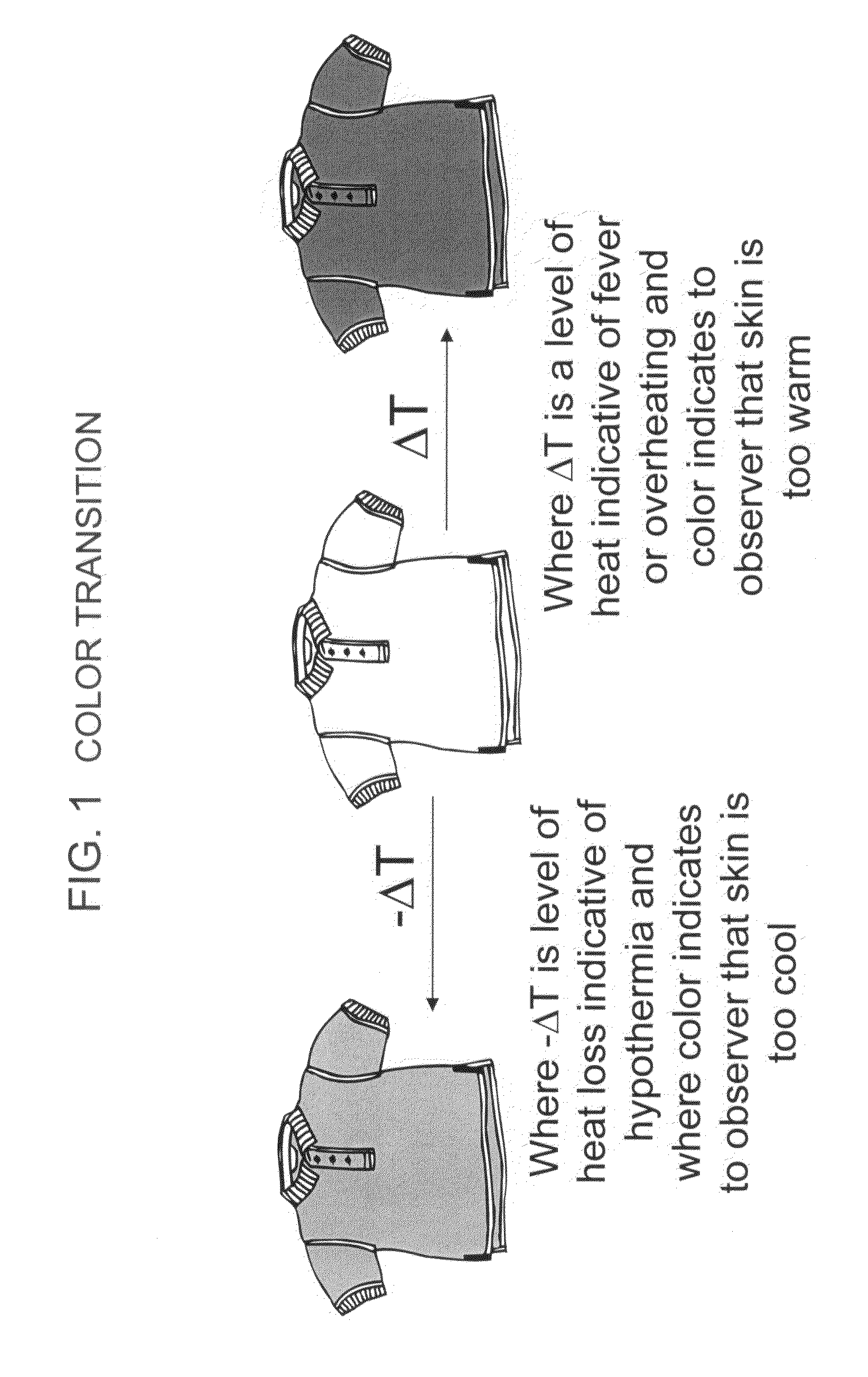
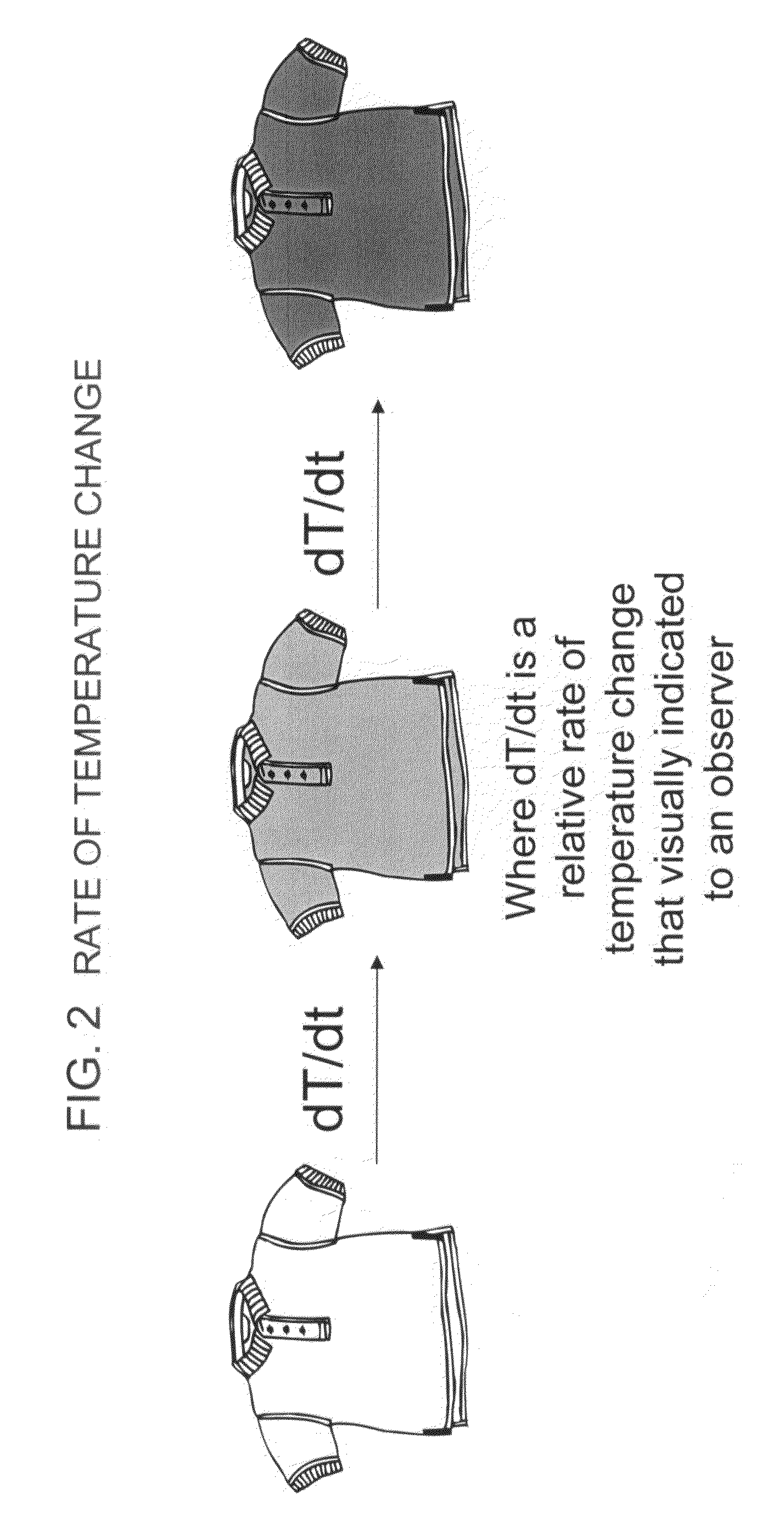
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
730results about "Thermometers using value differences" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
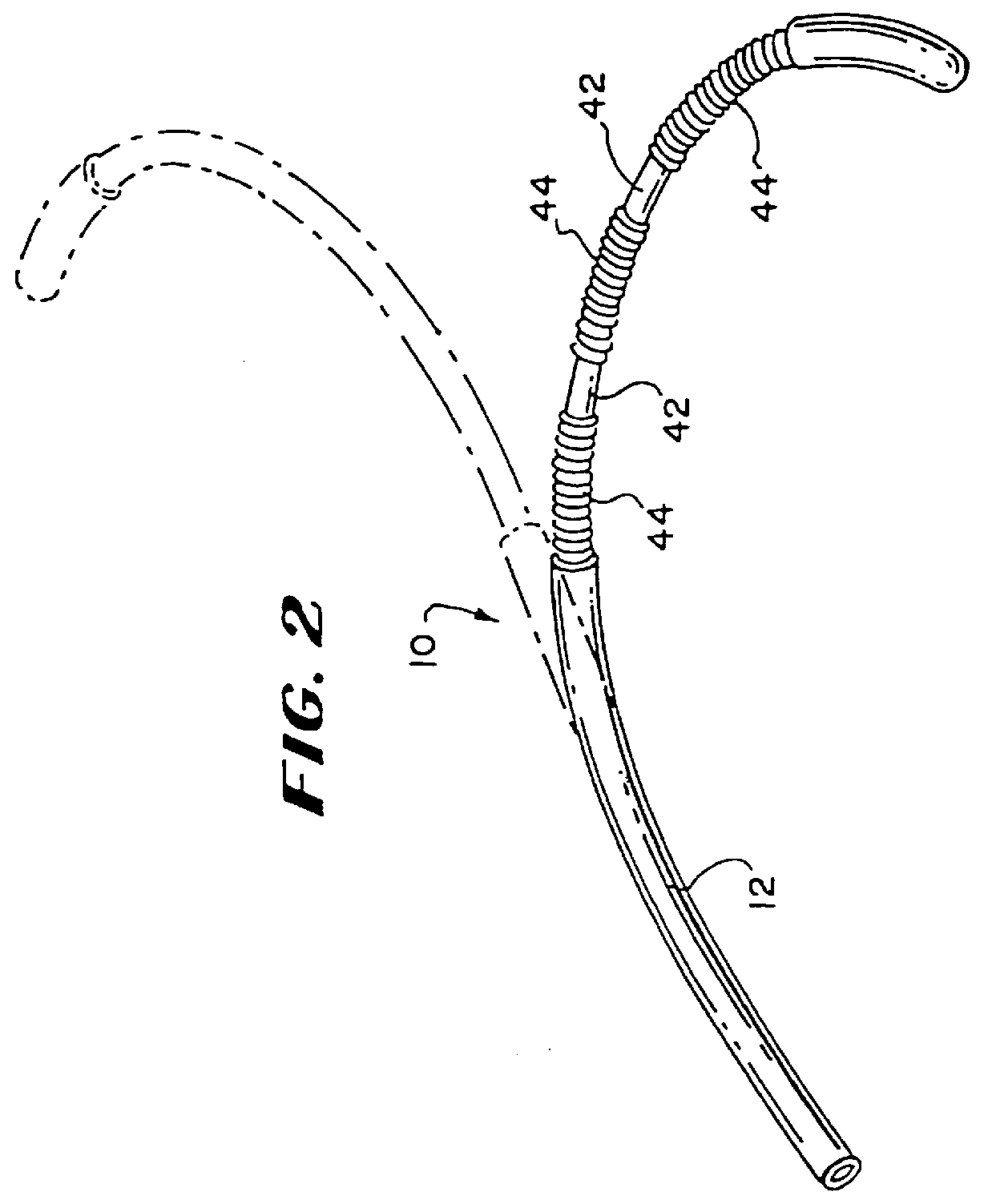
Flexible tissue ablation elements for making long lesions
Devices and methods for ablating body tissue. The devices include a support body and at least one elongated electrode. Adjacent windings are spaced apart to impart enhanced flexibility to the elongated electrode.
Owner:EP TECH
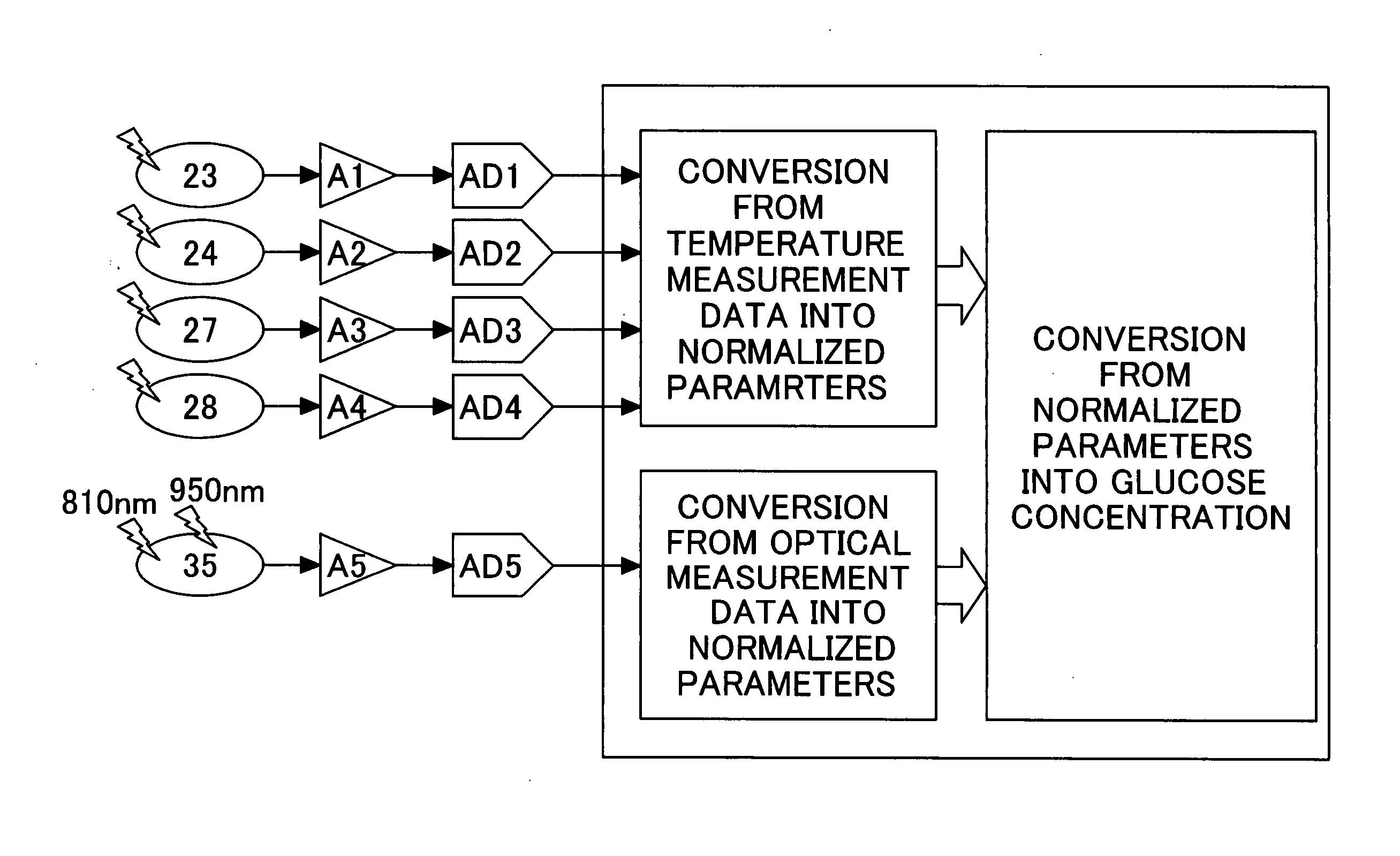
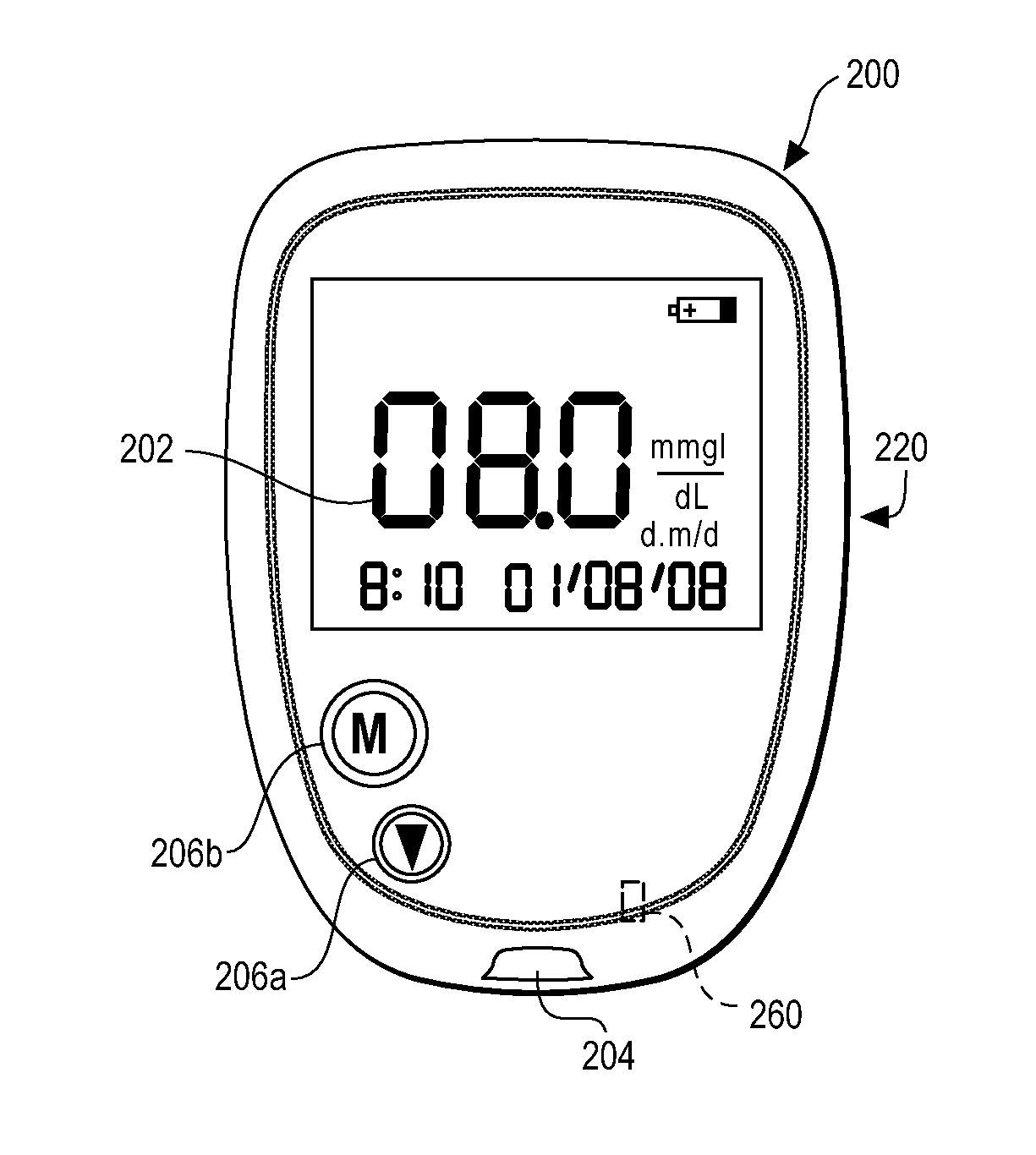
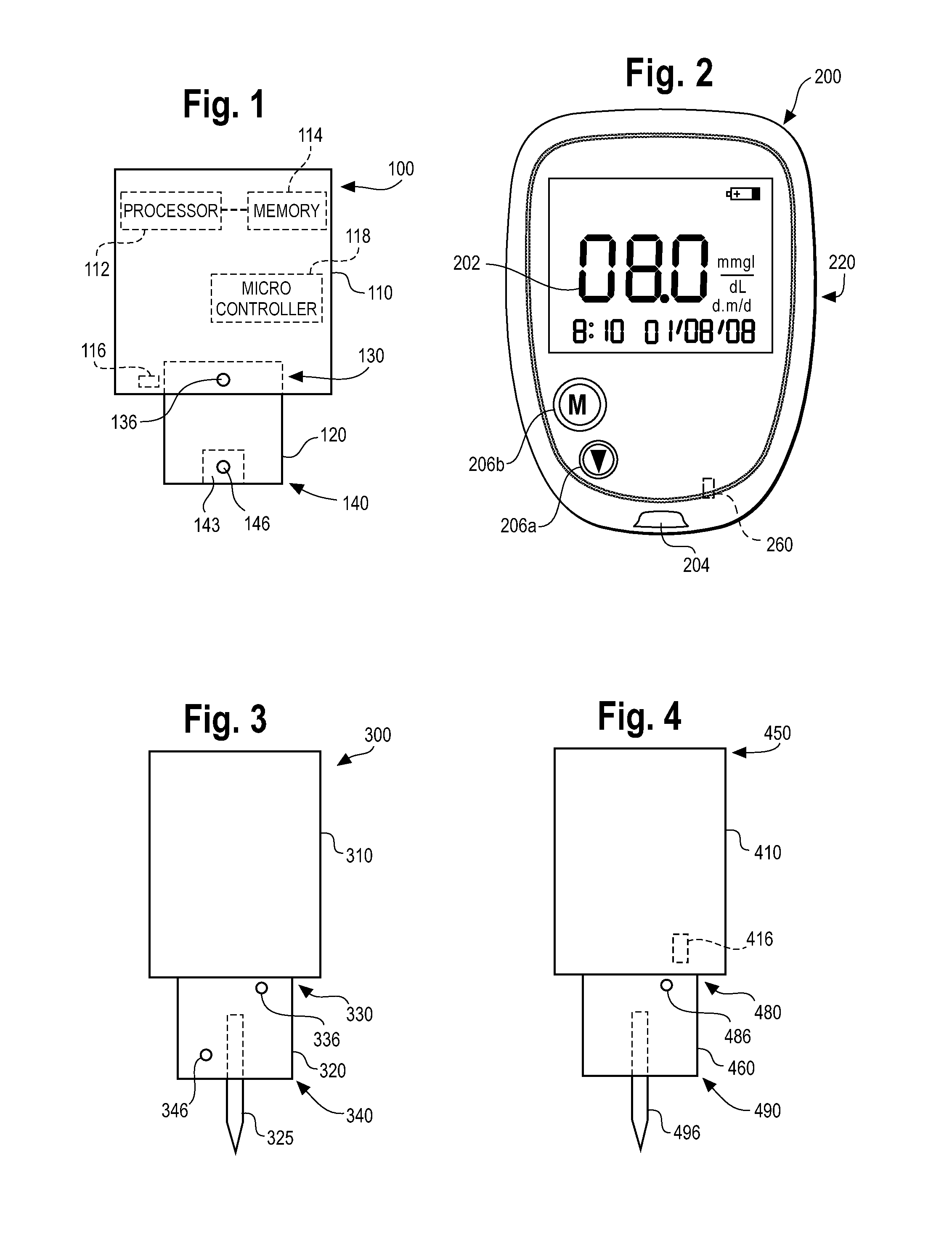
Blood sugar level measuring method and apparatus
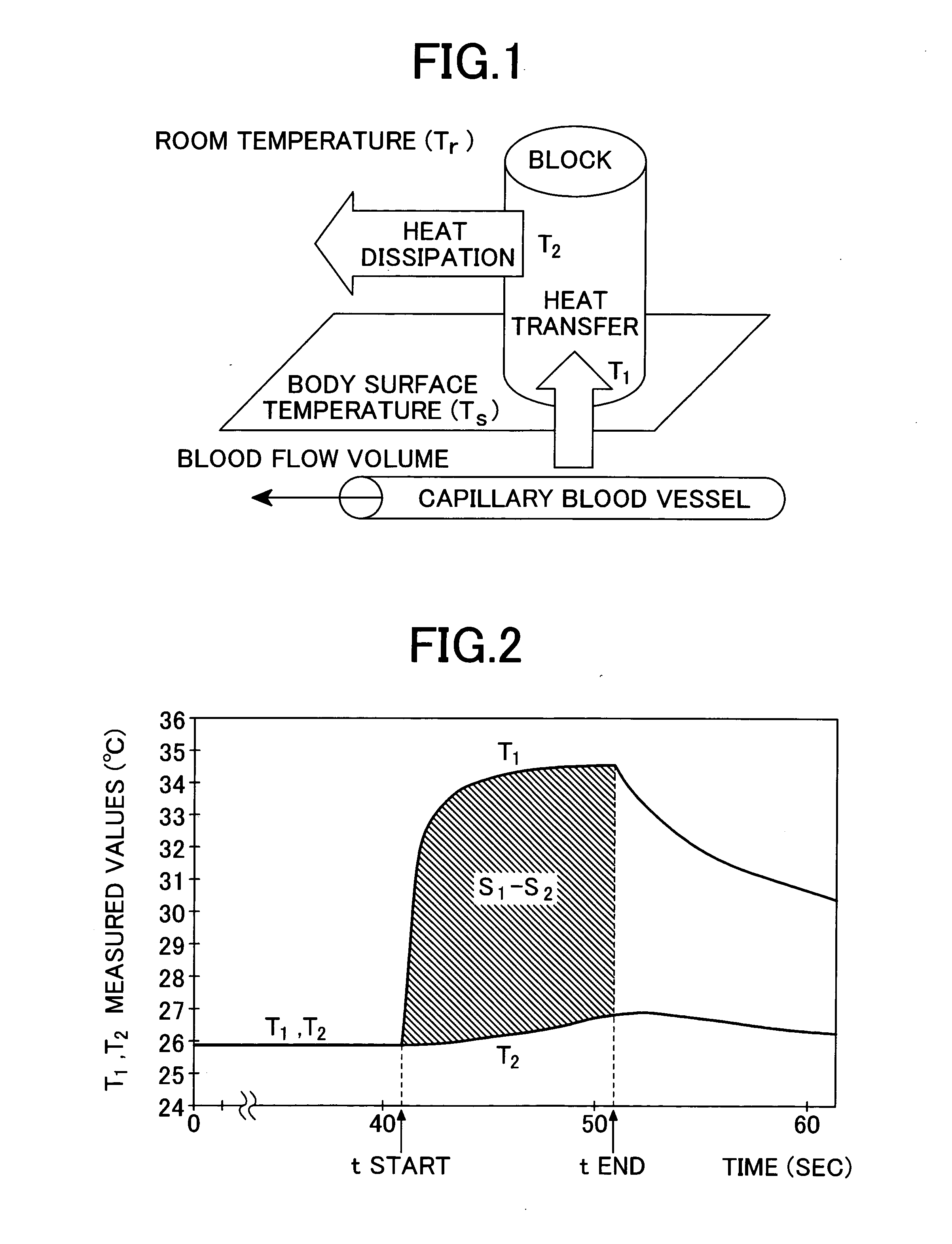
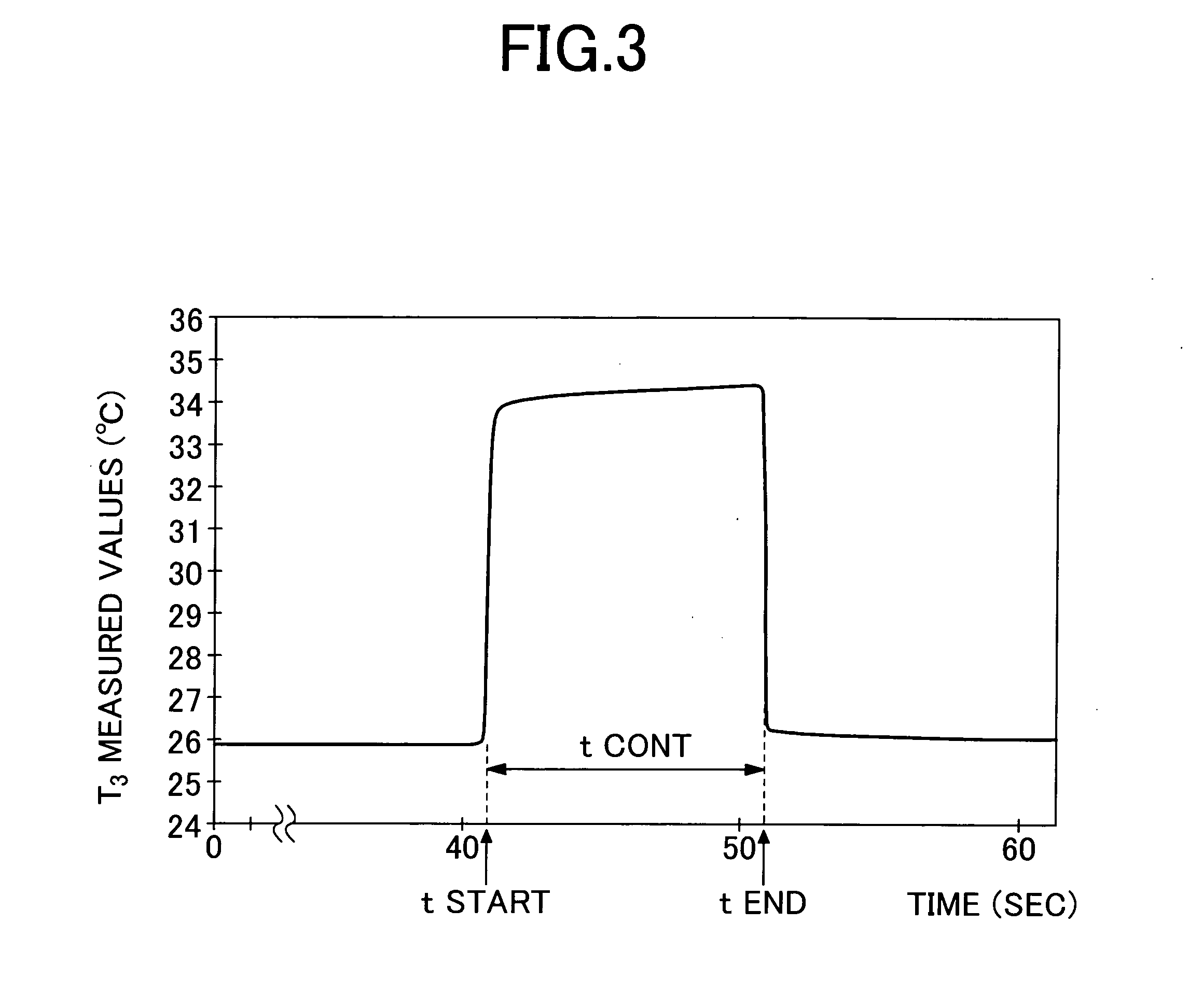
InactiveUS20050070777A1Thermometers using value differencesBody temperature measurementBiomedical engineeringBlood sampling
In a method and apparatus for determining the blood glucose concentration reliably and accurately based on temperature data obtained from a subject without requiring blood sampling, chronological changes in the output from a temperature detecting portion are monitored. Based on those chronological changes, the making of contact between a body surface and a body surface contact portion is detected, whereupon the acquisition of measurement data is started and an advance-notice display about the timing of departure of the body surface is made. The moment of departure of the body surface from the body surface contact portion is detected, and if that moment is before the noticed timing, or in the absence of detection of the departure of the body surface from the body surface contact portion even after a certain time following the noticed timing, an error display is made on the apparatus and the measurement is reset.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Detecting Energy and Environmental Leaks In Indoor Environments Using a Mobile Robot
InactiveUS20120078417A1Programme-controlled manipulatorThermometers using value differencesEngineeringTaking temperatures
Techniques for energy and environmental leak detection in an indoor environment using one or more mobile robots are provided. An energy leak detection system is provided. The energy leak detection system includes one or more mobile robots configured to move throughout at least a portion of a building and to take temperature and air flow measurements at a plurality of locations within the building. An environmental leak detection system is also provided. The environmental leak detection system includes one or more mobile robots configured to move throughout at least a portion of a building and to take airborne matter measurements at a plurality of locations within the building.
Owner:IBM CORP
Infrared ear thermometer
InactiveUS6435711B1Thermometer detailsThermometers using value differencesThermopileLinear relationship
An infrared ear thermometer includes a detector head housing, a heat sink, a recess formed in the heat sink, a thermopile sensor mounted within the recess, a thermistor, and temperature determination circuitry. The recess defines an aperture that limits the field of view of the thermopile sensor. The thermal capacities and conductivities of the heat sink and the thermopile sensor are selected so that the output signal of the thermopile sensor stabilizes during a temperature measurement. A method of determining temperature using the ear thermometer takes successive measurements, stores the measurements in a moving time window, averages the measurements in the moving window, determines whether the average has stabilized, and outputs an average temperature. A method of calculating a subject's temperature determines the temperature of a cold junction of the thermopile, looks up a bias and slope of the thermopile based upon the temperature of the cold junction, measures the output of the thermopile, and calculates the subject's temperature based upon a linear relationship between the output and the subject's temperature. The linear relationship is defined by the bias and the slope.
Owner:GERLITZ JONATHAN
Air conditioner and frost removal control method thereof
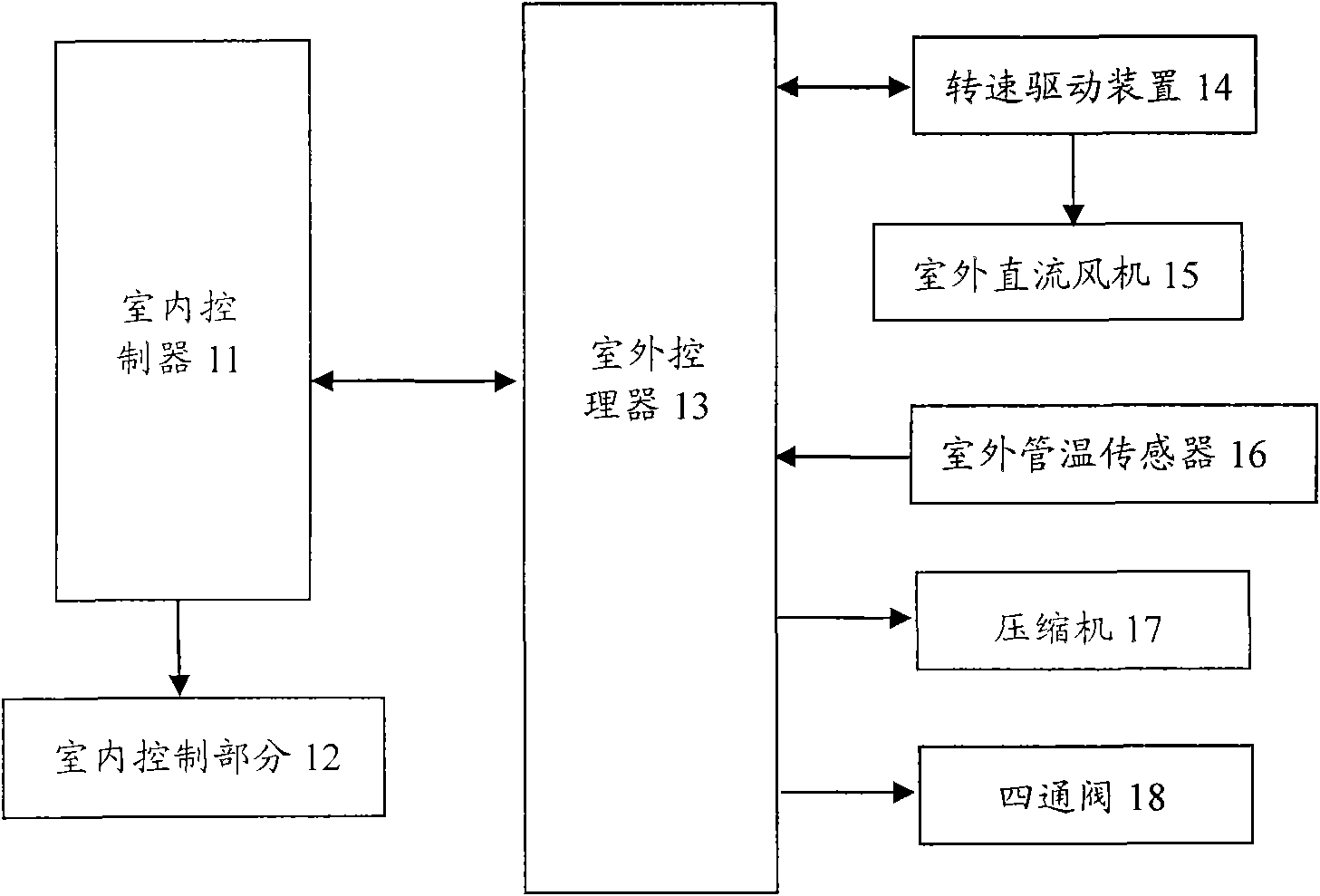
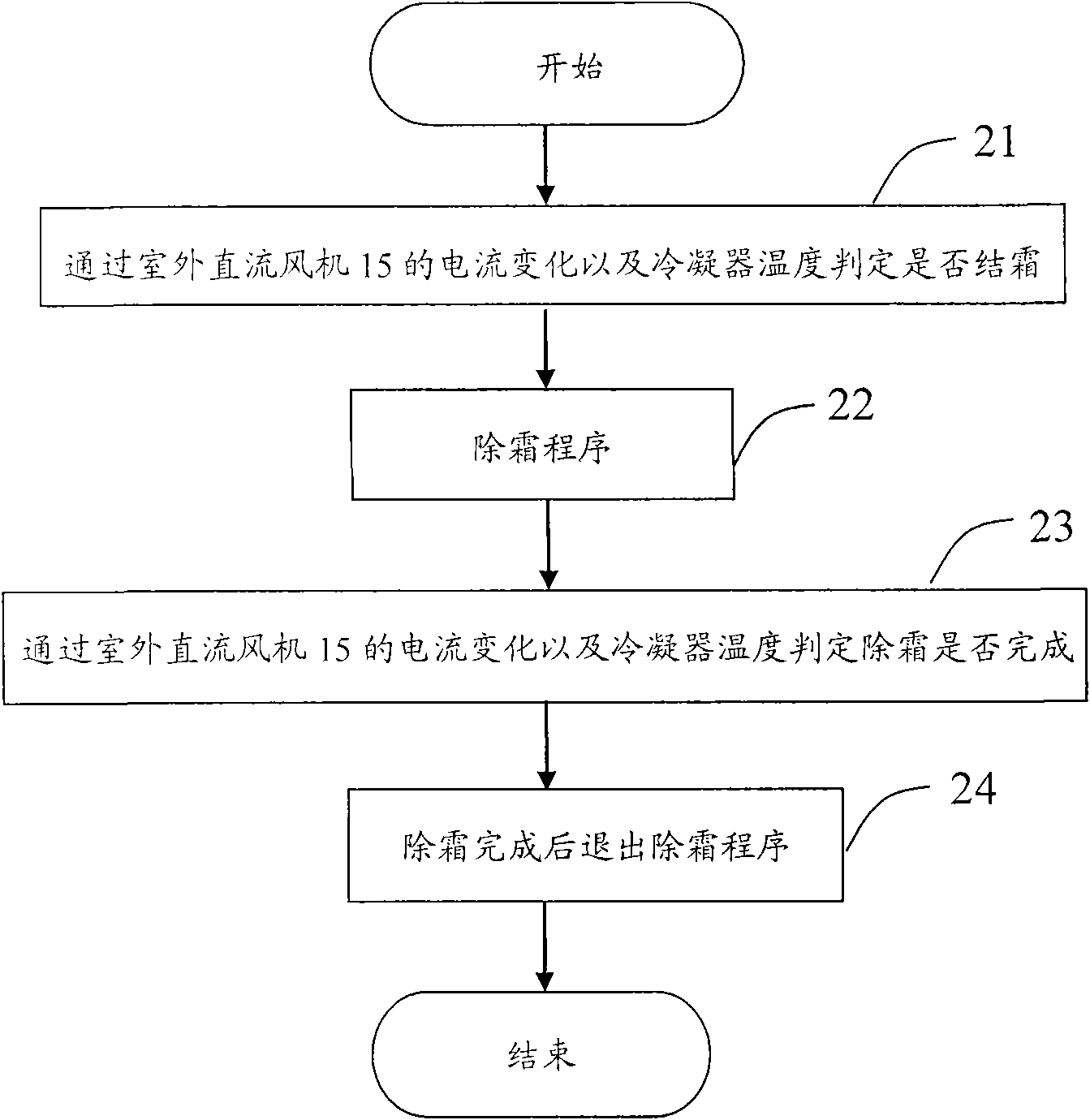
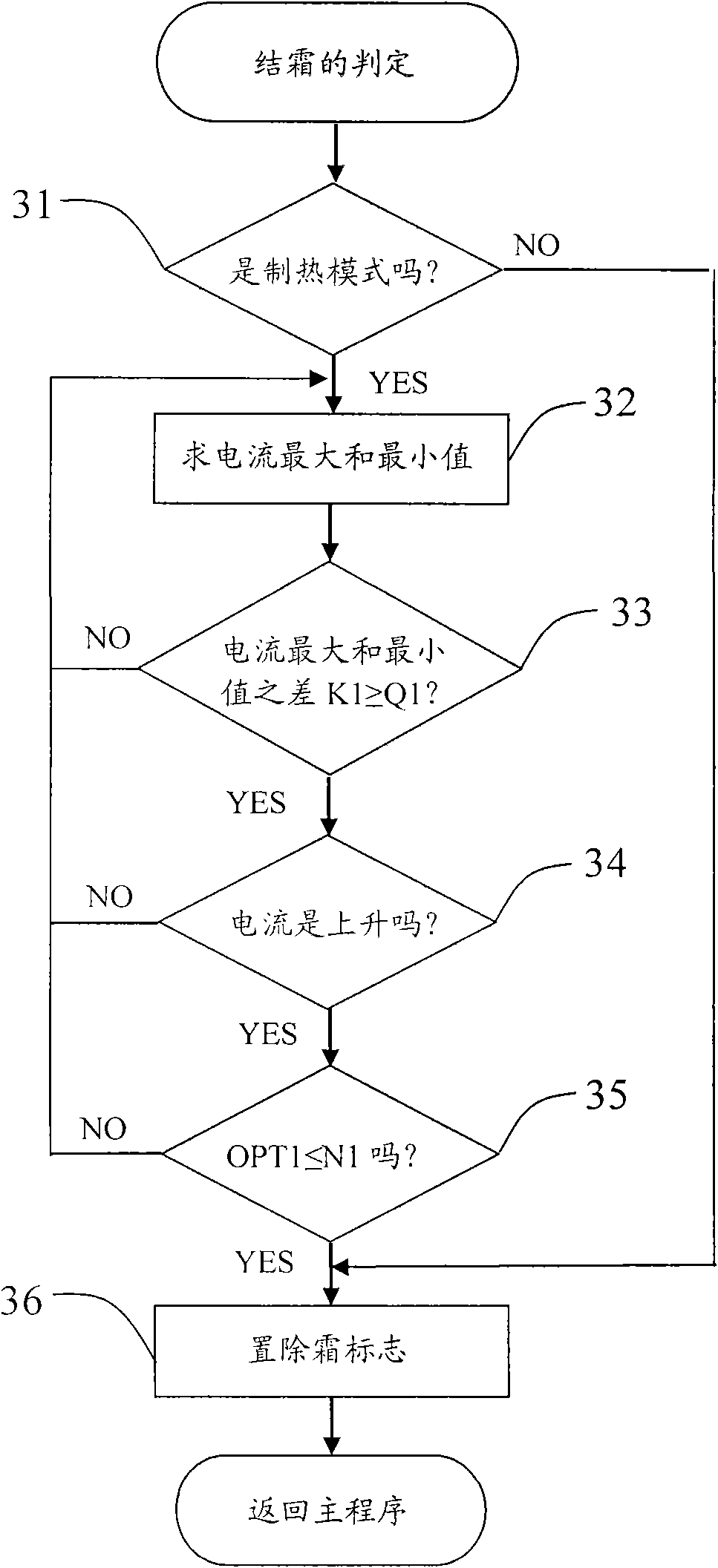
