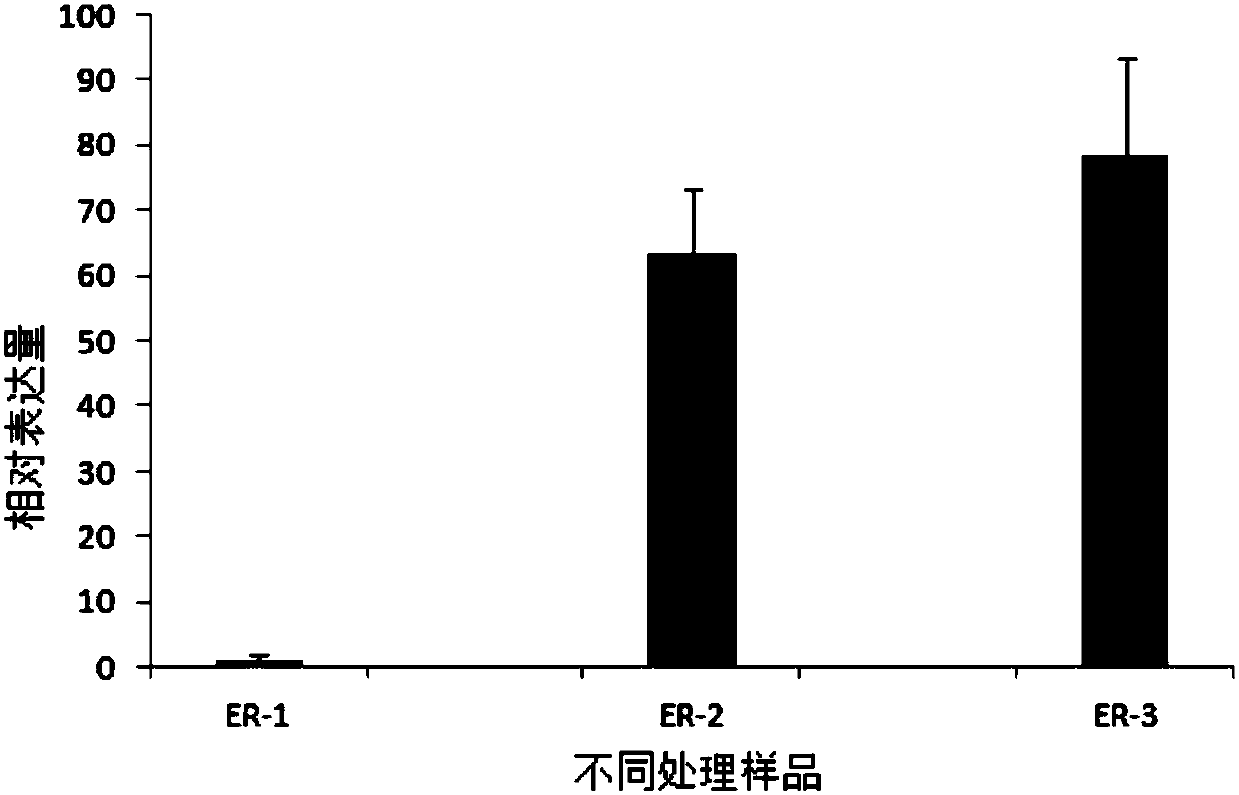
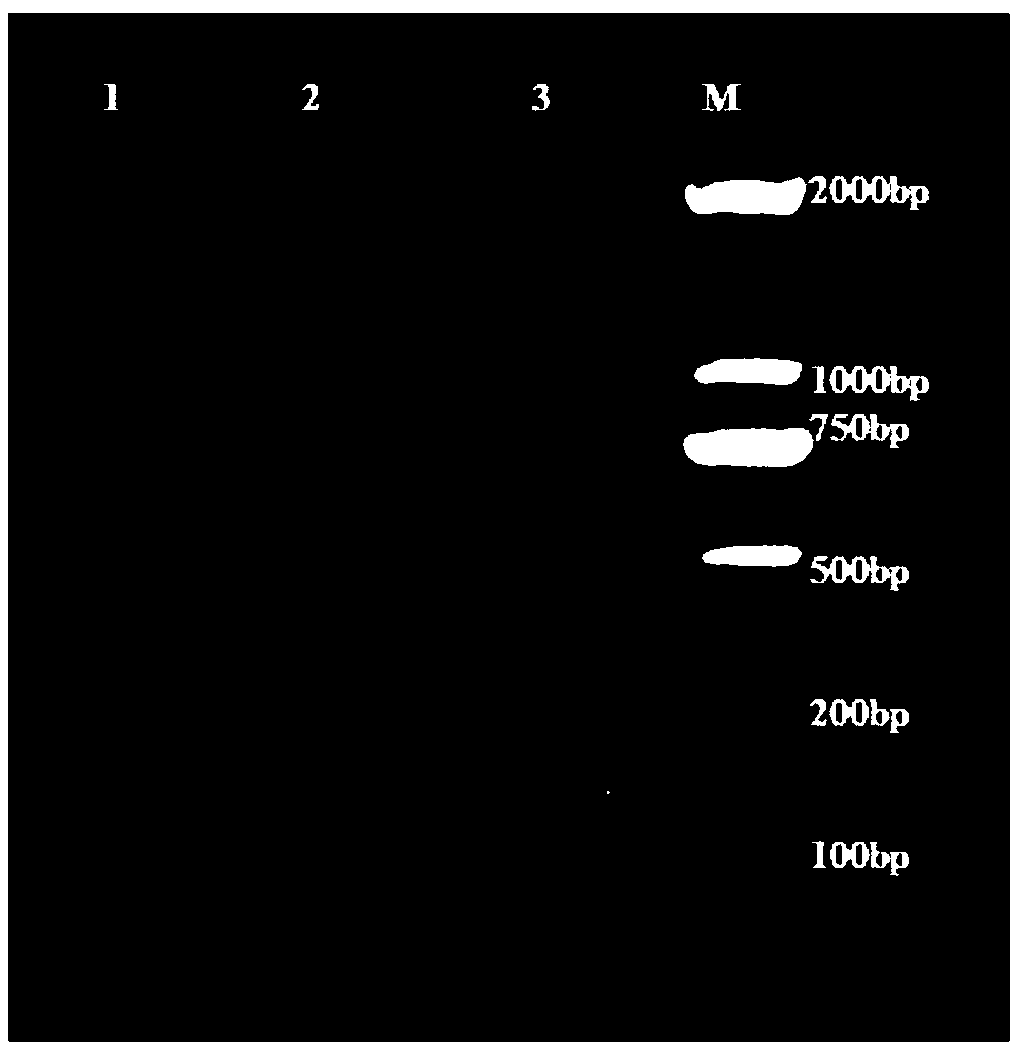
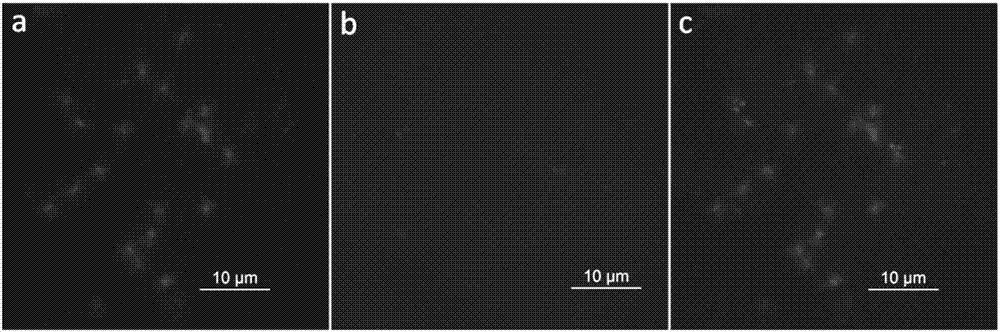
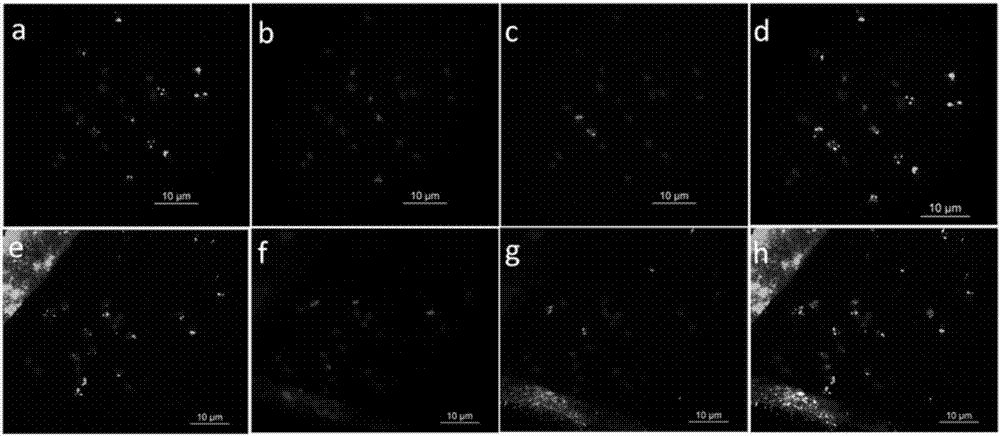
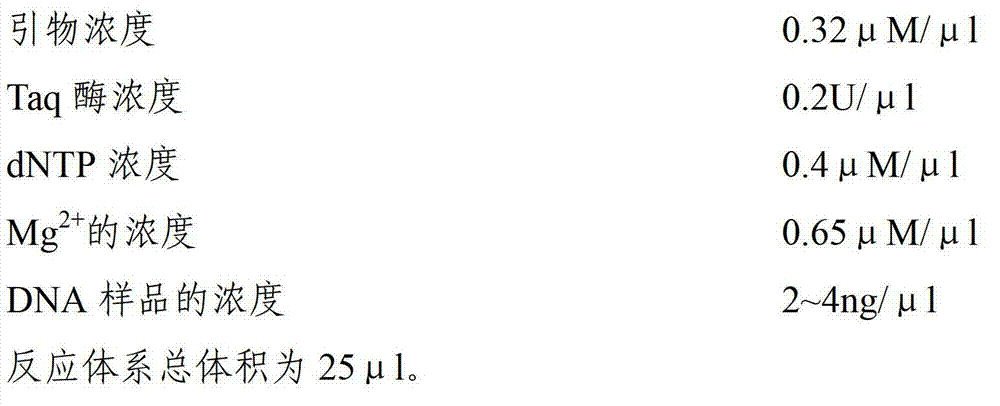Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
138 results about "Wild species" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Bacterial strain isolation and cultivation technique for Chinese wild species big fat mushroom
The invention related to technique of edible mushroom provides a cultivate technique and a method for separating bacterial strains Chinese wild mast mushroom. Wild source of mast mushroom in said invention is scarce for meeting the demand of market. Said invention performs artificial cultivation of mast mushroom by selection from different culture mediums and conditions. The technique of the invention is easy to master and its material for cultivating has broad source, as a result, can be extended generally in countryside.
