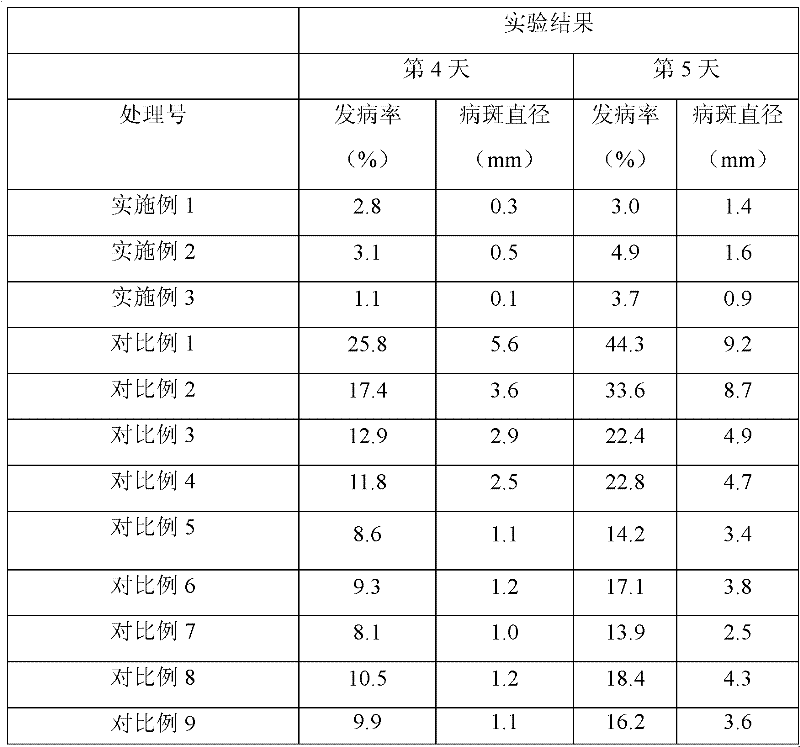
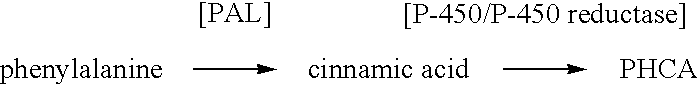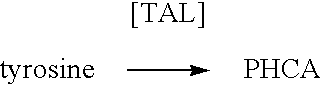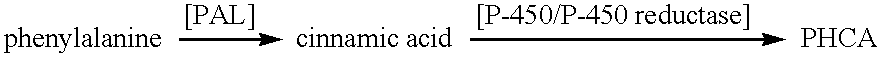Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
123 results about "Rhodotorula species" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Rhodotorula glutinis (Fresenius) F.C. Harrison is the type species of the genus Rhodotorula, a basidiomycetous genus of pink yeasts which contains 370 species.
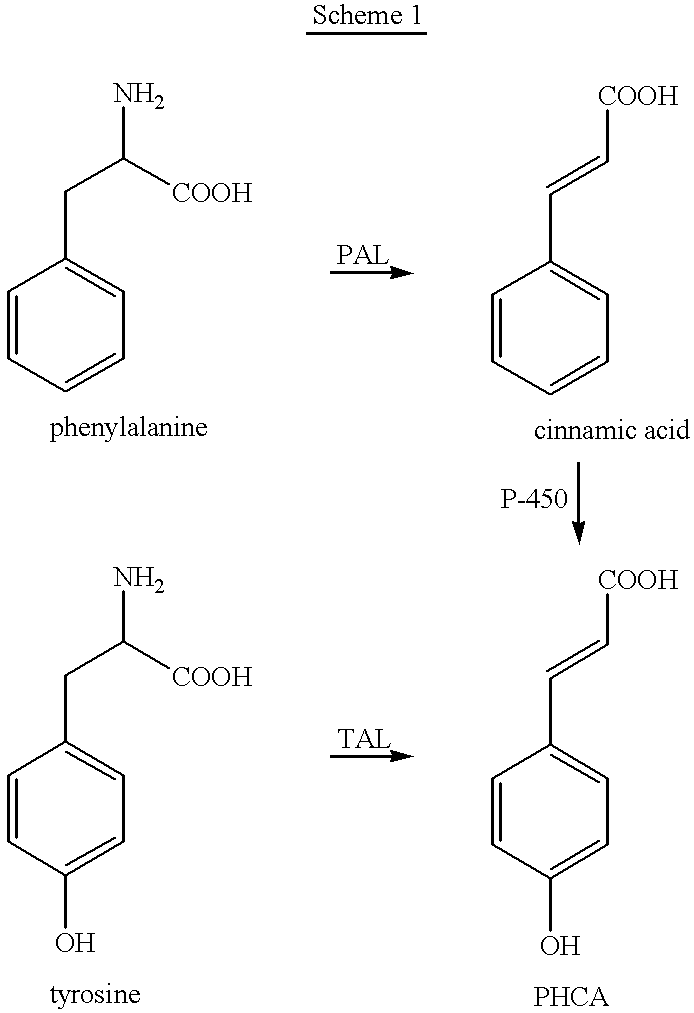
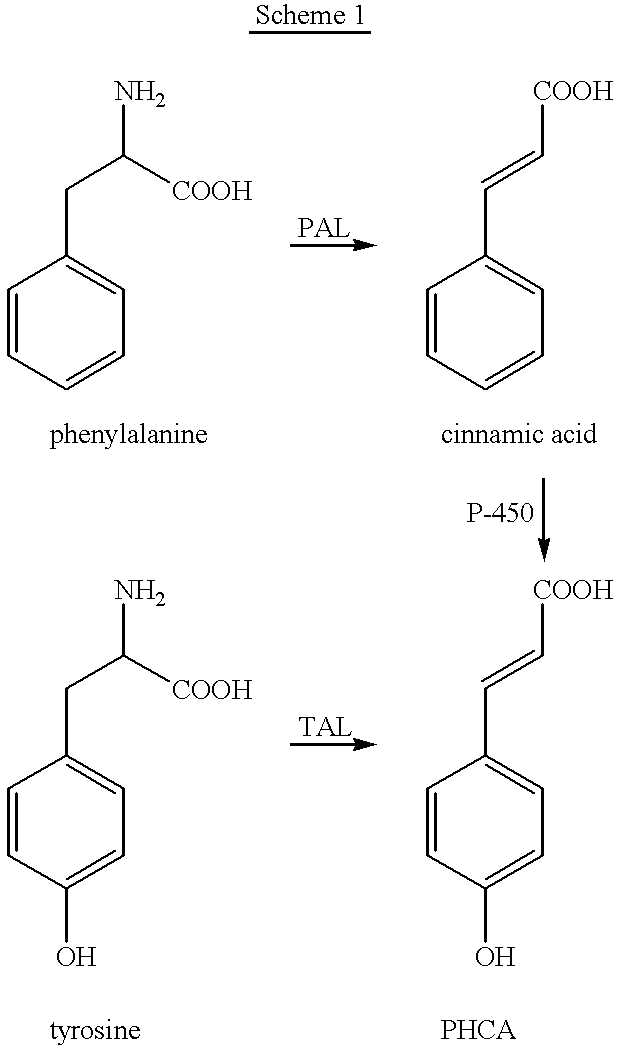
Bioproduction of para-hydroxycinnamic acid
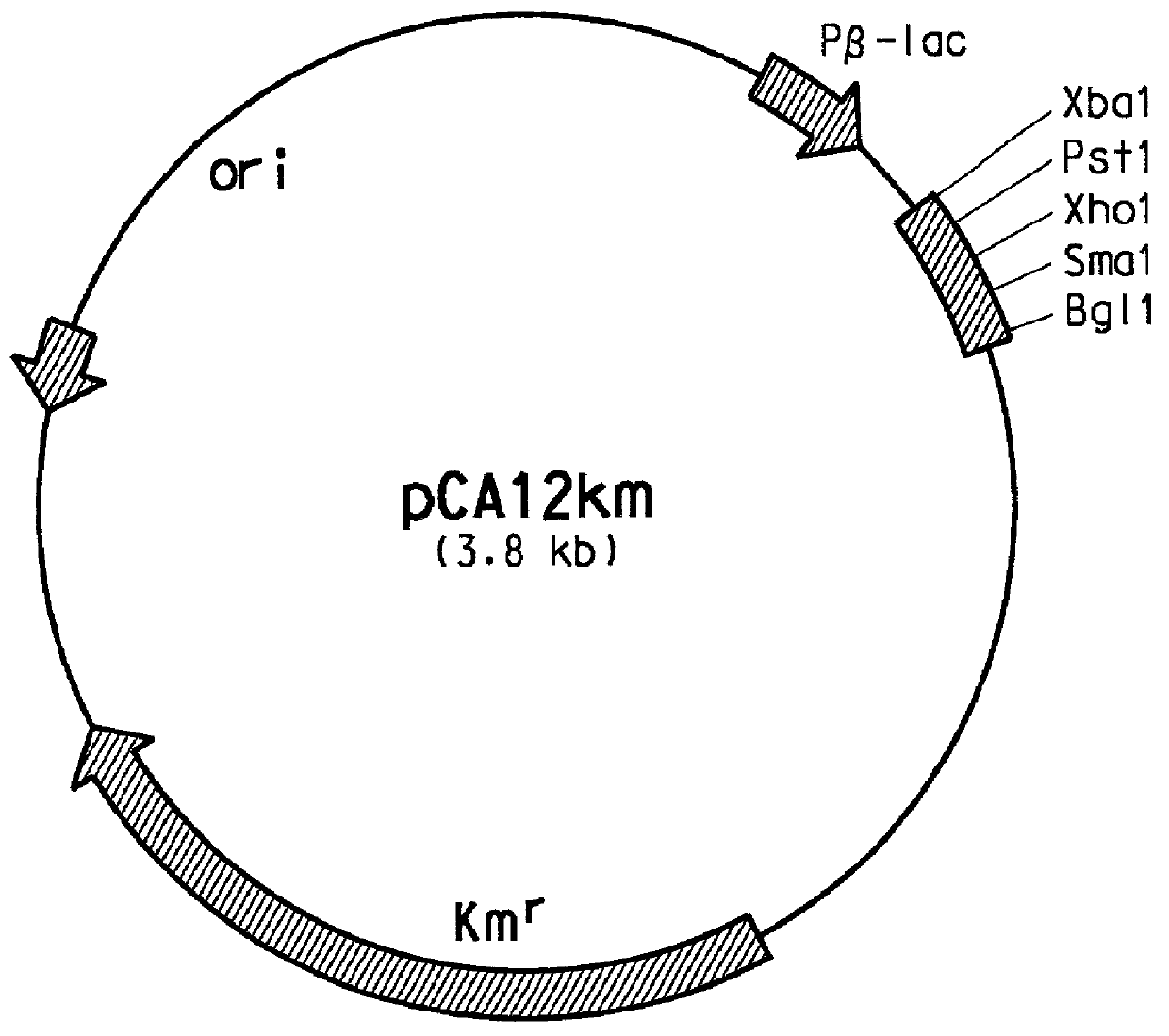
InactiveUS6368837B1Increased substrate specificityEnhanced TAL activityMicroorganism based processesOxidoreductasesEscherichia coliTyrosine
Owner:DUPONT US HLDG LLC
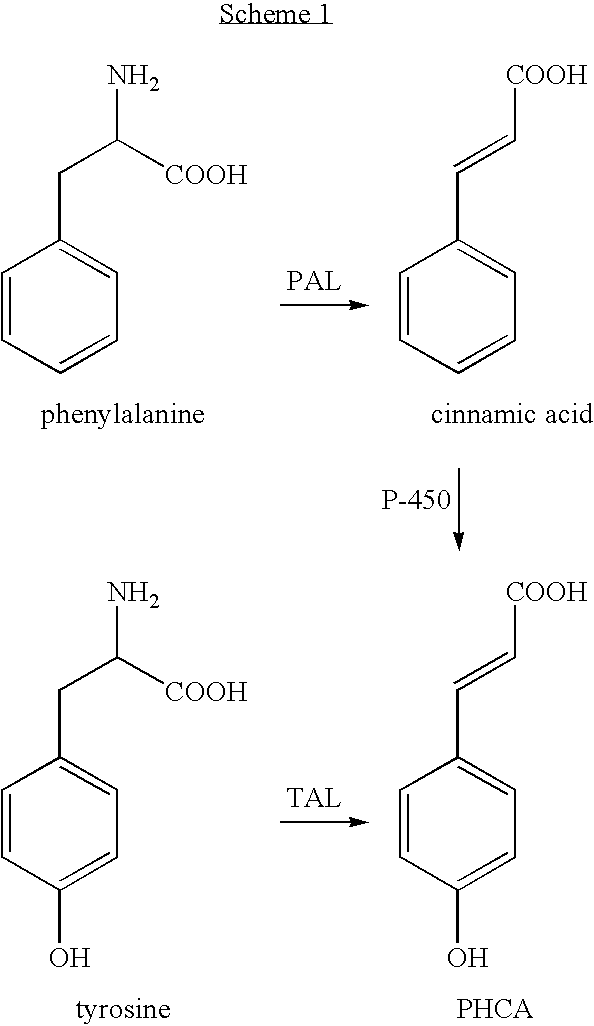
Bioproduction of para-hydroxycinnamic acid
The present invention provides several methods for biological production of para-hydroxycinnamic acid (PHCA). The invention is also directed to the discovery of new fungi and bacteria that possess the ability to convert cinnamate to PHCA. The invention relates to developing of a new biocatalyst for conversion of glucose to PHCA by incorporation of the wild type PAL from the yeast Rhodotorula glutinis into E. coli underlining the ability of the wildtype PAL to convert tyrosine to PHCA. The invention is also directed to developing a new biocatalyst for conversion of glucose to PHCA by incorporation of the wildtype PAL from the yeast Rhodotorula glutinis plus the plant cytochrome P-450 and the cytochrome P-450 reductase into E. coli. In yet another embodiment, the present invention provides for the developing of a new biocatalyst through mutagenesis of the wild type yeast PAL which possesses enhanced tyrosine ammonia-lyase (TAL) activity.
Owner:GATENBY ANTHONY A +4
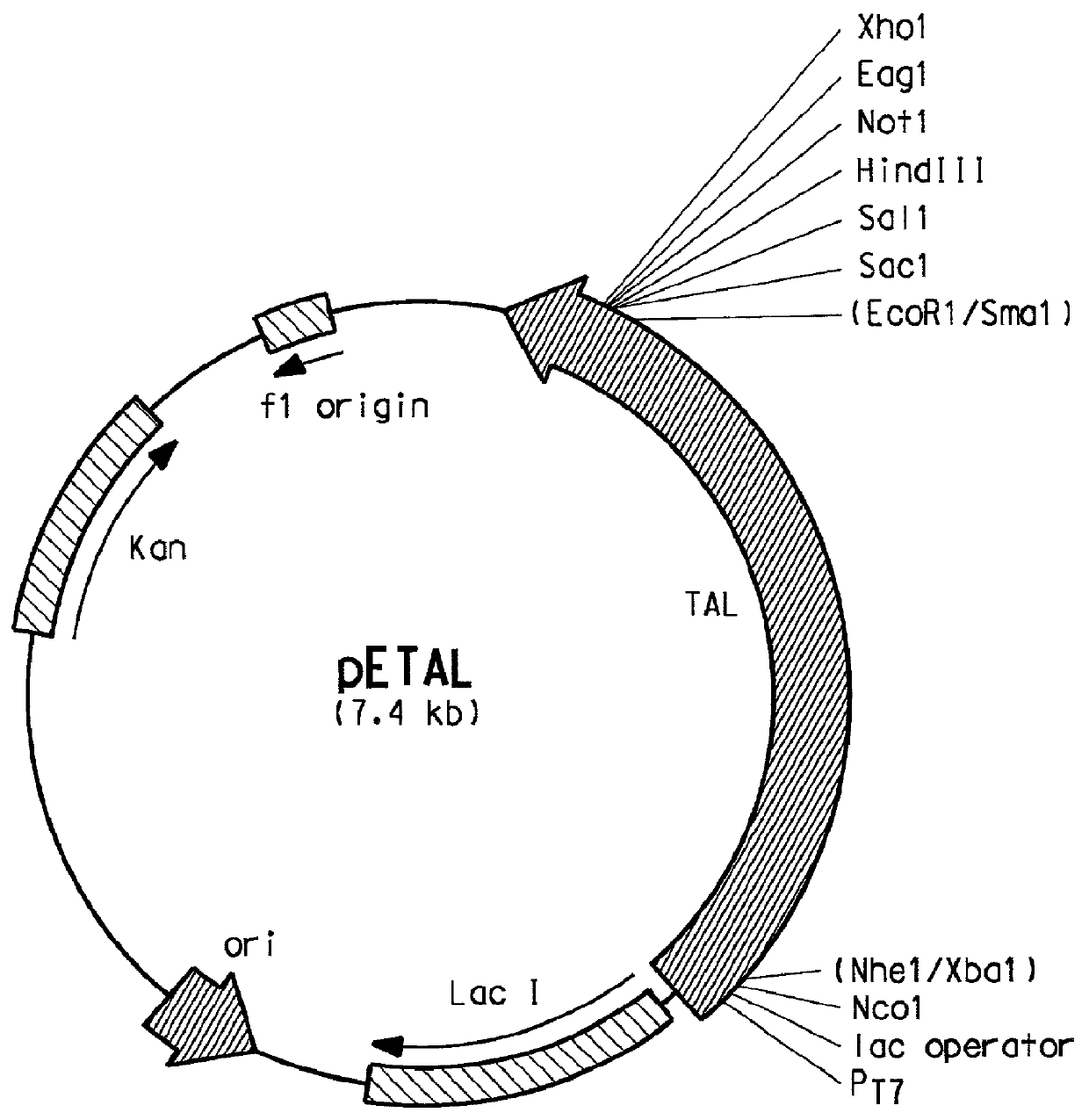
Polynucleotide encoding a mutant Rhodotorula glutinis tyrosine ammonia lyase polypeptide
The present invention provides several methods for biological production of para-hydroxycinnamic acid (PHCA). The invention is also directed to the discovery of new fungi and bacteria that possess the ability to convert cinnamate to PHCA. The invention relates to developing of a new biocatalyst for conversion of glucose to PHCA by incorporation of the wild type PAL from the yeast Rhodotorula glutinis into E. coli underlining the ability of the wildtype PAL to convert tyrosine to PHCA. The invention is also directed to developing a new biocatalyst for conversion of glucose to PHCA by incorporation of the wildtype PAL from the yeast Rhodotorula glutinis plus the plant cytochrome P-450 and the cytochrome P-450 reductase into E. coli. In yet another embodiment, the present invention provides for the developing of a new biocatalyst through mutagenesis of the wild type yeast PAL which possesses enhanced tyrosine ammonia-lyase (TAL) activity.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Method for extracting grease from oleaginous microorganisms