InactiveCN101660808AAccurate and smart defrostingThermometers using value differencesCurrent/voltage measurementFrostPower flow
The invention provides an air conditioner and a frost removal control method of the air conditioner. The air conditioner comprises a controller, an outdoor direct current fan, a condenser and a current detecting unit which detects the current changes of the outdoor direct current fan and feeds the detection result back to the controller. The frost removal control method of the air conditioner comprises the following steps: a, judging whether the air conditioner is frosted through the current changes of the outdoor direct current fan and the temperature of the condenser; and b, judging whetherthe frost removal is finished through the current changes of the outdoor direct current fan and the temperature of the condenser. The conditioner and the frost removal control method of the air conditioner can judge whether the condenser of the air conditioner is frosted and whether the frost removal is finished together by combining the temperature of the condenser with the current changes of theoutdoor direct current fan, and have the advantage of accurate and intelligent frost removal.
Owner:TCL CORPORATION
Method of temperature sensing
ActiveUS20060047480A1Thermometer detailsThermometers using value differencesProcess moduleEngineering
A method of diagnosing a temperature sensing system having a temperature sensor, a field processing module coupled to the temperature sensor, a bitbus, a fieldbus, and an auxiliary processing module communicating with the bitbus and the fieldbus. The method includes generating a temperature characteristic at the temperature sensor, processing the temperature characteristic at the field processing module, and generating field operating data including a temperature diagnostic parameter as a function of the temperature characteristic. The method also includes communicating the field operating data including the temperature diagnostic parameter over the bitbus from the field processing module to the auxiliary processing module, generating at the auxiliary processing module auxiliary field data as a function of the received field operating data, and communicating the auxiliary field data over the fieldbus.
Owner:WATLOW ELECTRIC MFG
Differential temperature sensor device for use in the detection of breast cancer and breast disease
InactiveUS6086247AImprove ease of useImprove comfortThermometers using value differencesSurgeryDiseaseGynecology
A differential temperature sensor device is provided for detecting differential temperatures in a human breast. A pad having a contoured design is covered with an adhesive layer having differing release forces on its two sides to insure sustained contact between the breast and temperature sensors and to ease removal after use. Temperature sensors are arranged in a useful pattern and covered with a silicon lidding which is removed prior to use. The device is especially useful for the detection of breast cancer and breast disease.
Owner:LIFE MEDICAL TECH
Method for estimating service life of motor, motor control system, blower system, and multicopter system
InactiveUS10374544B2Accurate estimateAC motor controlElectric motor controlControl systemMotor control
Owner:NIDEC CORP
Distributed diagnostic operations system
A distributed operations system having integrated diagnostics, a bitbus and a fieldbus and includes a field device for generating a field operating characteristic and a field processing module for receiving the field operating characteristic from the field device. The field processing module includes a field diagnostic component and a field communication component configured for communication over the bitbus. The field processing module is configured for generating field operating data including a field diagnostic parameter as a function of the field operating characteristic. An auxiliary processing module is configured for communicating with the bitbus and receiving the field operating data. The auxiliary processing module includes an auxiliary diagnostic component and an auxiliary communication component having a fieldbus interface and a gateway component. The auxiliary processing module is also configured for generating auxiliary field data as a function of the field operating data and for communicating the auxiliary field data over the fieldbus.
