Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
73 results about "Diffusion current" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
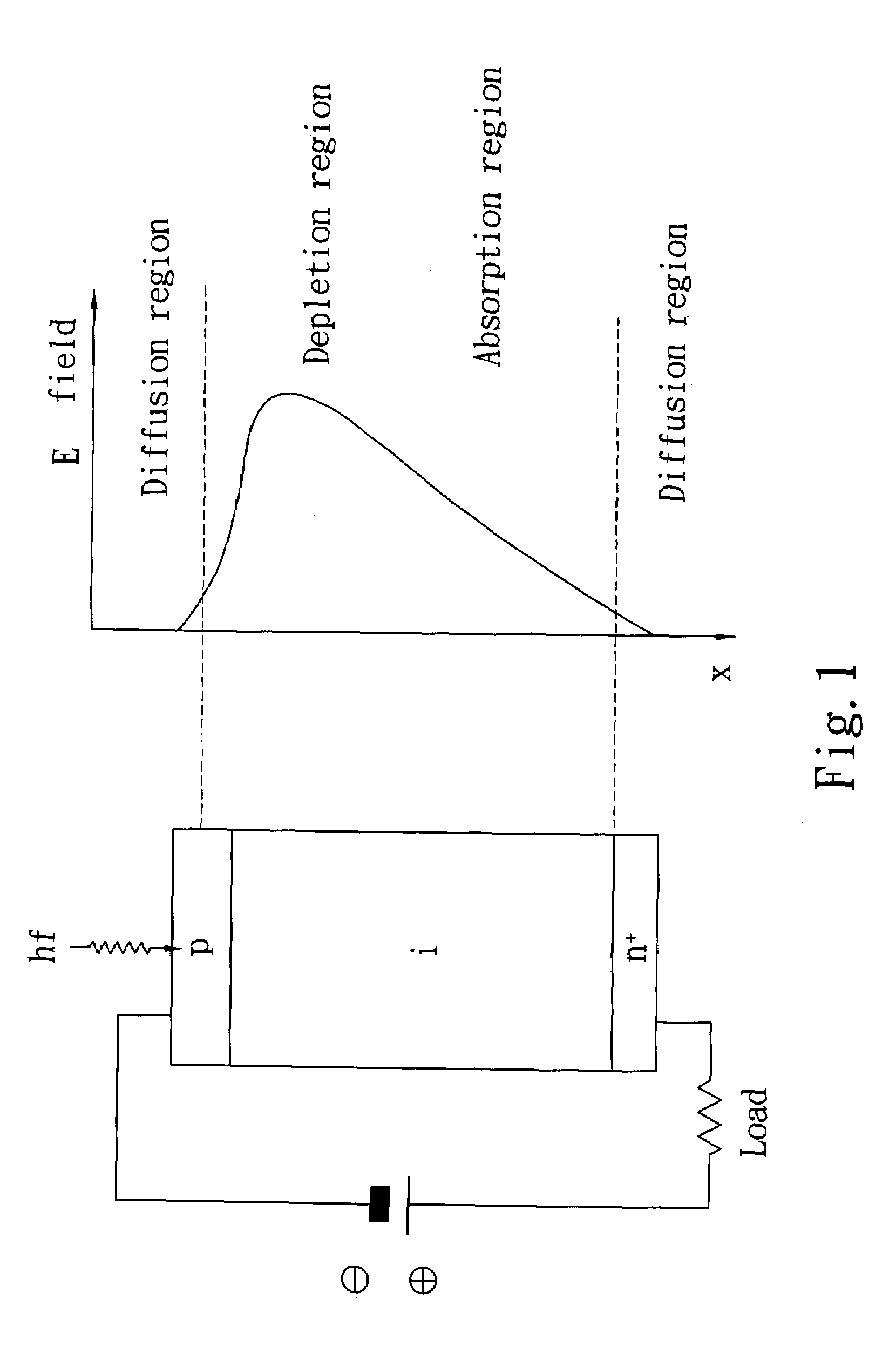
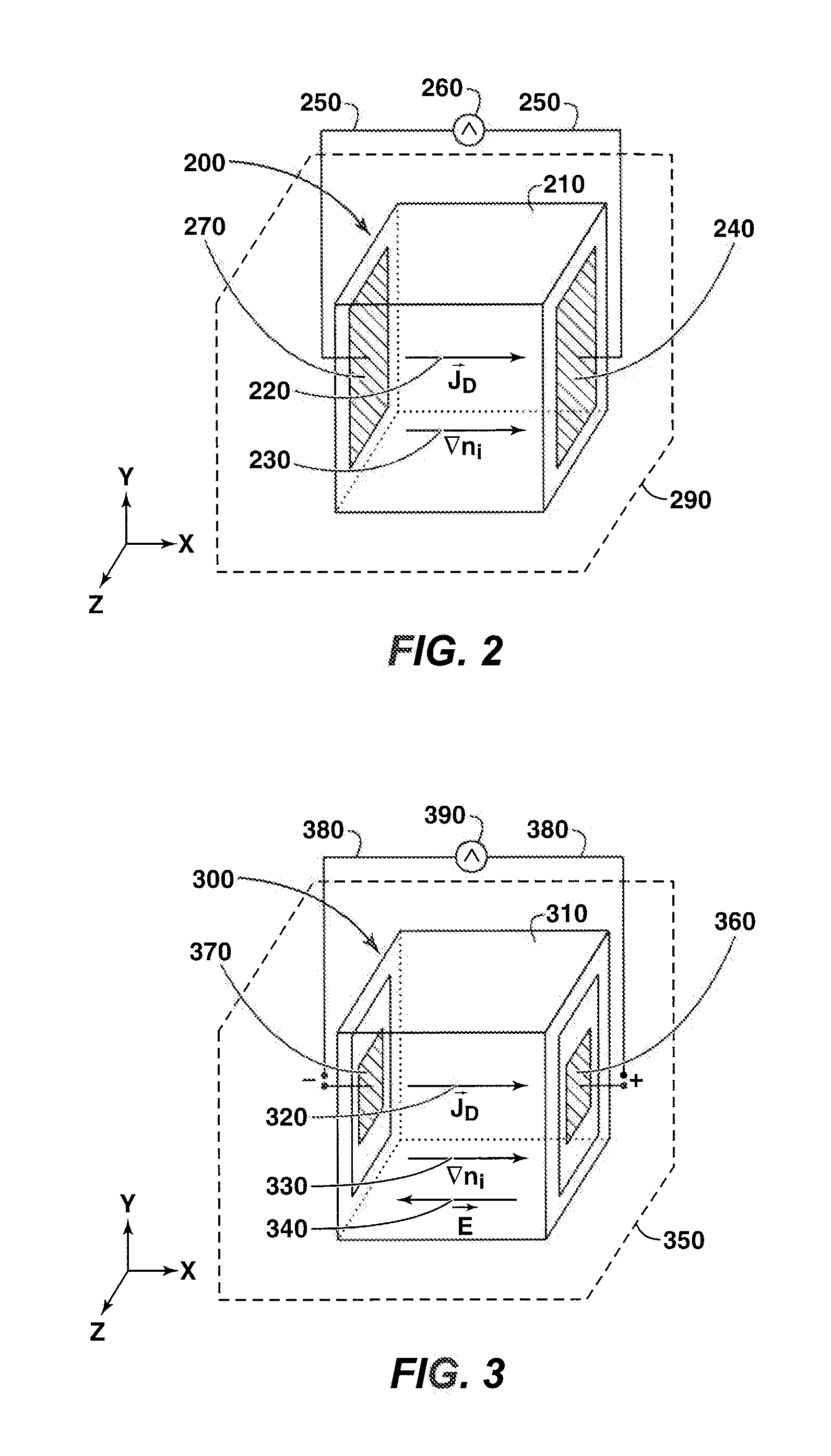
Diffusion Current is a current in a semiconductor caused by the diffusion of charge carriers (holes and/or electrons). This is the current which is due to the transport of charges occurring because of non-uniform concentration of charged particles in a semiconductor. The drift current, by contrast, is due to the motion of charge carriers due to the force exerted on them by an electric field. Diffusion current can be in the same or opposite direction of a drift current. The diffusion current and drift current together are described by the drift–diffusion equation.
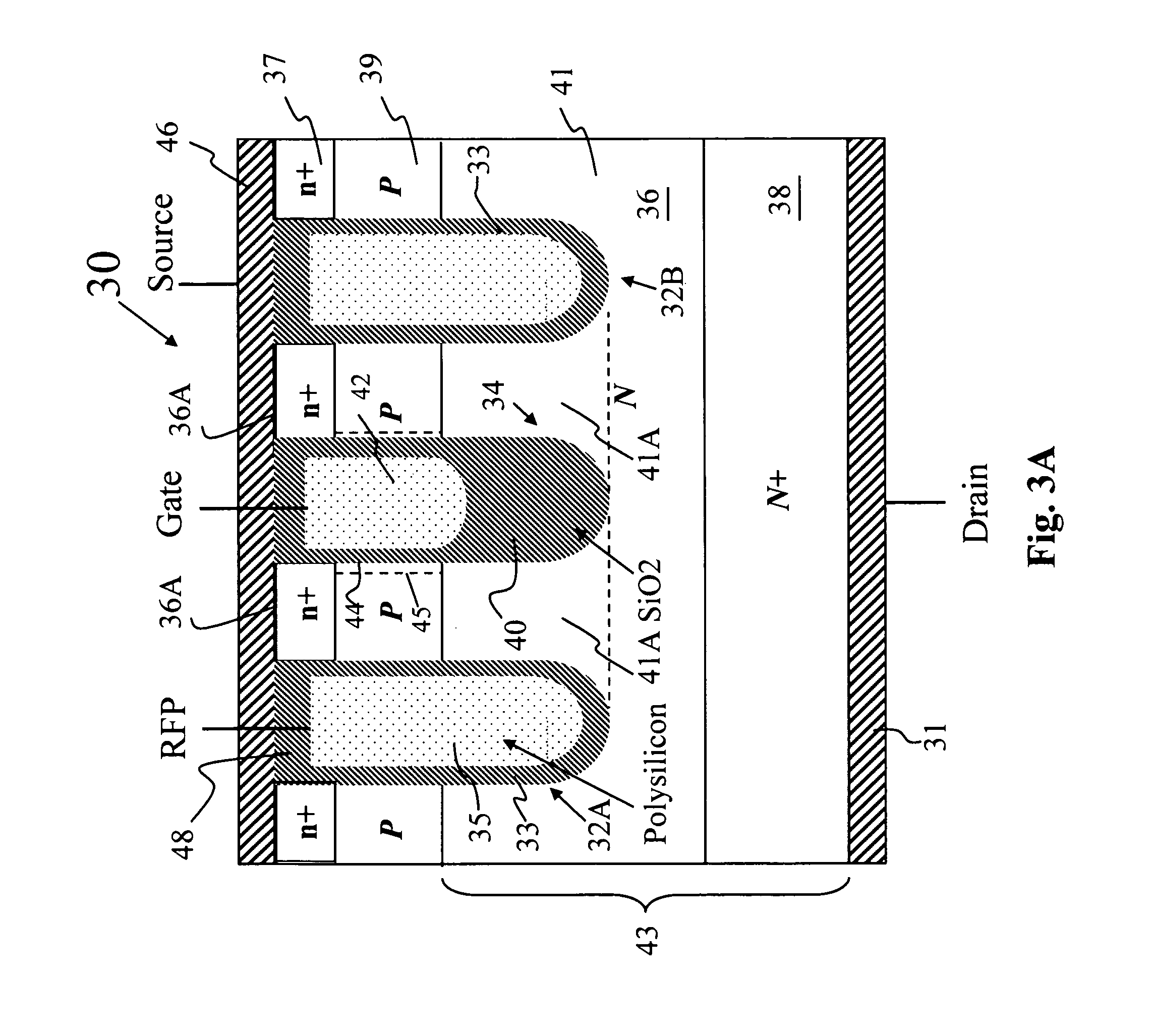
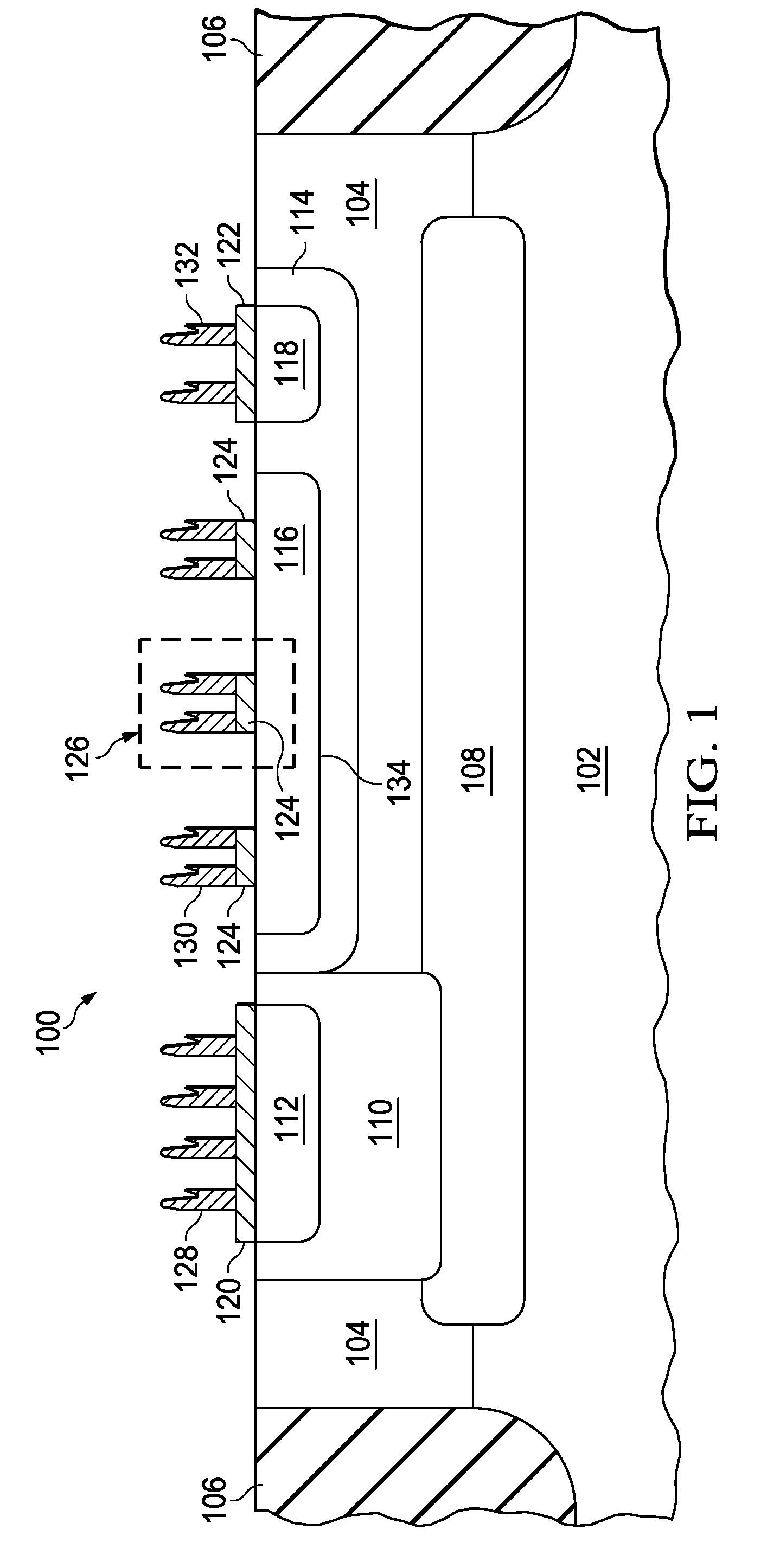
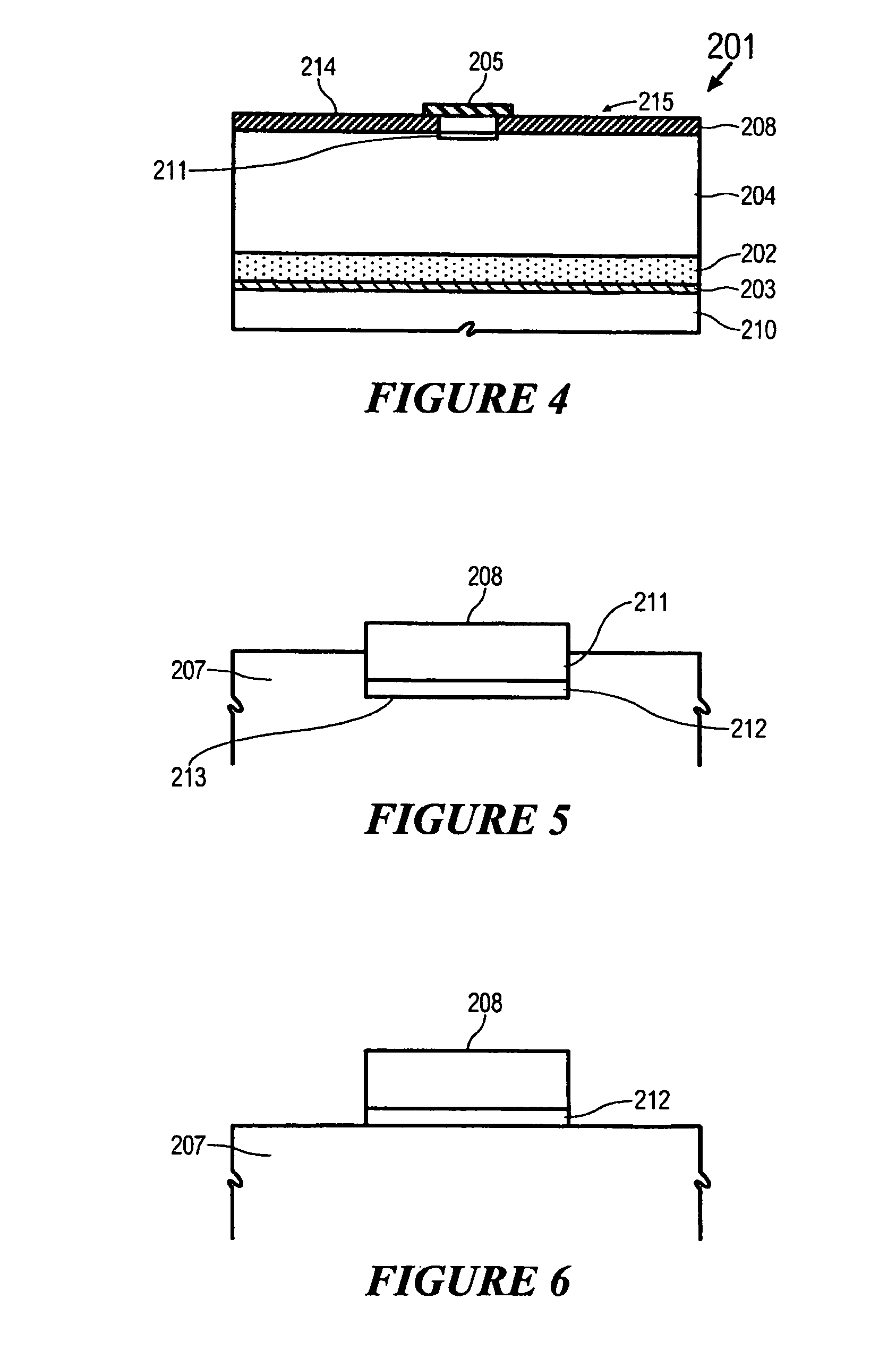
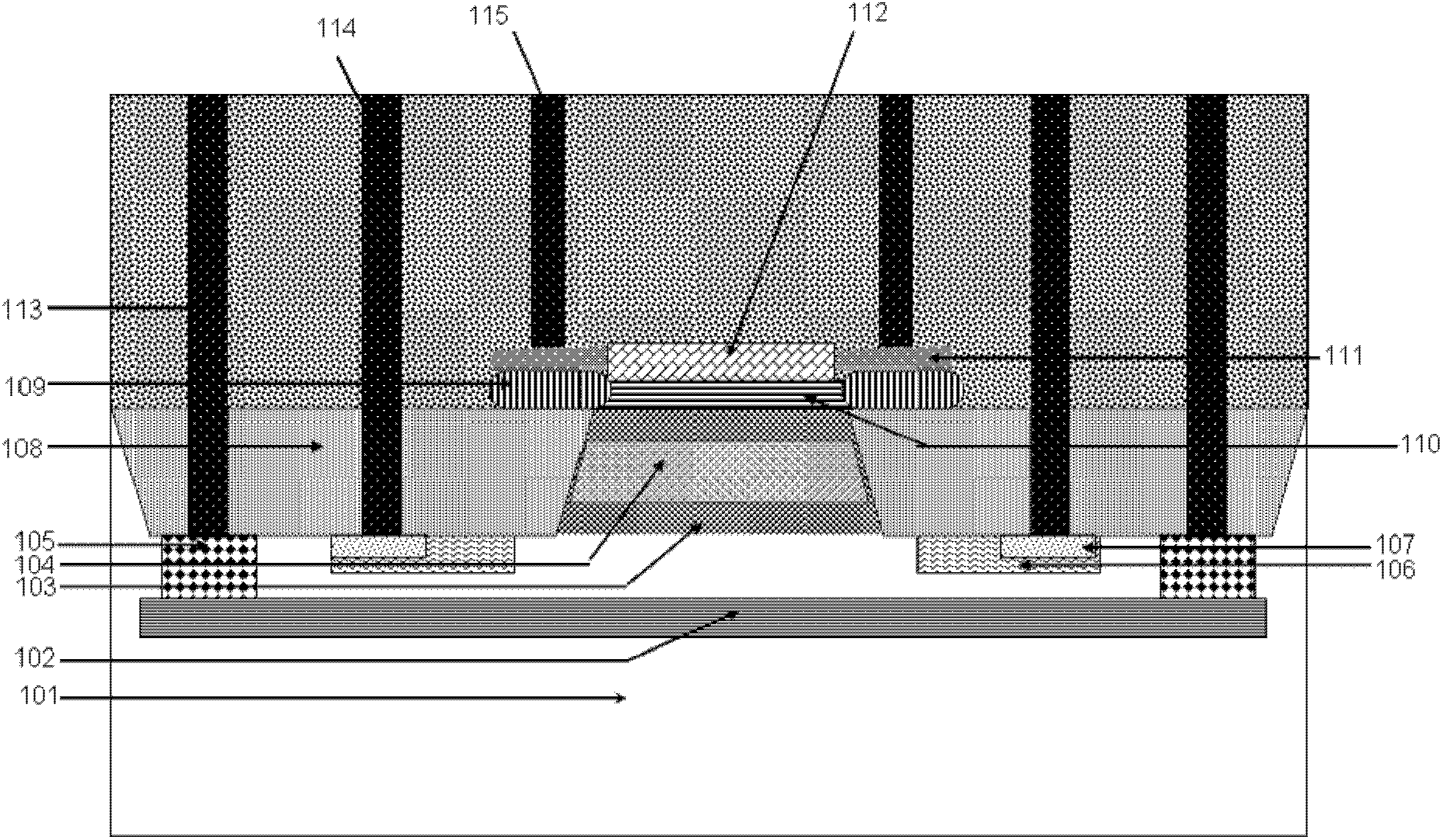
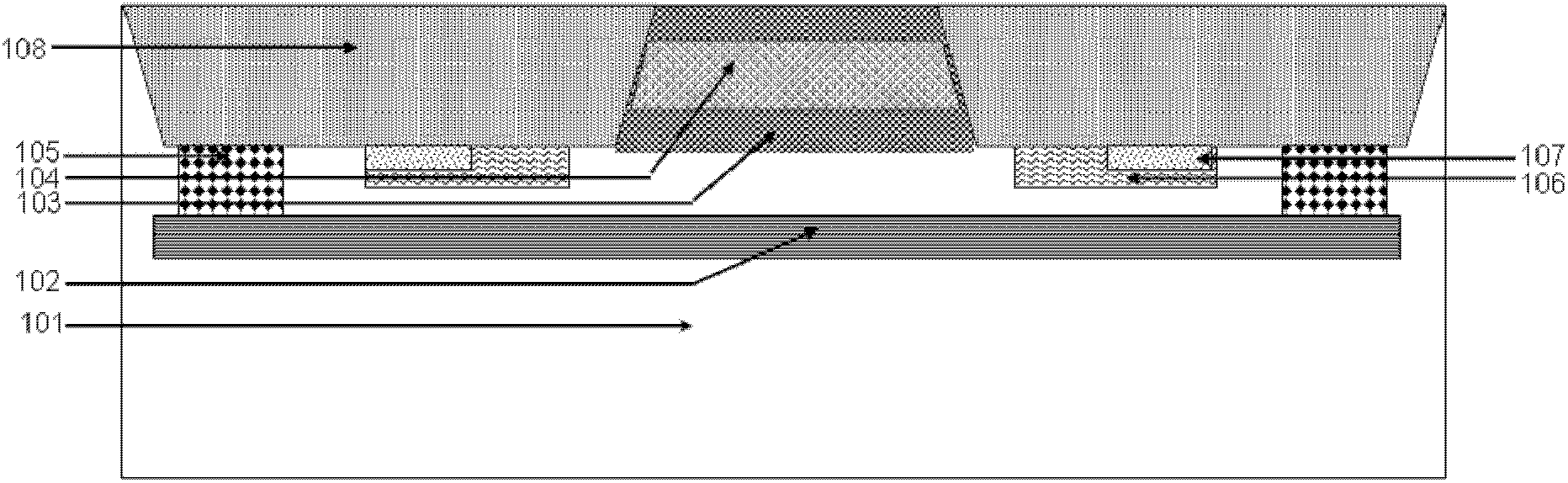
Power MOSFET with recessed field plate
ActiveUS20080073707A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingTrench mosfetReverse recovery
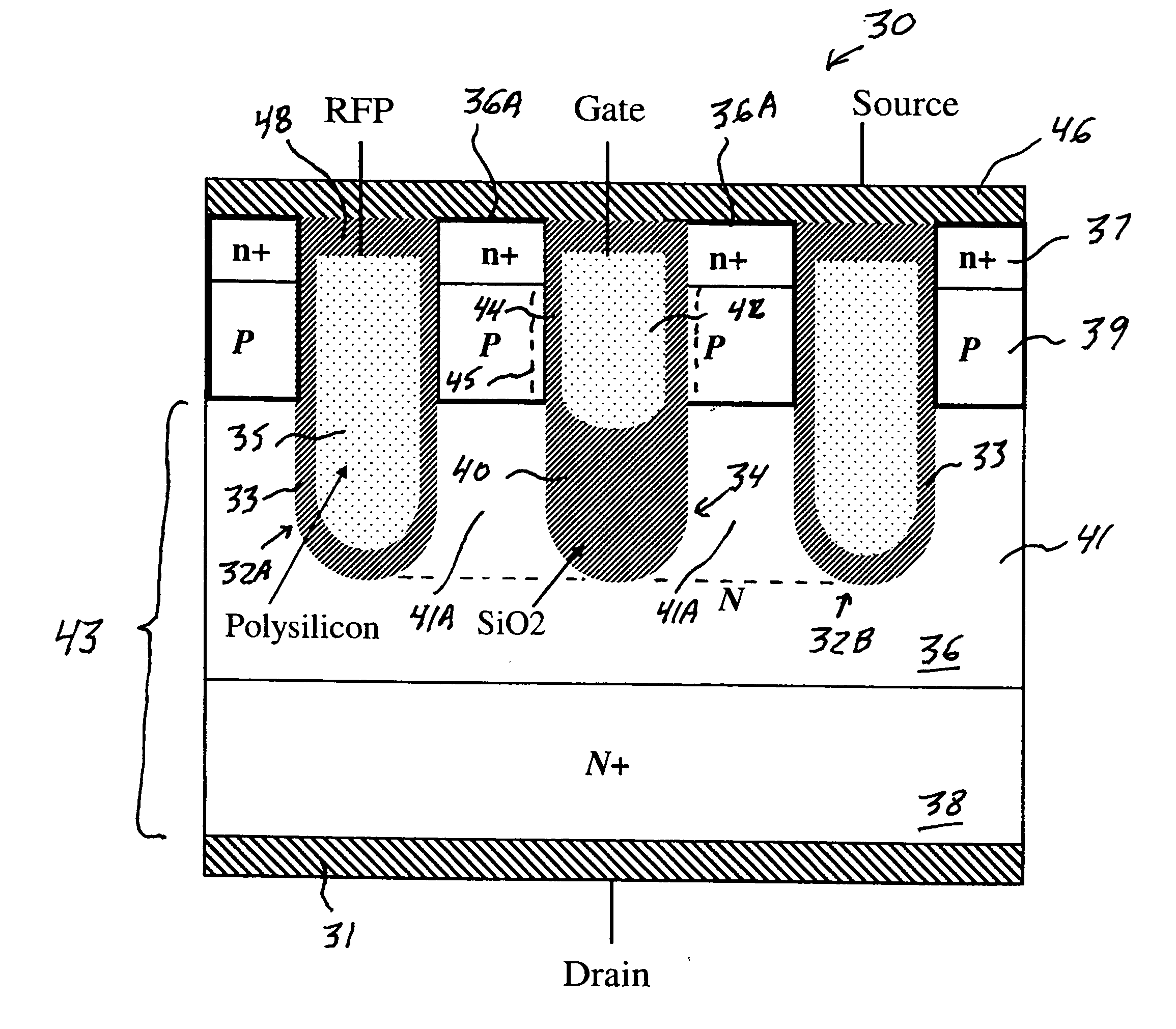
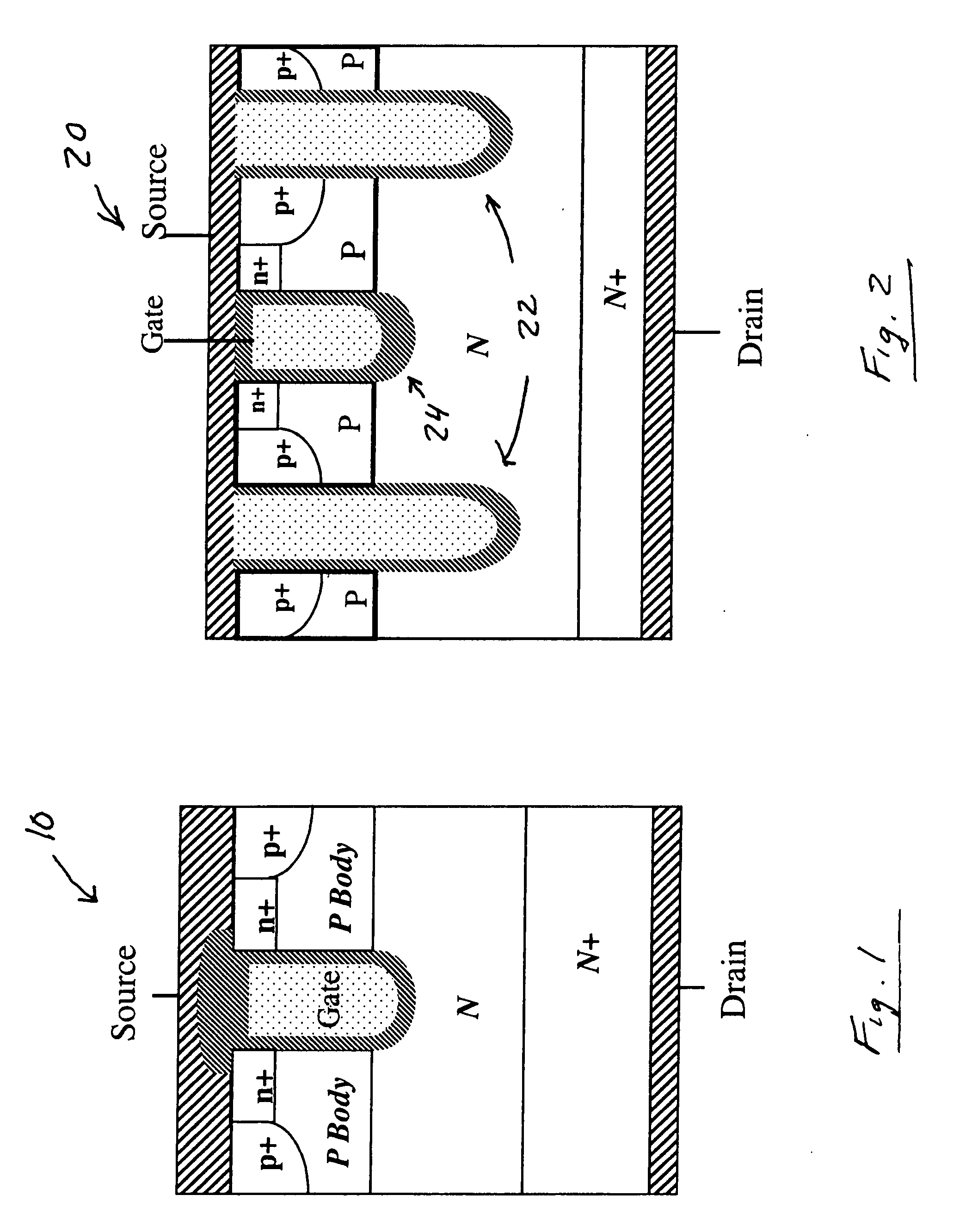
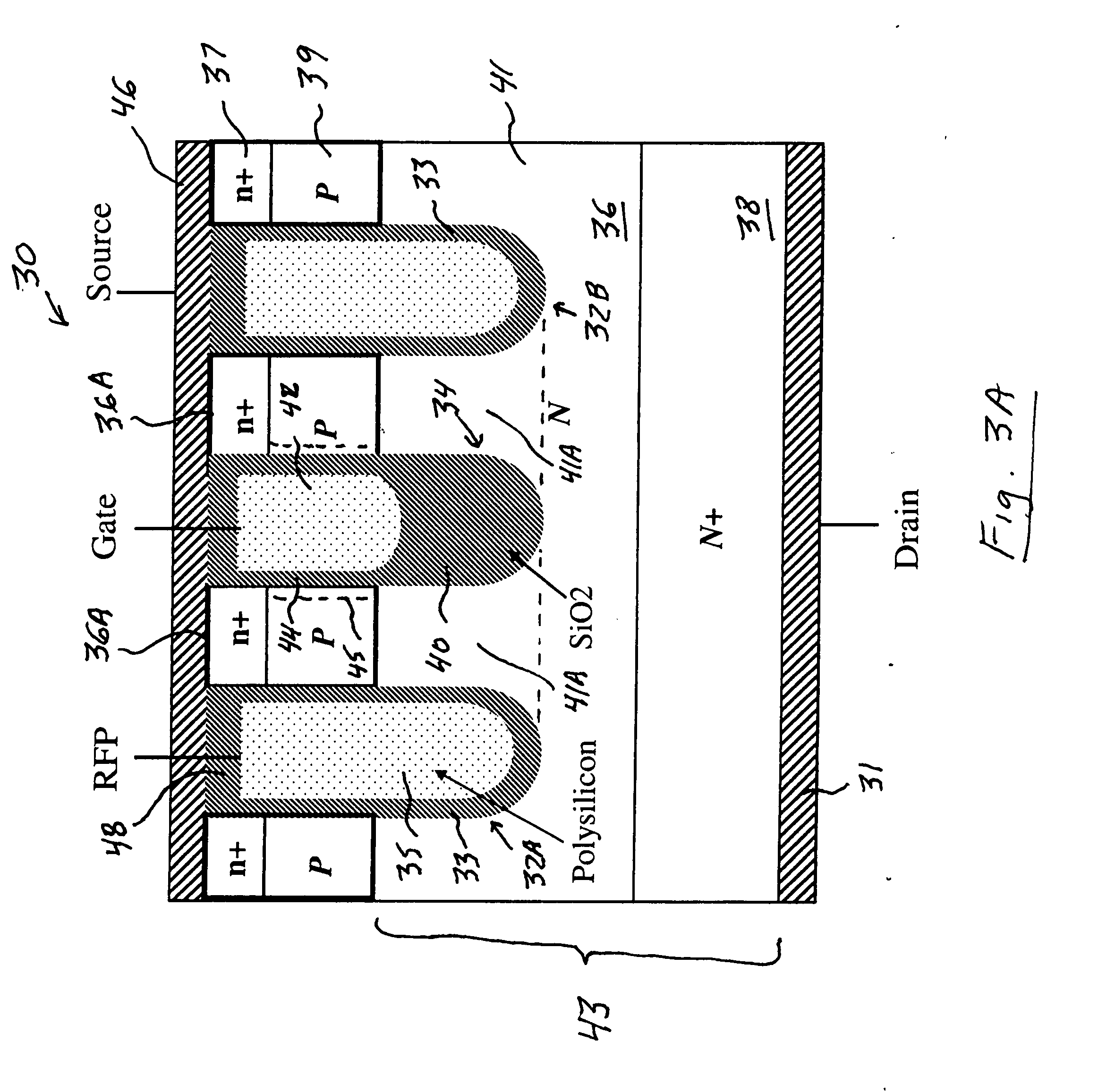
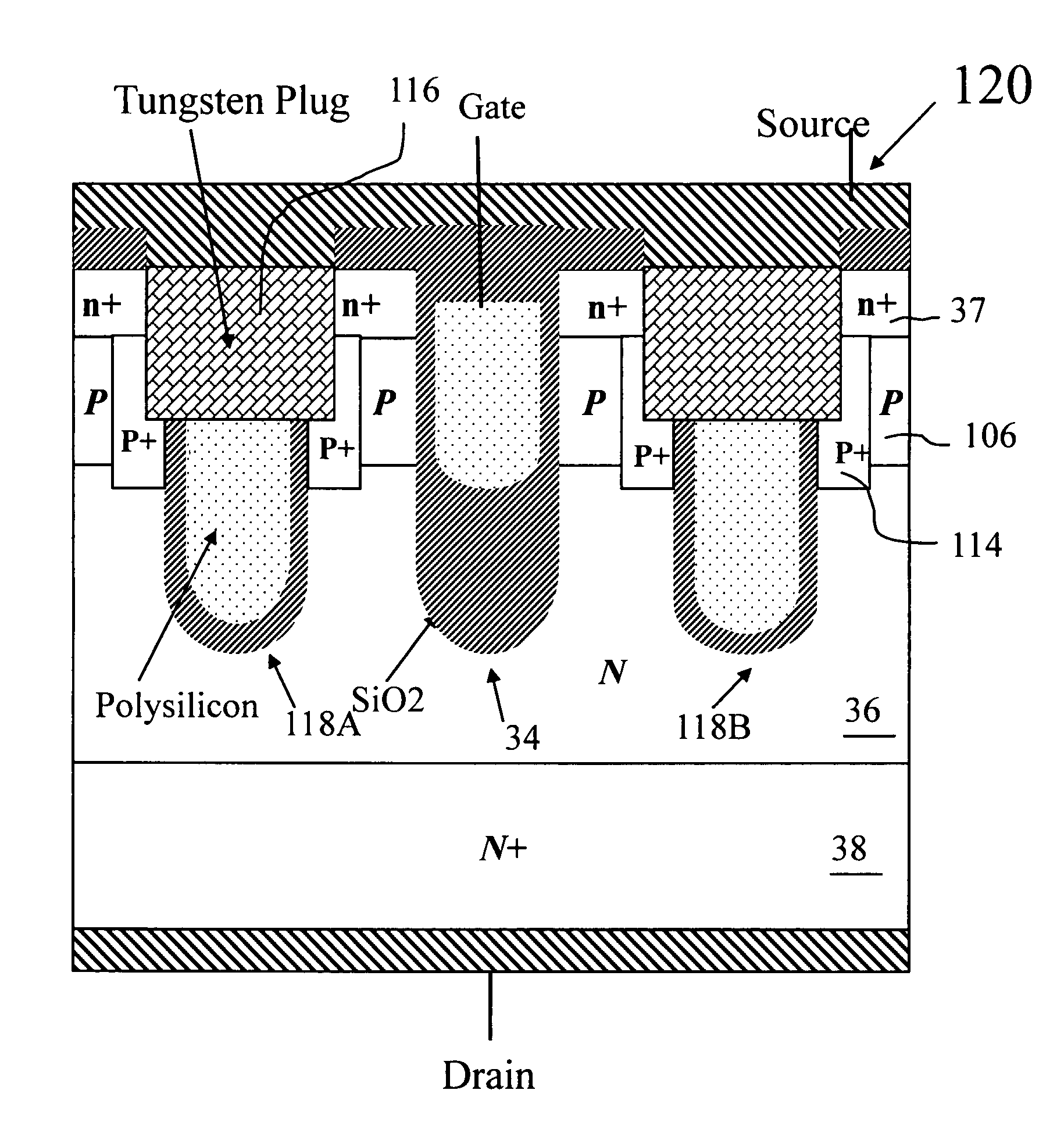
A trench MOSFET contains a recessed field plate (RFP) trench adjacent the gate trench. The RFP trench contains an RFP electrode insulated from the die by a dielectric layer along the walls of the RFP trench. The gate trench has a thick bottom oxide layer, and the gate and RFP trenches are preferably formed in the same processing step and are of substantially the same depth. When the MOSFET operates in the third quadrant (with the source / body-to-drain junction forward-biased), the combined effect of the RFP and gate electrodes significantly reduces in the minority carrier diffusion current and reverse-recovery charge. The RFP electrode also functions as a recessed field plates to reduce the electric field in the channel regions when the MOSFET source / body to-drain junction reverse-biased.
Owner:MAXPOWER SEMICON INC
Power MOSFET with recessed field plate
ActiveUS7843004B2Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingTrench mosfetReverse recovery
A trench MOSFET contains a recessed field plate (RFP) trench adjacent the gate trench. The RFP trench contains an RFP electrode insulated from the die by a dielectric layer along the walls of the RFP trench. The gate trench has a thick bottom oxide layer, and the gate and RFP trenches are preferably formed in the same processing step and are of substantially the same depth. When the MOSFET operates in the third quadrant (with the source / body-to-drain junction forward-biased), the combined effect of the RFP and gate electrodes significantly reduces in the minority carrier diffusion current and reverse-recovery charge. The RFP electrode also functions as a recessed field plates to reduce the electric field in the channel regions when the MOSFET source / body to-drain junction reverse-biased.
