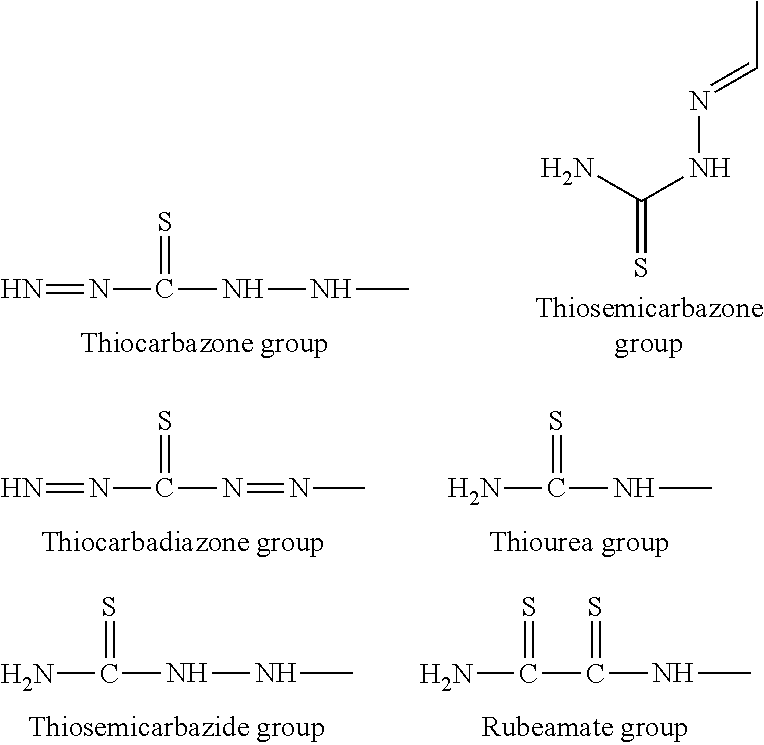
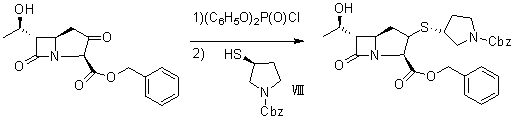Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
34 results about "Iodoacetic acid" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Iodoacetic acid is a derivative of acetic acid. It is a toxic compound, because, like many alkyl halides, it is an alkylating agent. It reacts with cysteine residues in proteins. It is often used to modify SH-groups to prevent the re-formation of disulfide bonds after the reduction of cystine residues to cysteine during protein sequencing.
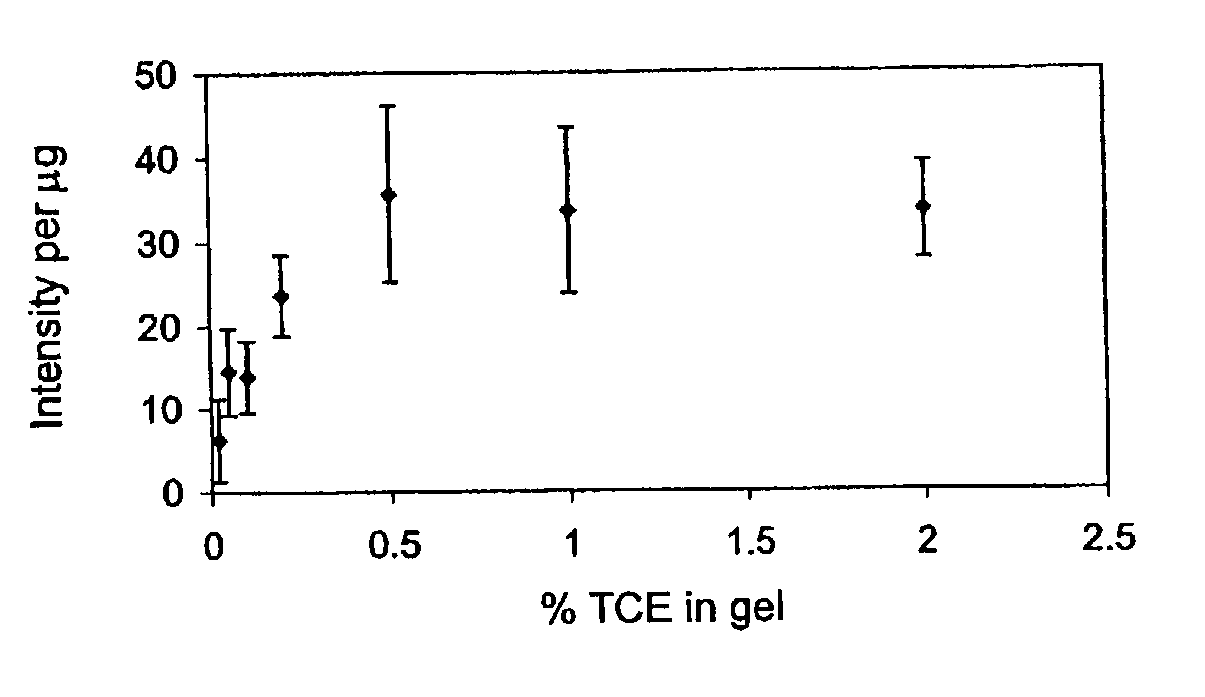
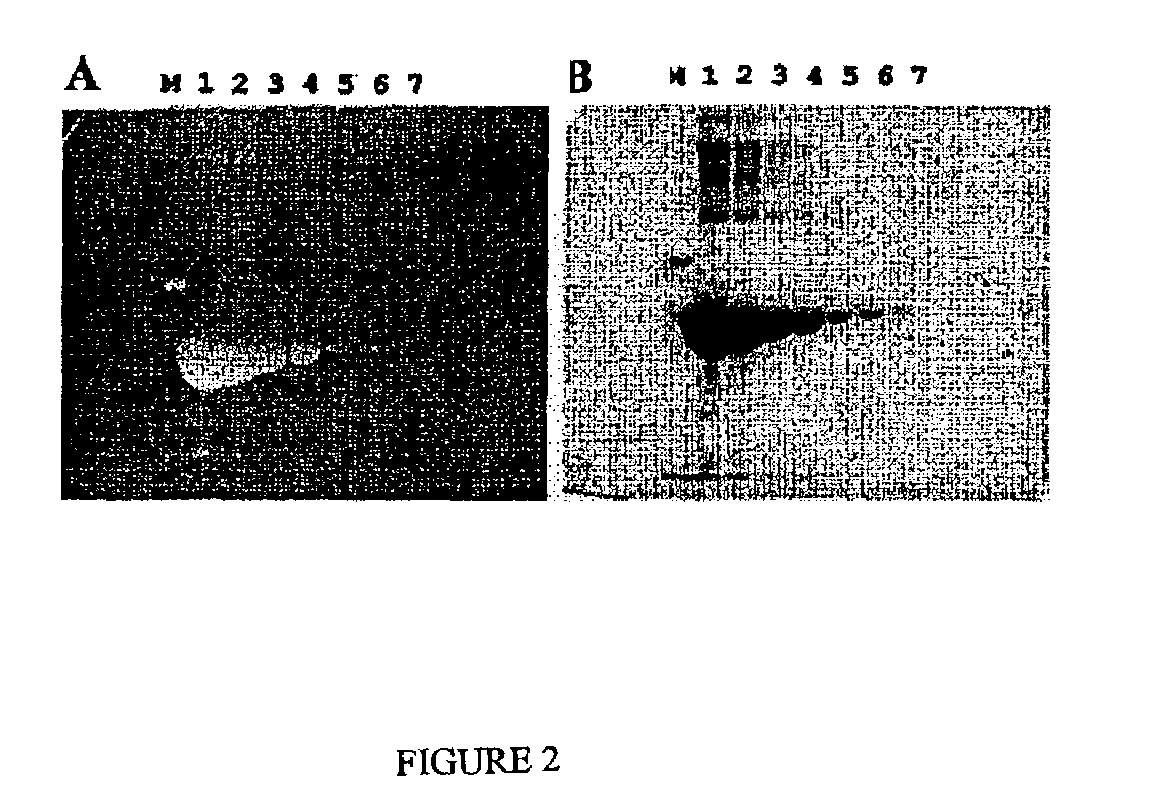
Fluorescent detection of proteins in polyacrylamide gels
ActiveUS7569130B2Laborious labelingLaborious staining stepElectrolysis componentsChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceSpectroscopyTryptophan
The mechanism of the UV light-induced reaction between the indole moiety of tryptophan and chloroform, and the structure of the modified tryptophan and polypeptides including such modified tryptophan residues. The excited indole moiety, which is formed upon UV light irradiation, emits a solvated electron which initiates a series of events that yield fluorescent derivatives that have CHO group covalently bound to the indole moiety. These derivatives are herein referred to as formyltryptophan, and are relatively stable. Similar reactions are observed when 5-hydroxytryptophan, 5-fluorotryptophan, or N-methylindolacetate are used in place of tryptophan, or when other haloalkanes, such as trichloracetic acid, trichlorethanol, trichlorethane, bromoform, and iodoactetate are used in place of chloroform. The derivatives can be used in a variety of applications in fluorescence spectroscopy, and for nuclear magnetic resonance, X-ray crystallography, infra-red spectroscopy, circular dicroism and mass spectroscopy. Additionally, the UV light-induced reaction between the indole moiety of tryptophan and haloalkanes can be used to prepare derivatives of tryptophan for chemical cross-linking studies of proteins and peptides.
Owner:UNIV TECH INT +1
Fluorescent detection of proteins in polyacrylamide gels
InactiveUS20100089753A1Without laborious labeling and staining stepElectrolysis componentsVolume/mass flow measurementSpectroscopyTryptophan
The mechanism of the UV light-induced reaction between the indole moiety of tryptophan and chloroform, and the structure of the modified tryptophan and polypeptides including such modified tryptophan residues. The excited indole moiety, which is formed upon UV light irradiation, emits a solvated electron which initiates a series of events that yield fluorescent derivatives that have CHO group covalently bound to the indole moiety. These derivatives are herein referred to as formyltryptophan, and are relatively stable. Similar reactions are observed when 5-hydroxytryptophan, 5-fluorotryptophan, or N-methylindolacetate are used in place of tryptophan, or when other haloalkanes, such as trichloracetic acid, trichlorethanol, trichlorethane, bromoform, and iodoactetate are used in place of chloroform. The derivatives can be used in a variety of applications in fluorescence spectroscopy, and for nuclear magnetic resonance, X-ray crystallography, infra-red spectroscopy, circular dicroism and mass spectroscopy. Additionally, the UV light-induced reaction between the indole moiety of tryptophan and haloalkanes can be used to prepare derivatives of tryptophan for chemical cross-linking studies of proteins and peptides.
Owner:UNIV TECH INT +1
Multielement composite foliar fertilizer
InactiveCN104591845AFast absorbencyQuick conversionMagnesium fertilisersAlkali orthophosphate fertiliserIron sulfatePlant growth
The invention relates to the field of fertilizers, and concretely relates to a multielement composite foliar fertilizer. The multielement composite foliar fertilizer is composed of the following substances in percent by mass: 10-20% of urea, 5-7% of diammonium phosphate, 3-5% of potassium sulfate, 0.05-0.15% of ferric sulfate, 0.02-0.04% of zinc sulfate, 0.03-0.05% of sodium molybdate, 0.1-0.3% of borax, 0.03-0.05% of magnesium sulfate, 0.07-0.09% of potassium chloride, 0.07-0.09% of iodoacetic acid, and 1-3% of a plant-growth regulator.