Owner:WATLOW ELECTRIC MFG
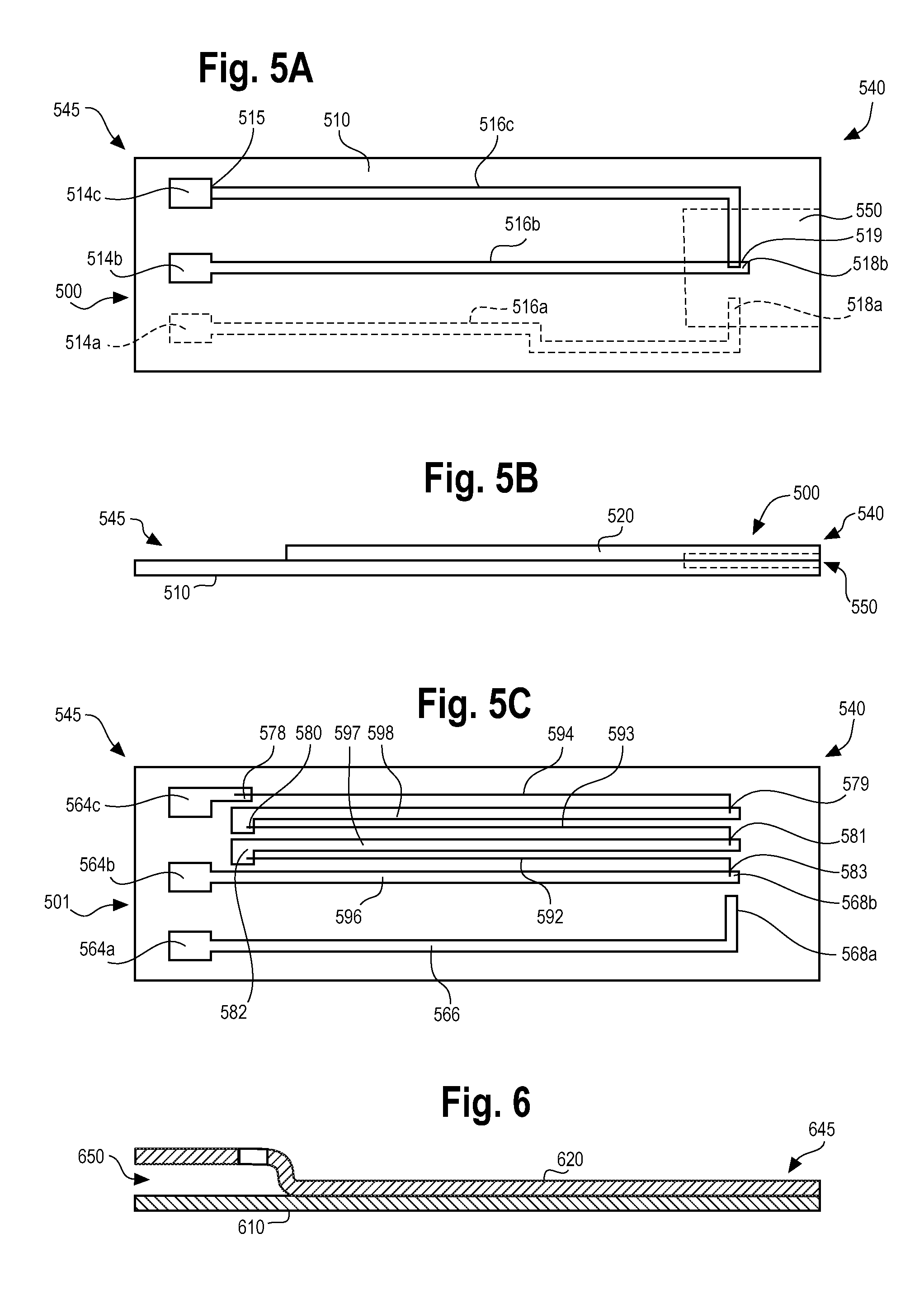
System and Apparatus for Determining Temperatures in a Fluid Analyte System
ActiveUS20100319436A1Thermometers using value differencesWeather/light/corrosion resistanceAnalyteEngineering
A test sensor includes a body, a first conductive trace, a second conductive trace, and a third conductive trace. The body includes a first region that has a fluid-receiving area, a second region separate from the first region, and a first temperature sensing interface disposed at or adjacent to the fluid-receiving area. The fluid-receiving area receives a sample. The first trace is disposed on the body, and at least a portion of the first trace is disposed in the first region. The second and third traces are disposed on the body. The third trace extends from the first to the second regions. The third trace is connected to the first trace at the first temperature sensing interface. The third trace includes a different material than the first trace. A first thermocouple is formed at the first temperature sensing interface. The thermocouple provides temperature data to determine an analyte concentration.
Owner:ASCENSIA DIABETES CARE HLDG AG
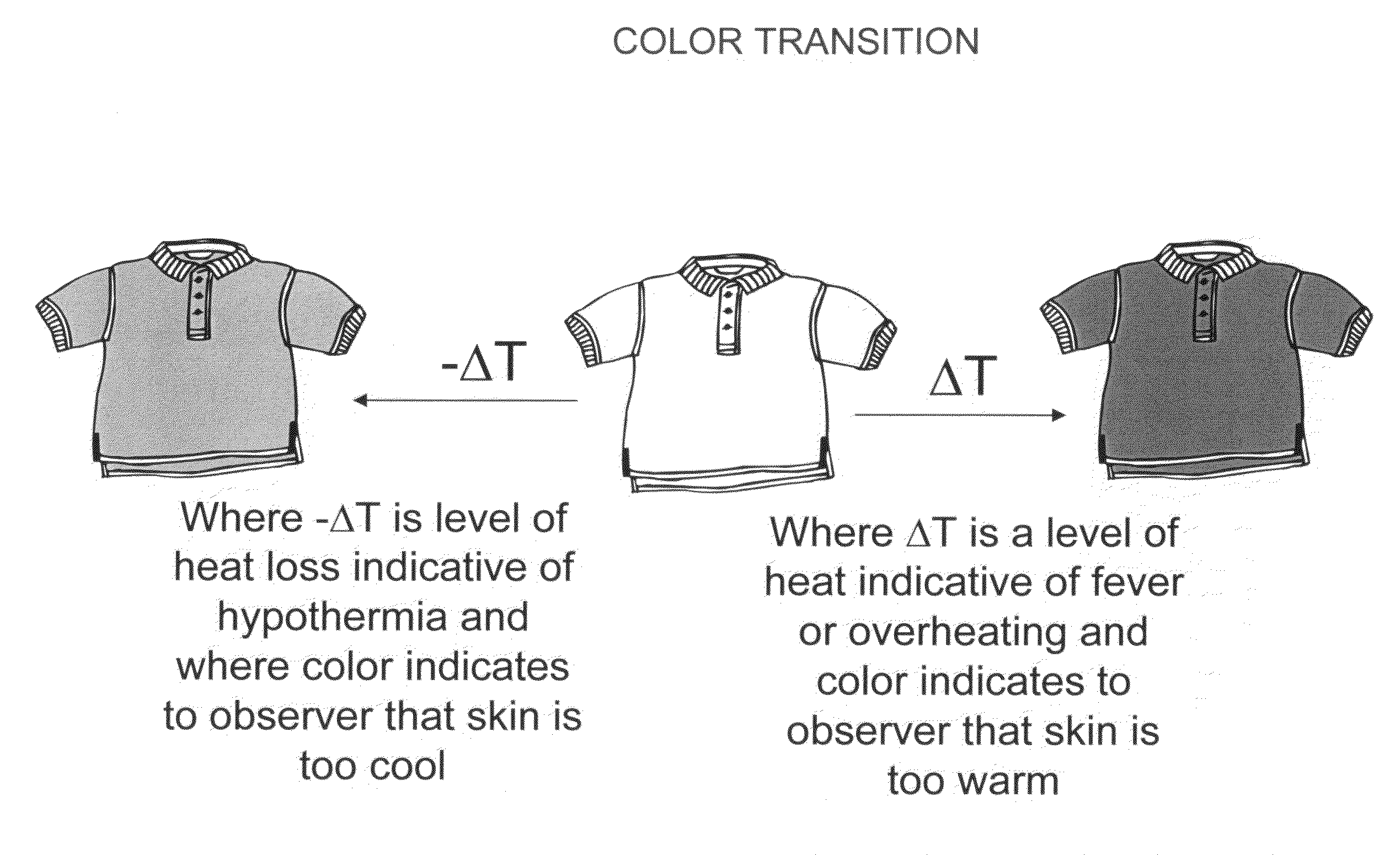
Method and articles for sensing relative temperature
ActiveUS20080279253A1Thermometer detailsThermometers using value differencesEngineeringImpaired Circulation
A method for determining the relative body temperature of a warm-bodied animal is described. The method, in part, involves an article of manufacture that provides a manifestation, or visually observable indication on an exterior surface, of a relative state of the warm-bodied animal's body temperature, either being too cold or too hot, as a measure against relative levels of hypothermia or hyperthermia, or poor circulation.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
Human body detecting method, device and air conditioner
ActiveCN104061662AAvoid disadvantagesEasy to control intelligentlyThermometers using value differencesSpace heating and ventilation safety systemsInfraredHuman body
The invention discloses a human body detecting method, device and air conditioner. According to the method, based on the character that human body temperature and indoor background temperature have obvious temperature difference, human body detecting is carried out through the temperature changing situation of various zones indoors, namely the method comprises the steps that current indoor temperature field data are obtained, and processed current indoor temperature field data are used as indoor current temperature, wherein indoor current temperature is the set of the current temperatures of pixel points in a pixel matrix corresponding to a temperature place; and then the indoor current temperature and the indoor background temperature corresponding to the indoor current temperature are subjected to differential treatment, the differential temperatures of the pixel points are obtained, pixel points with the differential temperatures not smaller than a preset threshold value are subjected to clustering, N heat sources are obtained, and finally heat sources with the number not smaller than the preset number of pixels are determined as human bodies. Human body detecting is achieved through the temperature changing situations of the zones indoors, various shortcomings of a current infrared detection mode are overcome, and detecting accuracy is improved.
Owner:GREE ELECTRIC APPLIANCES INC
Passive Microwave Assessment of Human Body Core to Surface Temperature Gradients and Basal Metabolic Rate
InactiveUS20120029369A1Enhances ability to quantifyEnhances to mapThermometers using value differencesBody temperature measurementDiseaseHuman body
A passive microwave thermography apparatus uses passive microwave antennas designed for operation, for example, at WARC protected frequencies of 1.400 to 1.427 GHz and 2.690 to 2.70 GHz (for core body gradient temperature measurement) and 10.68 to 10.700 GHz or higher microwave frequency (for surface body gradient temperature measurement) and a related directional antenna or antenna array to measure microwave radiation emanating from an animal, especially, a human body. The antennae may be radially directed toward a point within or on the surface of a human body for comparison with known temperature distribution data for that point and a given ambient temperature. Each frequency band may provide a plurality of adjacent noise measuring channels for measuring microwave noise naturally emitted by the human body. The apparatus measures short-term changes in, for example, core and body surface temperatures to establish a basal metabolic rate. Changes in core body temperature may be stimulated by the administration of food or certain organic and drug-related substances or stress to induce a change in basal metabolic rate over time. These changes correlate directly with a human subject's metabolism rate at rest and under certain dietary constraints and can be used to determine courses of treatment for obesity, metabolic disease, and other disorders. The apparatus can also be used to remotely monitor patients and subjects without physical contact.
