Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
53 results about "Cell deformation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Deformation of stably oriented cells increased with increasing shear stress and approached a value limited by cell surface area and volume. For isotonic media, over a wide range of external viscosities and shear stresses, deformation was greater for younger cells than for older cells. However, deformation vs.
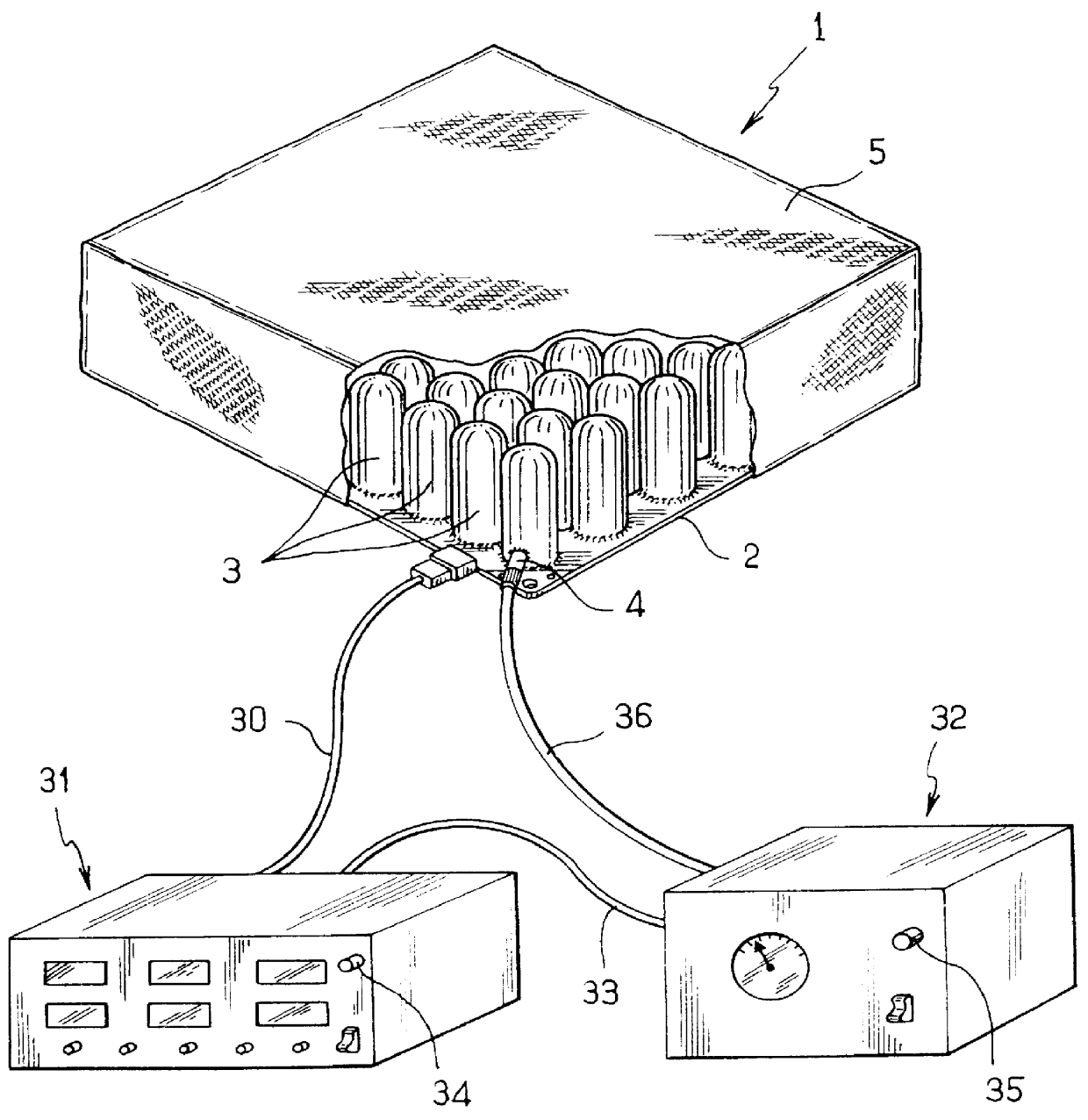
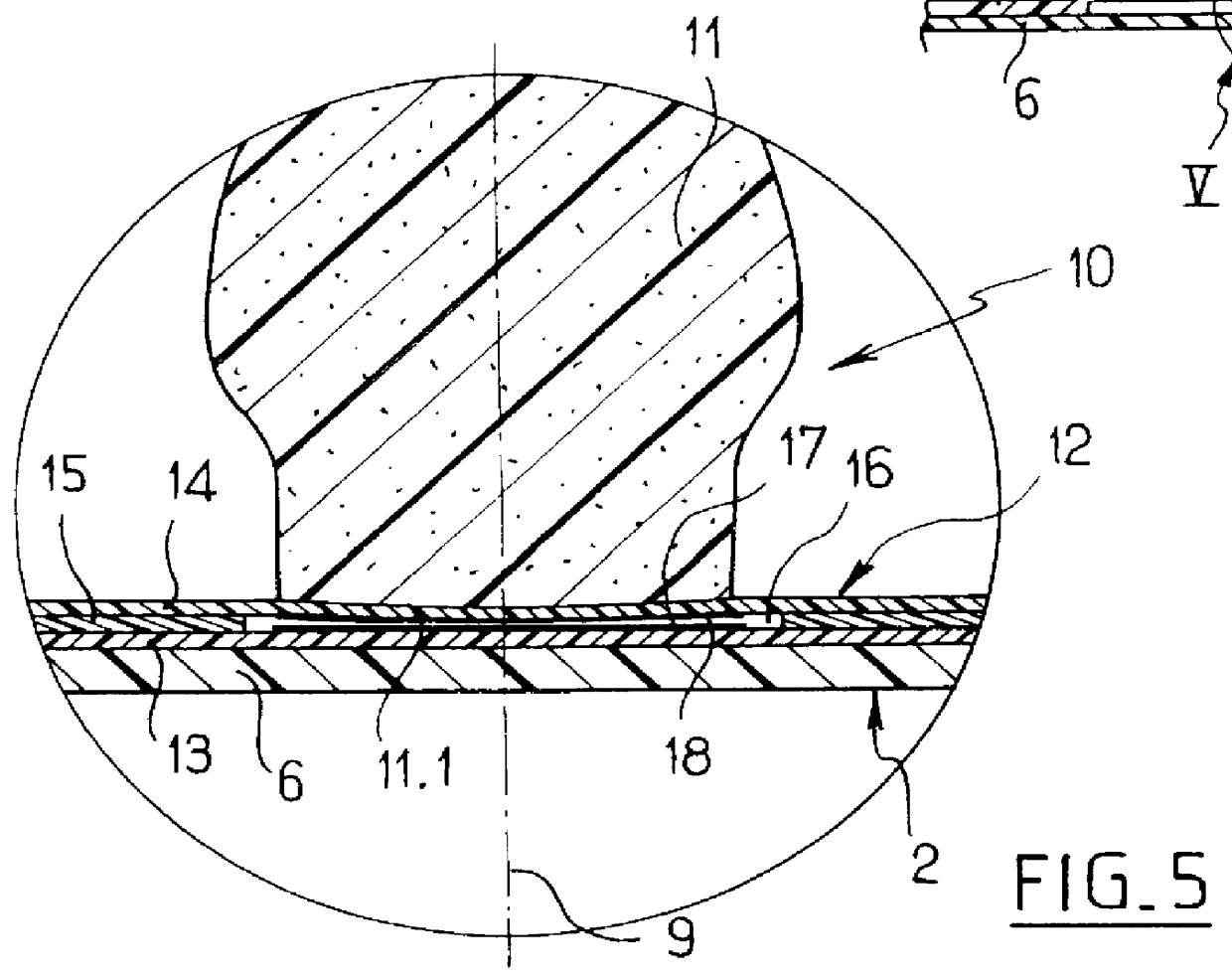
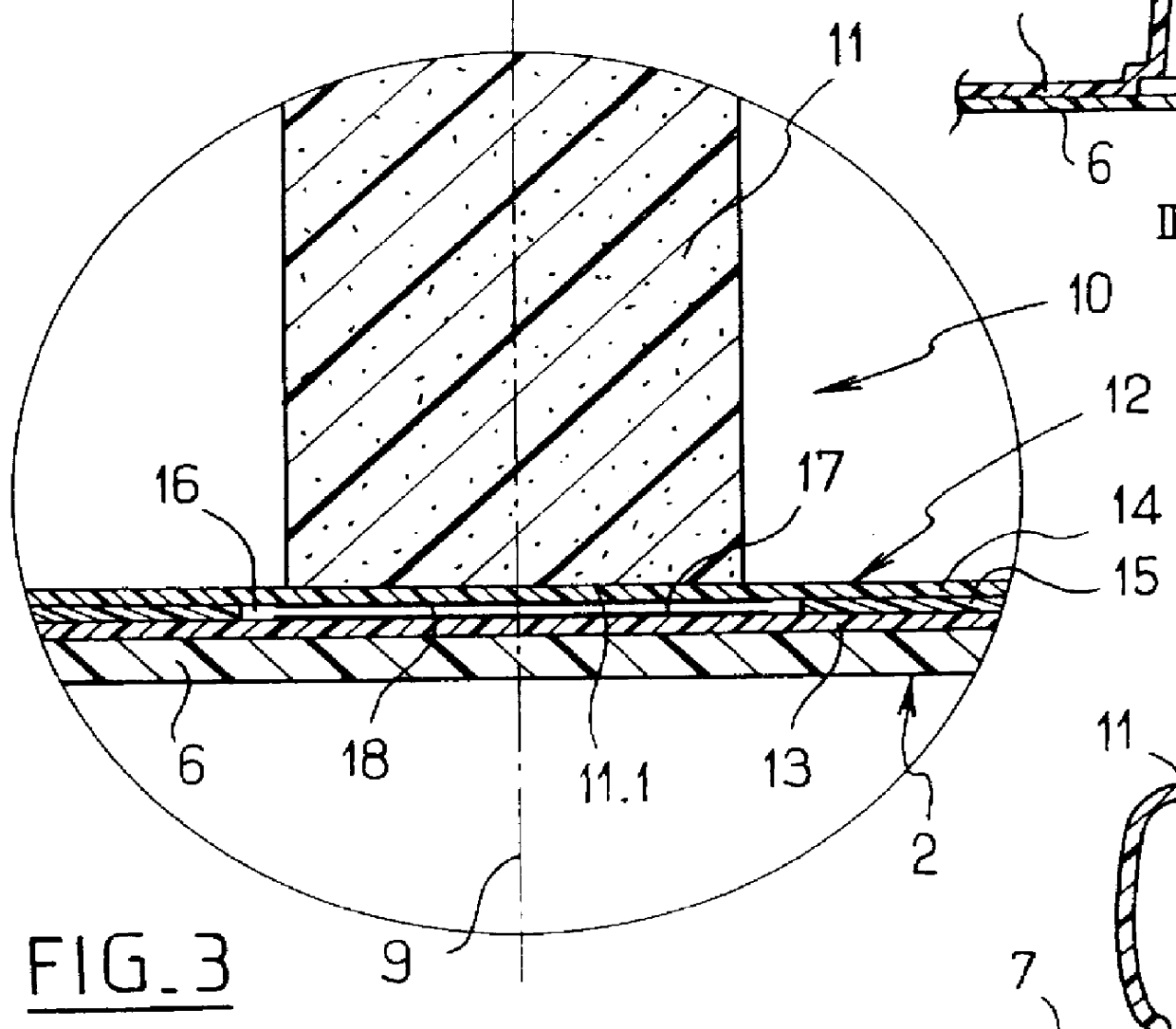
Pneumatic cushion having individually deformable cells
InactiveUS6154907AAdjustable pressureReduce pressureStuffed mattressesSpring mattressesBiomedical engineeringCushion
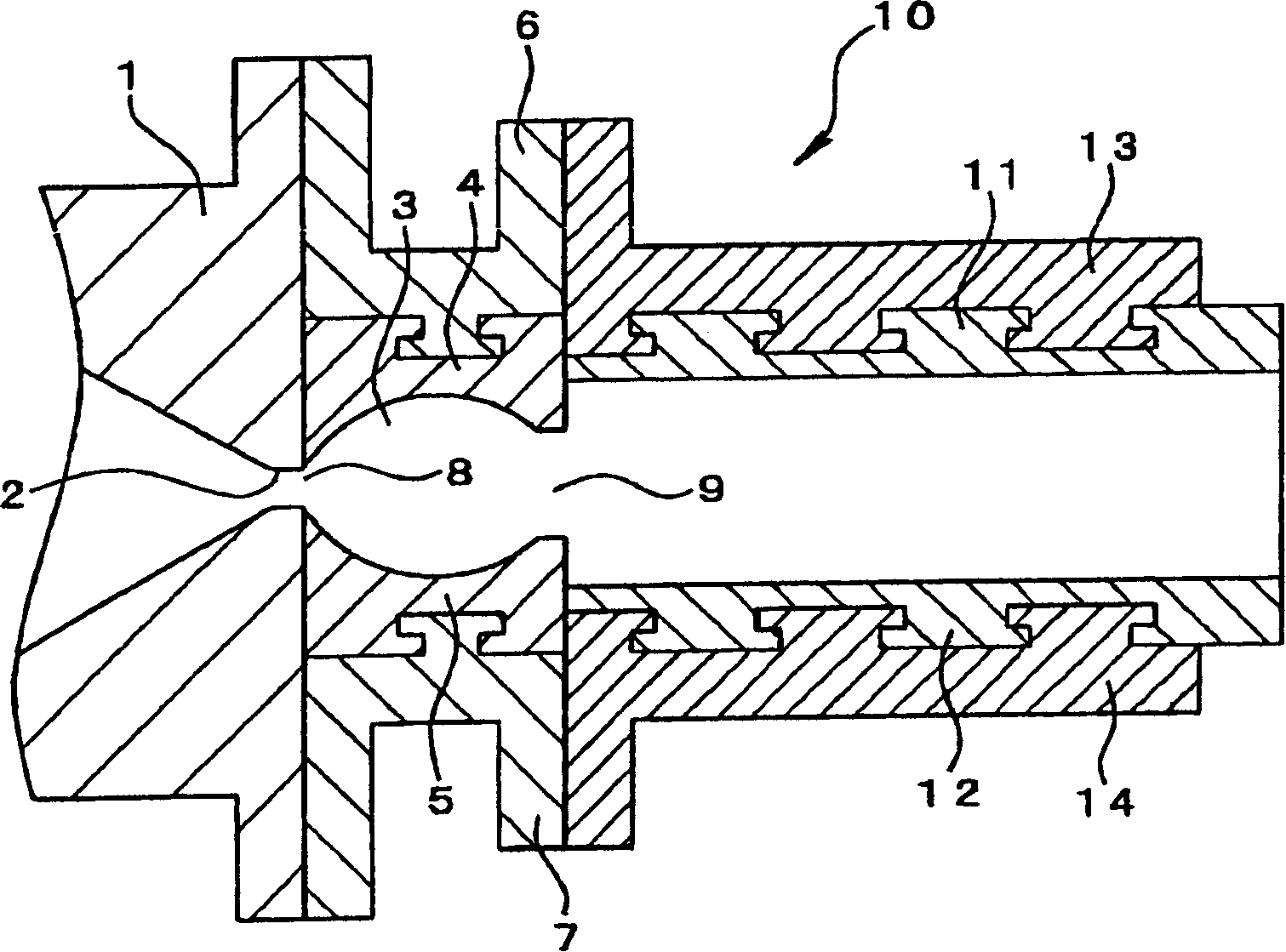
PCT No. PCT / FR98 / 01582 Sec. 371 Date Mar. 8, 1999 Sec. 102(e) Date Mar. 8, 1999 PCT Filed Jul. 20, 1998 PCT Pub. No. WO99 / 04673 PCT Pub. Date Feb. 4, 1999The invention relates to a pneumatic cushion (1) having a base sheet (2) from which there project a plurality of adjacent inflatable cells (3) that are individually deformable in height. At least some of the cells (3) are internally fitted with respective individual sensors of cell deformation that deliver electrical signals indicating that a determined threshold of deformation of a cell (3) has been crossed.
