Yeast strain for controlling pear patulin and application of yeast
A patulin and yeast technology, applied in fungi, microorganism-based methods, microorganisms, etc., can solve the problems of unsecured safety, pollution of the environment, drug resistance of fungi, etc., to ensure food safety. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
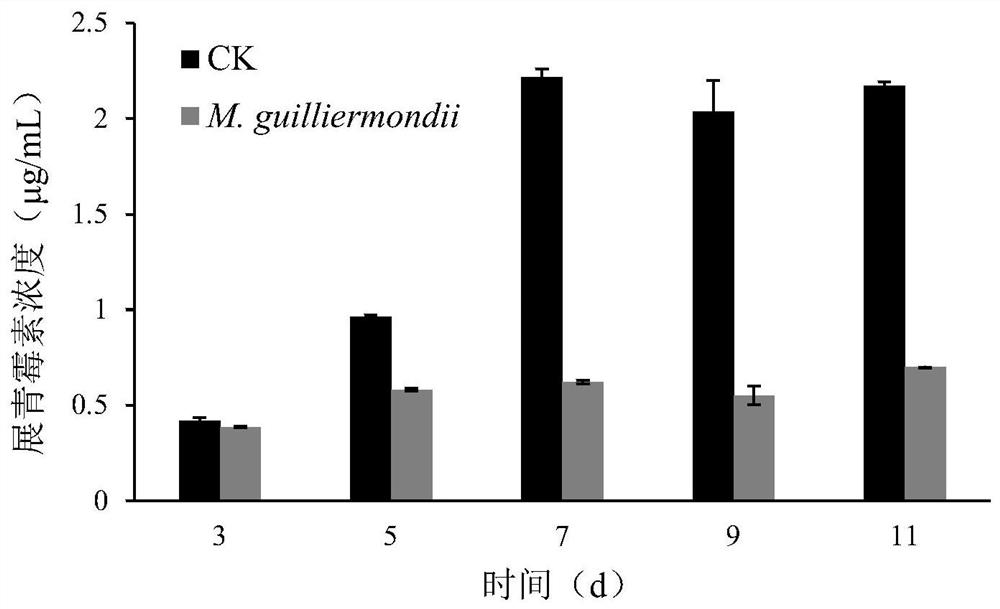
[0034] Control of Pichia mongolica Y1 on patulin in pome fruit wounds;
[0035] Pretreatment of pear fruits: select ripe pear fruits that are basically consistent with the relevant indicators such as fruit maturity and size, and are not damaged, and immerse them in tap water containing 0.3% sodium hypochlorite solution for disinfection for 1 to 2 minutes, rinse with clean water, and then dry them in the air;
[0036] Then use a sterilized hole puncher to form wounds of uniform size and depth on the equator of each fruit surface, and the pome fruits are divided into the experimental group and the control group; 30 μL is added to each wound in the experimental group at a concentration of 1× 10 8 cells / mL yeast suspension; add 30 μL of sterile water to each wound in the treatment group; after standing for 2 hours, add an equal amount of 30 μL to each wound in the experimental group and control group with a concentration of 1×10 5 spores / mL of P.expansum spore suspension; after n...
