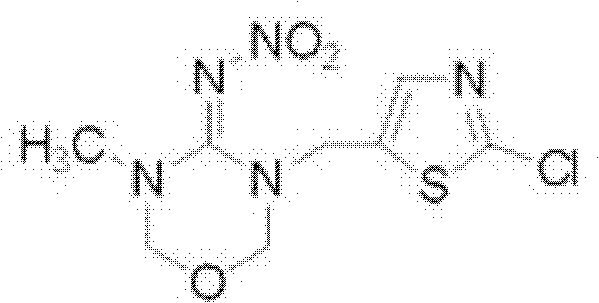
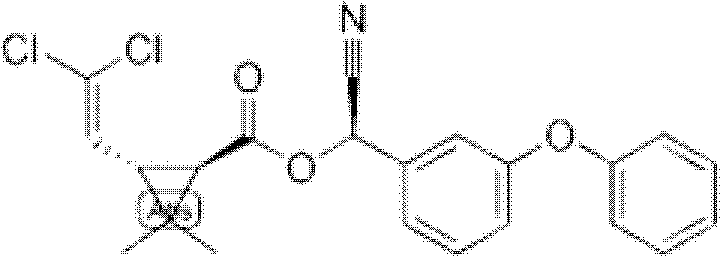
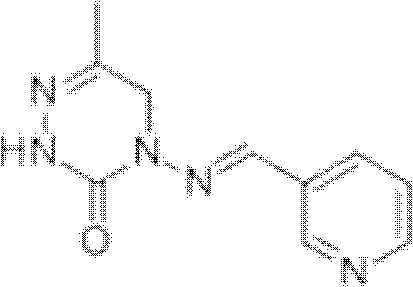
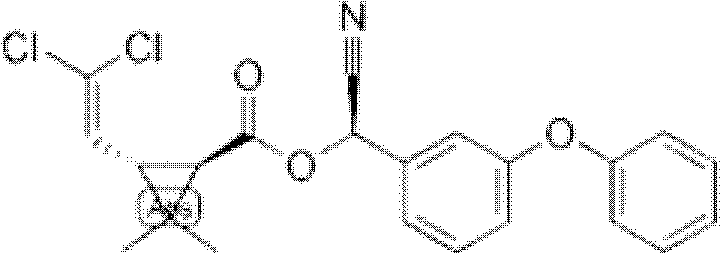
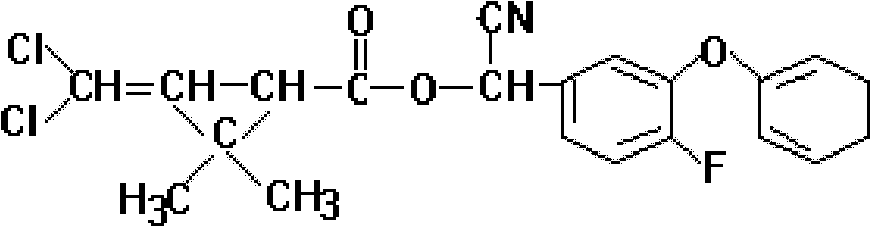Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
368 results about "Brown planthopper" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The brown planthopper (BPH), Nilaparvata lugens (Stål) (Hemiptera: Delphacidae) is a planthopper species that feeds on rice plants (Oryza sativa L.). These insects are among the most important pests of rice, which is the major staple crop for about half the world's population. They damage rice directly through feeding and also by transmitting two viruses, rice ragged stunt virus and rice grassy stunt virus. Up to 60% yield loss is common in susceptible rice cultivars attacked by the insect. The BPH is distributed in Australia, Bangladesh, Bhutan, Burma (Myanmar), Cambodia, China, Fiji, India, Indonesia, Japan, North and South Korea, Laos, Malaysia, Nepal, Pakistan, Papua New Guinea, Philippines, Sri Lanka, Taiwan, Thailand, and Vietnam. Their alternative host plant other than rice is Leersia hexandra.
Brown planthopper resistant rice gene Bph9 as well as molecular marker and application thereof
ActiveCN103667309AClear functionGood effectBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementBinding siteProtein
The invention provides a brown planthopper resistant rice gene Bph9 as well as a molecular marker and application thereof. The brown planthopper resistant rice gene Bph9 has a nucleotide sequence as shown in SEQ ID No.1 and a cDNA (complementary Desoxvribose Nucleic Acid) sequence as shown in SEQ ID No.2. The Bph9 gene is located between molecular markers InD2 and RM28466. The molecular markers closely linked with the gene also includes one of RM28438, InD28450, InD28453, InD14, InD28432, RM28481 and RM28486 which can be used for sieving the rice containing the brown planthopper resistant gene Bph9. The Bph9 gene belongs to the NBS-LRR (Nucleotide Binding Site-Leucine Rich Repeat) gene family; the encoded protein is related to the plant disease resistance; the Bph9 gene is transferred into common rice by virtue of genetic transformation and hybridization, and thus the resistance of rice to brown planthopper can be improved, so that the damage of brown planthopper is decreased, and the purposes of yield increase and yield stabilization are realized.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Molecular mark method for rice variety anti-brownspot gene site