Owner:POLY SYST INJECTION
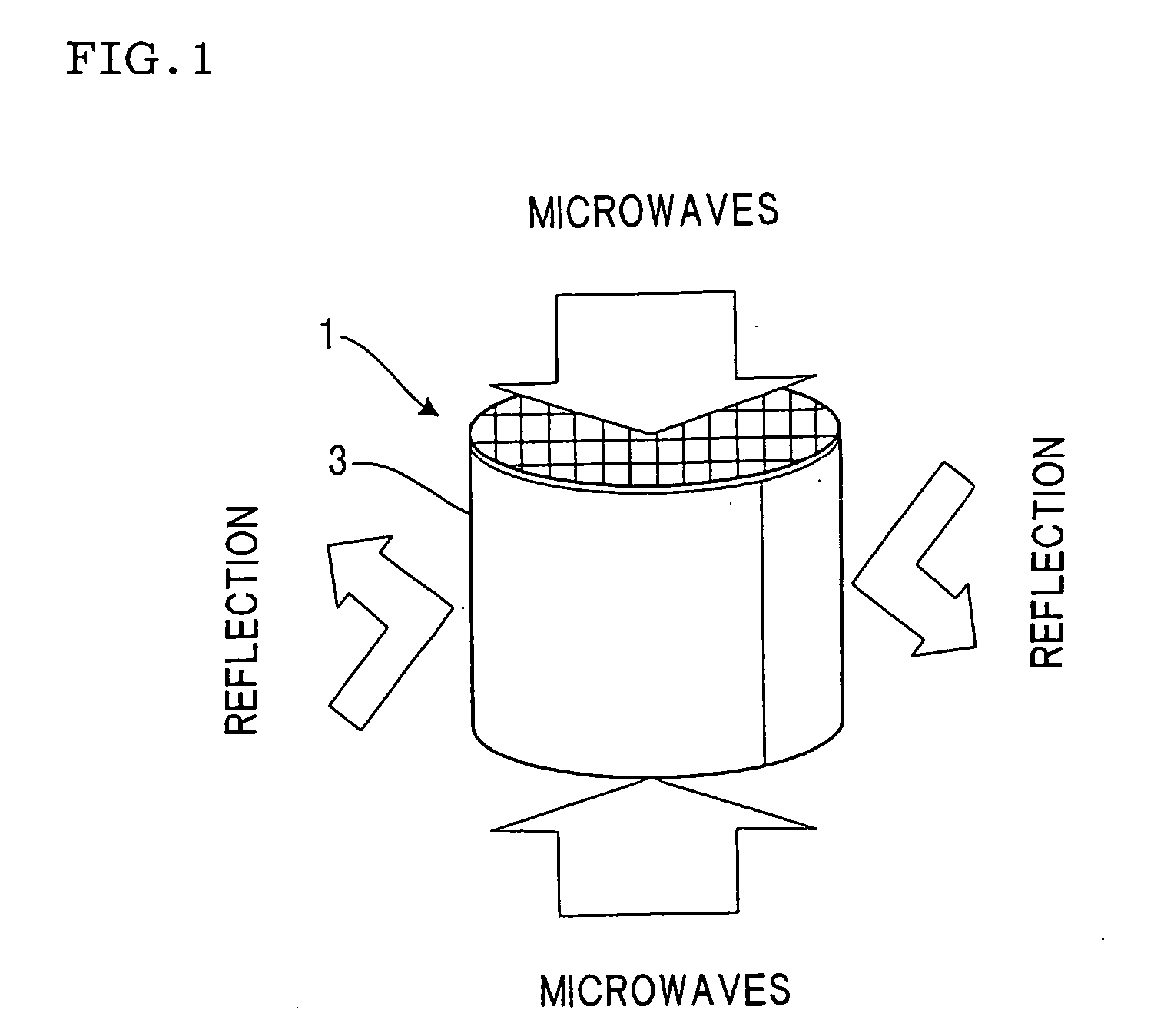
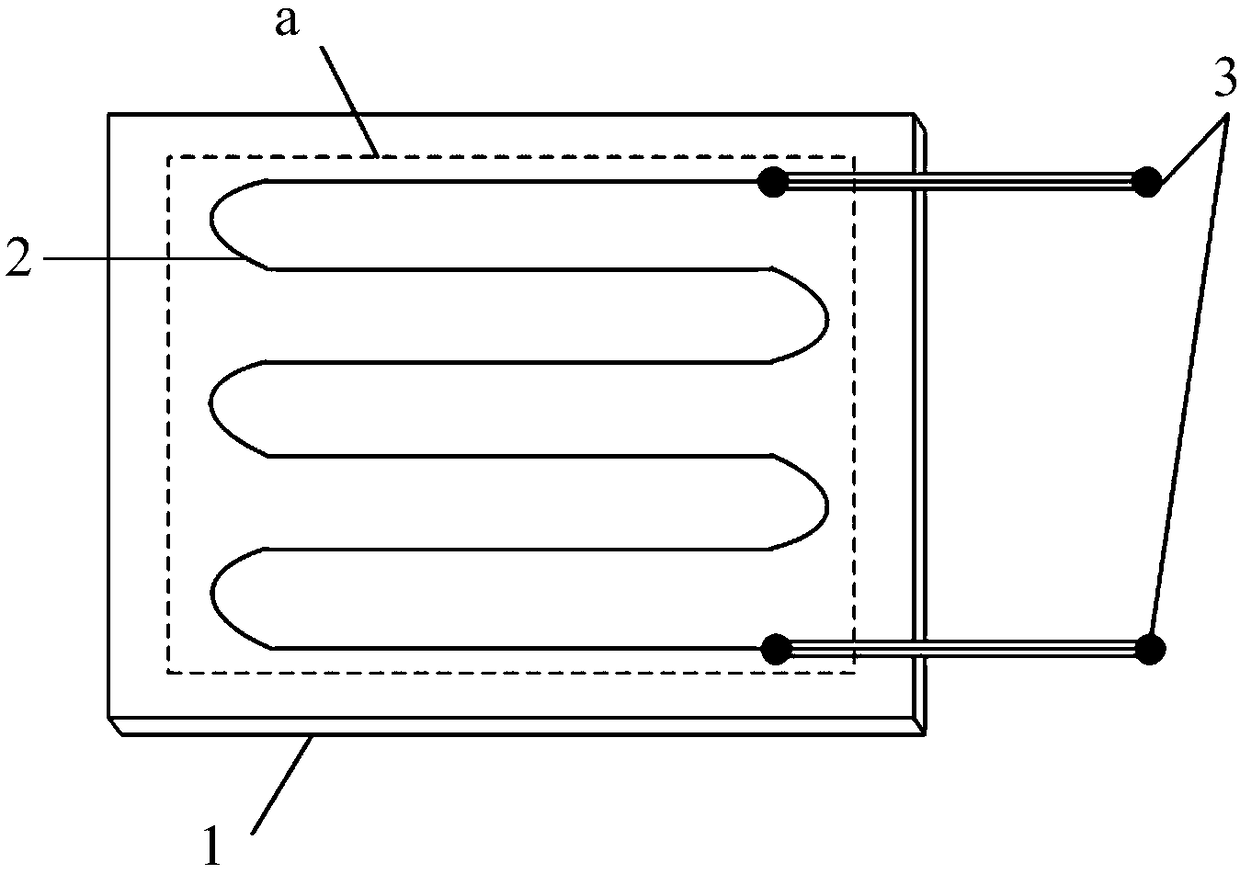
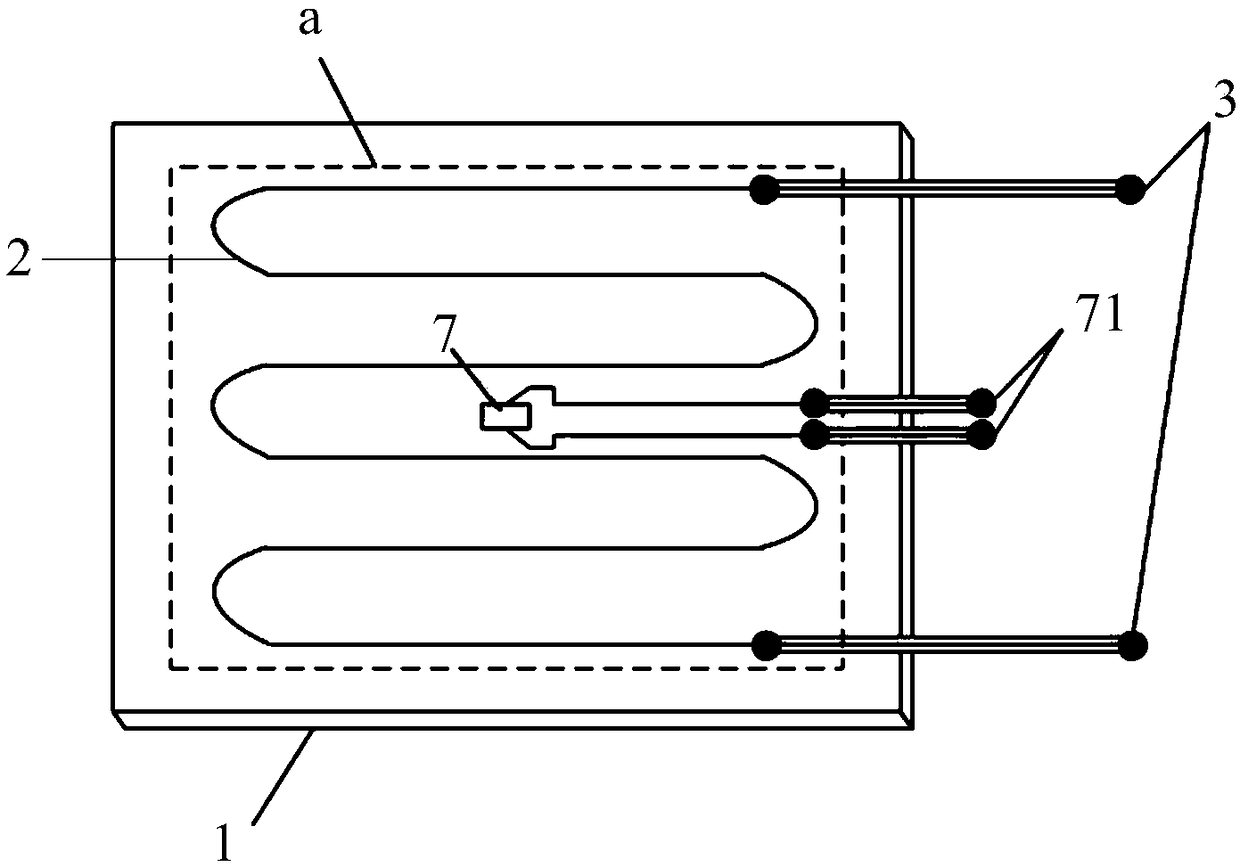
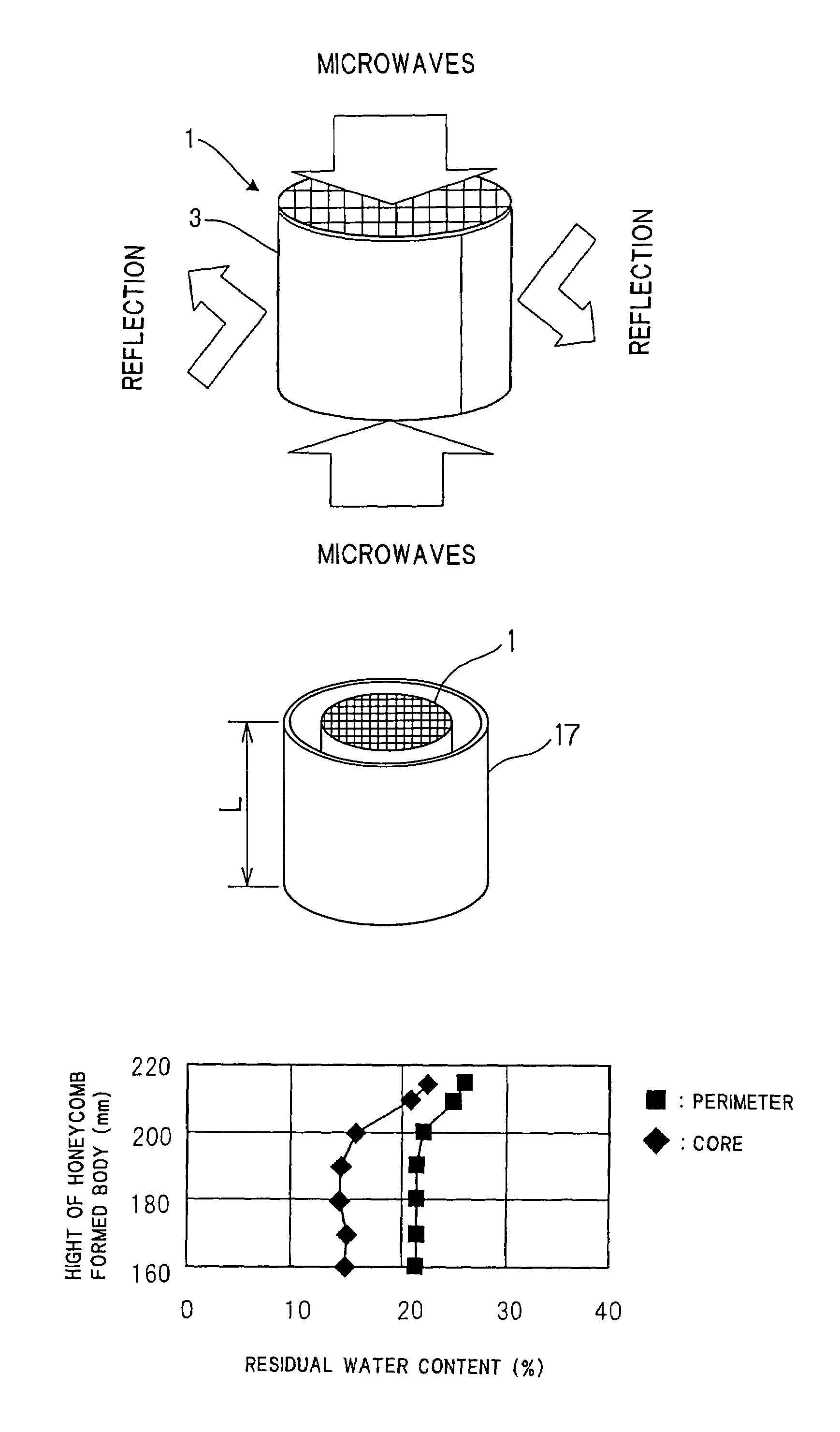
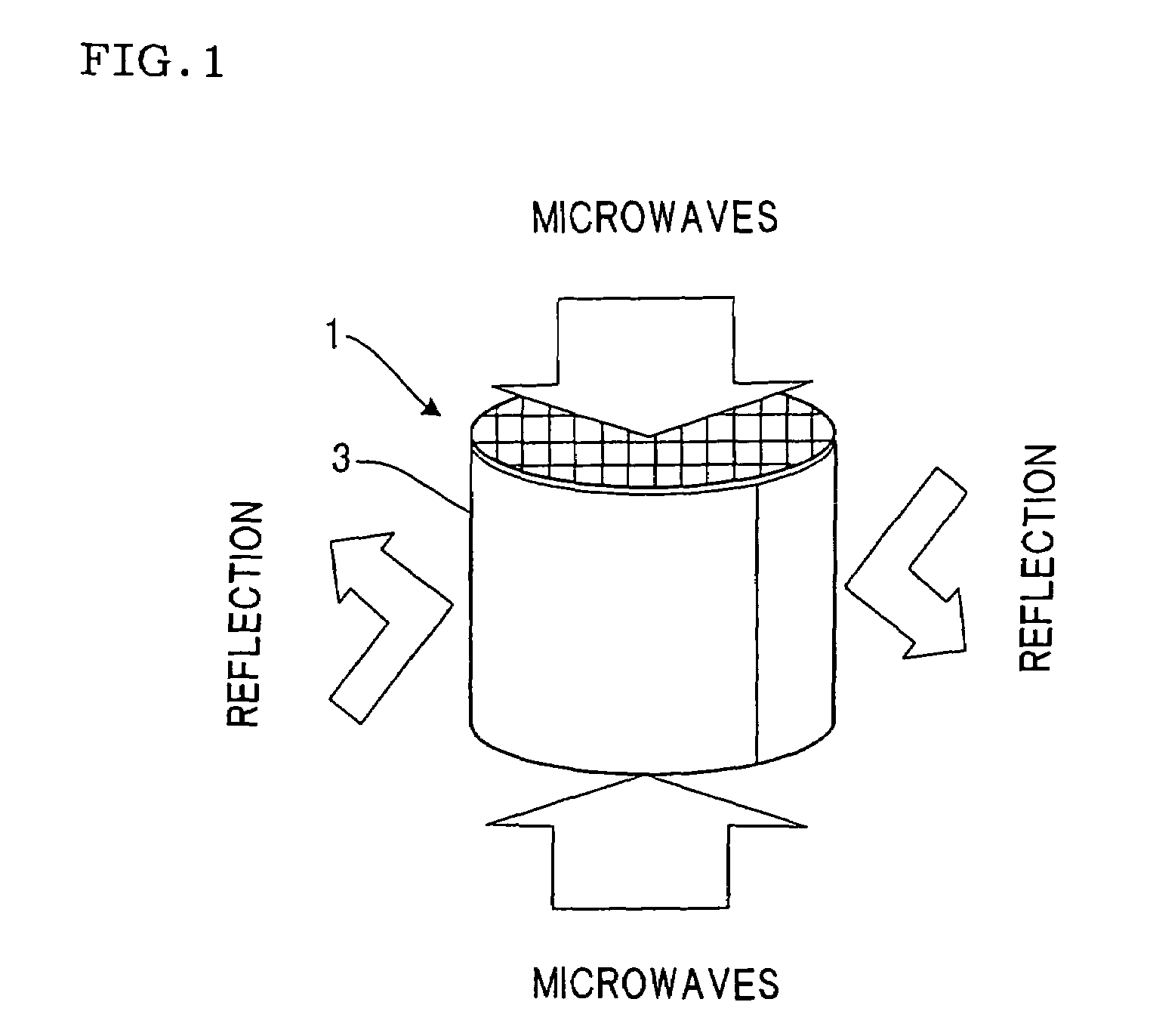
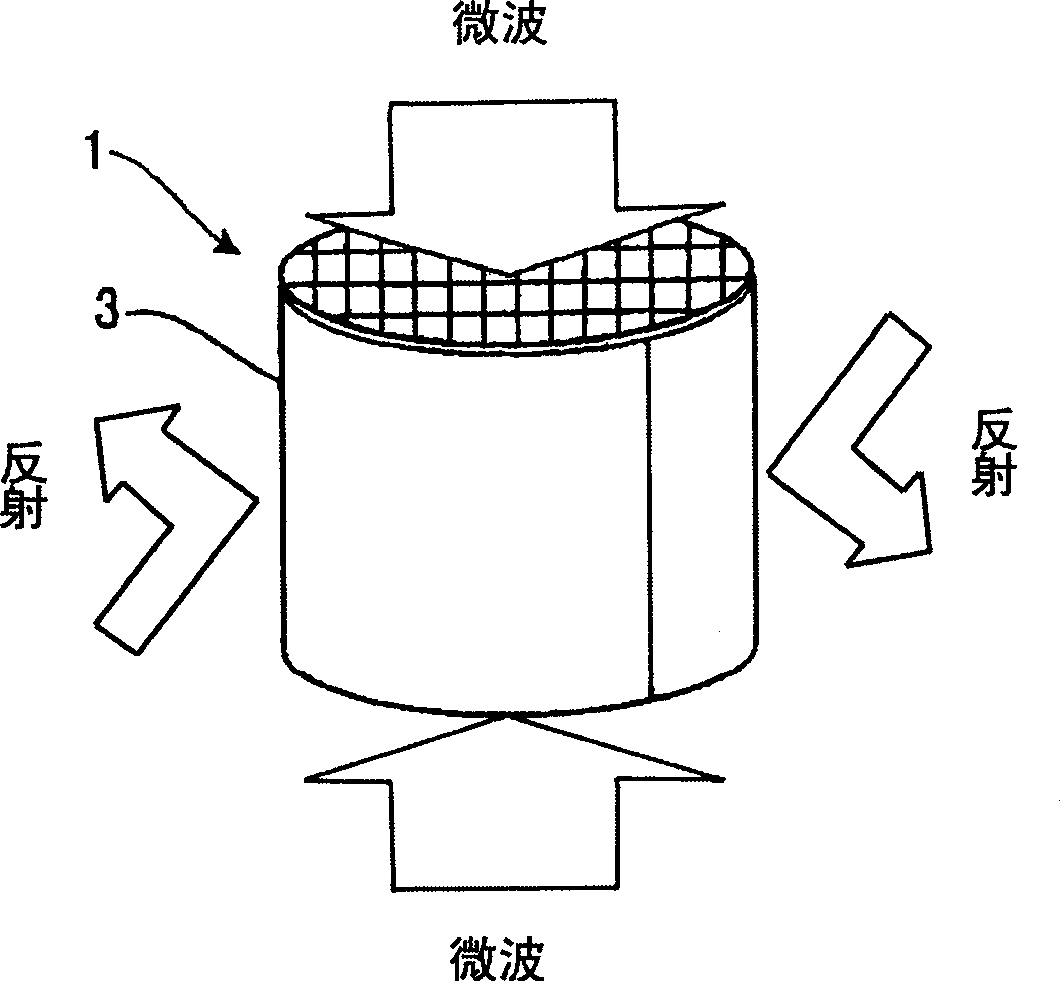
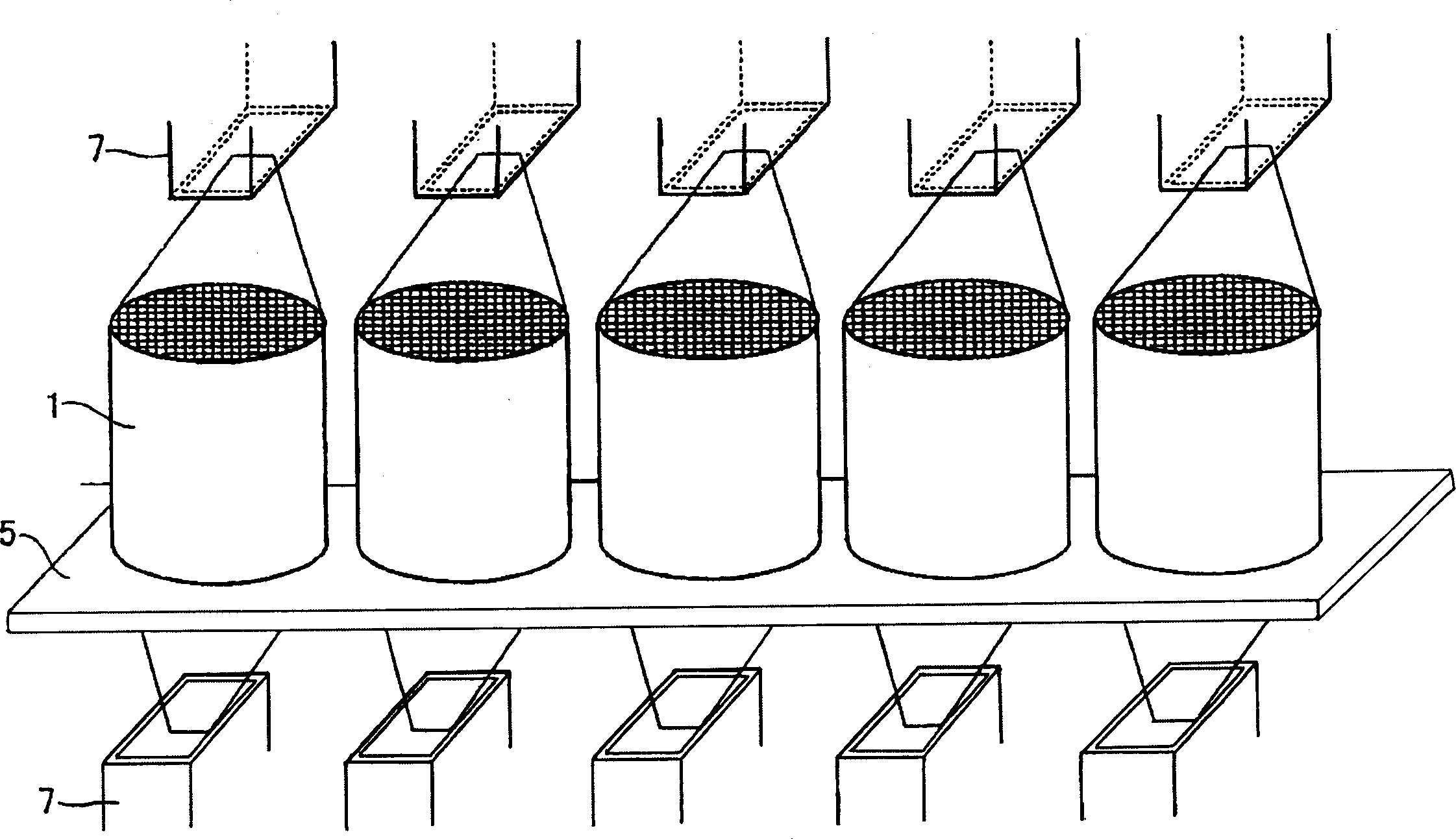
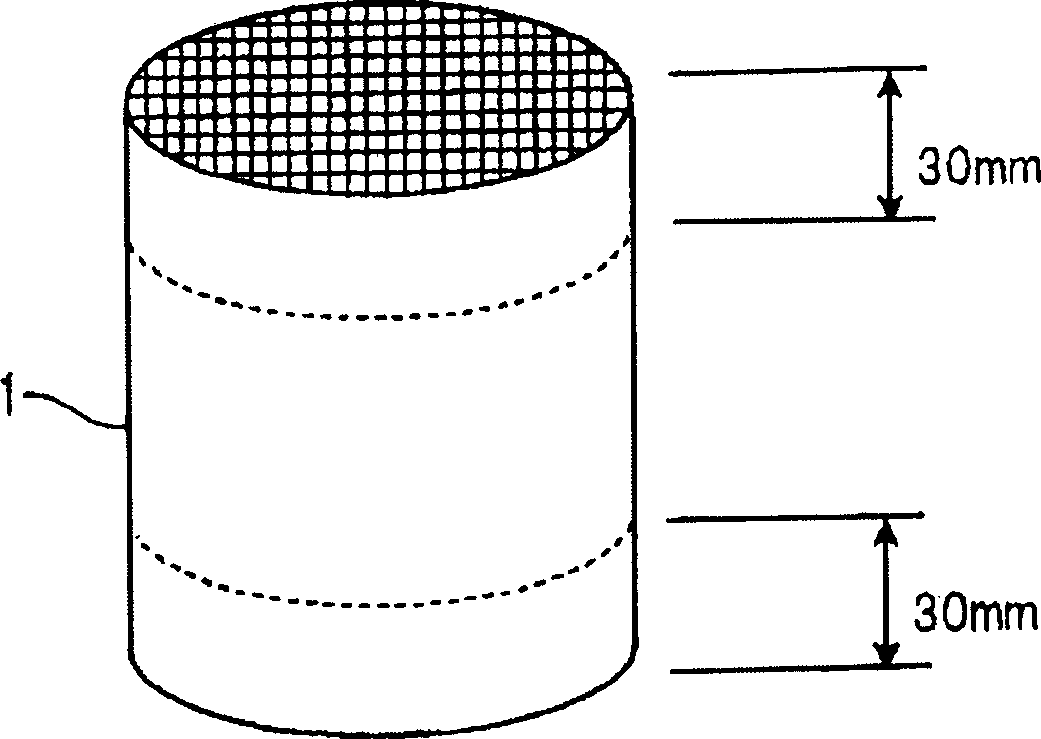
Microwave drying method of honeycomb formed bodies
ActiveUS20060042116A1Lot differenceReduce the differenceDrying solid materials with heatCeramic shaping apparatusHoneycombCell axis
A method for drying a honeycomb formed body using microwaves is provided. The method can reduce the difference in the drying speed inside the honeycomb formed bodies during the drying process and can dry the honeycomb formed bodies without cell deformation. The method comprises placing the honeycomb formed body in a drying furnace with the cell axis in the vertical direction and irradiating the honeycomb with microwaves at a frequency of 300-30,000 MHz. The difference of the water content in the vertical direction of the honeycomb formed body 1 is maintained at 0.3% per mm or less during microwave irradiation.