Owner:ICOVE DAVID +3
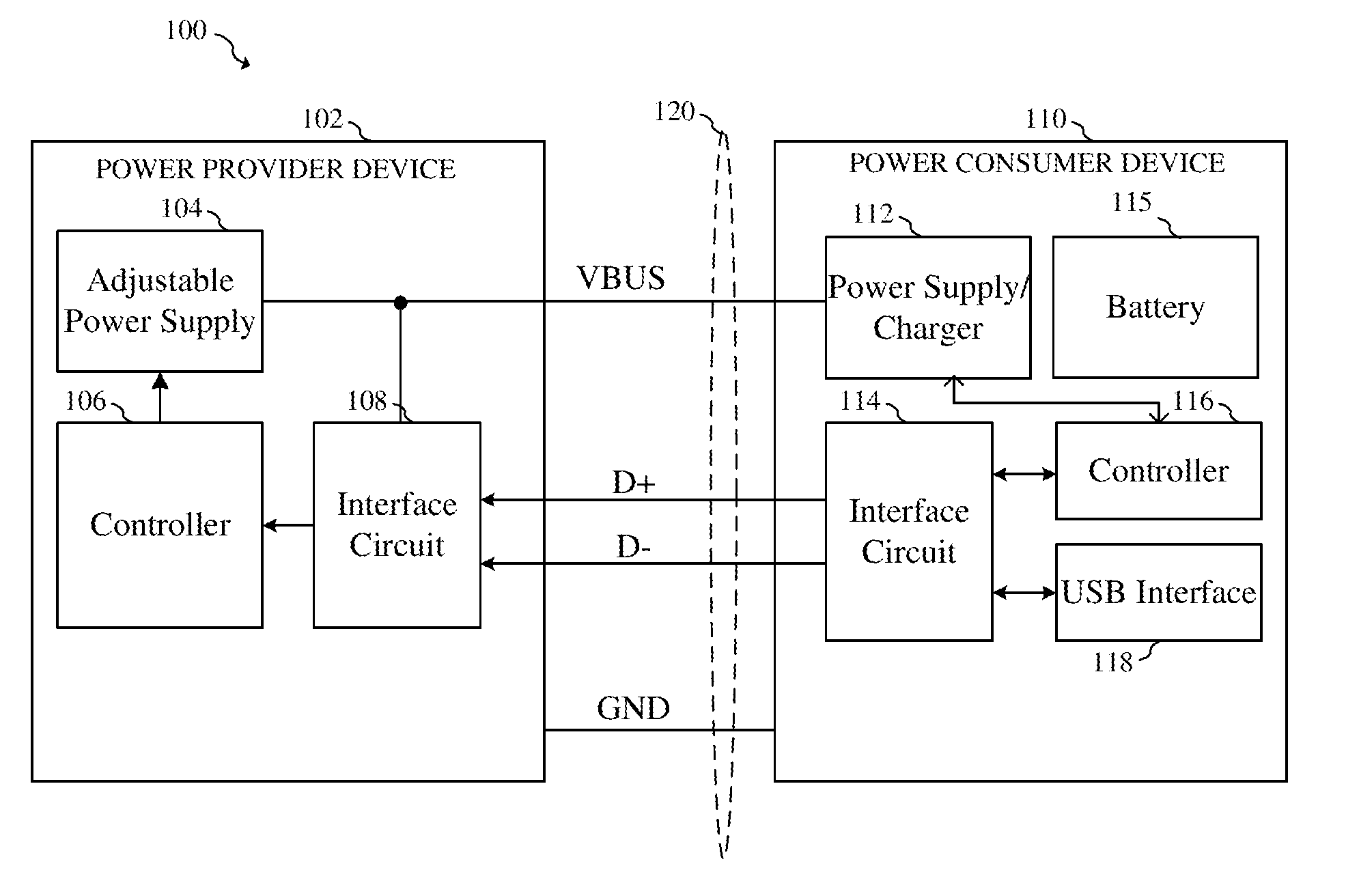
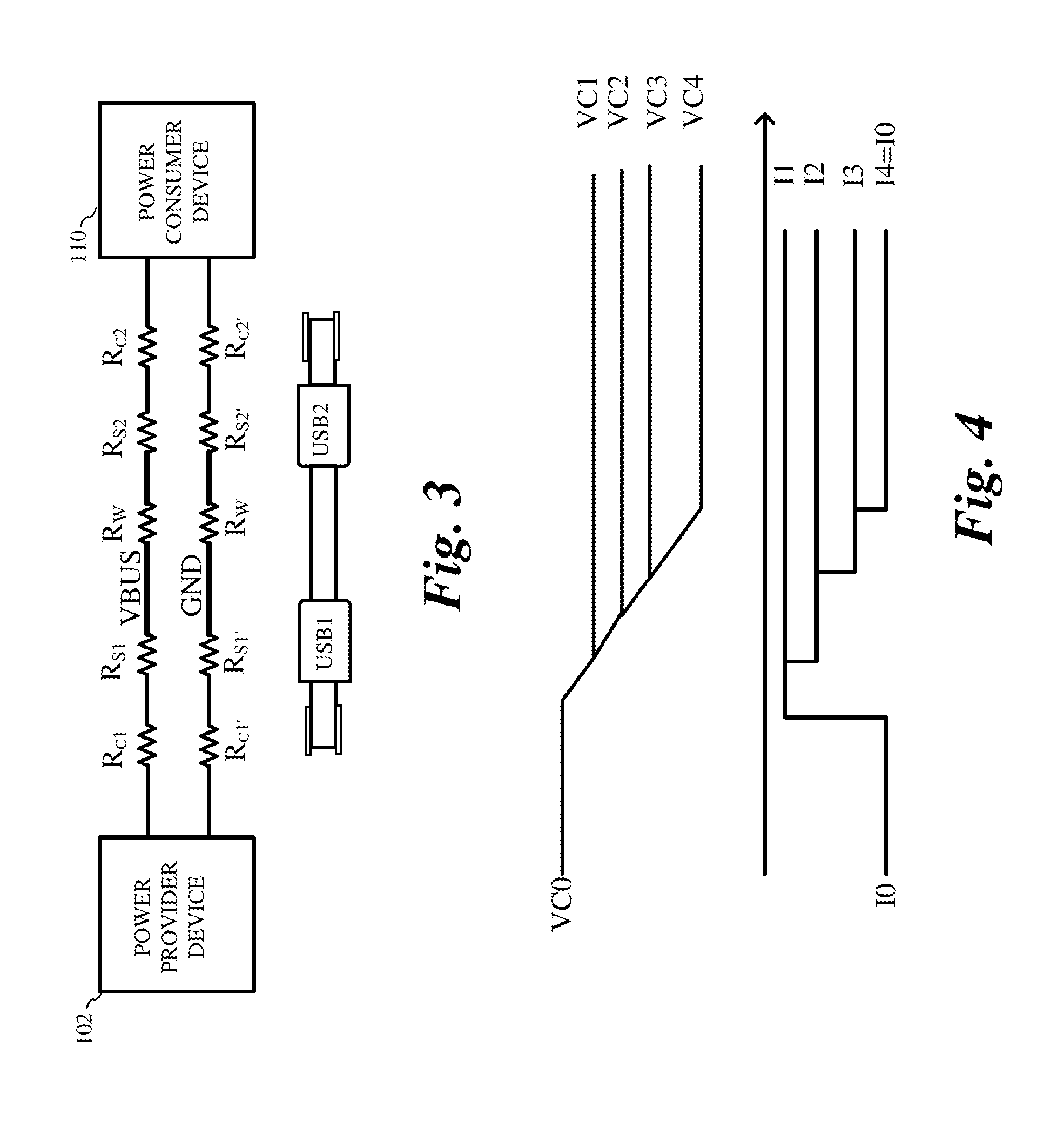
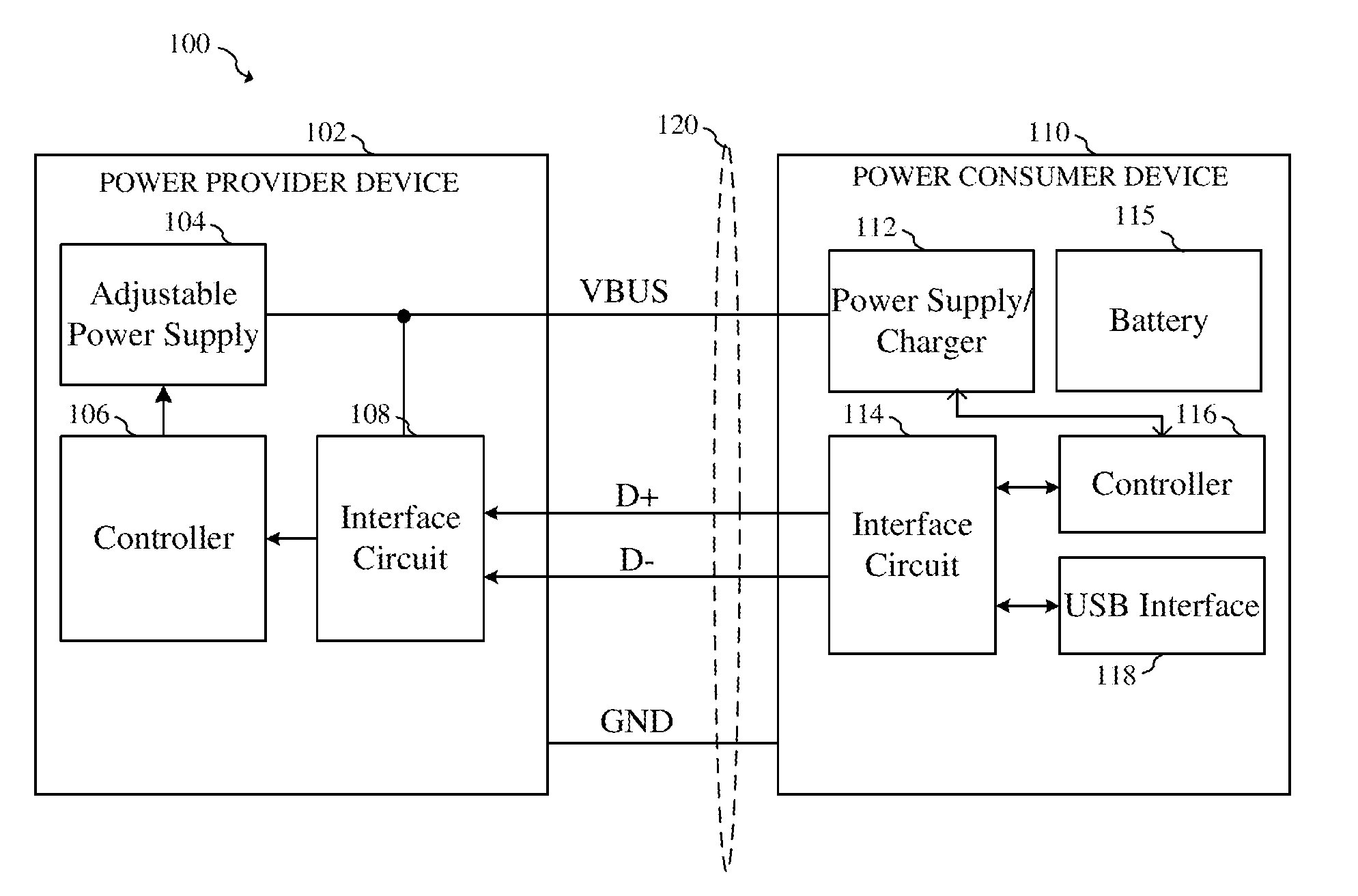
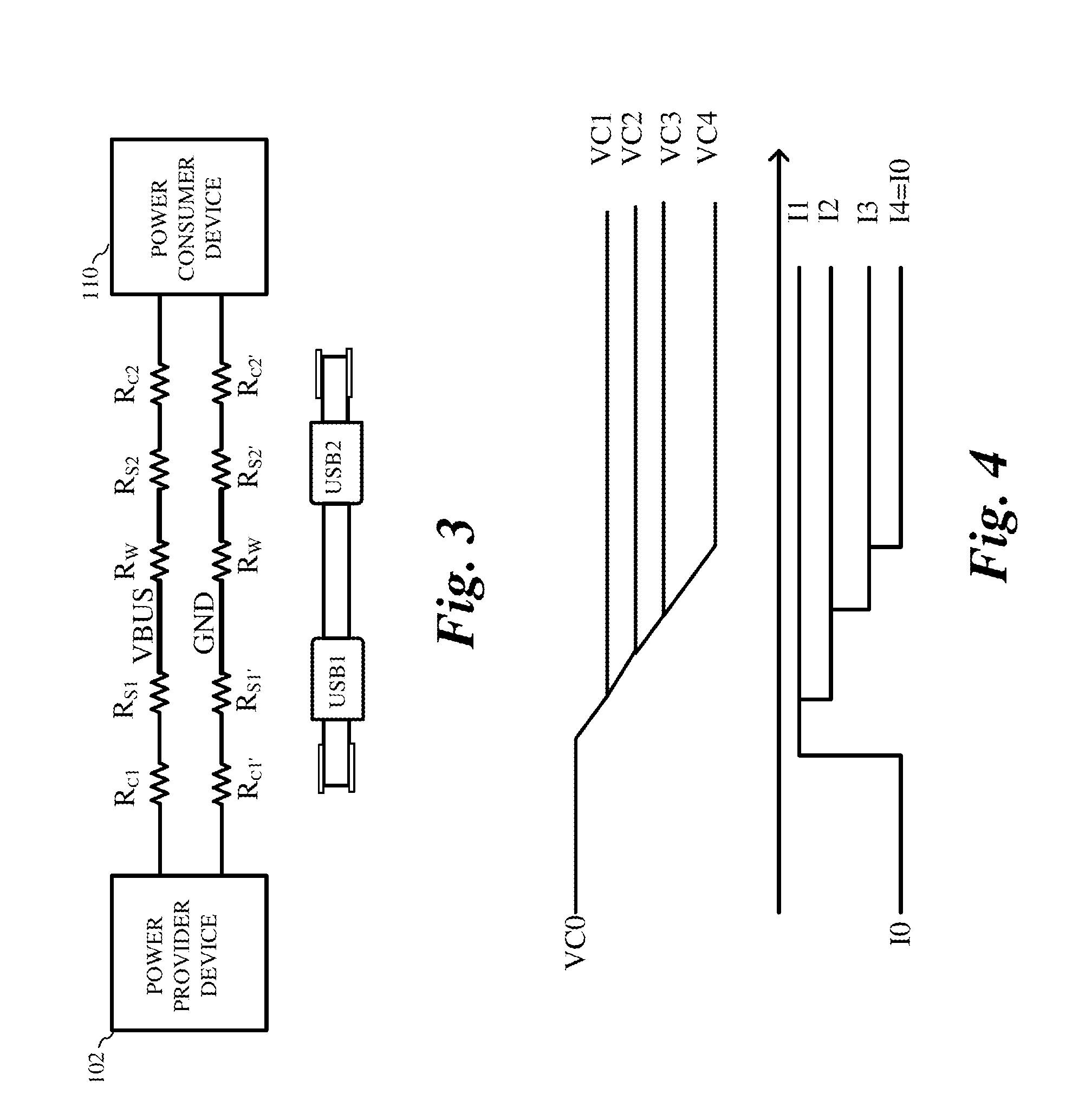
Cable quality detection and power consumer devices
ActiveUS9158325B1Batteries circuit arrangementsThermometers using value differencesElectric cablesElectric power
In one embodiment, a method includes receiving power at a power consumer device coupled to a power provider device by a cable. The received power is supplied at a first current at an input of the power consumer device and is supplied to a load in the power consumer device. The method includes measuring a rate of change of the voltage at the input of the power consumer device, and determining whether the rate of change of the voltage at the input of the power consumer device is less than a first target rate of change of voltage. The current received at the input of the power consumer device is reduced to a second current lower than the first current if the rate of change of the voltage at the input of the power consumer device is greater than the first target rate of change of voltage.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
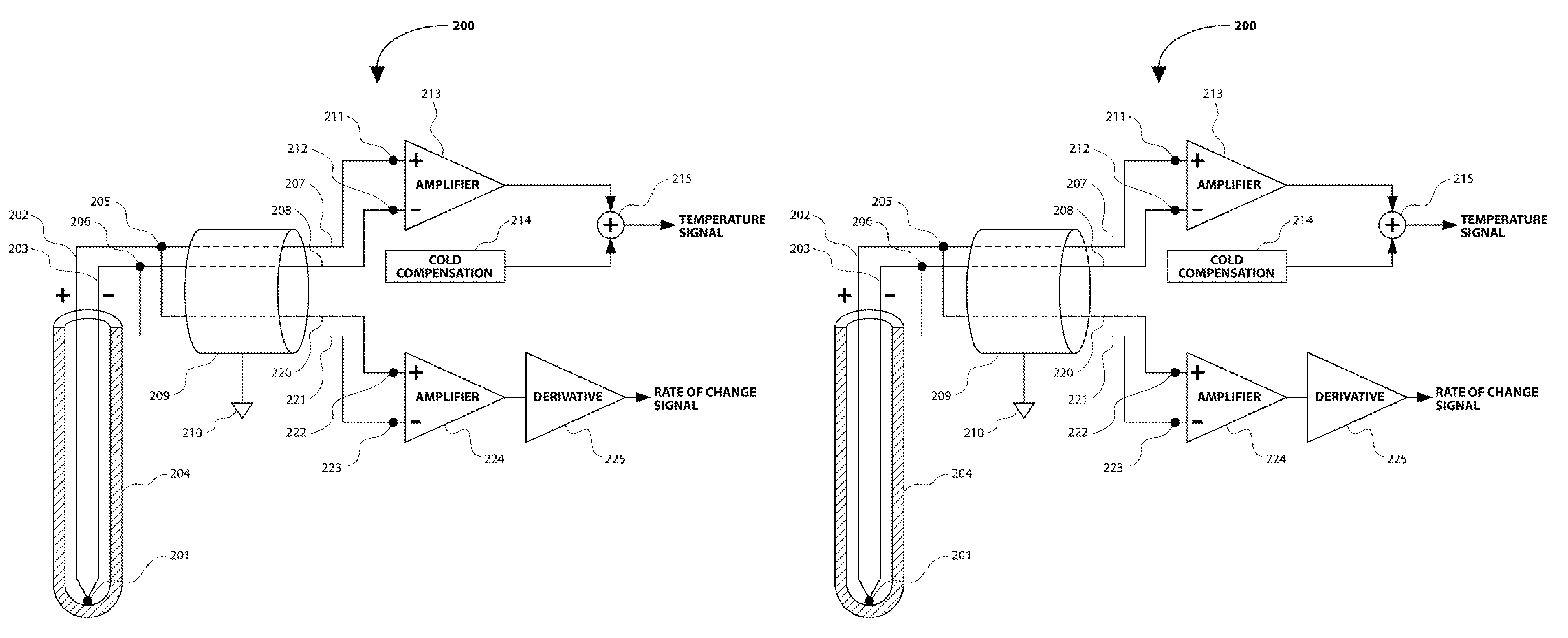
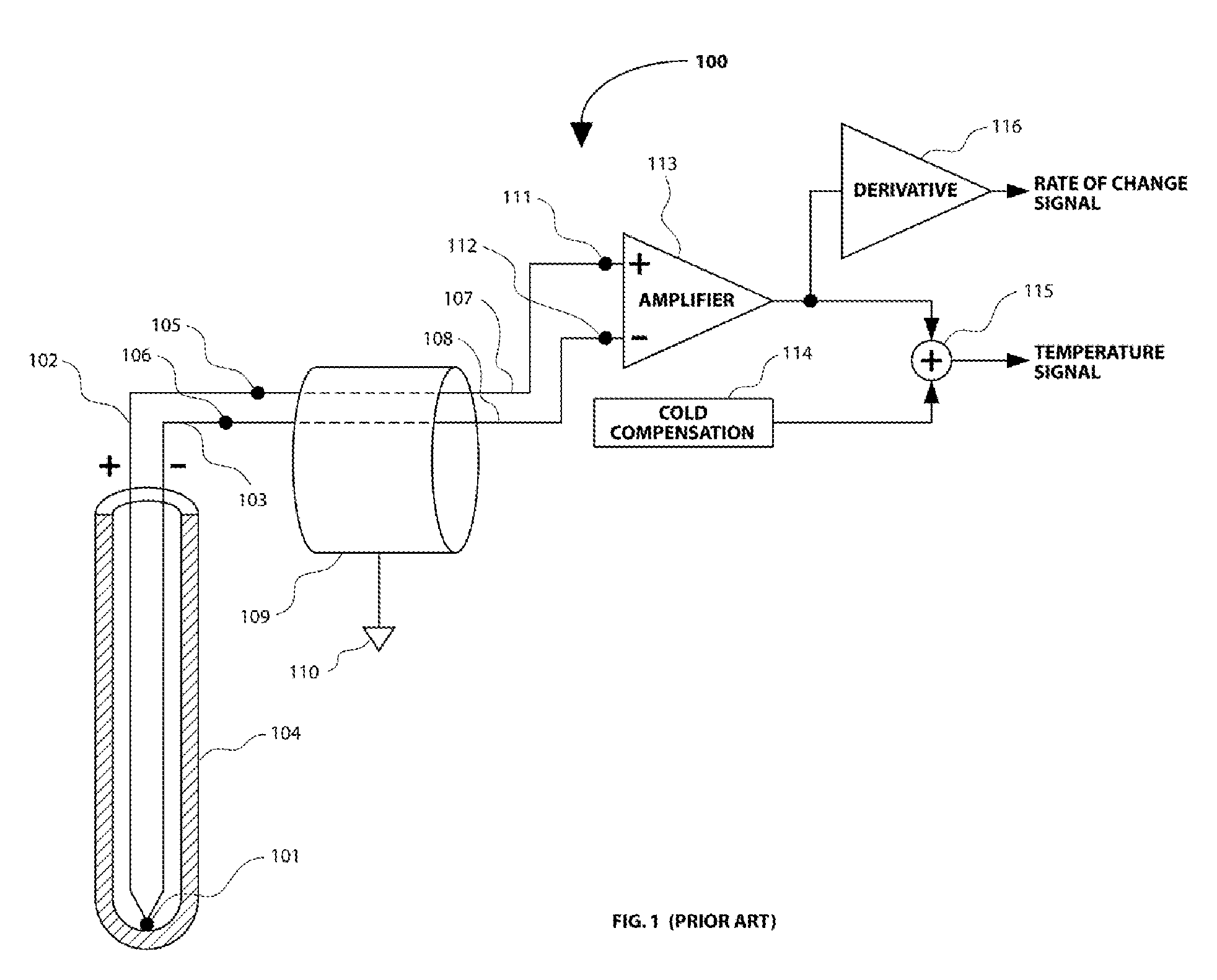
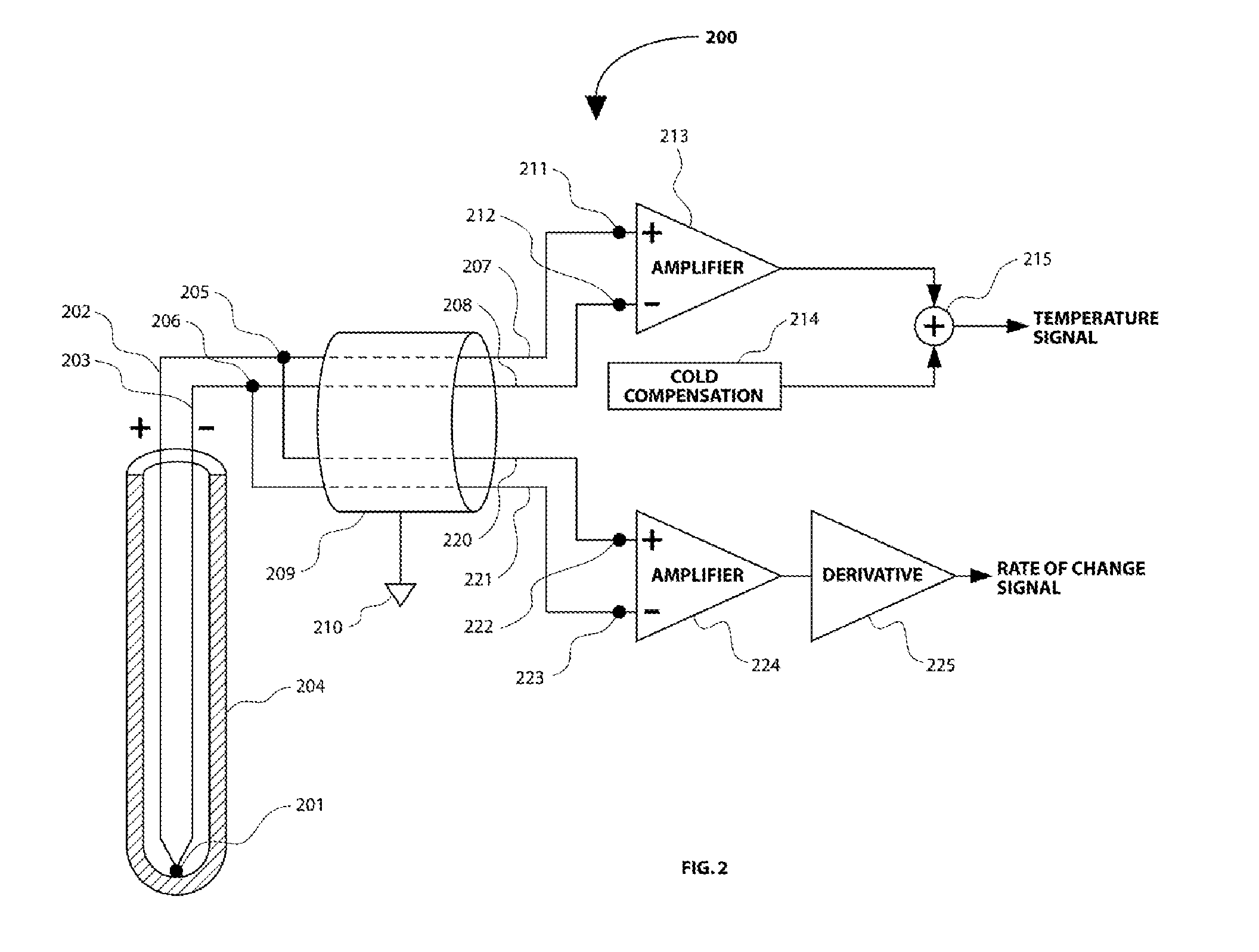
Method and apparatus for measurement of temperature and rate of change of temperature
InactiveUS8602643B2Accurate measurementHigh fidelity measurementThermometers using value differencesThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsElectrical conductorAlloy
A method and apparatus is presented for obtaining of accurate measurements of the temperature of a thermocouple and high fidelity measurements of the rate of change of the temperature of a thermocouple. A first sub-circuit is connected to the thermocouple with two conductors made of two different thermocouple alloys which are substantially the same as the alloys used in the construction of the thermocouple. A second sub-circuit is connected to the thermocouple with two conductors made of substantially identical material, such as copper. The first sub-circuit provides an accurate measurement of the temperature of the thermocouple. The second sub-circuit provides a high fidelity measurement of the rate of change of the temperature of the thermocouple.
Owner:GARDINER DAVID PHILLIP
Temperature sensitive color changing cable apparatus
A communication cable apparatus, such as an actual cable, a connector for a cable end, a jacks for receiving a cable connector, or a holder or tie for bundling cables, includes at least one component formed of a material which can change color. The color change is visible to a human observer and is indicative of a temperature of the component. One or more colors changes may occur to indicate one or more ranges of temperature.
Owner:COMMSCOPE INC
Temperature measuring device of a power semiconductor apparatus
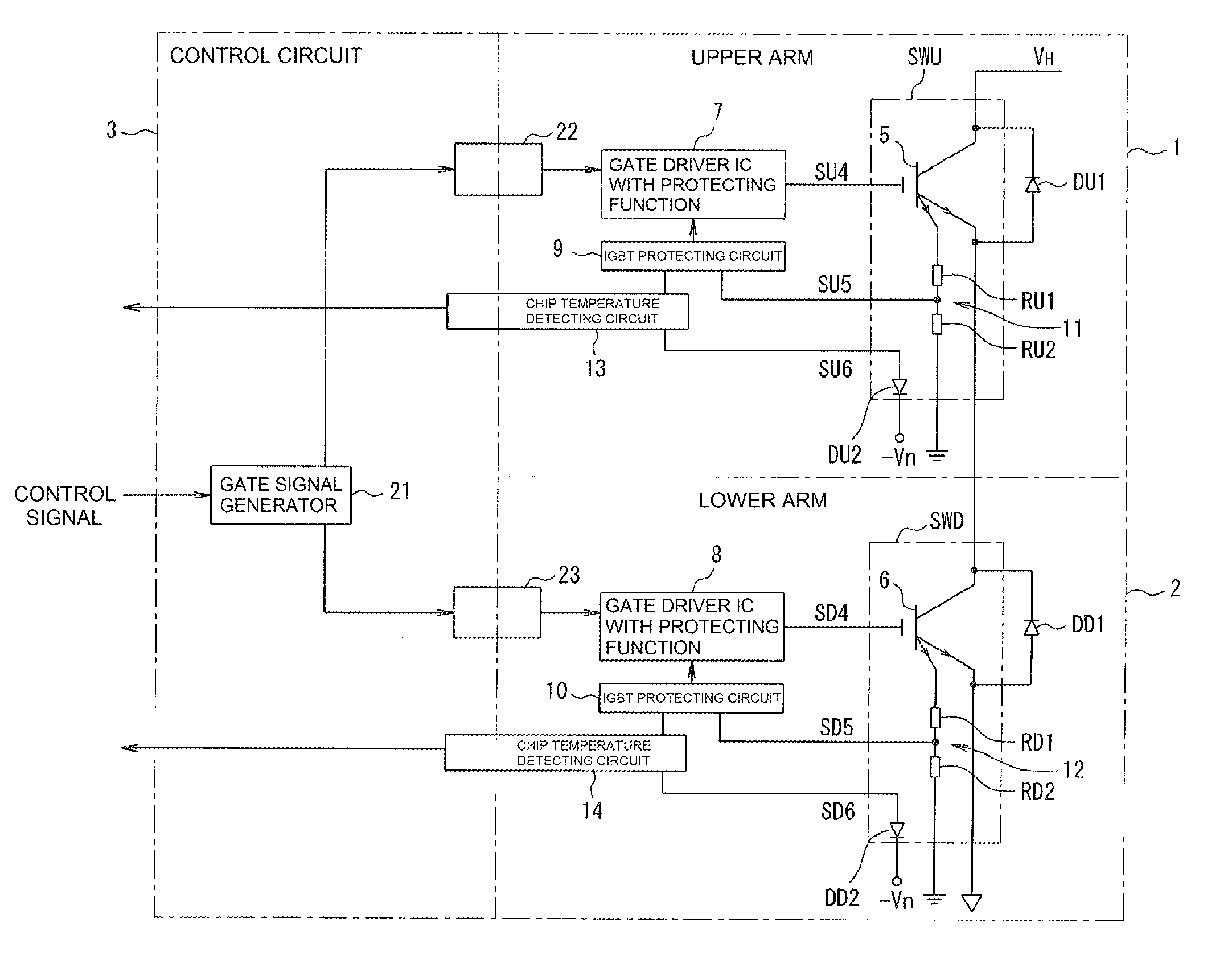
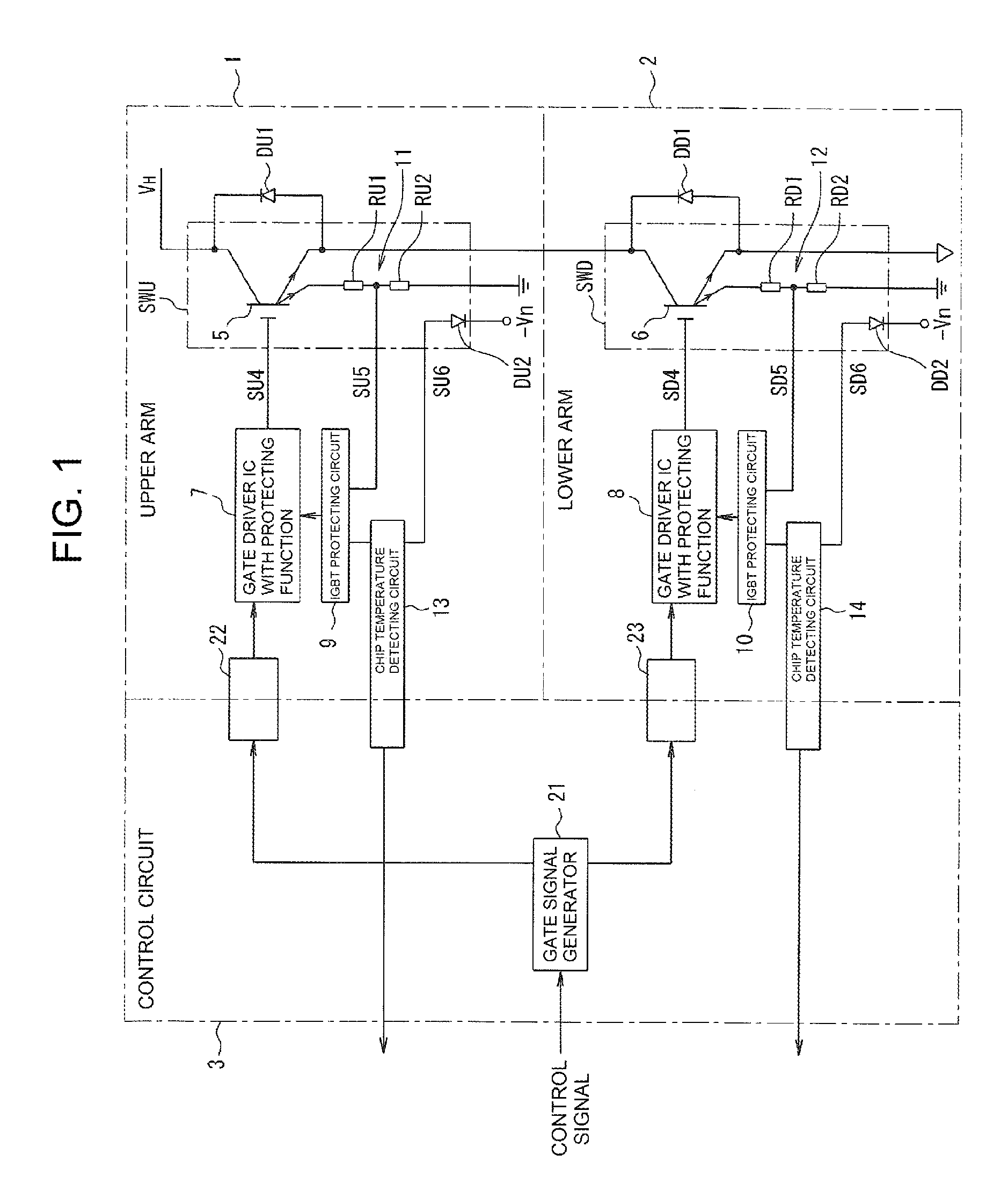
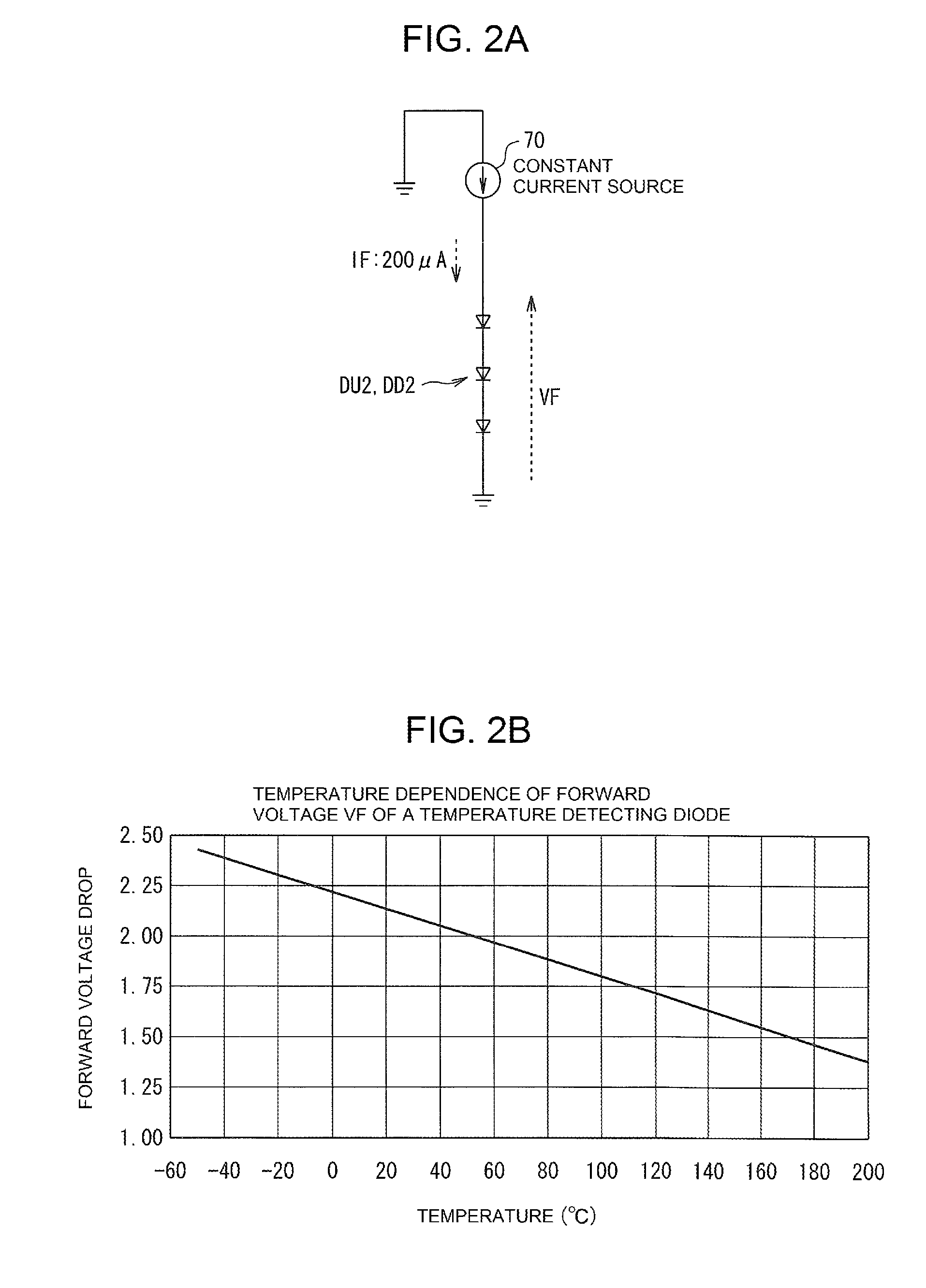
ActiveUS20130060499A1Easy to calculateEasy to operateThermometer with A/D convertersThermometers using value differencesVoltage referenceLine segment
A temperature measuring device of a power semiconductor apparatus that accurately detects chip temperature even where a gradient of the measured characteristic line segment is different from a designed gradient, including a chip temperature detecting circuit that includes an A / D converter delivering a measurement value of a digital converted forward voltage across a temperature detecting diode and an operational processing unit for calibration and chip temperature calculation. In calibration processing, different known reference voltages are applied by a reference connected in place of the diode and a gradient of the line segment connecting the measurement values is calculated. The gradient is stored in a memory with an offset correction value that is one of the measurement values. A chip temperature is calculated based on a forward voltage across the diode calculated based on the measurement value and the stored values of the gradient and the offset correction value.