InactiveCN102199482AReduce energy consumptionMild reaction conditionsFatty-oils/fats productionMicroorganismProteinase activity
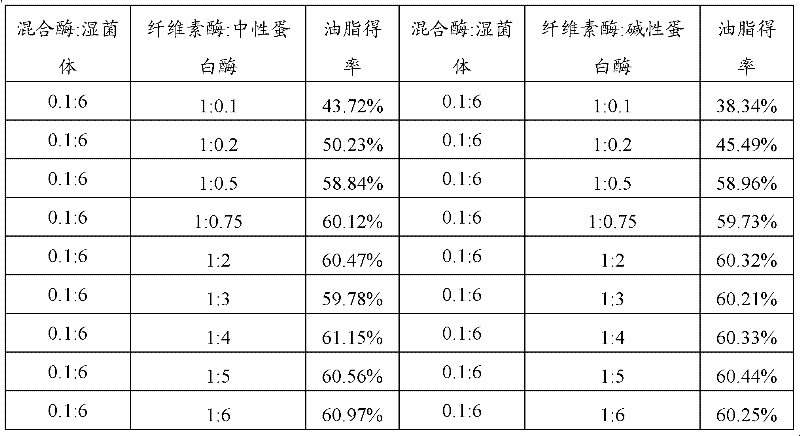
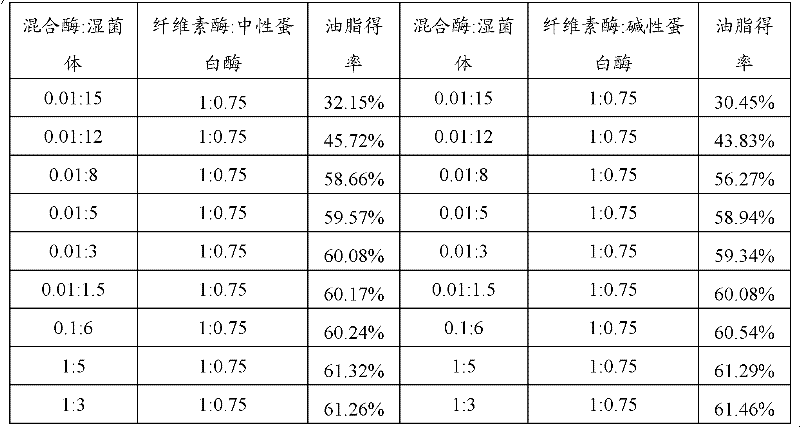
The invention relates to the field of microbial engineering, and discloses a method for extracting grease from oleaginous microorganisms. The method comprises the following steps of: mixing cellulose and protease to form mixed enzyme, hydrolyzing wet thalli of the oleaginous microorganisms, centrifuging, leaching an obtained precipitate, and desolventizing to obtain the grease, wherein the mass ratio of the cellulose to the protease is 1:(0.25-4); and the protease is neutral protease or alkali protease. In addition, the method also comprises the following steps of: hydrolyzing wet thalli of Rhodotorula glutinis by using the protease, centrifuging, leaching an obtained precipitate, and desolventizing to obtain the grease, wherein the protease is the neutral protease or the alkali protease;and the mass ratio of the protease and the thalli of the oleaginous microorganisms is (0.01-0.15):(1-10). By the method, the wet thalli are directly adopted for extraction, so that energy consumptionis reduced, reaction conditions are mild, the reaction has high specificity, the higher yield of the grease can be obtained with a smaller amount of enzyme, and extraction efficiency is higher; and the method is favorable for industrial production.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Bioproduction of para-hydroxycinnamic acid
InactiveUS20010053847A1Increased substrate specificityEnhanced TAL activitySugar derivativesBacteriaTyrosine ammonia-lyase activityTyrosine
The present invention provides several methods for biological production of para-hydroxycinnamic acid (PHCA). The invention is also directed to the discovery of new fungi and bacteria that possess the ability to convert cinnamate to PHCA. The invention relates to developing of a new biocatalyst for conversion of glucose to PHCA by incorporation of the wild type PAL from the yeast Rhodotorula glutinis into E. coli underlining the ability of the wildtype PAL to convert tyrosine to PHCA. The invention is also directed to developing a new biocatalyst for conversion of glucose to PHCA by incorporation of the wildtype PAL from the yeast Rhodotorula glutinis plus the plant cytochrome P-450 and the cytochrome P-450 reductase into E. coli. In yet another embodiment, the present invention provides for the developing of a new biocatalyst through mutagenesis of the wild type yeast PAL which possesses enhanced tyrosine ammonia-lyase (TAL) activity.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Tissue culturing, rapid propagating and transplanting method of Rhododendron mucronulatum Turcz.
