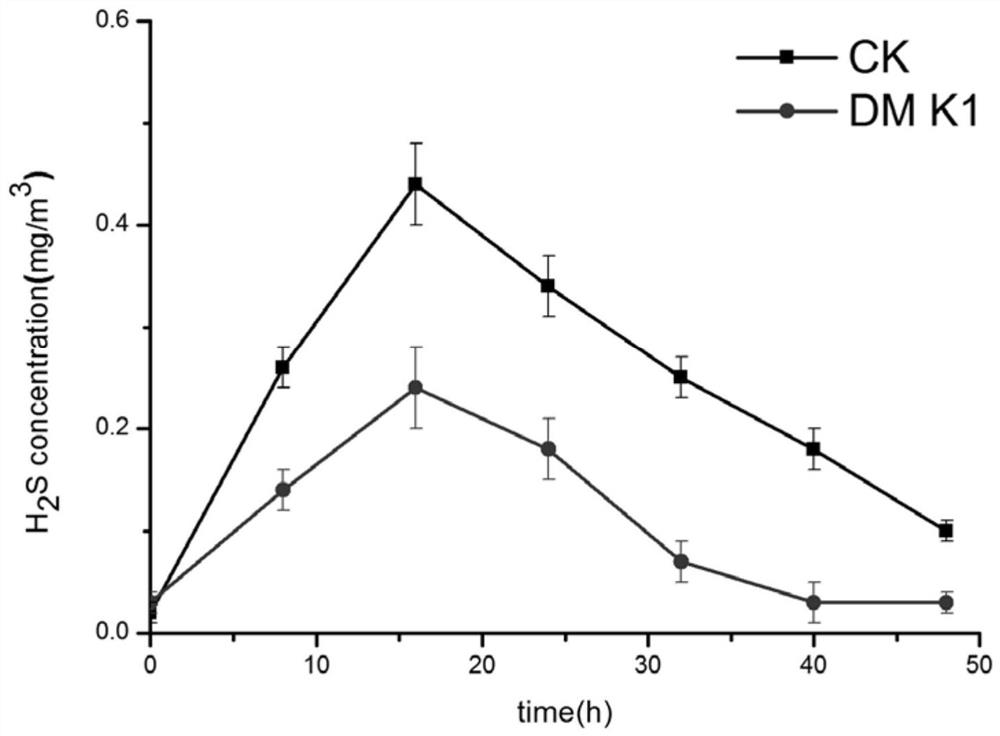
ActiveCN112159768AImprove deodorization efficiencyNo biohazardFungiDispersed particle separationMicrobial agentEnvironmental engineering
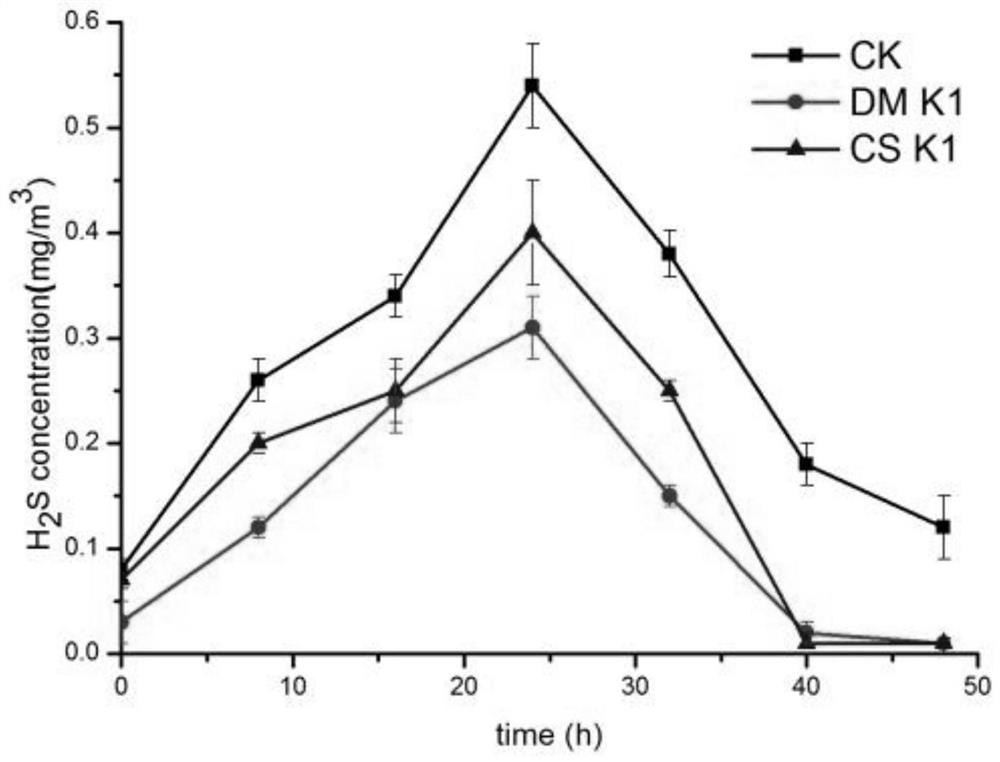
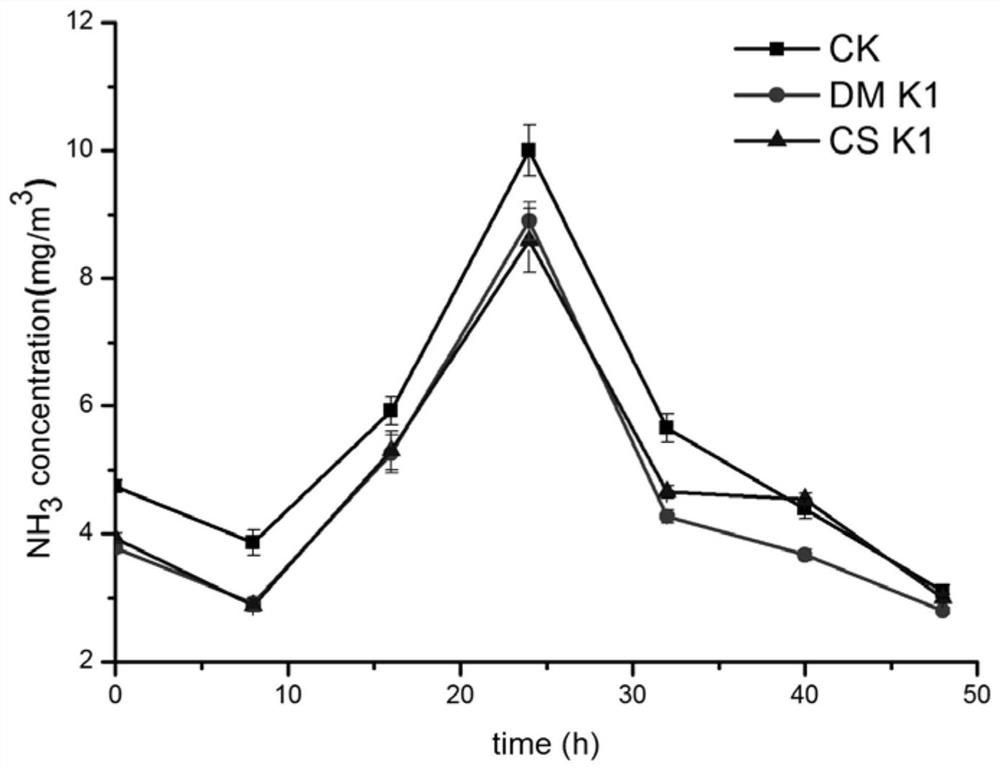
The invention discloses Meyerozyma guilliermondii K1 and an application thereof in biological deodorization, and belongs to the technical field of biology. The preservation number of the Meyerozyma guilliermondii K1 is CCTCC NO: M 2020191. The strain is high in deodorization efficiency and free of biological danger, and a biological deodorization microbial agent prepared from the Meyerozyma guilliermondii K1 has obvious degradation effects on odors generated by restaurant and kitchen waste, and has relatively good application potential.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Meyerozyma guilliermondii and method for treating high-salinity wastewater
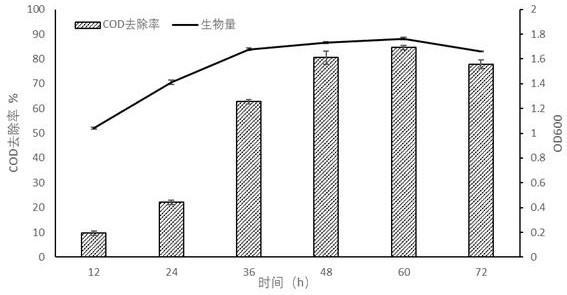
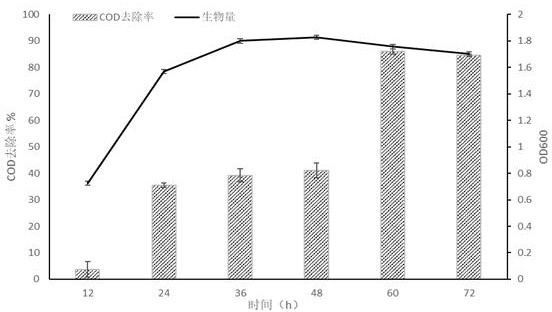
The invention discloses Meyerozyma guilliermondii, which is preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC) and has a preservation number of CGMCC No.18675. The methodfor treating high-salinity wastewater by using the meyerozyma guilliermondii comprises the following steps: gradually carrying out enlarged culture on a metschnikowia bicuspidate seed solution; and adding the bacterial liquid with the volume multiplied by enlarged culture into the high-salinity wastewater, and performing culturing. The method is simple to operate and low in cost, and has a COD removal rate on kelp processing produced high-salinity wastewater being 84.61 percent and a COD removal rate on undaria pinnatifida processing produced high-salinity wastewater being 75.50 percent to reach the emission standard of city pipe network.
Owner:DALIAN OCEAN UNIV +1
