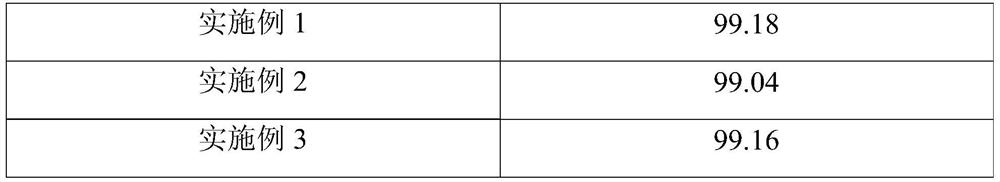
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
35 results about "Extractive metallurgy" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Extractive metallurgy is a branch of metallurgical engineering wherein process and methods of extraction of metals from their natural mineral deposits are studied. The field is a materials science, covering all aspects of the types of ore, washing, concentration, separation, chemical processes and extraction of pure metal and their alloying to suit various applications, sometimes for direct use as a finished product, but more often in a form that requires further working to achieve the given properties to suit the applications.
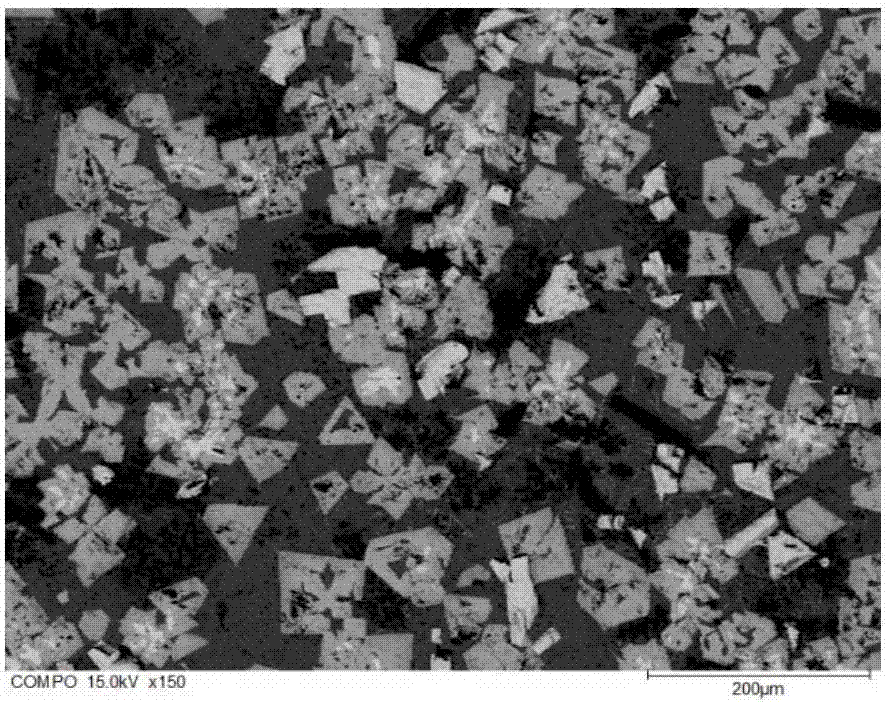
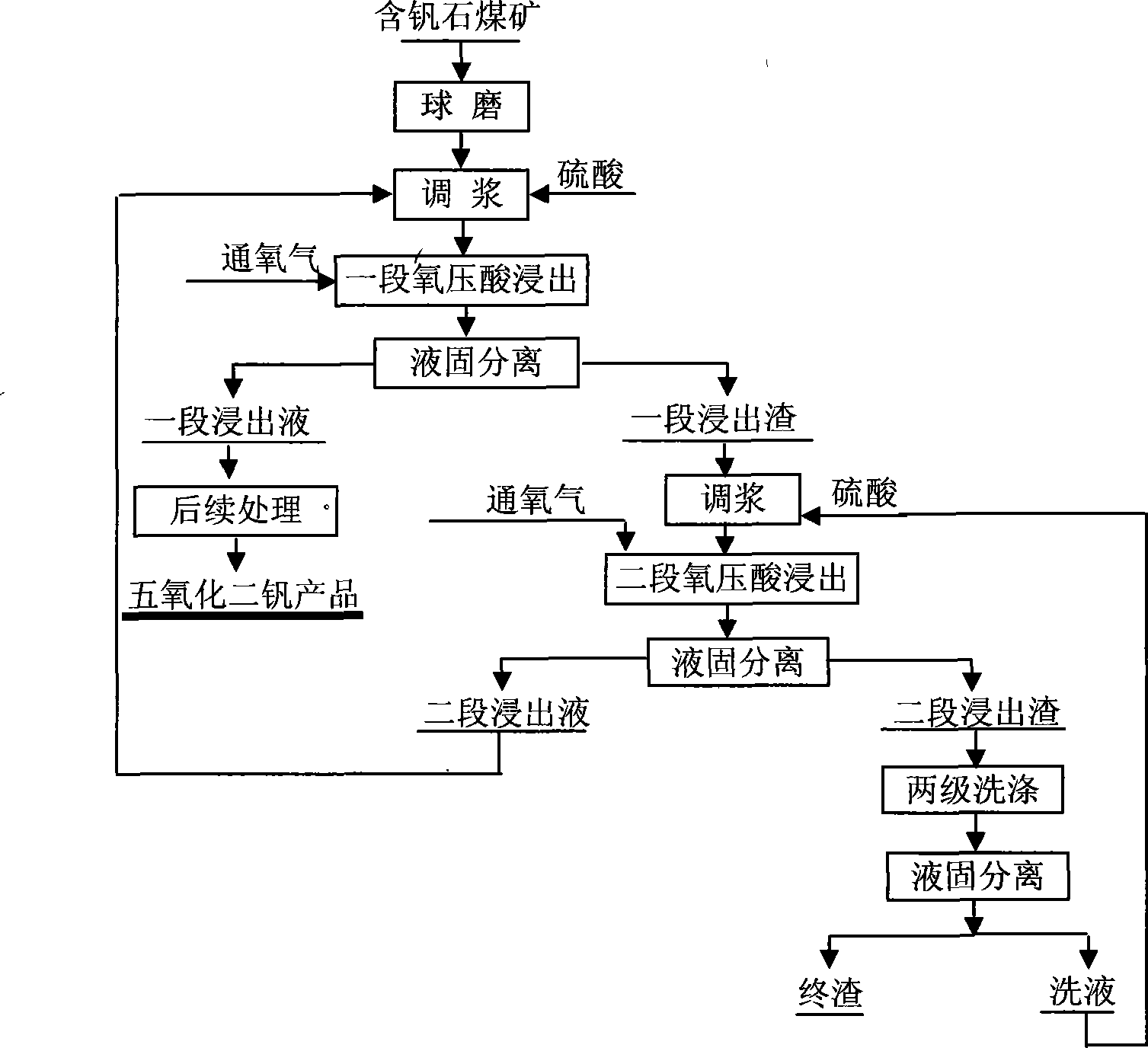
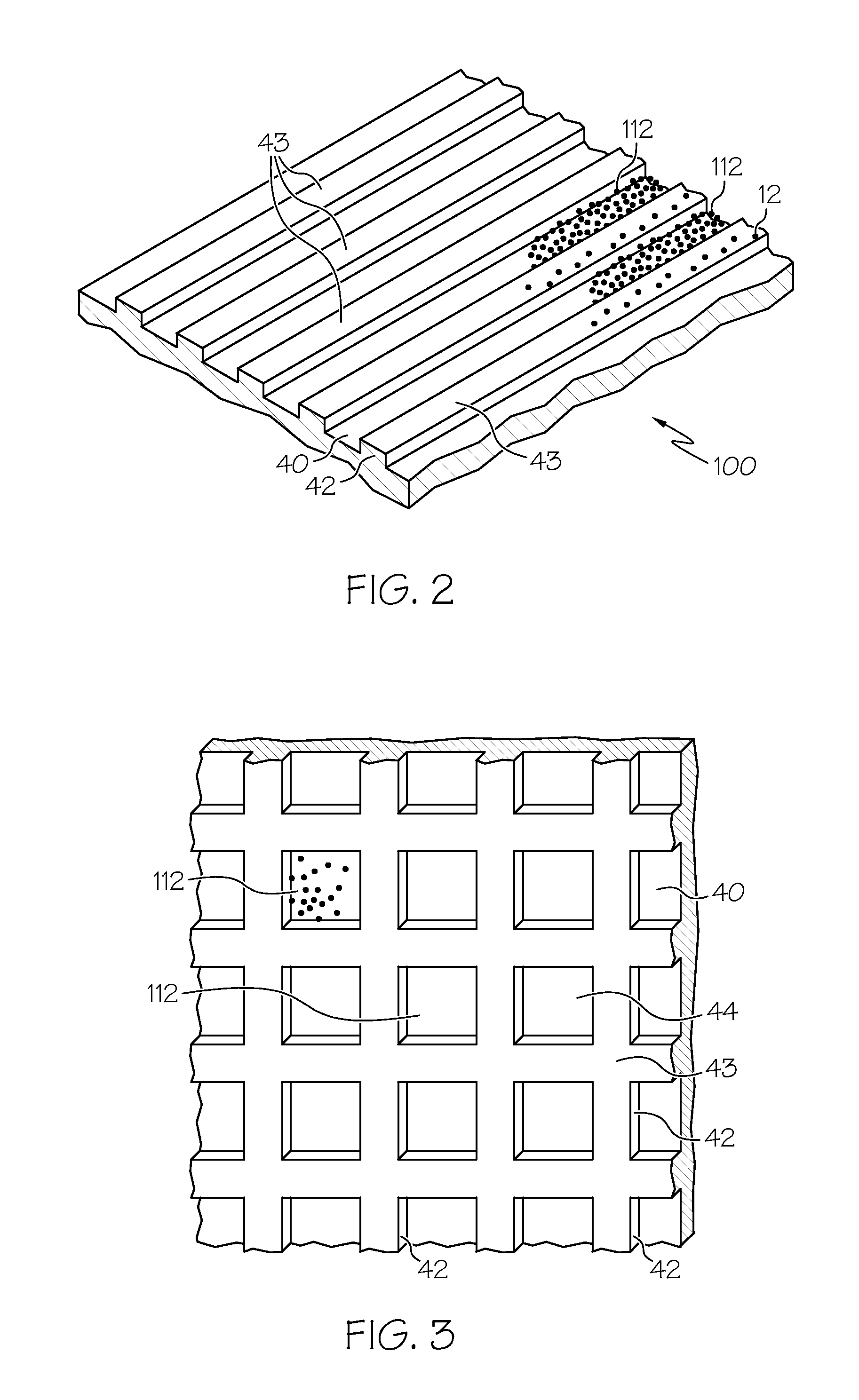
Method for leaching vanadium from vanadium-containing coal mine
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
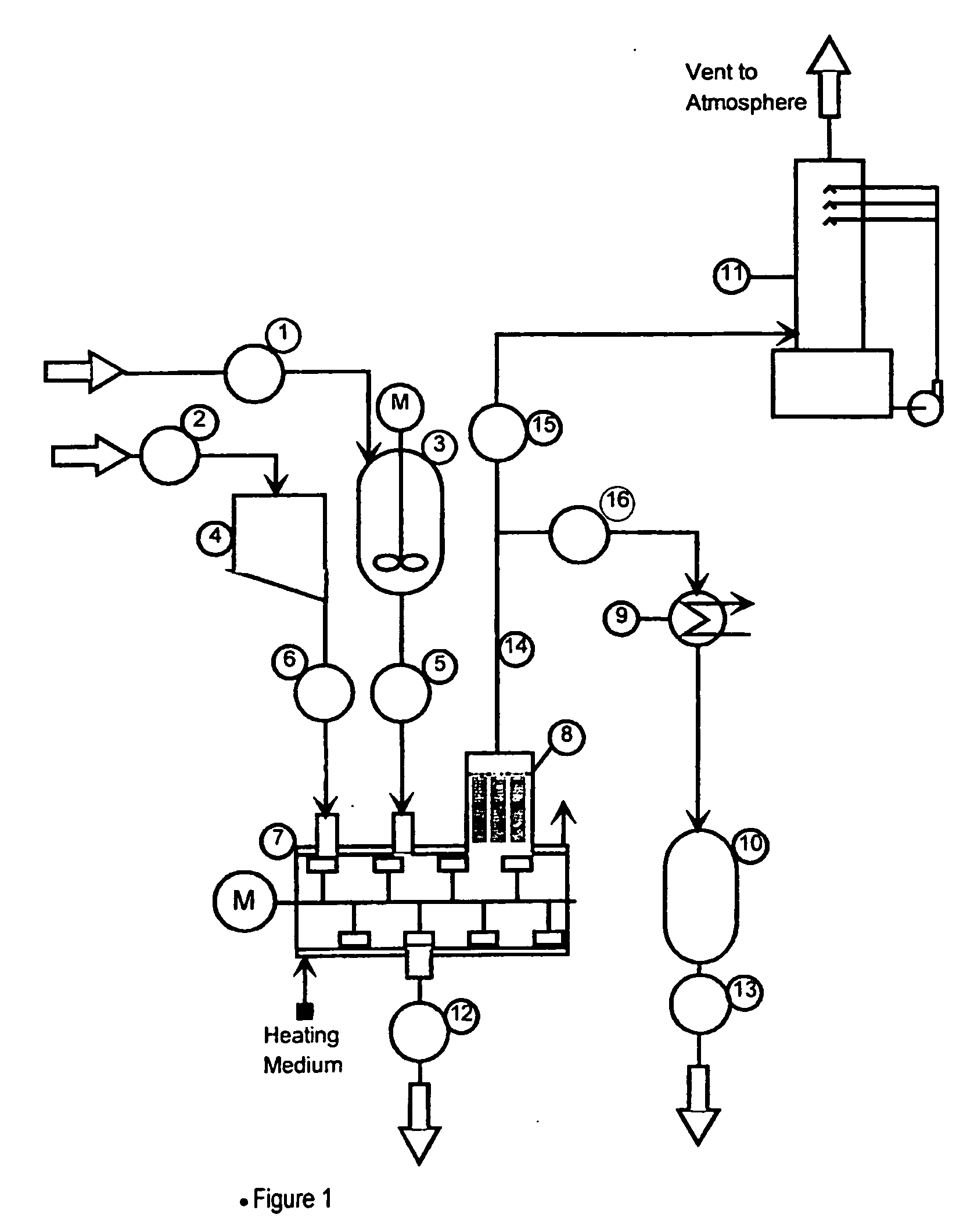
Process for the treatment of waste metal chlorides
InactiveUS20060183958A1Low costMaximize recoveryTitanium tetrachlorideSilicon oxidesMetal chlorideOrganic chloride compound
A process is described for treating the residues from metal chlorination processes wherein valuable volatile metal chlorides or metalorgano chlorides are recovered while low volatility metal chlorides and chloride complexes are reacted with a neutralizing humectant. The resulting neutral, dry solid is suitable for land fill disposal or for recovery of valuable metal constituents by extractive metallurgy techniques.