Owner:YANTAI NAKE ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION TECH
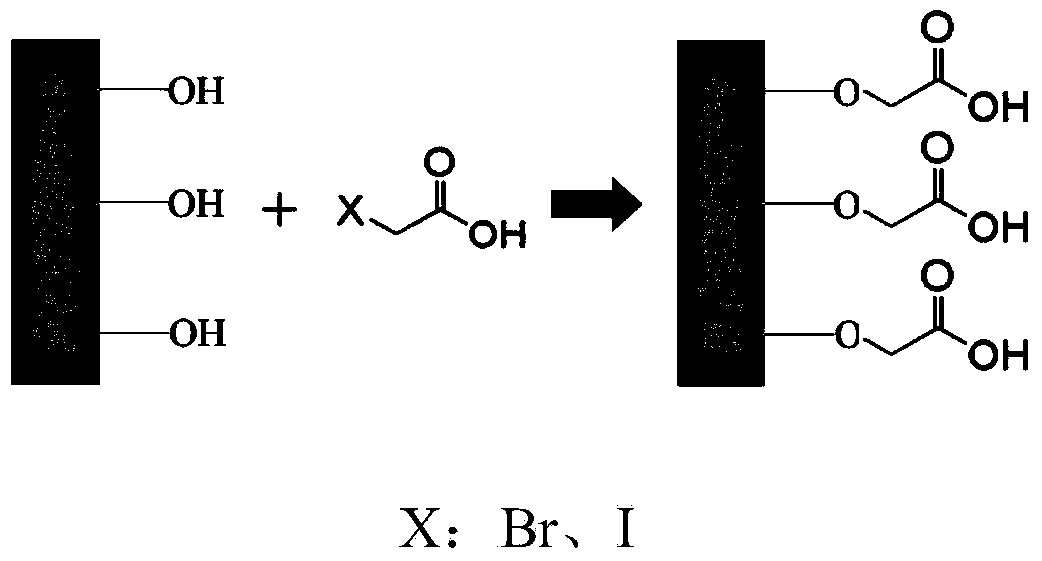
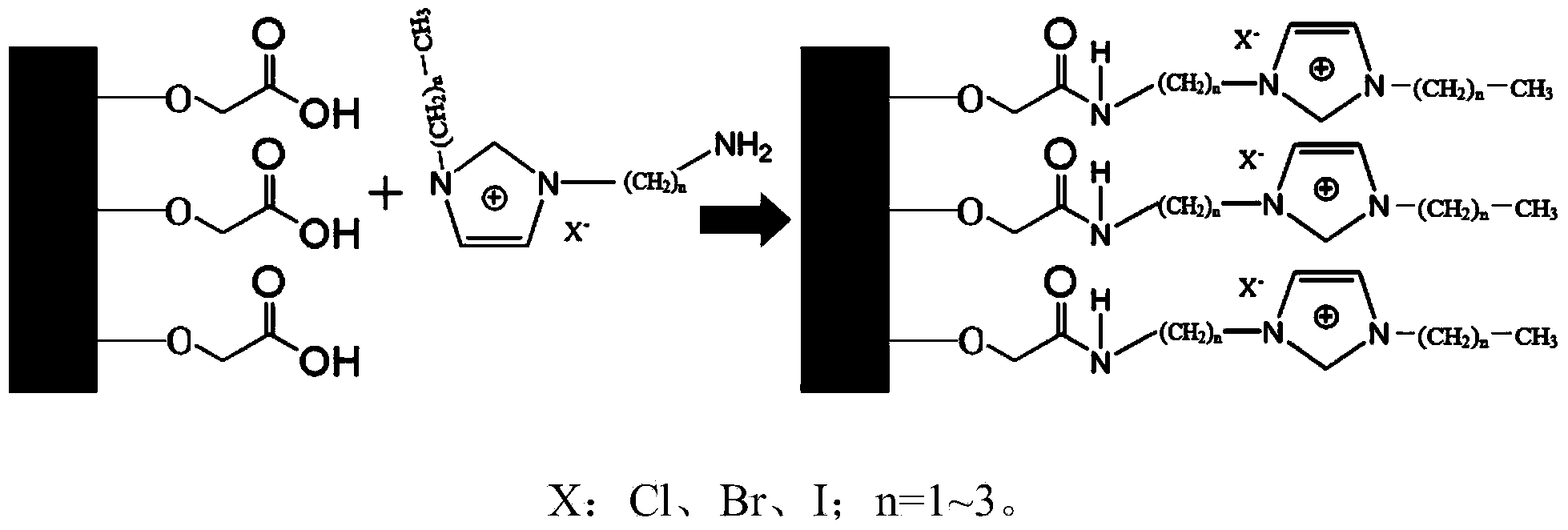
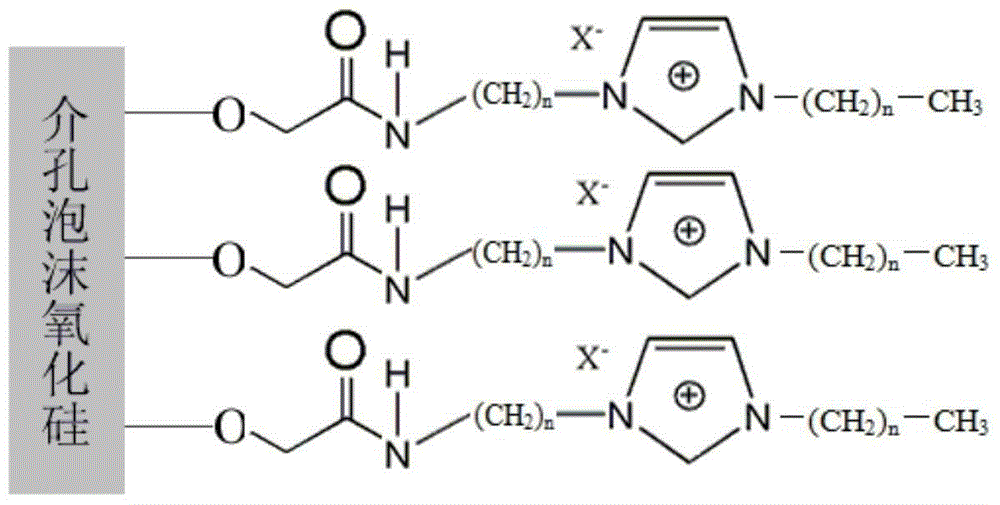
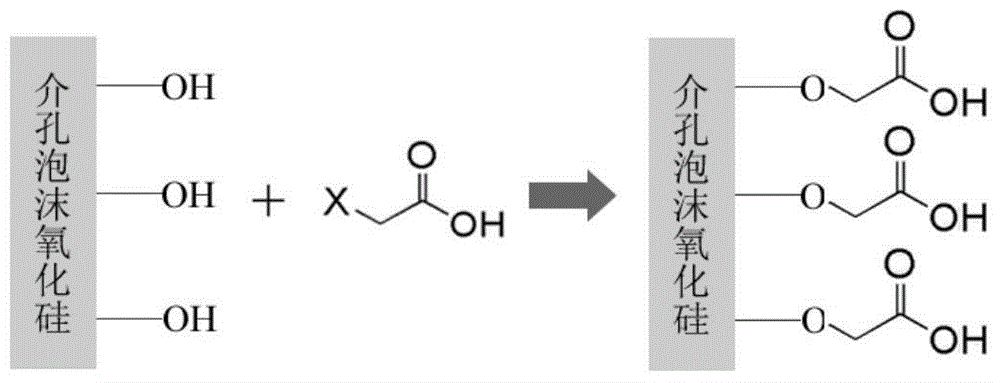
Solid catalyst for synthesizing cyclic carbonate and preparation method thereof
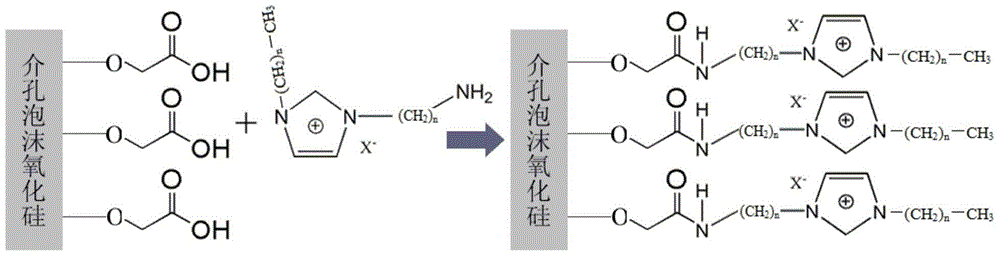
ActiveCN103521262AEffective fixed loadIncrease the number ofCatalyst carriersOrganic chemistryBromoacetic acidSilicon oxide
The invention relates to a solid catalyst for synthesizing cyclic carbonate and a preparation method thereof. In the catalyst, mesoporous foam silicon oxide is used as a carrier, bromoacetic acid or iodoacetic acid and an amino-containing imidazole ionic liquid are used as raw materials, and effective fixation of the ionic liquid on the mesoporous foam silicon oxide material can be realized through a two-step reaction so as to obtain the solid catalyst for synthesizing cyclic carbonate. The method is simple to operate, the obtained solid catalyst can be continuously reused through simple treatment after the reaction, thus the service life is long, the pollution is avoided, and the production cost is greatly reduced. By applying the solid catalyst to a process of synthesizing ethylene carbonate or propylene carbonate through a reaction between ethylene oxide or propylene oxide and carbon dioxide, a good catalysis effect is realized, the selectivity of the cyclic carbonate is higher than 95%, and the yield is higher than 85%.
Owner:CHANGZHOU XIAOGUO INFORMATION SERVICES
Catalyst containing palladium compound, preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN106000469AThe synthesis method is simpleSynthetic method is fastOrganic compound preparationOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsArylAcetic acid
The invention discloses a catalyst containing palladium compound, a preparation method and an application thereof. According to a compounding method of the palladium compound PdBr2(PPh3)2, o-chloro pyridine is taken as an initial raw material, reacts with methyl iodide and then reacts with tetra (triphenylphosphine) palladium. According to the compounding method of the palladium compound PdI2(PPh3)2, o-bromopyridine is taken as the initial raw material, reacts with iodoacetic acid and then reacts with tetra (triphenylphosphine) palladium. The method for compounding the target product provided by the invention is simple, easy to operate and control and also has the advantages of high product purity and high yield. Such a compound can be applied to the Heck coupling reaction of aryl halogen and ethyl acrylate and has ultrahigh catalytic activity.