Meyerozyma guilliermondii suspension for controlling postharvest diseases of cherry tomato fruits
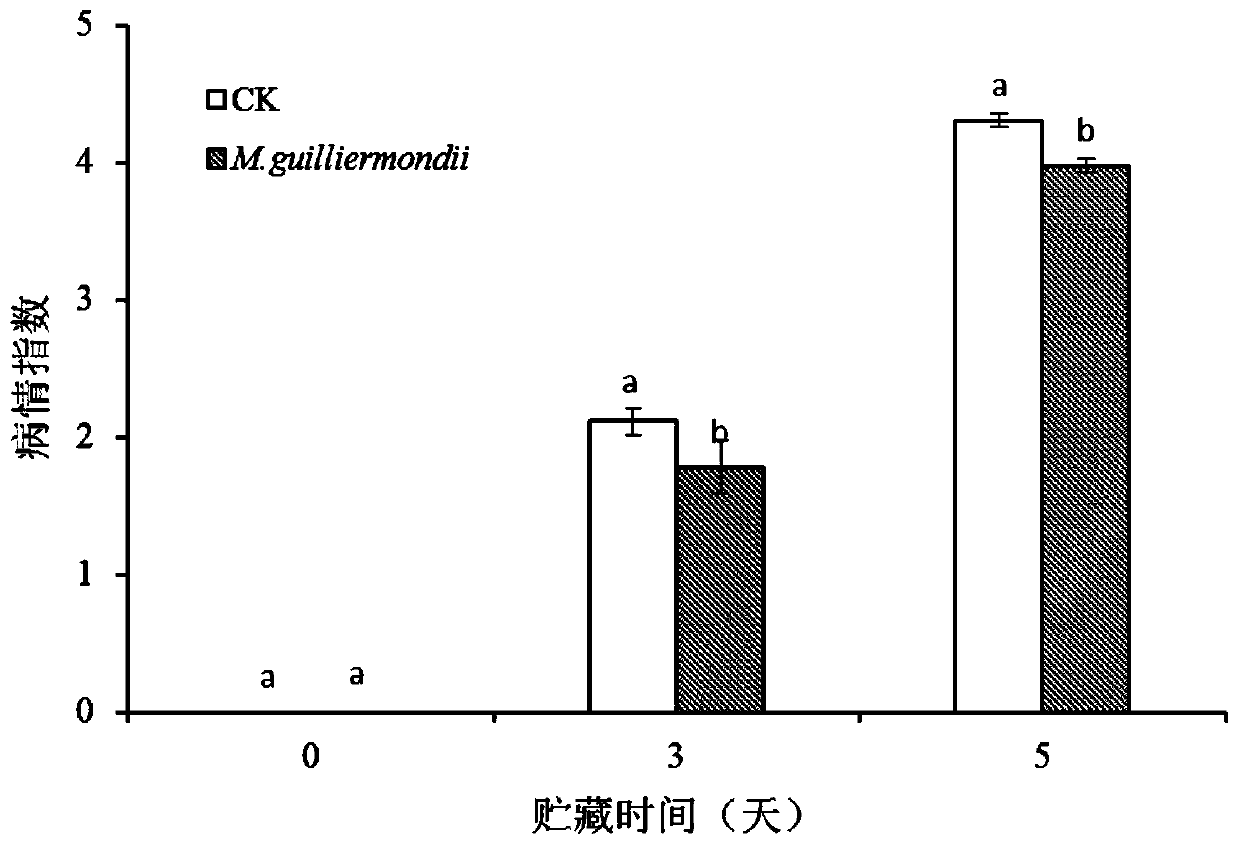
ActiveCN110050831AAbundant resourcesEasy to trainFungiFruit and vegetables preservationDistilled waterMicrobiology
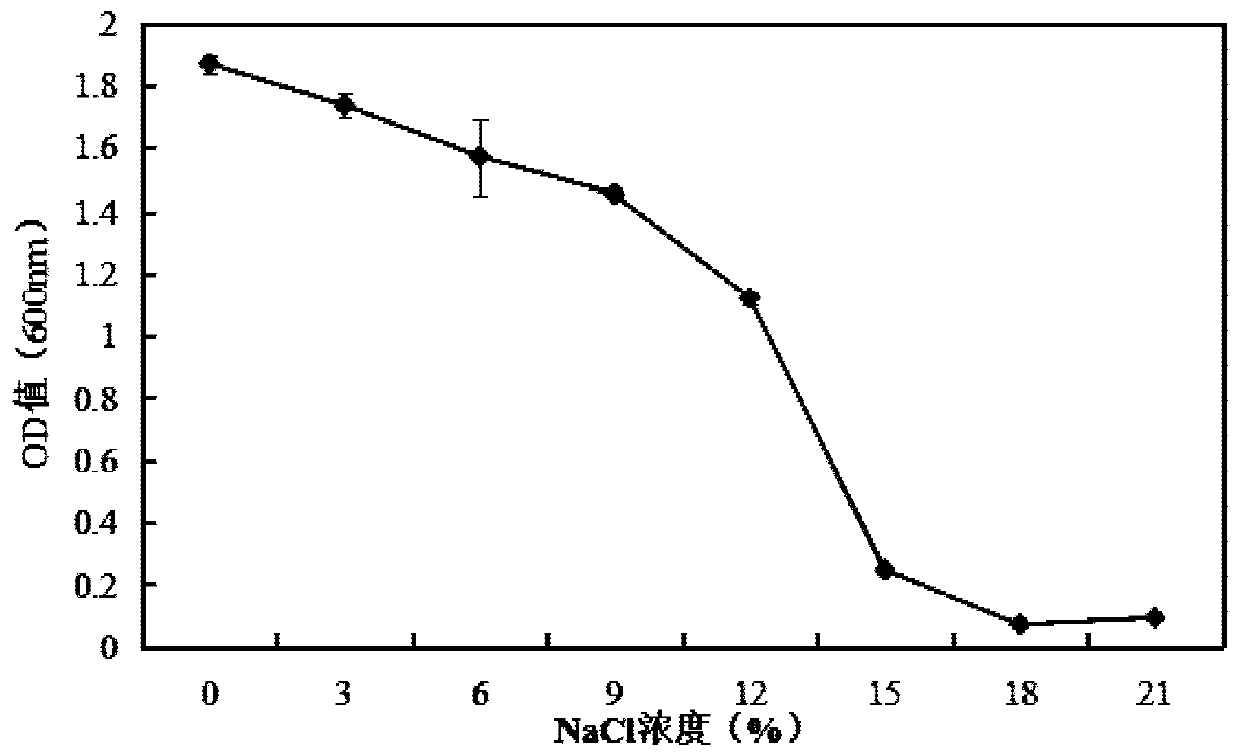
The invention discloses J-SS-CX which is meyerozyma guilliermondii with under the preservation number CGMCC NO.17240. The invention also discloses a meyerozyma guilliermondii suspension for controlling postharvest diseases of cherry tomato fruits. The preparation method of the meyerozyma guilliermondii suspension comprises the steps of inoculating meyerozyma guilliermondii J-SS-CX with an activated NYDA solid culture medium into an NYDB culture medium for one generation, then inoculating it into a NYDB culture medium containing 12% NaCl for culture, washing the obtained thalli with sterile distilled water and diluting it. The yeast preparation can effectively control postharvest diseases of fruits on the premise that a chemical bactericide is not used, and is convenient to operate, good in effect, low in cost, safe and environmentally friendly.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for preparing bioethanol by taking sodium alginate or algae as active ingredients
InactiveCN103614448BIncrease profitSave foodBiofuelsMicroorganism based processesMeyerozyma guilliermondiiBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENT
The invention discloses a method for preparing bioethanol by taking sodium alginate or algae as active ingredients. Fermentation culture medium taking sodium alginate as a carbon source can be adopted, or the fermentation culture medium taking algae treatment liquor as a carbon source can be adopted, the algae treatment liquor is obtained by adopting the following method: mixing algae