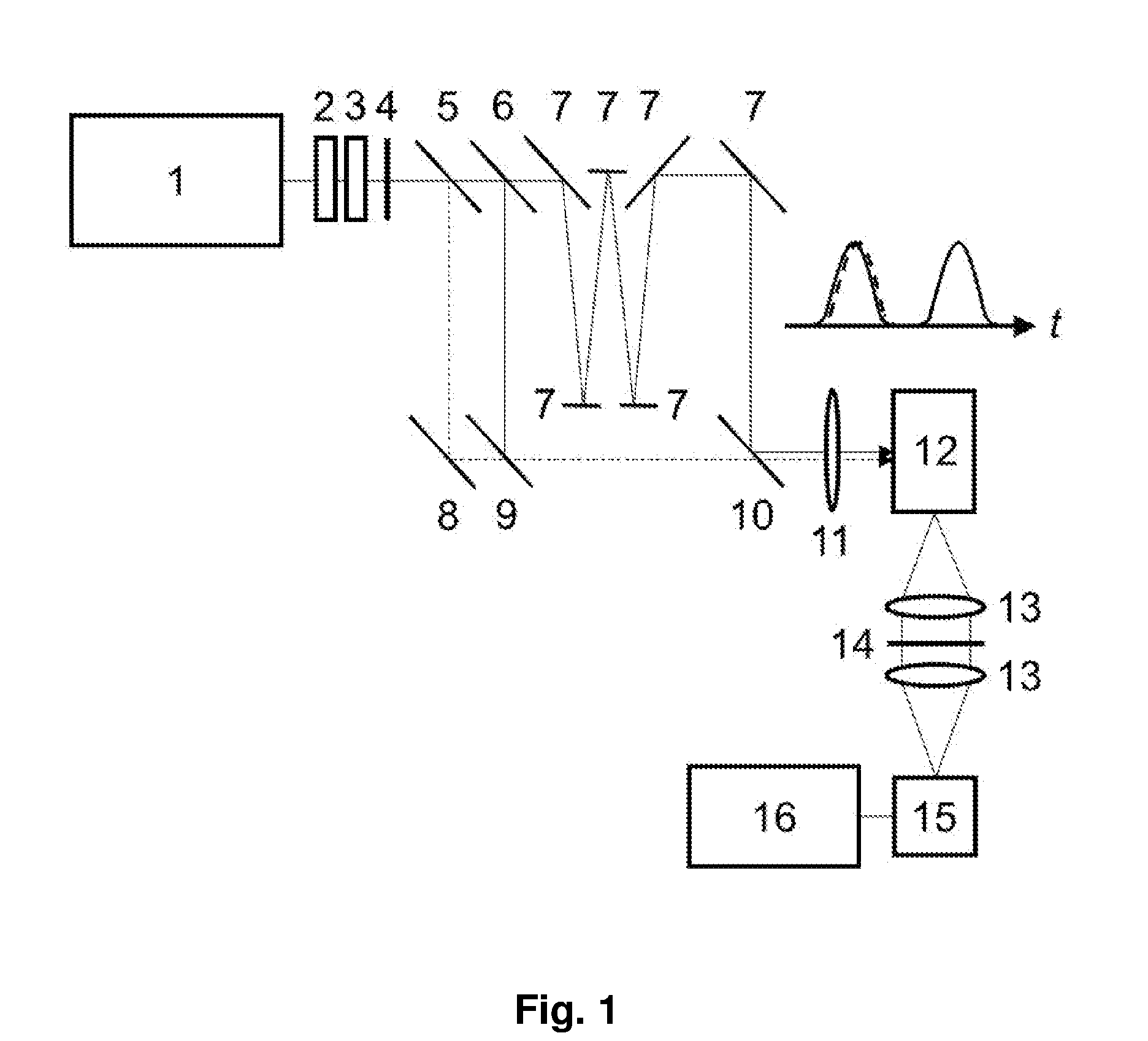
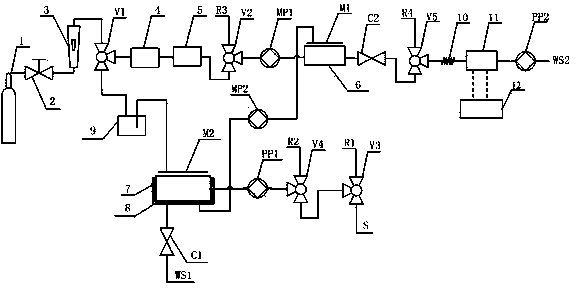
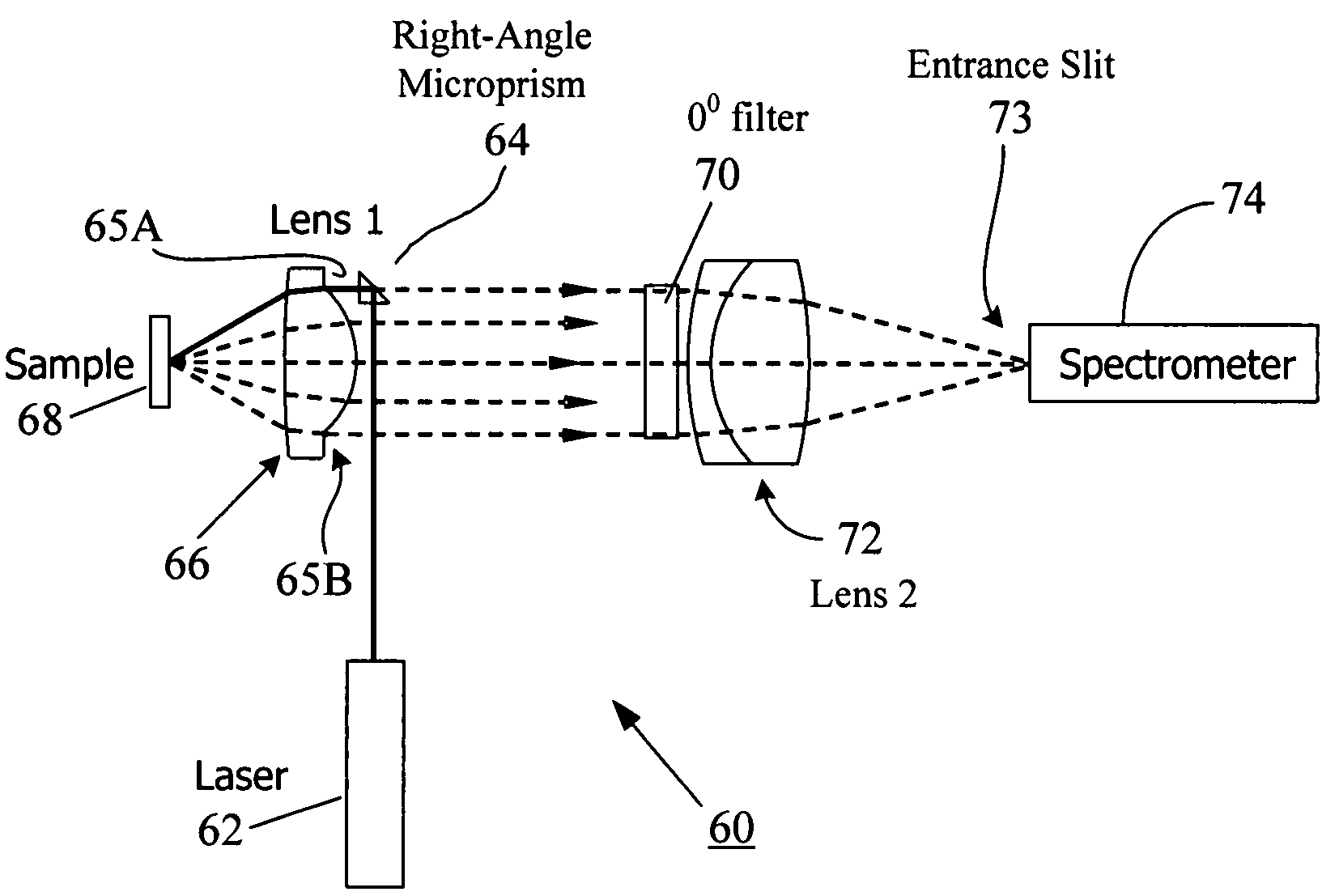
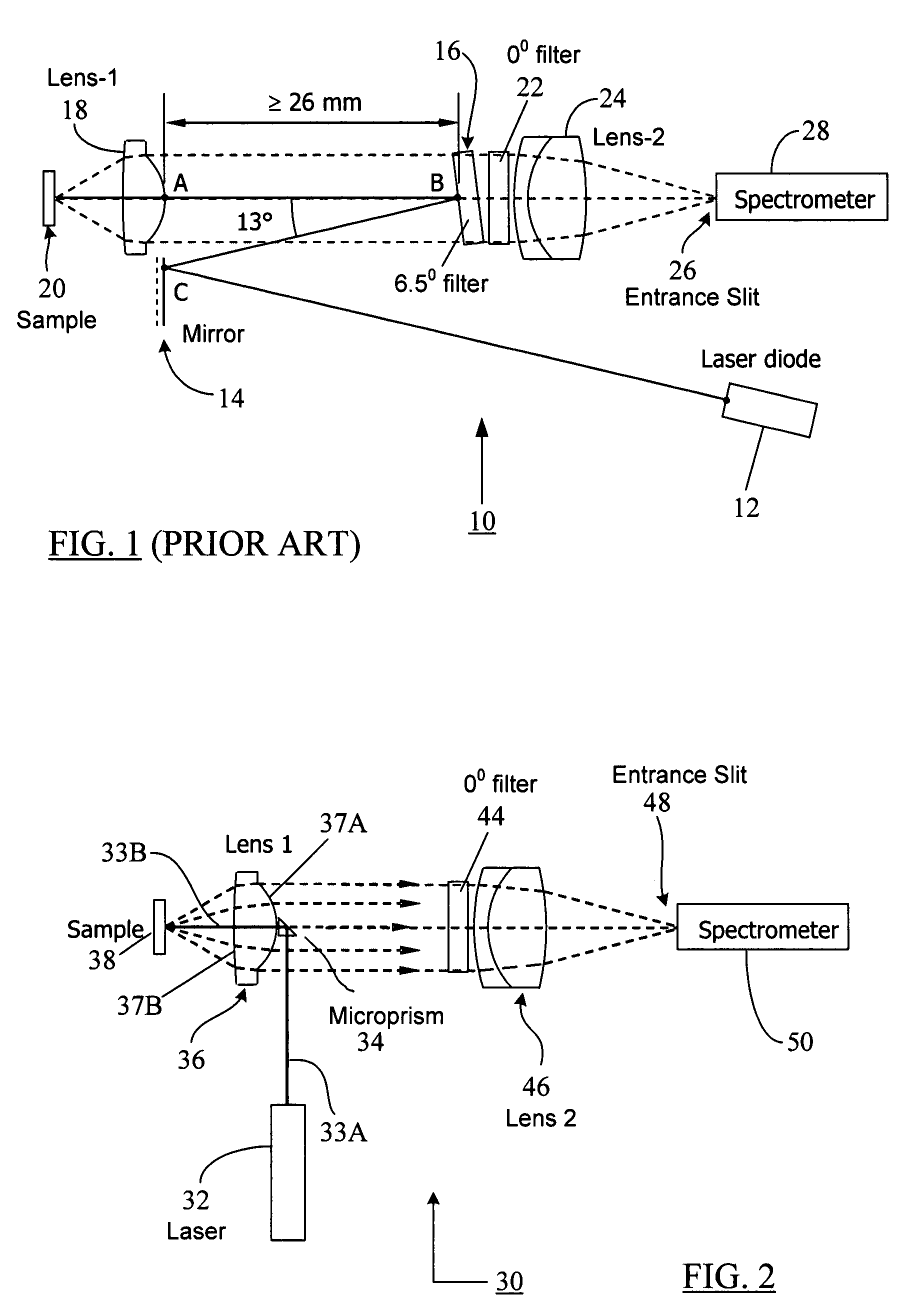
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
321 results about "Fluorescence Spectrophotometry" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Fluorescence spectroscopy (also known as fluorometry or spectrofluorometry) is a type of electromagnetic spectroscopy that analyzes fluorescence from a sample.
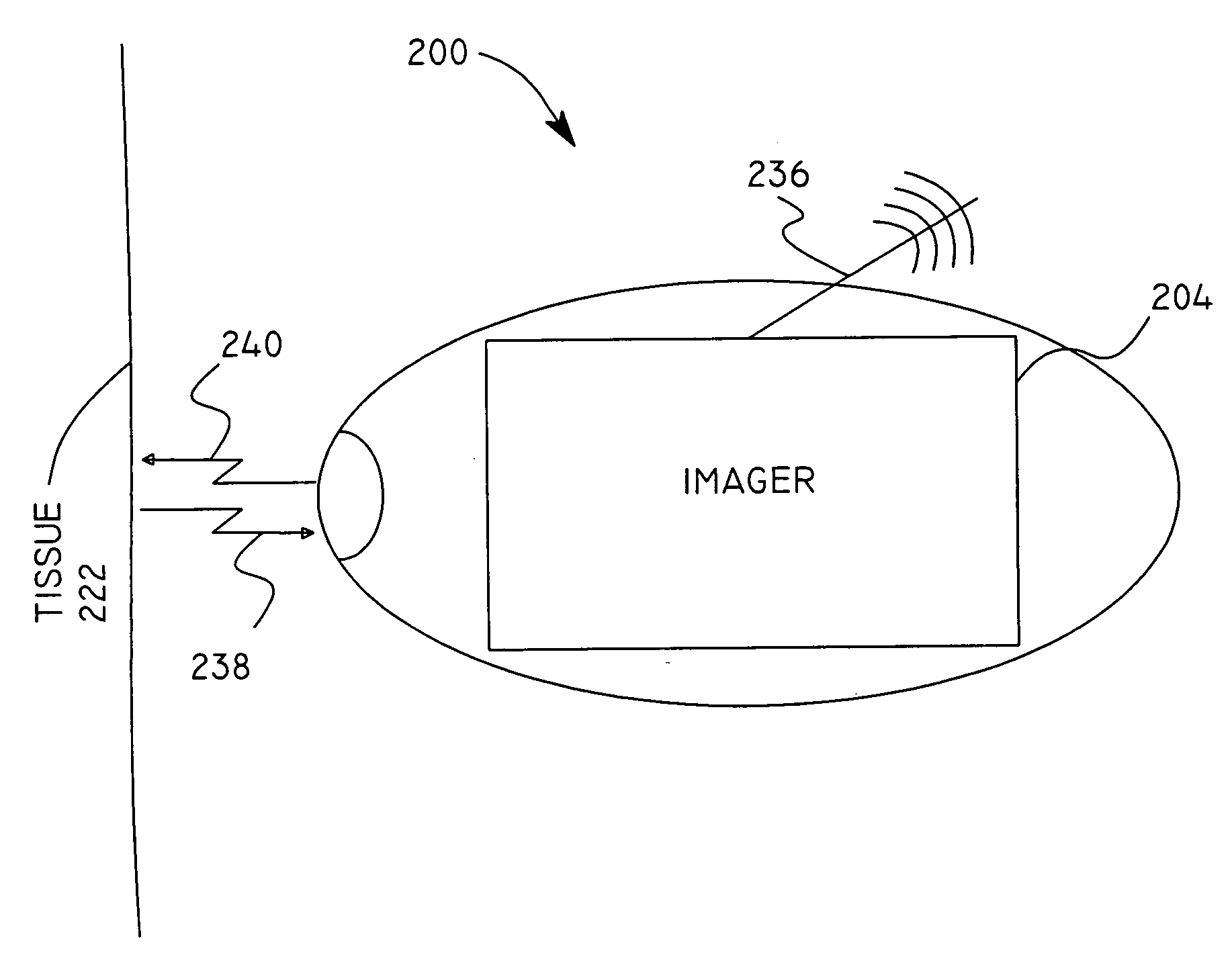
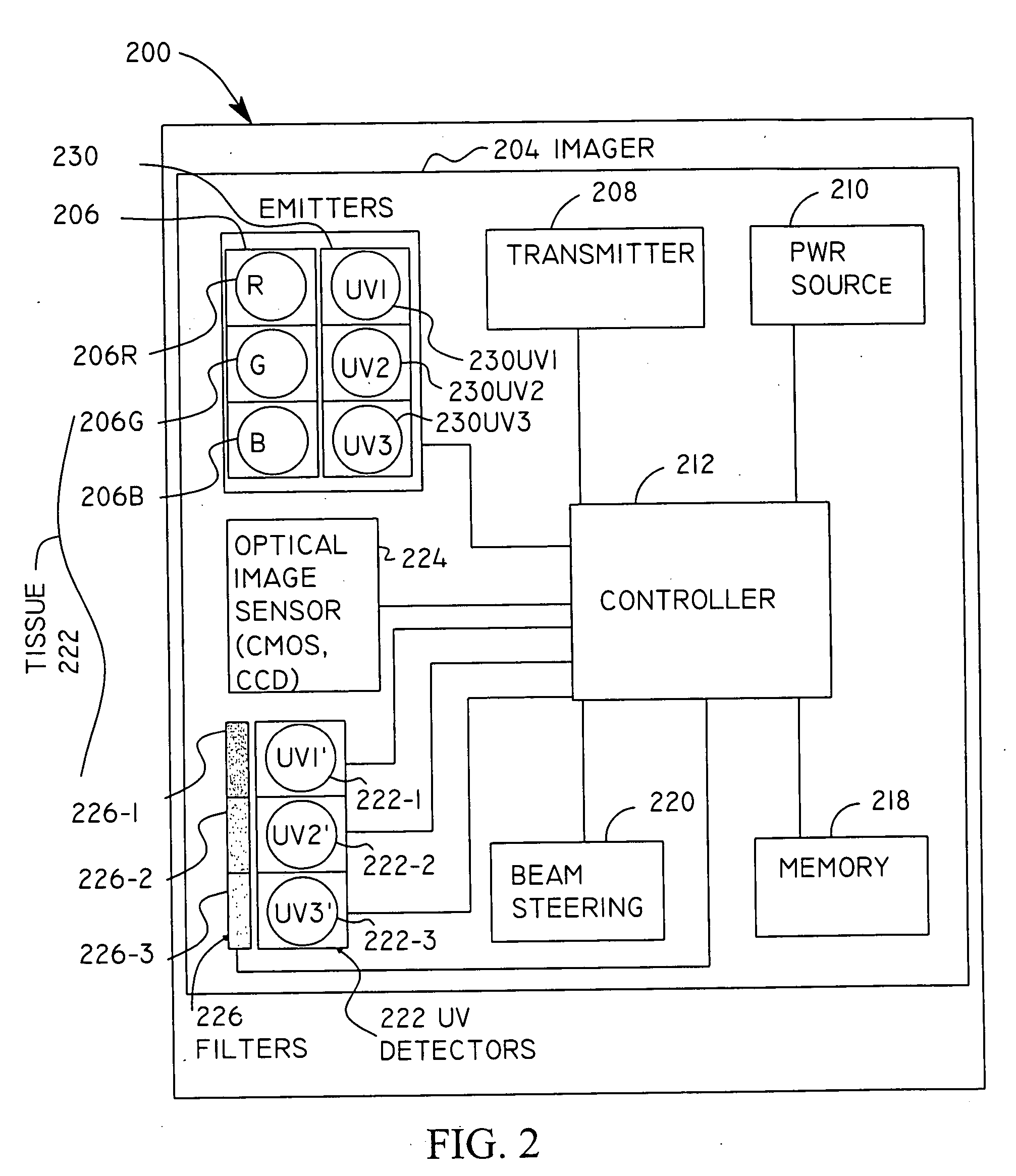
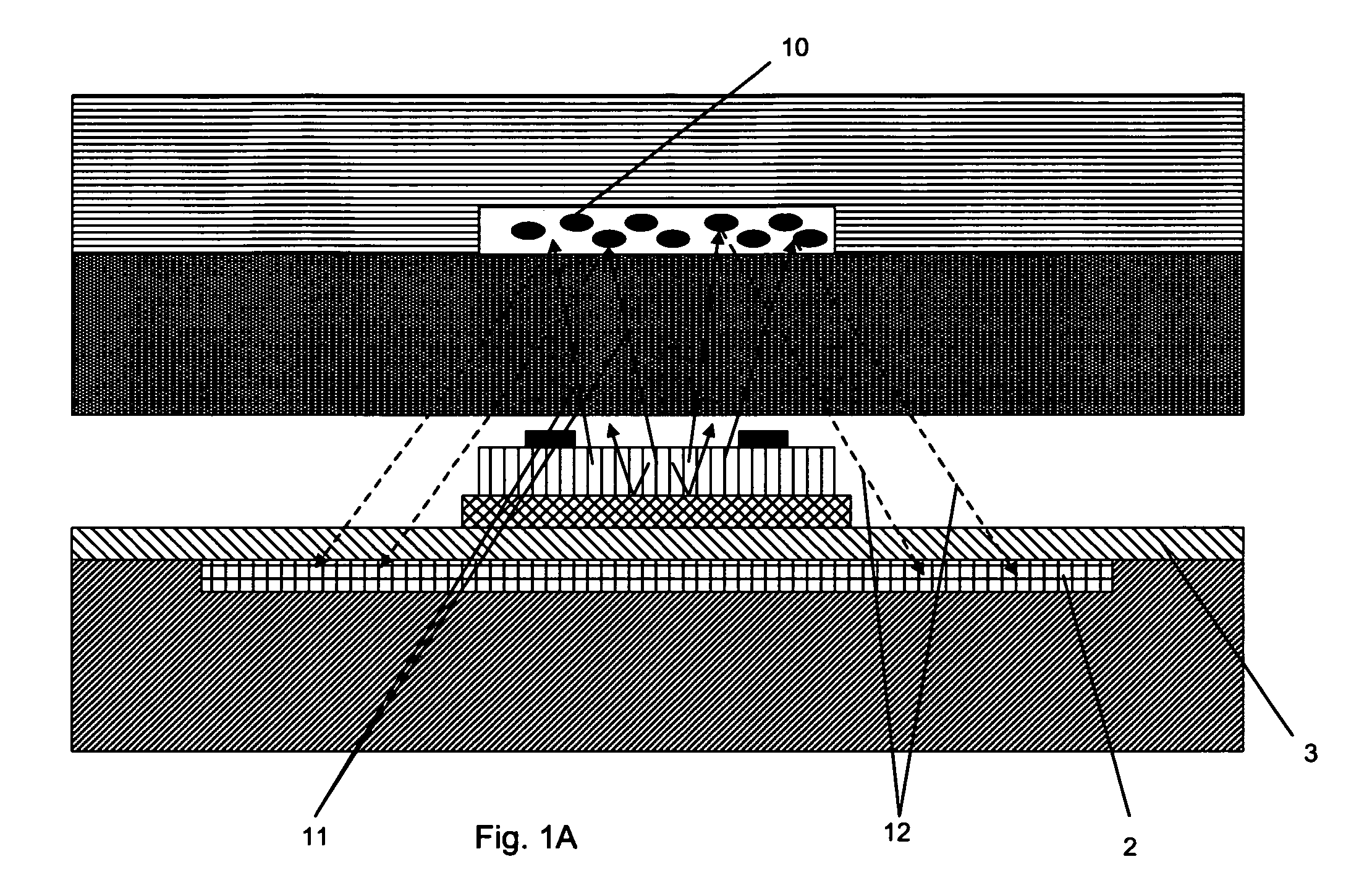
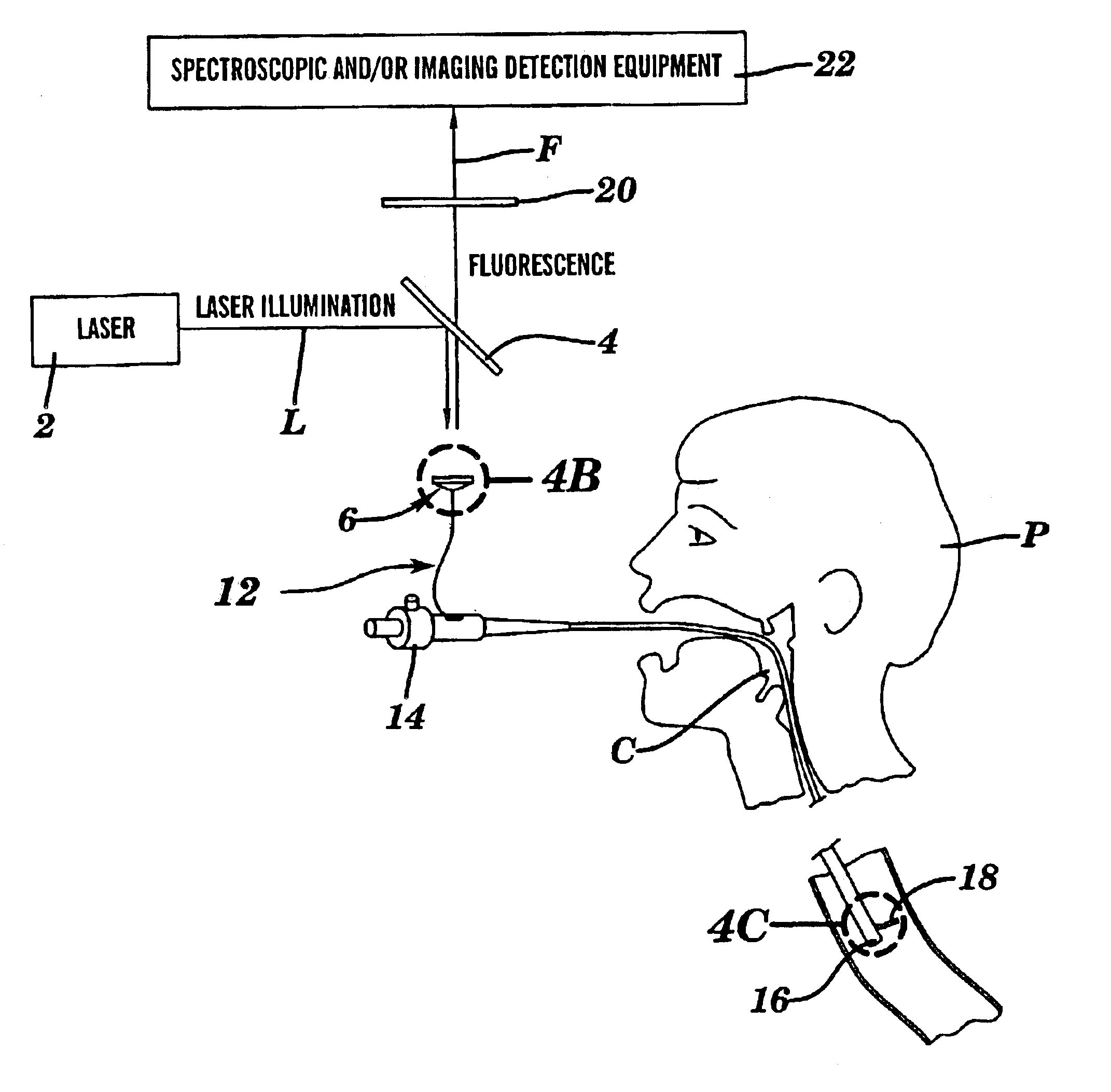
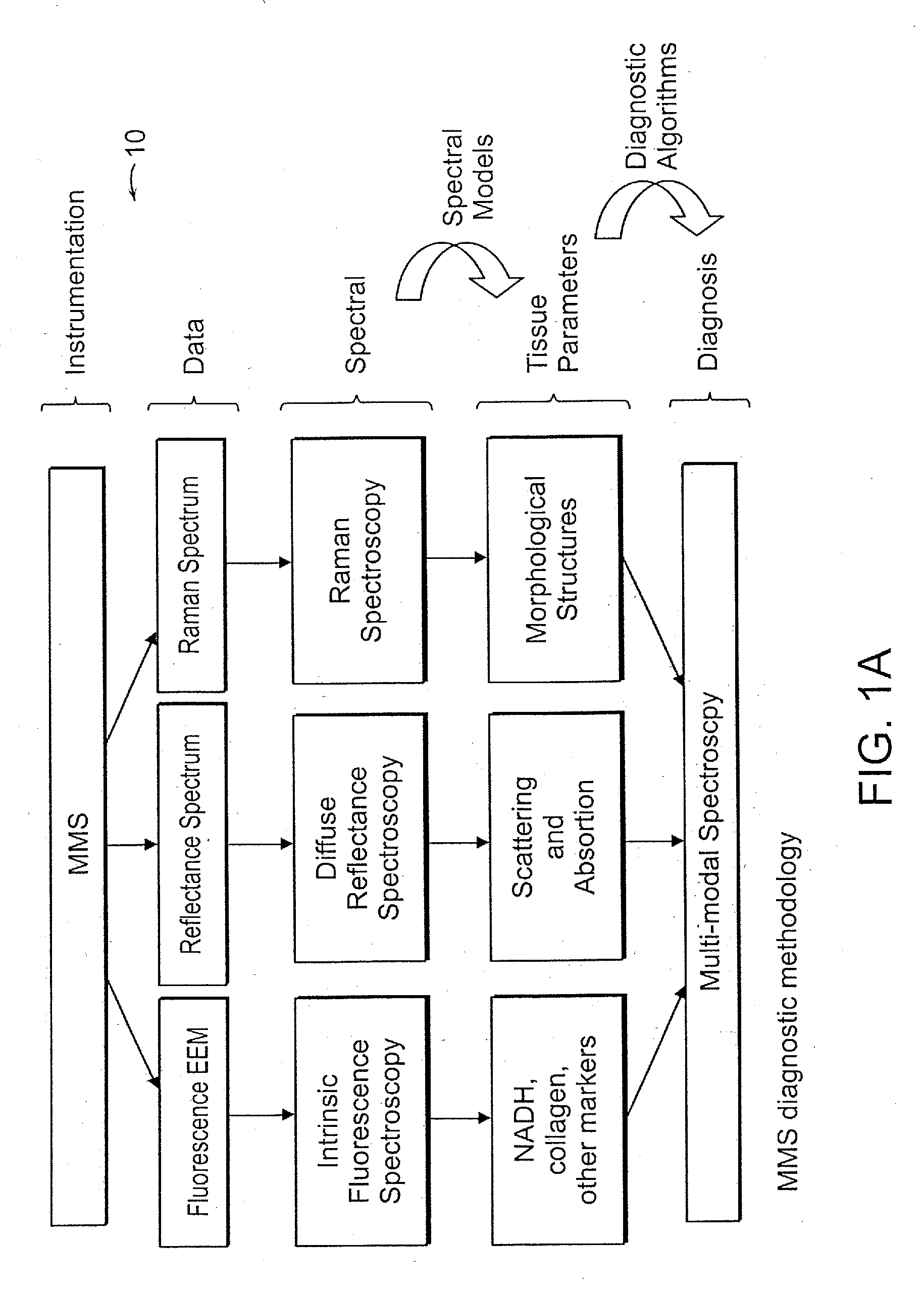
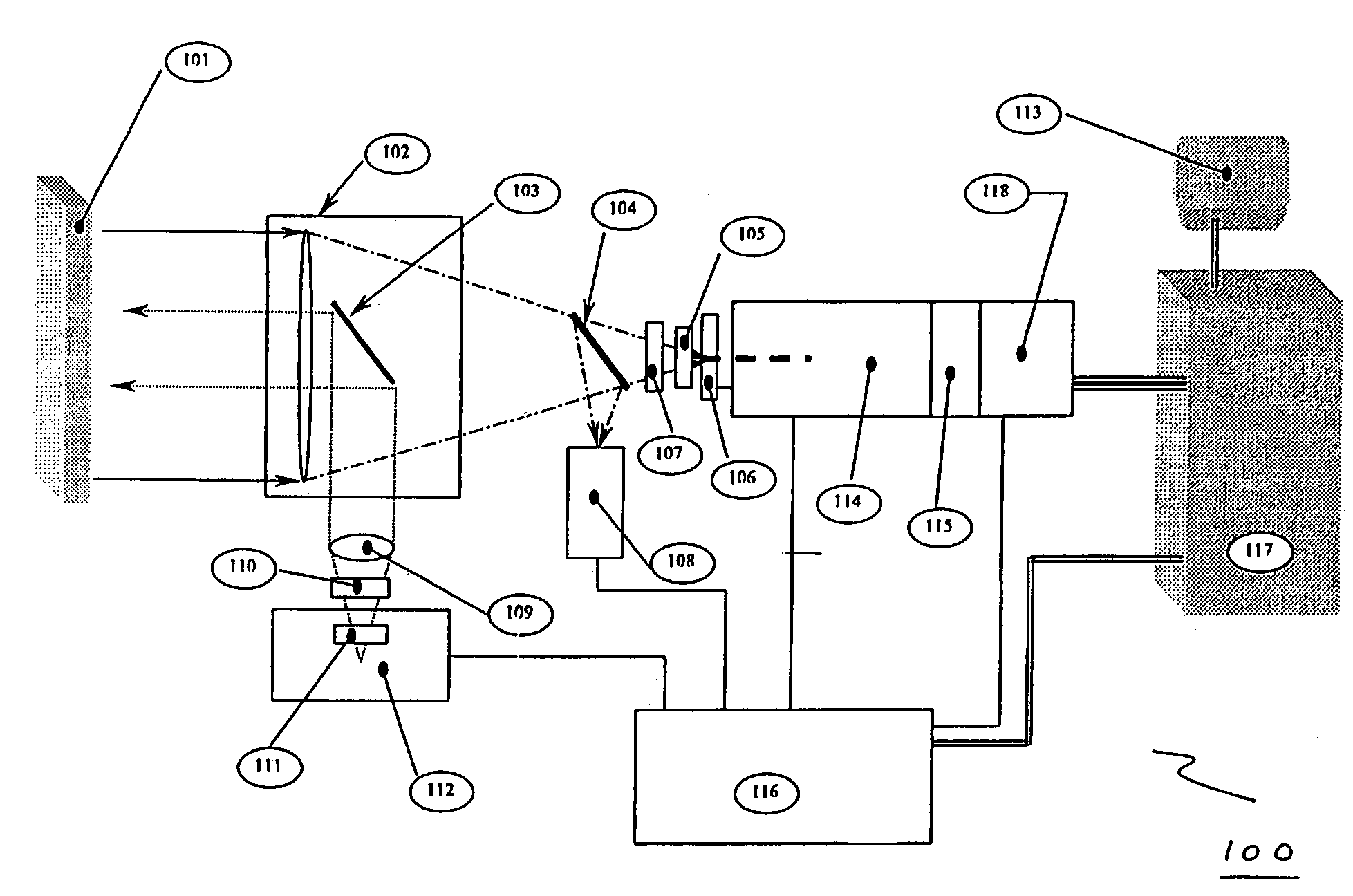
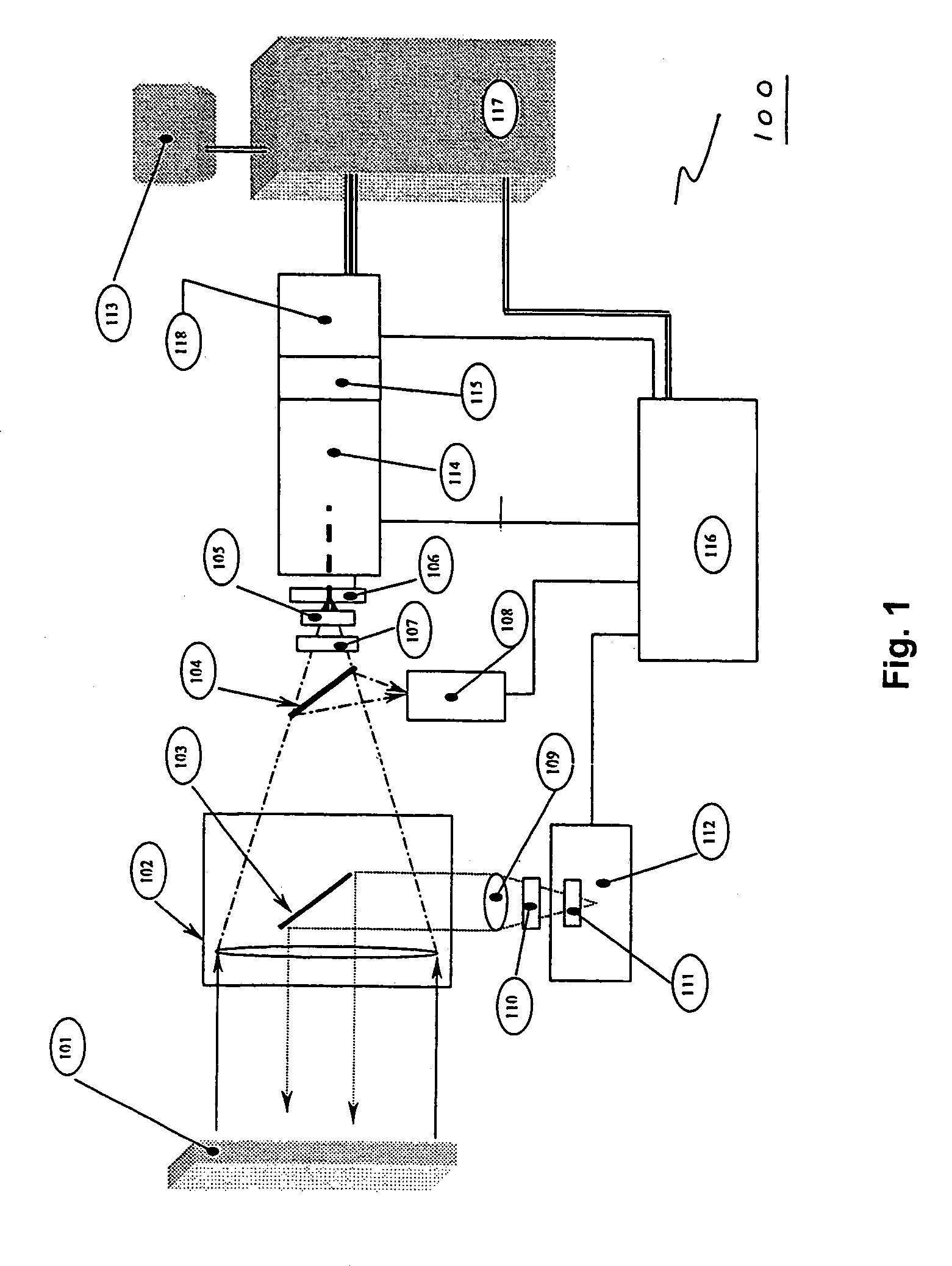
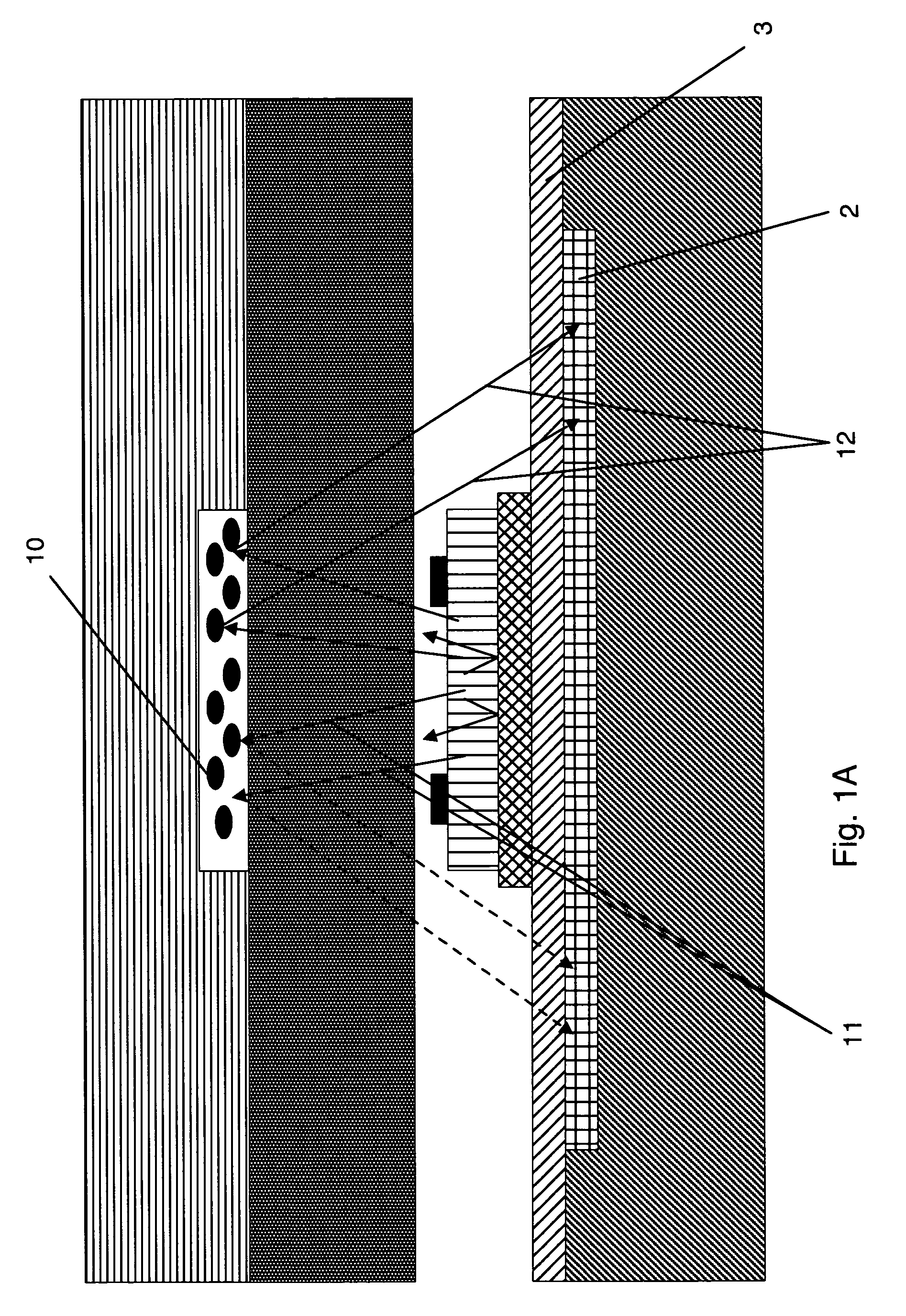
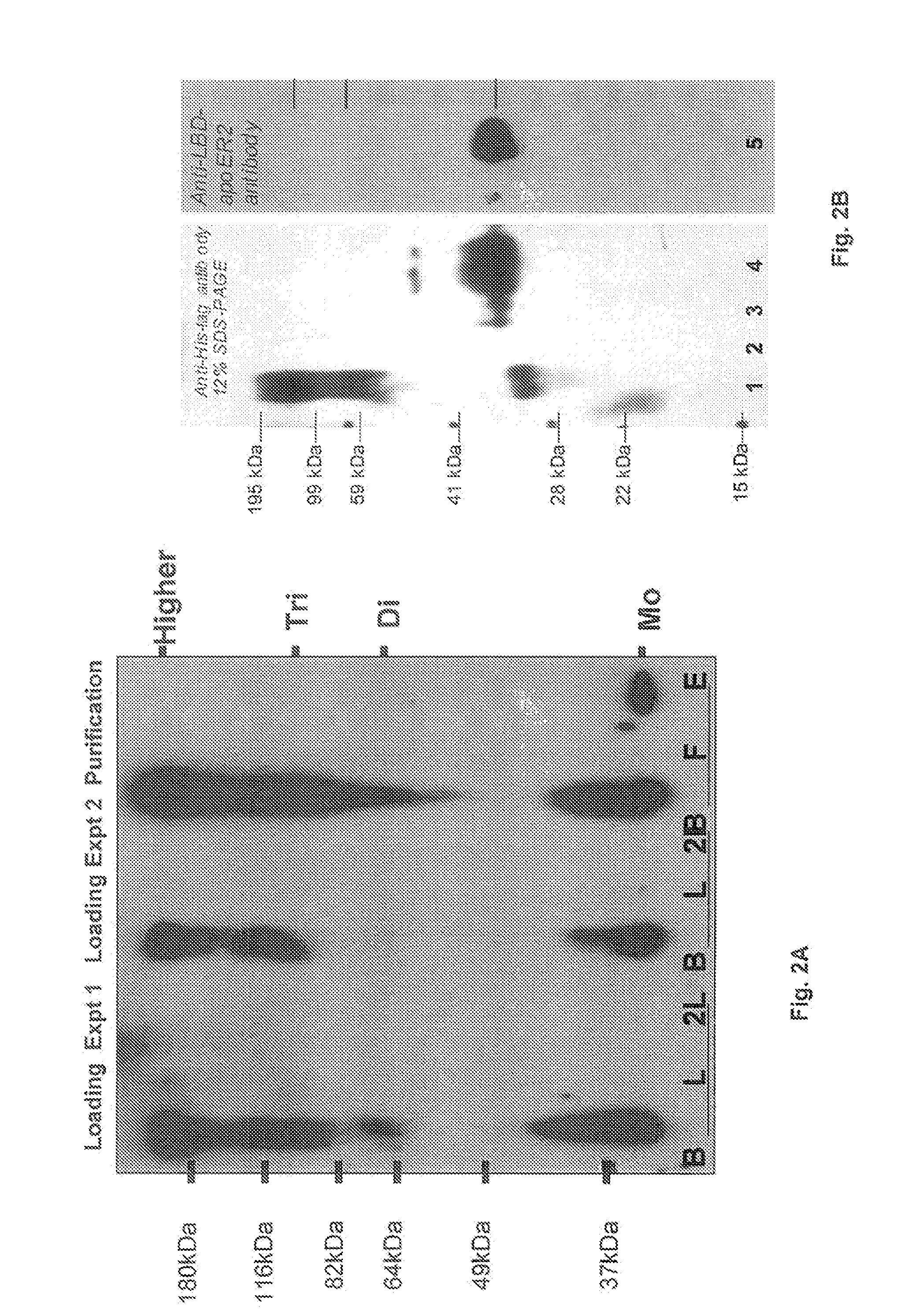
Micro-scale compact device for in vivo medical diagnosis combining optical imaging and point fluorescence spectroscopy
ActiveUS20050215911A1Timely non-invasive accurate detectionImprove the problemEndoscopesDiagnostics using fluorescence emissionCancer cellAbnormal cell
An apparatus and method for medical practitioners to detect the presence of abnormal cells including cancerous and pre-cancerous cells by using a transport capsule containing an imaging apparatus including UV sources and fluorescence detectors for obtaining images and fluorescence data of biological cells and tissue. The method includes the steps of scanning biological tissue using an ultra-violet (UV) source to obtain fluorescence data, transferring fluorescence data and / or images using a radio frequency (RF) or other suitable means to a personal computer (PC) system, analyzing the image and / or fluorescence data in the PC, identifying -tissues with precancerous and cancerous cells, and optionally determining their precise location, and assessing the accuracy of the calculated fluoroscopic images.
