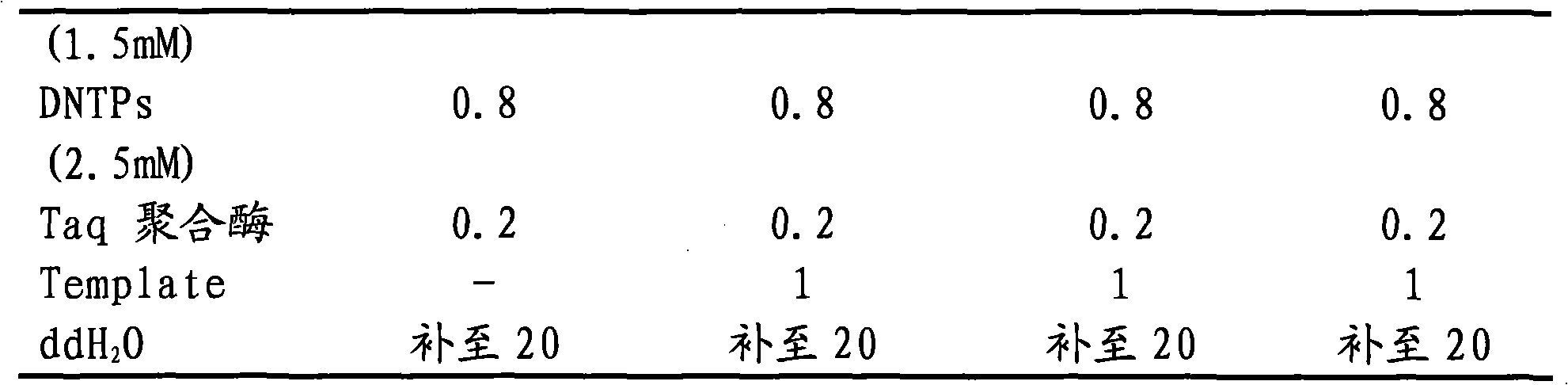
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
286 results about "293t cell" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
293T (or HEK 293T) is a human cell line, derived from the HEK 293 cell line, that expresses a mutant version of the SV40 large T antigen. It is very commonly used in biology for protein expression and production of recombinant retroviruses .
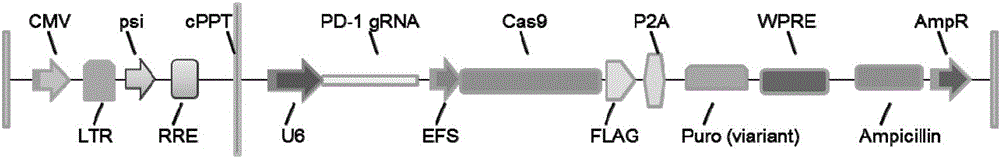
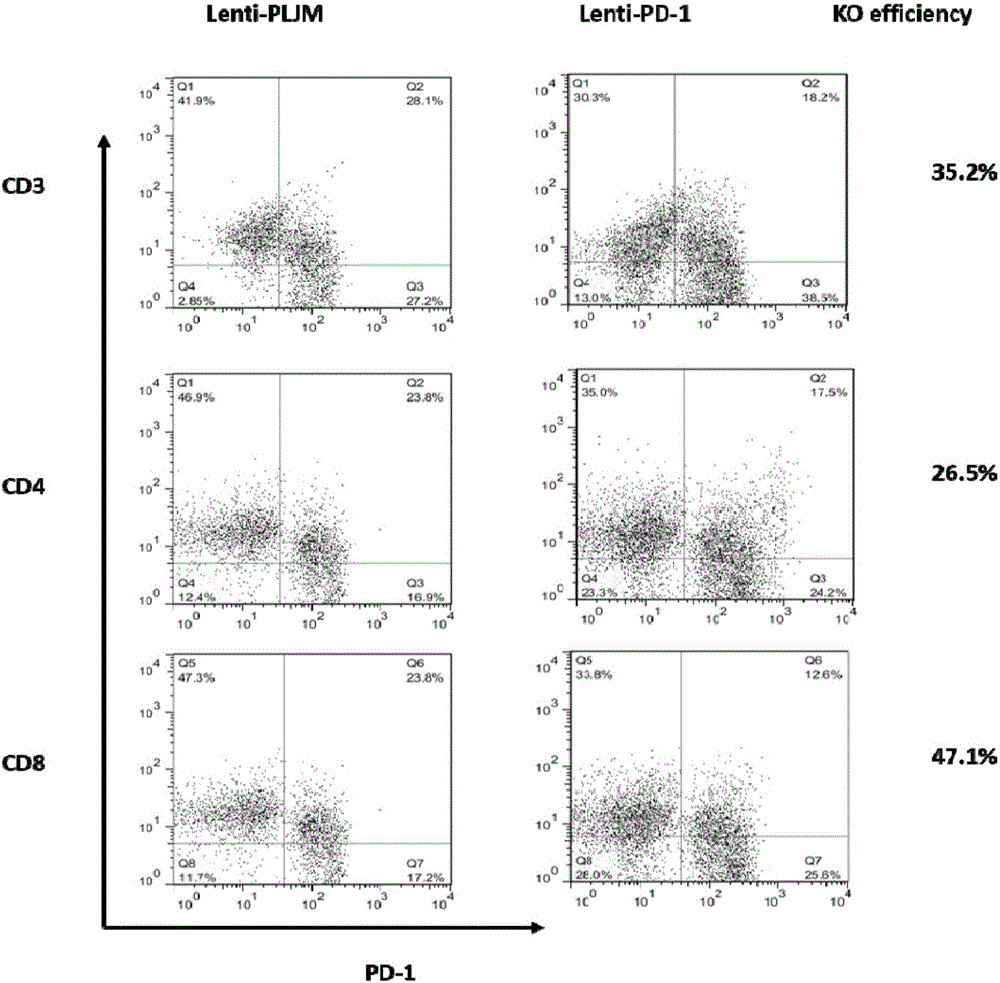
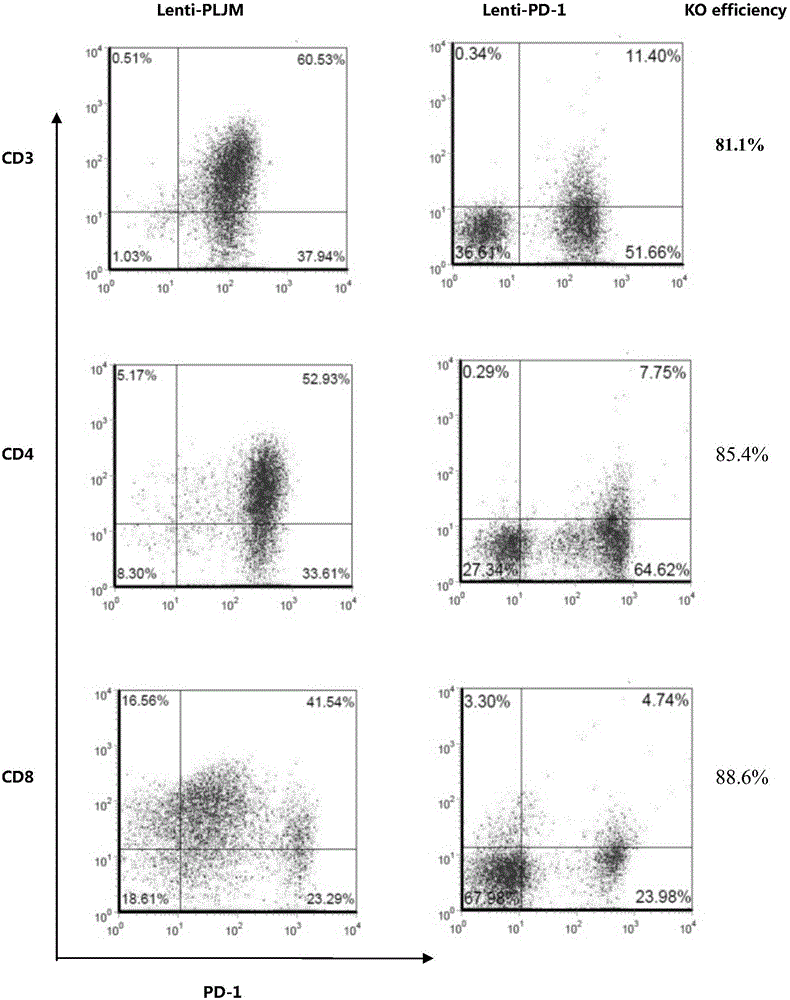
PD-1 gene recombinant virus plasmid, construction thereof, recombinant retrovirus Lenti-PD-1-Puro and packaging and application of recombinant retrovirus Lenti-PD-1-Puro
ActiveCN105671083AStrong specificityRelease the suppressed stateCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsUnknown materialsT cellViral infection
The invention discloses a PD-1 gene recombinant virus. The collection number of the recombinant virus Lenti-PD-1-Puro is CCTCC No:V201601. According to the PD-1 gene recombinant virus, PD-1gRNA sequences are cloned into a retrovirus plasmid Lenti-CRISPR / Cas9-Puro, and a PD-1 recombinant virus plasmid Lenti-CRISPR / Cas9-PD-1-Puro is obtained; then the PD-1 recombinant virus plasmid Lenti-CRISPR / Cas9-PD-1-Puro, a plasmid pSPAX and pMD2.G are jointly transfected by 293T cells, and packaging of the recombinant virus Lenti-PD-1-Puro is completed. After T cells of peripheral blood of tumor patients are infected by the PD-1 recombinant virus, PD-1 on the T cells is successfully knocked out, the inhibitory state of the T cells of the tumor patients is relieved, the capacity of attacking tumor cells of the T cells embellished by the PD-1 recombinant virus is recovered accordingly, and the effect of immune cell treating is achieved.