powder with water, and sterilizing; mixing algae powder with citric acid-sodium citrate buffer solution, regulating the pH value to be neutral with NaOH solution, adding cellulase which is 10% of the mass of algae powder, performing enzymolysis so that the cellulase is inactivated; mixing algae powder with aqueous sulfuric acid solution, and hydrolyzing. The method for preparing bioethanol comprises the steps of: inoculating 5% Meyerozyma guilliermondii strain seed solution into a sterilized fermentation culture medium, multiplying, then performing airtight anaerobic fermentation for 5-7 days at 28-32DEG C; distilling the fermented liquid to obtain bioethanol. According to the method, the bioethanol can be produced by utilizing marine algae resources; therefore, the commercial crops of grains and the like can be saved, cultivated land cannot be occupied and fresh water resources cannot be consumed; remaining solids after fermentation can serve as organic fertilizers, and the algae utilization rate can be improved; the method is simple and easy, and absolutely capable of carrying out industrial production.
Owner:YANSHAN UNIV
Yeast strain for controlling pear patulin and application of yeast
ActiveCN111705005AGood control effectEfficient degradationFungiYeast food ingredientsBiotechnologyMeyerozyma guilliermondii
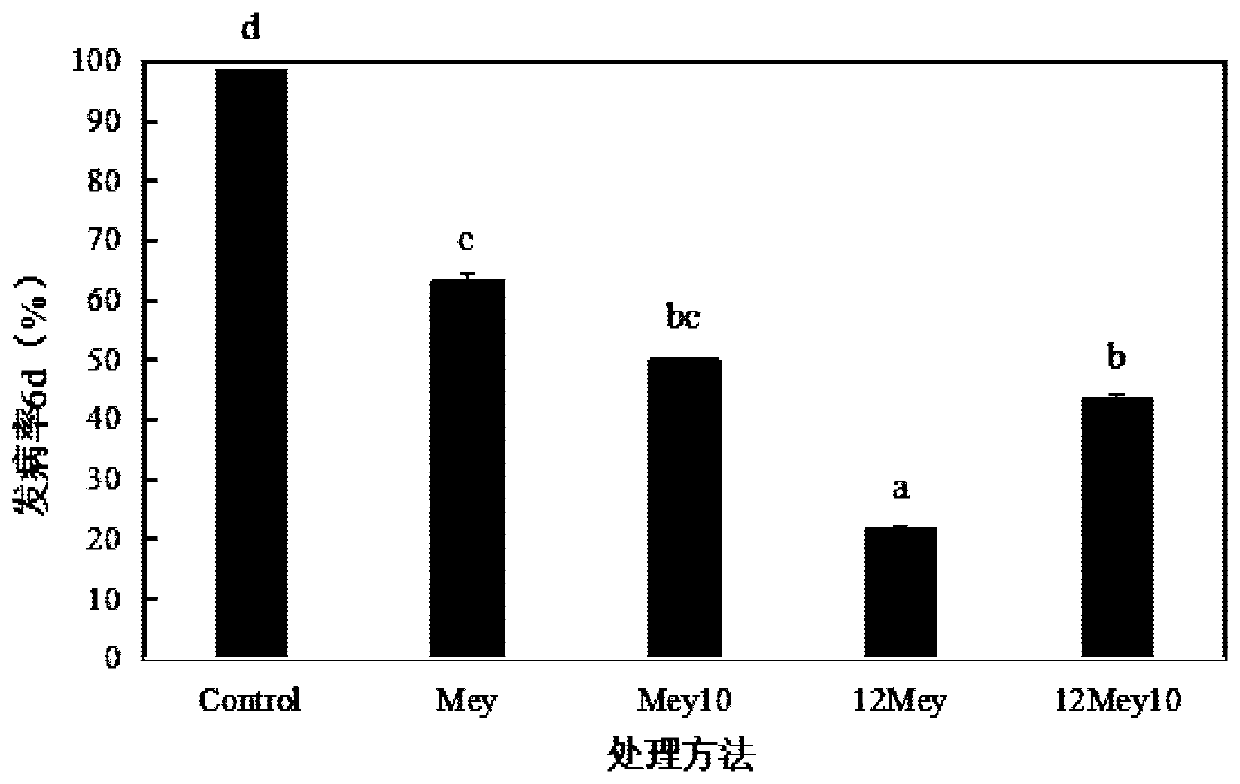
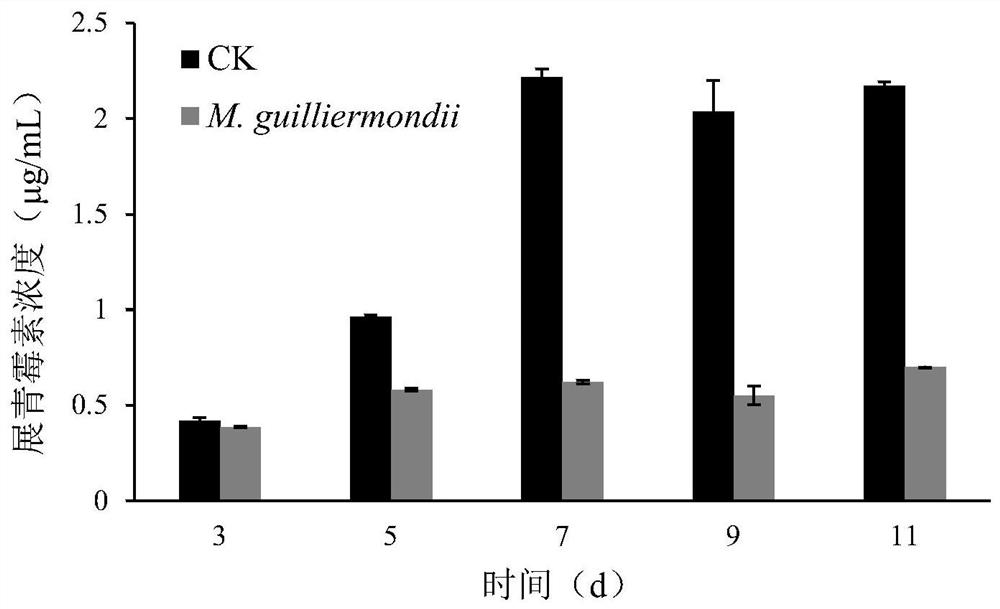
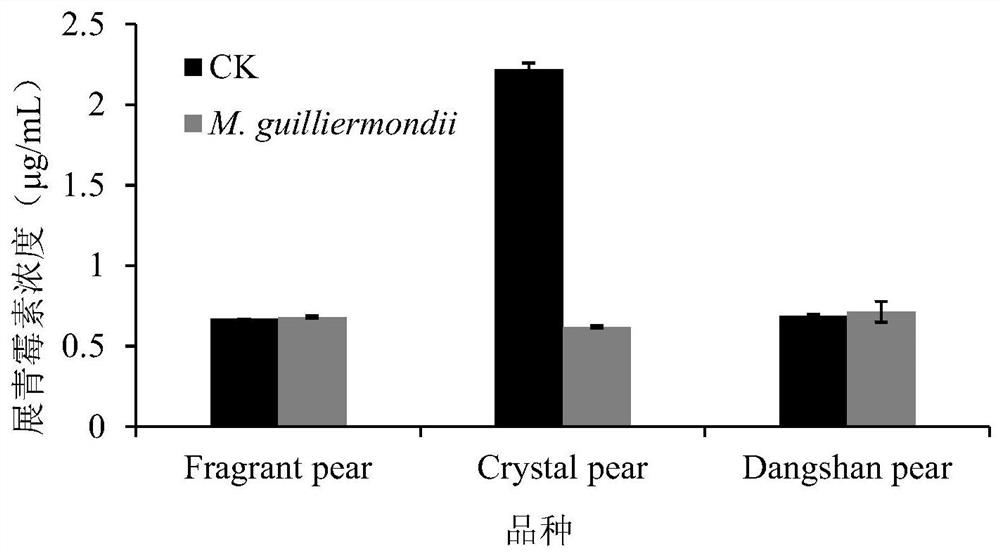
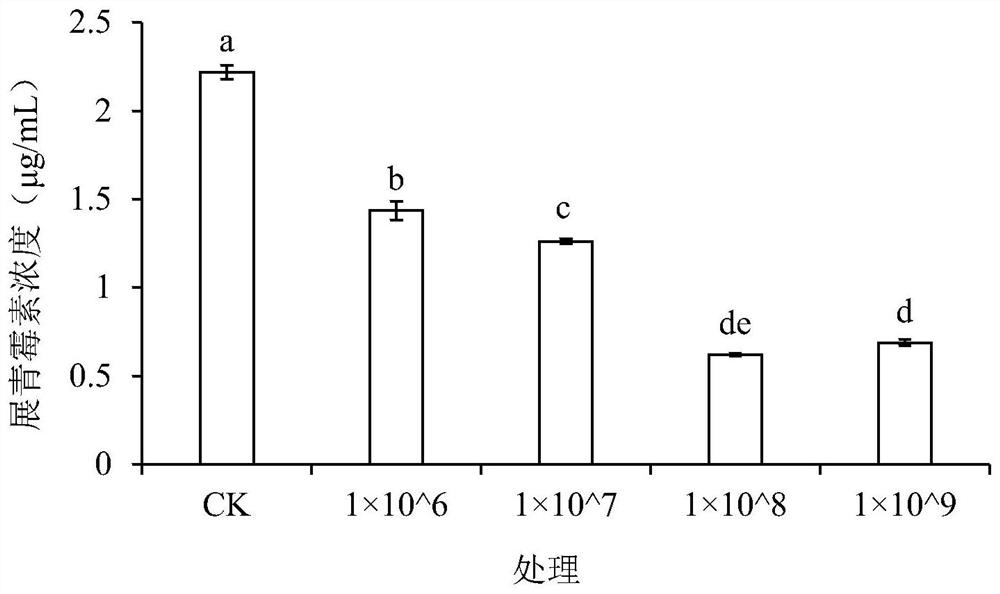
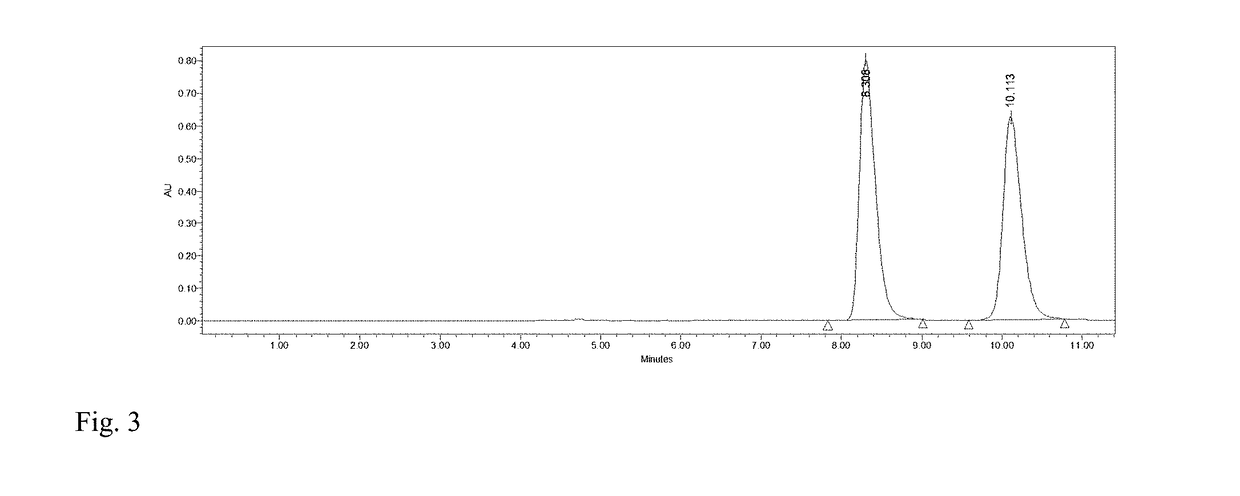
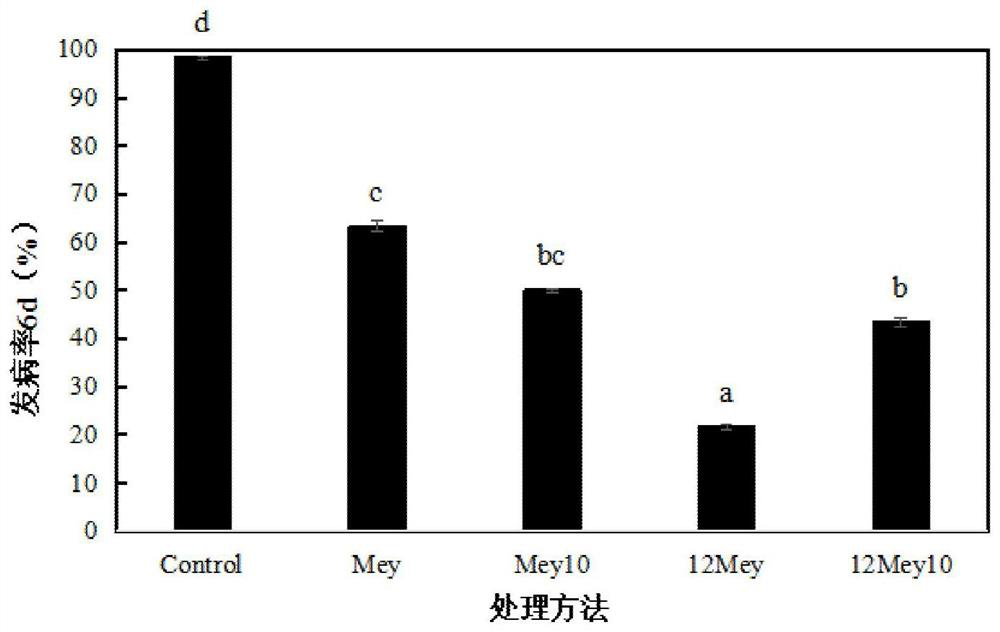