Owner:REC SILICON
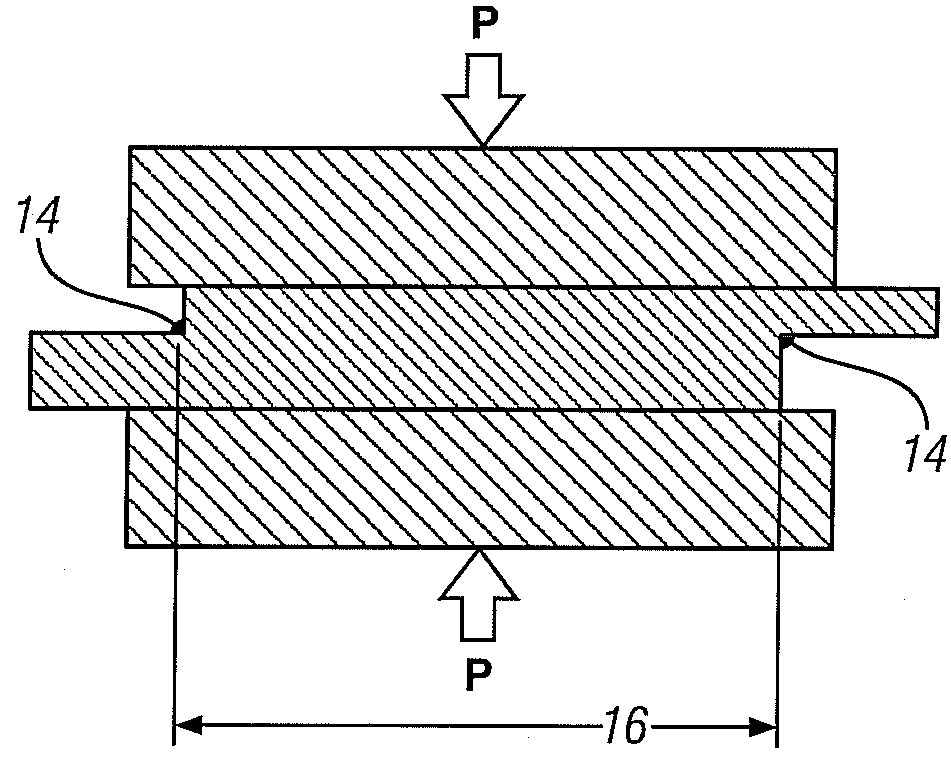
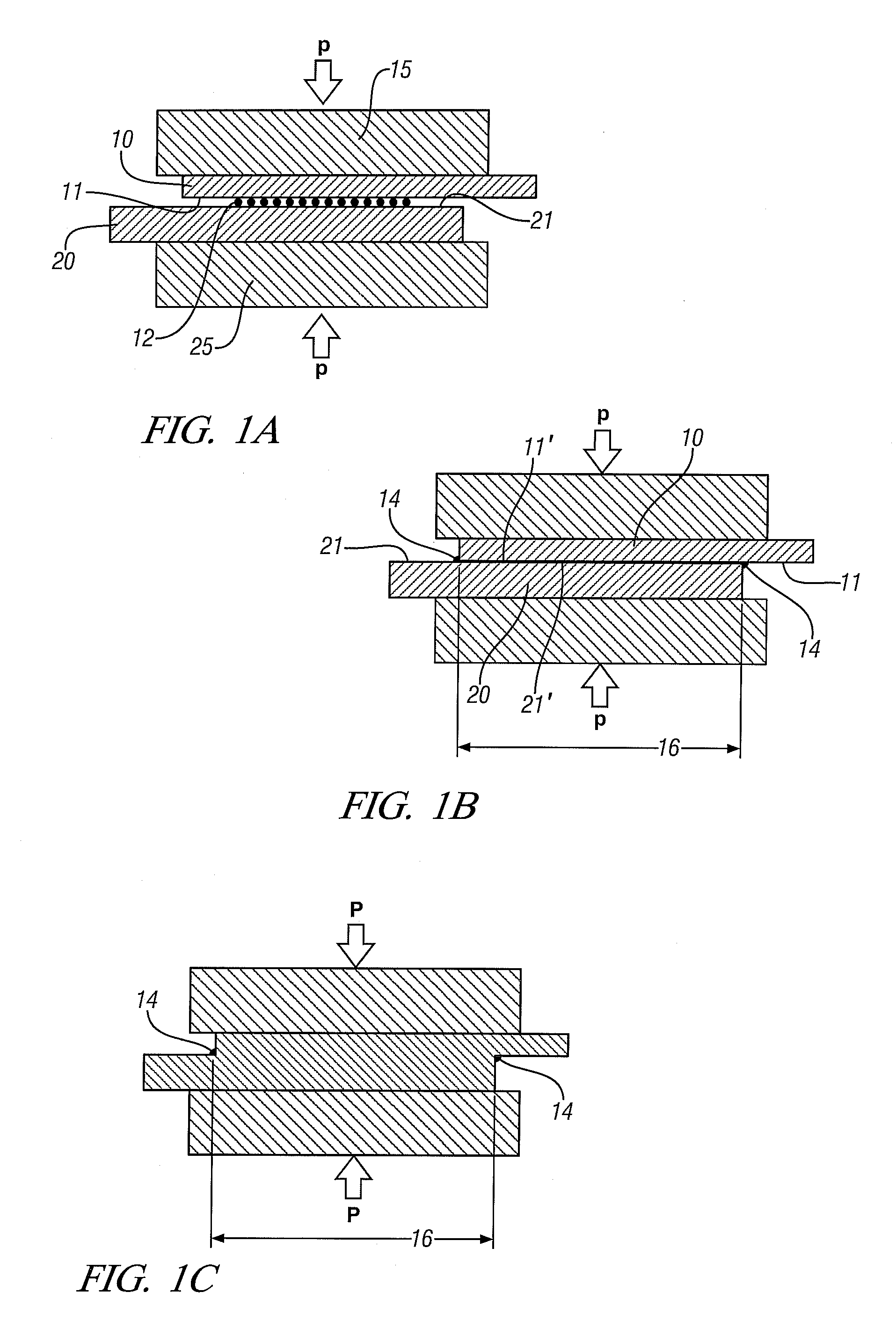
Welding light metal workpieces by reaction metallurgy
ActiveUS20100258537A1Minimize distortionDeformation MinimizationArc welding apparatusHigh frequency current welding apparatusReactive materialMaterials science
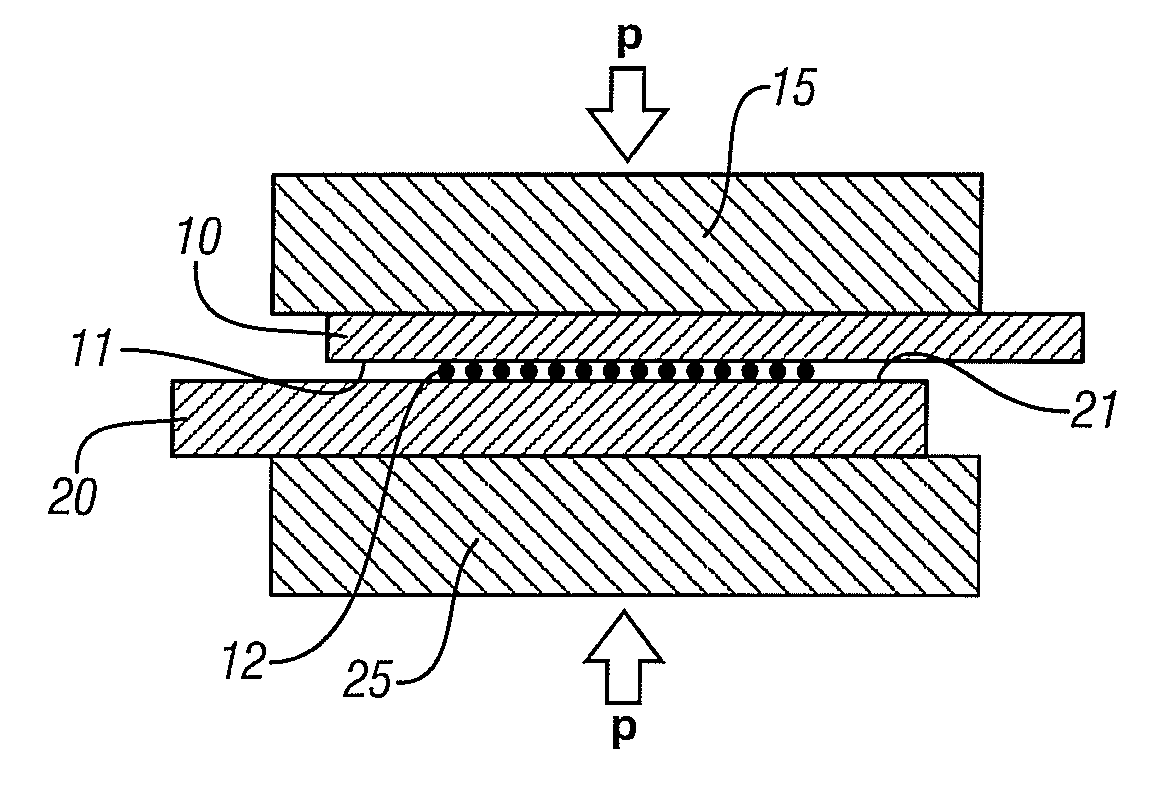
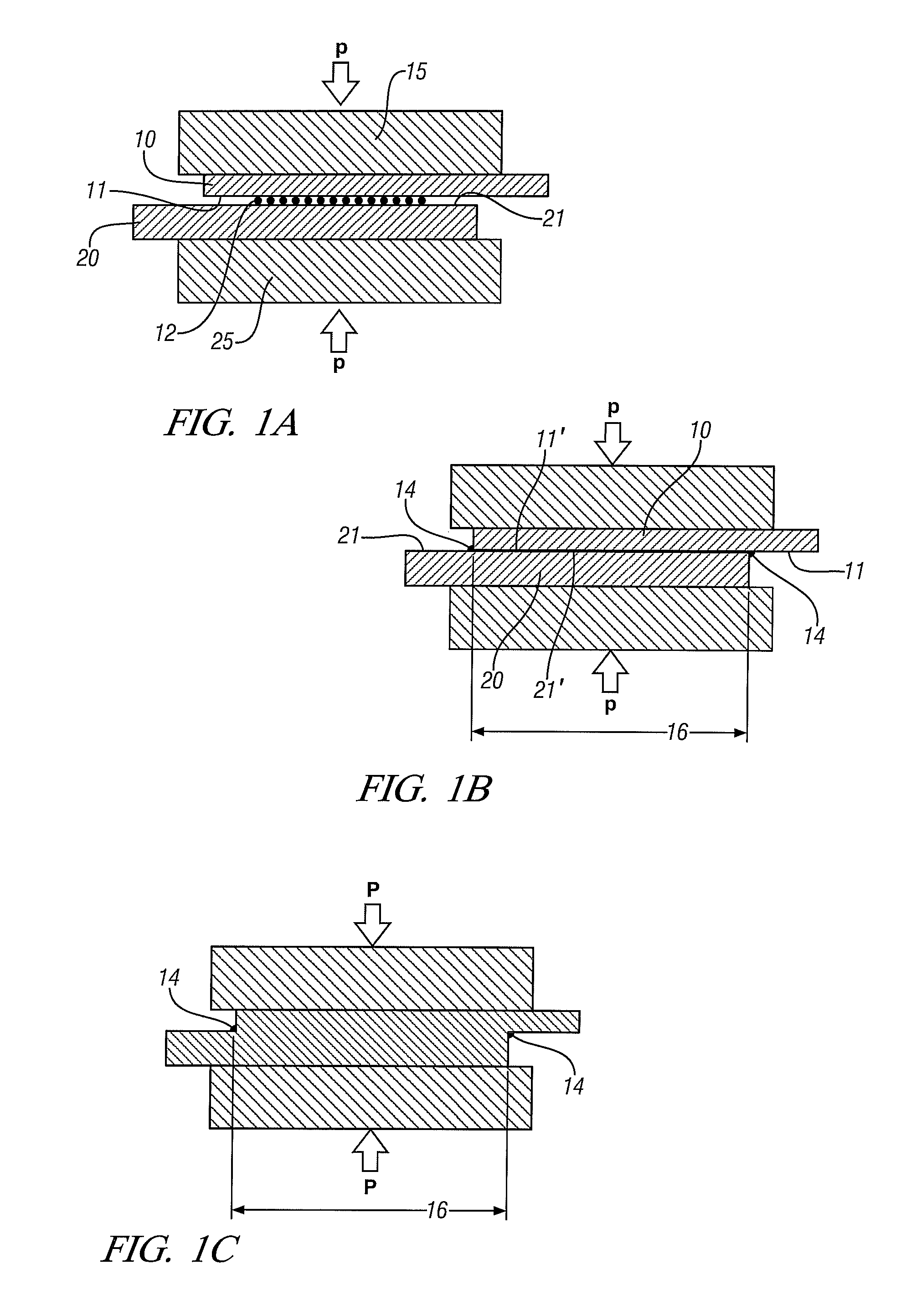
Aluminum alloy workpieces and / or magnesium alloy workpieces are joined in a solid state weld by use of a reactive material placed, in a suitable form, at the joining surfaces. Joining surfaces of the workpieces are pressed against the interposed reactive material and heated. The reactive material alloys or reacts with the workpiece surfaces consuming some of the surface material in forming a reaction product comprising a low melting liquid that removes oxide films and other surface impediments to a welded bond across the interface. Further pressure is applied to expel the reaction product and to join the workpiece surfaces in a solid state weld bond.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Method and device for condensing magnesium vapor generated by evaporation and heat absorption of magnesium liquid and coproducing refined magnesium
ActiveCN104674016ATake advantage ofReduce wasteProcess efficiency improvementEvaporationMaterials science
The invention relates to a method and a device for condensing magnesium vapor generated by evaporation and heat absorption of a magnesium liquid and coproducing refined magnesium and belongs to the technical field of extraction metallurgy or nonferrous magnesium metal. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out reverse phase change heat exchange on primary magnesium vapor in a first condensing section by taking evaporation and heat absorption of the magnesium liquid as a cooling manner, wherein the primary magnesium vapor is condensed to a liquid state; then evaporating the magnesium liquid to form higher-purity refined magnesium vapor due to the heat obtained by the magnesium liquid; then condensing the refined magnesium vapor to liquid refined magnesium; and continuously cooling and condensing residual vapor of the primary magnesium and refined magnesium in a second condensing section, wherein the primary magnesium and refined magnesium are condensed to solid crystal magnesium. According to the method and device provided by the invention, a magnesium liquid evaporator is used for condensing the primary magnesium vapor and further serves as a heat source for purifying the magnesium liquid. Parallel secondary cooling monomers are arranged in a secondary cooling section to realize alternate condensation and follow-up heating and re-melting. By adopting returned heating, heat demand on evaporation and remelting is realized by using heat energy of magnesium vapor condensation, so that high purity magnesium is coproduced and heat energy is fully utilized; the secondary cooling monomers are alternately condensed and remelted, so that the condensing rate is improved and the magnesium liquid is convenient to flow out and recycle.
