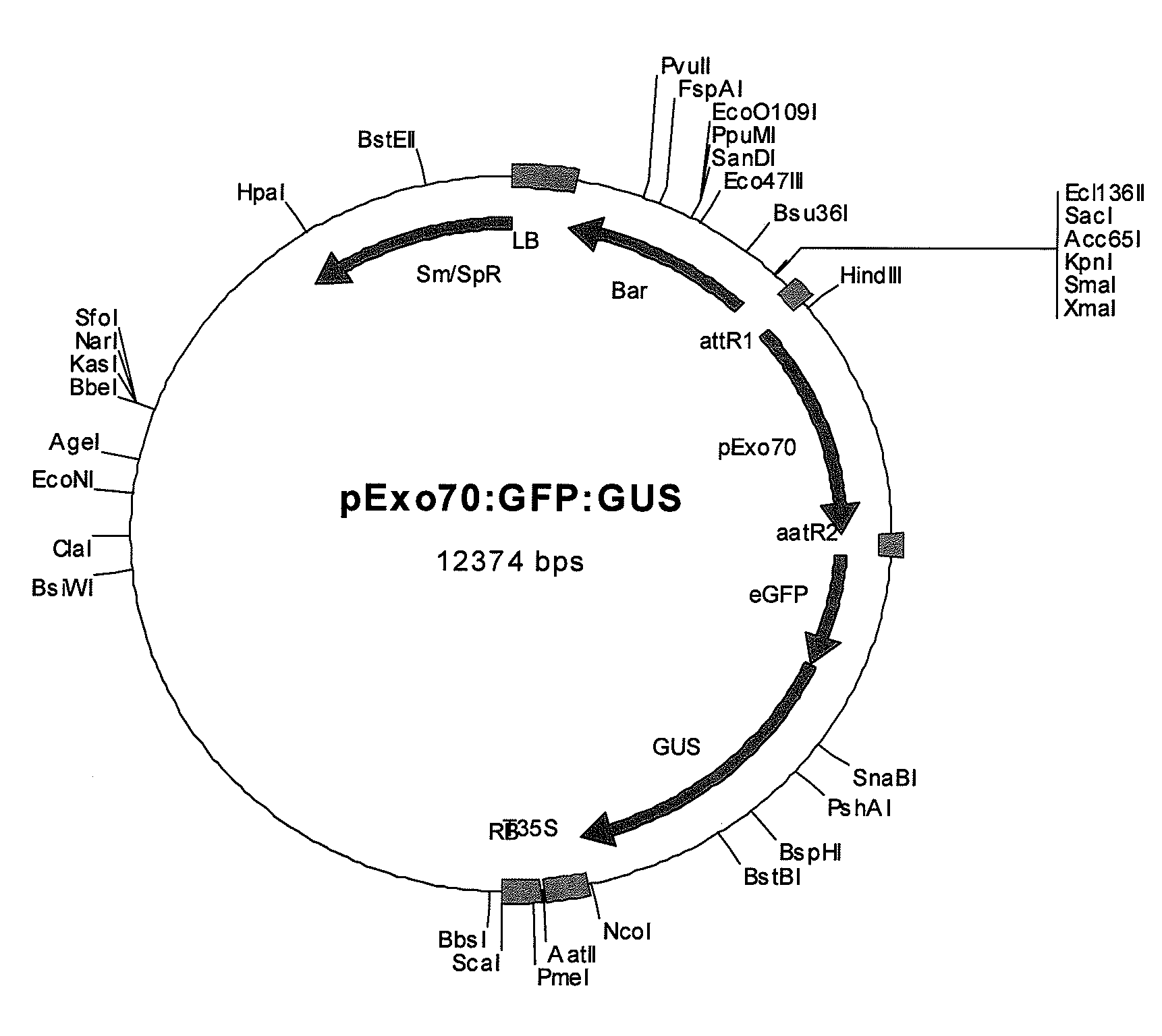
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
110 results about "Chromosome number" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In any given asexually reproducing species, the chromosome number is always the same. In sexually reproducing organisms, the number of chromosomes in the body (somatic) cells typically is diploid (2n; a pair of each chromosome), twice the haploid (1n) number found in the sex cells, or gametes.
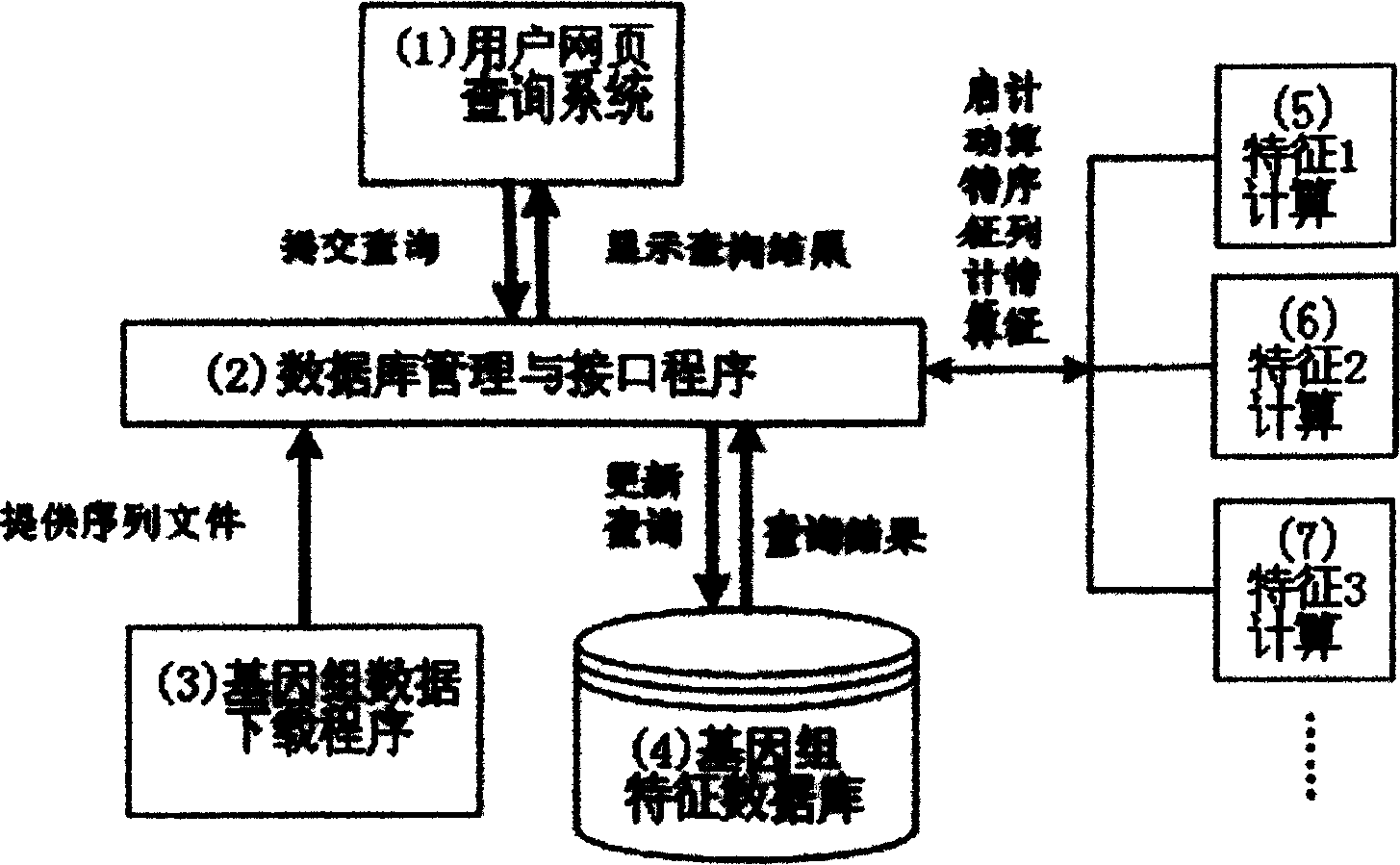
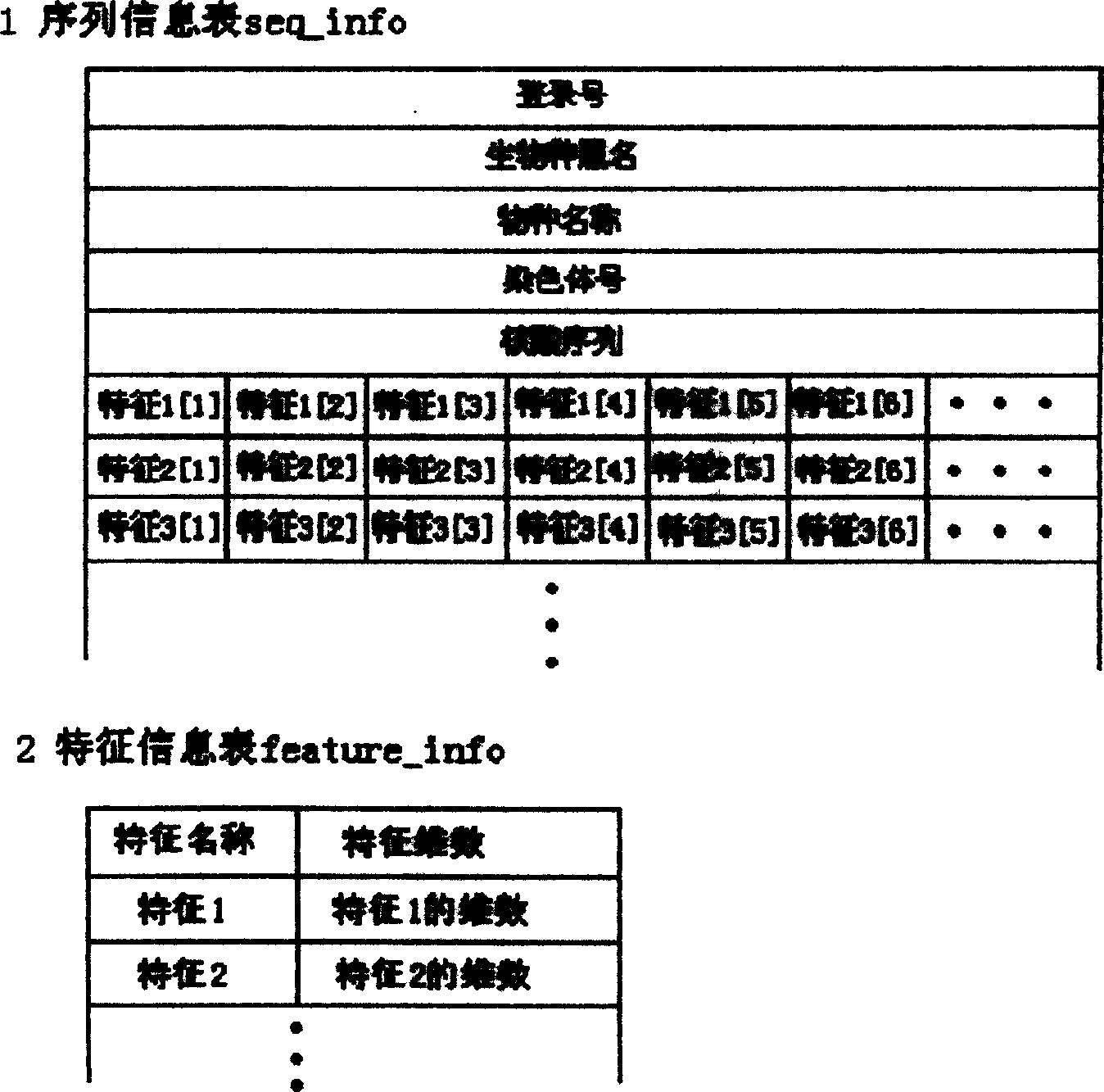
Method and device for quick contrast and analysis of short sequence for second-generation sequencing
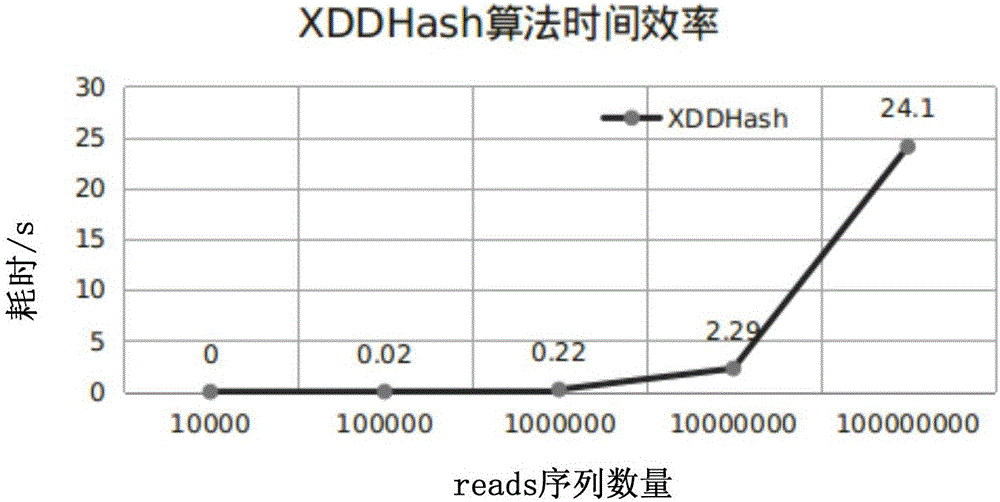
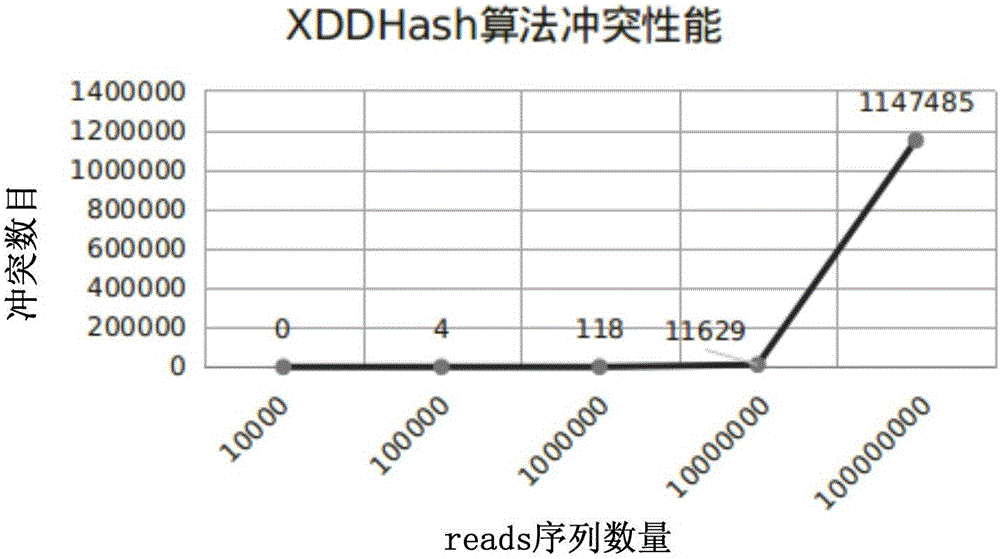
ActiveCN106295250AImprove time and efficiencyFaster thanSequence analysisSpecial data processing applicationsReference genesArray data structure
The invention discloses a method and a device for quick contrast and analysis of a short sequence for second-generation sequencing, which can solve the problems of low contrast efficiency and high memory occupation ratio of sequencing data. The method comprises the following steps of obtaining a DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) short sequence obtained by sequencing, and respectively mapping and encoding the DNA short sequence by a first hash algorithm and a second hash algorithm, so as to respectively obtain a first index and a second index; according to a preset index query library, the first index and the second index, contrasting the DNA short sequence and a reference gene group, wherein the index query library consists of an unit structure array, and each unit structure comprises value and index 2; storing the array