Owner:田绍义
Breeding method of drought resistant and cold tolerant Saccharum varieties/lines containing Erianthus fulvus Ness consanguinity
The invention discloses a breeding method of drought resistant and cold tolerant Saccharum varieties / lines containing Erianthus fulvus Ness consanguinity. The method provided in the invention makes use of Erianthus fulvus Ness wild species (E. fulvus) and Saccharum cultivars (Saccharum spp.) to perform "interspecific distant hybridization". The hybrid progenies undergo selection from a seedling stage, i.e. under conditions (dryland, high altitude) with natural environmental stress, thus obtaining new drought resistant and cold tolerant Saccharum varieties / lines suitable to plant at an altitude of over 1300 meters.
Owner:YUNNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Sweet potato distant hybridization breeding method with high success rate
InactiveCN101715724AEasy to operateIncrease success rateBiocidePlant growth regulatorsFlowering seasonWild species
The invention discloses a sweet potato distant hybridization breeding method with a high success rate, and relates to the technical field of plant innovation and new variety breeding of crops. The method comprises the following steps of: taking a wide-compatibility parental sweet potato Xushu 18 as a female parent, and regulating the flower season of the Xushu 18 to be synchronous with that of a wild specie sweet potato by a grafting and dark treatment method; performing water culture on a male parent and the female parent indoor to naturally take root and blossom; after the male parent and the female parent blossom, performing hybrid pollination; after pollinating, coating a hybridization treating fluid (40mg / L 6-benzyladenine, 45mg / L 2,4-dichlorphenoxyacetic acid and 40mg / L naphthylacetic acid) on the stem base of an ovary and the whole flower stalk, and continuously treating for 7 days; and for a combined hybridized ovule which stops early development, adopting immature embryo rescue technology. The hybridization method and a hybridization system of the invention have the advantages of high operability and high success rate. The method is also suitable for indoor directed hybridization of a field naturally blossoming sweet potato material and a conventional sexual hybridization breeding of the sweet potato.
Owner:XUZHOU ACAD OF AGRI SCI
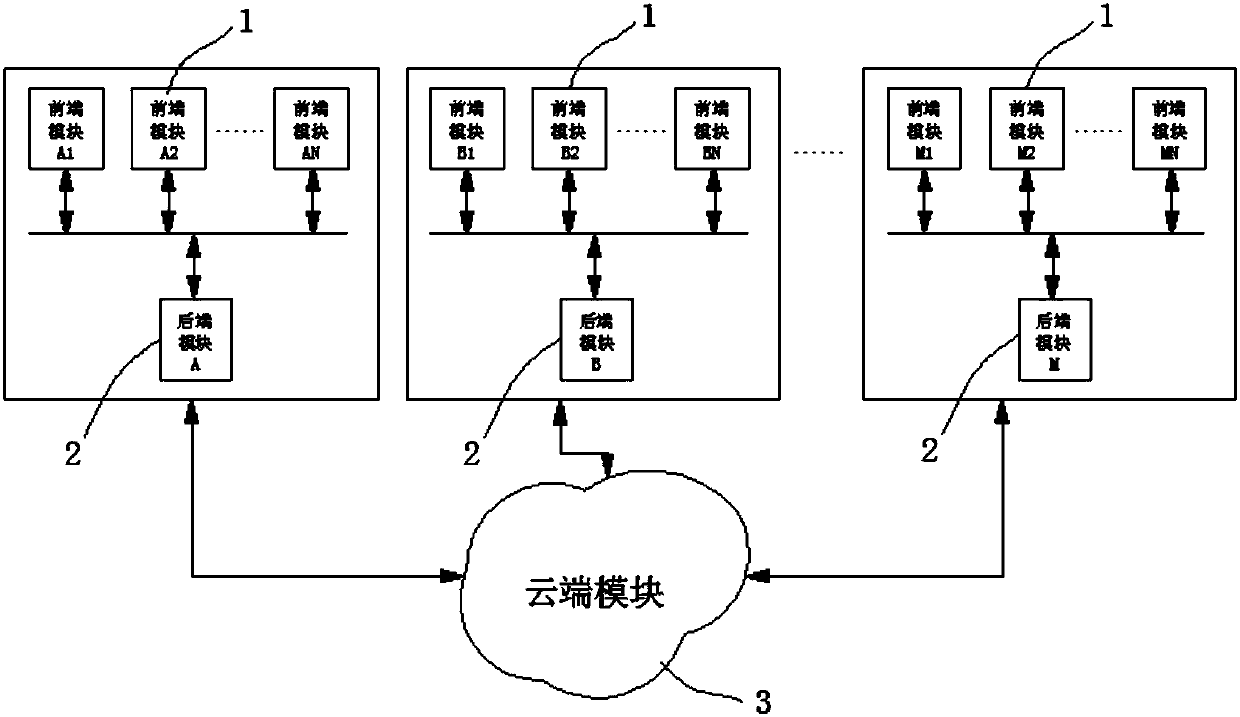
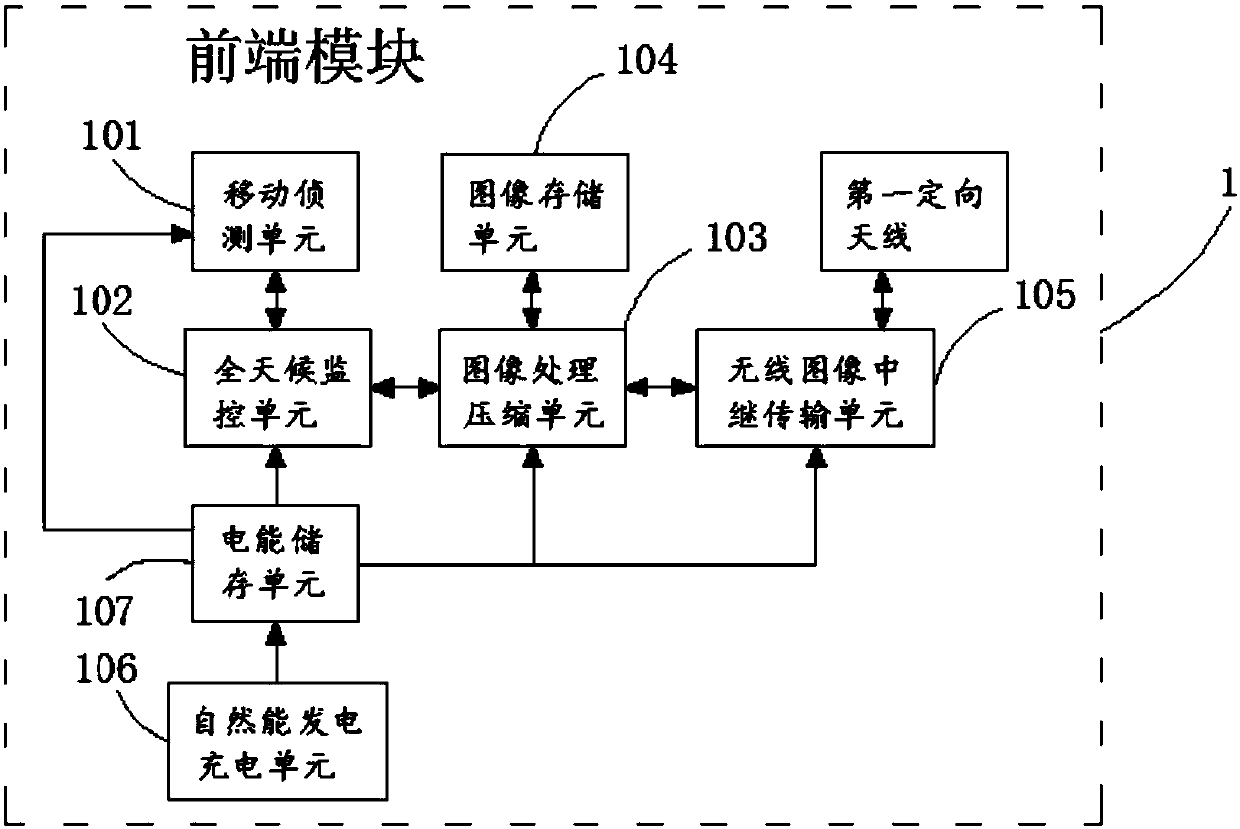
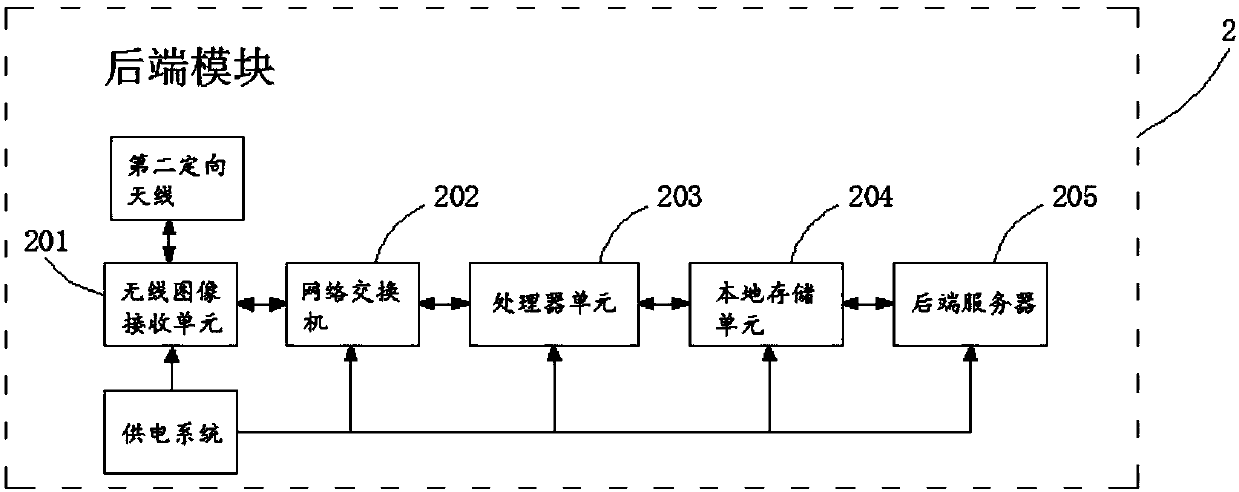
Wild animal monitoring system
InactiveCN107770494AAchieving processing powerRealize analysisTelevision system detailsColor television detailsWild speciesWildlife
The invention discloses a wild animal monitoring system. The wild animal monitoring system comprises multiple front modules, multiple rear modules and a cloud module; the front modules perform monitoring on a scenery in a set range, perform recording to generate an original image when a moving target enters a monitoring range, and perform processing and storage on the original image; the rear modules perform dynamic analysis, animal type recognition, animal number and animal age prediction, and animal activity rule analysis on the processed image, perform summarization on data obtained by theanalysis and write to a database to store; and the cloud module performs generalization and summarization on the data obtained by the analysis with reference to the previously received data, presentsthe data in a form of a data report, a chart, a curve and a distribution map, performs storage on the generalized and summarized data and sends to a set user. The data processing and analysis are implemented, and animal population type, number and activity rule are presented, such that a powerful data support is provided for a relevant department to control a balance of wild species and investigate the wild species.
Owner:SHENZHEN WANNEY SCI & TECH CO LTD
Plant anther specific promoter and its application
InactiveCN1912126AAvoid pollutionEnhanced insemination capacityFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionWild speciesAgricultural science
The invention discloses plant anther specificity promoter and its application. The promoter nucleotide sequence can be the one as (1) sequence table number one in question; or the one as (2), (1) in question nucleotide sequence complementary; or the one as (3), (1), or (2) in question which has 60% or above homology; or the one as (4), (1), (2), or (3) in question which can hybridized at strict hybridization condition. The inverse gene, small RNA, or expression vector can be used to transform host cell or tissue and its progeny cell to culture male sterile line plant, prevent transgene from polluting its wild species, landscaping plant, or crop species, etc.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Hibiscus cannabinus l. H040 cytoplasmic male sterility phyletic breeding method
InactiveCN101401540AReduce the risk of a majorReduce the cost of seed productionPlant genotype modificationWild speciesHibiscus