The invention belongs to the field of biotechnology, and relates to a yeast strain for controlling patulin and application of the yeast strain. The yeast is meyerozyma guilliermondii Y1, and the strain collection number is CCTCCC NO:M 2017270, and the yeast is used to degrade patulin or to control pear patulin and has a good control effect on the patulin in the whole crystal pear fruits or the wounds of the fruits; when the pears rot naturally, the concentration of patulin in a control group is 4.41 [mu]g / mL, and the content of the patulin of an experimental group using the meyerozyma guilliermondii Y1 is only 1.24 [mu]g / mL; the patulin content in the fruit wounds is 72% lower than that in the control group; at the same time, the yeast can directly degrade the patulin, when the concentration is 10 [mu]g / mL and the initial yeast concentration is 1*10<8> cells / mL, the patulin can be completely degraded, and the yeast degradation rate of the patulin by the yeast is the highest within 24-36h.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
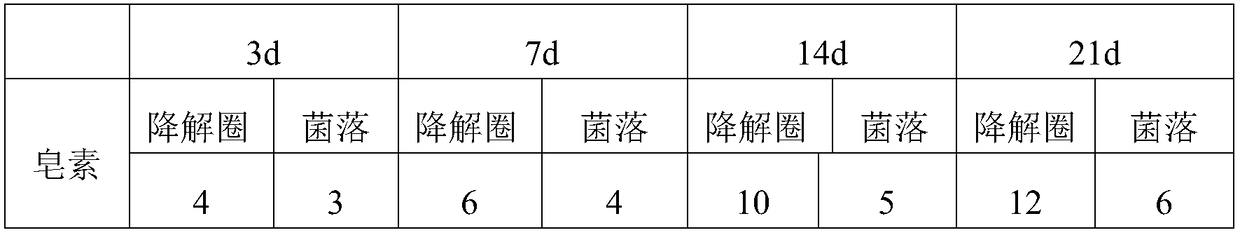
Complex microbial agent for degrading saponin and tannin
The invention provides a complex microbial agent for degrading saponin and tannin. The agent is composed of the microbial agents for degrading the saponin of bacillus amyloliquefaciens S301 and meyerozyma guilliermondii and the microbial agents for degrading the tannin of aspergillus awamori T301, wherein the volume ratio of the three microbial agents is (1-5):(1-5):(3:5). The complex microbial agent for degrading the saponin and tannin has the advantages that the complex microbial agent has the ability to degrade the saponin and the tannin, especially the saponin and tannin in sasanqua shell,sasanqua dregs and wood bits of pinus massoniana, and the degradation rate is 68% or above, the application of the complex microbial agent in the degradation of plant materials containing the saponin, tannin and the like has good prospects, and the application of the material rich in the saponin and tannin is greatly expanded.
