Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
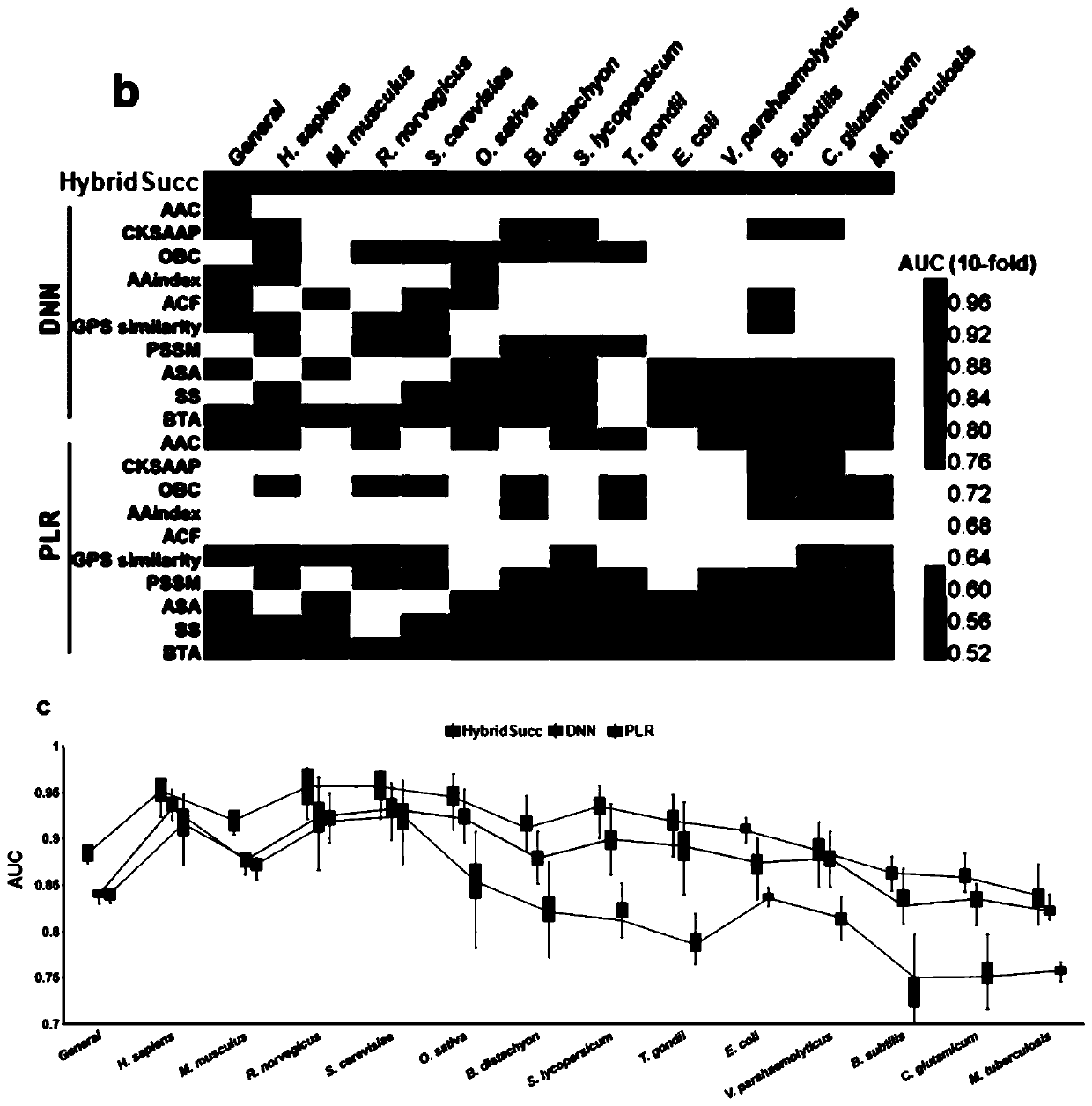
152 results about "Protein translation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Protein translation is the process by which a protein is created from a ribonucleic acid (RNA) template code. The strand of RNA, which contains the order for the protein’s amino acid sequence, binds to a special cellular organelle called a ribosome.
Kit for in vitro synthesis of protein and preparation method
ActiveCN106978349ALow costEasy to operateMicroorganism lysisMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyFreeze-drying
The invention provides a preparation method of a yeast cell extracting solution, the yeast cell extracting solution and a method for synthesizing protein in an in vitro system by virtue of the yeast cell extracting solution, as well as a kit containing the yeast cell extracting solution. The kit, which is more convenient than a conventional method, is applicable to protein synthesis in the in vitro system; transformation, culture and crushing can be prevented; a great amount of using time and cost can be saved; various types of proteins can be expressed, and influence of protein toxicity can be prevented; and a plurality of protein complexes can be expressed, without the use of a high temperature at 37 DEG C. In addition, as a raw material adopted by the invention, yeast cell is simple to cultivate, convenient to operate, rapid to propagate and relatively low in cost; a prepared yeast extract has a capacity of modifying translated protein, the yeast extract is suitable for large-scale preparation and has an advantage of industrial production; and the yeast cell extract, which is prepared into freeze-dried powder by virtue of a vacuum freeze-drying method and is preserved at low temperature or high temperature, is convenient to transport.
Owner:KANGMA SHANGHAI BIOTECH LTD
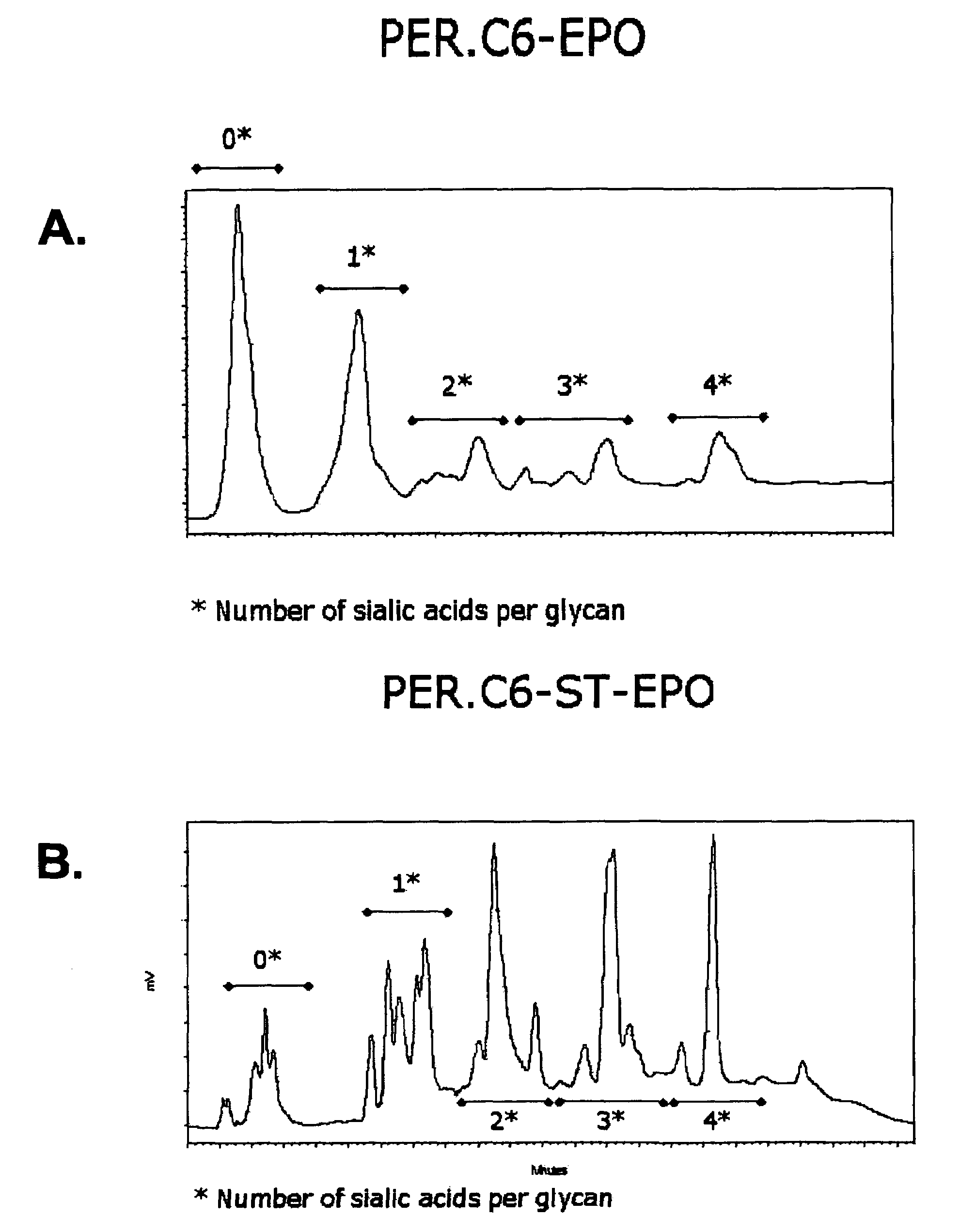
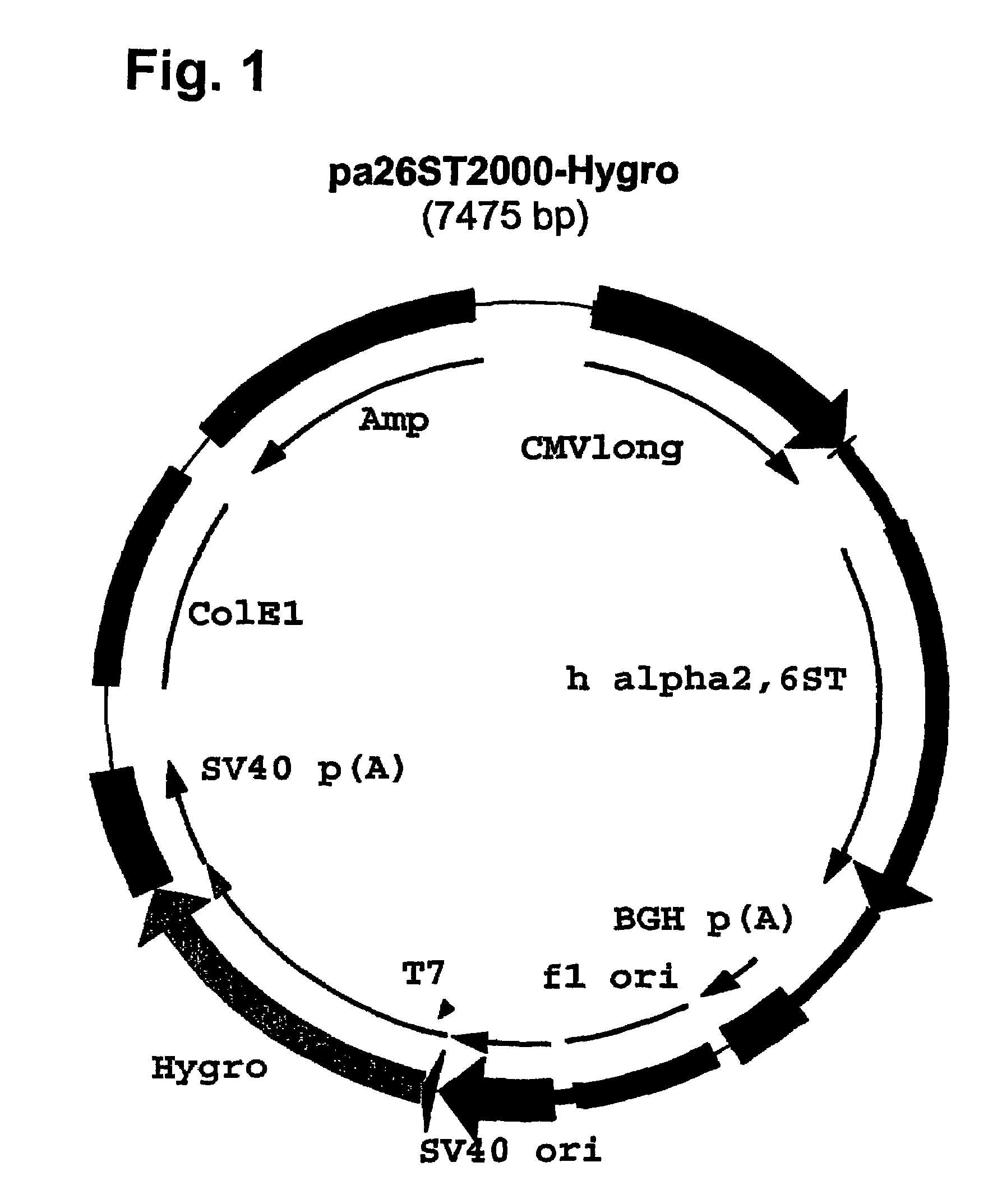
Compositions of erythropoietin isoforms comprising Lewis-X structures and high sialic acid content
InactiveUS7297680B2Improve system reliabilitySimplifies isolationOrganic active ingredientsVirusesHeterologousE1A Protein
Disclosed are immortalized human embryonic retina cells, having a nucleic acid sequence encoding an adenoviral E1A protein integrated into the genome of the cells, and further comprising a nucleic acid sequence encoding an enzyme involved in post-translational modification of proteins, such as a sialyltransferase, wherein said nucleic acid sequence encoding the enzyme involved in post-translational modification of proteins is under control of a heterologous promoter. Methods for producing recombinant proteins from such cells and obtaining such recombinant proteins having increased sialylation are provided as are novel compositions of isoforms of erythropoietin.
