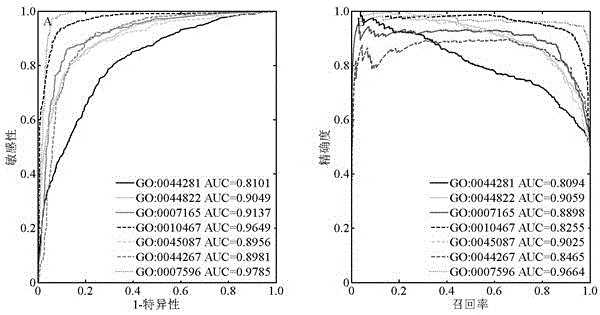
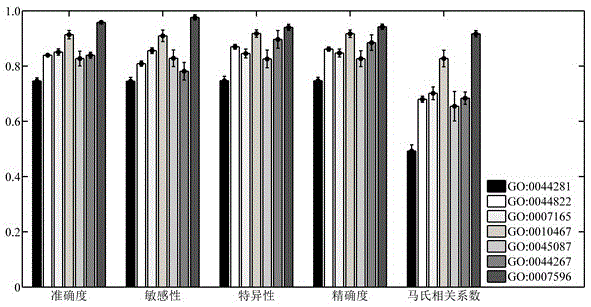
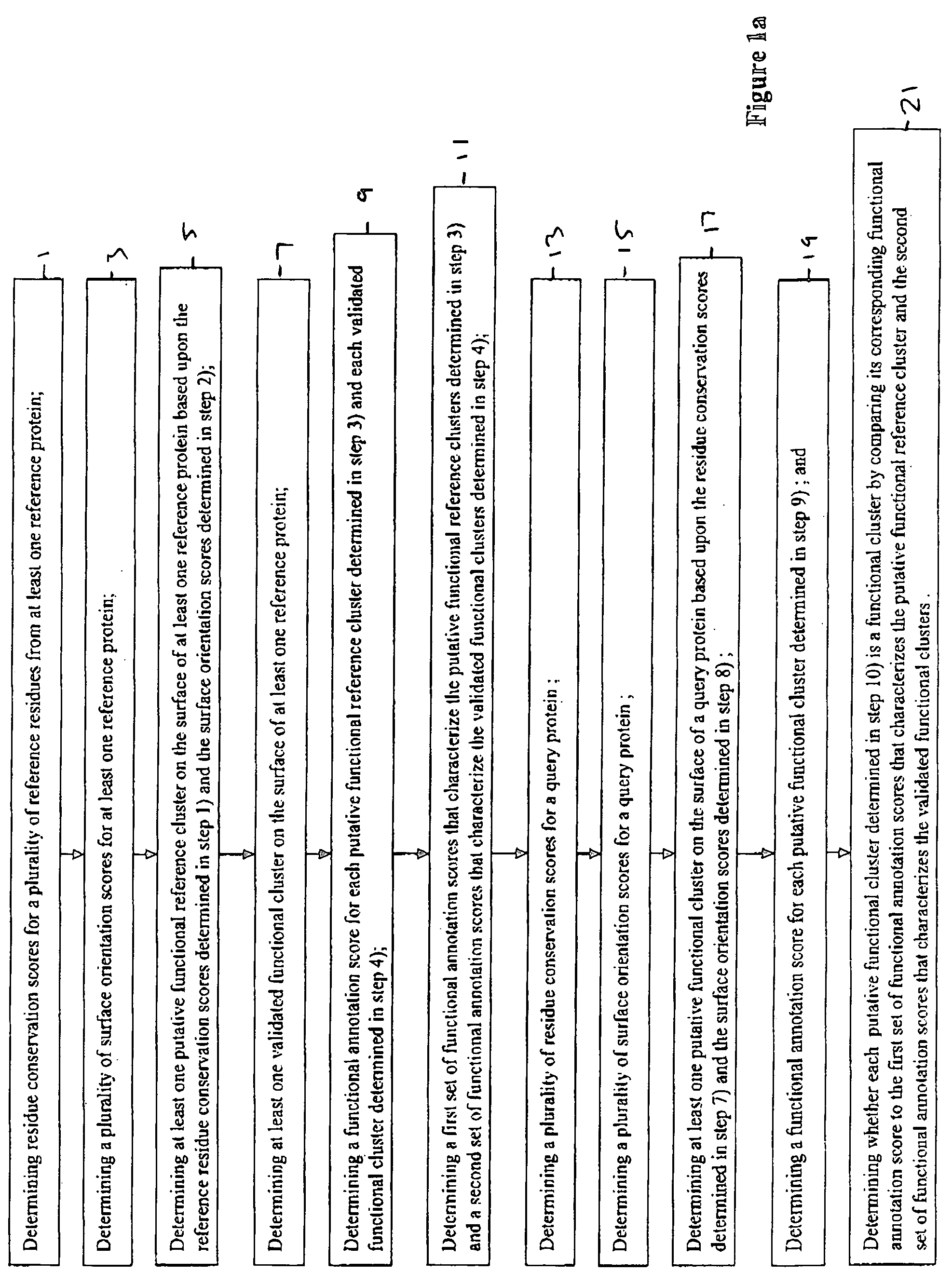
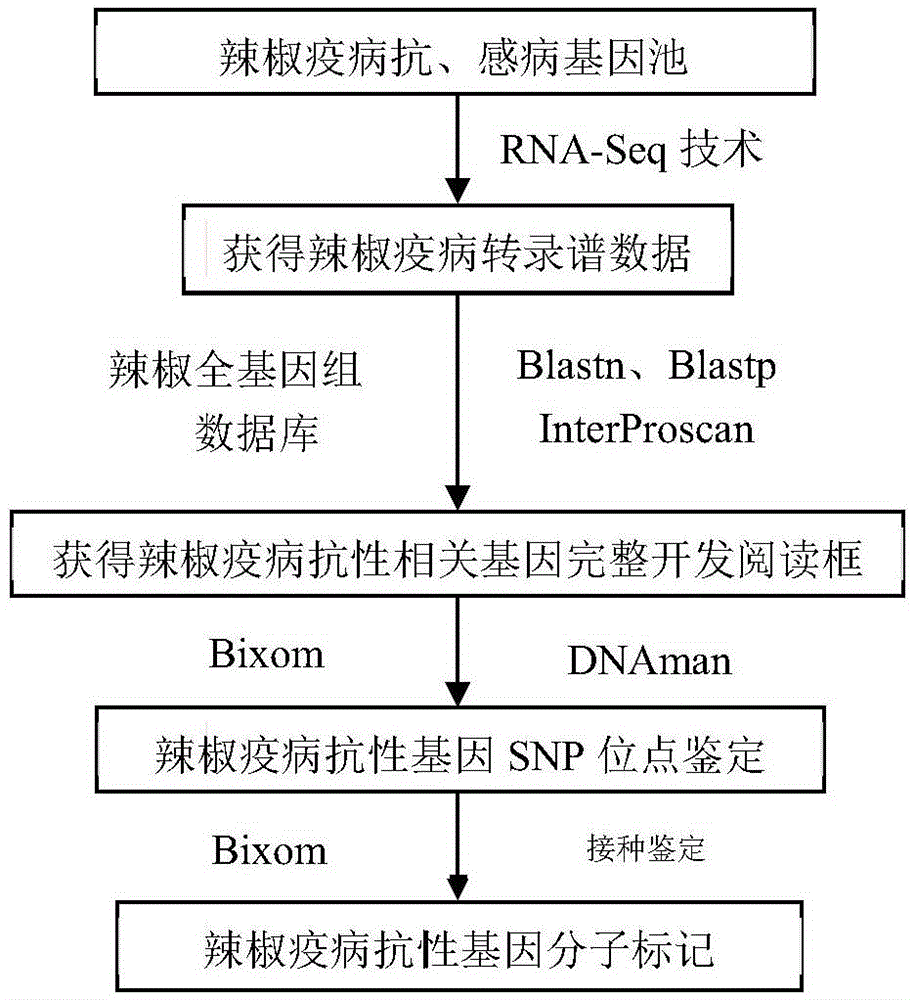
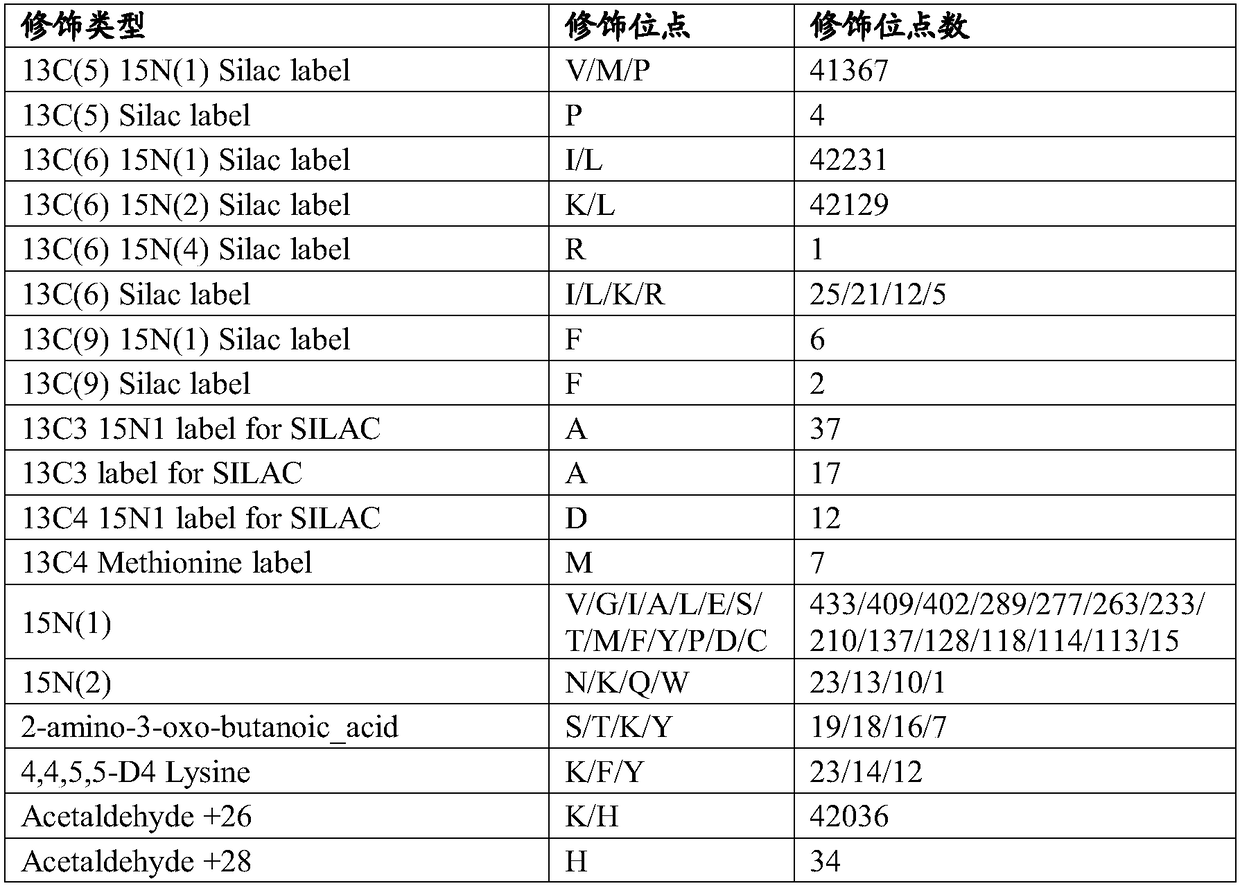
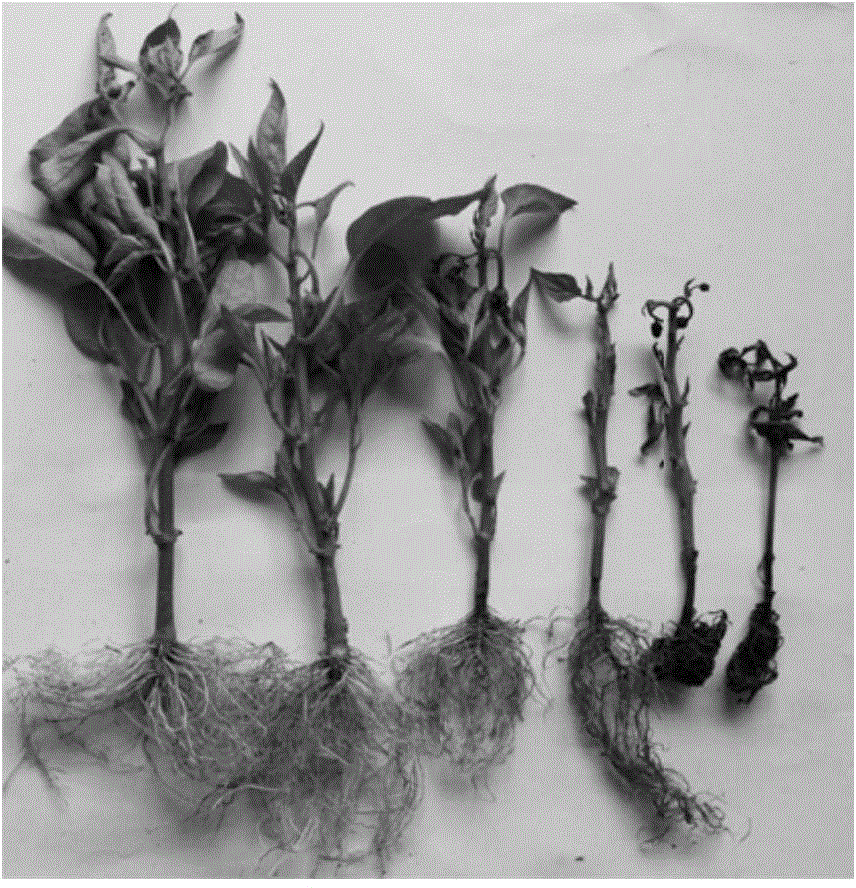Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
37 results about "Functional annotation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Systems and Methods for Analysis and Interpretation of Nucleic Acid Sequence Data
Systems and method for annotating variants within a genome can call variants from reads or receive called variants directly and associate the called variants with functional annotations and interpretive annotations. A summary report of the called variants, the associated functional annotations, and the associated interpretive annotations can be generated.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Systems and methods for analysis and interpretation of nucleic acid sequence data
InactiveUS20130091126A1Digital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsNucleic acid sequencingData system
Systems and method for annotating variants within a genome can call variants from reads or receive called variants directly and associate the called variants with functional annotations and interpretive annotations. A summary report of the called variants, the associated functional annotations, and the associated interpretive annotations can be generated.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Method for identifying protein functions based on protein-protein interaction network and network topological structure features
InactiveCN105138866ARobustSignificant predictive advantageSpecial data processing applicationsNODALData set
The invention discloses a method for identifying protein functions based on a protein-protein interaction network and network topological structure features. Firstly, a node and side-weighted protein-protection interaction network is established, wherein the node represents protein while the edge represents the interaction; then the nodes and the sides in the network are weighted by protein first-grade structural description and protein-protein interaction trust scoring; protection functional annotation data is collected to establish a data set, and a new protein with overall and local information network topological structure features is provided based on a graph theory; and finally, the protein functions are predicated by choosing features through adopting a minimum-redundancy maximum-correlation method and by modeling through a support vector machine. The protein function predication method is greatly better than the prior art, and has robustness on sequence similarity and sampling; and meanwhile, information of three-dimensional structure and the like of protein is not required, so that the method is simple, rapid, accurate and efficient, and the method is expected to be applied in the research fields of proteomics and the like.