Owner:THE CITY COLLEGE OF THE UNIV OF NEW YORK
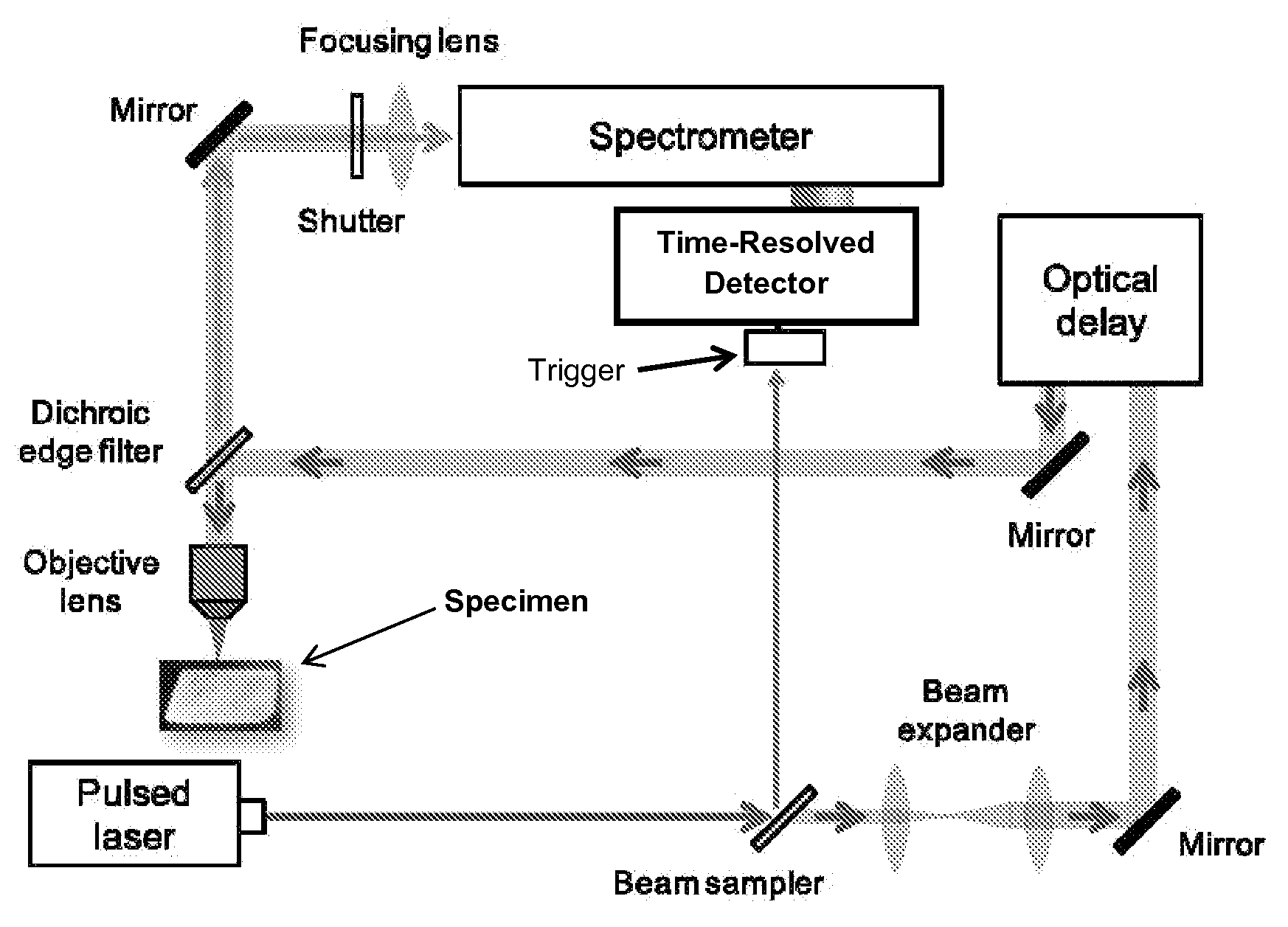
Time resolved laser raman spectroscopy using a single photon avalanche diode array
InactiveUS20130342835A1Radiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationLaser-induced breakdown spectroscopySpectrometer
A Raman spectrometer that employs a time-gated single photon avalanche diode array as a sensor is described. The spectrometer can also perform fluorescence spectroscopy and laser induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS). A laser is used to provide an excitation signal to excite a specimen of interest. A spectrometer is used to separate the various intensities over a range of wavelengths, which are then caused to impinge on the array to be recorded. The time-gated single photon avalanche diode array is triggered in synchrony with the excitation signal so as to allow time resolution of the response of the sample of interest to the excitation. The array can be time-gated to resolve signals that have shorter durations as a function of time while excluding signals that have a longer time duration. Raman and LIBS signals can be observed even from specimens that fluoresce strongly.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
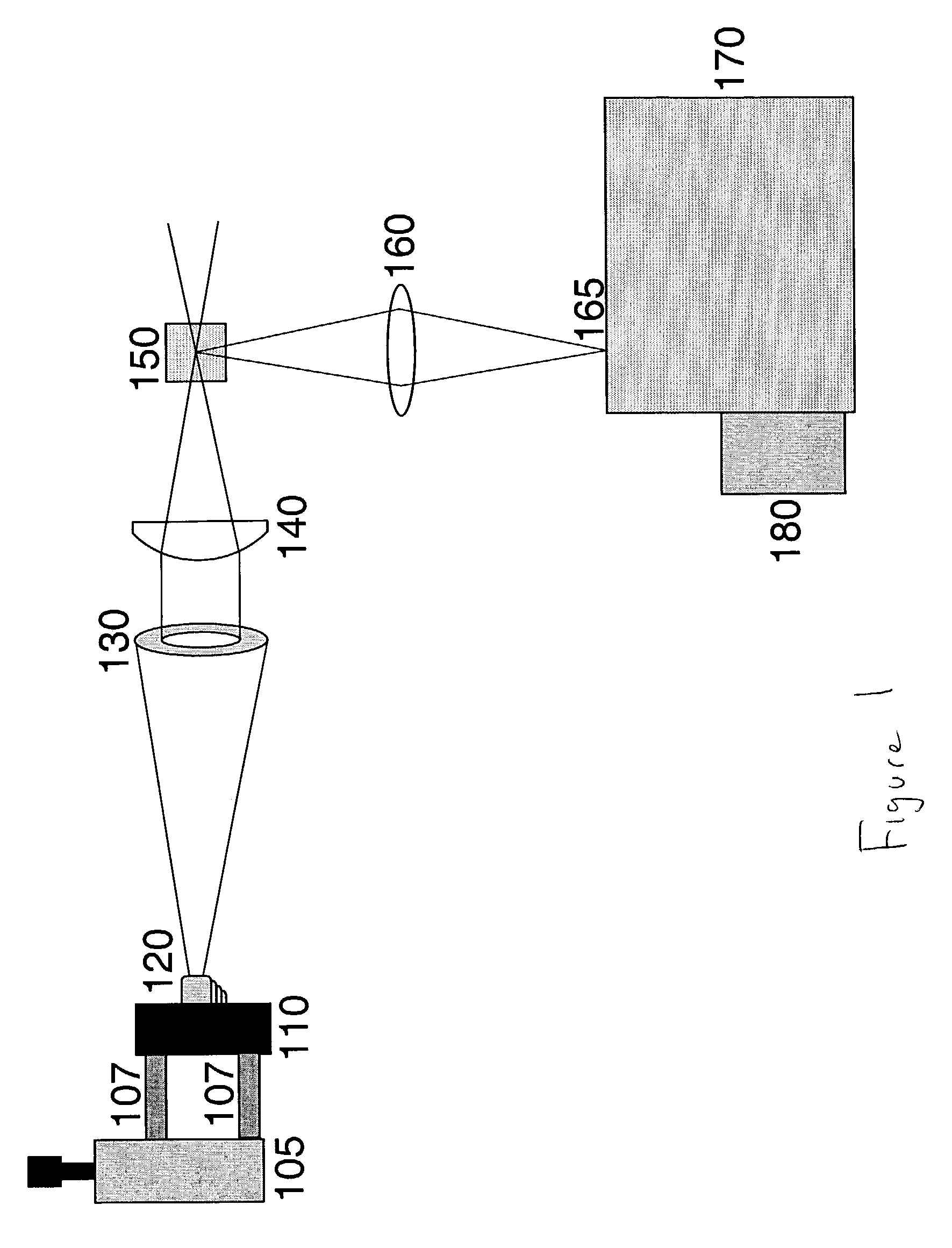
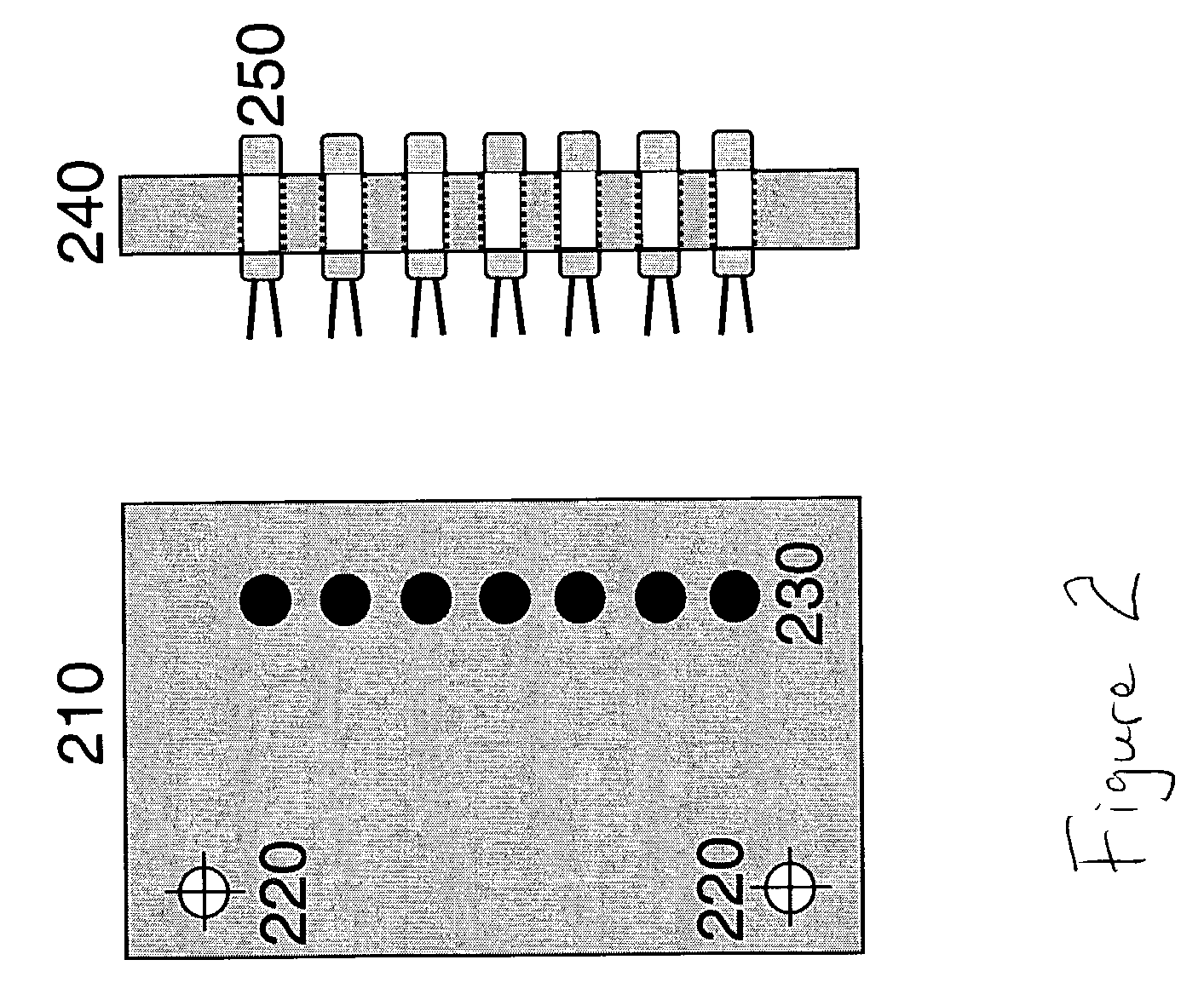
Integrated, fluorescence-detecting microanalytical system
InactiveUS20050157301A1Improve portabilityBroaden range of potential applicationChemiluminescene/bioluminescencePhotometryPhotovoltaic detectorsPhotodetector
The present invention relates to a functionally integrated microanalytical system for performing fluorescence spectroscopy. A source of fluorescence-exciting radiation, typically a LED, is integrated onto a substrate along with a photodetector and, in some embodiments, an optical filter. A pixel-to-point laser lift-off process is used to effect this component integration. For those cases in which a filter is required, a thin film bandgap filter is typically used, such as CdS or CdSxSe1-x (0<x<1). A disposable microchannel containing the sample and its fluorescent tag is mounted onto the integrated assembly of LED, photodetector and (optionally) filter. This configuration of components allows the microchannel and sample to be readily removed and replaced, facilitating rapid analysis of multiple samples. Multiple LEDS, detectors and filters (if present) can also be integrated onto the same substrate, permitting multiple wavelength analysis of the sample to be performed concurrently.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
System and methods for detection and identification of chemical substances
InactiveUS20050077476A1MinimizesHigh sensitivityRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationAnesthetic AgentSpectrograph
The invention provides a system and method utilizing, among other things, fluorescence spectroscopy in the ultraviolet portion of the electromagnetic spectrum to determine chemical species and concentrations. The basic measuring system includes optics, a spectrograph, a detector, and an energy source (“head” components), along with a computer and control electronics and power source capable of generating and detecting unique fluorescence signatures for individual and unique mixtures of chemical substances including, for example, prescribed and / or compounded medications, alcohol products, food types, synthetic drugs, narcotics, perfumes, liquids, and the like.
