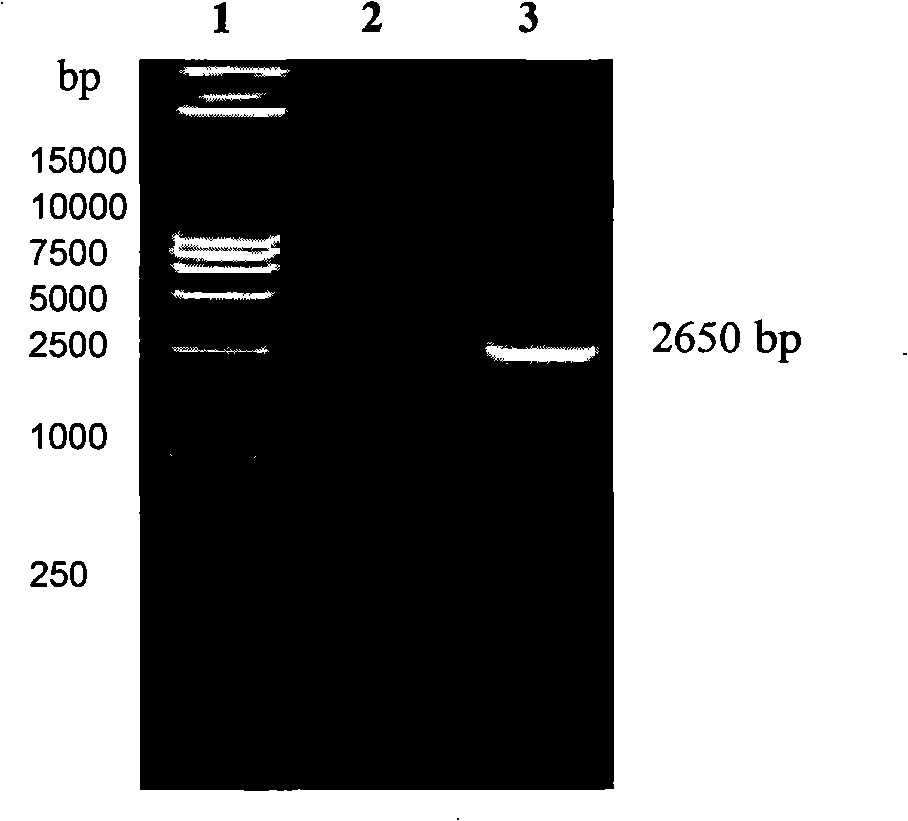
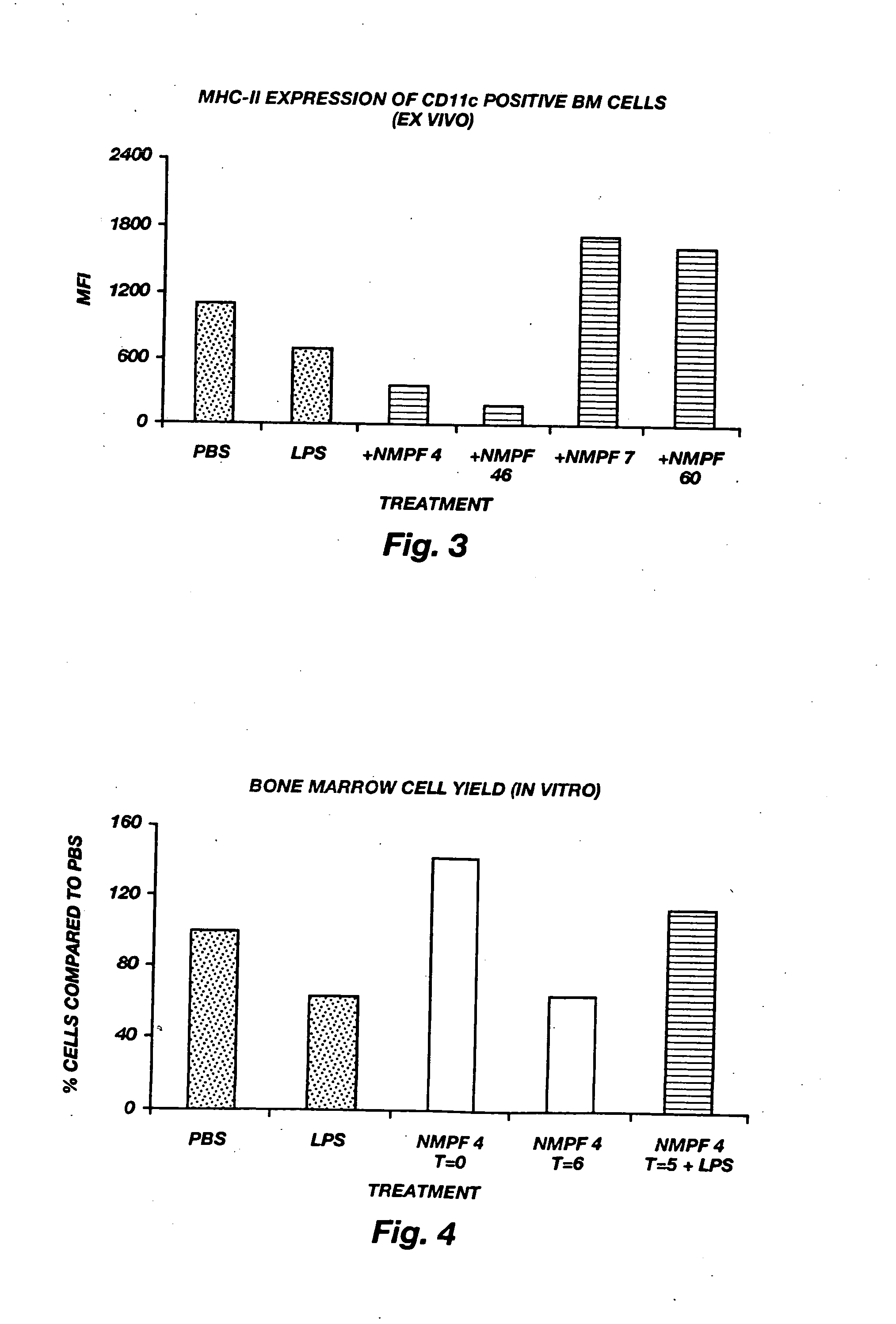
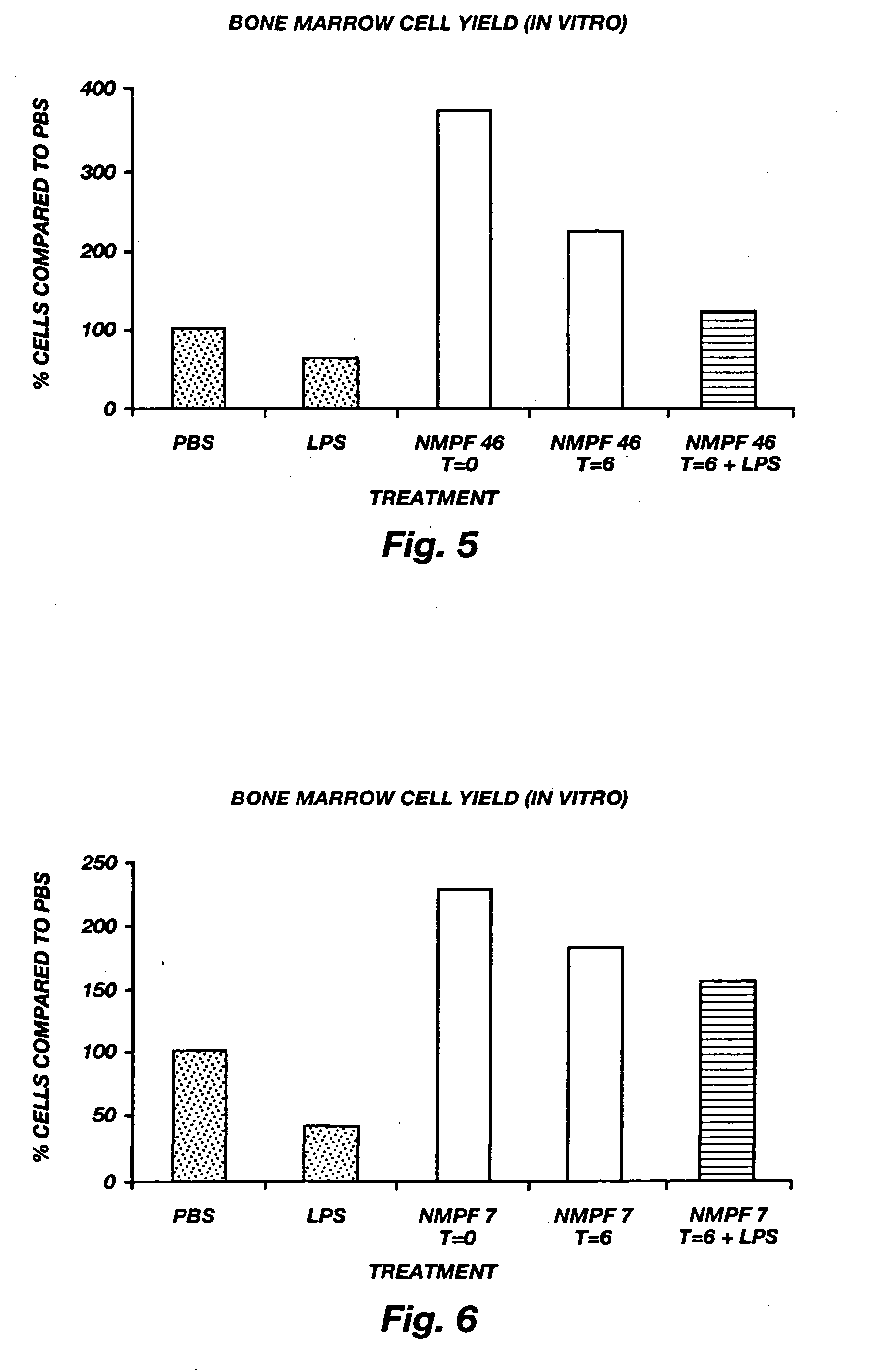
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
226 results about "Gene control" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Dietary supplement and method of processing same
InactiveUS20050158376A1Avoid contactMaintain curative effectBiocideHydroxy compound active ingredientsNatural sourceAntioxidant
A composition including small plant or synthetic molecules, such as resveratrol and quercetin, in their biologically active form, is provided. The small molecules may be derived from natural sources such as grapes or Giant Knotweed (botanical name Polygonum). The composition may be processed such that the gene-controlled biological activity of the small molecules is maintained. Specifically, the raw material for encapsulation must exhibit biological activity before and after encapsulation and be processed in an oxygen-free (nitrogen), dim light environment. The composition may further include at least one metal chelating agent as an antioxidant stabilizer, an antioxidant, and an emulsifier. The compositions are useful in the formation of a dietary supplement or drug.
Owner:RESVERATROL PARTNERS
Oligopeptide treatment of NF-κB mediated inflammation
InactiveUS7175679B2Reduced iron up-takeAccelerated deathAntipyreticAnalgesicsSignalling moleculesOligopeptide
The invention relates to the modulation of gene expression in a cell, also called gene control, in particular in relation to the treatment of anthrax. The invention provides a method for modulating expression of a gene in a cell comprising providing the cell with a signaling molecule comprising a peptide or functional analogue thereof.
Owner:BIOTEMPT
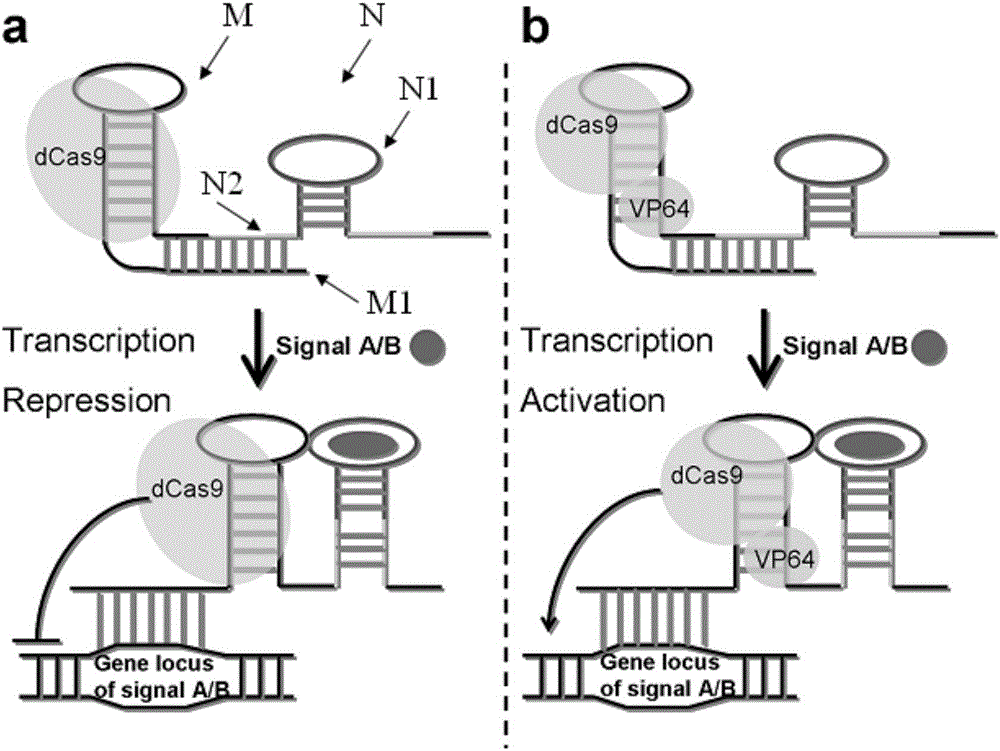
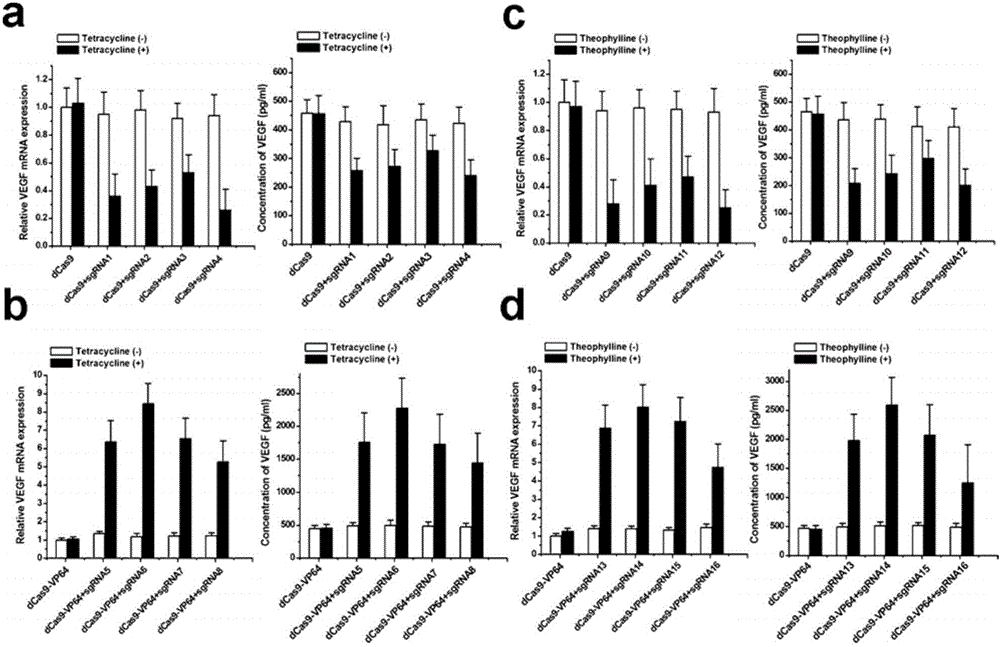
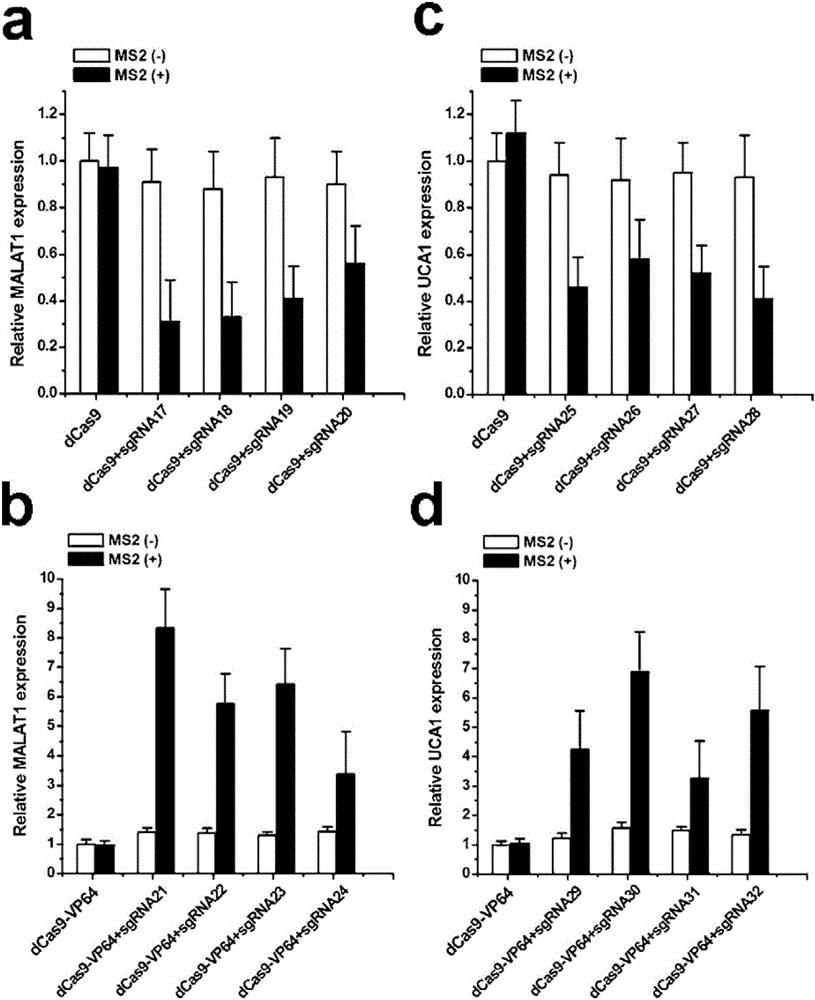
Gene control device and method based on CRISPR-Cas9
The invention discloses a gene control device and method based on CRISPR-Cas9. The device comprises a nucleotide sequence, wherein the nucleotide sequence is an sgRNA itself or can be transcribed into an sgRNA, the sgRNA structurally comprises a first part bonded with inactivated Cas9 protein and a second part connected to the 3'end of the first part, the 5'end of the first part is provided with an antisense sequence, and the second part is an aptamer sequence part which comprises a ligand binding part and an aptamer stem part; when no ligand exists, the aptamer sequence is pair-bonded with the aptamer stem part; when a ligand exists, the aptamer sequence is dissociated from the aptamer stem part so as to be pair-bonded with a target DNA. By integrating an RNA riboswitch bonded with a specific biological signal into the sgRNA, a bridge of cell signal intensity and gene expression intensity is established, any target gene can be activated or silenced on the basis that biological signal identification is achieved, and artificial connection is built between signal ligands and cytogene.