Owner:SYSU CMU SHUNDE INT JOINT RES INST +2
Method for determining functional sites in a protein
InactiveUS20050089878A1Simple methodMicrobiological testing/measurementBiostatisticsComputer scienceNon functional
The present invention relates to improved methods for determining functional residues on the surface of a query protein. The claimed methods rely on determining a plurality of functional annotation scores for a query protein and comparing these functional annotation scores to distributions of similar functional annotation scores derived from a plurality of reference proteins. Based upon these comparisons, a putative functional cluster may be annotated as a functional cluster or a non-functional cluster.
Owner:DEBE DEREK +2
Method for obtaining capsicum phytophthora resistance candidate gene and molecular marker, and application
InactiveCN104560973AAccurate identificationLarge amount of data informationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyData information
The invention relates to a method for obtaining a capsicum phytophthora resistance candidate gene and a molecular marker, and application. The method is used for obtaining the capsicum phytophthora resistance candidate gene by utilizing capsicum phytophthora transcriptome and whole-genome sequencing data information, differentially-expressed gene identification, bioinformatics analysis, molecular marker development and phytophthora inoculation identification and belongs to the technical field of capsicum biology. The method comprises the following steps: sequencing a phytophthora resistant and susceptible gene pool transcriptome obtained after phytophthora inoculation of an F2 population constructed by capsicum highly-resistant and highly-susceptible phytophthora materials, performing expression analysis and functional annotation on differential genes, extracting DNAs (Desoxvribose Nucleic Acid) of a capsicum phytophthora highly-resistant and highly-susceptible phytophthora material genome, performing primer design and PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) amplification, performing sequence difference analysis and SNP site identification, performing SNP specific primer design and validity verification, and performing other steps to efficiently obtain the capsicum phytophthora resistance candidate gene and the molecular marker. According to the method, the capsicum phytophthora resistance candidate gene can be accurately identified, and the effective molecular marker can be developed.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
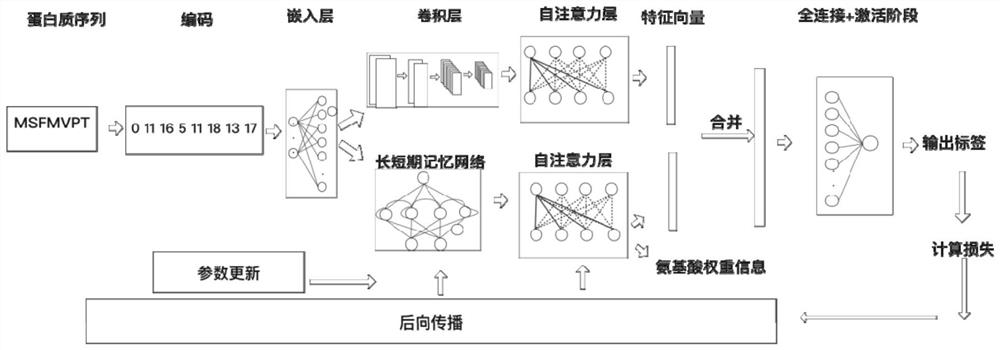
DNA binding protein identification and function annotation deep learning method based on self-attention mechanism
The invention discloses a DNA binding protein identification and function annotation deep learning method based on a self-attention mechanism. The method comprises the following steps: selecting a data set from a protein database, training and testing a constructed deep learning model by using the selected data set, and predicting whether protein can be combined with DNA by using the trained deeplearning model, wherein the deep learning model comprises a coding layer, an embedding layer, a long short-term memory neural network layer (LSTM), a convolutional neural network layer (CNN) and a self-attention layer (Self-Attention). Through a deep learning model based on a self-attention mechanism, whether the protein has a function of combining with DNA or not can be predicted according to primary sequence information of the protein, and an area with a combining function is found out.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
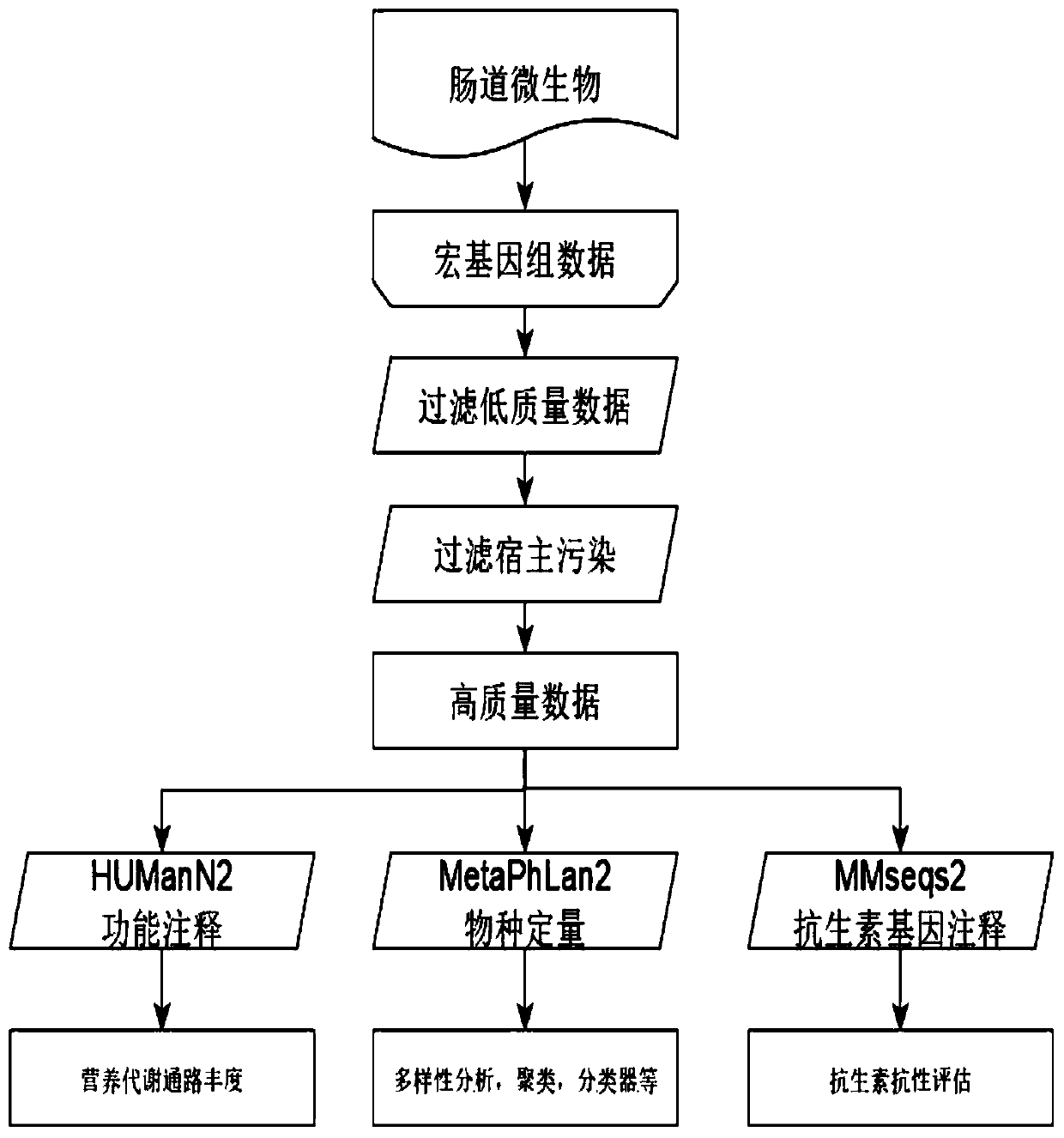
Metagenome data analysis method based on next-generation sequencing technology
PendingCN112071366ASolve incomplete problemsThe analysis process is reasonableCharacter and pattern recognitionHybridisationGenomicsContig
The invention discloses a metagenome data analysis method based on a next-generation sequencing technology, which comprises the following steps of: (1) carrying out quality control on original sequencing data to obtain clean reads; (2) performing species annotation on the clean reads subjected to the quality control; (3) performing statistical analysis on the sample diversity based on a species abundance matrix; (4) performing statistical analysis on species with significant differences among sample groups based on the species abundance matrix; (5) splicing and assembling the clean reads to obtain a contigs sequence; (6) packaging the contigs obtained by splicing and assembling into boxes to obtain bins; (7) carrying out gene annotation on the bins subjected to boxing; (8) performing statistical analysis on the genes with significant differences among the sample groups based on the gene abundance matrix; and (9) based on the gene annotation result, performing function and species annotation on the sequence. A whole process from metagenome next-generation sequencing data processing to species composition analysis, gene composition analysis and function annotation is provided, an accurate analysis result is provided for researchers, and the metagenomics problem is comprehensively analyzed.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
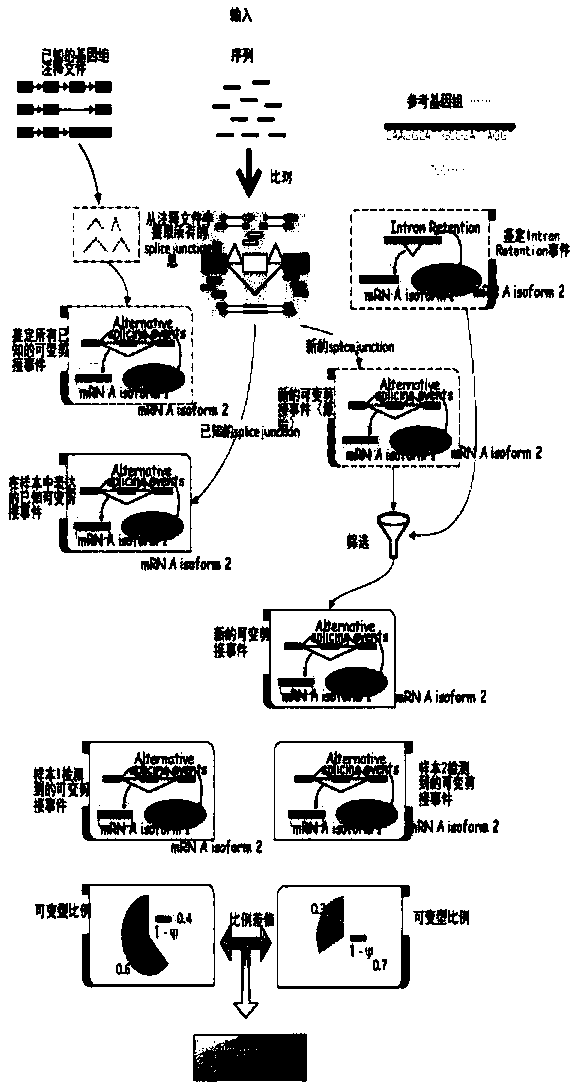
Eucaryon alternative splicing analysis method and system based on RNA-seq data
InactiveCN107766696AAccurate identificationHybridisationSpecial data processing applicationsAnalysis dataData filtering
The invention provides a eucaryon alternative splicing analysis method and system based on RNA-seq data. The method comprises the steps that transcriptome original sequencing data of one or more samples of a certain eucaryon with a reference genome and annotation is acquired through an illumina next-generation sequencing platform; unqualified data is filtered out, and the remaining data serves asto-be-analyzed data; next, basic analysis is performed, wherein the to-be-analyzed data of all the transcriptome samples is compared to the reference genome of the species, and a unique comparison result is screened out; expression quantities of all sample genes are calculated; the genes with significant difference expression are screened out; functional annotation and analysis are performed on the differential genes; then alternative splicing analysis is performed, wherein a known alternative splicing event is identified; a new alternative splicing event is identified; the difference betweenalternative splicing events of samples (sample groups) is analyzed; the correlation between alternative splicing and gene expression is analyzed; the alternative splicing analysis result is subjectedto statistical analysis, and a report is generated; and an alternative splicing visual graph is generated.