index offset of each unit structure as the corresponding index 1, namely the index value corresponding to the structure array, wherein K is the length of segment sequence; according to the contrast result, when the contrast result is correct, obtaining the value of the K-mer segment contrasted with the corresponding DNA short sequence, and determining the chromosome number of the corresponding DNA short sequence and the site on the chromosome.
Owner:北京普康瑞仁医学检验所有限公司
Gene analysis annotation method and device
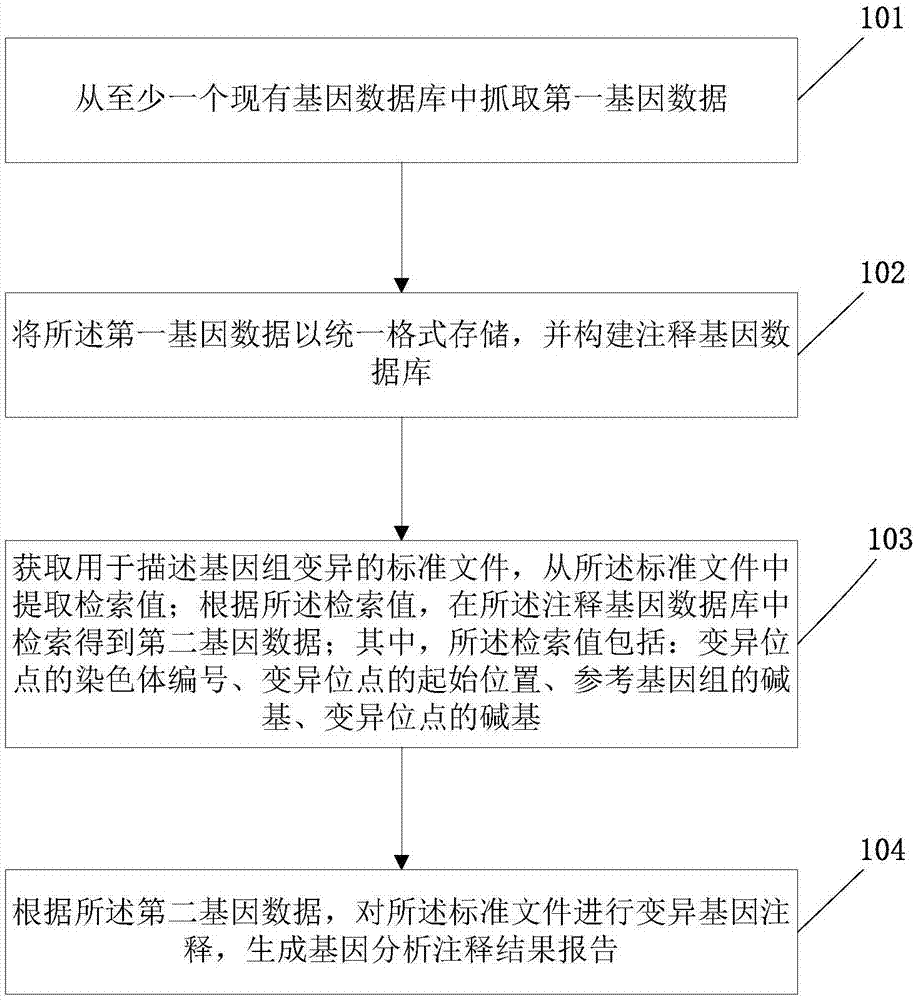
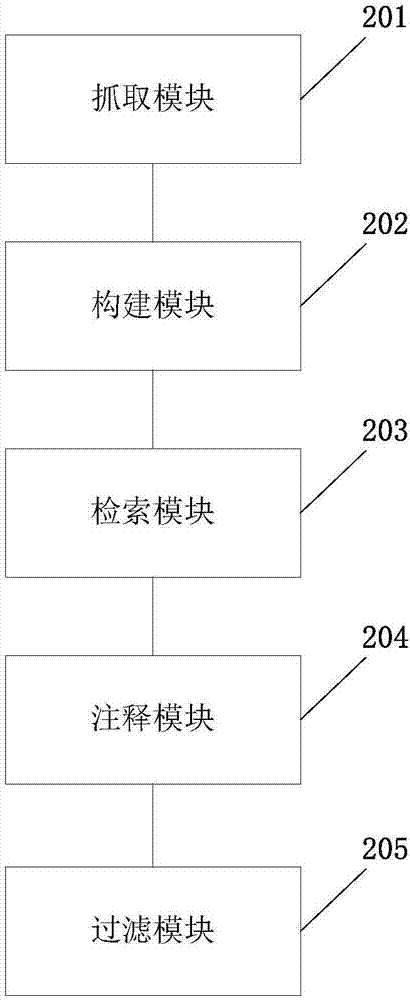
ActiveCN107194208AAccurate annotation of genetic analysisEfficient annotation of gene analysisBiostatisticsSpecial data processing applicationsGene AnnotationChromosome number
The invention discloses a gene analysis annotation method and device. The method comprises the following steps that: capturing first gene data from at least one existing gene database; storing the first gene data in a uniform format, and constructing an annotation gene database; obtaining a standard file used for describing genome variation, and extracting a retrieval value from the standard file; according to the retrieval value, carrying out retrieval in the annotation gene database to obtain second gene data, wherein the retrieval value comprises the chromosome number of a variation site, the starting position of the variation site, the basic group of a refereed genome and the basic group of the variation site; and according to the second gene data, carrying out gene annotation on the standard file, and generating a gene analysis annotation result report. By use of the method, the gene analysis annotation can be accurately and efficiently carried out.