Owner:NGK INSULATORS LTD
Cathode including insulation layer on cathode tab and secondary battery including the cathode
ActiveUS20140255778A1Reduce the possibilityImprove reliabilityElectrode carriers/collectorsPositive electrodesLithiumInsulation layer
Provided is a cathode including a cathode current collector, a cathode tab protruding from the cathode current collector, and an insulation layer coated with an insulating material on the cathode tab, and a secondary battery including the cathode. Since the cathode of the present invention includes an insulation layer on a cathode tab, the present invention may prevent an internal short circuit which may occur due to cell deformation or sharp edges of electrodes, which are formed during cutting of the electrodes in a preparation process of the battery, when the electrodes are stacked, or may prevent a physical short circuit between the cathode and the anode due to shrinkage of a separator in a high-temperature atmosphere. In a case where the cathode is used in a lithium secondary battery, safety and reliability in battery performance may be significantly improved.
Owner:LG ENERGY SOLUTION LTD
Collector, electrode, secondary cell, and capacitor
InactiveCN104798232AImprove productivityHybrid capacitor electrodesElectrode carriers/collectorsCapacitanceInternal pressure
Owner:FURUKAWA ELECTRIC CO LTD +2
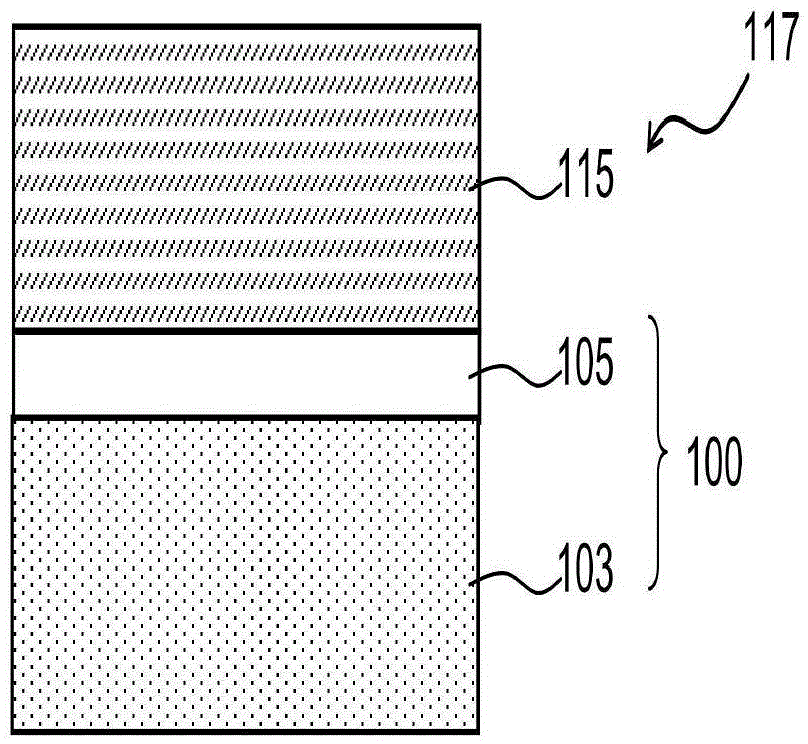
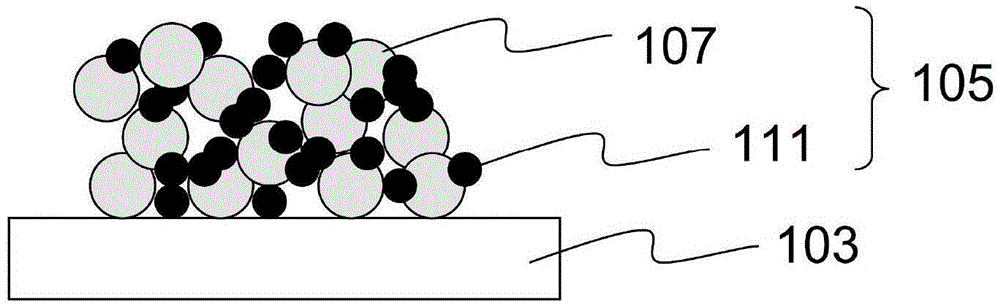
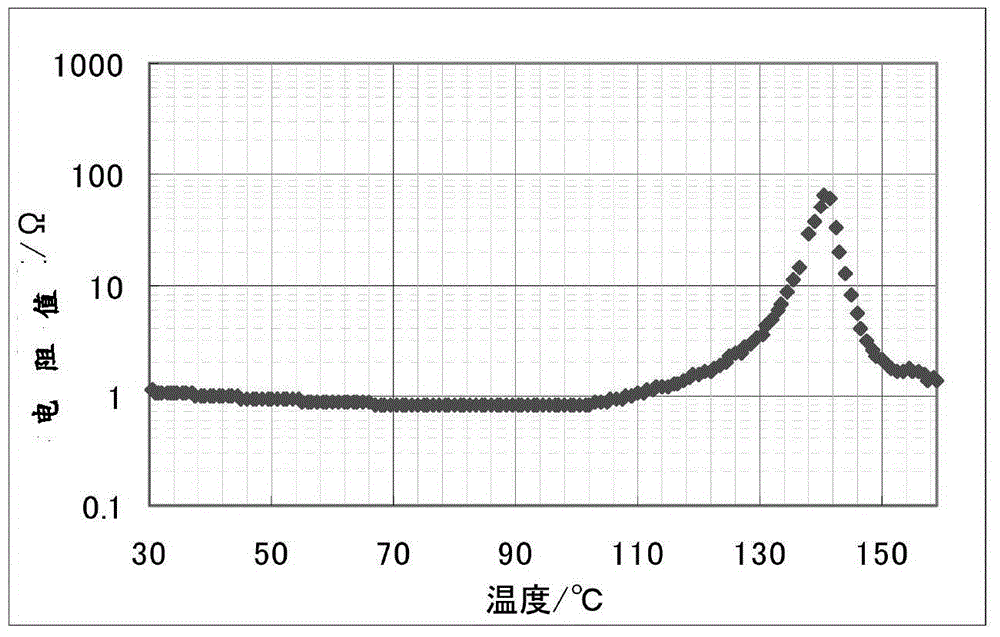
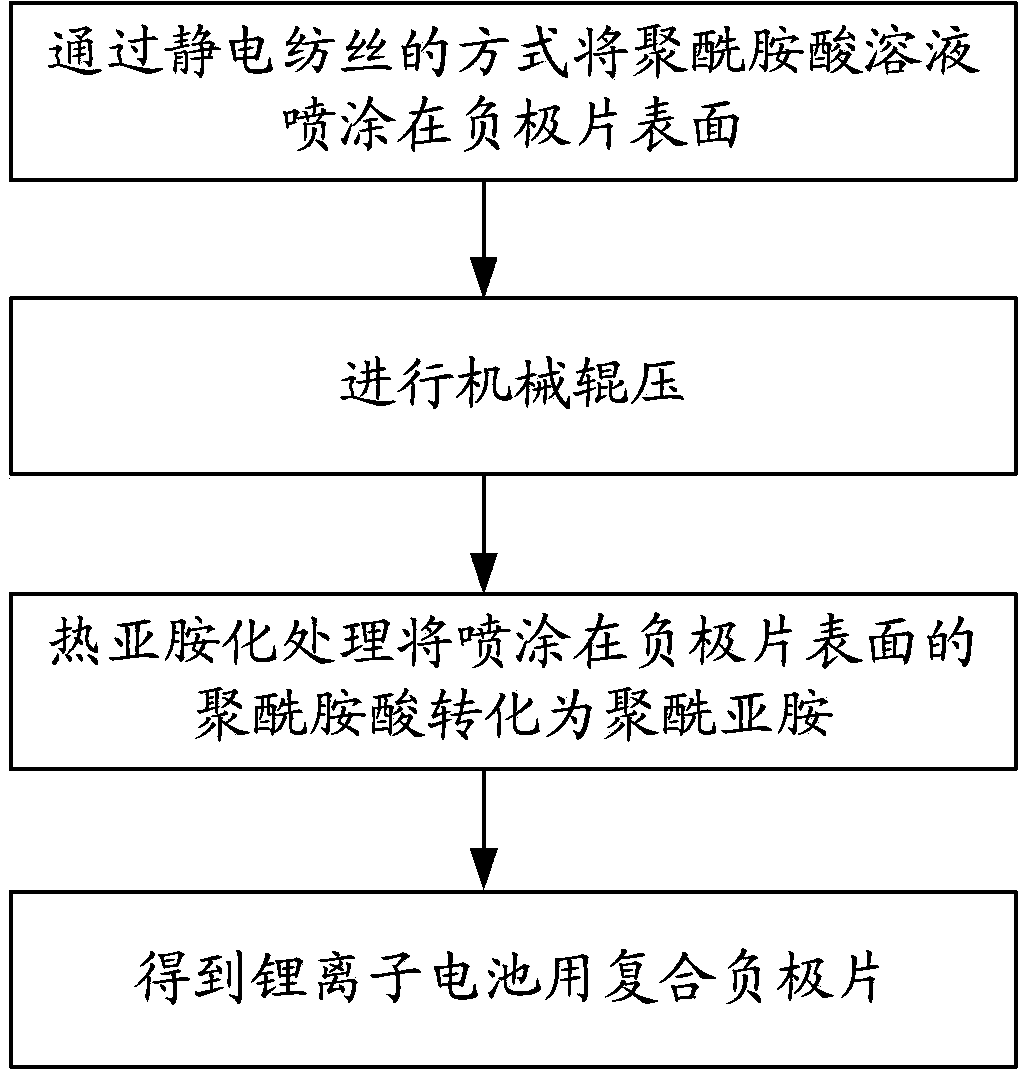
Composite negative plate for lithium ion battery as well as preparation method of composite negative plate and lithium ion battery
ActiveCN103682247AOvercome short circuitOvercoming the problem of battery deformationElectrode rolling/calenderingCell seperators/membranes/diaphragms/spacersPower batteryFiber
The invention provides a composite negative plate for a lithium ion battery as well as a preparation method of the composite negative plate and a lithium ion battery. The preparation method of the composite negative plate for the lithium ion battery comprises the following steps of spraying polyamide acid solution onto the surface of the negative plate in an electrostatic spinning manner, then mechanically rolling the negative plate, finally converting polyamide acid on the surface of the negative plate into polyimide through the heat imidization treatment, and forming a polyimide nanometer fiber membrane on the surface of the negative plate to obtain the composite negative plate for the lithium ion battery. By adopting the preparation method, the process of firstly independently preparing a positive plate, the negative plate and a diaphgram and then winding the diaphragm and the positive and negative plates in the prior art can be simplified, and the internal short circuit and cell deformation problems caused by the winding of the diaphragm and the positive and negative plates in the prior art can be solved. The lithium ion battery prepared by adopting the composite negative plate for the lithium ion battery is excellent in safety performance and long in service life and can be used as a high-capacity and power battery.
Owner:TONGDING INTERCONNECTION INFORMATION CO LTD
Lithium ion battery, coating separator and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN109148798AImprove barrier propertiesReduce short circuitSecondary cellsCell component detailsCoated surfaceElectrochemistry
The invention discloses a lithium ion battery, a coating separator and a preparation method thereof, comprising: a separator base material, wherein the separator base material is a porous polymer filmlayer; A first coating uniformly and continuously formed on at least one surface of the diaphragm substrate; A second coating layer dispersed at a predetermined pitch on the surface of the first coating layer or the surface of the diaphragm substrate by a conical deposit having a preset stacking shape. The first coating and the second coating of the coating diaphragm of the invention increase thebarrier action of the diaphragm between the positive electrode and the negative electrode, and reduce the probability of short circuit in the positive electrode and the negative electrode. The firstcoating also has good thermal stability to the diaphragm substrate. The second coating is sprayed by atomization, the cone-shaped deposit has little effect on the permeability of the membrane, and thegap provides a better channel for the flow and infiltration of the electrolyte. The second coating also possesses cold / hot pressing irreversible deformation and good adhesion, which reduces the riskof cell deformation and improves the electrochemical performance of the battery.
Owner:SUNWODA ELECTRIC VEHICLE BATTERY CO LTD
Cell deformation detection device and method, and terminal
InactiveCN108548517ASecondary cellsElectrical/magnetic solid deformation measurementElectricityComputer terminal
The embodiment of the invention discloses a cell deformation detection device and method, and a terminal; the cell deformation detection device comprises a deformation detection module and a control module; the control module and the deformation detection module are electrically connected; the deformation detection module is used for detecting cell deformations; the control module is used for determining whether the cell has deformation abnormity or not according to the deformation detection result of the deformation detection module; the deformation detection module and the control module arearranged, so the cell deformation detection device can have cell deformation detection and deformation abnormity determination functions, thus safely detecting cells.
Owner:VIVO MOBILE COMM CO LTD
Microwave drying method of honeycomb formed bodies
ActiveUS7197839B2Lot differenceReduce the differenceDrying solid materials with heatCeramic shaping apparatusHoneycombCell axis
A method for drying a honeycomb formed body using microwaves is provided. The method can reduce the difference in the drying speed inside the honeycomb formed bodies during the drying process and can dry the honeycomb formed bodies without cell deformation. The method comprises placing the honeycomb formed body in a drying furnace with the cell axis in the vertical direction and irradiating the honeycomb with microwaves at a frequency of 300–30,000 MHz. The difference of the water content in the vertical direction of the honeycomb formed body 1 is maintained at 0.3% per mm or less during microwave irradiation.