Owner:武汉生命之美科技有限公司
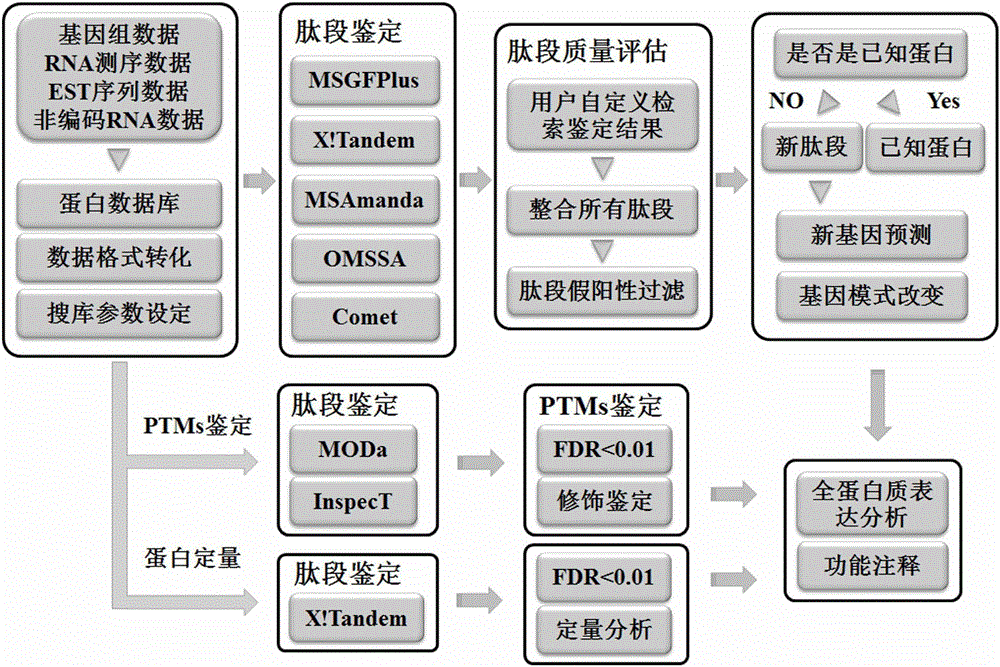
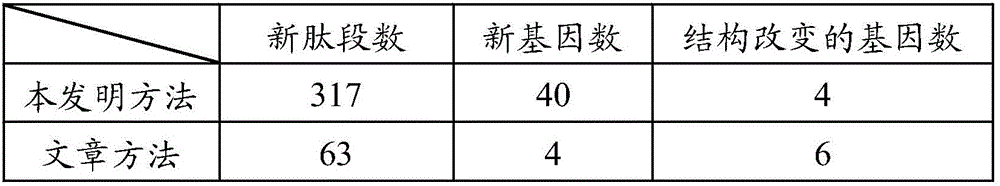
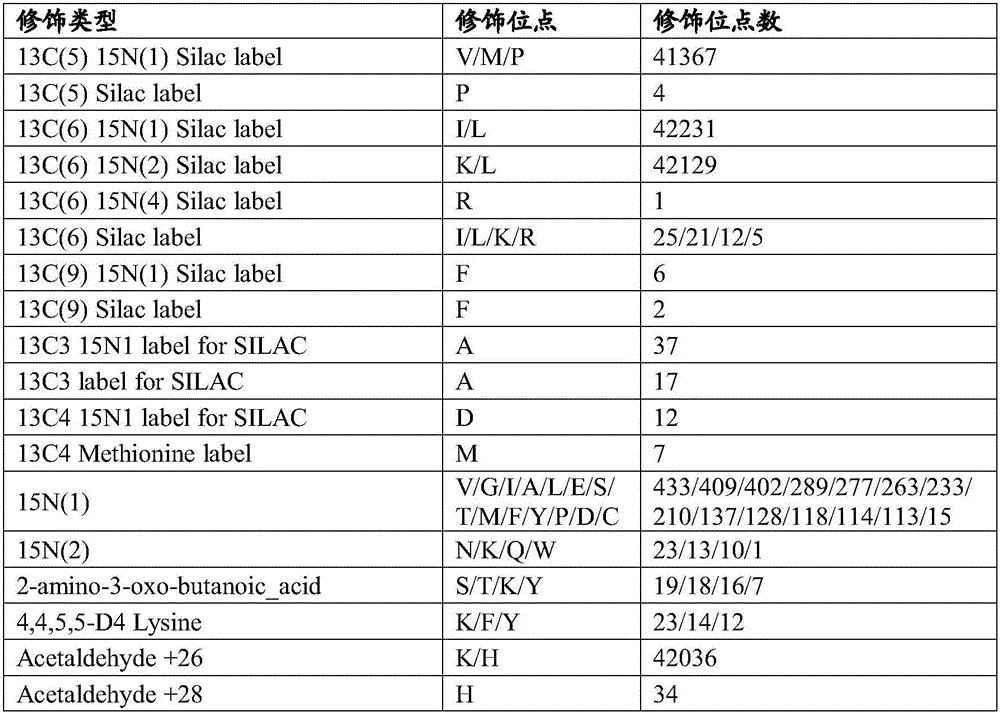
Method for analyzing data of prokaryotic proteogenomics rapidly and automatically
ActiveCN105956416AIncrease Identification CoverageImprove compatibilityProteomicsGenomicsDatabase fileMass spectrometric
The invention provides a method for analyzing data of prokaryotic proteogenomics rapidly and automatically. Users only need to provide mass spectral data and a corresponding database file and set a simple retrieval parameter; retrieval of data of proteogenomics can be completed; simultaneously, a user defined data retrieval result can also be compatible; therefore, the identification coverage rate of the data of proteogenomics is increased; in the method disclosed by the invention, library search engines of different algorithms are integrated in advance; disadvantages of a single retrieval method are made up; a user defined library search result can also be compatible; the method has good compatibility; the peptide fragment identification coverage rate is increased to the most extent; in the method disclosed by the invention, functional annotation of new genes is automatically completed; large-scale identification of protein post-translational modification and analysis of non-labelled quantitative proteomics are realized for the first time; and automatic and rapid deep analysis of the data of proteogenomics is really realized.
Owner:湖北普罗金科技有限公司
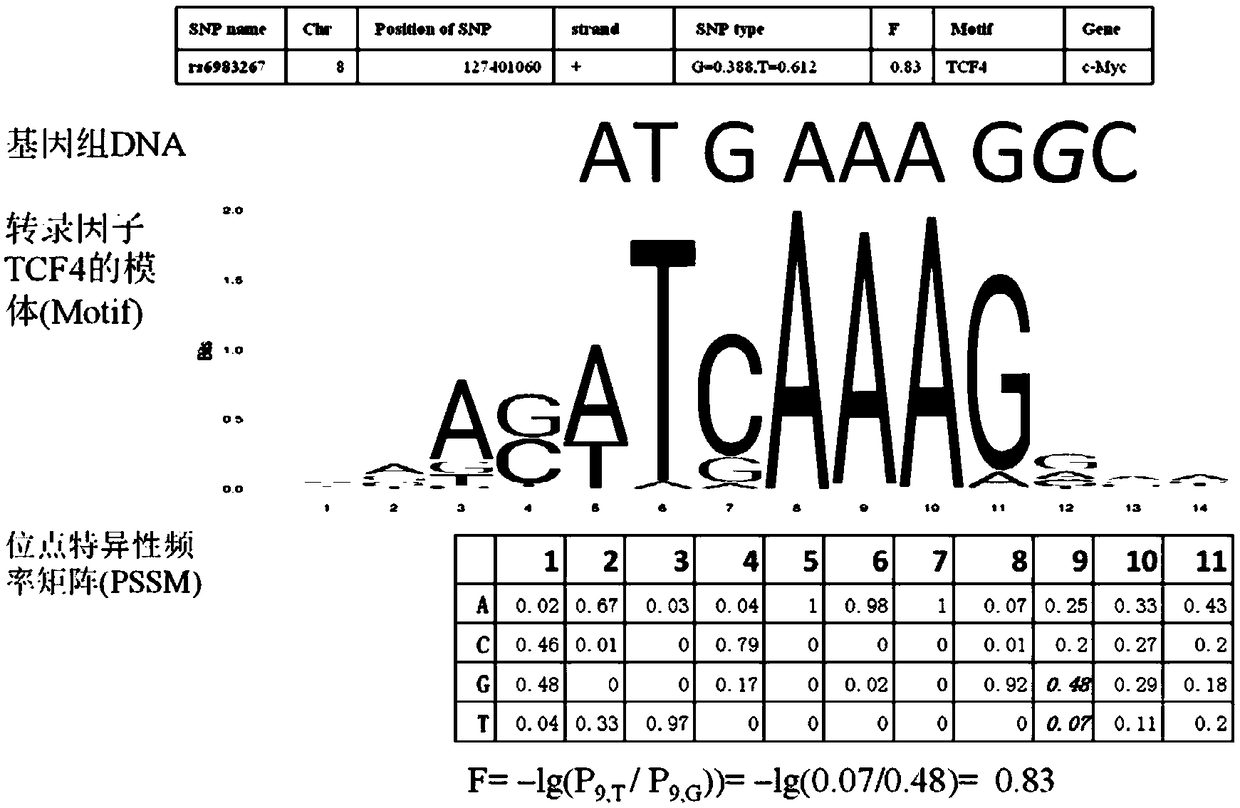
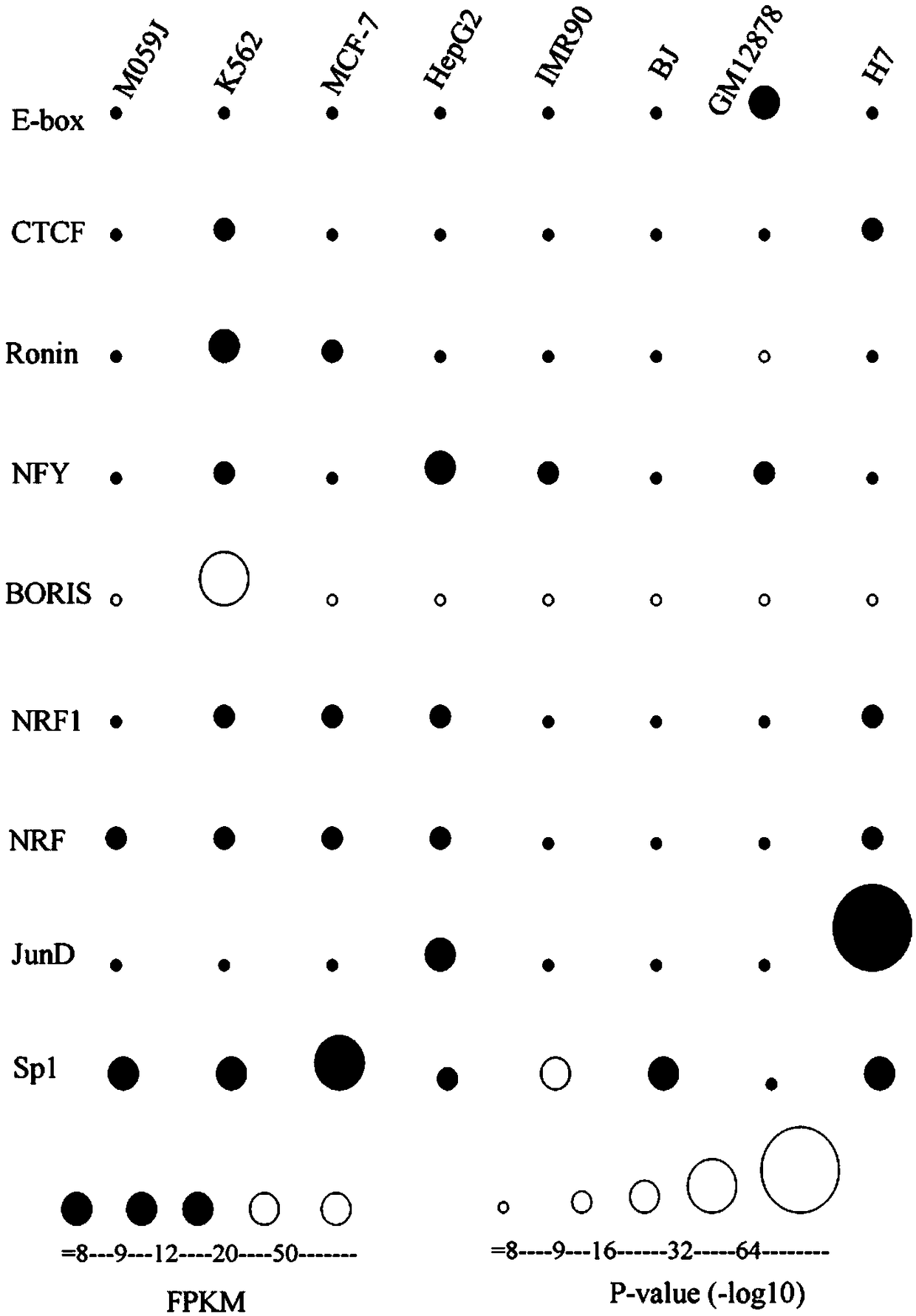
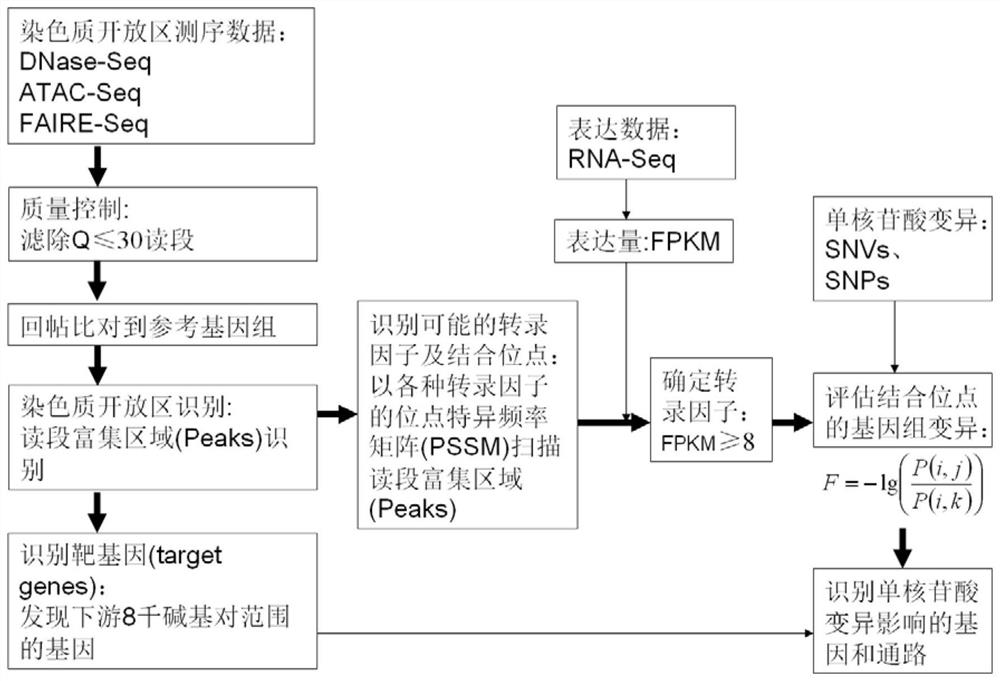
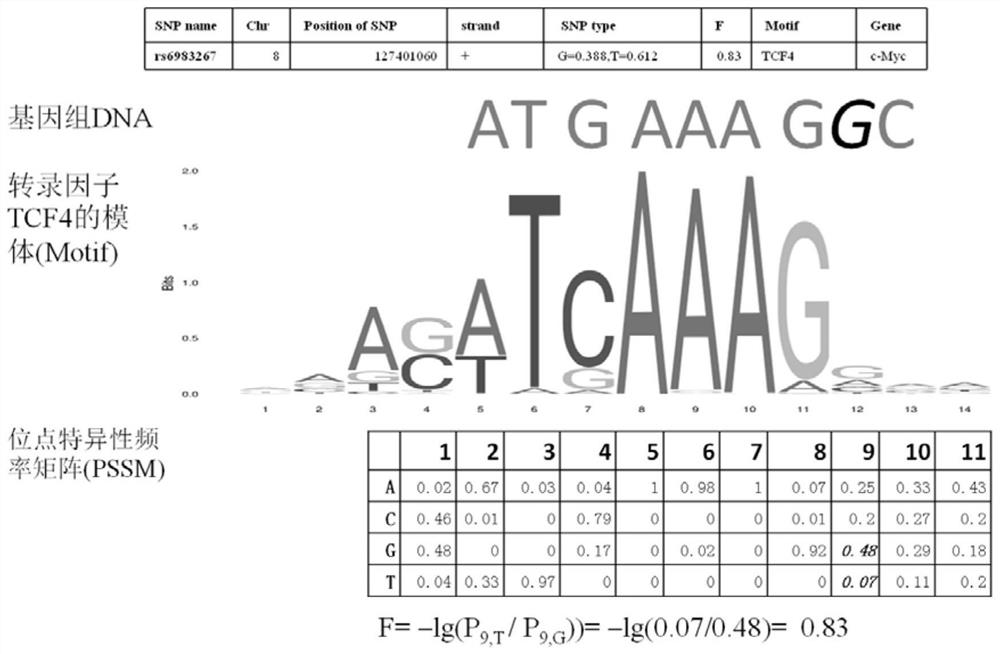
A method for functional prediction of single nucleotide genomic variation in a non-coding region
ActiveCN109033751ALow sequencing depth requirementAvoid time costSpecial data processing applicationsGenomic mutationNucleotide
The invention discloses a method for functional prediction of single nucleotide genomic variation in a non-coding region, which comprises the following steps: 1) identifying a chromatin open region; 2) identifying transcription factor bin sites; 3) assessing the role of single nucleotide variations: Based on the site-specific frequency