Owner:TIANJIN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
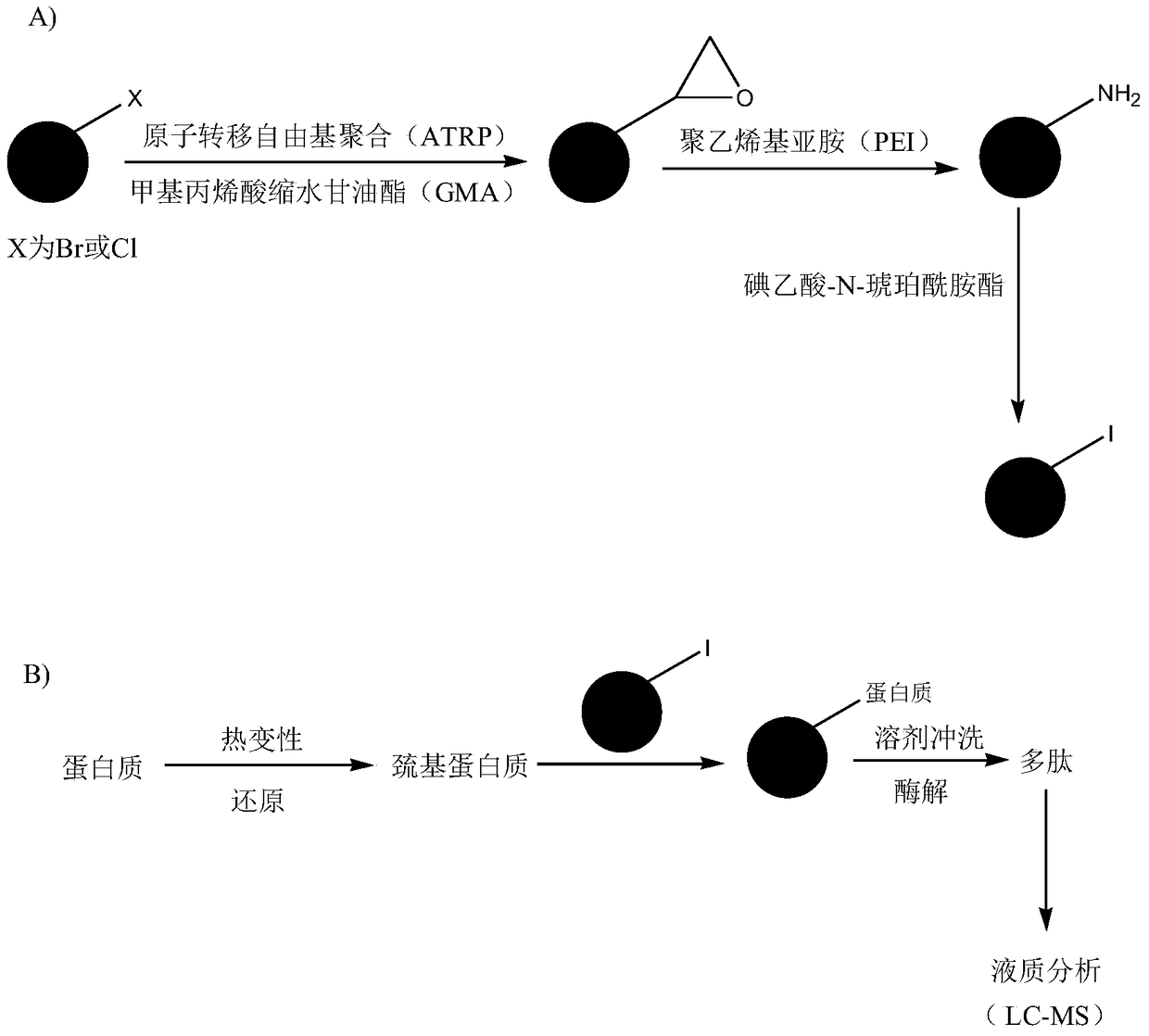
Preparation of protein solid-phase alkylation reagent, and solid-phase alkylation reagent and applications thereof
ActiveCN106632877AIncreased grafting capacityThe preparation process is simple and controllablePeptide preparation methodsLipid formationActive agent
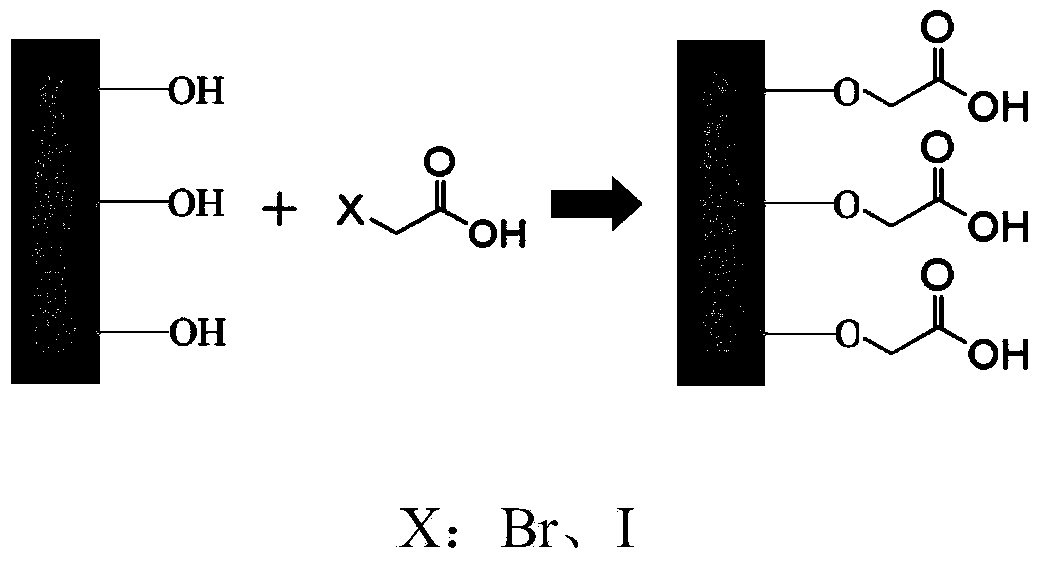
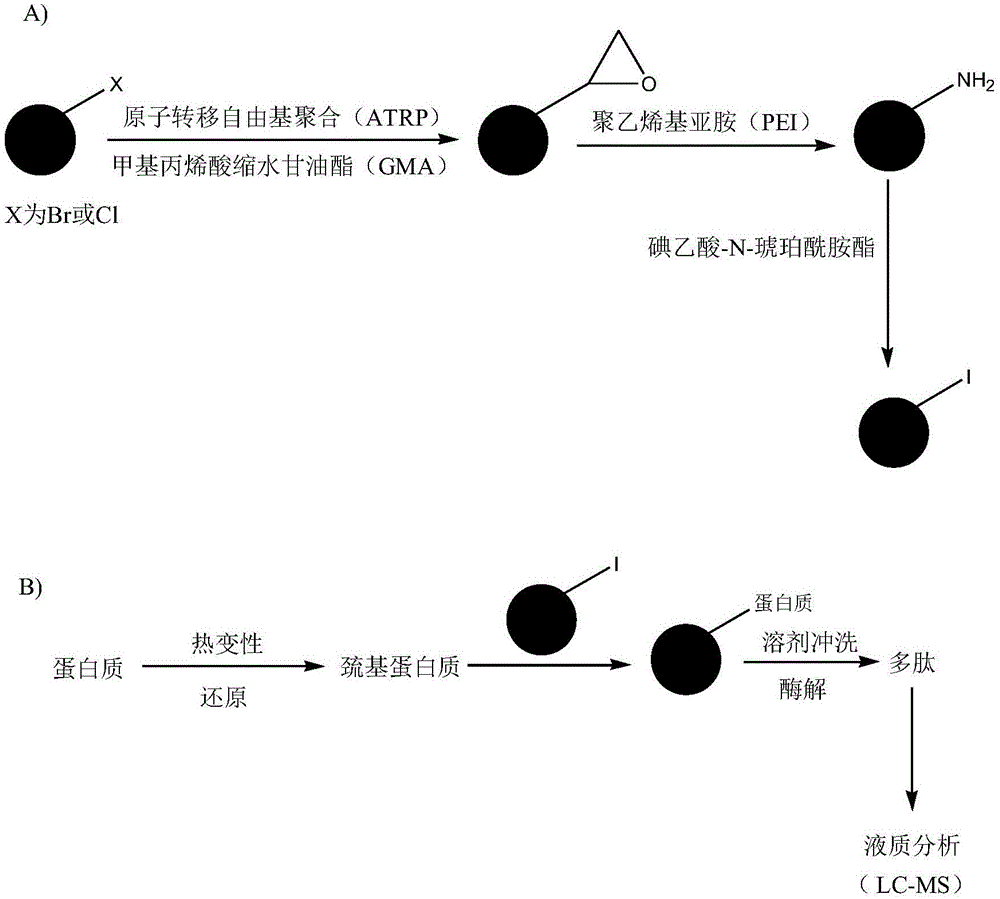
The present invention relates to a protein solid-phase alkylation reagent, preparation and applications thereof. According to the preparation, silica gel particles are used as a carrier, an epoxy group is modified on the surface of the carrier through atom transfer radical polymerization, and dendritic hydrophilic compounds such as polyethyleneimine and iodoacetic acid-N-succinamate are sequentially modified through covalent bonding to prepare the solid-phase alkylation reagent. According to the present invention, the reagent can selectively react with the mercapto group on proteins, and has advantages of high stability, simple operation, quick reaction and the like; compared to the traditional alkylation reagent, the protein solid-phase alkylation reagent of the present invention has the following advantages that by using the protein solid-phase alkylation reagent, rapid separation of proteins and other small molecules (such as saccharides, salts, surfactants, lipids, and the like) can be achieved, the protein purity can be improved, and the complexity of the sample can be significantly reduced; and the reagent has good surface hydrophilicity, and can significantly improve the recovery rate of proteins or hydrolyzates, such that the reagent is suitable for the selective reaction and the pretreatment of the mercapto group in proteins extracted from cells, tissues, body fluids, hairs, and the like.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
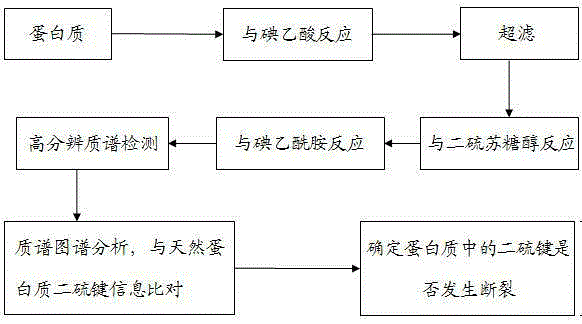
Method for detecting disulfide bond breakage of protein
Disclosed is a method for detecting disulfide bond breakage of protein. The method for detecting disulfide bond breakage of the protein comprises utilizing iodoacetic acid to react with free sulfydryl, removing unreacted iodoacetic acid through filtration, breaking the disulfide bonds inside the protein through dithiothreitol, utilizing ammonium iodoacetate to react with newly-produced sulfydryl, utilizing trypsin to hydrolyze the protein into polypeptide, detecting the mass to charge ratio information of the polypeptide through high-resolution mass spectrometry and comparing the mass to charge ratio information with the disulfide bond information of natural protein to determine whether the disulfide bonds break. The method for detecting disulfide bond breakage of the protein can be effectively used for determining whether the sulfydryl exists in a free or disulfide mode; the mass difference caused by reactions between the iodoacetic acid as well as the ammonium iodoacetate and the sulfydryl can be within 1Da, so that the difference between the two reactions can be determined very accurately through the high-resolution mass spectrometry; accurate judgment on whether the disulfide bonds of the protein break can lay the foundation for relevant theoretical researches and provide theoretical foundation for modification of specific proteins and actual production.
Owner:JIANGXI NORMAL UNIV
Method for extracting proteins and polysaccharides from brassica rapa
The present invention relates to a method for extracting proteins and polysaccharides from brassica rapa. The method comprises the following steps: pretreatment is conducted: brassica rapa beating andultrasound treating are conducted to prepare slurry; enzymatic hydrolysis is conducted: snailase and iodoacetic acid are added to the slurry simultaneously and pH is also adjusted to be weakly acidic; heating is conducted, the weakly acidic slurry is slowly heated and then cooling to a normal temperature is conducted; centrifuging is conducted: the cooled slurry is centrifuged to obtain a clear solution; salting-out is conducted: then the pH of the clear solution is adjusted to be weakly acidic again, a mixed solution of a saturated solution of ammonium sulfate and a saturated solution of sodium sulfate is added at a suitable temperature, and even stirring and placing for layering are conducted; and protein and polysaccharide extraction is conducted: after the layering, precipitated liquid at a lower layer is subjected to multiple dialysis at a certain temperature to remove salts to obtain brassica rapa proteins, and a supernatant is dried to obtain brassica rapa polysaccharides. Themethod is a simple method to extract the proteins and polysaccharides from the brassica rapa simultaneously, besides, an average extraction rate of the proteins can reach 5.5% or more, and an averageextraction rate of the polysaccharides can reach 7.9% or more.
Owner:河北中科汉禧生物科技有限公司 +1
A kind of solid catalyst for synthesizing cyclic carbonate and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103521262BEffective fixed loadIncrease the number ofCatalyst carriersOrganic chemistryBromoacetic acidSilicon oxide
Owner:CHANGZHOU XIAOGUO INFORMATION SERVICES
Method for selectively increasing haloacid dehalogenase yield
InactiveCN105483095AIncrease productionStable outputHydrolasesMicroorganism based processesHydroxybutyric acid3-chloropropionic acid
The invention discloses a method for selectively increasing haloacid dehalogenase yield. Pseudomonas strains DEH138 are adopted according to a mechanism that inducers induce microorganisms to generate induced enzymes, and a proper carbon source is selected and optimized to specifically increase L-2-haloacid dehalogenase yield. To be more specific, inducer halogenated compounds (chloroacetic acid, iodoacetic acid, 2-propanoate, 2-chloropropionic acid, 2-bromopropionate, 3-chloropropionic acid, 2-chlorobutyric acid, 2-bromobutyric acid, 2-chloride propionamide and 2-bromide propionamide) are added in a logarithmic phase or synchronously in mineral basal media containing auxiliary carbon sources (glycolic acid, lactic acid, hydroxybutyric acid or glucose) respectively, so that induced expression of L-2-haloacid dehalogenase can be promoted; meanwhile, quantity of D-2-haloacid dehalogenases different in chiral selectivity is kept stable, and the L-2-haloacid dehalogenase yield is finally selectively increased. The method is a novel production mode for acquiring dehalogenases with chiral selectivity.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
A method for detecting whether a protein disulfide bond is broken
A method for detecting whether a protein disulfide bond is broken is to use iodoacetic acid to react with free sulfhydryl groups in the protein, remove unreacted iodoacetic acid by ultrafiltration, and then use dithiothreitol to cut the disulfide bond in the protein, and then Use iodoacetamide to react with the newly generated sulfhydryl groups, use trypsin to hydrolyze the protein into polypeptides, use high-resolution mass spectrometry to detect the mass-to-charge ratio information of the polypeptides, and compare them with the disulfide bond information of natural proteins to determine whether the disulfide bonds occur fracture. The present invention can be effectively used to determine whether sulfhydryl exists in the form of free or disulfide bonds; the mass difference caused by the reaction between iodoacetic acid and iodoacetamide and sulfhydryl is within 1 Da, so the high-resolution mass spectrometry can be used to determine the two very accurately. The accurate judgment of whether the protein disulfide bond is broken can lay the foundation for related theoretical research and provide a theoretical basis for specific protein modification and actual production.