Owner:RES INST OF SUBTROPICAL FORESTRY CHINESE ACAD OF FORESTRY
Phytolacca acinosa fruit fermentation liquor as well as preparation method and application thereof
The invention relates to phytolacca acinosa fruit fermentation liquor and a preparation method thereof. According to the method, ripe phytolacca acinosa fresh fruits are used as a raw material, and eight kinds of mixed strains of Penicillium sublateritium, Golubevia pallescens, Aspergillus penicillioids, Aspergillus parvulus, Meyerozyma guilliermondii, Candida intermedia, Lodderomyces elongisporusand Aspergillus sydowii are taken as fermented strains, and secondary fermentation is carried out at a temperature of 18-32 DEG C. The preparation method is clear in fermentation strain and controllable in process. The prepared fermentation liquor is clear in chemical components and has remarkable anti-cancer activity.
Owner:衡阳市文龙野生蔬果研发种植农民专业合作社 +2
Meyerozyma guilliermondii and application of secreted extracellular protein
ActiveCN111778308AExpand sourceHigh catalytic activityMicroorganism based processesChemical recyclingMicroorganismPtru catalyst
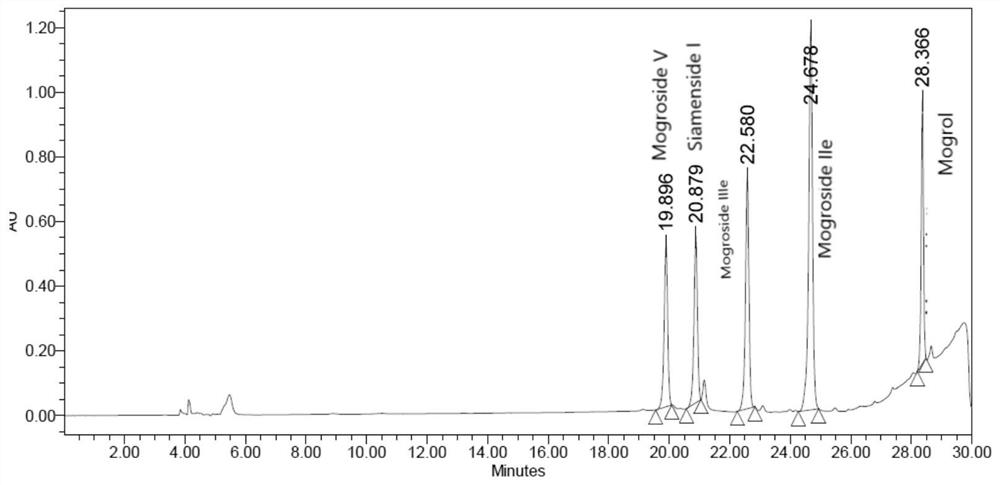
The invention discloses Meyerozyma guilliermondii and an application of secreted extracellular protein, relates to the technical field of microorganisms, and particularly relates to a method for efficiently synthesizing siamenoside I by using the Meyerozyma guilliermondii. According to the application, the catalytic function is achieved through the extracellular protein secreted by the Meyerozymaguilliermondii; the extracellular protein has relatively strong catalytic activity, has the characteristics of high catalytic efficiency, mild reaction conditions, strong specificity and the like, isexpected to be an ideal catalyst for efficiently synthesizing the siamenoside I, and widens the source of the siamenoside I.