Owner:JANSSEN VACCINES & PREVENTION BV
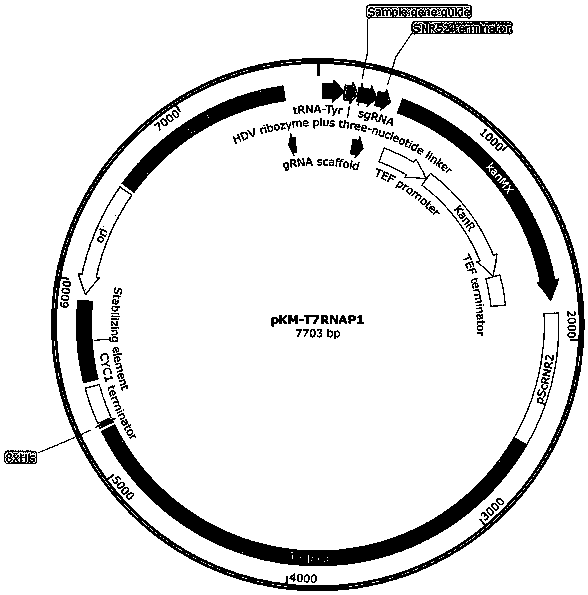
Nucleic acid construct for endogenously expressing RNA polymerase in cells
The invention provides a nucleic acid construct for endogenously expressing RNA polymerase in cells, and particularly discovers a novel nucleic acid construct capable of greatly enhancing protein translation efficiency. The nucleic acid construct consists of a promoter with specific promotion intensity (such as RNR2, ADH1, GAPDH, TEF1, PGK1 and SED1) and coding sequences of proteins of RNAP (suchas T7RNAP, T3RNAP, T4RNAP and T5RNAP), if the nucleic acid construct of the invention is applied into a yeast extracorporeal protein synthesis system, the activity of synthesized luciferase is quite high relative to light unit value (RLU), and the effect can be the same as the effect of T7RNAP added exogenously. The effect can reach up to 6.6* 107.
Owner:KANGMA SHANGHAI BIOTECH LTD
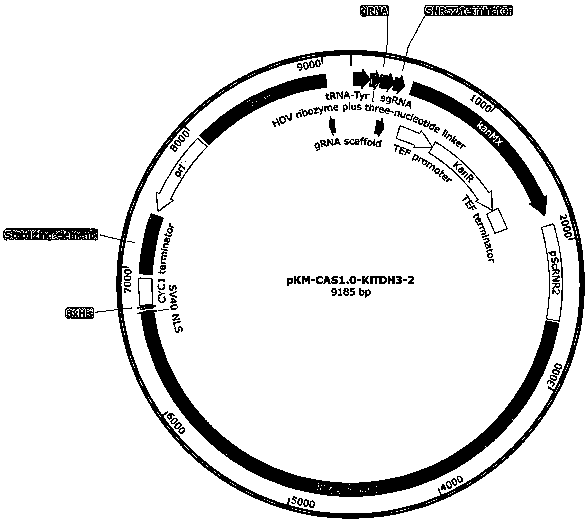
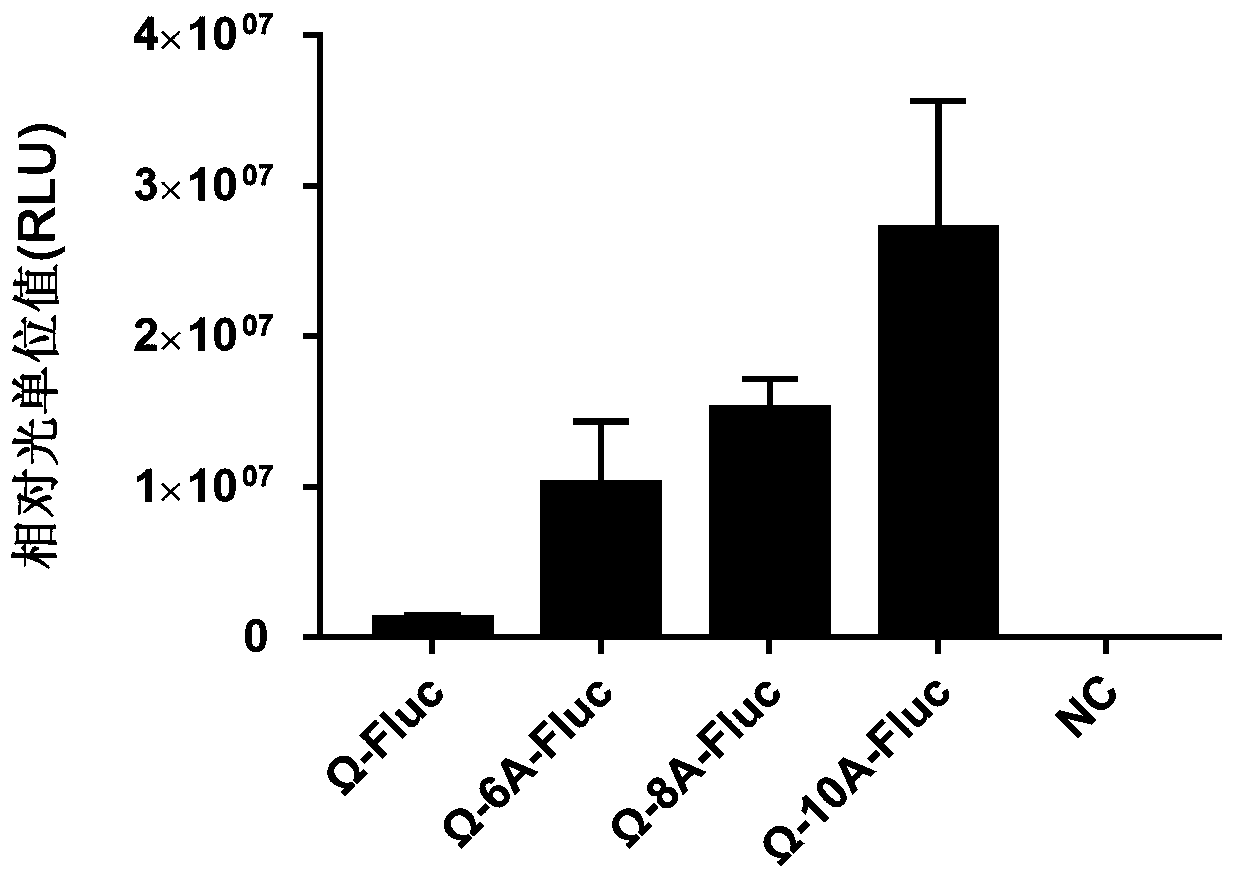
DNA element for high-throughput in vitro protein synthesis
The invention provides a DNA element for high-throughput in vitro protein synthesis, and specifically discloses a novel DNA element capable of greatly enhancing protein translation efficiency. According to the present invention, with the application of the DNA element in a yeast in-vitro protein synthesis system, the relative light unit value of the activity of the synthesized luciferase is enhanced by about 22.3 times compared to the DNA element containing only the omega sequence.
Owner:KANGMA SHANGHAI BIOTECH LTD
Preparation of fusion protein in deficiency of different structural domains and application of fusion protein to improvement of protein synthesis
The invention provides preparation of an eIF4G and Pab1 fusion protein in deficiency of different structural domains and application of the fusion protein to improvement of protein synthesis. Particularly, the fusion protein in deficiency of different structural domains is capable of changing in-vitro protein translation efficiency, wherein RNA1 and / or PABP structural domain deficiency of an eIF4Gelement can remarkably improve protein expression. In addition, the invention provides a preparation method of the infusion protein and a corresponding in-vitro protein synthesis system and method.
Owner:KANGMA SHANGHAI BIOTECH LTD
Protein synthesis system for increasing expression amount of foreign protein and application method of protein synthesis system