Owner:FUJI ELECTRIC CO LTD
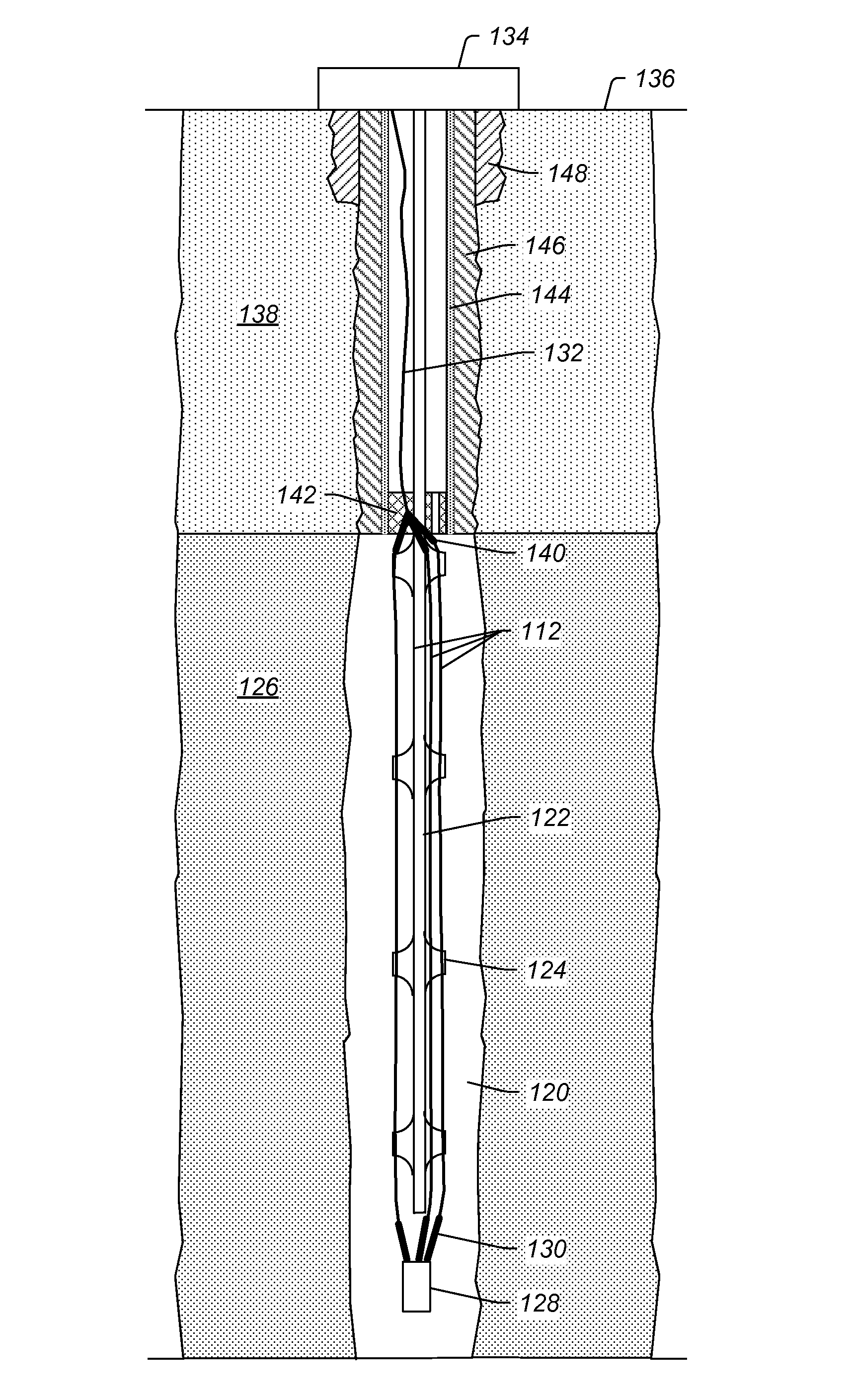
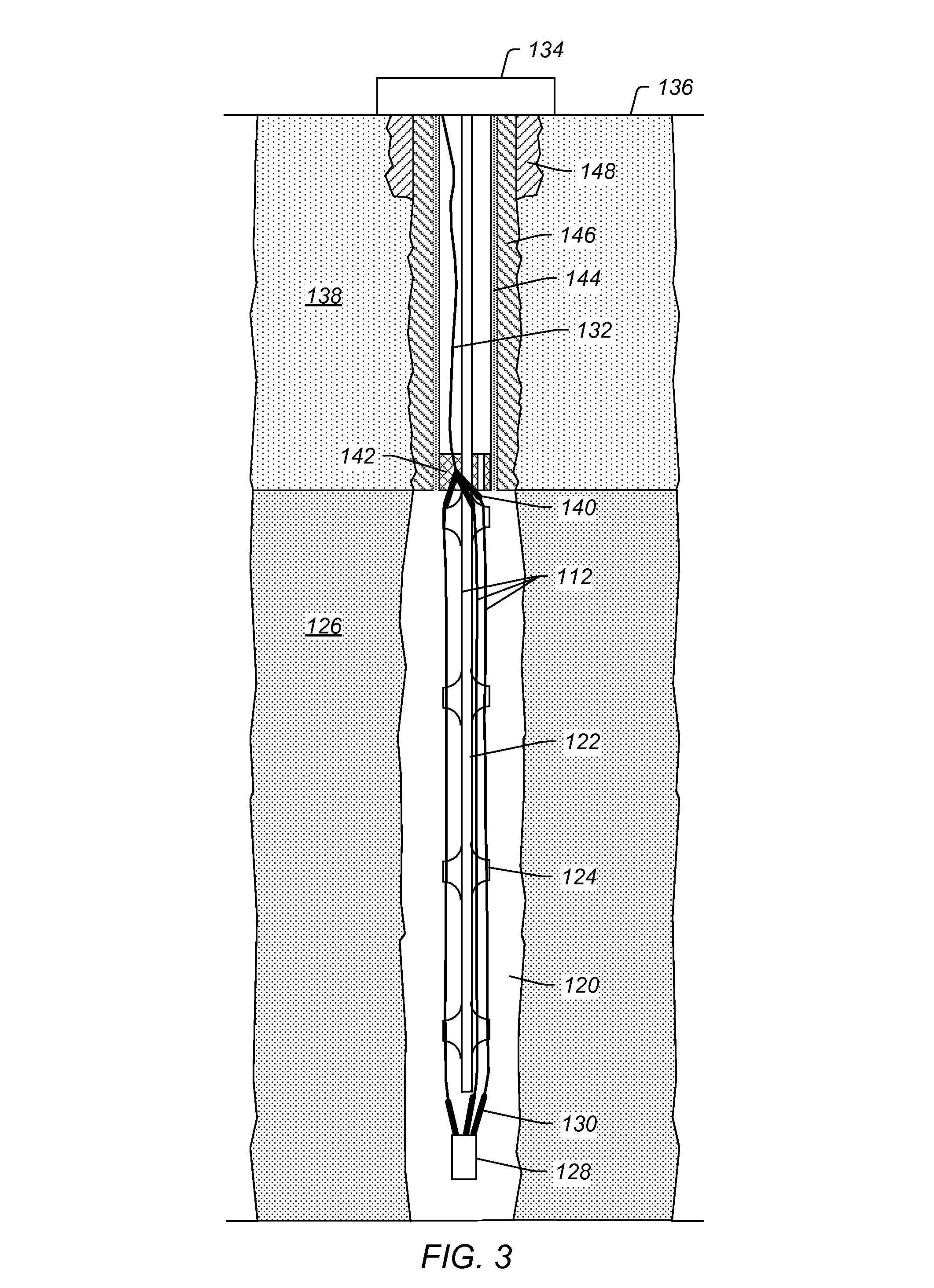
Methods for assessing a temperature in a subsurface formation
ActiveUS20110134958A1ConstructionsThermometers using value differencesElectrical conductorEngineering
Methods for assessing a temperature in an opening in a subsurface formation are described herein. A method may include assessing one or more dielectric properties along a length of an insulated conductor located in the opening and assessing one or more temperatures along the length of the insulated conductor based on the one or more assessed dielectric properties.
Owner:SHELL USA INC
Power supply apparatus
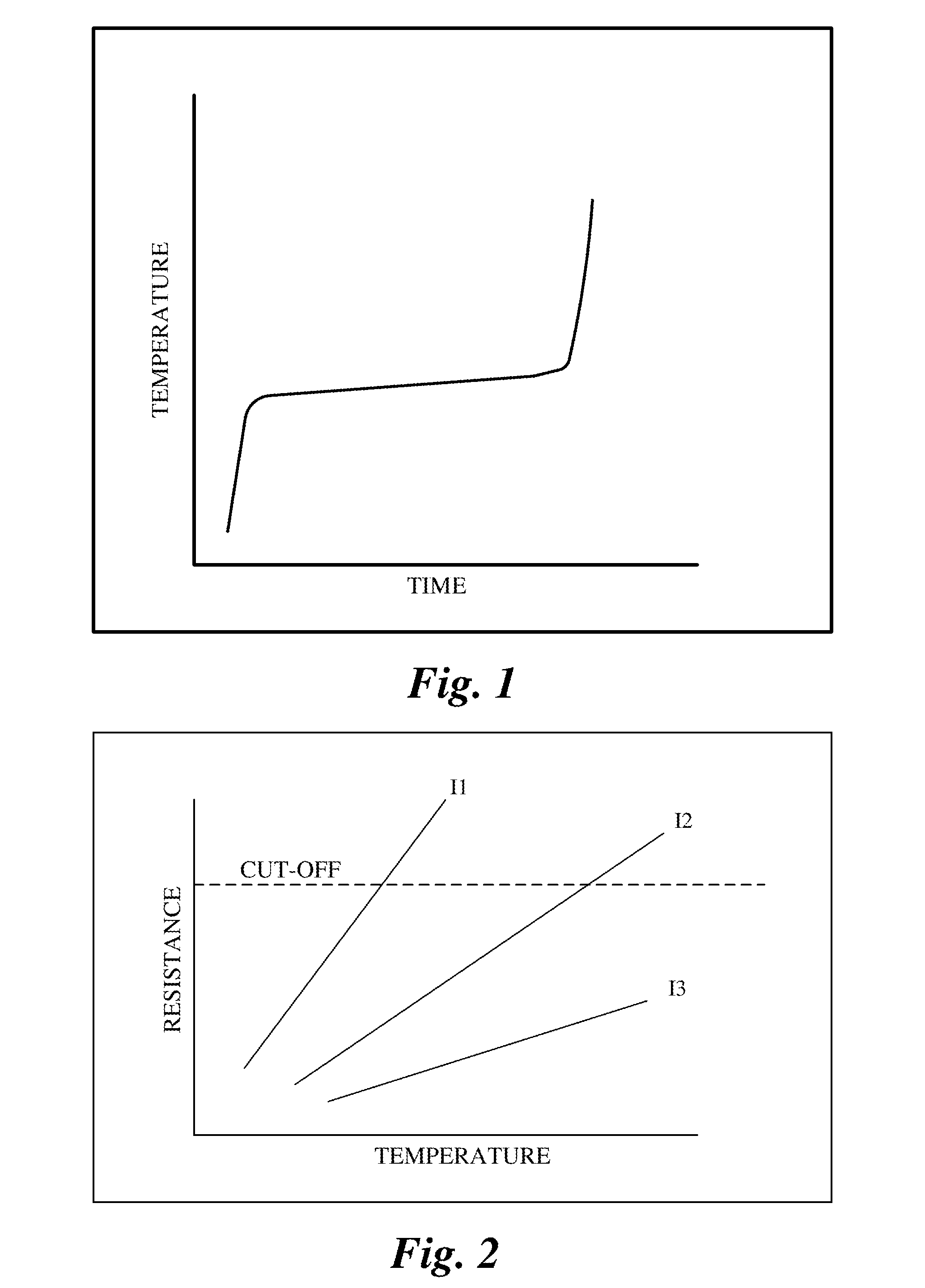
InactiveUS20050206347A1Simple circuit designReduce detection accuracyThermometer detailsBatteries circuit arrangementsElectrical batteryResistor
A power supply apparatus has a battery and a temperature detection circuit. The battery has n battery cells, and the temperature detection circuit has m temperature detection units. Each temperature detection units has a temperature sensor that is thermally coupled to one or more of the battery cells and whose electrical resistance decreases as the temperature of the battery cell or battery cells to which it is thermally coupled increases, a serial resistor that is connected in series with the temperature sensor, and a first diode whose cathode is connected to the node between the temperature sensor and the serial resistor. The serial circuit formed by the temperature sensor and the serial resistor receives a predetermined voltage such that, as the electrical resistance of the temperature sensor decreases, the voltage at the node decreases. The first diodes have anodes thereof connected together.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
Method of estimating temperature and device for the effecting same
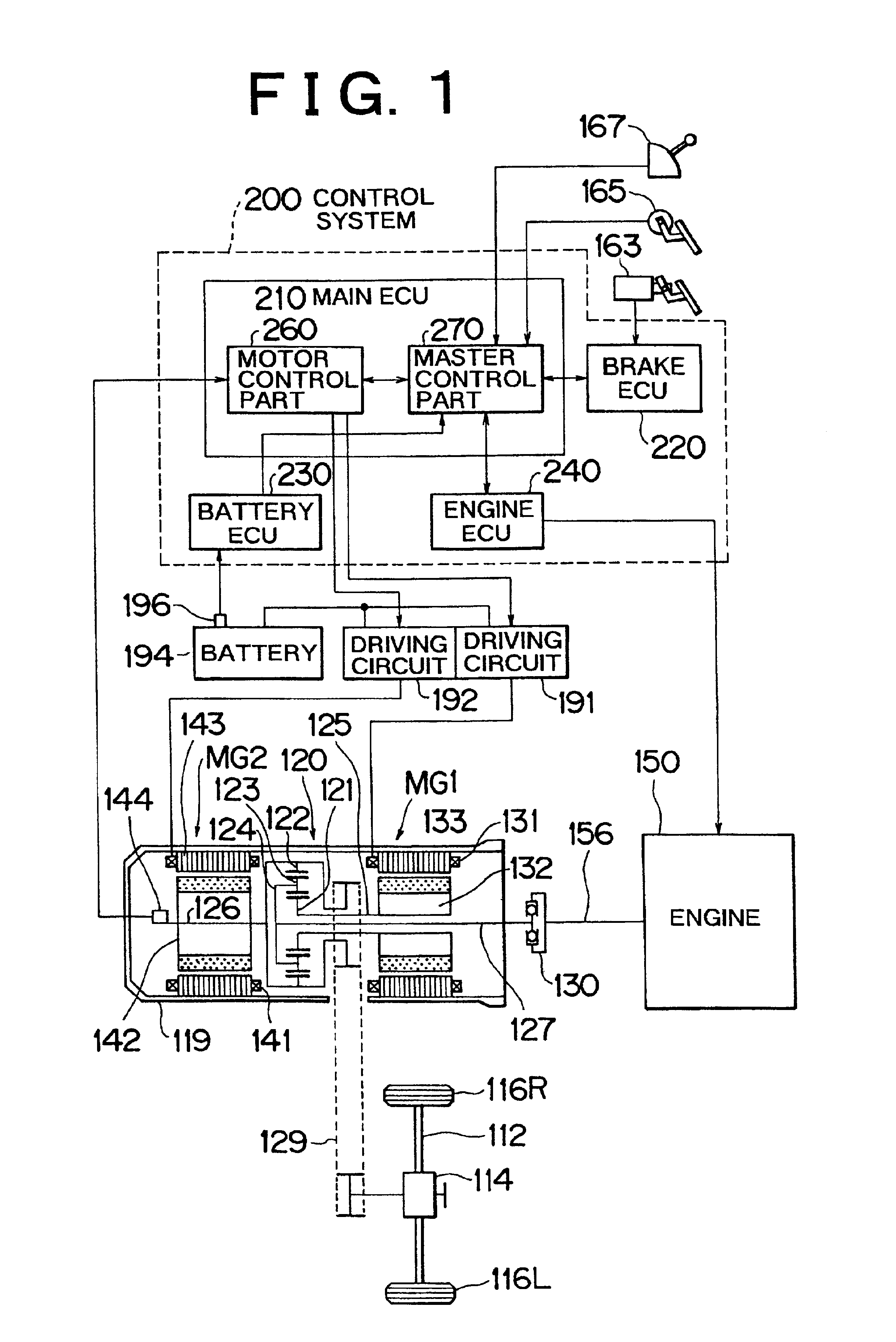
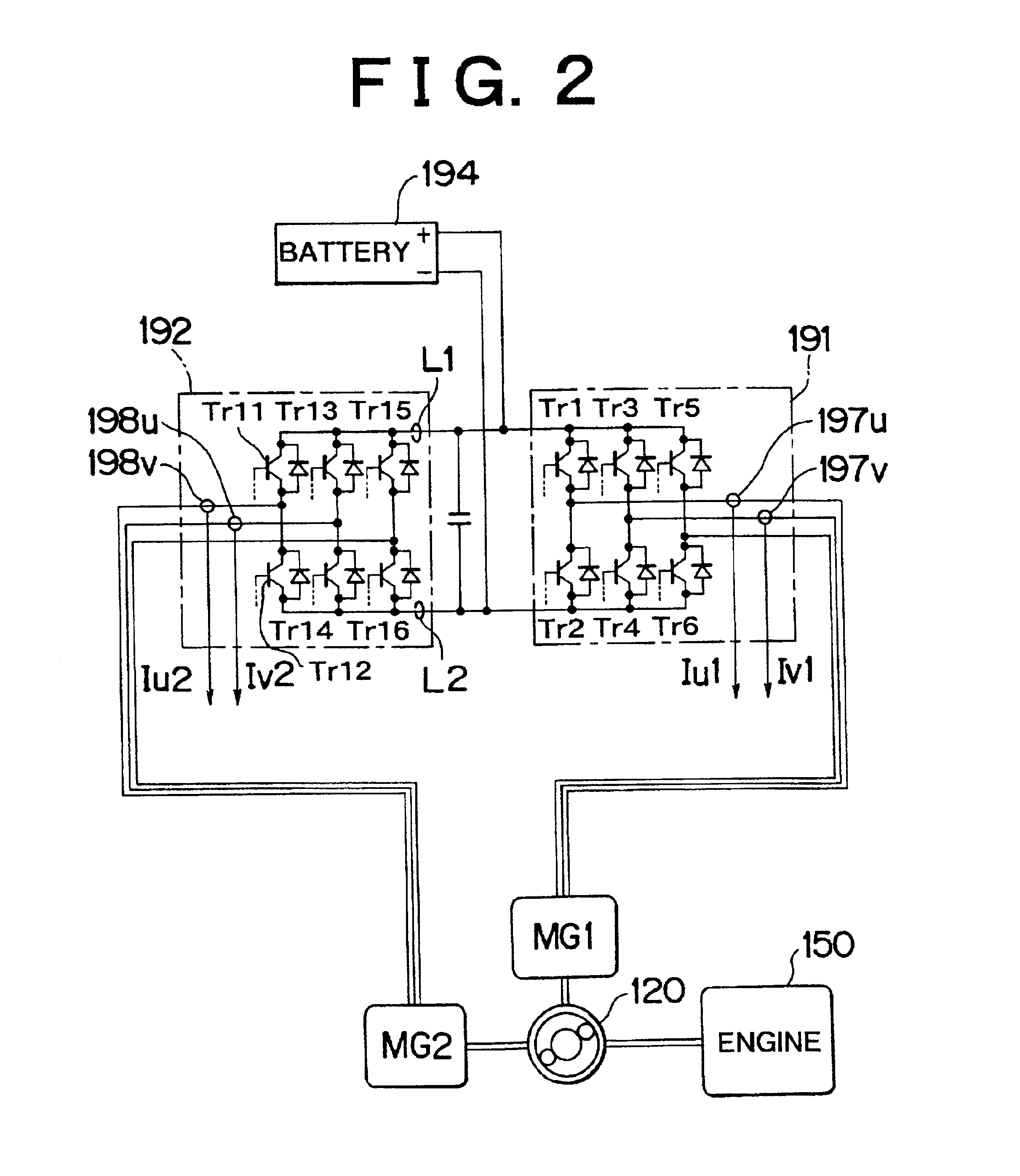
InactiveUS6854881B2Small heat capacityRapid temperature changeHybrid vehiclesThermometer detailsEngineeringTransistor
In accordance with the presence or absence of heat, a transistor shows a relatively rapid change, while a cooling water CLW shows a relatively gentle change. The temperatures of both members settle down to approximately equal temperatures when no heat is generated in the transistor. At this time, the temperature of one of the transistor or the cooling water and the amount of energization of the transistor are used to estimate the temperature of the other member. This method is applied to other temperature estimations, such as estimation of the temperature between a stator coil and a stator iron core of a motor etc.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Test apparatus for power circuits of an electrical distribution device