Owner:UNITED ELECTRONICS
Method for making hyacinth root tip chromosome slice
InactiveCN102183394AEvenly dispersedEasy to countPreparing sample for investigationBiotechnologyWater baths
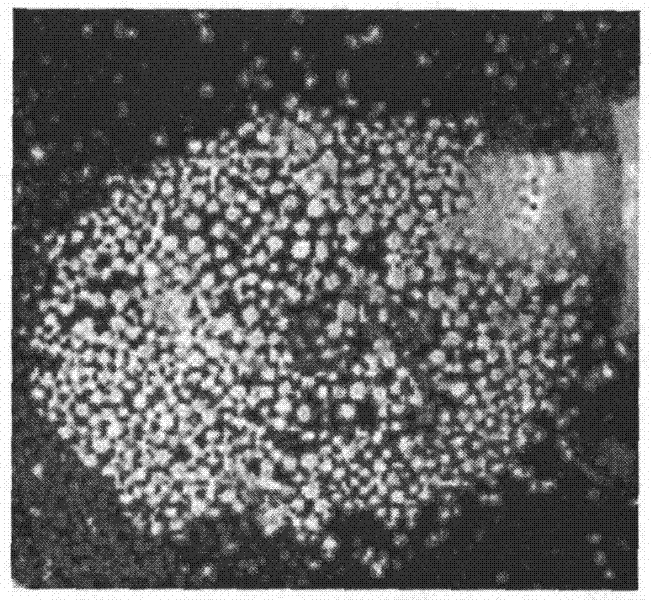
The invention provides a method for making a hyacinth root tip chromosome slice, which comprises the following steps: carrying out the low-temperature preprocessing by adopting a 1g / L colchicin solution; fixing by a Carnoy fixing solution; dissociating for 10 minutes by utilizing 1mol / L hydrochloric acid in a 60 DEG C water bath and rinsing by utilizing distilled water which is added with a small amount of NaOH; cutting the root tip into two parts along the longitudinal direction; dyeing for 10 minutes by utilizing a carbor fuchsin dyeing agent; rinsing by utilizing the distilled water after dyeing; making the slice by utilizing a tabletting method; and carrying out the microscopic examination and microphotograph under an Motic microscope. The method for making the slice provided by the invention has the advantages of simpleness and convenience in operation, uniform chromosome dispersion and shallow background; the number of chromosomes is easy to count; and the chromosome number accuracy which is obtained by adopting the slice making method provided by the invention is high.
Owner:SHENYANG AGRI UNIV
Technology for culturing unisexual hybrid scallop by utilizing purple scallop and bay scallop
ActiveCN101703016ARapid purificationClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaAquatic productOospore
The invention discloses technology for culturing a unisexual hybrid scallop by utilizing a purple scallop and a bay scallop, which relates to shellfish breeding technology for aquiculture. The technology comprises the steps of: utilizing two congeneric hermaphroditic scallops with same chromosome number; ripening the two scallops respectively to achieve the synchronous maturity; and then synchronously inducing the two scallops to spawn and spermiate; and acquiring sperms and ovum of the two scallops respectively for interspecies cross-insemination to culture the unisexual hybrid scallop. Obtained offsprings have separated sexes, have males and females, and also have hermaphroditic individuals; ovum from female individuals in the hybrid offsprings can be inseminated by any parental sperm and normally grow; and the hermaphroditic individuals in the hybrid offsprings can be used for quickly purifying a strain.
Owner:QINGDAO AGRI UNIV
Seaching method of genome sequence data based on characteristic
InactiveCN1598821AImprove search efficiencyImprove scalabilitySpecial data processing applicationsOriginal dataSequence database
The invention relates to an approach of searching gene group sequence database based on characters. Approximate sequence is searched in database according to sequence statistic character. The search method is as follows: search approximate sequence according to distance of statistic character, namely, basic information of different species' sequence group serial data, including sequence's database login number, species name, chromosome number, original data, basic group composition character and base pair relativity character is memorized in database. For any a gene snippet submitted by client, its eigenvalue is computed according to client's request and distance between the eigenvalue and all corresponding eigenvalue in database is computed to compare approximate sequence; the most approximate sequence is arranged and displayed by distance.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
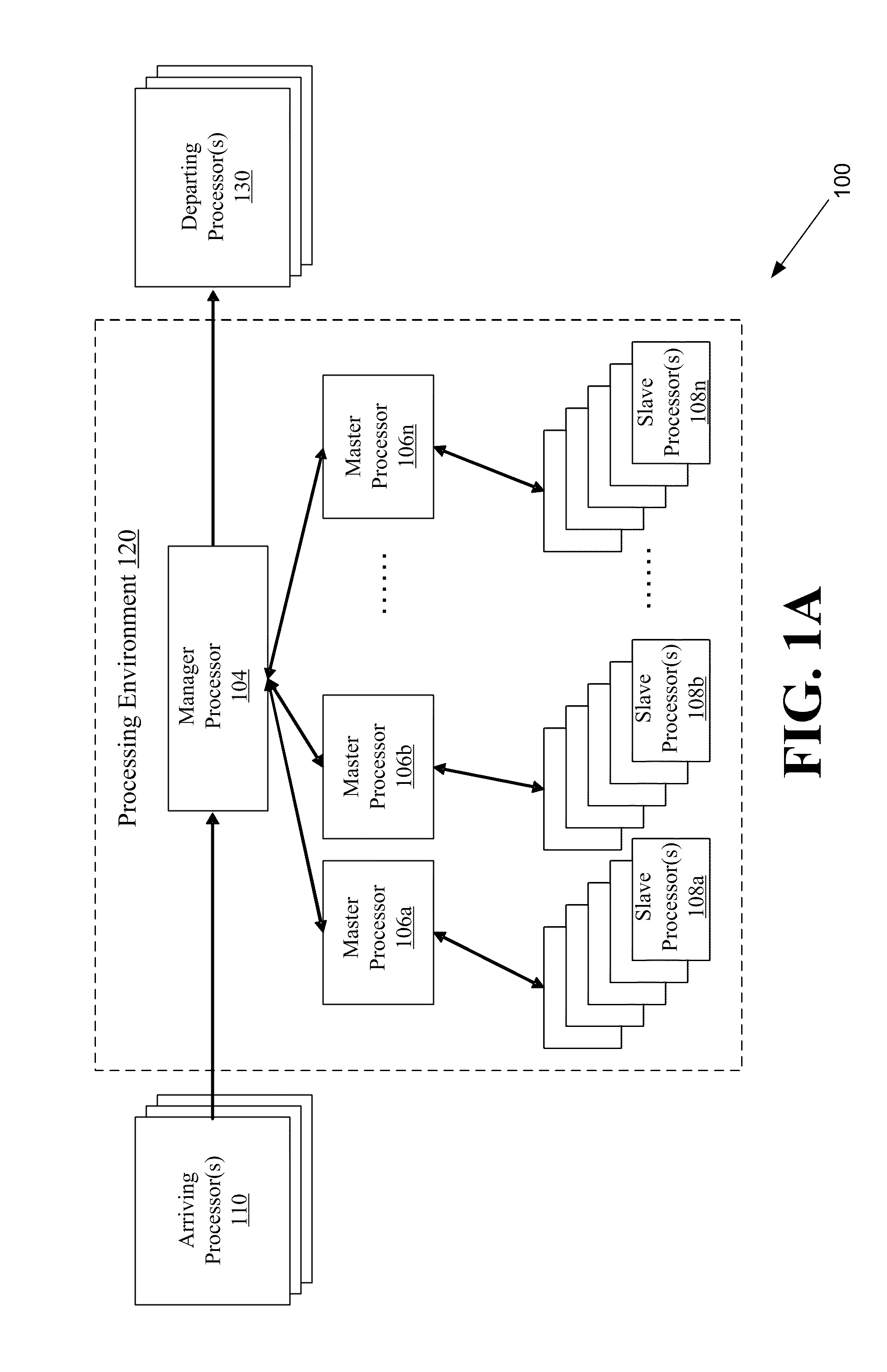
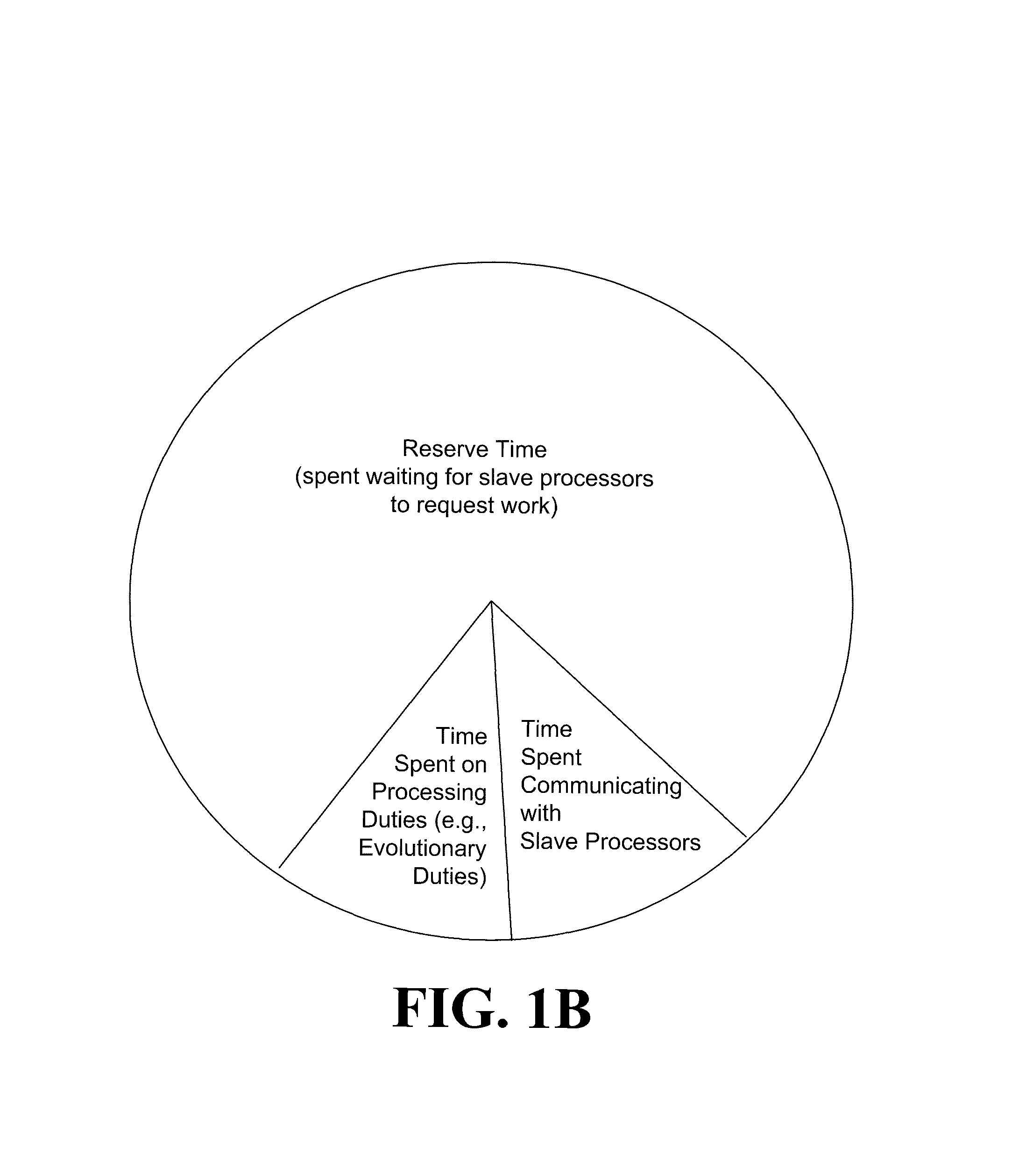
Systems and methods for parallel processing with infeasibility checking mechanism
ActiveUS8255345B2Digital computer detailsNeural learning methodsChromosome numberParallel processing