Owner:NGK INSULATORS LTD
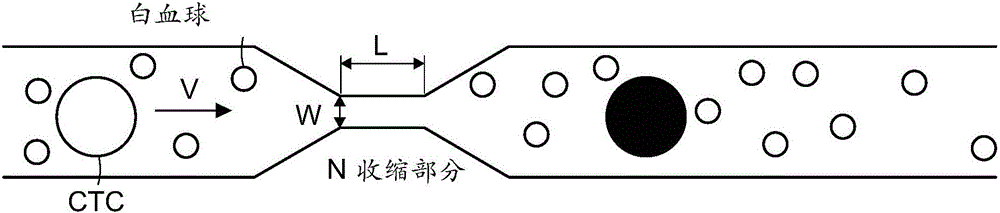
A cancer cell separation device based on cell deformation quantity and dielectrophoresis force and a control system
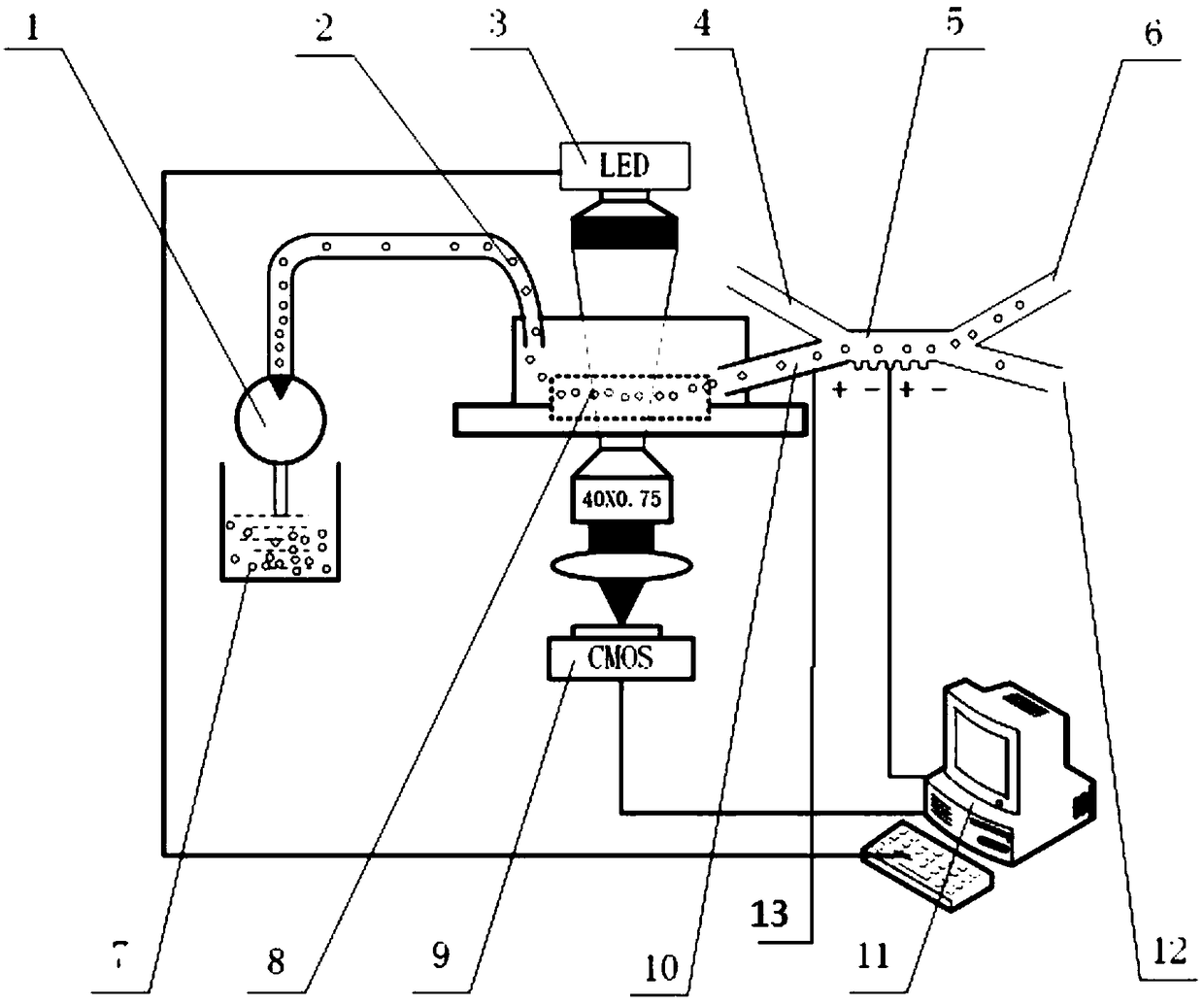
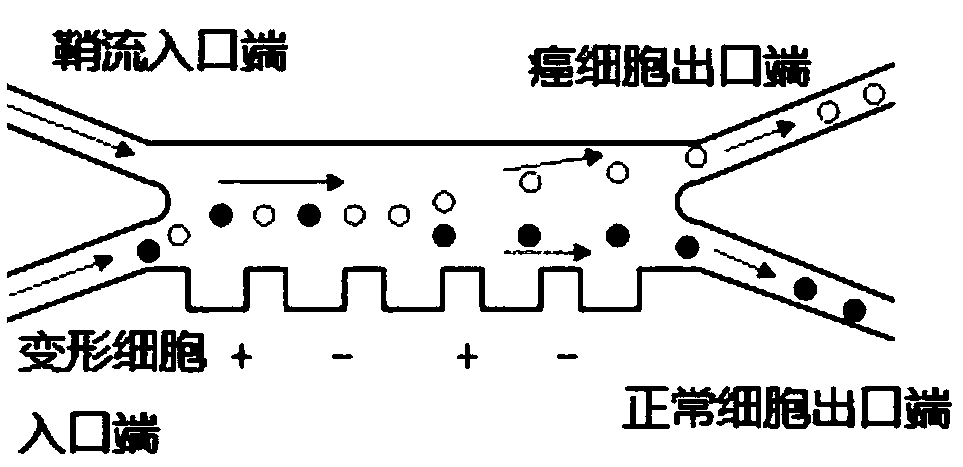
A cancer cell separation device based on cell deformation quantity and dielectrophoresis force and a control system are disclosed. The device includes a cell reservoir and an injection micropump. Oneend of the injection micropump extends into the cell reservoir and the other end is connected to an inlet end of a cell deformation quantity detection chip. An outlet end of the cell deformation quantity detection chip is connected to a deformed cell inlet end of a cancer cell separation chip. A CMOS high-speed camera is disposed below the cell deformation quantity detection chip to capture deformed cell images. A processor determines the deformation quantity of a deformed cell according to an acquired deformed cell image, and determines whether the deformed cell is a cancer cell or not according to the deformation quantity, and if yes, the processor outputs a drive signal to drive an electrode to generate dielectrophoresis force to allow the deformed cell to flow towards a cancer cell outlet end of the cancer cell separation chip. Through the device and the system, deformation quantity of cells can be detected rapidly, and cancer cells can be separated from blood samples of patients according to the difference in deformation quantity between the cancer cells and normal cells.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
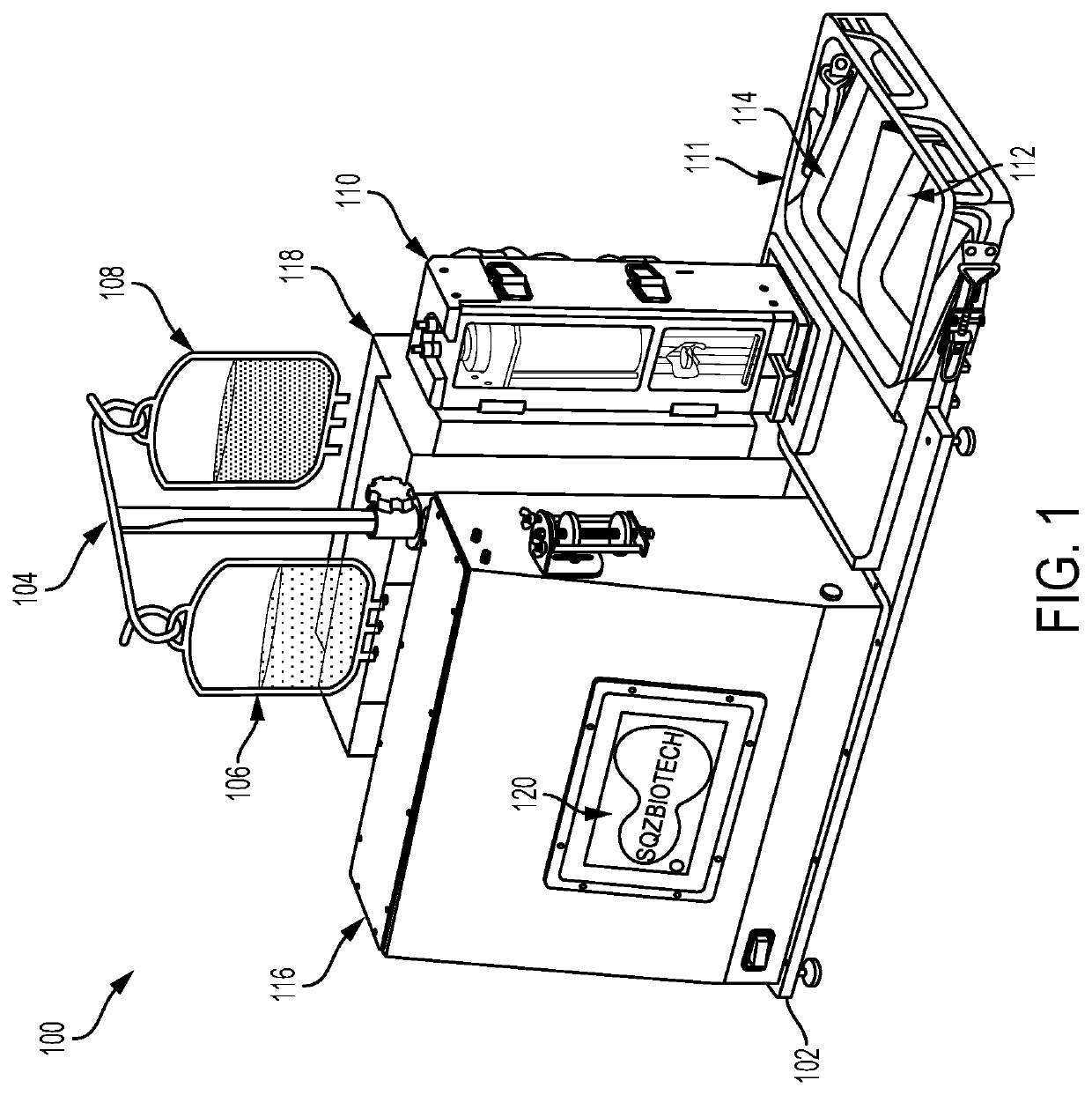
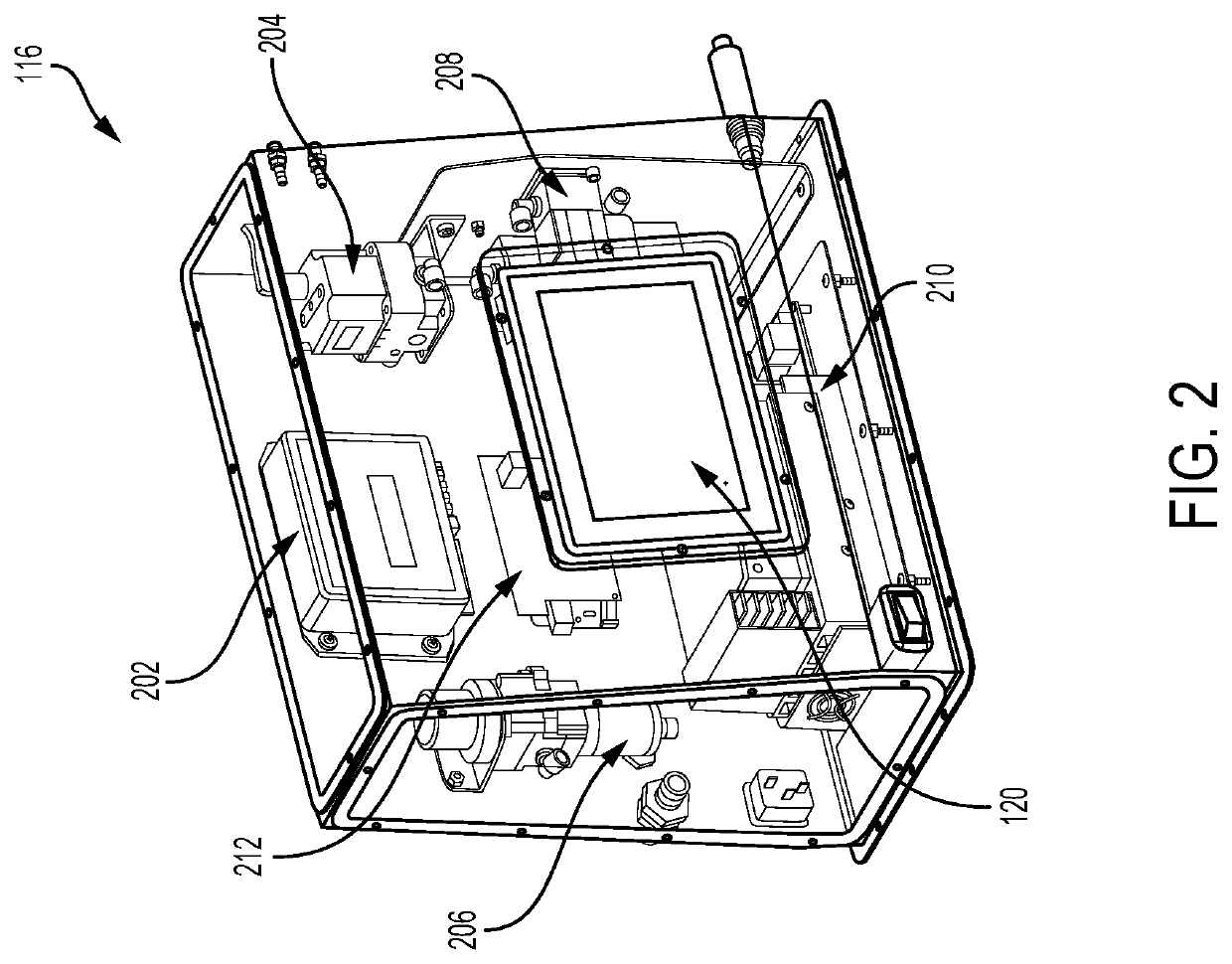
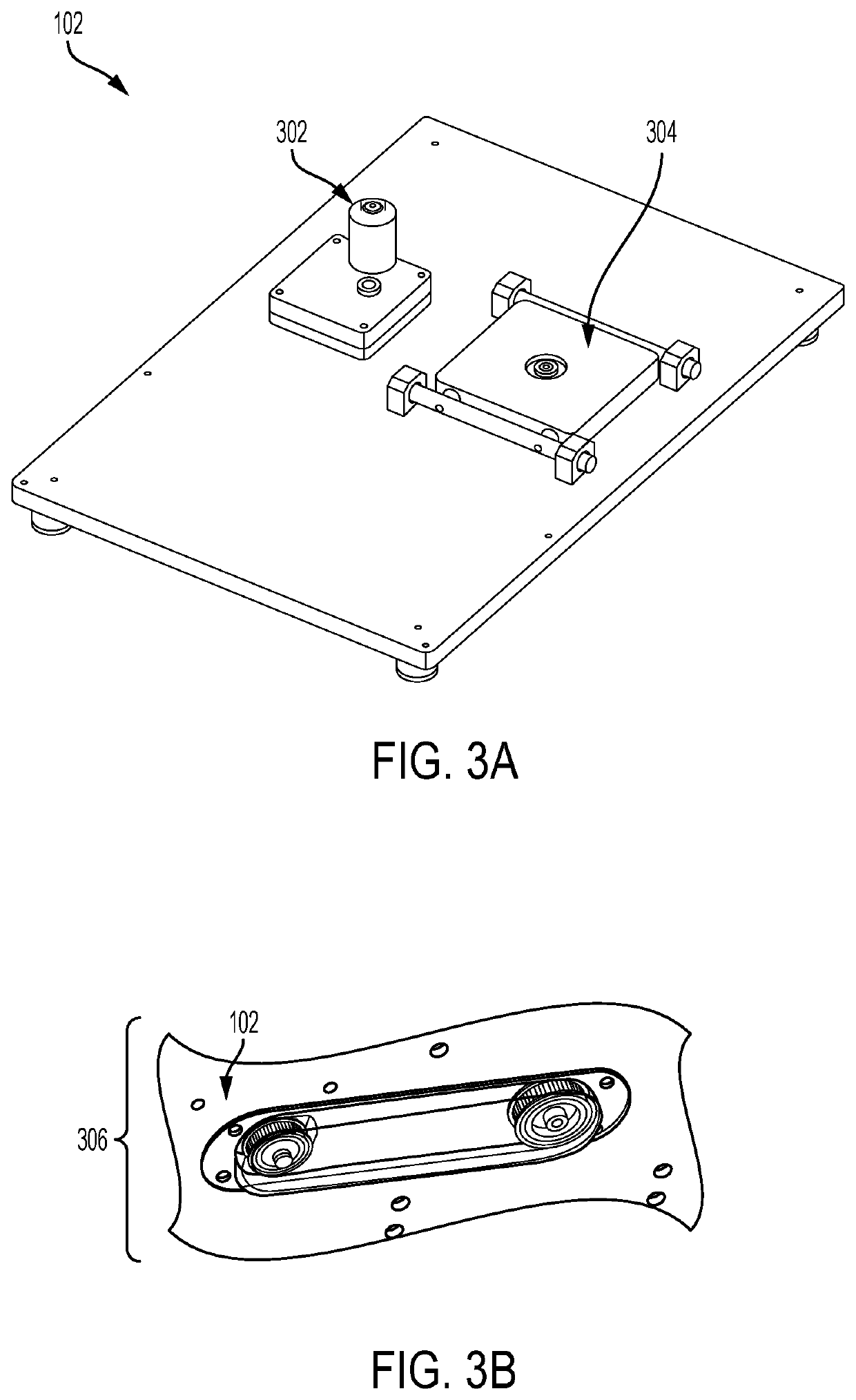
System for delivery of a payload into a cell
PendingUS20200332243A1Improve consistencyIncrease ratingsPreparing sample for investigationLaboratory glasswaresMechanical engineeringCellular membrane
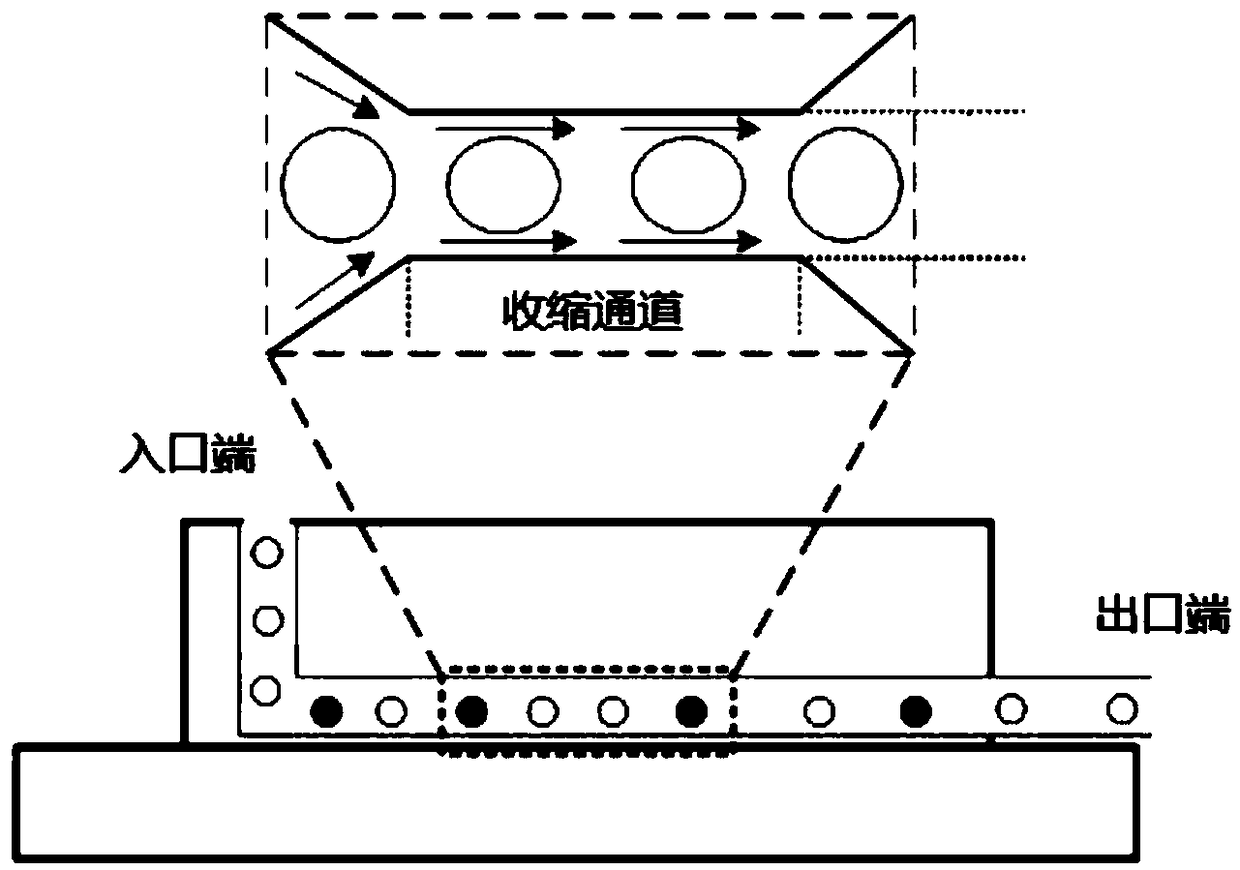
A system for delivering a payload to a cell that includes: a platform supporting an input container, an output container, and a receiver for receiving all or part of a disposable assembly, the disposable assembly including a preparation vessel and a constriction cartridge. The preparation vessel holds a cell suspension as it is prepared for passage through one or more cell-deforming constrictions, and the constriction cartridge houses a component that includes the one or more cell deforming constrictions. Passage through the cell-deforming constrictions causes perturbations in cell membranes to allow entry of a payload into the cells. The system includes one or more processors configured to receive input from a user and to automatically control pressure, temperature, agitation, and / or flow of the cell suspension as it passes through the input container, through the preparation vessel, through the constriction cartridge, and to the output container.
Owner:SQZ BIOTECH CO
Intelligent energy absorbing material and preparation method thereof
The invention provides a preparation method of a high temperature-resistant intelligent energy absorbing material. A damping and protecting material with a high buffering performance is prepared with energy absorbing gel as a filler and a silicone rubber foamed material as a base body. The energy absorbing gel spontaneously becomes hard from soft when being impacted, and absorbs energy in the becoming process in order to realize an effective protection effect, and the silicone rubber foamed material used as the structure base body also can absorb parts of impact energy through cell deformation when being acted, so the base body and the filler are simultaneously used to realize damping and buffering effects.
Owner:深圳市思创新材科技有限公司
Method for fixing fish brain tissue specimen through systemic heart perfusion
InactiveCN104568542AFix fixityTissue AutolysisPreparing sample for investigationSurgical veterinaryIntubationCommon cardinal veins
The invention discloses a method for fixing a fish brain tissue specimen through systemic heart perfusion. The method is mainly characterized in that after fish anesthesia, thoracotomy is performed on the periphery of a heart surface projection area of the fish, ventral aorta intubation is performed through the ventricle, common cardinal vein intubation is performed through the atrium, ligation with an operation thread is used for fixing, and an out flow tube is connected with a graduated vessel for measuring liquid out-flowing quantity; a constant-speed perfusion pump is used for perfusing normal saline through a perfusion tube, and a 10% formalin solution is adopted for reperfusion; when perfusion is started, a line is marked on the skull instantly and craniotomy is performed, and the perfusion time is then decided through combination of the perfusion quantity and the out-flowing quantity when the color of the brain tissue changes white; the brain is picked and placed in the 10% formalin solution to be fixed for 48 h after perfusion is stopped, and the brain tissue specimen with complete structure, normal form and good state is obtained. By means of the method, the problems of insufficient fixing, non-comprehensive fixing area, tissue autolysis, cell deformation and the like of the fish brain tissue can be solved effectively, the brain tissue specimen with more complete structure and more ideal state is obtained easily, and the natural form is retained better.
Owner:YANSHAN UNIV
Microwave drying method of honeycomb formed bodies
ActiveCN1740722AReduce drying speed differenceDrying solid materials with heatHearth type furnacesHoneycombCell axis
A method for drying a honeycomb formed body using microwaves is provided. The method can reduce the difference in the drying speed inside the honeycomb formed bodies during the drying process and can dry the honeycomb formed bodies without cell deformation. The method comprises placing the honeycomb formed body in a drying furnace with the cell axis in the vertical direction and irradiating the honeycomb with microwaves at a frequency of 300-30,000 MHz. The difference of the water content in the vertical direction of the honeycomb formed body 1 is maintained at 0.3% per mm or less during microwave irradiation.