Owner:MAXPOWER SEMICON INC
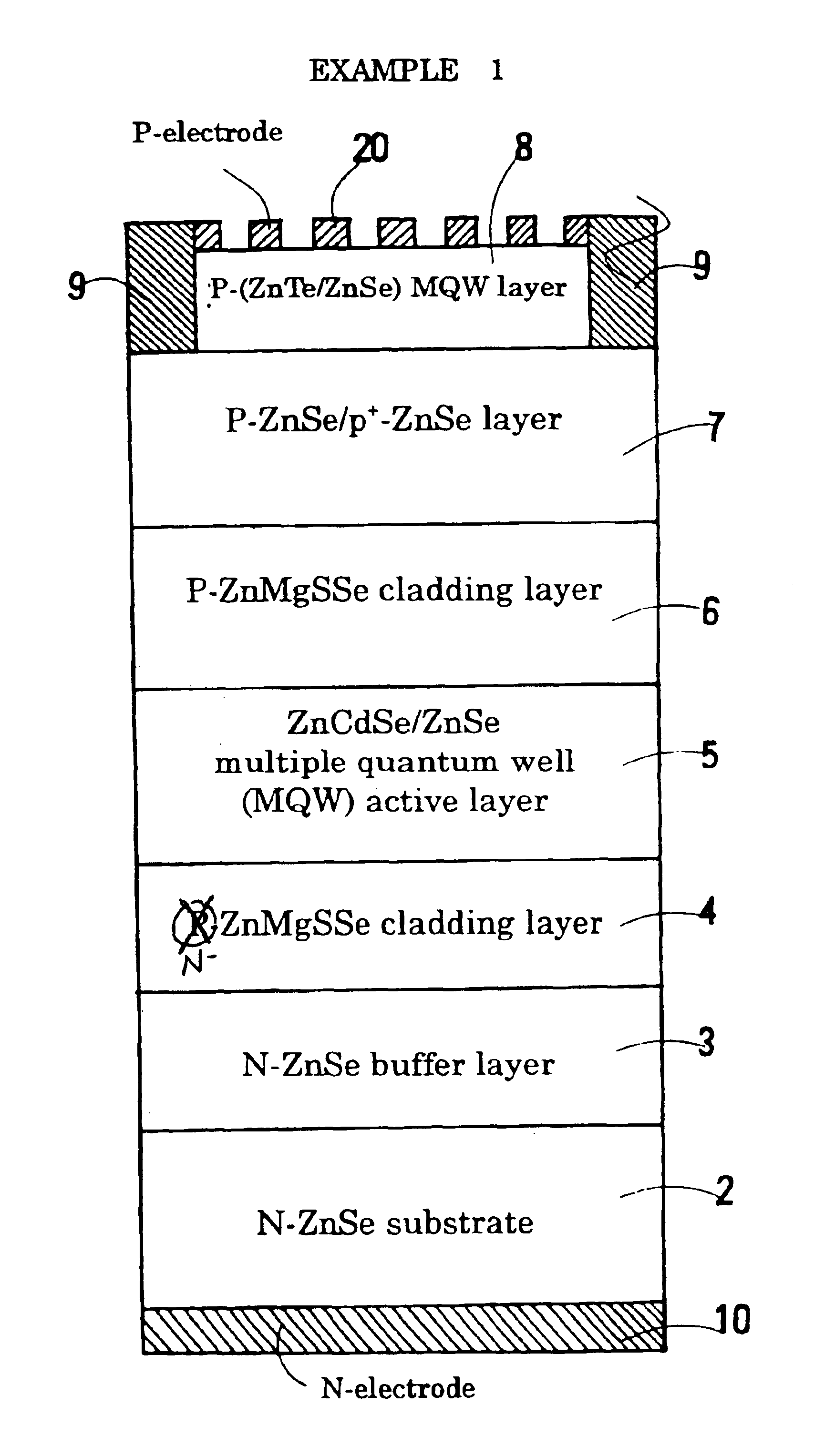
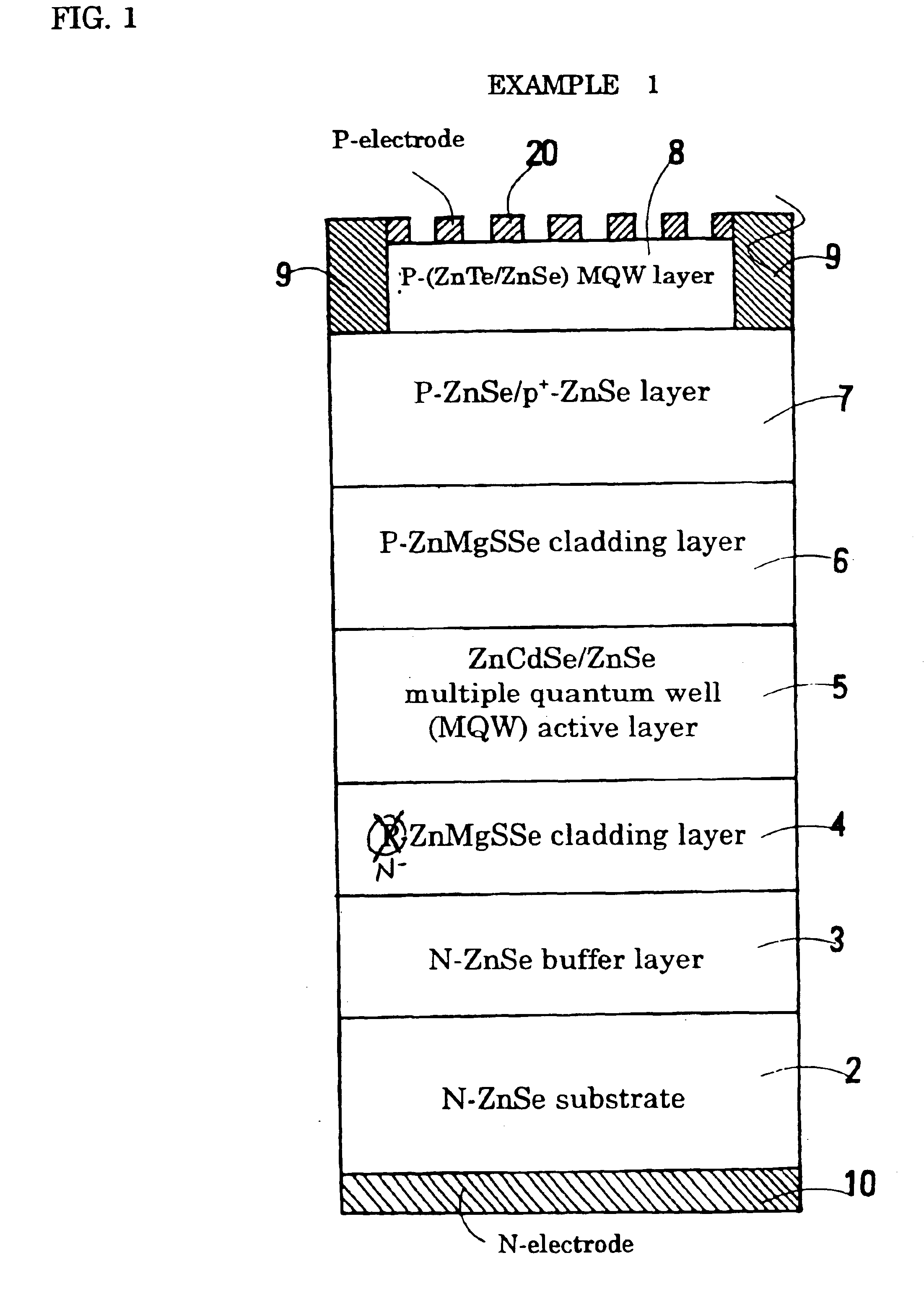
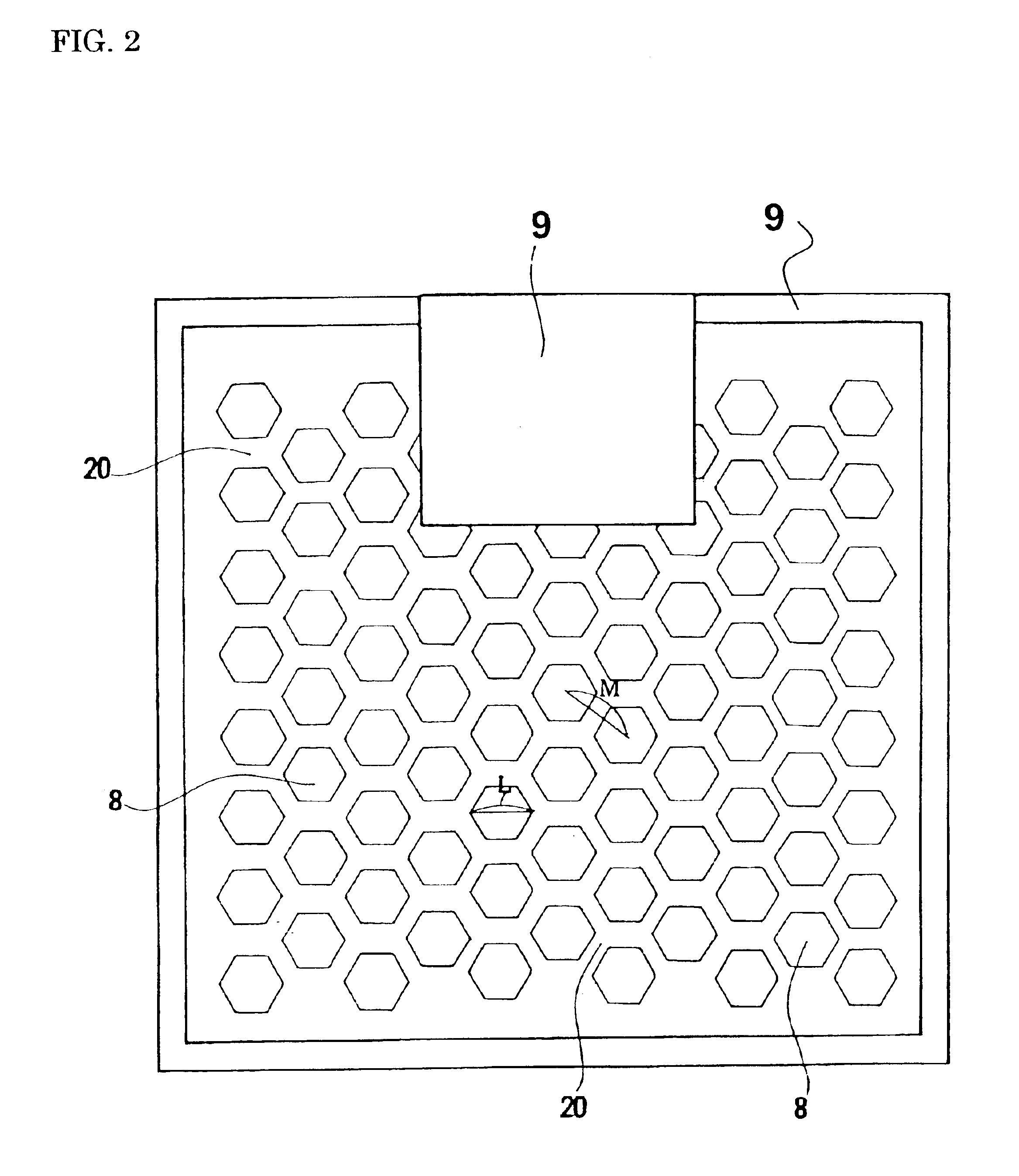
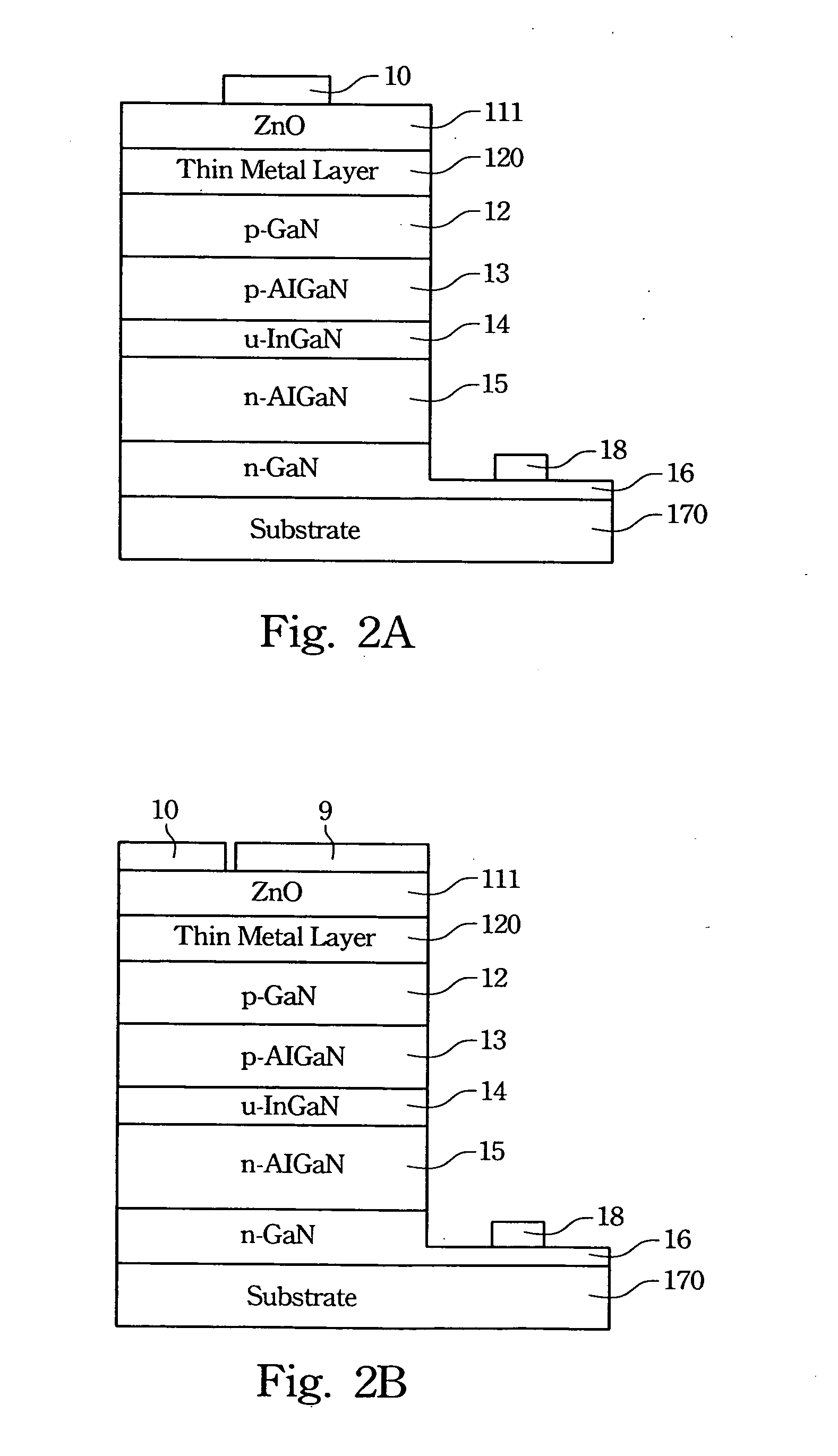
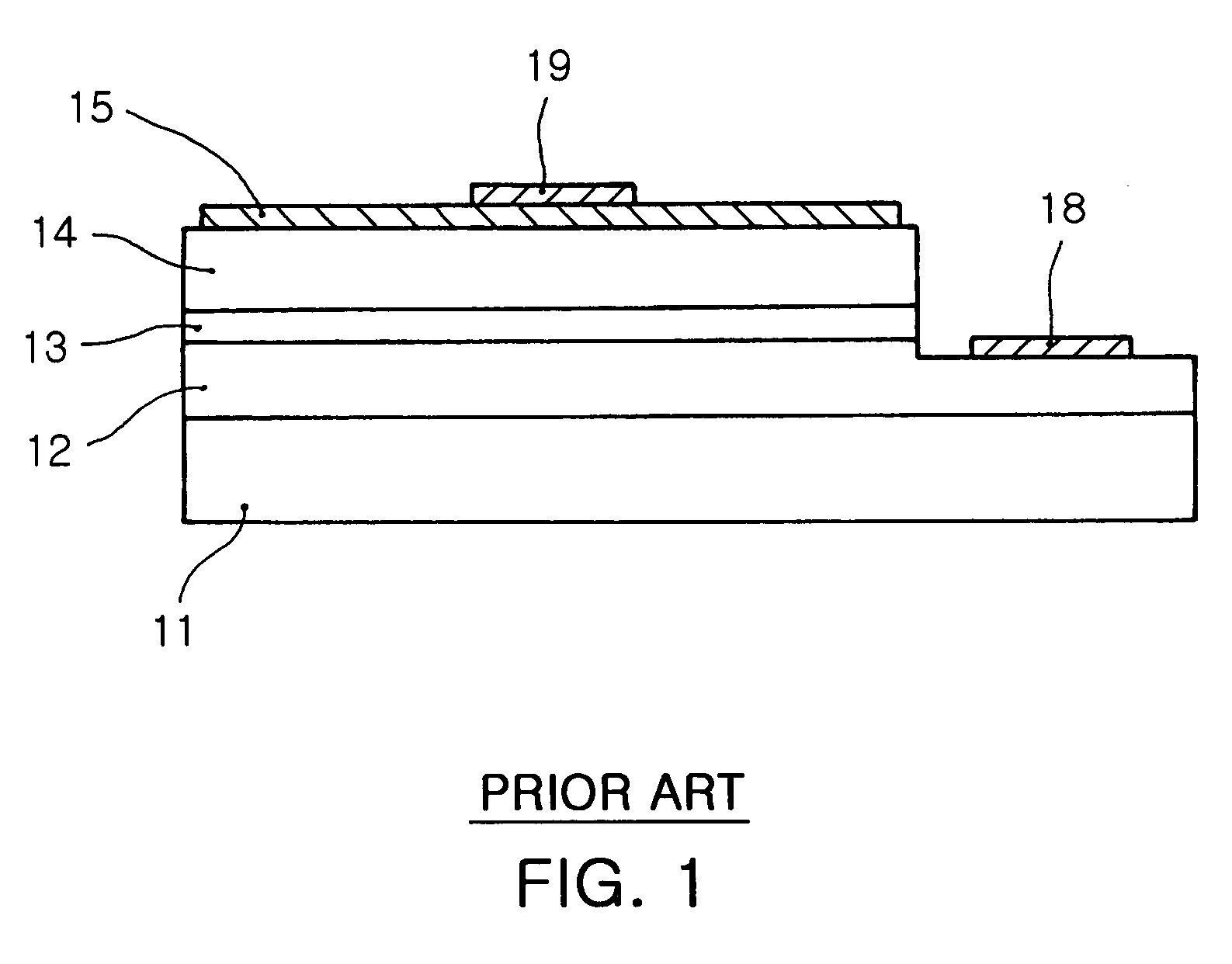
Structure of p-electrode at the light-emerging side of light-emitting diode
InactiveUS6903374B2High light transmittanceImprove light outputSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesTransmittanceContact layer
A structure of a p-electrode formed at the light-emerging side of an LED that comprises (a) an n-type semiconductor substrate, (b) an n-type cladding layer, an active layer, a p-type cladding layer, and a p-type contact layer formed on the substrate in this order, and (c) an n-electrode formed on the back face of the substrate. The structure of the p-electrode comprises a mesh-shaped semi-transparent thin-film metal electrode for diffusing electric current formed on the p-type contact layer and a bonding electrode for wire bonding. The metal electrode comprises a covering portion having a transmittance of at least 10% and an opening portion having an opening ratio of at least 20%. The bonding electrode is formed at the periphery of the p-type contact layer and is bonded directly to the mesh-shaped semi-transparent thin-film metal electrode. This structure can increase the intensity of the output light emerging from the p-side.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
P and N contact pad layout designs of GaN based LEDs for flip chip packaging
InactiveUS20050133806A1Efficient use ofIncrease current densitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesContact padSemiconductor materials
Based on the unique properties of the flip chip packaging process and GaN based LEDs with transparent substrates, new principles and methods for designing the layout of P contact pads and N contact pads are disclosed. The new designs of the present invention drastically increase the light extraction efficiency of LEDs by reducing the current crowding effect, increasing the uniformity of the spreading current in the active layer, and utilizing most of the available light emitting semiconductor material of the active layer. The present invention combined with the flip chip packaging process significantly improves the LEDs' heat dissipation.
Owner:PENG HUI +1
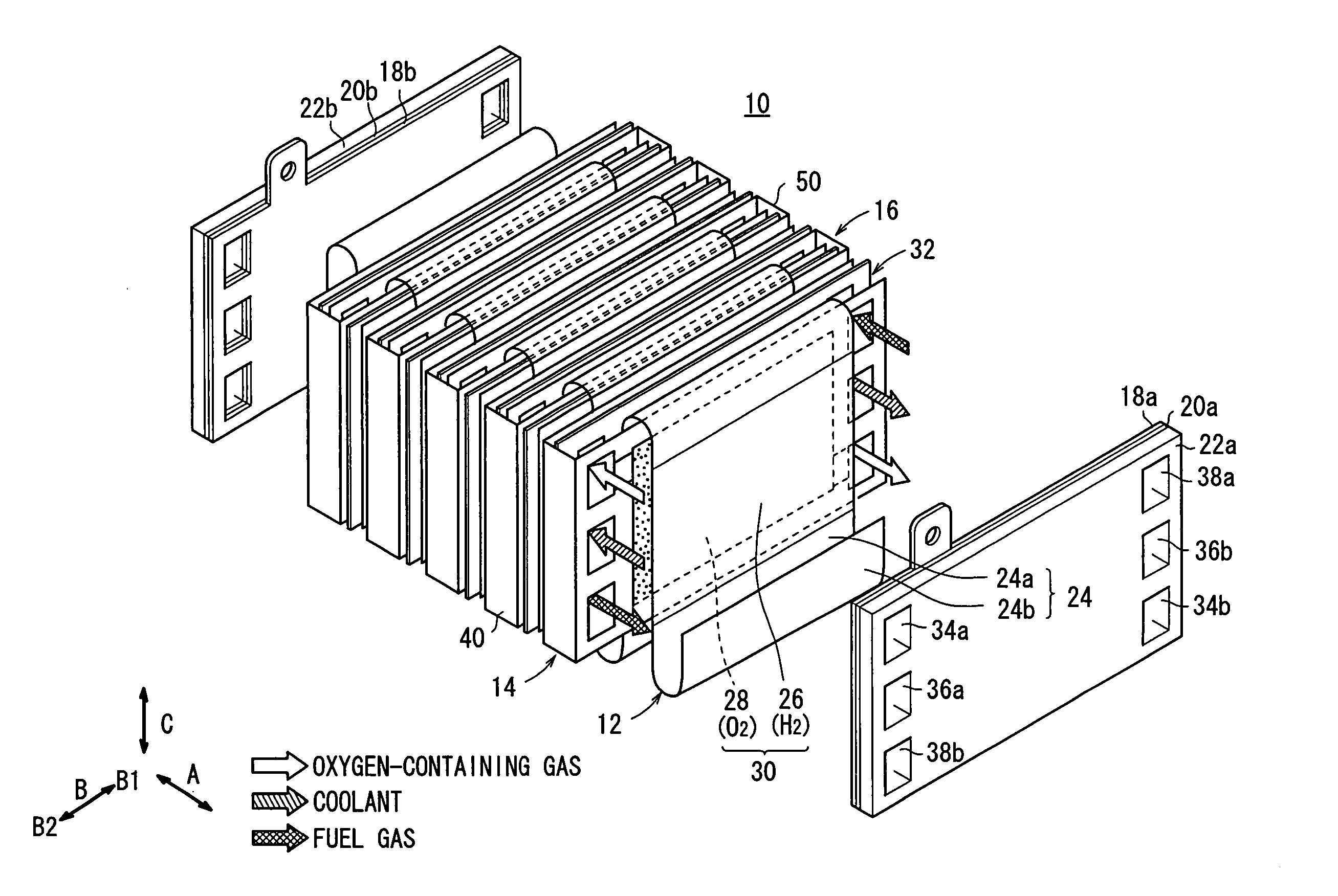
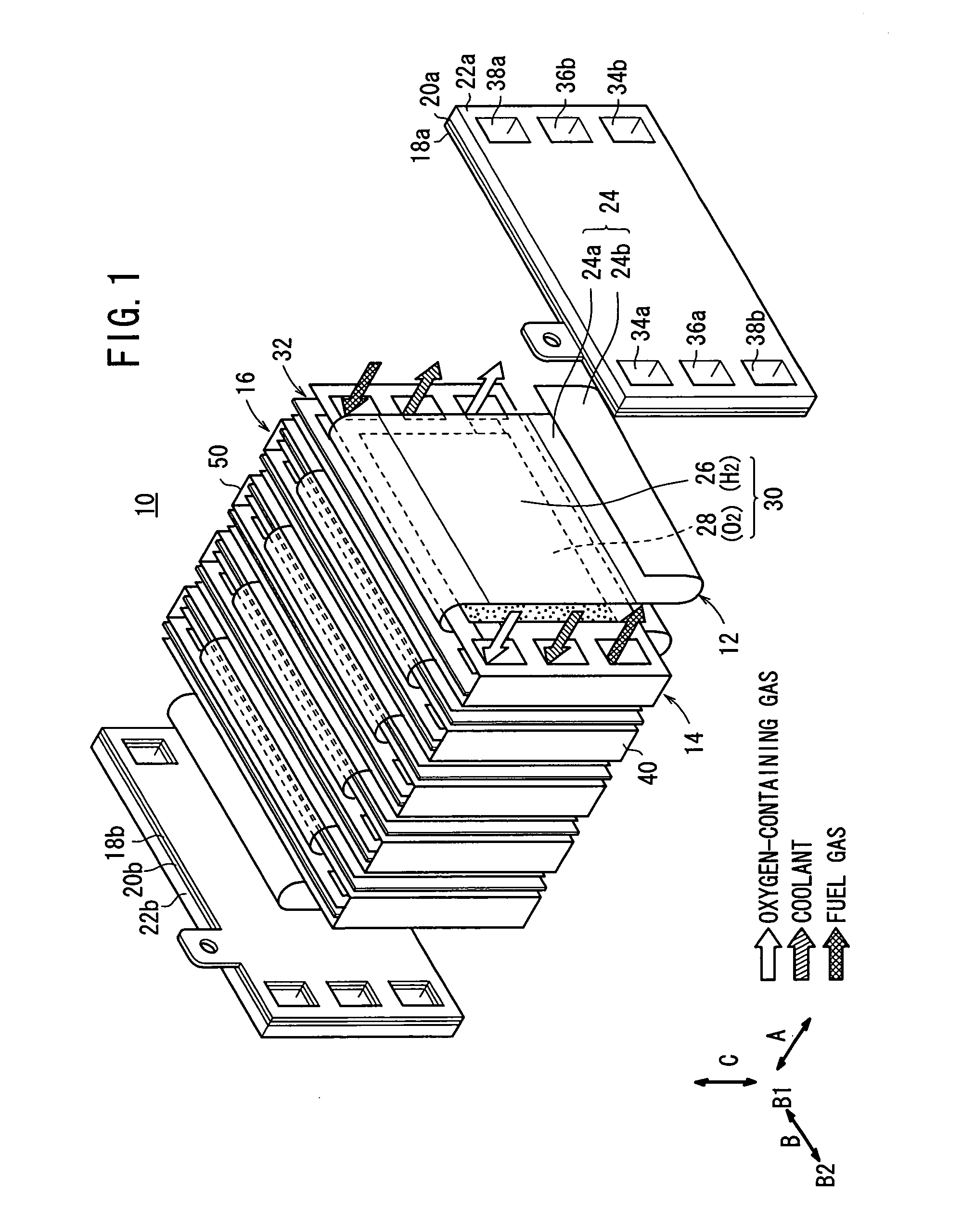
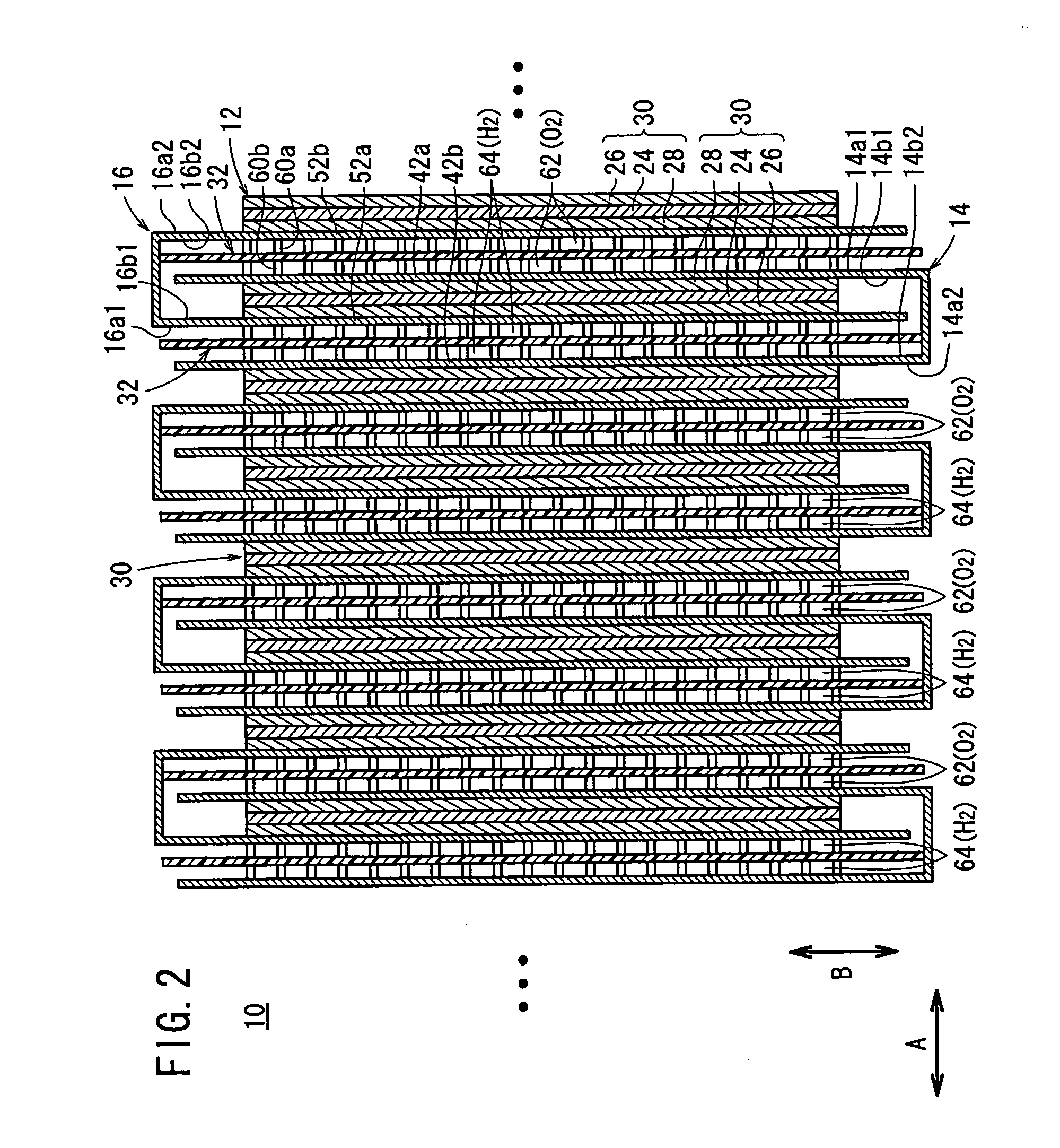
Fuel cell
InactiveUS20060210865A1Structural economyOperated easily and rapidlyFuel cells groupingFuel cell auxillariesPolymer electrolytesFuel cells
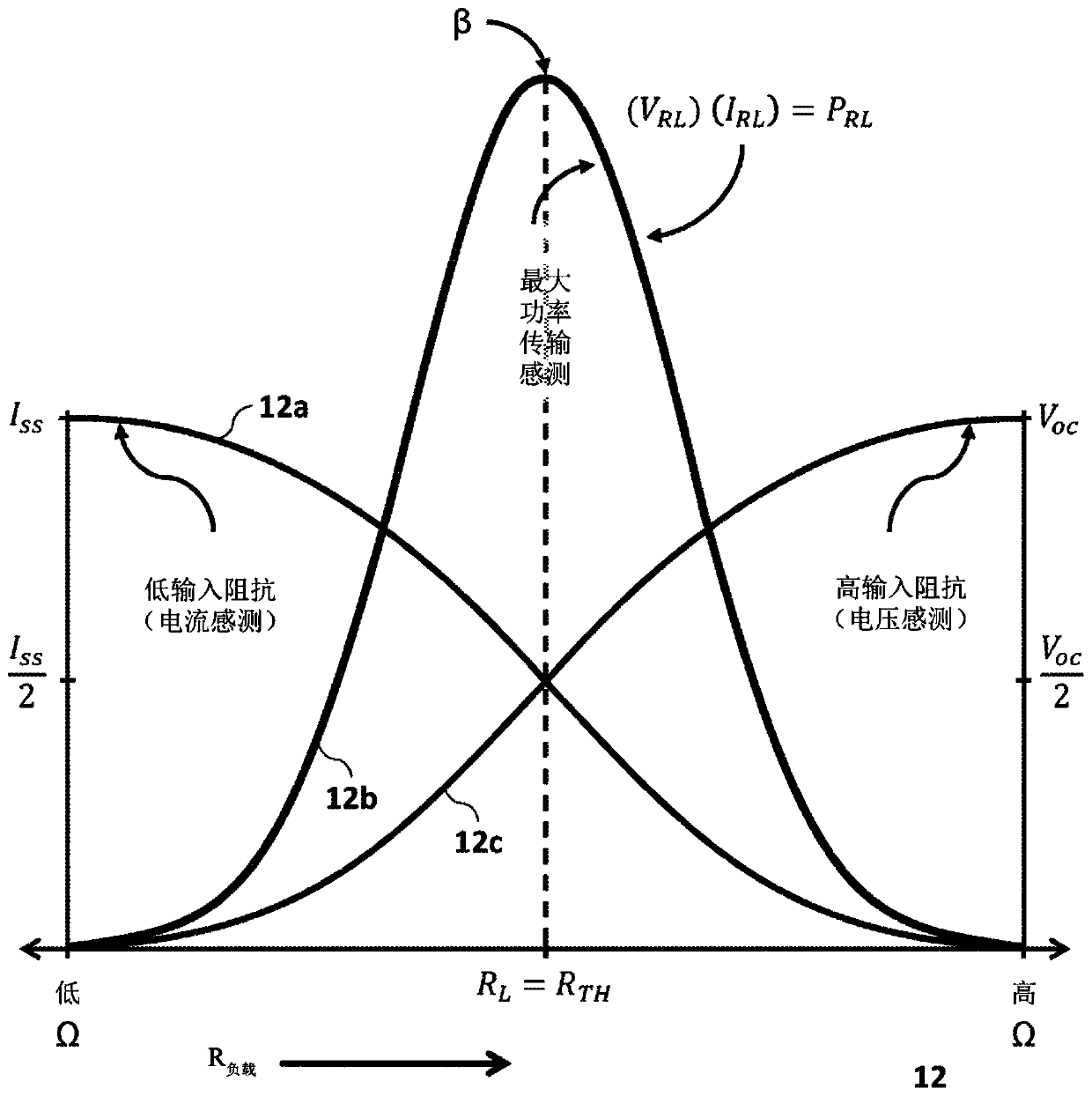
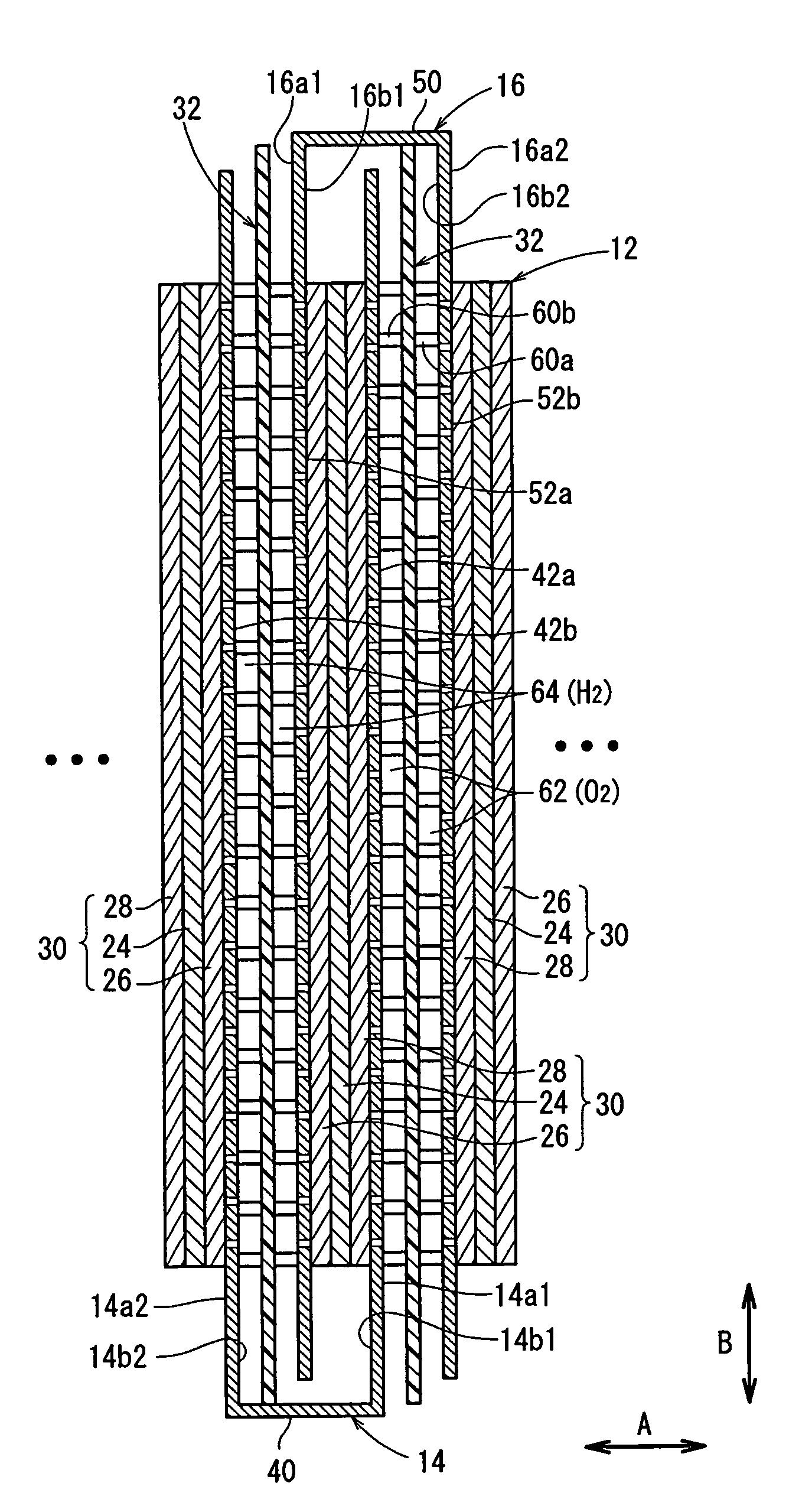
