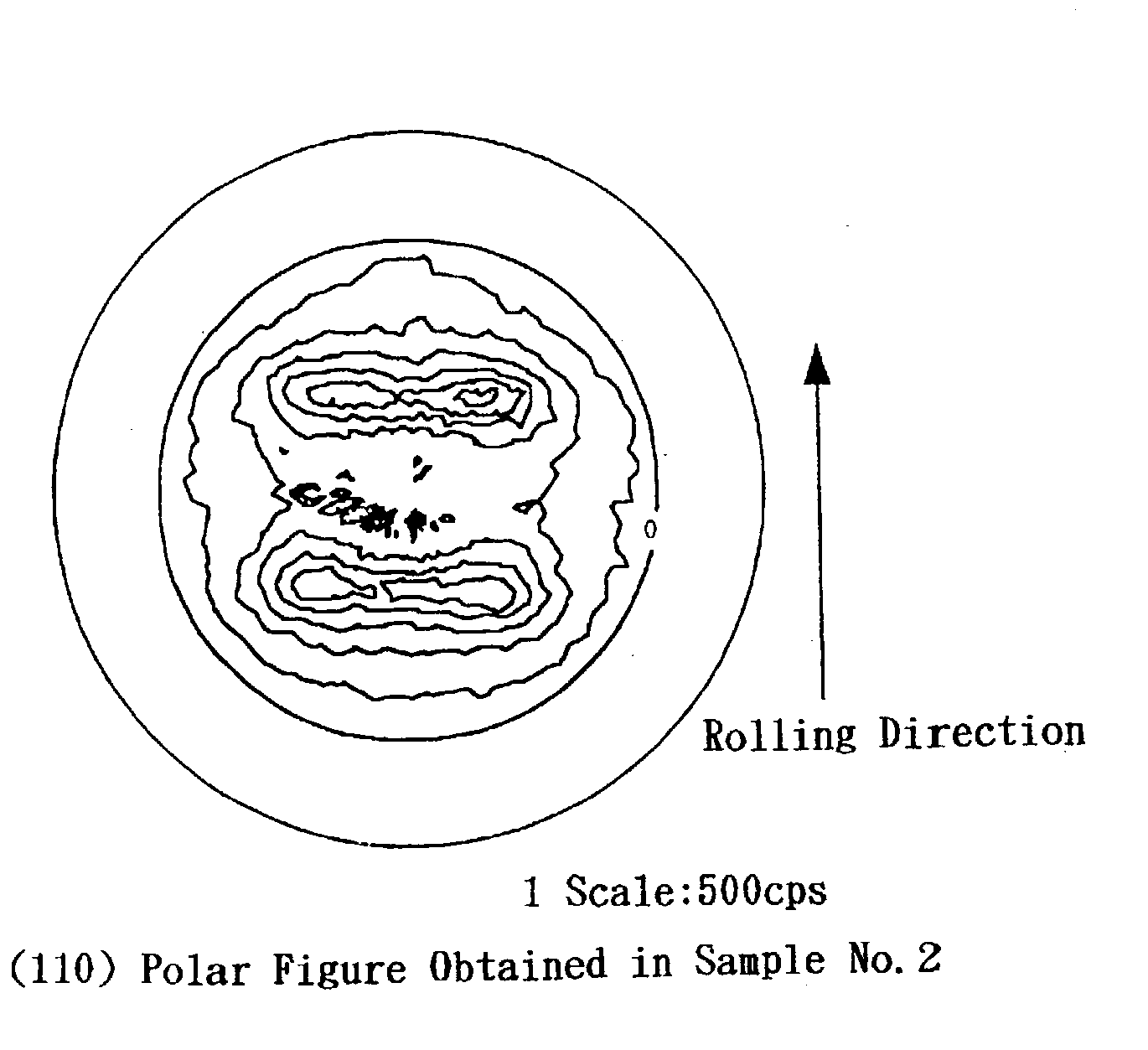
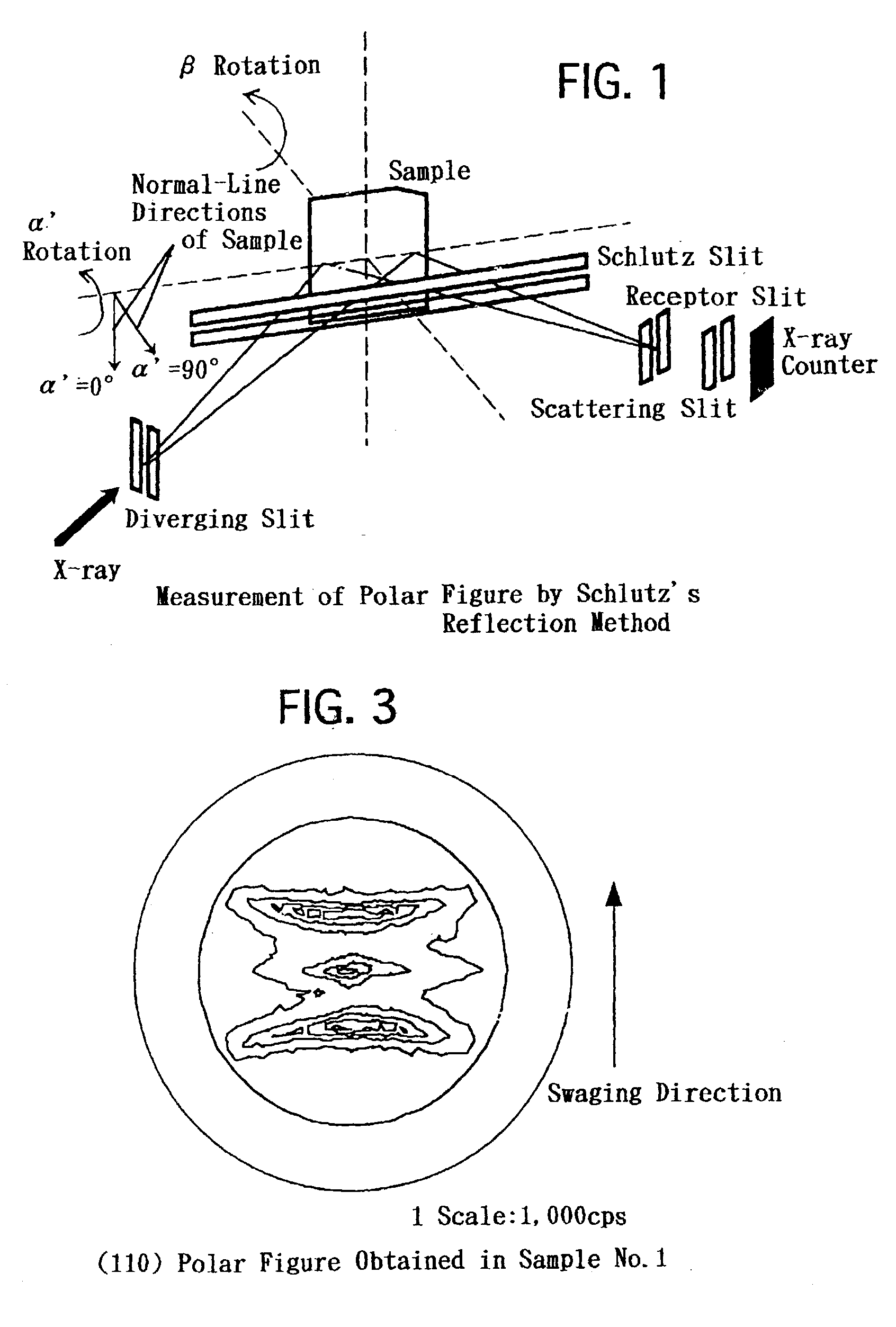
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
58 results about "Interstitial element" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
An interstitial element is an impurity found in "pure" metals or crystals. The quantity of these elements affect the physical properties of the host material. They can be introduced during the manufacturing process.