Systems and methods may include obtaining an input population of parent chromosome data structures, where each parent chromosome data structure provides having a plurality of genes representative of variables in which associated values are permitted to evolve; selecting pairs of parent chromosome data structures from the input population; allocating the selected pairs of parent chromosome data structures to respective ones of a plurality of slave processors, where each slave processor applies an evolutionary process to genes of the allocated pair to generate a plurality of child chromosome data structures; receiving a portion of the plurality of child chromosome data structures generated by the plurality of slave processors; merging the parent chromosome data structures with at least the received portion of the child chromosome data structures to generate a merged set of chromosome data structures; and identifying a portion of the merged set of chromosome data structures as an elite set of chromosome data structures.
Owner:THE AEROSPACE CORPORATION
Method for breeding polyploid royal paulownia by combination of in vitro culture and colchicine treatment
The invention provides a method of breeding fourfold paulownia tomentosa in the combination of isolated culture by using placentas as explants and colchicine treatment, comprising the following twelve steps: a. choice of parent; b. using placentas as best explants; c. placenta callus inducement; d. double treatment of placenta callus; e. callus recovery cultivation after treatment; f. callus division cultivation; g. sprout rooting cultivation; h. transplanting of seedling; i. morphological authentication of paulownia tomentosa plant polyploidy; j. chromosome number authentication of paulownia tomentosa plant polyploidy; k. flow cytometry analysis authentication of paulownia tomentosa plant polyploidy; l. authentication of paulownia tomentosa plant polyploidy in flowering period, etc. Compared with adult plants of other multiploid paulownia tomentosa, the fourfold paulownia tomentosa is characterized by big flower, thick leaf, no burliness, and the like, obviously different from twofold paulownia tomentosa, and has perfect ornamental value and growing vantage. The technology not only can be directly applied to breeding new types of paulownia tomentosa but also builds a fine foundation for polyploid breeding of other trees.
Owner:WUHAN POLYPLOID BIOTECH CO LTD
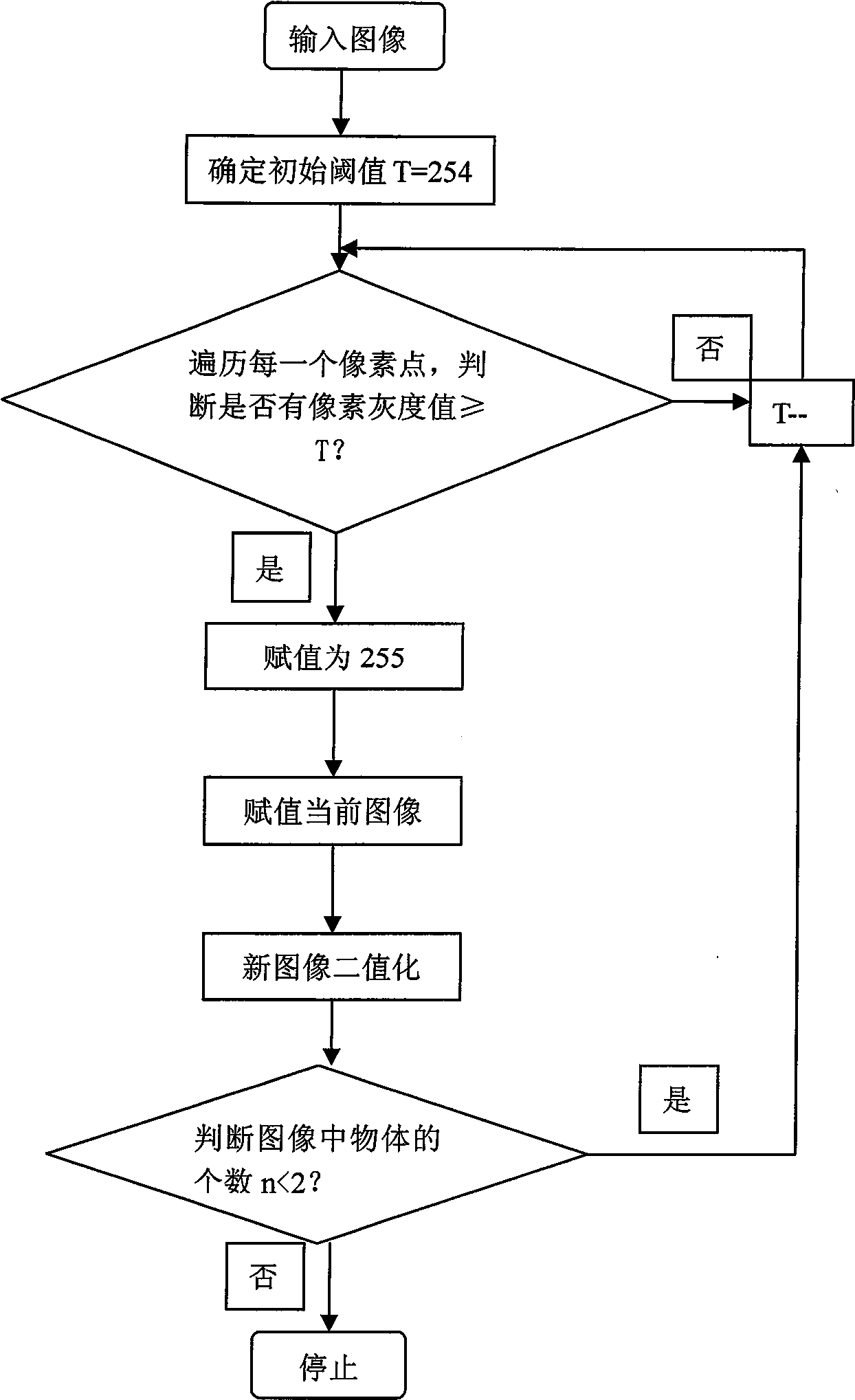
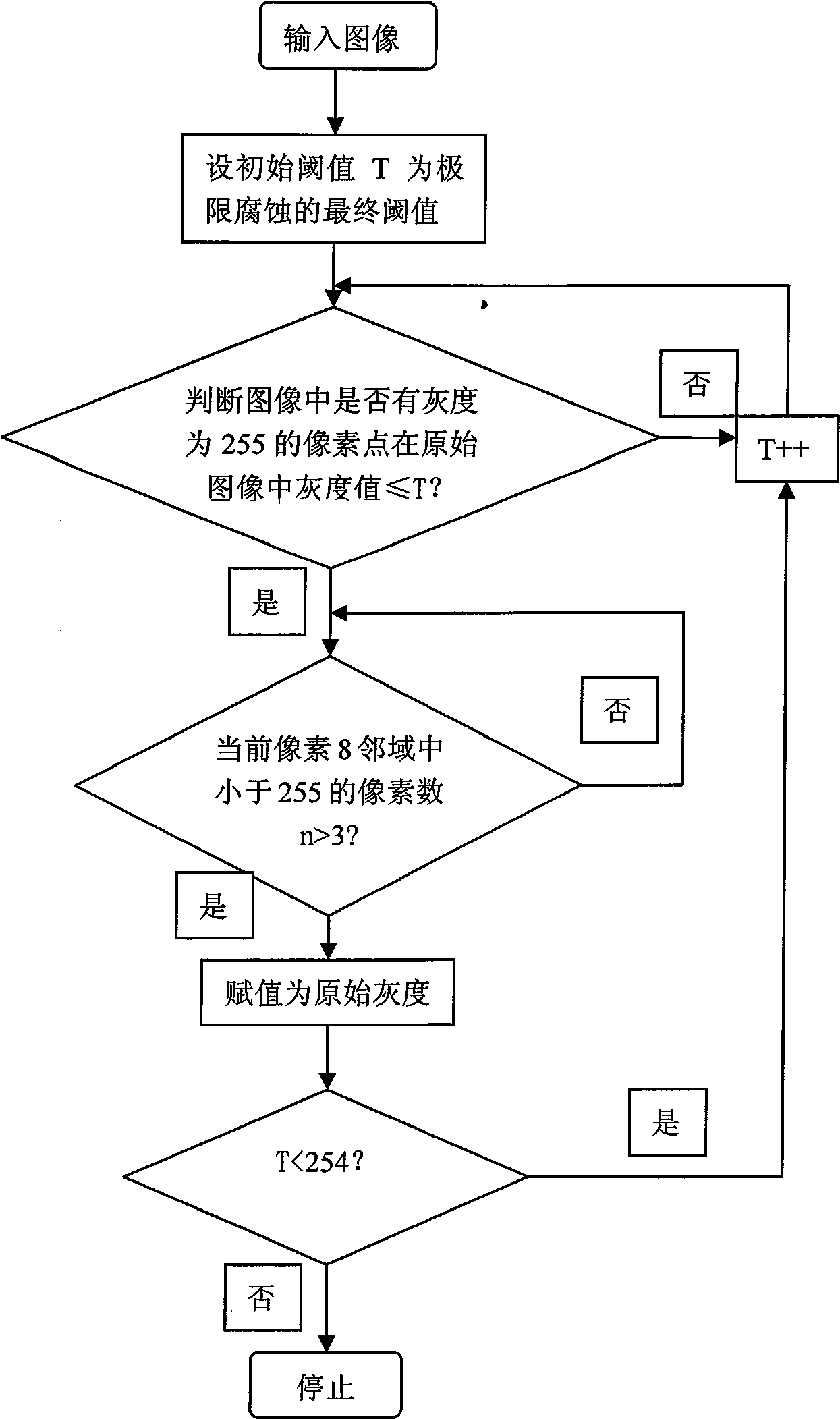
Grey scale characteristic graph-based automatic separation method for conglutinated chromosomes
InactiveCN101520890AHigh degree of automationGood Continuity Boundary EffectImage analysisState of artBoundary effects
The invention provides an automatic separation method for conglutinated chromosomes. The method firstly carries out immersion and corrosion processing operation based on a grey scale characteristic graph of chromosomes, and then carries out conditioned expansion recovery processing operation. The invention designs a grey scale characteristic graph-based morphological processing method to separate the chromosomes which are seriously conglutinated but are neither sheltered nor overlapped. The method solves the technical problems and fills up the technical vacancy of separating the chromosomes which are seriously conglutinated but are neither sheltered nor overlapped in the prior art, meets the requirements of accurately separating the conglutinated chromosomes and detecting the number of the chromosomes in medical fields of chromosome analysis, cell research, pathological analysis, and the like, and further improves the automaticity in a chromosome analysis system. The method provides individual chromosomes with good continuous boundary effect and independence for the automatic separation processing in the chromosome analysis system, and particularly keeps concave and convex details of original chromosome image boundary completely and clearly so as to improve the separation automaticity of the conglutinated chromosomes and the accuracy of the chromosome number counting.