Owner:安徽柯顿生物科技有限公司
MiR-126 full-length gene knockout kit based on CRISPR-Cas9 technology and application thereof
ActiveCN106566838AOvercoming the drawbacks of studying microRNA functionHigh knockout efficiencyNucleic acid vectorVector-based foreign material introductionSingle strandCell strain
The invention discloses a MiR-126 full-length gene knockout kit based on a CRISPR-Cas9 technology and an application thereof. CRISPR-Cas9 target sequences upstream and downstream a MiR-126 gene are preferably selected, and sgRNA single strands are designed and synthesized for the target sequences and built into a carrier. Through 293T cell strain transfection, sgRNA and trRNA constitute a specific recognition structure. Thus, Cas9 enzyme is guided to specifically shear the corresponding sequences at the two ends of the MiR-126 gene. Drug sieving is carried out constantly to get a MiR-126 full-length gene knockout cell strain. An optimal upstream and downstream sgRNA combination is obtained through drug sieving cell strain sequencing verification. The knockout efficiency of the combination is as high as 90% above. The kit built based on the combination can be used to carry out specific MiR-126 full-length gene knockout on a variety of cell lines such as 293T, a lung cancer cell line A 549 and a vascular endothelial cell HUVEC line.
Owner:上海伯豪生物技术有限公司
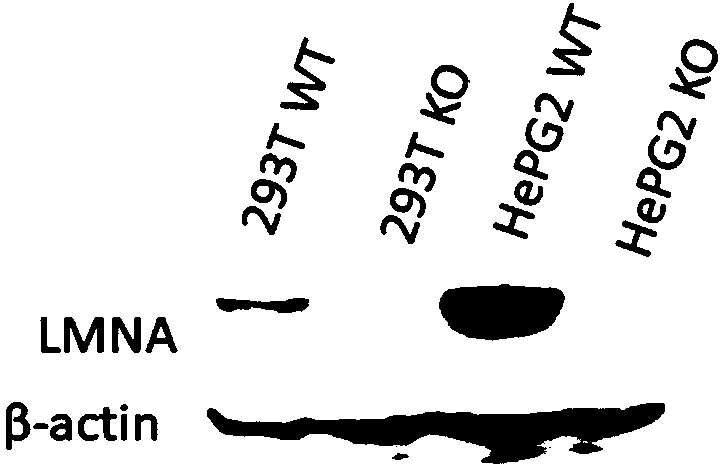
LMNA gene knocked-out cell line constructed on basis of CRISPR/Cas9 technology
InactiveCN108410911APrecise and Efficient KnockoutGenetically modified cellsStable introduction of DNAPremature agingPremature senility syndrome
The invention discloses an LMNA gene knocked-out cell line. The cell line is a 293T cell line or a HePG2 tumor cell line. Cells to be knocked out are transfected by plasmid vectors constructed by twopairs of gRNA as shown in SEQ ID NO. 1-4 or two pairs of gRNA as shown in SEQ ID NO. 7-10 on the basis of a crispr-cas9 technology, and then are subjected to resistance screening to obtain the cell line. The LMNA gene knocked-out cell line can be used for intervention drug screening cell models for diseases such as dilated cardiomyopathy, fat metabolic disorder syndrome and premature aging syndromes.
Owner:GUANGXI MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
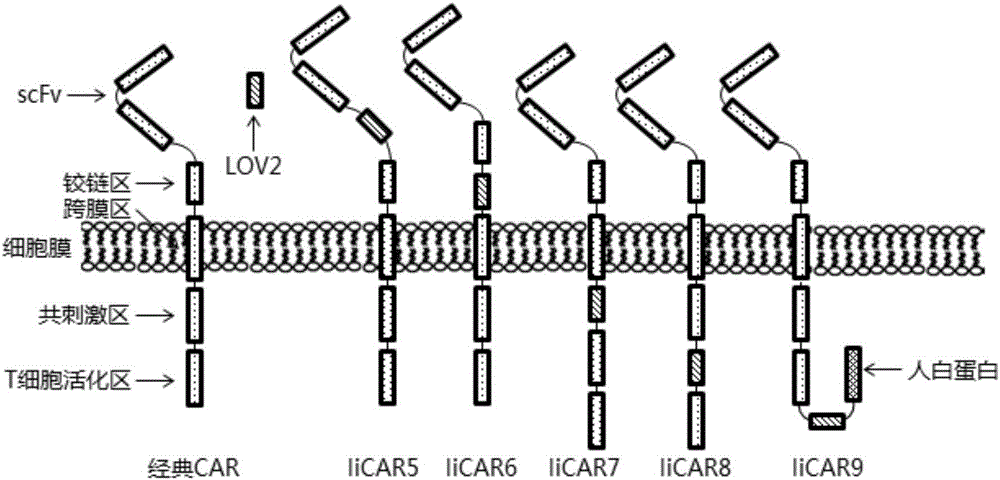
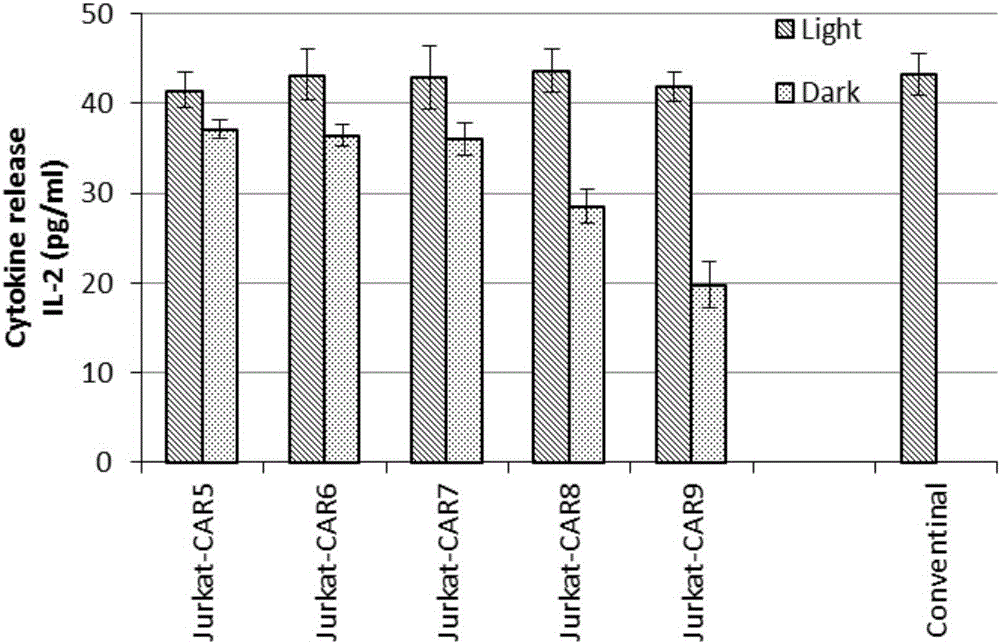
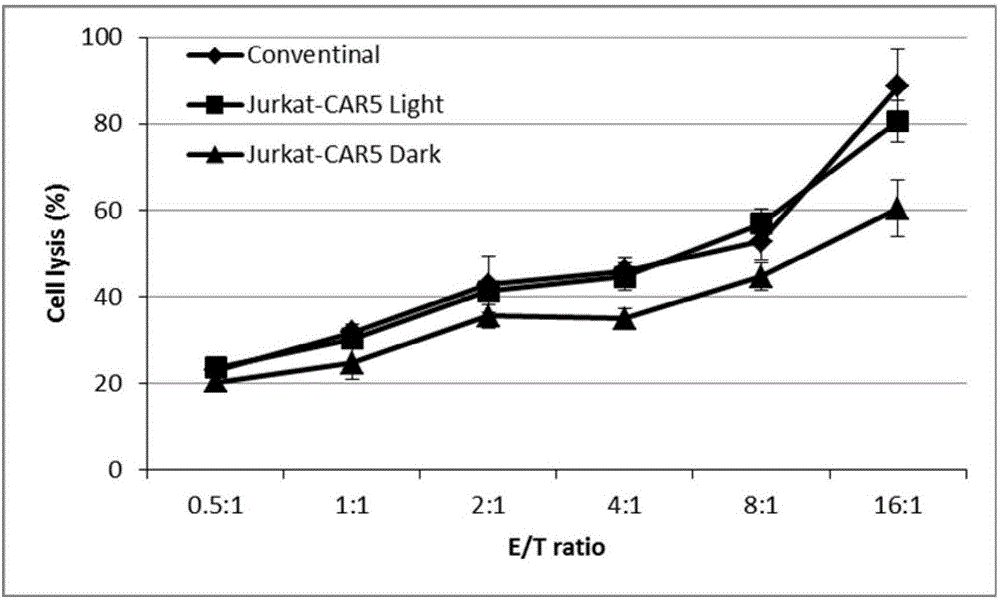
Novel chimeric antigen receptor and application thereof
ActiveCN106279438AImprove securityAdd control switchFermentationHybrid peptidesAntigenAntigen receptors
The invention discloses a recombined chimeric antigen receptor with a photoinduction element. The chimeric antigen receptor comprises an antigen combining area, a transmembrane structure area, a co-stimulatory signal transduction area and T cell signal transduction area functional structure domains, wherein the photoinduction element is inserted at the N terminal or C terminal of the recombined chimeric antigen receptor or between the functional structure domains. According to the chimeric antigen receptor, photoinduction element LOV2 genes are cloned into plasmids Lenti-EF1alpha-CD19CAR with a molecular cloning method to establish a co-expression vector of the recombined chimeric antigen receptor with the photoinduction element, 293T cells are used for packaging to obtain a lentiviral vector with photoinduction CAR molecules. After the recombined chimeric antigen receptor is expressed in T cells through the lentiviral vector, the damage toxicity of T cells is reversely controlled by LOV2, and an importable approach is provided for improving the safety of CAR-T in treating cancer clinically.