Owner:NGK INSULATORS LTD
Polystyrene serial resin extruded foam plate and its producing method
InactiveCN1392183AGood insulation performanceLow greenhouse effectThin material handlingApparent densityFoaming agent
A polystyrene resin extruded foam plate is obtained by extruding a foamable molten resin mixture comprising a mixed blowing agent containing the isobutane (except a chlorofluorocarbon and / or a fluorocarbon) and a polystyrene resin from a high-pressure zone to a low-pressure zone and has >=10 mm thickness and 25-60 kg / m3 apparent density. The residual amount of the isobutane in the foam plate is 0.45-0.80 mol based on 1 kg of the foam plate. Furthermore, the foam plate has 0.05-0.18 mm average cell diameter in the thickness direction and 0.7-1.2 cell deformation ratio (the average cell diameter in the thickness direction / the average cell diameter in the horizontal direction) and satisfies type 3 of the flammability standard of the polystyrene extruded foam heat insulating plate described in JIS A9511(1995) and further has <=0.028 W / mK thermal conductivity of the foamed plate.
Owner:JSP CORP
Soap embedded plant section method
InactiveCN101762412AShort preparation cycleShorten the timePreparing sample for investigationEngineeringHuman health
The invention relates to a soap embedded plant section method which adopts soap as embedding material, and overcomes the defects that the traditional paraffin section method is slow in speed, complicated in operation, large in cell deformation, expensive in expense, hard in obtaining a thin slice by hands, harmful for human health due to dimethylbenzene, and the like. The method has the advantages of short manufacturing period generally needing about five hours, fewer steps for the treatment of herbarium, small deformation of section preparation cells, low cost in manufacture of the slice, no hurt for the body of an experimenter, no environmental pollution, etc.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
Antimicrobial coatings
ActiveUS20180320000A1Improve economyPrevent adhesionBiocideOrganic active ingredientsLysisDisinfectant
A coating comprising a metal-organic framework, wherein the metal-organic framework having a zeolitic structure comprising at least one multivalent metal species and at least one organic ligand (such as zeolitic imidazolate framework (ZIF)). Said coating has a topography comprising an array of projections, and each projection having at least one tapered distal end. There is also provided a method of coating substrates with the disclosed coating and use of said coating as a disinfectant, an antiseptic, or an antibiotic. Such use is possible because the tapered distal end of the disclosed zeolitic structure exerting higher pressure on any microbial cell that comes into contact with the disclosed coating, thereby piercing through the cell membrane more easily, causing cell deformation and lysis.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
Optical-based cell deformability
Owner:COLORADO SCHOOL OF MINES
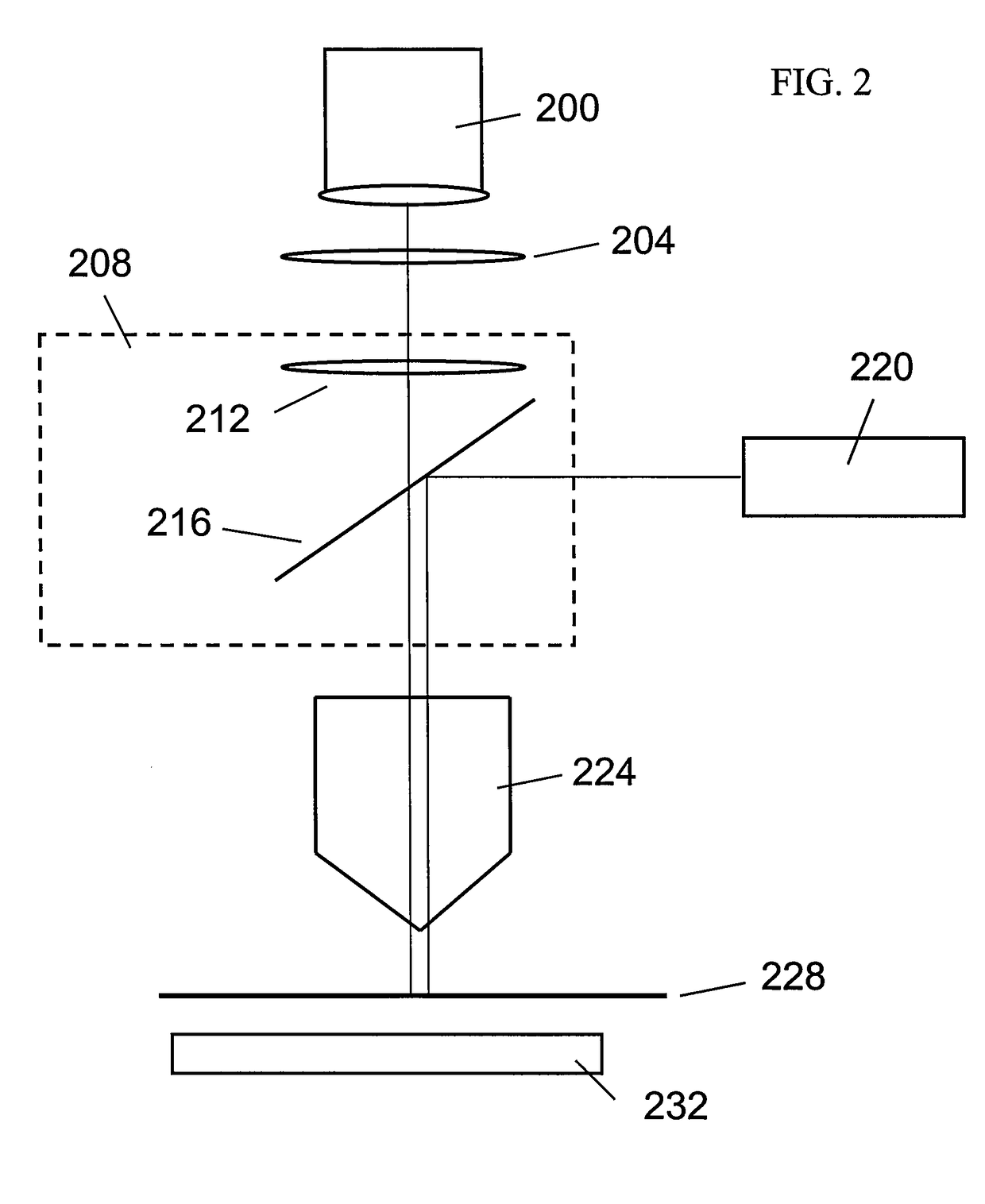
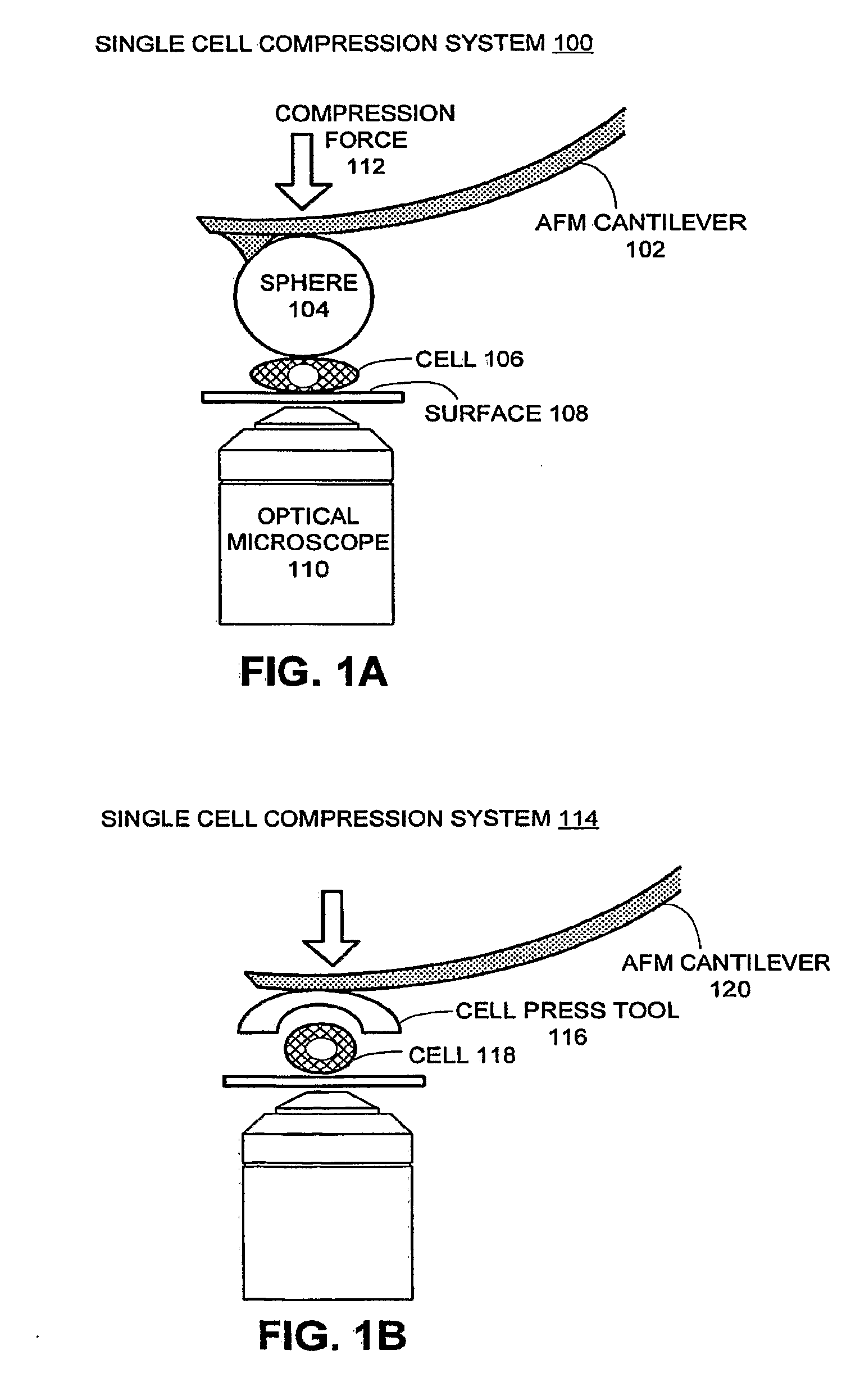
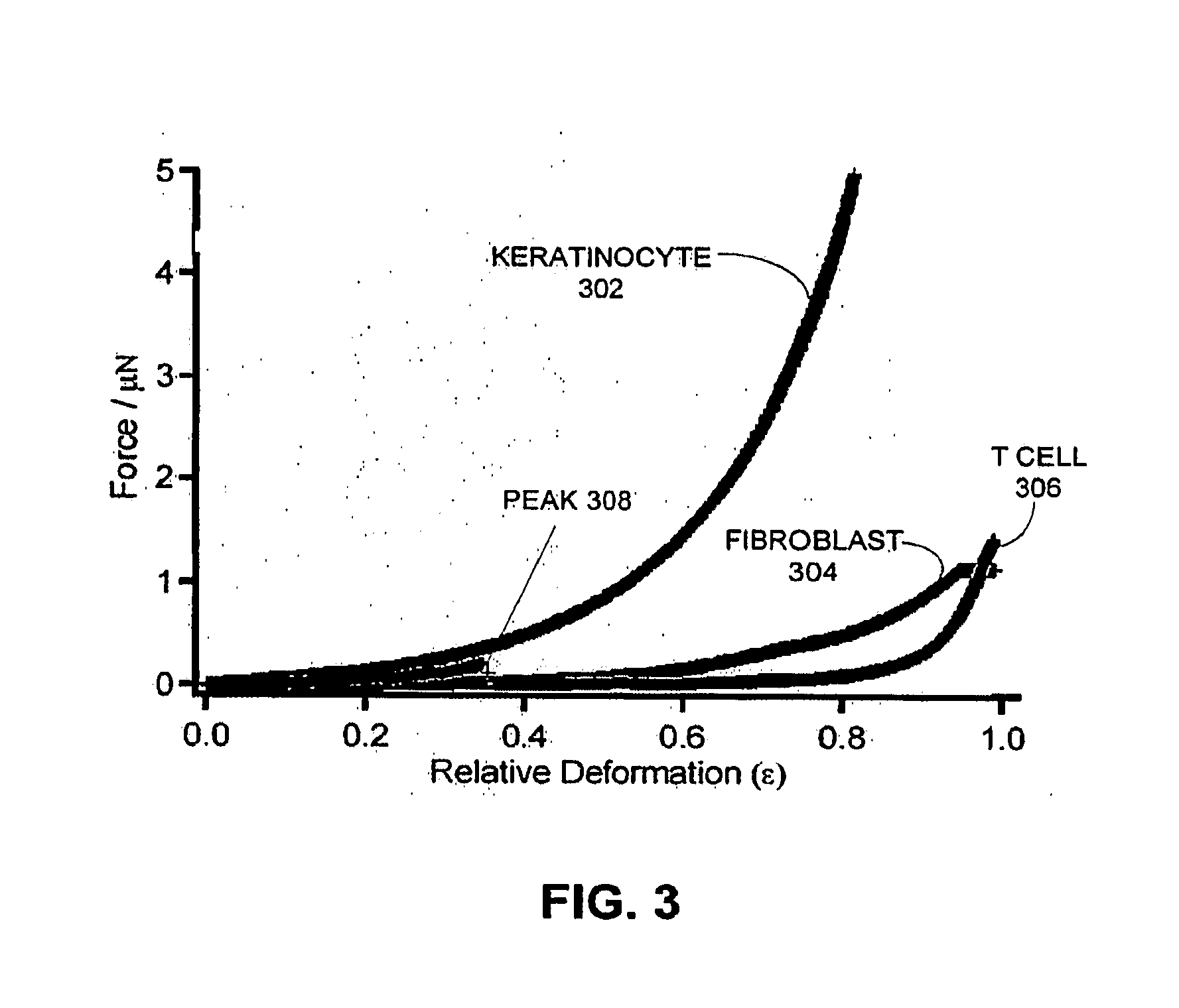
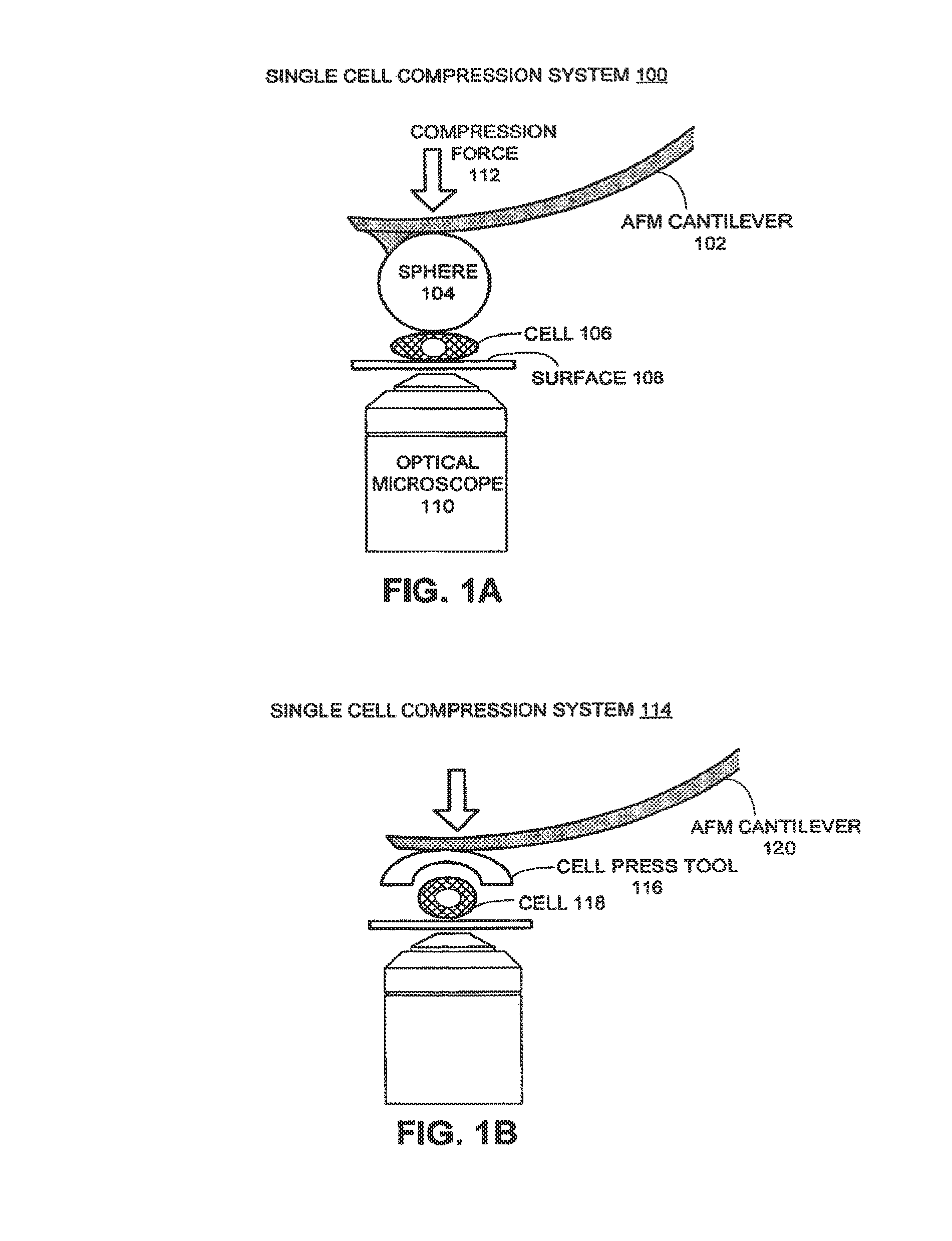
Method and system for measuring single cell mechanics using a modified scanning probe microscope
ActiveUS20090263850A1Small dimensionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCell mechanicsScanning electron microscope
One embodiment of the present invention provides a system that measures single cell mechanics using a scanning probe microscope. During operation, the system positions a modified probe of the scanning probe microscope above a cell which is located on a surface, wherein the modified probe is configured with a geometry for compressing the cell. The system then comprises the cell against the surface using the modified probe, thereby causing the cell to deform. Next, the system extracts mechanical properties of the cell from cell deformation behavior and cell response to the compression force.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Method suitable for in-situ hybridization of cherax quadricariratus gonadal tissue mRNA paraffin section
ActiveCN109988846ARealize the display effectClear specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementClimate change adaptationBiologyNucleoplasm
The invention provides a method suitable for in-situ hybridization of a cherax quadricariratus gonadal tissue mRNA paraffin section, and belongs to the technical field of in-situ hybridization. The method comprises the steps of gonadal tissue embedding, paraffin sectioning, in-situ hybridization, and photographing and recording. The sequence of a probe used in in-situ hybridization is as shown inSEQ ID NO.3. The probe has clear specificity on tissue positioning of a dsx gene, so that the display effect on the mRNA level of the dsx gene is realized. The method for mRNA in-situ hybridization ofthe paraffin section is established in cherax quadricariratus to research expression modes of related genes in the gonad, and the expression location of the sex-related genes of the cherax quadricariratus in the gonad can be clearly described. The method avoids tissue shrinkage and cell deformation while the dewaxing effect of the paraffin section is good, so that the tissue is still kept in theoriginal position, the tissue morphology is kept complete, the enzymolysis effect can be improved, cell coloring is good, nucleoplasm is clear, and the in-situ hybridization accuracy is finally improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG INST OF FRESH WATER FISHERIES