Owner:JIANGXI NORMAL UNIV
Pyrococcus produced high temperature alpha-glucosidase and enzyme producing method thereof
The invention discloses a method for high temperature Alpha-glucosidase generated through hot coccus (Thermococcus sp.HJ21). The invention also discloses a high temperature Alpha-glucosidase product which is obtained through the method, and the optimum temperature for the high temperature Alpha-glucosidase to act is 100 DEG C; the high temperature Alpha-glucosidase is warmed for 4 hours at 80 DEG C and retained 90 percent of the high temperature Alpha-glucosidase vitality, and the high temperature Alpha-glucosidase is warmed for an hour at 90 DEG C and retained 80 percent of the high temperature Alpha-glucosidase vitality; the suitable action PH of the high temperature Alpha-glucosidase is 7.0; the high temperature Alpha-glucosidase is stable in the PH value of 5.0 to 8.0; Fe<3+>, K<+>, Ag<+>, DTT and EDTA have the activation to the high temperature Alpha-glucosidase, and Cu<2+>, Al<3+>, Ni<2+>, iodoacetic acid and SDS have the inhibitory action to the high temperature Alpha-glucosidase; and the high temperature Alpha-glucosidase vitality is absolutely inhibited through 1mM Hg<2+>. The high temperature Alpha-glucosidase obtained through the invention is mainly applied in the production of the oligoisomaltose in the industry, and used as the diastatic enzyme preparation which can produce the high glucose syrup with the Alpha-amylase together in the starch processing industry.
Owner:HUAIHAI INST OF TECH
Preparation of protein solid-phase alkylation reagent, solid-phase alkylation reagent and application
ActiveCN106632877BIncreased grafting capacityThe preparation process is simple and controllablePeptide preparation methodsAlkyl transferIodoacetic acid
The invention relates to a protein solid-phase alkylation reagent and its preparation and application. Using silica gel particles as a carrier, epoxy groups are modified on the surface of the carrier through atom free transfer polymerization, and then dendrites are modified accordingly by covalent bonding. The hydrophilic compounds polyethyleneimine and iodoacetic acid-N-succinamide ester were prepared as solid-phase alkylation reagents. The reagent can selectively react with the sulfhydryl group on the protein, and has the advantages of high stability, simple operation and rapid reaction. Compared with traditional alkylation reagents, using this reagent, proteins can be rapidly separated from other small molecules (such as sugars, salts, surfactants, lipids, etc.), improving the purity of proteins and significantly reducing the complexity of samples. Due to the good hydrophilicity of the surface of the reagent, the recovery rate of protein or enzymatic hydrolysis product can be significantly improved. Therefore, this reagent is suitable for the selective reaction and pretreatment of sulfhydryl groups in proteins extracted from cells, tissues, body fluids, and hair.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
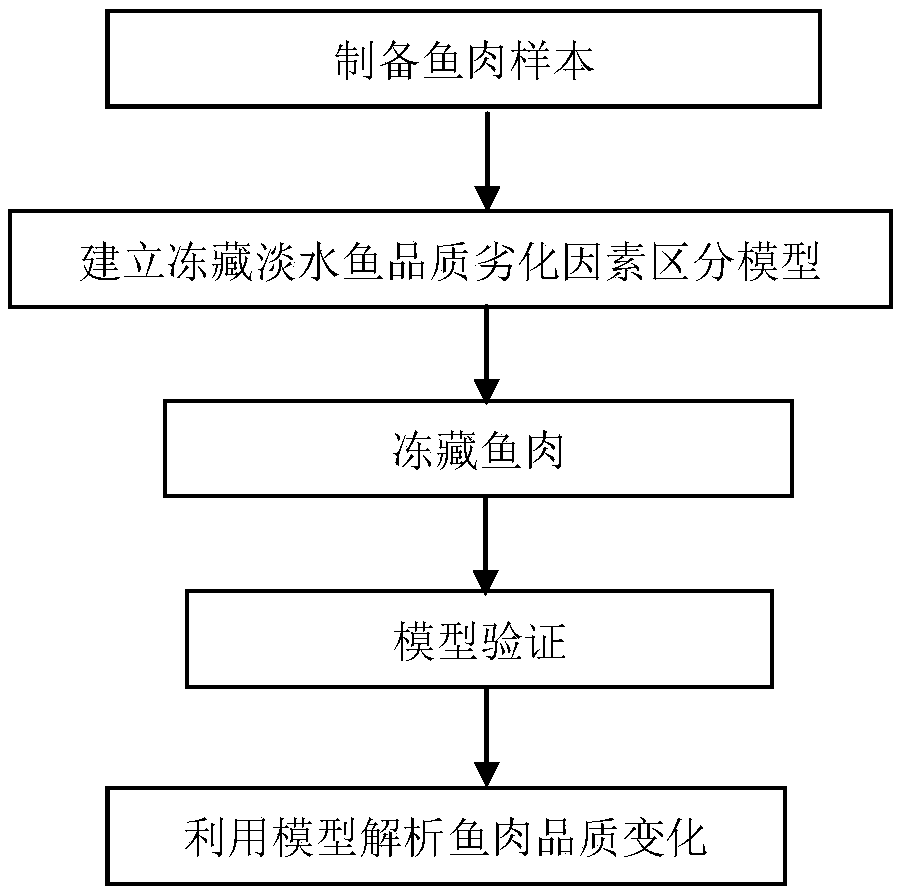
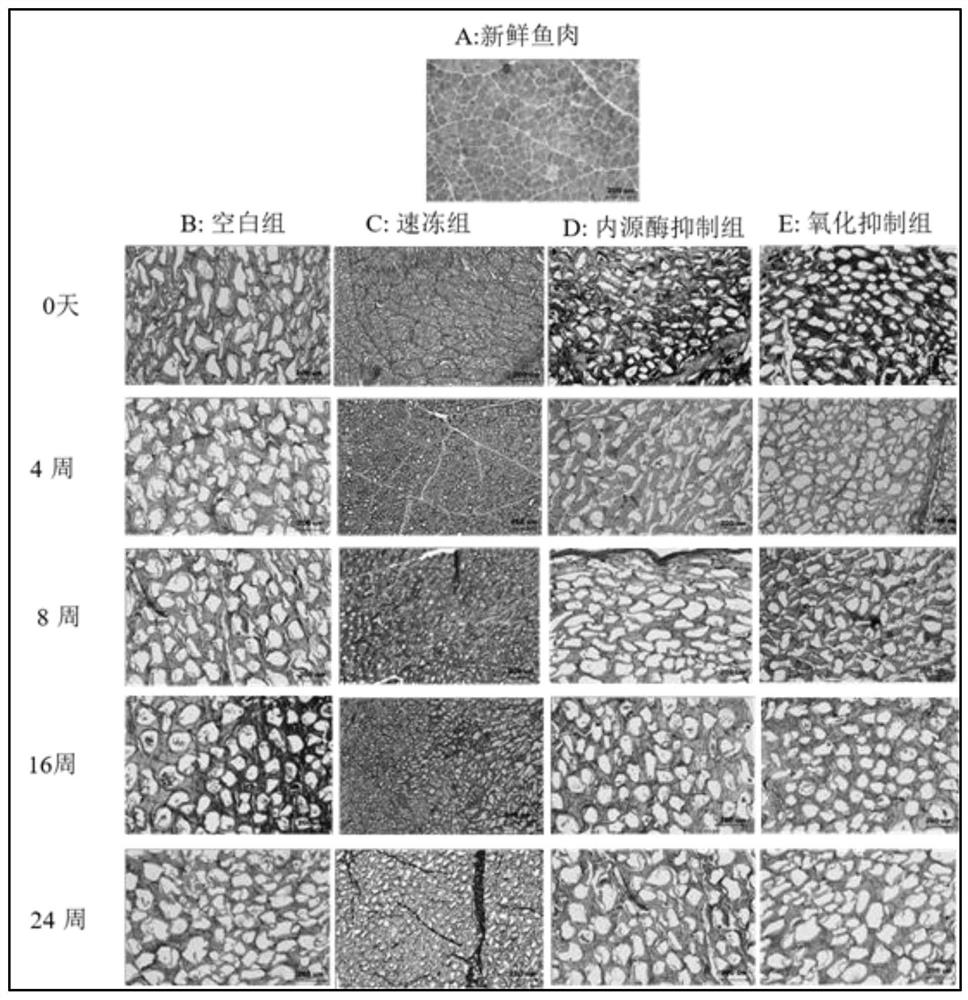
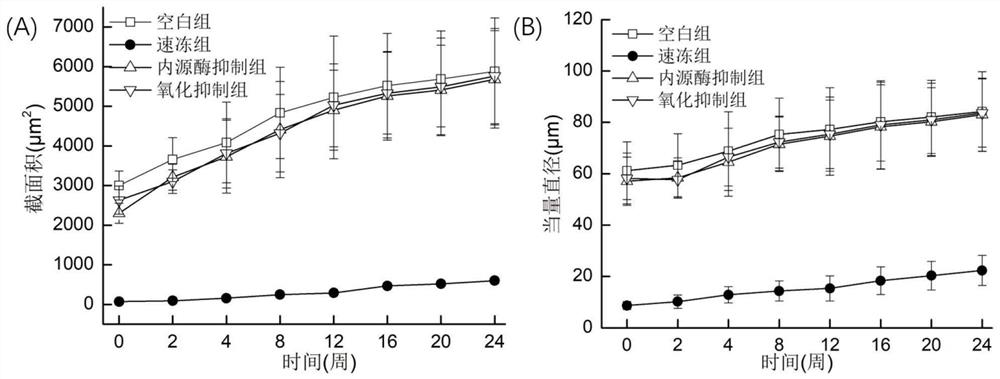
Model analysis method for distinguishing frozen storage fresh water fish meat quality degradation influence factor and application
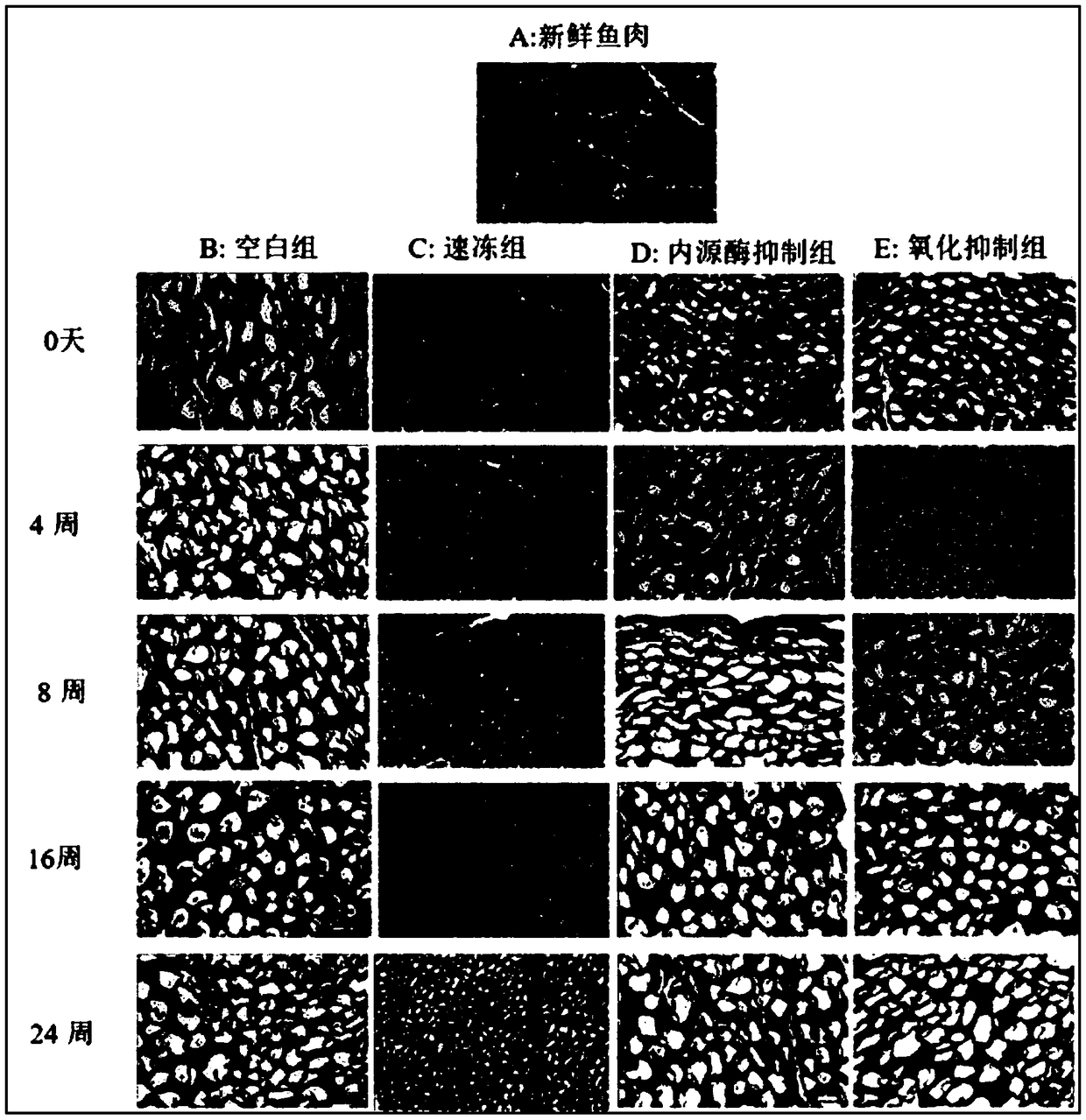
ActiveCN109444358AImprove preservationAvoid wastingPreparing sample for investigationMaterial analysis by optical meansFrozen storageFresh water organism
The invention discloses a model analysis method for distinguishing frozen storage fresh water fish meat quality degradation influence factors and application. The model analysis method comprises the following steps: taking fish meat samples; soaking a group A into water before freezing as a blank reference group; carrying out rapid freezing treatment on a group B with liquid nitrogen to inhibit generation of large ice crystals in the frozen storage process; treating a group C with iodoacetic acid to inhibit the activity of internal cathepsin in the frozen storage process; treating a group D with an antioxidant to inhibit an oxidation function in the frozen storage process; carrying out frozen storage on fish meat of all groups in a refrigerator at minus 5 DEG C or less; testing morphologychange of ice crystals of the fish meat of different groups in the frozen storage process; testing the activity of main internal cathepsin of the fish meat of different groups in the frozen storage process; testing the oxidation function of the fish meat of different groups in the frozen storage process; analyzing fish meat quality variation. By adopting the model analysis method, selective preservation is achieved according to storage demands, resource waste can be avoided, preservation conditions can be specifically selected, and the preservation effect can be improved.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method of Recovering Heavy Metal and Reagent for Recovery of Heavy Metal for Use in the Same
ActiveUS20130078726A1Variation in heavy metal recovery rate among samples is suppressedImprove reliabilitySemi-permeable membranesAnalysis using chemical indicatorsHeavy metal chelationIodoacetic acid