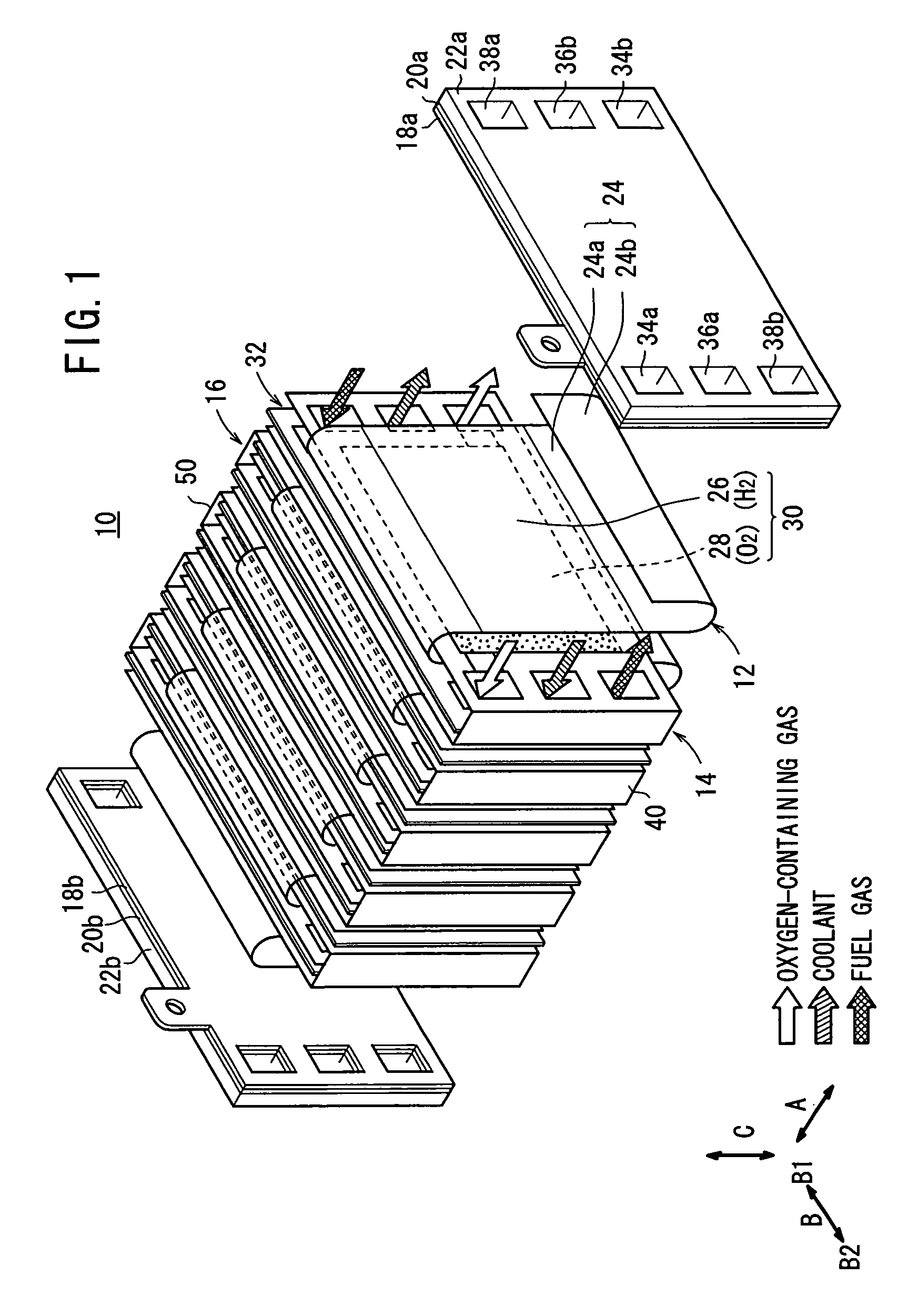
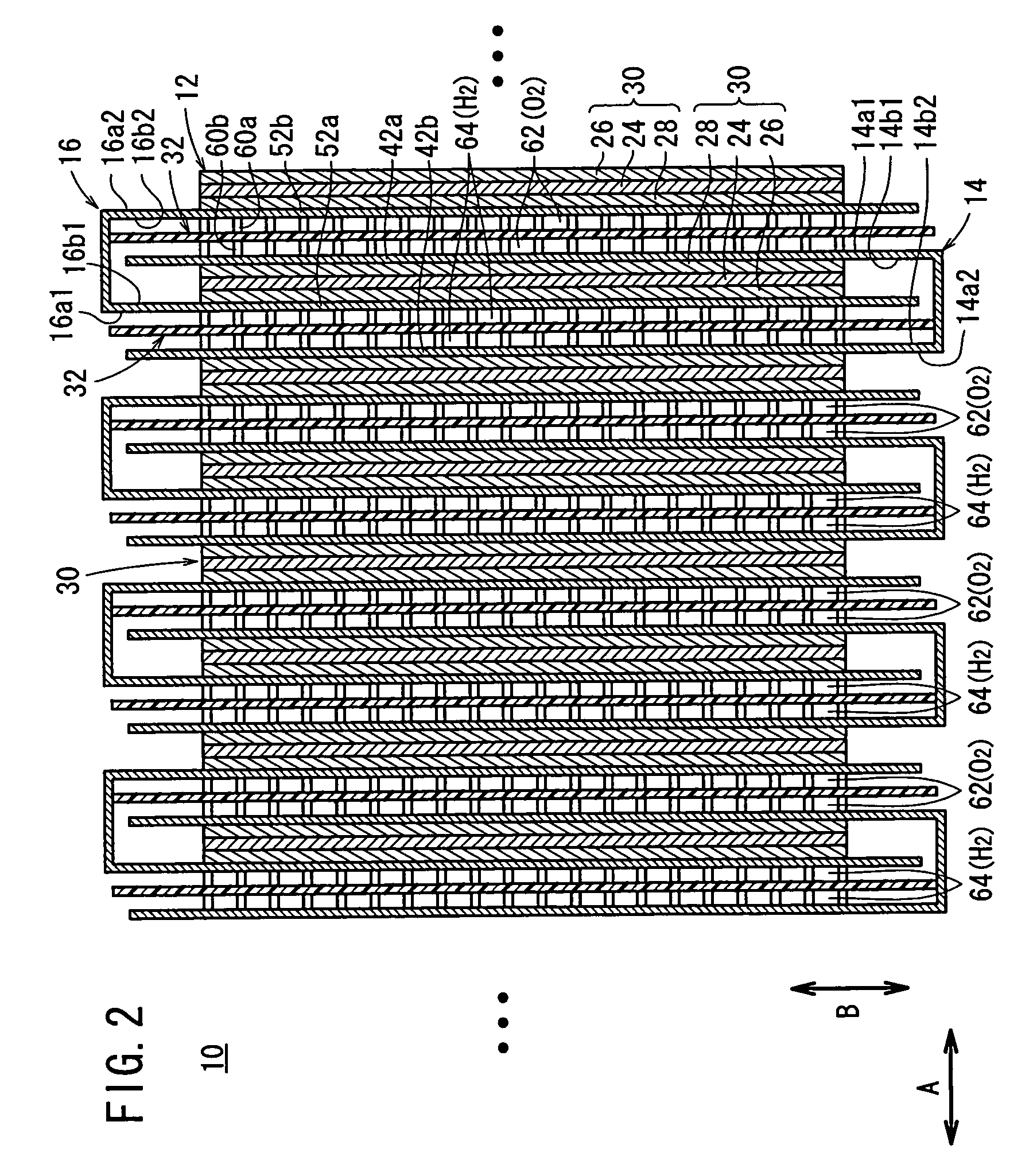
An electrolyte membrane / electrode web member includes an elongated solid polymer electrolyte membrane. A plurality of anodes and a plurality of cathodes are provided on one surface, and on the other surface of the solid polymer electrolyte membrane, respectively. First and second gas diffusion current collector members are inserted into the electrolyte membrane / electrode web member from both sides. Each of the first and second gas diffusion current collector members is formed by folding a single electrically conductive plate into a substantially U-shape. Electrical insulation is provided by interposing the insulating member between the first and second gas diffusion current collector members.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
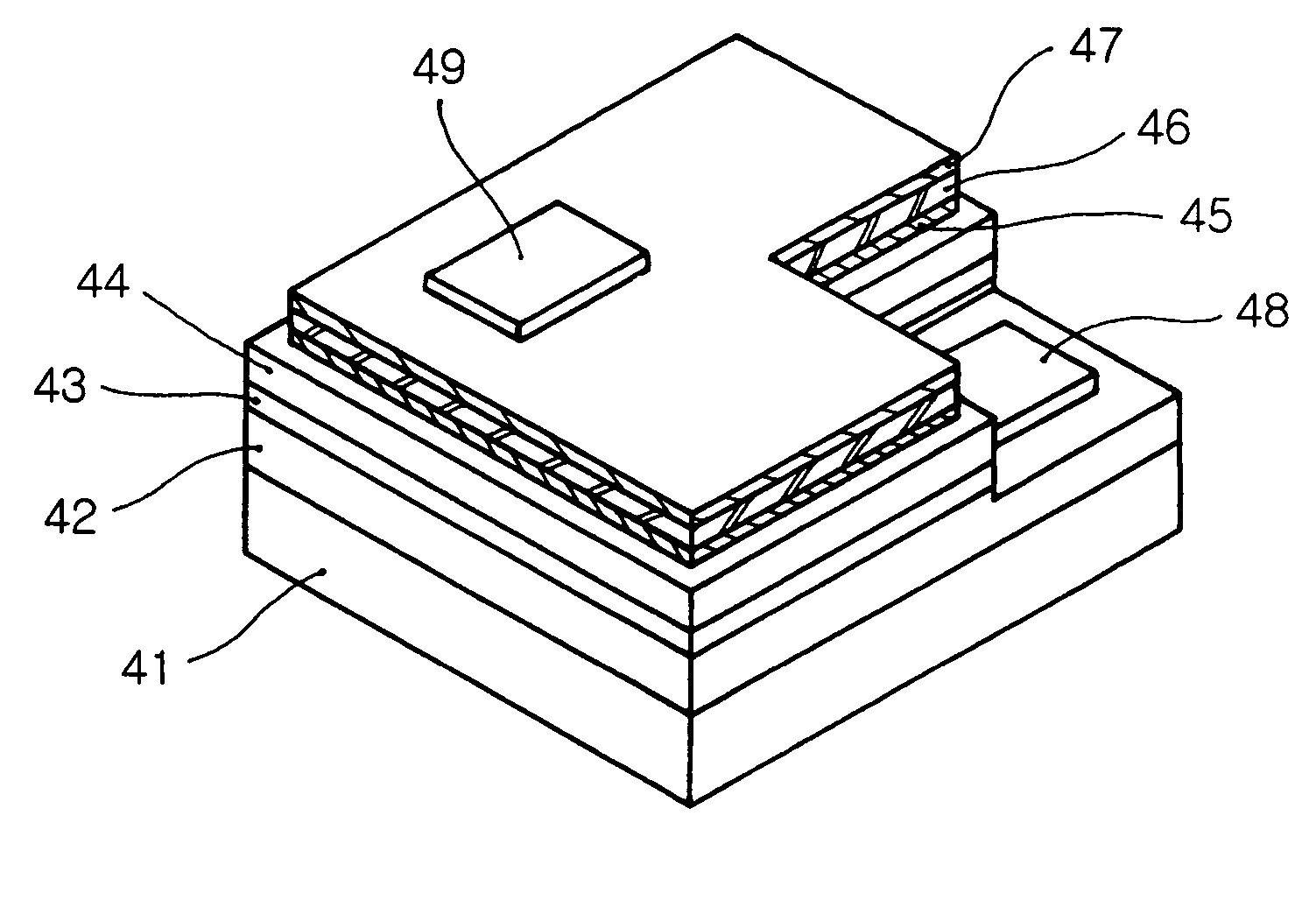
Flip chip type nitride semiconductor light emitting device and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveUS20050145875A1Increase brightnessImprove electric current diffusionSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesActive layerLight emitting device
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Transparent contact for light emitting diode
InactiveUS20050236630A1Smooth connectionSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesTransmittanceTransparent conducting film
A transparent conductive film is deposited between the electrode and semiconductor diode to spread the current evenly, reduce the series resistance and increase light transmittance at certain wavelength. ZnO film can be used as the transparent conductive film. The Ni / Au / ZnO film is found to have an increased light transmission compared with an annealed Ni / Au contact. The maximum optical transmission measured through the Ni / Au / ZnO film is 90%.
Owner:ARIMA COMP
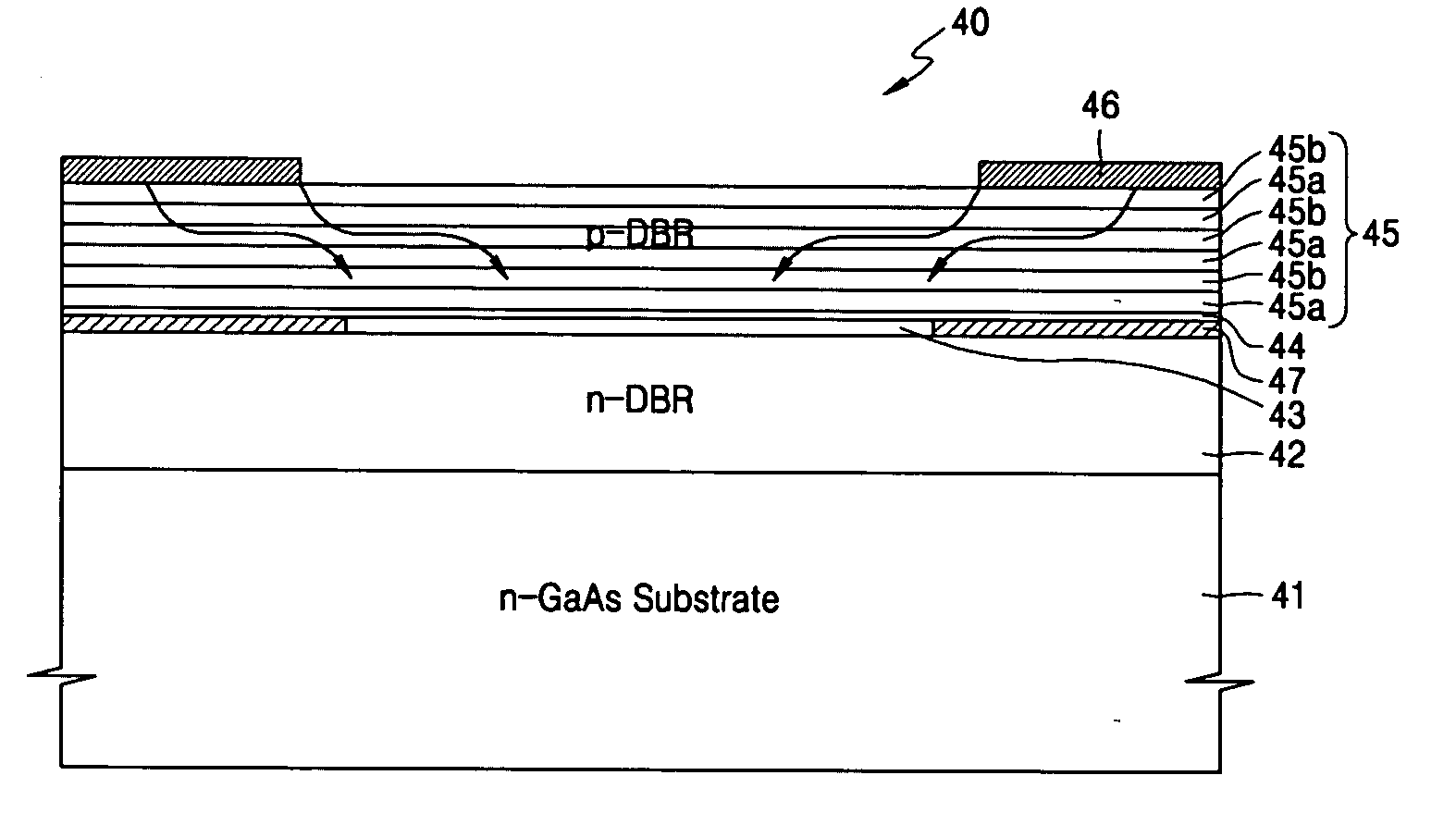
Laser pumping unit and high power laser device tunnel junction including the same
ActiveUS20060078027A1Doubling frequencyEasy to manufactureExcitation process/apparatusOptical resonator shape and constructionHigh power lasersQuantum well
Embodiments include a laser pumping unit and a high power vertical external cavity surface emitting laser (VECSEL) device including the same. The laser pumping unit easily diffuses current in a traverse direction by using a tunnel junction. The laser pumping unit may include a substrate, a lower distributed brag reflector (DBR) layer formed on the substrate, an active layer with a quantum well structure formed on the lower DBR layer to generate a light having a predetermined wavelength, a tunnel junction layer formed on the active layer to increase resistance in a vertical direction, and an upper DBR layer formed on the tunnel junction layer.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Determination device for metallic hydrogen diffusion current