Owner:CHENGDU BIOPURIFY LTD
Method for controlling postharvest diseases of broccoli and storing and preserving broccoli by using Meyerozyma guilliermondii
The invention belongs to the field of biological control of postharvest diseases, and relates to a method for controlling postharvest diseases of broccoli and storing and preserving the broccoli by using Meyerozyma guilliermondii. The Meyerozyma guilliermondii is identified as Meyerozyma guilliermondii Y1, and the preservation number is CCTCC NO: M 2019933. The method comprises the following steps: spraying a yeast suspension on the surface of disinfected broccoli to uniformly cover the surface of the broccoli; naturally airing the broccoli, placing the aired broccoli in a container, sealing the container with gauze, and then storing the sealed broccoli at the temperature of 20 DEG C to realize control of the postharvest diseases of the broccoli and storage and preservation of the broccoli. The disease index of the broccoli treated by the Meyerozyma guilliermondii is substantially reduced, yellowing of the broccoli is delayed, reduction of the contents of soluble sugar, vitamin C and chlorophyll and increase of the content of titratable acid are alleviated, the storage quality of the broccoli is not obviously affected, and reduction of the quality of the broccoli is alleviated to acertain extent; and on the other hand, the use of chemical bactericides is reduced, so the method is safe and environmentally-friendly, and has good economic and social benefits.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Yeast and use thereof in catalytical synthesis of 2,5-dihydroxymethylfuran
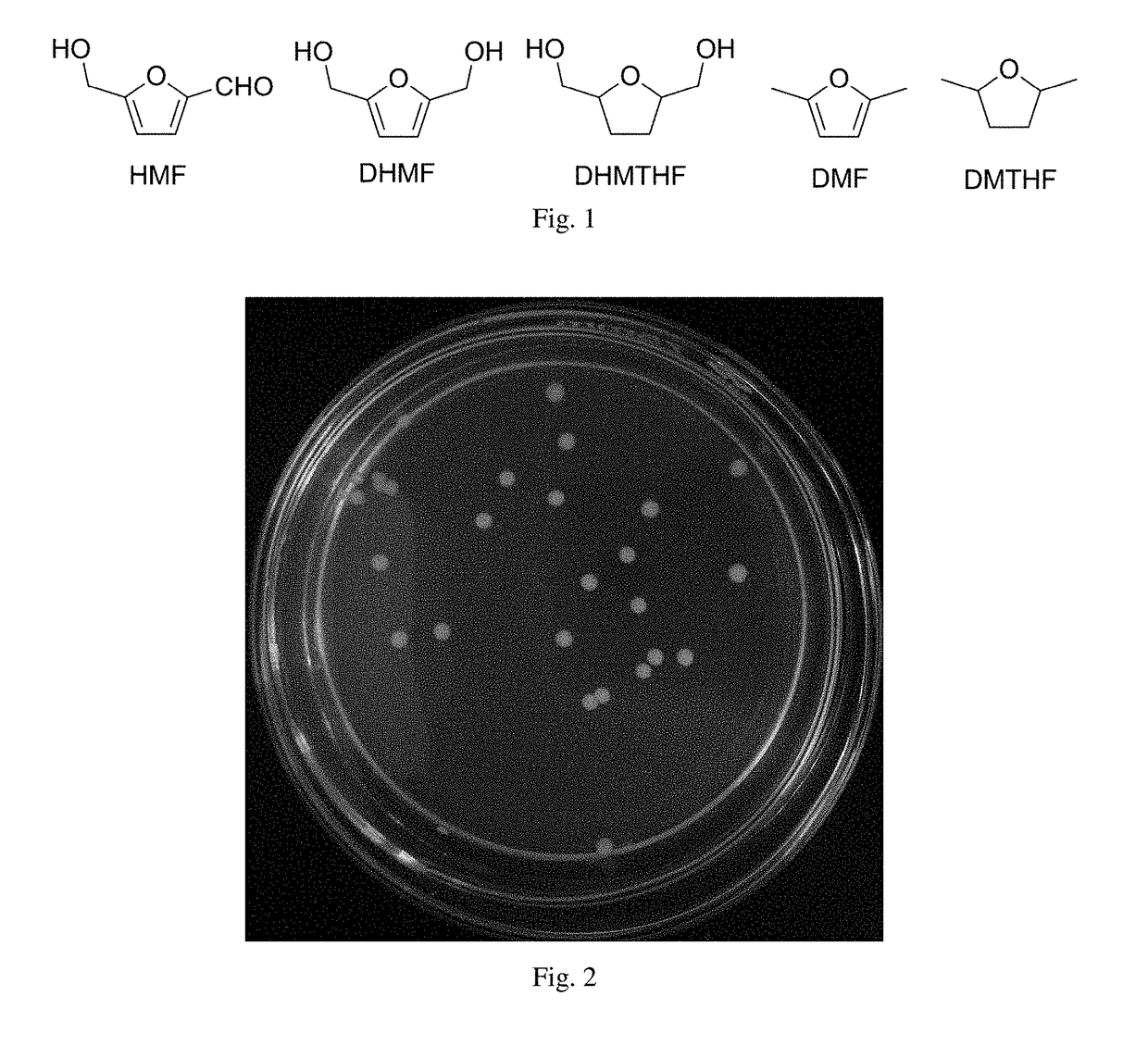
ActiveUS20190040430A1Improve efficiencyHigh selectivityMicroorganismsMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyFuraldehyde
A yeast strain and a method for the synthesis of 2,5-dihydroxymethylfuran using this strain are disclosed. The yeast strain is Meyerozyma guilliermondii SC 1103, which has been maintained in the China Center for Type Culture Collection (CCTCC, Wuhan, P.R. China) with an access No. of M2016144. The method for the synthesis of 2,5-dihydroxymethylfuran using this strain is described as follows: after pre-cultivation and cultivation, Meyerozyma guilliermondii SC 1103 cells are added into the buffer solutions containing 5-hydroxymethylfurfural and glucose; the biocatalytic reaction is conducted under designated conditions, thus affording 2,5-dihydroxymethylfuran. This disclosure has many advantages such as good selectivity, mild reaction conditions, environmental friendliness, high efficiency, and good yield.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Method for keeping flavor of seasoning bag for honey-stewed barbecue pork through microbial fermentation
PendingCN109259107AProduce moreImprove barrier propertiesMeat/fish preservation using chemicalsPolysaccharide/gum food ingredientsFlavorCooking & baking
The invention belongs to the field of microbial fermentation and food processing and particularly relates to a method for keeping the flavor of a seasoning bag for honey-stewed barbecue pork through microbial fermentation. The method comprises the following steps that after stretching, patting and cleaning preprocessing are sequentially conducted on very lean meat, cooking processing is performed,seasonings prepared through fermentation of Streptococcus thermophilus and Meyerozyma guilliermondii and a zinc gluconate solution are added to boil for gelatinization, the mixture is taken out and then is evenly mixed with seasonings, salting and baking are performed, then honey is applied, and the seasoning bag for the honey-stewed barbecue pork is packaged. The flavor loss of the pork chuck seasoning bag can be effectively reduced by adopting the method.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
Suspension of Pichia japonica for controlling postharvest disease of cherry tomato fruit
ActiveCN110050831BAbundant resourcesEasy to trainFungiFruit and vegetables preservationBiotechnologyFungicide
The invention discloses a kind of Pichia quaternary yeast J-SS-CX, which is Meyerozyma guilliermondii, and the deposit number is CGMCC NO.17240. The invention also discloses a Pichia moniliformis suspension for controlling postharvest diseases of cherry tomato fruits. The preparation method is as follows: Pichia moniliformes J-SS activated in NYDA solid medium ‑CX was inoculated into NYDB medium for one generation, and then inoculated into NYDB medium containing 12% NaCl for culture, and the obtained cells were washed and diluted with sterile distilled water. The invention can realize effective control of postharvest diseases of fruits without using chemical fungicides, and the yeast preparation is convenient to operate, has good effect, low cost, safety and environment-friendly.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Extract having effects of being preservative and fresh-keeping and application
InactiveCN107788105AAvoid pollutionAvoid security issuesFruit and vegetables preservationXanthomonas campestrisFreeze-drying
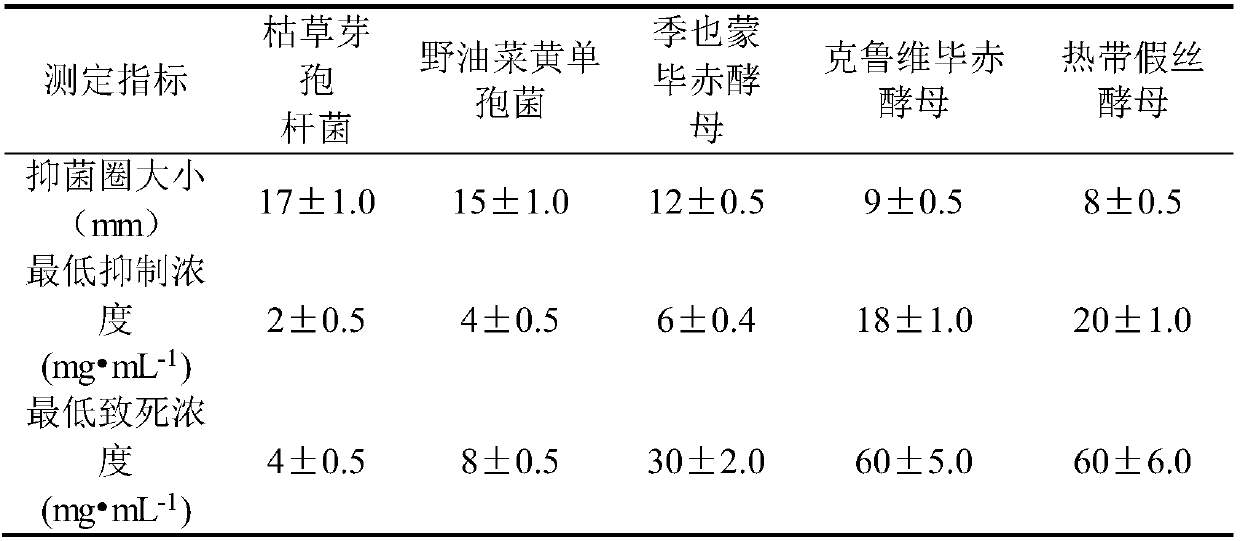