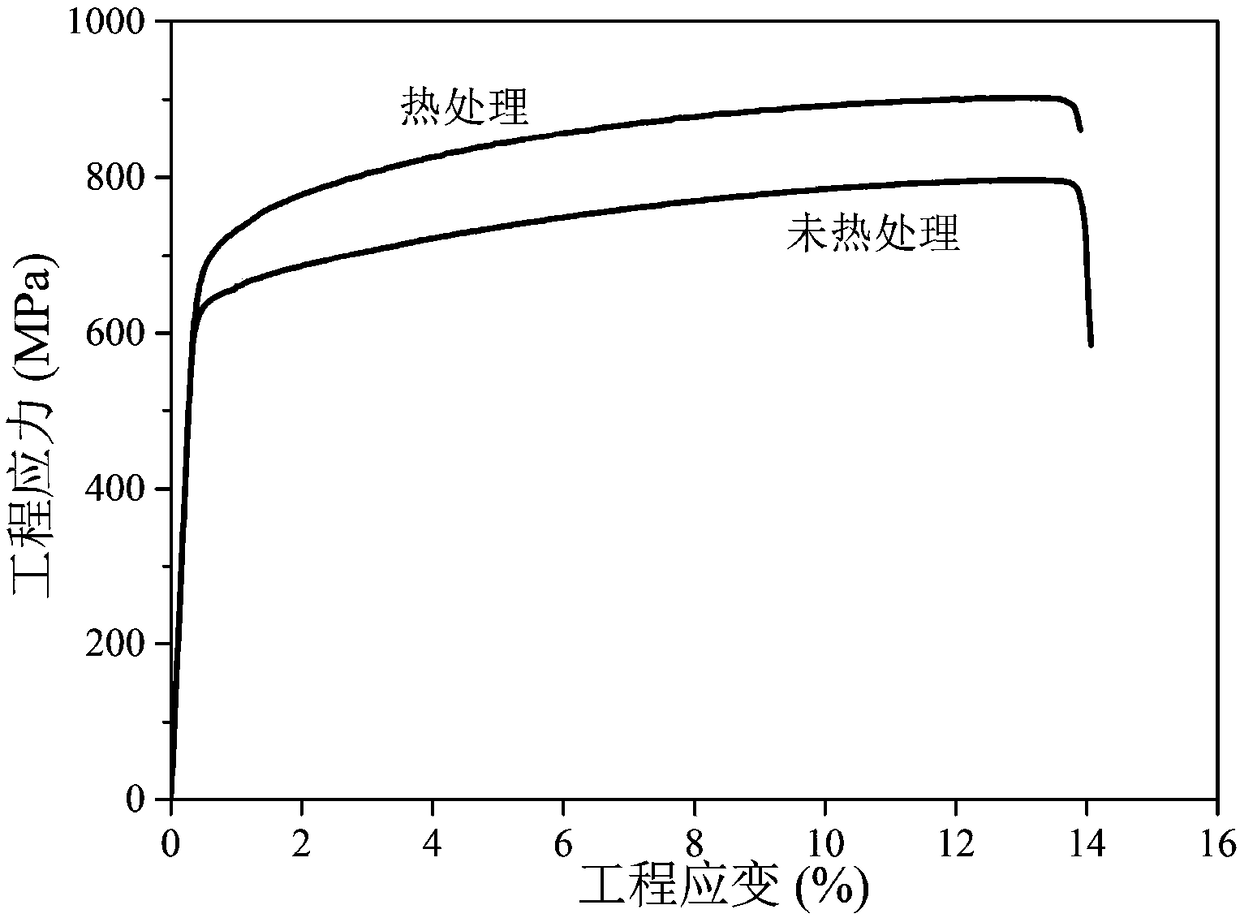
Method for preparing seamless titanium alloy tube for aircraft engine
The invention discloses a method for preparing a seamless titanium alloy tube for an aircraft engine. The seamless titanium alloy tube for the aircraft engine which meets corresponding requirements is manufactured by improving the technological plasticity of the titanium alloy tube material. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly, smelting a spongy cast ingot to introduce interstitial elements as little as possible; secondly, cogging and forging heated cast ingot at large deformation and repeatedly upsetting and stretching the cast ingot to ensure that as-cast coarse grains are completely crushed and thinned, thermally processing formed tube billet under vacuum to eliminate residual stress produced during tube billet extrusion so as to improve the plasticity of the tube billet; thirdly, cogging and rolling the tube billet at large deformation and further thinning the grains; and finally, annealing at a low temperature after cold rolling of intermediate rolling and finished product rolling to effectively control the coarsening of the grains. Therefore, full recrystallization can be ensured by prolonging the heating time, and mechanical property and processing property required by material consumption of the aircraft engine can be met under the condition that the tube structure is fully recrystallized.
Owner:WESTERN TITANIUM TECH
Preparation method of carbon-containing high-entropy alloy composite material
ActiveCN108213422AHigh yield strengthGuaranteed plasticityAdditive manufacturing apparatusIncreasing energy efficiencySelective laser meltingHigh density
The invention discloses a preparation method of a carbon-containing high-entropy alloy composite material. The method comprises the steps of (1) preparing high-entropy pre-alloyed powder, wherein thehigh-entropy pre-alloyed powder comprises at least four of metal elements of Fe, Co, Cr, Ni and Ni, and a C element; and (2) performing selective laser melting molding on the high-entropy pre-alloyedpowder; and performing following thermal treatment on the molded part to obtain the carbon-containing high-entropy alloy. According to the method, high-entropy alloys with outstanding plasticity, suchas Fe, Co, Cr and Ni, are used for preparing a substrate, so that the high plasticity remains after the selective laser melting molding; and meanwhile, an interstitial element C is introduced and issubjected to solid solution reinforcing, so that the yield intensity and the ultimate strength of the substrate can be obviously improved; the supercooling degree in the selective laser melting process is high, the interstitial element C can be uniformly dissolved into the substrate in a solid solution manner, and coarse and big carbide are not segregated and separated out, so that the plasticityof the material is ensured; a high-density (more than 99%) product is prepared through the selective laser melting mode.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Corrosion-resistance weldable titanium alloy with high strength and high impact toughness and preparation method thereof
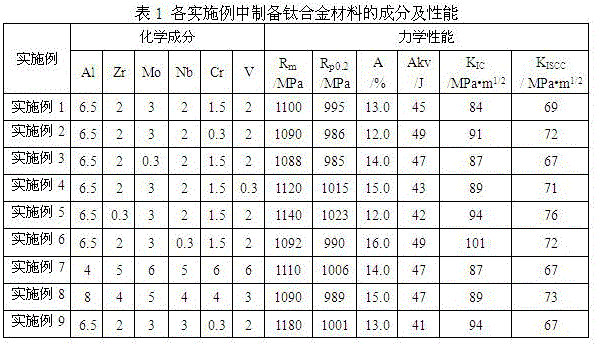
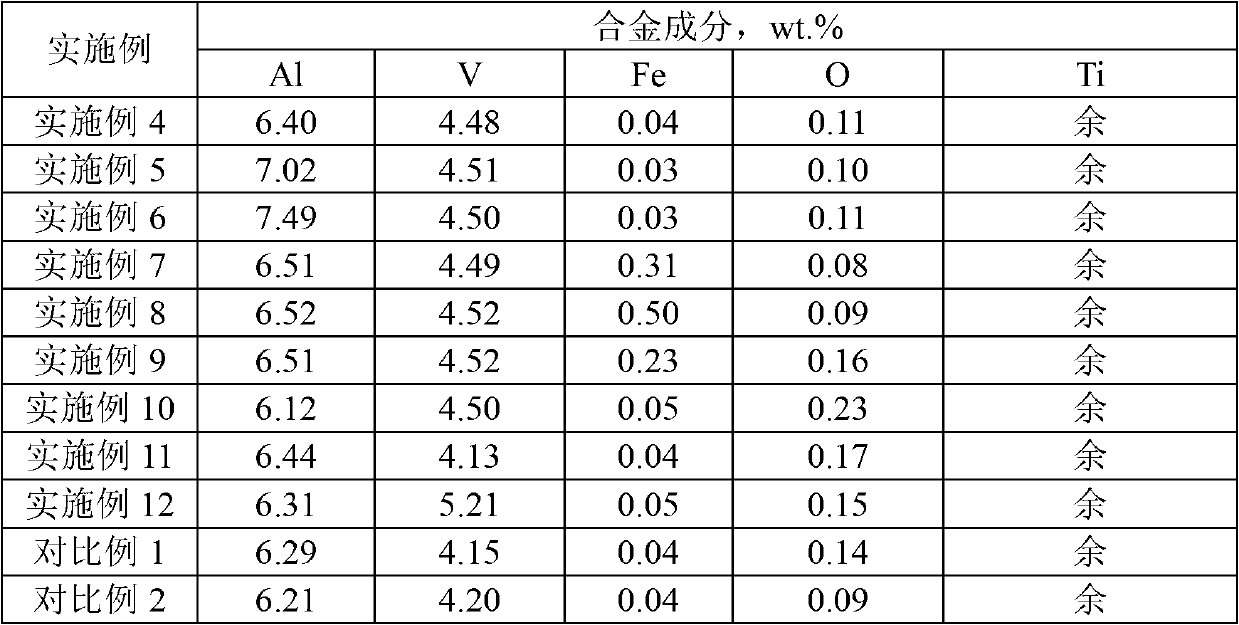
The invention discloses a corrosion-resistance weldable titanium alloy with high strength and high impact toughness, and relates to the technical field of titanium alloys. The corrosion-resistance weldable titanium alloy comprises the following components in percentage by mass: 4.0-8.0 wt.% of Al, 0.3-6.0 wt.% of Mo, 0.3-6.0 wt.% of V, 0.3-5.0 wt.% of Nb, 0.3-6.0 wt.% of Cr, 0.3-5.0 wt.% of Zr, aluminum equivalent [Al] not less than 6, molybdenum equivalent [Mo] not more than 8.0, and the balance of Ti, interstitial elements and inevitable impurity elements; the interstitial elements are C, H, O and N; and the mass percentage sum of all the elements in the titanium alloy is 100%. The titanium alloy material has comprehensive performances of high strength, high impact toughness, corrosion resistance and weldability, is excellent in cold and hot processing performance, and can be molded as forgings, thick plates and the like.
Owner:725TH RES INST OF CHINA SHIPBUILDING INDAL CORP
Casting manufacturing method of superconducting NbTi alloy