Owner:GUANGDONG VTRON TECH CO LTD
Pipless fructus momordicae and culture method thereof
ActiveCN101228843AHigh physiological advantageAvoid chimerasCultivating equipmentsPlant phenotype modificationMomordicaLoment
The invention discloses a seedless grosvenor momordica with high mogroside content, high whole fruit utilization rate and good taste, and a cultivating method for the seedless grosvenor momordica. The steps of the method are as follows: 1) cultivating and planting the diploid female and male seedlings of the grosvenor momordica; 2) when a male plant emerges a flower bud, inducing the formation of diploid big pollen; 3) picking the male flower that is induced to bloom and screen a diploid big pollen therein; 4) hybridizing the haploid oocyte of the diploid female plant after treating the diploid big pollen in the pollen germination solution, acquire the hybrid seeds after the female plant fruits; 5) propagating the hybrid seed into whole plant and then screening a triploid plant with the Chromosome number inspection; 6) planting the triploid plant and the diploid male plant, and carrying out artificial pollination to the male triploid plant with the male diploid plant when the plant is blooming, thus acquiring the seedless grosvenor momordica when the female plant fruits.
Owner:桂林亦元生现代生物技术有限公司
Method of real time detecting No.21 human chromosome number by quantitative PCR technology
InactiveCN1693480AQuick checkEasy to detectMicrobiological testing/measurementPcr ctppChromosome number
A method for detecting the number of human chromosomes NO.21 by real-time quantitative PCR technique in order to diagnoise the triple-21 syndrome includes such steps as using the genome-specific single-cope sequence as the molecular marker of chromosome, choosing part of non-polymorphic fragments of DSCR4 gene as target molecular marker, choosing part of fragments of RABIF gene as internal reference molecular marker, designing two pairs of primers and relative Taqman probes, amplifying said two sequences in a single tube by PCR, determining the relative value deltact, and determining the number of chromosomes No.21.
Owner:ATTACHED OBSTETRICS & GYNECOLOGY OSPITAL MEDICALCOLLEGE ZHEJIANG UNIV
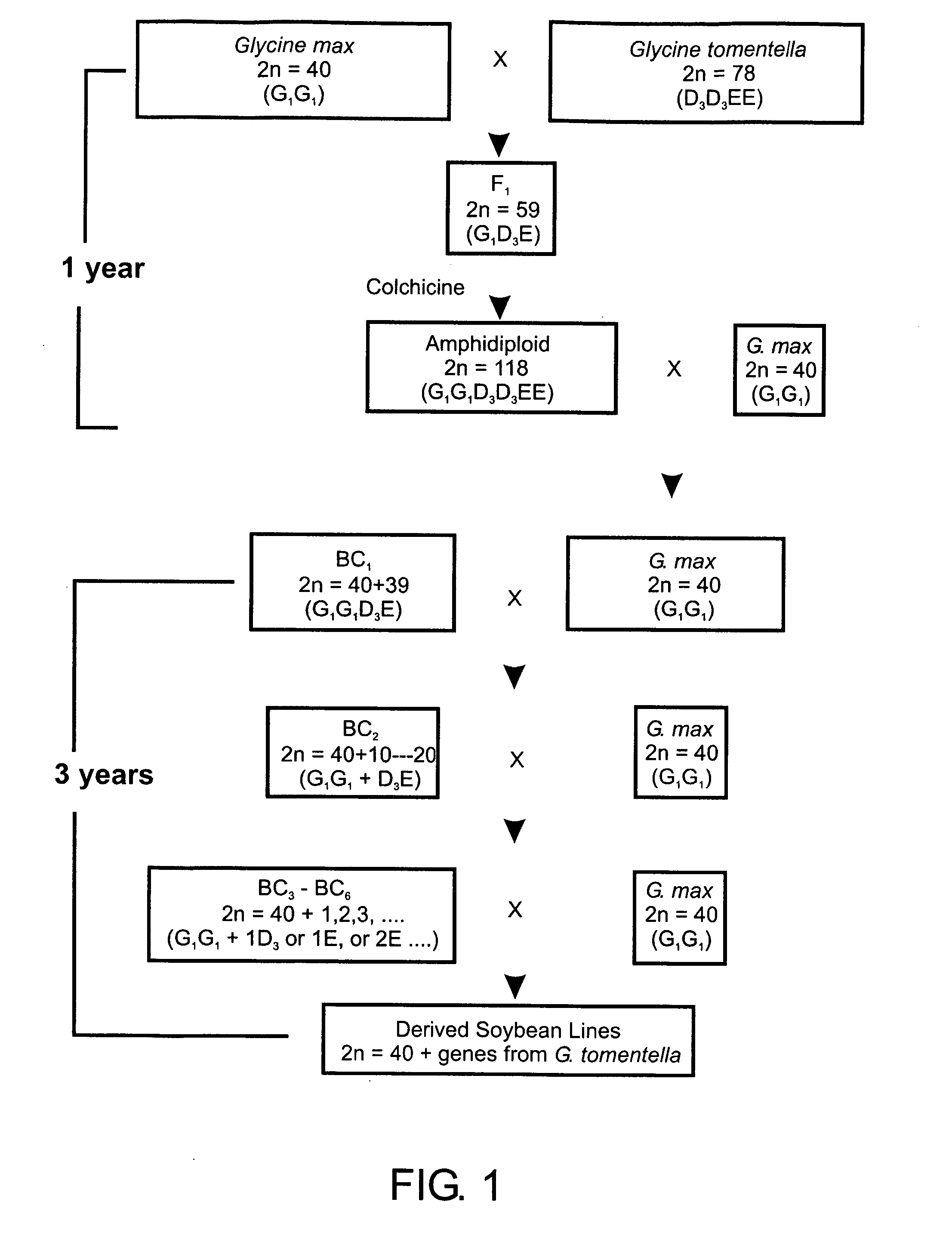
Methods for producing fertile crosses between wild and domestic soybean species
Methods for producing hybrids between domestic and wild soybean that are fertile and can be further bred with other soybean plants are provided, thus allowing transfer of desirable traits and genes from the wild soybean into the domestic soybean. This invention also provides novel media for producing callus and multiple somatic embryos, as well as novel media for producing multiple shoots from the embryos. The hybrid plants are made fertile by colchicine treatment to double their chromosome number so that they can be backcrossed into domestic soybean. These methods and media allow the production of elite soybean lines containing traits or genes from wild soybean as well as a minimum amount of additional wild soybean DNA. Backcrosses containing only one wild soybean chromosome can be produced, as well as sets of such backcrossed lines that each contain one chromosome from the wild ancestor, but collectively all the wild chromosomes from the hybrid ancestor. Plants and plant progeny and plant tissue (tissue including seeds) of plants produced by the foregoing methods are also provided. The methods do not require genetic modification, and thus this invention allows production of domestic soybean plants that are not genetically-modified organisms (non-GMO) but that express desirable traits derived from wild soybean.