The invention relates to a method for breeding kenaf H040 cytoplasmic male sterile line, and belongs to the technical field of breeding of crop male sterile lines. The method takes kenaf wild species H040 or filial generation inherited with cytoplasm of the kenaf wild species H040 as female parent, and takes UG 93 cytoplasmic male sterile maintainer line or kenaf common culture variety as male parent; the female parent and the male parent carry out saturated backcross; the H040 cytoplasmic male sterile line, which is similar to the male parent and is orderly and consistent and exhibits male sterility, is selected and bred; and the backcross female parent is the male sterile maintainer line. The method provides new source of the cytoplasm for the breeding of the kenaf male sterile line, and can combine hybridized combination with comparative advantages.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
Asexual propagation and culture technique for medium-sized pennisetum alopecuroides
The invention discloses an asexual propagation and culture technique for medium-sized pennisetum alopecuroides and relates to the technical field of introduction, domestication and culture of wild pennisetum alopecuroides. The asexual propagation and culture technique for the medium-sized pennisetum alopecuroides consists of an asexual propagation part and a culture management part and is completed according to the following steps of: A, performing asexual propagation which comprises root transplanting propagation and stem segment cuttage propagation; and B, performing culture management, wherein a nitrogenous fertilizer is applied at the seedling stage or in the period of seedling establishment, thinning is carried out at the seedling stage, scarification is carried out and weeds are removed after seedlings emerge in the first year, an ammonium phosphate composite fertilizer is applied at the tillering and jointing stage, the nitrogenous fertilizer and the ammonium phosphate composite fertilizer are applied supplementally after the pennisetum alopecuroides is mowed and grazed, and the pennisetum alopecuroides is mowed and utilized at the initial stage of earing and harvested at the mature stage at the end of October. The problems of a low maturing rate, a low emergence rate, propagation difficulty and the like in the actual production of the medium-sized pennisetum alopecuroides and other wild species of pennisetum alopecuroides are solved. The propagation speed of the medium-sized pennisetum alopecuroides can be rapidly improved. The technical support and the guarantee are provided for large-scale popularization and application of the species in the western region of China.
Owner:LANZHOU INST OF ANIMAL SCI & VETERINARY PHARMA OF CAAS
Method for identifying embryo abortion associated proteins of distant hybridization of chrysanthemum
InactiveCN103472182AAccurate identificationQuantitatively accurateComponent separationDevelopmental stageWild species
The invention discloses a method for identifying embryo abortion associated proteins of distant hybridization of chrysanthemum, and belongs to the field of chrysanthemum breeding and proteomics. The method comprises the steps of planting the small chrysanthemum as a female parent, taking wild chrysanthemum nankingense as a male parent for distant hybridization, cutting off pollinated inflorescences at different times after pollination, sampling ovaries with complete and plump morphological development and ovaries with abnormal and hollow morphological development respectively, immediately quick-freezing in liquid nitrogen after sampling, storing in a refrigerator at -80 DEG C, extracting proteins from samples by a TCA (Trichloroacetic Acid) / acetone precipitation method, quickly identifying differential proteins by an iTRAQ (Isobaric Tags for Relative and Absolute Quantitation) and mass-spectrometric technique, performing bioinformatic analysis, and obtaining the embryo abortion associated protein in the distant hybridization breeding of the chrysanthemum. The method can quickly and accurately identify the embryo differential proteins with different morphologies in different developmental stages during embryonic development of the chrysanthemum for the chrysanthemum and affinis wild species of the chrysanthemum, and a research foundation is provided for solving embryo abortion of the distant hybridization of the chrysanthemum.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method for predicting differentiation ability of rubber tree secondary milk tube in seedling stage
The invention relates to a method for predicting the differentiation capacity of the secondary milk vessels of rubber plants in a seedling stage which is characterized in following aspects: a) in October and November every year, sawing the branches of the rubber plant seeds that are stored in a seedling nursery, leading residue stumps to sprout branches which are stump shoots, and selecting the newborn stump shoots with 3 to 5 stretch units as the material; b) mechanically injuring a stem which lies in the first stretch unit of the stump shoot and has scale leaves; c) the mechanical injury processing is implemented in the season between March - July, and the processing day is sunny; d) the stump shoot biotemperature is the time when the leaves of the first stretch unit grow ripe and terminal bud lies in an inactive state. The mechanical injury method uses a single-side or double-side knife for scraping the epidermis and part of the cortical layers, and the scraped surfaces are directly exposed in air for 2 to 10 hours. The invention has the advantages that the invention well predicts the differentiation capacity of secondary milk vessels of Amazon wild species and Wickham species in the seedling stage.