The present invention provides a method of recovering a heavy metal by which the variation in heavy metal recovery rate among samples can be suppressed. A mixture of a sample and a chelating agent capable of chelating with a heavy metal is prepared. A complex between a heavy metal being in the sample and the chelating agent is formed in the presence of a masking agent for a thiol group in the mixture. The heavy metal in the sample is recovered by recovering the complex. By this method, a heavy metal can be recovered with suppressing the variation in the recovery rate among samples. The chelating agent preferably is 1,5-diphenyl-3-thiocarbazone (dithizone). As the masking agent, N-ethylmaleimide, iodoacetamide, iodoacetic acid, or the like can be used.
Owner:ARKRAY INC
Enrichment method of thiosulfated peptides
ActiveCN106854231AHigh bonding capacityEasy to operatePeptide preparation methodsEnrichment methodsHydrolysate
The invention relates to an enrichment method of thiosulfated peptides, and applications thereof. According to the enrichment method, a polyaminodendritic polymer is taken as a carrier, covalent modification with iodoacetic acid-N-succinamide is carried out so as to prepare a water soluble high-molecular compound capable of realizing selective reaction with mercapto peptides; the water soluble high-molecular compound is mixed with a protein enzymatic hydrolysate fully, an obtained product is placed on an ultrafiltration membrane, selective blocking of the mercapto peptides on the ultrafiltration membrane is realized via high speed centrifugation; and at last, a disulfide bond reducing agent is added onto the ultrafiltration membrane to realize selective release of the thiosulfated peptides from the high-molecular compound at a certain temperature; and the thiosulfated peptides are obtained via high speed centrifugation. Operation of the enrichment method is simple; flux is high; selectivity is high; and the enrichment method is used for large-scale enrichment of the thiosulfated peptides in complex proteome samples.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method of recovering heavy metal and reagent for recovery of heavy metal for use in the same
ActiveUS9873925B2Variation in heavy metal recovery rate among samples is suppressedImprove reliabilitySemi-permeable membranesAnalysis using chemical indicatorsHeavy metal chelationIodoacetic acid
The present invention provides a method of recovering a heavy metal by which the variation in heavy metal recovery rate among samples can be suppressed. A mixture of a sample and a chelating agent capable of chelating with a heavy metal is prepared. A complex between a heavy metal being in the sample and the chelating agent is formed in the presence of a masking agent for a thiol group in the mixture. The heavy metal in the sample is recovered by recovering the complex. By this method, a heavy metal can be recovered with suppressing the variation in the recovery rate among samples. The chelating agent preferably is 1,5-diphenyl-3-thiocarbazone (dithizone). As the masking agent, N-ethylmaleimide, iodoacetamide, iodoacetic acid, or the like can be used.
Owner:ARKRAY INC
Preparation method of glycine
InactiveCN109206329AAvoid energy-consuming cumbersome linksHigh yieldOrganic compound preparationAmino-carboxyl compound preparationIodideEvaporation
The invention discloses a preparation method of glycine, and belongs to a preparation method of amino acid. The preparation method comprises two-step reactions of replacement and ammoniation. The preparation method comprises the following specific steps: firstly performing a replacement desalting reaction between chloroacetic acid and an alcoholic solution of iodide under the heating condition, and then centrifuging or filtering after the reaction to respectively obtain chloride and an alcoholic solution of iodoacetic acid; and adding a catalyst into the alcoholic solution of iodoacetic acid,heating and introducing ammonia gas for ammoniation, and centrifuging or filtering after the reaction to respectively obtain glycine and a catalyst-containing alcoholic solution of iodide. The reaction liquid can be recycled, cumbersome energy-consuming links such as organic solvent extraction, rectification, evaporation, etc. can be saved; waste liquids that need environmental protection treatment are not generated; and yield and purity of the product can be improved. The preparation method has the following advantages: production cost is low; operation is simple; raw materials are easily available; and the preparation method meets the clean and environmental protection requirements and is suitable for industrial large-scale production.
Owner:刘笃琏
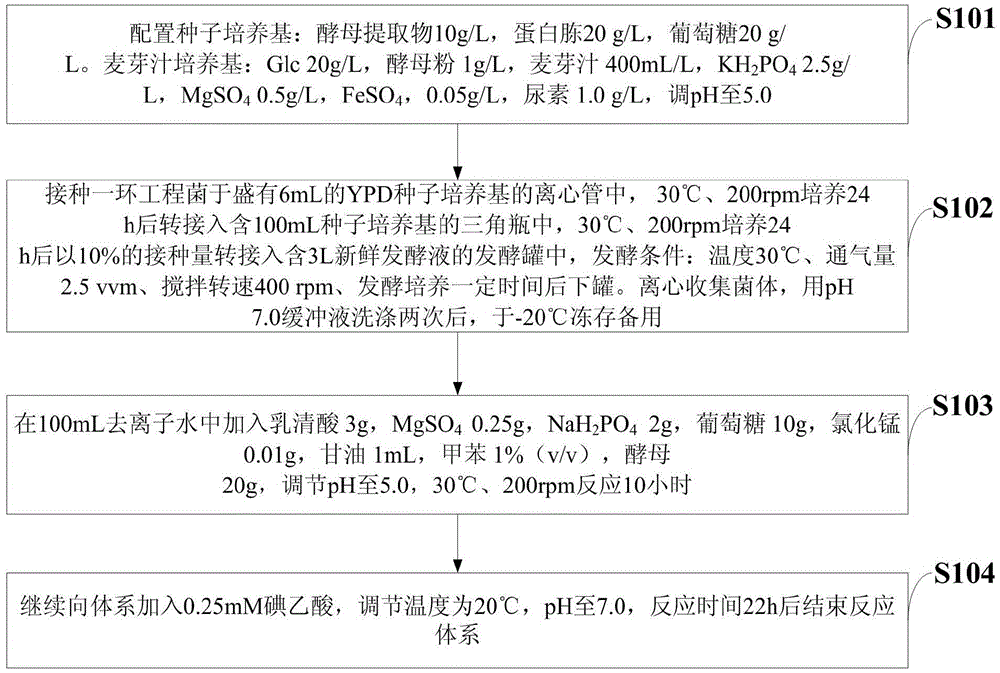
Fermentation technique for improving yield of uridylic acid produced by saccharomyces cerevisiae engineered strain
InactiveCN105524960AHigh yieldImprove the ability to produce UMPSugar food ingredientsMicroorganism based processesGlycerolFermentation
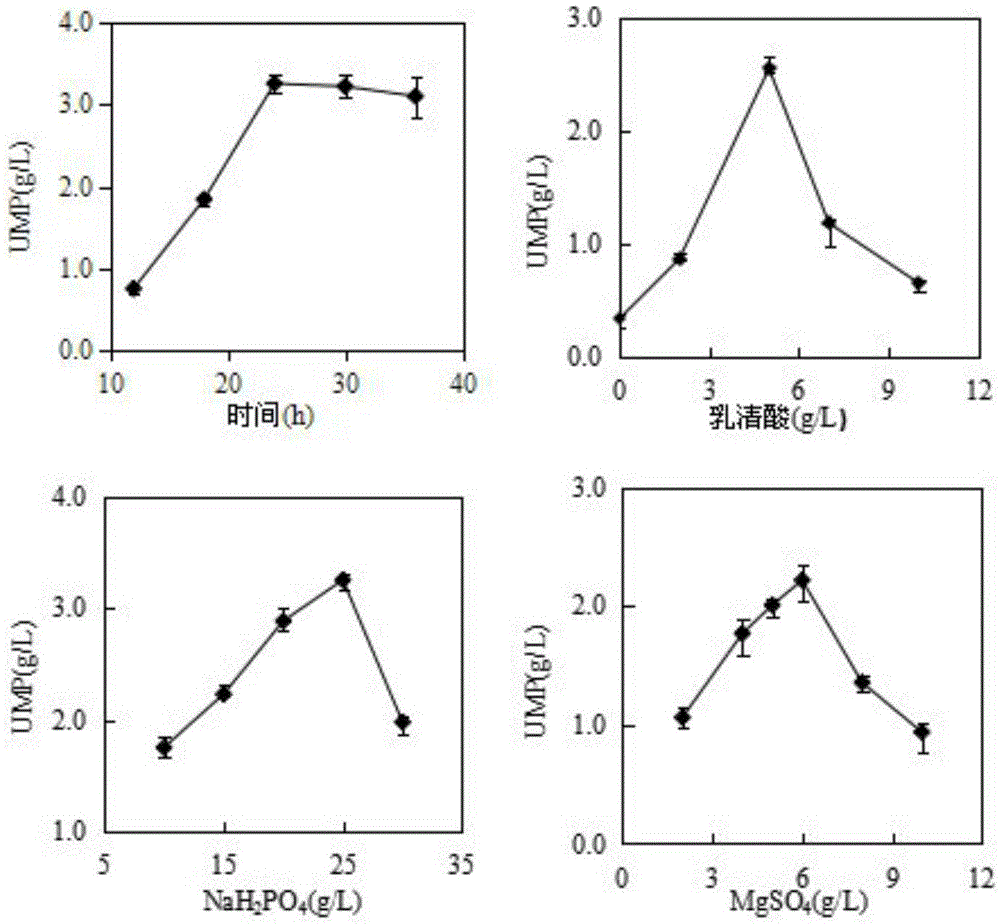
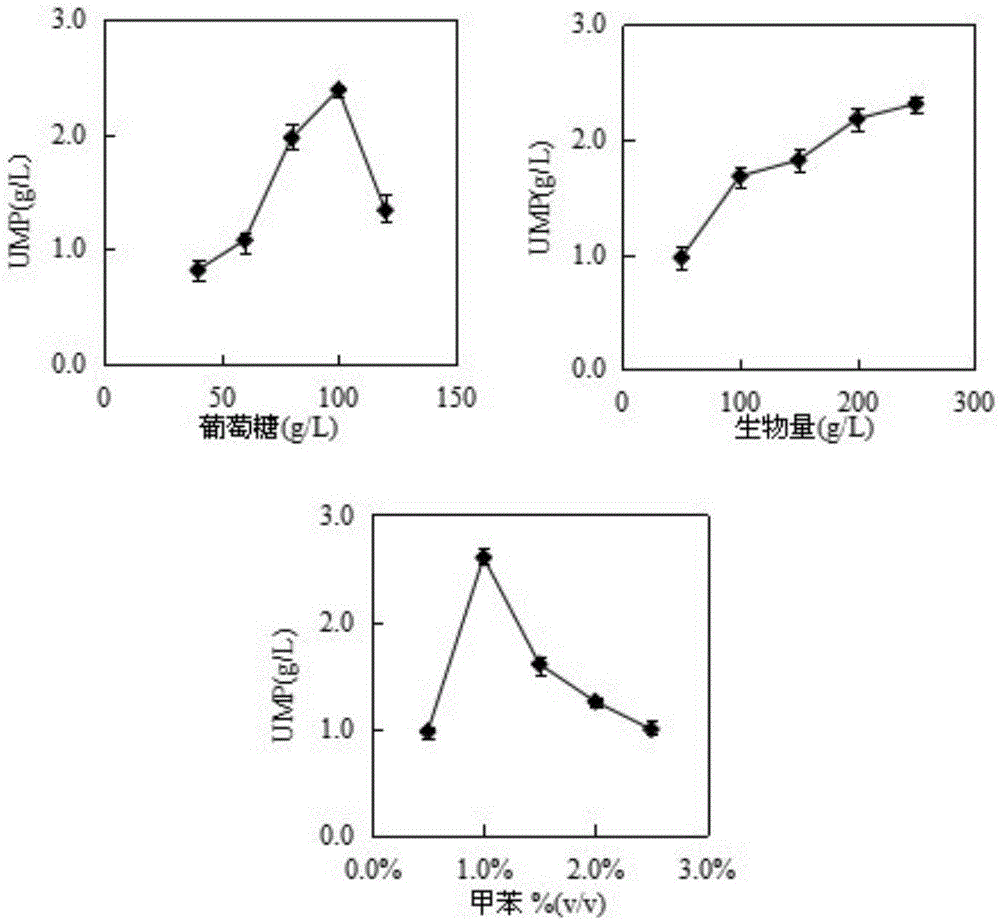
The invention discloses a fermentation technique for improving yield of uridylic acid produced by a saccharomyces cerevisiae engineered strain. The fermentation technique comprises the following steps: preparing a malt extract medium; adding 1-5g of orotic acid, 0.1-0.3g of MgCl2, 1-2g of KH2PO4, 5-15g of glucose, 0.005-0.02g of manganese chloride, 1mL of glycerol, 0.5-2% (v / v) of methylbenzene and 15-25g of a yeast to 100mL of de-ionized water, regulating pH to 5.0, and reacting at 30 DEG C under 200rpm for 10h; and continuing to add 0.2-0.5mM of iodoacetic acid to the system, regulating temperature to 20 DEG C and pH value to 7.0, and ending the reaction system after reacting for 20-25h. By virtue of the method disclosed by the invention, the yield of the uridylic acid produced by the engineered strain is improved; and the method is applicable to the industries of functional food, health care products and medicines.