InactiveCN1896281AEasy to detectNot affectedMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBrown planthopperGenotype
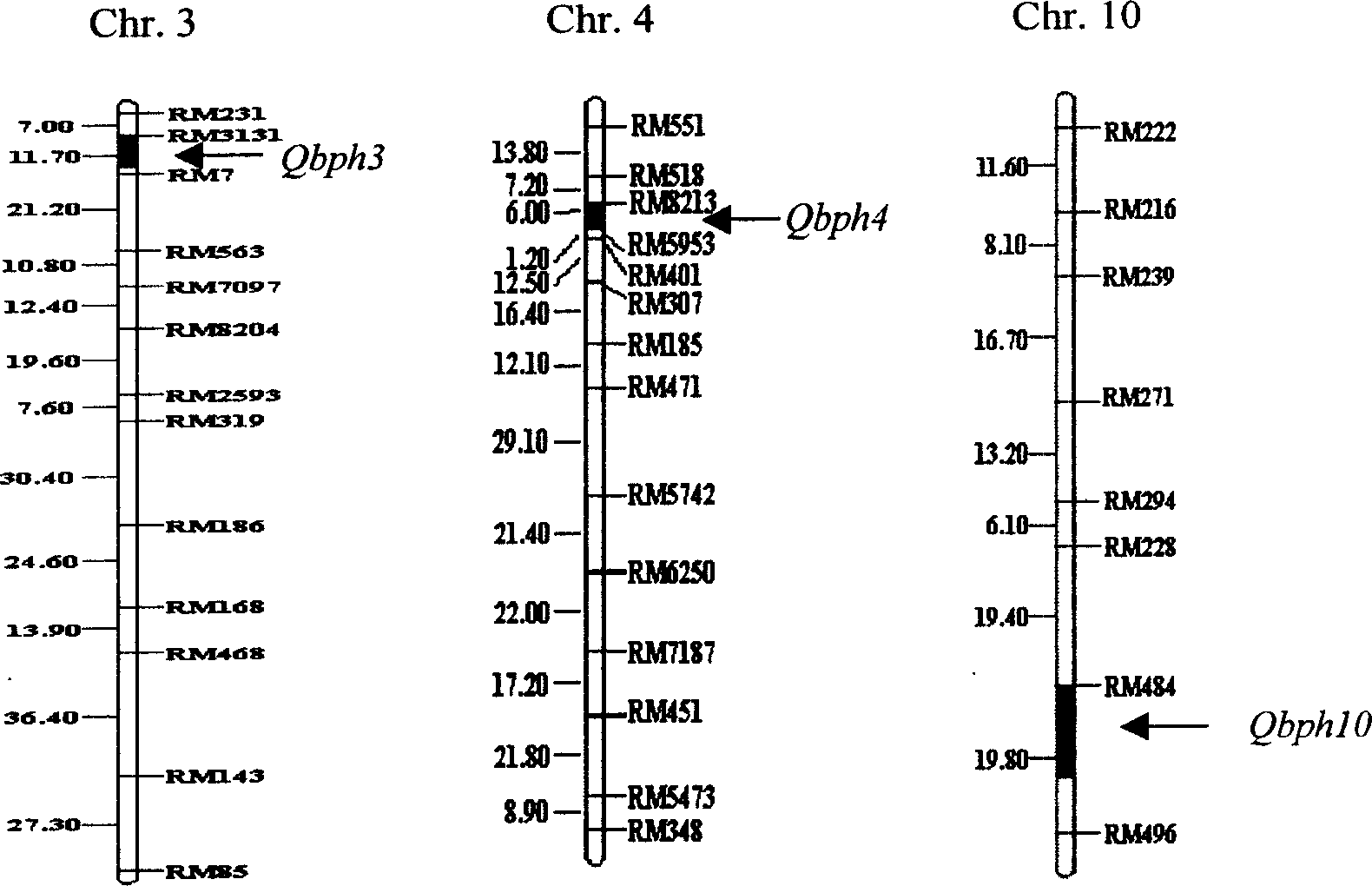
The present invention belongs to the molecular genetics field and relates to the molecular marker method of the major gene for brown planthopper resistance in the rice variety Rathu Heenati. Via genetic linkage analysis of the individual F2 plant genotype and the brown planthopper resistance level of each F2:3 family produced by hybridizing the insect-resistant variety Rathu Heenati with insect-susceptible variety 02428, the molecular markers RM8213 and RM5953 of the major gene loci Qbph4(Bph3) in the insect-resistant variety Rathu Heenati are obtained, the loci Qbph4(Bph3) is 3.6cM and 3.2cM distant from the markers RM8213 and RM5953 respectively. Detection of this major gene loci in Rathu Heenati and its derivatives via these molecular markers will increase the selection efficiency of brown plant hopper resistant rices.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
A kind of ultra-low volume liquid preparation containing thiamethoxam
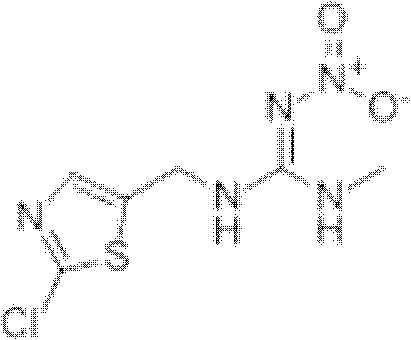
The invention discloses an ultra-low-capacity liquid preparation containing thiamethoxam, which uses thiamethoxam, or the compound of thiamethoxam and active component II as the active ingredient, and supplements the rest to 100% with auxiliary agents and solvents. Low-volume liquid preparation; active component II is beta-cypermethrin, pymetrozine, chlorantraniliprole, flubendiamide, tofenpyrad, azadirachtin, buprofezin, abamectin, and emamectin Any one of plain benzoate and diazinon. The invention can be used to control crop pests such as rice planthopper, rice leaf roller, brown planthopper, white-backed planthopper, striatellus striatellus, stem borer and rice thrips, and has the advantages of convenient processing, water saving, high work efficiency and good drug effect , long-lasting, synergistic and other advantages.