Owner:UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Begonia cultivating and planting method
InactiveCN102422809AWonderful and unique viewing valueEasy to transportPlant genotype modificationSelf-pollinationOrganic matter
The invention discloses a cultivating and planting method of a begonia named Yinjiao. According to the invention, an artificial pollination method is adopted, begonia dryadis irmsch. is adopted as a female parent, B.'White King' is adopted as a male parent, and sexual hybridization is carried out; an offspring individual plant is subject to self-pollination, and the variety Yinjiao is obtained through selective breeding from an F2 generation colony; the chromosome numbers of the parents and the filial generation are determined; and the variety Yinjiao obtained through the previous cultivationsteps is planted in humic soil under a temperature of 15-25 DEG C and an air relative humidity of 65-75%, where in the humic soil is air-permeating and is rich in organic matters. Also, the drainage of the humic soil is good.
Owner:KUNMING INST OF BOTANY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for cultivating corn allopolyploid by using unreduced gamete characteristic of tripsacum dactyloides
ActiveCN103609428AOvercoming reproductive barriersImprove stabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant genotype modificationHeterologousBridge material
The invention discloses a method for cultivating a corn allopolyploid by using an unreduced gamete characteristic of tripsacum dactyloides, belonging to the field of corn distance hybridization. The method comprises the steps of: hybridizing an MTF-1 (metal-responsive transcription factor) as a female parent with corn or tetraploid perennation corn as a male parent, and then selecting a filial generation plant which is capable of overwintering, namely a new corn allopolyploid, wherein the tiller number of the filial generation plant is more than 15 and the chromosome number of the filial generation plant is a sum of the chromosome number of a female parent and the chromosome number of the male parent. According to the method provided by the invention, the dysgenesis of corn affinis species is overcome and a good inheritance basis is provided for breeding ground-breaking corn species by using the bred corn allopolyploid as a bridge material transfer character. In addition, the method provided by the invention provides a model to breed allopolyploids of other species. The corn allopolyploid bred by the method provided by the invention is perennial, adopts vegetative propagation, and provides a material to corn allopolyploid origin and evolution research and allopolyploid breeding. The method provided by the invention is simple, is short in time, high in efficiency and small in workload.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
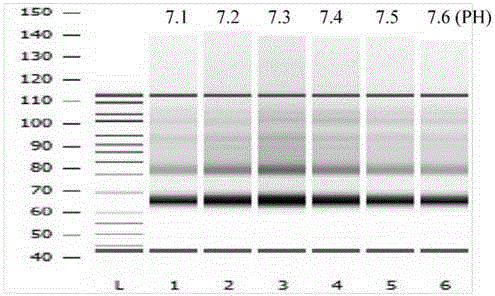
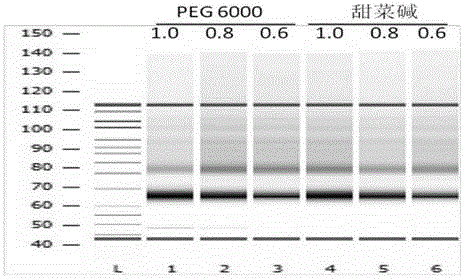
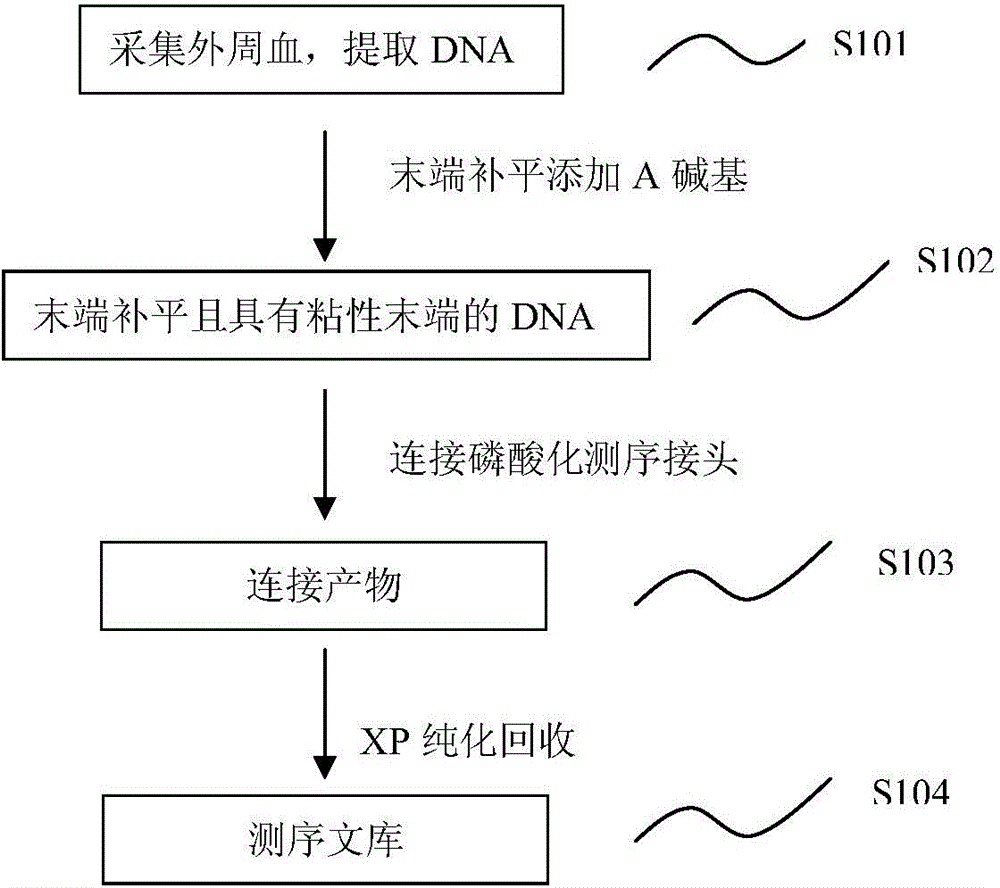
Method for detecting chromosome number variation of fetus
ActiveCN104694654AAccurate connectionEfficient and accurate connectionMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationModified dnaPhosphorylation
The invention discloses a reagent kit for detecting chromosome number of fetus and a method for detecting chromosome number of fetus that belong to the field of chromosome detection. The reagent kit comprises a reagent I that modifies DNA, phosphorylated sequencing linkers for linking two terminals of the modified DNA, a reagent II for linking the DNA phosphorylated sequencing linkers together, and a device for directly purifying the ligation product without amplifying by a primer. The provided method for detecting chromosome number of fetus comprises four steps, including a DNA extraction step, a DNA terminal modification step, a sequencing linker connection step, and a purification step. A sequencing library can be acquired without a PCR amplification. The disclosed reagent kit and the prepared library are able to achieve an efficient, precise and non-invasive effect for the detection of chromosome number of fetus.