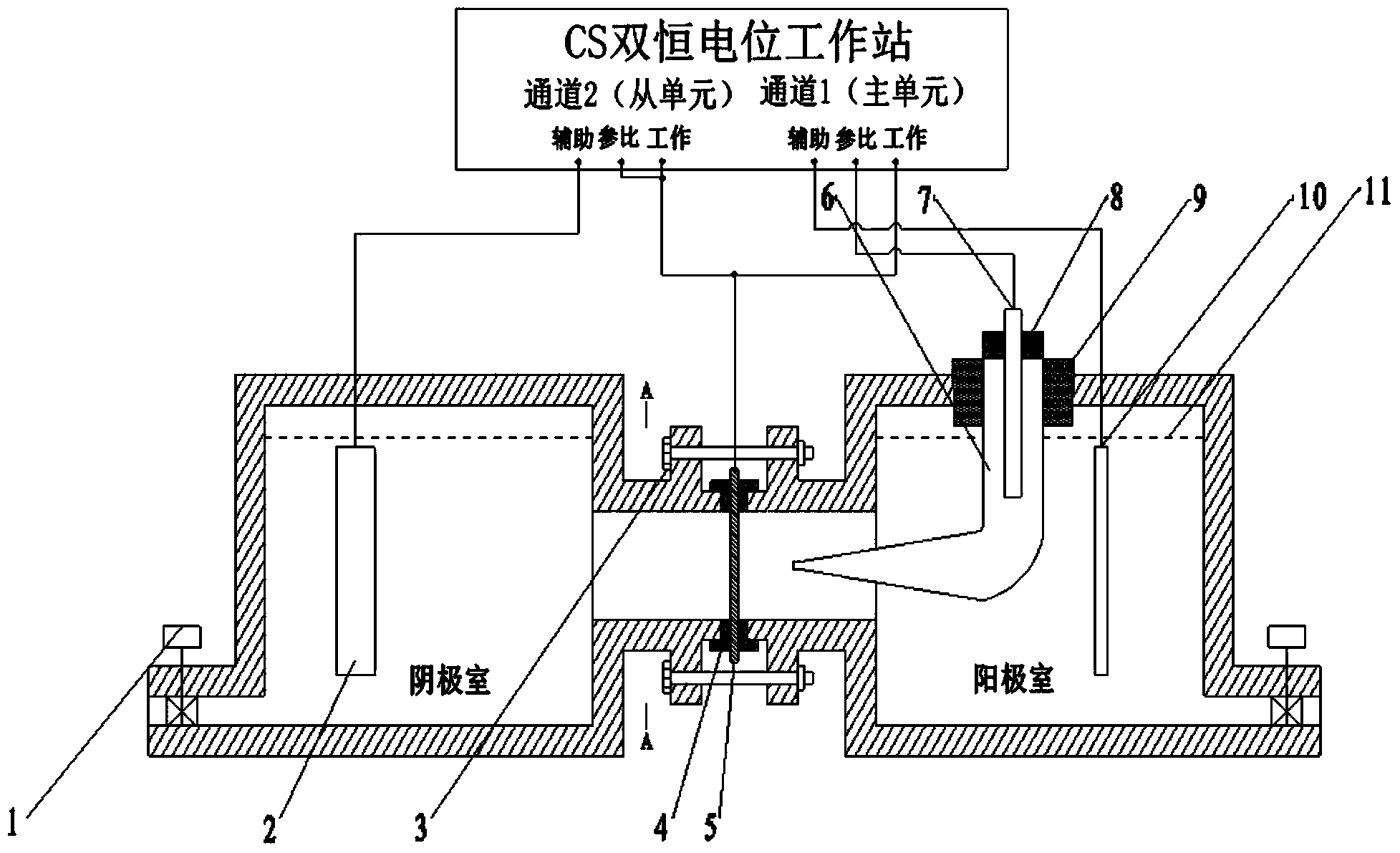
The invention discloses a determination device for metallic hydrogen diffusion current. The determination device comprises a cathode chamber, an anode chamber and a CS double constant potential workstation, wherein the cathode chamber and the anode chamber are communicated with each other; a hole provided with a drain valve is formed in the lower part of one side of each of the cathode chamber and the anode chamber; a beak bent-tube stretching from the anode chamber to a communicating channel is mounted at the top opening of the anode chamber through a tightened rubber plug, a saturated calomel reference electrode is mounted in the beak bent-tube through a rubber plug, and an auxiliary electrode II connected with a conducting wire is also arranged in the anode chamber and positioned near to one side of the beak bent-tube; an auxiliary electrode I connected with the conducting wire is also arranged in the cathode chamber; a sample connected with the conducting wire is clamped between the connecting end faces of the communicating channel through sealed rubber rings; the auxiliary electrode I, the sample, the saturated calomel reference electrode and the auxiliary electrode II are connected to related interfaces in the CS double constant potential workstation through the conducting wires. The determination device has the advantages that the good accuracy is realized, the operation is convenient, the measuring results are stable and reliable and the usage and maintenance cost is low.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Application of heteroatom-doped porous-carbon-coated Co9S8 composite catalyst
InactiveCN109713326AIncrease contact areaIncrease the active siteFuel and primary cellsCell electrodesPorous carbonPotassium hydroxide
The invention discloses an application of a heteroatom-doped porous-carbon-coated Co9S8 composite catalyst in an electrocatalytic oxygen reduction reaction, and belongs to the technical field of composite catalysts and electrocatalytic oxygen reduction and zinc-air batteries. The composite catalyst regards a nitrogen-oxygen-sulfur triple heteroatom-doped mixed type cobalt-based metal-organic framework material (abbreviated as Co-MOF) as a precursor, is obtained through subjecting the Co-MOF to carbonization, and is used for high-efficiency electrocatalytic oxygen reduction. In a 0.1 mol L<-1>potassium hydroxide electrolyte, the oxygen reduction half-wave potential of the catalyst is 0.78 V, the limited diffusion current is 5.45 mA cm<-2>. The zinc-air battery assembled by adopting the prepared catalyst is subjected to cyclic charge and discharge tests for 48 h, and the charge and discharge voltage difference does not change significantly, thereby indicating that the prepared catalysthas very high stability and has high practical application value.