Anti-bacterial patterned surfaces and methods of making the same
ActiveCN108777957AExhibit antimicrobial propertiesGrowth inhibitionBiocideMaterial nanotechnologyEscherichia coliCell membrane
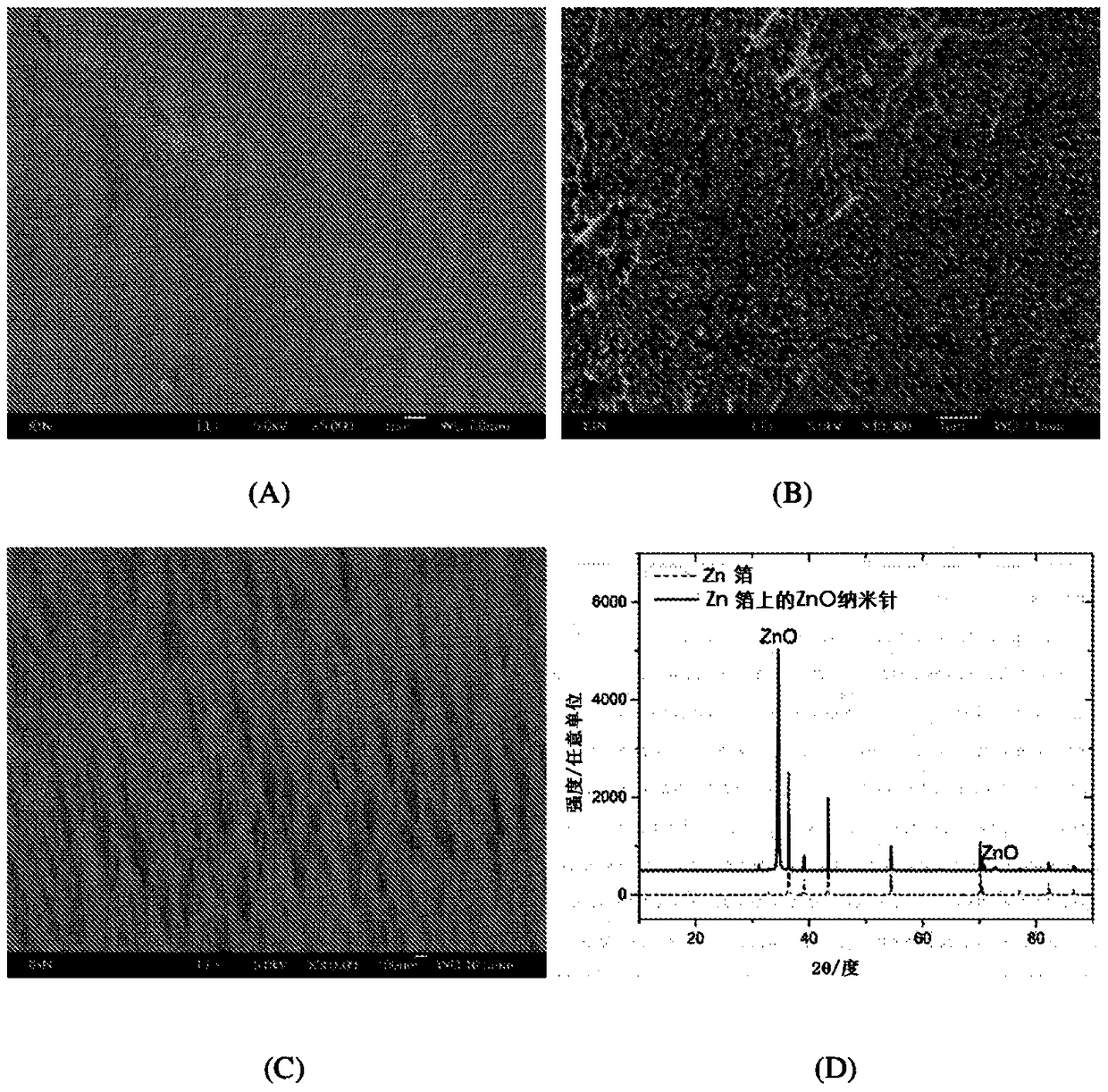
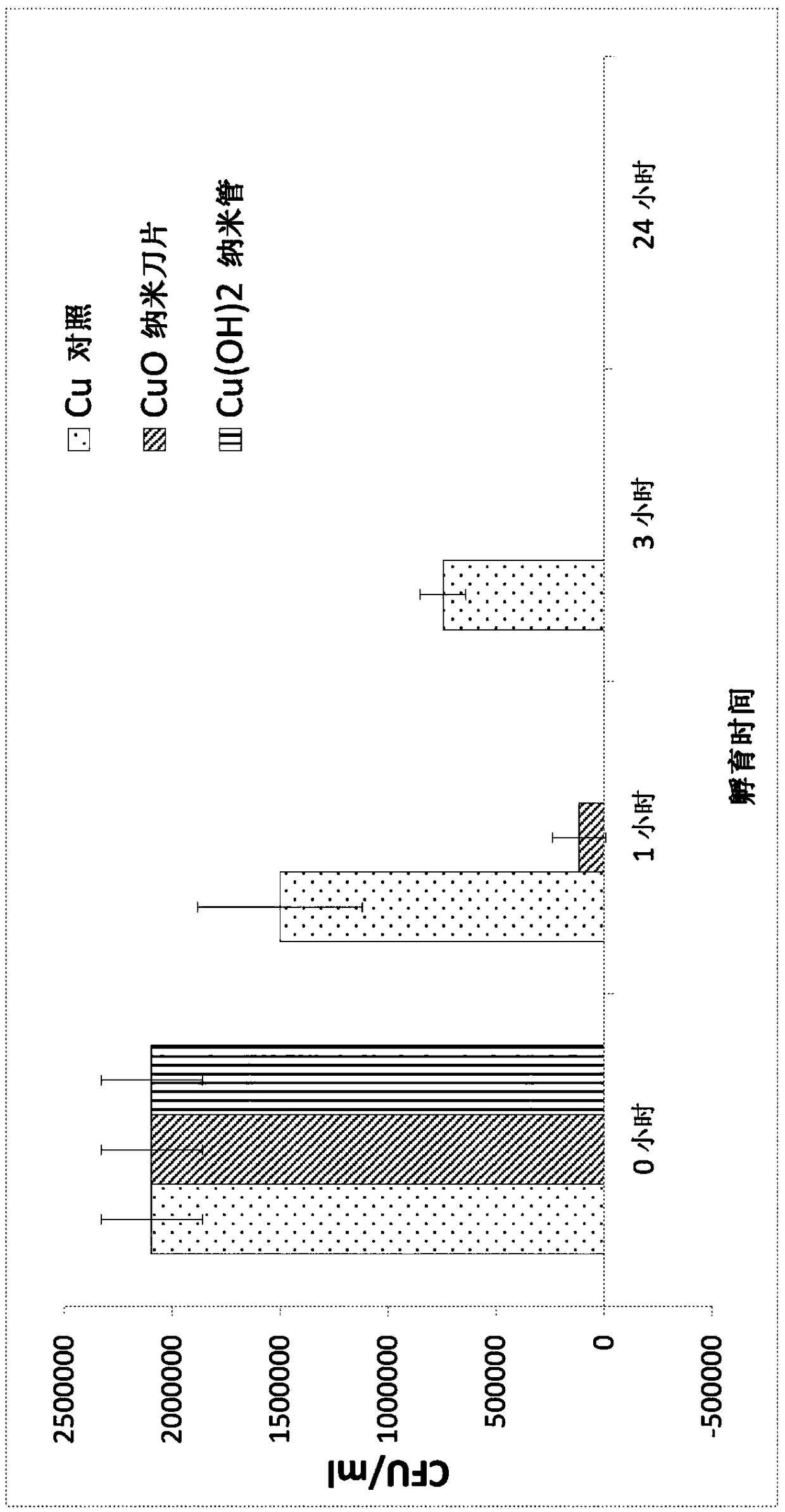
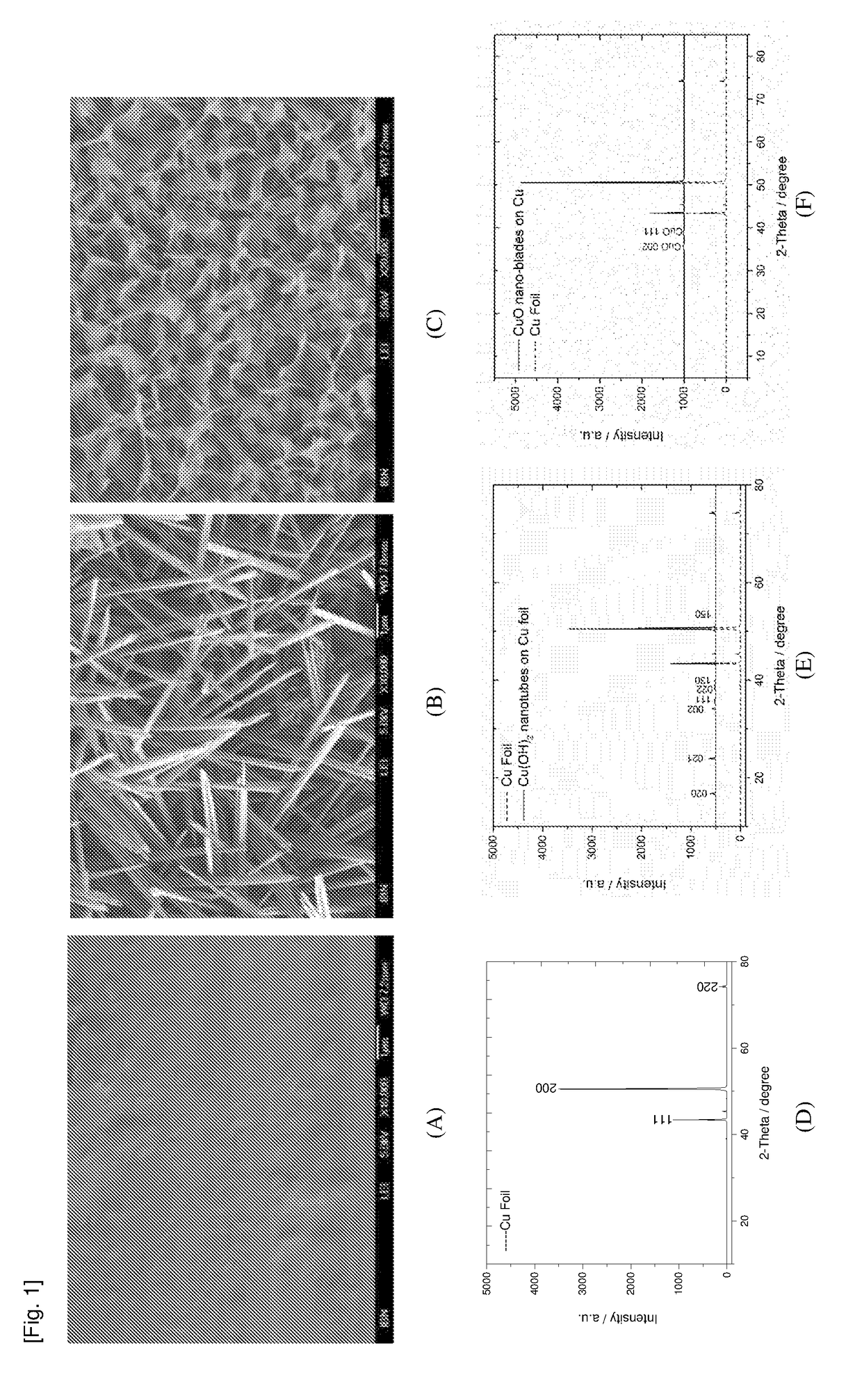
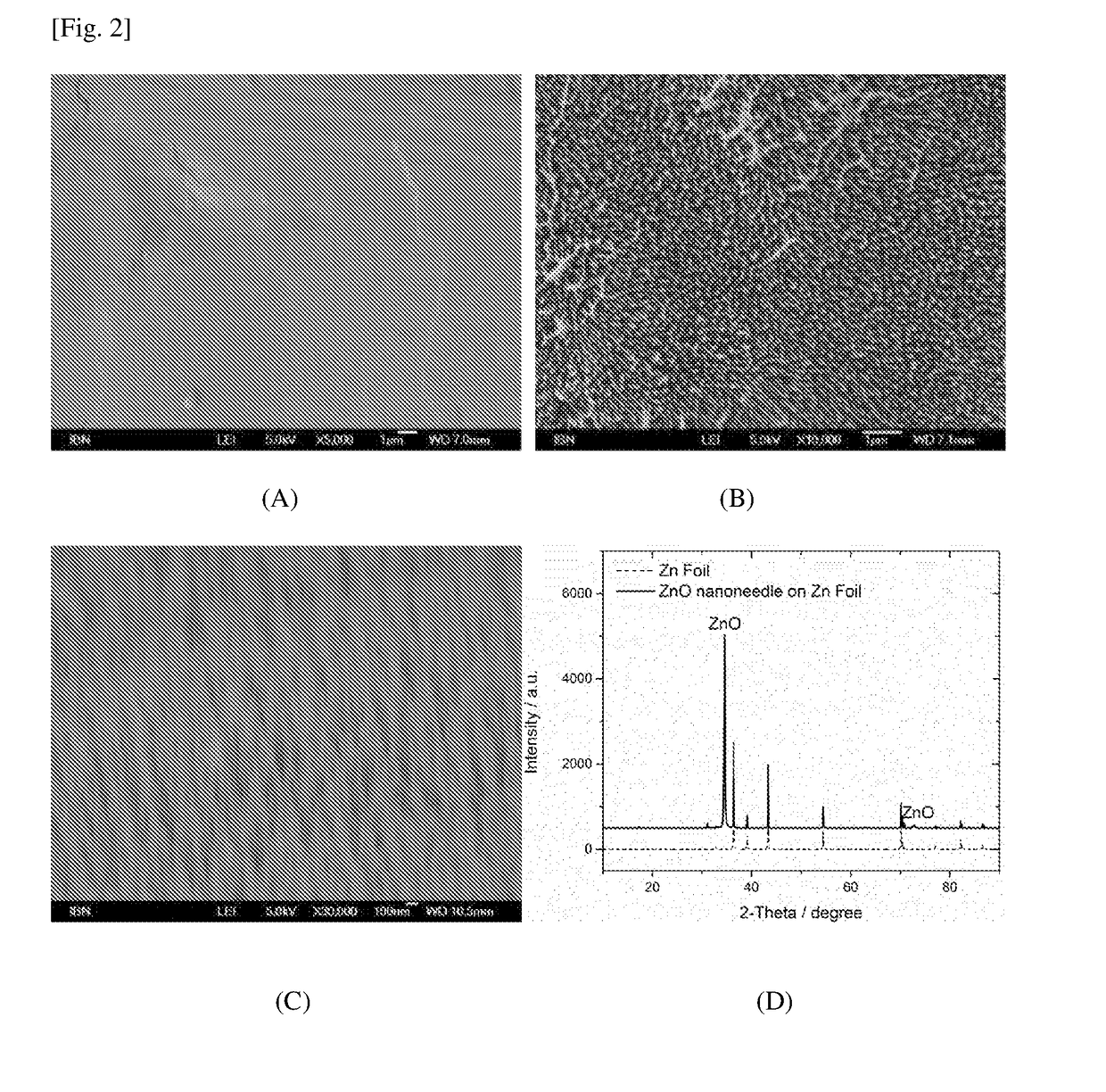
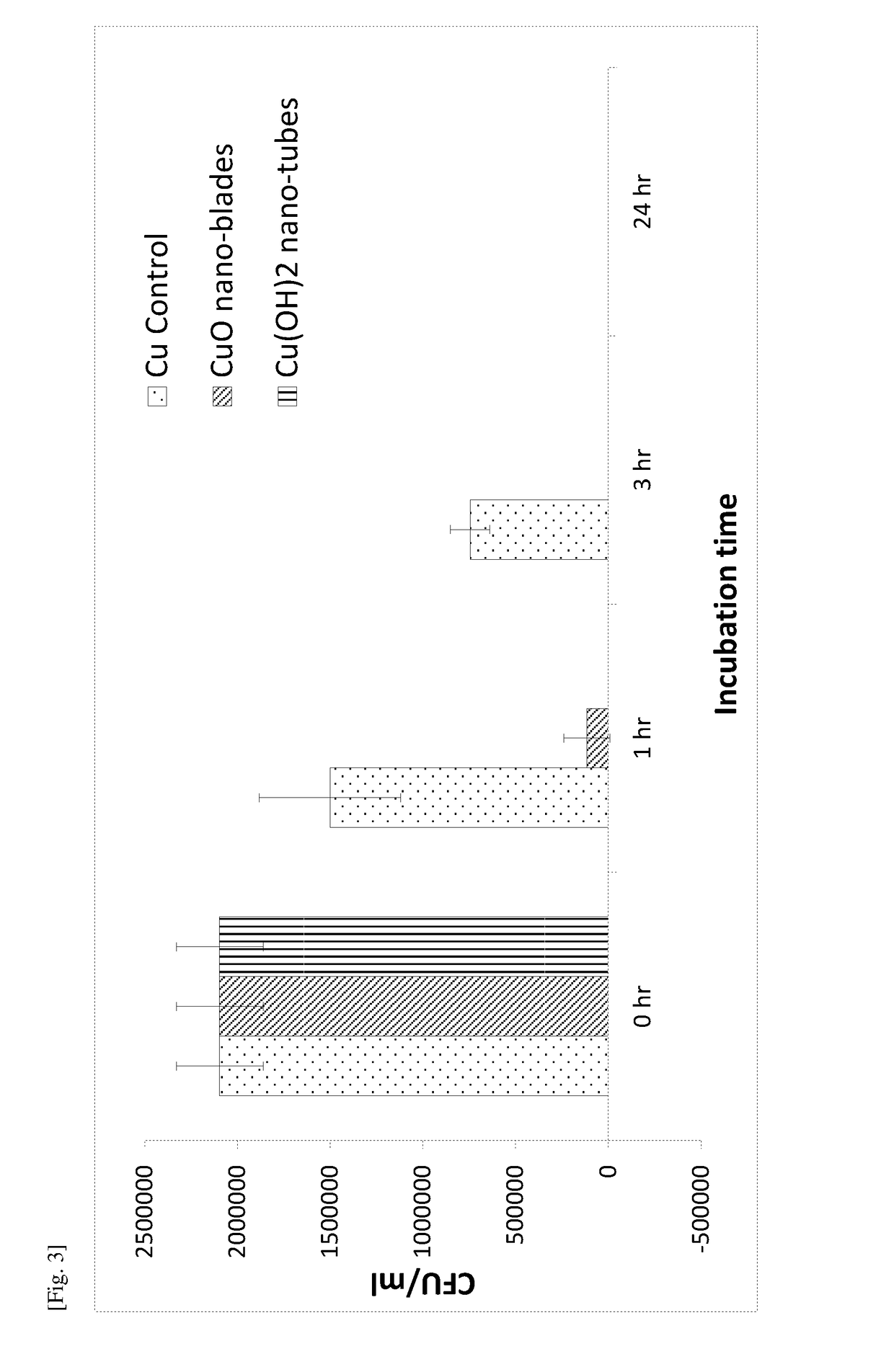
The present invention relates to a substrate comprising a plurality of integrally formed surface features, said surface features being micro-sized and / or nano-sized, said surface features comprising at least one pointed terminus. As a result of this unique surface, said substrate exhibits a biocidal activity because the terminal ends of said surface feature pierce through cell membrane of any microbial cell that comes into contact with the substrate, thereby causing cell deformation and lysis. The present invention also relates to a method producing said substrate. By a simple treatment of copper or zinc foil with a reagent solution comprising an alkali and an oxidizing agent, Cu(OH)2 nanotube arrays, CuO nano-blades and ZnO nano-needles are prepared. These surfaces are proven to be very effective in killing bacterial (such as E. coli) via a physical interaction.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
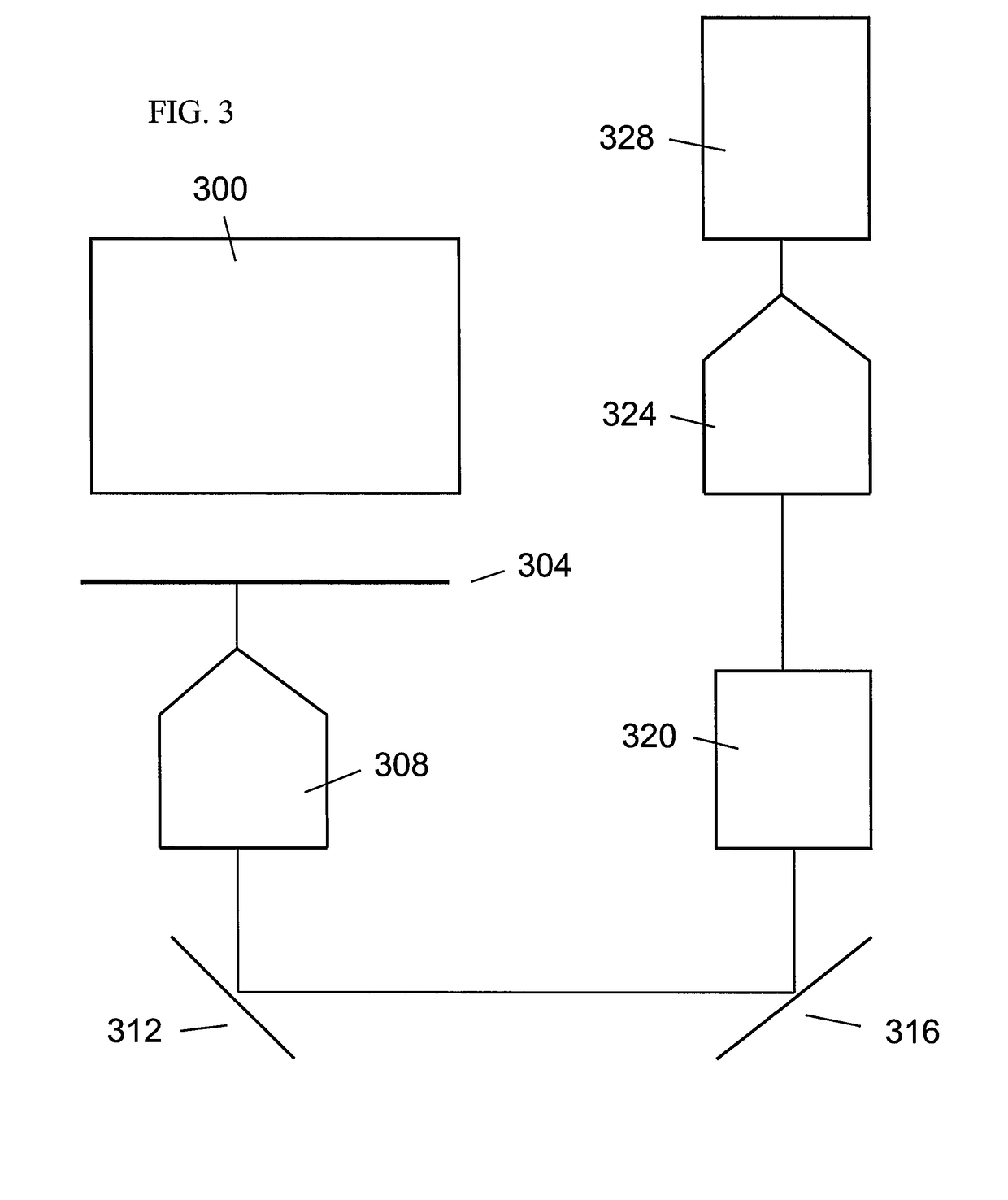
Method and system for measuring single cell mechanics using a modified scanning probe microscope
ActiveUS8323920B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCell mechanicsScanning electron microscope
One embodiment of the present invention provides a system that measures single cell mechanics using a scanning probe microscope. During operation, the system positions a modified probe of the scanning probe microscope above a cell which is located on a surface, wherein the modified probe is configured with a geometry for compressing the cell. The system then comprises the cell against the surface using the modified probe, thereby causing the cell to deform. Next, the system extracts mechanical properties of the cell from cell deformation behavior and cell response to the compression force.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
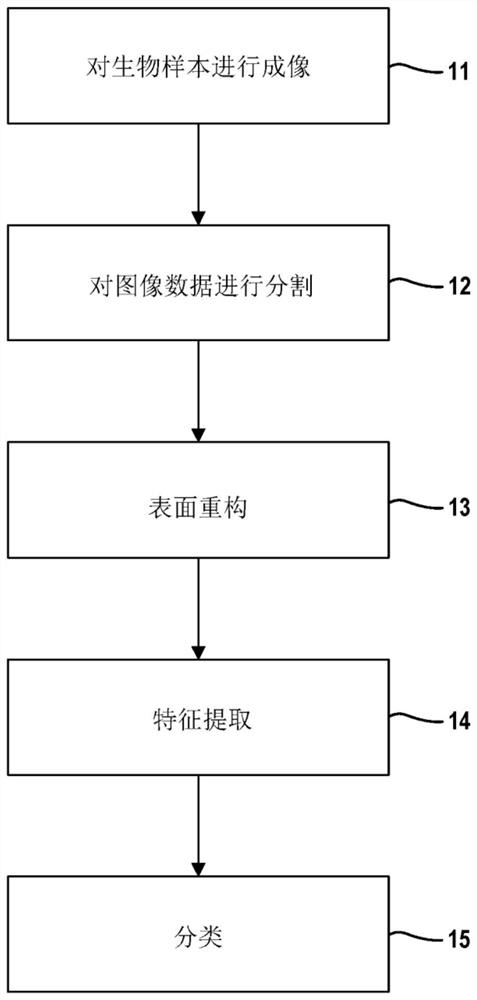
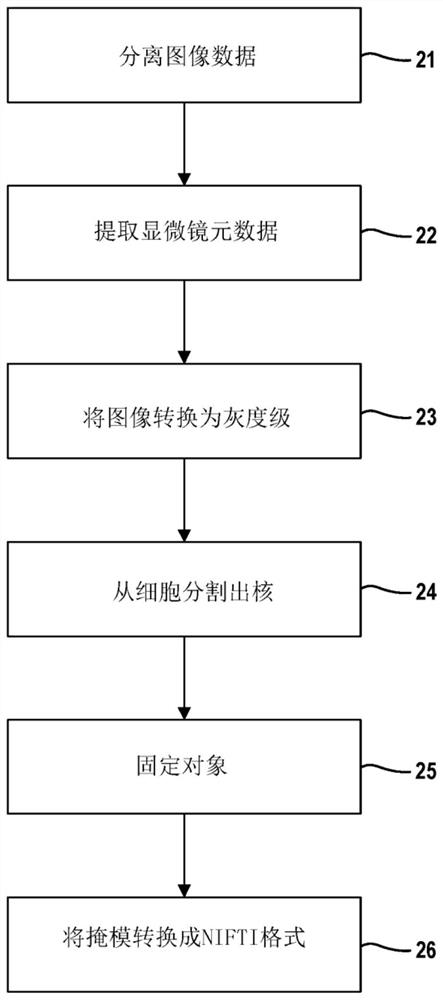
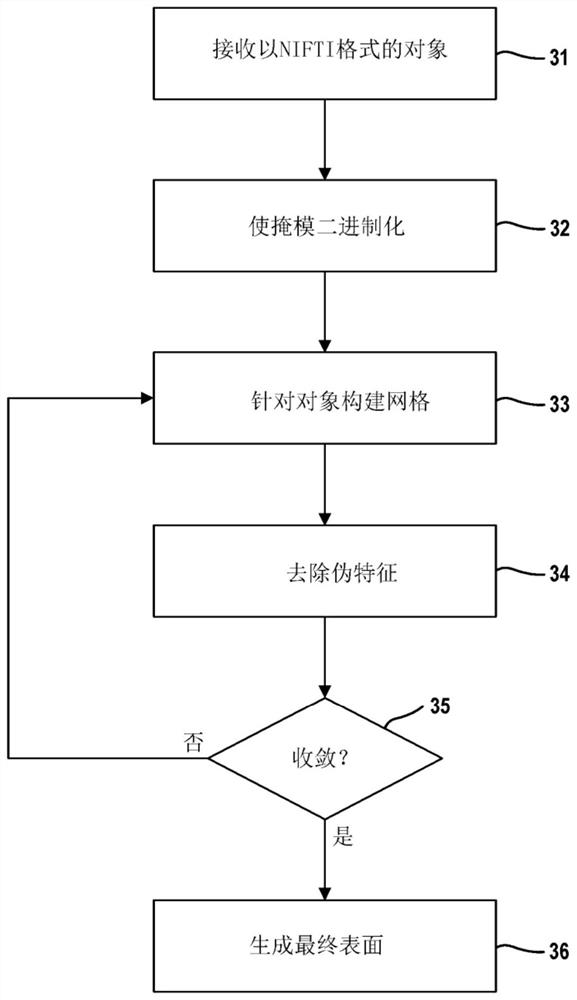
Three-dimensional cell and tissue image analysis for cellular and sub-cellular morphological modeling and classification
The ability to automate the processes of specimen collection, image acquisition, data pre-processing, computation of derived biomarkers, modeling, classification and analysis can significantly impactclinical decision-making and fundamental investigation of cell deformation. This disclosure combine 3D cell nuclear shape modeling by robust smooth surface reconstruction and extraction of shape morphometry measure into a highly parallel pipeline workflow protocol for end-to-end morphological analysis of thousands of nuclei and nucleoli in 3D. This approach allows efficient and informative evaluation of cell shapes in the imaging data and represents a reproducible technique that can be validated, modified, and repurposed by the biomedical community. This facilitates result reproducibility, collaborative method validation, and broad knowledge dissemination.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Anti-bacterial patterned surfaces and methods of making the same
InactiveUS20190037841A1Resolution of these surface features is notAdvantageous and cost-effectiveMaterial nanotechnologyBiocideLysisCell membrane
The present invention relates to a substrate comprising a plurality of integrally formed surface features, said surface features being micro-sized and / or nano-sized, said surface features comprising at least one pointed terminus. As a result of this unique surface, said substrate exhibits a biocidal activity because the terminal ends of said surface feature pierce through cell membrane of any microbial cell that comes into contact with the substrate, thereby causing cell deformation and lysis. The present invention also relates to a method producing said substrate. By a simple treatment of copper or zinc foil with a reagent solution comprising an alkali and an oxidizing agent, Cu(OH)2 nanotube arrays, CuO nano-blades and ZnO nano-needles are prepared. These surfaces are proven to be very effective in killing bacterial (such as E. coli) via a physical interaction.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
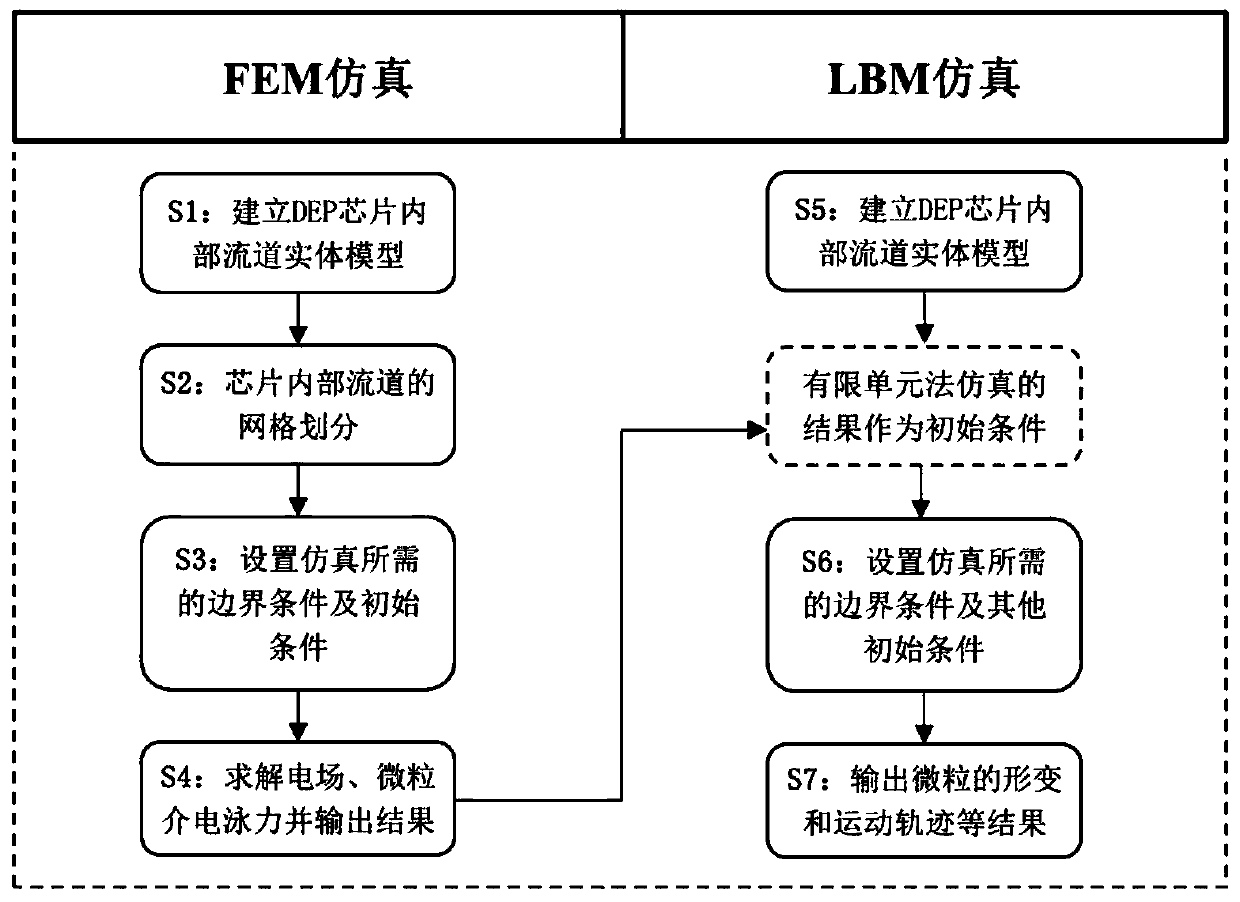
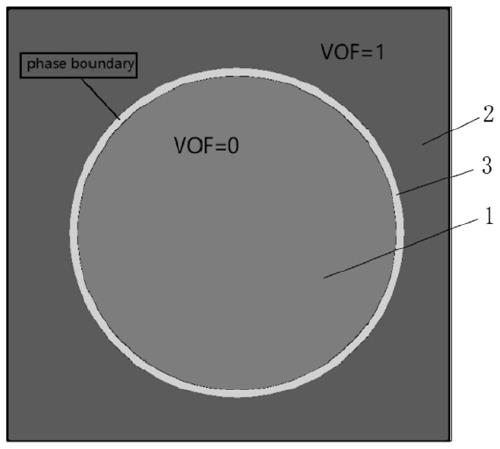
Indirect coupling simulation method of microfluidic dielectrophoresis sorting chip
PendingCN111475983ASimple structureDesign optimisation/simulationComputational theoretical chemistryElectrical field strengthDielectrophoretic force