Embodiment 2
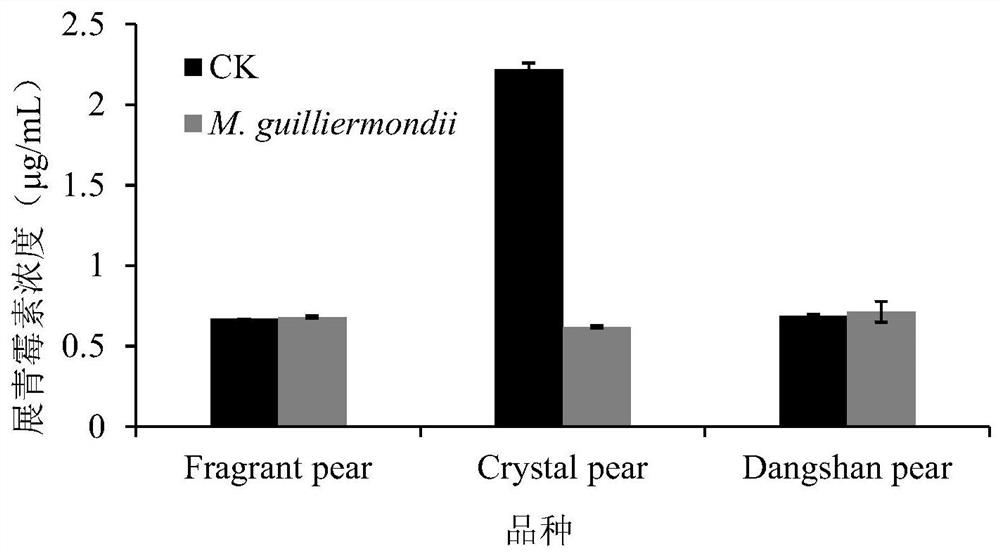
[0040] Control of Pichia mongolica Y1 on patulin in fruit wounds of different pome varieties;
[0041] After choosing the pear fruits (Crystal Pear, Fragrant Pear, Dangshan Pear) pretreatment of different varieties, the operation steps are the same as Example 1, only sampling on the seventh day;
[0042] According to the above-mentioned steps test, the control effect of Pichia mongoliana Y1 on the wound patulin of different varieties of pome fruit is as follows: figure 2 shown by figure 2 It can be seen that there is almost no difference in the content of patulin between the pear and Dangshanli experimental group using Pichia mongoliana Y1 and the control group without yeast, indicating that Pichia mongoliana Y1 has no effect on the pear and Dangshanli fruit. Patulin at the wound site had no controlling effect. Pichia mongoliana Y1 had a significant control effect on patulin in the fruit wound of Jingjing pear.
Embodiment 3
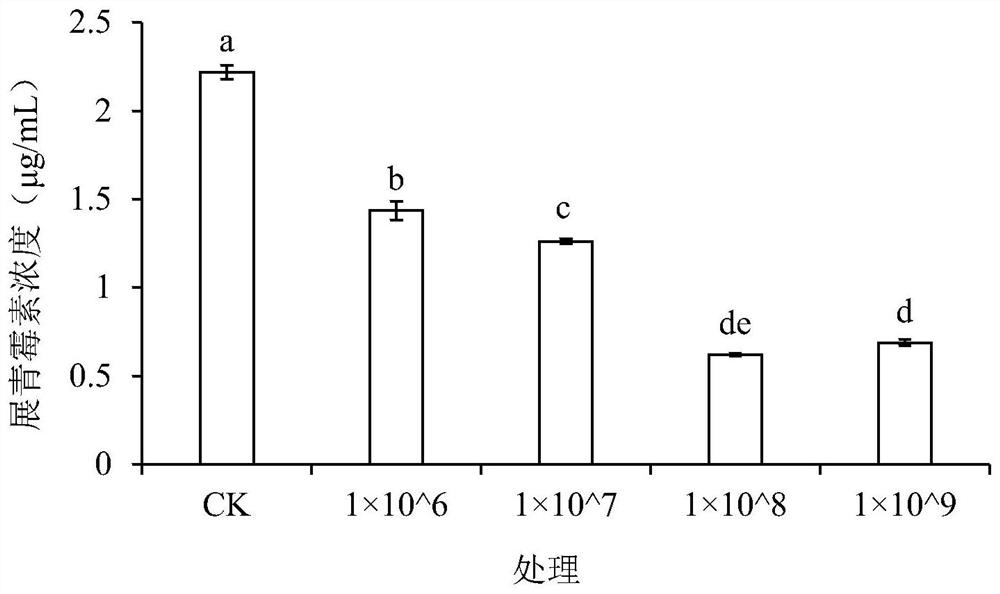
[0044] Control of patulin in pome fruit wounds by different concentrations of Pichia mongoliana Y1
[0045] After pretreatment of the pome fruit, a wound of uniform size and depth was formed on the equator of each fruit surface with a sterilized puncher, and the pome fruit was divided into 5 groups, recorded as group A, group B, and group C , groups D and E; add 30 μL of the following treatment solution to each wound equally: Group A 1×10 6 cells / mL of yeast; group B 1×10 7 cells / mL of yeast; group C 1×10 8 cells / mL yeast; D group 1×10 9 cells / mL yeast; E group sterile water; after standing for 2 hours, add an equal amount of 30 μL to each wound of the experimental group and the control group with a concentration of 1×10 5 Penicillium expansum (Penicillium expansum) spore suspension of spores / mL; After natural drying, put the treated fruit in a plastic basket, seal it with a plastic wrap, and cultivate it in a constant temperature and humidity incubator (20°C, RH 95%); Eac...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com