Owner:北京明谛生物医药科技有限公司
Method for cultivating aneuploid perennial forage grass variety by using corn heterologous polyploidy
ActiveCN103548674AOvercoming the Difficulty of Distant HybridizationNo resistancePlant genotype modificationHorticultureHeterologousNutritive values
The invention discloses a method for cultivating an aneuploid perennial forage grass variety by using a corn heterologous polyploidy and belongs to the field of corn distant hybridization. According to the method, MTF-1 (Tripsazea creammaize T.2n=76) cultivated by Sichuan Agricultural University is used as a female parent and teosinte is used as a male parent to be hybridized; a filial generation is selected from perennials, a wintering habit, a tiller number, a chromosome number and chromosome constitution to select the perennial heterologous aneuploid forage grass variety. According to the method, firstly, a heterologous aneuploid is used as the forage grass variety to be applied so as to creatively expand an application range of corn affinis species and explore a novel way for utilizing corn affinis specie materials; secondly, a material cultivated by the method is used as a bridge material and has a very great application value; furthermore, a vegetative propagation manner can be used for fixing a hybrid vigor and the variety is perennial, so that the production cost is very low, the yield and the nutritive value are high, and the economic benefit is great.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
Cultivation method for inducing autotetraploid of paulownia catalpifolia by colchicine
ActiveCN105432464AHigh induction rateShorten the timePlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsPaulowniaWoody plant
The invention introduces an effective inductive cultivation method for an autotetraploid of paulownia catalpifolia by using leaves of a diplontic paulownia catalpifolia tissue culture seedling. The method comprises: pre-cultivating the leaves of paulownia catalpifolia for 6 days, wherein the concentration of added colchicine is 30 mg / L, the concentration of dimethyl sulfoxide is 2%, and the soaking time is 48 hours; performing shake cultivation, wherein the induction rate of the tetraploid paulownia catalpifolia reaches 14.5%; detecting that the chromosome number of root tip cells of variant plants of paulownia catalpifolia is 80 by virtue of a chromosome counting method, wherein the chromosome number is two times of that of the corresponding diplontic paulownia catalpifolia; and detecting that the unicellular DNA content of the tetraploid leaves of the paulownia catalpifolia are two times of those of the corresponding diplontic paulownia catalpifolia by using a flow cytometer, showing that a tetraploid paulownia catalpifolia plant is obtained. The cultivation method for inducing autotetraploid of paulownia catalpifolia by colchicine disclosed by the invention has the advantages of being wide in material drawing, simple and convenient to operate, low in cost, high in induction rate and the like, and is of certain guiding significance for woody plants, the tetraploid of which is not easily obtained.
Owner:HENAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Industrial production method of Cymbidium germchit based on sexual hybridization
InactiveCN102301950AIncrease varietyProliferation line highCultivating equipmentsHorticulture methodsPollinationBottle
The invention relates to an industrial production method of Cymbidium germchit based on sexual hybridization. The method provided by the invention comprises the following steps of: firstly identifying chromosome number and ploidy of Cymbidium parents; selecting pairing hybridized combinations according to the ploidy; carrying out a sexual hybridization pollination of the Cymbidium; managing the pollinated Cymbidium; carrying out a nonsymbiotic germination culture on Cymbidium seeds; inducing and differentiating protocorms (PLBs) of the Cymbidium seeds; differentiating bigger seedlings of the Cymbidium; transplanting the Cymbidium seedlings into bottles; and managing the cultivation of the Cymbidium transplanted seedlings. On the basis of indentifying the chromosomes of the Cymbidium parents, the method provided by the invention selectively pairs the hybridized combinations and carries out the sexual hybridization pollination, so that the aims of improving varieties and breeding new varieties are achieved; then a lot of Cymbidium germchit can be industrially produced through a tissue culture method.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Method Of Producing Haploid And Doubled Haploid Plant Embryos, And Embryos, Plants, Progeny, Cells, Tissues And Seeds Obtainable By Method
The invention relates to a method for producing haploid plant embryos, comprising providing microspores or pollen that comprise cell division inducing molecules; pollinating an embryo sac cell, in particular an egg cell, of the plant of which the haploid embryo is to be made with the microspores or pollen; allowing the microspores or pollen to discharge the cell division inducing molecules in or in the vicinity of the embryo sac cell, in particular the egg cell, to trigger division thereof to obtain a haploid plant embryo. When doubled haploid plant embryos are to be produced doubling of the chromosome number takes place at a certain stage after pollination, in particular during cell division or after obtaining the embryo. The invention further relates to the embryos thus obtained, plants regenerated therefrom and progeny thereof.
Owner:RIJK ZWAAN ZAADTEELT & ZAADHANDEL BV
Two polyploid centella asiatica varieties and cultivation method thereof
The invention discloses two polyploid centella asiatica varieties and a cultivation method thereof. The cultivation method comprises the following steps of 1, selecting terminal buds of a diploid centella asiatica adult plant, and carrying out breeding of a tissue cultured seedling or callus tissue, 2, carrying out chromosome doubling induction culture and differentiation culture of tissue subcultured seedling or callus tissue by oryzalin, 3, cutting down novel buds obtained by the differentiation culture and carrying out cluster bud culture, 4, carrying out chromosome doubling identification of the cultured complete plants having roots, stems and leaves, screening the tetraploid plant, and planting the tetraploid plant to obtain the tetraploid centella asiatica variety, 5, carrying out artificial emasculation and pollination hybridization of the tetraploid plant and the diploid plant to obtain hybrid seeds (female parent 4N*male parent 2N or male parent 4N* female parent 2N, wherein F1 is 3x), and 6, breeding the hybrid seeds into complete plants, planting the plants, carrying out chromosome number detection and screening the triploid centella asiatica variety.
Owner:桂林亦元生现代生物技术有限公司
Maladera sp. spermary chromosome production and observation method
InactiveCN1828296APreparing sample for investigationColor/spectral properties measurementsAcetic acidColchicine
Wherein, with adult sperm cell of Maladera sp. As material, pre-processing for 6-14h with colchicine; using 0.4%KCl to hypotonic reaction for 30min; curing with methaol and glacial acetic acid (3:1) for 30-60min; finally, dyeing with Giemsa for 10-20min. this invention obtains clear chromosome with number as n = 9.
Owner:YUNNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Subfamily distant hybridization for German mirror carp and megalobrama amblycephala and application of tetraploid hybrid fishes
The invention discloses a subfamily distant hybridization for German mirror carp and megalobrama amblycephala. The method comprises the following steps of artificial dry-process fertilization on the ova of the pubescent German mirror carp and sperms of the megalobrama amblycephala by taking the German mirror carp as a female parent and the megalobrama amblycephala as a male parent, hatching fertilized ova at the water temperature of 19-20 DEG C, and breeding fries in a pond; then, detecting the DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) content, the chromosome number and the blood cell sizes of the fries by a flow cytometry DNA content determination method, a chromosome ploidy detection method of peripheral blood cell culture and a blood smear method, screening, and then preparing to obtain triploid hybrid fishes and tetraploid hybrid fishes. A tetraploid fish strain which is genetically stable and has four sets of crucian carp chromosomes can be formed by subsequent self-cross selective breeding of the tetraploid hybrid fishes, and the tetraploid fish strain can be used as a resource for breeding the infertile triploid fishes. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages that not only are the characters of hybrid offspring good but also a good foundation can be laid for variety breeding, and a precious resource is provided for subsequent breeding of new polyploid fishes.
Owner:湖南岳麓山水产育种科技有限公司
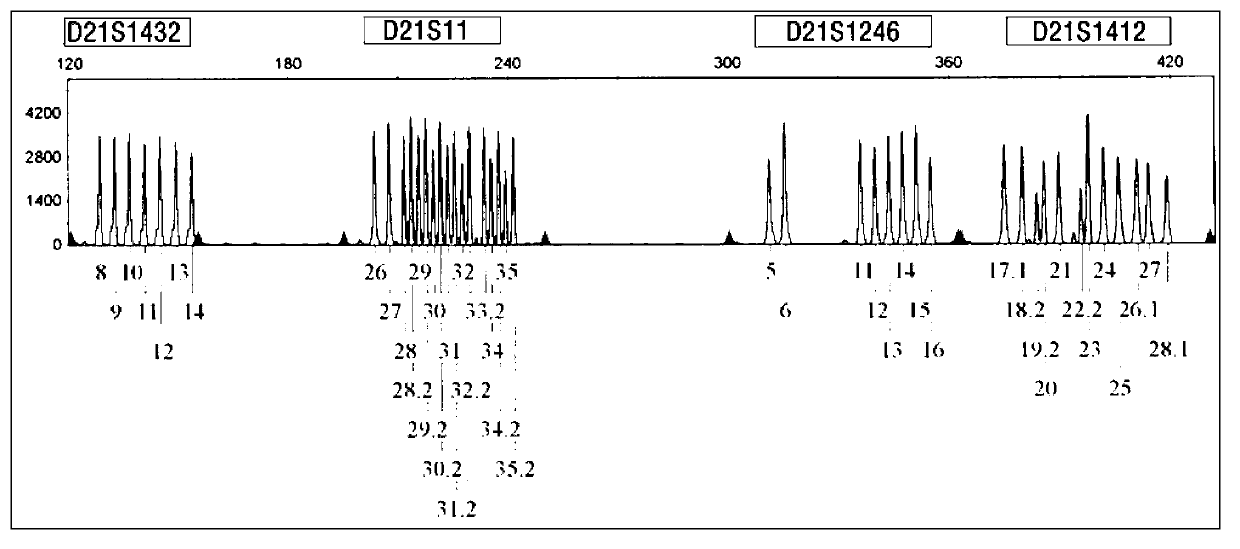
Kit for detecting genotype of human chromosome 21 STR (short tandem repeat)
ActiveCN103103267AHigh polymorphismImprove diagnostic capabilitiesMicrobiological testing/measurementPrenatal diagnosisGenetics
The invention provides a kit for detecting genotype of human chromosome 21 STR (short tandem repeat). The kit comprises an amplification reagent and an amplification product detection reagent and mainly contains primers of 12 pairs of fluorescent markers, a molecular weight internal label containing the size of 14 fragments, an allele typing standard product and a quality control product. According to the kit disclosed by the invention, when the kit is used, the required quantity of specimens is small, the diagnosis is fast, and the kit is suitable for villi, amniotic fluid, blood and other tissues, and can be used for not only prenatal diagnosis, but also source analysis of extra chromosomes of a 21-trisomy aborted fetus; the kit can precisely diagnose the genotype and is conductive to presentation of diagnosis result and laboratory quality evaluation; and the kit can further realize fast, accurate, automatic and high-throughput detection of the number of chromosomes 21 and realize quality controllability and standardization of a detection result, and thus has clinical application prospects.