Owner:北京领柯生物科技有限公司
Construction and application of farnesyl pyrophosphoric acid synthetase RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) interference recombinant lentivirus vector
InactiveCN101805750AOvercoming No Commercial AntibodyOvercoming low transfection efficiencyMetabolism disorderGenetic material ingredientsDiseaseFhit gene
The invention provides the construction for a farnesyl pyrophosphoric acid synthetase RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) interference recombinant lentivirus vector, which comprises the following steps of: sieving the most effective target sequence of an FDS (farnesyl diphosphate synthase) gene RNAi (RNA interference) in a tool cell 293T cell, synthesizing the double-stranded DNA of the most effective target sequence, connecting to a pGCSIL-GFP vector and successfully constructing the recombinant vector through enzyme cutting, sequencing and identification. Researches indicate that the constructed RNA interference vector LV-sh-FDS can downwards modulate the expression of an FDS mRNA (Messenger RNA) level in a neonatal rat cardiac myocyte, simultaneously can downwards modulate the expression of myocardial hypertrophy markers such as cell areas and marker genes beta-MHC (Myosin Heavy Chain) and BNP (Brain Natriuretic Peptide), additionally can effectively inhabit the activity of RhoA while downwards modulating the FDS, can be applied in preparing medicaments for treating myocardial hypertrophy diseases and also can be applied in preparing medicaments for cholesterol metabolic control.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for producing red blood cell drug containing L-ASPase II by in vitro induction
ActiveCN103224957ASmall toxicityPreserve form functionPeptide/protein ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsSide effectL asparaginase
The invention discloses a method for producing a red blood cell drug containing L-ASPase II (L-asparaginase) by in vitro induction. The method comprises the steps of: 1) using a lentiviral vector system to transform induced pluripotent stem (IPS) cells: I. constructing a pLenti6.3 / V5-GW / Em-GFP VerA-L-ASPase II plasmid; II. using 293T cells to perform packaging so as to generate high titer virus particles containing L-ASPase II; III. using the virus particles to transfect induced pluripotent stem cells; and 2) inducing the induced pluripotent stem cells in vitro to generate L-ASPase II-containing red blood cells: I. subjecting IPS cells to in vitro differentiation induction to form an erythroid body EB; and II. performing induced differentiation on EB to obtain mature red cells. The method provided in the invention performs genetic modification on IPS cells by the lentiviral vector system, and induces them in vitro to generate red blood cells containing L-ASPase II. The generated red blood cells can be used as a sustained release carrier of L-ASPase II, and also can maintain the original shapes and functions of red blood cells. The toxic and side effects of L-ASPase II are further reduced, so that the method lays a solid foundation for future clinical application.
Owner:厦门三一造血技术有限公司
Recombination cell line for stable expression of classical swine fever virus E2 and application thereof
InactiveCN105331636AResistance to virulent attacksStable in natureMicroorganism based processesAntiviralsHigh titer293t cell
The invention discloses a recombination cell line for stable expression of classical swine fever virus E2 and the application thereof. The recombination cell line is established after a lentivirus vector carries target genes to establish recombinant plasmids, then HEK-293T cell transfection is conducted, and generated high-titer virions are reinfected with HEK-293T cells. Stable expression is achieved, and a high protein expression level is kept after several passages. When a vaccine prepared with the recombination cell line is used for pig immunization, an animal organism can be induced to generate a high-potency classical swine fever virus neutralizing antibody, so that virulent attack of the classical swine fever virus is resisted.
Owner:GUANGZHOU BONIZZI BIOTECH CO LTD
Recombinant cell line for stable expression of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus S1 protein, vaccine and application
InactiveCN107619819AEase of mass productionGood antigenicityAntiviralsAntibody medical ingredientsEpidemic diarrheaAdjuvant
The invention discloses a recombinant cell line for stable expression of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus S1 protein, a vaccine and an application. The recombinant cell line is constructed by transfecting HEK-293T cells by virtue of recombinant plasmid which is constructed by carrying a target gene on a lentiviral vector, and then transfecting the HEK-293T cells by virtue of generated high-titer virus particles; and the recombinant cell line, which can achieve stable expression, can still keep an excellent protein expression level after several passages. The recombinant cell line for stable expression of the porcine epidemic diarrhea virus S1 protein provided by the invention has the characteristics of being easy for culture, rapid in proliferation, unlimited in expansion, stable in property and high in protein expression amount; and when the vaccine, which is prepared from the expression protein and adjuvants, is used for immunizing pigs, the generation of a high-titer porcine epidemicdiarrhea virus neutralizing antibody can be induced from animal bodies, and the piglets (the pigs) can resist strong attack of porcine epidemic diarrhea viruses.