The invention discloses a casting manufacturing method of a superconducting NbTi alloy. The casting manufacturing method comprises the following steps of carrying out purification and ingot casting of high-melting point metal Nb to obtain an Nb rod, pressing low-melting point sponge active metal Ti into a semi-cylindrical tile, carrying out assembly welding of the Nb rod and the semi-cylindrical tile in an inert gas protective atmosphere to obtain a consutrode, and carrying out electric arc melting more than twice. The superconducting NbTi alloy obtained by the casting manufacturing method has no impurities, high uniformity, less interstitial elements and good plasticity, and is conducive to manufacture of thin core rods suitable for large-scale application and alloy materials having a high current-carrying capability and a low cost.
Owner:NINGXIA ORIENT TANTALUM IND
Nickel-based deformation high temperature alloy being higher than 700 DEG C in service temperature and preparation method of same
The invention discloses a nickel-based deformation high temperature alloy being higher than 700 DEG C in service temperature and a preparation method of same. The alloy includes, by weight, 11.0-14.0% of Co, 15.0-17.0% of Cr, 3.3-4.3% of Mo, 3.3-4.3% of W, 1.6-2.7% of Al, 3.0-4.0% of Ti, 0.6-1.2% of Nb, 0.005-1.2% of Ta, 0.005-0.02% of B, 0.005-0.05% of C, 0.02-0.07% of Zr, 0.001-0.1% of Mg, 0-2.0% of V, 0.2-4.5% of Fe, 0.001-0.01% of Ce and the balanced being Ni. By controlling the content of low-interstitial element C, adding microelements Ce and Mg which are beneficial to hot-working plasticity, and adding a certain amount of Ta for regulating the ratio of precipitation strengthening elements Al, Ti, Nb and Ta, the alloy has the similar comprehensive performance as a second-generation powder high temperature alloy FGH96 at above 700 DEG C, but is greatly reduced in cost than the latter. The alloy has high reliability, is low in whole-life cost and is high in production efficiency.
Owner:CENT IRON & STEEL RES INST
Preparing method of Ti Al-based alloy plate
InactiveCN101758236AOvercome the defect of poor deformability during cold and hot processingLow melting pointTension/compression control deviceMetal rolling arrangementsRoom temperatureTitanium
The present invention discloses a preparing method of a Ti Al-based alloy plate, which relates to a preparing method of an alloy plate. The present invention solves the problems that the existing Ti Al-based alloy is not easy to process into to form at room temperature; Ti Al-based alloy plates prepared by powder metallurgy technique are easy to pollute by interstitial elements with many impurities containing oxygen; and Ti Al-based alloy plates prepared by casting metallurgy technique and precision casting art have the disadvantages of crude grain structure, low strength and loose structure. In the method, pure titanium grains are piled in a steel module to obtain a multi-hole titanium prefabricated body; an Al-Si alloy casting wire is cut into block bodies; the block bodies are arranged on the multi-hole titanium prefabricated body to be sintered to obtain a Ti - Al double alloy complex body; the Ti - Al double alloy complex body is coldrolled to obtain a Ti - Al double alloy complex plate; the Ti - Al double alloy complex plate is sintered again, and is cooled to room temperature; the Ti - Al double alloy complex plate is retreated from the steel module to obtain the Ti Al-based alloy plate. The Ti Al-based alloy is processed to be formed at the room temperature, so the Ti Al-based alloy plate has the advantages of compaction, even structure, thin grain structure and high strength, and the negative effect of oxidation and impurities is reduced.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
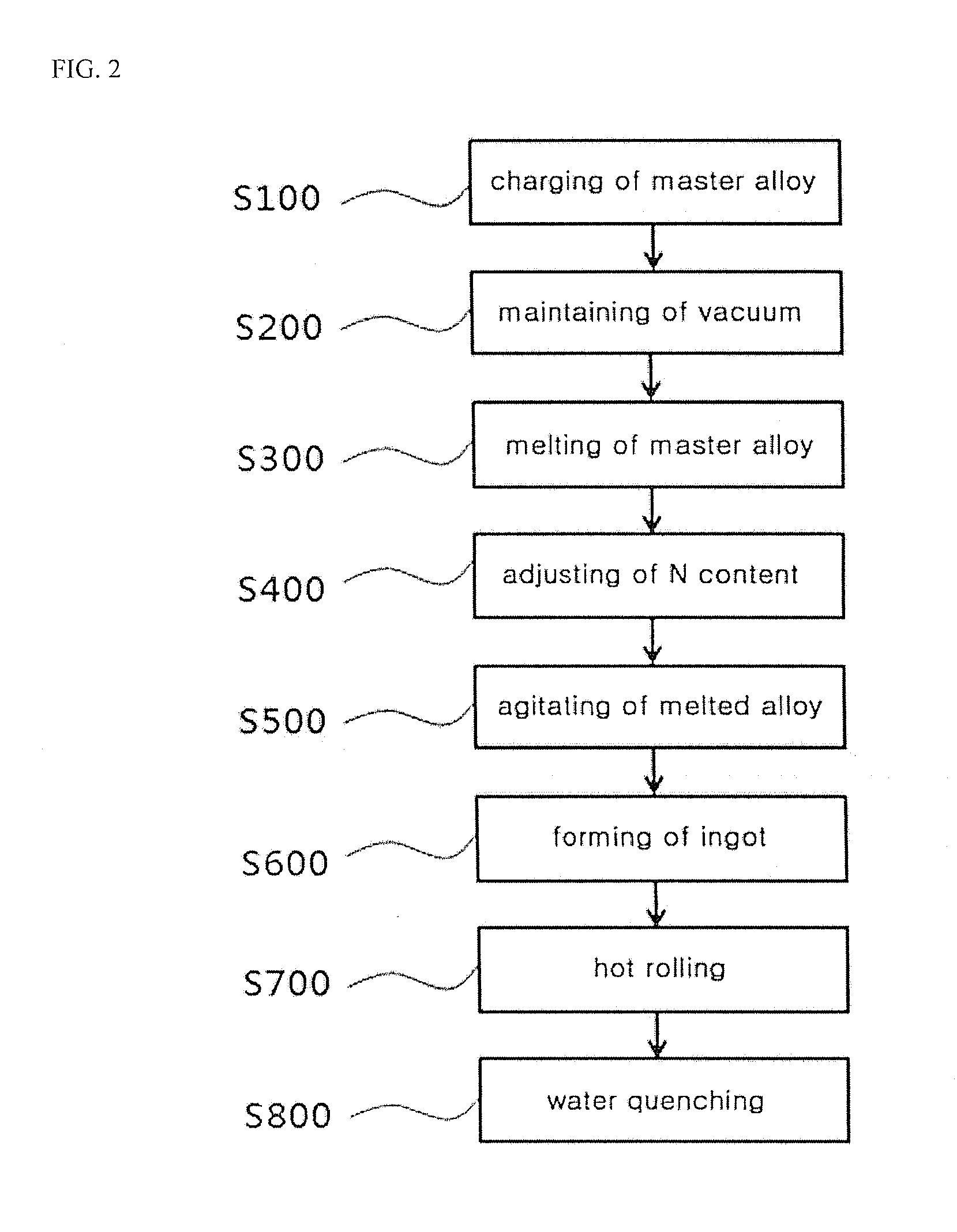
Preparation method for high-uniformity WSTi62441S titanium alloy ingot
The invention discloses a preparation method for a high-uniformity WSTi62441S titanium alloy ingot. The preparation method comprises the following steps of mixing 6.0 to 7.0 mass percent of Al, 1.0 to 2.5 mass percent of Sn, 3.5 to 4.5 mass percent of Mo, 3.0 to 4.5 mass percent of Zr, 0.20 to 0.25 mass percent of Si, 0.4 to 1.5 mass percent of W and the balance of Ti based on the total amount of 100 percent, performing electrode pressing and welding on the mixture to obtain a consumable electrode, and performing vacuum smelting on the consumable electrode for many times to obtain the high-uniformity WSTi62441S titanium alloy ingot. According to the preparation method, the problems of composition segregation, poor controllability in the content of impurities and an interstitial element and poor batch stability of the conventional preparation method are solved, the prepared WSTi62441S titanium alloy ingot is uniform in element composition and high in batch stability, and the preparation method is applied to the industrial production of WSTi62441S titanium alloy ingots in specifications of Phi560 to Phi720mm.