Owner:GAUNGXI TIANYUAN BIOCHEM
Brown planthopper resistant gene in rice and use thereof
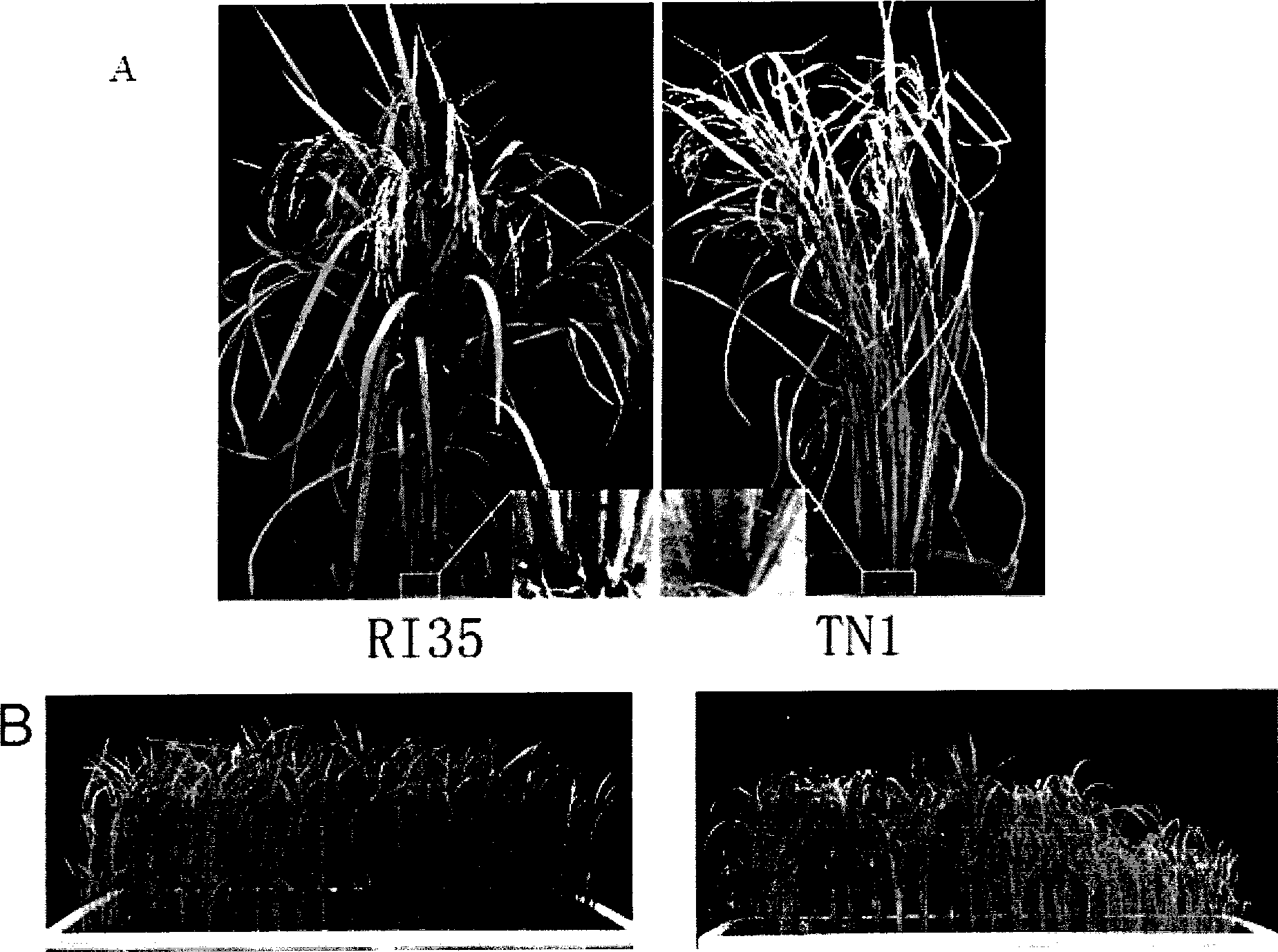
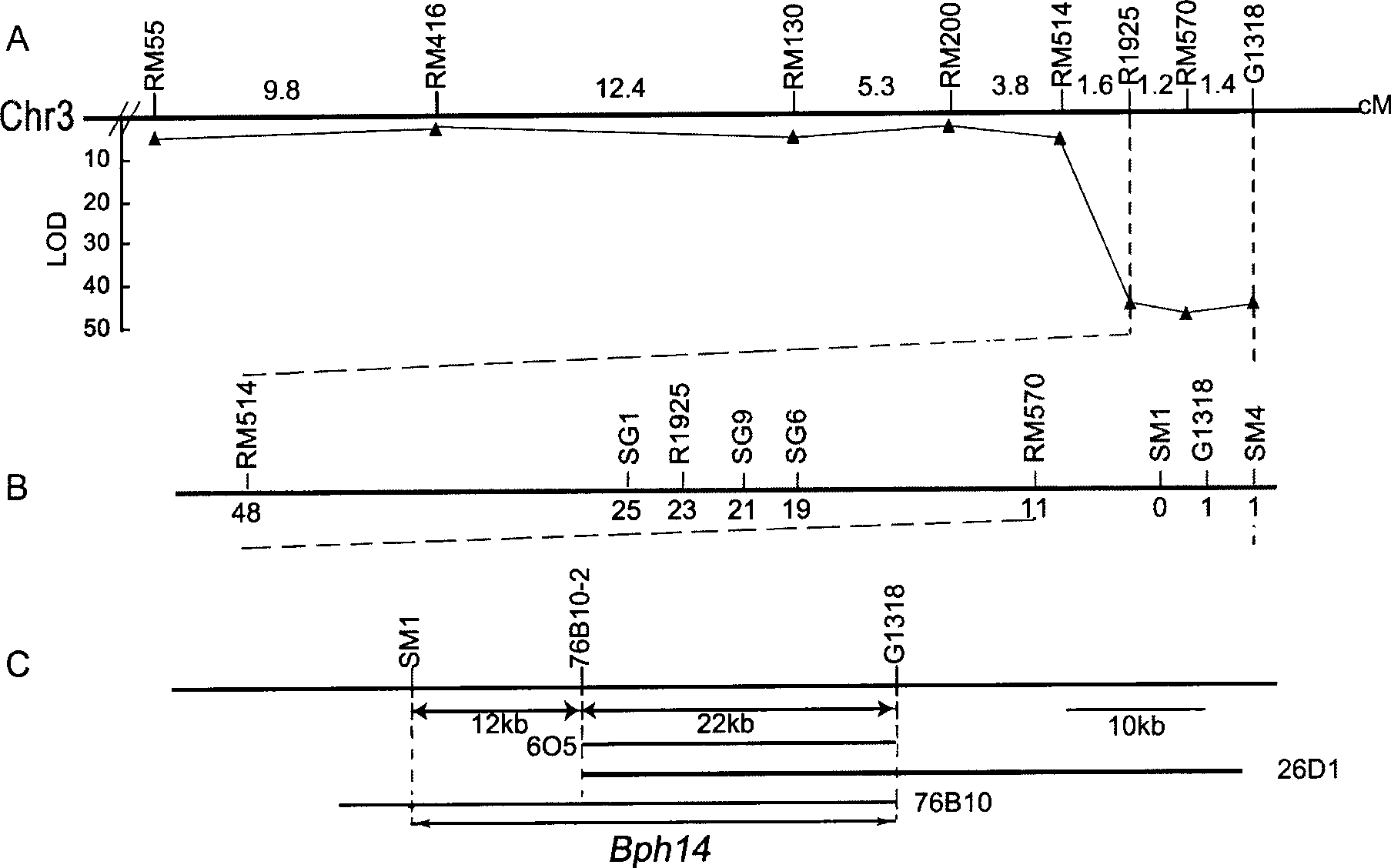
The invention provides a brown planthopper resistance gene Bph14 in rice. The gene has a nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID No. 1 and a cDNA sequence thereof is shown in SEQ ID No.2. The gene Bph14 of the invention belongs to CC-NBS-LRR gene family, and coded protein is related to plant disease resistance. The gene Bph14 has function of resisting the brown planthopper. Through genetic transformation and hybridization, the gene Bph14 is transferred into normal rice varieties, which can improve the resistance of the rice to the brown planthopper, thus reducing the damage caused by the brown planthopper and achieving the purposes of increasing and stabilizing the production of rice.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
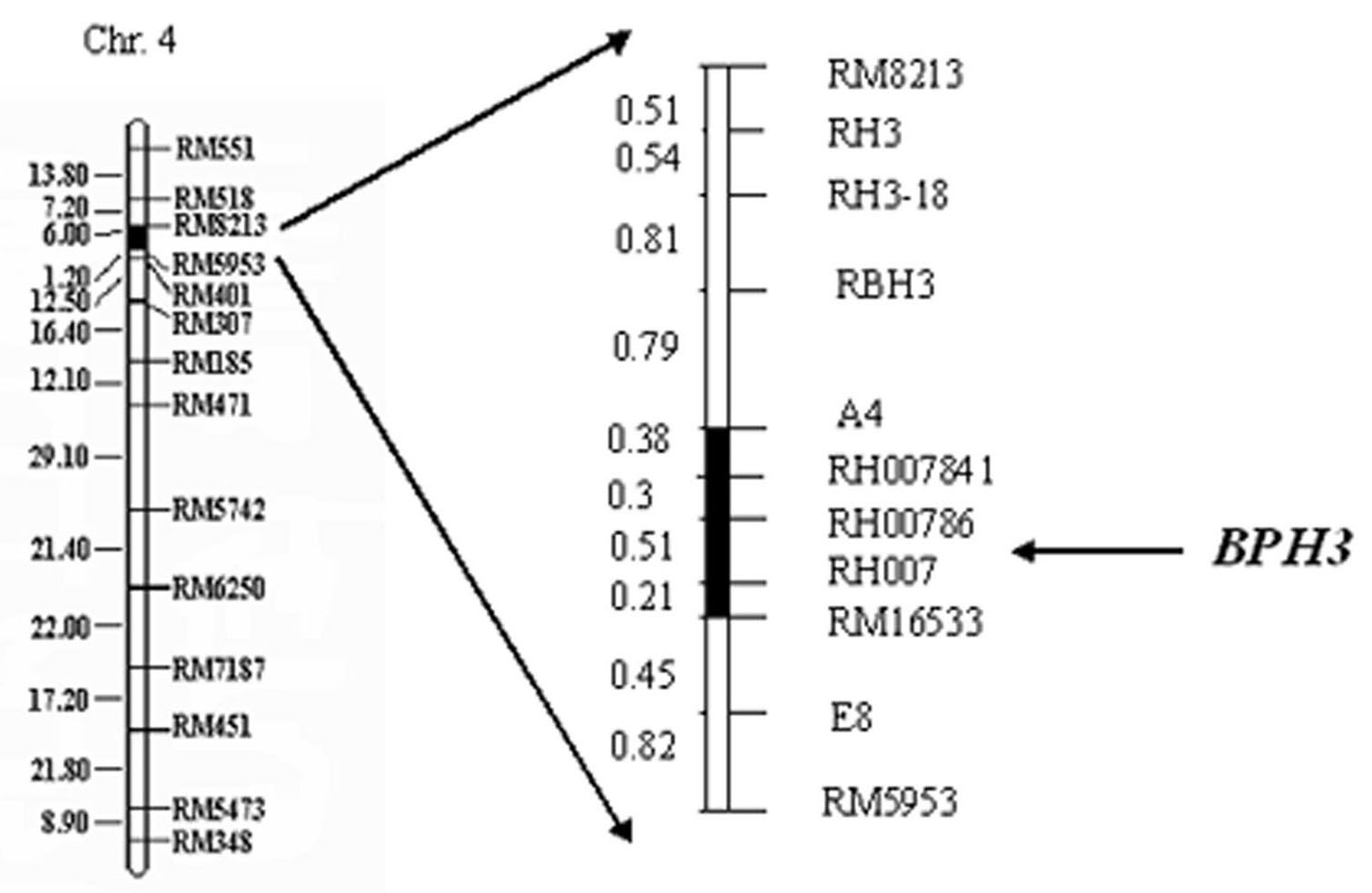
Molecular marker method of rice variety brown planthopper resistance main gene Bph3
InactiveCN101418349AQuick checkQuick filterMicrobiological testing/measurementBrown planthopperGene type