Owner:CDEX
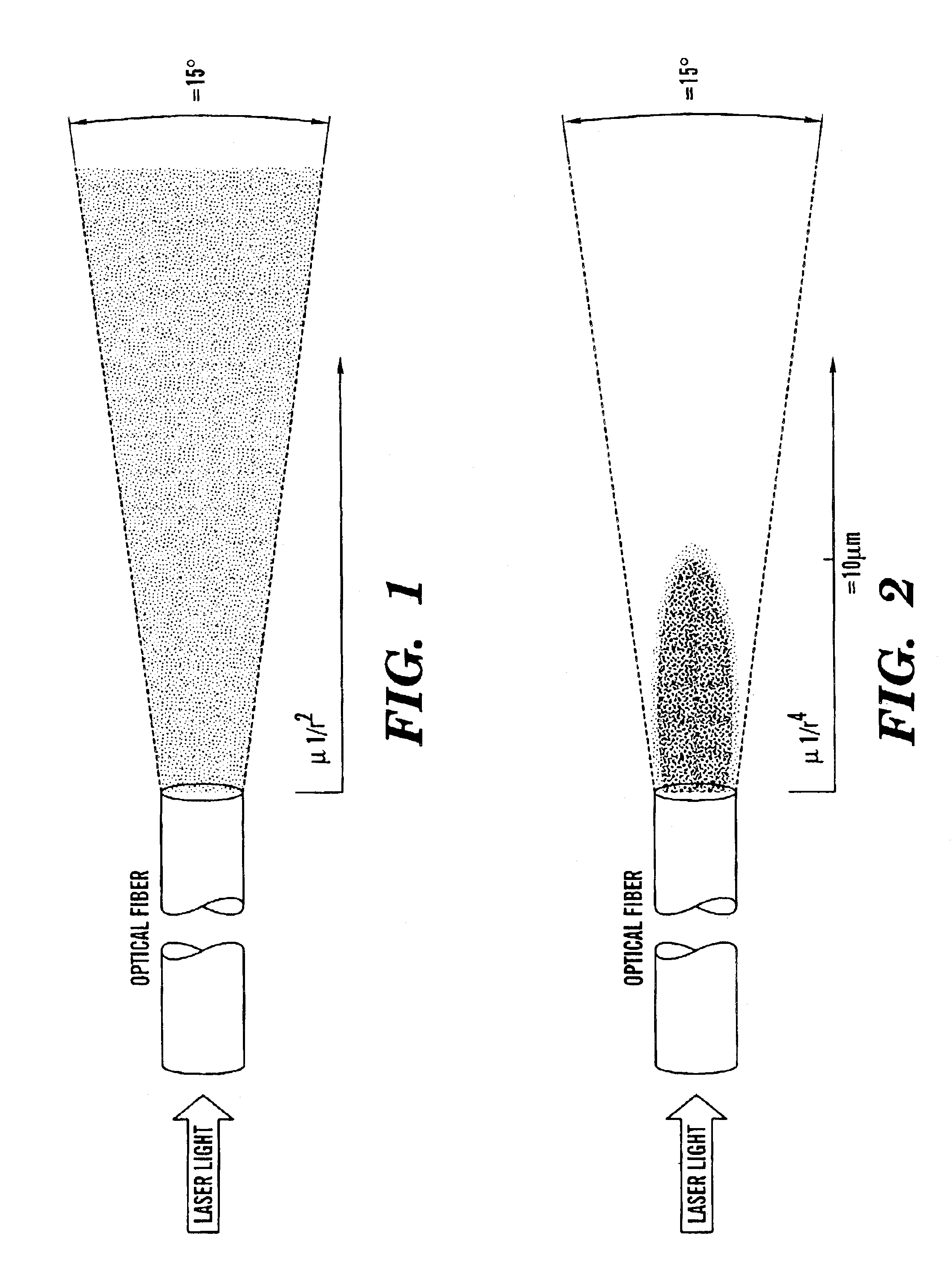
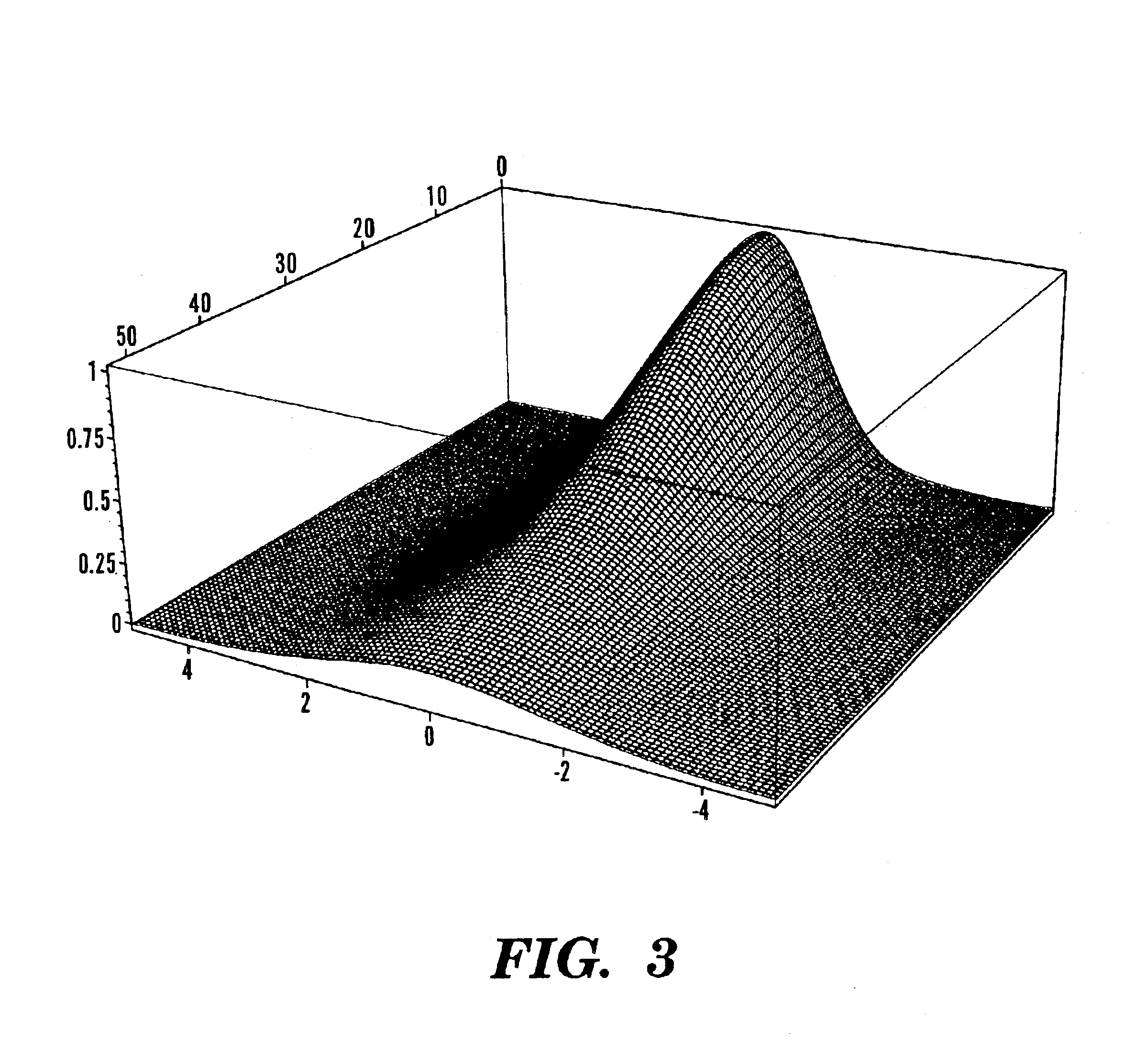
Use of multiphoton excitation through optical fibers for fluorescence spectroscopy in conjunction with optical biopsy needles and endoscopes
InactiveUS6839586B2Easy to resolveUseful spatial resolutionSurgeryDiagnostics using spectroscopyDiseaseEndoscope
The present invention is directed to a method of applying radiation through an optical fiber for detecting disease within a plant or animal or imaging a particular tissue of a plant or animal. In addition, fluorescence can be detected and localized within a subject by such application of radiation through an optical fiber. The radiation is effective to promote simultaneous multiphoton excitation. The optical fibers are used alone to examine internal regions of tissue, in conjunction with an optical biopsy needle to evaluate sub-surface tissue, or with an endoscope to evaluate tissue within body cavities.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
Portable optical fiber probe-based spectroscopic scanner for rapid cancer diagnosis
InactiveUS20120302892A1Overcoming distortionImprove accuracyDiagnostics using spectroscopyDiagnostics using fluorescence emissionDiseaseReflectance spectroscopy
A multimodal probe system for spectroscopic scanning of tissue for disease diagnosis. The system can use diffuse reflectance spectroscopy, fluorescence spectroscopy and Raman spectroscopy for the detection of cancerous tissue, such as tissue margin assessment.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
System and methods for detection and identification of chemical substances
InactiveUS7154102B2Lower potentialMinimize distribution and sale and useRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationSpectrographAlcohol products
The invention provides a system and method utilizing, among other things, fluorescence spectroscopy in the ultraviolet portion of the electromagnetic spectrum to determine chemical species and concentrations. The basic measuring system includes optics, a spectrograph, a detector, and an energy source (“head” components), along with a computer and control electronics and power source capable of generating and detecting unique fluorescence signatures for individual and unique mixtures of chemical substances including, for example, prescribed and / or compounded medications, alcohol products, food types, synthetic drugs, narcotics, perfumes, liquids, and the like.
Owner:CDEX
Method for the Fluorescent Detection of Nitroreductase Activity Using Nitro-Substituted Aromatic Compounds
A method utilising one or more fluorogenic probes, for the detection of nitroreductase activity. The non-fluorescent probes are reduced in the presence of nitroreductase to form fluorescent derivatives that may be detected using fluorescence spectroscopy. In particular, the method may be used to detect and / or identify a plurality of nitroreductase in a single test environment
Owner:AUCKLAND UNISERVICES LTD
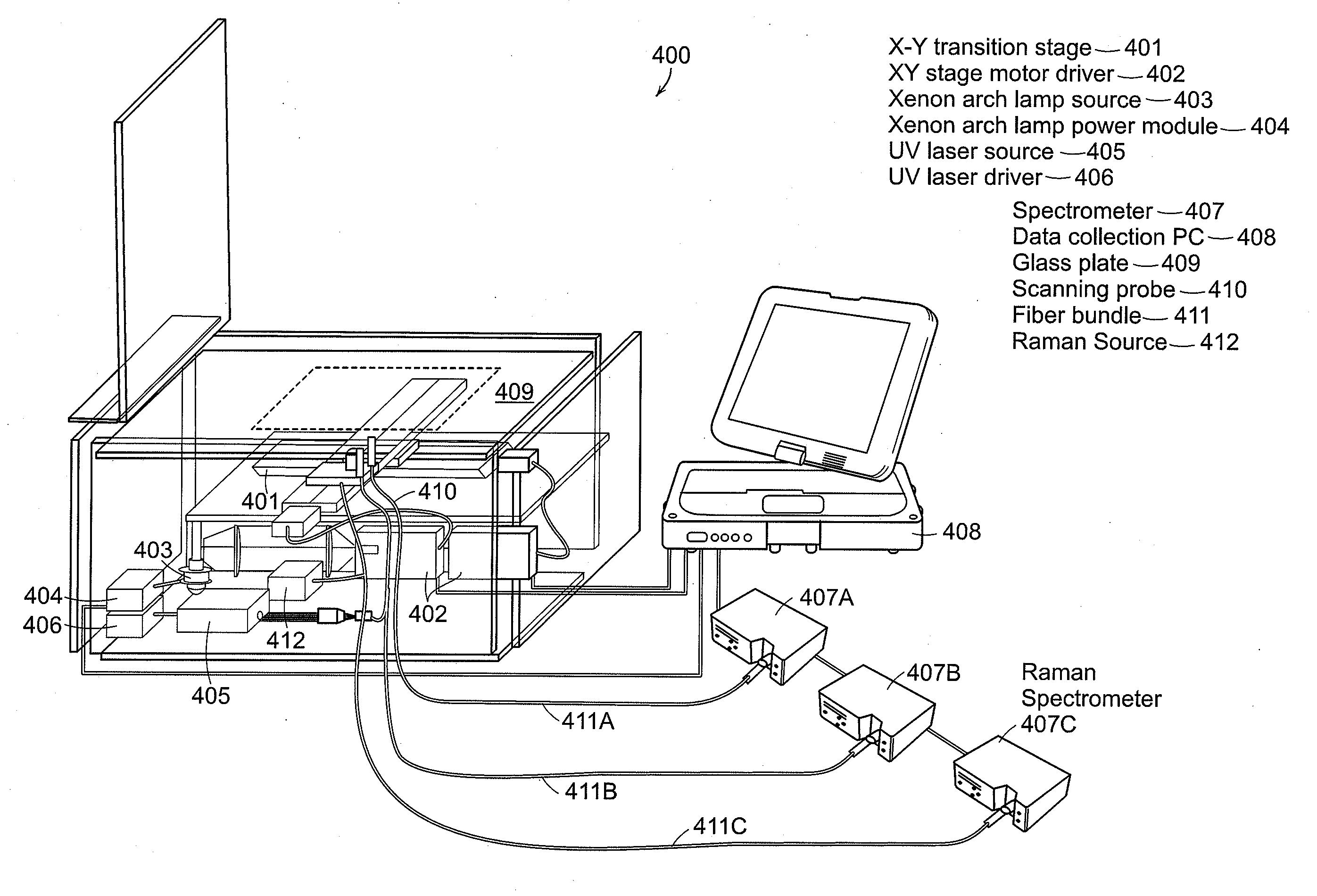
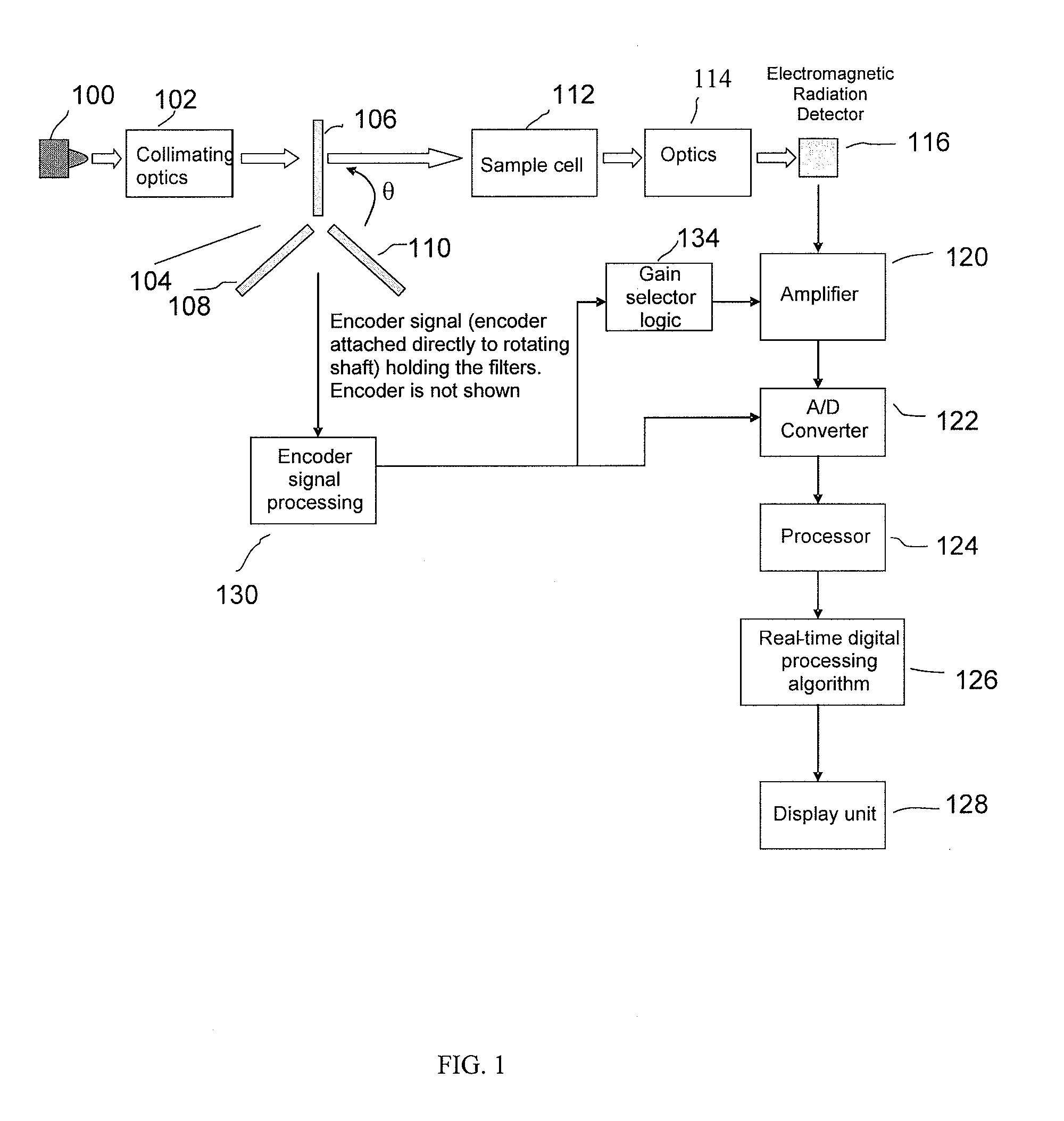
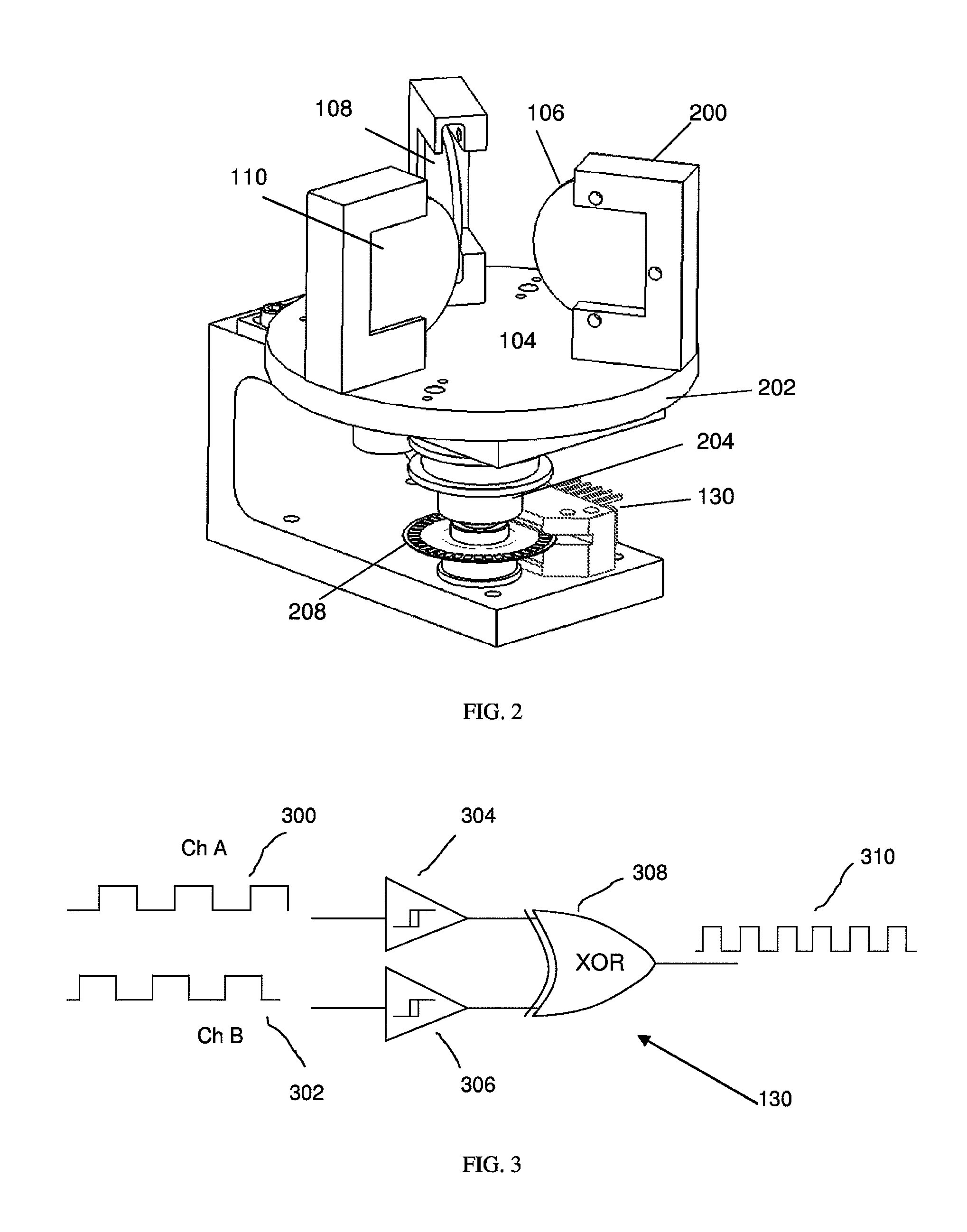
Methods and systems for chemical composition measurement and monitoring using a rotating filter spectrometer
ActiveUS20100027004A1Improve measurement stabilityAccurate and robust detectionRadiation pyrometryInterferometric spectrometrySpectroscopySpectrometer
The invention relates to methods and systems for measuring and / or monitoring the chemical composition of a sample (e.g., a process stream), and / or detecting specific substances or compounds in a sample, using light spectroscopy such as absorption, emission and fluorescence spectroscopy. In certain embodiments, the invention relates to spectrometers with rotating narrow-band interference optical filter(s) to measure light intensity as a function of wavelength. More specifically, in certain embodiments, the invention relates to a spectrometer system with a rotatable filter assembly with a position detector rigidly attached thereto, and, in certain embodiments, the further use of various oversampling methods and techniques described herein, made particularly useful in conjunction with the rotatable filter assembly. In preferred embodiments, the rotatable filter is tilted with respect to the rotation axis, thereby providing surprisingly improved measurement stability and significantly improved control of the wavelength coverage of the filter spectrometer.