Owner:GUANGZHOU BONIZZI BIOTECH CO LTD
Target quaternary ammonium salt cationic polymer lipid gene carrier, preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102234658ARich varietyHigh transfection efficiencyGenetic material ingredientsMacromolecular non-active ingredientsPositive controlQuaternary ammonium cation
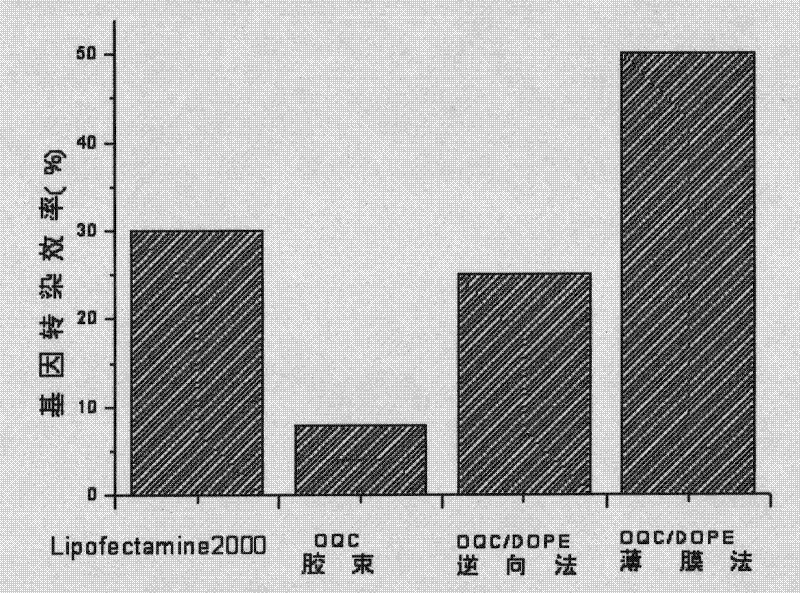
The invention discloses a target quaternary ammonium salt cationic polymer lipid gene carrier, a preparation method and an application thereof. The target quaternary ammonium salt cationic polymer lipid genetic carrier is characterized in that: a polymeric quaternary ammonium salt and lipid are adopted for preparing a quaternary ammonium salt cationic polymer lipid genetic carrier according to a mass ratio, wherein the mass ratio of the polymeric quaternary ammonium salt to the lipid is 0.05-20:1; then a assembly method or a modification method is adopted for modifying to prepare a folic acid or EGFR antibody modified cationic polymer lipid gene carrier. Results of gene transfection experiments show that: gene transfection efficiencies of the target quaternary ammonium salt cationic polymer lipid gene carrier in 293T cells and NIH-3T3 cells are the same as the gene transfection efficiencies of positive control lipofectamine of lipofectamine<TM>2000 in the 293T cells and the NIH-3T3 cells; the gene transfection efficiencies of the EGFR antibody modified cationic polymer lipid genetic carrier in liver cancer Huh-7 cells and breast cancer MCF-7 cells are higher than the gene transfection efficiencies of the lipofectamine<TM>2000 in the liver cancer Huh-7 cells and the breast cancer MCF-7 cells. The cationic polymer lipid genetic carrier system provided by the present invention has good biocompatibility and low cytotoxicity, and can be as an excellent non-viral gene delivery carrier.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF ONCOLOGY
Suspension acclimatization and serum-free acclimatization method for HEK (human embryonic kidney)-293T cells
ActiveCN103205396AStable growthGood dispersionBlood/immune system cellsMicrobiology processesKidneyChemically defined medium
The invention relates to a suspension acclimatization and serum-free acclimatization method for HEK (human embryonic kidney)-293T cells, and belongs to the field of biotechnology. The suspension acclimatization and serum-free acclimatization method includes acclimatizing the HEK-293T cells adaptive to adherent culture so that the HEK-293T cells are adaptive to suspension culture in culture media with serum; and acclimatizing the HEK-293T cells adaptive to suspension culture in the culture media with the serum in a serum reducing mode so that the HEK-293T cells are adaptive to serum-free acclimatization. The suspension acclimatization and serum-free acclimatization method has the advantages that the growth status of the HEK-293T cells cultured by the suspension acclimatization and serum-free acclimatization method is stable, the HEK-293T cells are high in dispersibility and are completely adaptive to suspension culture in the serum-free culture media with certain chemical compositions, and batch production can be carried out.
Owner:AKESO BIOPHARMA
Preparation method and application of CAR-T cell targeting B7H3
ActiveCN109880804AHas a lethal effectEnhance killing activityMammal material medical ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsBiologyLung cancer
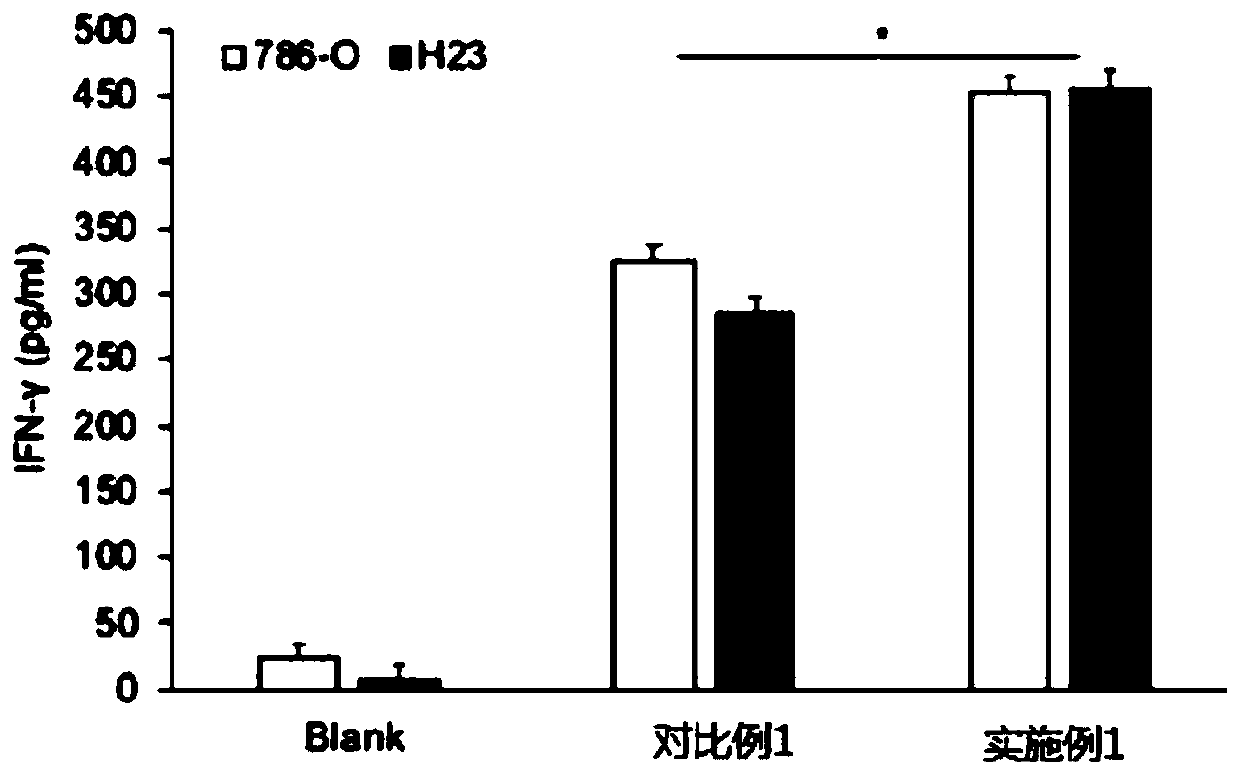
The invention relates to a preparation method of a CAR-T cell targeting B7H3. The preparation method includes first preparing a PBMC cell; then co-transfecting a 293T cell with a shuttle plasmid LV-B7H3 containing the CAR structure, a helper plasmid psPAX2 and an envelope plasmid VSV-G to obtain a packaged B7H3-CAR virus; then taking a PBMC cell, using anti-human CD3 and anti-human CD28 as activators, culturing and activating for 48 hours and adding the B7H3-CAR virus for infection. By means of the preparation scheme, the expression of IFN-gamma in the CAR-T cell is increased, and the cell killing activity is high. The CAR-T cell targeting B7H3 has a killing effect on various solid tumor cells, has high killing activity, is safe and effective, and can be used for immunotherapy of kidney cancer, lung cancer, liver cancer, glioma, ovarian cancer, breast cancer and the like.
Owner:XUZHOU MEDICAL UNIV
Six2 genetic expression-inhibiting shRNA, lentiviral expression vector and construction method of lentiviral expression vector
InactiveCN104195137AStable knockoutGood inhibitory effectAnimal cellsViruses/bacteriophagesLentivirusComputational biology
The invention discloses a Six2 genetic expression-inhibiting shRNA, a lentiviral expression vector and a construction method of the lentiviral expression vector. The Six2 genetic expression-inhibiting shRNA has a sequence of SEQ ID NO.2. The Six2 gene shRNA knockout lentiviral expression vector is obtained by inserting the shRNA into BamH I and EcoR I digestion sites of a vector plasmid pLVX-EF1alpha-IRES-Puro. The lentivirus pLV-shSix2 is obtained by transfecting the lentiviral vector plasmid and a packaging plasmid pLP1 and pLP / VSVG with a 293T cell. The screened shRNA which has a remarkable inhibiting effect on the Six2 genetic expression, and on the basis, the lentiviral expression vector and lentiviral, from which Six2 is knocked out, are successfully constructed, and a MES23.5 cell strain from which the Six2 gene is stably knocked out is obtained, thereby laying a good foundation for further researching the function of the Six2.