Owner:RUBBER RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF TROPICAL AGRI SCI
Simple sequence repeat (SSR) marker polymerase chain reaction (PCR) reaction method applied to chrysanthemum and related species thereof universally
ActiveCN102876790AHigh sensitivityGood repeatabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementWild speciesCrossostephium
The invention discloses a simple sequence repeat (SSR) marker polymerase chain reaction (PCR) reaction method universally applied to chrysanthemum and related species thereof. In a PCR reaction system, the primer concentration is 0.32 MuM / Mul; the Taq enzyme concentration is 0.2 U / Mul; the dNTP concentration is 0.4 MuM / Mul; the Mg<2+> concentration is 0.65 MuM / Mul; and the DNA concentration is 2 to 4 ng / Mul. Stripes obtained by the method for performing SSR molecular marker PCR reaction are clear and have high polymorphism and high repeatability. The method is simple in operation and commonly used in wild species and varieties of chrysanthemum, Ajania, Opisthopappus Shih and Crossostephium Less, and has a wide application prospect.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Method for quickly identifying differential protein during interaction of chrysanthemum pollen and stigma
InactiveCN102841126AOvercoming incompatibilityMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansWild speciesPetal
The invention discloses a method for quickly identifying differential protein during interaction of chrysanthemum pollen and stigma, belonging to the field of chrysanthemum proteomics. The method comprises the following steps of: performing distant hybridization work of chrysanthemum by taking cultured chrysanthemum as a female parent and wild chrysanthemum as a male parent; cutting off pollinated inflorescences in 1 h and 24 h after pollination; removing petals and sepals of ligulate flowers in the obtained inflorescences to obtain pistils; extracting a protein sample from the obtained pistils by using a TCA (Trichloroacetic Acid) / acetone precipitation method; and quickly identifying the differential protein by applying iTRAQ (Isobaric Tags For Relative And Absolute Quantitation) and a mass spectrum technology and performing bioinformatic analysis. Aiming at the chrysanthemum and wild species of related genera thereof, the invention provides a method for quickly and accurately identifying key differential protein during the interaction of the chrysanthemum pollen and the stigma for providing research foundation for solving the problem of distant hybridization incompatibility of the chrysanthemum.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
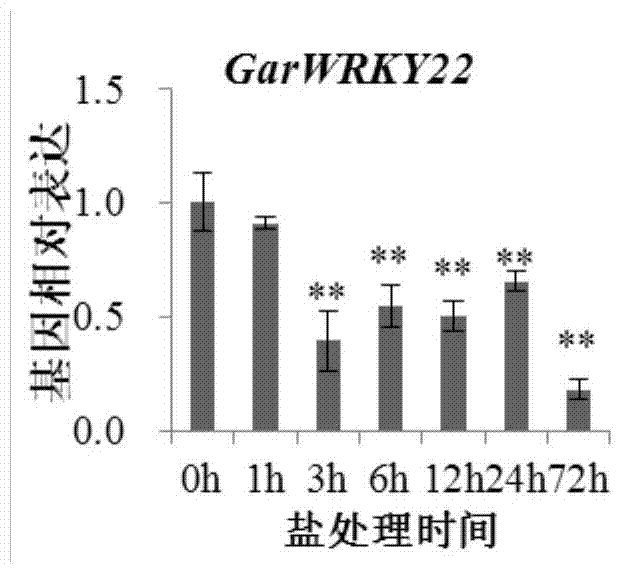
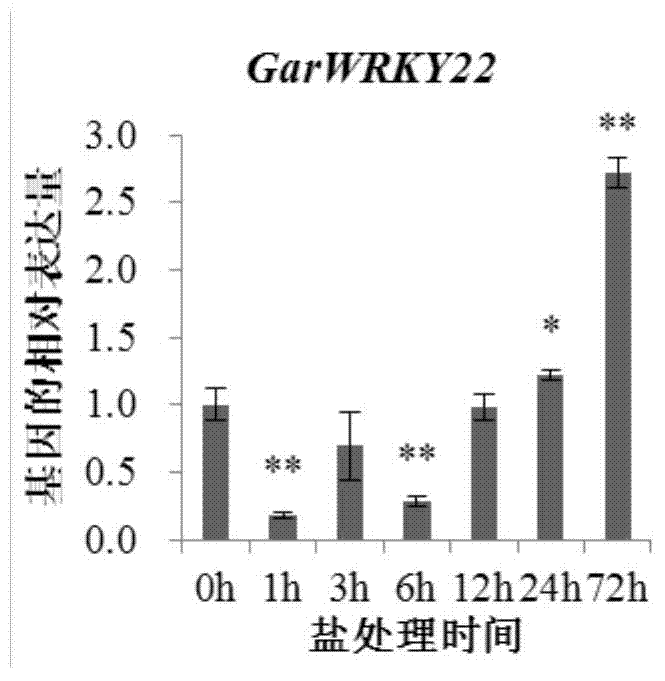
Cotton WRKY transcription factor GarWRKY22 for regulating salt tolerance of plants and application thereof
The invention discloses a transcription factor related to salt tolerance of cotton, namely gossypium wild species dry land cotton WRKY gene GarWRKY22 of which the sequence is disclosed as SEQ ID NO.2 in the sequence table. Electronic cloning and RT-PCR (reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction) techniques are utilized to separate the protein GarWRKY22 related to salt tolerance of cotton. The functional verification by converting Arabidopsis thaliana proves that the transcription factor can regulate the salt tolerance. When the gene is overexpressed, the salt tolerance of the plants is obviously lowered.
Owner:JIANGSU ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method for rapidly establishing medium-sized Chinese pennisetum herb tissue culture regeneration system by taking seeds as explants
InactiveCN104719158AEasy to operateEasy to completeHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureBiotechnologyWild species
The invention provides a method for rapidly establishing a medium-sized Chinese pennisetum herb tissue culture regeneration system by taking seeds as explants. The method mainly comprises the following steps: performing selection, disinfection and soaking on a medium-sized Chinese pennisetum herb raw material; performing inoculation, culture and differentiation on callus tissues; performing rooting culture on tissue culture seedlings; and performing acclimatization and transplanting. By adopting the method provided by the invention, an indoor rapid tissue culture regeneration system of medium-sized Chinese pennisetum herb wild species can be rapidly established, and the indoor rapid tissue culture regeneration system is an important foundation for further researching a molecular mechanism with low seed setting and germination rate; and moreover, the method is simple to operate and easy to complete.
Owner:LANZHOU INST OF ANIMAL SCI & VETERINARY PHARMA OF CAAS
Cultivating method of new species of anti-late blight and anti-beetle potato
The invention provides a cultivating method of a new species of an anti-late blight and anti-beetle potato, relating to a cultivating method of a new species of the potato with a cell culture technology. The method comprises the following steps of: electrically fusing a protoplast (A) which has anti-late blight gene, anti-beetle gene and anti-oxidation gene, and is separated from the wild species of the potato, with a protoplast (B) of the potato culturing species with wide adaptability to form into a fusion cell with the protoplast A and the protoplast B; generating a callus by means of cell culture, and generating a hybrid test tube plantlet of a regenerated somatic cell by means of induction; and further culturing the tissue culture test tube plantlet, transplanting the cultured tissue culture test tube plantlet into a glasshouse or a land for growing field crops, and generating a test tube first generation somatic cell hybridized potato to obtain the anti-diseases and insect cell hybrid potato, wherein the somatic cell hybridized potato has the good agronomic trait of the potato cultivating species and the anti-late blight and anti-beetle trait. The cultivating method provides a new available gene resource which can be used for improving the quality of the potato and improving the antioxidant activity of the potato cultivating species with the wild species.