The invention provides a protein synthesis system for increasing the expression amount of a foreign protein and an application method of the protein synthesis system. Specifically, a poly-nucleotide sequence or vector constructed by a strong promoter sequence is inserted in front of a nucleotide sequence for encoding an eIF4E binding protein, over-expression of eIF4E binding proteins such as Eap1and p20 can be achieved, and foreign protein synthesis is implemented by using the improved cell lysis buffer. The invention provides the protein synthesis system for increasing the expression amountof the foreign protein, and by adopting the synthesis system provided by the invention, the efficiency of protein translation can be remarkably improved.
Owner:KANGMA SHANGHAI BIOTECH LTD
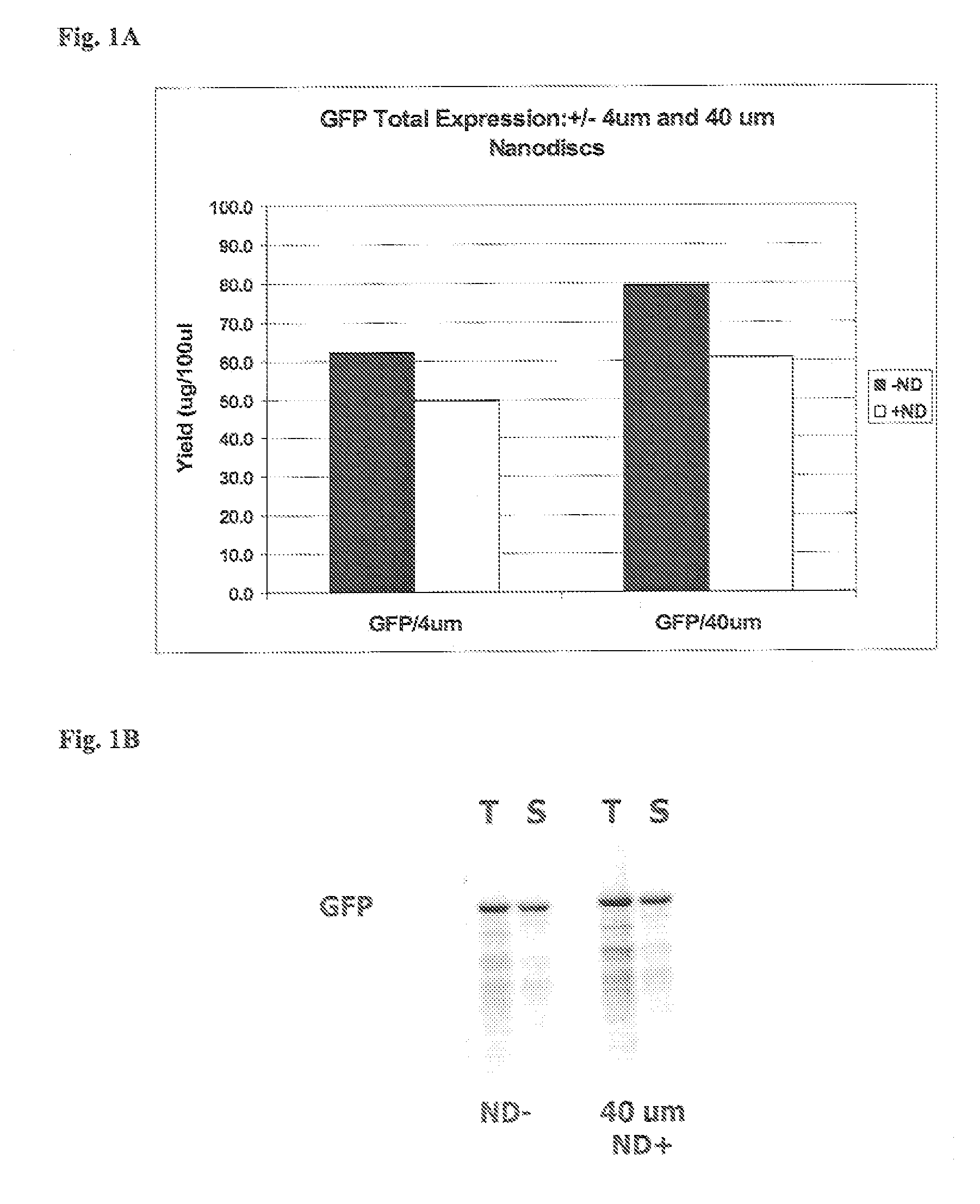
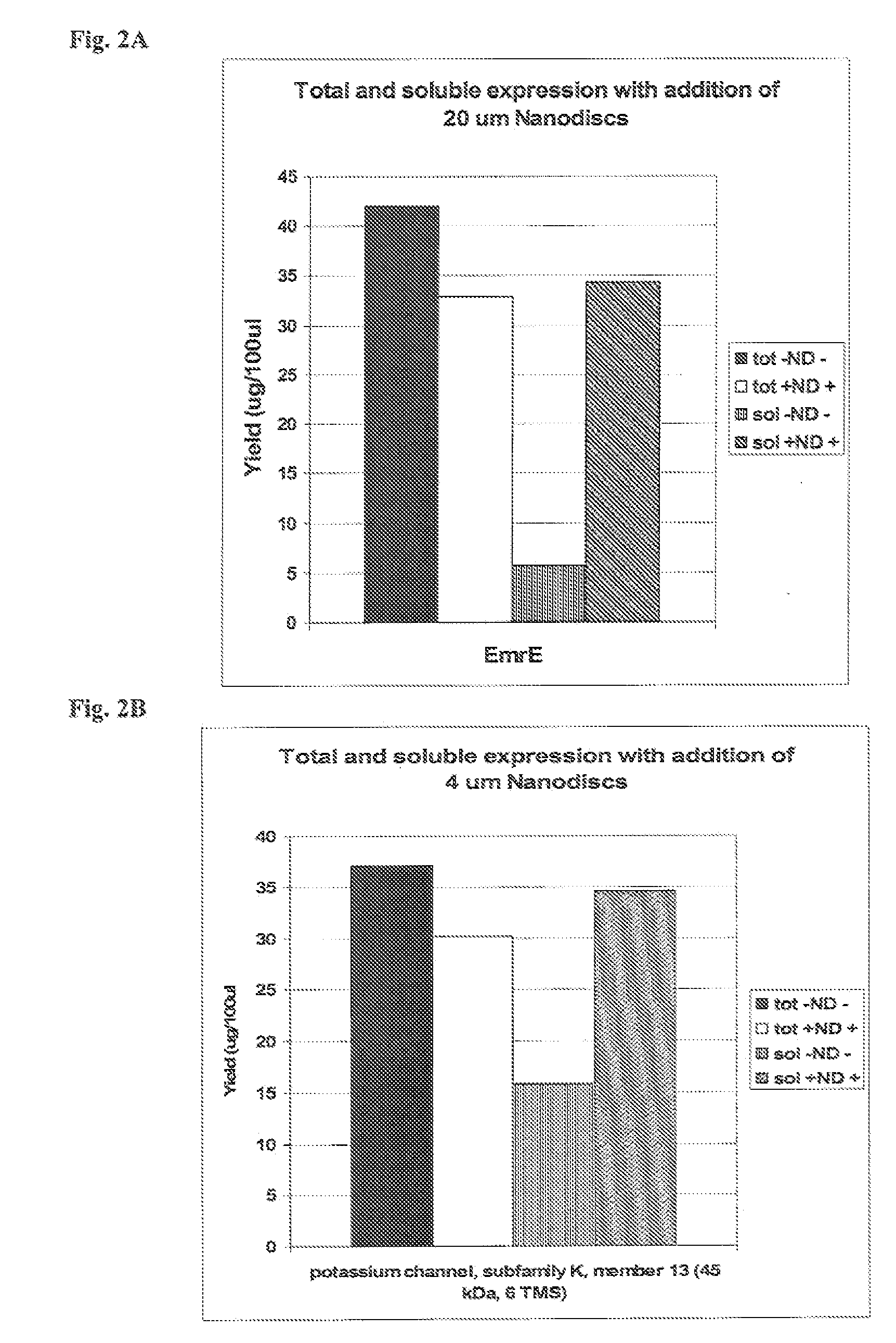
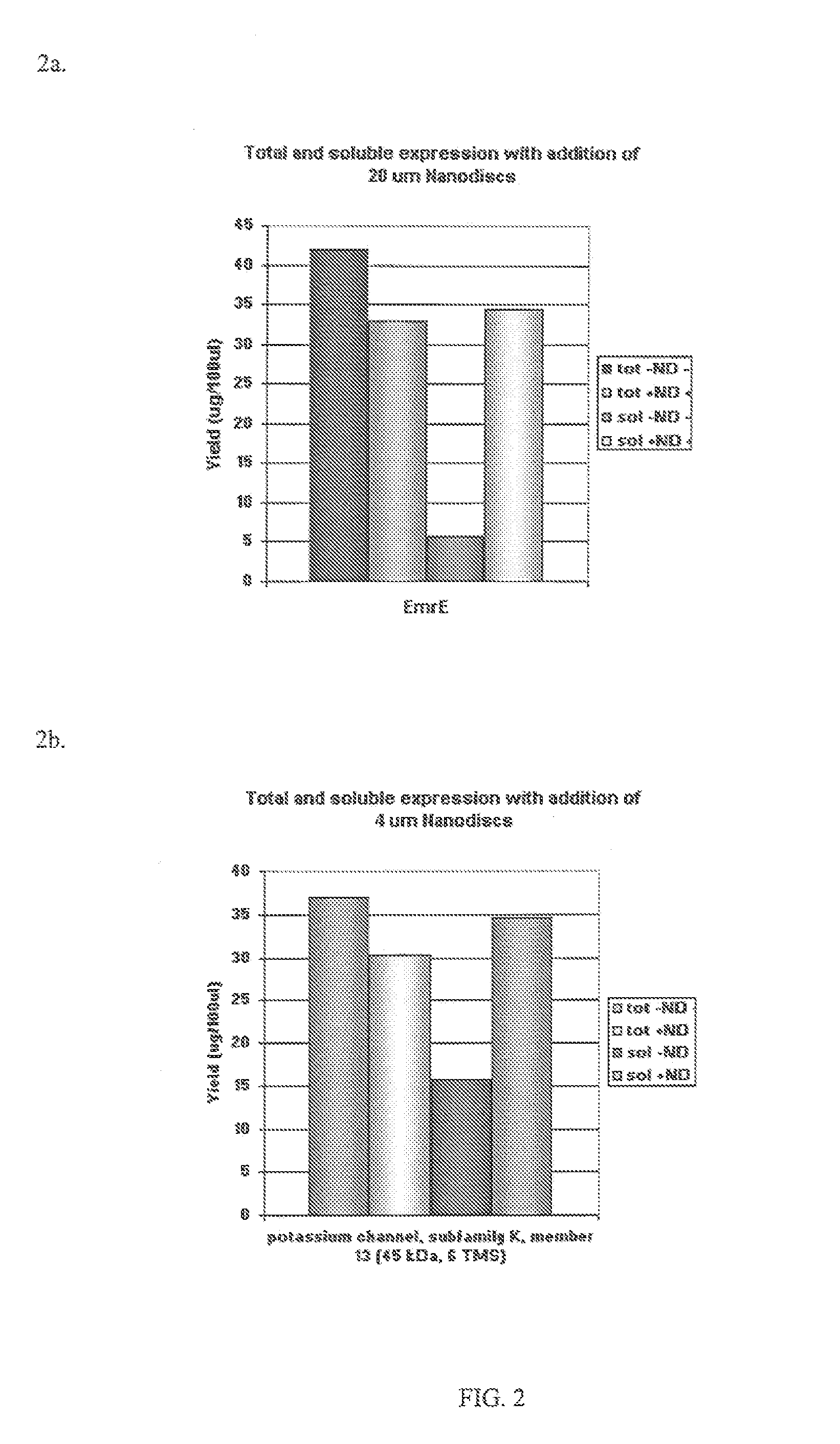
In vitro protein synthesis systems for membrane proteins that include adolipoproteins and phospholipid-adolipoprotein particles
In vitro protein synthesis systems and methods are provided that produce membrane proteins in soluble form. In some aspects, the invention provides methods of synthesizing proteins using in vitro protein synthesis systems that include an apolipoprotein, in which higher yields of soluble protein are produced than in the absence of the apolipoprotein. Apolipoproteins useful in the present invention include naturally occurring apolipoproteins, as well as sequence variants of wild-type apolipoproteins, and engineered apolipoproteins. The apolipoproteins can be provided in an in vitro protein synthesis system associated with lipid or not associated with lipid. The invention also provides compositions and kits for synthesis of proteins in soluble form, in which the compositions and kits include cell extracts for protein translation and at least one apolipoprotein biomolecule.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
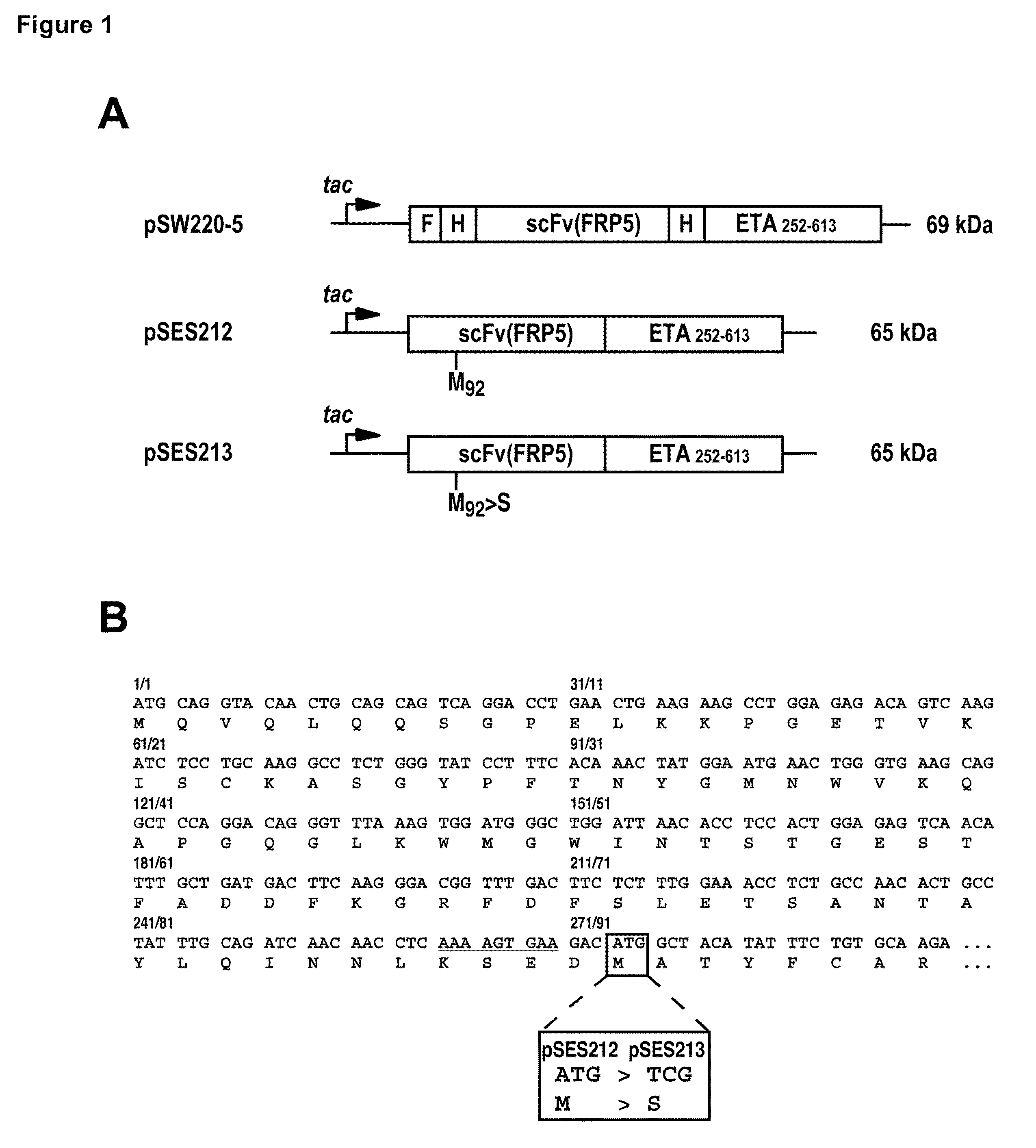
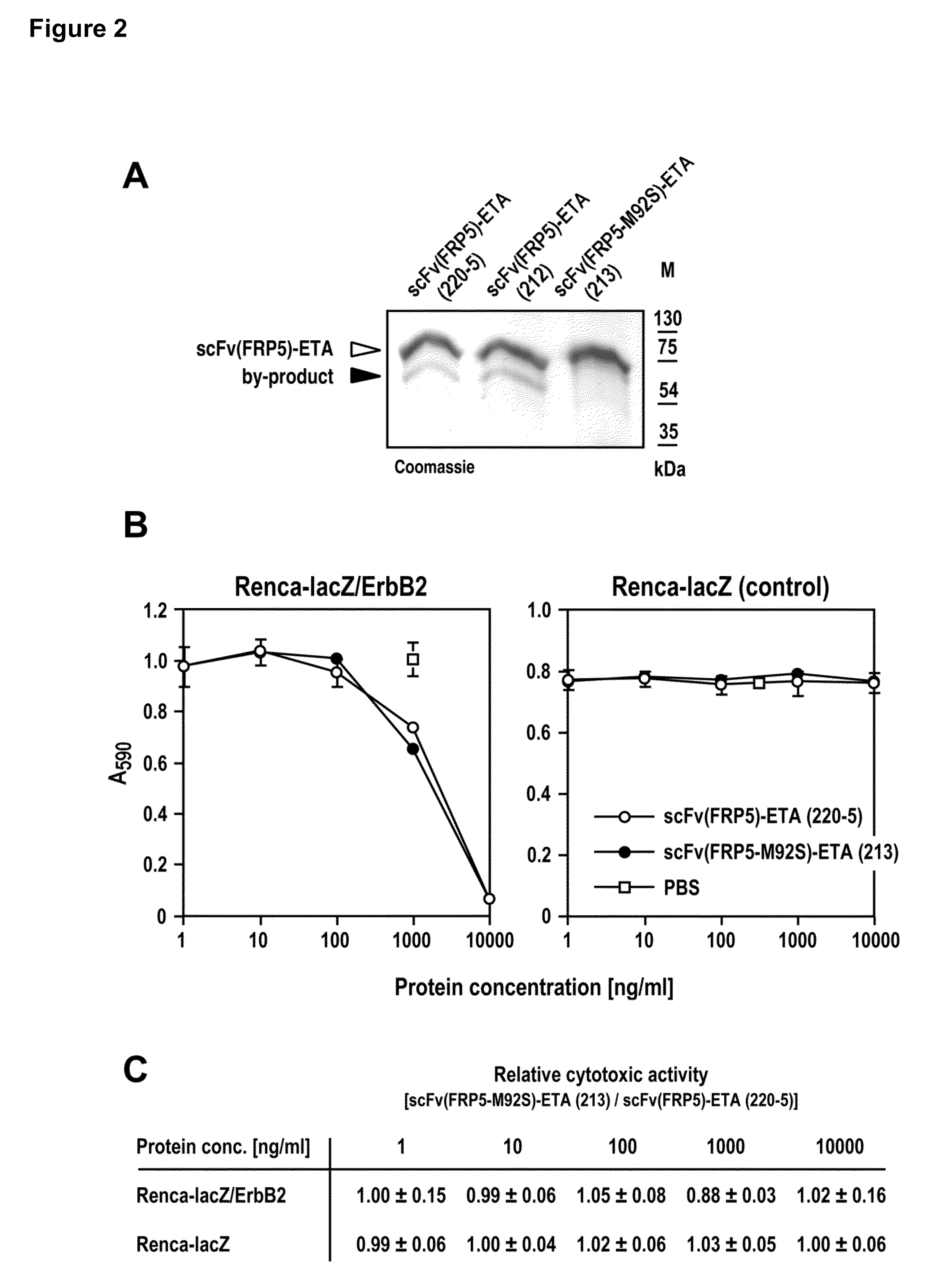
Optimized DNA and protein sequence of an antibody to improve quality and yield of bacterially expressed antibody fusion proteins
ActiveUS7887801B2Easy to produceHigh purityOrganic active ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsAntibody fragmentsDNA
Object matter of the invention is an optimized DNA sequence encoding the scFv(FRP5) antibody fragment. This novel sequence prevents the generation of the undesired by-product in the context of an scFv(FRP5)-ETA fusion protein, and possibly also other bacterially expressed scFv(FRP5)-containing fusion proteins. The DNA sequence of the scFv(FRP5) domain of scFv(FRP5)-ETA was modified by exchanging a distinct codon, thereby preventing an otherwise possible internal start of protein translation.