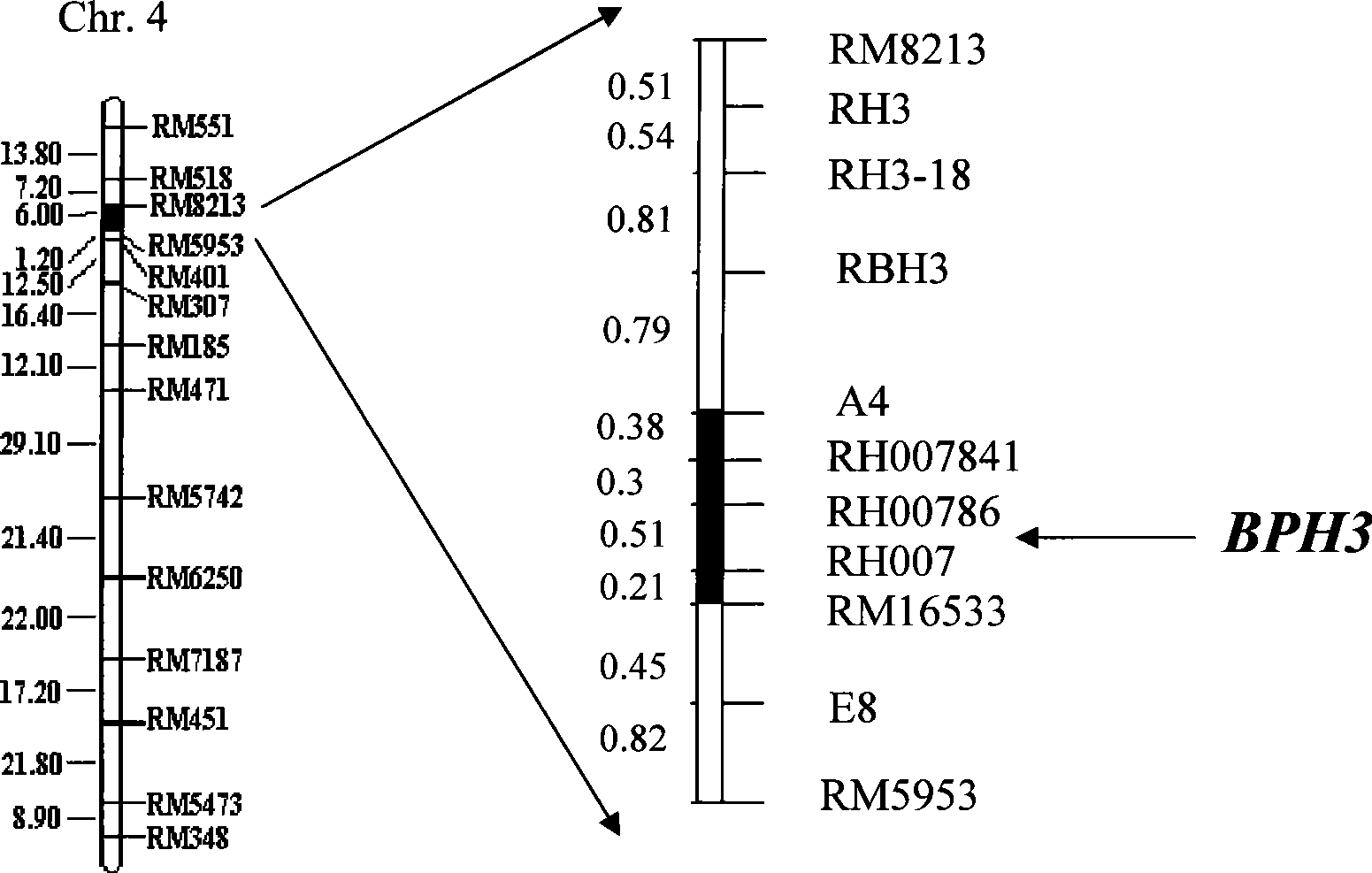
The invention relates to a molecule tagging method for a brown paddy plant hopper resistant master gene Bph3 of rice cultivars, which belongs to the technical field of genetic thremmatology. The brown paddy plant hopper resistant master gene Bph3 of an insect resistant variety Rathu Heenati is obtained by genetic linkage analysis of the brown paddy plant hopper resistant level of gene types of various single plants of F2 and various genealogies of F 2:3 obtained after hybridization of the insect resistant rice variety Rathu Heenati (female) and an insect susceptible variety 02428(male). The gene is positioned between a molecular marker A4 and a molecular marker RM16533, and the selection efficiency of three Indel indexes namely RH784, RH786 and RH007 of the interval is approximately 97 percent. Detection is made whether the insect resistant variety Rathu Heenati and derivative varieties (systems) of the insect resistant variety Rathu Heenati contain the master gene through the molecular markeres of the brown paddy plant hopper resistant master gene; the brown paddy plant hopper resistance level of the master gene can be predicted; and the selection efficiency of brown paddy plant hopper resistant rice can be greatly improved.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
A kind of ultra-low volume liquid preparation containing clothianidin
The invention discloses an ultra-low-volume liquid preparation containing clothianidin, which uses clothianidin, or clothianidin and active component II as the active ingredient, and supplements the rest to 100% with auxiliary agents and solvents. Low-volume liquid preparation; active component II is any one of beta-cypermethrin, beta-cyfluthrin, chlorantraniliprole, flubendiamide, abamectin or emamectin benzoate. The invention can be used to control crop pests such as rice planthopper, rice leaf roller, brown planthopper, white-backed planthopper, striatellus striatellus, stem borer and rice thrips, and has the advantages of convenient processing, water saving, high work efficiency and good drug effect , long-lasting, synergistic and other advantages.