Owner:HENAN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
P electrode structure on light exit side of LED
A structure of a p-electrode formed at the light-emerging side of an LED that comprises (a) an n-type semiconductor substrate, (b) an n-type cladding layer, an active layer, a p-type cladding layer, and a p-type contact layer formed on the substrate in this order, and (c) an n-electrode formed on the back face of the substrate. The structure of the p-electrode comprises a mesh-shaped semi-transparent thin-film metal electrode for diffusing electric current formed on the p-type contact layer and a bonding electrode for wire bonding. The metal electrode comprises a covering portion having a transmittance of at least 10% and an opening portion having an opening ratio of at least 20%. The bonding electrode is formed at the periphery of the p-type contact layer and is bonded directly to the mesh-shaped semi-transparent thin-film metal electrode. This structure can increase the intensity of the output light emerging from the p-side.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Light-emitting diode with passivation layer and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101944558AGood diffusion current effectLight evenlySemiconductor devicesDiffusion currentLight-emitting diode
The invention provides a light-emitting diode with a passivation layer and a preparation method thereof. The light-emitting diode comprises a base material, a light-emitting unit arranged on the base material, a first electrode, a second electrode and the passivation layer. The main improvement of the invention is that the passivation layer is arranged on the light-emitting unit and is positioned below the second electrode correspondingly; the passivation layer comprises a body part corresponding to the second electrode and an extension part connected at the periphery of the body part; the width of the extension part is L, wherein, L is more than or equal to 3 microns and is less than or equal to 20 microns; and the thickness of the passivation layer is D, wherein, D is more than or equal to 4 angstroms. The light-emitting diode of the invention is designed according to the appropriate width of the extension part and the thickness of the passivation layer, has good current diffusion effect, and achieves the purposes of the light-emitting uniformity and the promoted light-emitting efficiency.
Owner:UBILUX OPTOELECTRONICS CORP
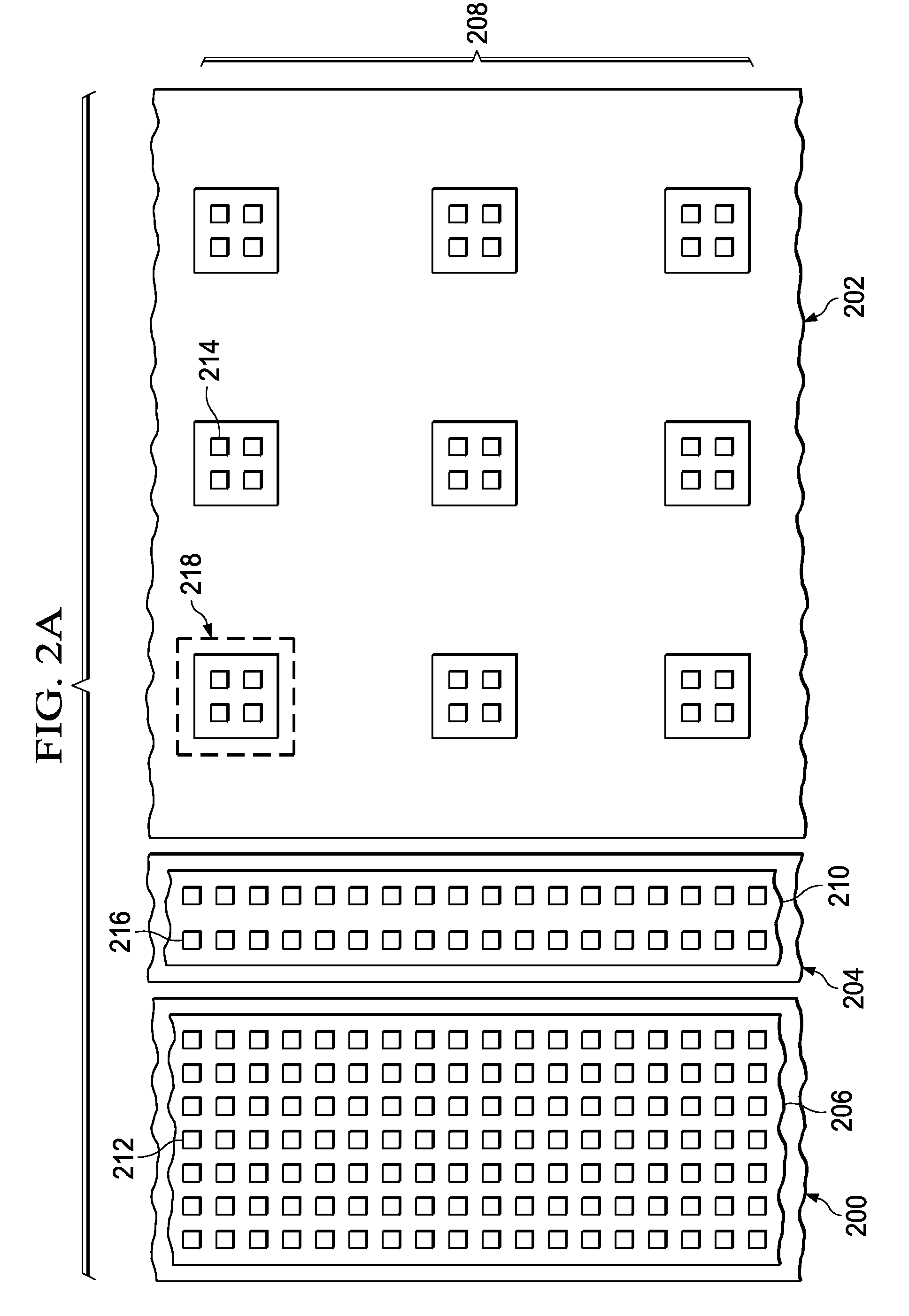
Emitter Ballasting by Contact Area Segmentation in ESD Bipolar Based Semiconductor Component
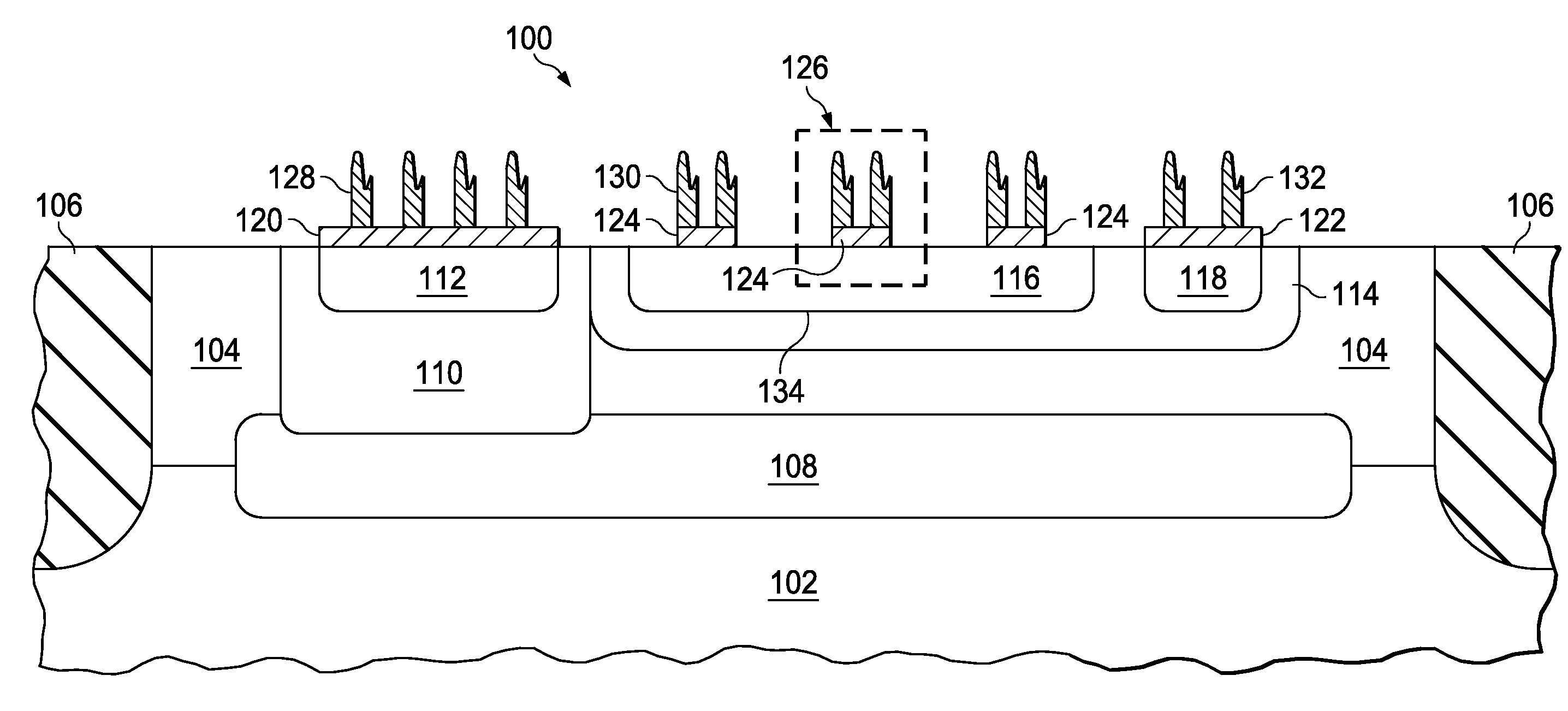
Integrated circuits (ICs) utilize bipolar transistors in electro-static discharge (ESD) protection circuits to shunt discharge currents during ESD events to protect the components in the ICs. Bipolar transistors are subject to non-uniform current crowding across the emitter-base junction during ESD events, which results in less protection for the IC components and degradation of the bipolar transistor. This invention comprises multiple contact islands (126) on the emitter (116) of a bipolar transistor, which act to spread current uniformly across the emitter-base junction. Also included in this invention is segmentation of the emitter diffused region to further improve current uniformity and biasing of the transistor. This invention can be combined with drift region ballasting or back-end ballasting to optimize an ESD protection circuit.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Magnetization reversal device, memory element, and magnetic field generation device
InactiveUS20120133007A1Low costGood effectMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsSolid-state devicesPower flowSpins
A magnetization reversal device includes a ferromagnetic 12 body which is provided in an interconnection of a non-ferromagnetic dot 11 so that a part or a whole of the ferromagnetic dot is three-dimensionally buried in the interconnection of said non-ferromagnetic dot, and a spin injection source 13 which generates a spin-polarized pure spin current without a flow of charges, and which is provided in the interconnection of the non-ferromagnetic dot 11 to be in contact therewith so that the interconnection of the non-ferromagnetic dot serves as a common electrode, and the pure spin current flows into the ferromagnetic dot 2 through the interconnection of the non-magnetic body by the spin injection source 13 due to a diffusion current, to thereby reverse magnetization of the ferromagnetic dot 12. By injecting the pure spin current, using this planar structure, it is possible to easily carry out the magnetization reversal of the ferromagnetic dot 12 even if it is a thick film ferromagnetic dot without being subjected to limitation of a spin diffusion length.
Owner:KYUSHU UNIV
Flip chip type nitride semiconductor light emitting device and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveUS7235818B2Increase brightnessImprove bindingSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesActive layerLight emitting device
Disclosed herein are a flip chip type nitride semiconductor light emitting device, which comprises a substrate for growing a nitride semiconductor material, an n-type nitride semiconductor layer formed on the substrate, an active layer formed on at least a part of the n-type nitride semiconductor layer, a p-type nitride semiconductor layer formed on the active layer, a bonding force providing layer formed on the p-type nitride semiconductor layer and adapted to provide a bonding force relative to the p-type nitride semiconductor layer, a reflective electrode layer formed on the bonding force providing layer, and adapted to reflect light produced in the active layer toward the substrate and to diffuse electric current, and a cap layer formed on the reflective electrode layer, and adapted to provide a bonding force between the reflective electrode layer and a bonding metal and to reduce contact resistance.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Coaxial Solar Cell Structure and Continuous Fabrication Method of its Linear Structure
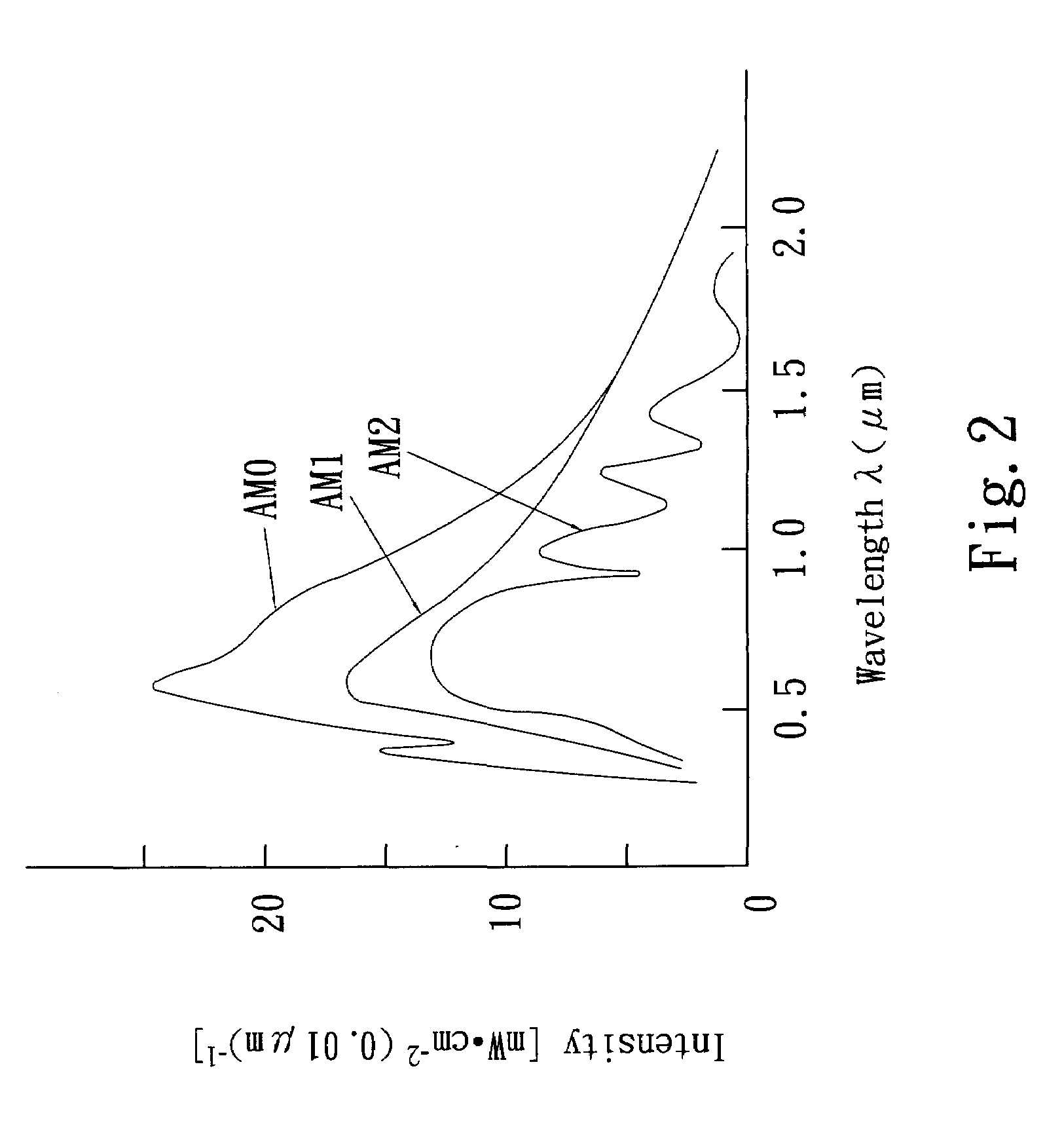
InactiveUS20100089448A1Low efficiencyMore materialSpecial surfacesCoatingsLength waveDiffusion current
A coaxial solar cell forces an exposed annular light receiving layers of a constant thickness to directly receive projection of light excitedly to generate pairs of electrons and holes that are driven by radial built-in electronic field formed on a PN junction to travel by the same distance paths to coaxial inner and outer electrodes. The photons directly enter an exposed drift region. The excited pairs of electrons and holes are separated by the even built-in electronic field to output current. Loss caused by crowding and recombination of diffusion current can be prevented. Photoelectric conversion efficiency improves without losing photon energy of short wavelengths projecting to the surface. The linear coaxial solar cell is fabricated by forming coaxial and annular semiconductor layers or compound films through deposition. Thus, it can be continuously fabricated by extending its length and mass production to reduce costs.