Owner:CHEMOTHERAPEUTISCHES FORSCHUNGINSTITUT GEORG SPEYER HAUS
In Vitro Protein Synthesis Systems for Membrane Proteins that Include Adolipoproteins and Phospholipid Adolipoprotein Particles
In vitro protein synthesis systems and methods are provided that produce membrane proteins in soluble form. In some aspects, the invention provides methods of synthesizing proteins using in vitro protein synthesis systems that include an apolipoprotein, in which higher yields of soluble protein are produced than in the absence of the apolipoprotein. Apolipoproteins useful in the present invention include naturally occurring apolipoproteins, as well as sequence variants of wild-type apolipoproteins, and engineered apolipoproteins. The apolipoproteins can be provided in an in vitro protein synthesis system associated with lipid or not associated with lipid. The invention also provides compositions and kits for synthesis of proteins in soluble form, in which the compositions and kits include cell extracts for protein translation and at least one apolipoprotein biomolecule.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Discovery method for protein post-translational modification
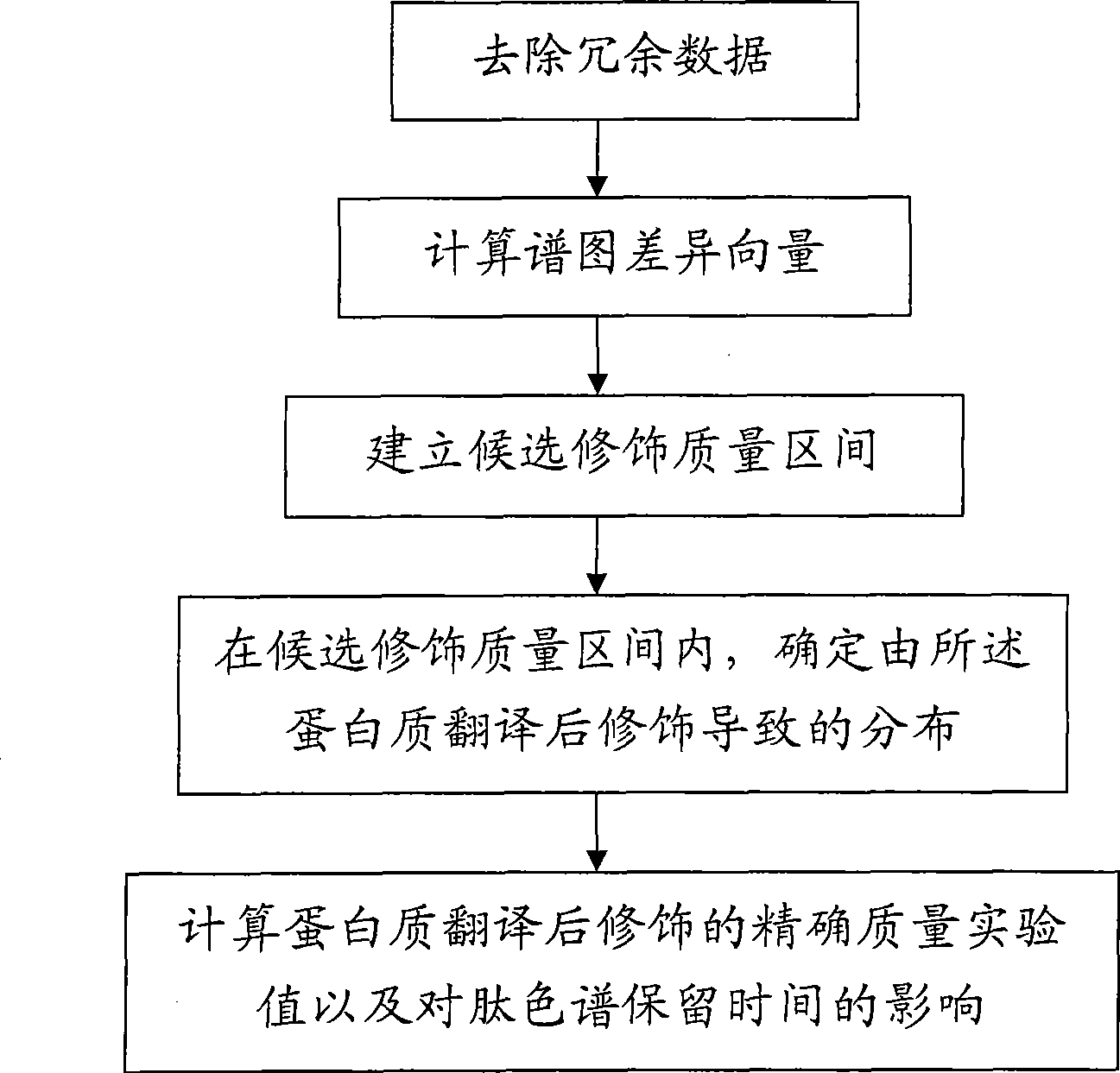
ActiveCN101477089ACalculation speedImprove accuracyComponent separationBiological testingProtein insertionRetention time
The invention provides a detecting method of post-translational protein modification. The method comprises the following steps: calculating spectrogram difference vectors among all spectrograms by means of peptide chromatogram retaining time and peptide quality in experimental tandem mass spectrum data of protein samples; establishing candidate modification mass intervals probably containing modification mass; estimating mixed distribution of the spectrogram difference vectors on each candidate modification mass interval, and calculating the standard deviation of each distribution inside the mixed distribution so as to determine distributions inside the candidate modification mass intervals caused by post-translational protein modification according to the standard deviation; calculating the average value of the distributions caused by post-translational protein modification; obtaining an accurate mass experimental value of the post-translational protein modification according to the mass component of the average value; and obtaining the influence of post-translational protein modification on peptide chromatogram retaining time according to the retaining time component of the average value. The detecting method has the advantages of high efficiency, accuracy and robustness.
Owner:INST OF COMPUTING TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Cyclic RNA and protein production method
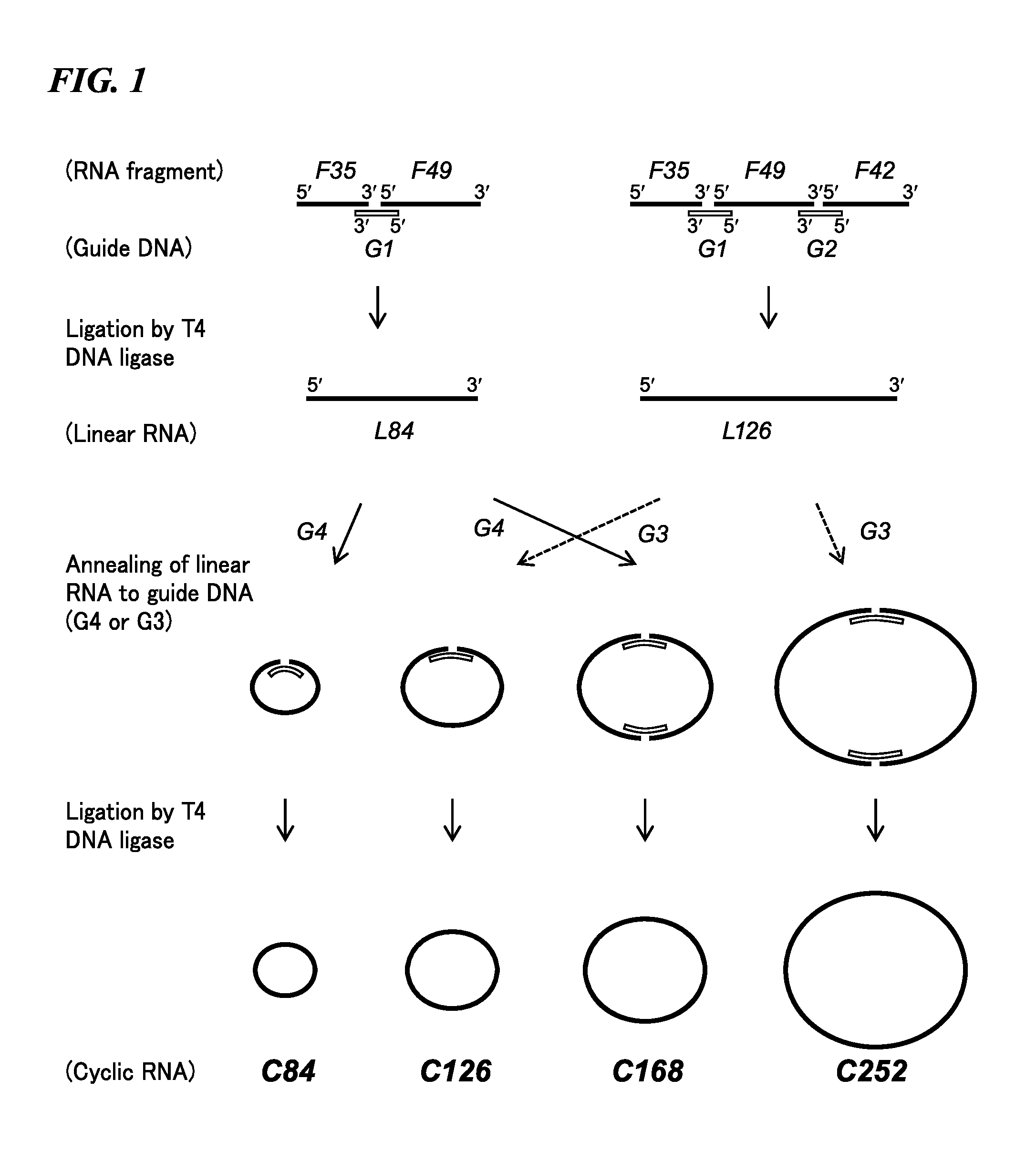
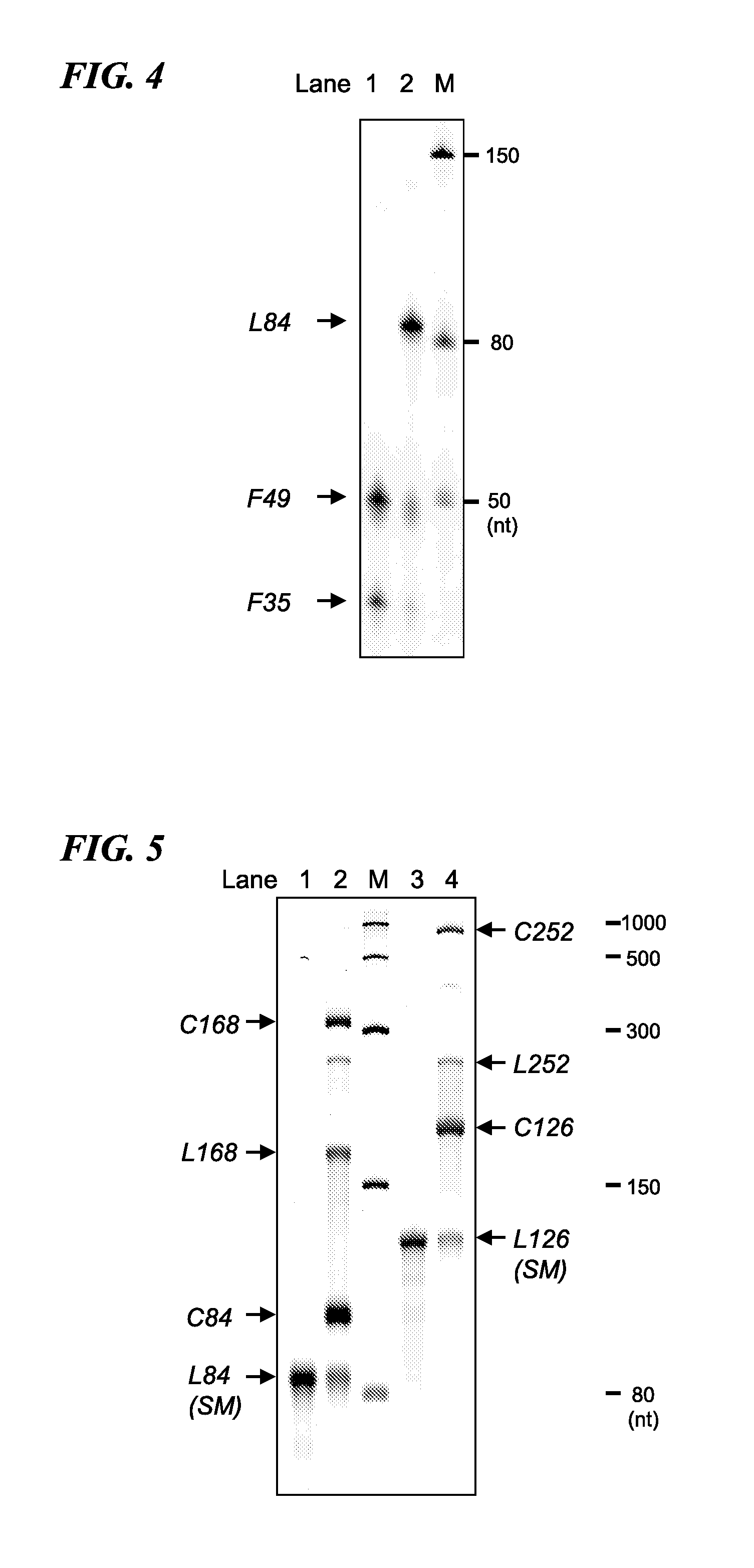
The present invention provides a cyclic RNA preferable for carrying out rotary protein translation in which translation domains other than that of the target protein are sufficiently short and translation efficiency is high, and a method for producing protein that uses this cyclic RNA as template. More specifically, the present invention provides a cyclic RNA that encodes a protein, has a full-length number of bases that is equal to or greater than 102 and is a multiple of 3, has at least one start codon, does not have a stop codon in the same reading frame as the start codon, and does not contain an internal ribosome entry site (IRES). In addition, the present invention provides a method for producing protein in a eukaryotic cell expression system that consists of using the aforementioned cyclic RNA as template and expressing a protein encoded by that cyclic RNA.