Owner:GAUNGXI TIANYUAN BIOCHEM
Set of paddy rice anti-brown-planthopper genes, coded protein thereof, and application thereof
ActiveCN103215237AIncrease resistanceGenetic improvementBacteriaTransferasesBrown planthopperGene engineering
The invention belongs to the technical field of gene engineering, and specifically relates to a set of paddy rice anti-brown-planthopper genes, and coded proteins thereof and an application thereof. The sequences of the paddy rice anti-brown-planthopper genes are represented by SEQ ID No.5-No.8. The sequences of the coded proteins are represented by SEQ ID No.1-No. 4. The paddy insect-resistance-related proteins influence the insect resistance of plant. The increase of the protein-coding gene can lead to insect resistance of susceptible plants, such that anti-brown-planthopper transgenic plants can be cultivated. The gene and the coded protein thereof can be used in plant genetic improvement.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method for preserving rice black-streaked dwarf virus indoor living bodies
ActiveCN102870743ASolve the technical problems that are difficult to maintain in vivo preservationOvercome technical bottlenecks that are difficult to preserve for a long timeHorticulture methodsAnimal husbandryRice black-streaked dwarf virusTriticeae
The invention provides a method for preserving rice black-streaked dwarf virus (RBSDV) indoor living bodies. According to the principle of the method, wheat serves as a virus source host, small brown planthopper imagoes carrying the RBSDV spread the virus on wheat seedlings, a descendant small brown planthopper nymphs obtain the virus from the wheat, and accordingly a large of small brown planthoppers with the virus are obtained at a short period under indoor feeding conditions. The method effectively overcomes the technical bottleneck in preserving a large number of RBSDV indoor living bodies in a long term, and a series of technical problems that an RBSDV virus source is difficult to preserve continuously through the living bodies, the conventional cycle of obtaining the virus source is long, virus feeding plants cannot be provided for a long term, and minimum of the instar of the virus feeding nymphs is difficult to operate, and the like are solved. The obtained small brown planthoppers with the virus can support rice and corn variety resistance identification at any time and can also serve as RBSDV purification and serum preparation materials, and the problems that materials are difficult to obtain and the virus content is low and the like in conventional purification are solved. By application of the method, research, development and utilization of the RBSDV are greatly accelerated.
Owner:JIANGSU ACAD OF AGRI SCI
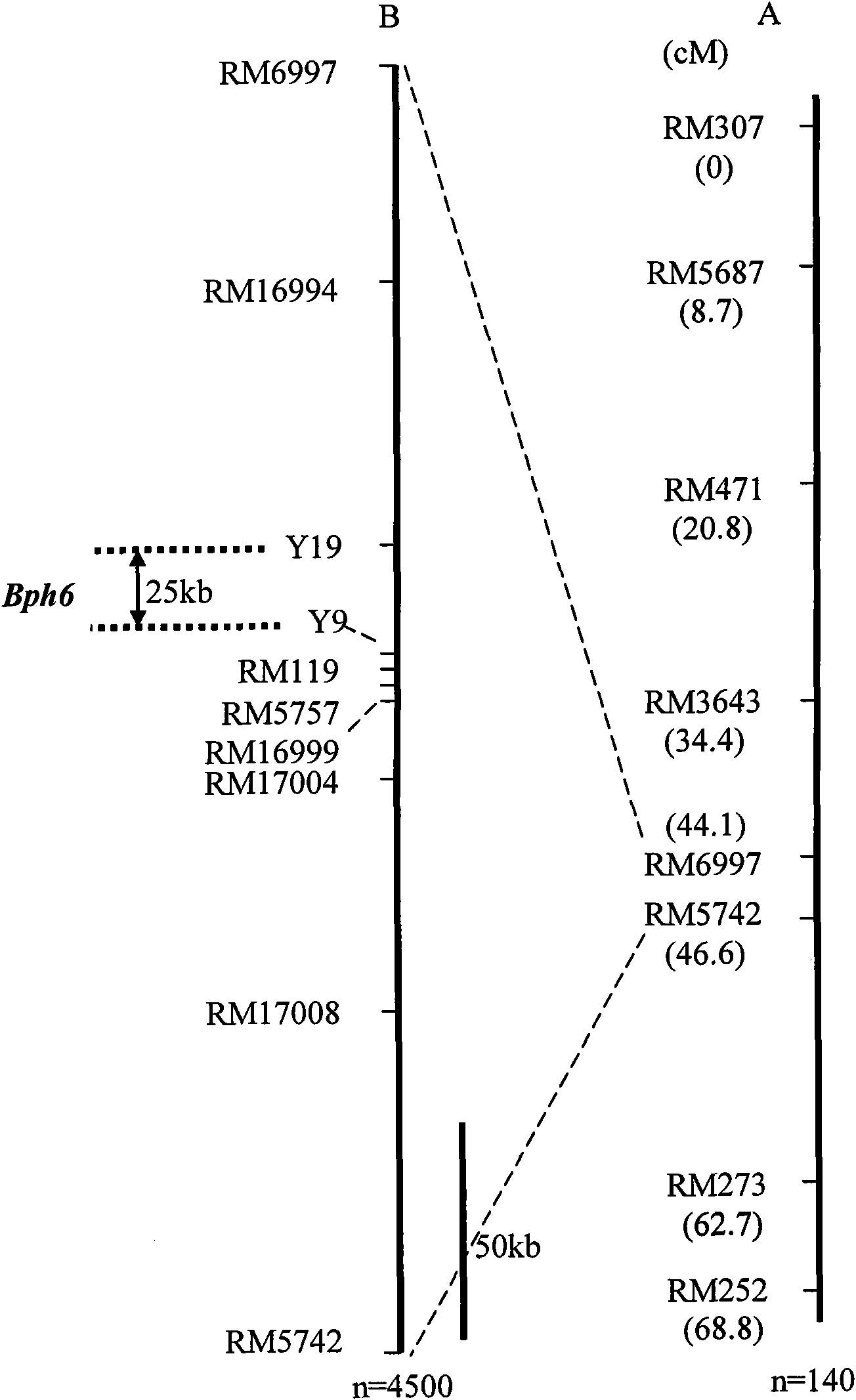
Molecular marker of major gene Bph6 resistant to brown planthopper and application thereof
InactiveCN101914531AQuick filterNot affectedMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyBrown planthopper
The invention provides a molecular marker of major gene Bph6 resistant to brown planthopper and an application thereof. The invention can obtain a pest-resistant cultivar Swarnalata resistance gene Bph6 and position the resistance gene between molecular marker Y1 and molecular marker Y9 by hybridizing a rice pest-resistant cultivar Swarnalata with 9311 (female) to obtain the genetype of each F2 plant and performing genetic linkage analysis by combining resistance levels resistant to brown planthopper of each family of F2:3. The molecular marker linked with the resistance gene is one of RM16994, Y19, Y9, RM119, RM5757, RM16999, RM17004 and RM17008. The molecular marker in the invention can effectively detect whether the major gene locus exists in the pest-resistant cultivar Swarnalata and derived varieties (strains) thereof, thus greatly improving the selection efficiency of rice resistant to brown planthopper and obtaining brown planthopper resistant rice varieties containing Bph6 gene.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Gene marker of major gene Bph14 for resisting brown planthopper in rice and application thereof