The invention relates to an extract having the effects of being preservative and fresh-keeping and an application of the extract. The extract is selected from peony, through ethanol / aqueous extraction, and then through freeze drying, dry powder is made; the extract has obvious restraining effect on bacillus subtilis, Xanthomonas campestris pv.campestris, Meyerozyma guilliermondii, Candida tropicalis and Pichia kluyveri; after thalli is treated with the extract, the electrical conductivity of bacterial liquid is instantaneously and rapidly increased within 1min, and the damage capacity to cellfilms is high; and fruits and vegetables are soaked or sprayed with the extract, the rotting rate and the weight loss rate of the fruits and the vegetables can be reduced, the loss of soluble solids and Vc is reduced, the extract has the effects of being preservative and fresh-keeping and can replace a chemical fresh keeping agent for preservation of the fruits and the vegetables, and the problemsthat a chemical preservation agent pollutes environment, and the food is unsafe, are solved.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Application of meyerozyma guilliermondii in aspect of degrading antibiotics
ActiveCN111528396APromote degradationIncrease profitClimate change adaptationFood scienceBiotechnologySulfadiazine
The invention discloses an application of meyerozyma guilliermondii in the aspect of degrading antibiotics or an application of the meyerozyma guilliermondii in the aspect of improving the degradationremoval rate of the antibiotics. First research finds that the meyerozyma guilliermondii can significantly degrade the antibiotics, especially sulfonamide antibiotics; and when the meyerozyma guilliermondii is applied to diseased animal meat and bone meal, a result shows that the degradation rate of sulfadiazine in the diseased animal meat and bone meal is close to 90%, and the degradation rate of protein is only about 2%, so that the utilization rate of the diseased animal meat and bone meal is greatly improved, and meanwhile the pollution of the antibiotics to the environment is reduced.
Owner:GUANGDONG OCEAN UNIVERSITY
A kind of Pichia monteriti and its application in biological deodorization
ActiveCN112159768BImprove deodorization efficiencyNo biohazardFungiDispersed particle separationBiotechnologyMeyerozyma guilliermondii
The invention discloses a Pichia guilliermondii (Meyerozyma guilliermondii) K1 and its application in biological deodorization, belonging to the field of biological technology. The deposit number of the Pichia guilliermondii K1 is CCTCC NO: M 2020191. The strain has high deodorizing efficiency and no biological hazard. The biological deodorizing bacteria agent made by using Pichia mongolica K1 has obvious degrading effect on the odor produced by kitchen waste, and has good application potential.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
A ketoreductase mutant with improved enzyme activity and its application
ActiveCN111454921BHigh substrate concentrationIncrease the number of cyclesBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMeyerozyma guilliermondiiEthyl acetate
The invention discloses a ketoreductase mutant with improved enzymatic activity and an application thereof, belonging to the field of biotechnology. It is derived from the wild-type ketoreductase of Meyerozyma guilliermondii, and can convert ethyl 4-chloroacetoacetate to generate (R) ‑4‑chloro‑3‑hydroxybutyrate ethyl ester, the ketoreductase mutant has higher alcohol dehydrogenase activity than the wild-type sequence, and has more than 90% similarity with SEQ ID NO.8. The ketoreductase mutant of the present invention has obviously high specific enzyme activity, which is 2-10 times higher than that of the wild-type ketoreductase, the reaction conditions are mild, the equipment requirements are low, the production process does not require high temperature or cooling, and the energy consumption is low. Enzyme catalysis has high efficiency, specific selectivity, and convenient purification. In addition, most of the solvent in the reaction is water, and there is no need to add solvents such as butyl acetate to form a two-phase reaction system. The three wastes discharge is low, and the preparation process is environmentally friendly.
Owner:NANJING LANGEN BIOLOGICAL SCI & TECH
Novel Methods for Production of Mannosylerythritol Lipids
ActiveUS20220127563A1Improve efficiencyLow costFungiChemical recyclingBiotechnologyCell culture media
The subject invention provides improved methods for producing mannosylerythritol lipids (MEL) using yeasts not previously known to produce MEL. In particular, Meyerozyma guilliermondii (Pichia guilliermondii) is cultivated in a specially-tailored nutrient medium and under cultivation conditions such that the yeast unnaturally produces MEL and / or MEL-like molecules in greater amounts and at increased rates than when using standard MEL production with, for example, Pseudozyma aphidis. Yeast culture compositions are also provided, comprising yeast cells, growth medium, and high concentrations of MEL.
