Application of meyerozyma guilliermondii in aspect of degrading antibiotics
A technology of antibiotics and yeast, applied in climate change adaptation, food science, etc., can solve the problems of less degradation technology of sulfonamide antibiotics, secondary pollution of meat and bone meal, and limited use range, etc., to achieve low cost, reduce pollution, and improve utilization rate Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] Embodiment 1 Degradation experiment of Pichia montaglia sulfadiazine
[0032] 1. Experimental method
[0033] The present invention detects the residual amount of sulfadiazine with LC / MS method, calculates the degradation rate, and concrete operation is:
[0034] Mass spectrometry conditions: spray voltage: 4.5kv; atomization flow: 3.0L / min; drying gas flow: 15L / min; collision pressure (CID): 230kPa.
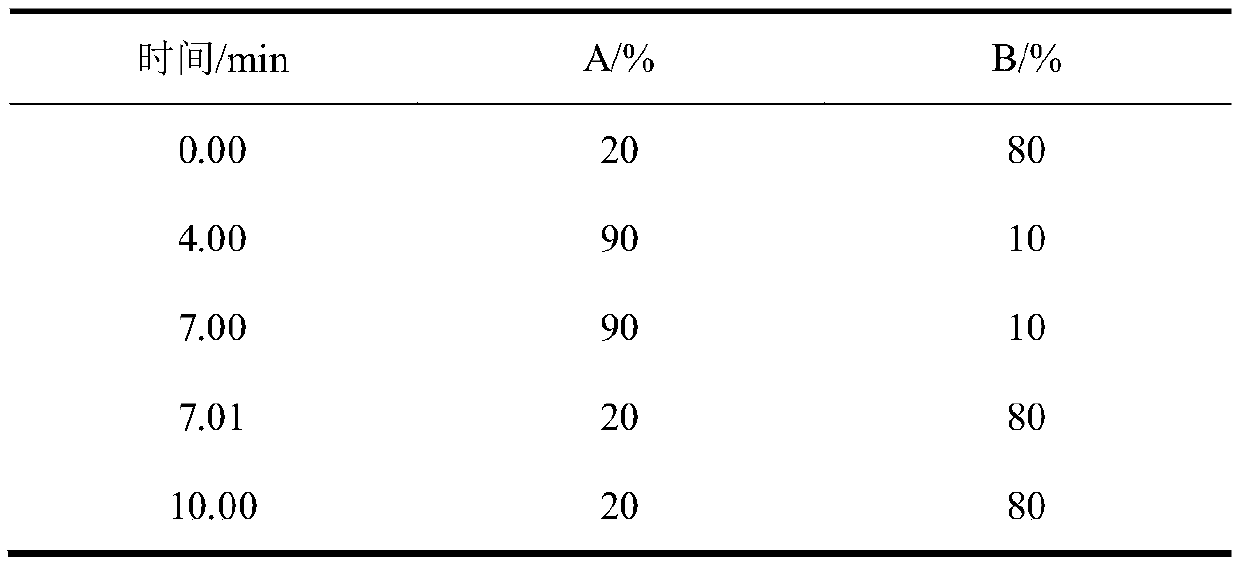
[0035] Liquid chromatography conditions: chromatographic column: Gold C18, 5 μm, 150mm×2.1mm (inner diameter); mobile phase: methanol A; ammonium acetate 5mmol / L (0.1% formic acid) aqueous solution B, see Table 1 for elution gradient, flow rate: 300 μL / min; column temperature: 30°C; injection volume: 10 μL.
[0036] Table 1 Liquid chromatography mobile phase gradient elution for separating drugs
[0037]
[0038] Dissolve sulfadiazine in an aqueous solution, dilute it with 5°Be wort to a final concentration of sulfadiazine of 25mg / L, 5mg / L, and 1mg / L, set 3 paralle...
Embodiment 2
[0041] Example 2 Degradation experiment of sulfadiazine in meat and bone meal of sick animals
[0042] Mix the diseased animal meat and bone meal with 3 times of water, add 1.5% molasses of the total weight, adjust the pH to 6.8, and prepare a fermentation medium, add it to the Erlenmeyer flask, and inoculate it into the fermentation medium after sterilization. Add 3% Pichia monteritiera seed liquid, and ferment for 3 days under the condition of 28°C.
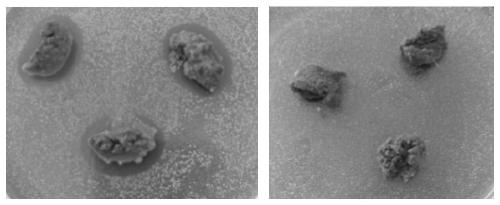
[0043] Take 0.2 g of the fermentation substrate on a nutrient agar plate containing Escherichia coli indicator bacteria, measure the diameter of the inhibition zone, and use the unfermented substrate as a blank control to compare the degradation of sulfadiazine before and after fermentation. Such as figure 1 As shown, the inhibitory effect of unfermented meat and bone meal on Escherichia coli is obvious, indicating that the antibiotic residue in meat and bone meal is relatively high, which can inhibit the growth of Escherichia...
Embodiment 3
[0045] Example 3 Degradation of Sulfadiazine in Meat and Bone Meal of Sick Animals
[0046] Mix the diseased animal meat and bone powder with 4 times of water, add 3% molasses of the total weight, adjust the pH to 5.5, and prepare a fermentation medium. After sterilization, add 2% Ji Yemeng to the fermentation medium Pichia pastoris seed liquid was fermented at 25°C for 4 days.
[0047]The measurement method is as in Example 2, and the results show that the residual amount of sulfadiazine in the meat and bone powder of sick animals before fermentation is 8.08 mg / kg, the content of sulfadiazine at the end of fermentation is 0.94 mg / kg, the degradation rate of sulfadiazine is 88.3%, and the degradation rate of protein was 2.6%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com