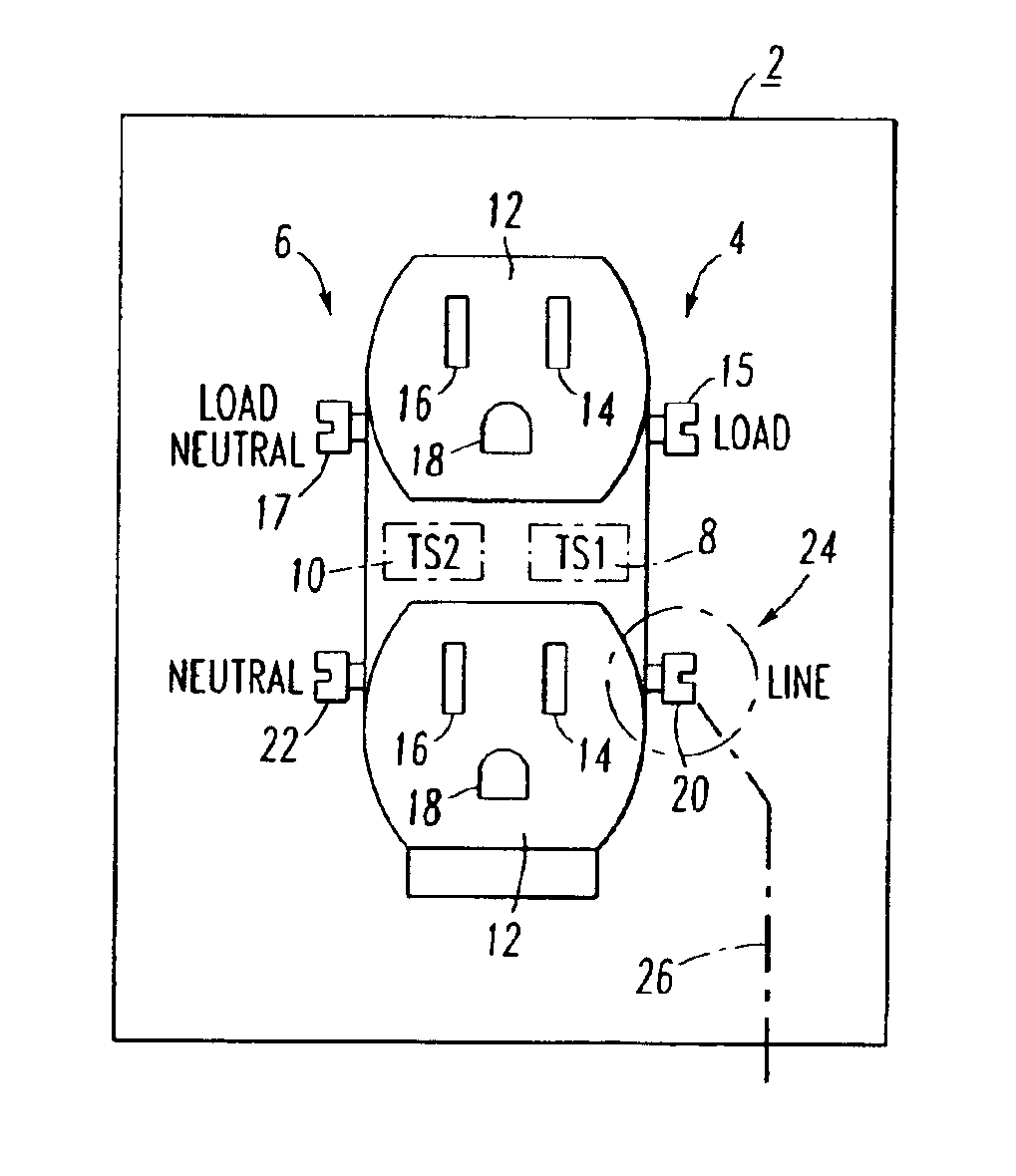
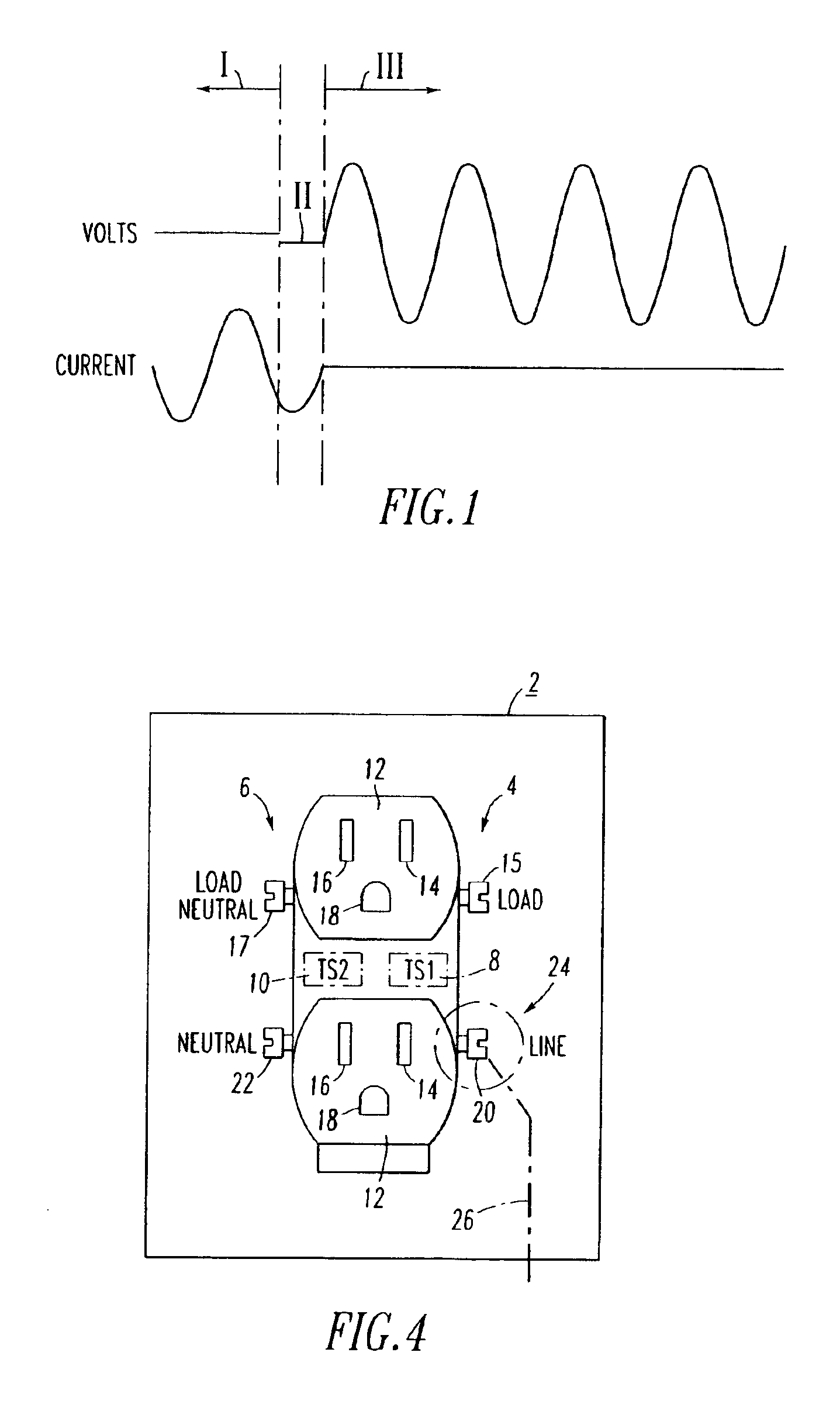
InactiveUS6948846B2Thermometer detailsThermometers using value differencesHigh resistanceElectricity
A glowing contact or high resistance test device includes a housing and first and second circuits substantially within the housing. The first and second circuits include first and second electrical plugs disposed from the housing and adapted to electrically engage and thermally communicate with line and neutral circuits, respectively, of an electrical receptacle. First and second diode temperature sensors are proximate the first and second circuits and the first and second electrical plugs, respectively. The first and second sensors output first and second signals representative of the first and second temperatures of the line and neutral circuits, respectively. An amplifier circuit determines a difference between the first and second signals. A window comparator circuit includes a light emitting diode, which displays an indication signal when the absolute value of the difference exceeds a predetermined value.
Owner:EATON INTELLIGENT POWER LTD
Thermal Stress Indicator
ActiveUS20110133939A1Electric signal transmission systemsThermometers using value differencesNon invasiveStress indicator
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
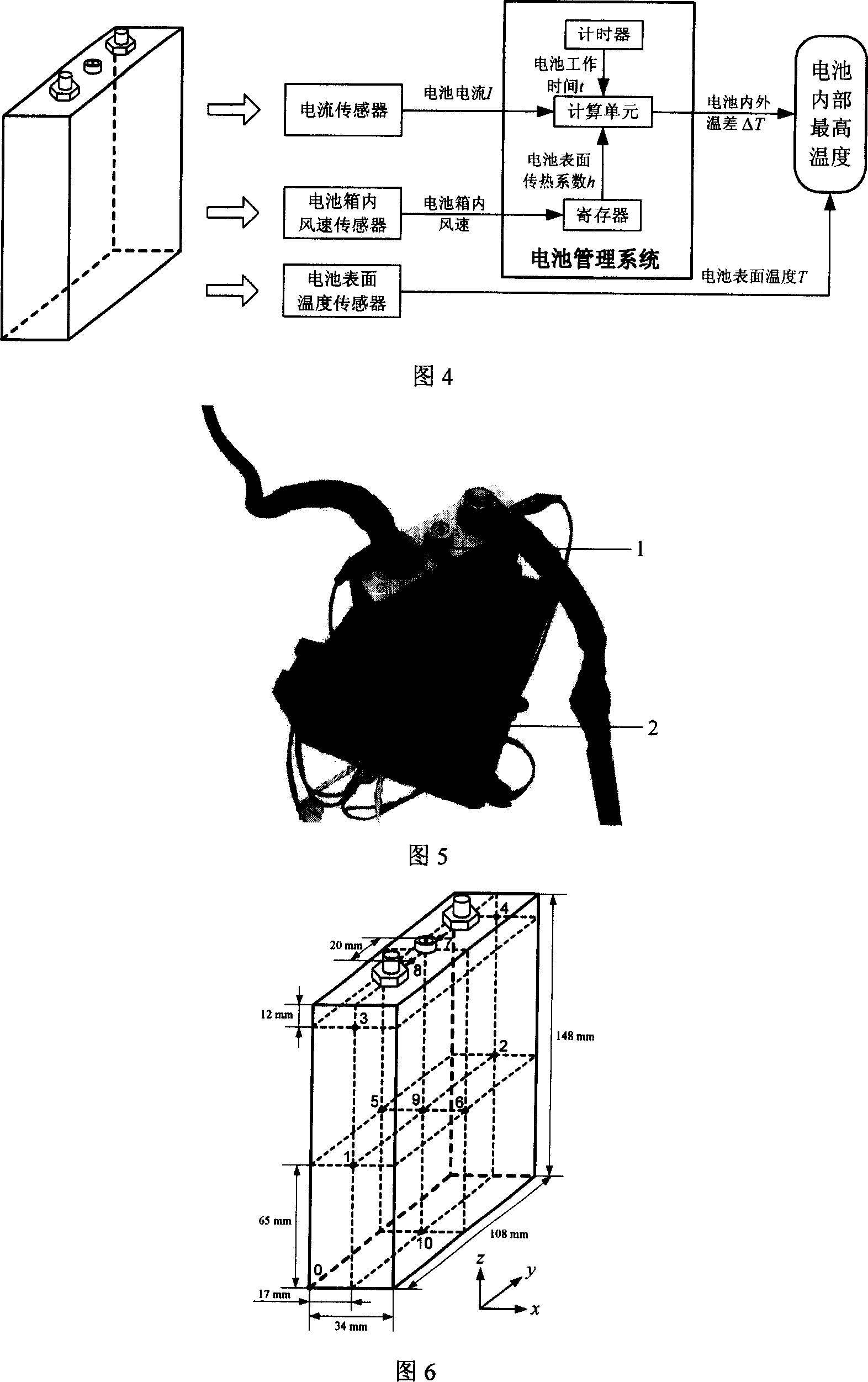
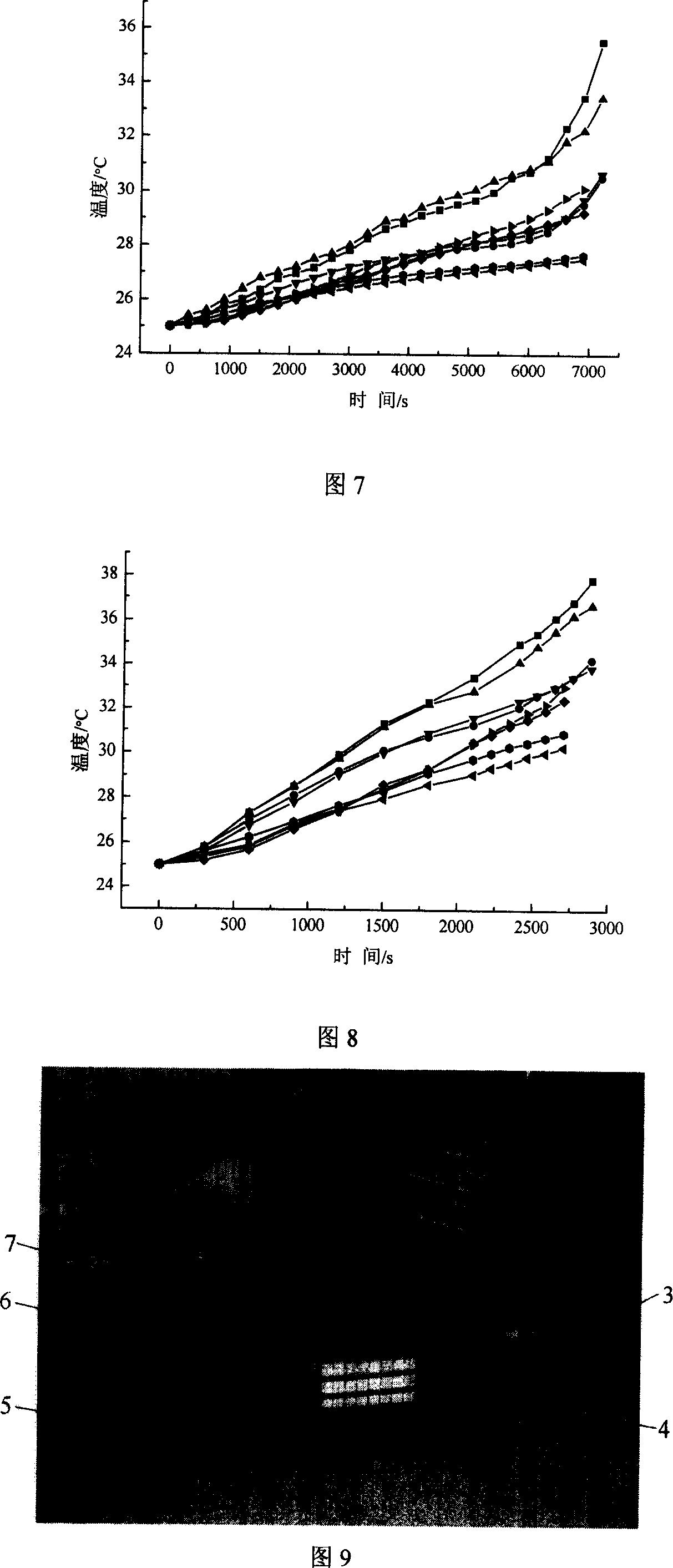
Method for real-time evaluating internal-external temperature difference of nickel-hydrogen electrokinetic cell
InactiveCN101013765AThermometers using value differencesSecondary cells servicing/maintenanceElectrical batteryEngineering
The invention relates to battery set thermal management technique, which is characterized by the following: getting nickel and hydrogen battery even thermal proportion based on experiment, thermal speed and battery balance motion temperature parameters; in computer, establishing battery thermal module to use software Fluent to get inside temperature field distribution; then using natural wind temperature difference and even current as input to establish one temperature difference module to reflect current, work time and surface transmission parameters.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Cable quality detection and power consumer devices
In one embodiment, a method includes receiving power at a power consumer device coupled to a power provider device by a cable. The received power is supplied at a first current at an input of the power consumer device and is supplied to a load in the power consumer device. The method includes measuring a rate of change of the voltage at the input of the power consumer device, and determining whether the rate of change of the voltage at the input of the power consumer device is less than a first target rate of change of voltage. The current received at the input of the power consumer device is reduced to a second current lower than the first current if the rate of change of the voltage at the input of the power consumer device is greater than the first target rate of change of voltage.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