Owner:BEIJING TECHNOLOGY AND BUSINESS UNIVERSITY
Pancreatic islet in-vitro culture surface parenchyma cell treatment method
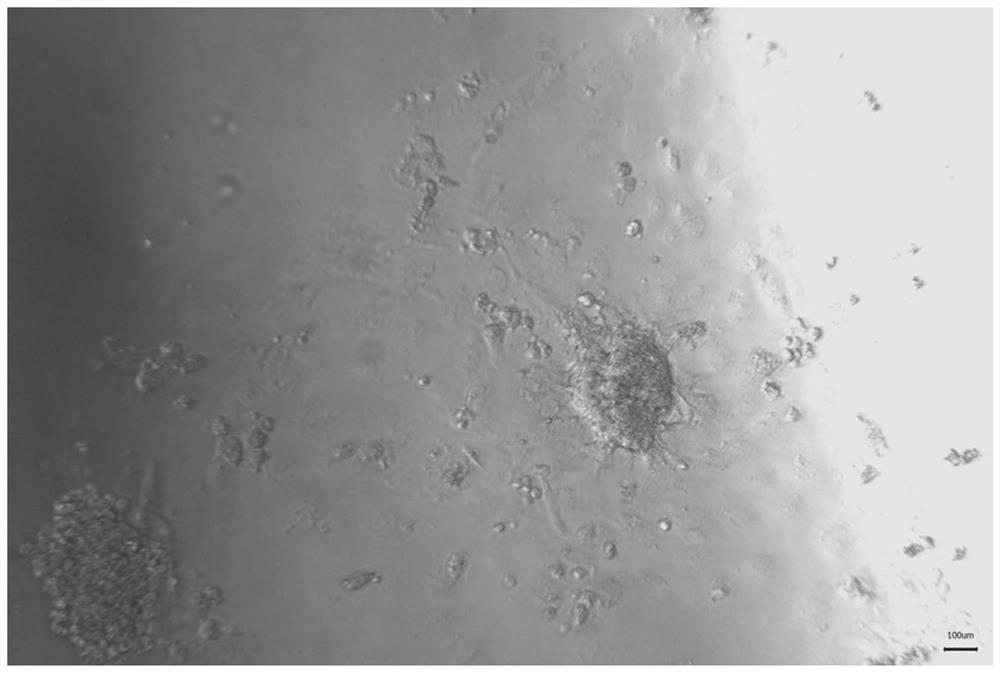
PendingCN113308433AAvoid damageReduce subsequent experimental stepsPancreatic cellsCulture processIodoacetic acidPancreas
The invention discloses a pancreatic islet in-vitro culture surface parenchyma cell treatment method. The method specifically comprises the following steps: adding iodoacetic acid with a proper concentration into an islet culture medium for culturing islet, and culturing for a period of time. The strong destructive effect of iodoacetic acid on cell membranes and the inhibition capability of iodoacetic acid on cell glycolysis are utilized, and hybrid cells (especially fibroblasts) on the surfaces of pancreas islets are treated by adjusting the concentration of iodoacetic acid in the culture medium and controlling the treatment time, so that subsequent experiment steps are reduced, and cell damage is reduced.
Owner:立沃生物科技(深圳)有限公司
A model analysis method and its application to distinguish the factors affecting the quality deterioration of frozen freshwater fish meat
ActiveCN109444358BImprove preservationAvoid wastingPreparing sample for investigationMaterial analysis by optical meansAnimal scienceIodoacetic acid
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Pyrococcus produced high temperature alpha-glucosidase and enzyme producing method thereof
Owner:HUAIHAI INST OF TECH
Method for high-throughput screening of high-yield sophorolipid strains
PendingCN111560367AHigh mutation rateHigh positive mutation rateBacteriaMutant preparationBiotechnologyIodoacetic acid
The invention discloses a method for high-throughput screening of high-yield sophorolipid strains. The method comprises the following steps: activating strains; carrying out combined mutagenesis on normal-pressure room-temperature plasma and sodium nitrite; carrying out relaxation culture; and carrying out multi-pressure culture; wherein the strain is candida mycoderma bacteria; in the step of multi-pressure culture, iodoacetic acid and malonic acid are combined for dual-pressure culture screening. According to the method, normal-pressure room-temperature plasma and sodium nitrite are combinedfor mutagenesis, relaxation culture is combined with double pressures of iodoacetic acid and malonic acid for screening, the mutation rate and the positive mutation rate of the strain are increased,the probability of obtaining the high-yield strain is increased, and then the high-yield strain with good genetic stability is obtained.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
Modified polyacrylonitrile ultra-filtration membrane, preparation method and application
InactiveCN112755788AImprove performanceImprove hydrophilicityMembranesUltrafiltrationPolymer scienceIodoacetic acid
The invention discloses a modified polyacrylonitrile ultra-filtration membrane, a preparation method and application, and belongs to the technical field of membrane preparation, the preparation method comprises the following steps: firstly preparing tetrazole grafted polyacrylonitrile, then grafting iodoethane, iodoacetic acid or 2-iodoethanol on the tetrazole grafted polyacrylonitrile, and performing membrane scraping to prepare the modified polyacrylonitrile ultra-filtration membrane. The anti-pollution performance is improved while the rejection rate is improved, and the overall performance of the ultra-filtration membrane is optimized.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Process for the production of acetic acid
ActiveCN106715379BEasy to understandOrganic compound preparationPreparation from carboxylic acid esters/lactonesIodoacetic acidDistillation
Owner:CELANESE INT CORP
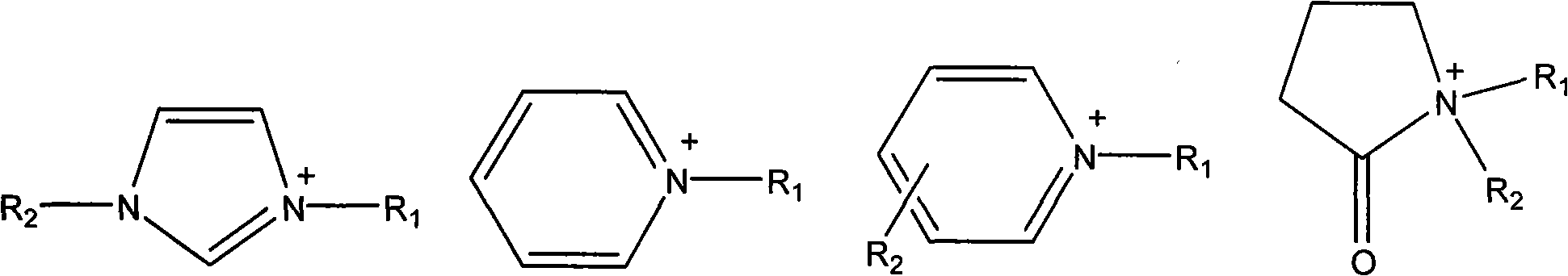
Ionic liquid containing cinnamyl functional groups and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101671304AImprove solubilityGood electrical and thermal conductivityOrganic chemistrySulfate radicalsTetrafluoroborate
The invention relates to ionic liquid containing cinnamyl functional groups and a preparation method thereof. The ionic liquid has a general formula of R<+>Y<->, wherein R is substituted or unsubstituted iminazole, pyridine or pyrrolidone containing cinnamyl functional groups, and Y is selected from chlorine, bromine, iodine, acetate radical, sulfate radical, phosphate radical, nitrate radical, thiocyanate radical, tetrafluoroborate radical, hexafluorophosphate racial, toluenesulfonate radical, and the like. The ionic liquid is a favorable novel green chemical material and has wide applicationprospects in the fields of organic synthesis, medicines, new materials, and the like. The preparation method has the advantages of convenient and easily-obtained raw materials, simple preparation process, mild reaction conditions, high production rate, simple after-treatment, green and environmental protection and the like and provides a foundation for researching and developing novel functionalionic liquid and industrial production application thereof.