Owner:PASON SYST
Integrated, fluorescence-detecting microanalytical system
InactiveUS7221455B2Improve portabilityBroaden range of potential applicationChemiluminescene/bioluminescencePhotometryPhotovoltaic detectorsPhotodetector
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
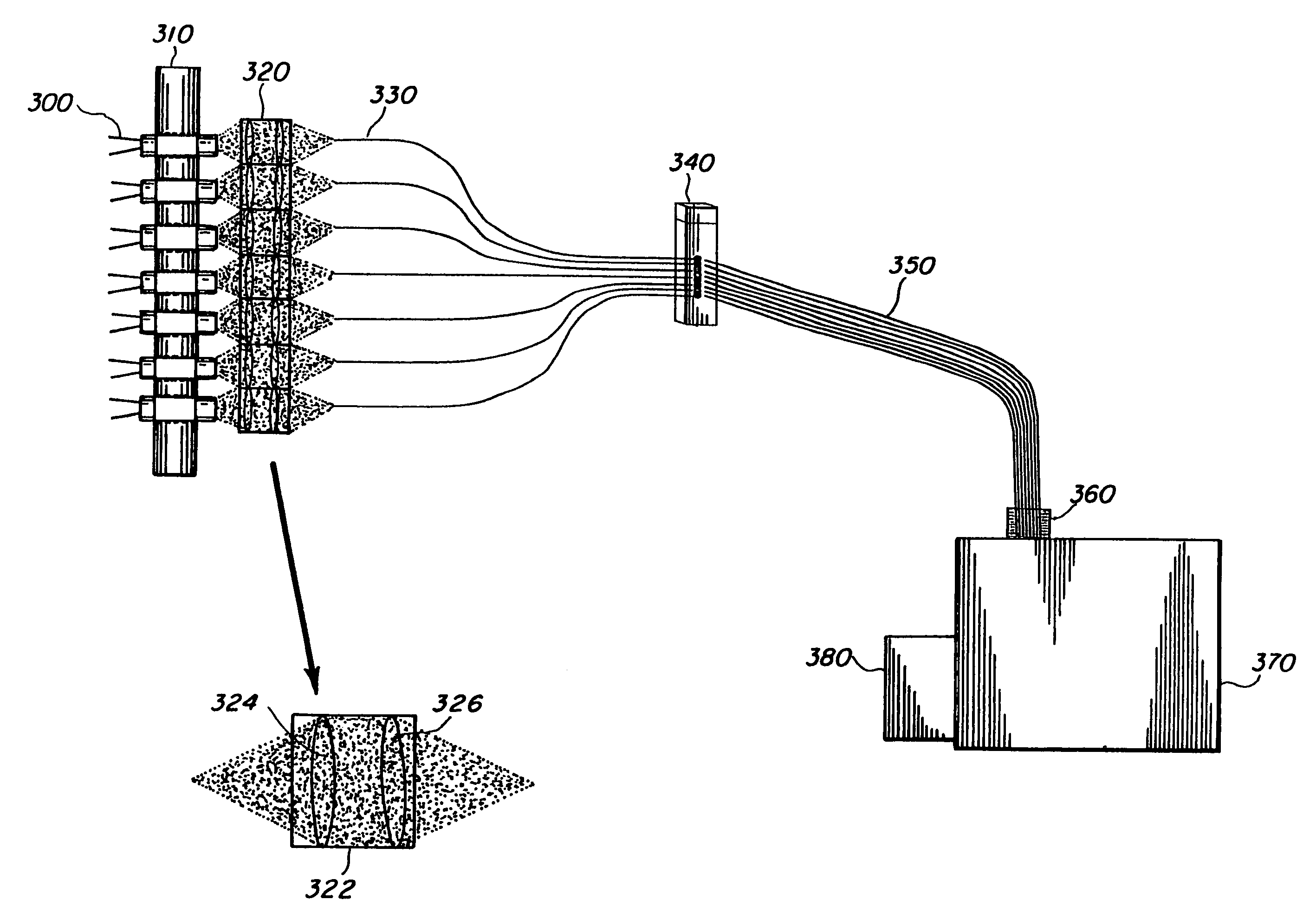
Light emitting diode (LED) array for excitation emission matrix (EEM) fluorescence spectroscopy
InactiveUS6985224B2Lower component costsEasy to useRadiation pyrometryRaman/scattering spectroscopySpectrographExcitation emission matrix
This invention discloses an Excitation Emission Matrix (EEM) fluorescence spectrometer system that uses an LED array to cause excitation emission matrix fluorescence that is imaged onto a spectrograph for sample identification and analysis. By using the LED array, the spectrograph requires only high spectroscopic resolution of about 1 to 5 nm in the fluorescence emission range and low excitation light resolution of about 14 to 73 nm in the excitation range. While individual LED optical excitation spectra may contain wavelength regions that overlap, as long as the various LEDs have different excitation wavelengths and intensities, spectral overlap does not preclude data analysis. The invention provides an EEM spectroscopy system that is not a high resolution such as a laser or lamp based excitation system, but instead uses a lower resolution, lower power LED system. The invention also provides results that are comparable to existing systems with lower component cost and lower power requirements while also optically stable, small, and easy to use.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
Fluorescent detection of proteins in polyacrylamide gels
ActiveUS7569130B2Laborious labelingLaborious staining stepElectrolysis componentsChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceSpectroscopyTryptophan
The mechanism of the UV light-induced reaction between the indole moiety of tryptophan and chloroform, and the structure of the modified tryptophan and polypeptides including such modified tryptophan residues. The excited indole moiety, which is formed upon UV light irradiation, emits a solvated electron which initiates a series of events that yield fluorescent derivatives that have CHO group covalently bound to the indole moiety. These derivatives are herein referred to as formyltryptophan, and are relatively stable. Similar reactions are observed when 5-hydroxytryptophan, 5-fluorotryptophan, or N-methylindolacetate are used in place of tryptophan, or when other haloalkanes, such as trichloracetic acid, trichlorethanol, trichlorethane, bromoform, and iodoactetate are used in place of chloroform. The derivatives can be used in a variety of applications in fluorescence spectroscopy, and for nuclear magnetic resonance, X-ray crystallography, infra-red spectroscopy, circular dicroism and mass spectroscopy. Additionally, the UV light-induced reaction between the indole moiety of tryptophan and haloalkanes can be used to prepare derivatives of tryptophan for chemical cross-linking studies of proteins and peptides.
Owner:UNIV TECH INT +1
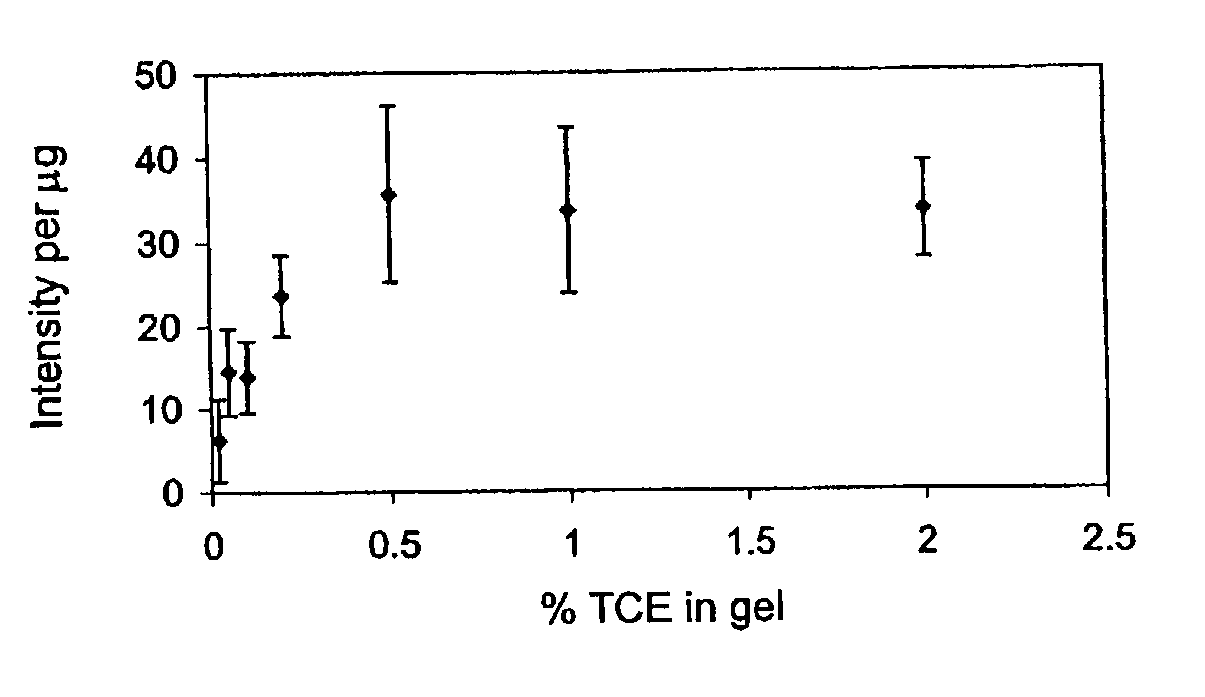
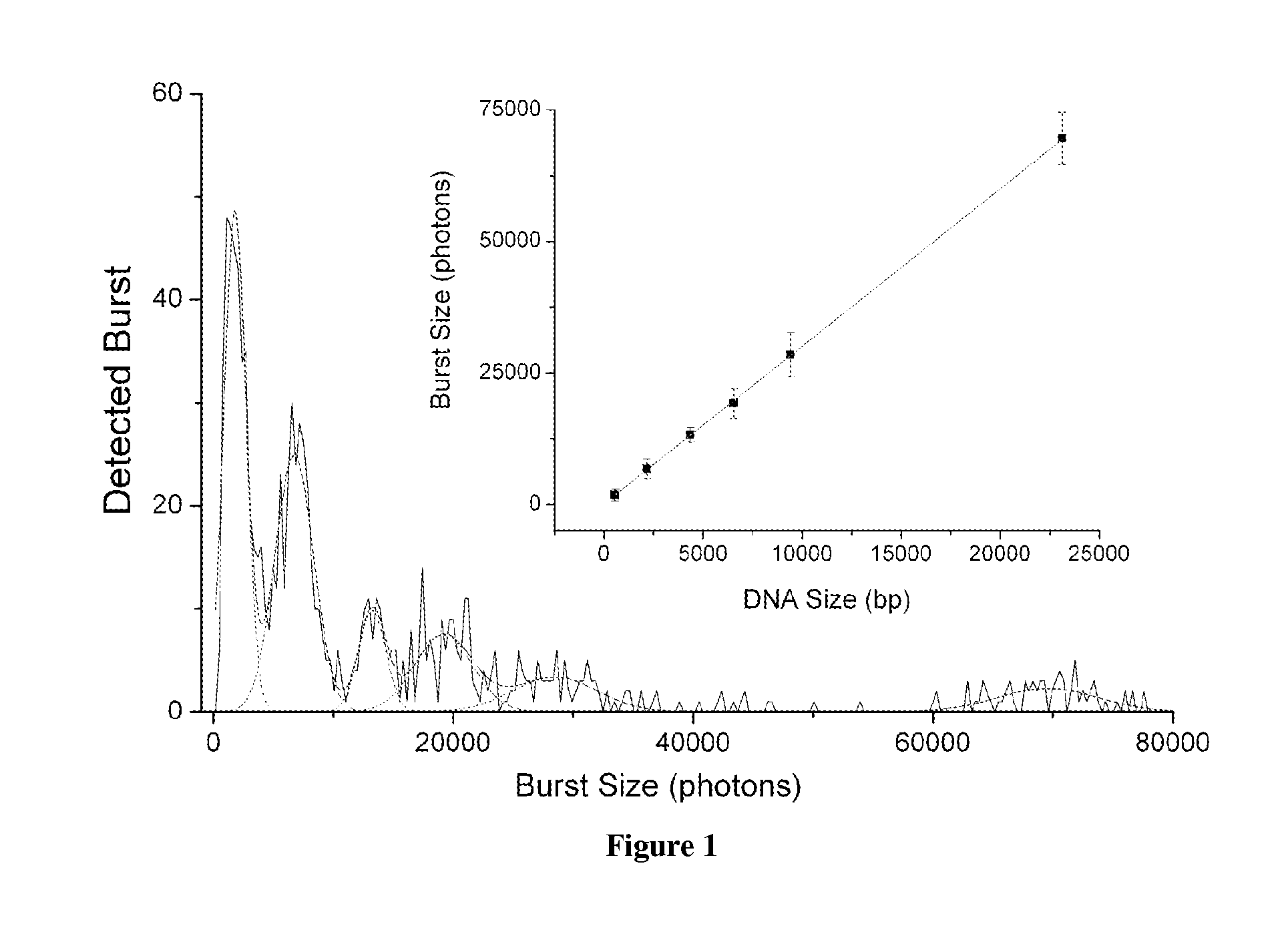
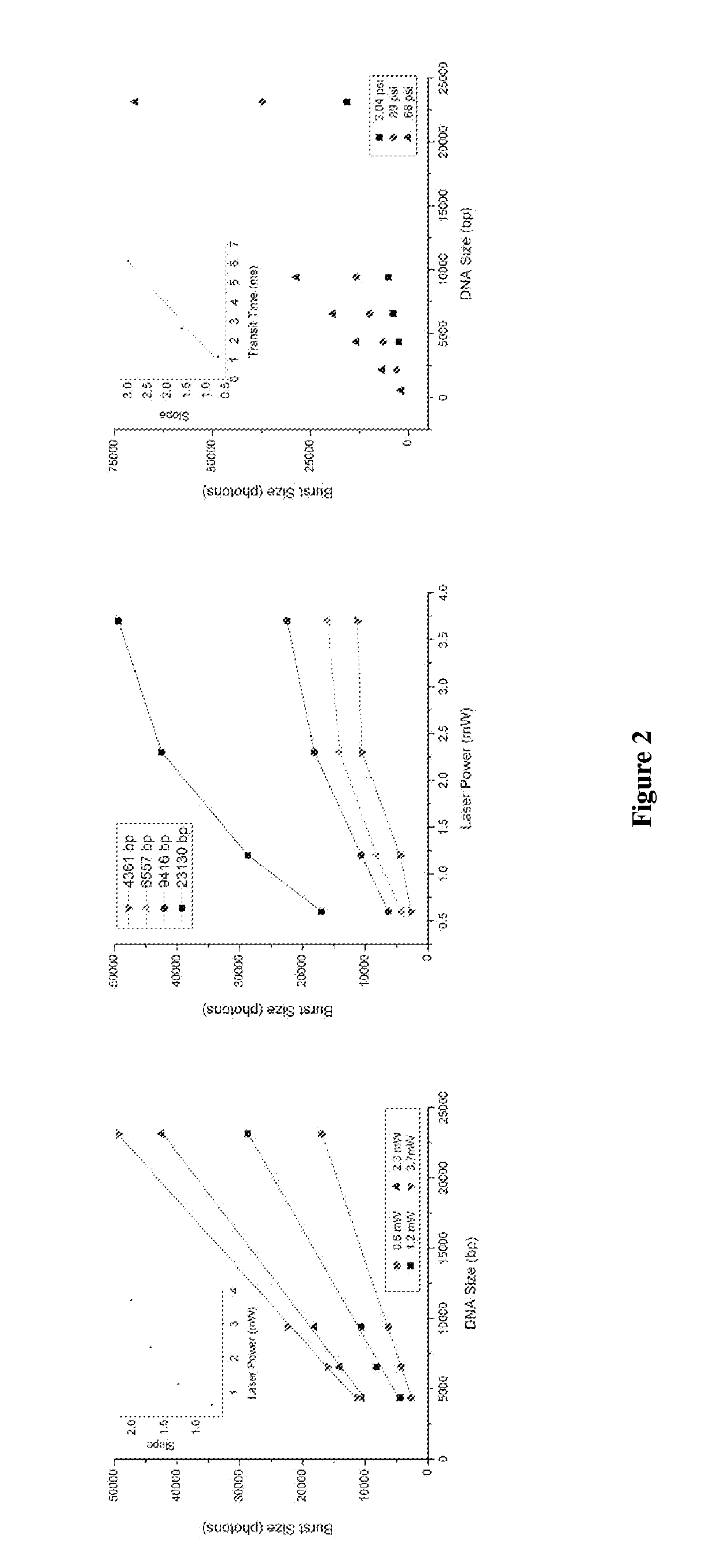
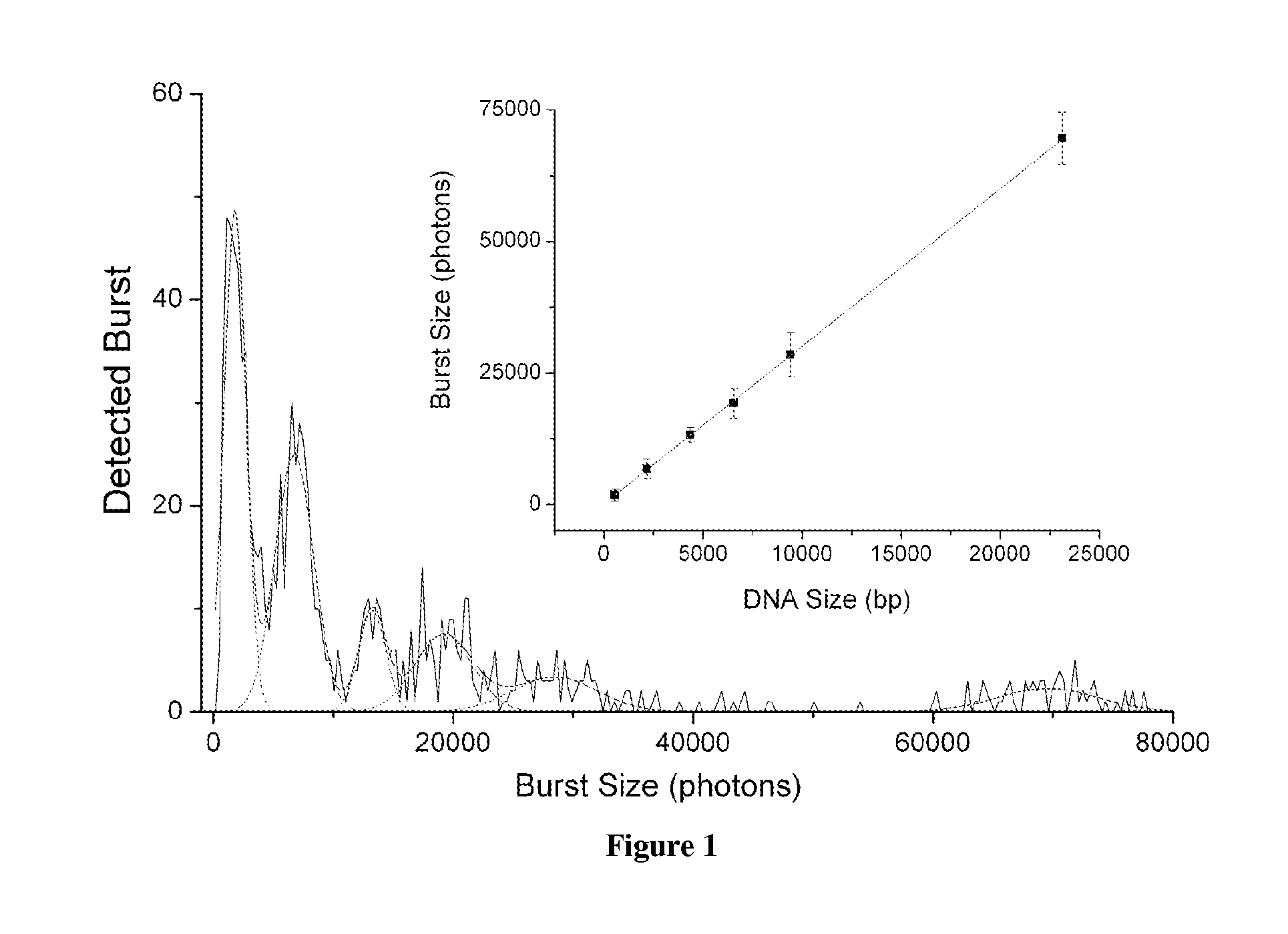
DNA integrity assay (DIA) for cancer diagnostics, using confocal fluorescence spectroscopy
The present invention relates, e.g., to a method for determining the size distribution of DNA molecules in a sample comprising cell-free nucleic acid, comprising labeling the DNA with a fluorescent dye in a stoichiometric manner, subjecting the DNA to molecular spectroscopy (e.g., cylindrical illumination confocal spectroscopy), analyzing suitable fluorescent burst parameters of the labeled DNA, and conducting single molecule DNA integrity analysis of the labeled DNA molecules in the sample. In one embodiment of the invention, the method is used as a diagnostic method for detecting cancer.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
DNA integrity assay (DIA) for cancer diagnostics, using confocal fluorescence spectroscopy
ActiveUS20110171741A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological testingFluorescence spectrometryMolecular spectroscopy
The present invention relates, e.g., to a method for determining the size distribution of DNA molecules in a sample comprising cell-free nucleic acid, comprising labeling the DNA with a fluorescent dye in a stoichiometric manner, subjecting the DNA to molecular spectroscopy (e.g., cylindrical illumination confocal spectroscopy), analyzing suitable fluorescent burst parameters of the labeled DNA, and conducting single molecule DNA integrity analysis of the labeled DNA molecules in the sample. In one embodiment of the invention, the method is used as a diagnostic method for detecting cancer.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Cellulose composites comprising hydrophobic particles and their use in paper products
InactiveUS20080041542A1Non-fibrous pulp additionNatural cellulose pulp/paperSolventAlkaline hydrolysis
Polymer composite films were prepared by solvent casting suspensions of quantum dots (QDs) in cellulose triacetate (CTA) solution. The films were robust and possessed the optical properties characteristic of QDs. Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) images of the films revealed that the QDs were well dispersed within the CTA film matrix. The selective alkaline hydrolysis of QD / CTA films in 0.1N NaOH over 24 hours resulted in the surface conversion of CTA to regenerated cellulose. Optical properties of the films were probed both before and after the hydrolysis reaction using fluorescence spectroscopy, and were found generally unaltered. The cellulose surfaces of the alkaline treated films allow for facile incorporation of the films into paper sheets.
Owner:ABITBOL TIFFANY +1
Fluorescent detection of proteins in polyacrylamide gels
InactiveUS20100089753A1Without laborious labeling and staining stepElectrolysis componentsVolume/mass flow measurementSpectroscopyTryptophan
The mechanism of the UV light-induced reaction between the indole moiety of tryptophan and chloroform, and the structure of the modified tryptophan and polypeptides including such modified tryptophan residues. The excited indole moiety, which is formed upon UV light irradiation, emits a solvated electron which initiates a series of events that yield fluorescent derivatives that have CHO group covalently bound to the indole moiety. These derivatives are herein referred to as formyltryptophan, and are relatively stable. Similar reactions are observed when 5-hydroxytryptophan, 5-fluorotryptophan, or N-methylindolacetate are used in place of tryptophan, or when other haloalkanes, such as trichloracetic acid, trichlorethanol, trichlorethane, bromoform, and iodoactetate are used in place of chloroform. The derivatives can be used in a variety of applications in fluorescence spectroscopy, and for nuclear magnetic resonance, X-ray crystallography, infra-red spectroscopy, circular dicroism and mass spectroscopy. Additionally, the UV light-induced reaction between the indole moiety of tryptophan and haloalkanes can be used to prepare derivatives of tryptophan for chemical cross-linking studies of proteins and peptides.