matrix of transcription factors, the effect of single nucleotide variations in the transcription factor binding site region on transcription factor binding is calculated, and the single nucleotide variations that significantly change the binding capacity of transcription factors are identified; the role of single nucleotide variations is further evaluated by viewing the biological pathway of the target gene of the transcription factor. The method recognizesa variety of transcription factors and their binding sites at one time through chromatin open region information and gene expression information, and realizes the functional annotation of non-coding region genomic mutation.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
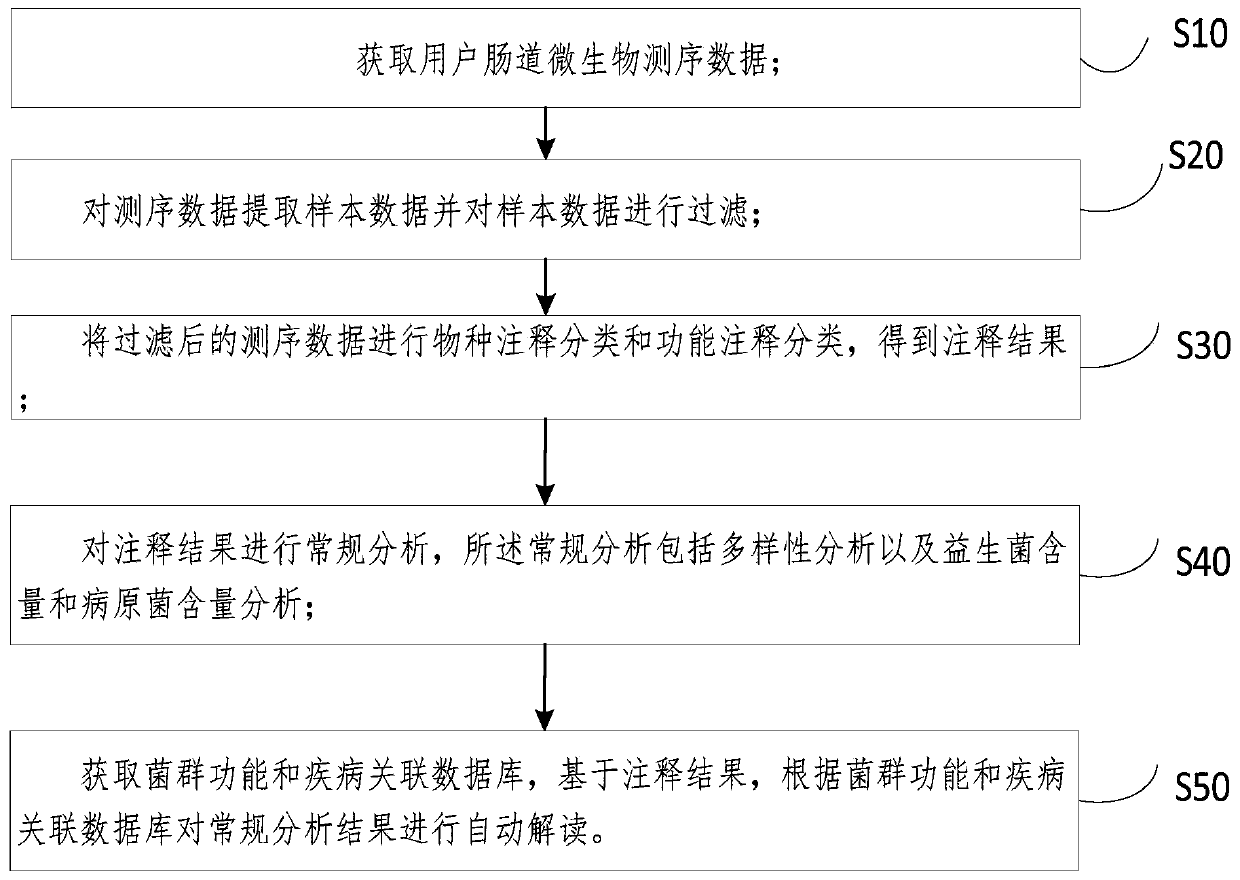
Enteric microorganism detection data analysis method, automatic interpretation system and medium
PendingCN111462819ARelieve pressureVarious formsBiostatisticsSequence analysisIntestinal microorganismsFlora
The invention discloses an enteric microorganism detection data analysis method, an automatic interpretation system and a medium. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring enteric microorganism sequencing data of a user; extracting sample data from the sequencing data, and filtering the sample data; performing species annotation classification and function annotation classification on the filtered sequencing data to obtain an annotation result; performing conventional analysis on the annotation result, wherein the conventional analysis comprises diversity analysis and probiotics content and pathogenic bacteria content analysis; and obtaining a flora function and disease association database, and based on the annotation result, automatically interpreting the conventional analysisresult according to the flora function and disease association database. According to the method, analysis and interpretation can be automatically executed, so that the working pressure is reduced, the generated analysis results are diversified in form and good in readability, the requirements of users are met, process and batch operations are conveniently carried out, and the workload of manual interpretation is small, visual and convenient.