InactiveCN1732759AHigh proliferation rateStable proliferationHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureCuckooFirst generation
The invention disclose a technique for the tissue culturing and breeding of the red-welcome cuckoo as well as the technique for domestication and replanting, which comprises the first generation culture of inducing the clump sprout by applying the germ-free seedling as explant, subculture for enrichment-culture, root-growing inducing for the clump sprout, water-planting for domestication before replanting the tissue culture sprout, the final replanting to flowerpot and getting the red-welcome cuckoo. The invention is suitable for the red-welcome cuckoo from different places, the k-factor of the clump sprout is high, the root is uniform, and the survival rate after the water-culture domestication is high and is suitable for the red-welcome cuckoo commercial production.
Owner:INST OF FORESTRY CHINESE ACAD OF FORESTRY
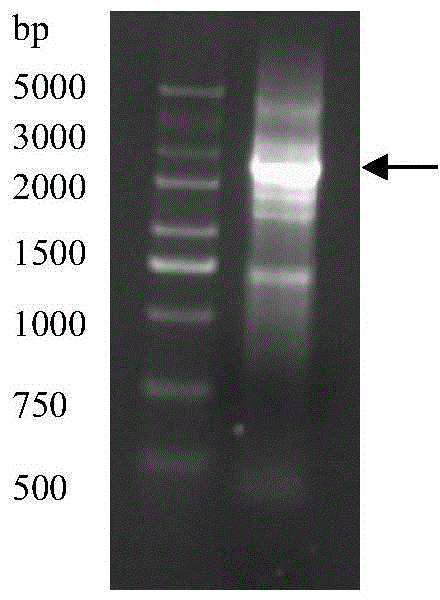
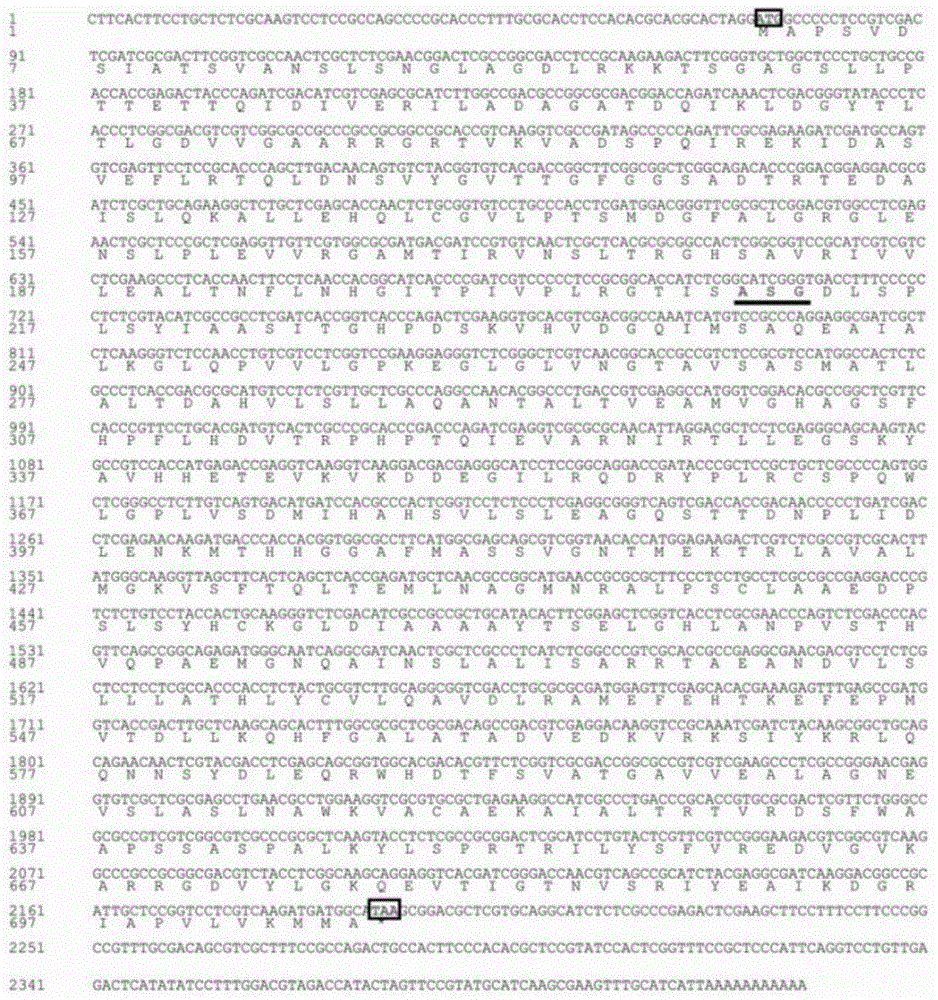
Method for acquiring rhodotorula glutinis phenylalanine deaminase gene sequence
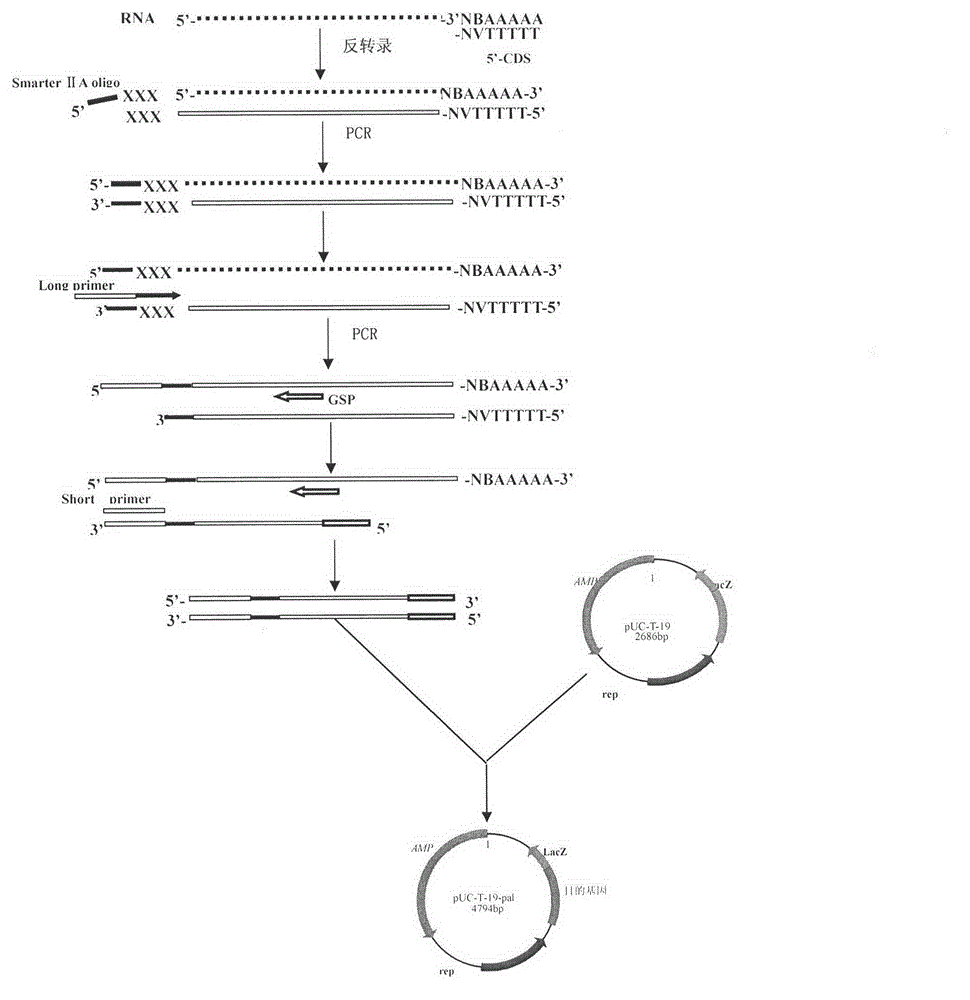
The invention discloses a method for acquiring a rhodotorula glutinis phenylalanine deaminase gene. The method comprises the following steps of: extracting RNA (Ribose Nucleic Acid); carrying out inverse transcription; carrying out PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) amplification; establishing a cloning vector pUCm-T-pal; and measuring a sequence to obtain a full-length phenylalanine deaminase gene sequence. The invention belongs to the technical field of gene clone. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of easiness for operation and higher efficiency and success rate.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for preparing Rhodotorula benthica fermentation feed
InactiveCN101433275AImprove digestion and absorption rateHigh nutritional valueFood processingAnimal feeding stuffNutritive valuesMicrobial transformation
The invention relates to a method for preparing ocean rhodotorula fermentation feed. The method comprises the preparation of solid fermentation base stock of soybean meal, the mixing of a nutrition replenishing agent and the preparation of a solid fermentation medium. The feed is characterized in that ocean rhodotorula and a lactobacillus strain are inoculated in the solid fermentation medium and are subjected to solid fermentation to obtain the ocean rhodotorula fermentation feed. The method has the advantages: 1. macromolecular protein in the soybean meal is decomposed into small molecular peptide which improves the digestive absorption rate of the protein and further balances the composition of amino acid through microbial transformation; 2. the fermentation feed is replenished with astaxanthin and other biological active substances introduced by the metabolism of rhodotorula glutinis, thereby improving the nutritive value of the feed; 3. lactobacillus in the fermentation feed has positive function on improving a microecological flora of intestinal tracts of bred animal; and 4. the method has low fermentation cost, low fermentation condition and equipment requirement, simple operation of process flow and small investment and is suitable for small-scale production of breeding households and feed processing factories.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Method for improving biomass and oil fat yield of microorganisms