Owner:THE SECOND PEOPLES HOSPITAL OF SHENZHEN
Gene regulatory peptides
InactiveUS20050214943A1Quick and easy approachThe process is simple and fastAntibacterial agentsAntipyreticSignalling moleculesExpression gene
The invention relates to the modulation of gene expression in a cell, also called gene control, in particular in relation to the treatment of a variety of diseases. The invention provides a method for modulating expression of a gene in a cell comprising providing the cell with a signaling molecule comprising a peptide or functional analogue thereof. Furthermore, the invention provides a method for identifying or obtaining a signaling molecule comprising a peptide or functional derivative or analogue thereof capable of modulating expression of a gene in a cell comprising providing the cell with a peptide or derivative or analogue thereof and determining the activity and / or nuclear translocation of a gene transcription factor.
Owner:BIOTEMPT
Genetically engineered bacterium producing tetrahydropyrimidine and structuring method and application thereof
ActiveCN105018403AIncrease productivityLow costBacteriaMicroorganism based processesChemical synthesisBiotechnology
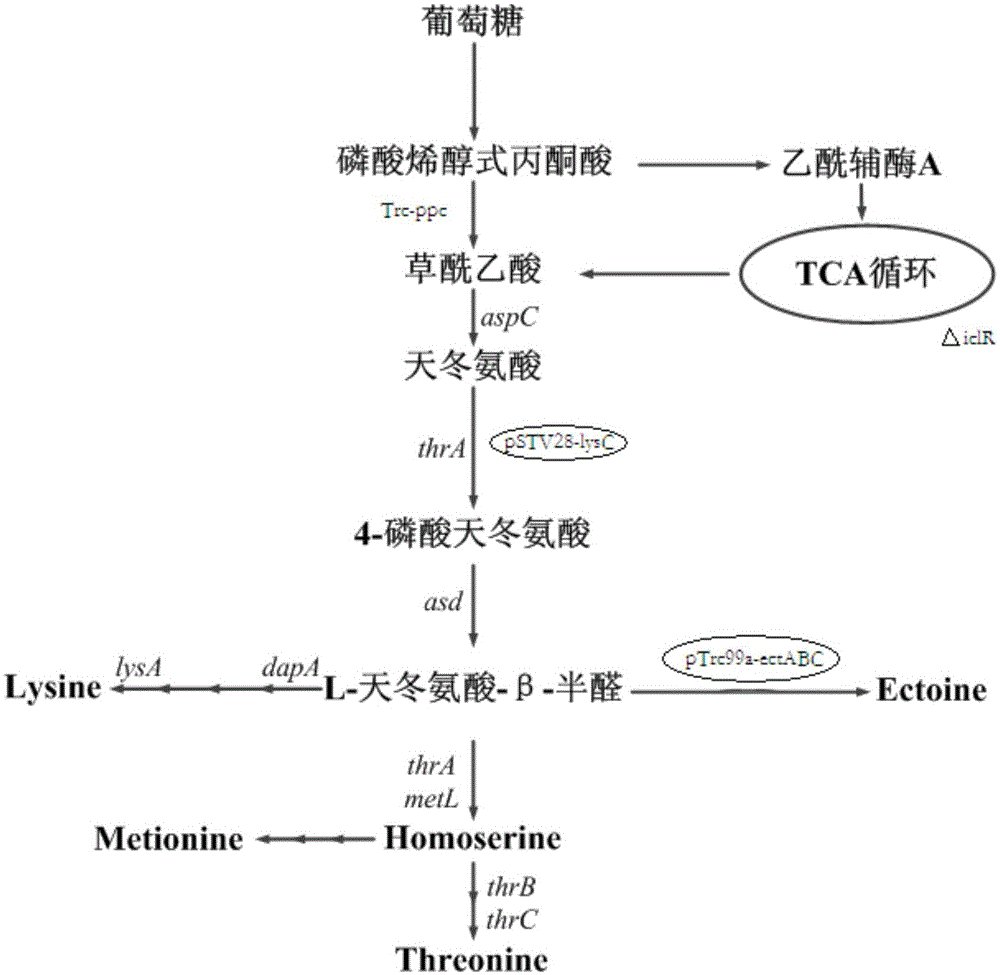
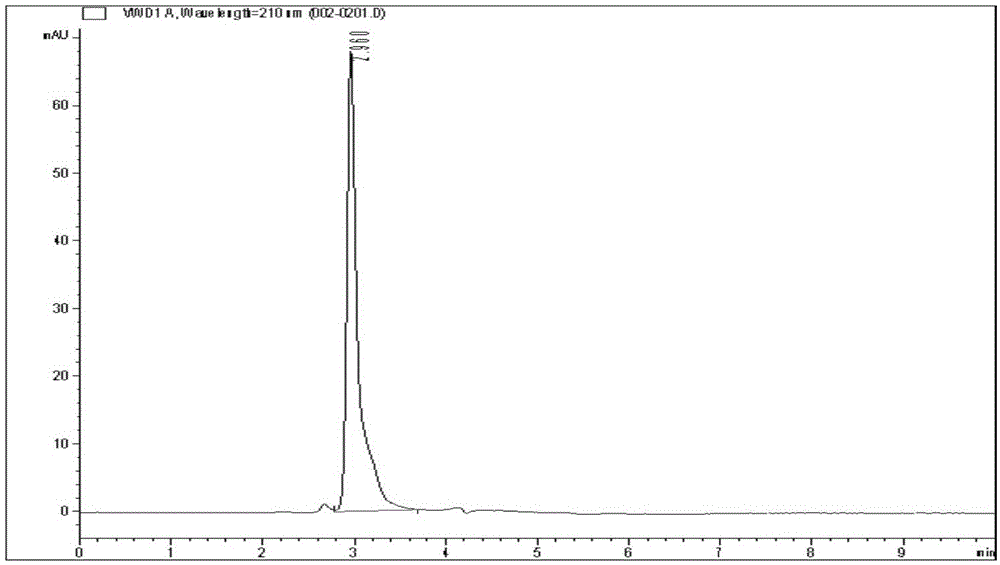
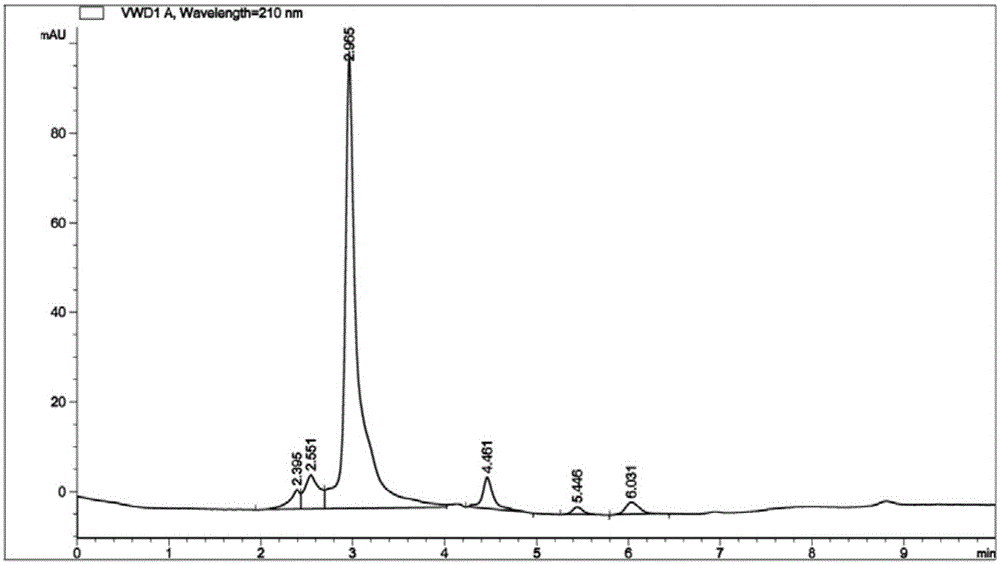
The invention relates to a genetically engineered bacterium producing tetrahydropyrimidine and a structuring method and application thereof. The genetically engineered bacterium is Escherichia coli with a specific genotype, comprises Halomonas-elogata-derived ectABC gene, has three gene deficiency variants including lysA, thrA and iclR and has corynebacterium glutamicum lysC gene controlled by a lac promoter and ppc gene controlled by a trc promoter. The defect that chemical synthesis methods have harsh reaction conditions and high energy consumption can be overcome by using the genetically engineered bacterium and utilizing glucose fermentation to produce tetrahydropyrimidine. The defect that Halomonas-elogata fermentation or enzyme-catalyzed methods are complex in process and high in production cost can be overcome. After fermentation for 20-28h, yield of tetrahydropyrimidine reaches 12-18g / L, and the genetically engineered bacterium has high industrial application value.