Owner:RIKEN
Small RNA numerator for differentiation of mesenchyma stem cell into hematopoiesis cell and function target point thereof
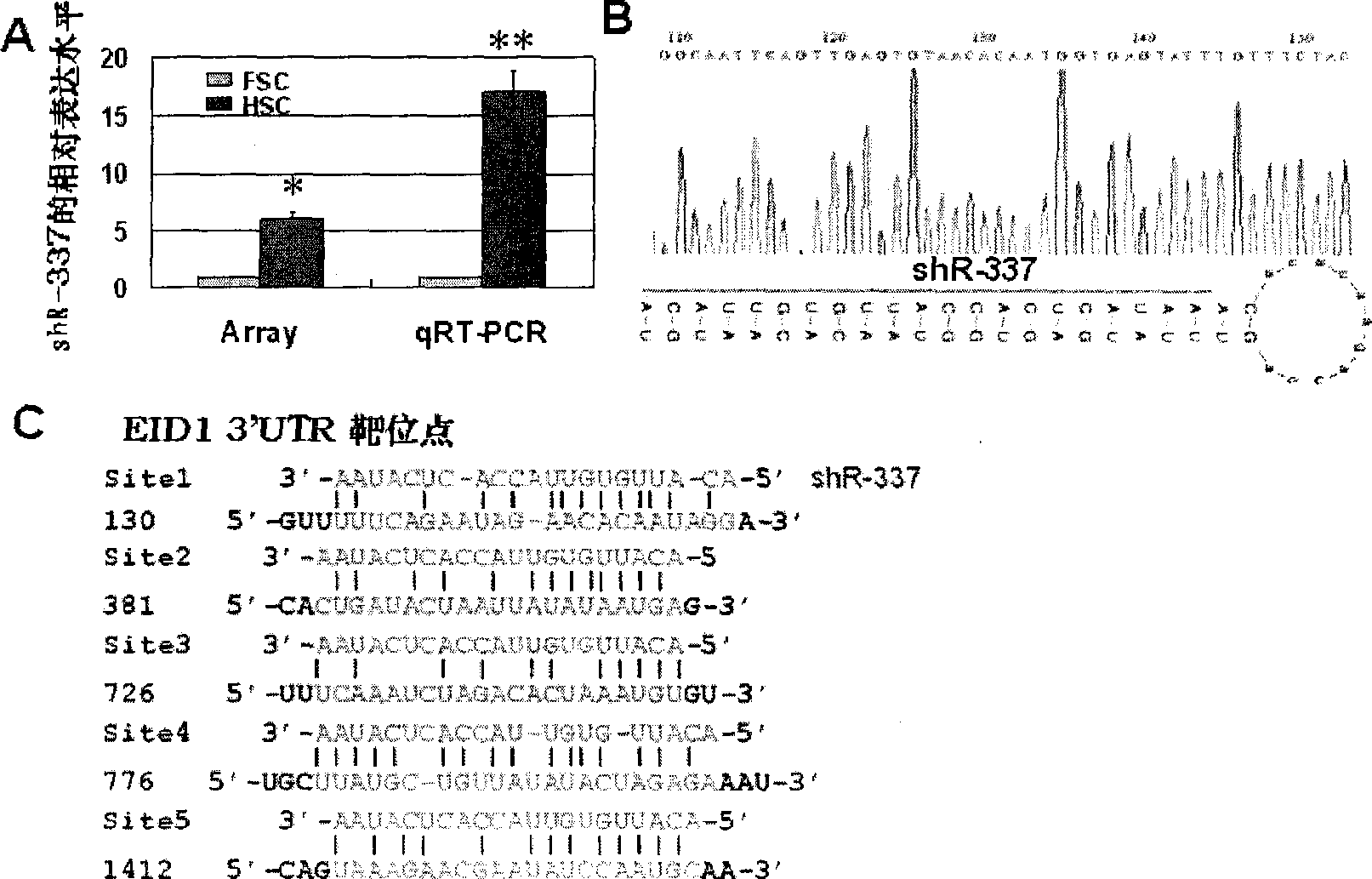
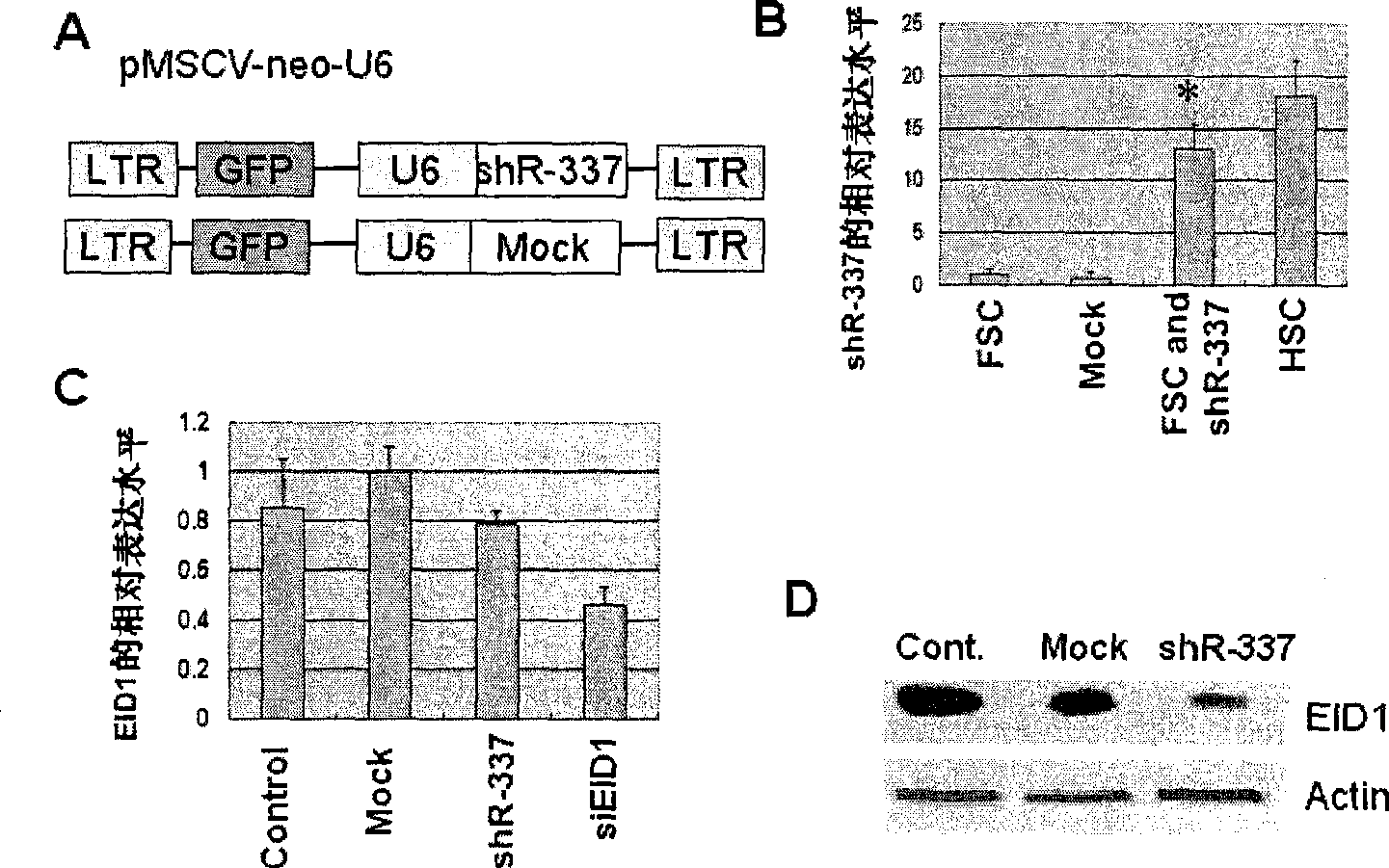
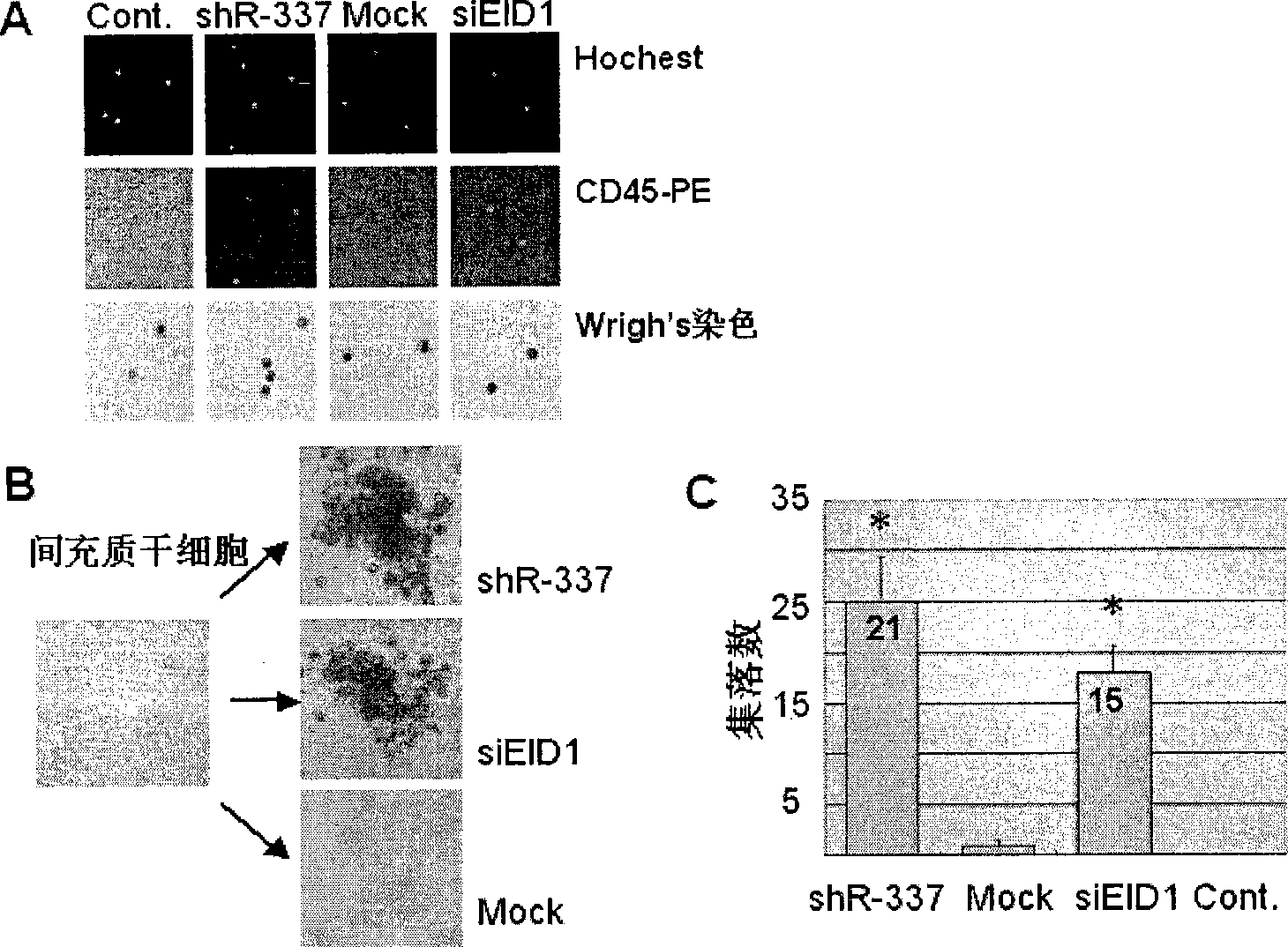
The invention provides small RNA (shR337) capable of differentiating hematopoietic stem cells (MSC) from human nonhematopoietic stem cells (HSC) such as mesenchymal stem cells (MSC). The discovery of the small RNA also provides an action target capable of differentiating the hematopoietic stem cells from the human nonhematopoietic stem cells such as the bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. The small RNA can restrict the protein translation of EIDI genes after being transfected to human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells to transform the human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into hematopoietic stem cells with CD45<+>surface antigen positive, and the hematopoietic stem cells with CD45<+>surface antigen positive can be further differentiated into myeloid cells and lymphoid cells. Mice in vivo experiments show that the differentiation of the small RNA to the mesenchymal stem cells is directional and undivided.
Owner:INSITUTE OF BIOPHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCIENCES
Assays and Devices For Identifying Pathogens
InactiveUS20110201013A1Avoiding complex reaction conditionEasy to manufactureMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysisBiologyRibosome
Provided are methods and devices for identifying pathogens based on protein translation from ribosomes isolated from the pathogens.
Owner:INVERNESS SWITZERLAND GMBH
Method for monitoring early treatment response
InactiveUS20060177378A1Early treatment responseMonitor early treatment responseCompounds screening/testingNMR/MRI constrast preparationsCell membranePositive response
Disclosed is a method for monitoring early treatment response of a cancer treatment comprising measuring by magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS), for example, proton MRS, the amount of Choline present in the tissue adjoining or surrounding the cancerous tissue before and after treatment; the treatment comprises administration of an angiogenesis inhibitor, for example, a VEGF inhibitor, whereby a decrease in the amount of Choline after treatment is indicative of a positive response. The decrease in the amount of Choline represents the decrease in the internal cell membrane as a result of down regulation of the organelles and their secretory granules and their transport vesicles. Disclosed also is a method for determining effectiveness of an angiogenesis inhibitor in the treatment of cancer. Also disclosed are methods of monitoring early treatment response in diseases where an angiogenesis effector, i.e., an inhibitor or promoter of angiogenesis, is employed. Also disclosed is a method for monitoring protein translation related to angiogenesis.
Owner:RECEPTOMON LLC
Method for analyzing data of prokaryotic proteogenomics rapidly and automatically
ActiveCN105956416AIncrease Identification CoverageImprove compatibilityProteomicsGenomicsDatabase fileMass spectrometric
The invention provides a method for analyzing data of prokaryotic proteogenomics rapidly and automatically. Users only need to provide mass spectral data and a corresponding database file and set a simple retrieval parameter; retrieval of data of proteogenomics can be completed; simultaneously, a user defined data retrieval result can also be compatible; therefore, the identification coverage rate of the data of proteogenomics is increased; in the method disclosed by the invention, library search engines of different algorithms are integrated in advance; disadvantages of a single retrieval method are made up; a user defined library search result can also be compatible; the method has good compatibility; the peptide fragment identification coverage rate is increased to the most extent; in the method disclosed by the invention, functional annotation of new genes is automatically completed; large-scale identification of protein post-translational modification and analysis of non-labelled quantitative proteomics are realized for the first time; and automatic and rapid deep analysis of the data of proteogenomics is really realized.