ActiveCN106754383AGood yieldMitigate disadvantagesFungiUnicellular algaeDry weightConcentrations glucose
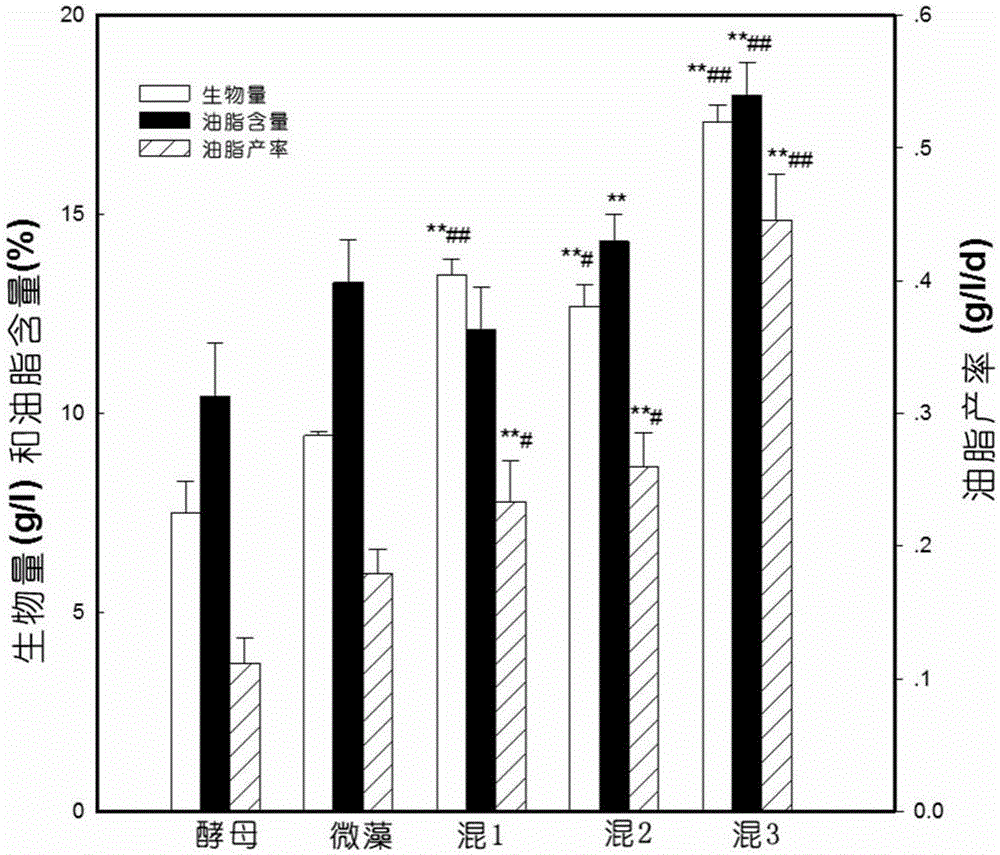
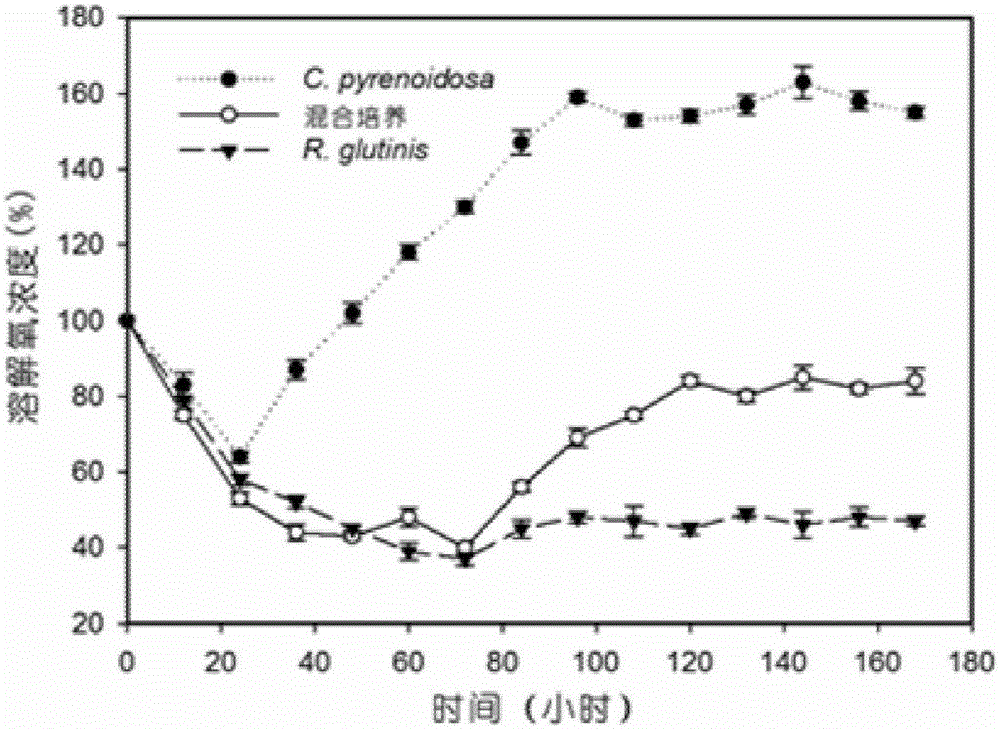
The invention discloses a method for improving the biomass and oil fat yield of microorganisms. The method comprises the following steps: (1) carrying out activated culture: respectively inoculating chlorella pyrenoidosa and rhodotorula glutinis cells into a culture medium, carrying out activated culture to a logarithmic phase, and taking a product as a seed solution; (2) respectively inoculating chlorella pyrenoidosa and rhodotorula glutinis into a shake flask according to different proportions, wherein each shake flask is internally filled with a culture medium, putting the shake flasks into a lighting shaker, and culturing; (3) respectively inoculating chlorella pyrenoidosa and rhodotorula glutinis cells into a BG11 culture medium, wherein the ratio of chlorella pyrenoidosa cell number to the rhodotorula glutinis cell number is equal to 3: 1, and the BG11 culture mediums contain 1.6g / L of yeast extract and have different glucose concentrations; putting the inoculated shake flasks into the lighting shaker, and culturing for 12 days; (4) after the culture is finished, centrifuging microbial cells, washing and carrying out freeze drying to obtain powder; the powder can be used for measuring and evaluating the dry weight concentration, total lipid content, fatty acid content and yield of the biomass. The method has the advantages that the biomass and oil fat yield of the oil-containing microorganisms are remarkably improved by utilizing a mixed culturing mode, and are 3-4 times or more than those of microorganisms cultured under a single culture condition; the method is relatively simple and convenient, and the energy consumption and the production cost are effectively reduced.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Rhodotorula glutinis oil genetic engineering strain and construction method and application thereof
ActiveCN102796675AImprove the lubrication effectImprove securityFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyLipid formation
The invention relates to a rhodotorula glutinis oil genetic engineering strain and a construction method and an application thereof. The construction method of the genetic engineering strain is mainly as follows: utilizing rDNA (recombinant deoxyribonucleic acid) of rhodotorula glutinis as a target sequence for homologous integration, using strong promoter genes PGK1 of saccharomyces cerevisiae and malate dehydrogenase genes ME of chaetomium cochloides to construct an expression vector to be introduced into rhodotorula glutinis, and enabling ME genes to obtain high-efficient expression in a rhodotorula glutinis body, wherein the content of lipid in a transformant is improved by 2.5 times in comparison with a wild strain. According to the construction method disclosed by the invention, key enzyme genes and a strong promoter for anabolism of the lipid are introduced on the basis that the anabolism of microbial oil is known, so that the lipid metabolism is regulated and controlled, and the yield of oil is improved. The genetic engineering strain can be applied to production of the microbial oil and development of functional oil related products, such as medicaments, health care products and the like.
