Selective delivery of material to cells
A technology of cells and blood cells, applied in the field of selective delivery of materials to cells
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0045] Whole blood or other cell suspensions are also processed with unlabeled and / or antibody-coated magnetic beads. These cells are then isolated using a high-fidelity, magnetic enrichment system for rare cells. A nanopore technology can also be used for high-purity isolation by imaging and automatically retrieving the desired individual cells from an elastic array of 84,672 subnanometer-sized pores.
[0046] Obtaining single, viable, pure, intact CTCs of different phenotypes allows characterization of the host from genomic to functional level efforts with immediate clinical and metastatic relevance. This method allows a highly sensitive and specific enrichment of live, distinct CTCs with reduced bias.
Embodiment 2
[0048] Magnetic nanoparticles were delivered to tumor cell lines & PBMCs. Nanoparticle delivery to EpCAM-expressing, epithelial cancer cell lines, such as HT-29, LNCaP, and SK-BR-3, was compared with bulk peripheral blood mononuclear cell (PBMC) suspensions derived from human blood.
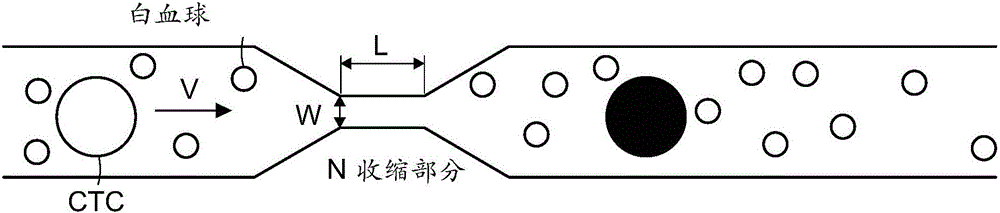
[0049] 10 nm iron oxide nanoparticles with a polyethylene glycol (PEG) surface coating were delivered into cancer cells mixed with whole blood, and the resulting target cell mixture was processed by using the cell separation device described above. For example, microfluidic delivery systems have been used to induce rapid mechanical deformation of cells to create transient voids in cell membranes (attached figure 1 ). The method has demonstrated the ability to deliver a range of materials, including proteins, RNA, DNA, and nanoparticles, to a variety of cell types, and is applicable to whole blood, a medium that typically poses problems for microfluidic systems.
[0050] Exemplary marker molecul...
Embodiment 3
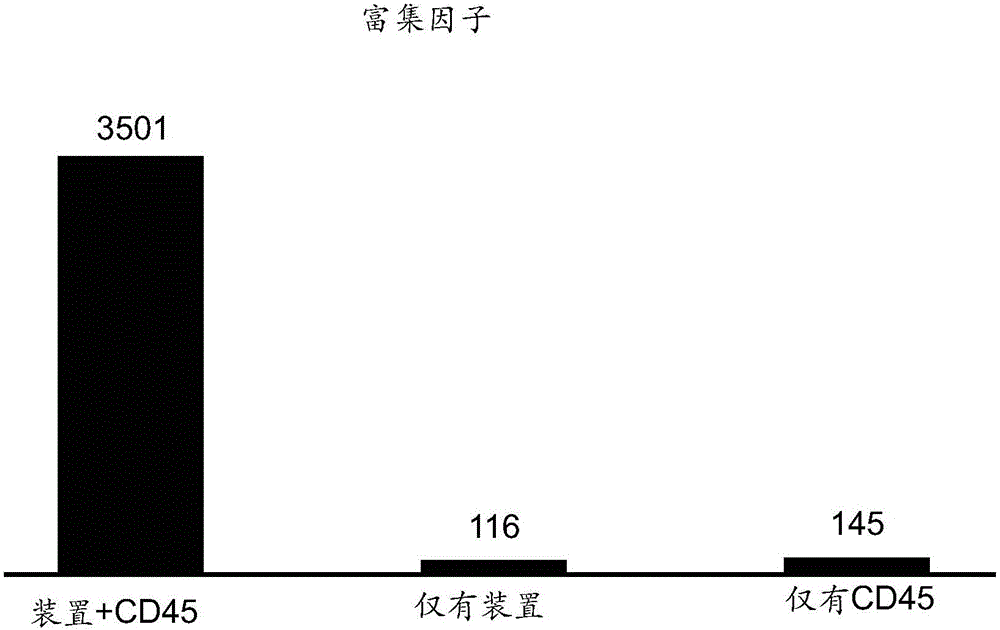
[0053] A combined immunological and morphological approach was performed as follows. After processing through the device based on cell size, the cells are treated with an antibody or other tumor cell specific ligand such as a fluorescently labeled anti-CD45 antibody. The sensitivity and specificity of three different isolation methods were compared: 1) device only, 2) anti-CD45 antibody only, 3) device + anti-CD45 antibody. Morphological markers (device) + immunolabeling (e.g. anti-CD45 antibody) were found to exhibit superior sensitivity relative to the other two techniques used alone (attached figure 2 ). For example, a 2-5 fold increase in sensitivity and / or a 2-5 fold increase in specificity compared to anti-CD45 antibody alone can be observed. Enrichment indices of more than one order of magnitude were observed (attached figure 2 ).
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Molecular mass | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com