InactiveCN103509791ANo genetic exchangeGood experimental repeatabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationForward primerResistant genes
The invention relates to a gene marker of a major gene Bph14 for resisting brown planthopper in rice and application thereof. The gene marker Bph14-M1 of Bph14 has the following sequences of forward and reverse primers: a forward primer of (5'-3') AGCCACTTGGTGAACTTATT, and a reverse primer of (5'-3') GATTGACGATGAGGAGACTT. The application method includes 1) extracting rice genomic DNA; carrying out PCR amplification on the rice genomic DNA by using the forward and reverse primers; and carrying out electrophoresis detection on amplification products. The invention employs the marker to assist selection and can accurately transform the brown planthopper resistant gene Bph14 in B5 to a brown planthopper susceptible cultivar and greatly improve the breeding efficiency of brown planthopper resistant varieties.
Owner:江西省农业科学院水稻研究所
Molecular marker of anti-nilaparvata-lugens major gene Bph3 of rice
InactiveCN101956019AQuick checkQuick filterMicrobiological testing/measurementBrown planthopperGenotype
The invention relates to a molecular marker of an anti-nilaparvata-lugens major gene Bph3 of rice and belongs to the technical field of genetic breeding. A genetic linkage analysis is preformed on a genotype of each single plant of F2 obtained by crossing an rice anti-insect variety RathuHeenati (female) with an insect-susceptible variety 02428 (male) as well as on an anti-nilaparvata-lugens level of each family of F2: 3, thereby obtaining the anti-nilaparvata-lugens major gene Bph3 of the anti-insect variety RathuHeenati. The gene is positioned between the molecular marker A4 and the molecular marker RM16533; the selection efficiencies of three Indel markers RH784, RH786 and RH007 in the interval are around 97%. The molecular marker of the anti-nilaparvata-lugens major gene is used for detecting whether the major gene is contained in the anti-insect variety RathuHeenati as well as derived varieties thereof (family), thereby forecasting the anti-nilaparvata-lugens level; therefore, the selection efficiency of the anti-nilaparvata-lugens rice is improved greatly.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Anti-Nilaparvata-lugens pesticidal protein, and coding gene and application thereof
The invention discloses an anti-Nilaparvata-lugens pesticidal protein, and a coding gene and application thereof. The protein is a) or b) as follows: a) protein composed of amino acid sequence disclosed as Sequence 2 in the sequence table; or b) protein with same functions subjected to substitution and / or deletion and / or addition of one or more amino acid residues on amino acid sequence disclosed as Sequence 2 in the sequence table. The experiment proves that the novel pesticidal protein disclosed by the invention has high toxicity for Nilaparvata lugens, provides a new strategy for resisting Nilaparvata lugens and has wide application prospects.
Owner:INST OF GENETICS & DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
A kind of ultra-low volume liquid preparation containing thiacloprid
The invention discloses an ultra-low-volume liquid preparation containing thiacloprid, which uses thiacloprid, or a compound of thiacloprid and active component II as the active ingredient, and supplements the rest to 100% with additives and solvents. Low-volume liquid formulation; active ingredient II is beta-cypermethrin, pymetrozine, chlorantraniliprole, flubendiamide, tofenpyrad, azadirachtin, buprofezin, abamectin or emamectin Any of the plain benzoates. The invention can be used to control crop pests such as rice planthopper, rice leaf roller, brown planthopper, white-backed planthopper, striatellus striatellus, stem borer and rice thrips, and has the advantages of convenient processing, water saving, high work efficiency and good drug effect , long-lasting, synergistic and other advantages.