Owner:湖北普罗金科技有限公司
Ribosomes with tethered subunits
An engineered ribosome that includes a tethered subunit arrangement is disclosed, in which the engineered ribosome supports translation of a sequence defined polymer. Methods for making and using the engineered ribosome are also disclosed, including a method for preparing a sequence defined polymer using the engineered ribosome and a method for preparing a sequence defined polymer using the engineered ribosome in a two-protein translation system. The engineered ribosomes may be utilized in methods for incorporating unnatural amino acids into a sequence defined polymer. Also disclosed are optimized polynucleotide sequences for use as tethers and Shine-Dalgarno / anti-Shine-Dalgarno sequences.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV +1
Applications of ZrO2 in the process for concentrating and purifying phosphorylated peptides
InactiveCN101284864ALarge specific surface areaHigh selectivityPeptide preparation methodsPhosphopeptidePhosphorylation site
The invention relates to the enrichment and purification of phosphopeptide in phosphoproteome, in particular to the application of ZrO2 in the enrichment and purification of phosphopeptide. ZrO2 nano material shows high specificity, selectivity, binding capacity and sensitivity at a phosphopeptide section; meanwhile, the affinity of the ZrO2 nano material to the specificity of phosphopeptide ensures that the material can be used in phosphoproteome during protein post-translational modification. Due to the specificity combination of ZrO2 with the phosphopeptide section in complex proteolysis sample, large-scale identification of phosphorylated protein and determination of phosphorylation sites can be realized through combining with MALDI-TOF MS and nano-LC MS / MS.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Dietary compositions containing alpha amino n-butyrate and methods of enhancing lean body mass
InactiveUS20080242727A1Increase synthesisDecrease protein catabolismBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseAlpha-Amino-N-Butyric Acid
A composition that may include branched chain amino acids, alpha amino n-Butyrate and / or alpha amino-n-valerate works synergistically to enhance lean body mass and prevent body mass breakdown. The composition may also be coupled with other agents to a) provide an increased level of amino acids and / or protein in the body's total pool or b) increase markers for protein translation or decrease markers of protein turnover. The composition may be administered in a variety of ways including capsules, tablets, powdered beverages, bars, gels or drinks. Increasing lean body mass is import to athletes looking to enhance performance, in the event of certain muscle wasting diseases, and to the general population that loses muscle mass as it ages.
Owner:ROMERO TIM +1
Replicative HBV (Hepatitis B Virus) vector carrying foreign gene and recombinant HBV generated after transfection and corresponding preparation method and application
ActiveCN103173492AGuaranteed high level of replicationPreserve the ability to reinfectMicroorganism based processesViruses/bacteriophagesHepatitis B virusVirus strain
The invention discloses a replicative HBV (Hepatitis B Virus) vector carrying a foreign gene and a recombinant HBV generated after transfection and a corresponding preparation method and an application. The vector separates overlaying genes C and P on an HBV genome by a molecular cloning technique based on originally expressed HBV plasmid to respectively form an integral opened reading frame where a protein translation starting sequence or a protease enzyme cutting site is inserted to respectively guide expression of foreign gene and gene P. The replicative HBV vector carrying the foreign gene transiently transfecting hepatoma carcinoma cell secretes the recombinant HBV. The recombinant HBV prepared from the HBV vector transfection cells provided by the invention can express the foreign gene and maintain the replicative and infecting capacity. The invention is suitable for constructing an HBV chronic infection animal model, an HBV cell model with cccDNA stably and automatically replicated and a traceable HBV strain, researching a molecular mechanism of HBV infection, replication, packaging and the like, and screening anti-HBV novel medicines.
Owner:BEIQIUEN INT PEACE HOSPITAL P L A
Method for Monitoring Early Treatment Response
InactiveUS20070218006A1Monitor early treatment responseMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesMagnetic measurementsCell membranePositive response
Owner:RECEPTOMON LLC
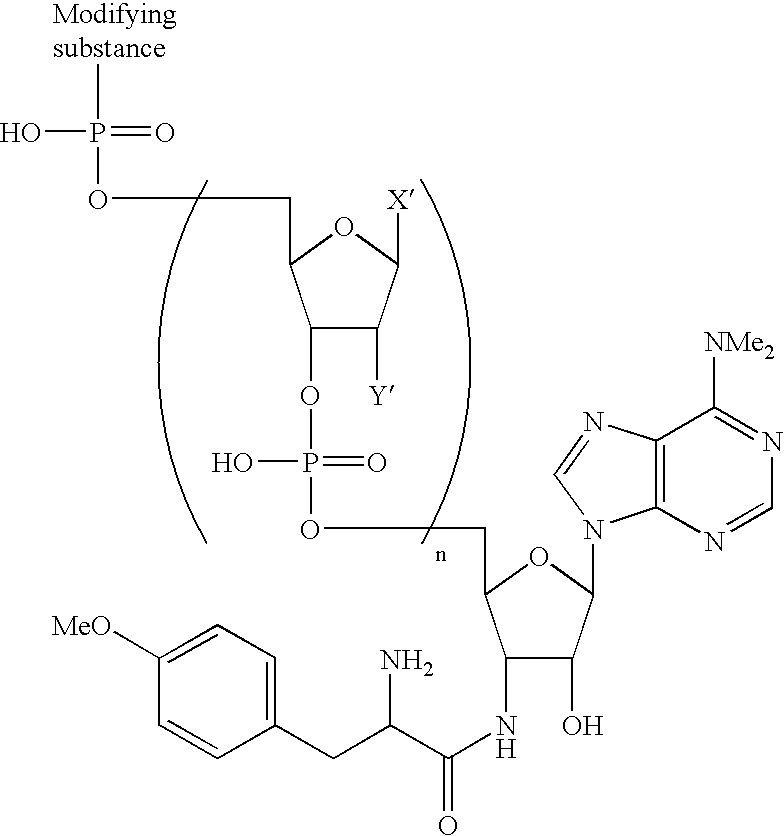
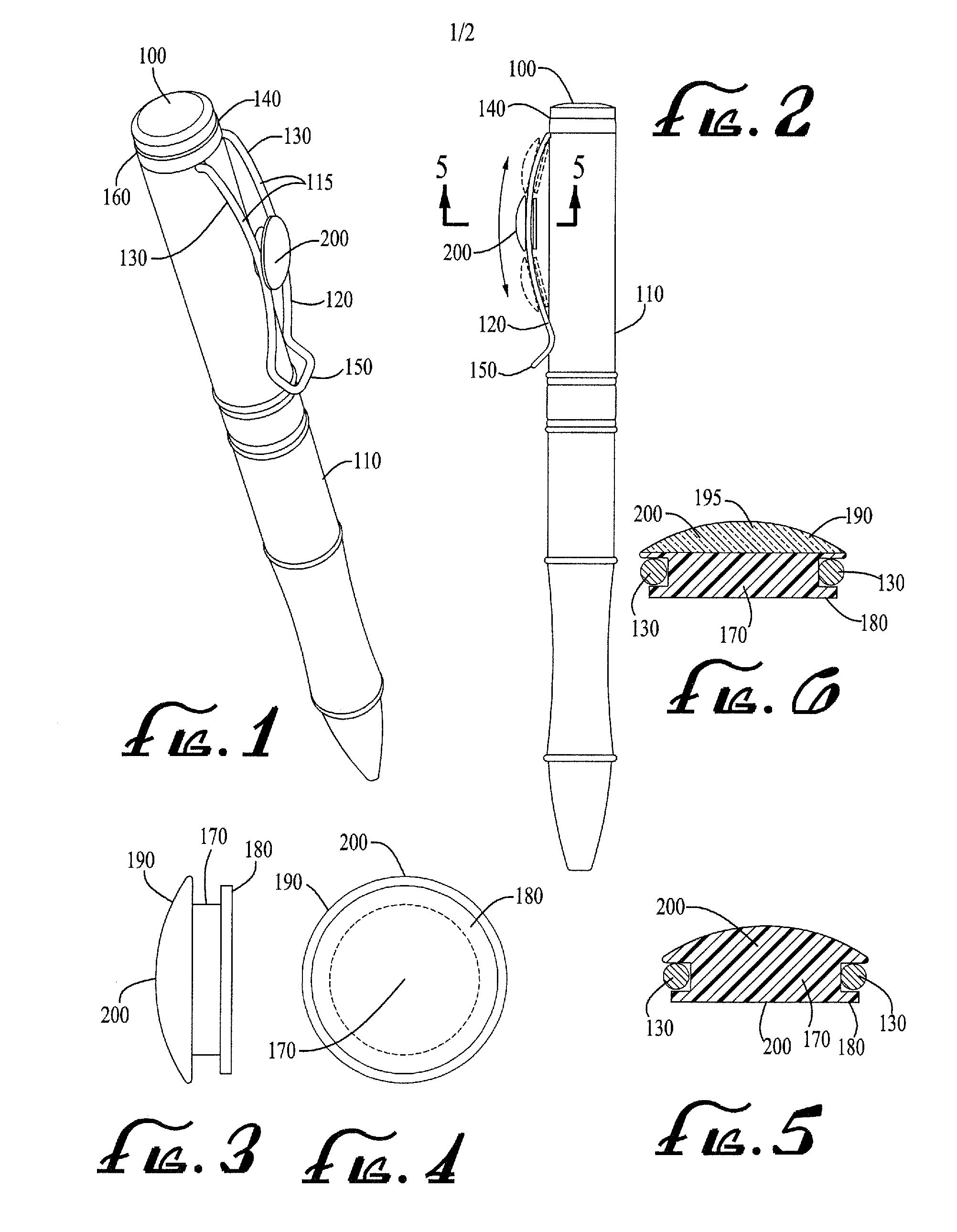
Recombinant template used for producing a carboxy-terminal modified protien and a method of producing a carboxy-terminal modified protein
A translation template comprising an ORF region coding for a protein, a 5′ untranslated region comprising a transcription promoter and a translation enhancer and locating on the 5′ side of the ORF region, and a 3′ end region comprising a poly-A sequence and locating on the 3′ side of the ORF region, is expressed in a translation system in the presence of an agent for modifying a C-terminal of a protein, which comprises an acceptor portion having a group capable of binding to a protein through a transpeptidation reaction in a protein translation system and a modifying portion comprising a nonradioactive modifying substance linked to the acceptor portion via a nucleotide linker, to cause protein synthesis and the synthesized protein is purified. Thus, the yield of modified protein in a method of modifying C-terminal of protein is improved and detection of protein interaction based on various intermolecular interaction detection methods is realized at an improved level.
Owner:IDAC THERANOSTICS
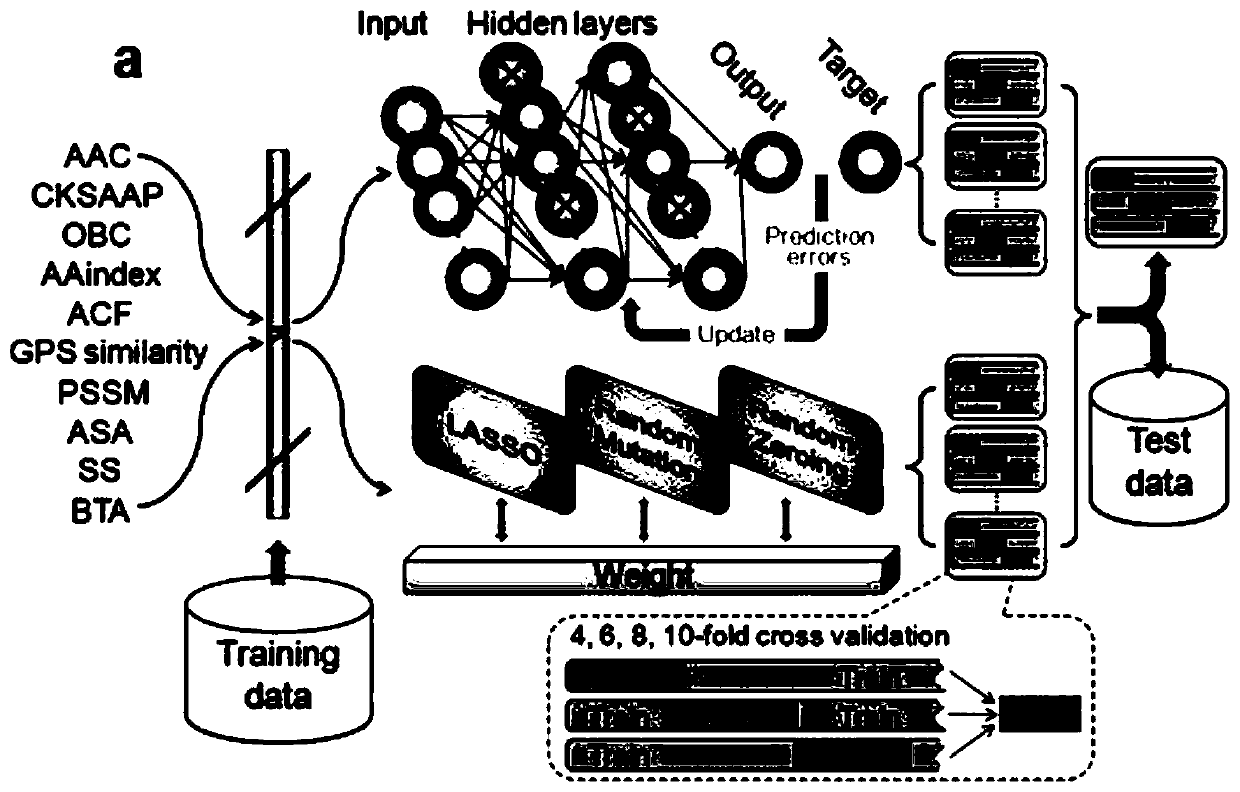
Protein coding method and protein post-translational modification site prediction method and system
ActiveCN110033822AImprove robustnessImprove accuracyInstrumentsMolecular structuresFeature codingProtein
The invention discloses a protein coding method and a protein post-translational modification site prediction method and system, belonging to the field of bioinformatics. The protein coding method includes collection of modification site information, position weight training, and coding of a peptide fragment to be encoded. The protein coding method and protein post-translational modification siteprediction method includes: collection of modification site information, feature coding, model training, and protein post-translational modification site prediction. The protein coding method and theprotein post-translational modification site prediction method and system construct prediction models for digital vector features of different types of positive and negative sites by using a deep neural network and penalty logistic regression, respectively, so as to obtain a plurality of prediction models, take the prediction results of each prediction model as new features and utilizing penalty logical regression to construct a final model, can capture more protein information, thus being conductive to improvement of the accuracy of prediction, and can quickly identify large-scale protein modification sites.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for monitoring protein translation
InactiveUS20070128114A1Monitor early treatment responseCompounds screening/testingIn-vivo radioactive preparationsCell membranePositive response
Disclosed is a method for monitoring early treatment response of a cancer treatment comprising measuring by magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS), for example, proton MRS, the amount of Choline present in the tissue adjoining or surrounding the cancerous tissue before and after treatment; the treatment comprises administration of an angiogenesis inhibitor, for example, a VEGF inhibitor, whereby a decrease in the amount of Choline after treatment is indicative of a positive response. The decrease in the amount of Choline represents the decrease in the internal cell membrane as a result of down regulation of the organelles and their secretory granules and their transport vesicles. Disclosed also is a method for determining effectiveness of an angiogenesis inhibitor in the treatment of cancer. Also disclosed are methods of monitoring early treatment response in diseases where an angiogenesis effector, i.e., an inhibitor or promoter of angiogenesis, is employed. Also disclosed is a method for monitoring protein translation related to angiogenesis.