Owner:西部超导材料科技股份有限公司
C+n austenitic stainless steel having high strength and excellent corrosion resistance, and fabrication method thereof
InactiveUS20110226391A1Economical efficiency can be improvedContent of nickel is minimizedManganeseBiocompatibility Testing
A C+N austenitic stainless steel with high mechanical strength and excellent corrosion resistance and a fabrication method thereof are provided. The C+N austenitic stainless steel consists of: 8 to 12 wt. % manganese; 15 to 20 wt. % chromium; 2 wt. % or less nickel; 4 wt. % or less tungsten; 2 wt. % or less molybdenum; 0.6 to 1.0 wt. % of total C+N content; a balance of iron; and unavoidable impurities. The austenitic stainless steel fabricated provides mechanical properties of a tensile strength of 850 MPa or higher and an uniform elongation of 45% or higher, obtained through controlling the contents of the interstitial elements and those of the substitutional elements. The alloy also provides corrosion resistance and a biocompatibility due to the minimized content of nickel which causes allergic reaction to the human body. Therefore, the C+N austenitic stainless steel is applicable in the fabrication of a variety of functional components and structural fields.
Owner:KOREA INST OF MASCH & MATERIALS
Alpha and beta combined titanium alloy wire for electron beam fused deposition rapid formed structural member with strength level of 920 MPa
The invention discloses an alpha and beta combined titanium alloy wire for an electron beam fused deposition rapid formed structural member with the strength level of 920 MPa. The alpha and beta combined titanium alloy wire is characterized in that an alpha phase is strengthened by an alloy element Al and an interstitial element O, and a beta phase is strengthened by an alloy element V and Fe, wherein the wire comprises the following components of: 6.2 to 7.5 weight percent of Al, 4.0 to 5.5 weight percent of V, 0.10 to 0.50 weight percent of Fe, 0.12 to 0.25 weight percent of O, the balance of Ti and inevitable impurity elements. The invention also provides the corresponding melting process, a thermal machining process and a thermal treatment process for the electron beam fused deposition rapid formed structural member. By the alloy wire, a requirement on the process for quickly forming by stacking the fuse wires of the electronic beams is met, and the titanium alloy structural member has relatively high mechanical performance. Great social benefits and economic benefits are created after the alloy wire is popularized and applied.
Owner:INST OF METAL RESEARCH - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
High strength/corrosion-resistant austenitic stainless steel with carbon - nitrogen complex additive, and method for manufacturing same
ActiveCN102428200AHigh tensile strengthImprove mechanical propertiesManganeseBiocompatibility Testing
The present invention relates to high strength / corrosion-resistant austenitic stainless steel with a carbon-nitrogen complex additive, and particularly, to an austenitic stainless steel with a carbon (C) and nitrogen (N) complex additive containing: 8-12 wt % of manganese (Mn); 15-20 wt % of chromium (Cr); less than 2 wt % of nickel (Ni); less than 4 wt % of tungsten (W); less than 2 wt % of molybdenum (Mo); 0.6-1.0 wt % of the total content (C+N) of carbon (C) and nitrogen (N); with the remainder being iron (Fe) and other unavoidable impurities, and to a method for manufacturing same. By controlling the content of the interstitial elements (C+N, C / N) and the substitution elements (Mn+Cr, Mn / Cr, or 0.5W+Mo), the austenitic stainless steel manufactured according to the present invention has a tensile strength of more than 850 MPa and uniform elongation of more than around 45%, thereby exhibiting excellent corrosion resistance as well as improving processability, and the content of Ni, a toxic alloy element, is minimized to improve biocompatibility, making the austenite stainless steel applicable to conventional and offshore structures, desalination facilities, and materials for oil and gas facilities / drilling, transportation and the like, which require high strength and high corrosion resistance, and may also be used to manufacture various functional parts for medical prosthetic materials, and accessories such as jewelry, watches, and the like.