Owner:YANG CHUN CHU
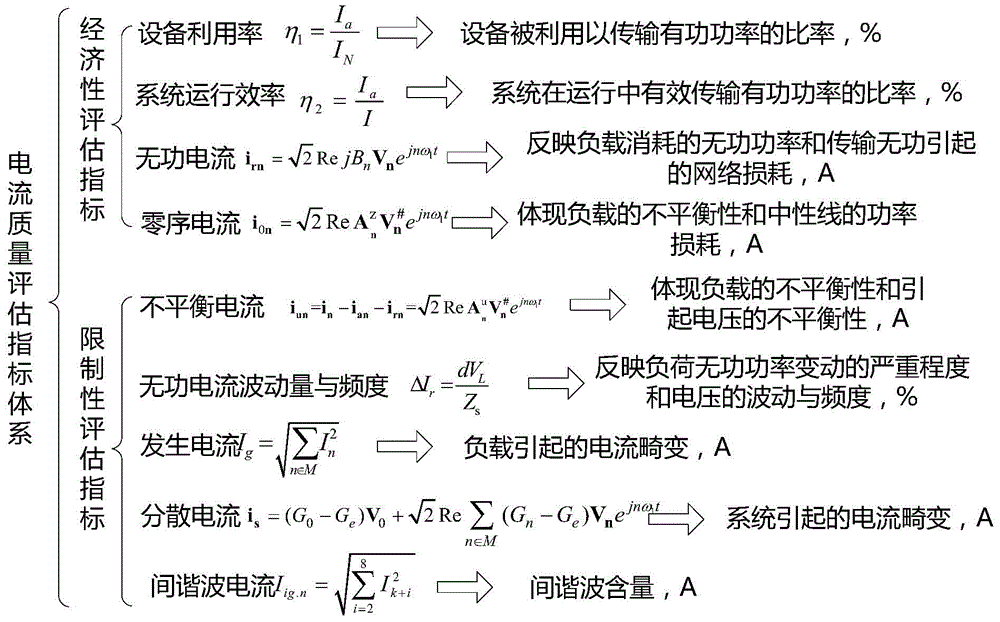
Electric power system current quality assessment method
ActiveCN104965112AImprove general performancePhysical concepts are clearCurrent/voltage measurementPower qualityDecomposition
The invention belongs to the electric energy quality analysis field, especially an electric power system current quality assessment method. The method comprises: firstly, performing Fourier decomposition on the voltage and current detected at a PCC, and dividing a voltage subset and a current subset obtained after decomposition into a harmonic portion and an interharmonic portion; secondly, for the harmonic portion, based on the harmonic wave power direction of each frequency, calculating harmonic voltages and harmonic current to obtain a current component under each frequency, and decomposing active current, diffusion current, reactive current, unbalanced current, zero sequence current and generation current; and finally, calculating each current component to obtain required current quality assessment indicators, i.e., a rate of equipment utilization, system operation efficiency, reactive current, zero sequence current, unbalanced current, reactive current fluctuation quantity and frequentness, generation current, diffusion current and interharmonic current. The assessment indicators are corresponding with real current quality phenomena one by one; an assessment system has clear concepts, and can effectively assess current quality in real engineering.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
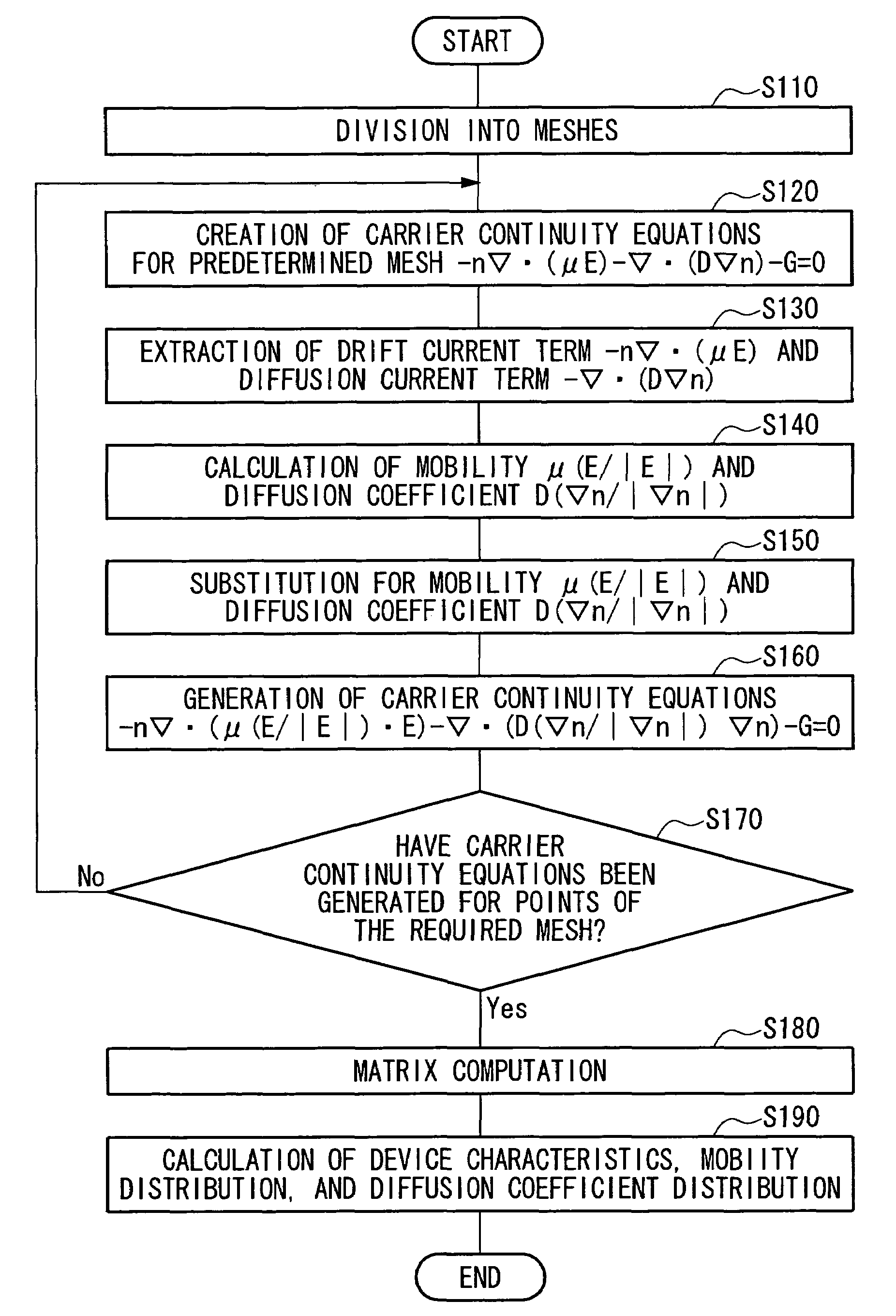
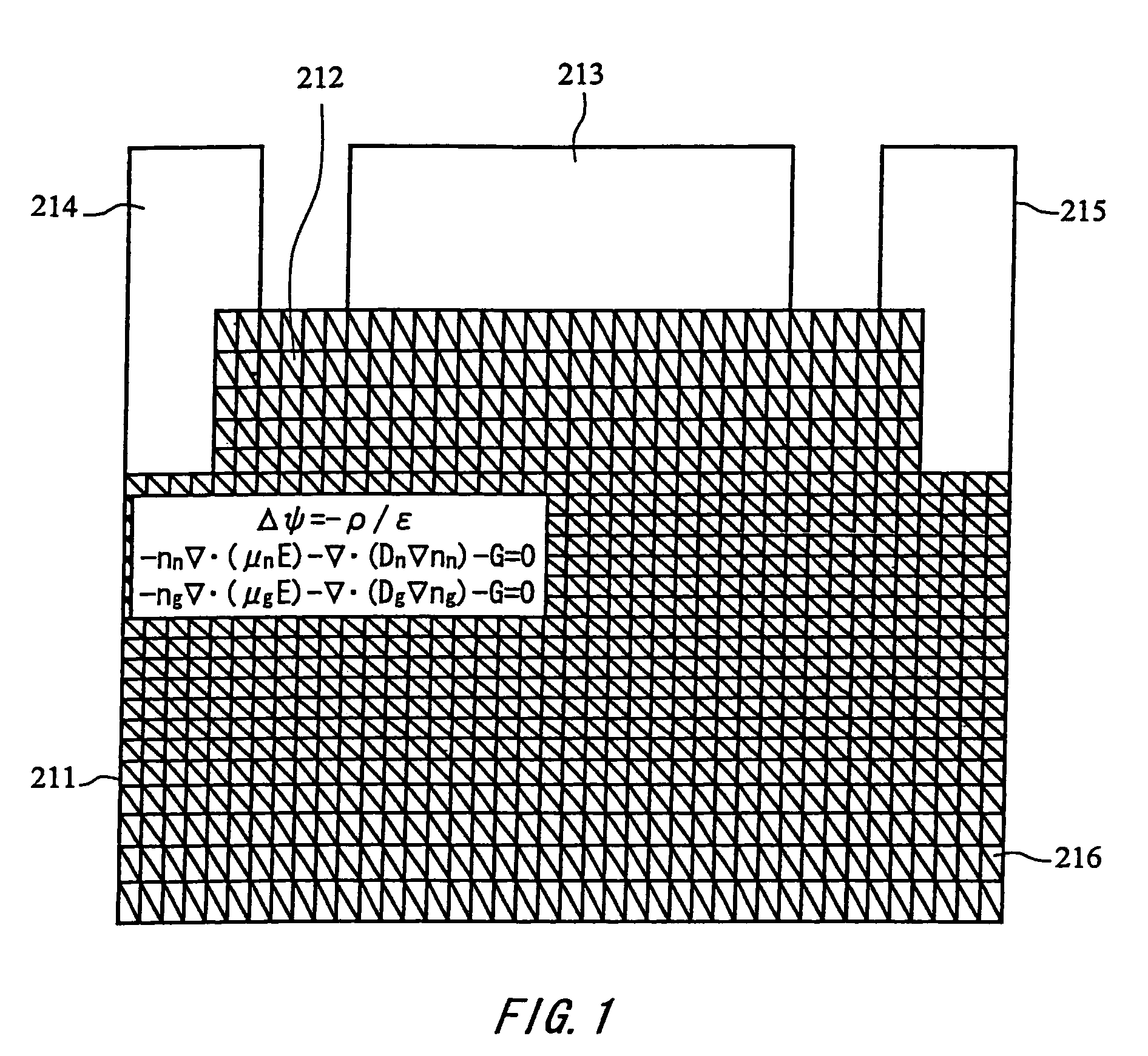
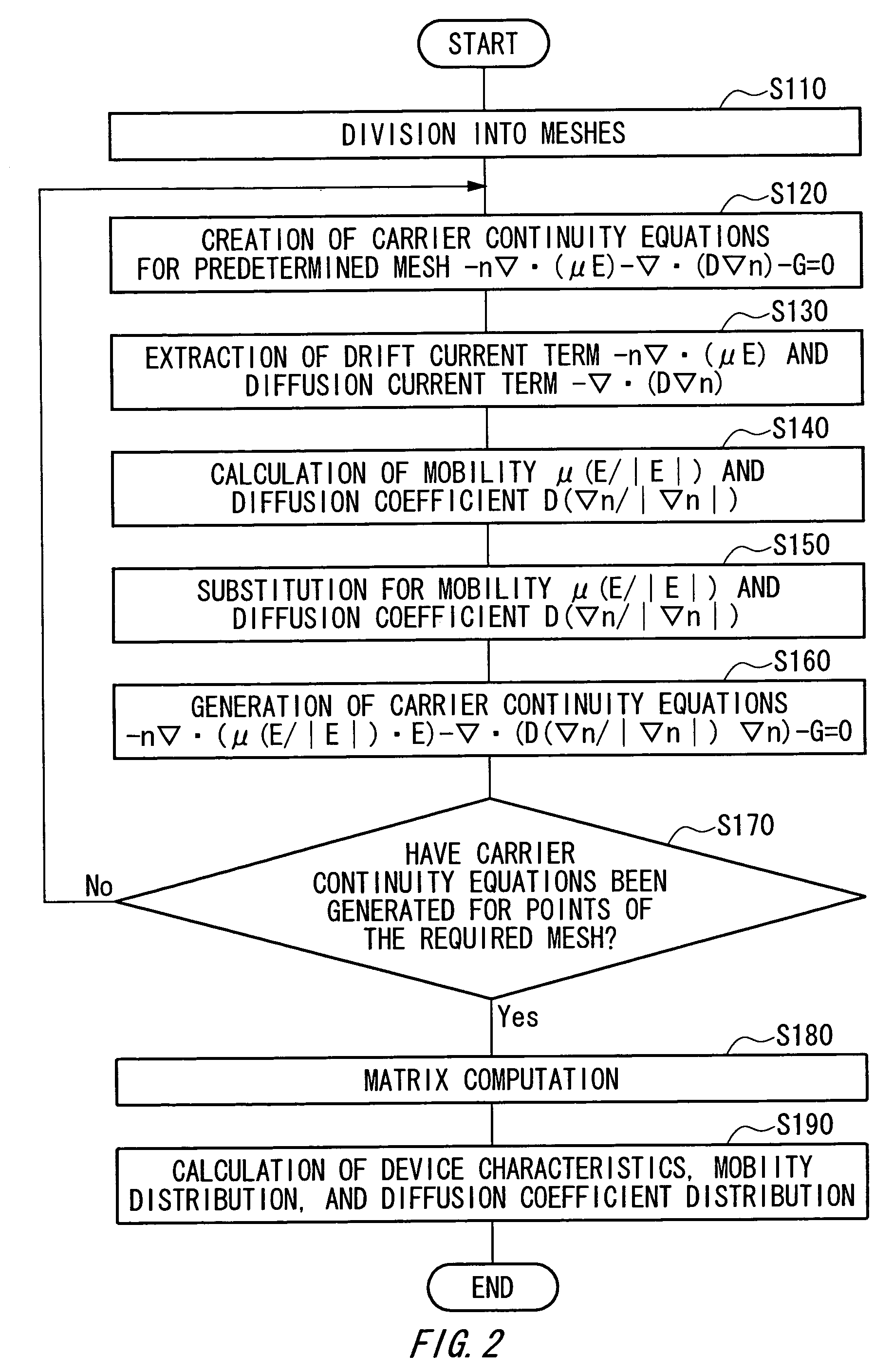
Semiconductor device simulation method, semiconductor device and fabrication method thereof, circuit board, electro-optical apparatus, and electronic device
The present invention provides an accurate and high-precision semiconductor device simulation method that is directed toward an electronic device whose physicality is not isotropic because the mobility of an organic thin film transistor, that employs an organic semiconductor, and the like, is highly dependent on field strength. In a semiconductor device simulation method which divides a semiconductor device of a two-dimensional structure or three-dimensional structure into meshes, and solves physical equations such as a potential equation and a carrier transport equation, for the meshes, a drift current resulting from an electric field and a diffusion current caused by a carrier density gradient are handled separately.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Free Charge Carrier Diffusion Response Transducer For Sensing Gradients
ActiveUS20110194376A1Obviates problemComplicates analysisThermometers using mean/integrated valuesThermometers using value differencesDiffusionPower flow
Devices for sensing gradients are constructed from material whose properties change in response to gradients. One embodiment of the device is a transducer (200) for sensing gradients that includes the material (210) and two or more electrodes (240, 270) coupled to the material. In one embodiment, gradients in a surrounding medium (110) modify the energy gap of the material in the transducer (130) producing a diffusion current density (150). The material is configured to connect to a current or voltage measurement device (520, 530, 540) where a measurement is used to determine the gradient in the medium (160). The devices can be used to measure pressure, temperature, and / or other properties. The transducer can be built on the same substrate as complementary circuitry. A transducer made of Indium. Antimonide is used in marine seismology to measure pressure gradients.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
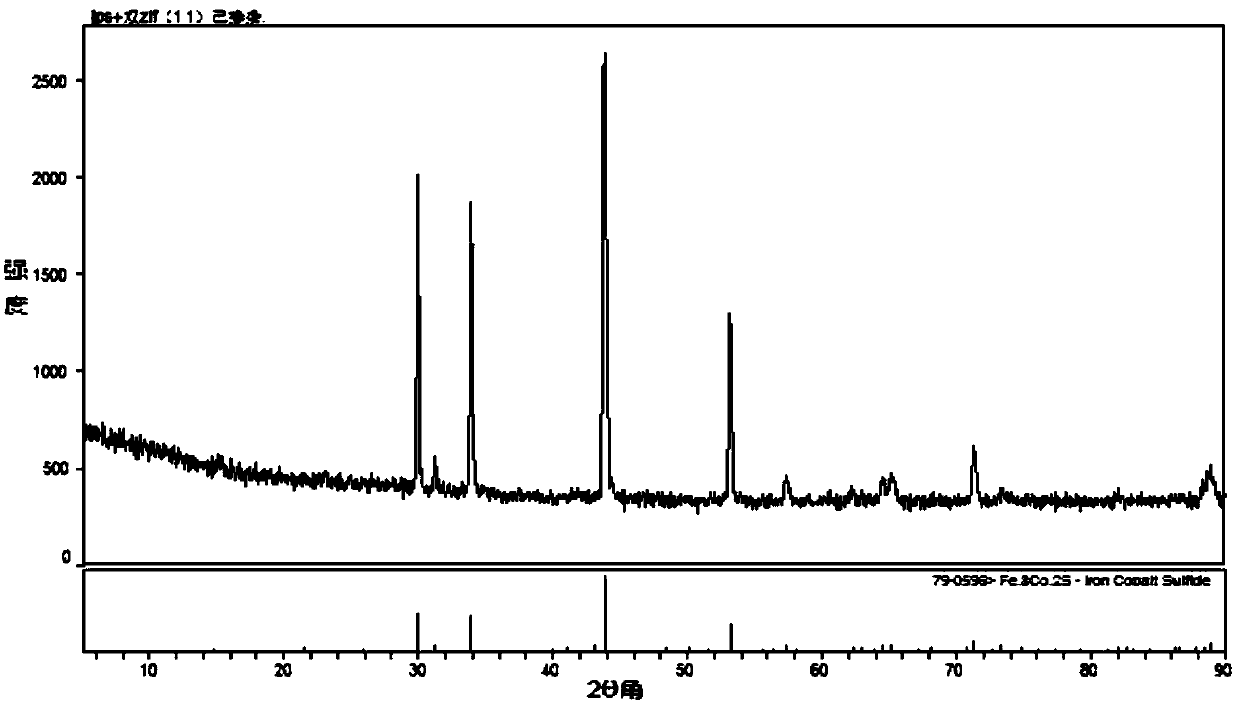
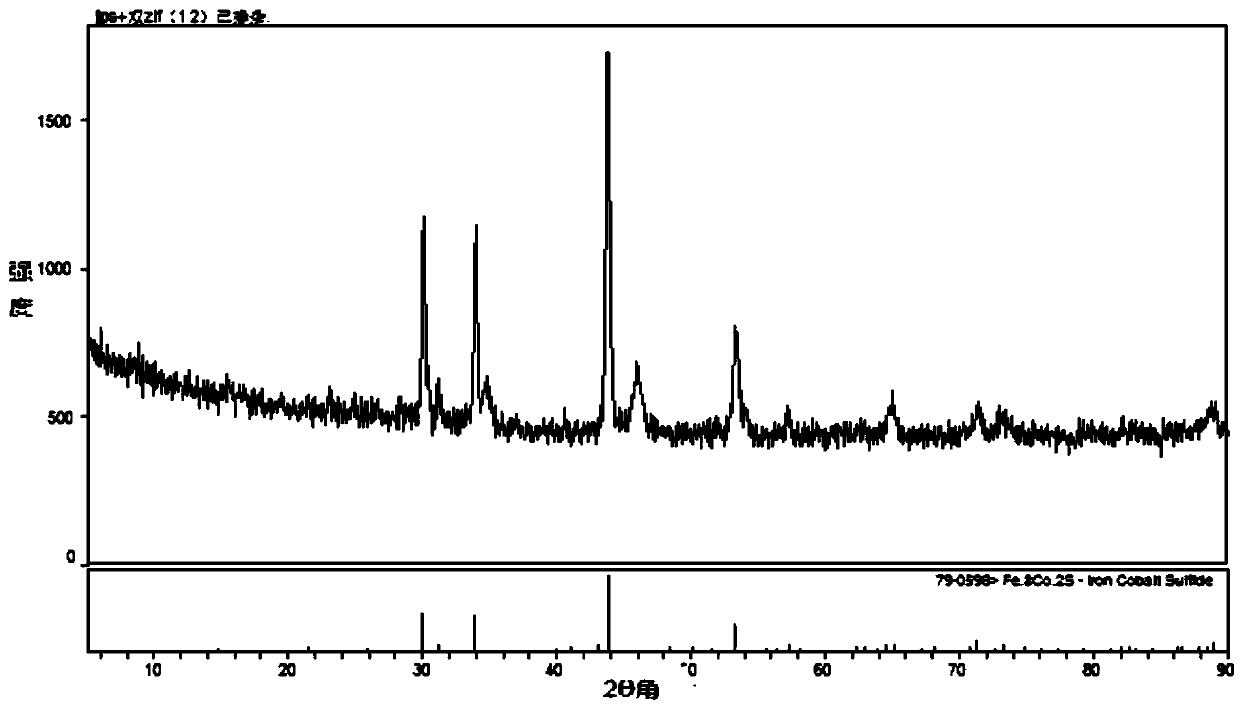
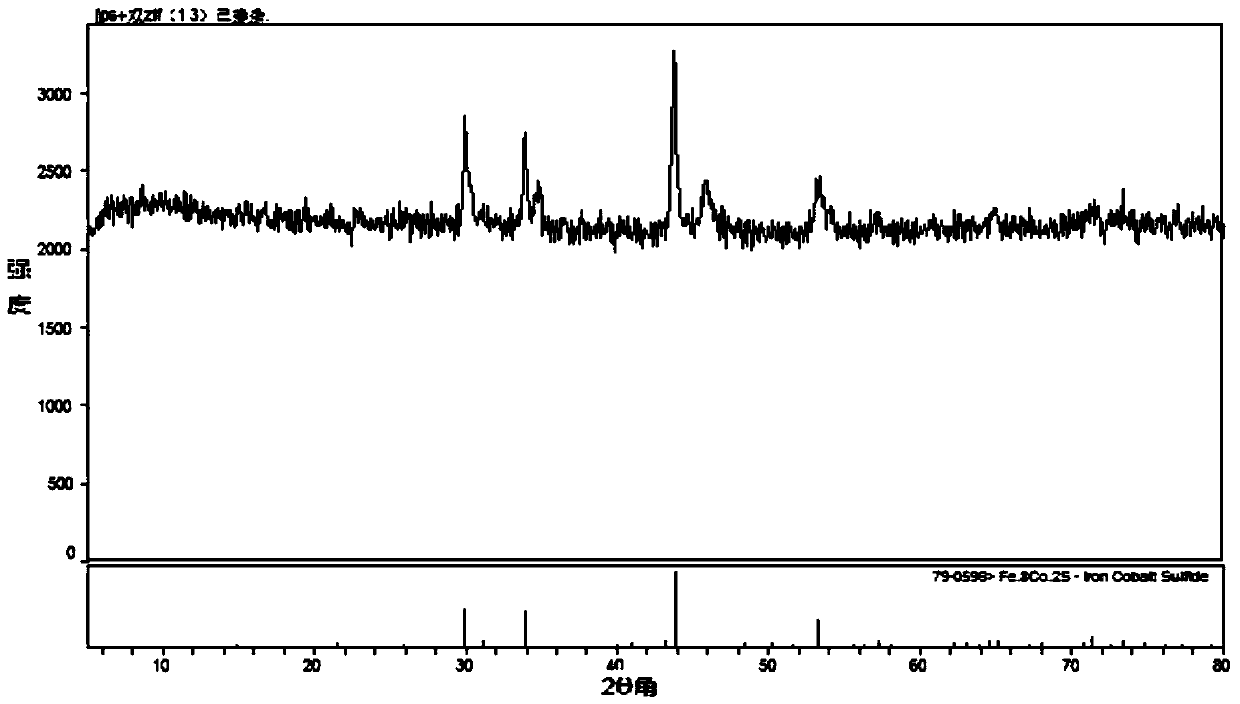
Application of metallic organic framework compound hollow microballoon loaded with iron cobalt sulfide
ActiveCN109659570ASimple preparation processLow costMaterial nanotechnologyCell electrodesMicrosphereCarbonization
The invention discloses an application of a metallic organic framework compound hollow microballoon loaded with an iron cobalt sulfide. The metallic organic framework compound hollow microballoon is applied to a fuel cell ORR catalyst for catalyzing the oxygen reduction reaction of a cathode. The metallic organic framework compound is prepared by a preparation method. The preparation method includes the steps: (1) providing polystyrene nano microballoons; (2) loading MOF derivatives with Fe and Co as metal ion centers on the polystyrene nano microballoons, ie, precursors; (3) performing high temperature carbonization on the precursors by calcining, so as to remove the polystyrene nano microballoons; and (4) performing sulfur doping on the carbonized product. The metallic organic frameworkcompound hollow microballoon has excellent electrocatalytic activity and can be used as a fuel cell ORR electrocatalyst. The optimal limited diffusion current density of the metallic organic frameworkcompound hollow microballoon is 4.1 mA / cm<-2>, and is close to the theoretical limited diffusion current density of platinum carbon of noble metal catalyst is 6 mA / cm<-2>, while the cost is lower.
Owner:YANGTZE UNIVERSITY
Oxygen reduction catalyst and preparation method thereof
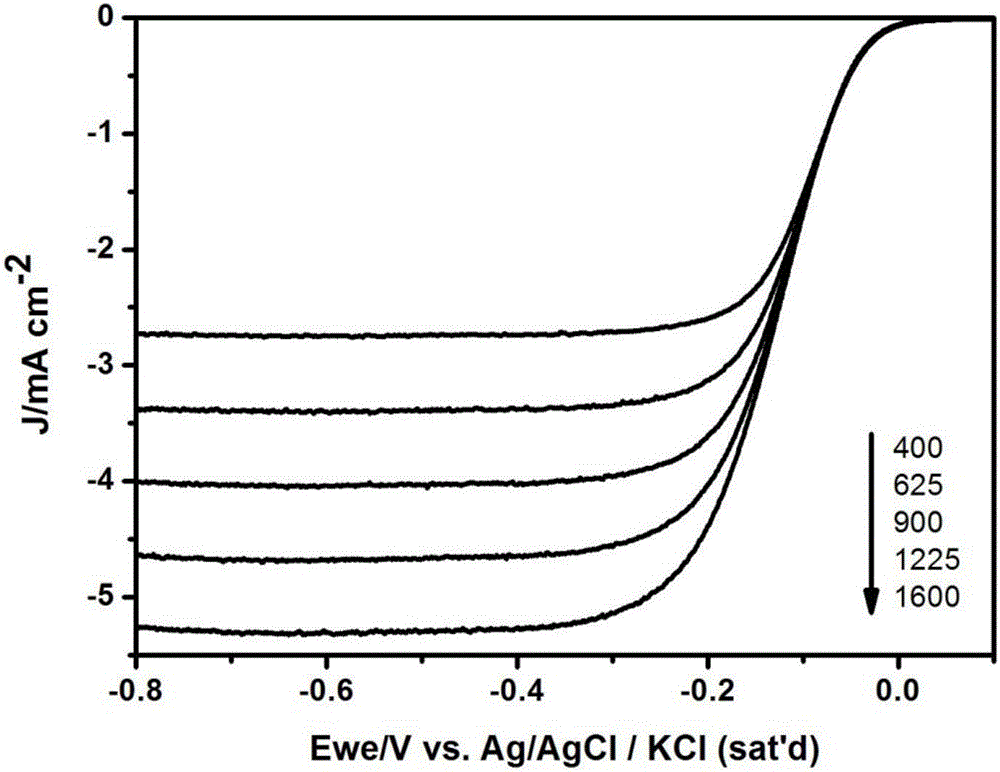
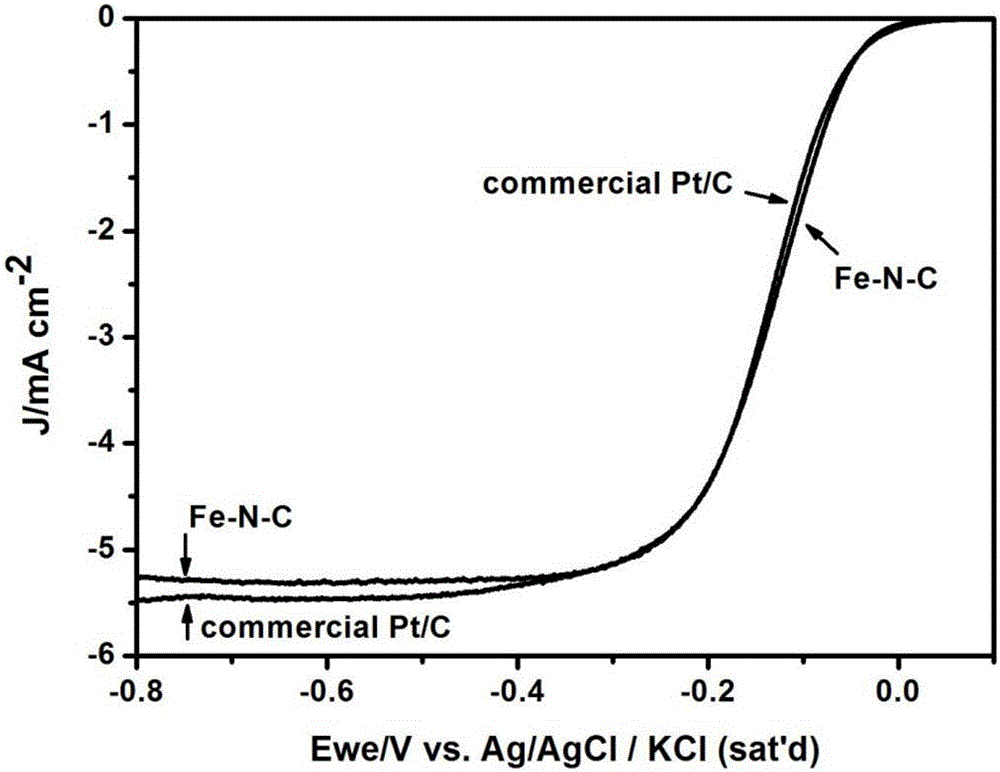
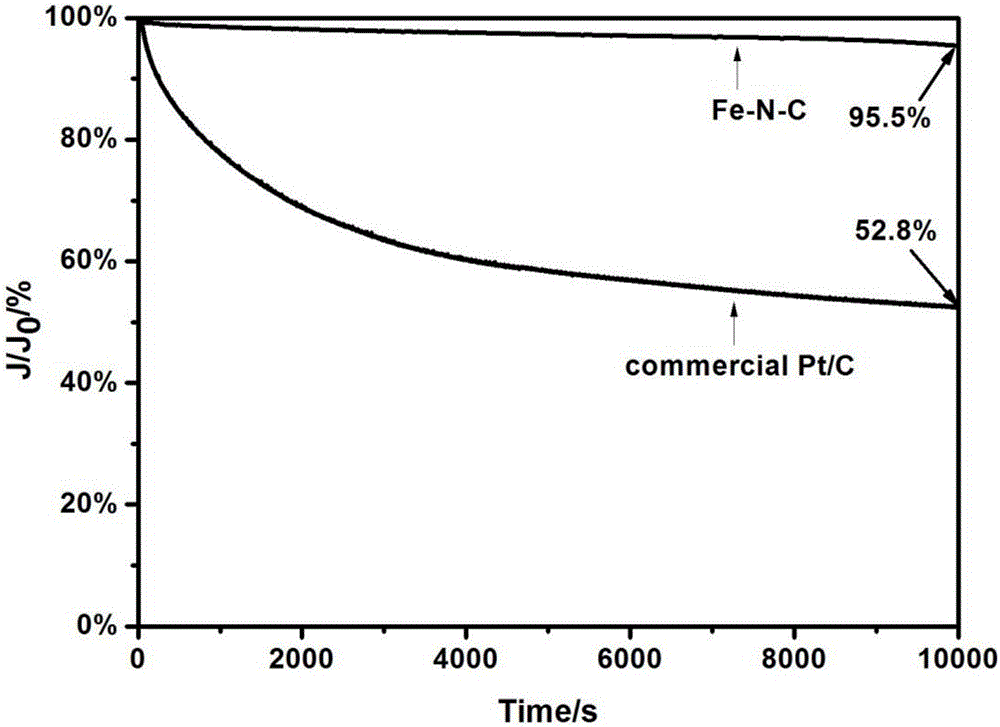
The invention provides an oxygen reduction catalyst and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method includes the steps of mixing a carbon support with a solvent to obtain a carbon support suspension liquid; mixing uric acid, molysite and the carbon support suspension liquid, and desolventizing to obtain a solid mixture; sintering the solid mixture at an inert atmosphere to obtain the oxygen reduction catalyst. According to a result of an embodiment, the oxygen reduction catalyst is provided with an take-off potential at -0.01v vsAg / AgC1 / KC1(sat'd), an extreme diffusion current of the oxygen reduction catalyst can reach to -5.25mA / cm<2> as tested in a 1600rpm rotating disk electrode test, and accordingly, the oxygen reduction catalyst is excellent in oxygen reduction performance. Compared with a commercial platinized carbon catalyst, the oxygen reduction catalyst is more correct in half wave point and much lower in decrement amount which is 4.5%.