Owner:合肥和晨生物科技有限公司
Recombinant bacillus subtitles capable of increasing yield of acetylglucosamine
InactiveCN107699533AReturn to normal growthIncrease productionBacteriaHydrolasesPhosphateAcetylglucosamine
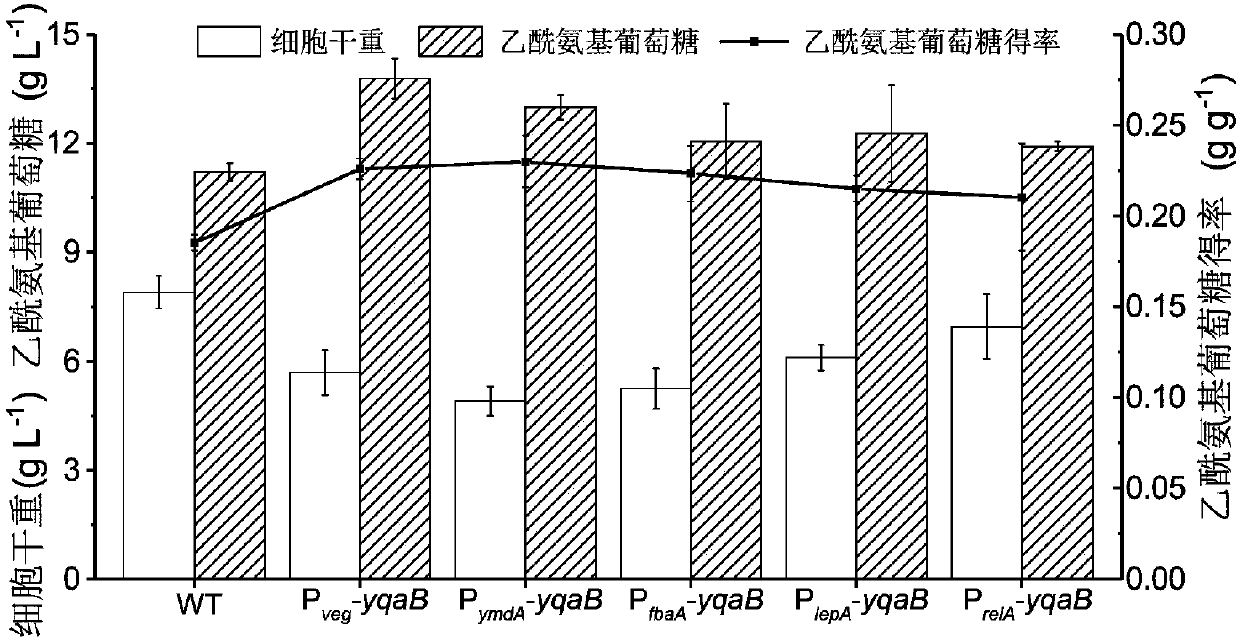
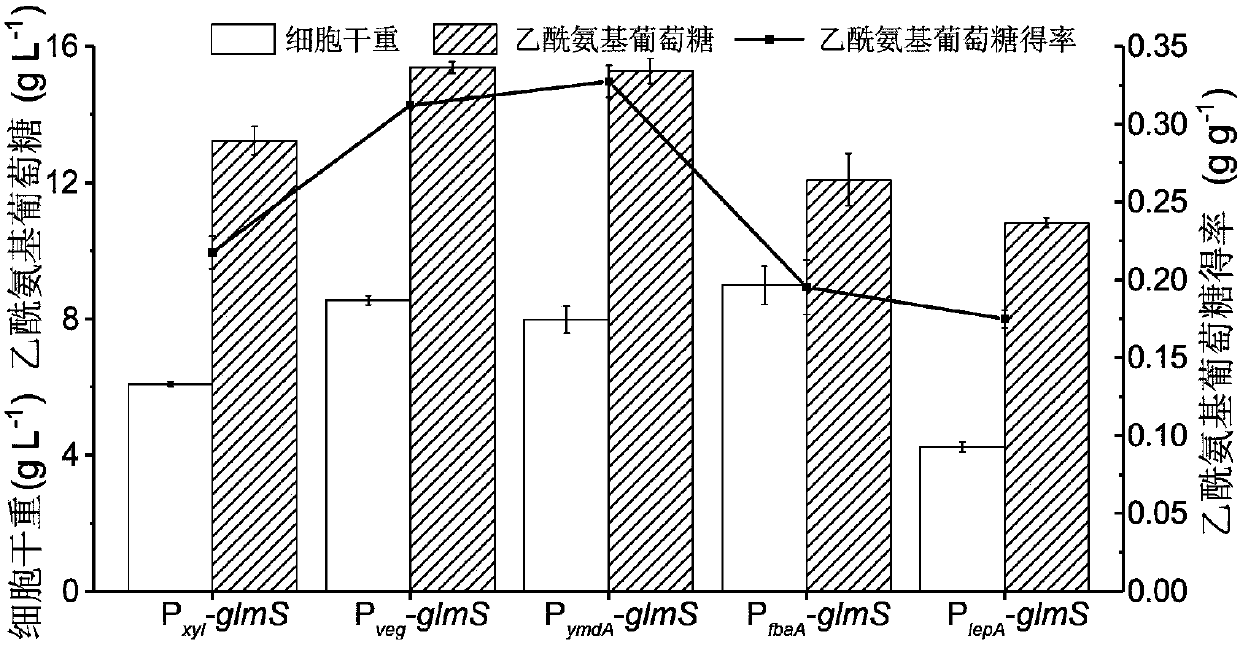
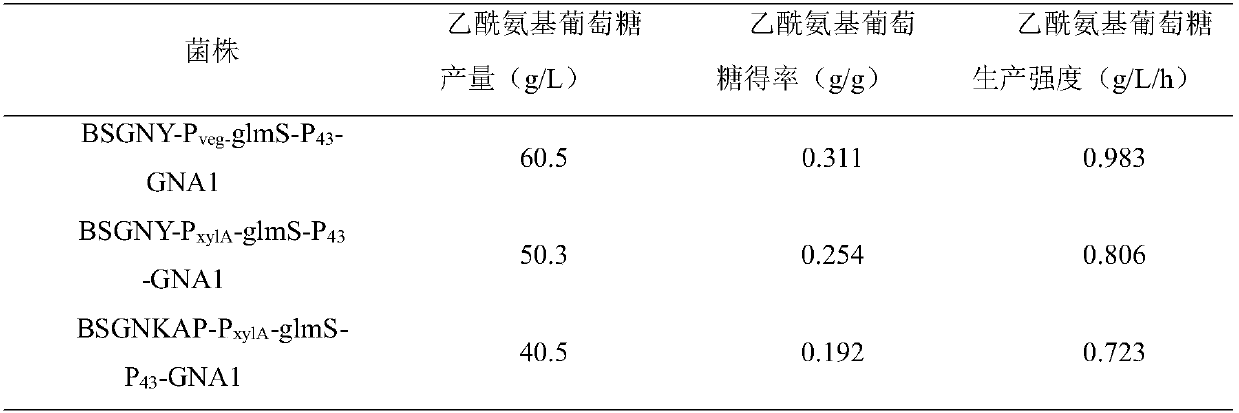
The invention discloses recombinant bacillus subtitles capable of increasing the yield of acetylglucosamine and belongs to the field of genetic engineering. The recombinant bacillus subtitles is characterized in that bacillus subtitles BSGNKAP-Pxy1A-glmS-P43-GNA1 is used as the original strain, a phosphatase yqaB gene controlled by a strong constitutive promoter Pveg is integrated to the genome, and the promoter of 6-phosphate glucosamine synthase is replaced by the strong constitutive promoter Pveg to obtain genetically engineered bacillus subtitles BSGNY-Pveg-glmS-P43-GNA1 accumulating the acetylglucosamine. The recombinant bacillus subtitles has the advantages that the yield of the acetylglucosamine of a 3L fermentation tank reaches 60.5g / L, the yield of the acetylglucosamine is 0.311g / g glucose, production intensity is 0.983g / L / h, the yield of the acetylglucosamine outside the cells of the recombinant bacillus subtitles is increased, and a foundation is laid for glucosamine production using metabolic engineering modified bacillus subtitles.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
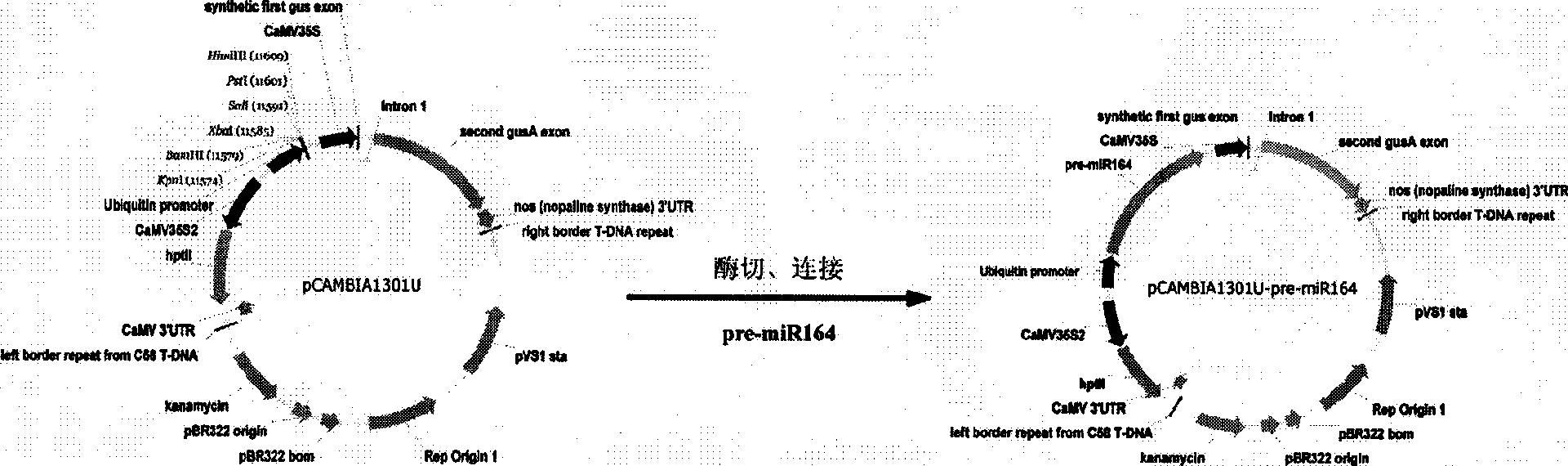
Function and application of miR164 genes in controlling development and fertility of root system of rice
InactiveCN101544987AVector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsBiotechnologyPlant roots
The invention relates to the technical field of rice gene engineering. Application of miR164 small RNA of rice for controlling development and fertility of a root system of a plant to genetic improvement of the rice is obtained through separation, cloning and functional verification, and the gene is one of the following nucleotide sequences: a DNA sequence shown in a sequence table SEQ NO:1 and an RNA sequence shown in SEQ NO:2. After connecting with an exogenous promoter, a nucleotide sequence containing miR164 precursor is transferred into the rice, the root system of the transgenic rice is developed and sterile, and the fertility can be recovered by externally applying hormone.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Magnetic resonance-based water treatment device
ActiveCN102485658AImprove bioavailabilityImprove biological activityWater/sewage treatment by magnetic/electric fieldsRadio frequencyDrug biological activity
The invention discloses a magnetic resonance-based water treatment device. The magnetic resonance-based water treatment device realizes water treatment through electromagnetic waves produced by magnetic resonance. The magnetic resonance-based water treatment device is characterized in that a power signal is subjected to transformation rectification by a transformation rectification circuit and then is input into a high-frequency inverter and a low-frequency inverter; radio frequency pulses having different frequency values are invertedly output by the high-frequency inverter and the low-frequency inverter; and the radio frequency pulses having different frequency values are transmitted to corresponding electromagnetic vibration wave transducers in a water treatment tank so that two different electromagnetic wave energy zones are formed. Through the magnetic resonance-based water treatment device, a water molecule is stimulated by resonance-supported radio frequency pulse energy waves and then splits and thus a hydrogen bond active force, an organization structure and an energy load capacity of water are changed. Water treated by the magnetic resonance-based water treatment device has the advantages that the bioavailability and the biological activity are improved; metabolism quality is improved; a free radical inhibition and removal capability is obtained; and a gene control capability is improved. The magnetic resonance-based water treatment device can produce health water, adopts a physical production technology and simple production processes, and has high production efficiency and a low cost.
Owner:易乾东
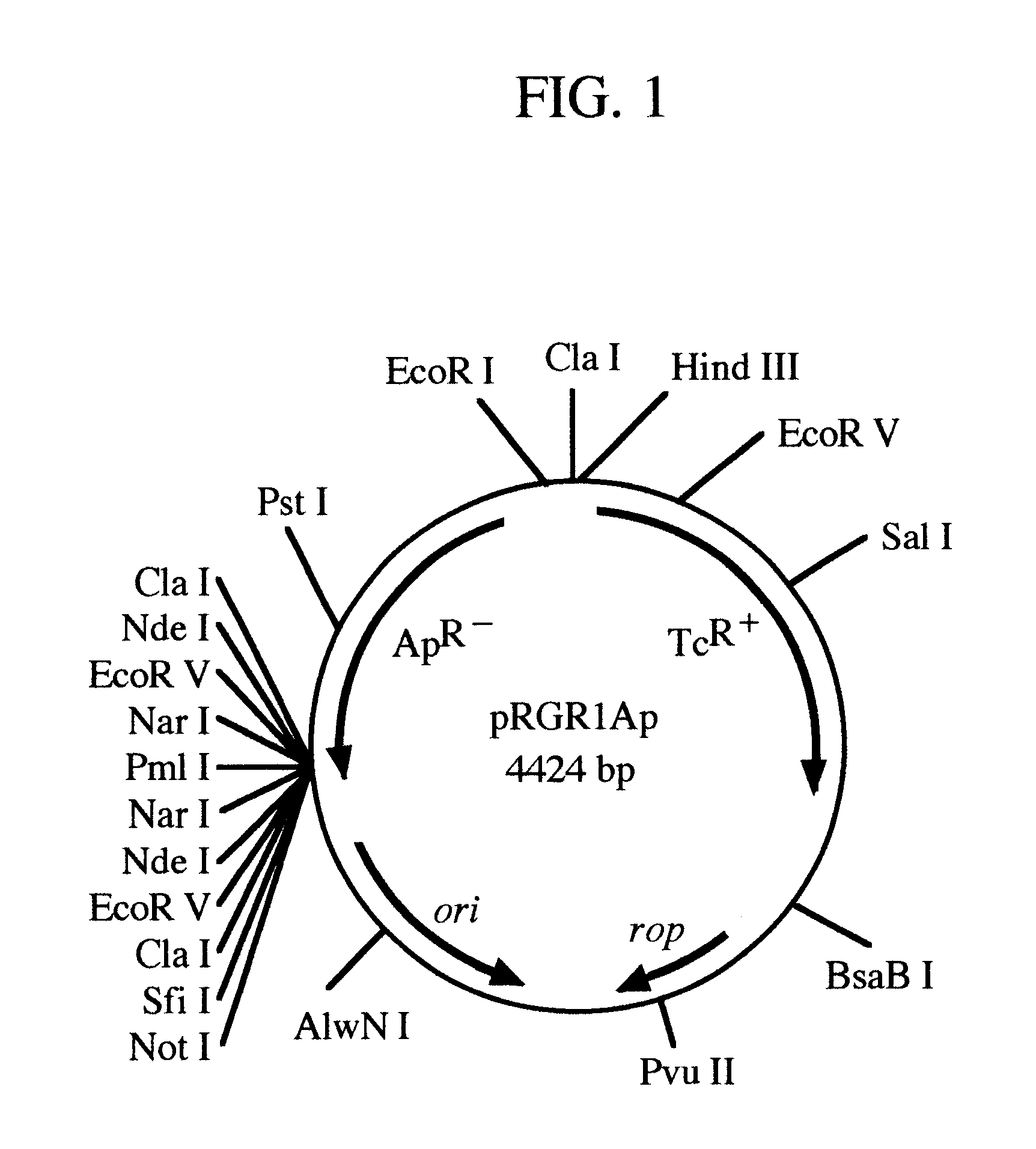
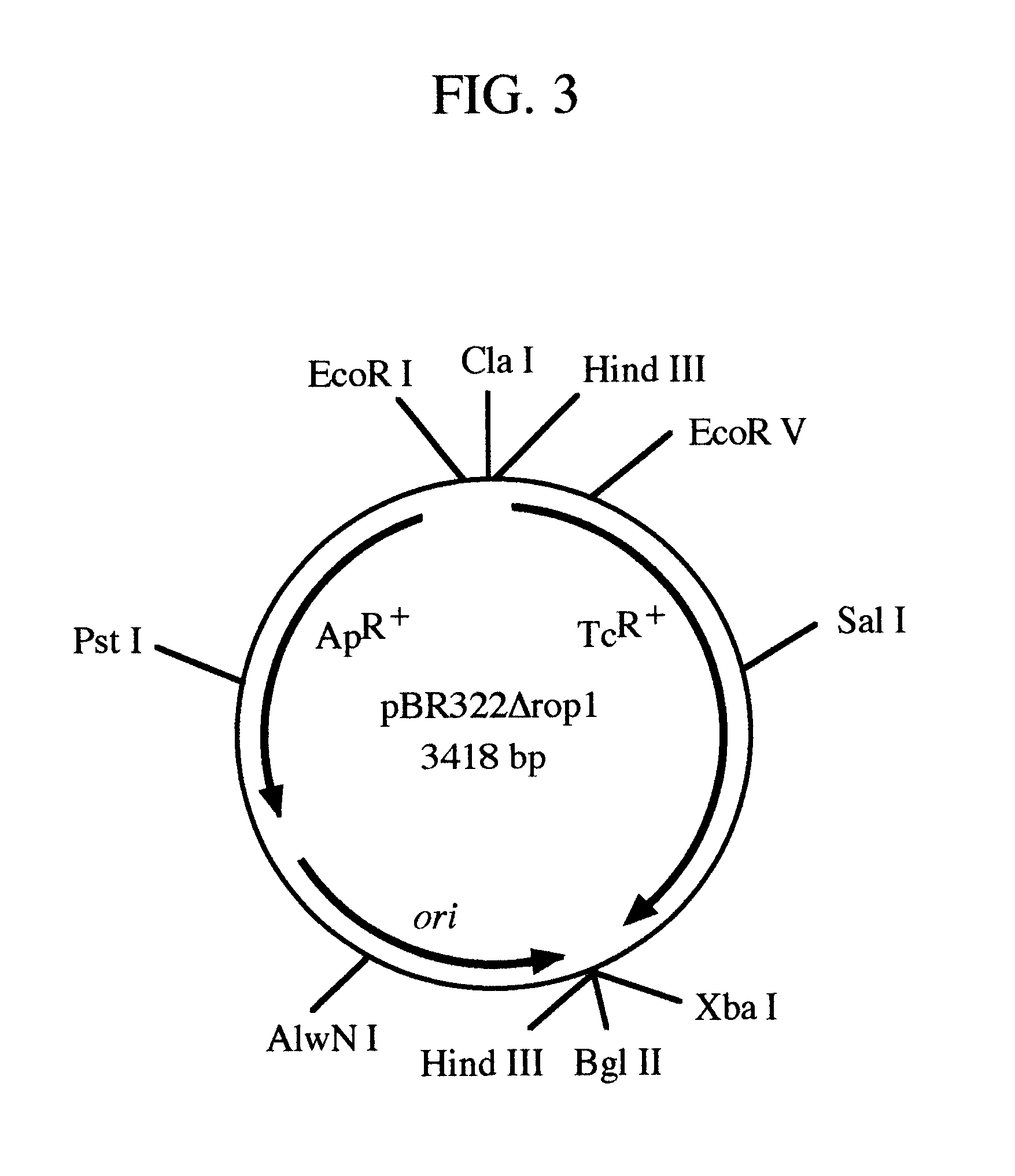
pRGR: a positive selection vector system for direct cloning of PCR amplified DNA fragments
InactiveUS6569678B1Easy extractionEliminate and greatly reduce generationFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionWild typeGene control
The present invention relates to the development of a positive selection vector based on insertional reconstruction of a reporter gene or of a regulatory gene controlling the expression of a reporter gene. The cloning vector carries a reporter gene or a regulatory gene with a mutation rendering the reporter or the regulatory gene protein functionally inactive. A primer carrying a nucleic acid sequence that corrects the mutation is used during PCR amplification of a targeted nucleic acid sequence, and the amplified DNA fragment is then ligated to the said vector thus reconstructing the wild-type reporter or regulatory gene.