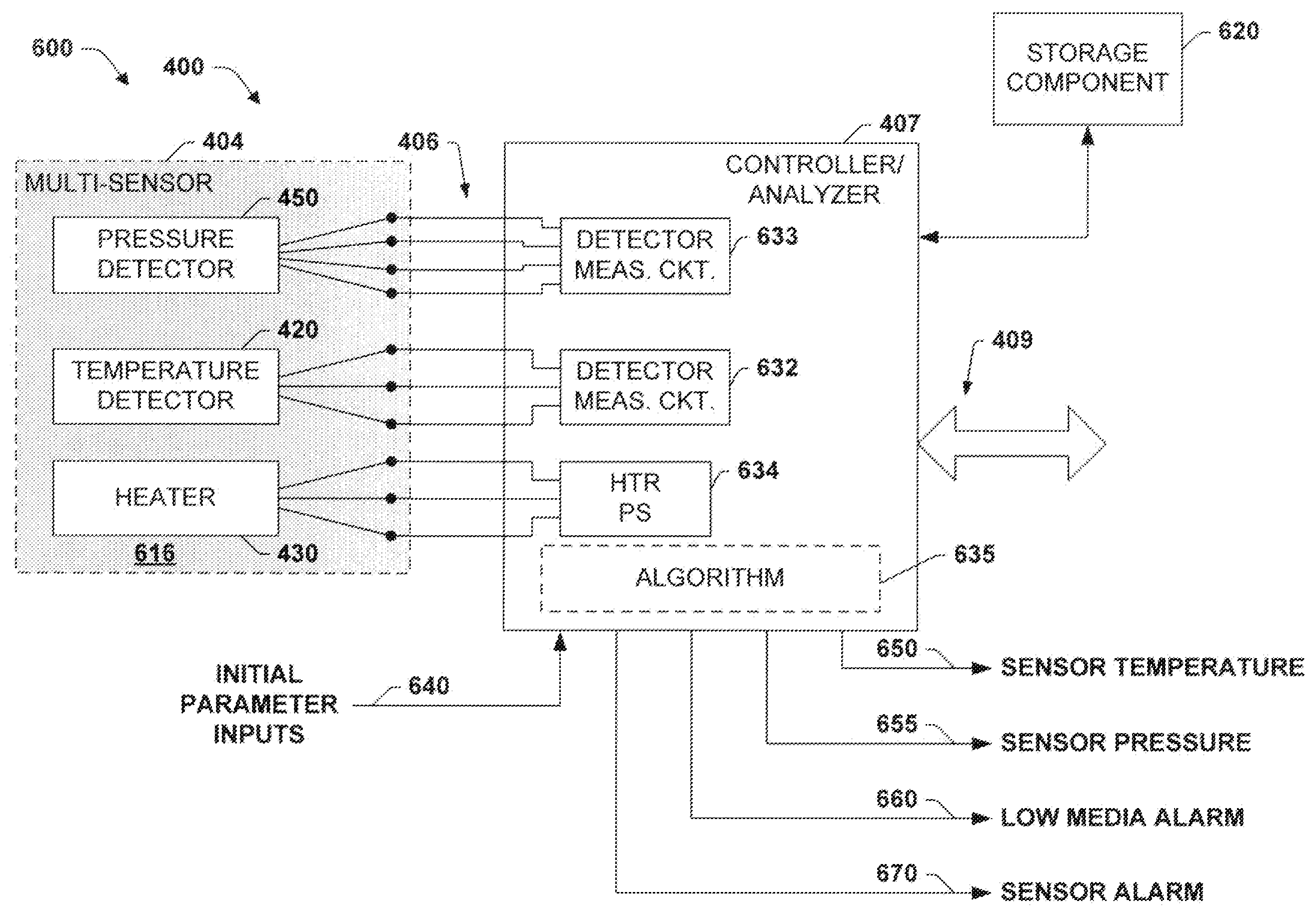
Integrated multi-sensor component
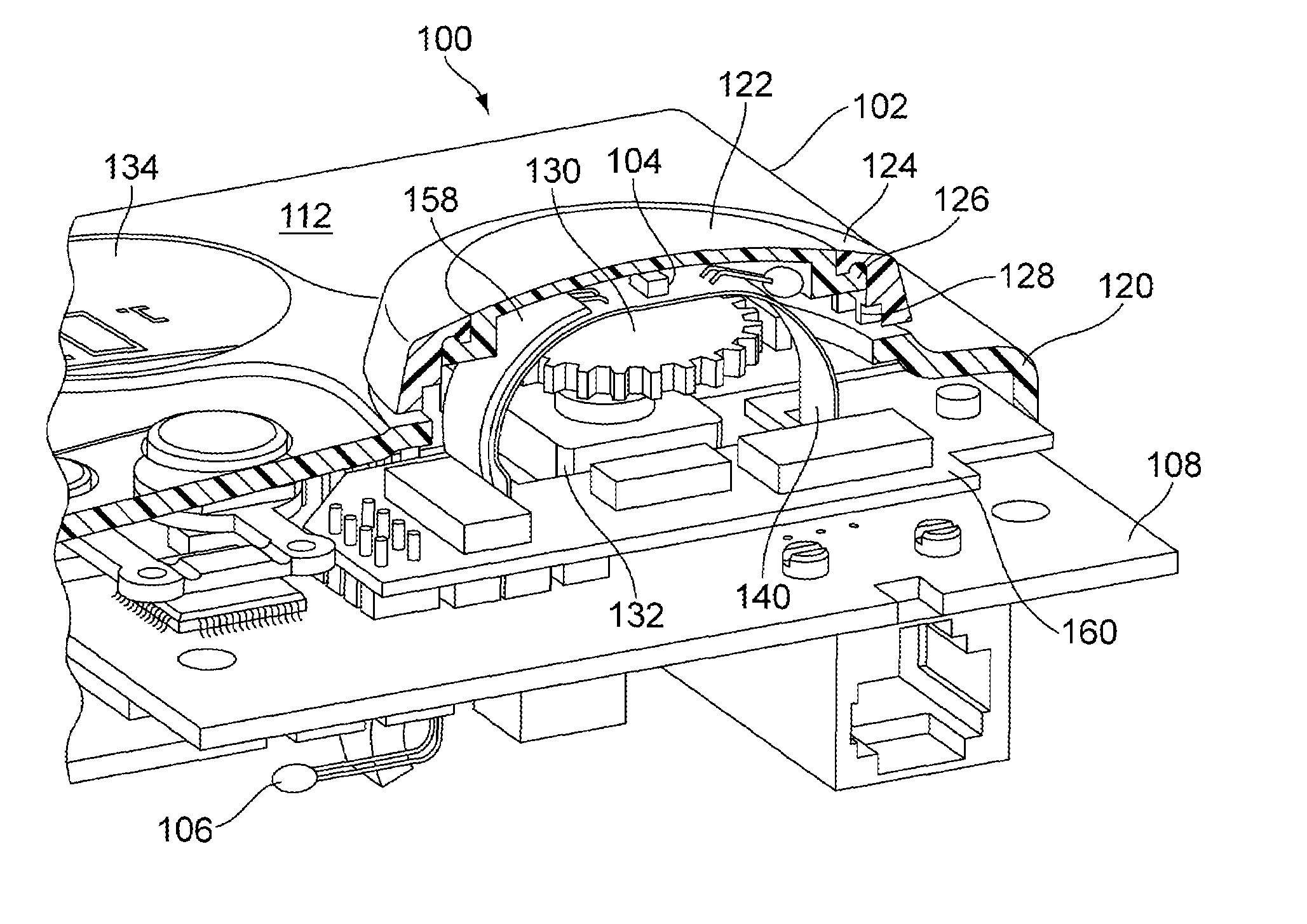
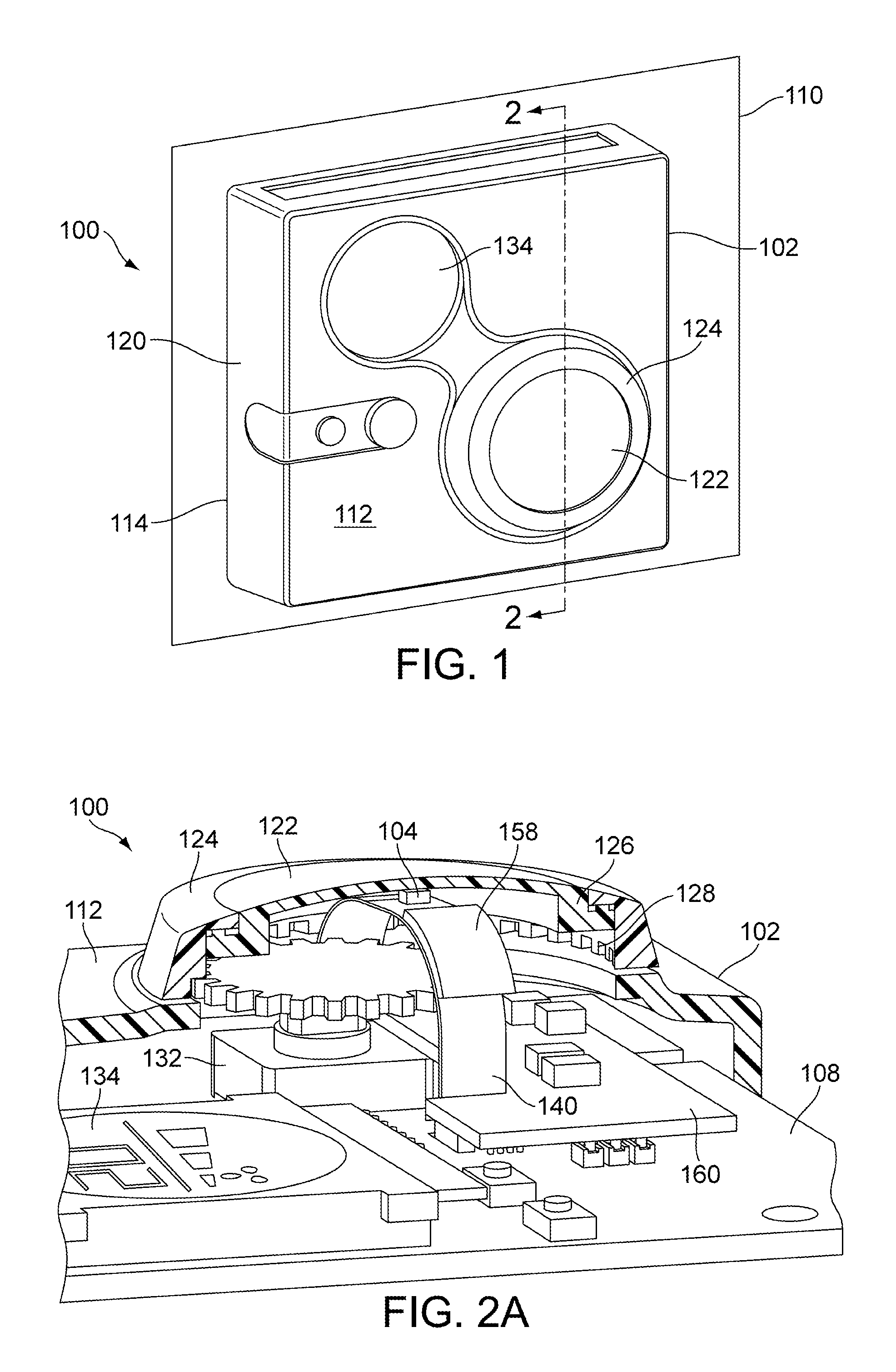
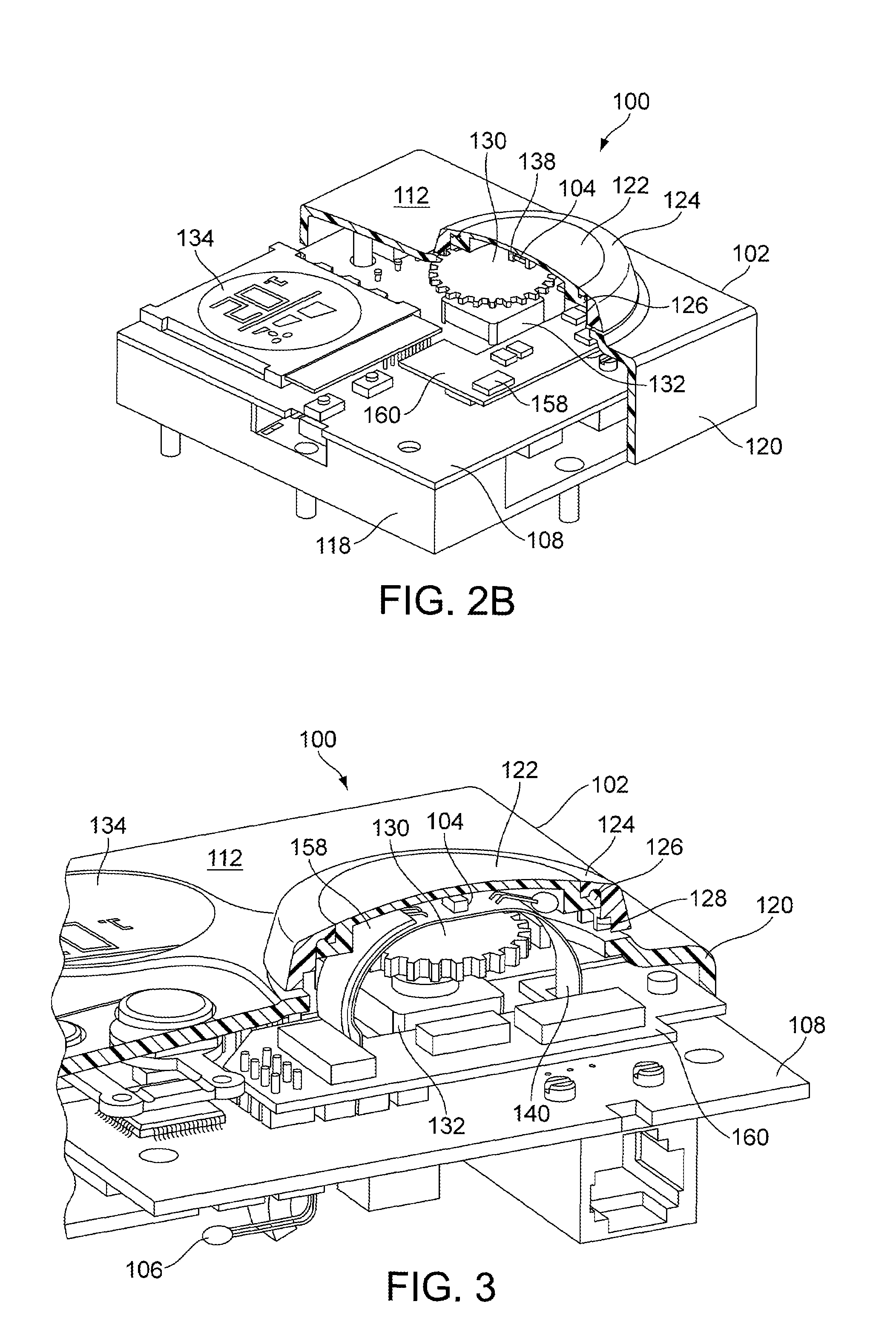
InactiveUS20100280788A1Eliminate needThermometer detailsMechanical apparatusTemperature responseThermal decay
A system and method is presented for a multi-sensor component for an HVAC system. The multi-sensor component comprises a sensor assembly, having a temperature detector for measuring a temperature of an object or medium, a presence detector to detect the presence of the object or medium against the sensor, and a pressure detector for measuring a pressure of the medium. The temperature, presence and pressure detectors may also be affixed within a single sensor housing. In a heating mode the multi-sensor component is heated by a heater, and in a cooling mode the multi-sensor component cools toward a temperature of the object or medium, and the temperature detector provides temperature data indicative of a temperature response comprising one of a temperature change, a rate of change and a time constant of a thermal decay rate of the multi-sensor component and the presence of the object or medium.
Owner:R W BECKETT
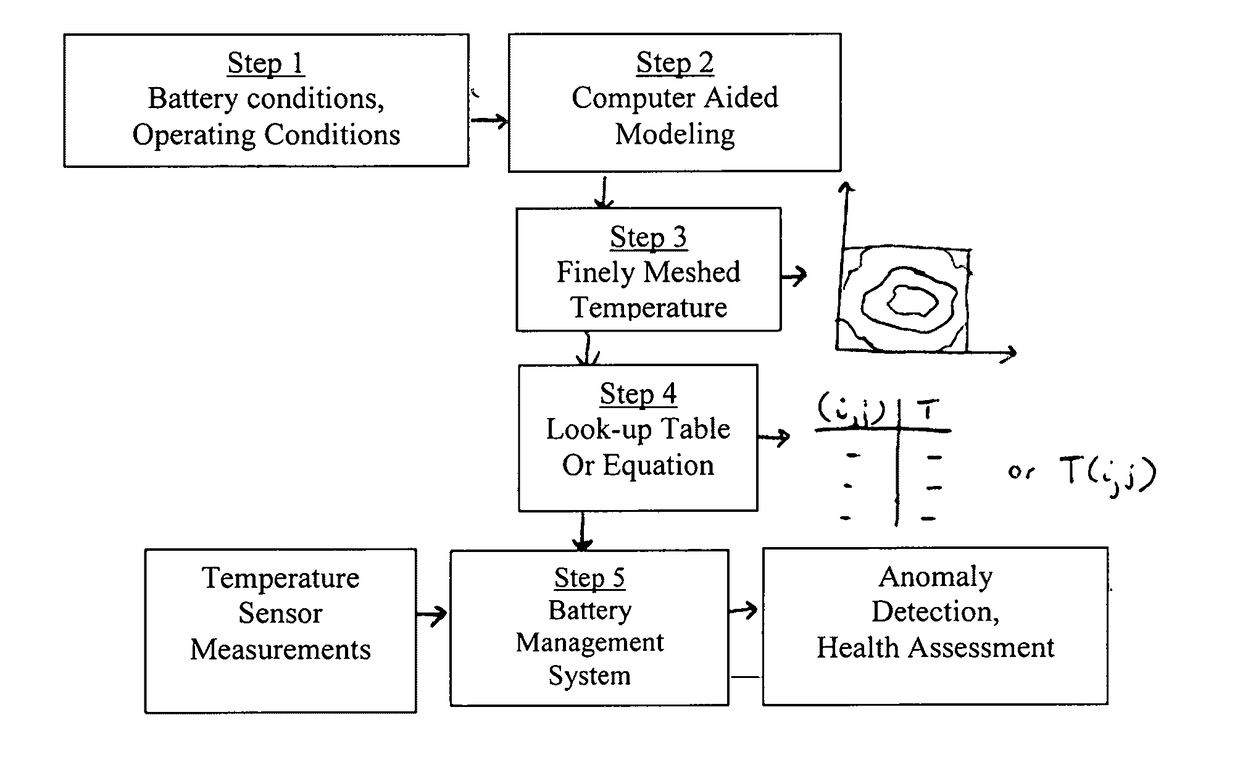
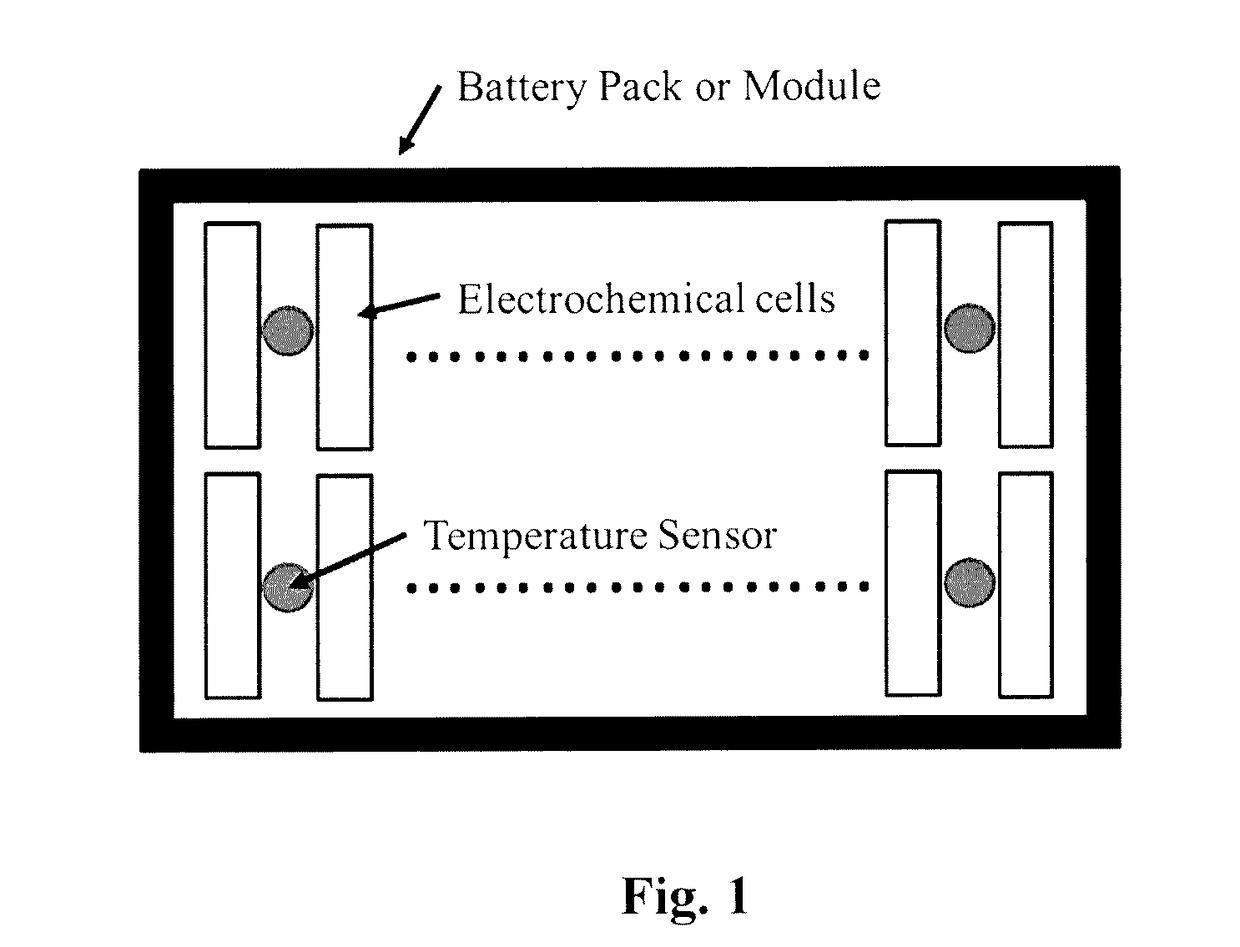
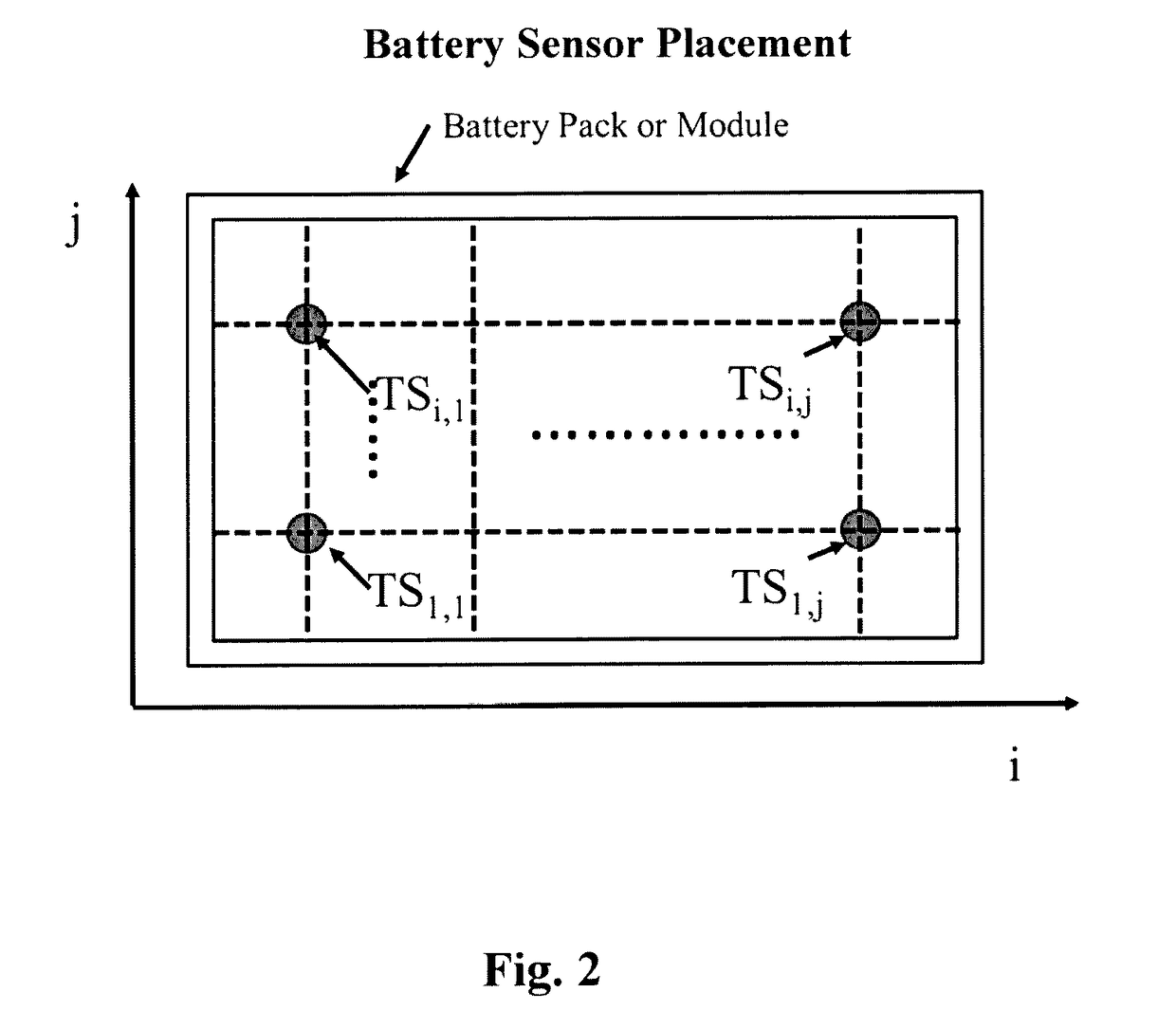
Thermal Monitoring of Battery Packs
InactiveUS20170117725A1Thermometer detailsThermometers using value differencesThermal monitoringComputer-aided
A computer-aided health monitoring method is described for thermal monitoring of a battery pack that consists of using modeling to determine temperature distributions representative of safe battery operating conditions and a technique is described for comparing sensor measurements to a look-up table of the pre-modeled temperature profiles under various operating conditions. In one embodiment a simplified model of temperature distribution is described.
Owner:OXFORDIAN
Methods for assessing a temperature in a subsurface formation
Methods for assessing a temperature in an opening in a subsurface formation are described herein. A method may include assessing one or more dielectric properties along a length of an insulated conductor located in the opening and assessing one or more temperatures along the length of the insulated conductor based on the one or more assessed dielectric properties.