Owner:UNIV TECH INT +1
Similarity index: a rapid classification method for multivariate data arrays
InactiveUS20090306932A1Rapid classification and analysisDigital computer detailsRaman scatteringData setSpectroscopy
Similarity Index: a rapid classification method for multivariate data arrays The present invention is directed to a method of determining the similarity between a first multivariate data set and a second multivariate data set. The method is versatile and can be applied to a number of different multivariate data sets, for example, a spectroscopy multivariate data set. In particular, the method may be applied to rapidly assess the similarity between fluorescence spectroscopy multivariate data sets. The method comprises the steps of representing the data of a first and a second multivariate data set in matrix form to yield a multivariate data matrix, wherein each multivariate data matrix has the same dimensions. Subsequently, the magnitude of an additive and subtractive combination of each multivariate data matrix is calculated. The concept of a penalty parameter is introduced to set a detectable limit of variance between said first multivariate data set and said second multivariate data set. The penalty parameter is ascribed a value and is used in combination with the magnitude of an additive and subtractive combination of each multivariate data matrix to determine a similarity value. The determined similarity value indicates the variance between said first multivariate data set and said second multivariate data set.
Owner:THE NAT UNIV OF IRELAND GALWAY
Method and composition for a protein transduction technology and its applications
ActiveUS20090298111A1Efficient deliveryBest protein transduction efficiencyPeptide/protein ingredientsMicroencapsulation basedSpectroscopyFluorophore
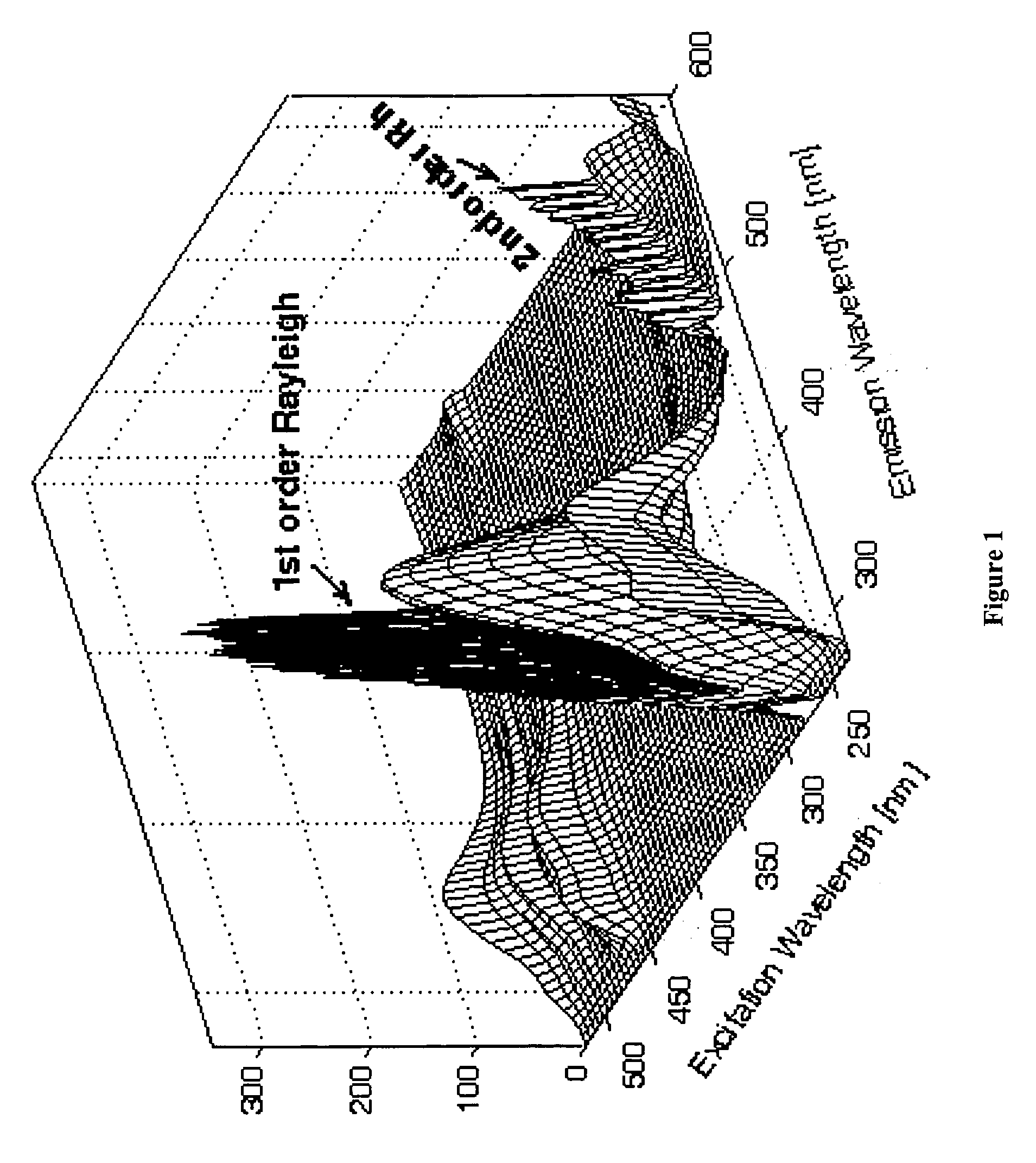
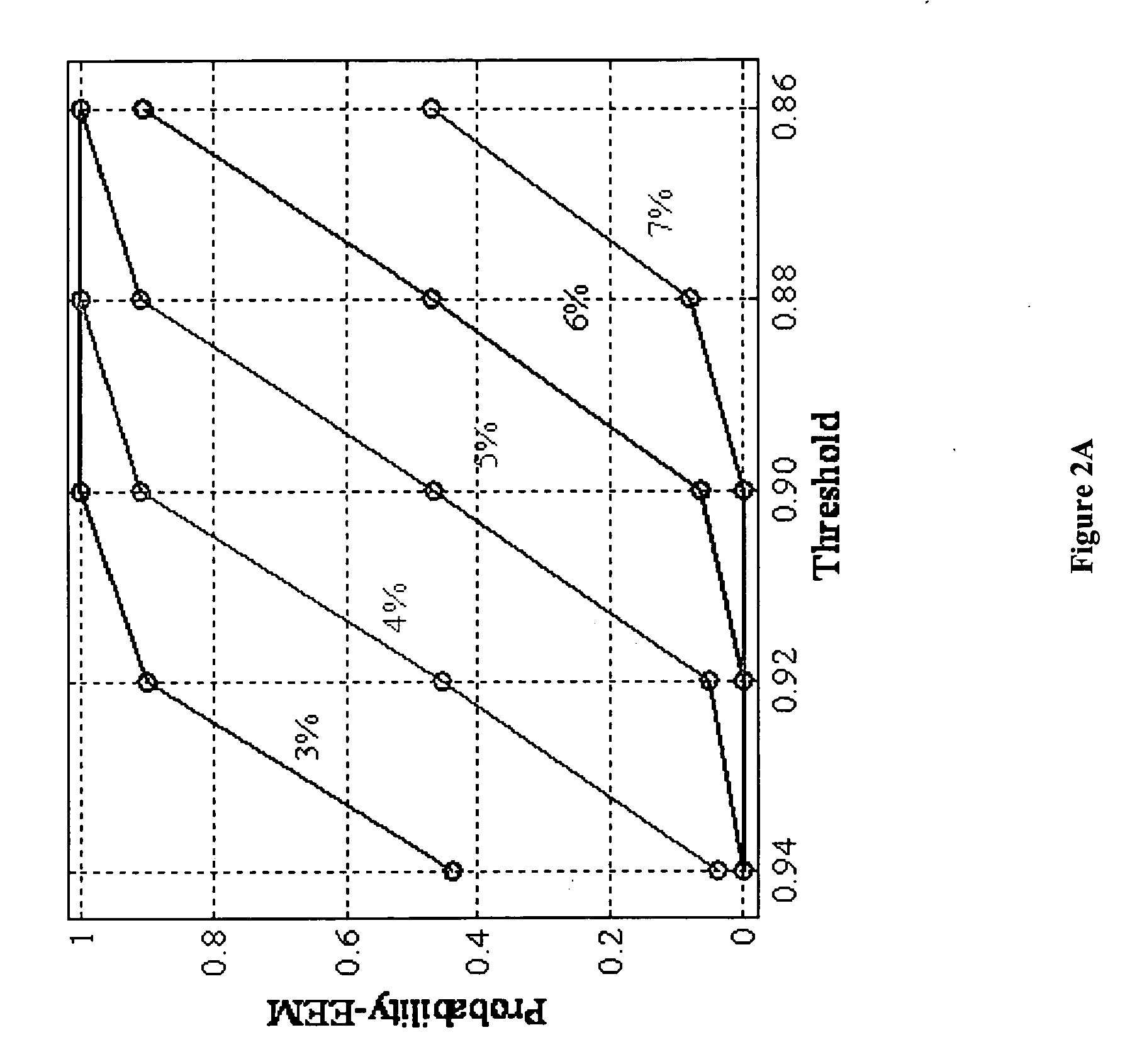
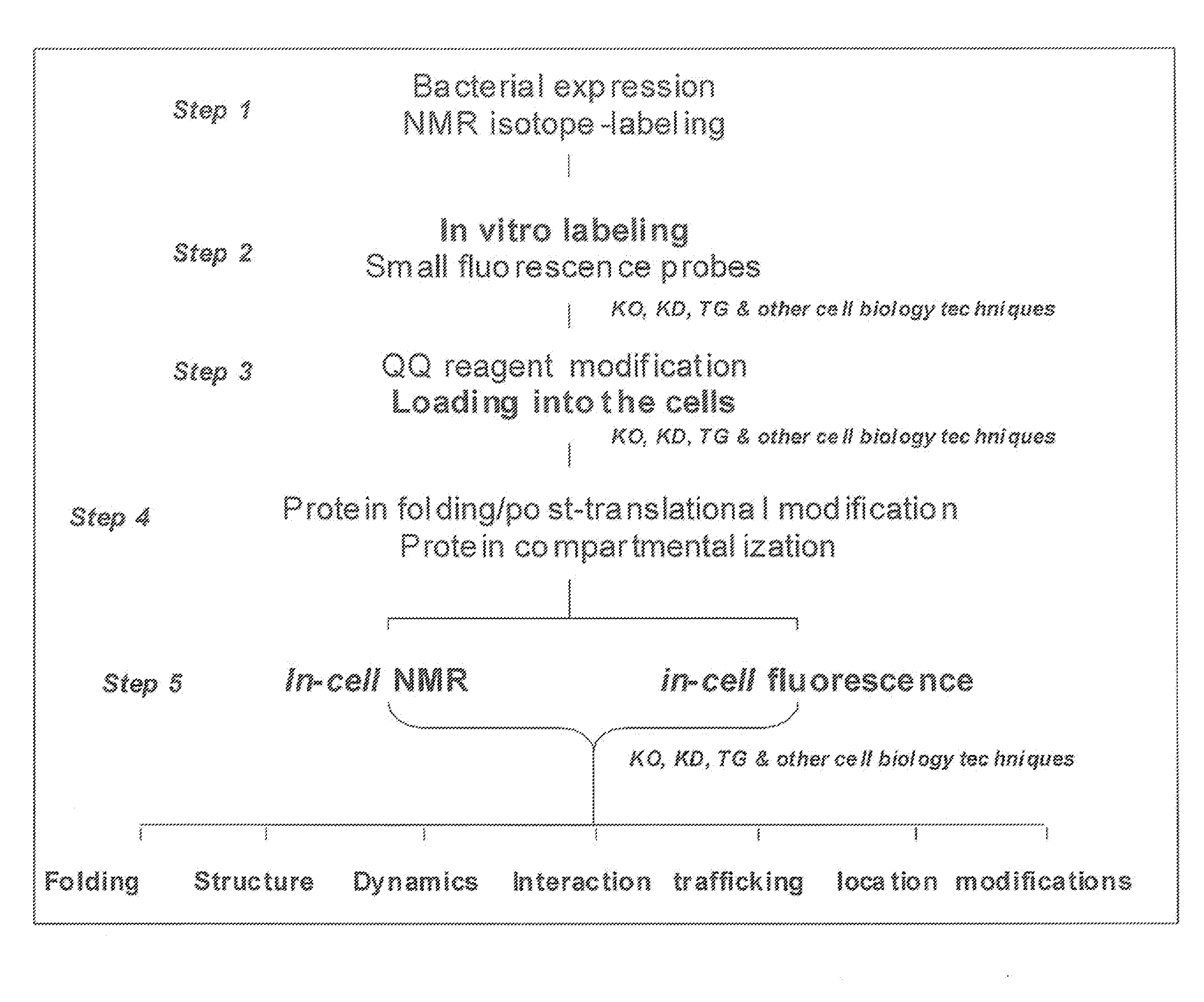
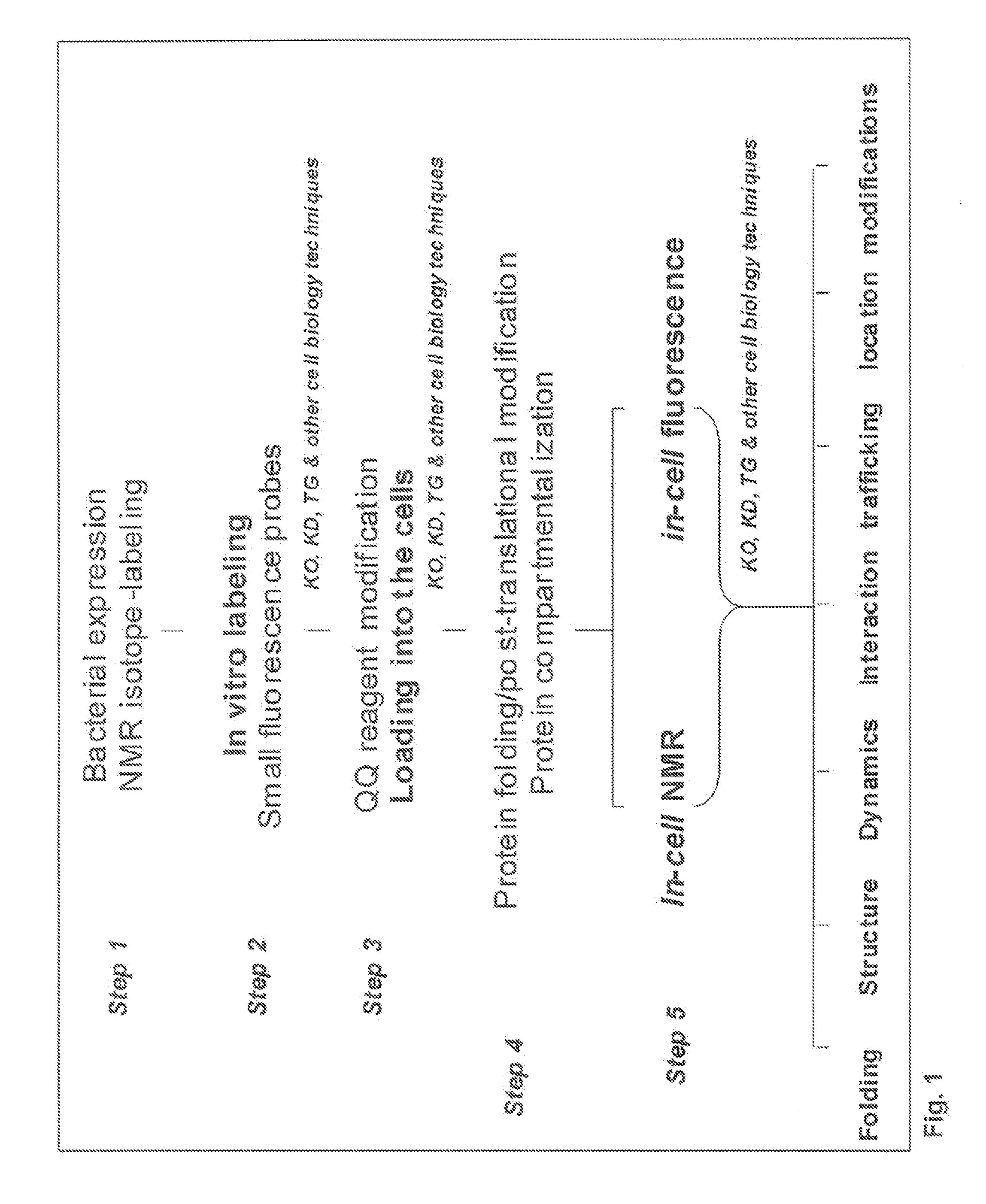
A protein transduction method for efficiently delivery of exogenous proteins into mammalian cells is invented, which has the capability of targeting different cellular compartments and protection from degradation of the delivered proteins from cellular proteases. A composition for treat proteins has cation reagents, lipids and enhancers in a carrier. The method can be used in a number of ways including: production of large quantities of properly folded, post-translationally modified proteins using mammalian cell machinery, a in-cell fluorescence spectroscopy and imaging using small molecule fluorophores and a in-cell NMR spectroscopy using living mammalian cells. The method permits cell biology at atomic resolution that is physiologically and pathological relevant and permits protein therapy to treat human diseases. The method can also be used to deliver exogenous protein inside mammalian cells, wherein the exogenous proteins follow a similar secretion pathway as that of the endogenous protein.