Owner:广州溯原生物科技股份有限公司
Orange biological preserving agent based on yeast, sodium bicarbonate and elicitor activity
InactiveCN102224843AInhibitionInhibition of developmentFruit and vegetables preservationSodium bicarbonateGram
The invention discloses an orange biological preserving agent based on yeast, sodium bicarbonate and elicitor activity, composed of cryptococcus laurentii suspension, rhodotorula glutinis suspension, rhodosporidium toruloides suspension, sodium bicarbonate, auxin, salicylic acid and water. The preserving agent has 1*1010-1*1012 cryptococcus laurentii cells, 1*1010-1*1012 rhodotorula glutinis cells, 1*1010-1*1012 rhodosporidium toruloides cells, 5-50 grams of sodium bicarbonate, 10-400mg of auxin, 1-100mg of salicylic acid and the reminder consisting of water per liter of the preserving agent. The accession number of cryptococcus laurentii is CGMCC No.3590, the accession number of rhodosporidium toruloides is IMI 394084, and the accession number of rhodotorula glutinis is CGMCC No.3589. The orange biological preserving agent disclosed in the invention can control orange postharvest diseases without using chemical bactericides.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Orange biological preservative based on antagonistic activities of three antagonistic yeasts
InactiveCN102224842AIntegration activityInhibitionFruit and vegetables preservationDiseasePreservative
The invention discloses an orange biological preservative based on antagonistic activities of three antagonistic yeasts, composed of cryptococcus laurentii suspension, rhodotorula glutinis suspension, rhodosporidium toruloides suspension and water. The preserving agent has 1*1010-1*1011 cryptococcus laurentii cells, 1*1010-1*1011 rhodotorula glutinis cells, 1*1010-1*1011 rhodosporidium toruloides cells1 and the reminder consisting of water per liter of the preserving agent. The accession number of cryptococcus laurentii is CGMCC No.3590, the accession number of rhodosporidium toruloides is IMI 394084, and the accession number of rhodotorula glutinis is CGMCC No.3589. The orange biological preserving agent disclosed in the invention can control orange postharvest diseases without using chemical bactericides.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for enhancing effect of rhodotorula glutinis on biologically controlling postharvest disease of fruit
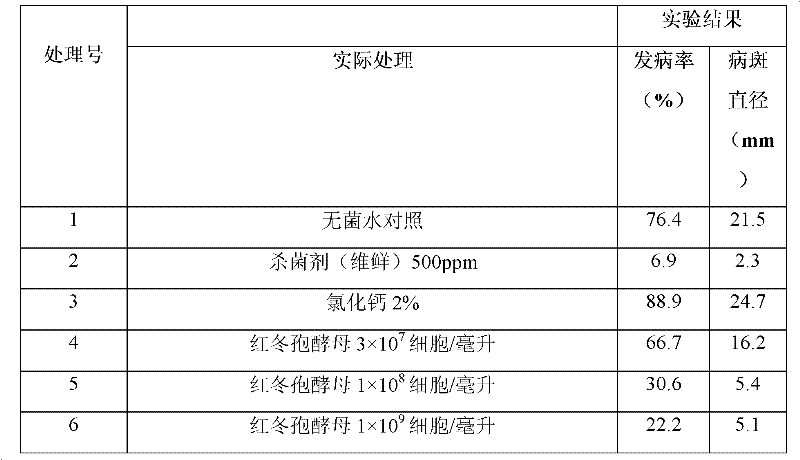
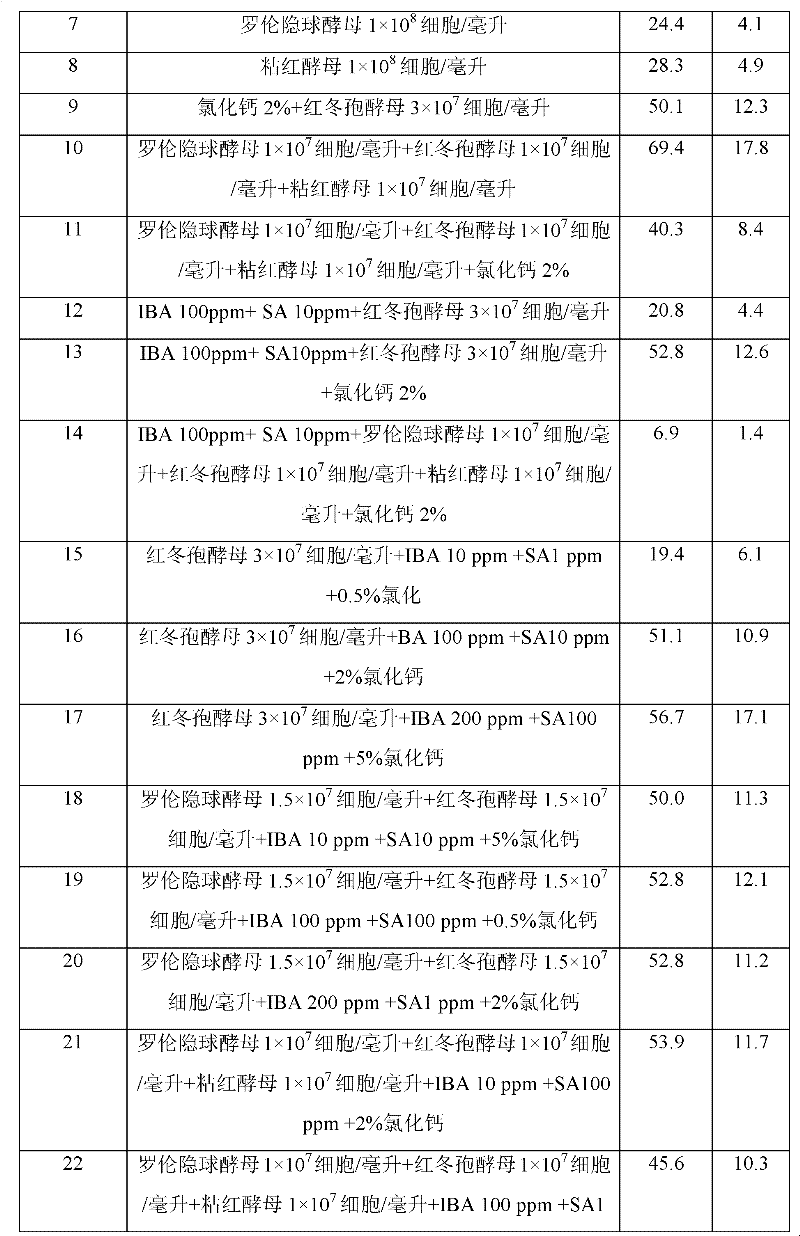
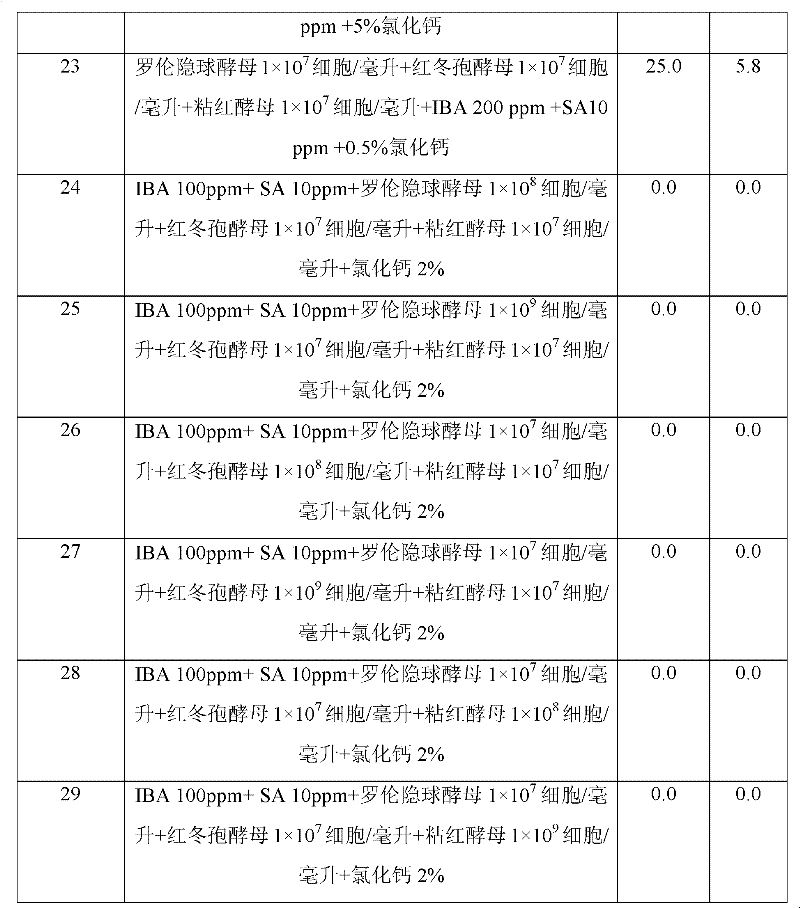
The invention discloses a method for enhancing effect of rhodotorula glutinis on biologically controlling a postharvest disease of a fruit, comprising the following steps of: activating the rhodotorula glutinis, inoculating the rhodotorula glutinis in an NYDB culture medium added with 0.01-1 percent of chitosan to carry out induction culture, and obtaining bacteria through centrifugation, wherein the NYDB culture medium is prepared from 5g of yeast extract, 8g of beef extract, 10g of glucose and 1000ml of purified water and has natural pH; preparing 1*106 / mL-1*109 / mL bacterial suspension by diluting the cell with sterile water; putting fruits into the bacterial suspension, immediately taking out after soaking for 30s, and naturally air drying; putting the fruits into a plastic basket; sealing with fresh-keeping film and storing at room temperature or under cold storage condition. The invention uses the rhodotorula glutinis after induction culture by the chitosan to replace a chemical fungicide to control the postharvest disease of fruit, prevents harm of using chemical fungicide to the human body and has remarkable economic benefit and social benefit.