Owner:康美华大基因技术有限公司
Method based on genome LoF loci to screening indirectly related kiwi fruit varietal character
InactiveCN106498070AAssociation Prediction AccurateImprove stabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementProteomicsActinidiaKiwi fruit
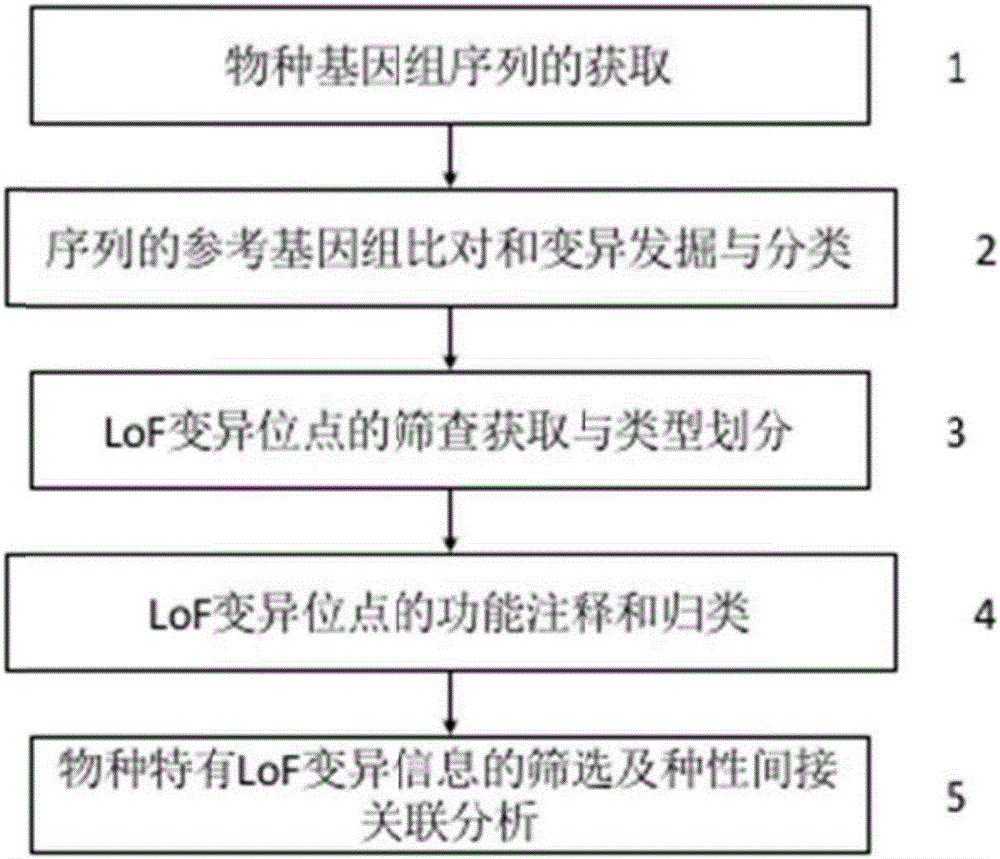
The invention discloses a method based on genome LoF loci to screening indirectly related kiwi fruit varietal character. The method includes: acquiring a variety genome sequence; comparing with a reference genome of the sequence, discovering and classifying mutation; screening and acquiring LoF mutation loci, and dividing types; performing functional annotation and classification on the LoF mutation loci; screening LoF mutation information unique to varieties, and performing varietal character indirect relation analysis. Compared with previous methods of direct artificial observation on varietal character of kiwi fruit variety and seed breeding experiment detection, the method has higher stability and repeatability, so that relation prediction on the varietal character of the variety is more accurate; by using the method, potential varietal character feature and breedable utilization value of a specific kiwi fruit variety can be quickly acquired and predicted, so that efficiency in resource evaluation and breeding application is improved greatly.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA BOTANICAL GARDEN CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Metabonomics and transcriptomics correlation analysis based method for screening key gene for synthesis of fritillaria alkaloid
InactiveCN108103176AIncrease alkaloid contentComponent separationMicrobiological testing/measurementCorrelation analysisAlkaloid
The invention discloses a metabonomics and transcriptomics correlation analysis based method for screening a key gene for the synthesis of fritillaria alkaloid. Specifically, the differential alkaloidand the content information of the differential alkaloid are obtained through the metabonomics analysis of three types of fritillaria, and meanwhile, the expression condition of the related gene in the synthetic route of the alkaloid is obtained through the functional annotation of the transcriptomics. The differential metabolin-gene dependence relation network is constructed through the correlation analysis, and the key gene for the synthetic route of the alkaloid, having a greater contribution to the content of the alkaloid in the fritillaria, is screened. The method provides important information for the further clarification of the synthesis mechanism of the alkaloid substance in the fritillaria, and provides an important evidence for increasing the content of fritillaria alkaloid bymeans of gene control and the like.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
Radix isatidis protein identification method
InactiveCN107192829AFast analysisGood repeatabilityComponent separationPreparing sample for investigationEnzyme digestionFunctional profiling
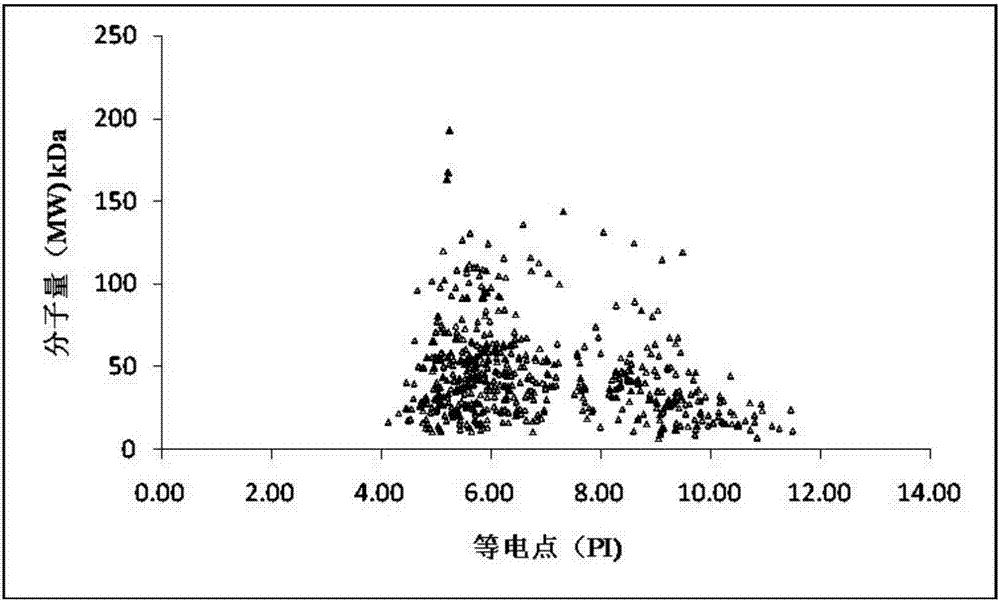
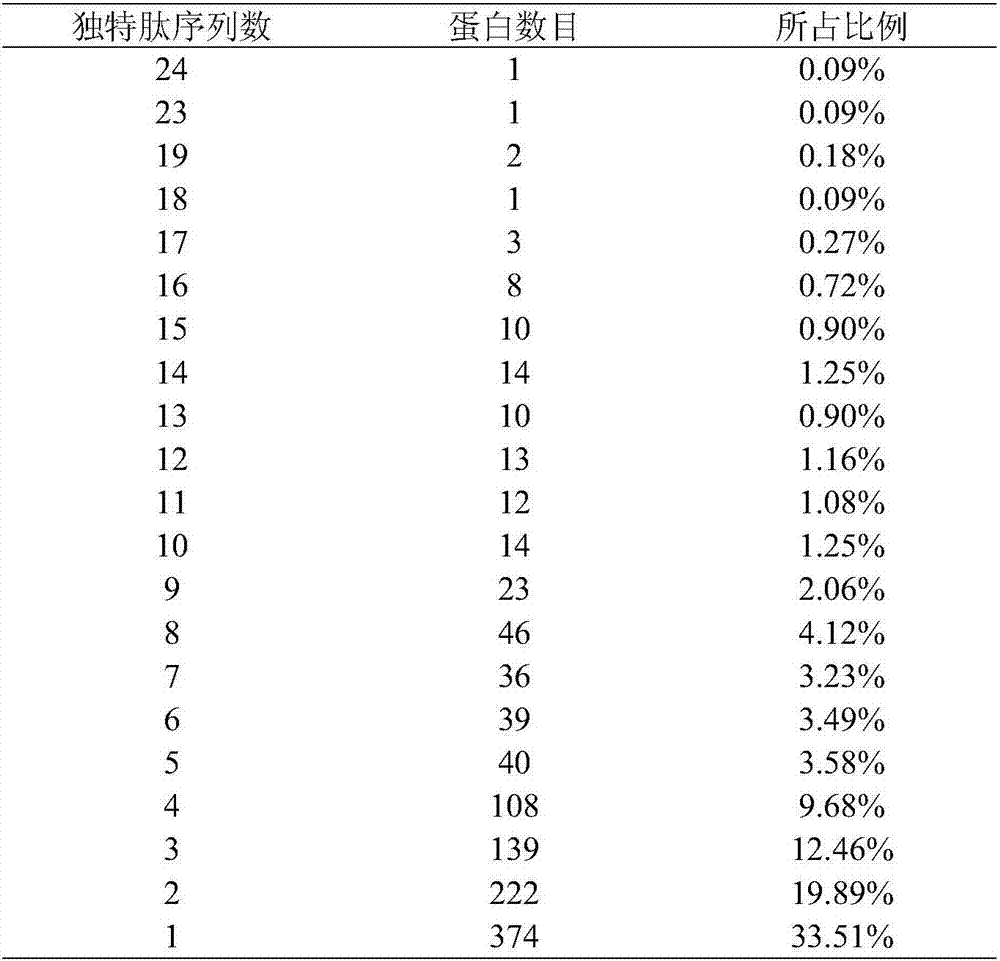
The invention discloses a radix isatidis protein identification method. The method includes: after radix isatidis is subjected to a series of pretreatment steps including grinding, decolorizing, splitting, enzyme digestion and the like, adopting a nanoliter liquid chromatograph / mass spectrometer for separation and mass spectrometric analysis, and adopting Mascot software for database retrieval and searching; subjecting identified proteins to functional annotation and pathway annotation by bioinformatics. The method is high in protein extraction rate and large in quantity of identified protein types, and in radix isatidis proteins, 1116 types of proteins and2589 unique peptide segments are identified, and the total number of high-reliability proteins (with unique peptide sequence matching numbers larger than or equal to 2) is 742 and accounts for 66.49%. The method is suitable for identification and functional analysis of proteins in traditional Chinese medicines such as radix isatidis and has a promising application prospect.
Owner:NANJING UNIVERSITY OF TRADITIONAL CHINESE MEDICINE
AD model rat hippocampus gene expression difference chart constructed by combining A beta and D-gal as well as determination method and application of AD model rat hippocampus gene expression difference chart
InactiveCN108588214AReduce excess spaceIncreased brain overloadMicrobiological testing/measurementProteomicsDifferentially expressed genesGene expression profiling
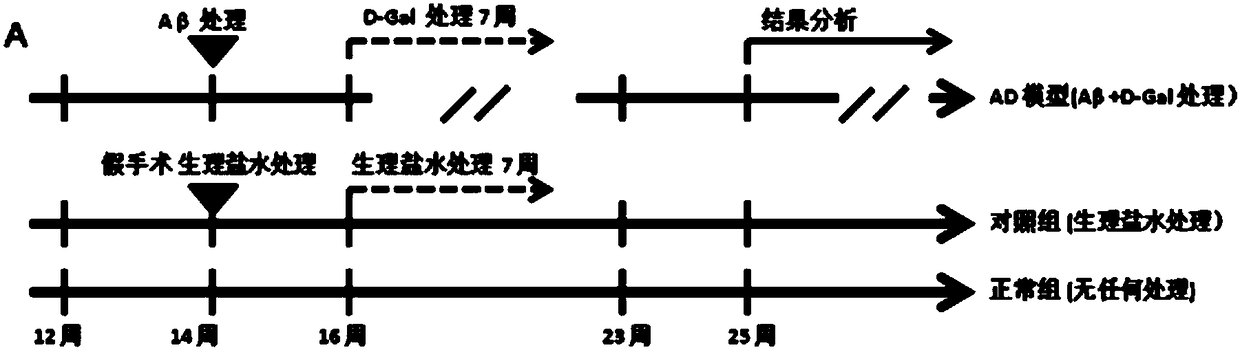
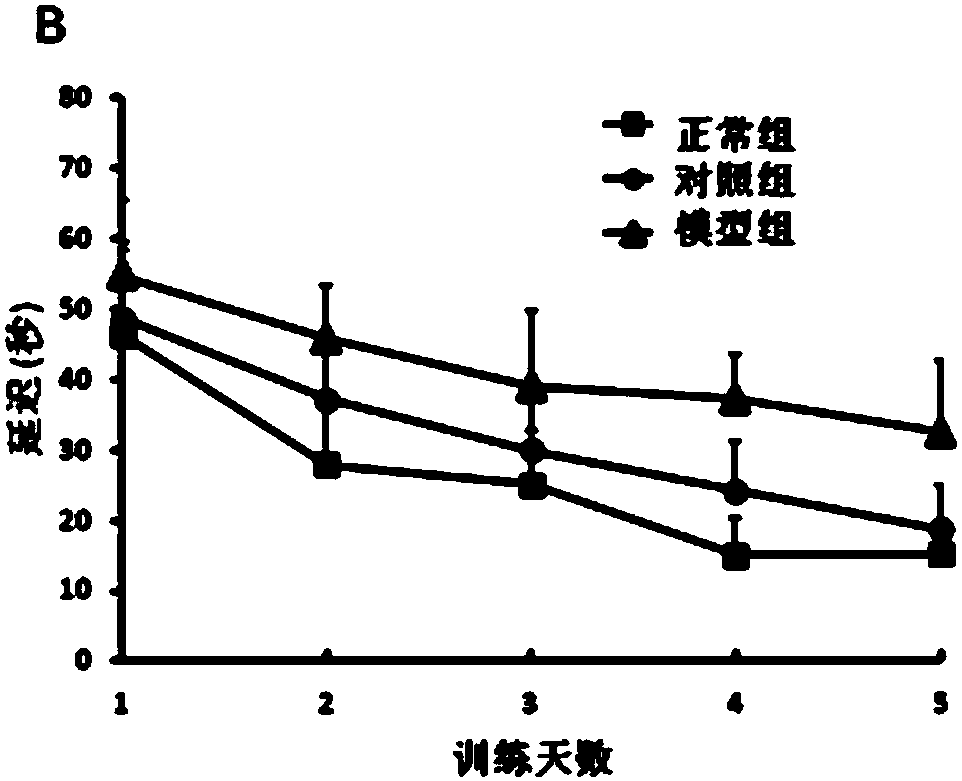
The invention relates to a construction method of an AD model rat hippocampus difference gene expression chart by combining Abeta and D-gal. The construction method comprises the following steps: firstly, treating a rat with the Abeta and the D-gal to establish an AD model rat; secondly, measuring memory damage of the AD model rat by using a Morris water maze so as to determine successful construction of the AD model rat; thirdly, obtaining hippocampus samples of an AD model group and a normal control group, and respectively obtaining gene chip data of all tested hippocampus gene expressions;fourthly, uploading all the gene chip data to gene chip data analysis software, obtaining differential expression genes and screening a gene spectrum of the differential expressions of the AD model rat; fifthly, carrying out functional annotation classification and a biological pathway analysis on the differently-expressed genes to reveal molecular basis associated with the AD. According to the construction method disclosed by the invention, the Abeta and the D-gal are used as a whole AD model to study the gene expression spectrum of the AD model rat hippocampus genes, so that other errors changing the expressions and induced by exogenous genes are effectively avoided.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Function candidate gene for affecting meat quality trait of pig and screening method of function candidate gene
The invention discloses function candidate gene for affecting the meat quality trait of a pig and a screening method of t function candidate gene. The function candidate geneisRXRG, GPI, CPT2 and / or GABARAPL1. The screening method comprises the following steps: (1), selecting longissimus muscles of two extreme pig breeds with large meat quality trait difference, extracting DNA, and independently creating databases; (2), performing whole genome DNA methylation sequencing on sample DNA databases by adoptingan MeDIP-Seq technology; (3), obtaining maps of whole genome DNA methylation levels of the two extreme pig breeds, and screeningdifferentialmethylationexpressed genes; (4), performing GO functional annotation and KEGG Pathway analysis on the differentialmethylationgenes, and screening out functional genes and regulatory pathways related to meat quality traits, such as fatty acid formation and decomposition; (5), performing DNA methylation and expression profileconjoint analysis through MeDIP-seq and RNA-seqtest results, and obtaining the function candidate gene of the meat quality trait of the pig. According to the method, the function candidate geneparticipatinginregulationof the meat quality trait of the pig is screened out, and a foundation is laid for the future deep research.