Owner:KOREA INST OF MATERIAL SCI
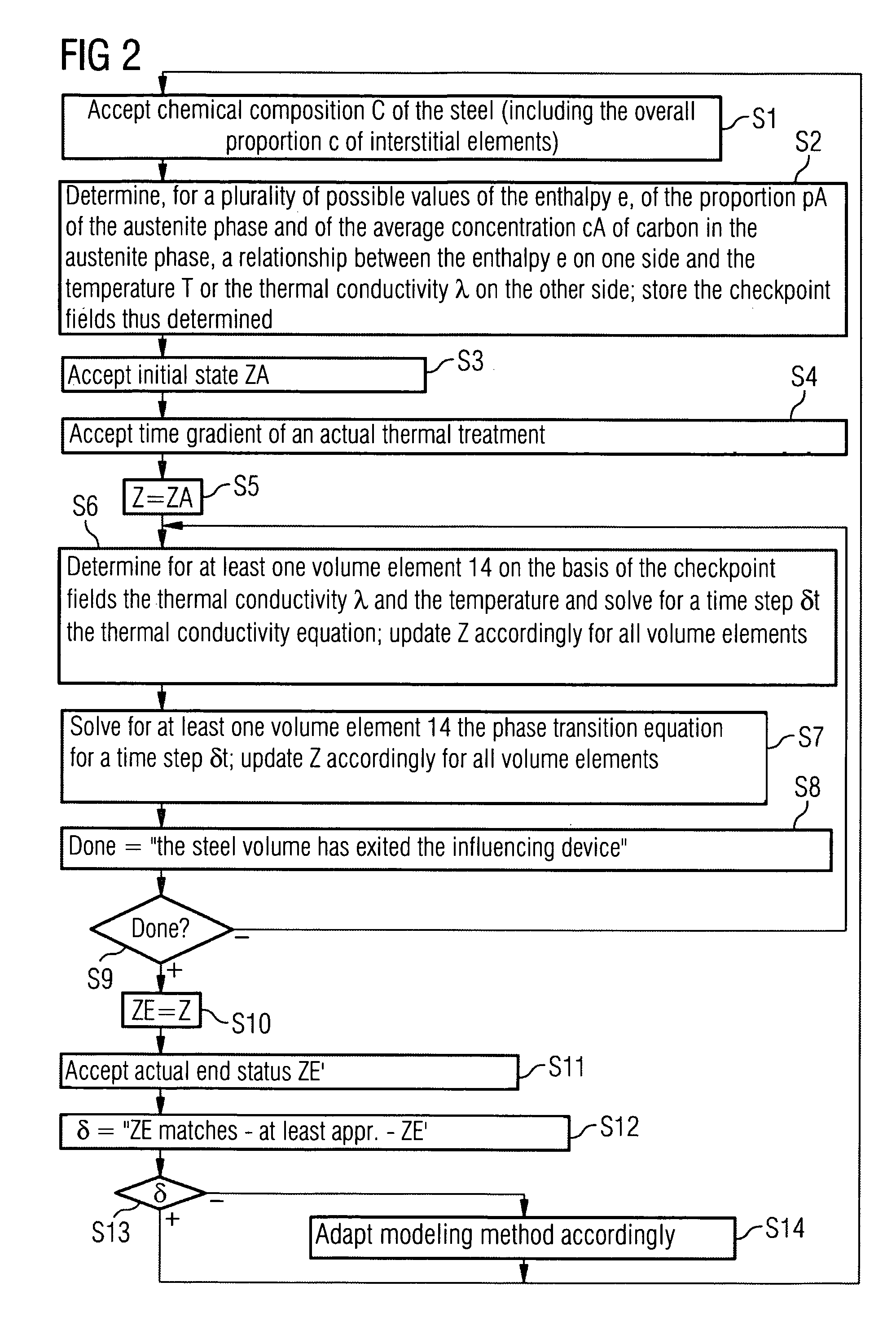
Method of Modeling the Time Gradient of the State of a Steel Volume by Means of a Computer and Corresponding Objects
InactiveUS20090265146A1Reduce the amount of calculationKeeping down the computing effortTemperature control deviceAnalogue computers for chemical processesMaterials scienceCementite
A steel volume is modeled in a computer by means of a plurality of volume elements. The state of the steel volume at a given time comprises, for each volume element, characteristic quantities of an enthalpy existing at said time in the respective volume element and percentages, in which the steel is available in the respective volume element at the time in austenite, ferrite and cementite phases. For at least one volume element, the computer determines the time gradient of the characteristic quantities by resolving thermal conductivity and phase transition equations. One of the characteristic quantities is a locally invariable mean interstitial element concentration within the volume element in the austenite phase thereof.
Owner:PRIMETALS TECH GERMANY
Thermal transfer coating
InactiveCN101305646ASemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesThermal barrier coatingMetal
The present invention discloses a thermal transfer coating comprising a plurality of metal bodies and a plurality of interstitial elements disposed between and connecting the plurality of metal bodies to one another. The metal bodies comprise an inner portion comprising a first metal and an outer portion comprising an alloy comprising the first metal and a second metal. The interstitial elements comprise the alloy of the outer portion.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Titanium alloy member
A titanium alloy member is characterized in that it comprise 40% by weight or more titanium (Ti), a IVa group element and / or a Va group element other than the titanium, wherein a summed amount including the IVa group element and / or the Va group element as well as the titanium is 90% by weight or more, and one or more members made in an amount of from 0.2 to 2.0% by weight and selected from an interstitial element group consisting of oxygen, nitrogen and carbon, and that its basic structure is a body-centered tetragonal crystal or a body-centered cubic crystal in which a ratio (c / a) of a distance between atoms on the c-axis with respect to a distance between atoms on the a-axis falls in a range of from 0.9 to 1.1. This titanium alloy member has such working properties that conventional titanium alloys do not have, is flexible, exhibits a high strength, and can be utilized in a variety of products.
Owner:KK TOYOTA CHUO KENKYUSHO
Processing and preparing method for high-strength high-precision Ti6Al4V titanium alloy tube
The invention discloses a processing and preparing method for a high-strength high-precision Ti6Al4V titanium alloy tube. The processing and preparing method comprises the following steps of: forginga Ti6Al4V titanium alloy bar billet with a uniform and fine tissue, adopting a box type resistance furnace to heat and preserve heat for the titanium alloy bar billet in a beta-phase area; rolling theheated titanium alloy bar billet into a tube billet through an oblique-rolling perforating machine; performing thermal treatment on the rolled bar billet, and performing thermal straightening by a straightening machine; and performing boring treatment on the inner surface of the thermally straightened tube billet, thereby obtaining the finished product titanium alloy tube. Through control on titanium alloy chemical components, especially interstitial elements O and Fe, large-deformation forging and rolling, reasonable heating and rolling temperature selection during processing and follow-up stress-relief annealing, the Ti6Al4V tube can obtain high strength; and thermal straightening and machining parameters are reasonably controlled, so that the prepared tube is good in surface quality, is high in wall thickness uniformity, and is excellent in plasticity; and the method is especially suitable for production of medium-specification high-strength Ti6Al4V titanium alloy tubes.
Owner:西安赛特思迈钛业有限公司
Preparing method of low-interstitial and large-size TC4 titanium alloy ingot
The invention discloses a preparing method of a low-interstitial and large-size TC4 titanium alloy ingot. The specific technical scheme comprises the following steps: choosing corresponding raw materials according to TC4 alloy components, carrying out proportioning and weighing, uniformly mixing the prepared raw materials through an automatic material mixing and distributing machine, adopting a ten-thousand-ton oil press to press the raw materials into a large-size integral consumable electrode, carrying out smelting to obtain primary ingots, welding two primary ingots to obtain a secondary consumable electrode, carrying out smelting to obtain a secondary ingot, and carrying out smelting again to obtain an ingot finished product. The preparing method has the advantages that through preparing the integral consumable electrode and three-step vacuum consumable smelting, the problems that the large-size TC4 titanium alloy ingot produced by the existing preparing technology is unstable in metallurgical quality and high in interstitial element content are solved, and the metallurgical quality of the large-size TC4 titanium alloy ingot is ensured.