Owner:CAPITAL NORMAL UNIVERSITY
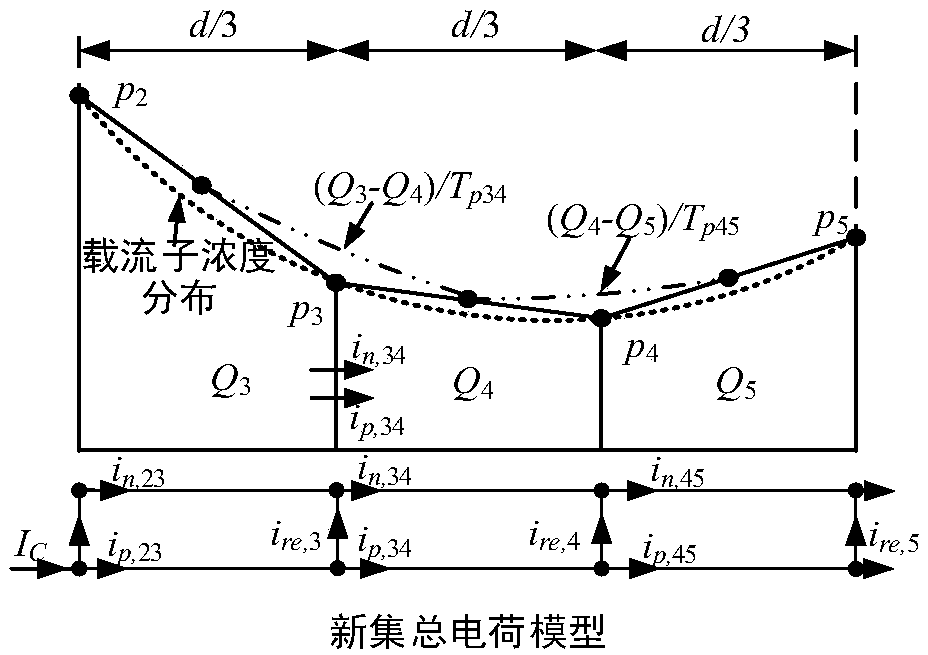
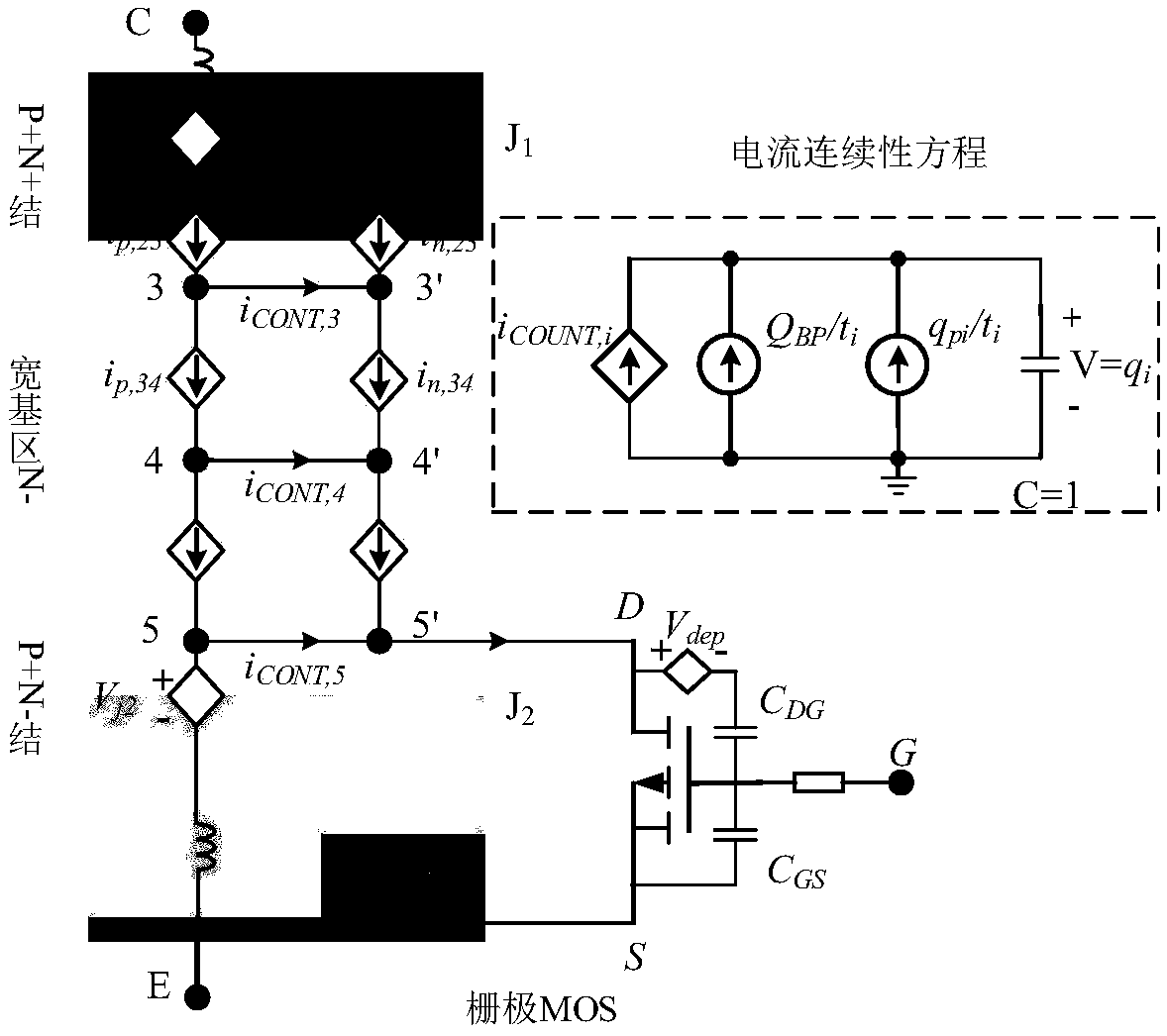
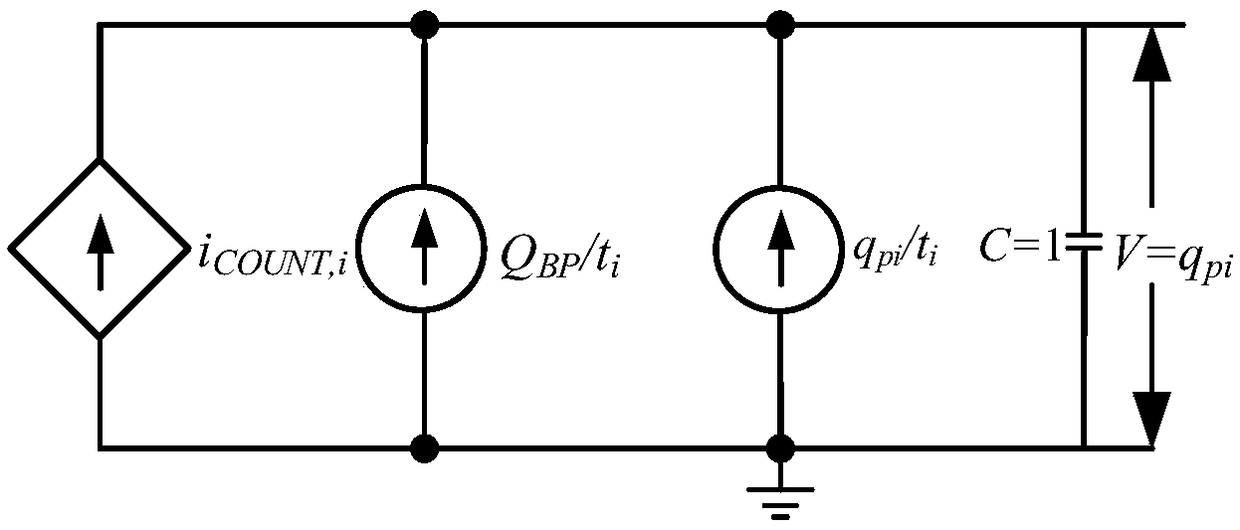
Wide base region lumped electric charge modeling method for large-power bipolar semiconductor device
ActiveCN108763696AImprove simulation accuracyReduce mistakesSpecial data processing applicationsElectron currentRecombination current
The invention discloses a wide base region lumped electric charge modeling method for a large-power bipolar semiconductor device. A wide base region is divided into n areas with equal width, and n pieces of lumped electric charges are adopted for independently expressing electric charge distribution in the n pieces of areas, wherein n is greater than or equal to 3; according to the electric chargedistribution of the area and an electric charge motion mechanism, drift current and diffusion current are defined; through a current density equation, hole current and electron current between adjacent areas are determined; according to a current continuity equation, recombination current caused by electric charges in each area is determined; and the hole current, the electron current and the recombination current are taken as a basis to establish a wide base region lumped electric charge model. By use of the method, the simulation accuracy of the wide base region lumped electric charge modelis improved, and therefore, the accurate calculation of an electric charge quantity in the wide base region of the large-power bipolar semiconductor device under multiple working conditions is realized.
Owner:NAVAL UNIV OF ENG PLA
Electrical current distribution in light emitting devices
InactiveUS8124994B2Minimize impactSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOhmic contactReflective layer
A light emitting device is disclosed that has a plurality of epitaxial layers including an active layer, at least one of a reflective layer and an ohmic contact on a first side of the epitaxial layers; and a layer of a conductive metal on a second side of the epitaxial layers and having a light emitting surface. A terminal is on the light emitting surface, the terminal comprising an array for diffusing electrical current and minimizing its effect on light output. The array may have a bonding pad, an outer portion, and a joining portion connecting the bonding pad and the outer portion; the outer portion and the joining portion being for current dissipation.
Owner:TINGGI TECH PTE
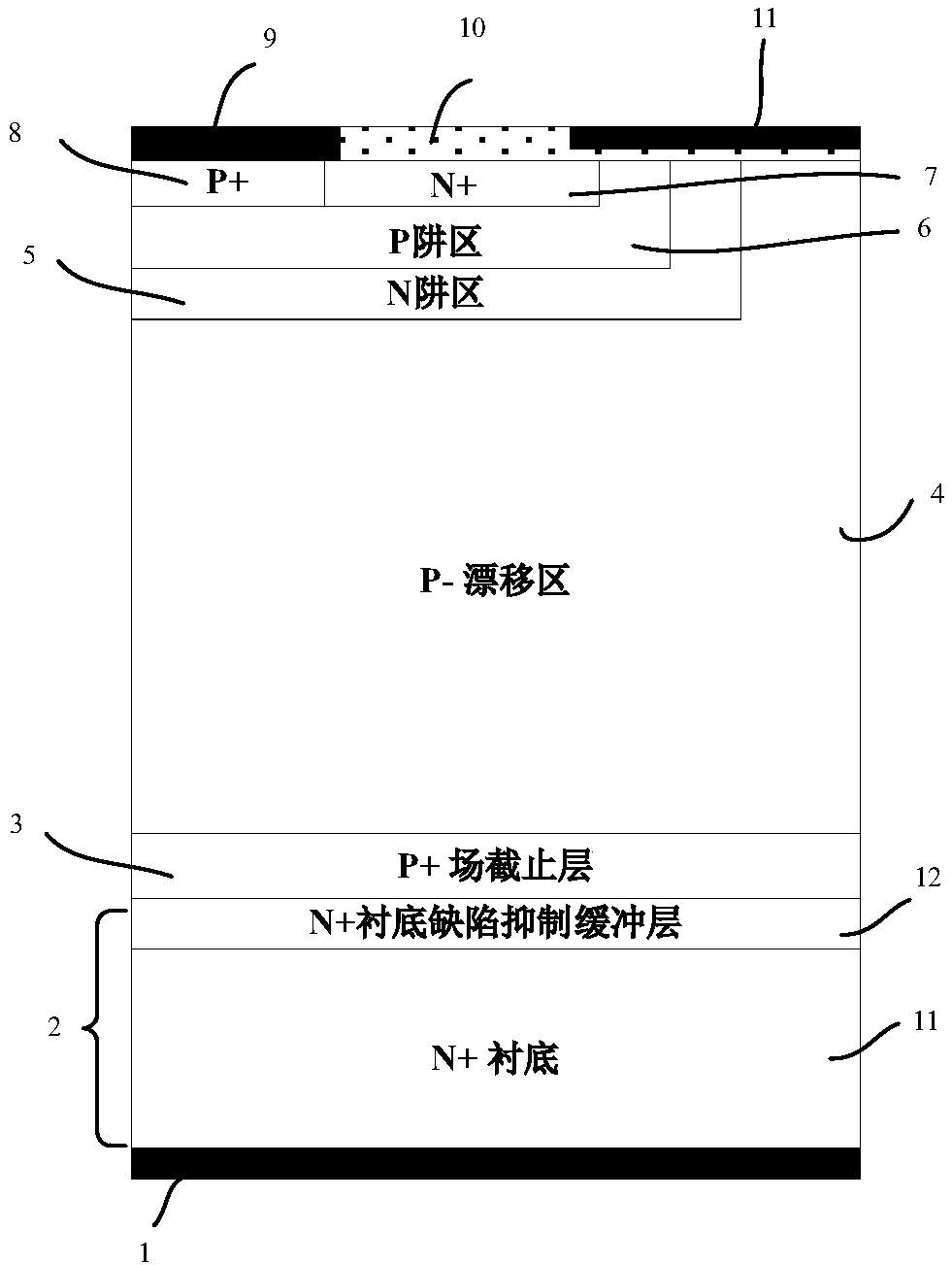
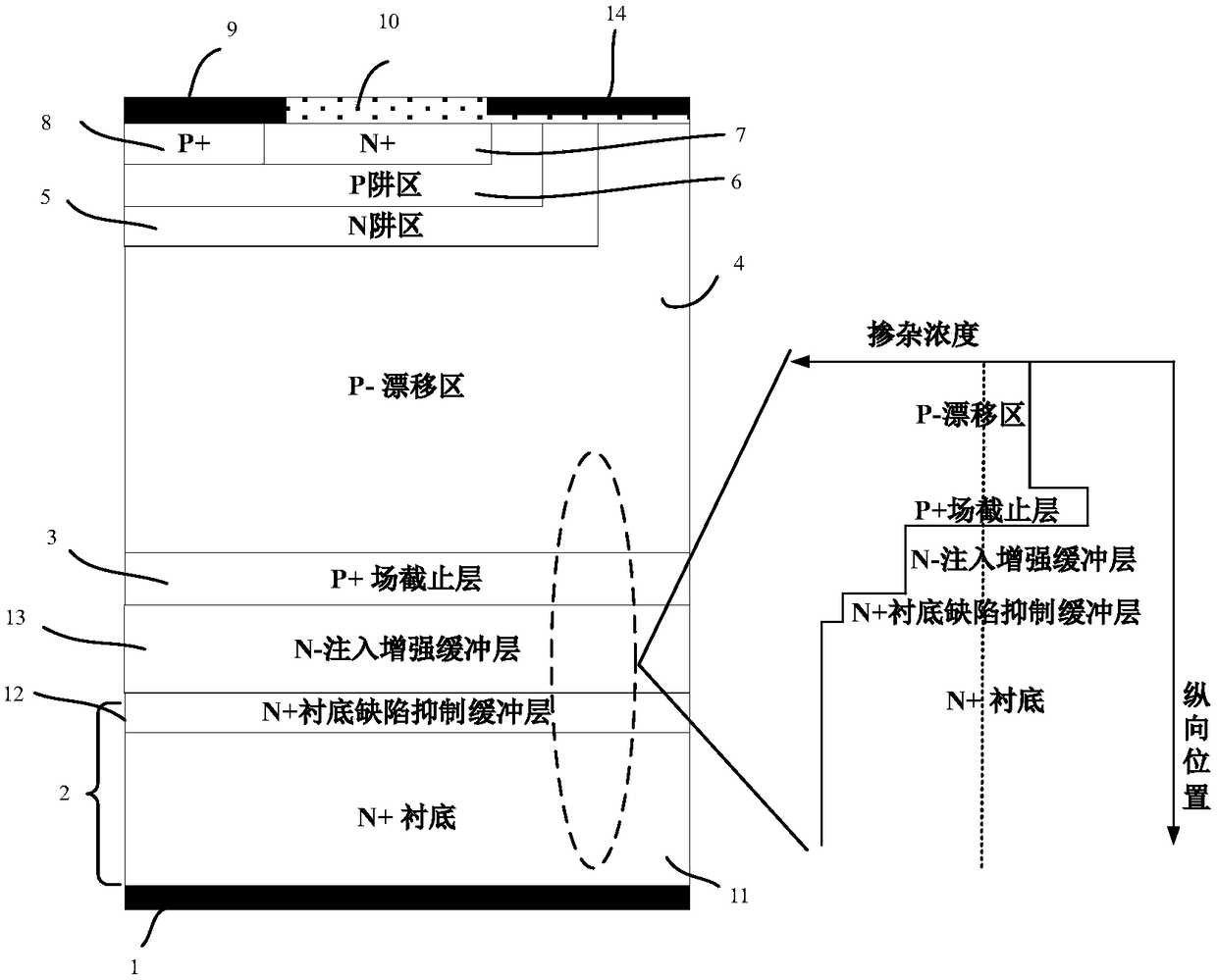
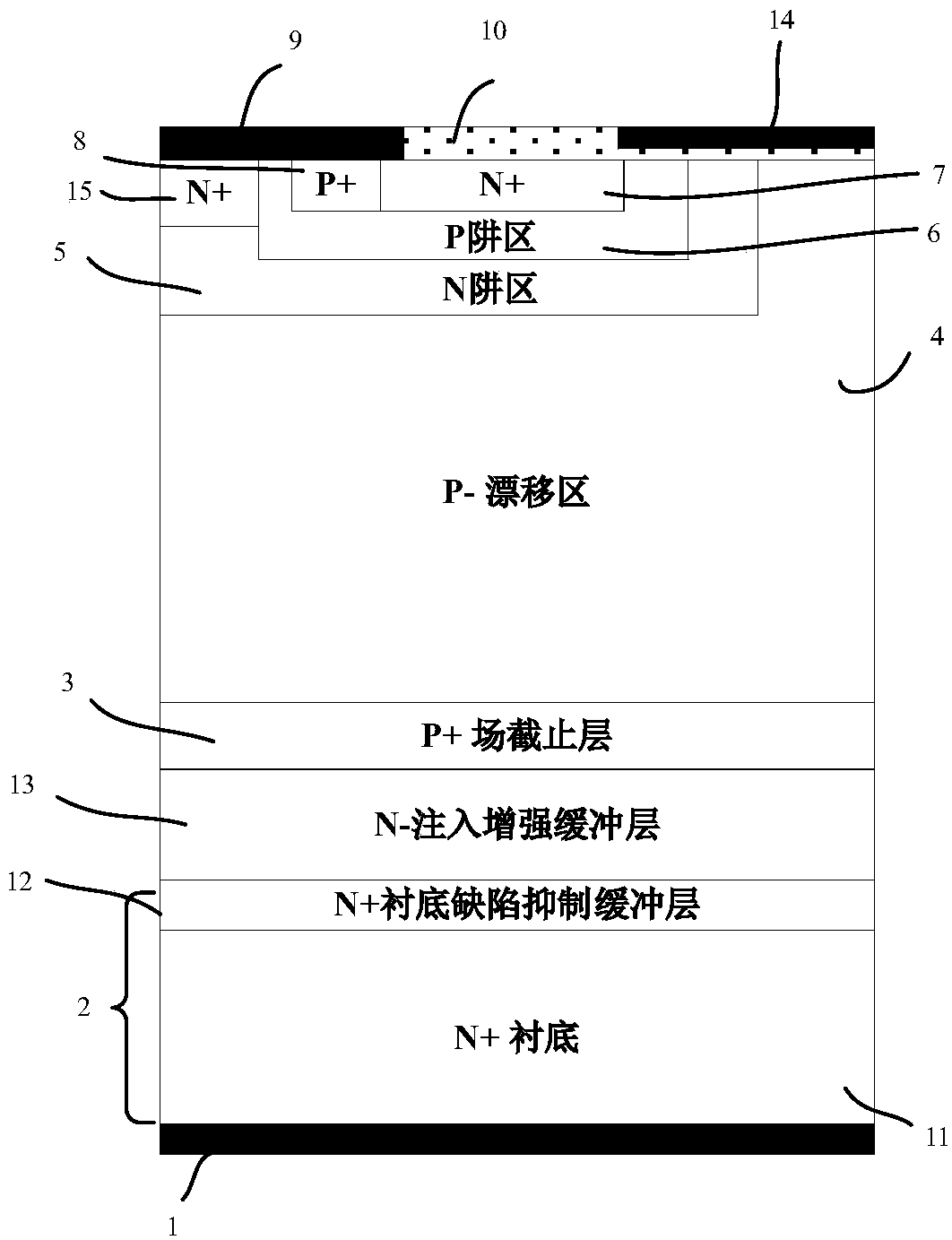
Silicon carbide MOS (Metal Oxide Semiconductor) controlled thyristor
The invention relates to the technology of power semiconductors, in particular to a silicon carbide MOS (Metal Oxide Semiconductor) controlled thyristor. The thyristor transforms the cathode region ofa conventional silicon carbide MCT (MOS Controlled Thyristor), and one N-IEB (N type-Injection Enhanced Buffer) layer is added below a P+ field stop layer. Since the N-IEB layer has low dosage concentration, the service life and the migration rate of a minority of current carriers in the region can be improved to increase the diffusion length of the minority of current carriers in a cathode structure so as to increase cathode injection efficiency. In addition, since a built-in electric field is generated due to a concentration difference between an N-type substrate and the N-IEB layer, the direction of the built-in electric field points to the N-IEB layer from the N-type substrate so as to prevent minority holes from diffusing to the N-type substrate from the N-IEB layer, so that minorityhole diffusion current is reduced, and therefore, the cathode injection efficiency is improved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Transverse parasitic plug-and-play (PNP) device in SiGe heterojunction bipolar transistor (HBT) technique and production method
ActiveCN102969349AImprove performanceReduce performanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesSalicideMetal silicide
The invention discloses a transverse parasitic PNP device in the SiGe HBT technique. An active region is isolated by field oxide of a shallow groove; a collector region comprises P-type buried layers formed at the bottom of the shallow groove and on two sides of the active region and P-type impurity ion implanted layers formed at the bottom of the shallow groove and connected with the P-type buried layers, wherein the transverse distance between each P-type buried layer and a base region is larger than 1 micron; the base region is formed by an N-type impurity ion implanted layer formed on the upper portion of the active region; and an emitting region is formed by a P-type SiGe epitaxial layer formed on the N-type impurity ion implanted layer of the active region and a polysilicon layer formed at the top of the shallow groove and connected with the P-type SiGe epitaxial layer, wherein the upper portion of the P-type SiGe epitaxial layer is provided with a silicide barrier layer. The invention further discloses a production method of the PNP device. According to the device and the method, the performances of the PNP device are improved, SiGe free of metal silicide is formed in the emitting region, loss of silicon for the metal silicide is reduced, the thickness of the emitting region is increased, base diffusion current is reduced, and the DC amplification factor is increased.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUAHONG GRACE SEMICON MFG CORP
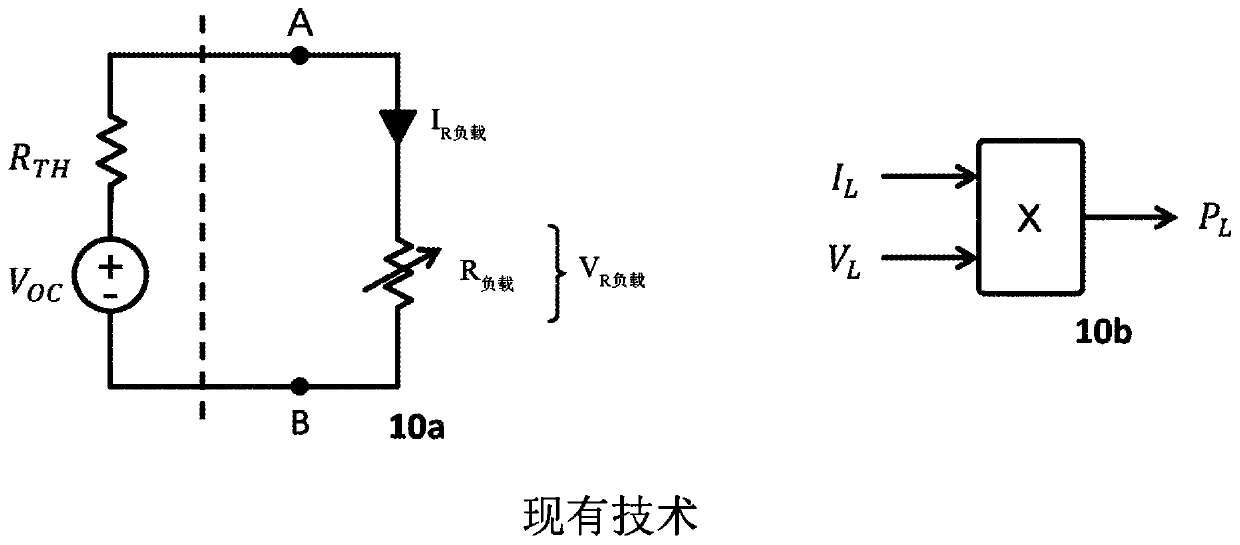
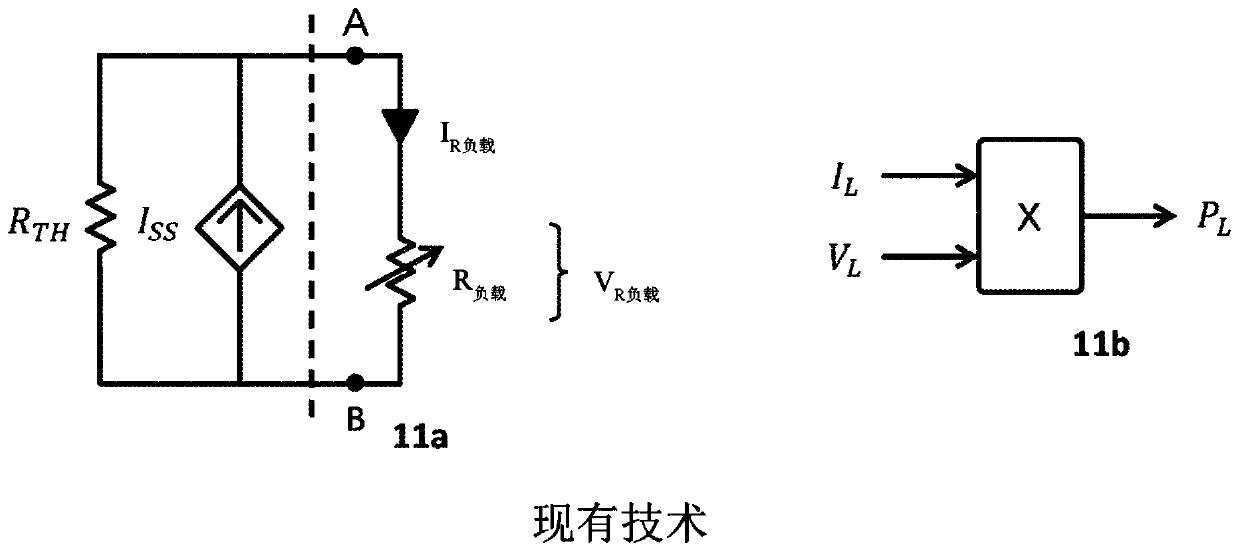
Low noise sensor amplifiers and trans-impedance amplifiers using complementary pair of current injection field-effect transistor devices
This invention relates to low noise sensor amplifiers and trans-impedance amplifiers using a complementary pair of current injection field effect transistor (iFET) devices (CiFET). CiFET includes an N-type current field-effect transistor (NiFET) and a P-type current field-effect transistor (PiFET), each of the NiFET and PiFET has a source, a drain, a gate, and a diffusion (current injection) terminal (iPort). Each iFET also has a source channel with a width and a length between the source and diffusion terminal, and drain channel with a width and a length between the drain and the diffusion terminal. A trans-impedance of the CiFET device is adjusted by a ratio of width / length of source channel over width / length of drain channel of the iFET and supply power voltage. In one configuration, the gate terminals of the NiFET and PiFET are connected together to form a common gate. In another configuration that common gate is configured as a voltage input for a high input impedance mode. Output voltage swings around a common mode voltage.