Owner:INST OF ANIMAL HUSBANDRY & VETERINARY MEDICINE ANHUI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
A method for rapid and automated analysis of prokaryotic proteomics data
ActiveCN105956416BIncrease Identification CoverageImprove compatibilityProteomicsGenomicsGenomicsDatabase file
The invention provides a method for analyzing data of prokaryotic proteogenomics rapidly and automatically. Users only need to provide mass spectral data and a corresponding database file and set a simple retrieval parameter; retrieval of data of proteogenomics can be completed; simultaneously, a user defined data retrieval result can also be compatible; therefore, the identification coverage rate of the data of proteogenomics is increased; in the method disclosed by the invention, library search engines of different algorithms are integrated in advance; disadvantages of a single retrieval method are made up; a user defined library search result can also be compatible; the method has good compatibility; the peptide fragment identification coverage rate is increased to the most extent; in the method disclosed by the invention, functional annotation of new genes is automatically completed; large-scale identification of protein post-translational modification and analysis of non-labelled quantitative proteomics are realized for the first time; and automatic and rapid deep analysis of the data of proteogenomics is really realized.
Owner:湖北普罗金科技有限公司
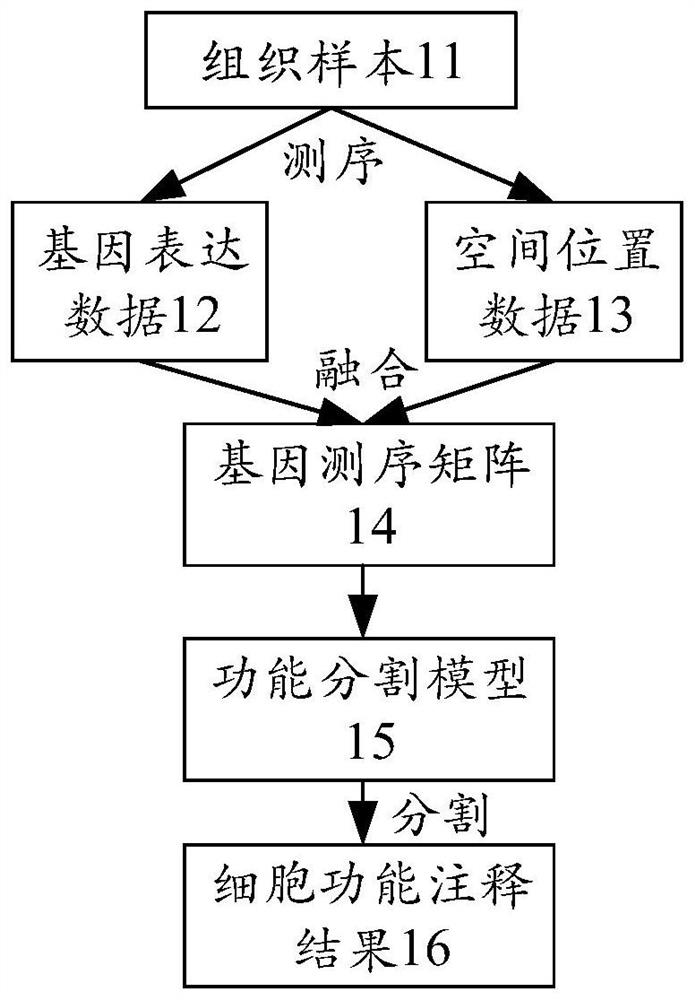
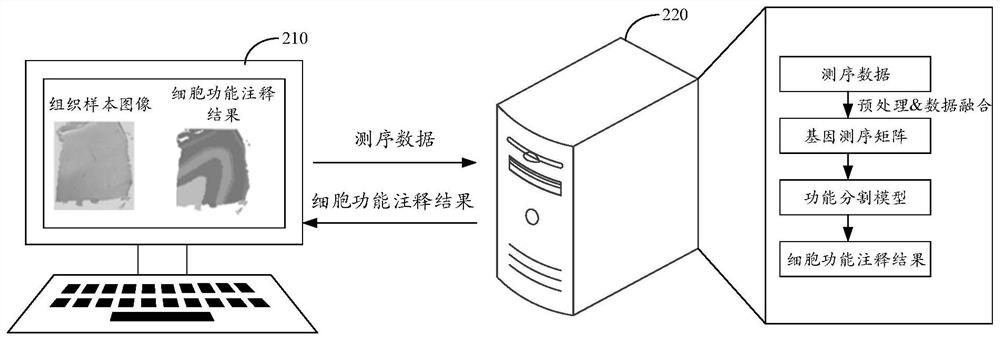
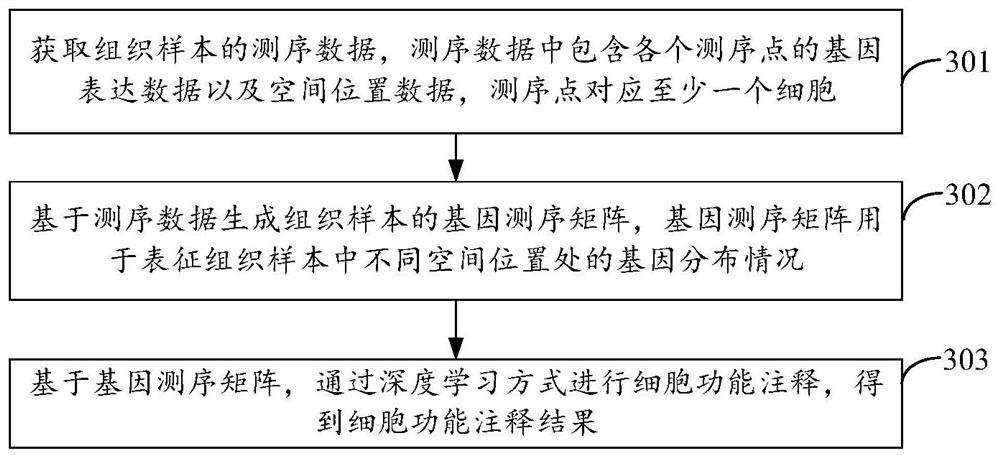
Cell function annotation method, device, equipment and medium
The invention discloses a cell function annotation method, device and equipment and a medium, and relates to the field of artificial intelligence. The method comprises: obtaining sequencing data of a tissue sample, the sequencing data comprising gene expression data and spatial position data of each sequencing point, and the sequencing point corresponding to at least one cell; generating a gene sequencing matrix of the tissue sample based on the sequencing data, wherein the gene sequencing matrix is used for representing gene distribution conditions at different spatial positions in the tissue sample; based on the gene sequencing matrix, cell function annotation is carried out in a deep learning mode, and a cell function annotation result is obtained. By adopting the scheme provided by the embodiment of the invention, the accuracy of cell function annotation can be improved.
Owner:TENCENT TECH (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
Monitoring gene silencing and annotating gene function in living cells
InactiveUS20080064040A1Direct effectSuitable for applicationMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingFluorescenceProtein translocation
The cell-based assays described in the present invention can be used to directly assess the sensitivity and specificity of the gene annotation reagent against its target, and to determine if a non-targeted gene participates in a pathway of interest or is functionally linked to another gene or protein. The combination of annotation reagents with such cell-based assays is useful for mapping genes (proteins) into cellular pathways on a genome-wide scale. Preferred assay embodiments include fluorescence or luminescence assays in intact (live or fixed) cells. Such fluorescence or luminescence assays include high-throughput or high-content assays for protein activity, subcellular localization, post-translational modifications, or interactions of proteins. Suitable assays may include protein-protein interaction assays; protein translocation assays; and post-translational modification assays. The invention can be used to assess the efficacy of any gene silencing experiment, to determine the level of gene silencing that is achieved, and to map novel genes into biochemical pathways, and to identify novel pharmaceutical targets. The results also demonstrate the feasibility of employing this strategy in genome-wide functional annotation efforts.
Owner:ODYSSEY THERA INC
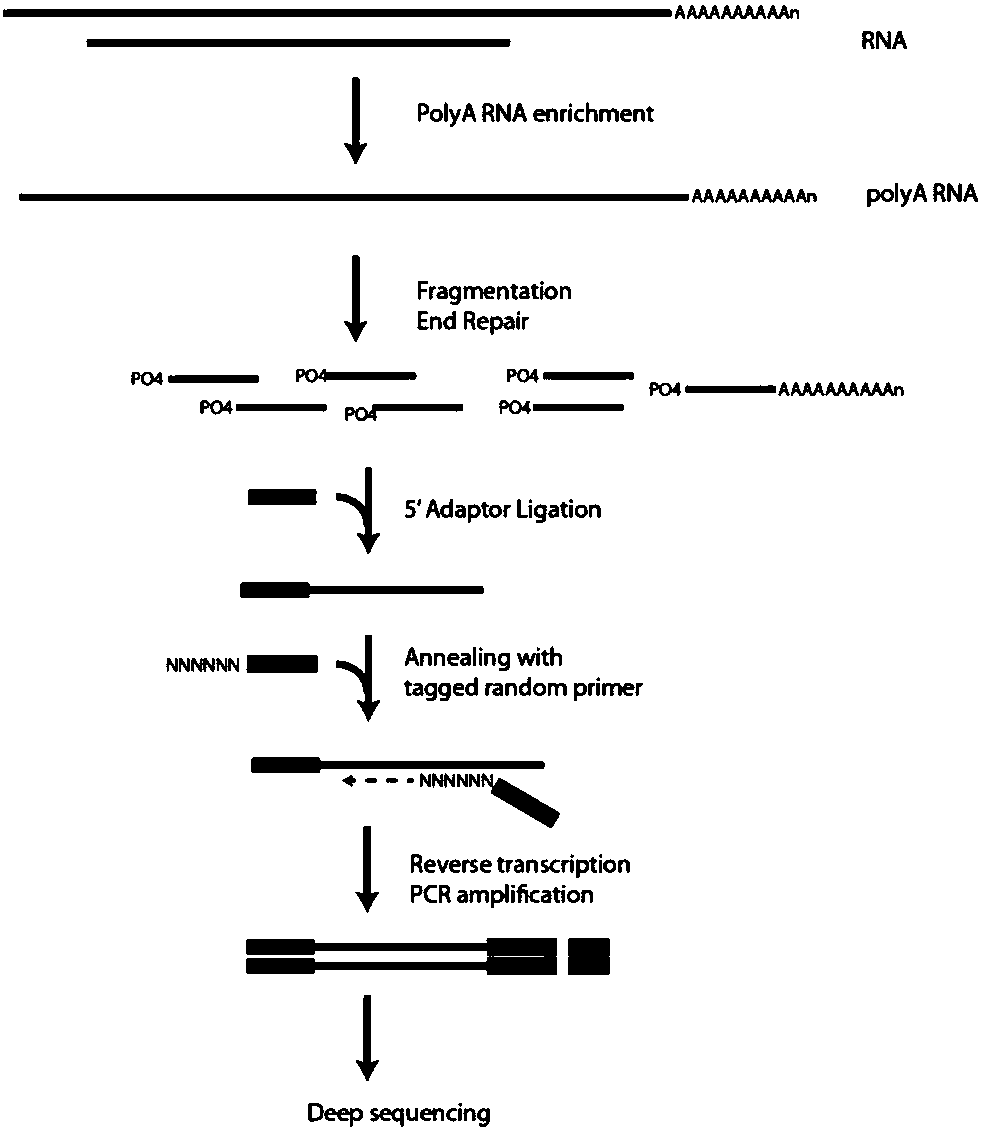
Method for obtaining transcriptome and functional genes of blumea balsamifera
PendingCN109423490AHigh content of active ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant peptidesPoly-A RNATotal rna
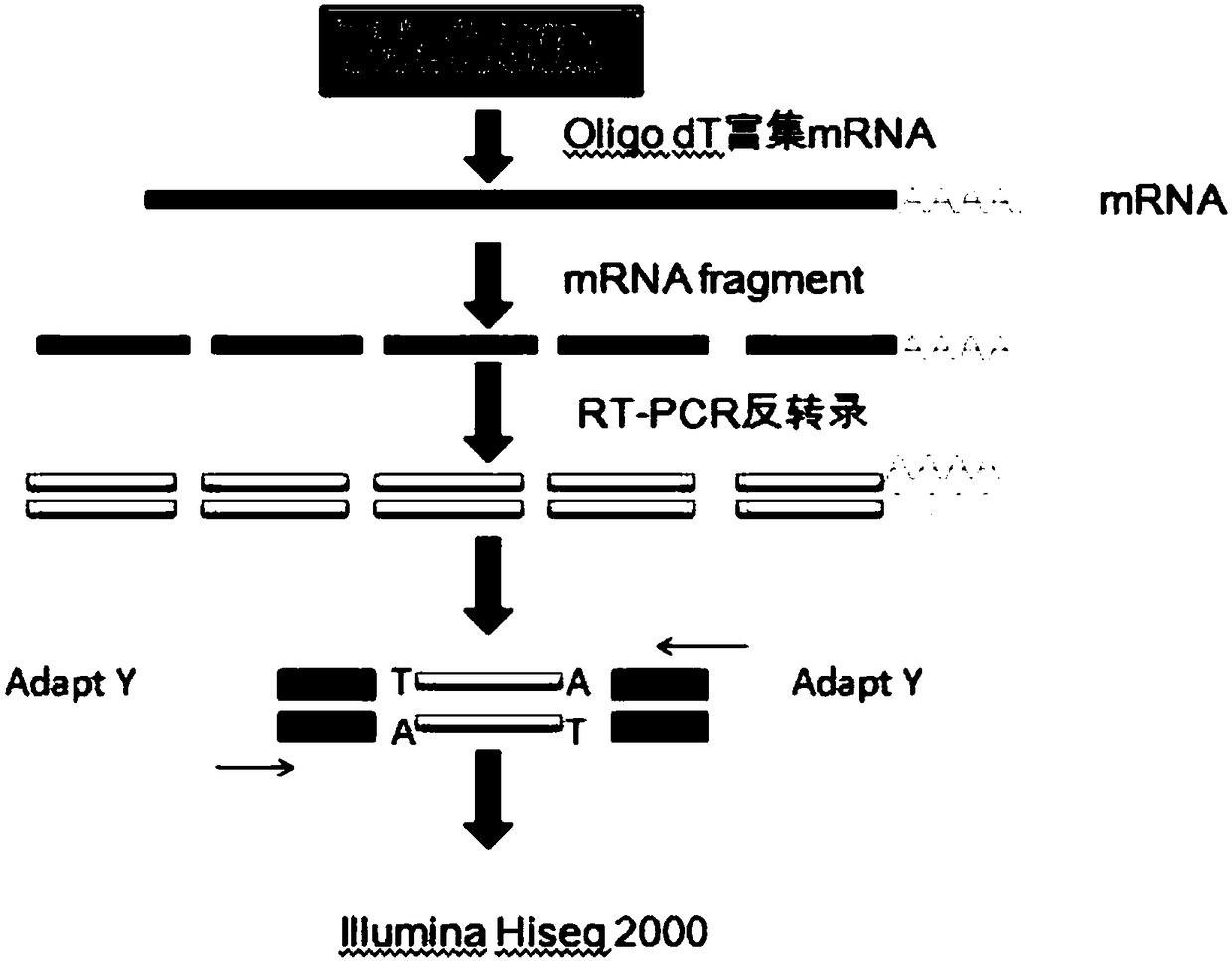
The invention provides a method for obtaining transcriptome and functional genes of blumea balsamifera. The method comprises (a) extracting the total RNA(ribonucleic acid) of blumea balsamifera, separating out mRNA (messenger RNA) with polyA (polyadenylation) at the 3' end, randomly breaking the mRNA, performing inverse transcription to synthesize double-stranded cDNA (complementary DNA); (b) sequencing an obtained sequence; (c) splicing and assembling a sequencing result to obtain Unigene and determining the orientation of the Unigene; (d) performing bioinformatics analysis on an obtained gene transcript to obtain the transcriptome and the function genes of blumea balsamifera. The method for obtaining the transcriptome and the functional genes of blumea balsamifera can help obtain 48197273 pieces of sequence information and 100341 Unigenes, involving 60477 pieces of information including RNA-seq names, sequence length and expression quantity, COG (cluster of ortholog genes) predication, COG functional annotations, KEGG (Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes) annotations, KEGG-pathway and GO (gene ontology) annotations, and 37283 pieces of information protein function annotationsfor performing CDS (coding sequence) prediction on the obtained sequence information.