Owner:重庆金世利航空材料有限公司
Element N and O co-doped ti-based amorphous composite and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to an element N and O co-doped ti-based amorphous composite and a preparation method thereof. The ti-based amorphous composite is formed by Ti, Zr, Nb, Cu, Be and doped interstitial elements N and O. The mass of the element N and the mass of the element O are determined according to the total mass of a quasi-molten alloy ingot. The element N and the element O are doped and introduced in the manner of adding TiN and TiO2 powder in the melting process. The adding range of the element N and the element O is controlled, and therefore the dendritic crystal volume fraction of an original Ti48Zr20Nb12Cu5Be15 amorphous composite is not changed, the solution strengthening effect of the element N and the element O in dendritic crystals is utilized, and the obtained element N and O co-doped ti-based amorphous composite has higher yield strength and meanwhile has strong breaking plasticity. Meanwhile, the adding amounts of the element N and the element O are adjusted and controlled, and therefore the mechanical property of the amorphous composite is adjusted, and the proper strength and plasticity are obtained accordingly.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Preparation method of in-situ synthesized ceramic phase reinforced titanium matrix composite and product
ActiveCN109971982AAvoid inert atmosphereEasy to operateTransportation and packagingMetal-working apparatusTitanium matrix compositesBoride
The invention discloses a preparation method of an in-situ synthesized ceramic phase reinforced titanium matrix composite and a product. The preparation method of the in-situ synthesized ceramic phasereinforced titanium matrix composite includes the following steps that titanium powder or titanium alloy powder is added into powder surface treating agents to prepare slurry; the surface treating agents can make the surface of titanium or the titanium alloy powder form an organic coating layer; composite powder is prepared by ball milling and powder mixing of the dried slurry with sintering andstrengthening additives, and the sintering and strengthening additives are calcium carbides or calcium borides; and after the composite powder is made into a blank, sintering treatment is carried out,and the product is prepared after cooling. According to the preparation method, oxygen increase in the preparation process is controlled by the surface coating technology, meanwhile the sintering andstrengthening additives are utilized to react with O, C and other interstitial elements remaining in a matrix, a multistage nano ceramic particle reinforcement phase is generated in situ, the mechanical properties of materials are improved, and thus the technical problem of high cost in preparation of a titanium matrix composite in the prior art is solved.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Titanium alloy member
A titanium alloy member is characterized in that it comprises 40% by weight or more titanium (Ti), a IVa group element and / or a Va group element other than the titanium, wherein a summed amount including the IVa group element and / or the Va group element as well as the titanium is 90% by weight or more, and one or more members made in an amount of from 0.2 to 2.0% by weight and selected from an interstitial element group consisting of oxygen, nitrogen and carbon, and that its basic structure is a body-centered tetragonal crystal or a body-centered cubic crystal in which a ratio (c / a) of a distance between atoms on the c-axis with respect to a distance between atoms on the a-axis falls in a range of from 0.9 to 1.1. This titanium alloy member has such working properties that conventional titanium alloys do not have, is flexible, exhibits a high strength, and can be utilized in a variety of products.
Owner:TOYOTA CENT RES & DEV LAB INC
Porous structured thermal transfer article
InactiveCN102066865ASemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesInterstitial elementThermal transfer
Provided is a porous structured thermal transfer article comprising a plurality of precursor metal bodies and a plurality of interstitial elements disposed between and connecting the plurality of precursor metal bodies to one another and a plurality of metallic particles at least partially embedded in the interstitial elements. The precursor metal bodies comprise an inner portion comprising a first metal and an outer portion comprising an alloy comprising the first metal and a second metal. The interstitial elements comprise the alloy of the outer portion.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