Owner:XUZHOU MEDICAL COLLEGE
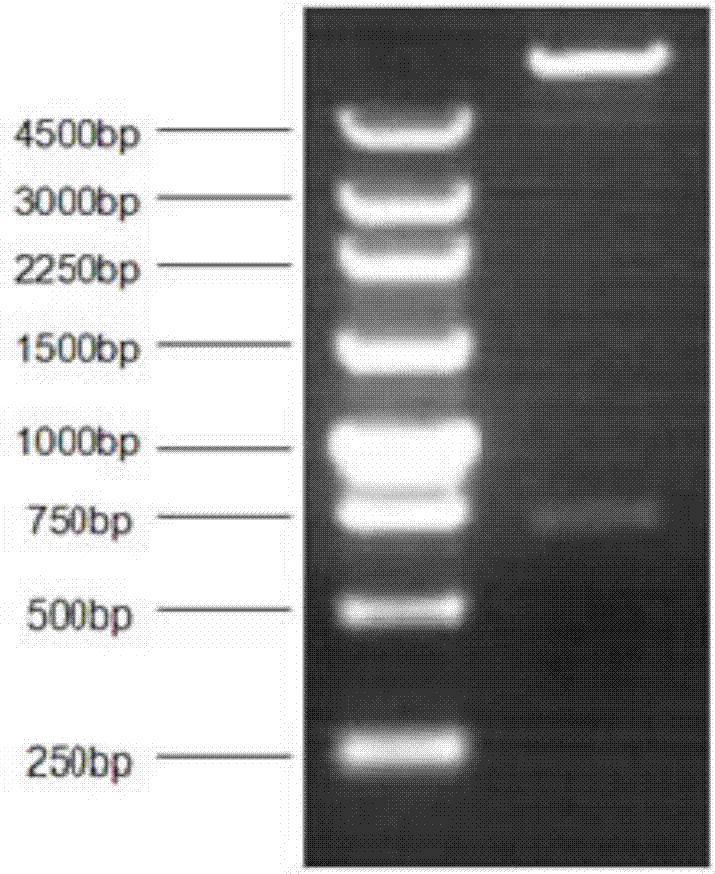
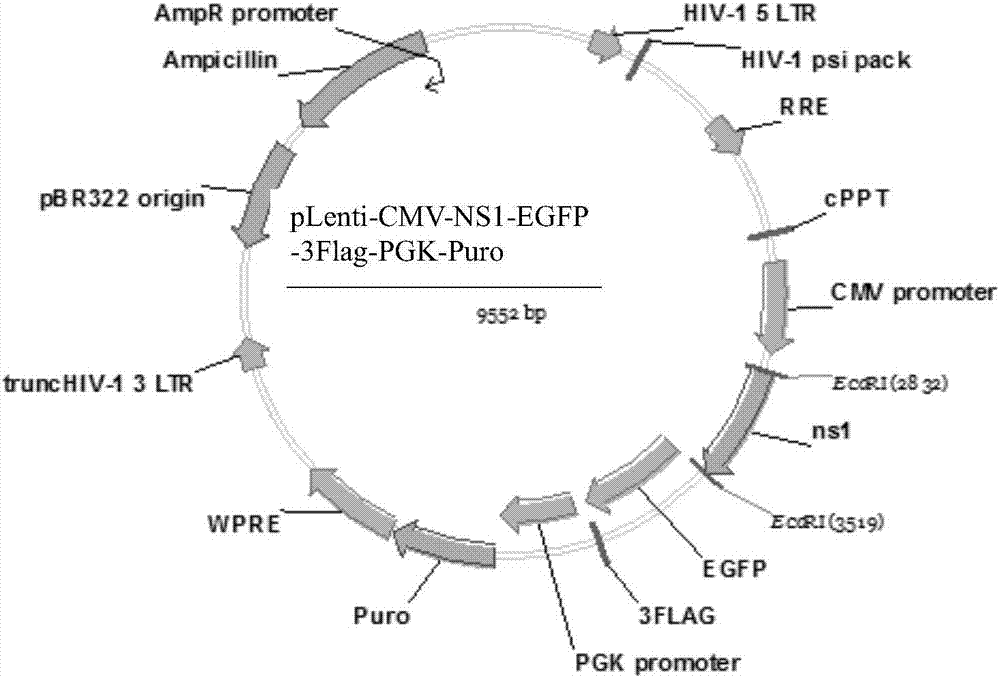
Building method of cell strain for stably expressing NS1(non-structural 1) protein
InactiveCN107190024AEasy to detectSsRNA viruses negative-senseVirus peptidesImmunofluorescenceWestern blot
The invention relates to a building method of a cell strain for stably expressing NS1 (non-structural 1) protein. An NS1 gene is inserted in an EcoR I polyclone site of a pLenti-CMV-EGFP-3Flag-PGK-Puro carrier; a built pLenti-CMV-NS1-EGFP-3Flag-PGK-Puro recombinant plasmid and a virus packaging plasmid are used for 293T cell cotransfection; culture, toxin elimination, virus liquid supernatant collection and filtering are performed to obtain recombinant lentivirus liquid. Packaged recombinant lentivirus infection A549 cells are subjected to puromycin screening, immunofluorescence and Western blot identification to obtain the cell strain for stably expressing NS1 protein. A recombinant lentivirus system is used for preparing the cell strain fusing tag protein capable of stably expressing the NS1 protein. The cell strain provides a good tool for studying the biological function of the NS1 protein.
Owner:LIAONING UNIVERSITY
Method for building model for collectively evaluating bioavailability and toxicity of cadmium accumulation in food for human body
InactiveCN102680654AAccurate evaluationThe result is accurateMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansTesting foodCell layerChronic toxicity testing
The invention relates to a method for building a model for collectively evaluating bioavailability and toxicity of cadmium accumulation in food for a human body, and the method comprises the following steps of (1) food sample digestion and determination liquid acquiring: a, grinding a food sample after the food sample is collected, and sequentially digesting the food sample by sequentially adopting gastric juice and intestinal juice; and b, centrifuging the digested mixed liquid, collecting supernate to be sterilized through high pressure; (2) independently culturing Caco-2 cells and 293T cells; (3) combined culture of Caco-2 cells and 293T cells: moving an insertion groove with the Caco-2 cells into a hexagonal-porous plate with the 293T cells to be continuously cultured for 24h; (4) evaluation of bioavailability and toxicity of cadmium: placing the food sample determination liquid on a Caco-2 cell layer of a combined culture model, simultaneously adding iso-osmotic incubation liquid on a 293T cell layer, and continuing the culture for 24h; in the chronic toxicity test, maximally collectively culturing the sample for 10d; and (5) detecting indexes. The method has characteristics of simpleness in operation, easiness in controlling test conditions, small pollution, economical efficiency, accurate result and the like, and also has the advantages for collectively evaluating the bioavailability and toxicity. The method is suitable for evaluating the safety of the cadmium accumulation in grains, vegetables and animal food.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
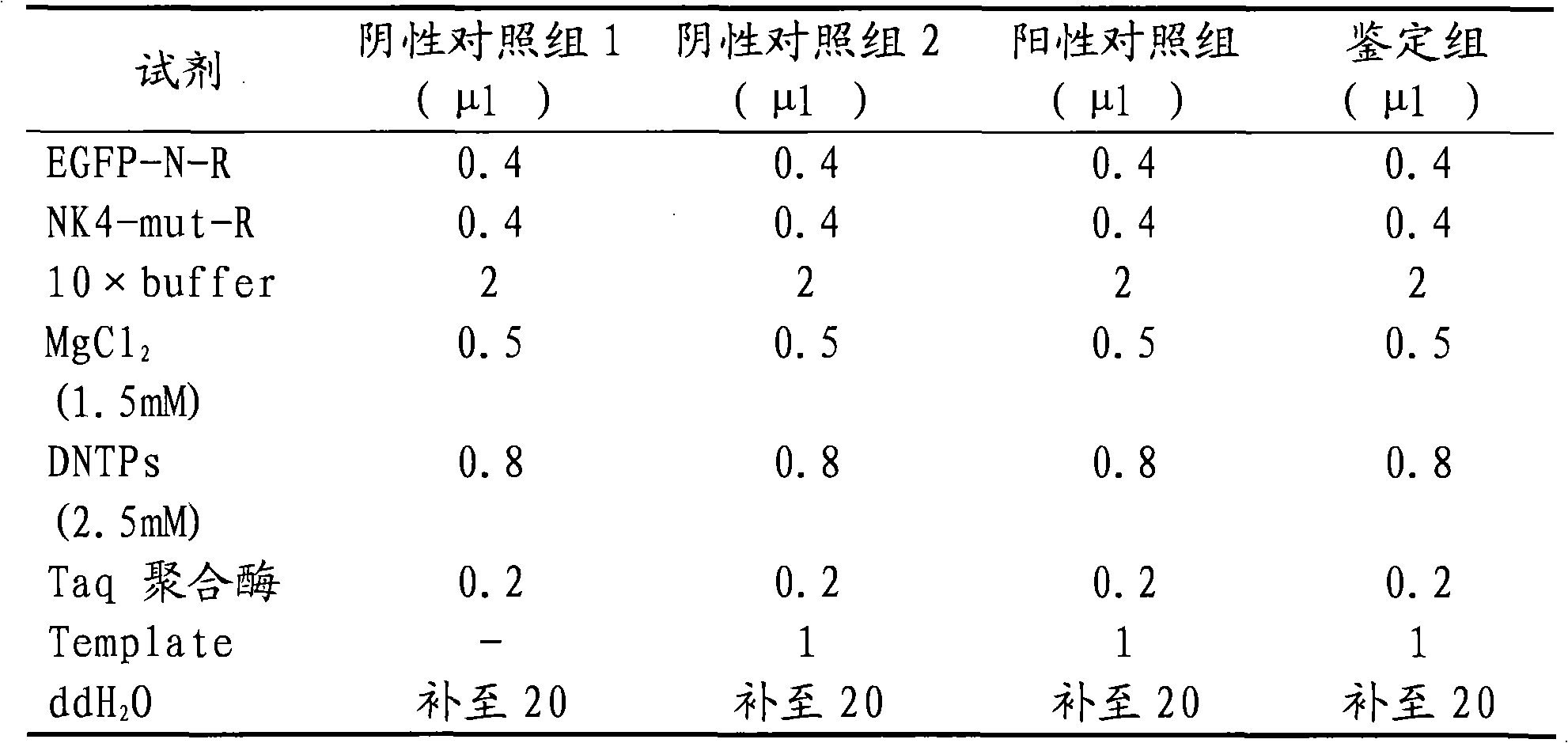
Preparation method of bone mesenchymal stem cell carrying NK4 gene and application thereof
InactiveCN101912618AGrowth inhibitionImprove tumor inhibition rateGenetic material ingredientsDigestive systemBALB/cGastric carcinoma
The invention discloses a preparation method of bone mesenchymal stem cells carrying NK4 genes and application thereof in medicine for treating gastric cancer. The preparation method comprises the following steps: extracting the NK4 genes from an HGF plasmid, using an in-Fusion technology to directionally clone the NK4 genes to a slow virus expression carrier plasmid, constructing an NK4-EGFP fusion gene recombinant slow virus carrier plasmid (pGC-FU-NK4) and then co-transfecting a 293T cell with the pGC-FU-NK4, a pHelper1.0 carrier and a pHelper2.0 carrier, packaging to produce NK4 overexpression slow virus particles (Lenti-NK4), using slow virus (Lenti-NK4) carrying NK4-EGFP fusion gene to transfect the bone mesenchymal stem cells to establish in vitro bone mesenchymal stem cells to stably express the NK4 genes. Balb / C nude mice animal experiments prove that the NK4 gene therapy taking BMSCs as a carrier can obviously inhibit the growth of subcutaneous transplant tumor of gastric cancer with high tumor inhibition efficiency, and the NK4 gene therapy is a good gene therapeutic method for gastric cancer.