Owner:LOCUS SOLUTIONS IPCO LLC
A strain of Pichia monteriti and its application
The invention relates to a biocontrol bacterial strain Y-1 for preventing and treating fungal diseases of grapes and its application in the prevention and treatment of grape diseases, belonging to the technical field of biological control of plant diseases. The bacterial strain is Meyerozyma guilliermondii Y‑1, and the strain preservation number is CCTCC NO: M2015814. The above-mentioned Pichia guilliermondii (Meyerozyma guilliermondii) Y-1 is used to prepare a biocontrol agent for preventing and treating grape diseases, which has a significant control effect on various pathogenic fungi. The active ingredient of the biocontrol preparation provided by the present invention, Pichia guilliermondii (Meyerozyma guilliermondii) Y‑1, has stable control effect, long-lasting effect and wide spectrum of disease prevention, and is environmentally safe and not suitable for drug resistance; The method has the advantages of fast speed, simple culture conditions, easy storage and industrial production; it can also improve the activity of defense-related enzymes in plants, and has good development and application prospects.
Owner:QINGDAO AGRI UNIV
A ketoreductase mutant for producing (r)-4-chloro-3-hydroxybutyric acid ethyl ester
ActiveCN111575256BHigh substrate concentrationHigh coenzyme cycle timesBacteriaMicroorganism based processesHydroxybutyric acidNucleotide
The invention discloses a ketoreductase mutant for producing (R)-4-chloro-3-hydroxybutyric acid ethyl ester, belonging to the field of biotechnology, which is derived from the wild-type ketoreductase of Meyerozyma guilliermondii and can convert Ethyl 4-chloroacetoacetate is converted to generate (R)-4-chloro-3-hydroxybutyric acid ethyl ester, which has higher alcohol dehydrogenase activity compared with the wild-type sequence, and the sequence of the ketoreductase mutant is SEQ ID NO.2, the enzyme activity of the ketoreductase mutant is at least 2-10 times higher than that of the wild-type ketoreductase. The ketoreductase mutants of the present invention and polynucleotides encoding such mutants can be prepared using methods commonly used by those skilled in the art. Mutants can be obtained by in vitro recombination encoding the enzyme, mutagenesis of polynucleotides, DNA shuffling, error-prone PCR, and directed evolution methods, among others.
Owner:NANJING LANGEN BIOLOGICAL SCI & TECH
Strain of meyerozyma guilliermondii and its use in methods of catalytic synthesis of 2,5-dihydroxymethylfuran
ActiveUS10662452B2Improve efficiencyHigh selectivityMicroorganismsChemical recyclingBiotechnologyFuraldehyde
A yeast strain and a method for the synthesis of 2,5-dihydroxymethylfuran using this strain are disclosed. The yeast strain is Meyerozyma guilliermondii SC 1103, which has been maintained in the China Center for Type Culture Collection (CCTCC, Wuhan, P.R. China) with an access No. of M2016144. The method for the synthesis of 2,5-dihydroxymethylfuran using this strain is described as follows: after pre-cultivation and cultivation, Meyerozyma guilliermondii SC 1103 cells are added into the buffer solutions containing 5-hydroxymethylfurfural and glucose; the biocatalytic reaction is conducted under designated conditions, thus affording 2,5-dihydroxymethylfuran. This disclosure has many advantages such as good selectivity, mild reaction conditions, environmental friendliness, high efficiency, and good yield.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Breeding of Yeast Strain Producing Nitrilase and Its Application in Biotransformation of Nitrile Compounds
ActiveCN107022497BIncrease vitalityExcellent nitrile conversion abilityFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnology3-Hydroxypropionic acid
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Polyethylene-degradable Pichia guilliermondii
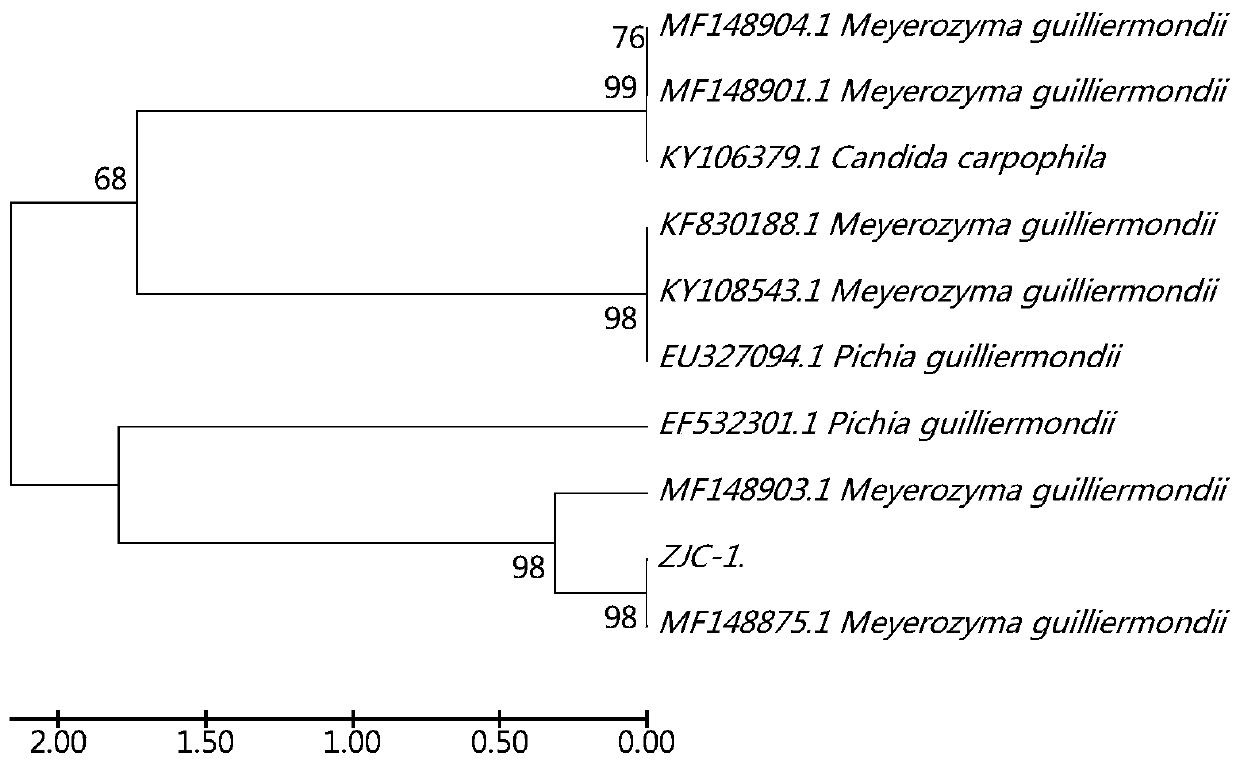
The invention relates to a strain of polyethylene-degradable Pichia guilliermondii, and relates to a strain of Pichia guilliermondii. The invention provides a train of Pichia guilliermondii which can degrade polyethylene and provides a new bacterial source for the biodegradation of polyethylene. The Pichia guilliermondii is Meyerozyma guilliermondii ZJC-1, and is deposited in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center, with the preservation address being No.3, Courtyard 1, Beichen Road, Chaoyang District, Beijing, the preservation date being December 17, 2018, and the preservation number being CGMCC No. 16956. The Meyerozyma guilliermondii ZJC-1 provides a new bacterial source for biodegradable polyethylene, and is used to degrade polyethylene.
Owner:NORTHEAST FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com