WSTi64E high-damage-tolerance super-large-size titanium alloy cast ingot and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a WSTi64E high-damage-tolerance super-large-size titanium alloy cast ingot which is composed of the following elements in percentage by weight: 5.8-6.5% of Al, 3.6-4.4% of V, 0.10-0.25% of Fe, 0.01-0.05% of C, 0.05-0.12% of O, less than 0.03% of N, less than 0.0125% of H, and the balance of Ti and inevitable impurities. The total amount of the impurity elements does not exceed 0.10%. The invention also discloses a preparation method of the titanium alloy. The WSTi64E high-damage-tolerance super-large-size titanium alloy cast ingot has the advantages of high transverse and longitudinal uniformity of chemical components and lower impurity content, successfully makes a breakthrough in the chemical component uniformity control technology of industrial 5t and 8t large-size cast ingots, reduces the burning loss of the aluminum element in the smelting process, effectively controls the interstitial element content, and avoids the niggerheads formed by the high-melting-point vanadium element and other metallurgical defects.
Owner:西部超导材料科技股份有限公司
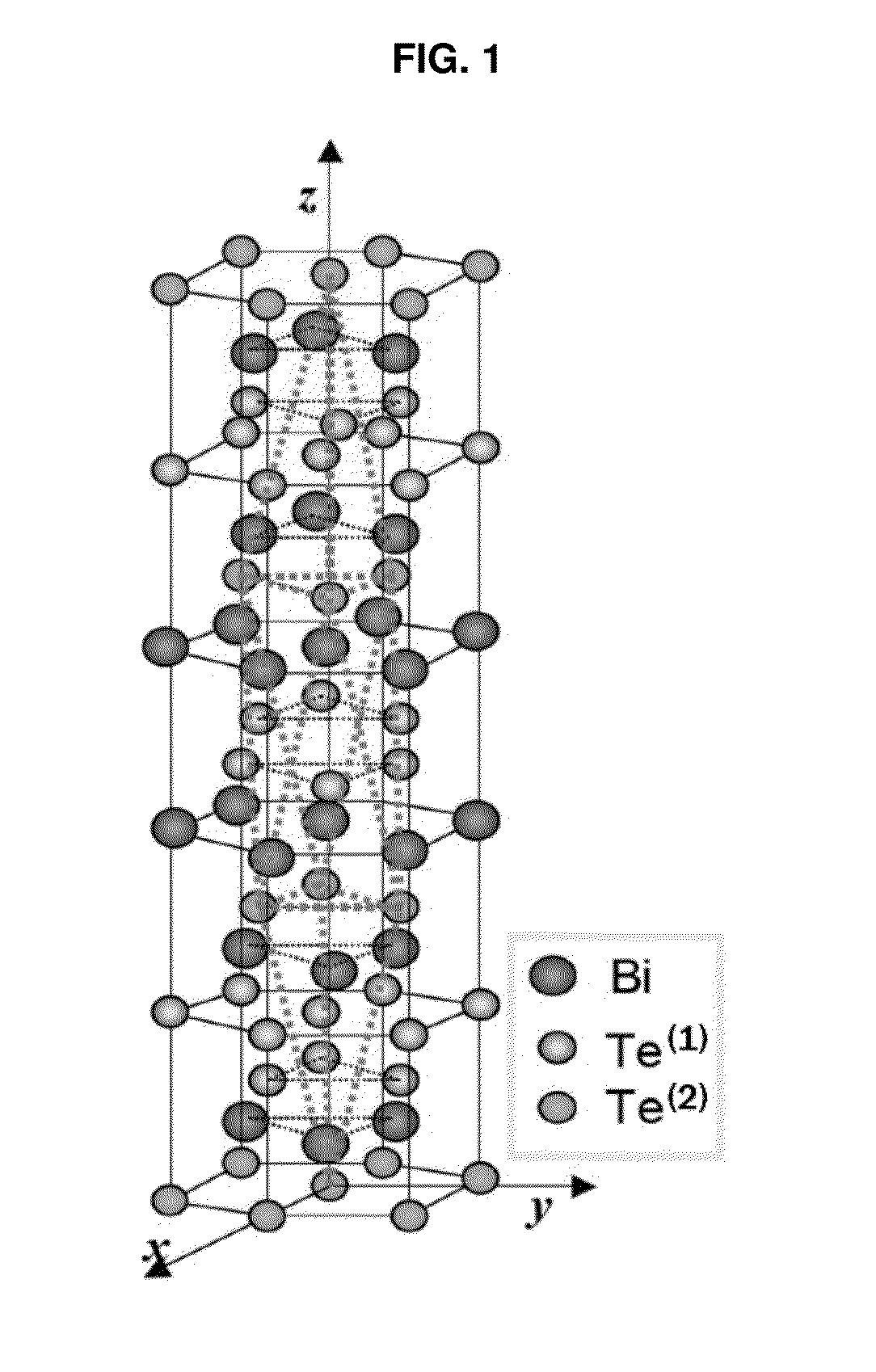
Te-based thermoelectric material having complex crystal structure by addition of interstitial dopant
InactiveUS20150372212A1Improve thermoelectric performancePolycrystalline material growthThermoelectric device manufacture/treatmentThermoelectric materialsDopant
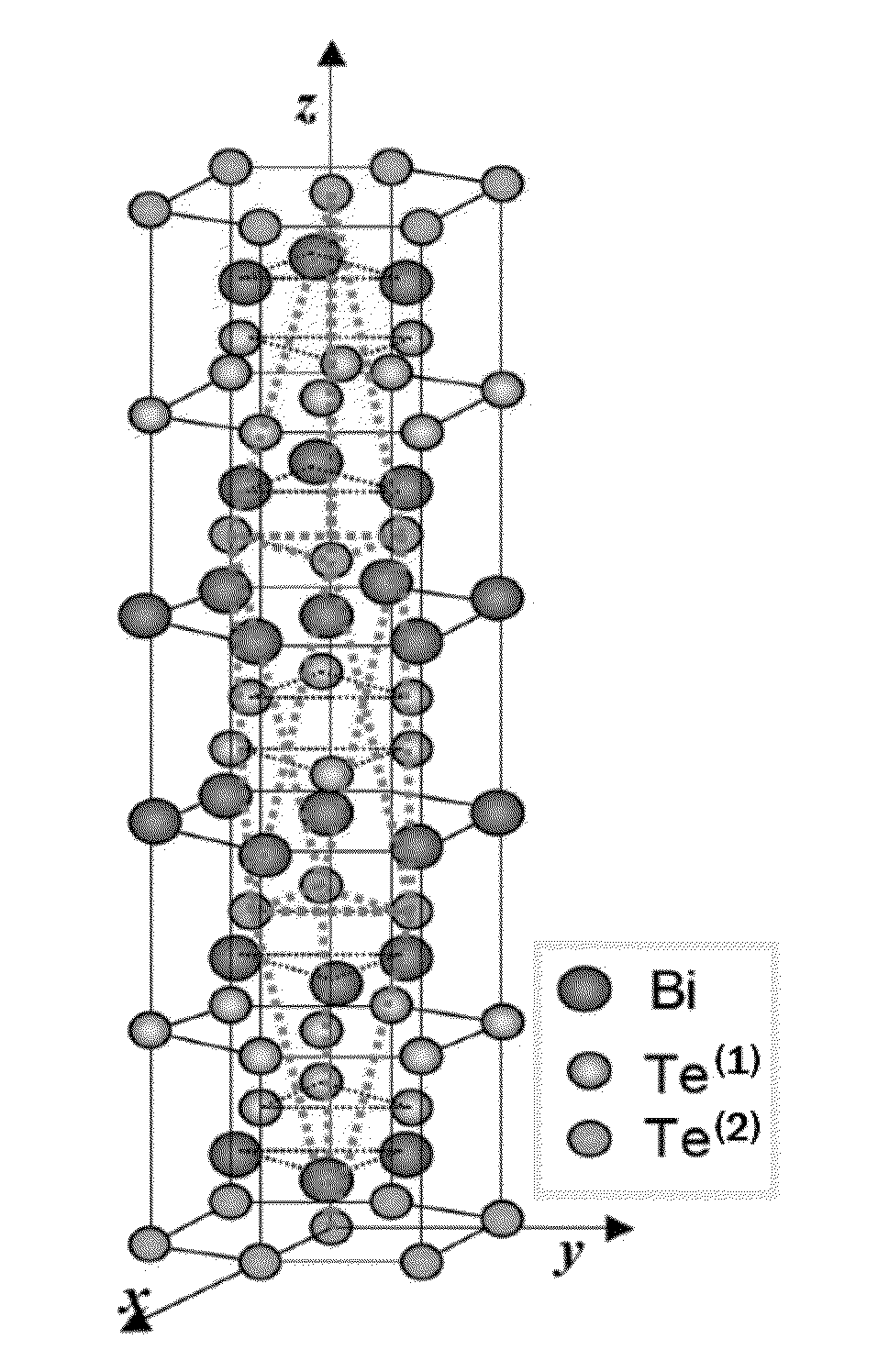
This invention relates to a Te-based thermoelectric material having stacking faults by addition of an interstitial dopant, including unit cells configured such that A-B-A-C-A elements are stacked to five layers, in which A element of a terminal of a unit cell and A element of a terminal of another unit cell are repeatedly stacked by a van der Waals interaction, wherein an interstitial element as the dopant is located at an interstitial position between the repeatedly stacked A elements adjacent to each other, thus generating stacking faults of the repeatedly stacked unit cells to thereby form a twin as well as a complex crystal structure different from the unit cells (where A is Te or Se, B is Bi or Sb, and C is Bi or Sb).
Owner:KOREA ELECTROTECH RES INST
Nitriding catalyst
InactiveCN103526152AAvoid harmNitriding effect is goodSolid state diffusion coatingRare-earth elementNitrogen
The invention provides a nitriding catalyst which is an alloy with a general formula of RTxMy, wherein R is one of rare earth metals: La, Ce, Pr, Nd, Y, Sm and the like or combination thereof, T is one of metals: Fe, Co, Ni, Mn, Ti, V, Cr, Si, Al, Mg, Sn, Zn and the like or combination thereof, M is one of interstitial elements: H, B, C, N, P and the like or combination thereof, x is ranged from 1 to 20 and y is ranged from 1 to 10. According to the nitriding catalyst provided by the invention, the temperature of gas nitriding in nitrogen-containing atmospheres such as nitrogen or ammonia gas can be remarkably reduced.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for reduced n+ diffusion in strained si on sige substrate
InactiveUS20050054145A1Type of reductionVacancy concentration is reducedSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesTrappingEngineering
The first source and drain regions are formed in an upper surface of a SiGe substrate. The first source and drain regions containing an N type impurity. Vacancy concentration in the first source and drain regions are reduced in order to reduce diffusion of the N type impurity contained in the first source and drain regions. The vacancy concentration is reduced by an interstitial element or a vacancy-trapping element in the first source and drain regions. The interstitial element or the vacancy-trapping element is provided by ion-implantation.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Short-process preparation method for high-purity nickel strip material
ActiveCN112474864AAvoid pollutionHigh yieldFurnace typesWork heating devicesSensor materialsIntegrated circuit
The invention belongs to the technical field of nickel material processing and particularly relates to a short-process preparation method for a high-purity nickel strip material. In the short-processpreparation method, high-purity nickel powder is subjected to hot isostatic pressing sintering to form a compact nickel blank body after being filled into a casing, vacuumized and sealed and welded, and then a plate strip material is formed after hot rolling and cold rolling are performed. According to the short-process preparation method for the high-purity nickel strip material, oxygen, nitrogenand other interstitial element impurities are not introduced in the casing and nickel blank hot isostatic pressing sintering process, pollution of air preheating oxidation to internal high-purity nickel is avoided by the hot rolling with the casing, and compared with a traditional high-purity nickel preparation process, the short-process preparation method for the high-purity nickel strip material is short in technological process, low in technical difficulty, high in yield and suitable for scale production and has important application prospects in the high-tech fields of magnetic recordingmaterials, magnetic sensor materials, photoelectric materials, integrated circuits, aero-engines and the like.