Owner:祝荫
Preparation of cell growing slide assembly of CBA (cytometric bead array) kit for detecting MOG-IgG, CBA detection kit and application of CBA detection kit
InactiveCN107299111AGood repeatabilityStrong specificityCell dissociation methodsBiological material analysisCell strainBead array
The present invention relates to the preparation of a cell slide assembly for a CBA kit for detecting MOG-IgG, the CBA detection kit and its application. The preparation method of the cell slide assembly is as follows: S1: construction of MOG plasmid; S2: overexpression of MOG gene Lentiviral packaging; S3: Construction of a cell line (MOG-293T cell line) overexpressing the MOG gene; S4: Preparation of cell slide components. The kit includes cell slide assembly, anti-human IgG-FITC secondary antibody, blocking solution, PBS and mounting medium; the kit can be used for detection of MOG autoimmune IgG antibody in clinical samples. The kit of the invention has the advantages of simple operation, strong detection specificity, high sensitivity, good repeatability of experimental results, can be popularized and applied, and can be used for detection of MOG autoimmune IgG antibody in clinical samples.
Owner:GENERAL HOSPITAL OF PLA
Cell strain for expressing African swine fever virus CD2v protein and application of cell strain
ActiveCN110759973AEase of mass productionStable expressionSsRNA viruses positive-senseVirus peptidesClassical swine fever virus CSFVAfrican swine fever
The invention belongs to the field of biomedical genetic engineering and immunology, and particularly relates to a cell strain for expressing African swine fever virus CD2v protein and an applicationof the cell strain. The cell strain for expressing the African swine fever virus CD2v protein, provided by the invention, is obtained by optimizing and synthesizing a nucleic acid sequence of the African swine fever virus CD2v protein, constructing a recombinant lentiviral vector containing an ASFV-CD2v gene, packaging lentivirus, infecting HEK-293T cells and screening. The cell strain for expressing the African swine fever virus CD2v protein provided by the invention has biological characteristics similar to those of parent cells and is beneficial to large-scale production of antigen protein;the expression protein can obtain native conformation and modification processing close to virus protein in expression cells, has good antigenicity, and is easy for mass production.
Owner:GUANGZHOU BONIZZI BIOTECH CO LTD +1
Method for constructing stable cell strain secreting expression protein
PendingCN107043786ALow costImprove efficiencyGenetically modified cellsNucleic acid vectorProtein targetLentivirus
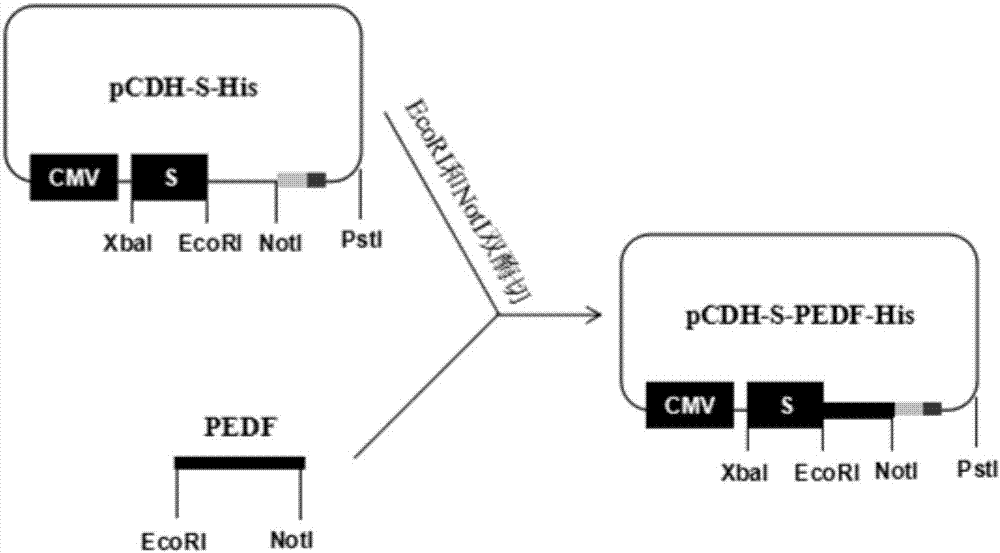
The invention belongs to the field of biotechnology and particularly relates to a method for constructing a stable cell strain secreting an expression protein. The method comprises the following steps: with a recombinant lentiviral vector pCDH-S-His as a skeleton, constructing a target protein gene to the recombinant lentiviral vector pCDH-S-His to obtain a recombinant plasmid pCDH-S-P-His; co-transfecting the recombinant plasmid and helper plasmids pSPAX2 and pMD2.G with 293T cells by using a PEI transfection method to obtain a recombinant lentivirus; transducing the obtained lentivirus to the 293T cells, and performing puromycin screening to obtain a plurality of monoclonal cell strains; detecting the content of target protein in each cell supernatant by an Elisa method; determining a high-expression cell strain. Compared with a traditional plasmid transfection method, the method provided by the invention has the advantages of short experimental period, high positive rate and good stability of the cell strain.