Owner:ATTACHED OBSTETRICS & GYNECOLOGY OSPITAL MEDICALCOLLEGE ZHEJIANG UNIV +2
Method for identifying carnation chromosome number by bud
InactiveCN101613755AAddressing the Disadvantages of Poor DispersionSolve hard-to-count puzzlesMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by optical meansBudMaterial resources
The invention provides a method for identifying carnation chromosome number by bud, comprising: obtaining bud anther, ovary wall and corolla tissue, pre-treating ice water mixture, fixing by stationary liquid, dyeing, dissociating with hydrochloric acid, tabletting and microscopic examining. Compared with the traditional method that a root tip tissue is used for chromosome tabletting, the invention solves the disadvantages of few visual filed cells, difficult microscopic examination and poor chromosome dispersion during root tip chromosome tabletting, and overcomes the problems of long rootage period for carnation cutting seedling and time and labor wasting for cutting; compared with stem tip chromosome tabletting, the invention overcomes the interference problem of non-meristematic cell or reserve substance or secretion, chromosome tabletting can be realized only by using buds, which does not damage plant growing state and has convenient material resource; in addition, a plurality of metaphase cells exist, so that the difficulties of small carnation chromosome, huge quantity and hard counting of the chromosome can be solved. Thus, when plants bloom, the effective method is that the bud is used for chromosome tabletting.
Owner:FLOWER RES INST OF YUNNAN ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Fine mapping of chromosome 17 quantitative trait loci and use of same for marker assisted selection
InactiveCN1809644AMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationBiotechnologyMarker-assisted selection
Disclosed herein is fine mapping of a quantitative trait locus on Chromosome 17 which is associated with meat traits, growth and fatness. The quantitative trait locus correlates with several major effect genes which have phenotypic correlations with animal growth and meat quality which may be used for marker assisted breeding. Specific polymorphic alleles of these genes are disclosed for tests to screen animals to determine those more likely to produce desired traits.
Owner:IOWA STATE UNIV RES FOUND
Breeding method of brassica napus capable of being specially adopted as green manure
The invention relates to a breeding method of brassica napus variety capable of being specially adopted as a green manure. The method comprises that brassica oleracea type hybrid brassica campestris is selected as the female parent and is subjected to interspecific hybridization with white brassica parachinensis to obtain a F1 generation hybrid species; the F1 generation hybrid species and the female parent are subjected to backcrossing to obtain BC1F1 seeds; the seeds are cultivated and are subjected to selfing to obtain BC1F2 seeds; the single plant having the chromosome number close to the brassica campestris female parent is selected to carry out selfing to obtain BC1F3 seeds; the single plant having the chromosome number n of 19 is further selected to carry out selfing to obtain BC1F4 seeds; and the BC1F4 seeds are subjected to subsequent multi-generation selfing, wherein the short growth period of the plant is adopted as the main limiting target character during the multi-generational selfing process and the consistent directional system selection in the line is performed until the brassica napus variety capable of being specially adopted as the green manure is obtained. With the breeding method of the present invention, the brassica napus variety capable of being specially adopted as the green manure and with characteristics of short growth period, strong adaptability, high biological yield and low seed production cost can be bred out.
Owner:湖南省作物研究所
Artificial cultivation and seedling industrial production method of dendrobium nobile polyploid compound
ActiveCN102239806APromote growthStrong disease resistancePlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsPollinationBottle
The invention relates to an artificial cultivation and seedling industrial production method of a dendrobium nobile polyploid compound, which comprises the following steps of: carrying out artificial pollination in a flowering period of common dendrobium nobile, inoculating harvested seeds in a 1 / 2MS liquid nutrient medium for nonsymbiotic germination cultivation, transferring protocorm of seeds in a proembryo stage into a 1 / 2MS liquid nutrient medium containing 0.01% of colchicin for mutagenesis cultivation, then transferring into 1 / 2MS solid nutrient medium for cultivation till seedlings ofdendrobium nobile are formed, carrying out flowering cultivation on tetraplont seedlings with chromosome numbers of 2n=76, taking tetraplont as a female parent and diploid as a male parent or taking diploid as a female parent and tetraplont as a male parent for hybridization to obtain the triploid; transferring triploid hybridized seeds in a formation early state into the 1 / 2MS liquid nutrient medium containing 0.01% of colchicin for carrying out artificial mutation hexaploid treatment for 150-180h, and then transferring into the 1 / 2MS solid nutrient medium till the seedlings are formed, selecting seedlings with chromosome numbers of 2n=114 as tetraplont dendrobium nobile for carrying out bottle seedling transplanting, and finally cultivating and managing according to a conventional method till flowering. The invention lays the foundation for the popularization of new varieties of the dendrobium nobile.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Cell line for lowly-metastatic clear cell carcinoma of kidney of Han Chinese
InactiveCN101550407AMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesCancer cellKidney
The invention discloses a cell line for lowly-metastatic clear cell carcinoma of kidney of Han Chinese, namely LoMeT-ccRcc CCTCC No.C200910. The cell line can grow for a long time in vitro and be stably handed down, has epithelioid cell form, and has no contact inhibition. The cell is heteroploid, chromosome number and structure are aberrant. Immunohistochemistry shows masculine CA9 and CD133. A flow cytometry analyses and finds out that CA9 and CD133 expression is obviously enhanced in the condition that cell is handed down for many times. The cell line has lowly-metastatic trend after the cell is handed down continuously. The recovery rate of the cell line after being frozen is more than 80%, the recovered cell growth state accords with the original cell. The cell line of the invention is used for establishing a cell model for sieving and preparing medicines that is used for dialogising, preventing and treating clear cell carcinoma of kidney.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
Slide preparation method for discriminating chromosome number of Avena magna, Triticum aestivum or filial generation of Avena magna and Triticum aestivum
InactiveCN105510095AEfficient identificationGood dispersionPreparing sample for investigationBiotechnologyEnzymatic hydrolysis
The invention discloses a slide preparation method for discriminating the chromosome number of Avena magna, Triticum aestivum or a filial generation of Avena magna and Triticum aestivum. The method comprises the following steps: pretreatment; fixation; enzymatic hydrolysis; acidolysis; post-hypotonic treatment; post-fixation; slide preparation; slide compression; etc. Through improvement of conventional methods, the slide preparation method provided by the invention can effectively discriminate the chromosome number of Avena magna, Triticum aestivum or the filial generation of Avena magna and Triticum aestivum. Experimental results show that a slide prepared by using the slide preparation method has a good number of cell division phases and good chromosome dispersion, and high repeatability and reliable results are obtained. Thus, a novel method is provided for discriminating the chromosome number of Avena magna, Triticum aestivum or the filial generation of Avena magna and Triticum aestivum, and technical support is provided for hybridization and seed selection of Avena magna and Triticum aestivum.
Owner:CAPITAL NORMAL UNIVERSITY
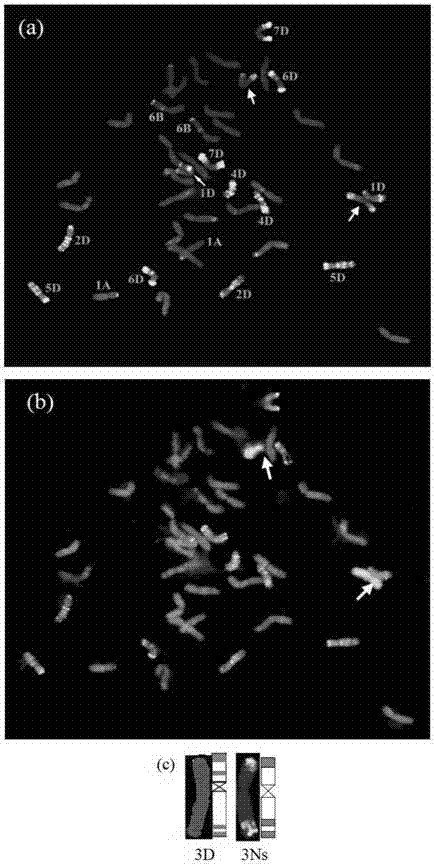
Wheat-tritileymus 3D (3Ns) alien substitution line cultivation method and identification method
InactiveCN103688846AAccurate and effective identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant genotype modificationGermplasmFluorescence in situ hybridization
The invention discloses a wheat-tritileymus 3D (3Ns) alien substitution line cultivation method, comprising the following steps: (1) hybridizing tetraploid durum wheat and octaploid tritileymus, authenticating every generation, and screening single plants with chromosome number (2n=42) and tritileymus Ns genome chromosomes; and (2) bagging the screened single plants, conducting selfing, and breeding a wheat-tritileymus alien substitution line with two tritileymus Ns genome chromosomes at the F5 generation. Furthermore, the invention also discloses an identification method for the quality of a wheat seed, and the identification method comprises a fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) method and an EST-STS (Expressed Sequence Tag-Sequence Tagged Sites) tag identification method. A wheat-tritileymus 3D (3Ns) alien substitution line cultured by using the method disclosed by the invention is remarkably improved on the aspects of agronomic traits such as plant height, ear length, tiller number and the like.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Three-dimensional inducing method for inducing spermatogonia stem cell to differentiate into functional sperm cell in vitro
ActiveCN106434536ACapable of fertilizationCulture processCell culture active agentsMatrigelMale infertility
The invention relates to a three-dimensional inducing method for inducing a spermatogonia stem cell to differentiate into a functional sperm cell in vitro, and belongs to the field of bioengineering. On the basis of acquiring the spermatogonia stem cell, a three-dimensional culture system is established through Matrigel, a key factor for inducing differentiation is added, the spermatogonia stem cell is induced to differentiate in vitro to obtain the sperm cell having a fertilization ability, the sperm cell obtained through induction is identified through an immunocytochemical method, the chromosome number of the sperm cell obtained through induction is detected through fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH), and the fertilization ability and the viability of the sperm cell obtained through induction are detected through round spermatid injection (ROSI). The application provides an excellent model for the molecular mechanism of the human sperm, and in addition, a functional gamete is provided for an azoospermia patient, so that a male infertility patient can have a child of his own.
Owner:何祖平
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com