Owner:牛强
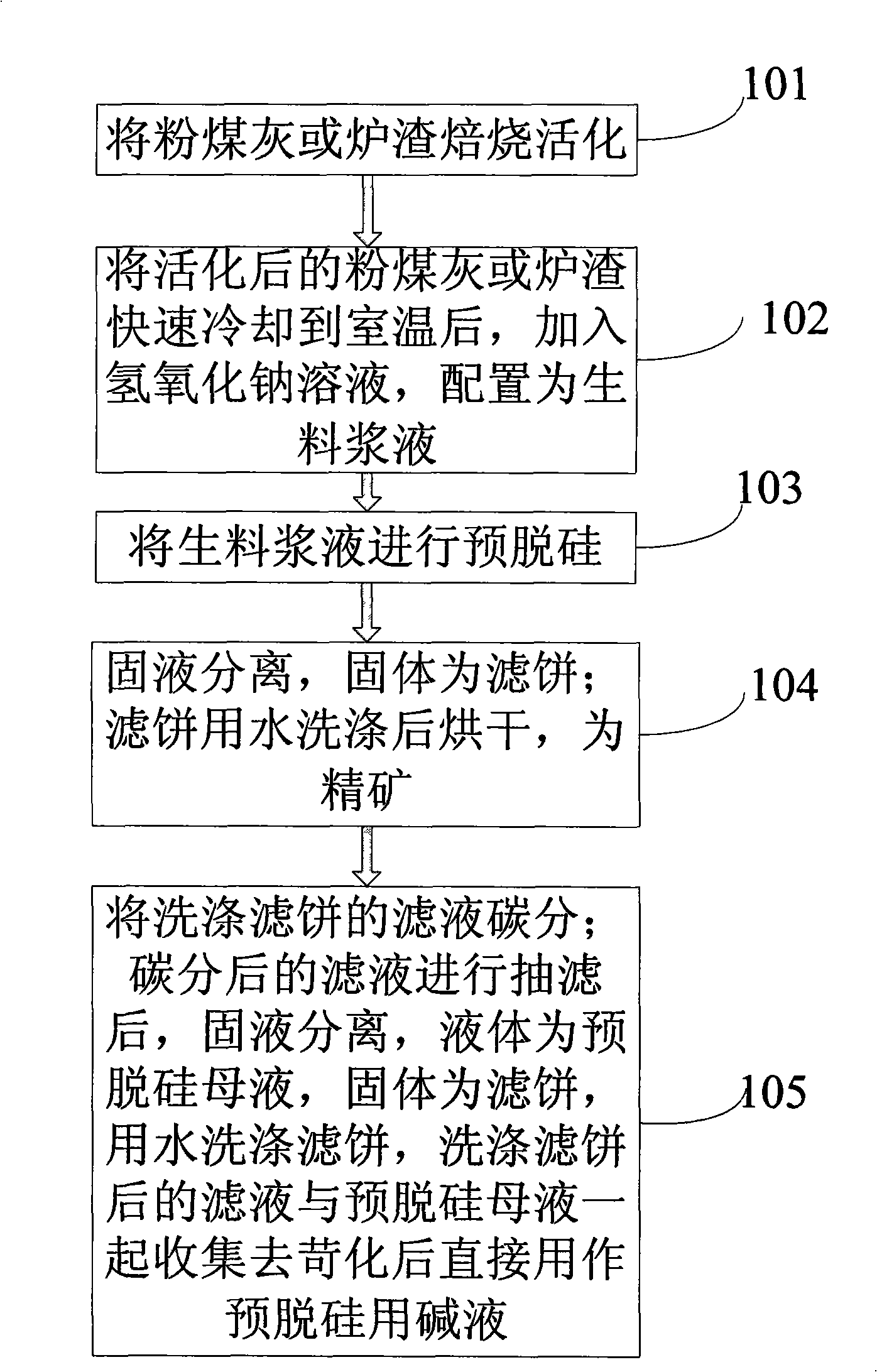
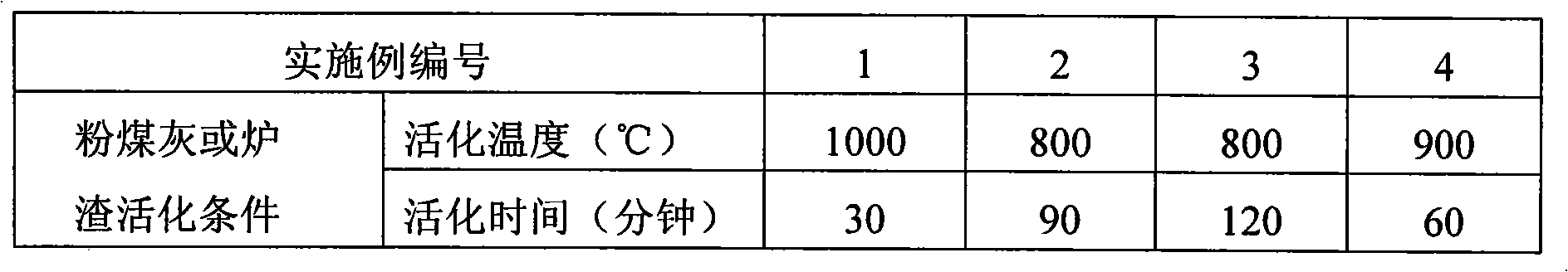
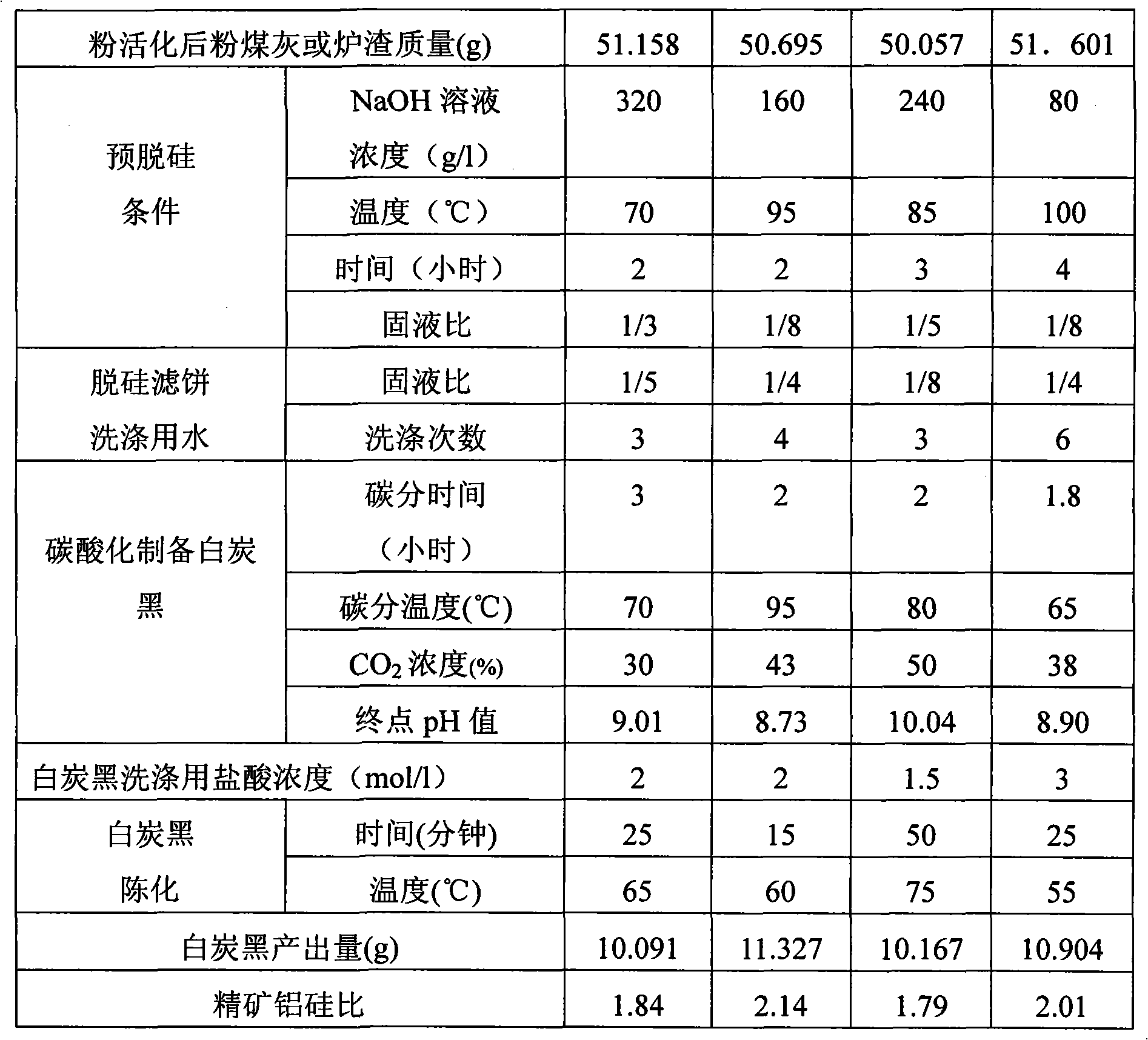
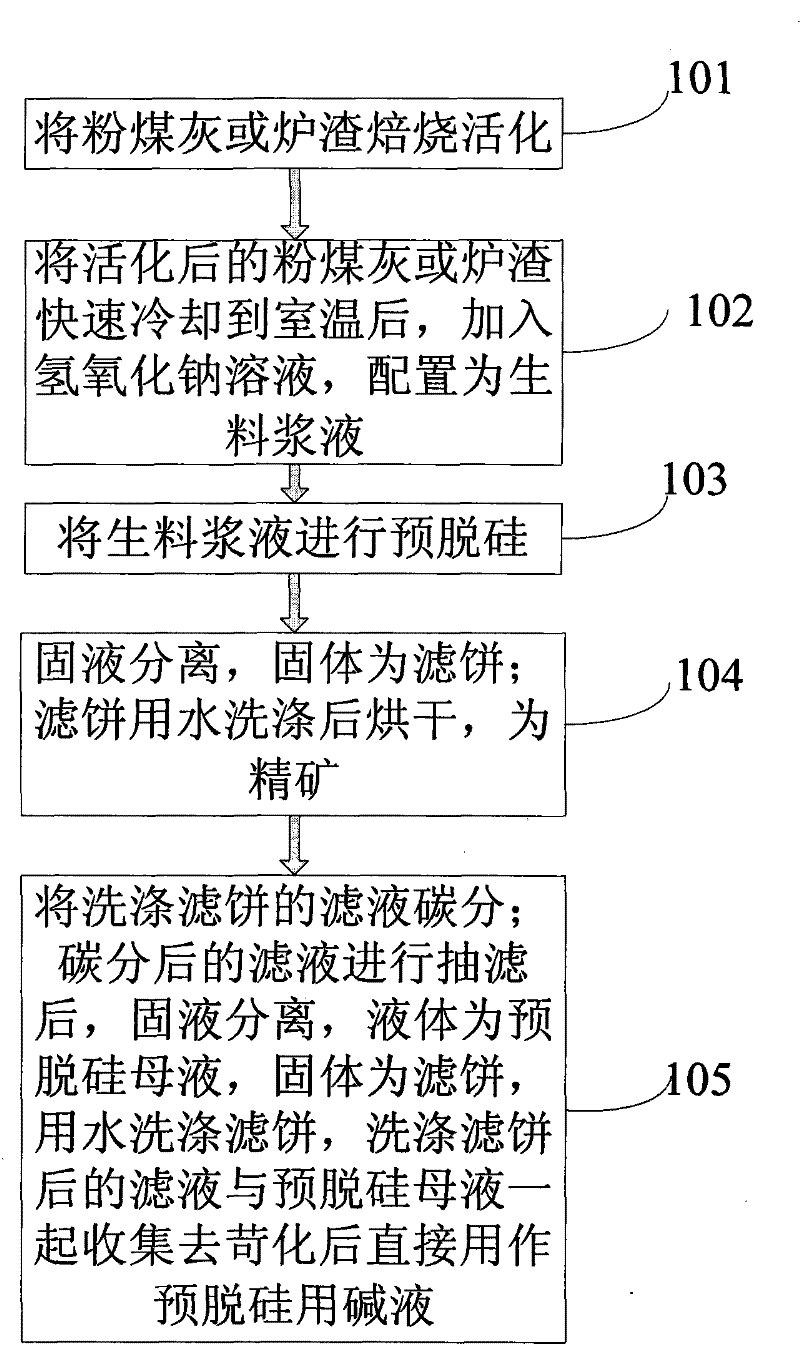
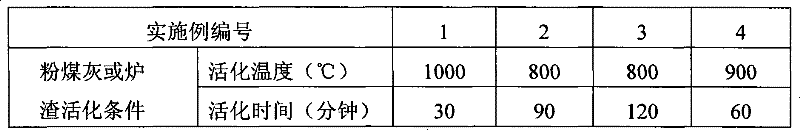
Pre- desiliconizing method from fly ash or slag
ActiveCN101306928AReduce energy consumptionIncrease Al-Si RatioSolid waste managementSlagSilicon oxide
The invention relates to a method for the comprehensive application of fly ash or slag, in particular to a method for the predesilication of the fly ash or the slag. The method mainly comprises the process flows including the baking and the activation of the fly ash or the slag, the formula process of the raw meal of activated the fly ash or the slag and a sodium hydroxide solution and the production of white carbon black. Through adopting a technological line during which the fly ash or the slag are baked and activated at first and then a sodium hydroxide solution is used to extract noncrystalline silicon oxide at a low temperature, the method ensures that the mass ratio of aluminum oxide and silicon oxide of desilicated fly ash reaches to 2.14; therefore, the method breaks a new path to take the fly ash or the slag as a raw material source for extracting metallurgical-grade aluminum oxide, thereby increasing the comprehensive utilization value of the fly ash and the slag.