Owner:合肥知恩生物技术有限公司
Method for constructing laryngeal cancer cell line for stably expressing green fluorescent protein
InactiveCN108949697AShort screening cycleMeet different throughput needsGenetically modified cellsPeptidesProtein CBamHI
The invention belongs to the technical field of cell research, and particularly relates to a method for constructing a laryngeal cancer cell line for stably expressing the green fluorescent protein. The method comprises the following steps: (1) designing and synthesizing a primer; (2) digesting the gene sequence of pLenti-puro carrier plasmids with BamHI and XhoI according to the gene sequence andpLenti-puro sequence of the green fluorescent protein, and connecting digested products to obtain a target carrier pLenti-puro-GFP; (3) verifying the carrier pLenti-puro-GFP with endotoxin extraction, digesting the pLenti-puro-GFP plasmids with BamHI and XhoI, and detecting the gene sequence by agarose gel electrophoresis, and sequencing the carrier pLenti-puro-GFP plasmids to detect the sequencesituation of the GFP-LC3; and (4) co-transfecting a 293T cell with the carrier pLenti-puro-GFP plasmids and a lentivirus package carrier, collecting virus supernatant, and transfecting a laryngeal cancer cell Hep-2 with the virus supernatant, infecting for 24 hours, then adding a culture medium containing puromycin, screening the cell, and observing under high content until a stable strain is obtained.
Owner:FIRST HOSPITAL OF SHANXI MEDICAL UNIV
Methacrylic ester polymer, compounds thereof as well as preparation methods and application of all
InactiveCN101659722AEfficient transfectionHas in vitro immune efficacyVector-based foreign material introductionPlasmid dnaIn vivo
The invention discloses a mercaptyl-terminated (2-dimethylamino ethyl) polymethacrylic ester polymer, a self-assembled and modified nano-gold compound (PDMAEMAGNPs) of the polymer as well as a compound of the polymer and plasmid DNA; and the invention also discloses preparation methods of the polymer and the compounds as well as the application of all in carrier as genes. When the concentration ofthe compounds of PDMAEMAGNPs and GFP DNA (green fluorescent protein expression DNA) is 30Mug / mL, the transfection efficiency to HEK 293T cell is 30 percent, and the survival rate to HEK 293T cell, HeLa cell and 293 cell is more than 80 percent. The PDMAEMAGNPs / CpG ODN (human CpG oligodeoxynucleotide) compound has remarkable effects in gene therapy in vitro and in vivo. The suppression ratio to tumor growth of the PDMAEMAGNPs / p53 DNA (tumor suppressor gene) is 30-37 percent.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF APPLIED PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
CAR-NK cell, and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN108300698AStrong ability to secrete factorsImprove anti-tumor effectMammal material medical ingredientsNucleic acid vectorPeripheral blood mononuclear cellBiological activation
The invention relates to a CAR-NK cell, and a preparation method and an application thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: S1, synthesizing a CAR sequence; S2, integrating theCAR sequence into a lentiviral target vector plasmid to obtain a target plasmid; S3, mixing the target plasmid with a 293T cell, performing culturing, collecting the obtained virus liquid, and concentrating the virus liquid to obtain the virus concentrate of the target plasmid; S4, collecting autologous plasma and peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC), adjusting the cell density with an activation culture medium, performing cell culturing, transferring obtained cells into a new cell culturing bag, continuing culturing, adding a proliferation culturing medium, and obtaining the NK cell after the culturing is finished; and S5, adding the virus concentrate of the target plasmid to the NK cell, and performing incubation to obtain the CAR-NK cell. The CAR-NK cell has very strong factor secretion ability and tumor inhibition ability, and the transfection method for preparing the CAR-NK cell is efficient and stable.
Owner:深圳市沃英达生命科学有限公司
Cell line for stable expression of peste des petits ruminants virus receptor Nectin-4 and construction method of cell line
InactiveCN107805628AEasy to separate workGood genetic stabilityImmunoglobulin superfamilyFermentationVector systemCell culture supernatant
The invention discloses a cell line for stable expression of a peste des petits ruminants virus receptor Nectin-4 and a construction method of the cell line. According to the invention, by virtue of asynthetic Nectin-4 gene and on the basis of a lentiviral vector system, a recombinant plasmid pLOV-eGFP-Nectin-4 is constructed. The recombinant plasmid, together with pSPAX2 and pMD2.G plasmid, is applied to co-transfection of a 293T cell, so that retrovirus-like particles are obtained. A supernatant-infected MDBK cell is cultivated by virtue of cells containing the retrovirus-like particles, and puromycin screening and purifying are conducted, so that the MDBK cell for stable expression of Nectin-4 protein is obtained, and the MDBK cell is named as MDBK-Nectin-4. Through the construction ofthe cell line, an experimental material is provided for deep research of an interaction between PPRV and the receptor Nectin-4 and for the clinical rapid isolation of the PPRV is provided.
Owner:ANHUI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method for suspension domestication of 293T cells
PendingCN109280636AEasy to operateEasy to useEmbryonic cellsUrinary tract/kidney cellsSerum free mediaSerum concentration
The invention provides a method for preparing a suspended 293T cell line cultured in low serum. The method includes the following steps: (1) resuscitating and cultivating mammalian cells to obtain theadherently cultured 293T cells, and digesting the 293T cells with trypsin; (2) culturing the adherently cultured 293T cells in a serum-free medium supplemented with a certain amount of serum, and continuously culturing the 293T cells to adapt to the serum-free medium supplemented with a certain amount of the serum; and (3) repeating the continuous cultivation procedure in the step (2) and gradually reducing serum addition amount in the serum-free medium until a serum concentration is 0 to obtain the suspension cultured 293T cell. The method of the invention has the advantages of simple operation, convenient use, low cost and good safety. An in vitro expansion culture method of 293T cell suspension culture requires no special equipment, and the operation is simple and feasible. The 293T cell suspension culture can has broad prospects in basic research and clinical applications.
Owner:HRAIN BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Monoclonal cell strain of human embryo kidney cell 293T-C10 as well as preparation and application of monoclonal cell strain
InactiveCN102911911ALow toxicityToxic titer is stableMicroorganism based processesViruses/bacteriophagesScreening methodEmbryo
The invention relates to the field of biotechnology, in particular to a monoclonal cell strain of a human embryo kidney cell 293T-C10 for packaging viruses as well as a screening method of the monoclonal cell strain. 293T cell mycoplasmas are removed, monoclonal screening is carried out during logarithmic growth period to obtain uniform monoclonal cells, different transfection and virus removal efficiencies are compared, and screening is carried out to obtain the monoclonal cell strain. Such cell strain has a collection number of CCTCC C201281, is very high in transfection efficiency and virus packaging stability, is remarkably improved in virus removal efficiency of 293T cells than that before screening, and can infect a majority of tumors and other cells to be infected without ultracentrifugation, so as to meet most of experimental demands.