Owner:SYNTHEGEN SYST
Continuous recessive character backcrossing technology
InactiveCN101637119AShorten breeding timeImprove time and efficiencyPlant genotype modificationHybrid seedTyping
The invention discloses a continuous recessive character backcrossing technology which is characterized by taking a material which contains no target recessive genes and is ready to be improved as a recurrent parent, and taking a material which contains the target recessive genes as a donor parent; taking the recurrent parent as the parent to be hybridized with the donor parent and harvesting hybrid seeds of the first generation F1 and recurrent parent seeds; and planting the hybrid seeds of the first generation F1 and the recurrent parent seeds till the planting of a group containing backcross hybrid seeds of the second of n generations BCn F2 and till the typing into a target recessive gene isogenic line of the recurrent parent. The invention also discloses a method for creating a purpleleaf marker isogenic line by applying the continuous recessive character backcrossing technology and also a method for transferring new purple leaf marker nucleus sterile line by taking the purple leaf marker isogenic line as an intermediate material. In the methods, a selfing process is combined with a next backcrossing process for the treatment in one season, therefore, the time efficiency is improved by about 50 percent, a small number of dominant-gene-controlled unsuitable characters of existing fine-quality parents can be fast improved, and useful recessive characters can be fast imported to the present high-level heredity background.
Owner:LIANYUNGANG ACAD OF AGRI SCI
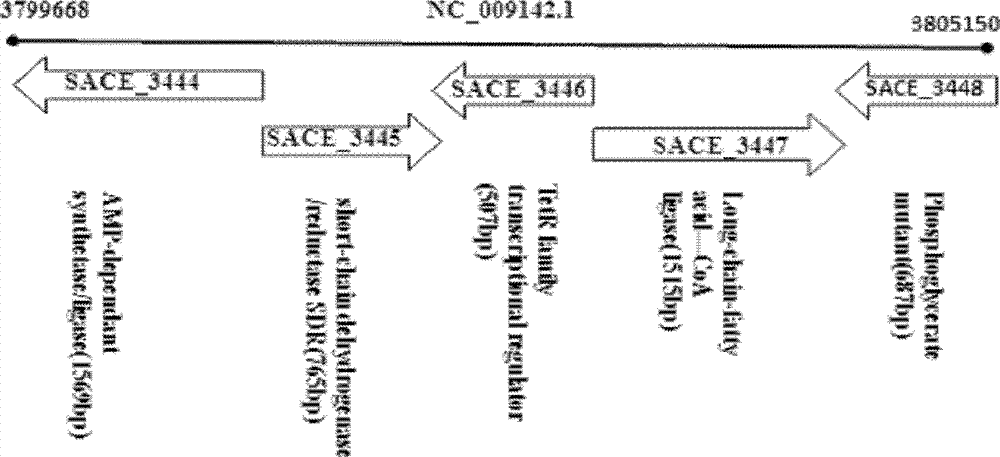
Method for improving erythrocin yield through inactivation saccharopolyspora erythraea SACE_3446 gene
The invention discloses a method for improving erythrocin yield through a negative control gene SACE_3446 on an inactivation saccharopolyspora erythraea chromosome. Saccharopolyspora erythraea is used for producing erythrocin. The erythrocin and derived drugs of the erythrocin such as clarithromycin, azithromycin and telithromycin are used widely in clinic. Erythrocin high-producing strain screening is very important in industrial production. The erythromycin biosynthesis negative control gene SACE_3446 is screened from a saccharopolyspora erythraea TetR family. Compared with erythrocin yield of an original strain, deletion mutants of the saccharopolyspora erythraea SACE_3446 is improved remarkably, the erythrocin is returned to low yield after gene complementation of the SACE_3446, and therefore the SACE_3446 gene is a erythromycin biosynthesis negative control gene. The inactivation saccharopolyspora erythraea SACE_3446 gene can improve the erythrocin yield through a genetic engineering way. Due to the fact that erythromycin biosynthesis gene control is a network system, upstream and downstream control factors acted by SACE_3446 control factors can be found by using the SACE_3446 as an object. The erythrocin yield can also be improved by changing upstream or downstream control factor genes of the saccharopolyspora erythraea SACE_3446 control factors.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY
Control of hypocotyllength and flowering time by COL8 gene
The present invention provides an isolated nucleic acid including a nucleotide sequence encoding COL8, which controls hypocotyl length and flowering time in a plant. It is found that plants over-expressing COL8 under long day conditions show slight hypocotyl elongation and delayed flowering in comparison with the wild type. In addition, COL8 and FKF1, which is a circadian-clock related gene, are found to be localized at the same site in a plant cell, indicating the existence of an interaction between the two.
Owner:KAGAWA UNIVERSITY
SVP gene controlling flowering time of plants
The present invention relates to SVP protein which controls the flowering time of plants originating from Arabidopsis, a gene encoding SVP protein, a recombinant vector comprising said gene, a plant transformed with said recombinant vector, a method of controlling flowering time of plants by using said gene, and a method of searching a protein or a gene which controls the flowering time of plantsby using said SVP protein or said gene encoding the same.
Owner:SEOUL NAT UNIV R&DB FOUND
Bicistronic mRNA coexpression gene transporter and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102994536AAchieve multiple gene co-expressionVector-based foreign material introductionBicistronic mrnaNuclear matrix
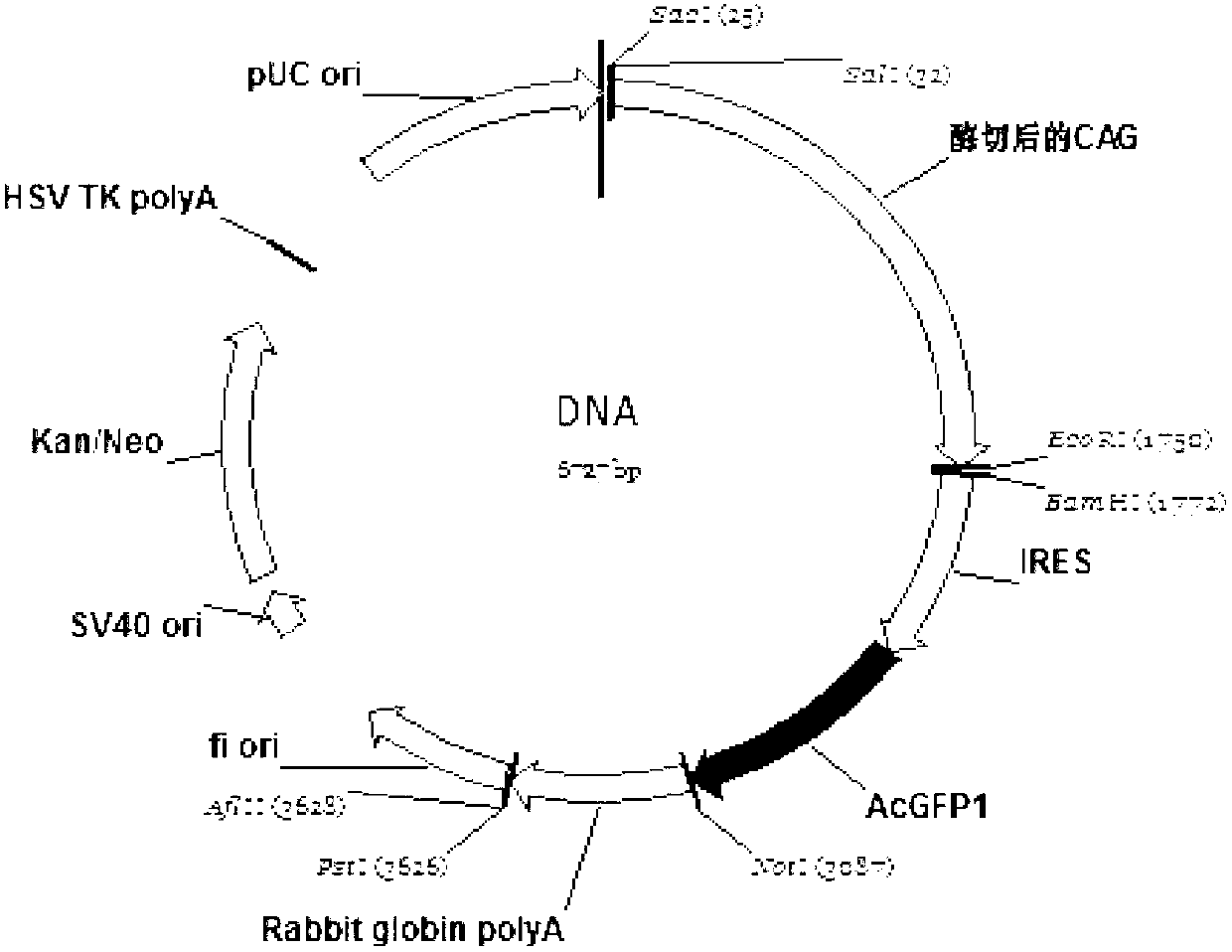
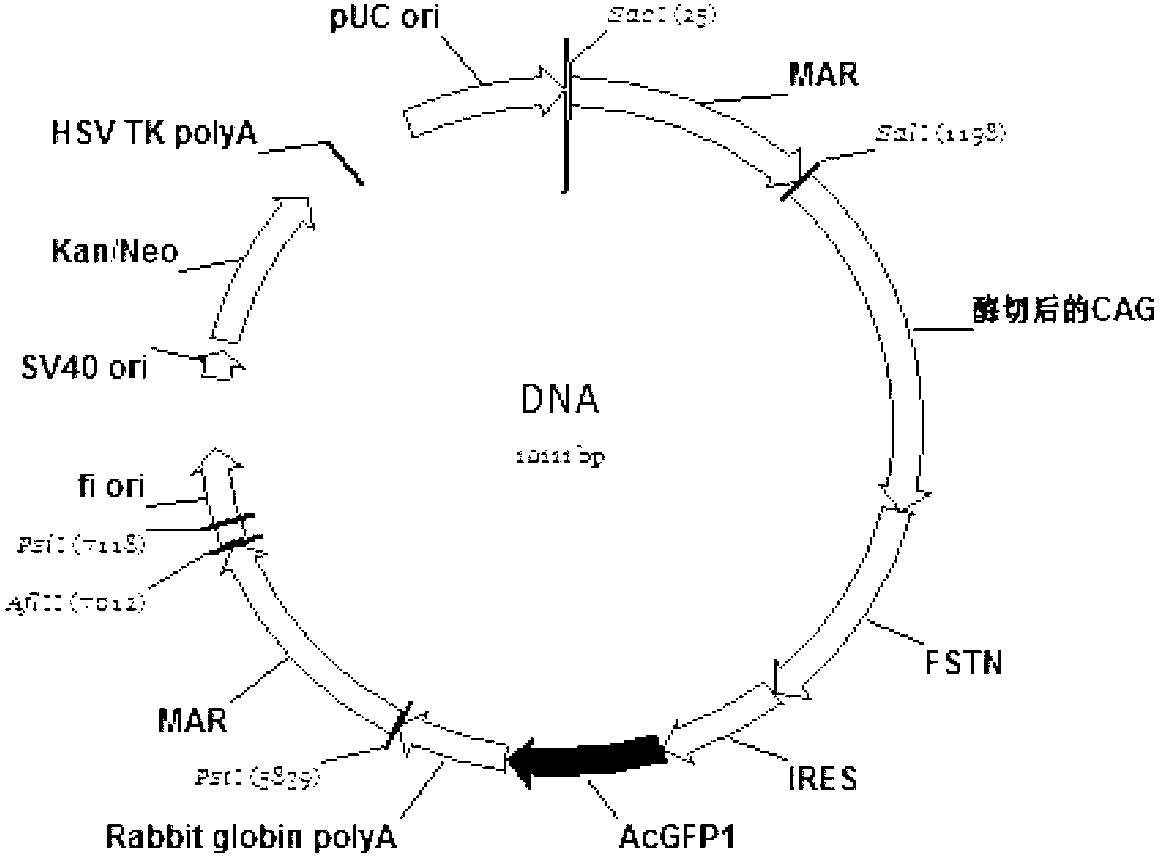
The invention relates to a bicistronic mRNA coexpression gene transporter and a preparation method thereof. The gene order of the gene transporter is SEQ ID No. 15; the gene transporter from 5' end to 3' end comprises bovine Nuclear matrix binding region MAR, artificially constructed combined promoter CAG, Profilin gene FSTN, internal ribosome entry site (IRES), green fluorescent protein AcGFP gene and Rabbit globin poly A signal region; the preparation method comprises the following steps: constructing a carrier pCAG-IRES2-AcGFP1; obtaining FSTN gene and inserting the pCAG-IRES2-AcGFP1 carrier; obtaining the sequence of MAR and inserting the pCAG-IRES2-AcGFP1 carrier; constructing a plasmid carriers so as to obtain the bicistronic mRNA coexpression gene transporter. The gene transporter is not only pure and safe gene transporter but also realizes dual-gene coexpression in any combination, achieves the purpose of multi-gene coexpression through repeated utilization of IRES, and provides new thinking and route for improving the shape of dual or multiple gene control such as economic character.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA UNIVERSITY
Rice bacterial leaf blight resistance related gene OsABA2 and application thereof
ActiveCN107475210AEnhanced blight resistanceBlight increasedHydrolasesOxidoreductasesAgricultural scienceNucleotide
The invention discloses a rice bacterial leaf blight resistance related gene OsABA2 which consists of nucleotide sequences of SEQ ID No.2 as shown in the specification. The invention further discloses a rice lesion mimic gene which is capable of remarkably improving the resistance of rice to bacterial leaf blight, and a lesion mimic mutant can be acquired through gene edition on the OsABA2 gene. Novel functions of the OsABA2 gene are discovered, and the lesion mimic mutant acquired after the OsABA2 gene is knocked off through gene edition can be applied to rice bacterial leaf blight resistance breeding; meanwhile, the lesion mimic trait is controlled by a single recessive nuclear gene, and hybrid identification and selection can be relatively simple to implement in transgenosis or crossbreeding; and in addition, the lesion mimic gene is derived from nonglutinous rice and has a great promotion function on bacterial leaf blight resistant breeding of the nonglutinous rice.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
DNA polymorphism-based methods for identifying field resistance of rice to rice blast
InactiveUS6963020B1Conveniently and accurately selected indoorReduce laborPlant genotype modificationRice plantsOryza
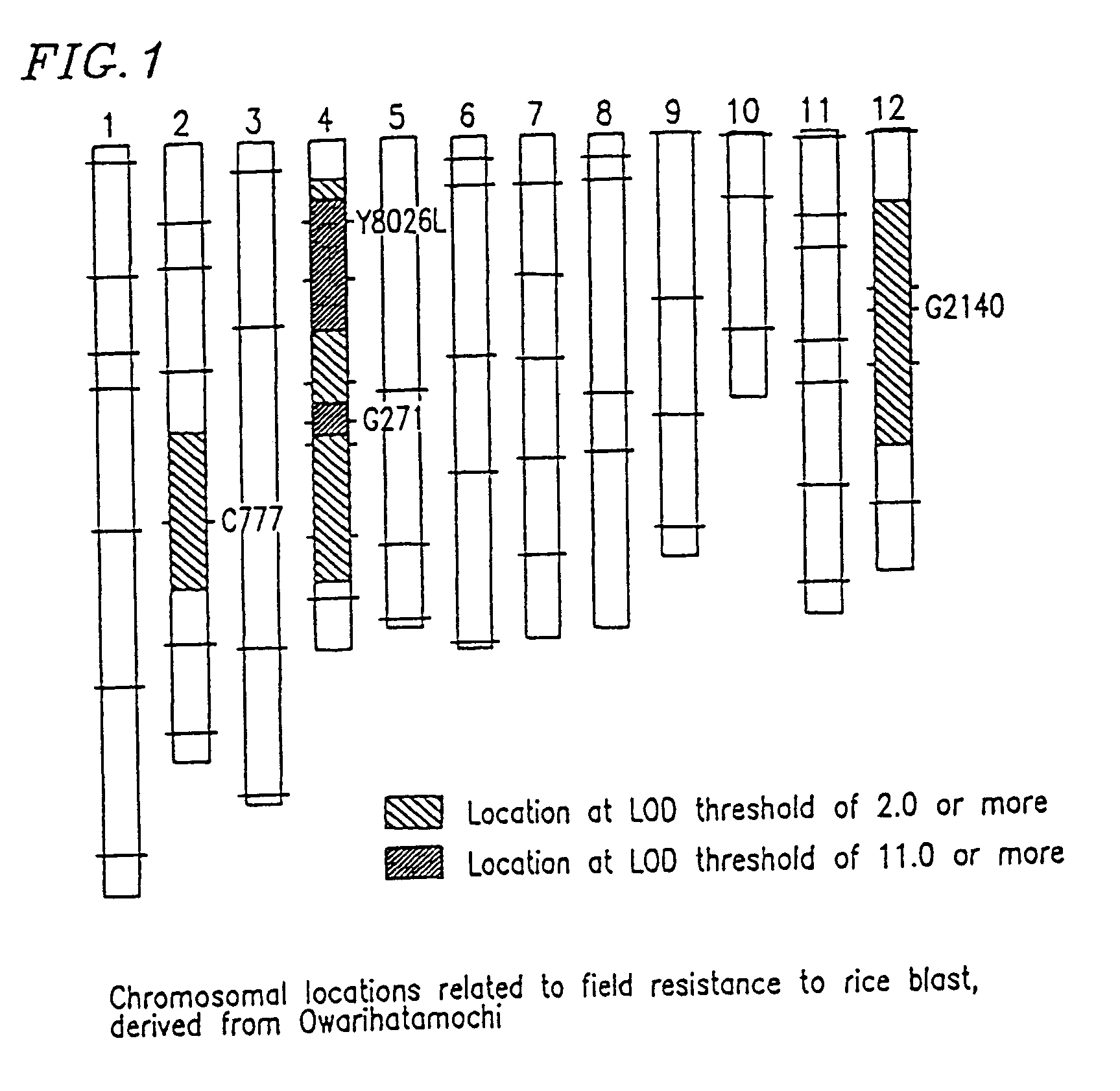
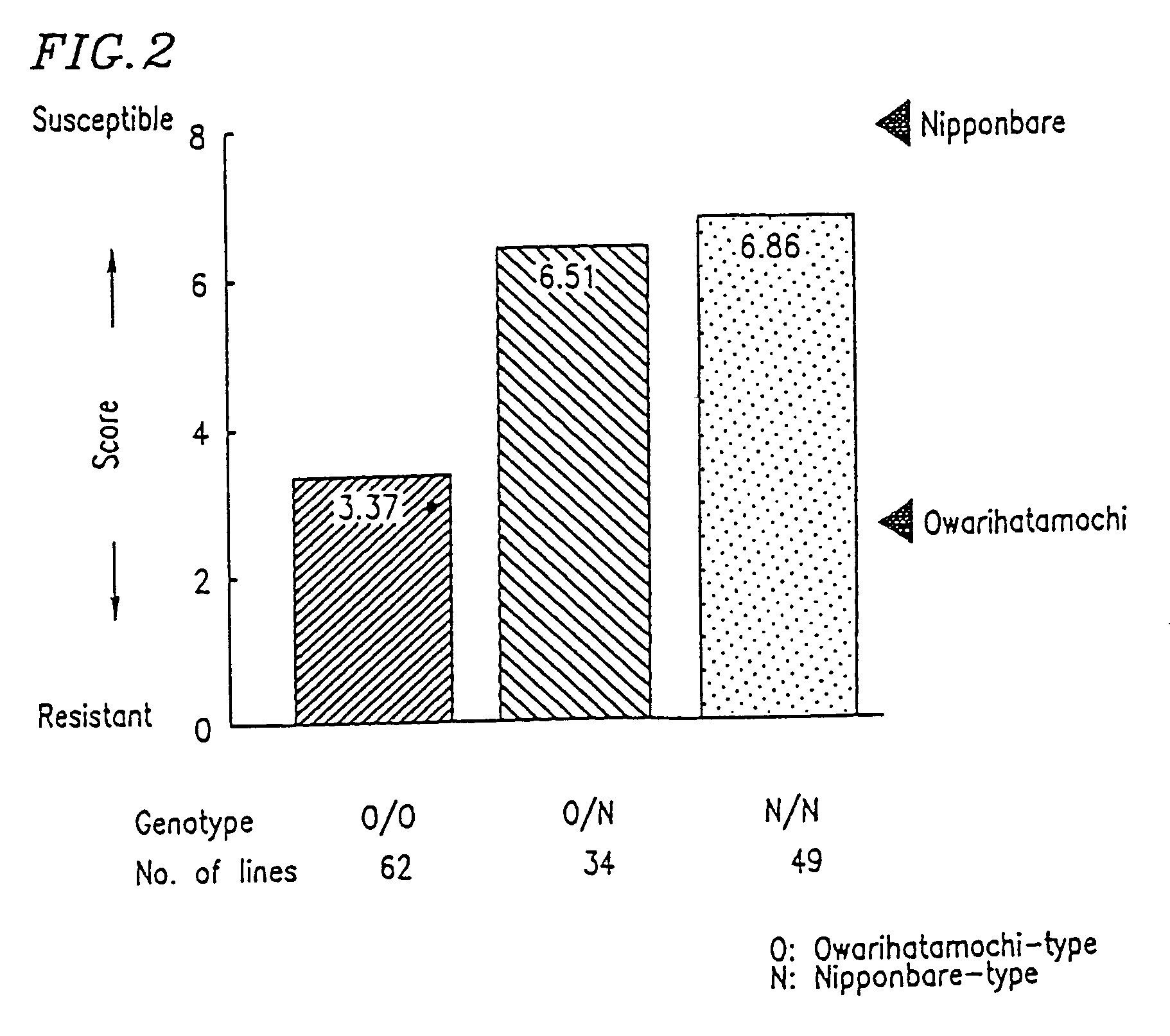