Owner:WAYNE STATE UNIV
Spectroscopic chemical analysis methods and apparatus
ActiveUS7525653B1Reduce weightRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationSpectroscopie ramanAcousto-optics
Owner:PHOTON SYST
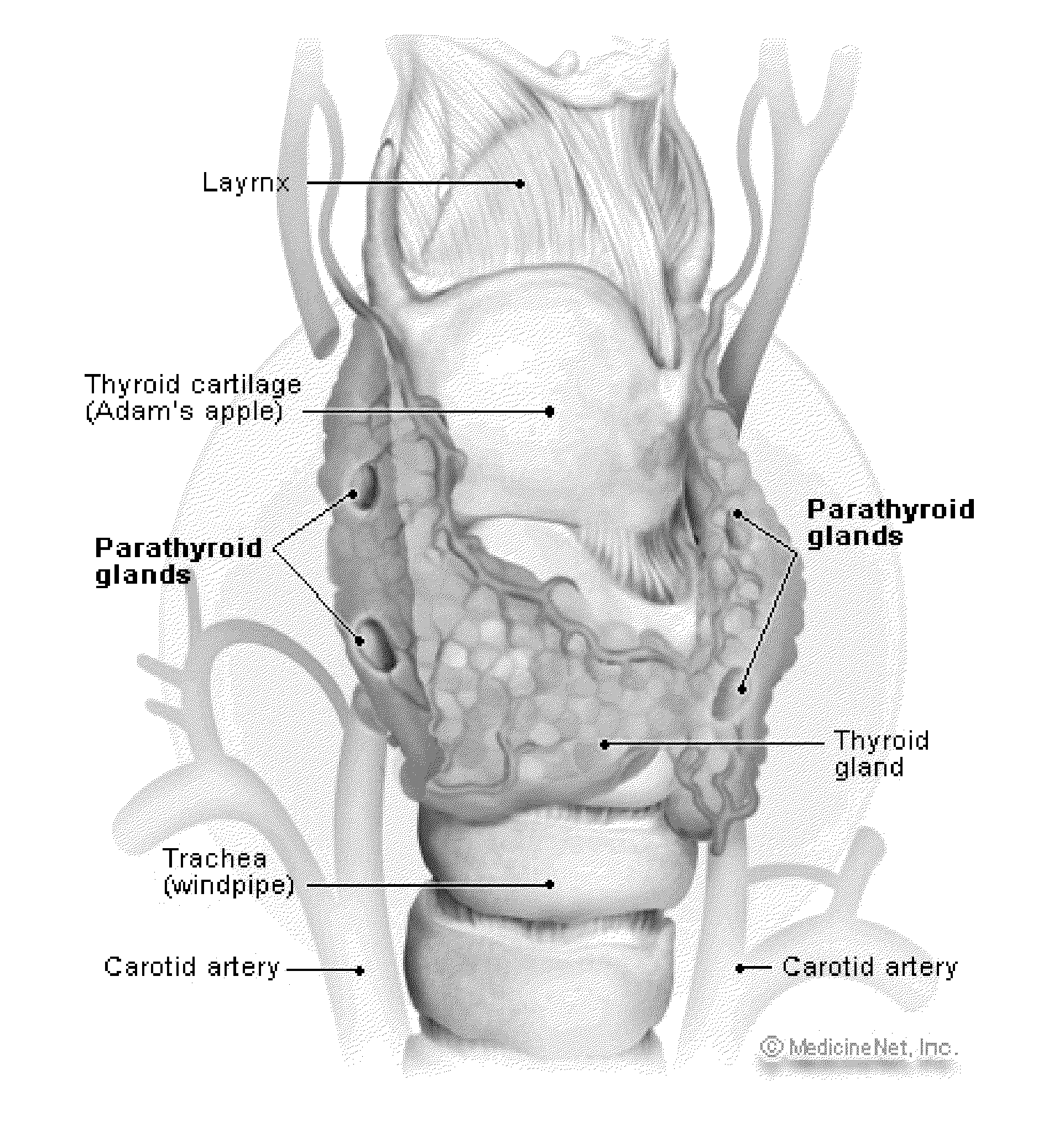
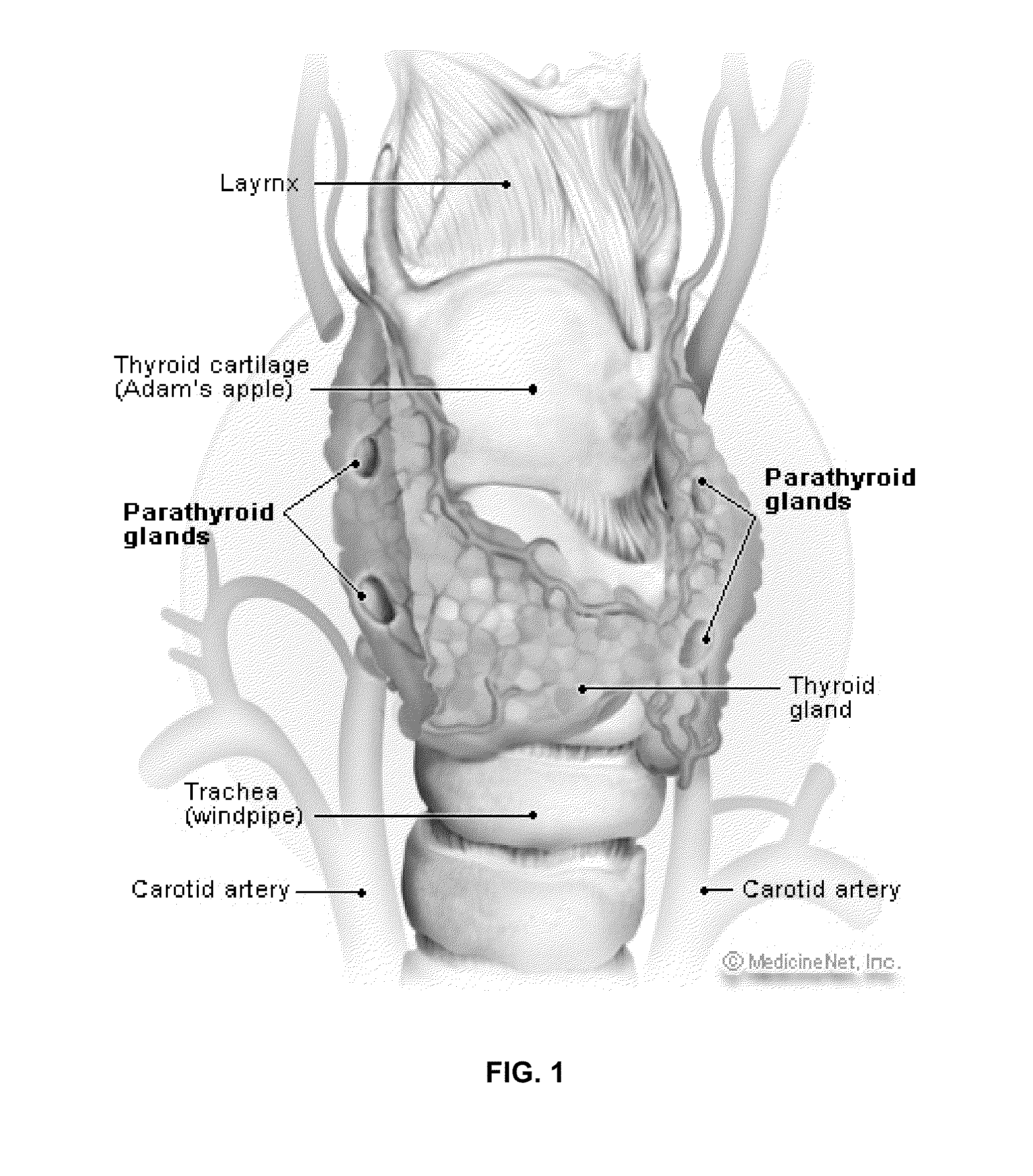
Intra-operative use of fluorescence spectroscopy and applications of same
ActiveUS20120010483A1Improve the level ofSurgical navigation systemsDiagnostics using spectroscopyEndocrine surgeryParathyroid Gland Tissue
In one aspect, the present invention relates to a process for intra-operatively providing anatomical guidance in endocrine surgery. In one embodiment, the process includes the steps of illuminating tissues in the neck area of a living subject with a beam of light having a predetermined wavelength, obtaining Raman data from light scattered from the illuminated tissues, finding Raman signatures corresponding to thyroid or parathyroid tissues from the obtained Raman data, and identifying the thyroid or parathyroid tissues from the corresponding Raman signatures.
Owner:VANDERBILT UNIV
Integrating sphere device for optical measurement
InactiveCN101915609AGood symmetryImprove cooling effectPhotometryOptical measurementsColor measurement
The invention discloses an integrating sphere device for optical measurement, relates to the technical field of optical measurement and aims to solve the problems of poor symmetry, ineffective heating control of a light source and non-adjustable flux of a sampling port existing in the conventional integrating sphere device structure. A first half integrating sphere shell and a second half integrating sphere shell of the device are fastened together to form a hollow sphere shell; a central light barrier is fixed at the central position of a joint surface of the first half integrating sphere shell and the second half integrating sphere shell; a joint between an adjustable light source and the first half integrating sphere shell is provided with a sampling hole; a slit device is fixed between the adjustable light source and the sampling hole; a stray light eliminating device is fixed on the second half integrating sphere shell through a screw thread; a position on which the second half integrating sphere shell is fixed with the stray light eliminating device is provided with a light emitting hole; and a detection hole is formed on the lower part of the light emitting hole on the second half integrating sphere shell. The integrating sphere device is suitable for fields such as the measurement of the radiation quantity of a light-emitting diode (LED) or various lamps, color measurement, fluorescence spectroscopy and the like.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Atmospheric environment pollution monitoring system and detection method
The invention relates to atmospheric environment pollution monitoring system and detection method, in particular to a device for acquiring fluorescence spectra generated by the interaction of the short-pulse laser and the atmosphere and the quantitative analysis of the fluorescence spectra. The system comprises a short-pulse laser, a light path part, a fluorescence spectrum acquiring part and a data processing and analyzing part. The system is characterized in that the pulse femtosecond laser sent out by a pulse femtosecond laser device goes into a sample cell via a femtosecond laser focusing lens group and a reflector, the lens group simulates the self focusing by the laser kerr effect, shatters gas molecules to generate multi-photon / tunnel ionization, and sends out nonlinear fluorescence spectra, the spectra are imaged by the lens group and are obtained by a spectrophotometer and a CCD (Charge Coupled Device) by detection, and the spectra respectively go into a sort module and a quantification module after going into a filtering module to be subject to the gas sorting and the quantitative analysis. The invention can carry out the nonlinear fluorescence spectrum analysis on gases of extensive wave bands from infrared to ultraviolet, can simultaneously monitor multiple gaseous pollutants, and has good instantaneity.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
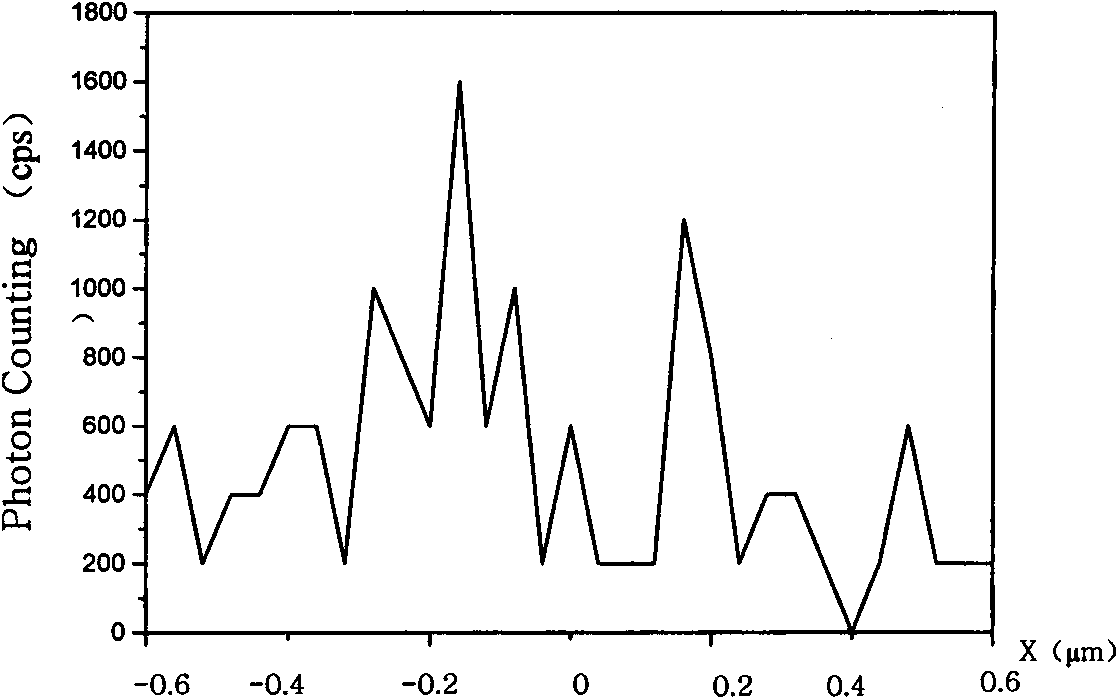
Method for fast optical tracking of single molecule and device thereof
ActiveCN101655460AInhibition of the effects of fluorescent signal detectionFluorescence/phosphorescencePhoton detectionOpto electronic
The invention discloses a method for fast optical tracking of a single molecule and a device, and relates to a technology for detecting single-molecule fluorescence spectroscopy and signal processing.The method uses the single-photon detection technology for detecting molecular fluorescence, analyzes the detected position with strongest fluorescence strength for determining the position of the single molecule, controls a nano-translation stage by feedback of a computer for tracking the position of the molecule and realizes the fast tracking of the motion trajectory of the molecule. The methodadopts the low-frequency sine wave modulation for triggering a laser signal of a single-molecule sample, thereby improving the signal-to-noise ratio. Compared with the prior art, the method adopts the single-photon detection technology, thereby being capable of determining and fast tracking the position of the single molecule in a relatively fine manner; the central position of the optoelectronicfeedback control nano-translation stage is changed along with the position of the single molecule, thereby being capable of reflecting the motion trajectory of the single molecule in a real-time manner; and the use of the modulation and demodulation technology can effectively suppresses the impacts of background noise on the detection of a fluorescence signal of the single molecule.
Owner:SHANXI UNIV
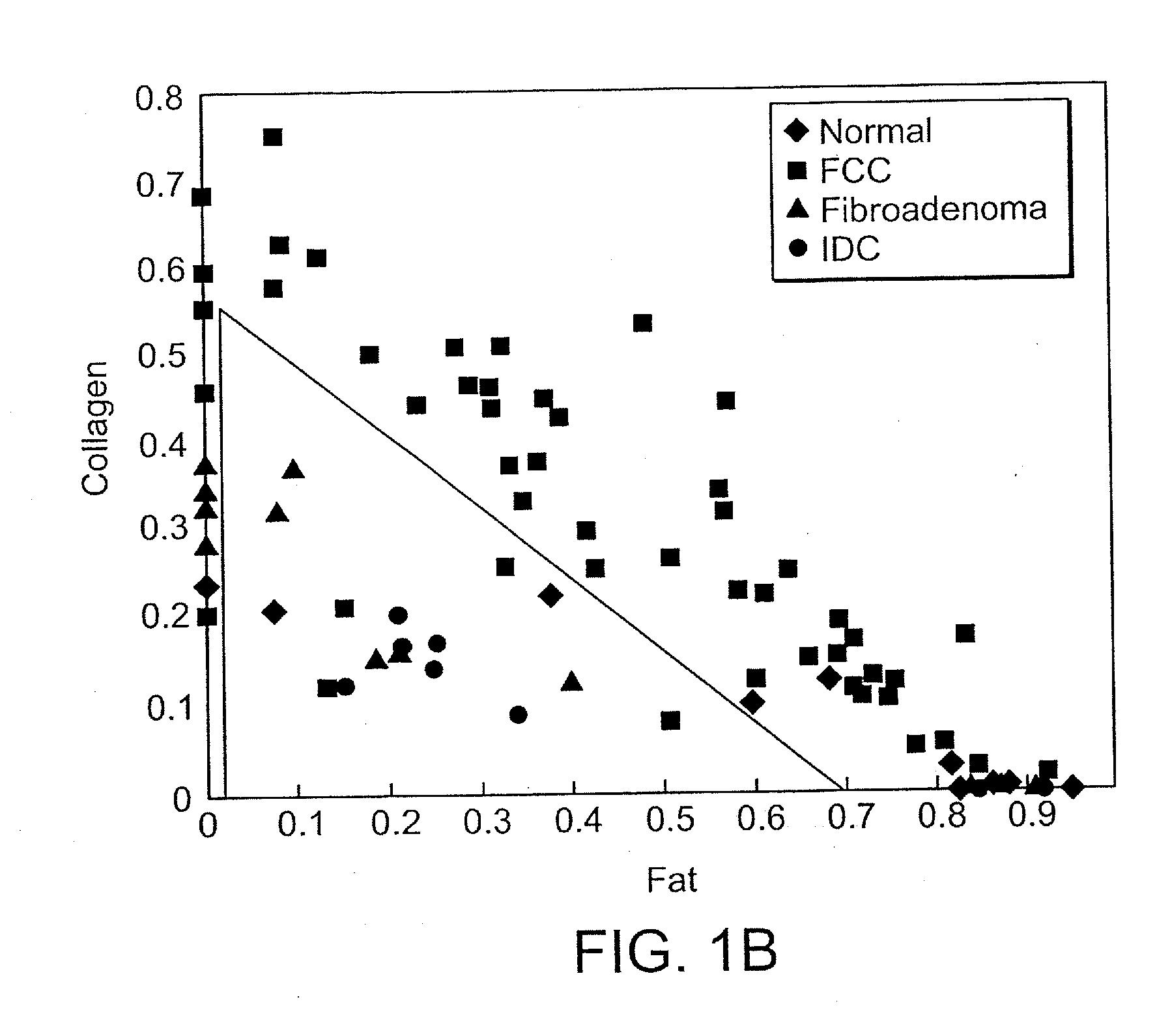
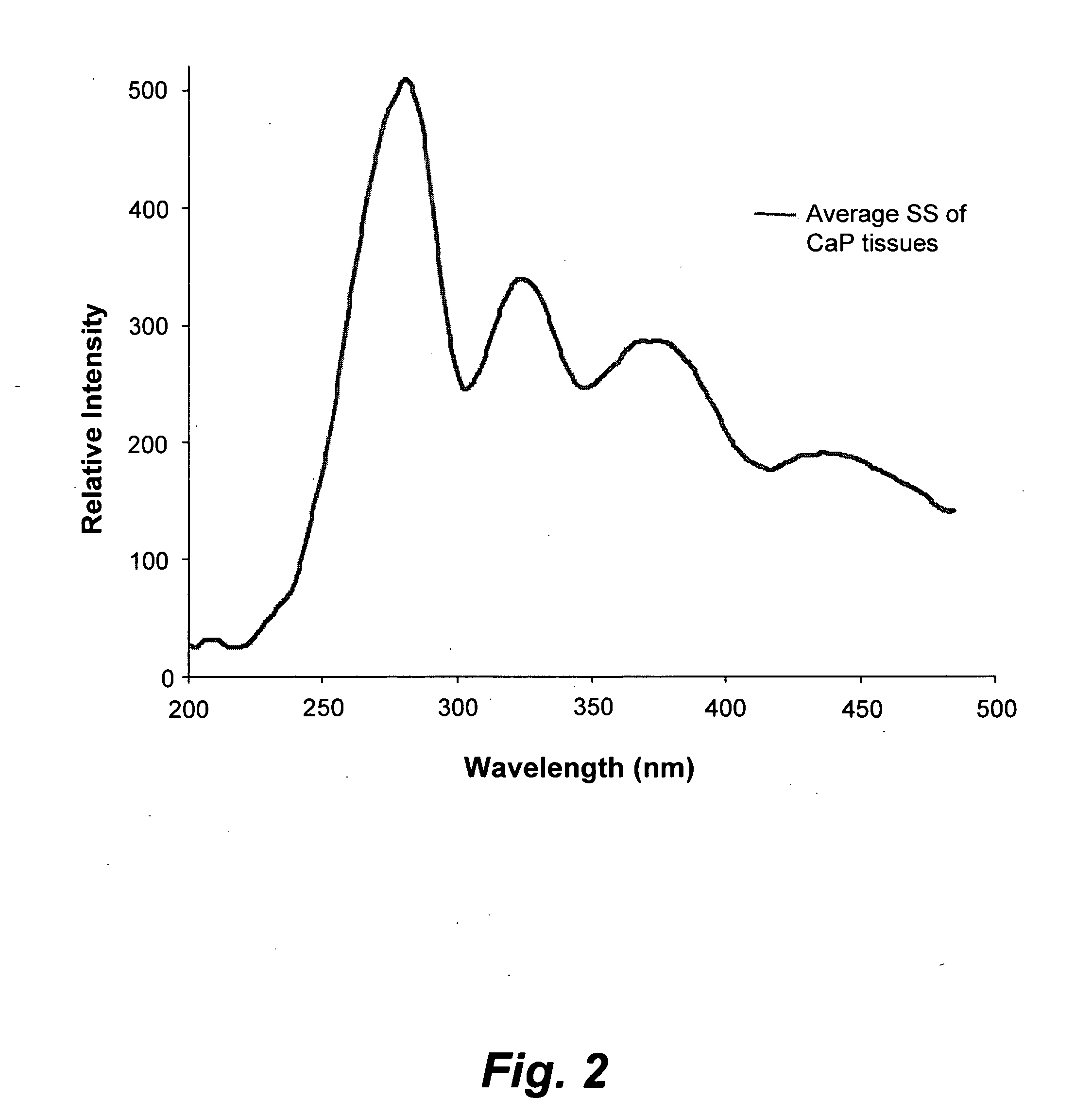
Method for discriminating between benign and malignant prostate tumors
The method for discriminating between benign and malignant prostate tumors relates to analyzing samples of blood, urine and tissue by fluorescence spectroscopy in order to detect the presence of naturally occurring molecules in the fluids and tissue that serve as biomarkers indicative of cancer in the human body. The analysis can be carried out based on fluorescence emission spectra, fluorescence excitation spectra and synchronous (emission and excitation) spectra of bio-samples. The detection, diagnosis, and follow-up and also discrimination between malignant and benign prostate tumors may be made by comparison of ratios of fluorescence emissions and / or excitation intensities of tryptophan, tyrosine, elastin, collagen, bile pigments, NADH, flavins and various species of porphyrins.