Owner:LELING XISEN POTATO IND GROUP
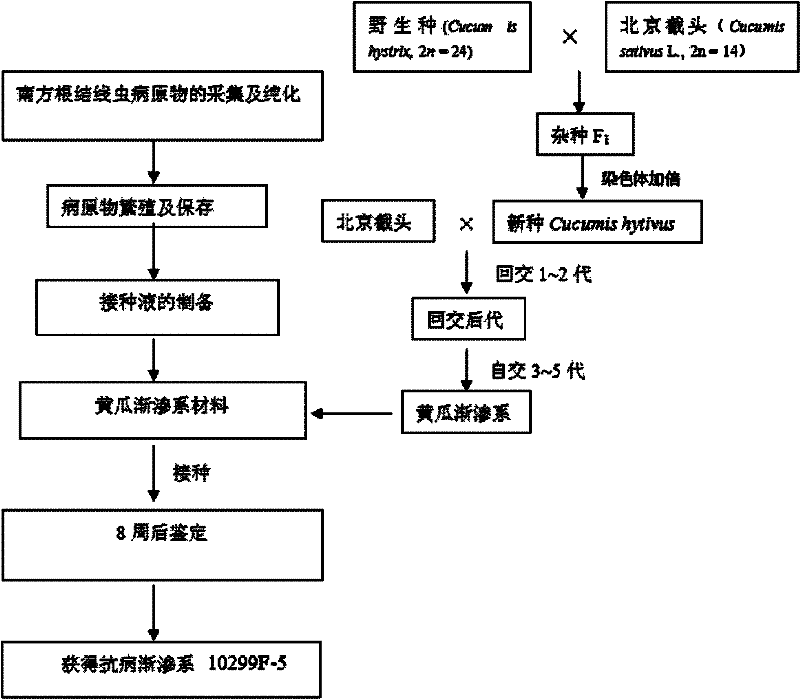
Cultivation Method of Cucumber Introgression Line Material Resistant to Meloidogyne incognita
InactiveCN102257953ABroaden the genetic baseStrong plant growthHorticulture methodsPlant genotype modificationWild speciesGenetic Materials
The invention belongs to the field of seed breeding in biotechnology, and relates to a method for cultivating cucumis sativus L introgression line material for resisting meloidogyne incognita. The method comprises the following steps of: performing the interspecific hybridization of wild species and cultivated species, doubling chromosomes to obtain new amphidiploid species, and performing backcross and selfing to obtain an interspecific introgression line; identifying the cucumis sativus L introgression line by a method of inoculating artificial seedling stage spawn liquid to obtain the cucumis sativus L interspecific hybridization introgression line material for resisting meloidogyne incognita, wherein an identification result indicates that disease indexes of the introgression line 10299F-5 are 2.0, and the introgression line 10299F-5 has disease-resistant expression. The cultivating cucumis sativus L interspecific hybridization introgression line material for resisting meloidogyneincognita is high in an economical character, and can be used as a breeding material directly, so the blank of cucumis sativus L resources for resisting meloidogyne incognita is filled, a reference is provided for the inoculation identification of other plants, and useful genetic materials are provided for improvement on cucumis sativus L species, the transfer of disease-resistant genes, gene positioning, molecular marks, gene cloning and the like in future.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Synthetic peptide vaccines for foot-and-mouth disease
InactiveCN101353373ASsRNA viruses positive-senseViral antigen ingredientsWild speciesImmune profiling
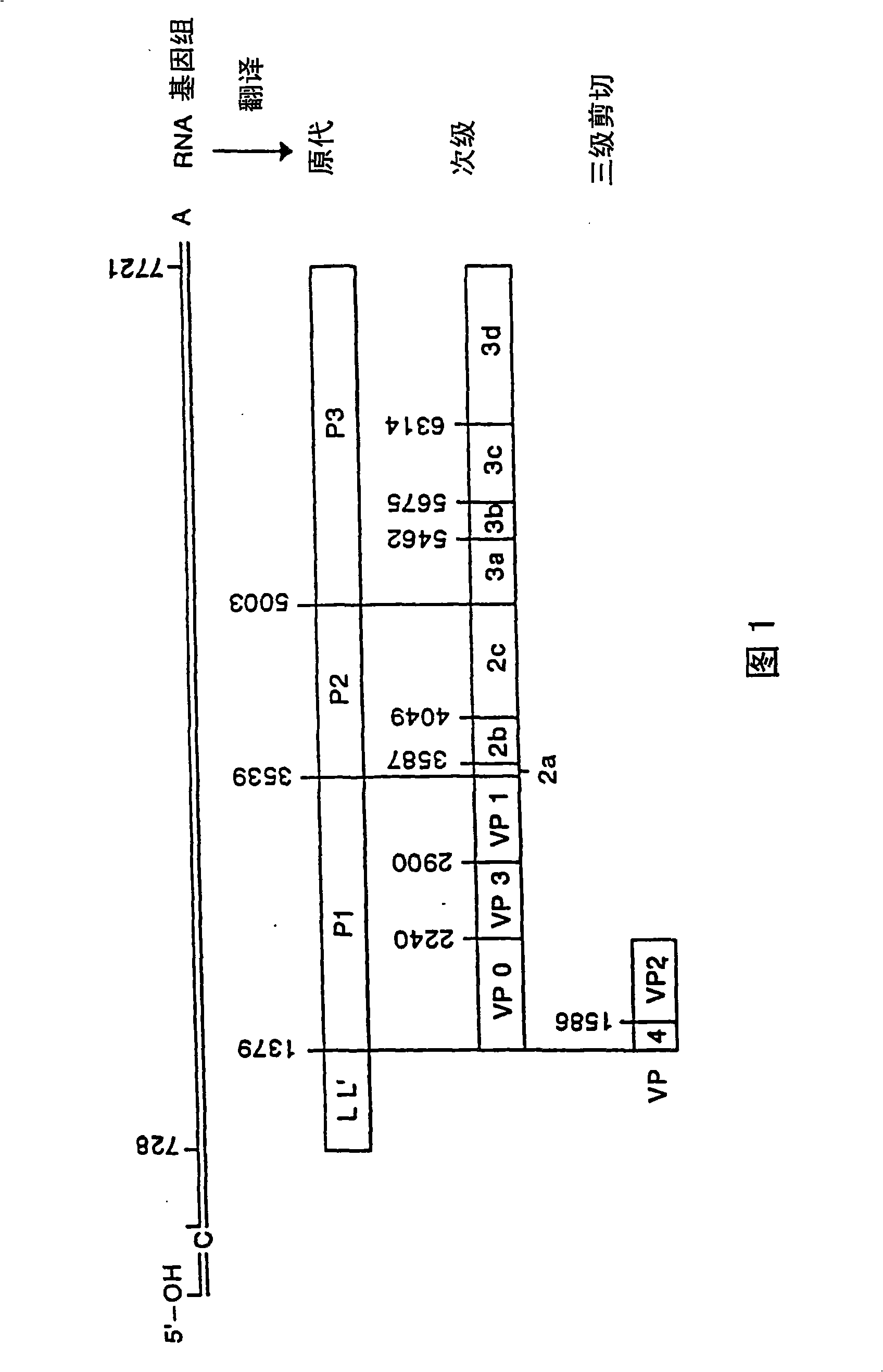
The present invention relates to the use of a peptide composition as an immunogen, with each peptide contained therein comprising a target antigenic site derived from the VP1 capsid protein of Foot-and-Mouth Disease Virus (FMDV). The antigenic site is covalently linked to a helper T cell epitope and, preferably, to other immunostimulatory sequences, preferably by conventional peptide bond(s) through direct synthesis, for the prevention of FMDV infection and eradication of Food-and-Mouth Disease (FMD). More particularly, the present invention relates to the use of such peptide composition as an immunogen to elicit the production in animals including swine, cattle, sheep, goets and susceptible wild species, of high titer polyclonal antibodies that can effectively neutralize, in vitro, multiple strains or serotypes of FMDV, and to the use of such composition as a vaccine to prevent, and / or reduce the incidence of, FMDV infection regardless of serotype, and thus affect the eradication of FMD. The present invention also relates to the peptides used in the compositions, and to immunoassays and / or diagnostic kits containing one or more of these peptides, and methods of diagnosing FMDV inmammals using such materials.