A method for identifying resistance of a rice plant to rice blast is provided. More particularly, a method for identifying resistance of a rice plant to rice blast by testing a genotype of the rice genome using a DNA marker (G271), which is closely linked to a gene controlling the field resistance to rice blast, is disclosed. The disclosed invention allows for evaluation of the field resistance of a rice plant to rice blast using a DNA marker, thereby allowing for a resistant variety to be conveniently and accurately selected. The disclosed invention contributes to reducing the time and labor that have conventionally been required for cross breeding, and is useful in developing novel rice varieties having a high degree of field resistance to rice blast.
Owner:NAT INST OF AGROBIOLOGICAL SCI
ST cell lines for stably expressing T7 RNA polyase, constructing process and applications thereof
InactiveCN101285054AEnzymesVector-based foreign material introductionMicroorganism preservationFluorescence
The invention discloses a cell line ST / T7 capable of stably expressing T7RNA polymerase, the microorganism preservation number of which is: CGMCC No.24444. In the invention, a T7RNA polymerase gene is inserted into a eukaryotic expression vector pIRES2-EGFP to get the pIRES2-EGFP-T7 to transfect ST cells to obtain the cell line ST / T7 capable of stably expressing T7RNA polymerase. Through RT-PCR detection, expression plasmid containing a red fluorescent protein gene controlled by T7 promotors can be used to transfect the cell line so as to observe the expression of red fluorescent protein in a transcription product amplified form a ST / T7 cell to the T7RNA polymerase. The cell line ST / T7 can provide reverse T7RNA polymerase for use in reverse genetic manipulation of RNA-virus such as hog cholera virus, etc., and can be used as transcription and expression systems in vitro for research on genic structures and functions.
Owner:HARBIN VETERINARY RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
High-throughput method for segregating quantitative character regulatory gene
InactiveCN101544974AAvoid false positivesImprove screening efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationTotal rnaCandidate Gene Association Study
The invention discloses a high-throughput method for segregating a quantitative character regulatory gene, which comprises the following steps of: 1) construction of a target character segregation population, in which the population is a population in two parent hybridization progenies (F2 and F3), a DH system and a RIL; 2) mixing of extreme samples and segregation of total RNA in the population, in which a progeny segregation population is divided into three categories according to character phenotype; 3) gene expression analysis, in which the difference and sameness of gene expressions between two extreme mixed samples are compared by utilizing a gene expression analysis method, namely one of chip, EST sequencing, subtraction, cDNA-AFLP, and the like; and 4) acquisition and verification of a candidate gene, in which a differential expression gene between the two extreme mixed samples is found and is a candidate regulatory gene related to target character, and the function of the gene is verified through transgene, gene expression, molecular marker correlation and a contribution rate analysis method to obtain a target gene with regulatory character phenotype. The method is suitable for the segregation of a certain quantitative character regulatory gene controlled by multigene of all organisms, and is a simple, quick, high-throughput and economical gene segregation method.
Owner:INST OF OIL CROPS RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Oligopeptide treatment of ischemia reperfusion injury
InactiveUS20090042807A1Reduce productionModulate translocationAntibacterial agentsNervous disorderSignalling moleculesNo production
The invention relates to the modulation of gene expression in a cell, also called gene control, in particular, in relation to the treatment of ischemic-reperfusion injury. The invention provides a method for modulating expression of a gene in a cell comprising providing the cell with a signaling molecule comprising a peptide or functional analogue thereof. The invention provides a method of treating ischemia-reperfusion injury in a subject by reducing NO production by the subject's macrophages, the method comprising: administering to the subject a composition comprising: means for reducing production of NO by a cell, together with a pharmaceutically acceptable excipient.
Owner:BIOTEMPT
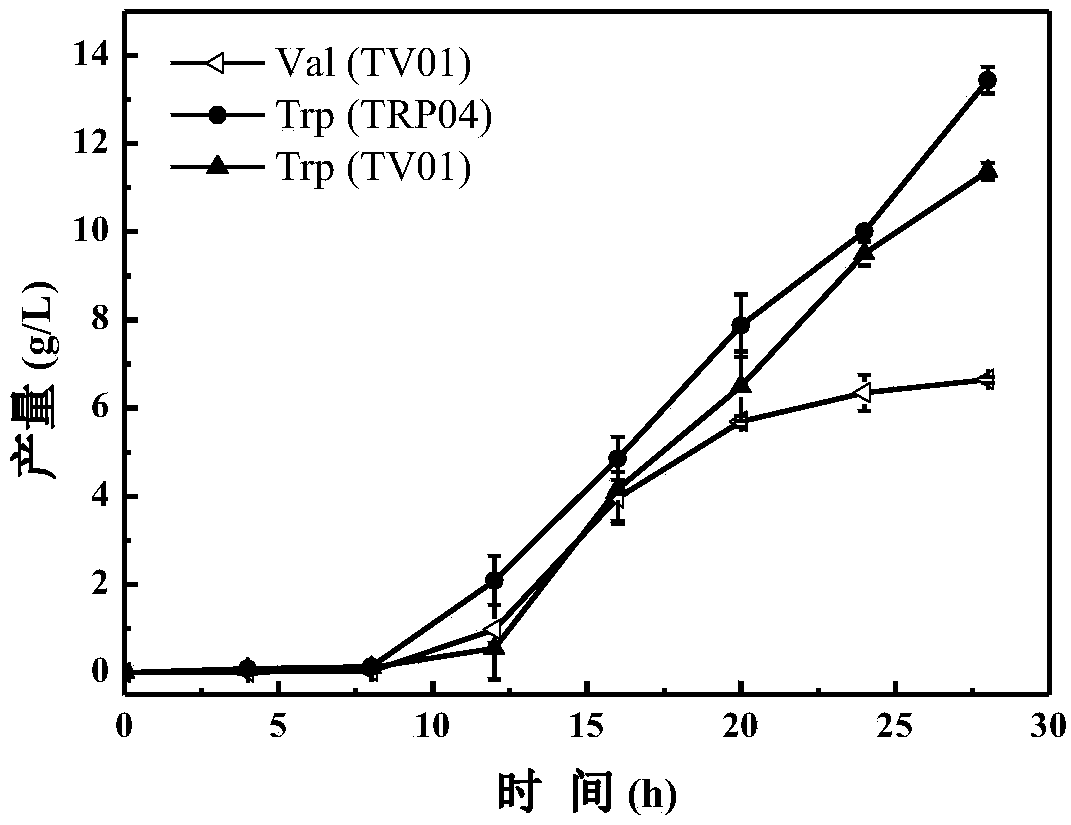
Escherichia coli genetically engineered bacterium and application of escherichia coli genetically engineered bacterium to synchronous production of L-tryptophan and L-valine through fermentation
ActiveCN108913642AEfficient use ofClear genetic backgroundBacteriaTransferasesEscherichia coliBiotechnology
The invention provides an escherichia coli genetically engineered bacterium for the synchronous high yield of L-tryptophan and L-valine, and application thereof. The genetically engineered bacterium is obtained through the steps that on a genome of escherichia coli, trpE (S40F) mutation is introduced while a promoter of tryptophan operon is replaced with a Ptrc promoter; an aroG (S180F) gene controlled by the Ptrc promoter is integrated to a tyrR locus; a serA (H344A, N364A) gene controlled by a Plac promoter is integrated to a yjiV pseudo gene locus; a glnA gene controlled by the Plac promoter is integrated to a ycjV pseudo gene locus; and then a bacillus subtilis alsS gene controlled by the Ptrc promoter is integrated to a yghx pseudo gene locus. Shaking flask fermentation is conducted through a strain to be able to accumulate the L-tryptophan within 22-28 h to 10-14 g / L, meanwhile the accumulation amount of valine reaches 5-7 g / L, and the total acid-producing ability is improved by50% or so compared with that of a tryptophan producing strain; and meanwhile, strain OD600 is different slightly, growth problems are avoided, but the acid-producing ability per strain is obviously improved by 120%, and effective utilization of carbon sources and cells is improved greatly.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
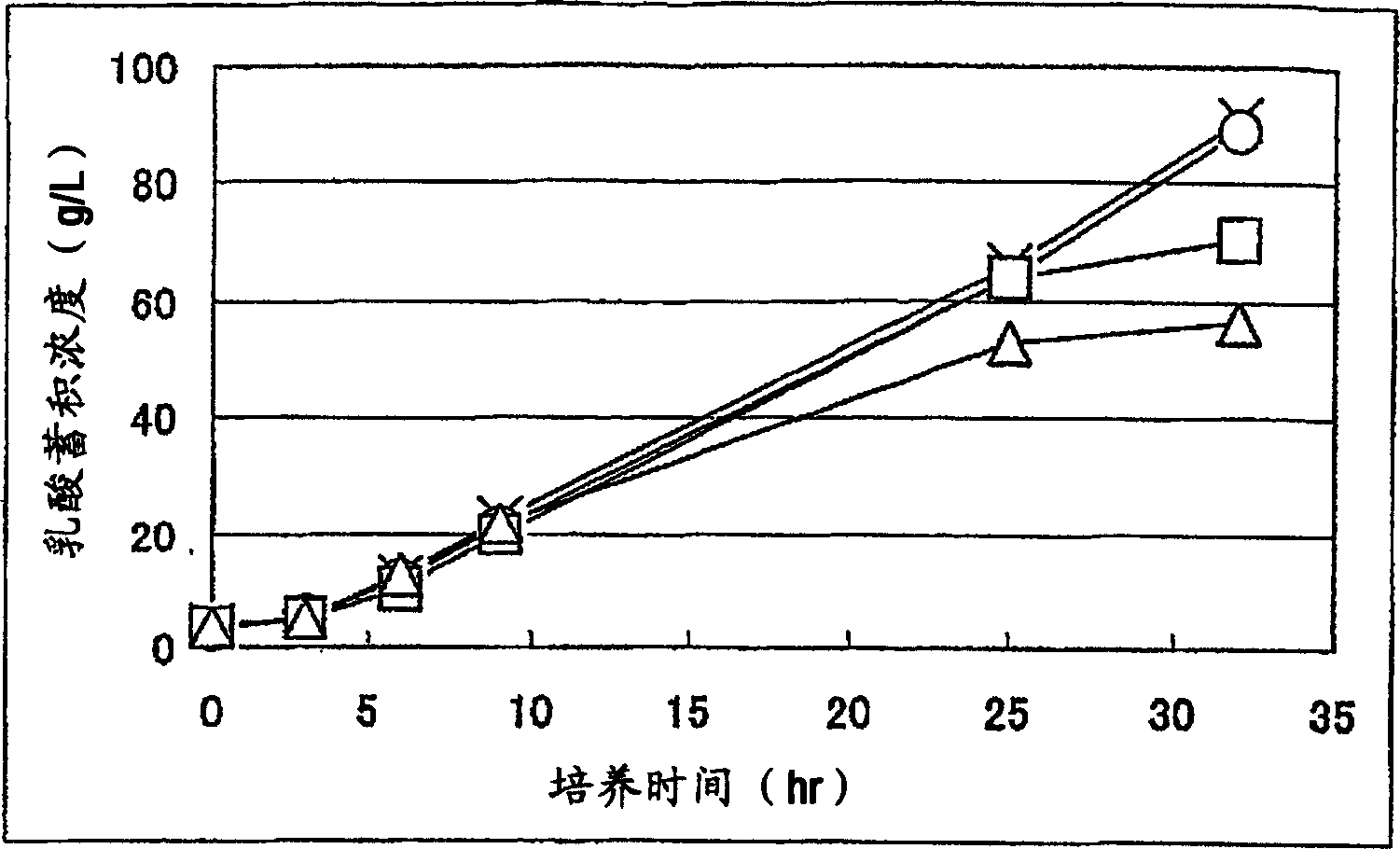
Biocatalyst for producing d-lactic acid
ActiveCN1856577AImprove productivityHigh purityBacteriaRecombinant DNA-technologyD-lactic acid dehydrogenase activityEscherichia coli
It is intended to provide a process for highly producing D-lactic acid. It is also intended to provide a process for highly selectively producing D-lactic acid having a high optical purity with the formation of little organic acids as by-products. D-Lactic acid is produced by culturing a microorganism having inactivated or lowered pyruvate formate-lyase activity and elevated Escherichia coli-origin NADH-dependent D-lactic acid dehydrogenase (ldhA) activity, a microorganism having inactivated or lowered FAD-dependent D-lactic acid dehydrogenase activity, or a microorganism as described above having a TCA cycle, inactivated or lowered malic acid dehydrogenase activity and inactivated or lowered aspartic acid ammonia-lyase activity. The ldhA activity is elevated by ligating a gene encoding ldhA to a promoter of a gene controlling the expression of a protein, which participates in a glycolysis system, a nucleic acid biosynthesis system or an amino acid biosynthesis system, on genome.