Owner:无棣鑫岳化工集团有限公司
Method for preventing fruit postharvest diseases
InactiveCN101697750AReduce decay rateExtended shelf lifeFruits/vegetable preservation by irradiation/electric treatmentFruits/vegetable preservation by coatingDiseaseDisinfectant
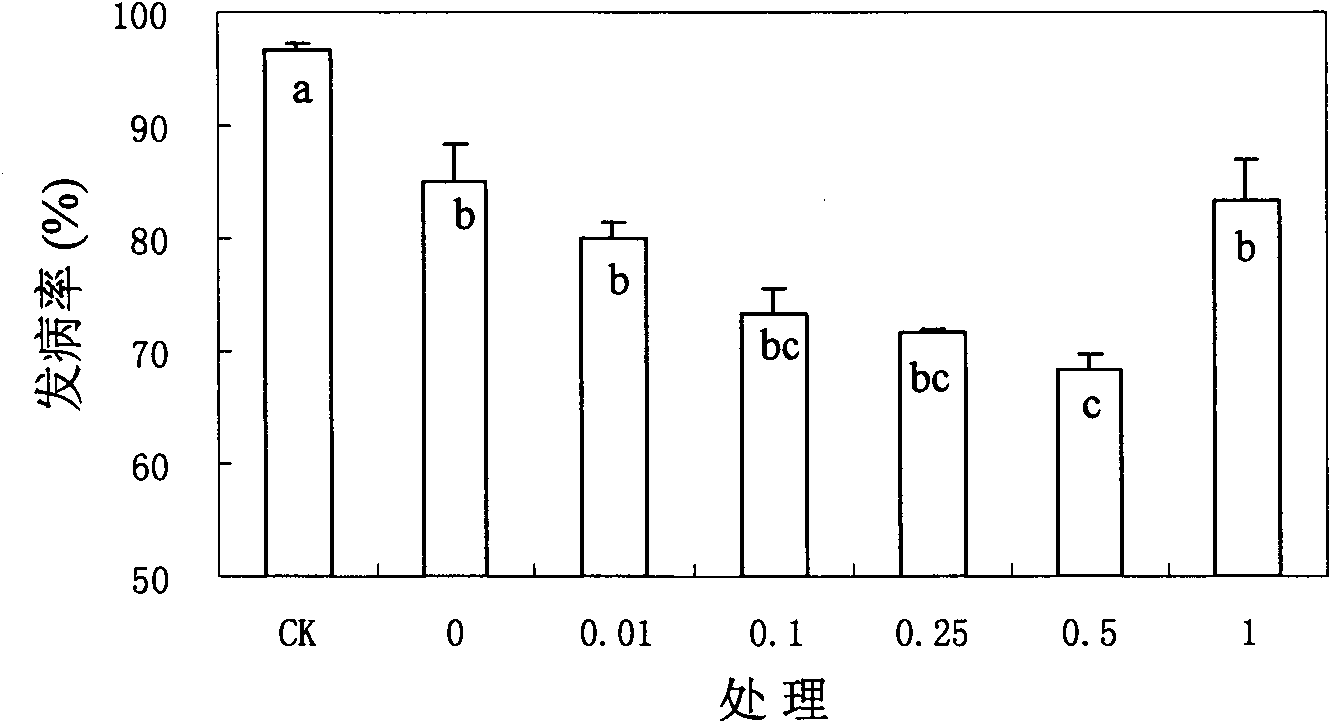
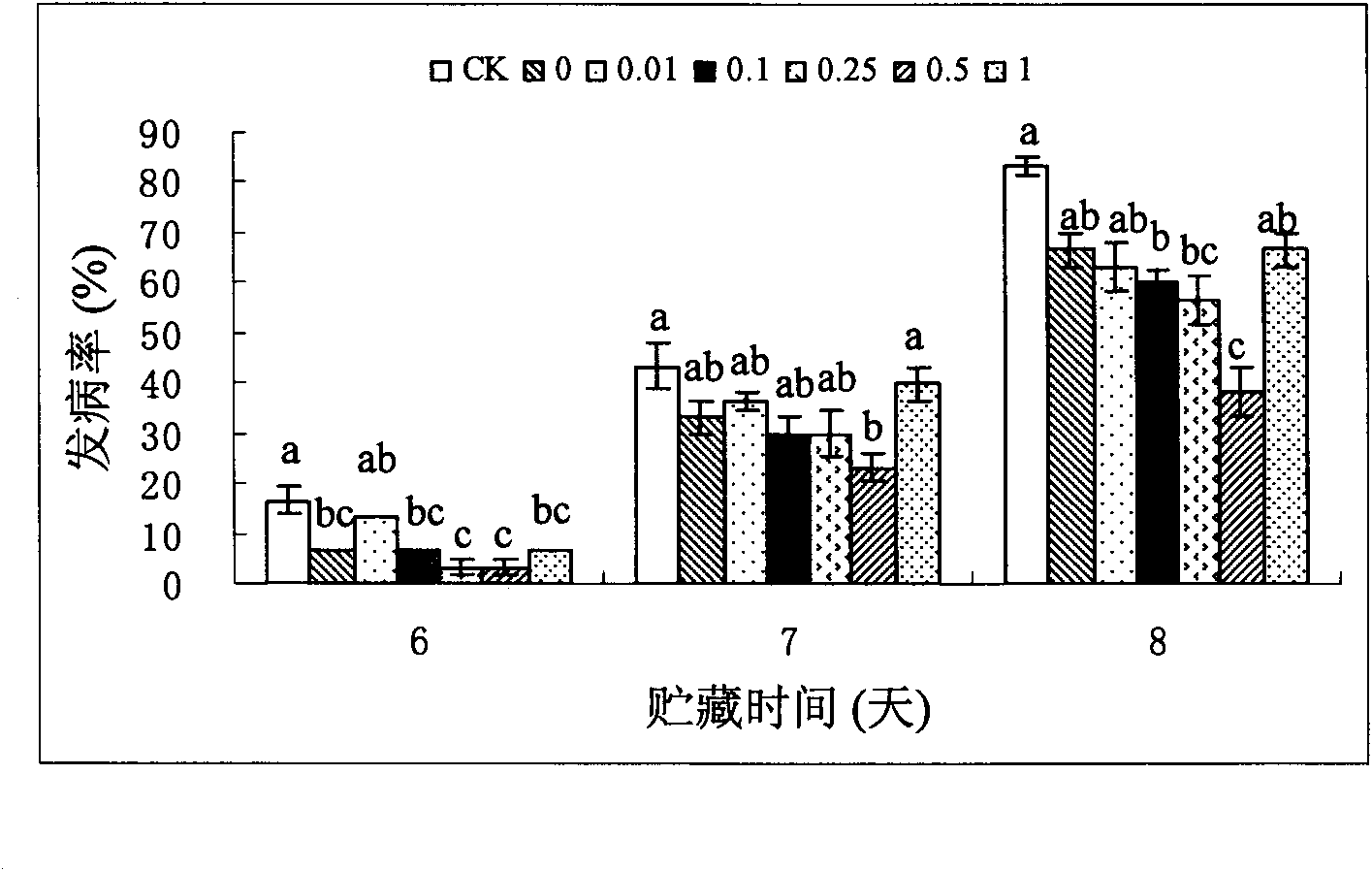
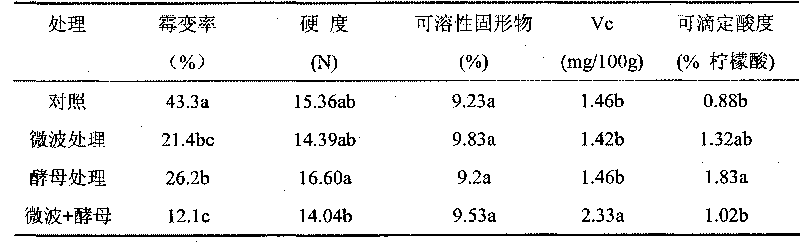
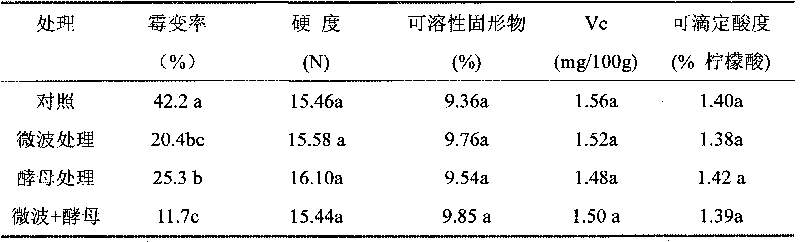
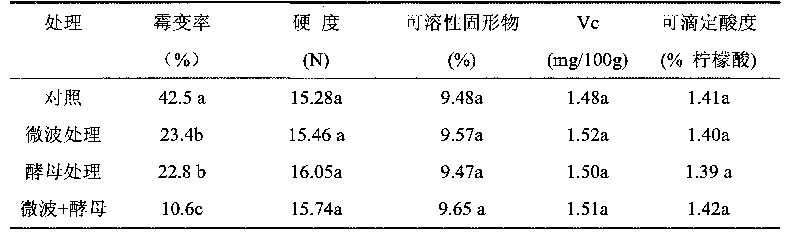
The invention provides a method for preventing fruit postharvest diseases, relating to prevention on fruit postharvest diseases and storing and refreshing method. Fruits are placed in microwave at 2450MHz and 0.25-0.45KW to be treated for 1-4 minutes, taken out to be placed at room temperature for 20 minutes, then immersed into 1x10<7>-1x10<9>ps / ml cryptococcus laurentii or rhodotorula glutinis solution and immediately taken out after immersion for about 30 seconds, then air drying is carried out, the fruits are placed in a plastic crate and stored under the conditions of room temperature or cold storage (20 DEG C) after sealed by preservative film. Through test, the combination of microwave and antagonism yeast can effectively prevent and treat fruit diseases caused by pathopoiesia mould, reduce fruit rotting rate and prolong fruit shelf life without destroying fruit storage quality or nutrition. The method of combining microwave treatment and bio-controlling micro-organism treatment used in the invention is simple in use, convenient in operation and low in cost, can avoid harm to human caused by using chemical disinfectant and pollution to environment and has significant economic benefit and social benefit.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Biological preservative for oranges
InactiveCN102246850AInhibitionInhibition of developmentFruit and vegetables preservationPreservativeSalicylic acid
The invention discloses a biological preservative for oranges, consisting of cryptococcus laurentii suspension, rhodotorula glutinis suspension, rhodosporidium suspension, salicylic acid, auxin, calcium chloride and water, wherein each liter of preservative contains 1*1010-1*1012 cryptococcus laurentii cells, 1*1010-1*1-12 rhodotorula glutinis cells, 1*1010-1*1012 rhodosporidium cells, 1-100mg of salicylic acid, 10-20mg of auxin, 5-50g of calcium chloride and the balance of water; the preservation number of the cryptococcus laurentii is CGMCC (China General Microbiological Culture Collection) NO.3590, the preservation number of the rhodosporidium is IMI (Innovative Medicines Initiative) 394084 and the preservation number of the rhodotorula glutinis is CGMCC NO.3589. The biological preservative for oranges, which is disclosed by the invention, can be used for effectively controlling postharvest diseases of orange fruits on the premise of no use of chemical bactericide.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
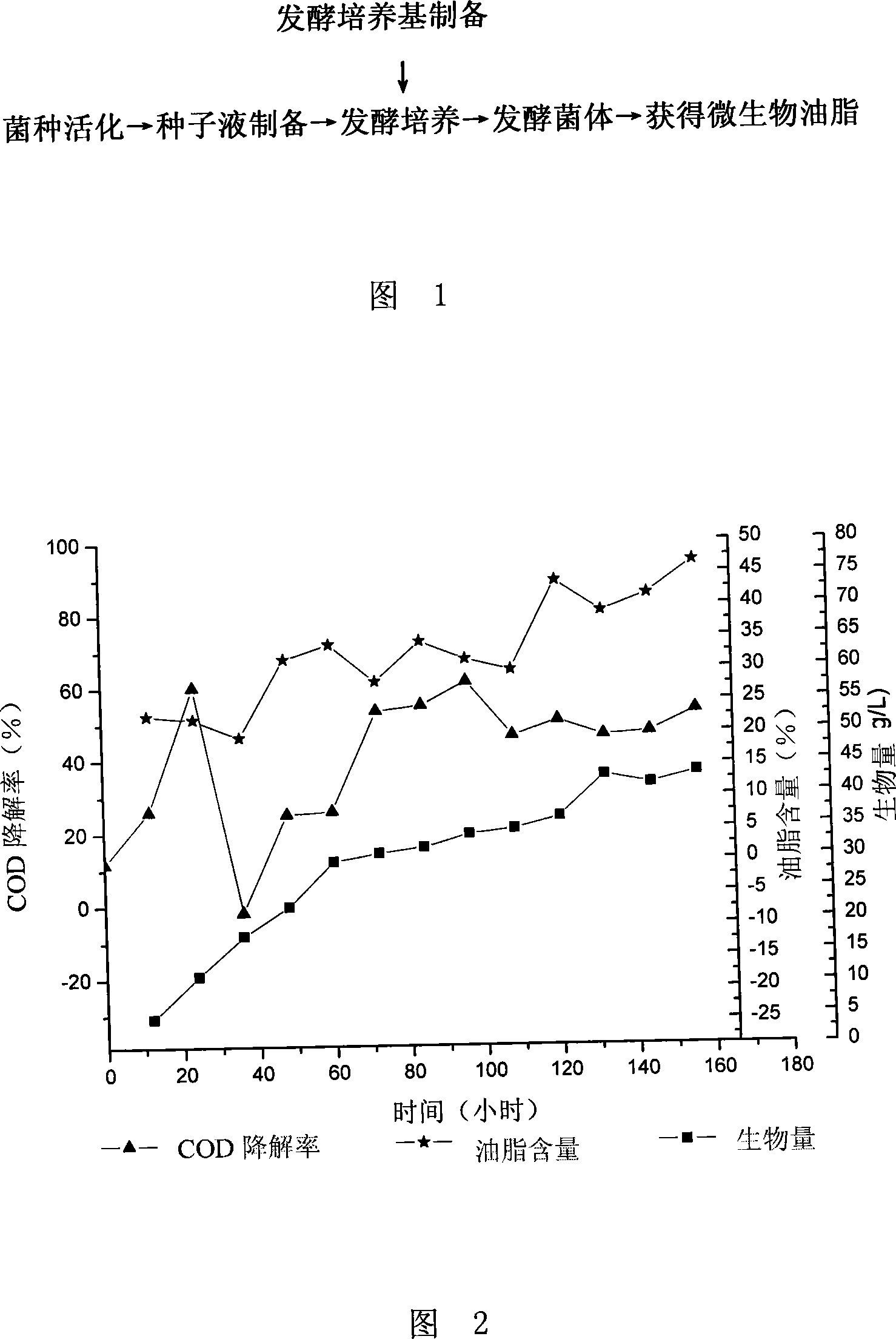
Method for treating industrial waste and fermentation production of microbial oil by microorganism as well as special strain thereof
The invention discloses a method for utilizing industrial wastes to produce microbial grease by means of fermentation and a special strain Rhodotorula glutinis Rh.g CGMCC No.2258. The method of the invention is a method for utilizing the industrial wastes (such as waste water of industrial production like starches, monosodium glutamate, paper making and so on, and / or fermentation industrial residues like soya residues and so on) as culture media to produce the microbial grease through fermentation of the Rhodotorula glutinis; the microbial grease obtained by the method also can be taken as material lipid to prepare biodiesel, and conversion rate can reach 80 to 99 percent. The production method of the microbial grease has the advantages of simple operation, low cost and high use value, and not only pollution of high concentration wastes which are discharged by fermentation industries like starches, monosodium glutamate, paper making, soya residues, etc. on the environment can be reduced but also the wastes can be converted into treasures by using the wastes to produce the grease which is a product in short supply in the current market, thereby the aim of resource utilization of the wastes is reached.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Intestine-regulating constipation-removing enzyme and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103815491ABalance quantitySmooth stoolYeast food ingredientsFood ingredient functionsAdditive ingredientHansenula anomala
The invention relates to an intestine-regulating constipation-removing enzyme and a preparation method thereof. The enzyme comprises the following raw materials in percentage by weight: 5% of figs, 10% of sophora flowers, 15% of celery, 20% of pears, 20% of apples, 2% of radix paeoniae alba, 4% of plantain, 3% of liquorice, 20% of mulberries, 2% of dandelion, 20% of flaccid knotweed herb and 80% of coarse rice. The preparation method comprises the following steps: 1. steaming the coarse rice in the raw materials, alcoholizing the steamed coarse rice and the flaccid knotweed by hansenula anomala and saccharomyces cerevisiae, and after alcoholizing, adding water, acetifying by acetobacter pasteurianus and clostridium butyricum; 2. grinding the other materials, alcoholizing by honey yeasts, hansenula anomala, rhodotorula glutinis, saccharomyces cerevisiae and streptomyces microflavus, after finishing the steps 1 and 2, mixing according to a ratio of 1 to 1, lactifying by lactobacillus lactis and plant lactobacilli, and fermenting to obtain suspension liquid as the intestine-regulating constipation-removing enzyme. The intestine-regulating constipation-removing enzyme has the effects of promoting production of body fluid, moistening the lung and facilitating intestinal tract movement, and is suitable for crowds with constipation.
Owner:SUZHOU KEDA WEILONG INFORMATION TECH
Preparation method of high-activity ocean rhodotorula glutinis powder
InactiveCN101748075AFast growthHigh activityFungiMicroorganism based processesUltrafiltrationRhodotorula species