Owner:TIANJIN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
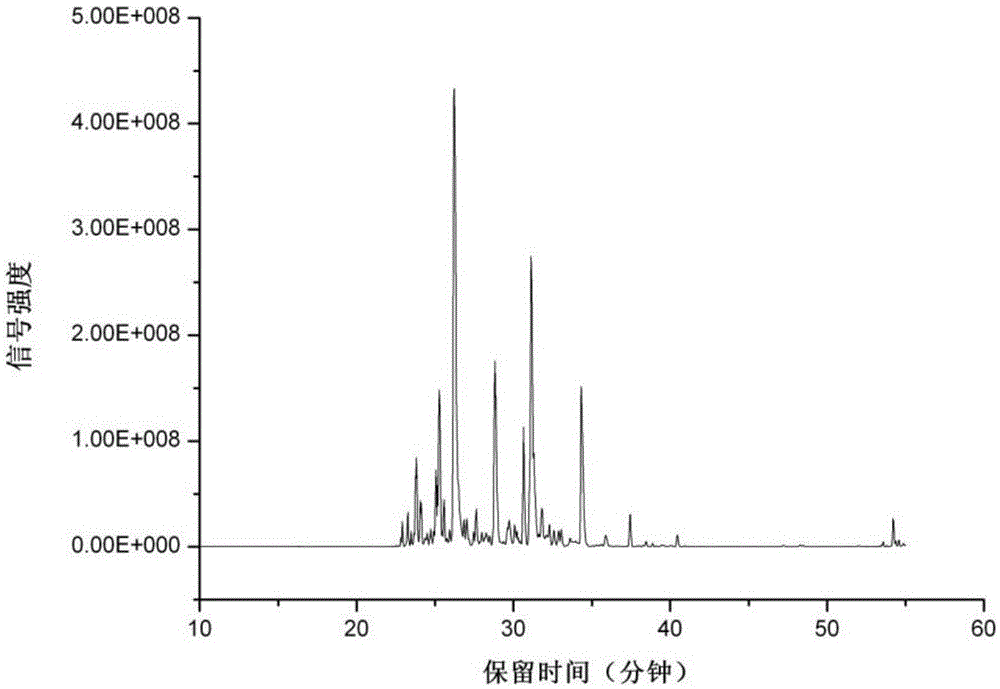
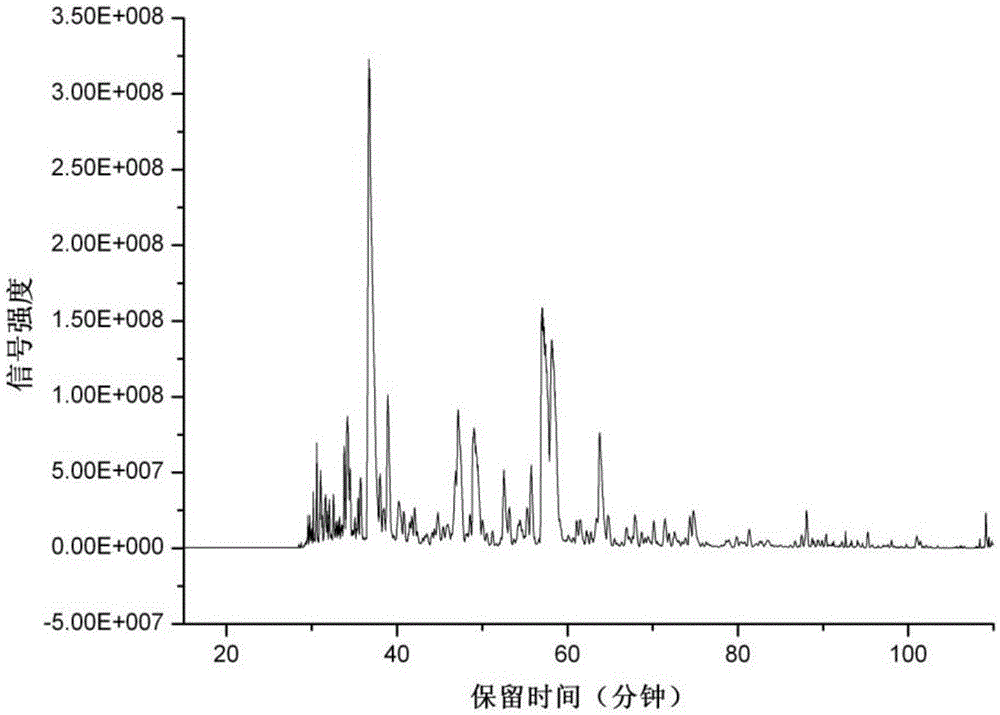
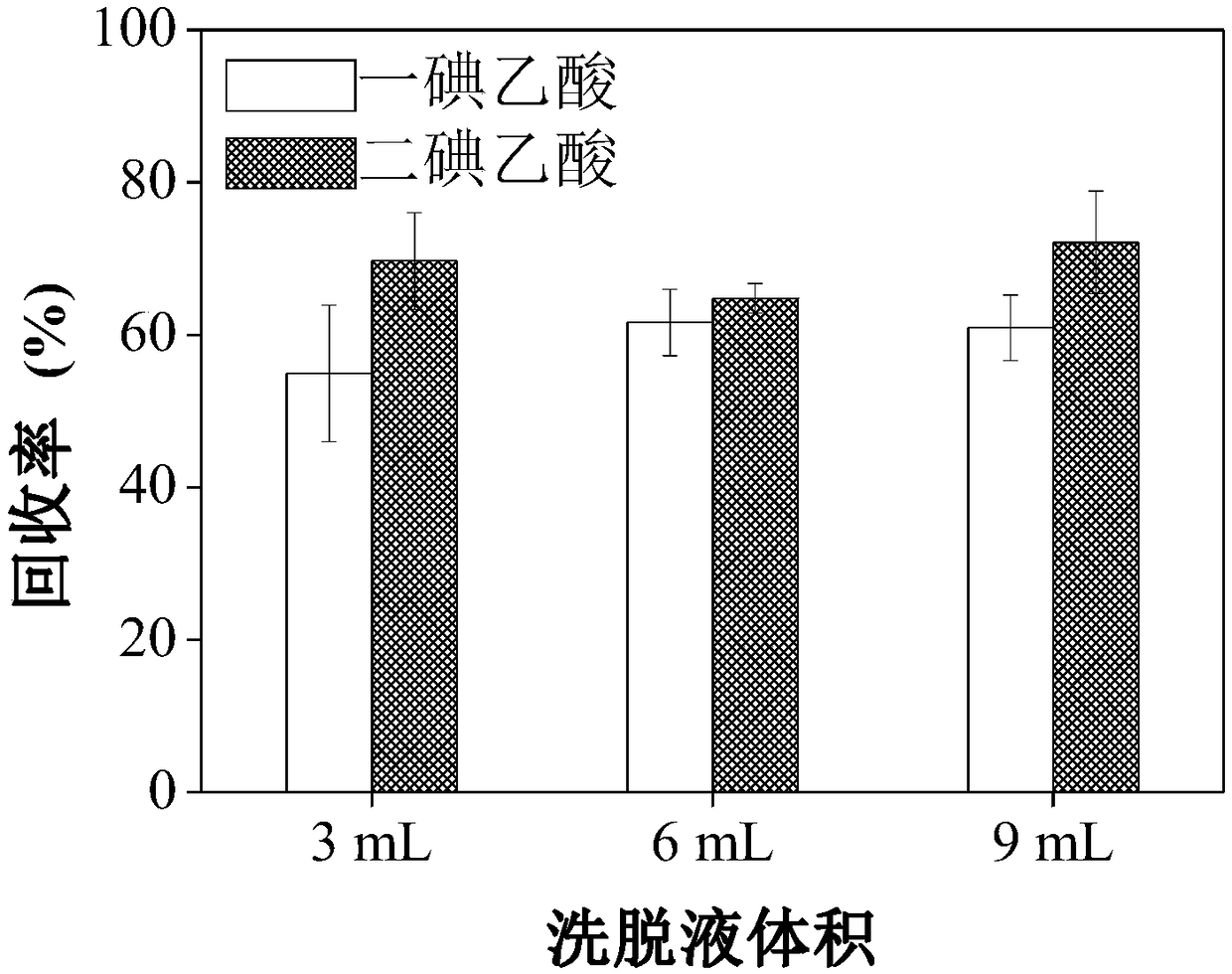
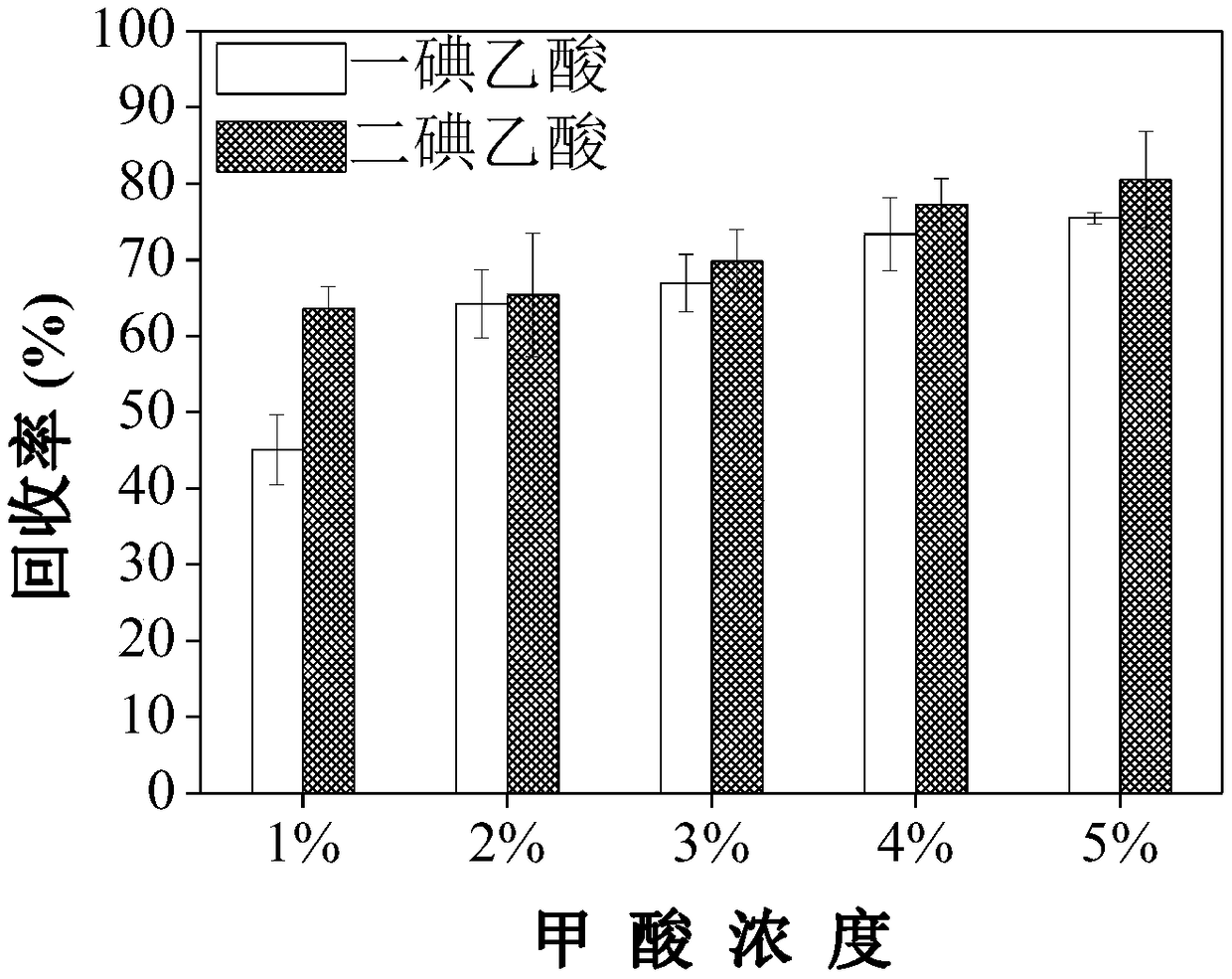
Analysis method for simultaneously detecting iodoacetic acid and aromatic iodide disinfection by-product in water
InactiveCN109212081AHigh recovery rateSimple and fast operationComponent separationAcetic acidDisinfection by-product
The invention discloses an analysis method for simultaneously detecting iodoacetic acid and aromatic iodide disinfection by-products in water, belongs to the field of chemical analysis, and solves theproblems in the existing liquid-liquid extraction method of low iodoacetic acid recovery rate, high detection limit and the like. The analysis method takes an Oasis MAX (Waters) column as a solid phase extraction column, and optimizes the extraction conditions including eluent component, eluent volume, sample pH and the like, wherein the recovery rates of monoiodoacetic acid and diiodoacetic acidare all greater than 70%. Compared with the traditional liquid-liquid extraction method, the analysis method for simultaneously detecting the iodoacetic acid and aromatic iodide disinfection by-products in water is more suitable for analyzing the iodoacetic acid in water, is also suitable for the analysis of the aromatic iodide disinfection by-products in water, and is simple and convenient to operate, and high in recovery rate, sensitivity and accuracy.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Process for the production of acetic acid
ActiveUS10550059B2Carboxylic preparation from carbon monoxide reactionCarboxylic compound separation/purificationPtru catalystReaction rate
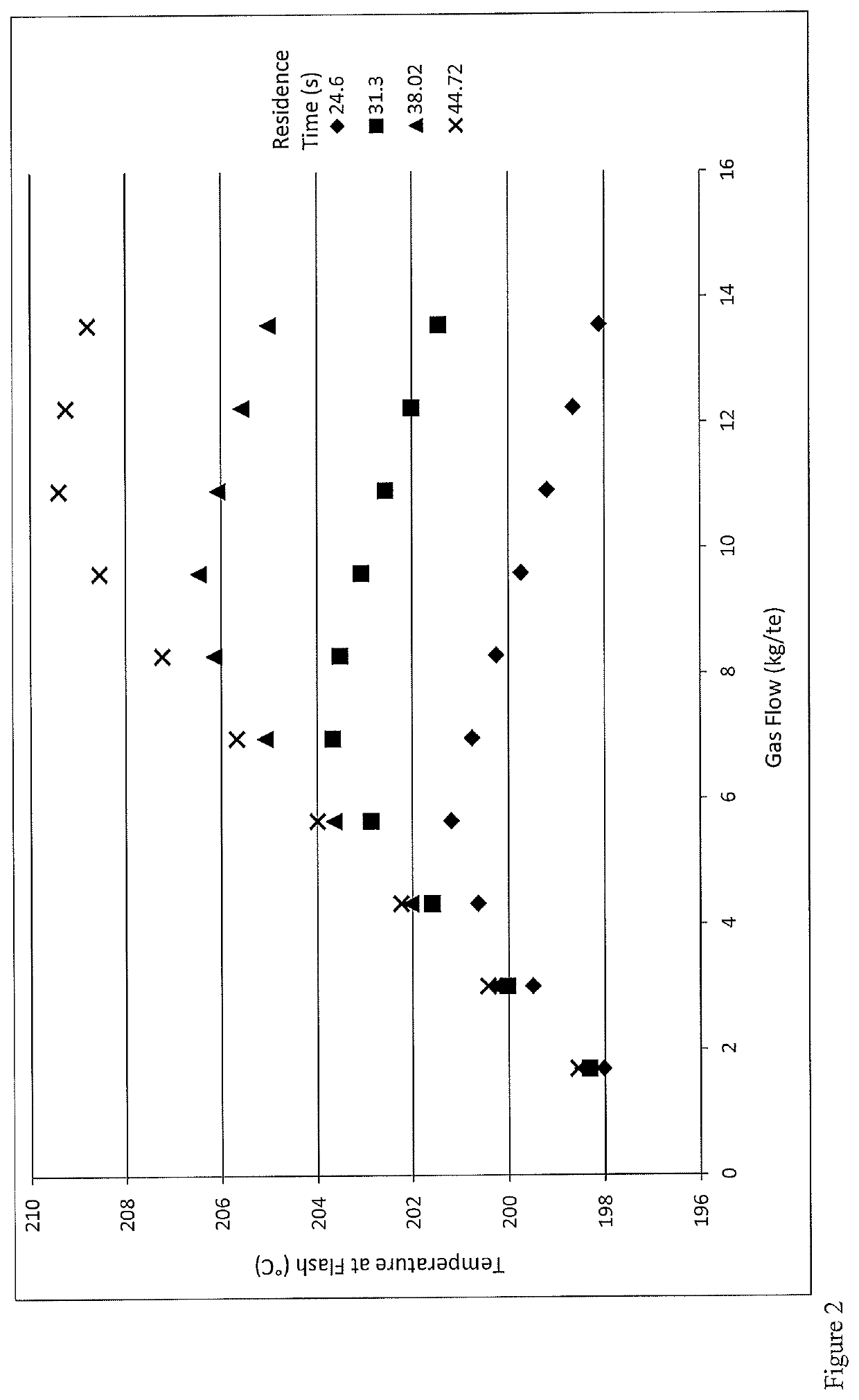
A process for the production of acetic acid which process comprises the steps of. (a) introducing methanol and / or a reactive derivative thereof and carbon monoxide into a first reaction zone containing a liquid reaction composition comprising a carbonylation catalyst, optionally a carbonylation catalyst promoter, methyl iodide, methyl acetate, acetic acid and water, (b) withdrawing at least a portion of the liquid reaction composition from the first reaction zone; (c) passing at least a portion of the withdrawn liquid reaction composition to a second reaction zone, wherein a gas feed comprising carbon monoxide is added to the liquid reaction composition withdrawn from the first reaction zone at one or more points upstream of the second reaction zone, one or more points within the second reaction zone, or a combination of one or more points upstream of the second reaction zone and one or more points within the second reaction zone; and (d) passing at least a portion of the liquid reaction composition from the second reaction zone into a flash separation zone to form: a vapour