Owner:MITSUI CHEM INC
Molecular mechanisms for gene containment in plants
Owner:UNICROP LTD
Rice chlorophyll synthase mutant gene and its application in gene engineering
InactiveCN101096676AHas chlorophyll synthase activityHigh homologyEnzymesVector-based foreign material introductionAgricultural scienceNucleotide
The invention discloses a nucleotide sequence of rice chlorophyll synthase mutation gene Osygl1 and gene engineering application in the gene engineering domain, which is characterized by the following: the cDNA sequence of Osygl1 is SEQ ID NO.1 and its coded amino acid sequence is SEQ ID NO.2; the gene OsYGL1 is a chlorophyll synthase gene in the rice, which participates the synthesis of chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b to display component expression; the mutation of the gene leads the leaf of rice to become yellow green, which can be genetic mark to identify the kind in the agricultural manufacturing and rice genetic breeding.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Prodenia litura gene engineering virus No.3 and building method thereof
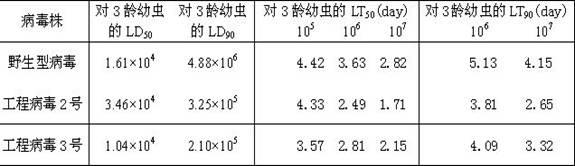
InactiveCN102329783AFast insecticideLow dose effectMicroorganism based processesViruses/bacteriophagesWild typeUridine diphosphate
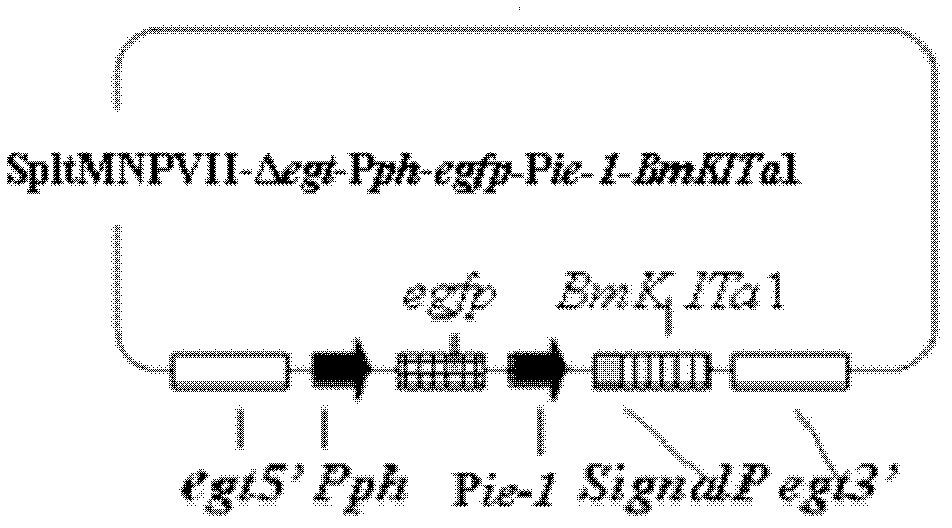
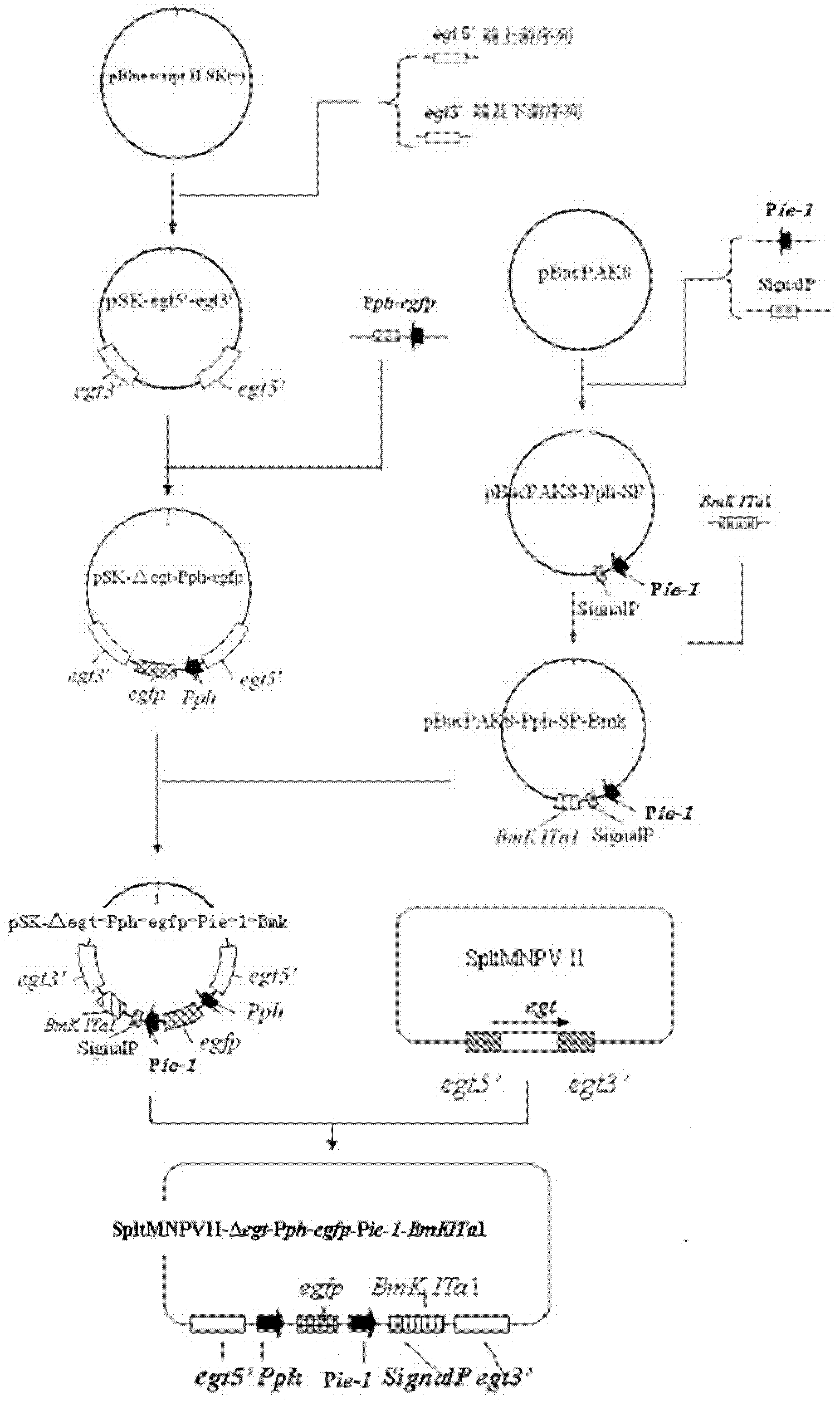
The invention discloses a prodenia litura gene engineering virus No.3 and a building method thereof, in particular relates to a prodenia litura gene engineering virus used for carrying out deficiency and recombination on a wild type virus (SpltMNPV II) by utilizing a gene engineering method. The genome of the virus is deficient in an egt gene, namely an ecdysteroid UDP (uridine diphosphate) glucosyltransferase gene; and at the site of the deficient egt gene, a BmKITa1 gene controlled by a wild type virus, namely an early gene-1(ie-1) starter, and a marker gene, namely an enhanced green fluorescent protein (egfp) gene, which is controlled by the wild type virus, namely a polyhedron gene (ph) starterare inserted. The prodenia litura gene engineering virus No.3 disclosed by the invention has the advantages of faster insecticidal speed, less dosage effect and better field application effect compared with the wild type virus. Compared with the prior art, the prodenia litura gene engineering virus No.3 provided by the invention has less dosage effect and lower LT50 at low dose (105 polyhydral bodies / larva).
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Specific gene controlling growth of Arabidopsis vascular bundle and application thereof