The invention relates to a new method for preparing high-activity ocean rhodotorula glutinis powder. The method comprises the following steps: beer yeast is taken as a raw material and hydrolyzed by hydrolase to be a basal medium after filtering; after ocean rhodotorula glutinis is inoculated at deep fluid for aerobic culture, and an ultrafiltration membrane is utilized in time to concentrate fermentation liquor and collect rhodotorula glutinis thallus; and the concentrated rhodotorula glutinis is mixed evenly with excipient to form wet cenobium, and then the wet cenobium are transmitted to expansion drying equipment by a screw stem for instantaneous drying at low temperature to obtain the rhodotorula glutinis dry powder of which the rhodotorula glutinis thallus reaches 10-20 billion / g, and the viable yeast content reaches above 60%. The rhodotorula glutinis prepared by the preparation method of the invention has high growth speed, high density of yeast as per unit volume and short incubation time; the ultrafiltration membrane is adopted to concentrate culture solution, which has small damage to thallus and easily keeps high activity of the concentrated rhodotorula glutinis; granulation is not needed after the concentrated rhodotorula glutinis solution and the excipient are mixed; and the obtained wet cenobium can directly enter the expansion drying equipment to for instantaneous drying at low temperature, thus ensuring high activity ratio of the rhodotorula glutinis powder in the whole production technology process.
Owner:DALIAN RES & DESIGN INST OF CHEM IND
Method for preparing rhodotorula glutinis feed
The invention provides a method for preparing a rhodotorula glutinis feed. The method comprises the following steps of: preparing a primary fermentative strain of 5 degree Be wort by using the rhodotorula glutinis as a parent strain; inoculating the primary fermentative strain into the 5-degree Be wort in a weight ratio of 10 percent; after 12 hours, continuously feeding a nutrient source containing 2 percent of maltose, 0.2 percent of urea and 0.1 percent of ammonium sulfate in 16 hours; culturing for 48 hours, wherein the viable count of the rhodotorula glutinis in the fermentation broth is more than or equal to 109 per milliliter, and the rhodotorula glutinis is used as a secondary fermentative strain; inoculating the secondary fermentative strain accounting for 5 to 8 percent of a distiller grain fermentation medium; tiling the uniformly stirred fermentation medium in a fermenting tank to ferment at the temperature of between 28 and 30 DEG C for 60 hours, wherein the thickness of the medium is between 20 and 25cm; and drying the strain by hot wind through a feed drier at the temperature of between 50 and 60 DEG C until the moisture of the strain is lower than 5 percent, and packaging the strain to obtain the rhodotorula glutinis feed finished product.
Owner:黑龙江大荒春酒业有限公司
Application method of microbial inoculum capable of controlling cadmium-polluted farmland by in-situ converting
ActiveCN107099298ALarge amount of processingEasy to operateAgriculture tools and machinesFungiRhodotorula speciesBioremediation
The present invention relates to the field of microbial remediation of cadmium contamination, and discloses an application method of a microbial inoculum capable of controlling a cadmium-polluted farmland by in-situ converting, and the microbial inoculum includes Acidiphilium cryptum, Candida rugosa, Acetobacter diazotrophicus, Rhodotorula glutinis and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Through expanding culture of the microbial inoculum, the bacteria concentration reaches more than 1 x 10<9> / mL, he microbial inoculum is sprayed directly to the soil surface of the cadmium-polluted farmland by a small-dosage multi-time multi-point method, average 14-20L of the microbial inoculum liquid is applied to per square meter of the farmland, the soil and the repair microbial inoculum are evenly mixed by turning over, and the turning-over depth is 25-35cm. The application method of the microbial inoculum has the advantages of wide application range, repeated use of the microbial inoculum, large processing capacity, simple operation and low cost, can improve the conversion efficiency of the microbial inoculum to 50% or more, and has broad application prospects in the field of heavy metal contaminated soil remediation.
Owner:HUNAN AGRI BIOTECH RES CENT +1
Microbial oil preparation method with biodiesel byproducts as carbon sources
ActiveCN104212848AReduce manufacturing costEfficient use ofBiofuelsMicroorganism based processesMicrobial oilMicroorganism
The invention provides a microbial oil preparation method with biodiesel byproducts as carbon sources and belongs to the technical field of microbial oil preparation. According to the microbial oil preparation method, microbial oil is prepared with the biodiesel byproducts serving as the carbon sources and rhodotorula glutinis 32489 serving as the oil-producing microorganisms. Therefore, the problem of high cost when glucose or pure glycerine (AR) is used as the carbon sources to prepare microbial oil is solved, and crude glycerine is effectively used; the components of the produced microbial oil are almost as same as those of vegetable oil. Compared with vegetable oil, microbial oil has the advantages of being short in the preparation cycle and free of occupying arable land, is a cheap non-crop biomass raw material to prepare biodiesel, can reduce the preparation cost of biodiesel, and has a wide application prospect.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Biological organic fertilizer produced by using erythromycin bacterium residues and preparation method of biological organic fertilizer
InactiveCN105924271AHigh nutrient contentFacilitate sorption storageBio-organic fraction processingAnimal corpse fertilisersRhodotorula speciesFermentation
The invention discloses a biological organic fertilizer produced by using erythromycin bacterium residues and a preparation method of the biological organic fertilizer. The biological organic fertilizer is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 37-43 parts of sheep manure, 27-33 parts of the erythromycin bacterium residues, 7-13 parts of bone meal, 12-18 parts of attapulgite powder, 2-8 parts of sawdust, 0.04-0.08 part of polyglutamic acid, and 0.35-0.41 part of microbial bacteria, wherein the microbial bacteria comprise rhodotorula glutinis, high temperature fermentation bacteria and functional bacteria in a ratio of 1.8:1:1. The biological organic fertilizer is prepared by the method comprising the following processes: (1) a process of degrading the bacterium residues; (2) a process of performing fermentation to prepare a fertilizer; and (3) a process of performing crushing and screening. According to the biological organic fertilizer disclosed by the invention, abundant nutrients are obtained from the bacterium residues, and the polyglutamic acid and the bone meal are added to improve the nutrient content, so that the nutrient content is high; the polyglutamic acid and protein can be quickly absorbed and utilized by crops under the action of the functional bacteria, so that the fast-acting property is good; and the abundant nutrients are obtained from waste bacterium residues, a small amount of the bone meal and the polyglutamic acid are added to improve the nutrient content, and a high-cost chemical fertilizer is not needed to be added, so that the production cost is low.