Owner:无锡市东杨新材料股份有限公司
Method for processing titanium alloy screw nut of high-end intelligent mobile phone
The invention relates to a method for processing a titanium alloy screw nut of a high-end intelligent mobile phone, belonging to the technical field of screw nut processing. The method comprises the following steps: smelting in vacuum, forging, milling, rolling, stretching and circling, performing mechanical surface treatment, stretching, annealing, broaching, straightening, polishing, forming pattern, milling and tapping. According to the method, the content of interstitial elements C, O and N and impurity element Fe is strictly controlled, the toughness of the screw nut is remarkably improved, and the screw nut which is produced by using the method is relatively good in plasticity and toughness and good in welding property and low-temperature use property; with the cooperative production of mechanical processing and manual processing, the quality of a product is ensured, the production efficiency of the product is improved, and the method has the characteristics of high production pass percent, high production efficiency and the like, and solves the problems of processing and production difficulty, and the like.
Owner:贵州顶效经济开发区沈兴实业有限责任公司
Structured thermal transfer article
InactiveCN101305256ASemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesMaterials scienceMetal
Structured thermal transfer article comprising a plurality of metal bodies and a plurality of interstitial elements disposed between and connecting the plurality of metal bodies to one another. The metal bodies comprise an inner portion comprising a first metal and an outer portion comprising an alloy comprising the first metal and a second metal. The interstitial elements comprise the alloy of the outer portion.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Method for reduced N+ diffusion in strained Si on SiGe substrate
InactiveUS20050145992A1Type of reductionReduce concentrationTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingTrappingEngineering
The first source and drain regions are formed in an upper surface of a SiGe substrate. The first source and drain regions containing an N type impurity. Vacancy concentration in the first source and drain regions are reduced in order to reduce diffusion of the N type impurity contained In the first source and drain regions. The vacancy concentration Is reduced by an interstitial element or a vacancy-trapping element in the first source and drain regions. The interstitial element or the vacancy-trapping element is provided by ion-implantation.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
A kind of processing method of high-end smartphone titanium alloy nut
The invention relates to a processing method for a high-end smart phone titanium alloy nut, belonging to the technical field of nut processing. It includes the following steps: vacuum melting, forging, turning, rolling, stretching and rounding, mechanical surface treatment, stretching, annealing, broaching, straightening, polishing, drawing, turning, tapping. The present invention strictly controls the content of interstitial elements C, O, N and impurity element Fe, significantly improves the toughness of nuts, and the nuts produced by this method have better plasticity, toughness, good welding performance and low-temperature use performance, and its The combination of mechanical processing and manual processing ensures the quality of the product and improves the production efficiency of the product. It has the advantages of high production pass rate and high production efficiency, and solves the problems of difficult processing and production.
Owner:贵州顶效经济开发区沈兴实业有限责任公司
Method of modeling the time gradient of the state of a steel volume by means of a computer and corresponding objects
InactiveUS8170853B2Keeping down the computing effortImprovement effortsTemperature control deviceAnalogue computers for chemical processesMaterials scienceCementite
A steel volume is modeled in a computer by means of a plurality of volume elements. The state of the steel volume at a given time comprises, for each volume element, characteristic quantities of an enthalpy existing at said time in the respective volume element and percentages, in which the steel is available in the respective volume element at the time in austenite, ferrite and cementite phases. For at least one volume element, the computer determines the time gradient of the characteristic quantities by resolving thermal conductivity and phase transition equations. One of the characteristic quantities is a locally invariable mean interstitial element concentration within the volume element in the austenite phase thereof.
Owner:PRIMETALS TECH GERMANY
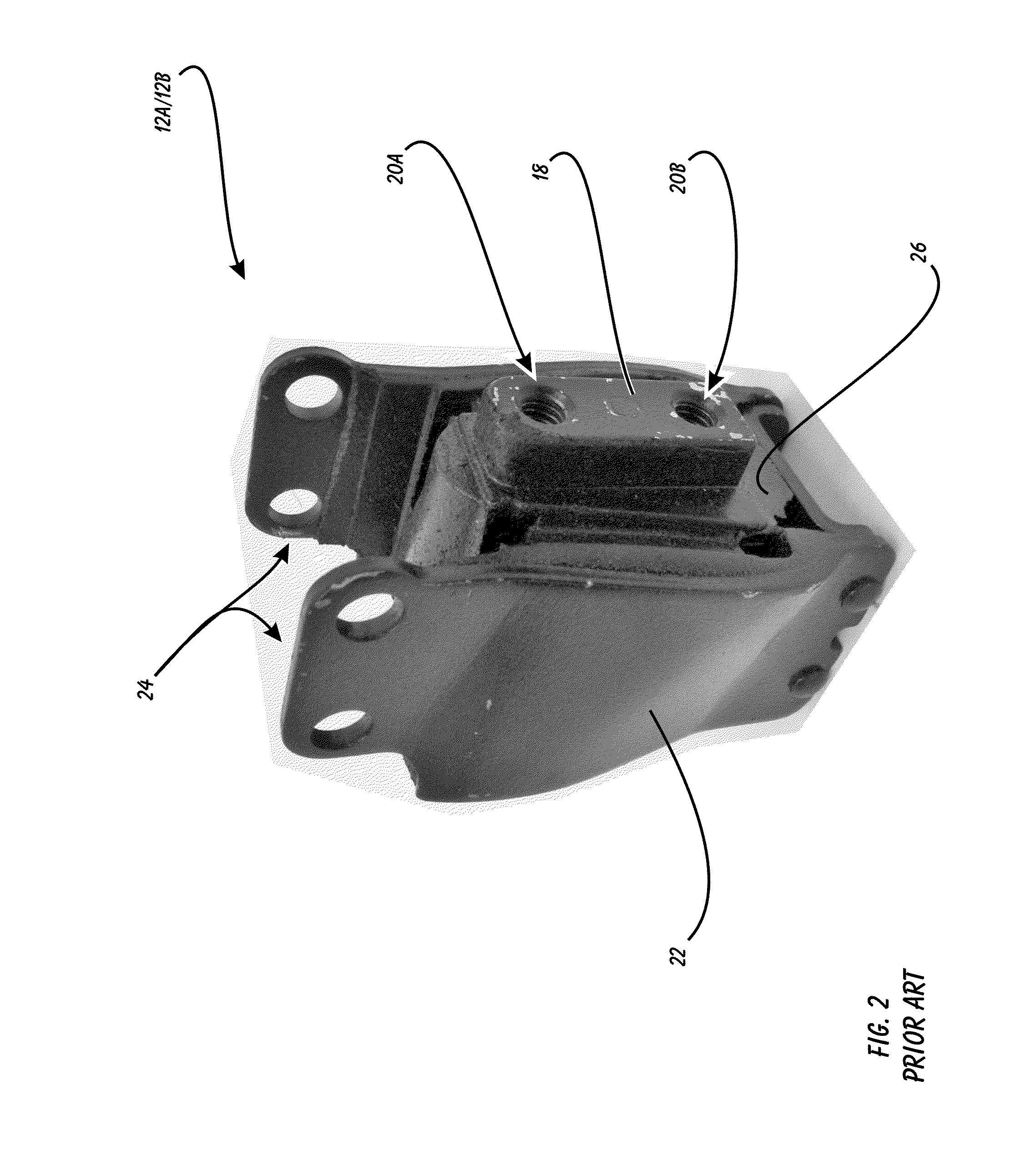
Motorcycle Engine Mount Having Improved Stiffness
InactiveUS20160251046A1Increase stiffnessLong-term durabilityCycle springsCycle standsOriginal equipment manufacturerLong term durability
A Motorcycle Engine Mount having Improved Stiffness. The device is a bolt-in replacement for the Original Equipment Manufacturer engine mounts for FXD_series Harley Davidson motorcycles. The device has a single-piece, hardened steel outer frame, and a interstitial formed from urethane (rather than rubber) having a durometer reading of 40-60. The outer frame and inner frame attachment elements are both formed with a plurality of apertures through them so that they will be infilled with urethane when the urethane is injected to form the interstitial element. This infilling will bond the three elements together for long-term durability. There are also front and rear retention plates made from hardened metal to further stabilize and bond the inner frame attachement element to the urethane interstitial element.
Owner:ORE JEREMY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com