Owner:SHELL USA INC
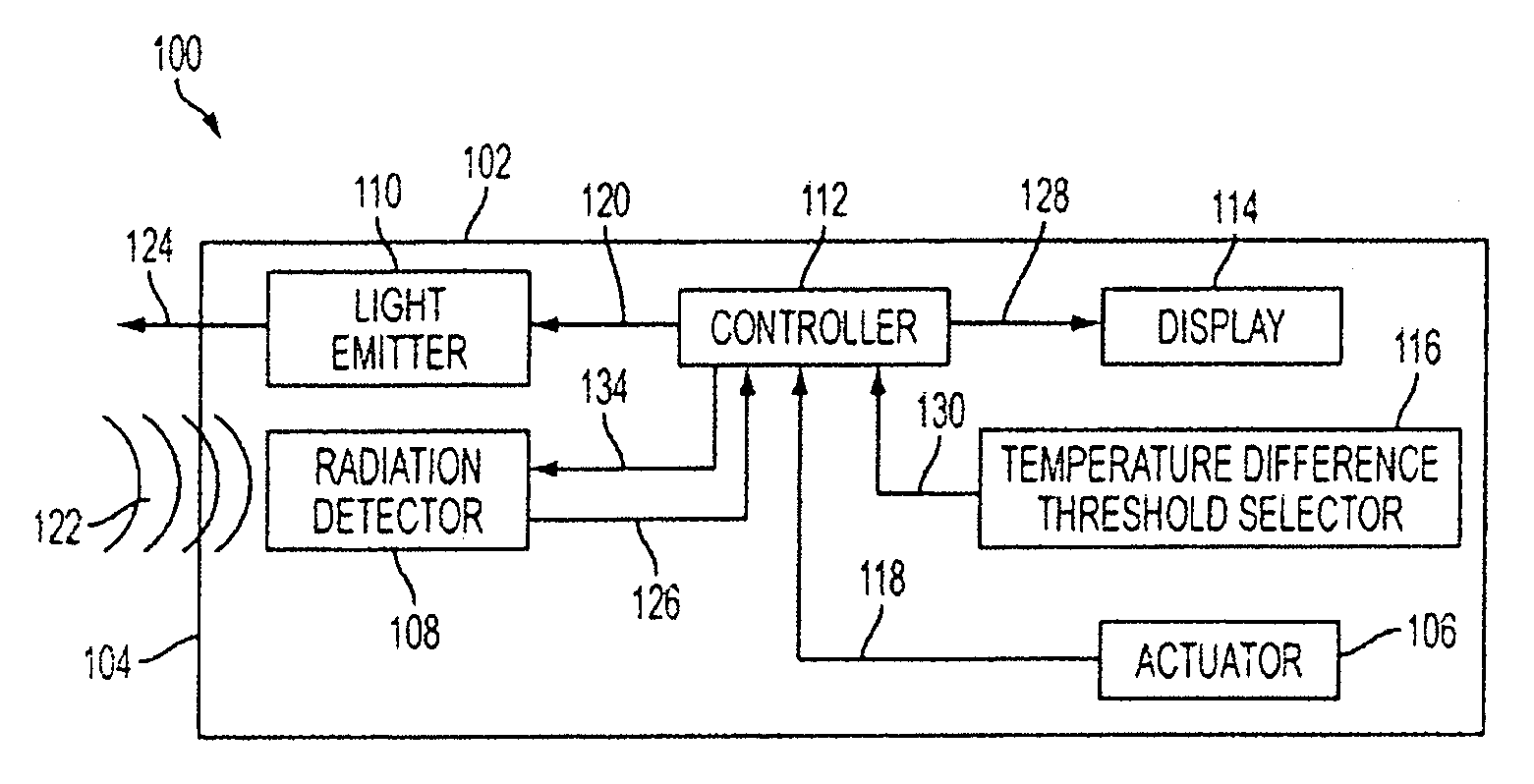
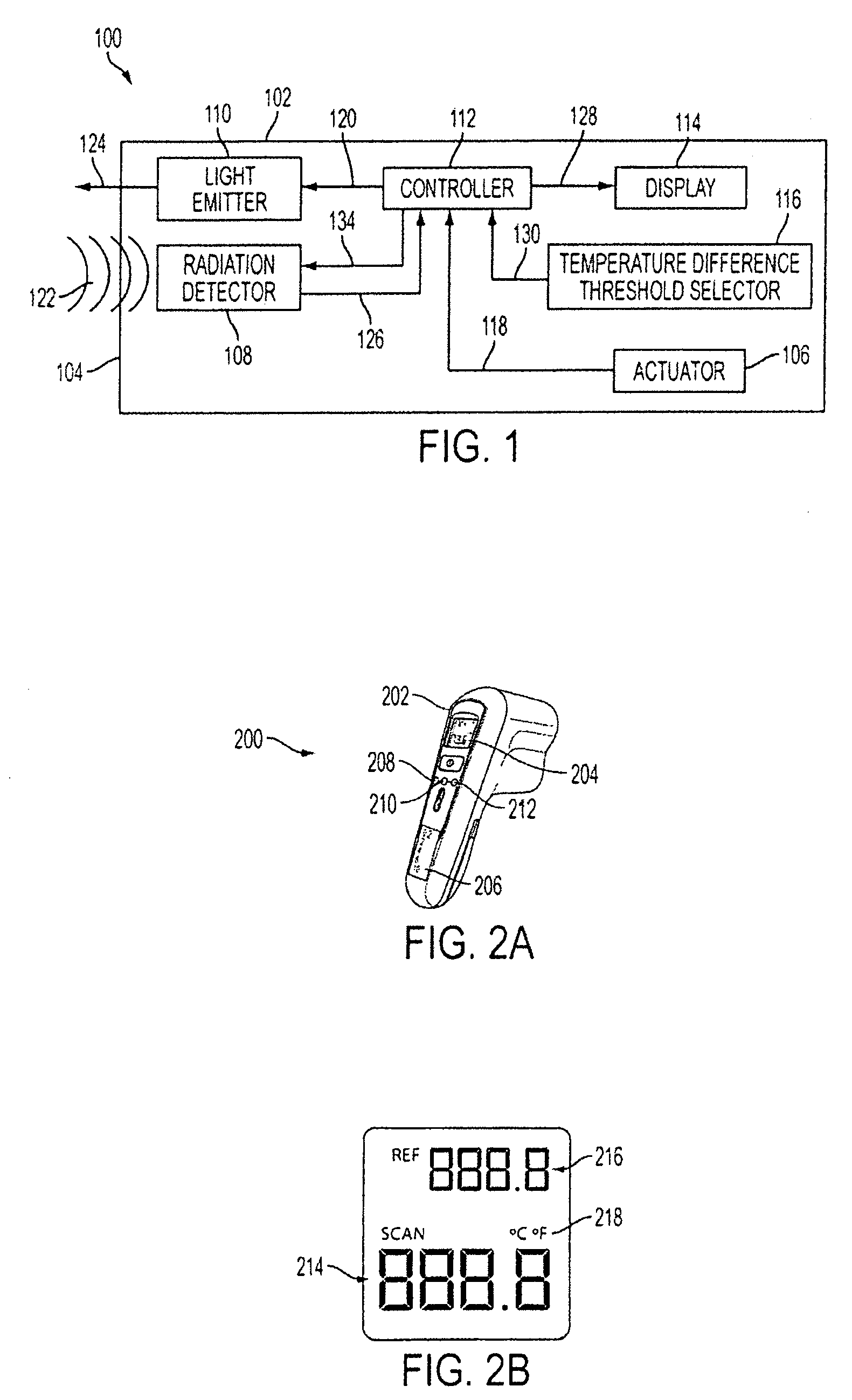
Non-contact thermometer
ActiveUS20090304042A1Thermometers using value differencesRadiation thermographyEngineeringTemperature difference
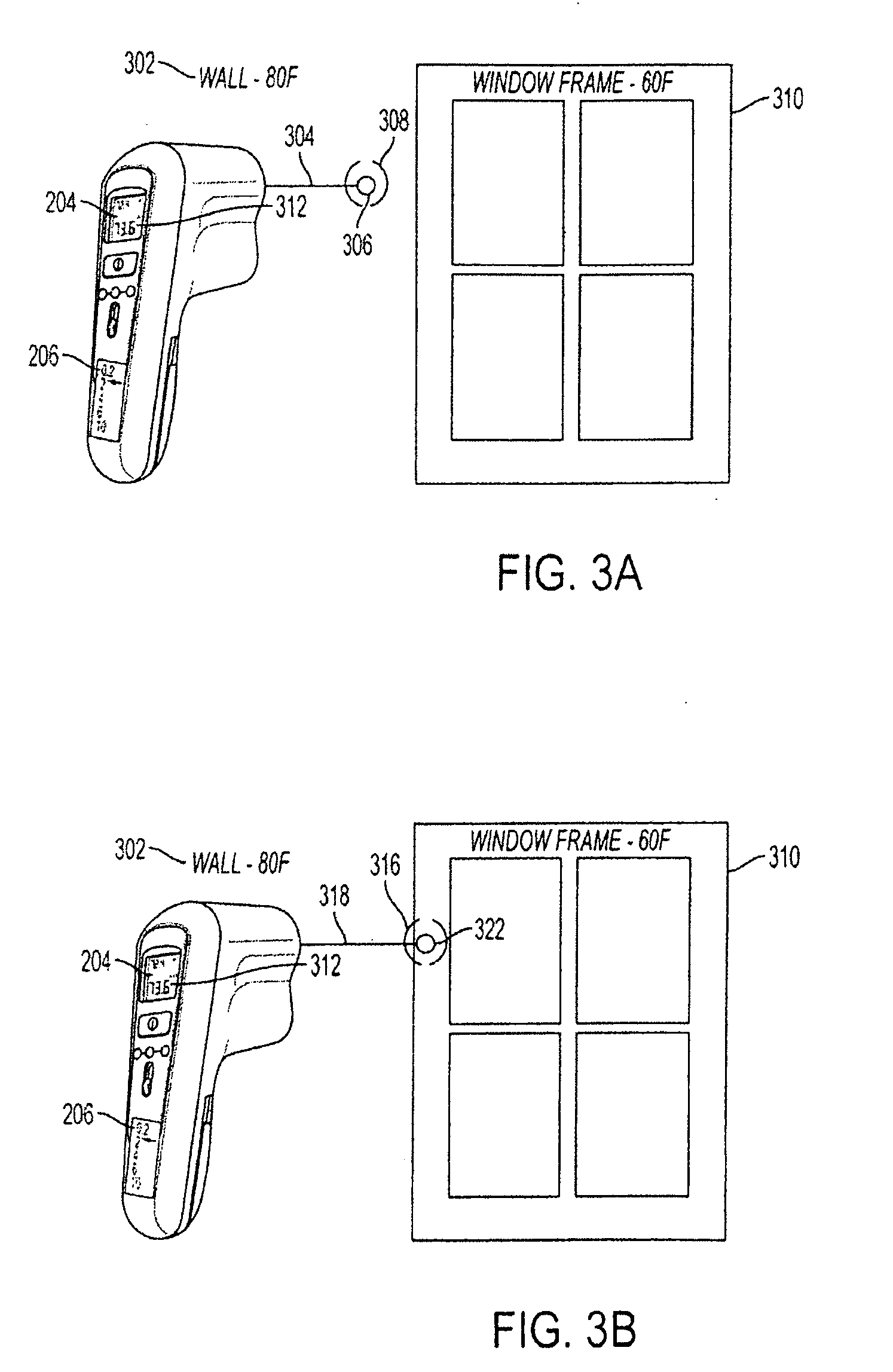
The present invention is drawn to a non-contact thermometer that is operable to emit a first light having a first color to create a spot of a first color at a reference target and to detect the temperature of the reference target. The non-contact thermometer is additionally operable to establish a temperature difference threshold. In use, once a temperature difference threshold is selected and once the temperature of the reference target is detected, the non-contact thermometer may detect a temperature of another target. Further, if the detected temperature of the other target is outside of the temperature difference threshold as compared to the temperature of the reference target, the non-contact thermometer is operable to emit a second light having a second color to create a spot of a second color at the other target.
Owner:BLACK & DECKER INC
Temperature sensing device
ActiveUS7395173B2Good estimateAvoid missed connectionsThermometer detailsThermometers using value differencesEngineeringElectrical and Electronics engineering
The present invention relates to a temperature sensing device with a first temperature sensor mounted to a housing at a first location proximate a first surface of the housing. The first temperature sensor senses a first temperature while a second temperature sensor senses a second temperature. A processor circuit is coupled to the first and second temperature sensors and a mounting device is coupled to either the housing or the processor circuit. The mounting device mounts the second temperature sensor at a second location proximate a second surface of the housing which is spaced apart from the first surface. The processor circuit is configured to estimate a third temperature based on the first and second temperatures and a distance between the first and second locations which is an estimate of a temperature at a third location.
Owner:JOHNSON CONTROLS TECH CO
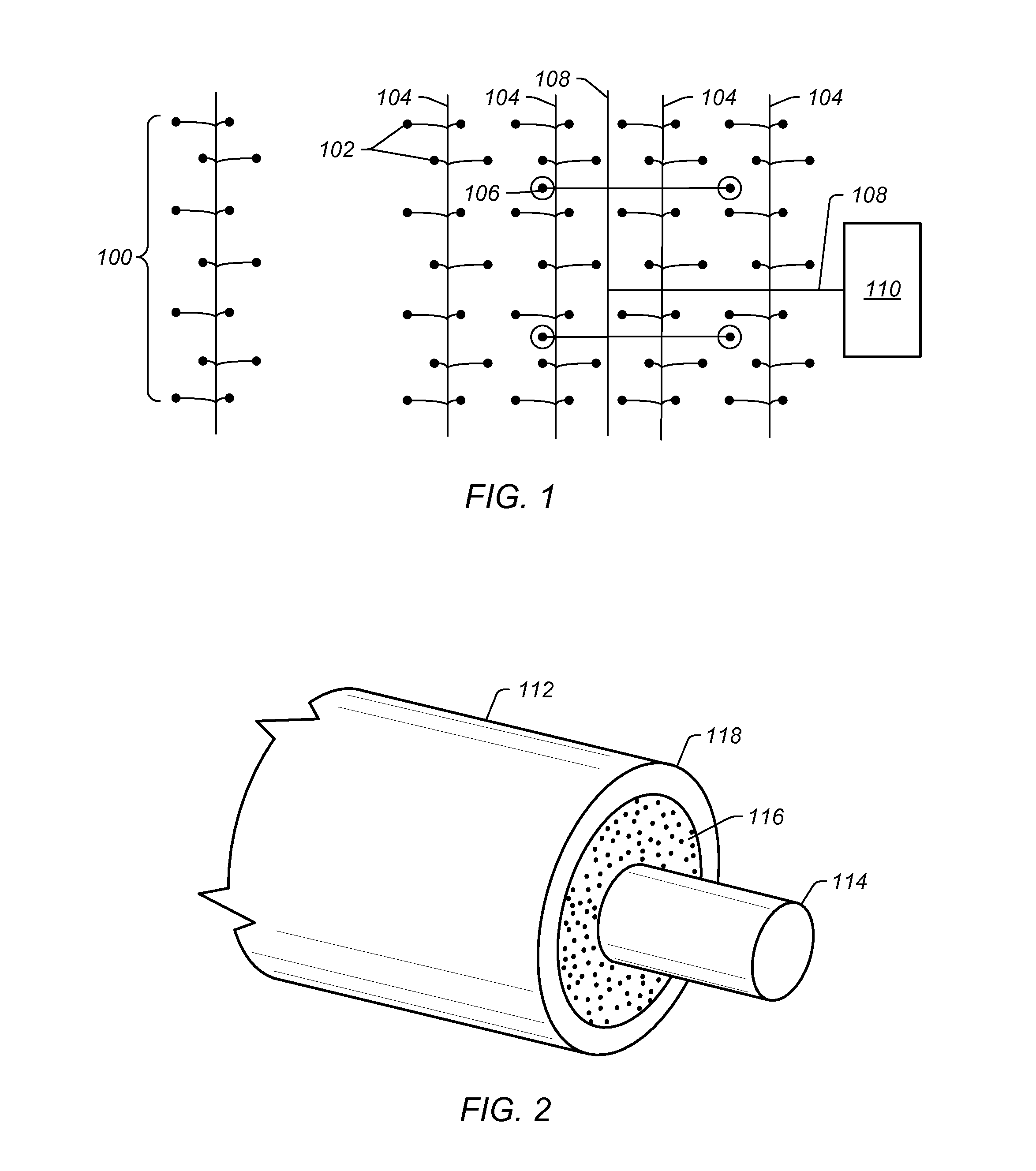
Multiple temperature resistance characteristic sensing cable and its sensor
InactiveUS20090059998A1Thermometers using mean/integrated valuesThermometers using value differencesElectrical resistance and conductanceElectrical conductor
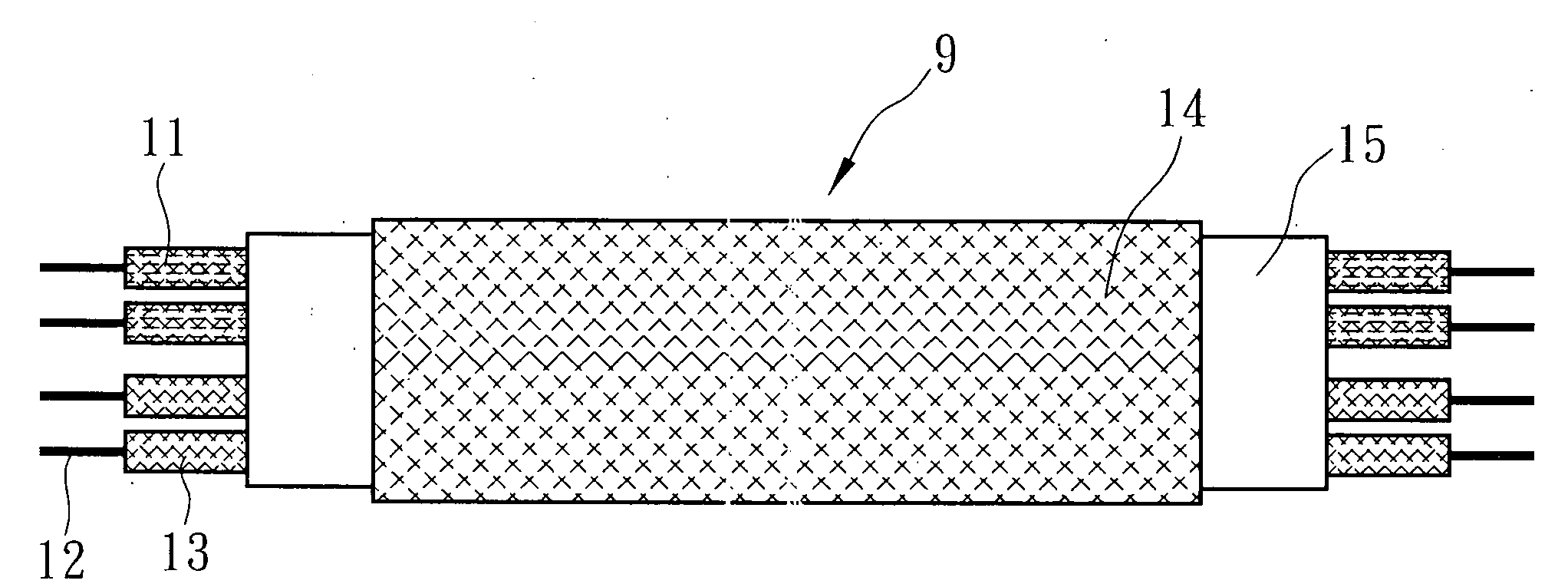
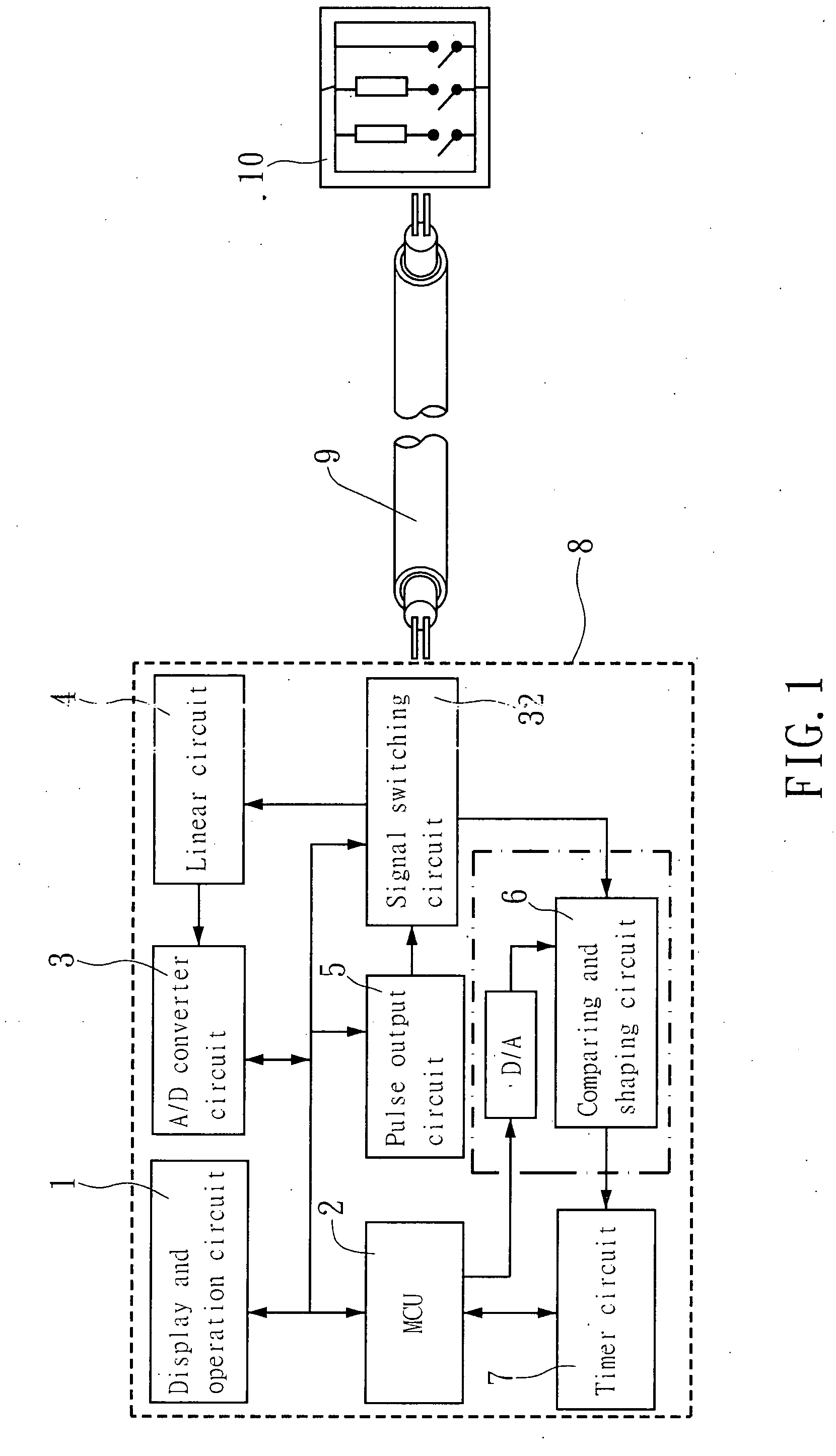
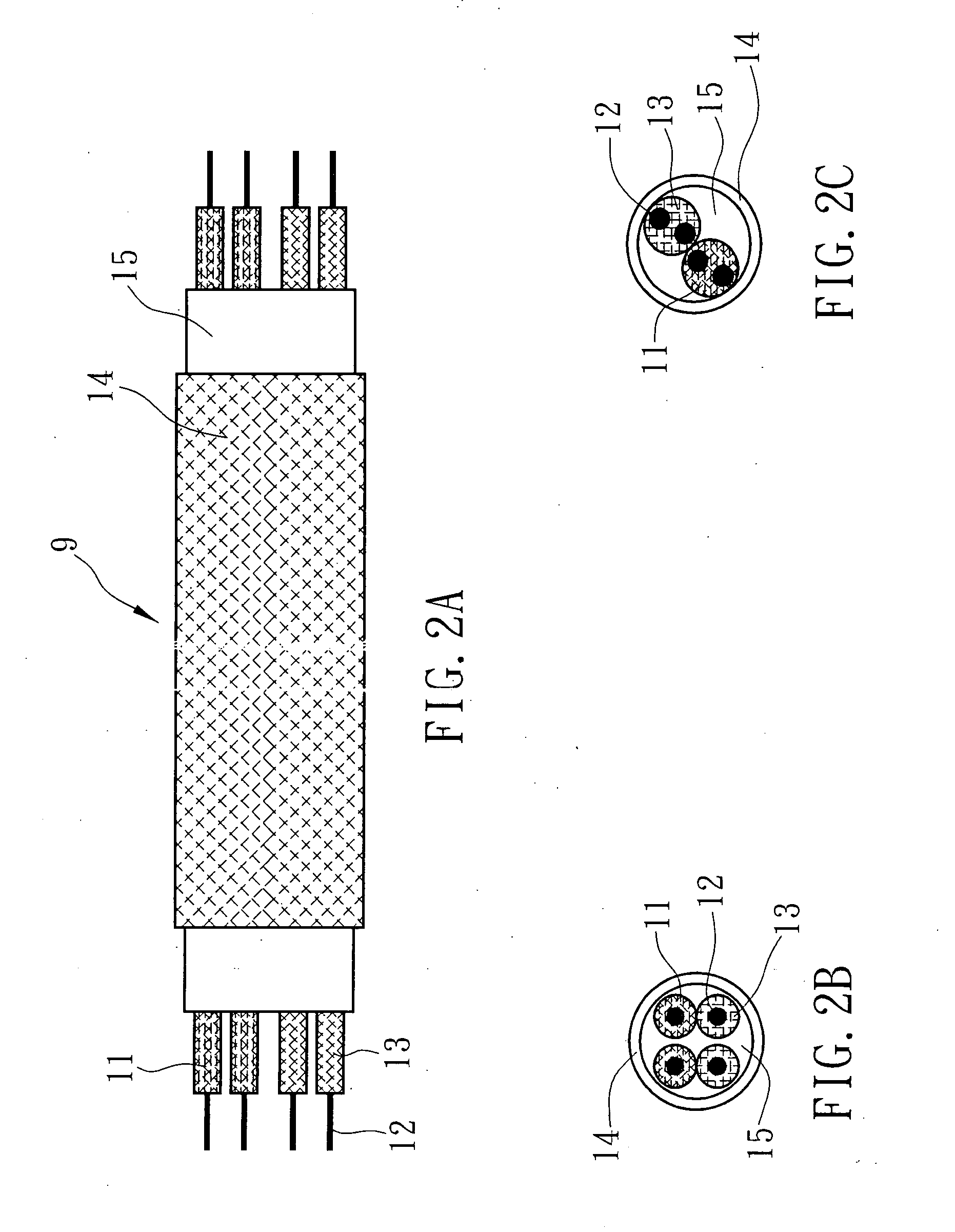
A multiple temperature resistance characteristic sensing cable comprised of 1˜6 metal conductors with restorable insulation layer. Each cable contains different temperature resistance characteristic, and is wrapped by 1-2 layers of outer sheath. The metal conductors are wrapped by 1-2 insulation layers and twisted together. These twisted wires are inside the 1-2 layers of outer sheath. The temperature sensor comprises an interface unit, a sensing cable corresponding to temperature resistance characteristics, and a cable terminal unit. The interface unit comprises a signal amplifier and linear circuit, an A / D converter, a microprocessor, a display and operation circuit, a pulse output circuit, and a timer circuit. The temperature sensor realizes the differential temperature, fixed temperature or differential fixed temperature alarm among low, mid and high temperature sections.
Owner:HOU BILLY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com