Owner:RECEPTOMON LLC
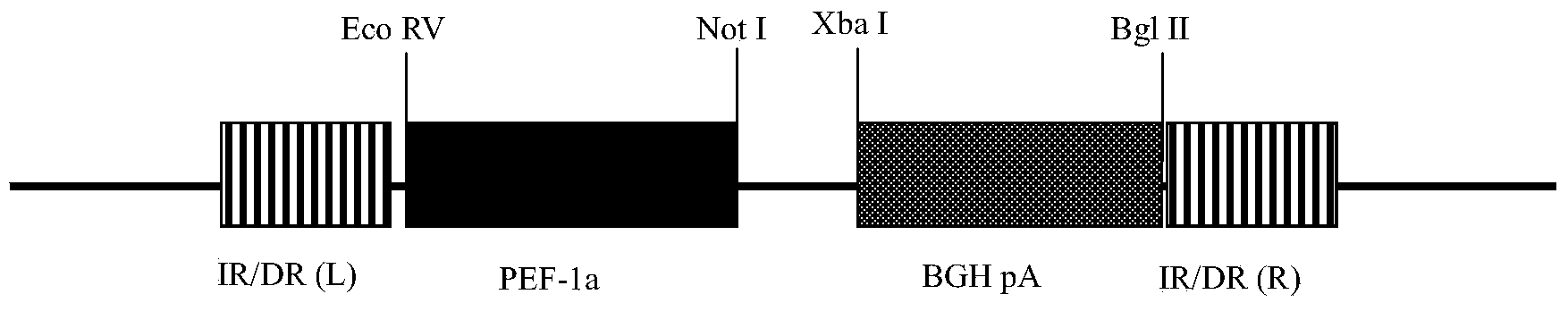
Transposable element carrier expressing pig telomerase reverse transcriptase, building method thereof and application in building pig immortalization cell line
ActiveCN103923942AVector-based foreign material introductionForeign genetic material cellsBiotechnology researchVaccine Production
The invention provides a building method of a transposable element carrier expressing pig telomerase reverse transcriptase, and application in building a pig immortalization cell line, and belongs to the field of biotechnology research. The building method includes the steps of cloning of a promoter of a pig protein translation elongation factor 1a and detection of transcriptional activity, building of an SB transposable element expression vector and exogenous gene integration, pig telomerase reverse transcriptase cDNA cloning, activity detection and building of the pig fibroblast immortalization cell line. Compared with other methods, the pig immortalization cell line built through the transposable element carrier comprises non-transformed normal cells, does not contain resistance genes, virogenes or oncogenes, and is suitable for cell physiological function researching, pig virus separation cultivation and vaccine production.
Owner:ZHONGCHONG XINNUO BIOTECH TAIZHOU CO LTD
Systems and methods for measuring translation activity in viable cells
ActiveUS20100267030A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsImage resolution
Systems for measuring protein translation and methods for measuring overall translation activity in viable cells or subcellular compartments is disclosed. The methods identify general ribosomal activity, if desired at sub-cellular resolution, thereby providing a signal indicating the rate of any of the steps of protein synthesis selected from initiation, elongation, termination or recycling. The translation system can be used to identify translation modulators in high-throughput-screening (HTS).
Owner:ANIMA CELL METROLOGY
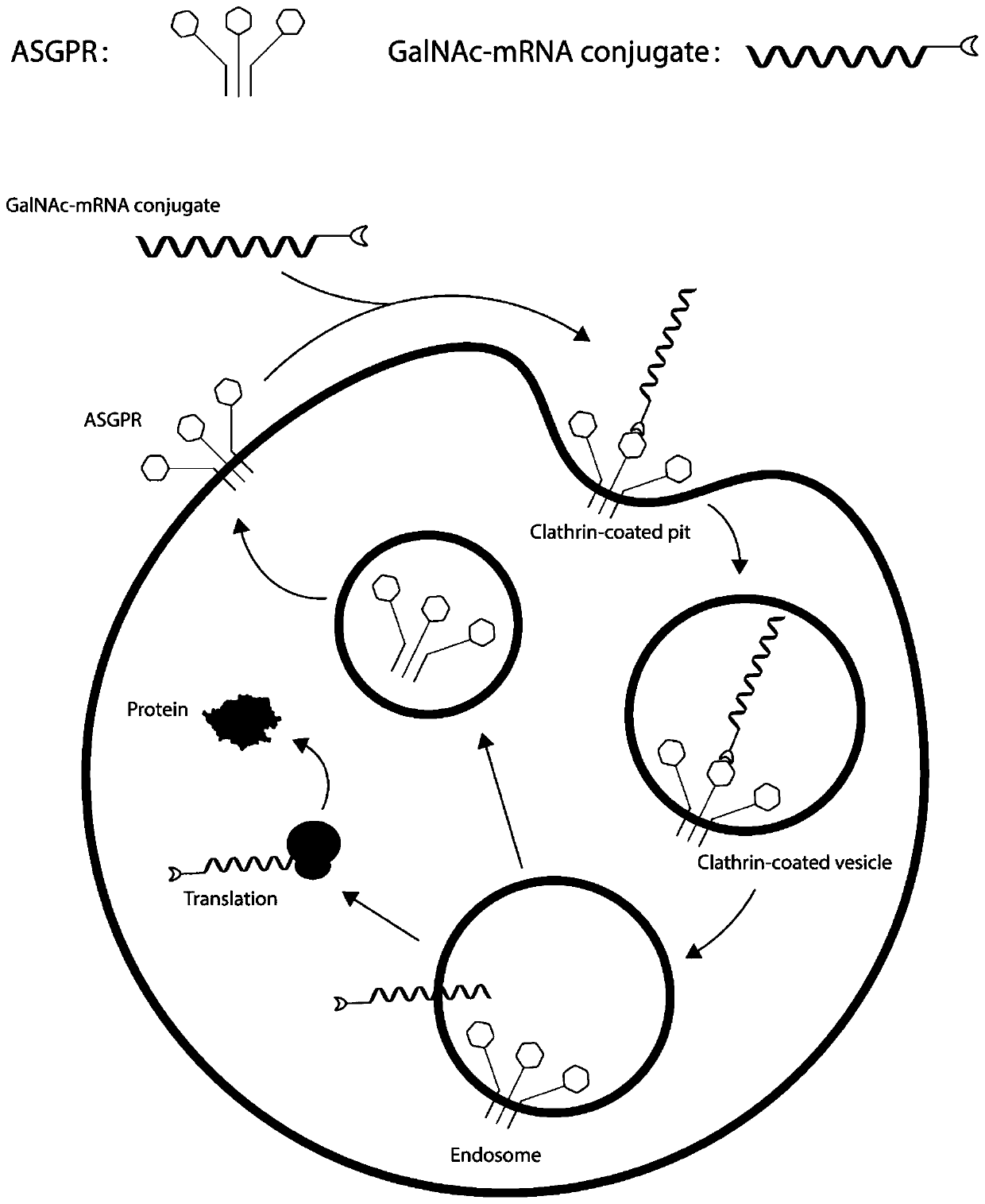
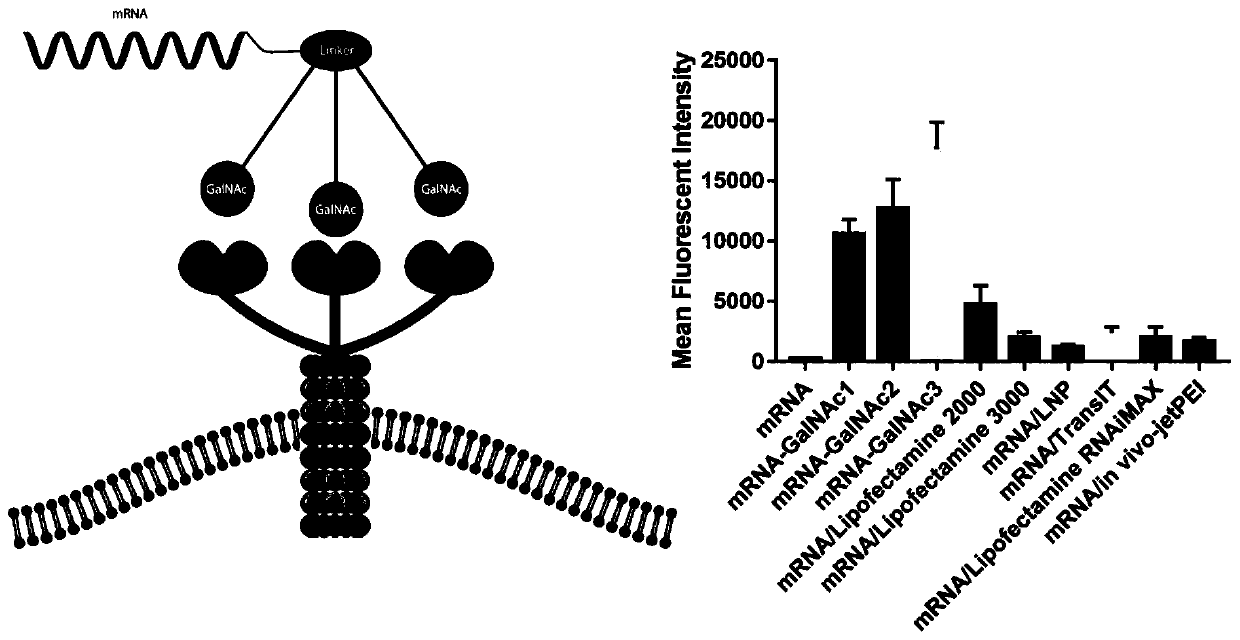
MRNA targeting molecule based on combination of N-acetylgalactosamine polypeptide and preparation method of mRNA targeting molecule
ActiveCN111041025AImprove efficacySolve the technical challenges of targeted deliveryGenetic material ingredientsDigestive systemGeneticsA-DNA
The invention provides an mRNA (messenger ribonucleic acid) targeting molecule based on N-acetylgalactosamine polypeptide and a preparation method of the mRNA targeting molecule. A plasmid vector containing a DNA fragment formed by sequentially connecting a promoter, a target gene, a specific protease cleavage sequence and a polypeptide GBD sequence capable of being combined with N-acetylgalactosamine is transcribed to obtain mRNA, the mRNA is connected with a DNA-puromycin connector under the action of T4 ligase, through protein translation and shearing with a specific protease, an mRNA-puromycin-GBD compound is obtained, and the mRNA-puromycin-GBD compound is combined with the GBD protein sequence under the action of N-acetylgalactosaminyl transferase to form an mRNA-puromycin-GBD-GalNAccompound to complete the GalNAc modification of the mRNA; in the mRNA drug delivery process, the purpose of accurate drug delivery is achieved, and the drug effect of mRNA drug molecules is improved.