Owner:北京世纪地和控股有限公司
Battery tab joint by reaction metallurgy
ActiveUS20110303736A1Minimize distortionDeformation MinimizationPrimary cell to battery groupingCell component detailsMetal alloyAluminum metal
Copper metal or metal alloy workpieces and / or aluminum metal or metal alloy workpieces are joined in a solid state weld by use of a reactive material placed, in a suitable form, at the joining surfaces. Joining surfaces of the workpieces are pressed against the interposed reactive material and heated. The reactive material alloys or reacts with the workpiece surfaces consuming some of the surface material in forming a liquid-containing reaction product comprising a low melting liquid that removes oxide films and other surface impediments to a welded bond across the interface. Further pressure is applied to expel the reaction product and to join the workpiece surfaces in a solid state weld bond.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
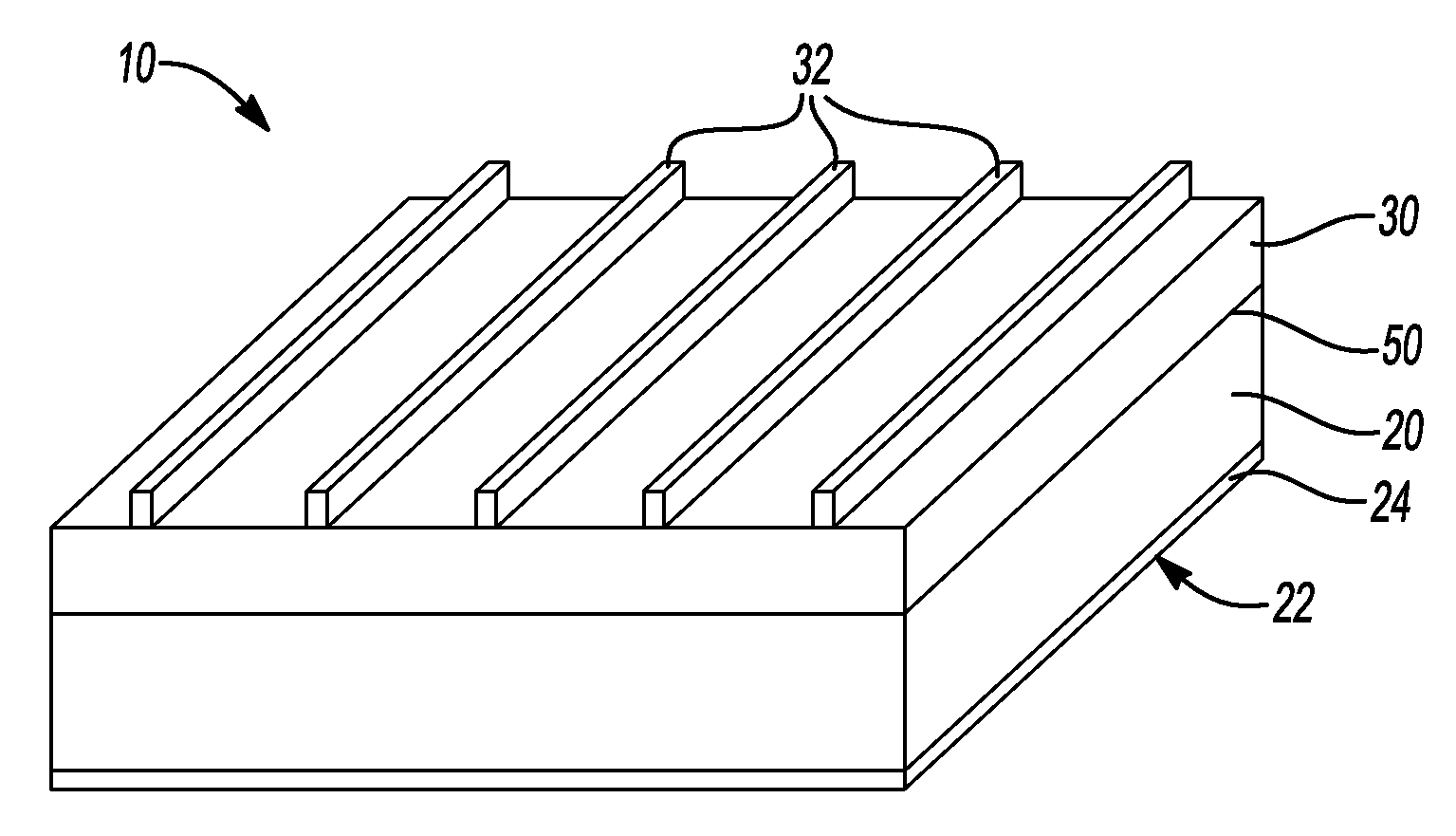
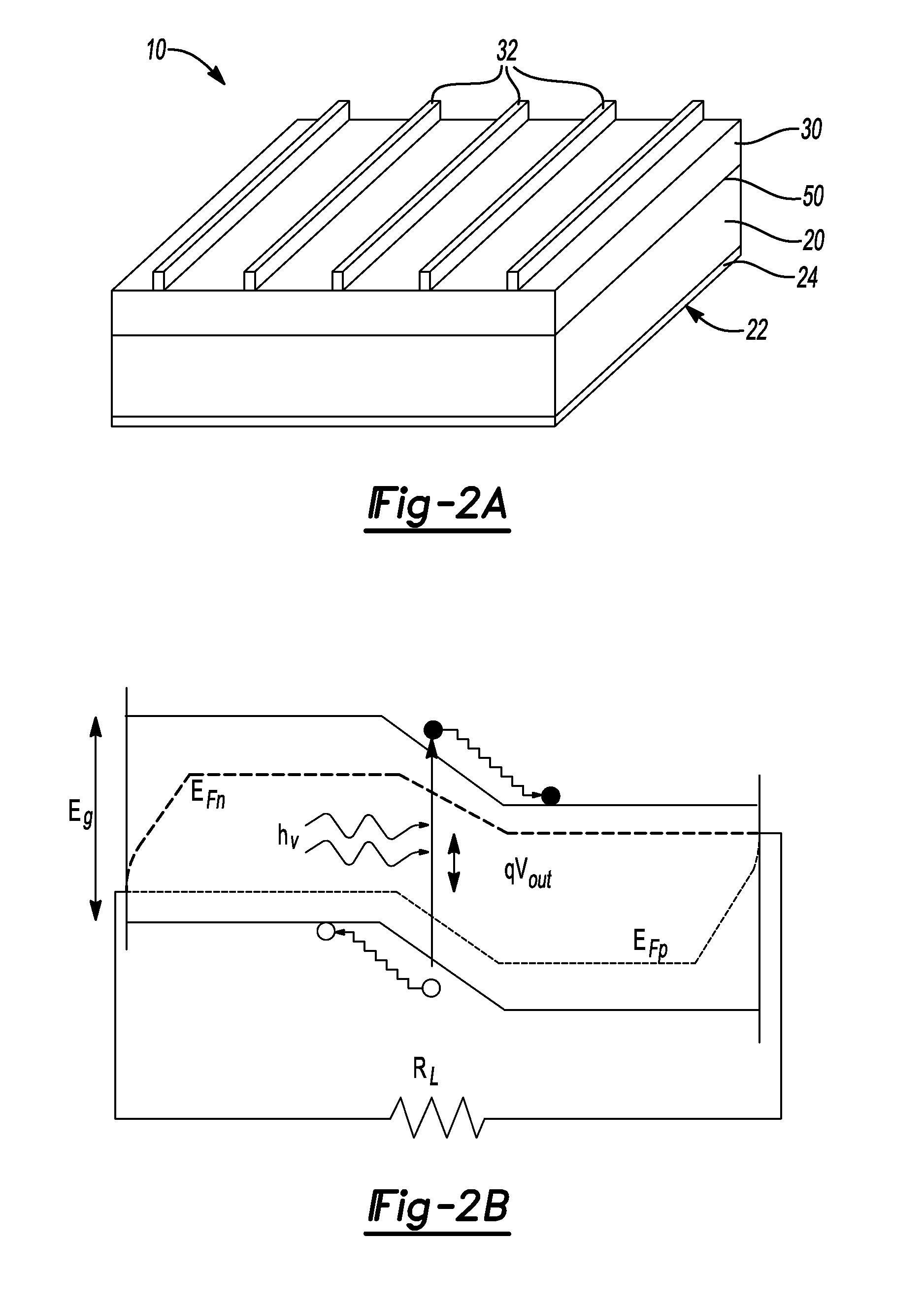
Silicon-based solar cell with eutectic composition
ActiveUS20120152354A1Eliminate costly purification stepLow costNon-metal conductorsFinal product manufactureHeterojunctionMicrometer
Growth and characterization of low cost, and high efficiency micro- and nanostructured p-n heterojunction solar cells through eutectic solidification are provided. Eutectic solidification results in self-assembly of lamellar or rod-like domains with length scales from hundreds of nanometers to micrometers that can be used for efficient extraction of minority carriers in metallurgical-grade materials. The material having a eutectic or near-eutectic composition can be used in making a low-cost and efficient inorganic solar cell.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Vacuum electrothermal magnesium smelting apparatus with protector
ActiveCN104651636AReduce adverse effectsImprove securityProcess efficiency improvementDc arc furnaceThermal insulation
The invention relates to a vacuum electrothermal magnesium smelting apparatus with a protector, belonging to the technical field of nonferrous metal magnesium extraction metallurgy. The apparatus comprises an electric-heating vacuum electric furnace, wherein the lower part is provided with a liquid outlet, and the upper part is provided with a liquid injection port, a feed port and a magnesium vapor outlet; the magnesium vapor outlet is communicated to a magnesium vapor condensing chamber through a sealed thermal-insulation pipeline, and then connected to a vacuum pump; the liquid outlet of the vacuum electric furnace is positioned inside a vacuum deslagging chamber; and the vacuum electric furnace and vacuum deslagging chamber are arranged inside an argon protective chamber. The vacuum magnesium smelting reactor (especially hollow cathode direct-current arc furnace) by using electricity as the heat source has high electrothermal power, is suitable for large-scale production, and greatly enhances the productive capacity of metal magnesium. The peripheral argon protective barrier can prevent air from leaking into the magnesium smelting furnace, which can cause severe safety production accidents, thereby greatly enhancing the safety of the magnesium smelting production device. The vacuum electrothermal magnesium smelting apparatus implements continuous production, greatly enhances the single-furnace magnesium yield, and obtains the original metal magnesium with lower impurity content.
Owner:牛强
Battery tab joint by reaction metallurgy
ActiveUS8590768B2Minimize distortionMinimize unwanted deformationPrimary cell to battery groupingCell component detailsMetal alloyAluminum metal
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
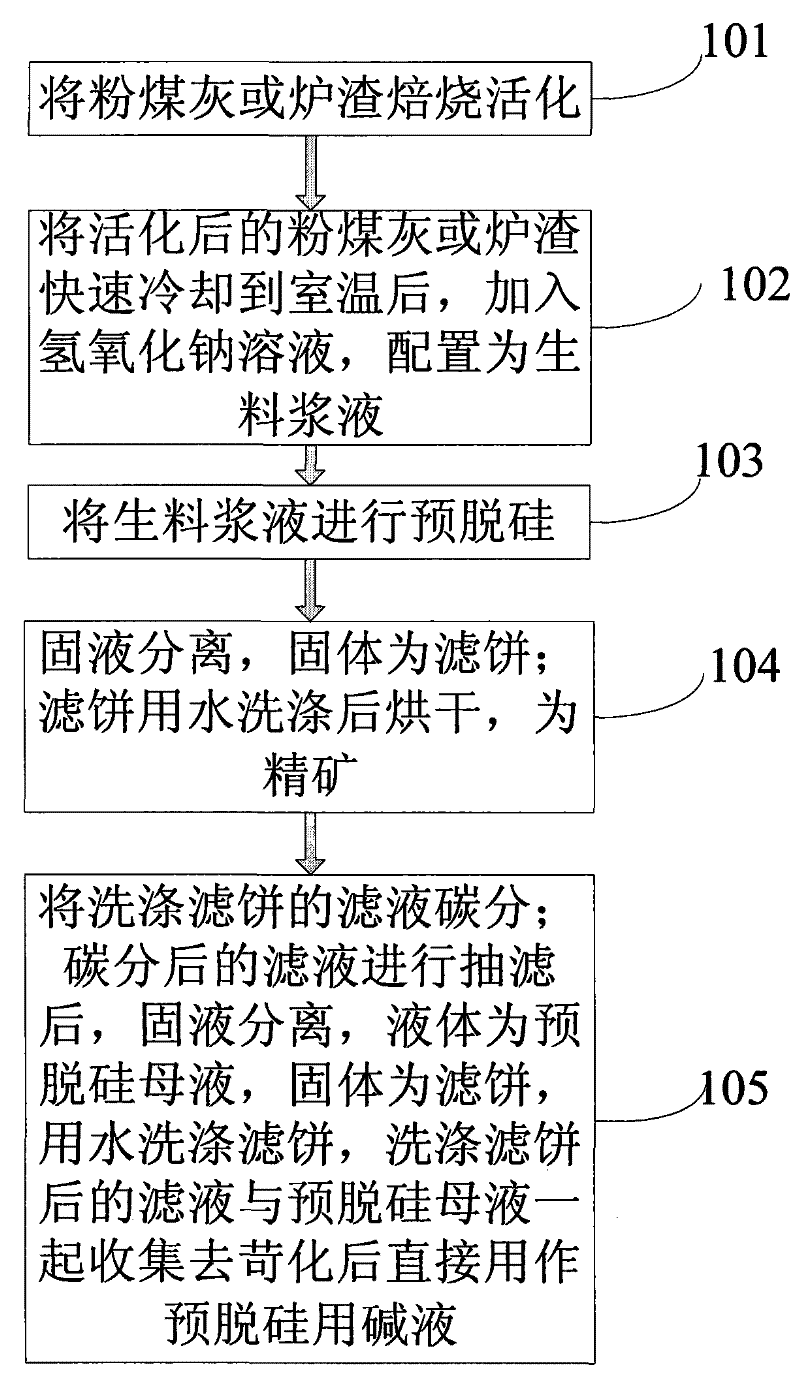
Pre- desiliconizing method from fly ash or slag
ActiveCN101306928BIncrease Al-Si RatioReduce the amount of raw material to be burnedSolid waste managementCooking & bakingSlag
The invention relates to a method for the comprehensive application of fly ash or slag, in particular to a method for the predesilication of the fly ash or the slag. The method mainly comprises the process flows including the baking and the activation of the fly ash or the slag, the formula process of the raw meal of activated the fly ash or the slag and a sodium hydroxide solution and the production of white carbon black. Through adopting a technological line during which the fly ash or the slag are baked and activated at first and then a sodium hydroxide solution is used to extract noncrystalline silicon oxide at a low temperature, the method ensures that the mass ratio of aluminum oxide and silicon oxide of desilicated fly ash reaches to 2.14; therefore, the method breaks a new path totake the fly ash or the slag as a raw material source for extracting metallurgical-grade aluminum oxide, thereby increasing the comprehensive utilization value of the fly ash and the slag.