Owner:TROPICAL CORP STRAIN RESOURCE INST CHINESE ACAD OF TROPICAL AGRI SCI
Third-generation full-length transcriptome sequencing result analysis method suitable for Sequel sequencing
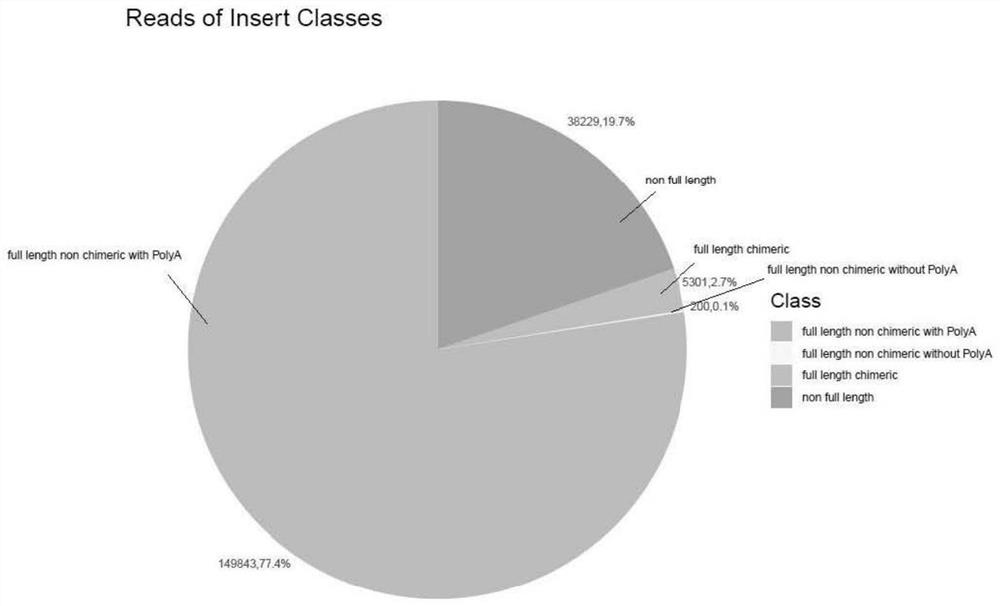
The invention discloses a third-generation full-length transcriptome analysis method suitable for a Sequel sequencing platform, which is characterized by comprising the following steps: 1, a sequencing data filtering step; 2, a sequencing data comparison step; 3, a transcript annotation step; 4, an ORF prediction step; 5, a transcript function annotation step; 6, a fusion gene analysis step; 7, aLncRNA prediction step; 8, variable shear analysis step; and 9, a variable polyadenylation analysis step. According to the method, the running speed is higher, annotation on the transcript is finer compared with common matchannot software, and the type of the transcript is more convenient to analyze.
Owner:南京派森诺基因科技有限公司
A method for predicting the function of unknown genes in maize based on the dynamic correlation between gene expression and traits
ActiveCN107058525BMicrobiological testing/measurementHybridisationCorrelation analysisExpression gene
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
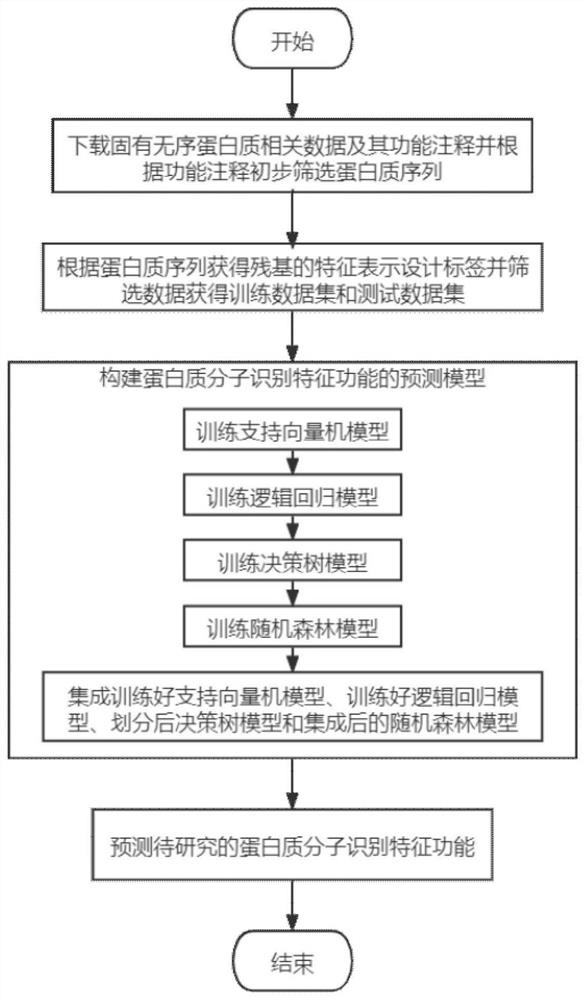
Molecular recognition feature function prediction method based on ensemble learning
PendingCN113936748AImprove accuracySimplify the experimental processMolecular entity identificationKernel methodsDrug targetEnsemble learning
The invention discloses a molecular recognition feature function prediction method based on ensemble learning, and mainly solves the problem that an existing molecular recognition feature predictor cannot further divide molecular recognition feature functions. According to the scheme, the method comprises the following steps: downloading inherent disordered protein data and functional annotations thereof, dividing training data and test data, performing feature representation on a protein sequence, and designing a residue tag of the protein sequence; selecting a single-input binary association strategy machine learning model; training different machine learning models by using the training data; integrating training results of different machine learning models by using an integration strategy to collect a prediction model; and inputting to-be-researched protein sequence data into the prediction model, and outputting a molecular recognition feature function prediction result of the protein. The method is simple in experimental process, low in resource consumption, low in cost and high in reliability of prediction results, can be used for predicting molecular recognition features in protein sequences, and provides reference for drug target acting positions.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
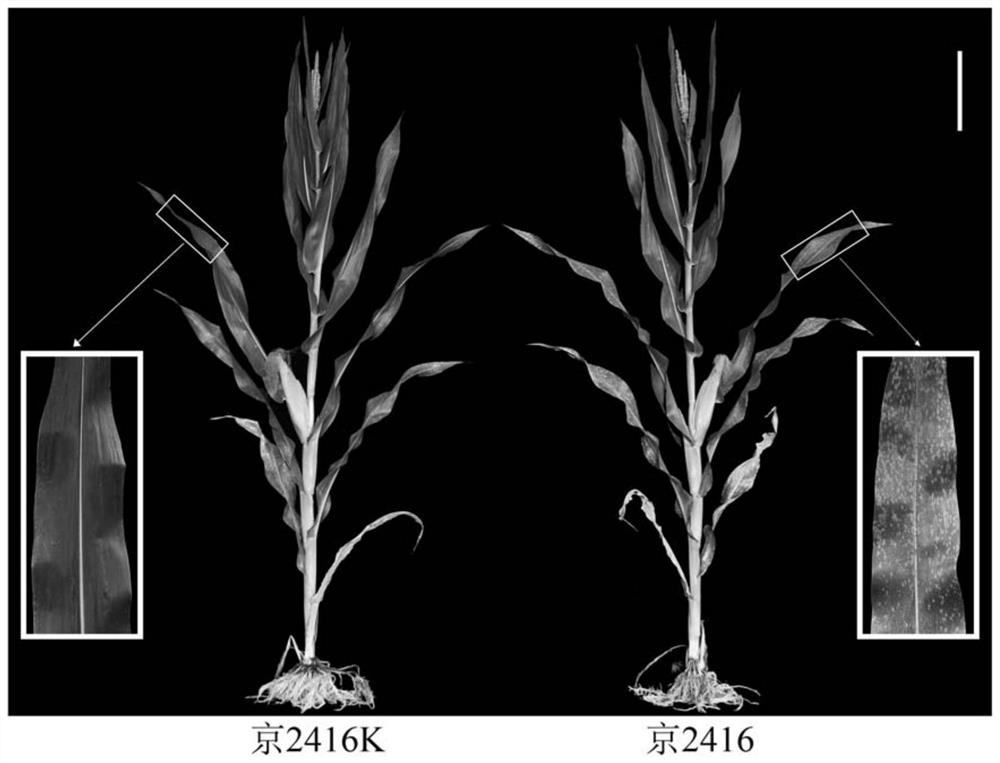
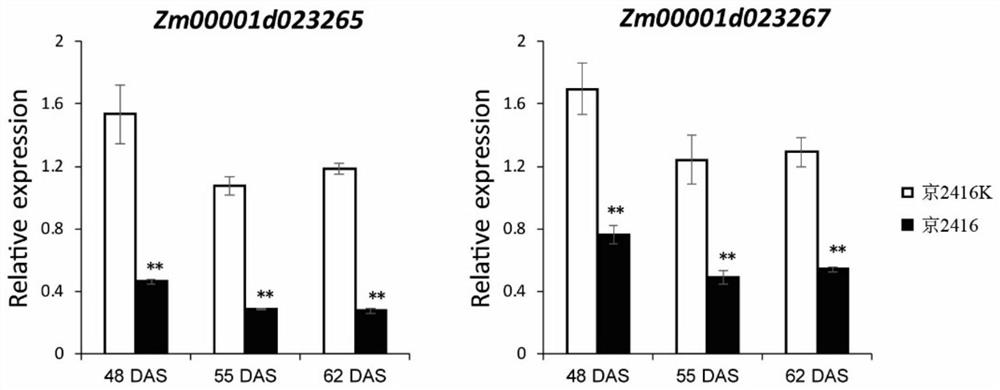
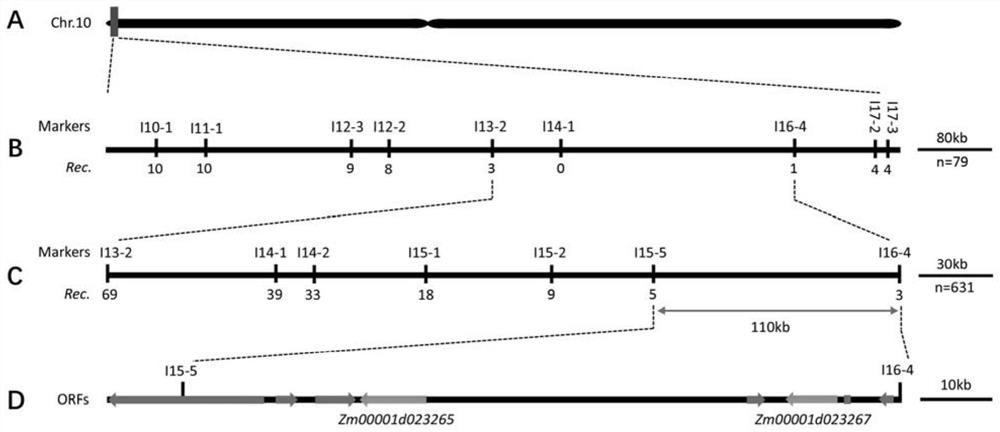
Corn southern rust resistance gene and application thereof
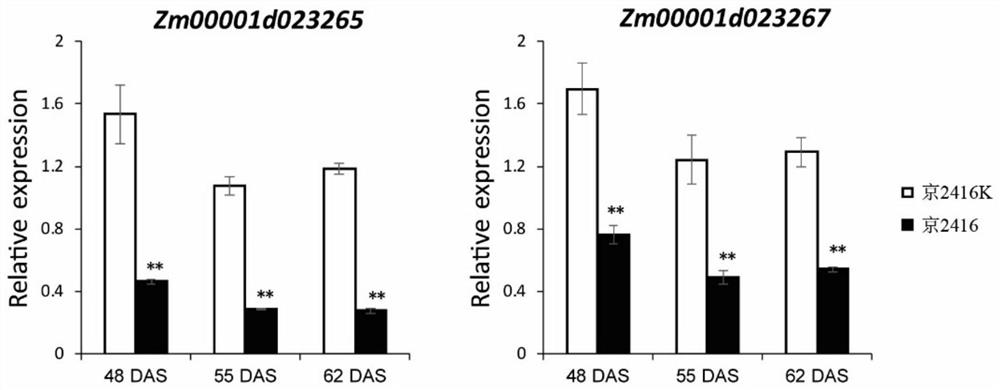
The invention discloses a corn southern rust (Puccinia polysora Underw) resistance gene and application thereof. F2 segregation population of inbred line Jing 2416 and Jing 2416K is used for genetic analysis, and the result shows that the resistance gene contained in the Jing 2416K is a single dominant gene and is named as RppM. The application comprises the following steps of positioning RppM in an interval of a short arm 110-kb of a corn chromosome No. 10 through BSA re-sequencing analysis and genetic linkage analysis, performing function annotation analysis, sequence comparison analysis and expression quantity analysis on candidate genes in the interval, determining Zm00001d023265 and Zm00001d023267 as the candidate genes of the RppM, and performing molecular cloning on the two genes to obtain coding region sequences of the two genes. Transgenic experiment verification proves that the two genes both have the function of improving the resistance of the corn to the southern rust disease, and new resistant materials and gene resources are provided for corn resistance breeding.