Owner:SHENZHEN RHEGEN BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
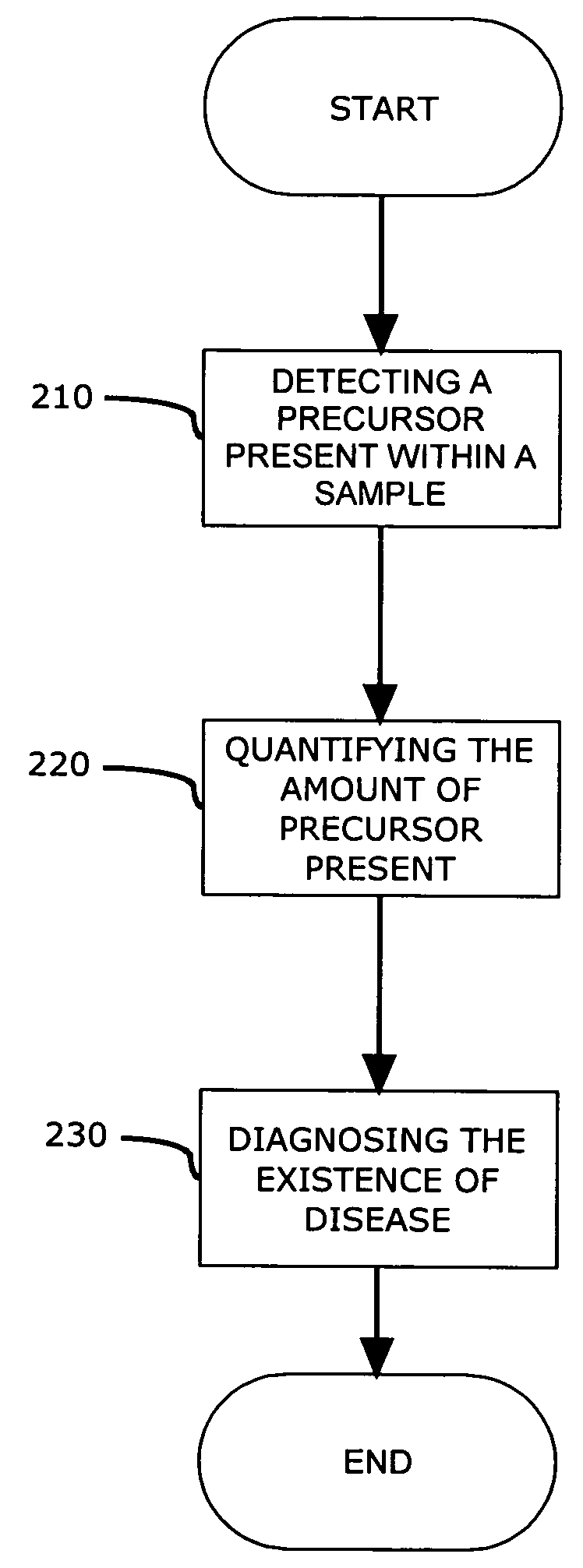
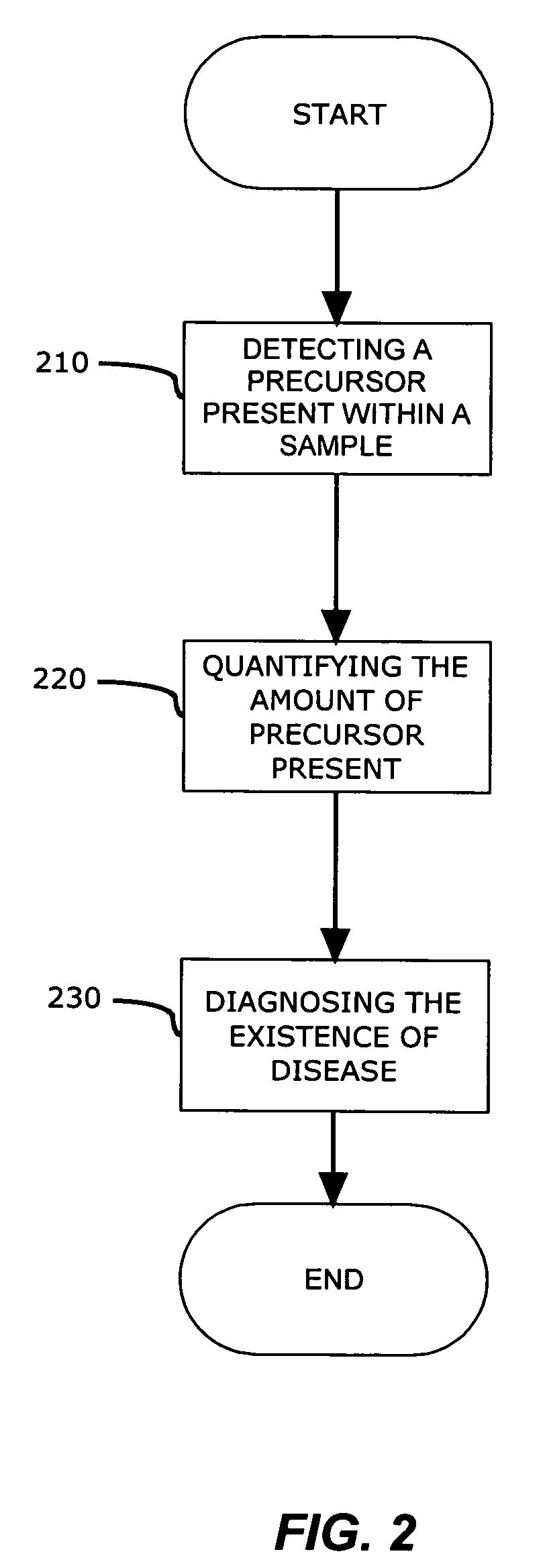
Precursors and enzymes associated with post translational modification of proteins implicated in isoform generation of PCNA
InactiveUS20090123487A1Rapid and minimally invasiveReliable determinationSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementGenomeEnzyme
The current invention provides a method for detecting the presence of a genomic or proteomic precursor(s) within a sample, wherein the precursor(s) provide an indication of the presence or the capability of expression modulation of various other proteins which may, either directly or indirectly, provide an indication, promote, and / or be responsible for the post translational modification of the PCNA.
Owner:ROTHHAAR KATIA
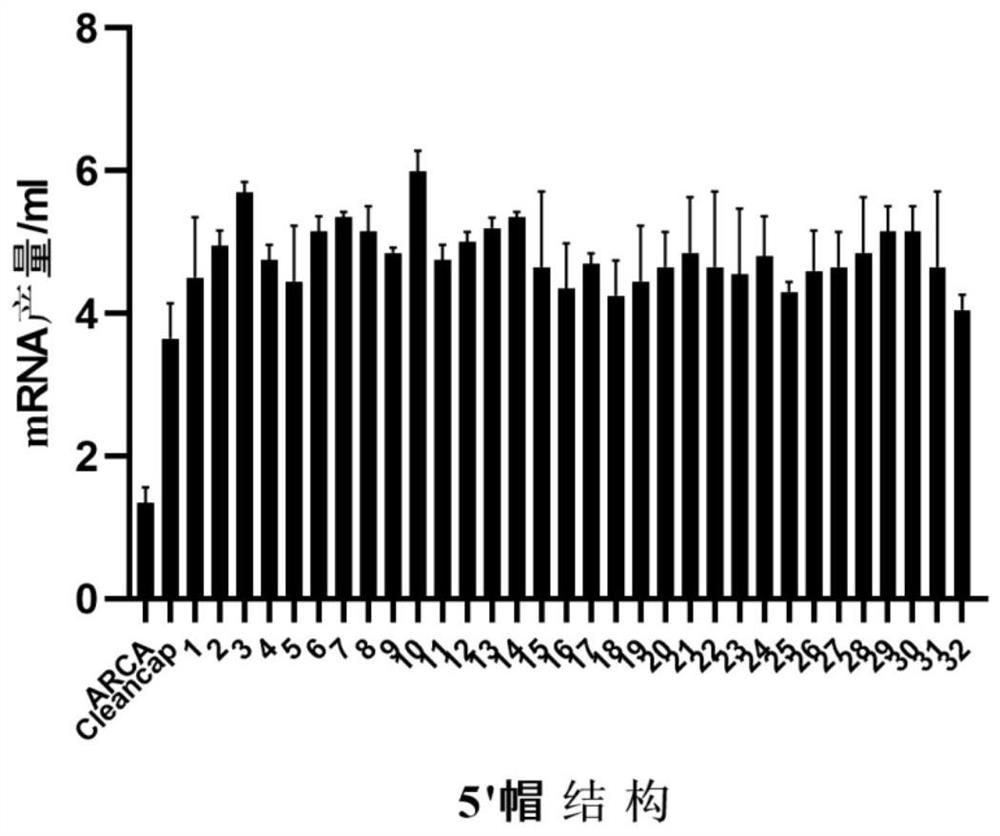
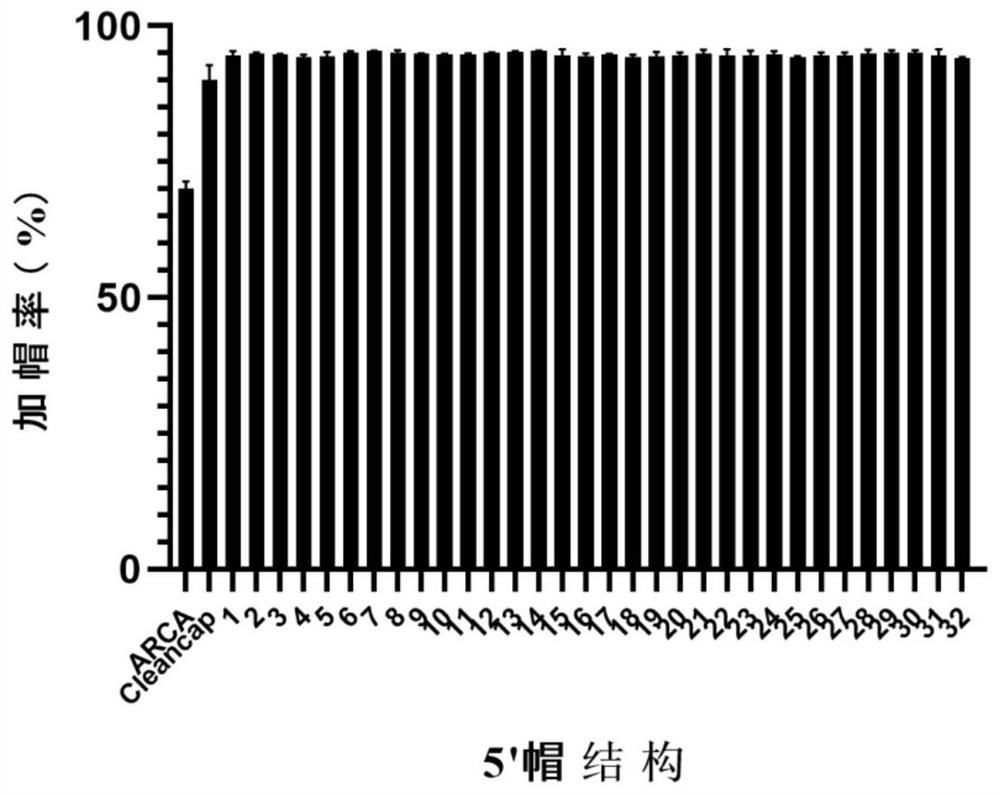
Novel Cap2 structure 5' cap analogue and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN111944864AHigh synthesis efficiencyImprove capping efficiencySugar derivativesFermentationBiochemistryGene engineering
The invention provides a novel Cap2 structure 5' cap analogue and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of gene engineering. The molecular formula of the novel Cap2 structure 5' cap analogue is selected from any of m7G (5') ppp (5 ') (2' OMeA) p (2 'OMeG), m7G (5') ppp (5') (2 'OMeG) p (2' OMeG) and the like. The novel Cap2 structure 5' cap analogue provided by the invention has higher synthesis efficiency, higher capping efficiency, lower immunogenicity and higher protein translation efficiency.
Owner:SHENZHEN RHEGEN BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Protein post-translational modification positioning method
InactiveCN104820011AEfficient distinctionAccurately determineMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansIsomerismsMass spectrometric
The invention relates to a protein post-translational modification positioning method. On the basis of original primary and secondary mass spectrum data base searching, loci of protein post-translational modification are determined by feature matching ions, and high efficiency and accuracy in distinguishing of position isomerism or combination isomerism of post-translational modification of different proteins can be realized by the aid of characteristic ions during protein identification and data base searching of mass spectrum data, so that protein post-translational modification positioning is realized. Compared with the prior art, the method has the advantages that accuracy in high-throughput protein post-translational modification positioning is remarkably improved, comprehensive post-translational modification identification results can be acquired, and protein post-translational modification loci are determined accurately. In addition, the method is applicable to high-throughput proteome analysis and especially applicable to accurate structural identification and efficient analysis of tandem mass spectrums and spectrums with a great quantity of post-translational modification proteins (such as proteomes and the like).
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
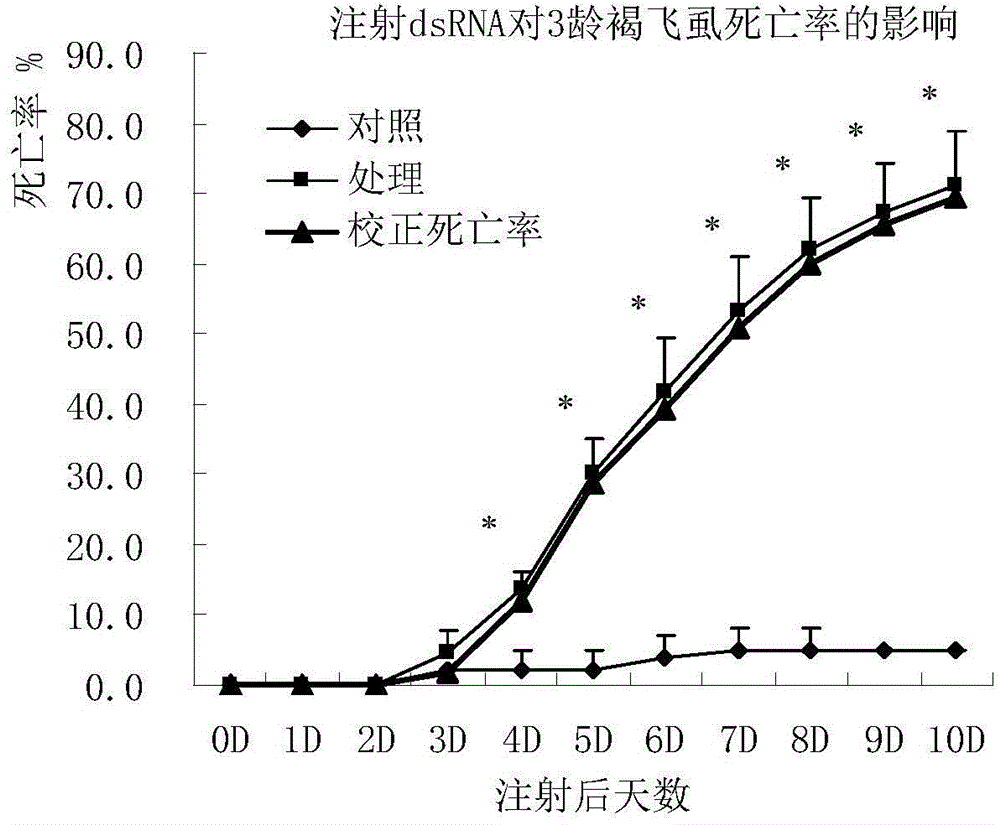
Brown planthopper protein translation elongation factor NlEF1gamma, and encoded protein and application thereof
The invention discloses a brown planthopper protein translation elongation factor NlEF1gamma, an encoded protein, synthesized dsRNA, and an application thereof in controlling brown planthopper pest diseases. The gene performs an important function in maintaining the normal growth and development processes of brown planthoppers. When the function is inhibited, brown planthopper nymph growth is slower, brown planthopper nymph size is smaller, and brown planthopper nymph dies because it couldn't develop into adult. When the function of the gene in a brown planthopper female adult is inhibited, its ovaries stop developing and it couldn't spawn normally. According to the invention, brown planthoppers are injected and fed with the dsRNA of the gene fragment. With both means the brown planthopper death rates reach 70% and brown planthopper spawning amounts are 0. Sequence and data bases are provided for establishing novel strategies for controlling pests with an RNA interference technology. The application has significant lethal and ovarian development inhibition effects against brown planthoppers. Therefore, the gene can be sued as an effective target for controlling the pest with an RNAi technology.
Owner:CHINA NAT RICE RES INST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com