Owner:北京世纪地和控股有限公司
Battery tab joint by reaction metallurgy
The invention relates to a battery tab joint by reaction metallurgy. Concretely, copper metal or metal alloy workpieces and / or aluminum metal or metal alloy workpieces are joined in a solid state weld by use of a reactive material placed, in a suitable form, at the joining surfaces. Joining surfaces of the workpieces are pressed against the interposed reactive material and heated. The reactive material alloys or reacts with the workpiece surfaces consuming some of the surface material in forming a liquid-containing reaction product comprising a low melting liquid that removes oxide films and other surface impediments to a welded bond across the interface. Further pressure is applied to expel the reaction product and to join the workpiece surfaces in a solid state weld bond.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Device and method for preparing aluminum oxide by roasting crystalline aluminum chloride hexahydrate in rotary kiln
ActiveCN104058436ARealize comprehensive utilizationAluminium oxide/hydroxide preparationBottom ashCombustion
The invention provides a device and a method for preparing aluminum oxide by roasting crystalline aluminum chloride hexahydrate in a rotary kiln, wherein the kiln head part of the roasting rotary kiln is connected with a combustion fan and a heavy oil heater by use of pipelines; a feeding hole formed at the bottom end of the kiln head part of the roasting rotary kiln is communicated with a cooling kiln; the outlet of the cooling kiln is communicated with a belt packing machine; the kiln tail part of the roasting rotary kiln is communicated with a bottom ash outlet of a cyclone separator and a feed pipe. The crystalline aluminum chloride hexahydrate material to be roasted is fed into the roasting rotary kiln via the feed pipe from the kiln tail part of the roasting rotary kiln; the crystalline aluminum chloride hexahydrate material goes oppositely to flue gas and has drastic heat and mass transfer reaction with the flue gas, and thus is transformed into an aluminum oxide powder; the aluminum oxide powder is taken as the product and discharged into the cooling kiln. The device and the method are capable of extracting the metallurgical aluminum oxide from the crystalline aluminum chloride successfully; meanwhile, hydrochloric acid can be recovered from the flue gas generated and used for previous sections, and therefore, comprehensive utilization of coal ash is realized.
Owner:BEIJING HANGHUA ENERGY SAVING ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION TECH CO LTD
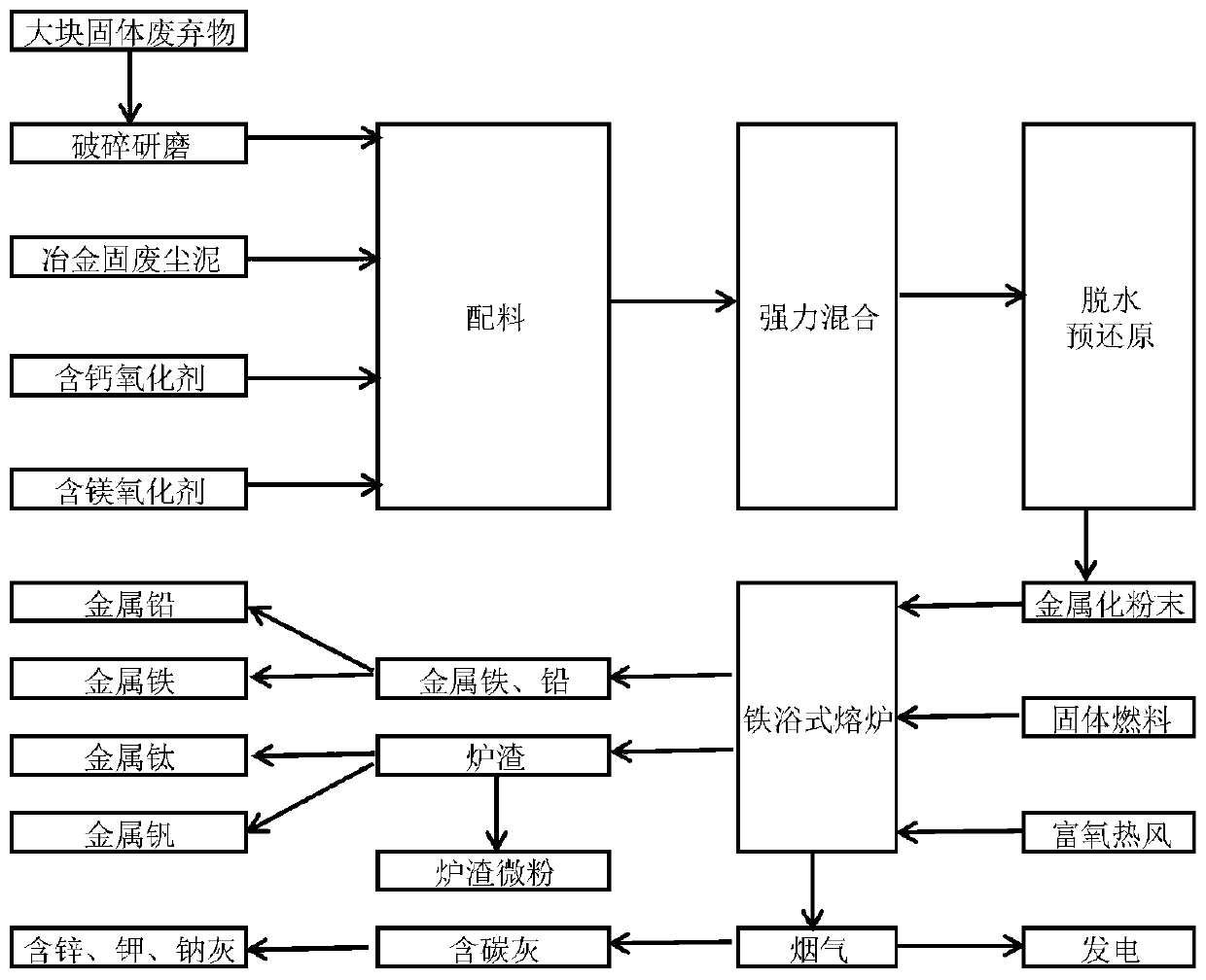
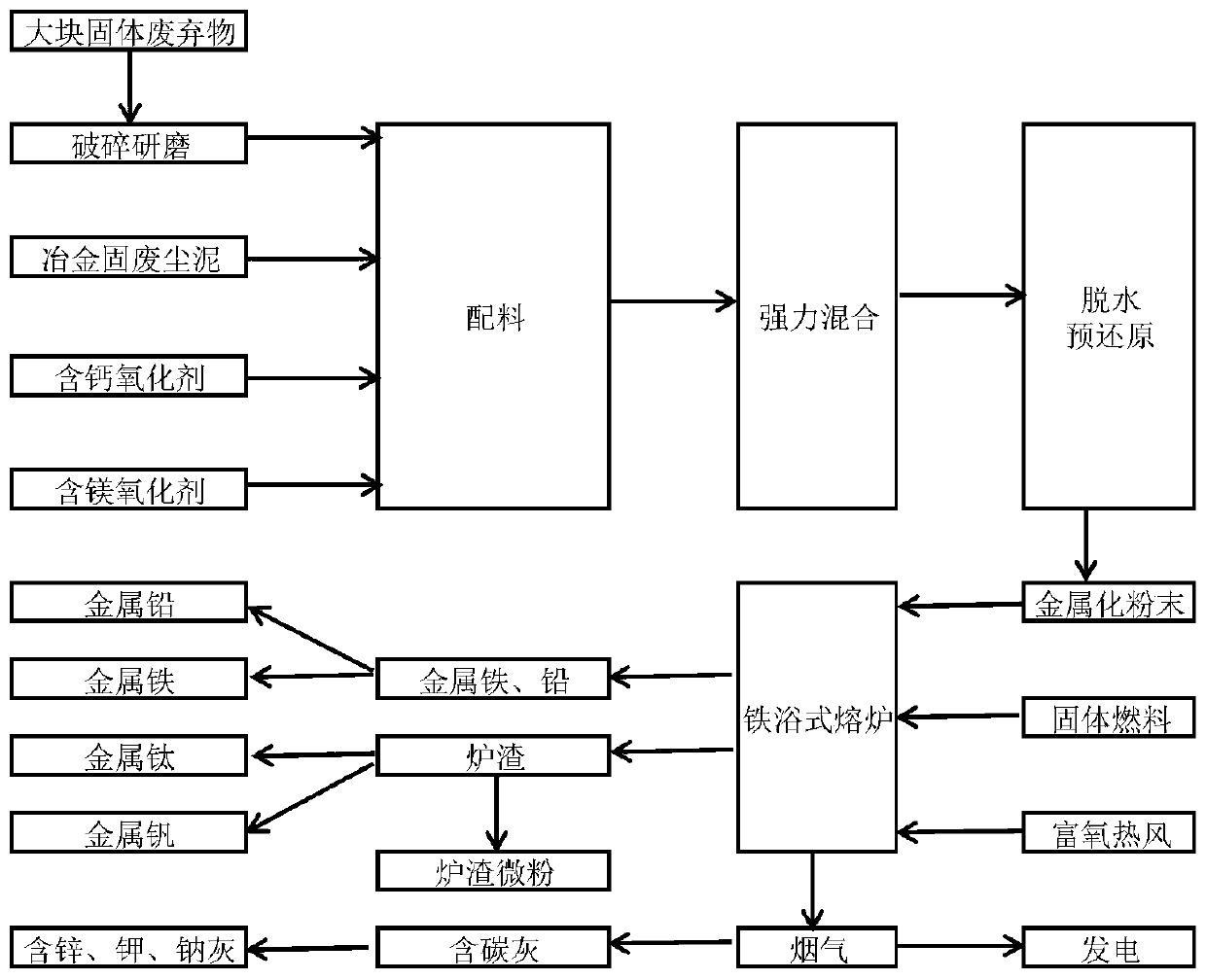
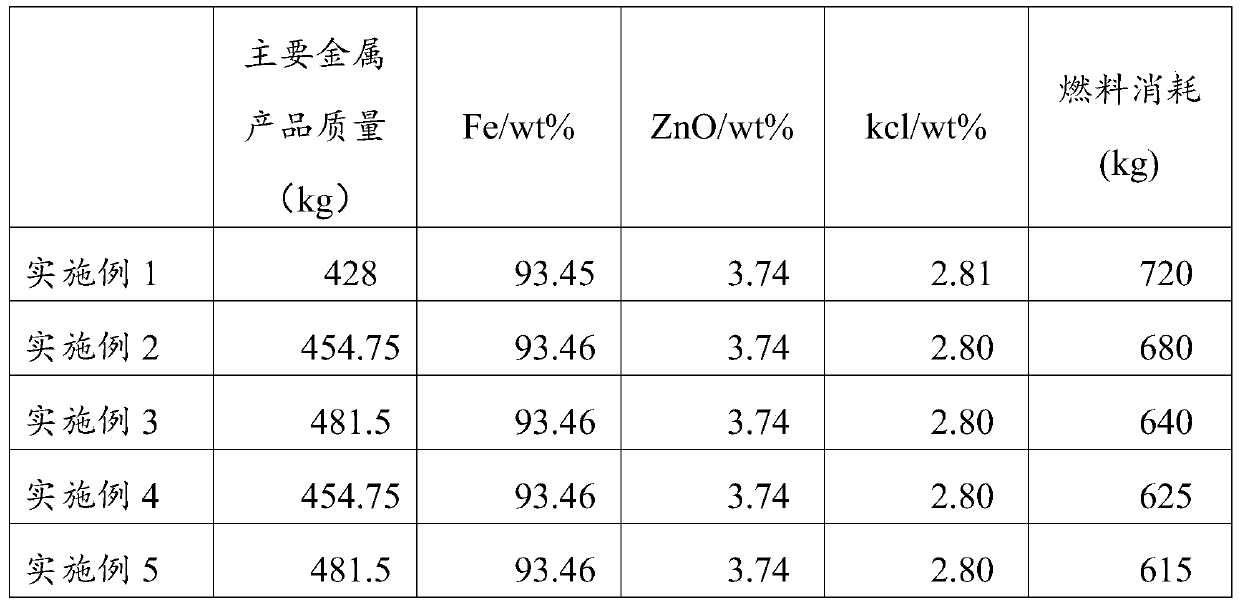
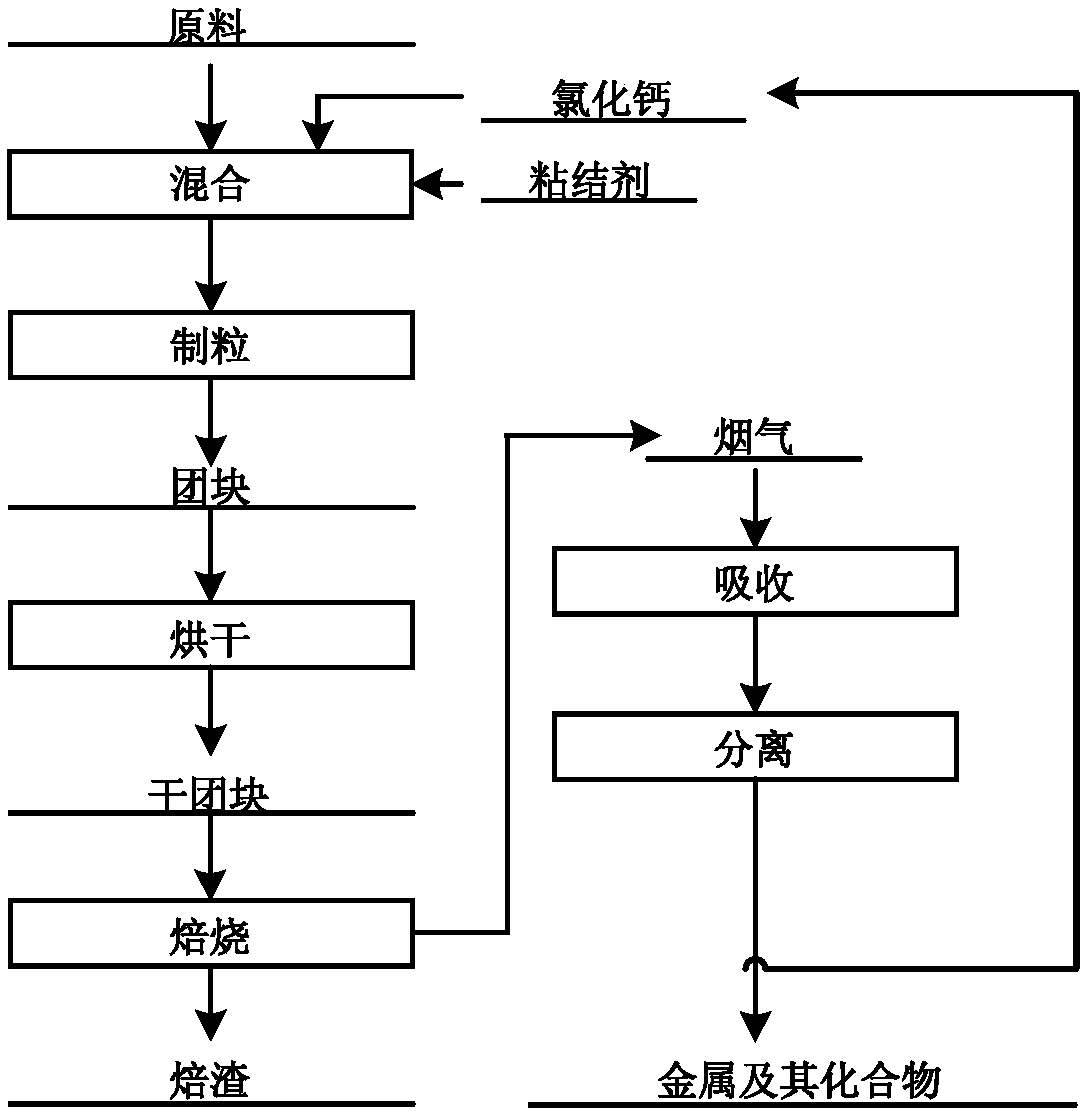
Handling method for metallurgy solid waste
The invention discloses a handling method for metallurgy solid waste. The technological method uses metallurgy solid waste (metallurgy production environment dedusting ash, sintering dust, pelletizingdust, blast furnace dust, converter mud dust, electric furnace mud dust, steel slag and steel rolling mud solid waste and the like) as the main raw materials, and calcium-containing oxide, magnesium-containing oxide and non-coking coal are matched to perform iron bath type smelting reduction through a spraying mode to extract products like Fe, K, Na, Zn, Ti and V in the metallurgy solid waste. The dependence of pyrogenic attack of metallurgy solid waste on coke, sintering, pelletizing and agglomeration is removed really, one-step treatment of metallurgy solid waste is achieved, gradual separation is achieved, all elements are extracted, and thorough treatment is achieved. The whole method is simple and efficient, and industrial production is easy.