The invention discloses an indirect coupling simulation method of a microfluidic dielectrophoresis sorting chip, and relates to the technical field of dielectrophoresis. The method comprises the following steps: establishing a phase field model in a multiphase flow; adopting a finite element method to obtain dielectrophoretic force which changes along with time and space and is borne by particles;inputting the dielectrophoresis force as an external force item into the phase field model in the multiphase flow, and solving the phase field model in the multiphase flow to realize indirect coupling; adopting a lattice Boltzmann method to calculate the phase field model in the multiphase flow, calculating electric field intensity distribution in a chip and track and characterize motion trails of the particles. The advantages of the finite element grid method for solving the electric field can be exerted, the advantages of the lattice Boltzmann method for solving micro-scale flow and flexible cell deformation can also be exerted, the chip structure can be optimized according to the simulation result, and a new thought is provided for design and manufacturing of the microfluidic dielectrophoresis chip.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
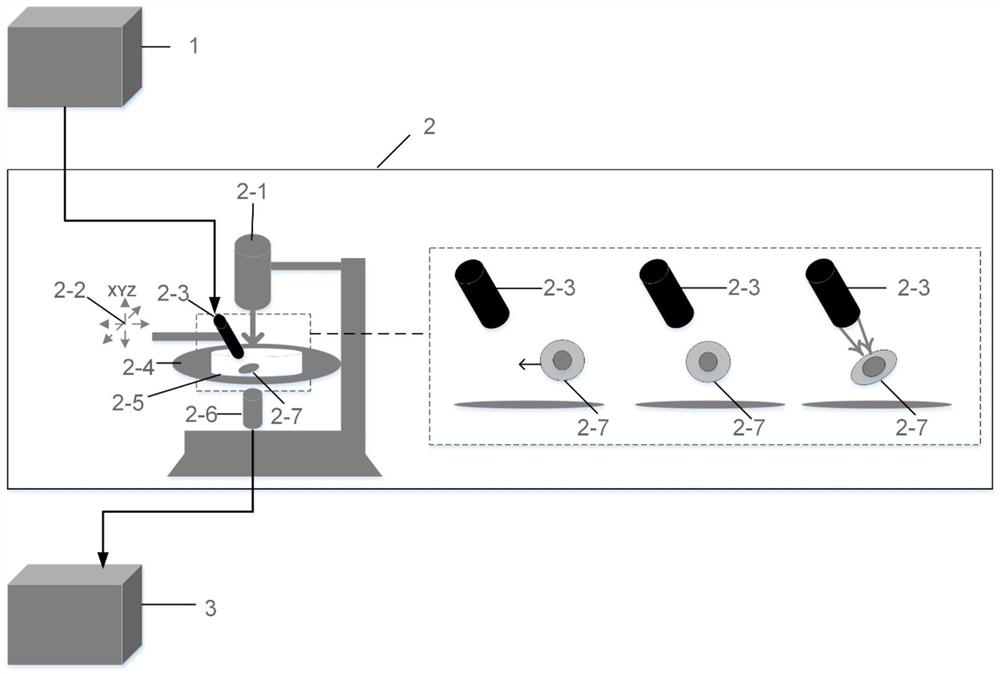
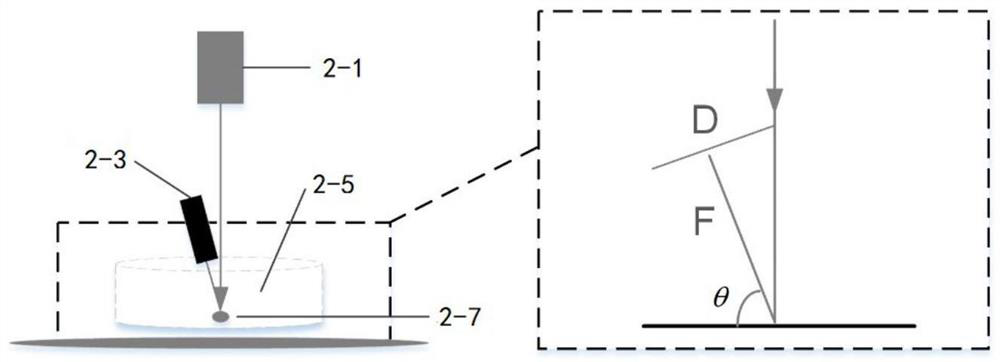
Device and method for testing mechanical properties of biological cells by using acoustic radiation force
PendingCN114441412AAchieve captureAchieve normal functionIndividual particle analysisEngineeringMechanical engineering
The invention discloses a device and a method for testing mechanical properties of biological cells by acoustic radiation force, and the device comprises an ultrasonic module, a test module and an analysis module; the test module comprises an inverted biological microscope, a cell culture dish is movably placed on the operation platform, an irradiation light source is arranged above the perpendicular bisector of the operation platform from top to bottom, and a lens cone connected with the analysis module is arranged below the operation platform; the ultrasonic module is connected with the ultrasonic focusing transducer; a probe at the front end of the ultrasonic focusing transducer is obliquely immersed into the culture dish from the upper part of the operation platform; the analysis module acquires images from the lens cone and realizes real-time dynamic acquisition and processing of image signals; an ultrasonic focusing transducer is driven by an ultrasonic module, acoustic radiation force is generated, target cells in a cell culture dish are captured, force is applied to the target cells, a cell deformation image is captured and extracted by an analysis module, a cell boundary diagram is drawn, and then the cell deformation quantity is calculated.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Antimicrobial coatings
ActiveUS10519323B2Prevent adhesionAvoid developmentBiocideOrganic active ingredientsLysisDisinfectant
A coating comprising a metal-organic framework, wherein the metal-organic framework having a zeolitic structure comprising at least one multivalent metal species and at least one organic ligand (such as zeolitic imidazolate framework (ZIF)). Said coating has a topography comprising an array of projections, and each projection having at least one tapered distal end. There is also provided a method of coating substrates with the disclosed coating and use of said coating as a disinfectant, an antiseptic, or an antibiotic. Such use is possible because the tapered distal end of the disclosed zeolitic structure exerting higher pressure on any microbial cell that comes into contact with the disclosed coating, thereby piercing through the cell membrane more easily, causing cell deformation and lysis.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
Method for nanotube-height-aided control of cytoskeleton change
InactiveCN106093475AMaterial nanotechnologyX-ray spectral distribution measurementCell adhesionOsteoblast
The invention discloses a method for nanotube-height-aided control of cytoskeleton change. The method comprises steps of performing anodization of pure titanium or low-modulus biphase titanium using an organic solvent; representing the microscopic structure of an anodization product using a microscopic means; preparing a titanium metal piece of nanopore and naotube microstructures; separating bone narrow mesenchymal stem cells, adhering three-generation cells on a surface-modified metal piece for incubation; observing cell adhesion effects by MTT, DYPI nuclear staining and SEM; placing the metal testing piece for cell incubation in culture holes of an aseptic elastic plate, and placing the metal testing piece in a universal testing system in a constant temperature state and providing the metal testing piece with different periods, frequencies and load compressive stress; and observing and testing cell deformation with a SEM electron microscope or optical microscope, and detecting representation of cell proliferation and differentiation. The method enables the elastic deformation signal of a modified titanium substrate surface to be amplified, thereby influencing osteoblast adhered on the modified titanium substrate surface to receive greater simulation, and leading to larger cytoskeleton change.