Owner:潘峰
Efficient synthesis and extraction method for blueberry anthocyanin
ActiveCN104561223ARelease completelyEasy to synthesizeMicroorganism based processesFermentationUltrafiltrationFreeze-drying
The invention discloses a method for efficiently synthesising and extracting anthocyanin in blueberry, and specifically discloses a synthesis and extraction preparation technology for blueberry anthocyanin. The method comprises the following steps: culturing blueberry cells by high hydrostatic-pressure assisted microbial fermentation, and extracting blueberry anthocyanin by ultrafiltration chromatography; breaking the cell walls of blueberry fruits by virtue of a high hydrostatic-pressure assisted microbial metabolite to adequately release anthocyanin; adding producing enzymes of L-phenylalanine, rhodotorula glutinis and the like to promote synthesis for precursors which are not converted to anthocyanin in blueberry into anthocyanin simultaneously; subjecting the fermentation liquor to treatment of centrifuging, ultrafiltration separation, chromatographic purification, vacuum freeze-drying and the like to obtain anthocyanin with the purity of 99.31%, wherein the extraction amount of anthocyanin is increased by 15-30%. The method disclosed by the invention is simple to operate, clean and harmless in generation process, low in cost, high in anthocyanin yield, high in purity, without the need of human intestinal microbial degradation, high in medical treatment health value, suitable for large-scale production application, and extremely high in market prospect.
Owner:广东维思奇食品有限公司
Biological preservative for cherry and tomato fruits and use thereof
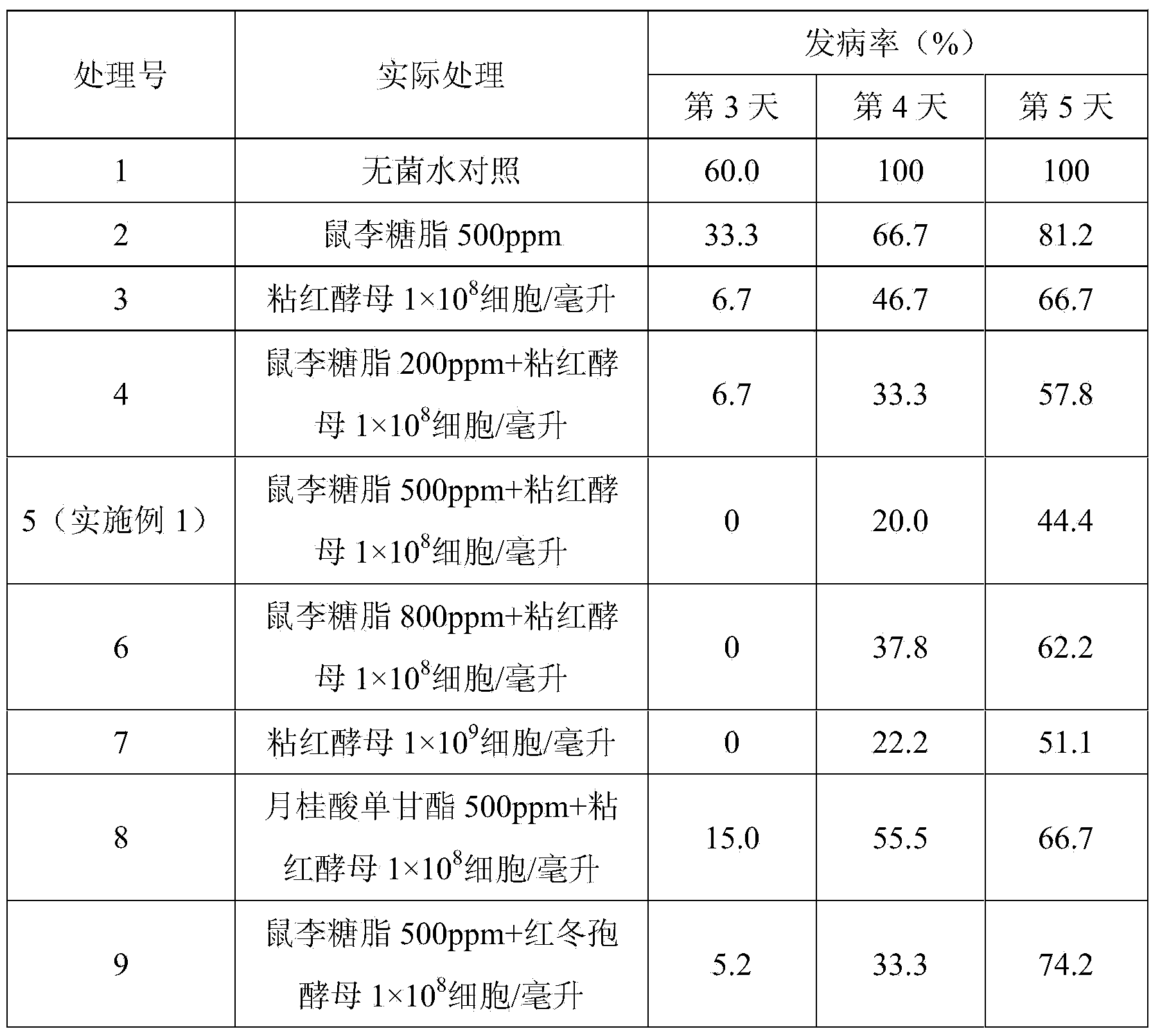
InactiveCN103766474AInhibitionInhibition of developmentFruit and vegetables preservationRhamnolipidPreservative
The invention discloses a biological preservative for cherry and tomato fruits and use thereof. Per L of biological preservative is prepared from 1*10<10>-1*10<12> rhodotorula glutinis cells, 400-600mg of rhamnolipid and the balance of water. The rhodotorula glutinis cells are rhodotorula glutinis (Rhodotorula glutinis) ZJU11; the preservation number is CGMCC NO.3589; the rhamnolipid is concentrated rhamnolipid of which the glycolipid content is 70-90%. By using the biological preservative for cherry and tomato fruits, not only can decaying of the cherry and tomato fruits be delayed, but also the quality of the cherry and tomato fruits can be ensured.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Water quality improver and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN107176626APromote decompositionImprove qualityTreatment using aerobic processesWater/sewage treatment by ion-exchangeDecompositionNormal growth
The invention discloses a water quality improver and a preparation method thereof. The water quality improver is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 30 to 40 parts of soybean, 40 to 50 parts of corn, 20 to 30 parts of composite biological enzyme, 15 to 25 parts of bacillus subtilis, 10 to 20 parts of enterococcus faecalis, 18 to 25 parts of photosynthetic bacteria, 10 to 18 parts of bacterium nitrobacter, 15 to 23 parts of oxygen producer, 17 to 23 parts of ion exchanger, 1 to 1.5 parts of wall-broken yeast powder, 22 to 30 parts of nano-silver, 11 to 15 parts of HA salt, 5 to 8 parts of microelement, 2 to 4 parts of vitamin, 5 to 10 parts of rhodotorula glutinis, and 33 to 45 parts of medical stone powder. The water quality improver provided by the invention is simple in preparation method, low in cost, and capable of reducing bottom mud organic matters of aquaculture water, thickening an aerobic layer, accelerating growth and reproduction of aerobes and decomposition of organic pollutants, and can provide micronutrient required for normal growth of aquatic products so as to improve the quality of the aquatic products.
Owner:NINGBO JUNCHUAN MUNICIPAL GARDEN ENG CO LTD
Plant growth regulator and production thereof
InactiveCN101406203AImprove disease resistanceImprove defenseBiocidePlant growth regulatorsSilicic acidRare earth
The invention relates to a plant growth regulator and a method for producing the same. The plant growth regulator is characterized by comprising raw materials according to the following weight ratio: 1 to 20 weight portions of copper sulfate, 1 to 50 weight portions of zinc sulfate, 1 to 30 weight portions of manganese sulfate, 1 to 40 weight portions of ferric sulfate, 1 to 25 weight portions of sodium molybdate, 0.1 to 1 weight portion of amino acid, 1 to 20 weight portions of nucleic acid protein, 0.001 to 0.002 weight portion of vitamin E, 2 to 6 weight portions of agricultural rare earth, 1 to 30 weight portions of silicic acid, 5 to 20 weight portions of sugar, and 1,000 to 2,000 weight portions of water, wherein each one hundred weight portions of the regulator contains 0.5 weight portion of potato polyphenol oxidase complex, 0.5 weight portion of rhodotorula glutinis L-phenylalanine ammonia-lyase complex, 0.5 weight portion of earthworm superoxide dismutase, 0.5 weight portion of seaweed bioactive substances, and 0.5 weight portion of anti-pest composite.
Owner:刘国辉
Microbial viable bacteria combination and preparation method thereof
the invention discloses microbe viable bacteria combined agent and preparing method, which consists of Bacillus subtilis and Rhodotorula glutinis, wherein the Bacillus subtilis is seeded firstly and then Rhodotorula glutinis, which need 15-100 h as combined culturing time.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE SCIENCES
Method for culturing synthetic bacteria in rapid growth and acid production and obtained synthetic bacteria
The invention discloses a method for culturing synthetic bacteria in rapid growth and acid production and obtained synthetic bacteria. Original strains mainly comprise Acidiphilium cryptum, Candida rugose, Acetobacter diazotrophicus, Rhodotorula glutinis and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Pyrrhotite powder is added into a culture medium, strain inoculation quantity ranges from 5.0*10<6> / liter to 8.0*10<6> / liter, and aeration culture is performed. By the method, efficient acid production mixed bacteria can be rapidly and substantially cultured, and the pH (potential of hydrogen) of solution is reduced to be around 2.0. The bacteria are applied to rapid leaching treatment for heavy metal contaminated soil and wide in prospect.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV +1
Rhodotorula glutinis phenylalanine deaminase gene and application thereof
InactiveCN104131017AIncrease enzyme activityImprove stabilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesRhodotorula speciesPhenylalanine
The invention discloses a rhodotorula glutinis phenylalanine deaminase gene and an application thereof, and belongs to the field of biotechnology. Cloning of the phenylalanine deaminase gene plays an important role in biosynthesis of L-phenylalanine by an enzyme method. The phenylalanine deaminase gene is obtained by extracting rhodotorula glutinis RNA and carrying out reverse transcription to obtain the full-length phenylalanine deaminase gene, wherein the full length of the gene is 2121 bp, and 705 amino acids are encoded. Phenylalanine deaminase gene resources are further expanded, and a scientific basis is provided for molecular modification of phenylalanine deaminase and improvement of the stability and catalytic activity of enzymes.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Microbial preparation for urban garbage percolate treatment and application thereof
Provided is a microbial preparation for urban garbage percolate treatment and an application thereof. The invention relates to a microbial preparation for urban sewage treatment and an application thereof. Viable bacteria in the microbial preparation comprise euryhaline bacteria bacillus cereus, Bacillus marisflavi, rhodopuesdomonas pulstris and rhodopseudomonas acidophila, Nitrosomonas europaea, marine pseudomonas and paracoccus denitrificans and yeast rhodotorula glutinis. The invention further provides a production method of the microbial preparation. According to the microbial preparation, the effect on treating garbage percolate is obvious, operation is convenient, and the microbial preparation has better application and promotion value.
Owner:NINGBO BLUE ENVIRONMENT SCI & TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com