Owner:班友合
Method for creating metallurgical steelmaking production line building information model
The invention relates to a construction management technical method. A method for creating a metallurgical steelmaking production line building information model comprises the following steps: collecting metallurgical project basic documents, and establishing a one to one correspondence relation of modeling personnel and project management personnel; extracting related plant infrastructure data of a steel plant, carrying out three-dimensional site layout, and carrying out basic modeling; extracting metallurgical steelmaking equipment data, and creating an equipment family library; extracting related electromechanical data, and carrying out a professional detailed design of electromechanical pipeline models; extracting model information according to a project information model application point, and outputting a document meeting the application requirements; and sharing the above-mentioned file and an application file to a project management cloud platform for relevant personnel to inspect and guide site operation. By adoption of the method provided by the invention, the installation positions of various facilitates can be intuitively and accurately understood prior to the construction, and possible construction schemes, equipment installation and other difficulties can be found in the construction process, thereby optimizing the construction process and improving the construction process.
Owner:SHANGHAI BAOYE GRP CORP
Welding light metal workpieces by reaction metallurgy
ActiveUS20150158113A1Mobility is suitableMinimize distortionWelding/cutting auxillary devicesAuxillary welding devicesReactive materialMagnesium alloy
Aluminum alloy workpieces and / or magnesium alloy workpieces are joined in a solid state weld by use of a reactive material placed, in a suitable form, at the joining surfaces. Joining surfaces of the workpieces are pressed against the interposed reactive material and heated. The reactive material alloys or reacts with the workpiece surfaces consuming some of the surface material in forming a reaction product comprising a low melting liquid that removes oxide films and other surface impediments to a welded bond across the interface. Further pressure is applied to expel the reaction product and to join the workpiece surfaces in a solid state weld bond.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
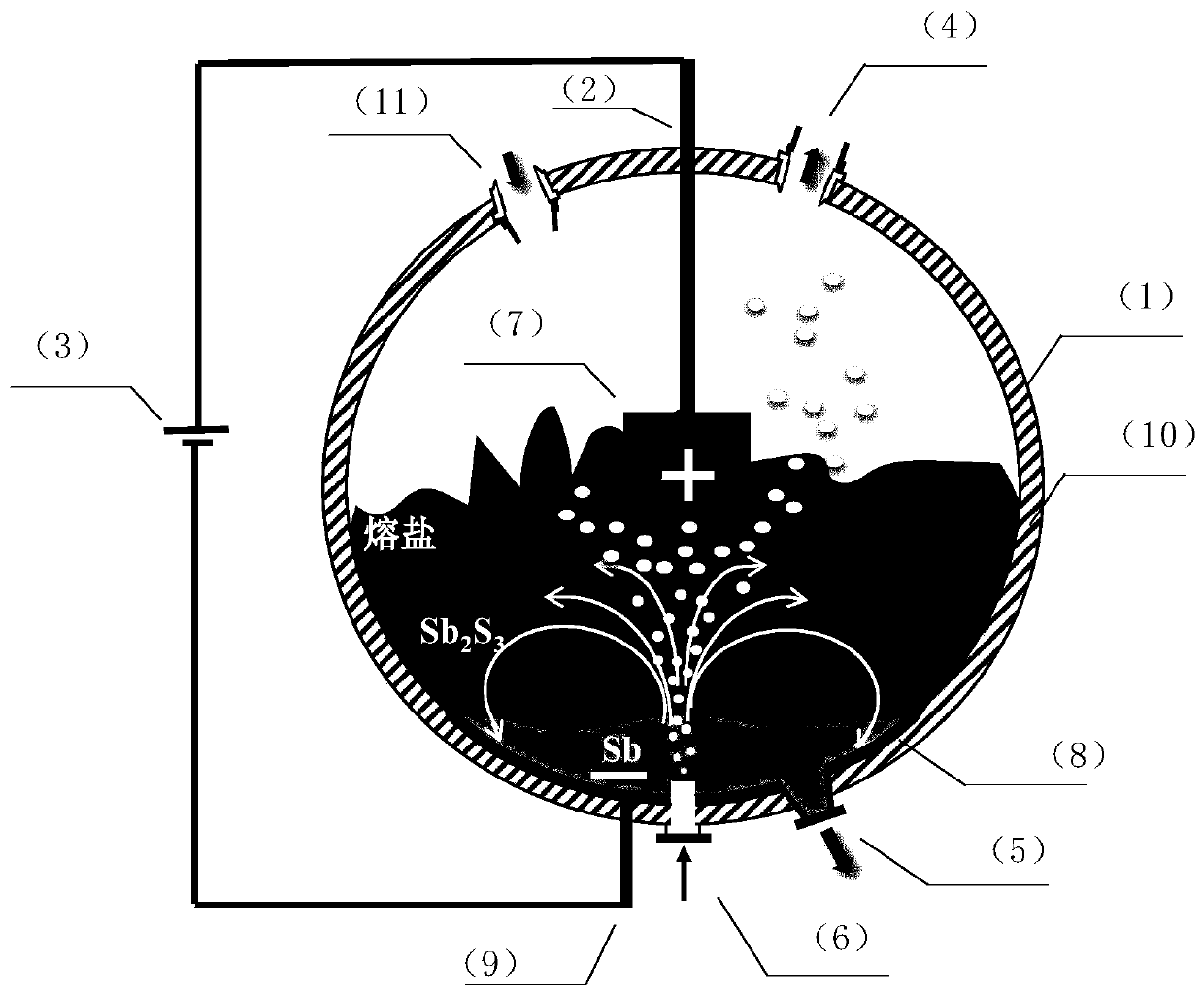
Method and device for molten salt electrolysis of materials containing antimony sulfide
ActiveCN111172563AEnhanced mass transferPromote "coagulation and sedimentationElectrolysis componentsElectrolysisMolten bath
The invention discloses a method and device for molten salt electrolysis of materials containing antimony sulfide. The materials containing antimony sulfide and inert molten salt are mixed and put into an electrolysis device for heating electrolysis smelting, inert gas is blown in the smelting process to stir a molten pool, a liquid antimony melt layer is obtained through gradual enrichment on thelower layer in the device along with proceeding of low-temperature molten salt electrolysis, and the elementary substance sulphur is obtained in a smoke collecting device through gradual enrichment.According to the method and the device, molten salt ion mass transfer is enhanced, high-quality antimony and the elementary substance sulphur are produced by one step, and the issue that low-concentration SO2 pollutes the environment in traditional antimony pyrometallurgy is avoided. The method and the device have the advantages of being low in energy consumption, high in antimony direct yield, clean and environmentally friendly. The device is simple and practical, and good antimony and sulphur extractive metallurgy effects can be obtained when the device is used for treating antimony sulfideconcentrate in cooperation.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
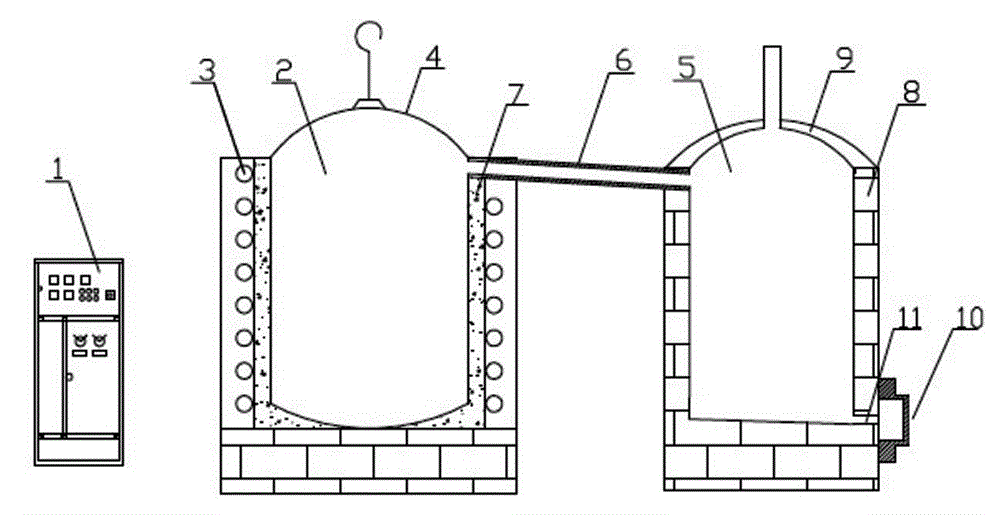
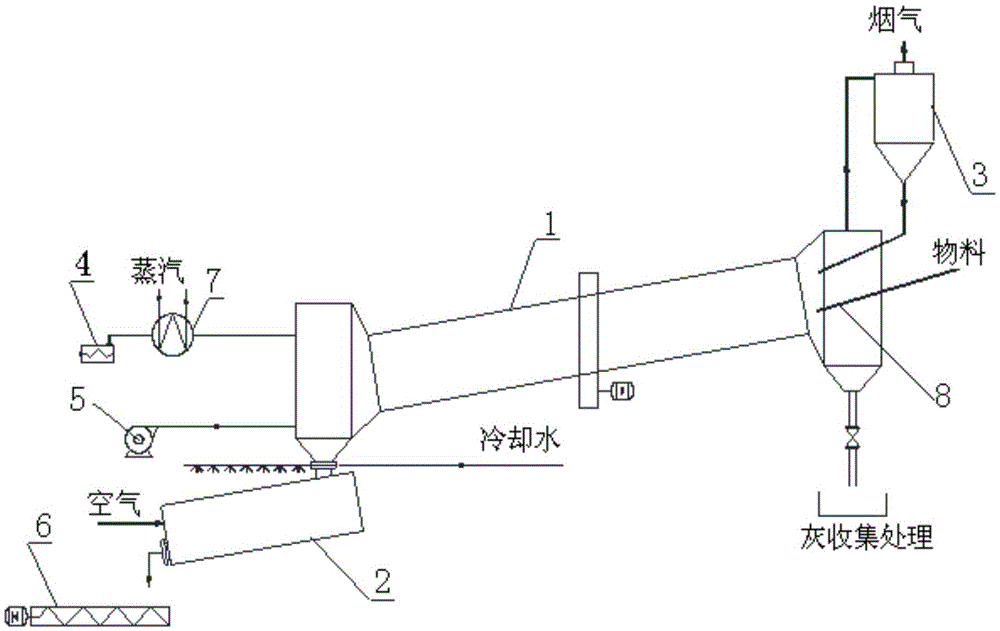
Method for separating and recycling zinc from secondary zinc resource by using distilling-condensing device
InactiveCN103146933AEasy extractionShort processProcess efficiency improvementEconomic benefitsEngineering
The invention discloses a method for separating and recycling zinc from secondary zinc resource by using a distilling-condensing device, belongs to the field of thermometallurgy, in particular relates to an extraction metallurgy technique of metal zinc, and relates to a method and a device for separating and recycling zinc from the secondary zinc resource. The method comprises the following steps of: adding a secondary zinc material in which the zinc content is greater than 30wt% into an evaporation tank, sealing the top cover, powering on a sensing heating coil to increase the temperature, increasing the temperature inside the evaporation tank to be at 900-1150 DEG C, generating a zinc liquid and evaporating, preserving the temperature of the zinc steam and introducing into a condenser, condensing and coacervating at the inner of a condensing chamber so as to form liquid zinc, opening the outlet at the lower part of the condenser to discharge the liquid zinc from the outlet, and ingoting so as to obtain zinc ingots. The method is simple in equipment and convenient in operation and has the characteristics of high recovery rate, wide material application range, good economic benefit, rapid investment return and the like.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH TECH IND SALES MANAGEMENT
Welding light metal workpieces by reaction metallurgy
ActiveUS8963042B2Mobility is suitableMinimize distortionArc welding apparatusHigh frequency current welding apparatusReactive materialMagnesium alloy
Aluminum alloy workpieces and / or magnesium alloy workpieces are joined in a solid state weld by use of a reactive material placed, in a suitable form, at the joining surfaces. Joining surfaces of the workpieces are pressed against the interposed reactive material and heated. The reactive material alloys or reacts with the workpiece surfaces consuming some of the surface material in forming a reaction product comprising a low melting liquid that removes oxide films and other surface impediments to a welded bond across the interface. Further pressure is applied to expel the reaction product and to join the workpiece surfaces in a solid state weld bond.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Method for extracting copper with solvent
ActiveUS20060147360A1High industrial valueHigh extraction rateSolid sorbent liquid separationGold compoundsSolventExtractive metallurgist
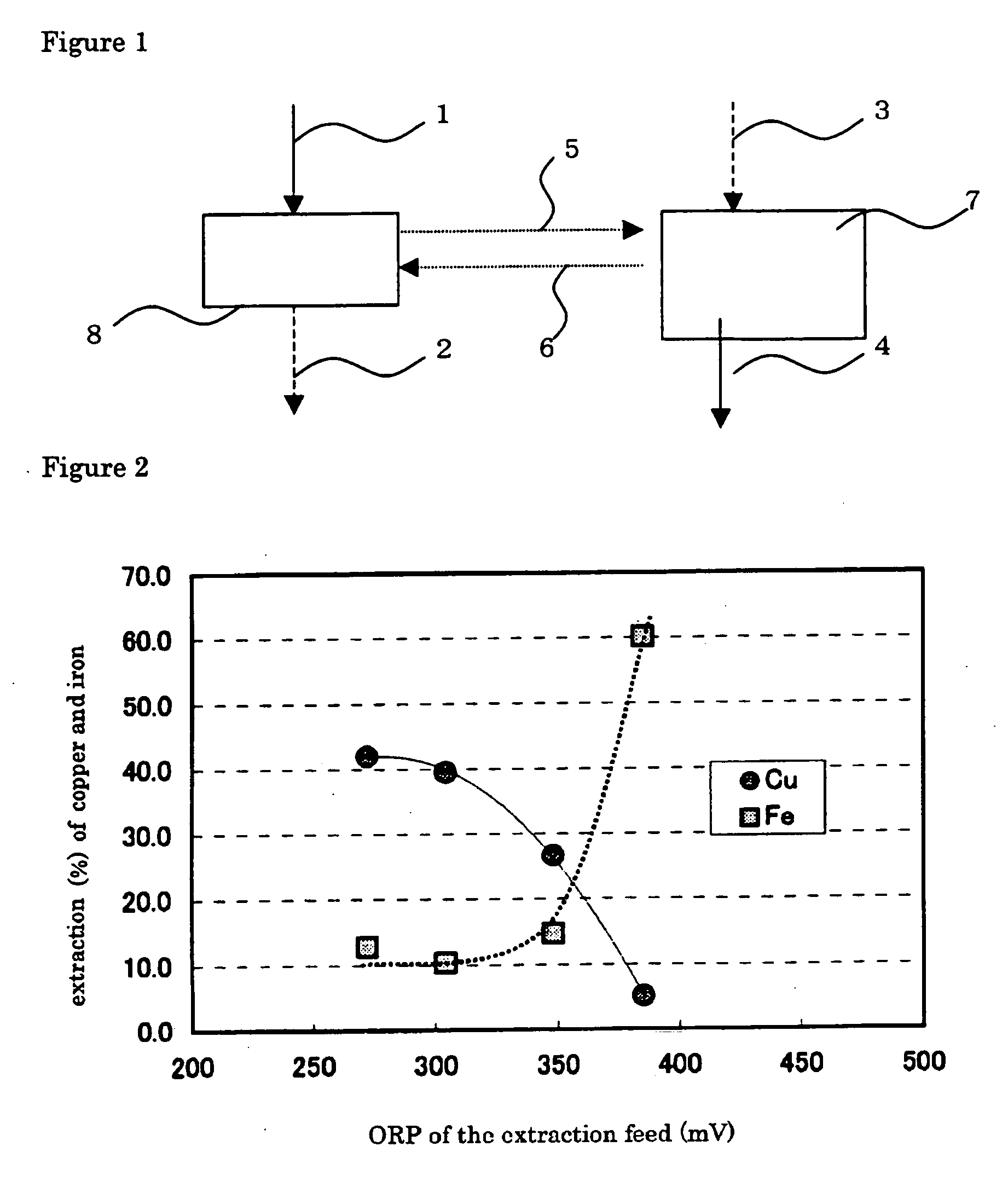
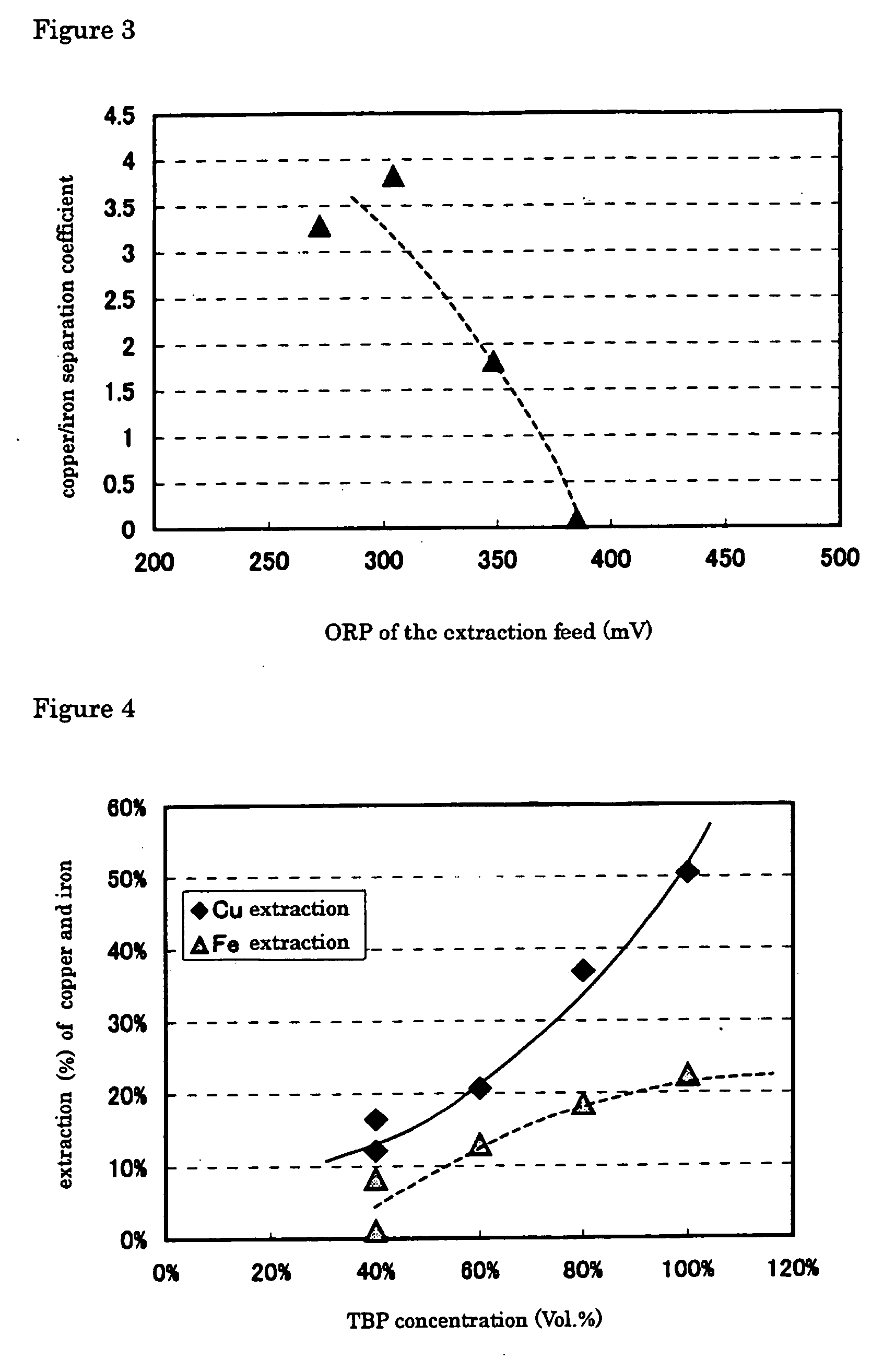