Owner:KING SAUD UNIVERSITY
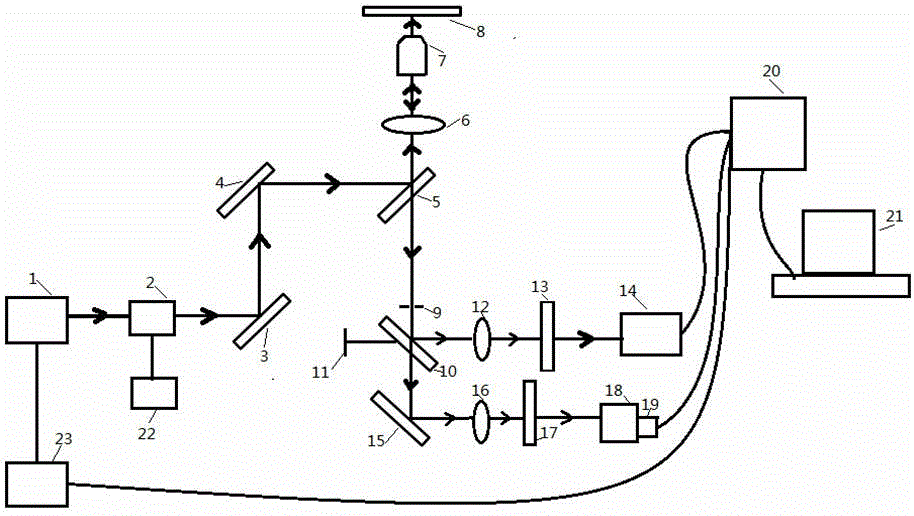
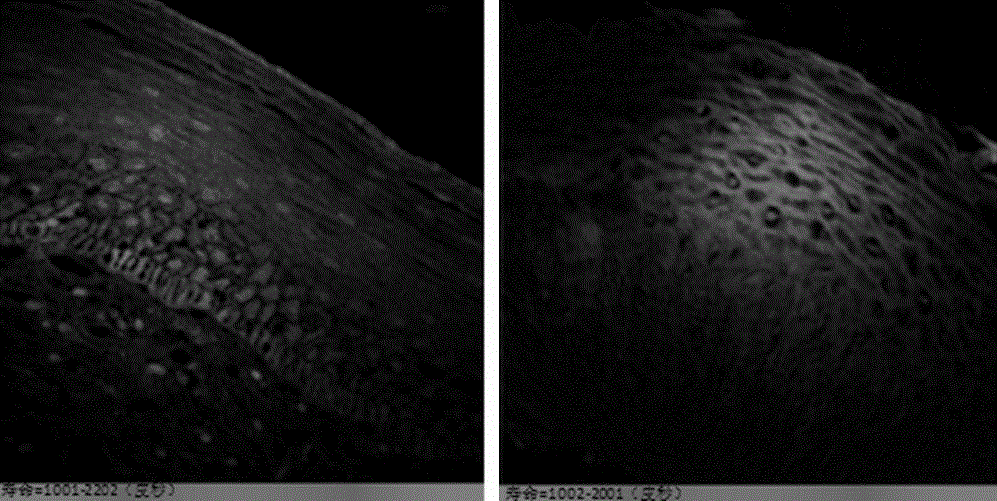
Early cancer diagnosis device based on combination of auto-fluorescence lifetime imaging and fluorescence spectroscopy
The invention belongs to the technical field of medical equipment, in particular to an early cancer diagnosis device based on combination of auto-fluorescence lifetime imaging and fluorescence spectroscopy. The auto-fluorescence lifetime imaging detection and fluorescence spectroscopy detection are coupled with a laser scanning confocal microscope for observing cytologic morphology of a biological sample. The device comprises a laser scanning confocal microscope device and two fluorescence signal acquisition devices; different detectors receive fluorescence lifetime information and fluorescence spectroscopy information respectively, and a computer processing system processes the auto-fluorescence lifetime information and fluorescence spectroscopy information. The multiple dimensional information of fluorescence images, fluorescence lifetime and fluorescence spectroscopy of the biological sample can be detected directly, early detection and diagnosis of various cancers can be implemented, and the application prospect is promised in the fields of biomedicine and clinical diagnostics.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Free cholesterol analogs bearing a boron dipyrromethene difluoro (bodipy) fluorophore in the side chain and method of preparation and use thereof
The present invention relates to free cholesterol analogs bearing a boron dipyrromethene difluoro (BODIPY) fluorophore in the side chain and methods of preparation. The compounds of the present invention can be used in fluorescence spectroscopy and fluorescence microscopy to visualize the exchange, distribution, and trafficking of free cholesterol between living cells and to monitor the movement of free cholesterol between ordered and disordered lipid domains in membranes.
Owner:RES FOUND THE CITY UNIV OF NEW YORK
Loaded double-metal hydrogenation catalyst, and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN105521792AEvenly distributedFully loadedCatalyst activation/preparationMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsFluorescenceHydrodesulfurization
The invention provides a loaded double-metal hydrogenation catalyst, and a preparation method and application thereof. The catalyst comprises a gamma-Al2O3-contained carrier and active metal components loaded on the gamma-Al2O3-contained carrier, wherein the active metal components comprise a group-VIB metal component and a group-VIII metal component which have the following characteristics: through the analysis of an X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, the mol ratio of the group-VIB metal atom to the Al atom on the surface of the catalyst is measured to be 0.11 to 0.25, and the mol ratio of the group-VIII metal atom to the Al atom on the surface of the catalyst is measured to be 0.01 to 0.10; and through the analysis of an X-ray fluorescence spectroscopy, the mol ratio of the group-VIII metal atom to the group-VIB metal atom in the catalyst is measured to be 0.2 to 1. The loaded double-metal hydrogenation catalyst prepared by using the method provided by the invention has good dispersibility, active-centre accessibility and structural stability, significantly improves hydrodesulphurization property of the catalyst, and has good industrial application prospects.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Method and apparatus for detecting and discriminating biological from non-biological species
InactiveUS20170059488A1Raman/scattering spectroscopyDiagnostics using spectroscopyHydrocotyle bowlesioidesPollen
This invention concerns the field of sample identification, in particular a method and apparatuses for identifying or discriminating biological species from non biological species, both as individual particles and as components of a composition, by pump-probe fluorescence spectroscopy for time-resolved detection or imaging. The method uses the finding that the UV-induced fluorescence of biological molecules is varied, in particular is depleted, by the addition of visible radiation, whereas this does not occur with non-biological organic molecules. The invention discriminates the fluorescence signals of bio and non-bio particles or species using a differential approach, i.e. the comparison. of the total fluorescence recorded with and without additional visible radiation. This allows to discriminate biological particles comprising aromatic amino-acids (AA), like peptides, proteins, bacteria, viruses, pollens, spores, etc., from non-biological particles, like aromatic (AH) or polyaromatic hydrocarbons (PAH), carbonaceous aerosols, soot, etc.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF GENEVA
Device and method for on-line detection of sulfide concentrations in water sample by utilization of fluorescence spectrophotometry
ActiveCN103364385ARealize detectionEasy to operateFluorescence/phosphorescenceSulfideMaterial resources
The invention discloses a device and a method for on-line detection of sulfide concentrations in a water sample by utilization of fluorescence spectrophotometry. The device comprises a sample acidification component, a gas extraction component, a solution absorption component, a gas supply component, a fluorescence detection component, and the like. The invention further provides the method for on-line sulfide detection by using the device. The device and the method have advantages of stable and reliable detection results, rapid and accurate detection processes, good reproducibility, stable and reliable results, capability of achieving automatic detection processes, capability of continuously real-time on-line monitoring for a long time and capability of saving human and material resources.
Owner:青岛觅海科技有限公司
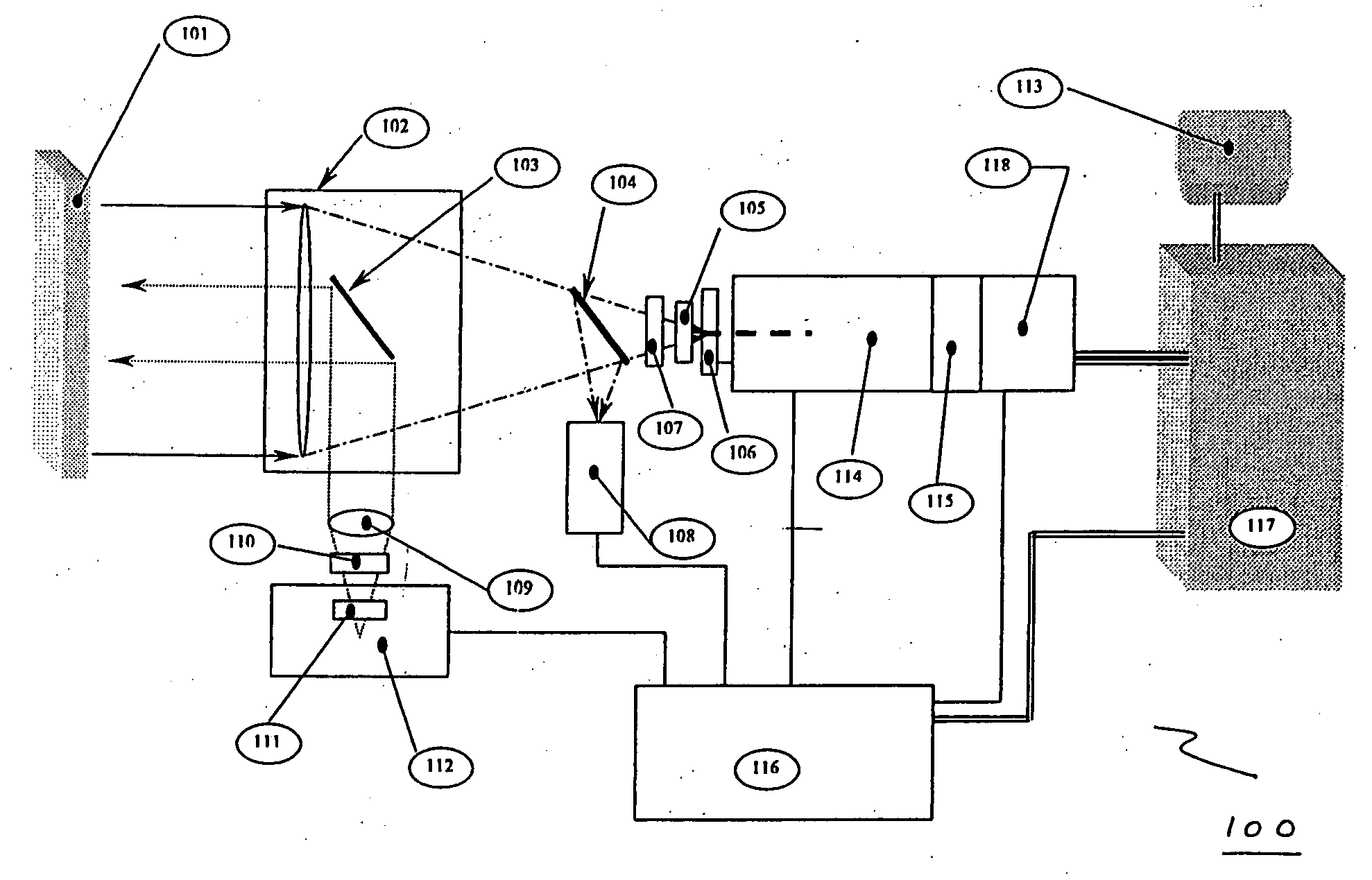
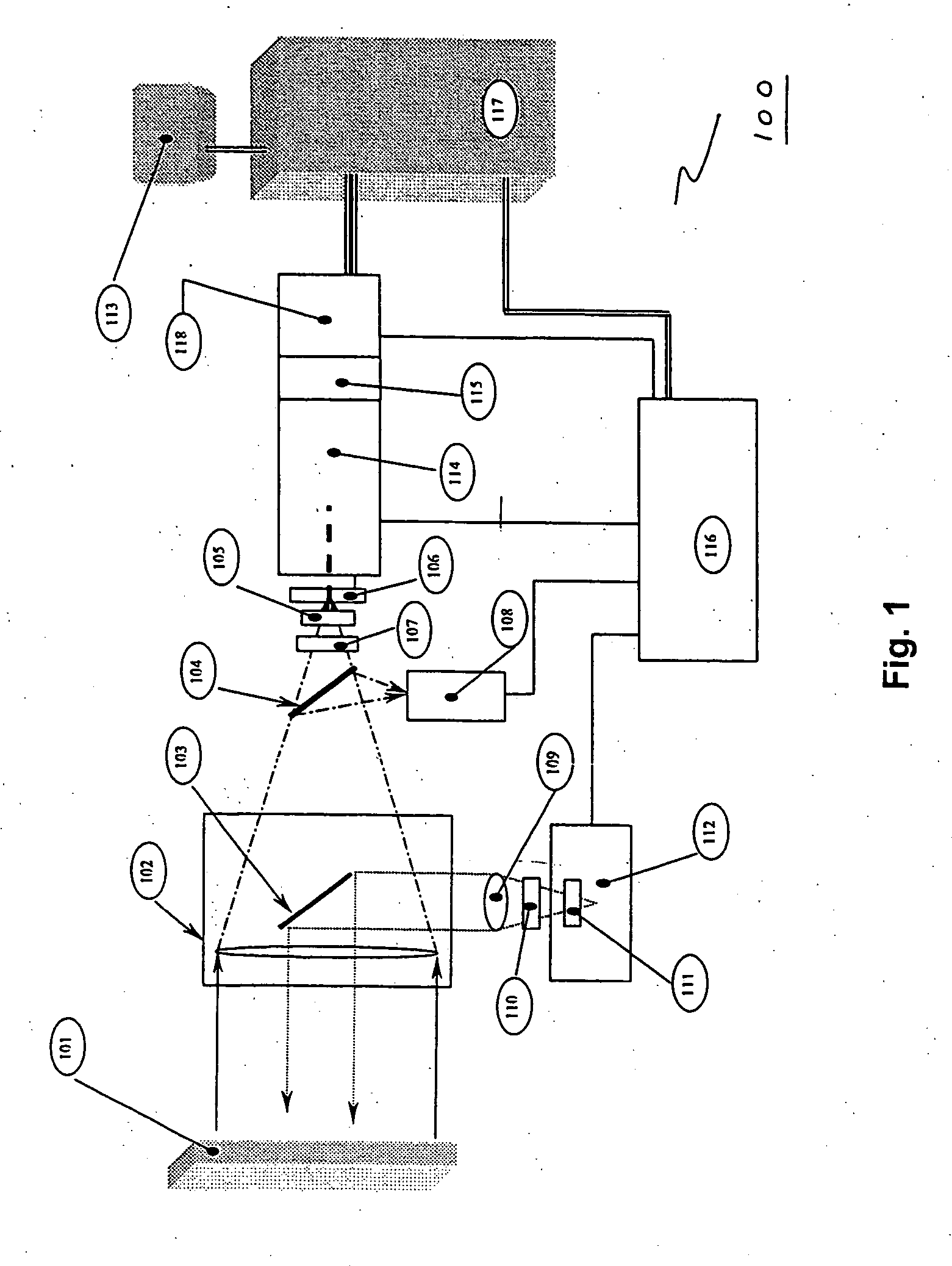
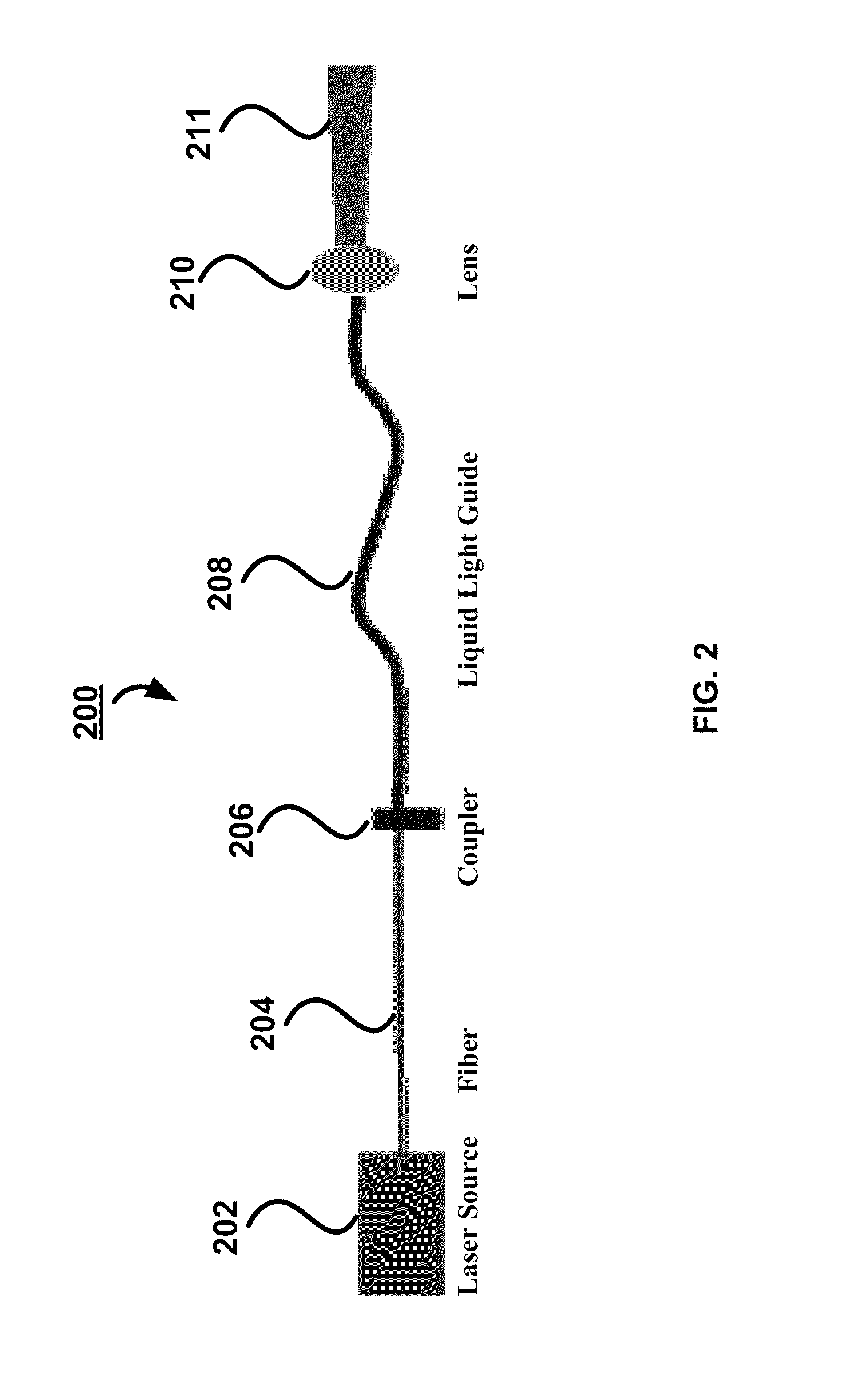
Compact Raman or fluorescence excitation system
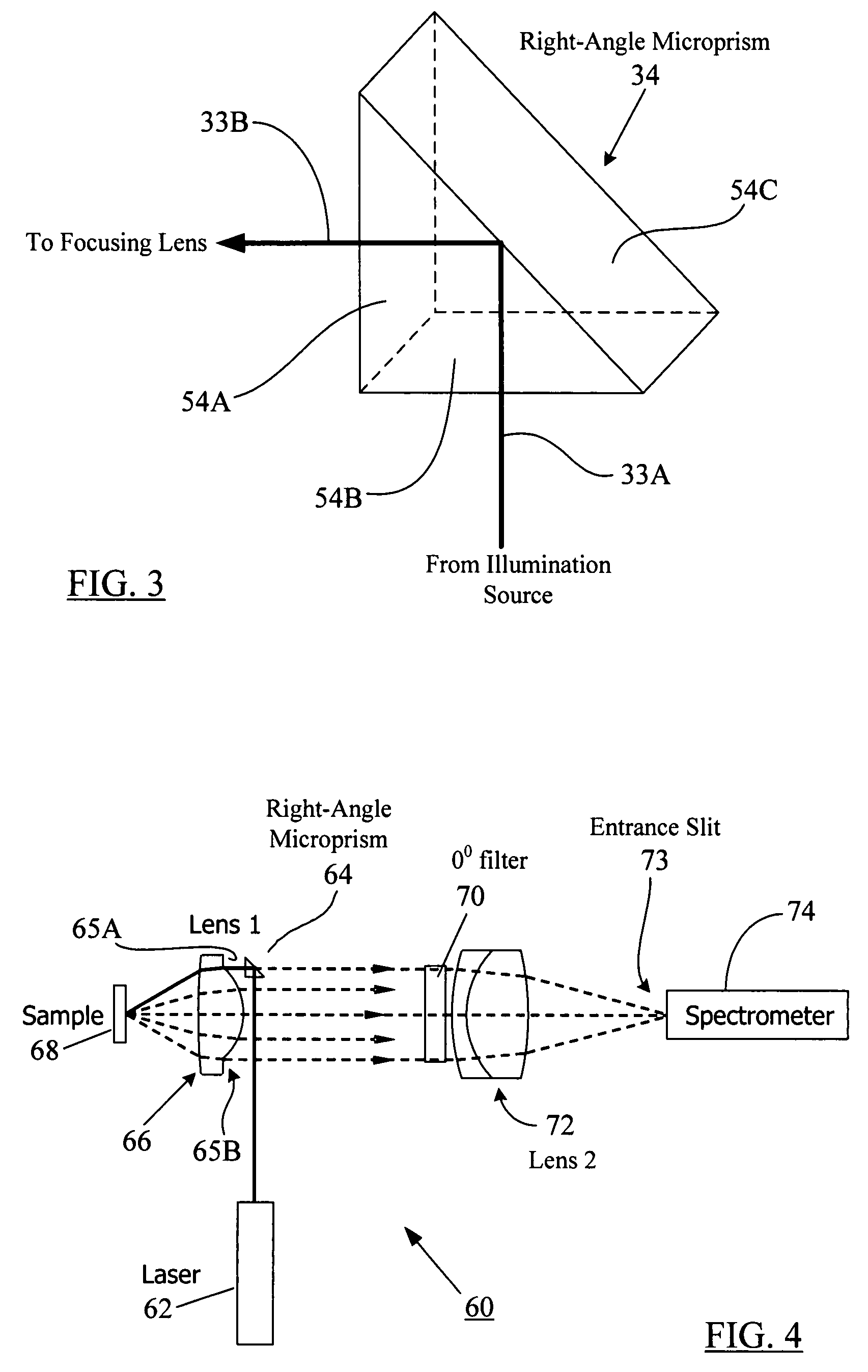
ActiveUS7573570B2Simple system configurationRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationOn boardSpectroscopy
A compact Raman and fluorescence spectroscopy system that uses a microprism or micromirror based optical structure to accomplish the introduction of excitation radiation with compactness and simplified system configuration for portable or mobile spectroscopy applications. A microprism may be glued to a surface location of a focusing lens in the system to directly receive the illumination signal without intervening optical components. Alternatively, the microprism may be simply placed in close physical proximity of the focusing lens without being glued thereto. On the other hand, a micromirror may be used instead of the microprism. The illuminating photons received by the microprism or micromirror may be directly transferred to the sample under investigation via the focusing lens. The compact system may be made portable and may further include an on-board spectrometer with or without a display unit. For chemical detecting applications, a detector (e.g., a CCD array) may also be provided along with the spectrometer.
Owner:CHEMIMAGE TECH LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com