Owner:SHANGHAI SHEN LIAN BIOMEDICAL CORP
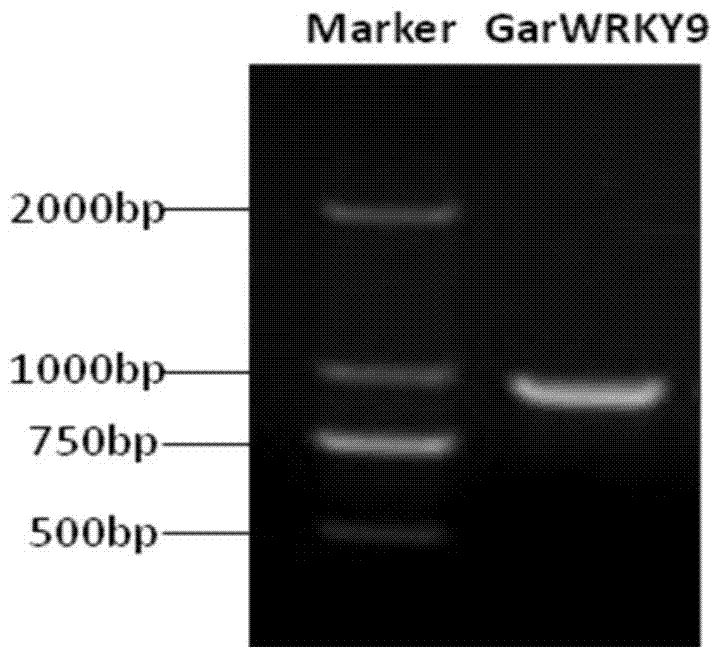
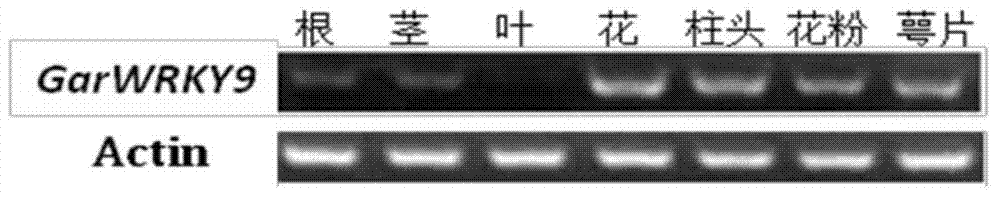
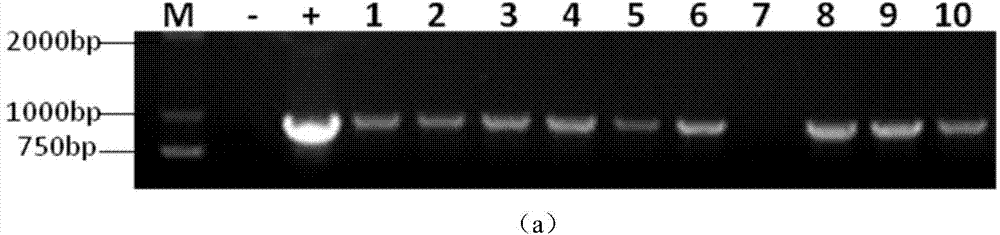
Gossypium aridum WRKY transcription factor GarWRKY9 for regulating blossoming of plant and application
InactiveCN104725496AEarly boltingEarly floweringPlant peptidesFermentationWild speciesAgricultural science
The invention discloses a transcription factor relevant to blossoming of gossypium aridum, namely gossypium wild species gossypium aridum WRKY gene GarWRKY9, which is characterized in that the transcription factor has a sequence as SEQ ID NO. 2 (Sequence Identifier Number 2) shown in a sequence table. The protein GarWRKY9 relevant to the blossoming of gossypium aridum is separated by using electronic cloning and RT-PCR (Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction) technologies, functional verification is conducted by transgenic arabidopsis, and the transcription factor is proven to be able to advance the blossoming of a plant.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
Culturing method for wild lucid ganoderma strain
InactiveCN107750814APromote growthImprove solubilityCultivating equipmentsMushroom cultivationWild speciesVitality
The invention provides a method for cultivating wild ganoderma strains, which relates to the technical field of mushroom cultivation. The method for cultivating wild ganoderma strains comprises the following steps: (1) preparation of tissue culture medium, (2) obtaining cultivated species, (3) ) the cultivation of test tube species, (4) the cultivation of wild Ganoderma lucidum bacterial classification; the present invention is by selecting wild Ganoderma lucidum as cultivated species, and then cultivated species obtains test tube species through test tube cultivation, and then transforms into original species in the test tube, and then from original species to female Finally, the mother bell is connected to the wood and cultivated at a constant temperature until it is covered with hyphae to obtain the cultivated species. The invention is very rigorous in the process from material selection to cultivation, avoiding repeated cultivation of cultivated strains, and improving the formula of the medium. The cultivation process is optimized, it is not easy to cause the degradation of the strain, the mycelium is strong, and the anti-miscellaneous bacteria performance is good. The strain cultivated by the method of the present invention has tenacious vitality and high medicinal value, which can lay a solid foundation for the high-quality and high-yield cultivation of Ganoderma lucidum. good foundation.
Owner:贺州市金子山生态灵芝林下种植专业合作社
Method for planting large-leaved gentian in sloping field
InactiveCN102318476AReduce laborGuaranteed germination rateFertilising methodsPlant protective coveringsWild speciesLand resources
The invention relates to a method for planting large-leaved gentian in a sloping field, belonging to the technical field of converting wild species of large-leaved gentian into domestic species, providing a method for planting large-leaved gentian in the sloping field and solving the technology of converting wild species into domestic species and saving precious land resources of China. The technical scheme adopted by the invention comprises the steps of: placing large-leaved gentian seeds in an overwintering mode under the conditions of natural north temperature and more than 85% of humidity for 15 to 90 days; processing the seeds at 12h to 30h before planting; mixing and stirring 0.5 to 2 parts of herbicide and 0.1 to 1 part of herbicide with 10 to 15 parts of seeds to obtain processed seeds; selecting the sloping field with elevation of 1500 to 4300m and gradient of 15 DEG to 55 DEG as a planting field; turning up the field within one week before planting, wherein turning depth is from 15cm to 30cm; fertilizing organic fertilizers of 7000 to 8000kg / hectare; planting the processed seeds in a strip cropping or broadcast sowing mode in the processed field, wherein sowing quantity is from 20 to 30kg / hectare and sowing depth is from 5mm to 15mm; covering a layer of crop straws with the thickness of 10mm to 20mm on the field after planting; and keeping a row spacing of 10cm to 25cm and a plant spacing of 1cm to 15cm in a manual seedling selecting method after seedlings emerge. The method provided by the invention is applied to the technical field of large-scale planting of large-leaved gentian in the sloping field.
Owner:SHANXI SHENGJI AGRI ANIMAL HUSBANDRY DEV
Factory breeding method for virus-free seedlings of salviae miltiorrhizae
PendingCN107810855AImproves root productionHigh transplant survival ratePlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsWild speciesSalvia miltiorrhiza
The invention relates to a factory breeding method for virus-free seedlings of salviae miltiorrhizae, in particular to a factory breeding method for wild species, cultivated species or varied speciesof salviae miltiorrhizae which is severe in quality degradation, lower in yield and short in resources, and belongs to the technical field of plant varieties breeding. The factory breeding method forvirus-free seedlings of salviae miltiorrhizae comprises the following steps: (1) selecting tender leaves or stem tips of the salviae miltiorrhizae to perform virus-free treatment; (2) culturing the tender leaves or stem tips of the salviae miltiorrhizae in an initial inducible-proliferation culture medium; (3) performing differentiation culture on salviae miltiorrhizae callus in a differentiationculture medium; (4) performing root induced culture on the seedlings of salviae miltiorrhizae in a root inducing culture medium; (5) exercising the seedlings of salviae miltiorrhizae; and (6) performing field transplanting for seedlings of salviae miltiorrhizae. The factory breeding method can realize quick and factory breeding for excellent salviae miltiorrhizae variety (system) or strain systemand cherish endangered salviae miltiorrhizae resources.
Owner:许文胜
Hemsleya amabilis tissue culture and later propagation method
InactiveCN107646689AAvoid lostRealize artificial cultivationPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsWild speciesFirst generation
The invention belongs to the field of agricultural high technologies and specifically relates to a hemsleya amabilis tissue culture and lateral propagation method. The method comprises the following steps of initial medium preparation, explants sterilization and treatment, inoculation and culture, subculture medium preparation and inoculation, rooting culture, seedling hardening and transplantation. The method disclosed by the invention overcomes loss of effective ingredients cultured under a specific environment of a laboratory in the prior art and achieves artificial cultivation of wild varieties. Detection shows that dihydrocucurbitacin, cucurbitacin and hemsleya amabilis saponins all can be detected from the hemsleya amabilis propagated by the method disclosed by the invention, and contents of the dihydrocucurbitacin, the cucurbitacin and the hemsleya amabilis saponins are equivalent to that of the dihydrocucurbitacin, the cucurbitacin and the hemsleya amabilis saponins in wild hemsleya amabilis. The method disclosed by the invention improves a qualified seedling percentage of hemsleya amabilis seedlings, shortens a cultivation period, keeps effectiveness of the wild hemsleya amabilis and has an application prospect in the aspects of preserving, protecting, developing and utilizing wild hemsleya amabilis resources and the like.