A process for efficient separation / recovery of copper involving selective extraction of the copper ion with the aid of an organic extractant from an aqueous chloride solution containing copper and one or more concomitant elements, discharged from an extractive metallurgy of non-ferrous metals or the like, and subsequent stripping. The process of solvent extraction of copper which treats an aqueous chloride solution containing copper and one or more concomitant elements to separate / recover copper, comprising the first step for selective extraction of copper from the aqueous chloride solution by mixing the solution with an extractant of organic solvent composed of tributyl phosphate as the major component after adjusting the solution at an oxidation-reduction potential of 0 to 350 mV (based on an Ag / AgCl electrode), and the second step for stripping of copper by mixing the extractant in which copper is stripped with an aqueous solution.
Owner:SUMITOMO METAL MINING CO LTD
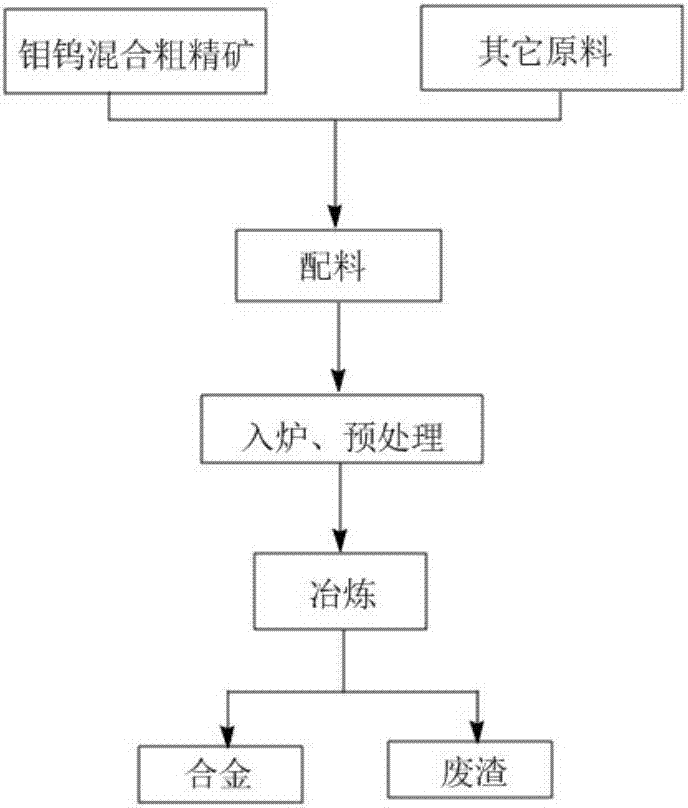
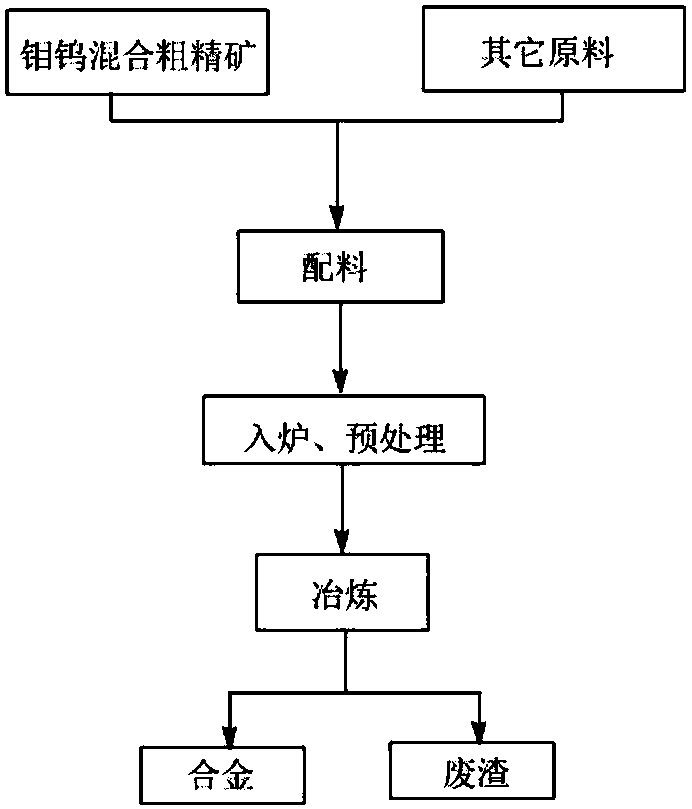
Molybdenum-tungsten-iron alloy and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to molybdenum-tungsten-iron alloy and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of mineral extractive metallurgy. The preparation method of molybdenum-tungsten-iron alloy comprises the following steps: adding the following raw materials such as calcium oxide, molybdenum and tungsten mixed crude concentrate, silicon iron and scrap iron into a crucible in sequence, rising the temperature to 400-600 DEG C, performing heat preservation for 3-5 min, continuously rising the temperature to 1500-1700 DEG C, performing heat preservation again for 1-3 min, and cooling, so as to obtain the molybdenum-tungsten-iron alloy. According to the preparation method of molybdenum-tungsten-iron alloy provided by the invention, molybdenum and tungsten mixed crude concentrate, calcium oxide, silicon iron and scrap iron are taken as the raw materials, the process is simple, and the required smelting time is as short as 1-3 min; compared with other methods, the preparation method has the advantages that the separation and purification processes of molybdenum and tungsten mixed crude concentrate are avoided, the smelting time is greatly reduced, the production cost is reduced, the resource utilization ratio is improved, and economic benefits are increased.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU MINERALS COMPOSITIVE UTILIZATION RES INST CHINESE GEOLOGICAL ACAD
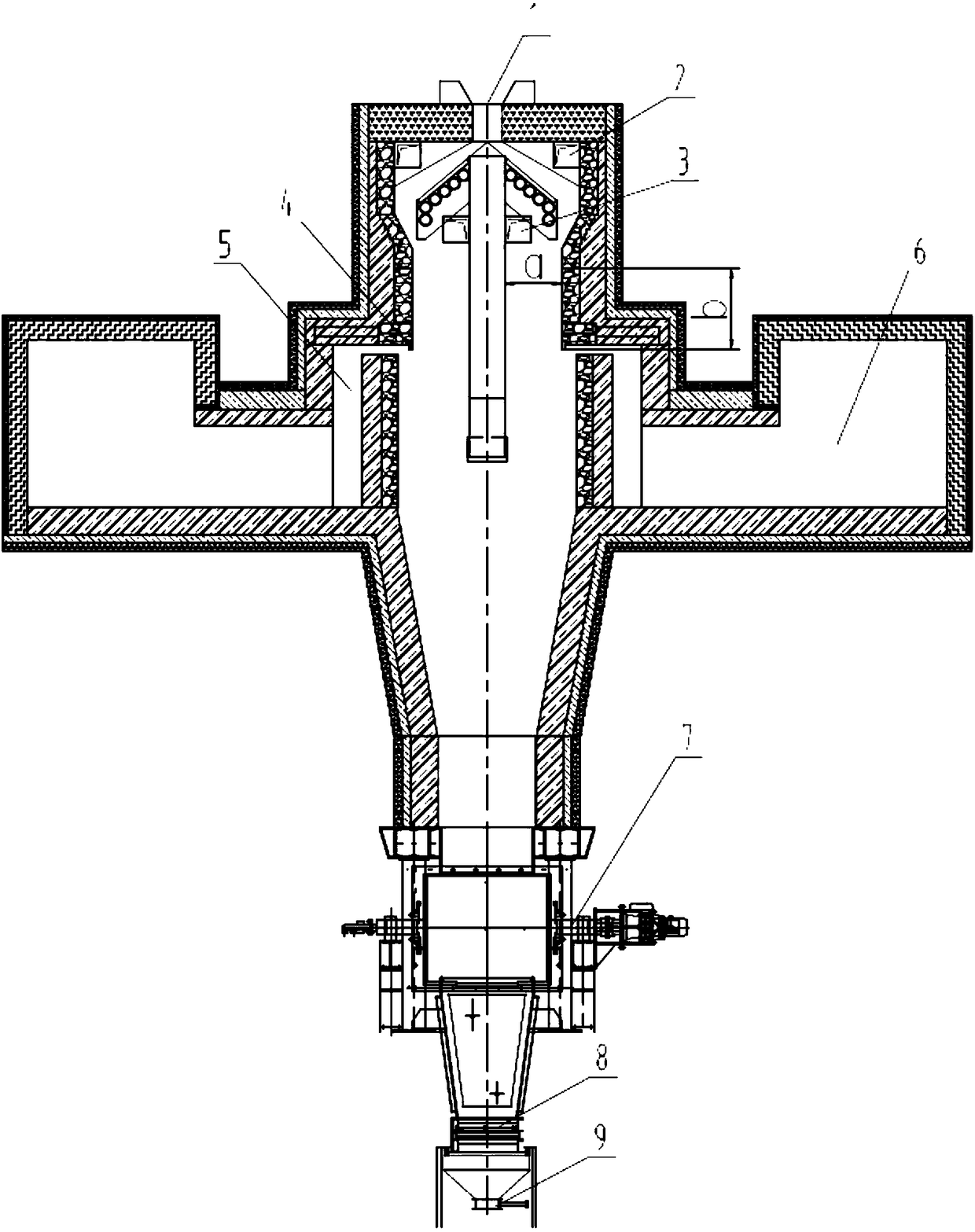
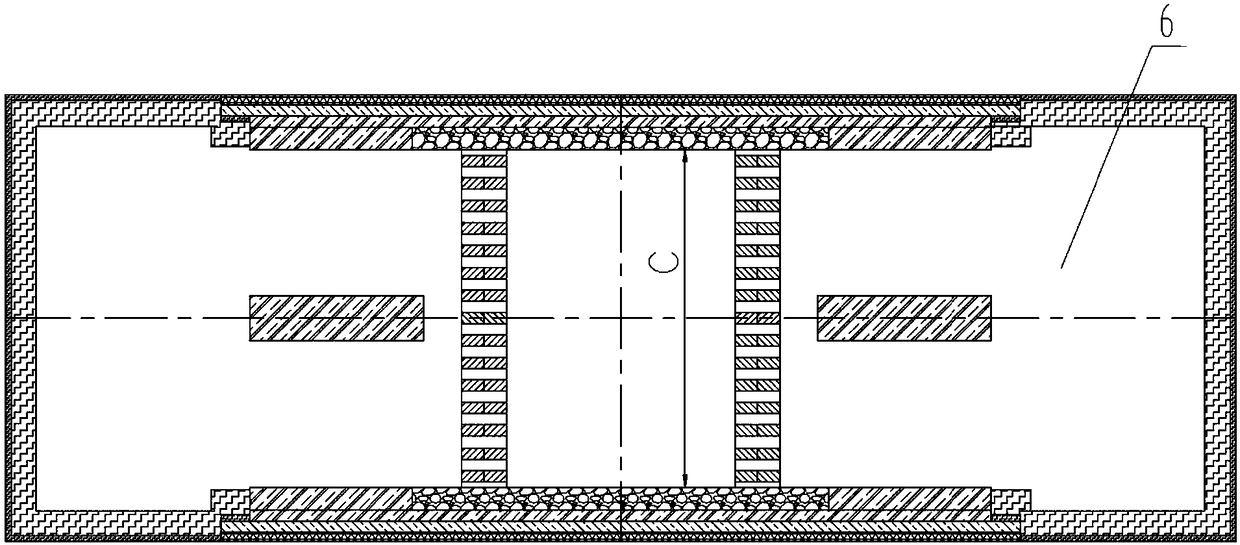
High temperature chlorination shaft furnace
InactiveCN108061461AStrong flame penetrationUniform product qualityVertical furnacesCombustion chamberShaft furnace
The invention relates to a high temperature chlorination shaft furnace, and belongs to chloridizing roasting shaft furnaces in the metallurgical industry. Raw materials are calcium chloride containingpellets, gold, silver, copper, lead, zinc, tin and cobalt in metallurgical and beneficiation waste residues can be extracted, and oxidation pellets can be produced. The high temperature chlorinationshaft furnace comprises a feeding device, a roasting chamber, burning chambers, a cooling discharging device and a chlorination metal gas discharging device. The burning chambers are located on one ortwo sides of the roasting chamber, and communication is achieved through a flame path. Extraction openings are located on one or two sides of the lower portion of a feeding opening, the high temperature chlorination shaft furnace is high in temperature rising capacity, sensitive in temperature controlling, even in heating, not prone to nodulation and good in product quality coincidence, and a nodule destroying device is arranged.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +2
A kind of vanadium extraction process of stone coal vanadium ore
InactiveCN108251661BHigh extraction rateIncrease profitProcess efficiency improvementMetal impuritiesIon exchange
Owner:CHANGCHUN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
A device and method for preparing alumina by roasting hexahydrate crystalline aluminum chloride in a rotary kiln
ActiveCN104058436BRealize comprehensive utilizationAluminium oxide/hydroxide preparationBottom ashCombustion
Owner:BEIJING HANGHUA ENERGY SAVING ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION TECH CO LTD
Method for extracting vanadium from low-grade vanadium-containing raw material and recycling wastewater
PendingCN114350951AAffect recyclingImprove filtering effectWaste water treatment from metallurgical processWater/sewage treatment by neutralisationCalcium sulfiteMaterials science
The invention relates to the technical field of vanadium extraction metallurgy, and discloses a method for extracting vanadium from a low-grade vanadium-containing raw material and recycling wastewater. The method comprises the following steps: (1) adding a low-grade vanadium-containing raw material and calcium sulfite into water for pulping, then adding sulfuric acid for leaching, adjusting the pH value of a system to 2-3 after the reaction is finished, and carrying out solid-liquid separation to obtain residues and leachate; (2) adjusting the pH value of the leachate to 5.5-7 for vanadium precipitation, and filtering to obtain a vanadium precipitate and primary wastewater; (3) adding water, sulfuric acid and a phosphorus removal agent into the vanadium precipitate for reaction, and performing solid-liquid separation to obtain filter residues and vanadium liquid; (4) adding urea into the vanadium liquid to precipitate vanadium, filtering to obtain vanadium hydroxide and secondary wastewater, and calcining the vanadium hydroxide to obtain vanadium pentoxide; the primary wastewater is neutralized by lime and then returns to the step (1) for use; and returning the secondary wastewater to the step (3) for use. According to the method, the recycling of the wastewater can be realized while vanadium is extracted, and the method has a good application prospect.
Owner:PANGANG GROUP RESEARCH INSTITUTE CO LTD
Method for recovering vanadium from calcified vanadium extraction tailings
PendingCN114350981AAvoid lostSettle the lossProcess efficiency improvementCalcium sulfiteMaterials science
The invention relates to the technical field of extraction metallurgy, and discloses a method for recovering vanadium from calcified vanadium extraction tailings. The method comprises the following steps: (1) adding the calcified vanadium extraction tailings and calcium sulfite into water for pulping, then adding sulfuric acid for leaching, adjusting the pH value of a system to 2-3 by using lime and / or limestone after the leaching is finished, and then carrying out solid-liquid separation to obtain residues and a leaching solution; (2) adjusting the pH value of the leachate to 5.5-7 by using magnesium carbonate and / or manganese carbonate to precipitate vanadium, and then filtering to obtain vanadium precipitate and wastewater; (3) adding a sodium hydroxide solution and an oxidizing agent into the vanadium precipitate for reaction, performing solid-liquid separation after reaction to obtain filtrate A and filter residue A, and controlling the weight ratio of vanadium element to phosphorus element in the filtrate A to be greater than or equal to 600; and (4) calcium oxide is added into the filtrate A for vanadium precipitation, and filtrate B and filter residues B are obtained through solid-liquid separation. According to the method, the vanadium in the calcified vanadium extraction tailings can be effectively recycled, and the vanadium loss in the vanadium extraction process can be reduced.