InactiveCN101824433AConvenient researchImprove qualityVector-based foreign material introductionVascular bundleVascular tissue
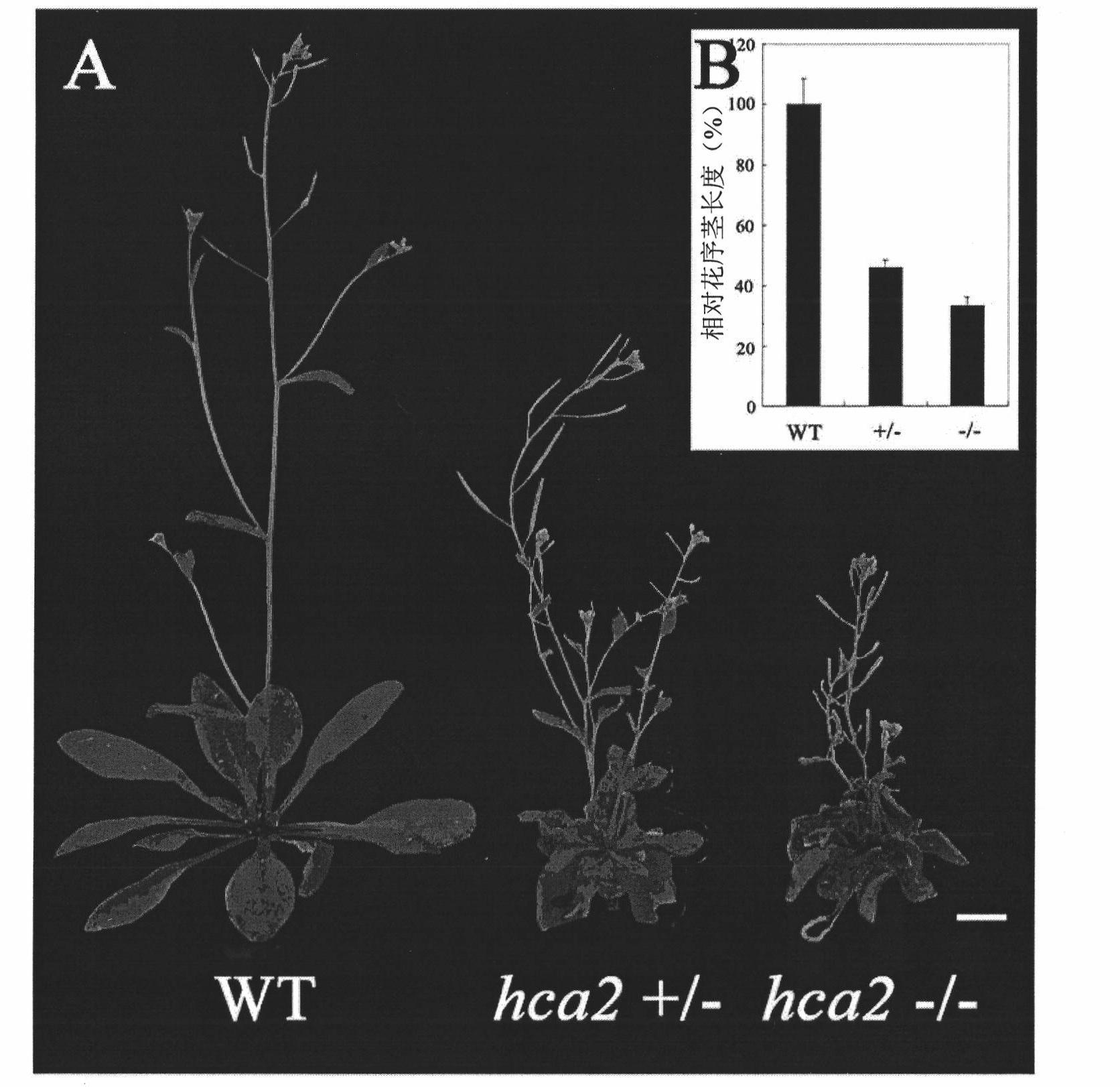
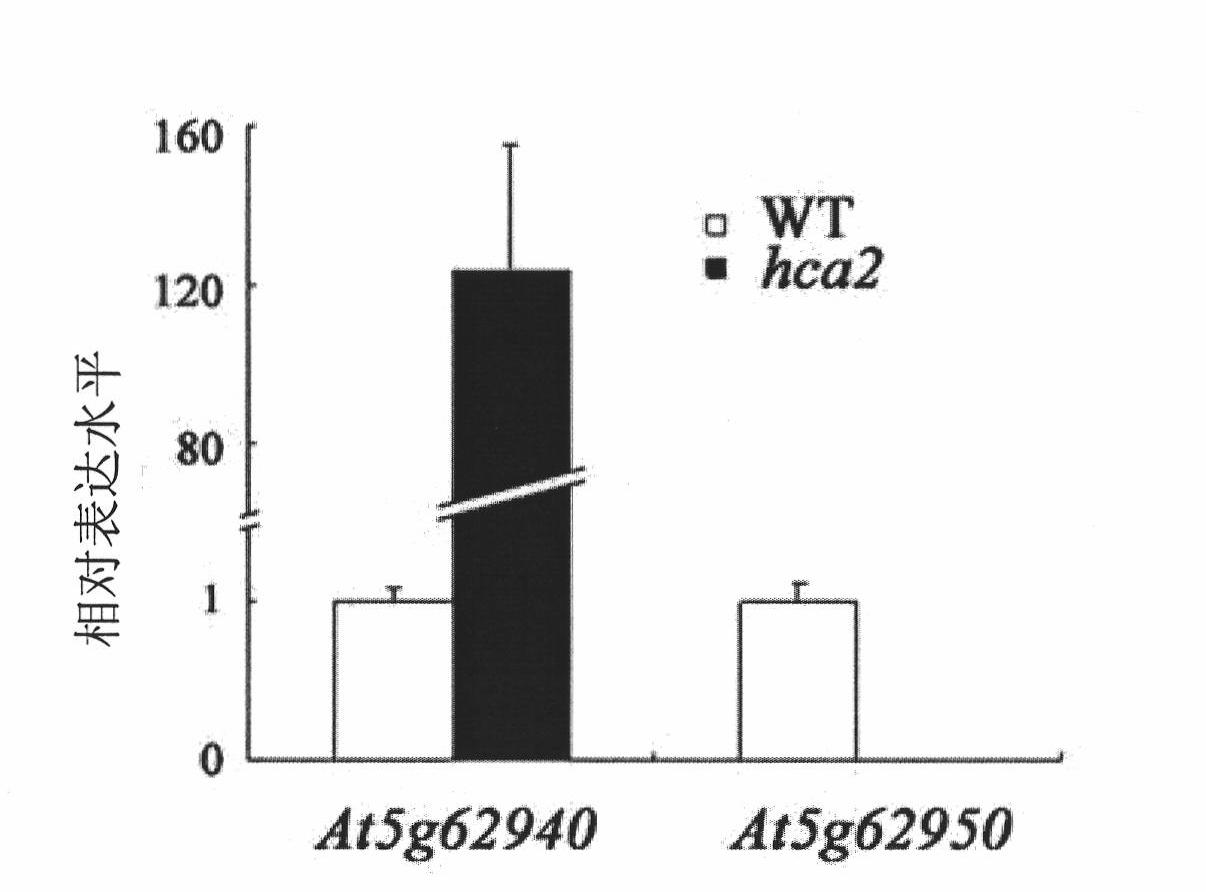
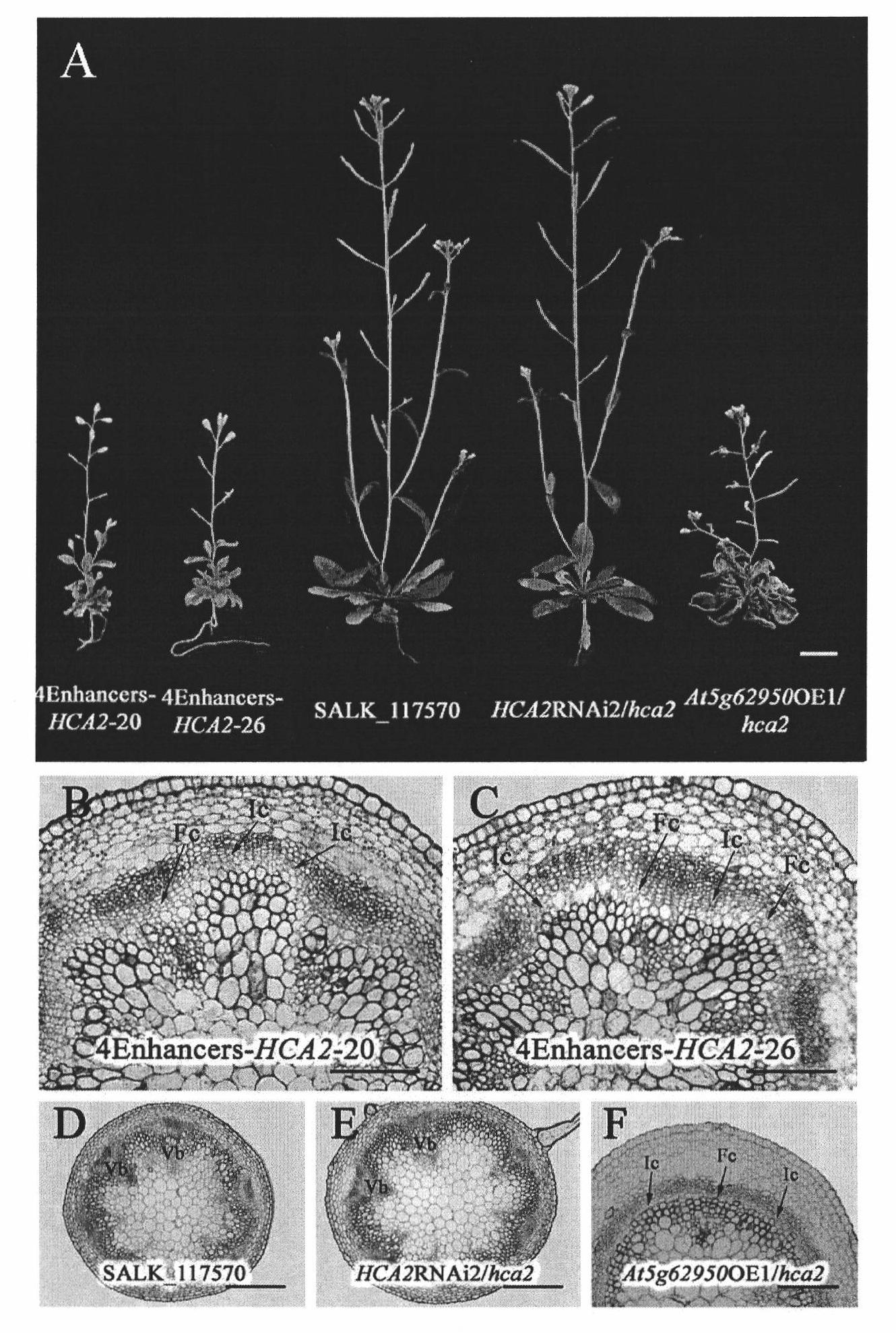
The present invention discloses a specific gene controlling growth of Arabidopsis vascular bundle and application thereof. The gene codes the protein of amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID No.2 in sequence list and the genome gene is AT5g62940; the corresponding cNDA sequence is shown in the SEQ ID No.1 of the sequence list. As shown from research, the gene codes a transcription factor which is positioned in a core and has trans-activation activity, but the transcription factor which can regulate the formation of the Arabidopsis interfascicular cambium and the growth of vascular tissue is the transcription factor which is found as the first transcription factor for regulating the interfascicular cambium in Arabidopsis. In a transgenic gene plant, overexpression of the gene can thicken the stem of the plant, but inhibiting the expression of the gene in the plant can inhibit the occurrence of the interfascicular cambium. Therefore, the gene can be used for regulating the thickness of the stem, researching the woody plants with growth strength of secondary growth, and improving the quality. The gene has wide application prospect in regulating thickness growth and growth of the wood, flowers and plants.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Molecular mechanims for gene contaiment in plants
InactiveUS20040107457A1Reduce negative impactClimate change adaptationOther foreign material introduction processesHeterologousIntein
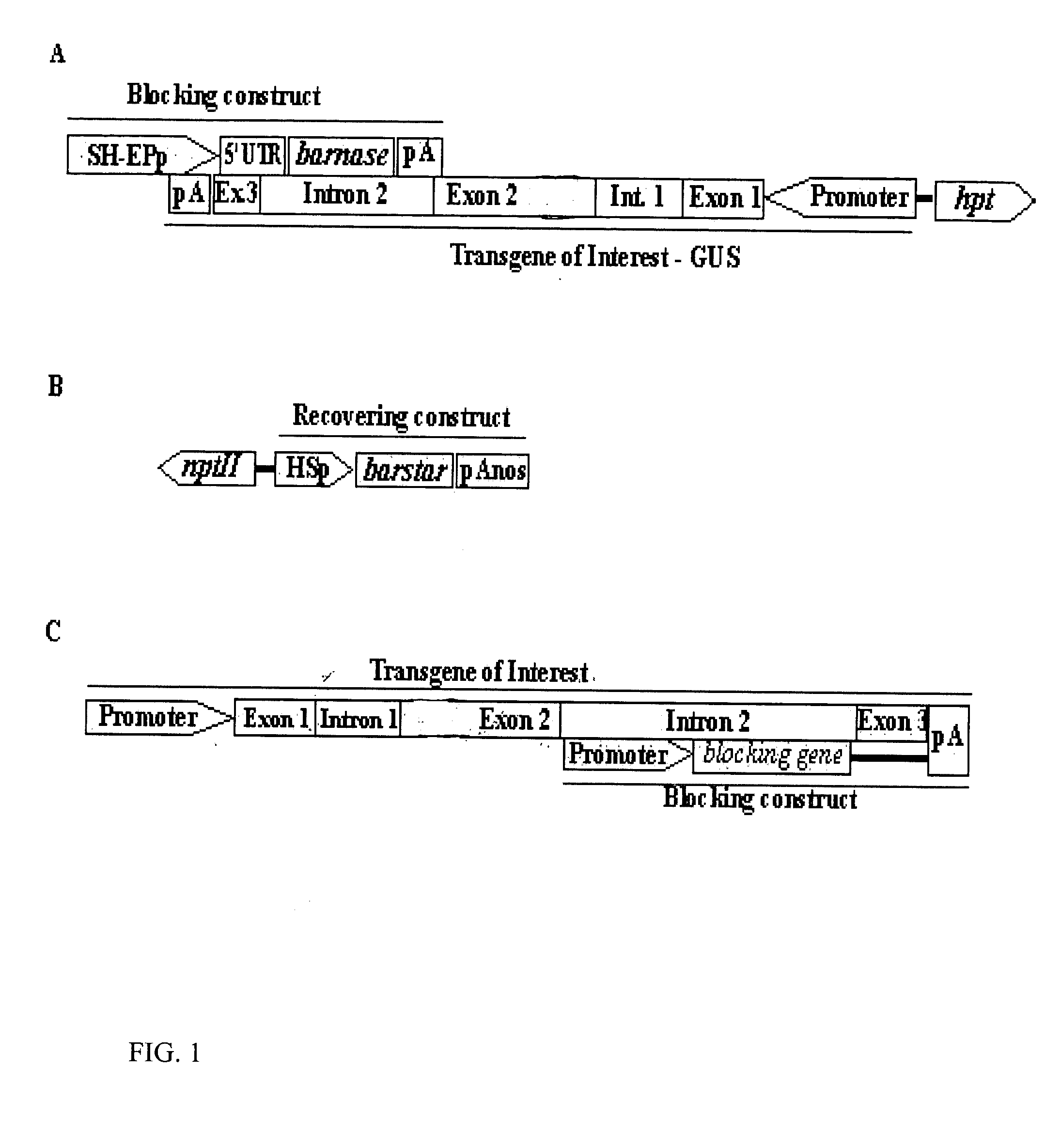
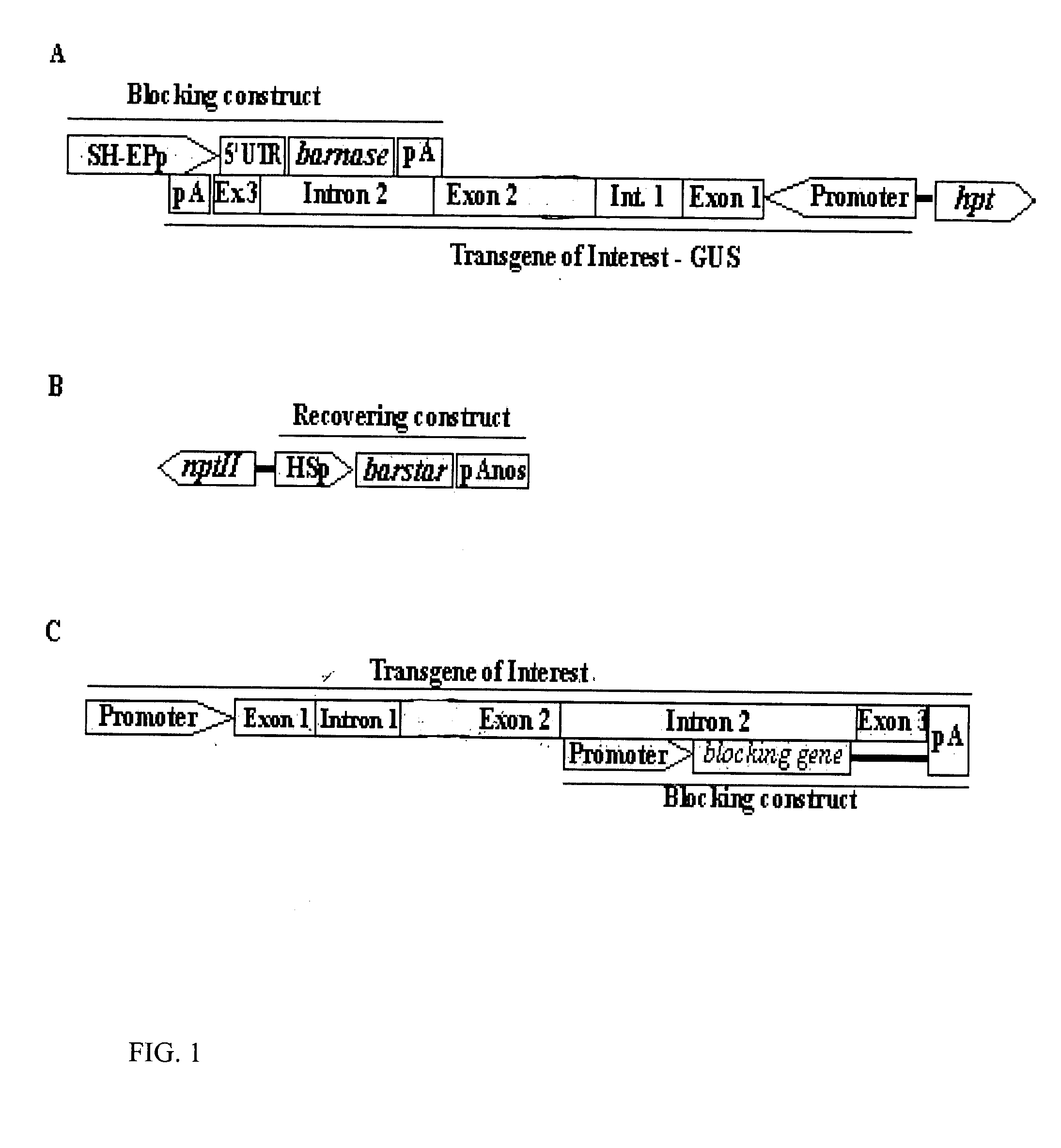
The present invention provides a molecular mechanism for gene containment in sexually reproducing transgenic plants. The mechanism is achieved with a molecular construct comprising a blocking construct (BC) that is inserted fully or partially into an intron of a transgene of interest (TGI). The TGI encodes desired gene products, such as heterologous or homologous proteins, peptides or other useful products. The expression of the BC leads to block of at least one molecular or physiological function that is essential for development or reproduction of the transgenic plant. Thereby the BC expression leads to death or incapacity of sexual reproduction of the plant. Moreover, the mechanism comprises an externally applicable recovering tool to recover the functions blocked by the BC. The recovering tool may be a recovering construct (RC).