fraction, which comprises acetic acid, methyl iodide, methyl acetate and low pressure off-gas; and, a liquid fraction, which comprises carbonylation catalyst and optional carbonylation catalyst promoter; wherein the flow rate in kg of gas feed comprising carbon monoxide which is added to the second reaction zone per tonne of liquid reaction composition being passed to the flash separation zone (kg / te), is in the range of from 0.5FG to 1.2FG, wherein FG is defined according to equation 1: (1) FG=(0.296086962×tr)+(0.369636×RR)+(0.295878701×GP0.8134)−23.3448 wherein, tr is the residence time (seconds) of the liquid reaction composition within the second reaction zone which is calculated using equation 2: (2) tr=V2 / Ff wherein, V2 is the volume of the second reaction zone (m3) and Ff is the volumetric flow rate of liquid reaction composition to the flash separation zone (m3 / s), RR is the reaction rate of the liquid reaction composition passed to the second reaction zone at the temperature at which it is withdrawn from the first reaction zone (mol / litre / hour), and Gp is the purity of the gas feed comprising carbon monoxide which is added to the second reaction zone expressed as the mass fraction of carbon monoxide in the gas feed.
Owner:INEOS ACETYLS UK LTD
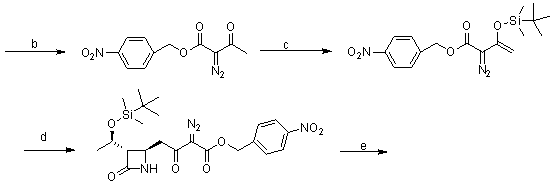
Synthesis method of panipenem and intermediates thereof
The invention discloses a synthesis method of panipenem and intermediates thereof. The synthesis method comprises the following steps of: synthesizing intermediates 4R-[4a,5b,6b(R)]-carbonyl-6-(1-hydroxyethyl)-7-oxo-1-aza bicyclo[3.2.0] hept-2-ene-2-benzyl carboxylate (compound VII) and N-benzyl formate-3-(S)-3-mercaptopyrrolidine (compound VIII); and activating methylene with an iodization method to finally synthesize panipenem. In the method, high-danger azide or high-cost diphenyl iodoacetic acid is not used, and benzyl alcohol and benzyl chloroformate are used for replacing p-nitro benzylalcohol and p-nitro benzyl chloroformate used in the traditional process, thus the synthesis method has good reaction effect and low cost.
Owner:湖南欧亚药业有限公司
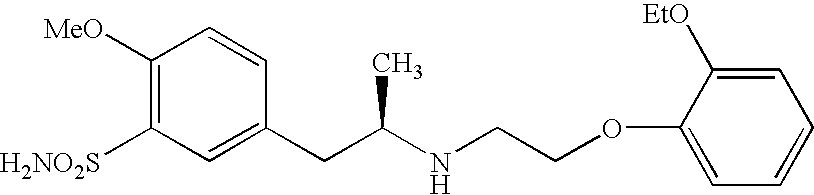
Method of preparing optically pure phenethylamine derivatives
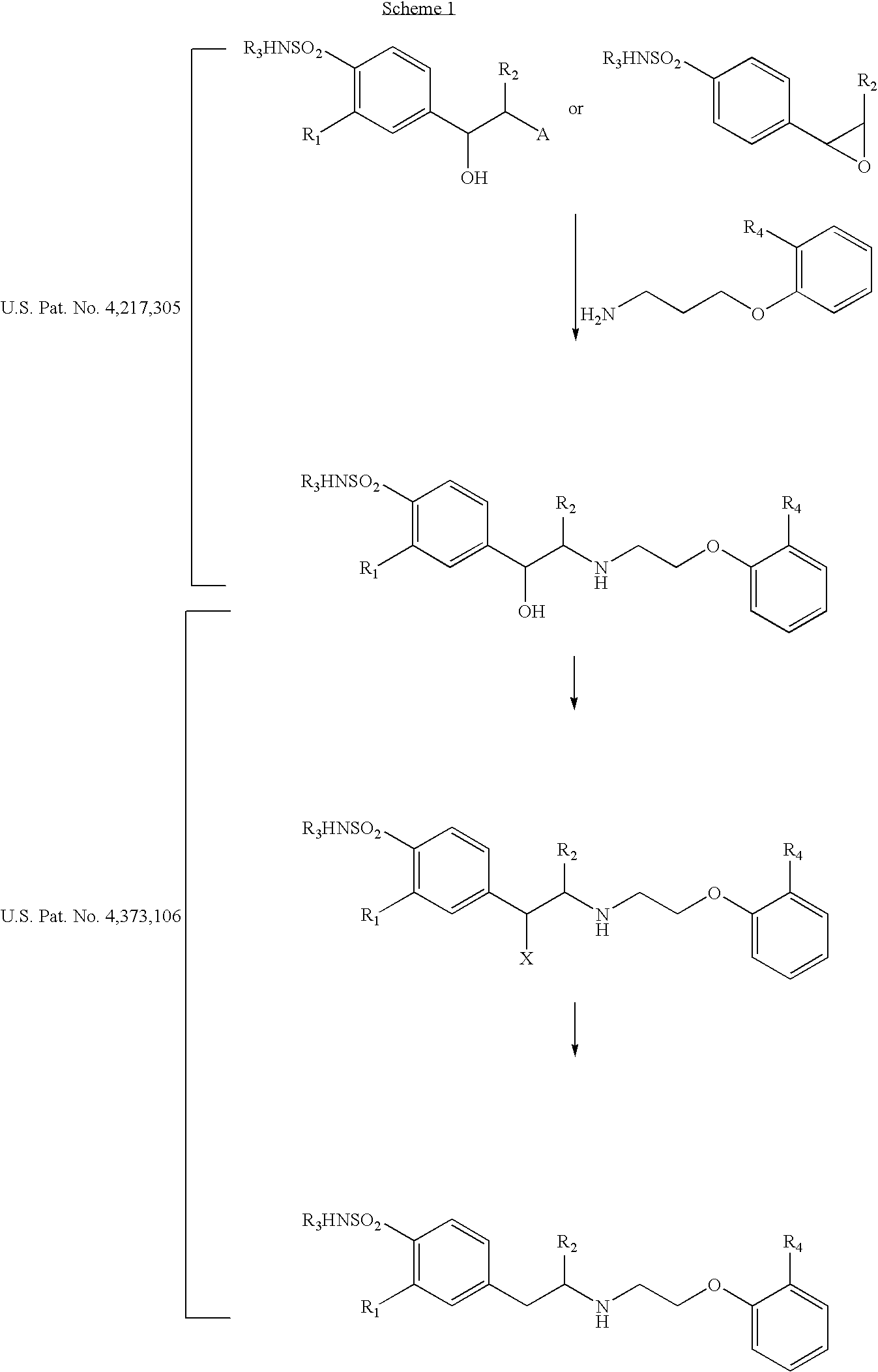
InactiveUS7329780B2Improve efficiencyOrganic compound preparationOrganic chemistry methodsIodoacetic acidFluoroacetic acid
Provided is a method of preparing an optically pure compound having formula 1 or its salts. The method includes: reacting (R)-2-(4-methoxy-3-aminosulfonyl-phenyl)-1 -methylethylamine or its salts with a compound selected from the group consisting of chloroacetic acid, bromoacetic acid, fluoroacetic acid, iodoacetic acid, α-halogenoacetic acid anhydride, and α-halogenoacetyl halide in the presence of a base or an acylating agent.
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com