Owner:PANGANG GROUP RESEARCH INSTITUTE CO LTD
Method and device for condensing and co-producing refined magnesium by evaporating and endothermic magnesium vapor from magnesium liquid
The invention relates to a method and a device for condensing magnesium vapor generated by evaporation and heat absorption of a magnesium liquid and coproducing refined magnesium and belongs to the technical field of extraction metallurgy or nonferrous magnesium metal. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out reverse phase change heat exchange on primary magnesium vapor in a first condensing section by taking evaporation and heat absorption of the magnesium liquid as a cooling manner, wherein the primary magnesium vapor is condensed to a liquid state; then evaporating the magnesium liquid to form higher-purity refined magnesium vapor due to the heat obtained by the magnesium liquid; then condensing the refined magnesium vapor to liquid refined magnesium; and continuously cooling and condensing residual vapor of the primary magnesium and refined magnesium in a second condensing section, wherein the primary magnesium and refined magnesium are condensed to solid crystal magnesium. According to the method and device provided by the invention, a magnesium liquid evaporator is used for condensing the primary magnesium vapor and further serves as a heat source for purifying the magnesium liquid. Parallel secondary cooling monomers are arranged in a secondary cooling section to realize alternate condensation and follow-up heating and re-melting. By adopting returned heating, heat demand on evaporation and remelting is realized by using heat energy of magnesium vapor condensation, so that high purity magnesium is coproduced and heat energy is fully utilized; the secondary cooling monomers are alternately condensed and remelted, so that the condensing rate is improved and the magnesium liquid is convenient to flow out and recycle.
Owner:牛强
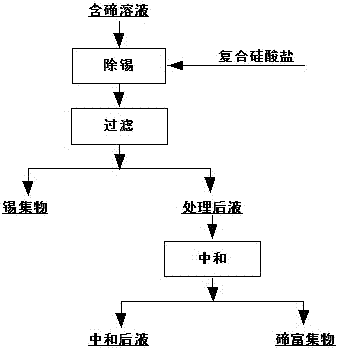
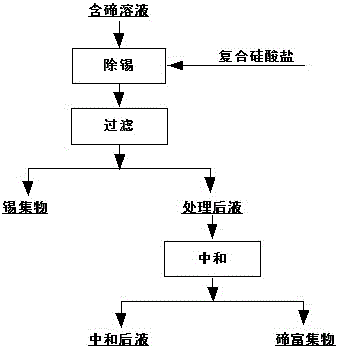
A method for deep tin removal in tellurium-containing solution
The invention belongs to the technical field of extractive metallurgy of nonferrous metals, and specifically relates to a method for deep removal of tin in a tellurium-contained solution. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: adding a composite silicate additive into the tellurium-contained solution, controlling a mass ratio of the composite silicate additive to tin in the tellurium-contained solution to be (0.2-2): 1, a reaction temperature to be 50 to 90 DEG C and a reaction time to be 2 to 12 hours, after deposition is completed, carrying out filtering, then subjecting obtained filtrate to acid neutralization, and carrying out filtering so as to obtain enriched tellurium. The method provided by the invention can realize deep removal of tin, and can obtain enriched tellurium with a tellurium content reaching 60% or above.
Owner:JIANGXI COPPER
Method for deep removal of tin in tellurium-contained solution
The invention belongs to the technical field of extractive metallurgy of nonferrous metals, and specifically relates to a method for deep removal of tin in a tellurium-contained solution. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: adding a composite silicate additive into the tellurium-contained solution, controlling a mass ratio of the composite silicate additive to tin in the tellurium-contained solution to be (0.2-2): 1, a reaction temperature to be 50 to 90 DEG C and a reaction time to be 2 to 12 hours, after deposition is completed, carrying out filtering, then subjecting obtained filtrate to acid neutralization, and carrying out filtering so as to obtain enriched tellurium. The method provided by the invention can realize deep removal of tin, and can obtain enriched tellurium with a tellurium content reaching 60% or above.
Owner:JIANGXI COPPER
A kind of molybdenum tungsten iron alloy and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to molybdenum-tungsten-iron alloy and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of mineral extractive metallurgy. The preparation method of molybdenum-tungsten-iron alloy comprises the following steps: adding the following raw materials such as calcium oxide, molybdenum and tungsten mixed crude concentrate, silicon iron and scrap iron into a crucible in sequence, rising the temperature to 400-600 DEG C, performing heat preservation for 3-5 min, continuously rising the temperature to 1500-1700 DEG C, performing heat preservation again for 1-3 min, and cooling, so as to obtain the molybdenum-tungsten-iron alloy. According to the preparation method of molybdenum-tungsten-iron alloy provided by the invention, molybdenum and tungsten mixed crude concentrate, calcium oxide, silicon iron and scrap iron are taken as the raw materials, the process is simple, and the required smelting time is as short as 1-3 min; compared with other methods, the preparation method has the advantages that the separation and purification processes of molybdenum and tungsten mixed crude concentrate are avoided, the smelting time is greatly reduced, the production cost is reduced, the resource utilization ratio is improved, and economic benefits are increased.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU MINERALS COMPOSITIVE UTILIZATION RES INST CHINESE GEOLOGICAL ACAD
Method and device for molten salt electrolysis of materials containing antimony sulfide
ActiveCN111172563BEnhanced mass transferPromote "coagulation and sedimentationElectrolysis componentsElectrolysisMolten bath
The invention discloses a method and device for molten salt electrolysis of materials containing antimony sulfide. The materials containing antimony sulfide and inert molten salt are mixed and put into an electrolysis device for heating electrolysis smelting, inert gas is blown in the smelting process to stir a molten pool, a liquid antimony melt layer is obtained through gradual enrichment on thelower layer in the device along with proceeding of low-temperature molten salt electrolysis, and the elementary substance sulphur is obtained in a smoke collecting device through gradual enrichment.According to the method and the device, molten salt ion mass transfer is enhanced, high-quality antimony and the elementary substance sulphur are produced by one step, and the issue that low-concentration SO2 pollutes the environment in traditional antimony pyrometallurgy is avoided. The method and the device have the advantages of being low in energy consumption, high in antimony direct yield, clean and environmentally friendly. The device is simple and practical, and good antimony and sulphur extractive metallurgy effects can be obtained when the device is used for treating antimony sulfideconcentrate in cooperation.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com