Owner:UNICROP LTD
Quaternary ammonium type cationic starch gene controlled release vector material and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN102408488AGood biocompatibilityQuick combinationGenetic material ingredientsGene therapySide effectIce water
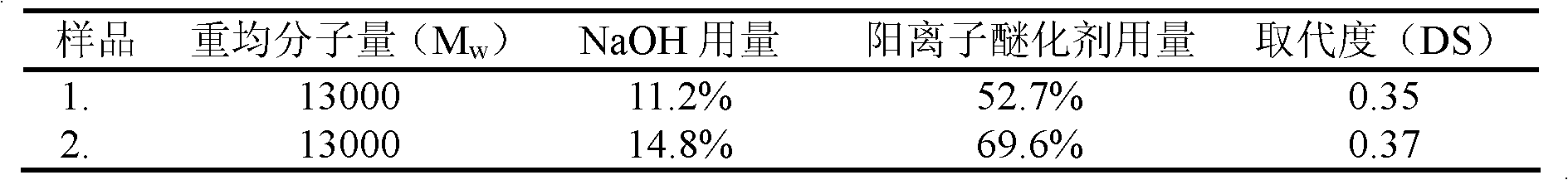
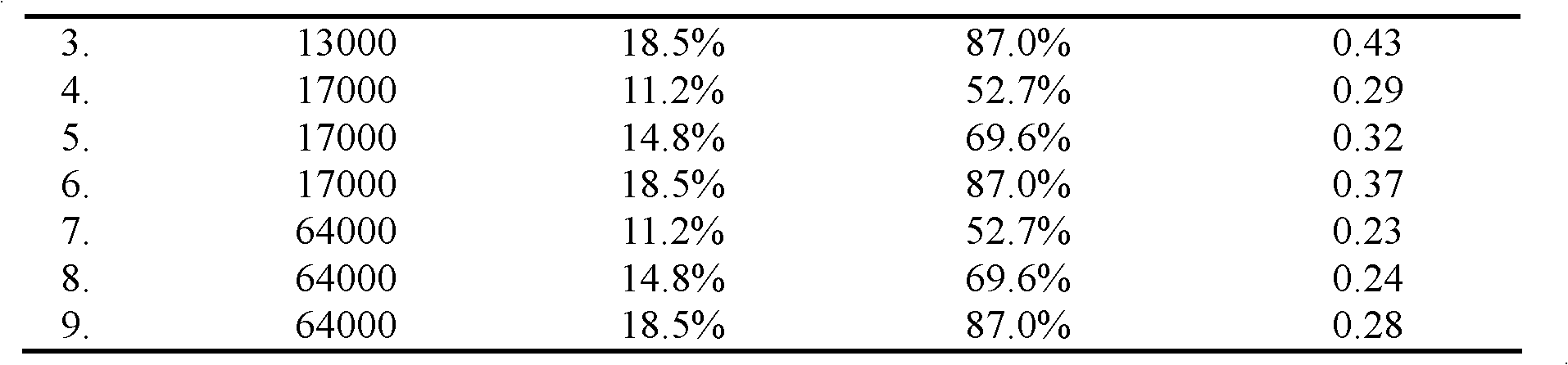
The invention discloses a quaternary ammonium type cationic starch gene controlled release vector material, and a preparation method and an application thereof; the preparation method particularly comprises the following steps: allowing starch which has a water content of 4.7-13.5% and a weight-average molecular weight of 13000-64000 Da to mix and react with a mixed system of solid caustic soda, water, and a quaternary ammonium type cationic etherifying agent which are stirred and well mixed through an ice water bath in a kneader by a dry method under a condition with a temperature of 25-30 DEG C and a rotating speed of 40-100 r / min for 12-48 hours; after the reaction is completed, washing, drying, and crushing to obtain the quaternary ammonium type cationic starch gene controlled releasevector material. An application of the vector material prepared by the invention as a non-viral vector material in gene therapy realizes the controlled release of gene drugs, improves the drug bioavailability, reduces the toxic and side effect of the drugs and the vector.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
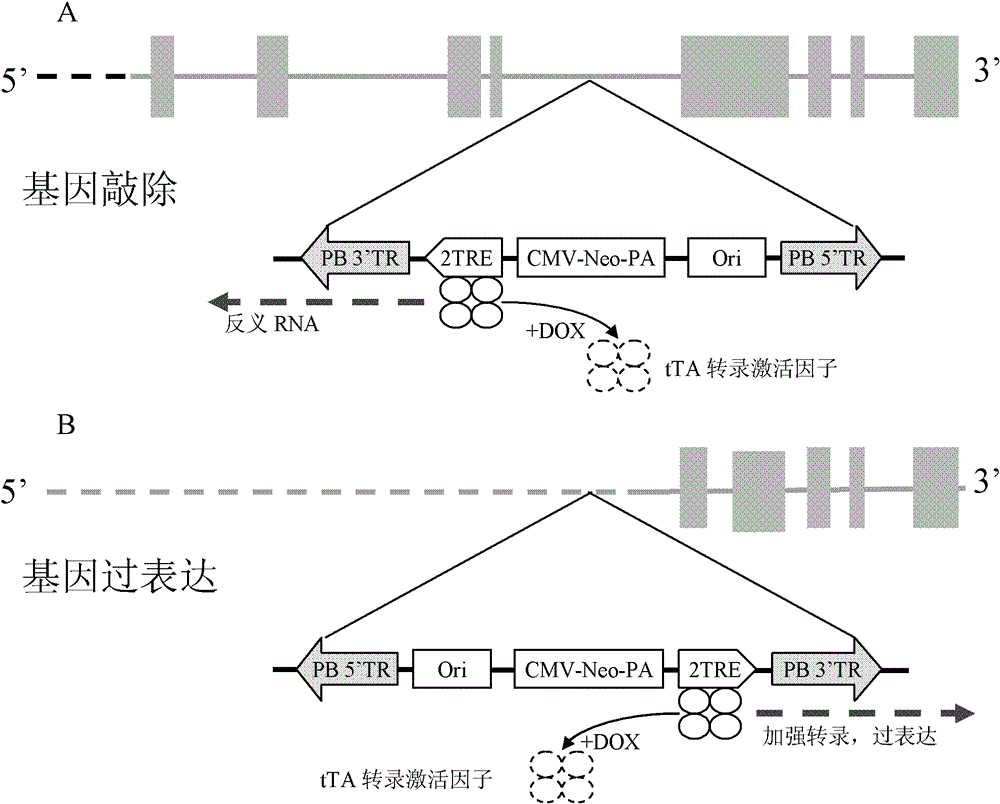
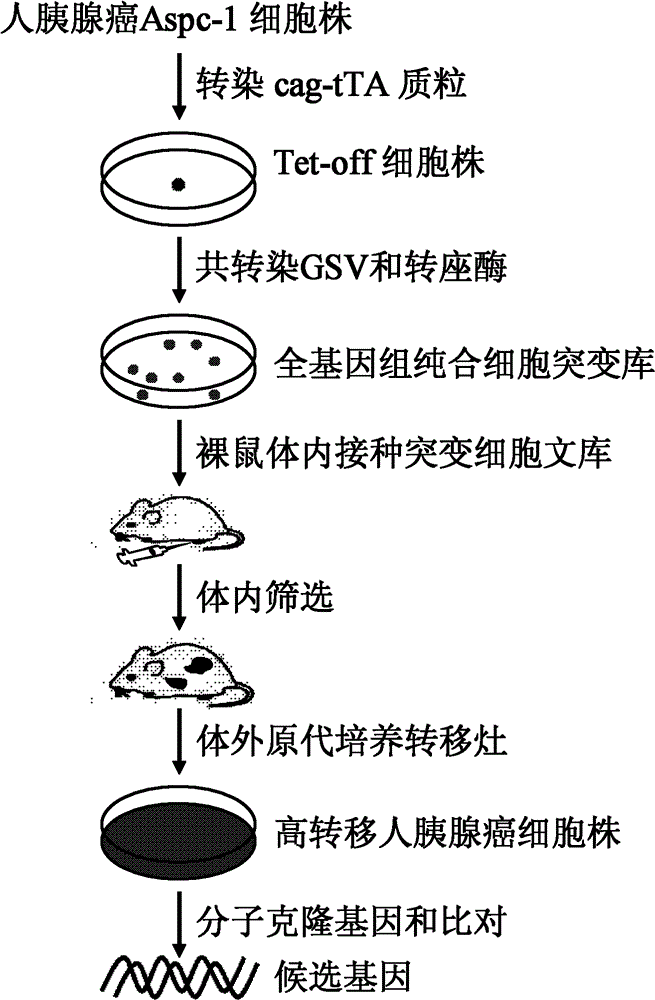
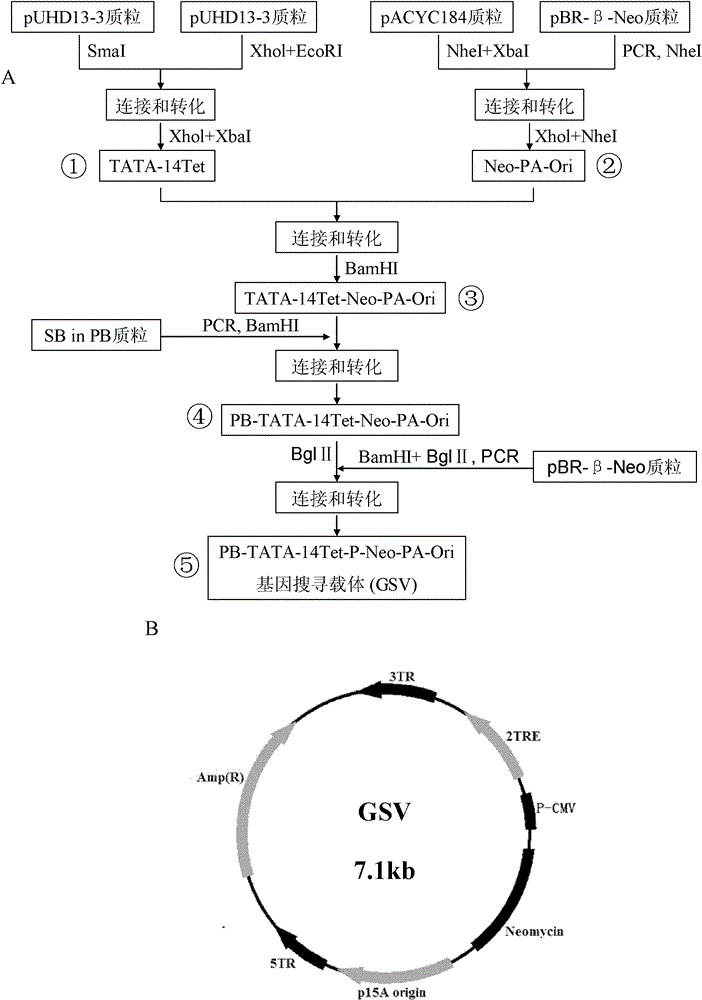
Gene search vector, random gene mutation control method and application thereof
InactiveCN102747096AGenetic material ingredientsImmunoglobulins against animals/humansRandom mutationHuman tumor
The present invention relates to a gene search vector, a random gene mutation control method and application thereof. Specifically, the present invention relates to a vector for gene search system, a random gene control method, a method for screening high transfer human tumor cell lines, a method for screening a gene for improving human tumor cell line transfer, a whole-genome random mutation library obtained by using the random gene control method, pharmaceutical application of the gene obtained by using the method for screening gene for improving human tumor cell line transfer, pharmaceutical application of an inhibitor of the gene, and pharmaceutical application of an inhibitor of an expression product of the gene. The gene obtained by the method of the invention, the inhibitor of the gene, the expression product of the gene and the inhibitor of the expression product of the gene can be applied to development of specific antitumor drug.
Owner:THE INST OF BASIC MEDICAL SCI OF CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
Application of GRMZM2G417164 in stomata development
ActiveCN107723296AImprove stress resistancePlant peptidesFermentationAgricultural scienceGene engineering
The invention relates to the technical field of maize gene engineering, in particular to application of a maize GRMZM2G417164 gene in adjustment of stomata development. The maize GRMZM2G417164, serving as a transcription factor, regulates some genes associated with the stomata development, and adjusts an associated process of maize stomata development. A series of experiments prove that a proteincoded by the GRMZM2G417164 gene controls transfer of a signal from a guard mother cell to a subsidiary mother cell and a final longitudinal division of the guard mother cell to form a guard cell. After the gene is mutant, a plant cannot form a normal guard cell and a normal subsidiary cell. Therefore, deep research and analysis on GRMZM2G417164 gene functions has an important theoretical significance and a practical application value for exploring a maize stomata development mechanism and improving maize resistance.
Owner:HENAN UNIVERSITY
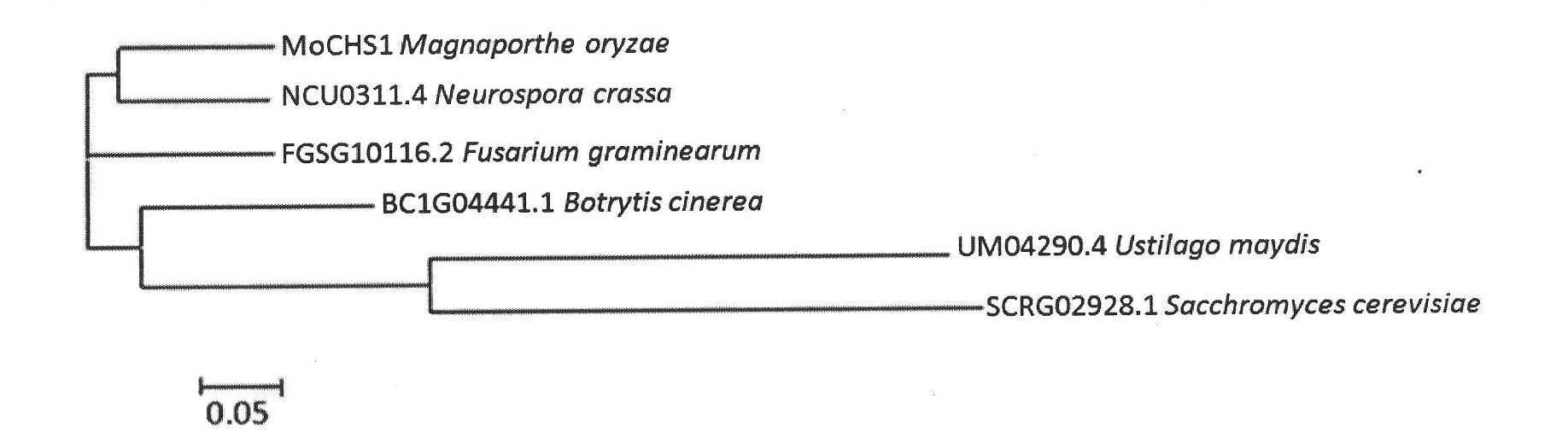
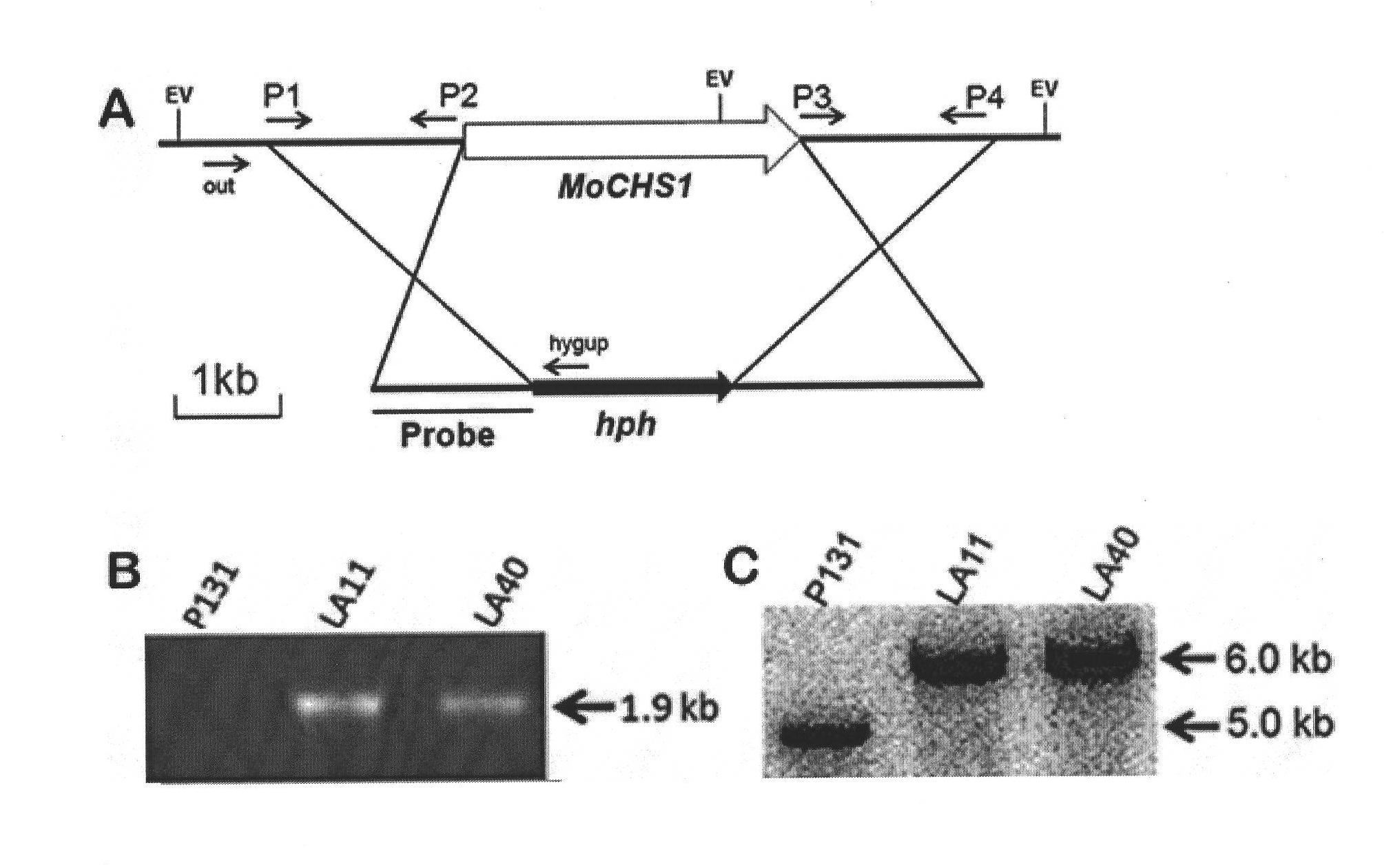
Function and usage of magnaporthe oryzae MoCHS1 gene and coded protein thereof
InactiveCN102021185AReduce incidenceReduce formation rateDepsipeptidesFermentationNucleotideAntifungal drug
The invention discloses the function and the usage of a magnaporthe oryzae MoCHS1 gene and a coded protein thereof. The gene controls the conidium form, the conidium yield, the appressorium formation rate and the pathogenicity of magnaporthe oryzae. The gene as well as the cDNA and the coded protein thereof respectively comprise nucleotide or amino acid sequences SEQ ID No: 1, No: 2 and No: 3 in the sequence list. The knockout of the MoCHS1 gene causes the change of the form establishment of the magnaporthe oryzae conidium; the conidium is reduced and has no diaphragm or has only one diaphragm; the yield of the conidium is decreased to 2% of wild type bacterial strains; the formation rate of the appressorium is decreased to 60% of the wide type bacterial strains; and the infestation capability on rice vanes is obviously decreased. The protein coded by MoCHS1 or / and the expression or the modification of the homologous protein in other pathogenic fungi can be taken as important candidate targets and can be used for designing and screening novel antifungal drugs.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com