Owner:临沧惠康中药材资源开发有限公司
Pinellia ternata allopatric detoxification breeding and planting cultivation method
InactiveCN106718004ASolve the problem that cannot be continuedWell-proportioned particlesCultivating equipmentsPlant cultivationContinuous croppingDisease
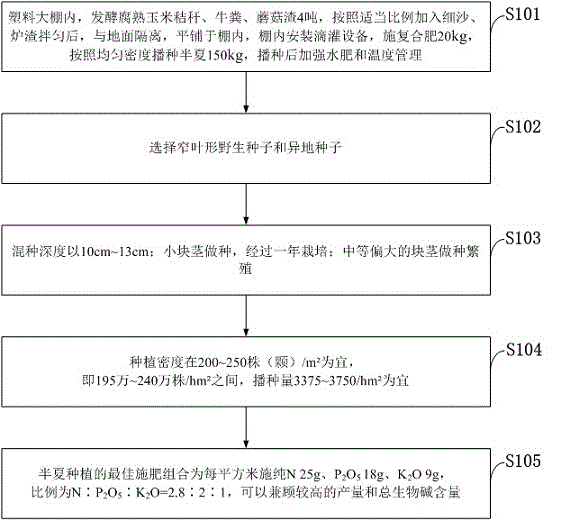
The invention belongs to the technical field of pinellia ternata planting, and discloses a pinellia ternata allopatric detoxification breeding and planting cultivation method. The method comprises the steps that thoroughly-decomposed corn stalk, cow dung and mushroom residues are fermented, silver sand, slag and compound fertilizer are added to be mixed evenly, and then drip irrigation equipment is installed inside a greenhouse; narrow leaf shaped wild species and allopatric species are selected as seeds; the mixed seed depth is 10-13 cm properly; the seed sowing amount is 3,375-3,750 kg / hm<2> properly; according to the most fertilizer combination for pinellia ternata planting, 25 g of pure N, 18 g of P2O5 and 9 g of K2O are applied in each square meter, and the ratio of N to P2O5 to K2O is 1.8:2:1. The yield reaches 1,000 kg / 667 m<2>; no disease or weed exists, the drying rate is high, workers are reduced by 15 per 667 m<2>, the cost is reduced by 750 yuan per 667 m<2>, 3a or more is adopted continuously after a matrix material is disinfected, and the problem that continuous cropping cannot be performed on pinellia ternata is solved.
Owner:天水农业学校
Method for improving domestication survival rate of distant-hybridization tissue cultured seedlings of cucumbers
InactiveCN103430851APromote reproductionImprove germination ratePlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsWild speciesBud
The invention relates to a method for improving the domestication survival rate of distant-hybridization tissue cultured seedlings of cucumbers, belonging to the field of biotechnology. The method is mainly used for propagation and preservation and domestication seedling of hybridization materials of cucumber species and provides technical guarantee for application of a distant hybridization technology to cucumber breeding. The method mainly includes the steps of performing embryo rescue to obtain aseptic seedlings, carrying out induced differentiation on adventitious buds, carrying out regeneration bud extension and rooting culture and domestication transplanting, and regulating and controlling a specially prepared culture medium and external environment conditions. The method is simple in operation, has low requirements on raw materials and laboratory facilities, and has extremely good effects. According to the method, the obtained distant-hybridization tissue cultured seedlings have strong functional roots, the domestication period is shortened, and the survival rate of transplanting is improved. The method can provide a stable and high-efficiency regeneration seedling domestication system for hybridization of two individuals from different cucumber species and hybridization of two individuals from the same cucumis genus, and can be used for preservation and propagation and preservation of treasured cucumis wild species and transplanting seedling of common cucumber tissue cultured seedlings.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Primers for IMP molecular markers of tobacco
InactiveCN101899436AMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationWild speciesNicotiana tabacum
The invention relates to the field of plant genetic engineering, and aims to provide primers for IMP molecular markers of tobacco. The primers have nucleotide sequences shown as SEQ ID NO:1 to SEQ ID NO:10. The invention belongs to the technology of new biomolecular markers of the tobacco. The provided primers can be used for the IMP molecular markers of the tobacco. The fields for the IMP molecular markers mainly comprise (1) auxiliary selection breeding of the molecular markers of the tobacco, namely the selection breeding for tobacco varieties; (2) the construction of a genetic map of the tobacco; (3) the positioning and discovery of important functional genes of the tobacco; (4) the early diagnosis and screening of specific properties of the tobacco; and (5) the judgment of the genetic relationship of the tobacco (such as the mixing of the tobacco varieties, the analysis of the tobacco and wild species thereof and the like).
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV +1
Cotton whole genome 40K mononucleotide site, and application thereof in cotton genotyping
ActiveCN113308562AImprove detection accuracyImprove detection levelMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyWild species
The invention provides a cotton whole genome 40K mononucleotide site, and application thereof in cotton genotyping. The cotton whole genome 40K mononucleotide site is obtained through a VCF file obtained based on three-population re-sequencing, a cotton genome TM-1V_2.1 is taken as a reference, a target segment is preliminarily screened from site information in data, and then the probe corresponding to the target segment is synthesized; 13 cotton varieties are selected for data testing, and 13 upland cotton materials including one wild species, one semi-wild species and 11 cultivated species are selected for chip detection; according to a detection result, a target area with good uniformity is preferentially selected, and overall uniform distribution is ensured; and finally screening is performed to obtain the 40K mononucleotide site. The application of the site can greatly improve the genotype detection accuracy, improve the detection level and reduce the detection cost, and provides important technical support for molecular breeding of cotton.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
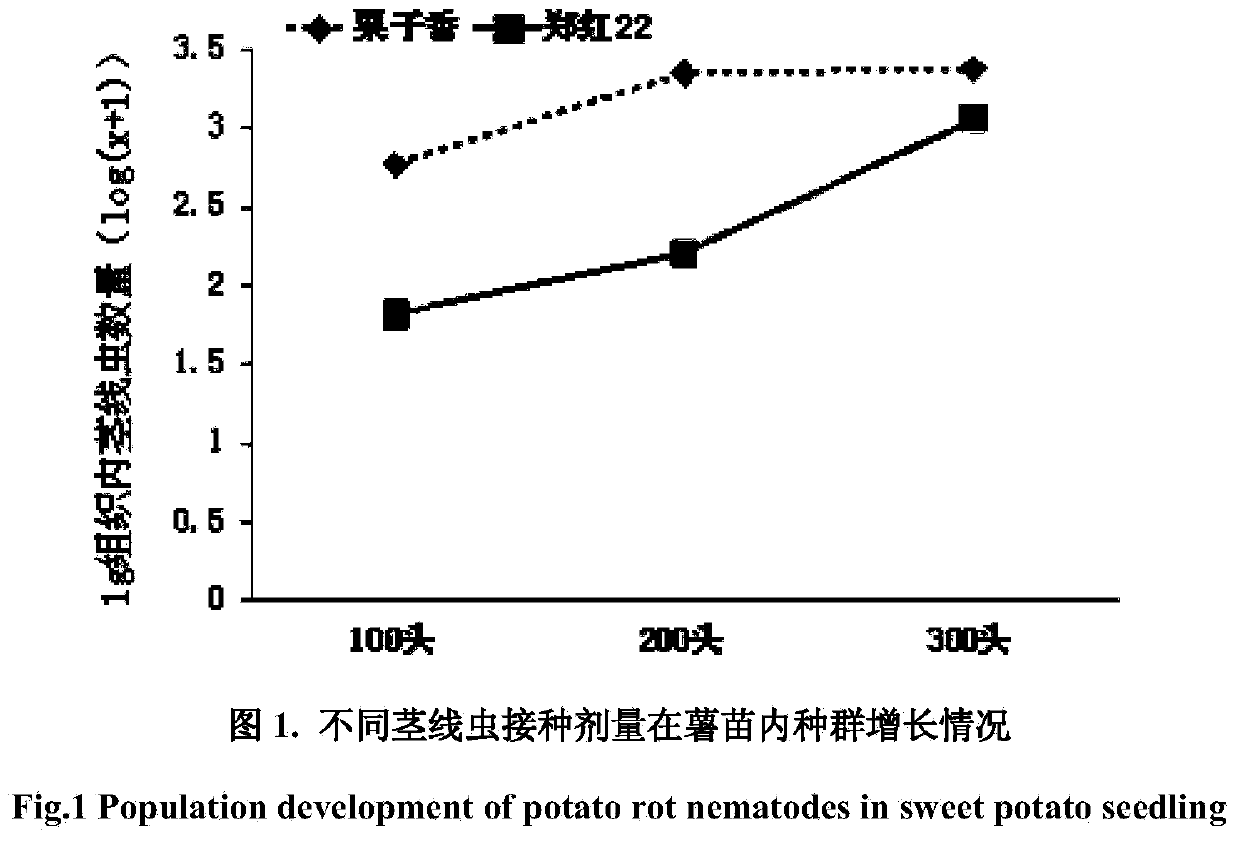
Stem nematode disease resistance identification method for sweet potato related wild species
InactiveCN103798044AAvoid pollutionFully reflect the level of resistanceHorticulture methodsAnimal husbandryWild speciesDisease
The invention discloses a stem nematode disease resistance identification method for sweet potato related wild species, and belongs to disease resistance identification methods of related wild species of crops. The identification method comprises the steps that the sweet potato wild species to be identified are planted into flowerpots containing sterilized soil, and one seedling is planted in each flowerpot; two hundred stem nematode worms are inoculated to each wild seedling by the adoption of the root dripping method, and the seedlings are cultivated at 25 DEG C, 80 percent of humidity, and a photoperiod of 14 / 10(L / D); the seedlings are watered appropriately each day, and the humidity of the soil in the flowerpots is controlled to be within the range of 18 percent-25 percent; after the seedlings are cultivated for 40 days, the subterraneous stems of the wild species are dug out and are vertically split with dissecting scissors, the stem nematode disease damage areas in the stems are measured, disease indexes are divided according to the ratio of the damaged areas to the stems, and the resistance levels of the wild species are determined. The processing means of the identification method is scientific and effective, the operation process is simple, the experimental period is short, and pollution to the environment by the test materials can be avoided. Besides, test results can comprehensively embody the levels of resistance to the stem nematode disease of the sweet potato related wild species.