Owner:上海溥生生物科技有限公司
Respiratory syncytial virus pre-fusion F protein and application thereof
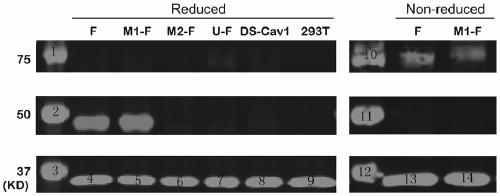
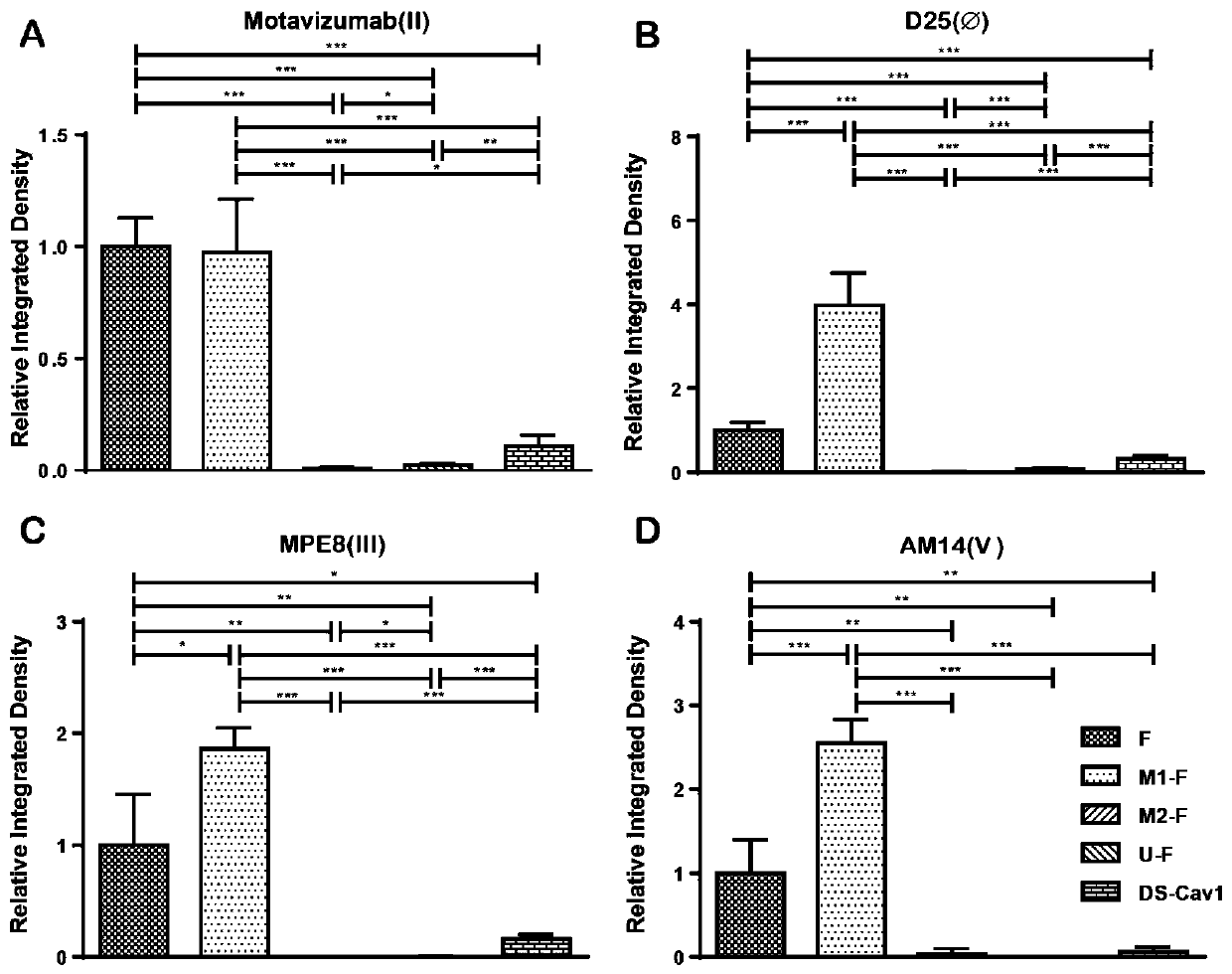
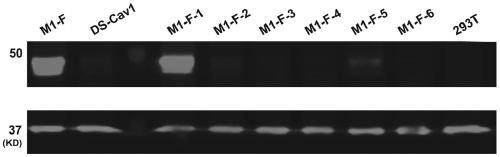
ActiveCN110054668AStable structureExpression did not decreaseSsRNA viruses negative-senseVirus peptidesF proteinWild type
The invention provides a respiratory syncytial virus pre-fusion F protein and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of respiratory syncytial virus vaccines. The pre-fusion F proteinis formed in the way that the 106th, 108th and 109th amino acids of a wild-type F protein are mutated from Arg to Asn, the 104th amino acid is mutated from Asn to Cys, the 155th amino acid is mutatedfrom Ser to Cys, or the 58th amino acid is mutated from Thr to Cys, and the 190th amino acid is mutated from Ser to Cys. A first furin cleavage site of the mutant wild-type F protein makes the structure of Pre-F more stable, the expression amount is not decreased, and the pre-fusion epitope of M1-F expression in 293T cells is significantly increased. The second mutation of the amino acid site of the F protein forms a disulfide bond, achieves the more stable pre-fusion epitope compared to the wild type, and is suitable for other strains of human RSV. The protein is suitable for various vaccineforms with the RSV F protein as the antigen, such as nucleic acid vaccines, protein vaccines, vector vaccines and recombinant virus particle vaccines.
Owner:BEIJING JIAOTONG UNIV
Method of preparing stem cell line for excreting insulin by using slow virus vectors of coding multiple exogenous gene
InactiveCN101100677AEasy to buildImprove practicalityVector-based foreign material introductionForeign genetic material cellsStem cell lineCell strain
Production of secretory insulin dry cell system by encoded various exogenous gene slow virus carrier is carried out by copying pWPST, cloning various insulin regulating genes to the carrier, transfecting 293T cell, packing, collecting virus grains, concentrating and transfecting human embryo pancreas dry cell. It's simple, efficient and practical, it can obtain one, two or three kinds of exogenous gene cells, which are in different expression and meet different needs.
Owner:CHINA JAPAN FRIENDSHIP HOSPITAL
Mediating method of RNAi (ribonucleic acid interference) utilizing lentiviral vector
InactiveCN102206645AStrong inhibition of replicationStrong inhibition of expressionMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationControl systemNucleic acid sequencing
The present invention relates to a mediating method of RNAi (ribonucleic acid interference) utilizing a lentiviral vector. The method comprises the following specific steps of: firstly carrying out homology analysis on the nucleic acid sequence of relevant viruses to find out conserved regions and designing siRNA (small interfering ribonucleic acid) corresponding to the conserved regions of the related viruses; and cloning the siRNA to an expression plasmid pLVTH, then co-transfecting 293T cells together with pCMV-dR8.91 and pMD2.G, collecting the supernatant of the transfected cells, carrying out ultracentrifugation, purification and concentration to obtain a high-titer lentiviral vector expressing the siRNA, then carrying out cotransduction into target cells together with LV-tTR-KRAB, and strictly controlling the acting time and dose of siRNA drugs utilizing tetracycline analogue DOX. Because of high transduction rate and a stringent control system, the mediating method can actually evaluate the in-vivo antiviral action of the siRNA and can track the whole process of drug interference action, thus having clinical application prospects.
Owner:成都康珞生物科技有限公司
Cell strain capable of stably expressing Cas9 protein as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN110951782AAvoid the risks of integrationImprove cutting efficiencyHydrolasesGenetically modified cellsCas9Homomeric
The invention discloses a cell strain capable of stably expressing Cas9 protein as well as a preparation method and an application thereof. According to the method, a Cas9 protein expression gene, anantibiotic selection marker gene and a fluorescence marker gene are introduced into a 293T cell of a tool cell through a CRISPR / Cas9 system; after positive clone cell strains are obtained through resistance and fluorescence screening, the screening marker is cut off through the CRISPR / Cas9 system, and finally the cell strains which can stably express Cas9 protein and do not have any screening marker are obtained. The cell strain constructed by the invention is constructed on the basis of a CRISPR / Cas9 gene editing system and a homologous recombination principle, and is integrated at a safety site-AAVS1 site in the tool cell genome in a fixed point mode; the Cas9 protein can be stably expressed and does not screening marker is obtained, so that the tool cell strain of a subsequent screeningexperiment is not influenced.
Owner:湖南普拉特网络科技有限公司
Method for transfecting and marking iPS cells of three-fusion reporter genes mediated by lentivirus
InactiveCN102174471AMeet the requirements of histological testingAvoid damageGenetic engineeringFermentationBiotechnologyMixed culture
The invention discloses a method for transfecting and marking iPS cells of three-fusion reporter genes mediated by lentivirus, comprising the following steps: 1. mixing plasmids, psPAX2 and pMD2G carrying fluc-mrfp-ttk, mixing the mixed plasmids with an EntransterTM-H reagent, adding the mixed plasmids into 293T cells for mixed culture, and performing centrifugation and concentration; 2. using pancreatin to digest iPS cells and carrying out resuspension, inoculating the iPS cells to a tissue culture medium coated by Matrigel for culturing; and 3. adding concentrated virus in steps 1 to the iPS cells and culturing the virus, separating and purifying the positive iPS cells of the mrfp. The method in the invention carries out three-fusion reporter gene marking on the iPS cells, thus being capable of carrying out real-time, positioning and quantitative tracking detection on the iPS cells in animals. The method causes less damage to the iPS cells and features high transfection efficiency of more than 25%.
Owner:INST OF BASIC MEDICAL SCI ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI OF PLA
Preparation method of gene mutation and fusion gene positive reference
The invention aims to provides a preparation method of a gene mutation and fusion gene positive reference. The preparation method comprises the following steps: with a lentivirus or a retrovirus, usedfor integrating a foreign gene in a cell genome, as a vector, preparing a sequence meeting different gene mutations or fusion genes, and after the sequencing validation is error-free, embedding in the cell genome through the virus, screening out a monoclonal cell line with gene mutation or fusion gene from a drug, thereby obtaining the continual positive reference. The cell line is preferably 293T cell line, the mutation can be conducted at a single mutation site of a single gene, multiple site mutations of a single gene and multiple site mutations of multiple genes, and the fusion gene canbe a single fusion gene,and can also be multiple fusion genes connected in series. The preparation method has the advantages of being rapid, accurate, simple, low in cost, high in sensitivity, and capable of realizing mass production, and application and popularization in the markets are facilitated.
Owner:辽宁琦润生物科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com