Owner:CIRCUIT SEED LLC
Fuel cell with interweaving current collector and membrane electrode assembly
InactiveUS7794891B2Structural economyOperated easily and rapidlyFuel cells groupingFuel cell auxillariesPolymer electrolytesFuel cells
An electrolyte membrane / electrode web member includes an elongated solid polymer electrolyte membrane. A plurality of anodes and a plurality of cathodes are provided on one surface, and on the other surface of the solid polymer electrolyte membrane, respectively. First and second gas diffusion current collector members are inserted into the electrolyte membrane / electrode web member from both sides. Each of the first and second gas diffusion current collector members is formed by folding a single electrically conductive plate into a substantially U-shape. Electrical insulation is provided by interposing the insulating member between the first and second gas diffusion current collector members.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
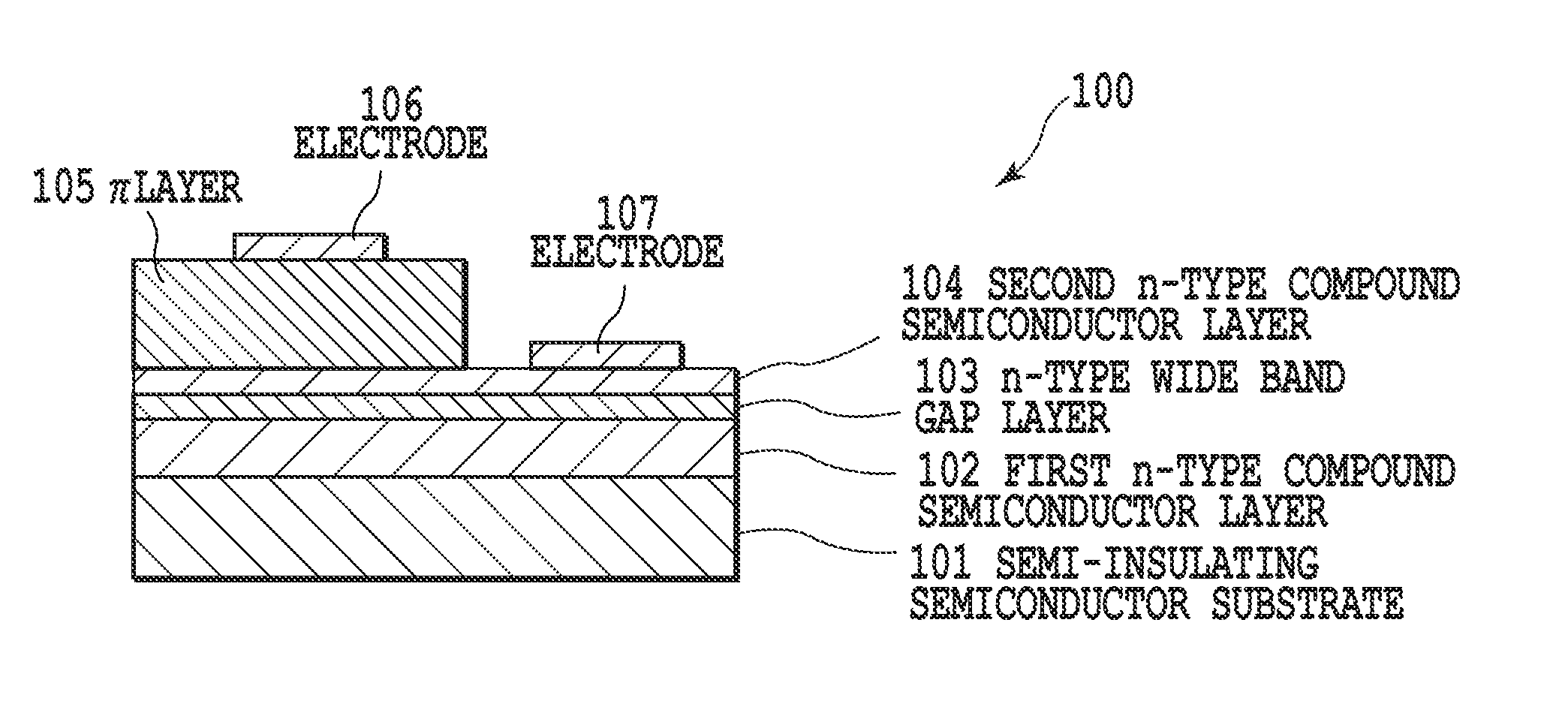
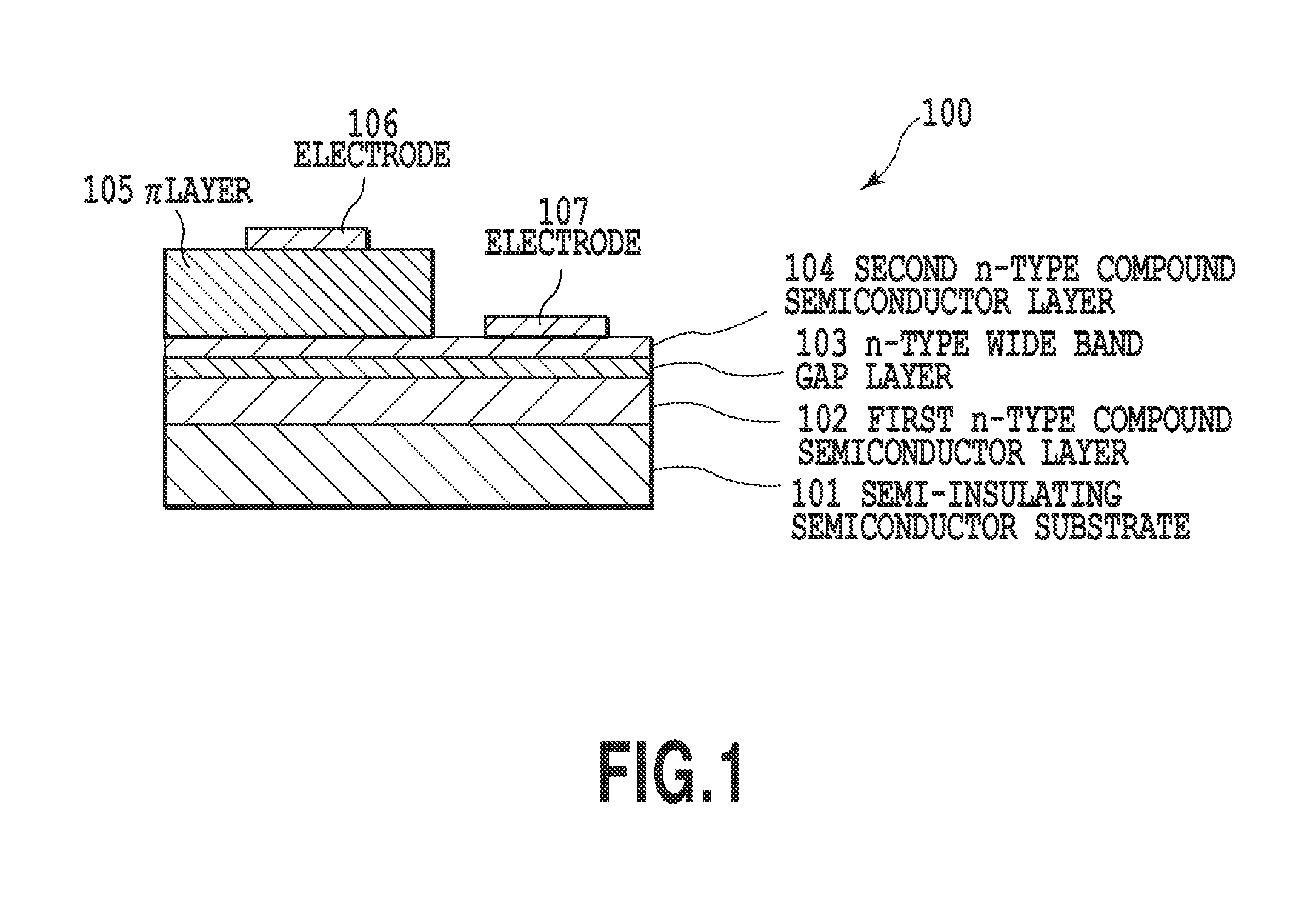
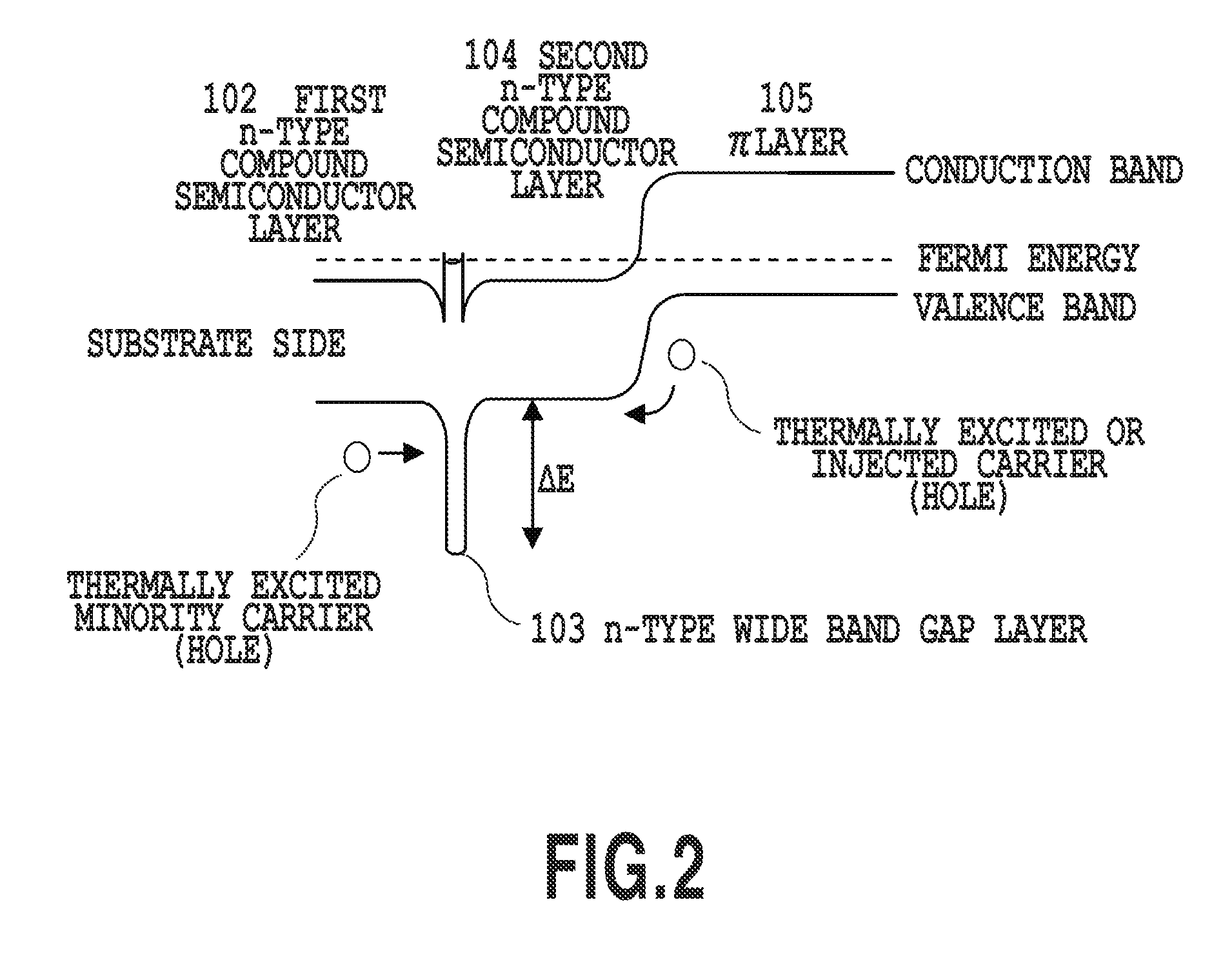
Infrared light emitting device
ActiveUS20110018010A1High diode resistanceTotal current dropSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingValence bandPower flow
Provided is an infrared light emitting device in which dark current and diffusion current caused by thermally excited holes are suppressed. Thermally excited carriers (holes) generated in a first n-type compound semiconductor layer (102) tend to diffuse in the direction of a π layer (105). But, the dark current by holes is reduced by providing an n-type wide band gap layer (103) with a larger band gap than the first layer (102) and the π layer (105) that suppresses the hole diffusion between the first layer (102) and the π layer (105). The wide band gap layer (103) has a band gap shifted relatively to valence band direction by n-type doping and thereby more effectively functions as a diffusion barrier for the thermally excited holes. Namely, the band gap and n-type doping of the wide band gap layer (103) are adjusted to suppress diffusion of the thermally excited carriers.
Owner:ASAHI KASEI ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Semiconductor light emitting device
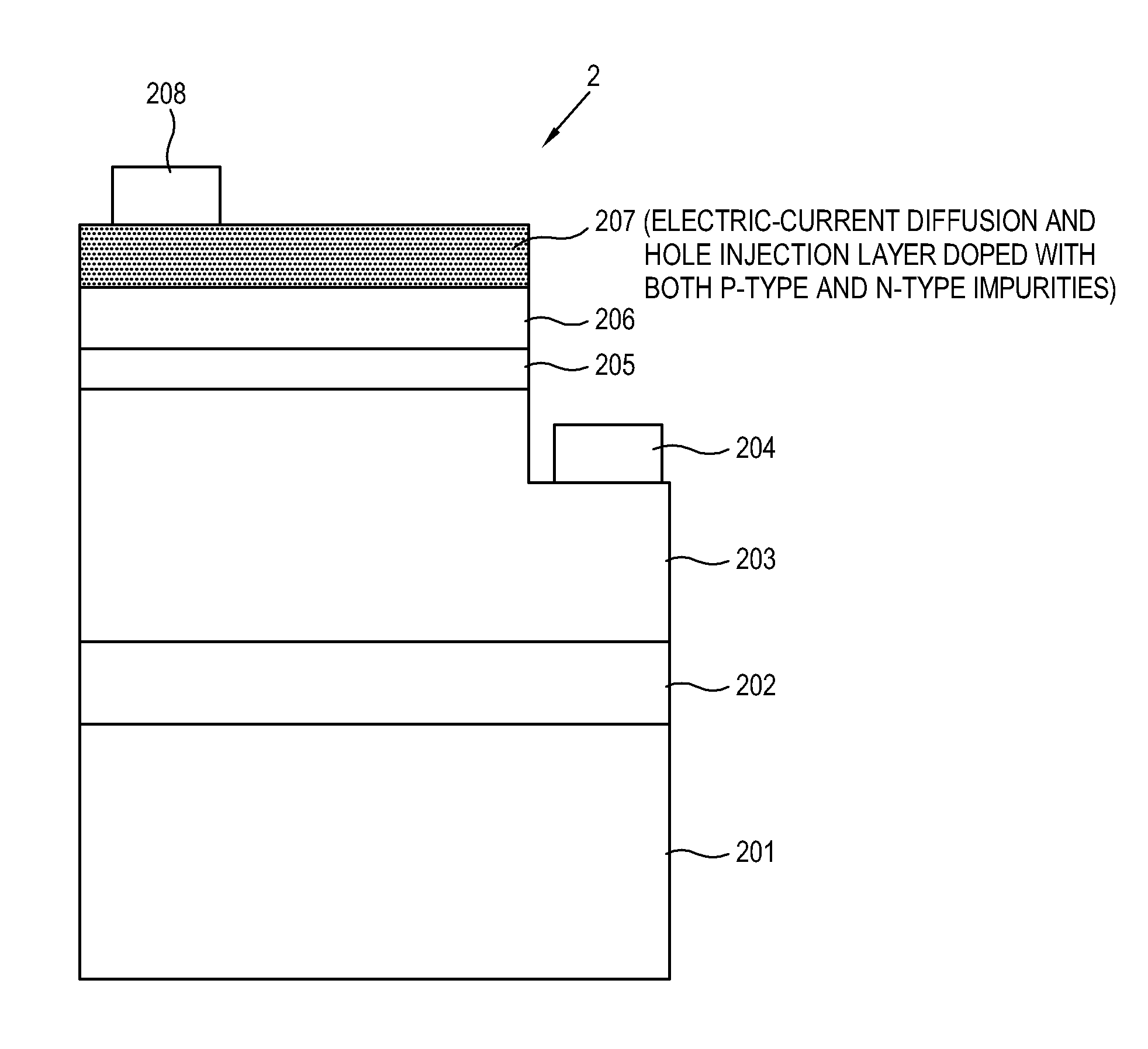
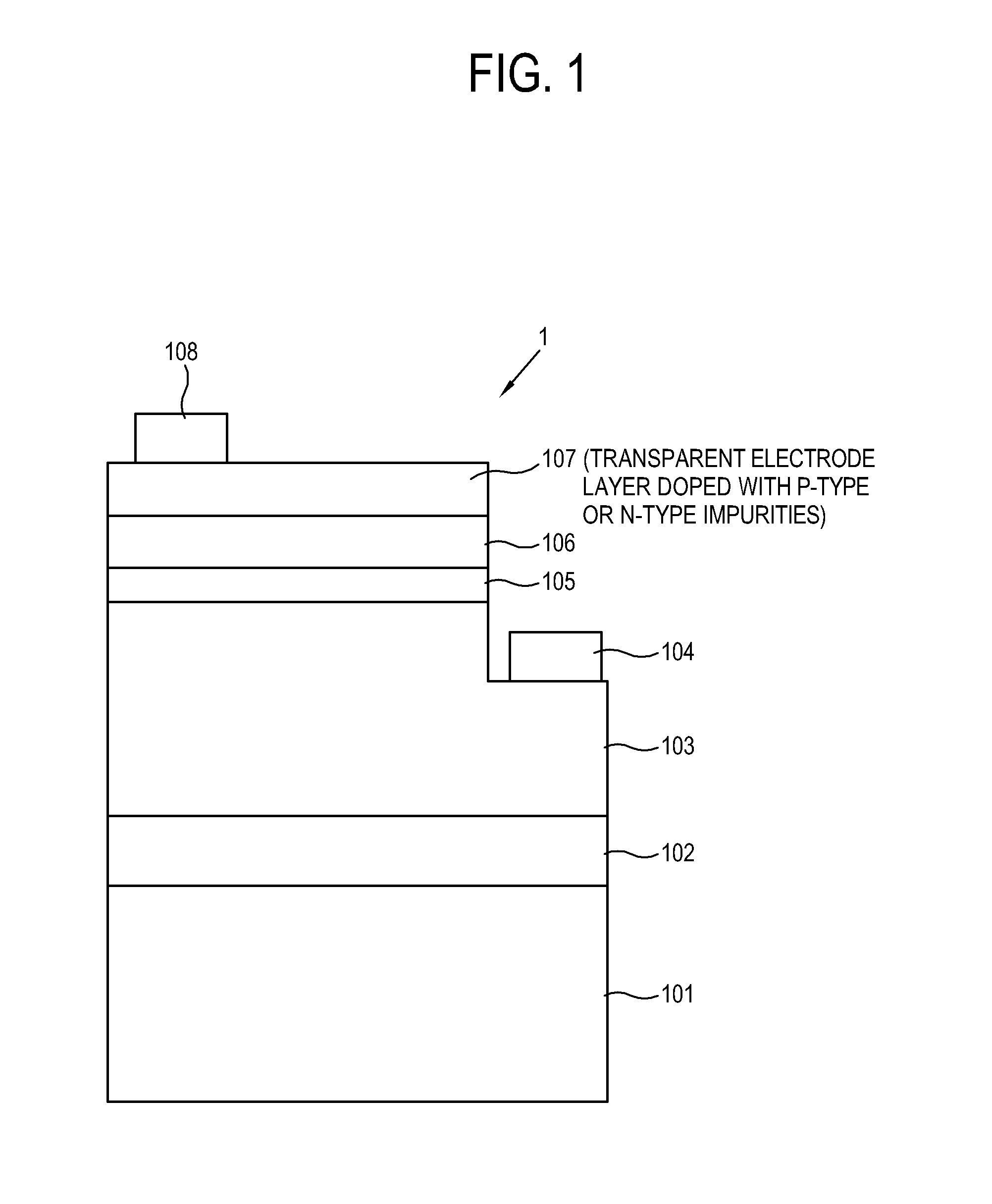
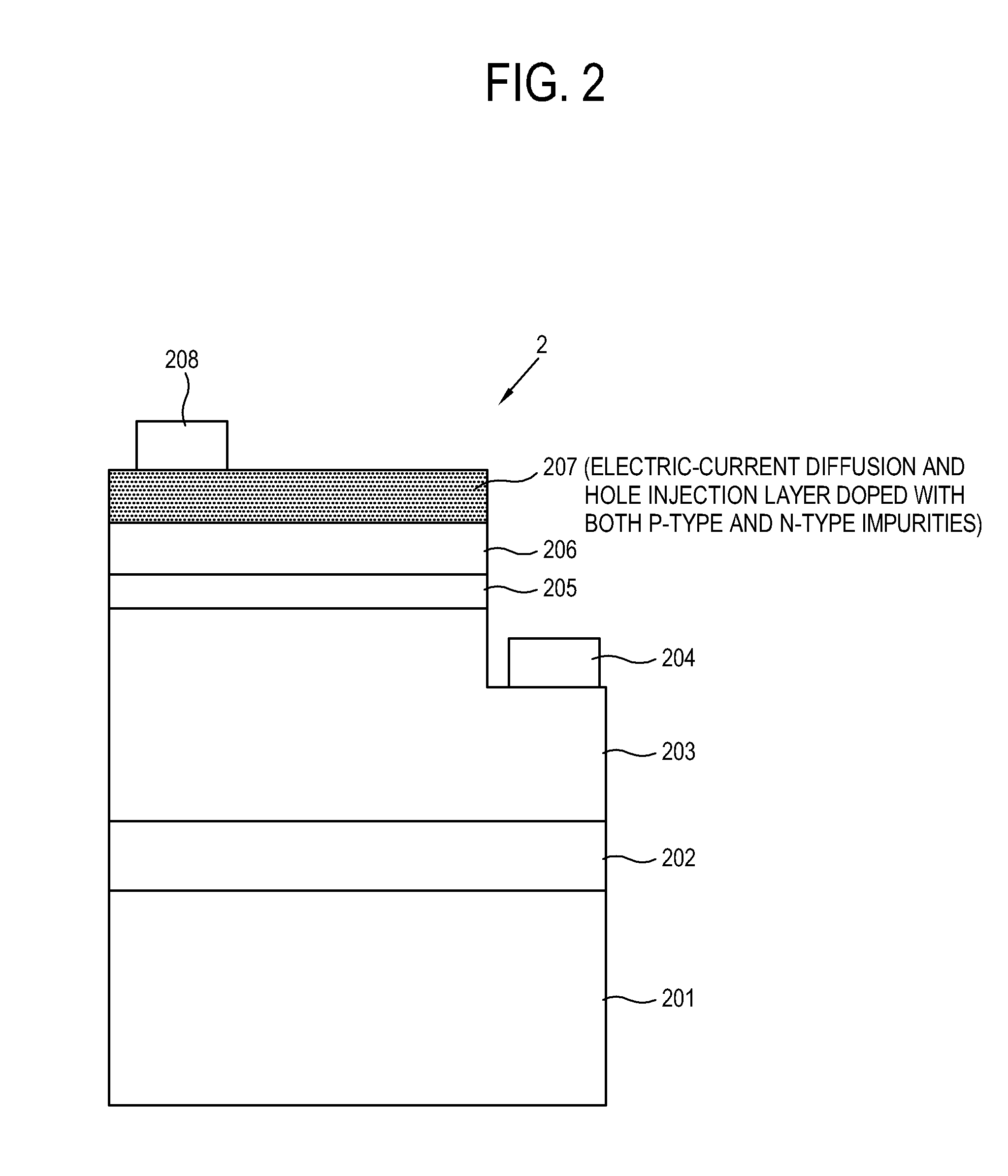
InactiveUS20120168718A1High trafficSpread evenlySemiconductor devicesHole injection layerQuantum well
Disclosed is a semiconductor light emitting device including: a substrate; an n-type semiconductor layer giving an electron when receiving voltage; a p-type semiconductor layer giving a hole when receiving voltage; an active layer provided between the n-type semiconductor layer and the p-type semiconductor layer and including a quantum well structure to facilitate coupling between an electron and a hole; an n-type electrode including conductivity for applying voltage to the n-type semiconductor layer; a p-type electrode including conductivity for applying voltage to the p-type semiconductor layer; and am electric-current diffusion and hole injection layer provided between the p-type semiconductor layer and the p-type electrode and doped with n-type impurities and p-type impurities for diffusing an electric current and injecting a hole between the p-type electrode and the p-type semiconductor layer. With this, ohmic contact is decreased, flow of an electric current is improved, diffusion of the electric current is more uniformized, and injection of a hole is improved between the electrode and the semiconductor layer of the semiconductor light emitting device, thereby maximizing efficiency of a device.
Owner:QUANTUM DEVICES
Photodiode
ActiveUS7141833B2Attenuation bandwidthBlurring responseSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCharge carrierPhotodiode
Apart from a semiconductor substrate and a photosensitive region in the semiconductor substrate, which comprises a space charge zone region for generating a diffusion current portion and a diffusion region for generating a diffusion current portion, a photodiode includes an insulation means in the semiconductor substrate for at least partially confining the diffusion region against an adjacent surrounding region of the semiconductor substrate. The reduction of the bandwidth of photodiodes by the smearing of the response of the photodiode by the diffusion current is alleviated by providing an insulation means in the semiconductor substrate, which confines the diffusion region against the surrounding semiconductor substrate and hereby on the one hand reduces the number of charge carriers contributing to the diffusion portion by reducing the diffusion region, in which the diffusing charge carriers are generated, and on the other hand by “sucking off” diffusing charge carriers generated in the shrunk diffusion region by the insulation means, which is why same do not contribute to the photocurrent.
Owner:MAGNOLIA LICENSING LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com