Owner:JIANGSU XUZHOU SWEET POTATO RES CENT
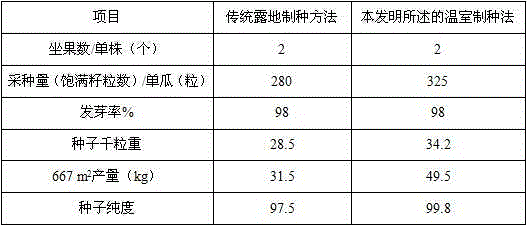
Method for producing seeds by adopting cucumis melo facility in greenhouse
ActiveCN104663426AReduce growth impactPrevent floweringPlant genotype modificationWild speciesPollination
The invention relates to a method for producing seeds by adopting cucumis melo facility in a greenhouse. According to the method, seeds of cucumis melo are produced in the solar greenhouse in early spring, the ratio of male and female parents is 1:5, male parents are 7 days earlier sown than female parents, planting and thorough watering are performed after a seedling has three leaves and one bud, intertillage is performed, a mulching film is covered, single stem training is performed on the female parents, vine-hanging cultivation is performed, pinching is performed when the seedling has 20-22 leaves, 16-19 nodes are used for fruit reserving, 3-4 vines are reserved for the male parents and hung, lateral buds are removed, 3-4 lateral vines are selected for pollination, emasculation is performed on female flowers at four o'clock in the afternoon one day earlier before the female flowers blossom, male flowers are well sleeved with sleeves, the well-sleeved male flowers are picked up at 5-7 o'clock next day, the emasculated female flowers are subjected to cross pollination at 7-10 o'clock and well sleeved with bags after pollination is completed, three hybrid melons are reserved, and two melons are selected when the three hybrid melons grow to the size of an egg. According to the method, the greenhouse is used for seed breeding of the cucumis melo, the flowering periods of wild species of various cucurbitaceae and vegetables are avoided, cross breeding probability is reduced, the seed purity is greatly improved, influence of adverse weather on melon growth is reduced, and the produced seed quality is better guaranteed.
Owner:山东省寿光市三木种苗有限公司
Erianthus fulvus calmodulin-like gene ErCML30 under low-temperature stress expression in erianthus fulvus wild species
InactiveCN108048469ANothing producedStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant peptidesWild speciesResource development
The invention discloses an erianthus fulvus calmodulin-like gene ErCML30 under low-temperature stress expression in erianthus fulvus wild species, a special primer for amplifying the erianthus fulvuscalmodulin-like gene ErCML30, a method for detecting difference expression of the gene in low-temperature stress of the erianthus fulvus wild species, and a specific primer. The expression quantity ofthe gene is constantly increased when the erianthus fulvus wild species are under low-temperature stress, and the gene directly participates in low-temperature stress response. The technical supportis provided for understanding the resistance mechanism of the gene as well as important germplasm resource development and utilization of the erianthus fulvus wild species serving as new cold-resistant sugarcane species.
Owner:YUNNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
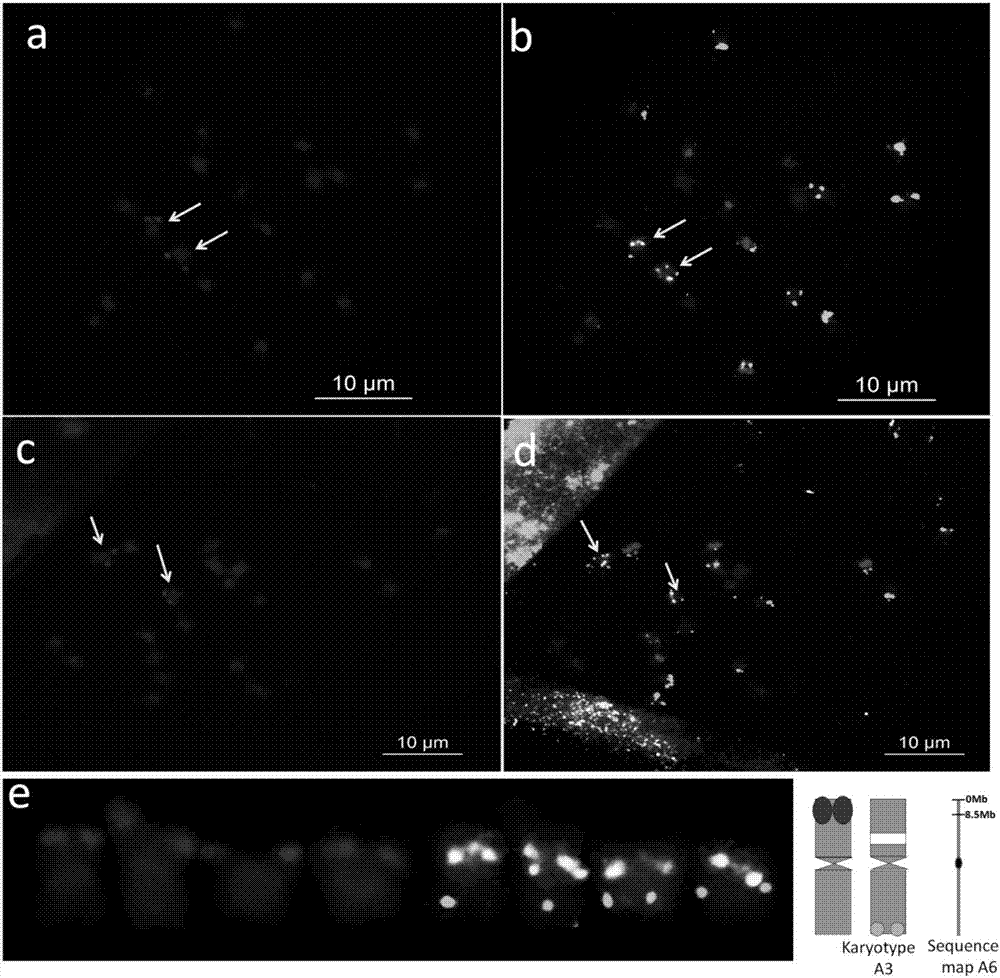
Method for corresponding peanut genome chromosome sequence map to actual karyotype chromosome number
ActiveCN107130033AConvenient researchEfficient use ofMicrobiological testing/measurementWild speciesIn situ hybridisation
The present invention discloses a method for corresponding a peanut genome chromosome sequence map to an actual karyotype chromosome number. According to the method, a peanut chromosome single copy oligonucleotide library is developed by using a peanut wild species A.duranensis genome sequence sketch, and the correspondence between the peanut genome chromosome sequence map and the actual karyotype chromosome number is achieved through probe labeling and sequential fluorescence in situ hybridization. According to the present invention, the correspondence between the sequence map of the A6 chromosome of the peanut wild species A.duranensis genome and the chromosome having the actual karyotype chromosome number of A3 is firstly achieved, such that the foundation is established for the integration of peanut genome information, chromosome labeling information and genetic linkage map information so as to develop the new approach for the revealing of the peanut chromosome exchange, recombination and evolution law; and the method can be used for the development of peanut breeding research, can establish the foundation for the construction of the peanut physical map and the physical locating of the single gene, and can promote the research and utilization of the gene.
Owner:HENAN ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method for artificially regulating and controlling photoperiod and hybridization of sugarcane in inland high latitude area
InactiveCN101180944ASexual interbreedingHorticulture methodsPlant genotype modificationWild speciesHigh latitude
The invention relates to an artificial regulation of photoperiod and hybridization of sugarcane in high-latitude areas in the hinterland. In a photoperiod room, the method of fixing and decreasing the day length is adopted to conduct photoperiodic induction; artificial crossing is carried out after booting and flowering of the sugarcane so as to realize sexual hybridization of the sugarcane in the high-latitude areas in the hinterland. The method solves the problems of difficult flowering and asynchronous flowering period of the sugarcane in the high-latitude areas in the hinterland by artificially controlling the light, temperature, humidity and adopting comprehensive cultivation and management measures to induce flowering and early flowering of sugarcane, which results in not only the booting and flowering of shy flowering parents and conventional parents, but also the synchronization of flowering of the cultivar, original stock, and wild species of the sugarcane and treating with the cross combination preparation so as to realize sexual hybridization of the sugarcane in the high-latitude areas in the hinterland and meet the demand of conventional breeding, and creation and utilization of germplasm resources of the sugarcane in the hinterland.
Owner:SUGARCANE RES INST OF YUNNAN ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com