Owner:BEIJING ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE & FORESTRY SCIENCES
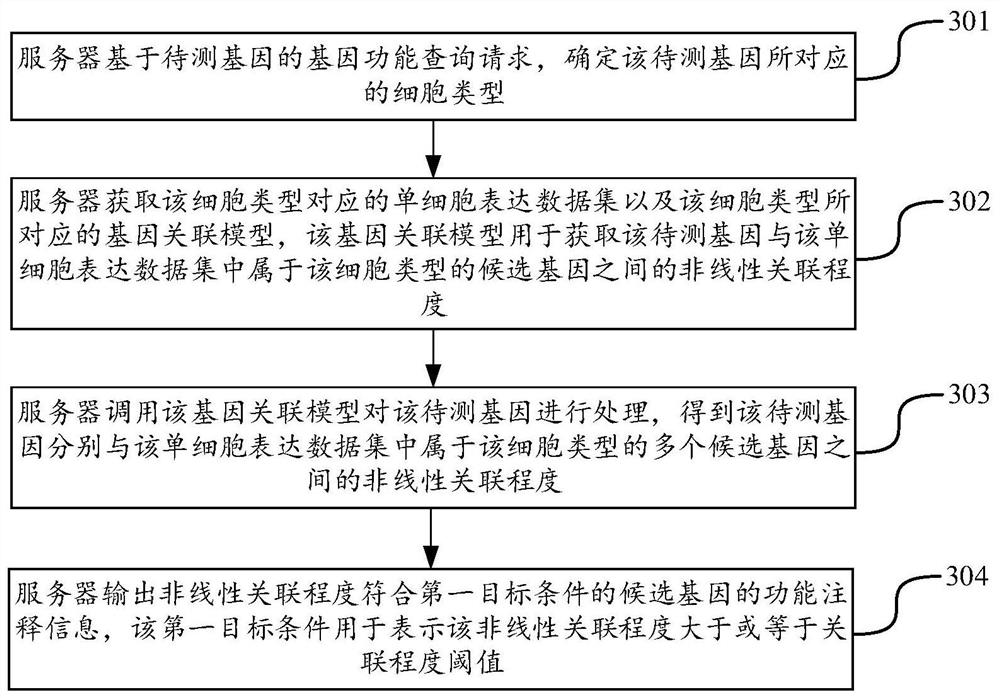
Gene data processing method and device, computer equipment and storage medium
PendingCN114765062AImprove accuracyProteomicsGenomicsCandidate Gene Association StudyLinear relationship
The invention discloses a gene data processing method and device, computer equipment and a storage medium, and belongs to the technical field of computers. According to the method, the gene association model corresponding to the cell type to which the to-be-detected gene belongs can be called through the gene function query request of the to-be-detected gene, and the nonlinear association degree between the to-be-detected gene and the known candidate gene is mined; the candidate genes with high nonlinear correlation degree are used for labeling the function annotation information of the to-be-detected genes, the mode of extracting the nonlinear relation by calling the gene correlation model is completely different from the mode of extracting the linear relation in the traditional statistics, the candidate genes with higher similarity with the to-be-detected genes can be deeply mined, and the accuracy of the to-be-detected genes is improved. The similarity is implicit non-linear similarity instead of non-linear similarity, so that the accuracy of the gene data processing process is greatly improved.
Owner:TENCENT TECH (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
A functional prediction method for single-nucleotide genomic variation in non-coding regions
ActiveCN109033751BLow sequencing depth requirementAvoid time costProteomicsGenomicsBinding siteNucleotide
The invention discloses a method for predicting the function of a single nucleotide genome variation in a non-coding region, comprising the following steps: 1) identification of an open chromatin region; 2) identification of a transcription factor binding site; 3) evaluation of a single nucleotide variation Role: Based on the site-specific frequency matrix of transcription factors, calculate the impact of single nucleotide variations located in the binding site region of transcription factors on the binding of transcription factors, and identify single nucleotide variations that significantly change the binding ability of transcription factors; further Assess the effect of single nucleotide variants by looking at the biological pathways of transcription factors' target genes. This method uses chromatin open region information and gene expression information to complete the identification of multiple transcription factors and their binding sites at one time, and realize the functional annotation of genomic variation in non-coding regions.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Maize southern rust resistance gene and its application
ActiveCN113372424BIncrease resistancePlant peptidesFermentationCandidate Gene Association StudyTransgene
The invention discloses a maize southern rust resistance gene and its application. The present invention utilizes the F of the inbred line Jing 2416 and Jing 2416K 2 Genetic analysis of the isolated population showed that the resistance gene contained in Jing 2416K was a single dominant gene, named RppM. Through BSA resequencing analysis and genetic linkage analysis, RppM was located in the 110-kb interval of the short arm of maize chromosome 10, and the candidate genes in this interval were subjected to functional annotation analysis, sequence alignment analysis and expression analysis to determine Zm00001d023265 and Zm00001d023267 are candidate genes of RppM, and molecular cloning of the two genes was carried out to obtain the coding region sequences of the two genes. The transgenic experiments proved that both genes have the function of improving the resistance of maize to southern rust, providing new resistance materials and gene resources for maize resistance breeding.
Owner:BEIJING ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE & FORESTRY SCIENCES
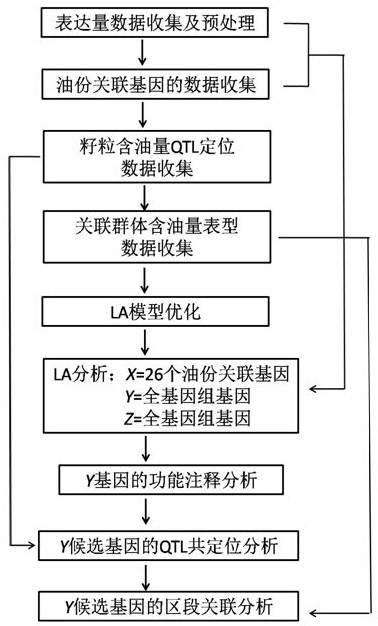
A method for mining oil metabolism mechanism of corn kernels based on dynamic association analysis
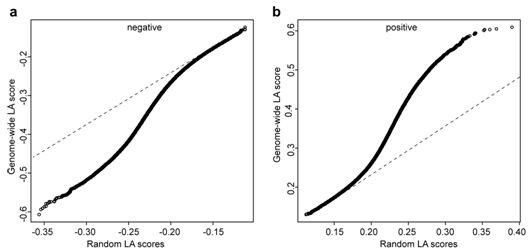
InactiveCN106929579BValid identificationIdentifiable regulatory relationshipsMicrobiological testing/measurementBiostatisticsCandidate Gene Association StudyGene coexpression
The invention belongs to the fields of plant molecular biotechnology and gene engineering and particularly relates to a method for exploring a lipid metabolism mechanism of corn kernels based on dynamic association analysis. The method specifically comprises the following steps: collecting gene expression quantity data of a corn selfing line; collecting gene data associated with oil content of the corn kernels; collecting oil content data of the kernels of association group formed by the corn selfing line; establishing a dynamic association analysis LA model; exploring a control gene for controlling dynamic change of a coexpression mode of 26 oil content associated genes in a whole genome range, and authenticating a candidate gene dynamically associated with the coexpression mode of the 26 oil content associated genes; carrying out function annotation on the candidate gene; detecting whether the candidate gene is in a QTl section of oil content characters; and carrying out section association analysis on oil content phenotype data of the corn selfing line. By taking the control of dynamic association of the coexpression mode of the known oil content associated genes as a key point, the control gene for controlling lipid metabolism of the kernels can be rapidly and effectively authenticated.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
A deep learning approach for DNA-binding protein identification and functional annotation based on self-attention mechanism
The invention discloses a deep learning method for DNA binding protein identification and functional annotation based on a self-attention mechanism. A data set is selected from a protein database, and the constructed deep learning model is trained and tested by using the selected data set, and then the trained deep learning model is used for training and testing. The deep learning model can predict whether protein can bind to DNA; wherein, the deep learning model includes coding layer, embedding layer, long short-term memory neural network layer (LSTM), convolutional neural network layer (CNN) and self-attention Layer (Self‑Attention). Through the deep learning model based on the self-attention mechanism, the present invention can predict whether it has the function of binding with DNA according to the primary sequence information of the protein, and find out the region with the binding function.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
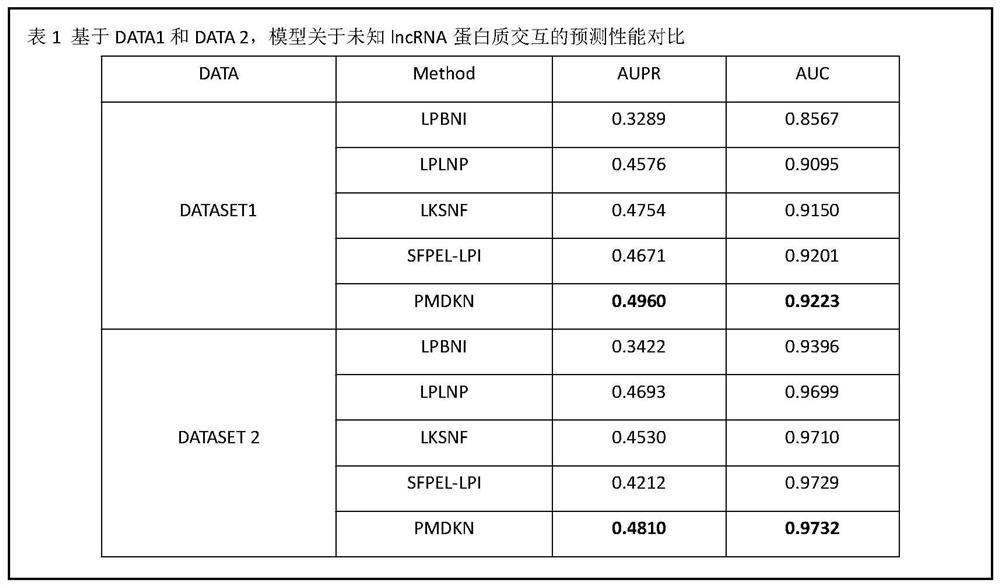
A lncRNA-protein Association Prediction Method Based on Projected Neighborhood Nonnegative Matrix Factorization
ActiveCN110491443BEfficient forecastingEfficient use ofCharacter and pattern recognitionProteomicsNonnegative matrix factorisationProtein Interaction Networks
The invention discloses a lncRNA-protein association prediction method based on projected neighborhood non-negative matrix decomposition. First, according to the lncRNA sequence, lncRNA expression profile data, protein sequence, GO function annotation data of protein and the interaction network of lncRNA and protein, calculate A variety of lncRNA features, protein features, lncRNA similarity matrix and protein similarity matrix are obtained. Secondly, the integrated lncRNA similarity network is obtained by fusing multiple lncRNA similarity networks, and the integrated protein similarity network is obtained by fusing multiple protein similarity networks. Finally, combining the integrated lncRNA(protein) similarity network and multiple lncRNA(protein) features, a feature-projected neighborhood nonnegative matrix factorization algorithm is proposed to predict potential lncRNA-protein interactions. The present invention can not only accurately predict new lncRNA-protein interactions, but also predict new proteins (lncRNA) that are not associated with any lncRNA (protein), effectively avoiding high human and material resource consumption caused by biochemical experiments.
Owner:HUAZHONG NORMAL UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com