Owner:SHANGHAI NINTH PEOPLES HOSPITAL SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Selective delivery of material to cells
Isolating or identifying a cell based on a physical property of said cell can include providing a cell suspension; passing said suspension through a microfluidic channel that includes a constriction; passing the cell suspension through the constriction; and, contacting said cell suspension solution with a compound. The constriction can be sized to preferentially deform a relatively larger cell compared to a relatively smaller cell.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Lateral cavity acoustic transducer (LCAT) for shear-induced cell transfection
ActiveUS11052395B2Reduce deliveryImprove throughputLaboratory glasswaresOther foreign material introduction processesTransducerBiology
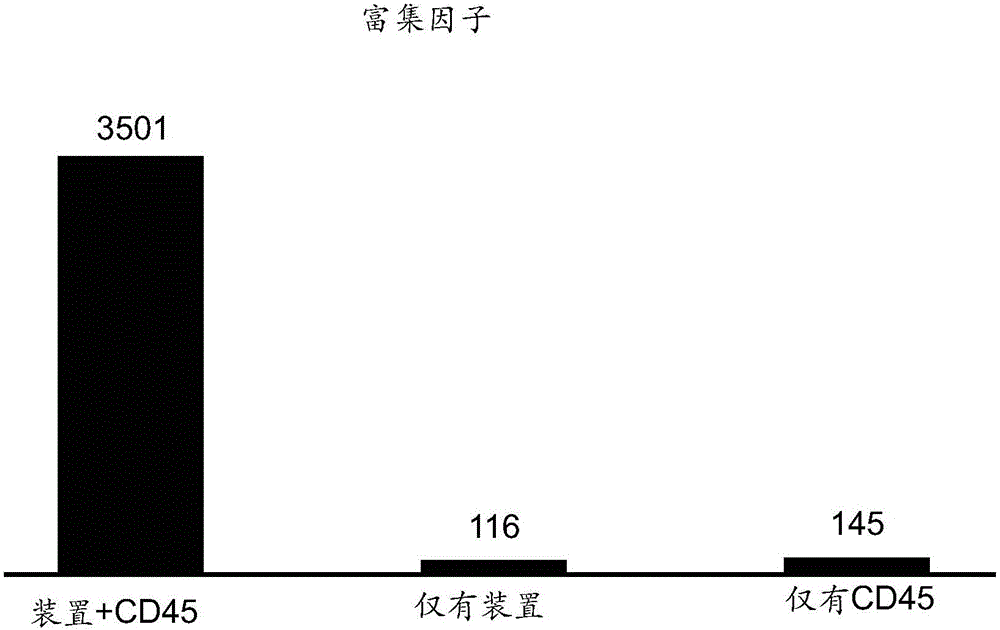
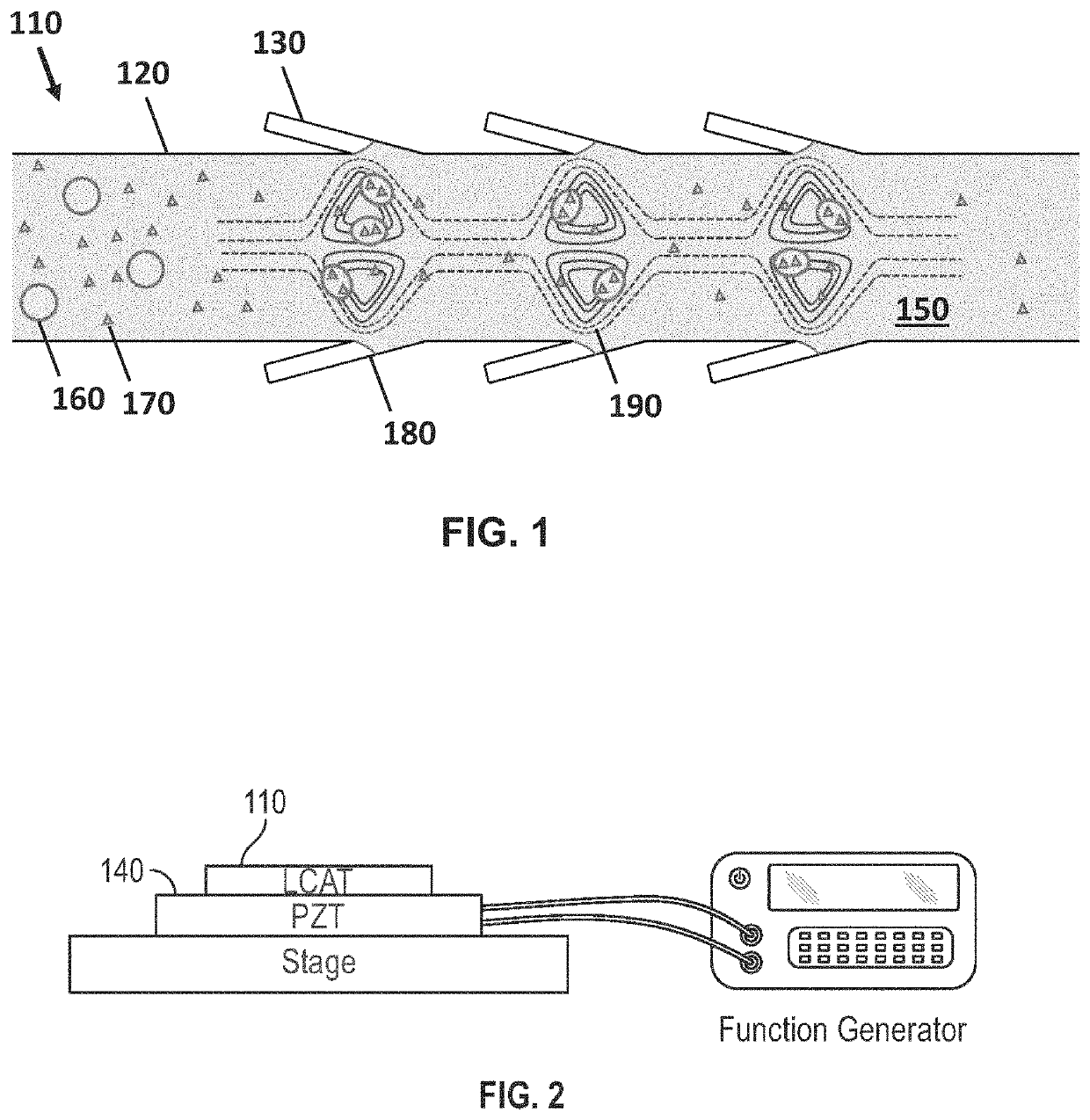
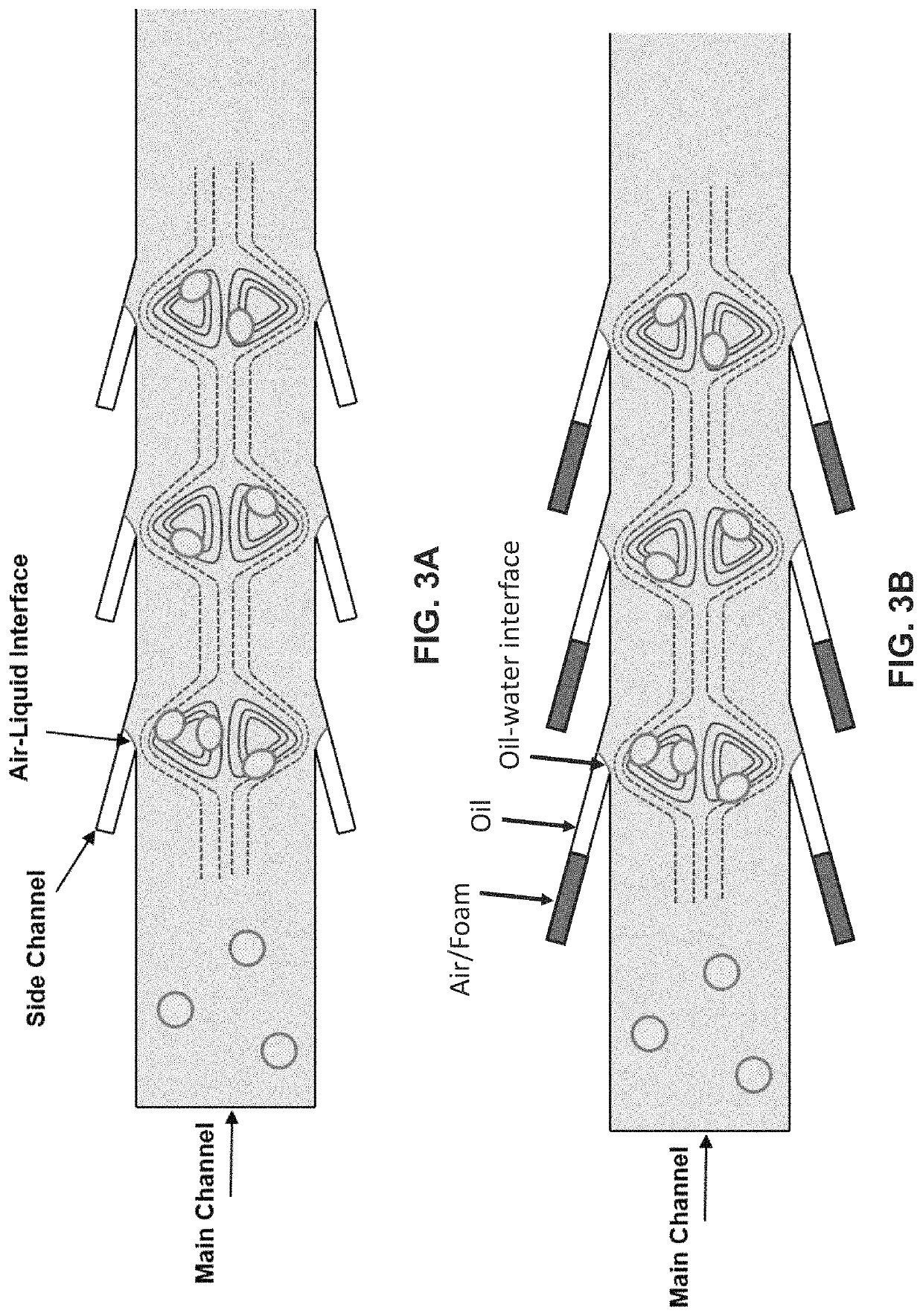
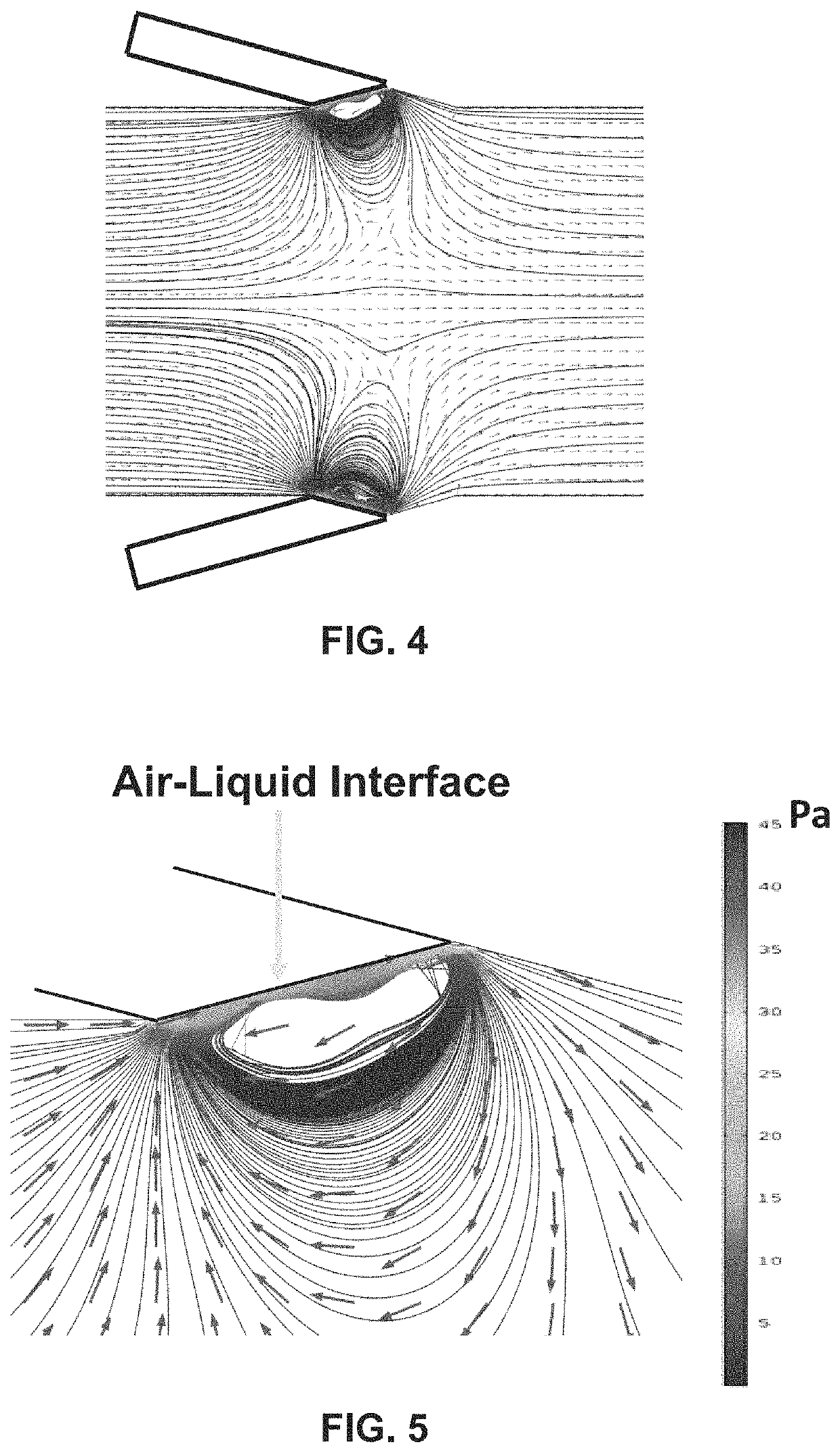
The present invention features the use of lateral cavity acoustic transducers (LCATs) to apply mechanical stimuli on cells. LCATs utilize the generated acoustic microstreaming vortices to trap cells and apply tunable shear-induced cell deformation on them. The present invention may use such a portable, automated, and high throughput device for shear-induced cell transfection.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
High-flux micro-fluidic system for researching mechanical and biochemical signal induced single cell dynamic response and use method thereof
PendingCN114836314AEfficient captureEffective controlBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsHigh fluxBiomedical engineering
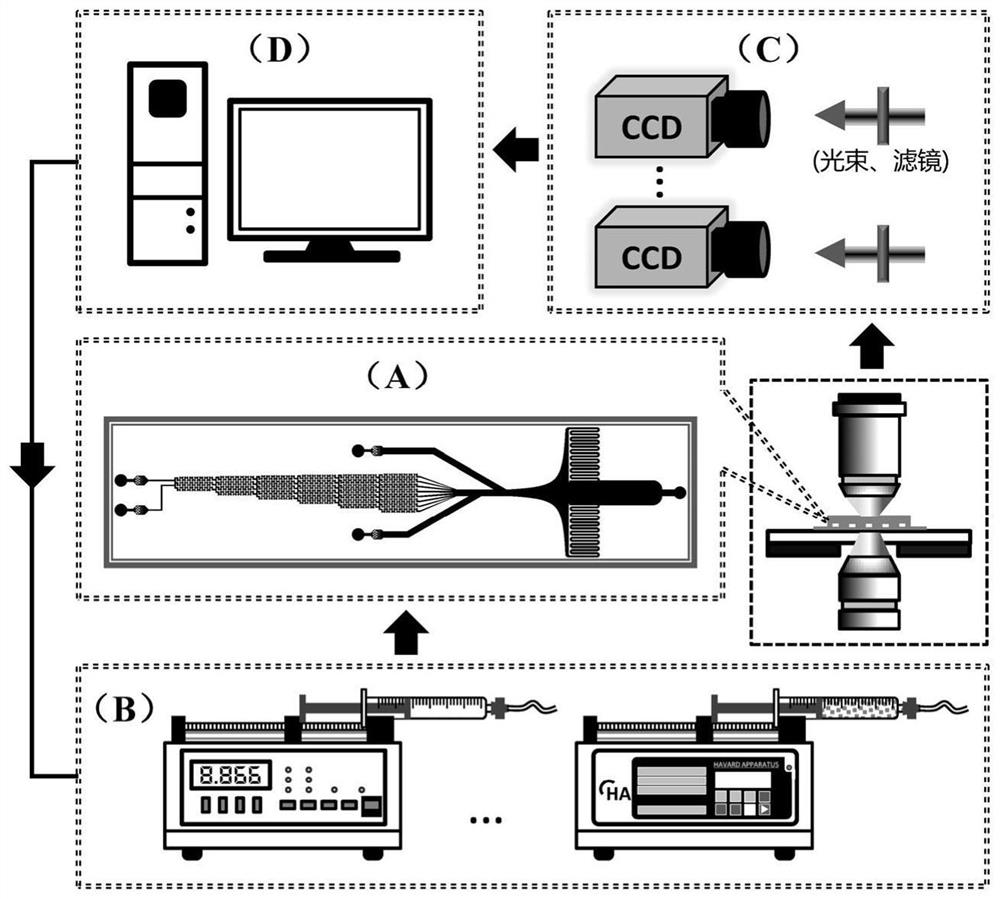
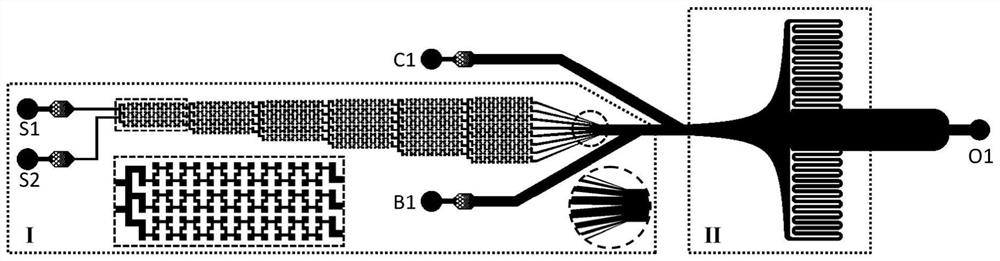
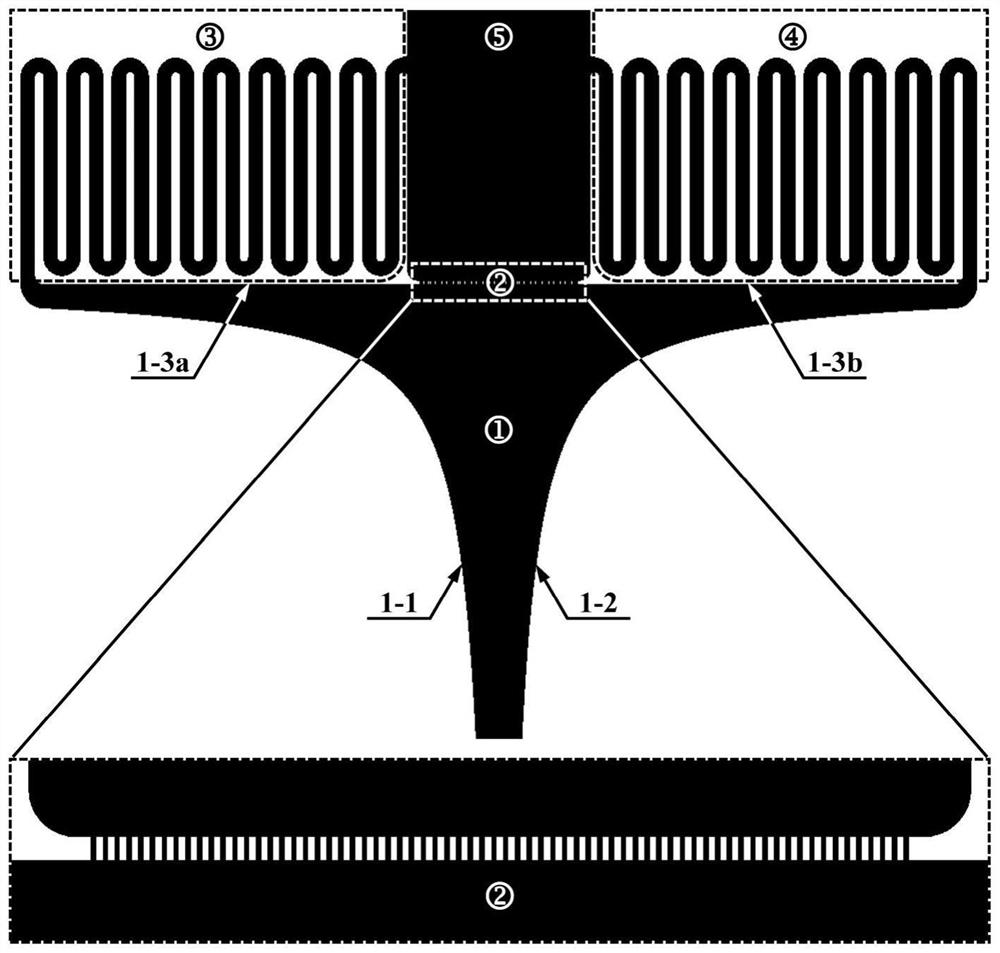
The invention relates to a high-flux microfluidic system for researching mechanical and biochemical signal induced single cell dynamic response and a use method thereof, and belongs to the field of cell biology experimental devices. The system comprises a micro-fluidic chip and a peripheral loading, detection and control device. The loading device is combined with the control device, so that a large number of single cells can be captured or controlled, and different dynamic mechanical and biochemical stimulation signals can be accurately loaded to the cells. The control device receives dynamic image information such as single cell deformation, motion trail and biochemical signal space-time distribution observed by the detection device in real time and pressure / flow value in the loading device, so as to feed back and control the loading device, control the single cell deformation process and accurately control the micro-channel flow field and biochemical signal transmission. The dynamic mechanics and biochemical microenvironment of in-vivo cells can be accurately simulated. According to the invention, efficient capture and control of a large number of single cells can be realized, and the method can be used for cell biology research such as analysis of dynamic response and mechanism of the single cells under stimulation of different dynamic mechanical and biochemical signals.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com