Owner:GAUNGXI TIANYUAN BIOCHEM
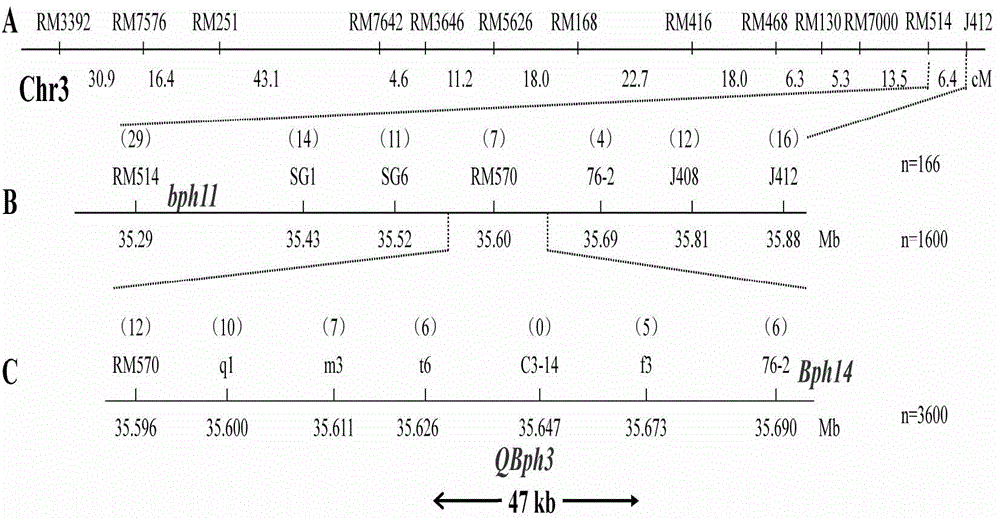
Molecular marker for rice brown planthopper-resistance QBph3 and QBph4 genes
InactiveCN105087553AImprove reliabilityEasy to identifyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAgricultural scienceGenotype
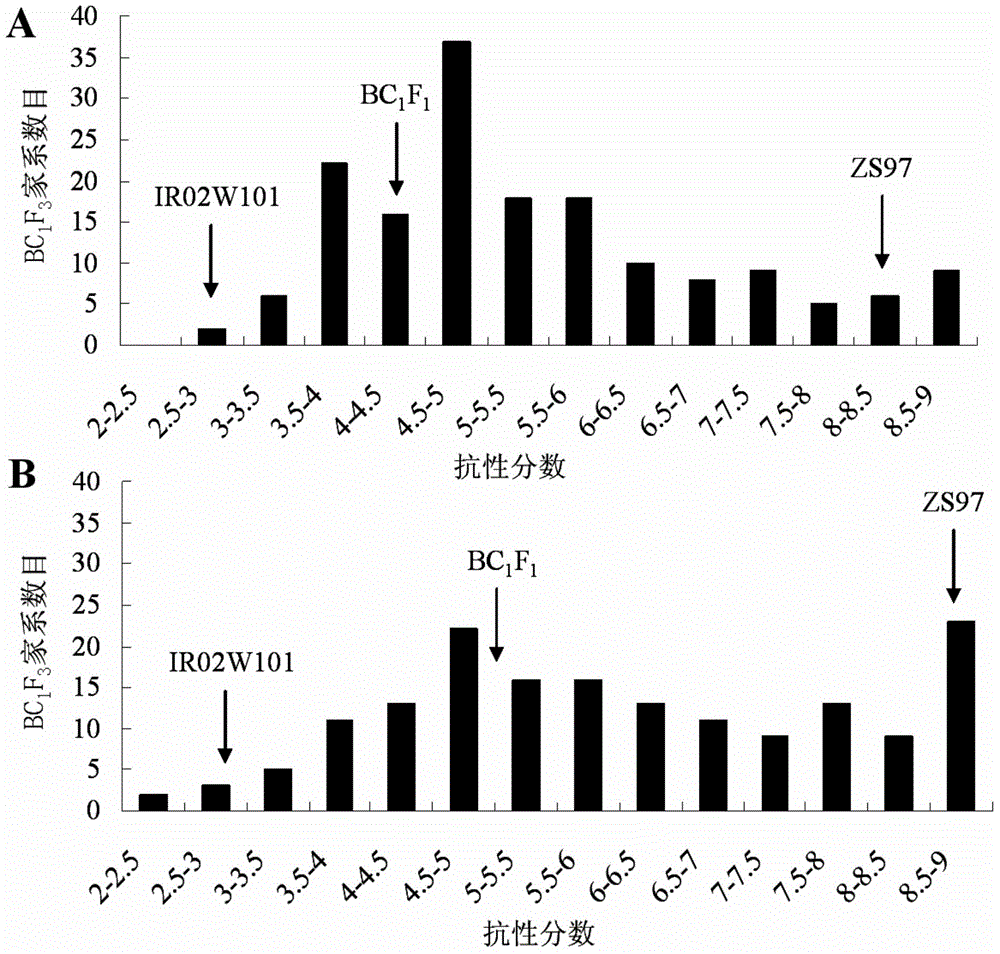
The invention belongs to the technical field of preparation of a rice molecular marker, and in particular relates to a molecular marker for two rice brown planthopper-resistance major genes QBph3 and QBph4 which are simultaneously derived from a pest-resistance introgression line IR02W101. The molecular marker comprises the following steps: carrying out crossing, self-crossing and backcrossing on Zhenshan97, which is an herbivore-susceptible variety, and IR02W101 so as to obtain genotypes of various BC1F2 single plants; carrying out genetic linkage analysis in accordance with brown planthopper-resistance grades of various F2: 3 lines during seedling stage; precisely locating a resistance gene QBph3 of the IR02W101 between long-arm markers t6 and f3 of the 3rd chromosome so as to obtain a co-segregative marker c3-14 as well as closely linked markers q1 and m3; and precisely locating QBph4 between short-arm markers p17 and xc4-27 of the 4th chromosome so as to obtain closely linked markers p6, p9, c4-5, xc4-7, HJ16, J417 and IN156. The molecular marker disclosed by the invention can be used for effectively detecting whether the pest-resistance introgression line IR02W101 and derived varieties thereof contain the major gene site or not.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Carrier plant system for protecting and increasing number of rice field rice planthopper parasitic wasps
InactiveCN103609373AImprove the effect of prevention and controlReduce usagePlant protectionAnimal husbandryBrown planthopperPlanthopper
The invention discloses a carrier plant system for protecting and increasing the number of rice field rice planthopper parasitic wasps. The carrier plant system comprises three parts, namely, carrier plants, substitute hosts and the parasitic wasps, wherein the carrier plants are grassy weed blighted grain grass and clubhead cutgrass herbs, the substitute hosts are main phytophagous insect false brown planthopper on the grassy weed blighted grain grass and the clubhead cutgrass herbs, and the parasitic wasps are mainly anagrus nilapartvatae pang et wang. The system servers as a species pool of natural enemies of the rice planthopper and used for unceasingly breeding the parasitic wasps, the biological control efficiency of the rice planthopper can be effectively improved, and the number of the times of using pesticides can be lowered by 2 to 3 in one season. The system has the advantages of being long in action time, easy to operate and high in practicability.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE SCIENCES
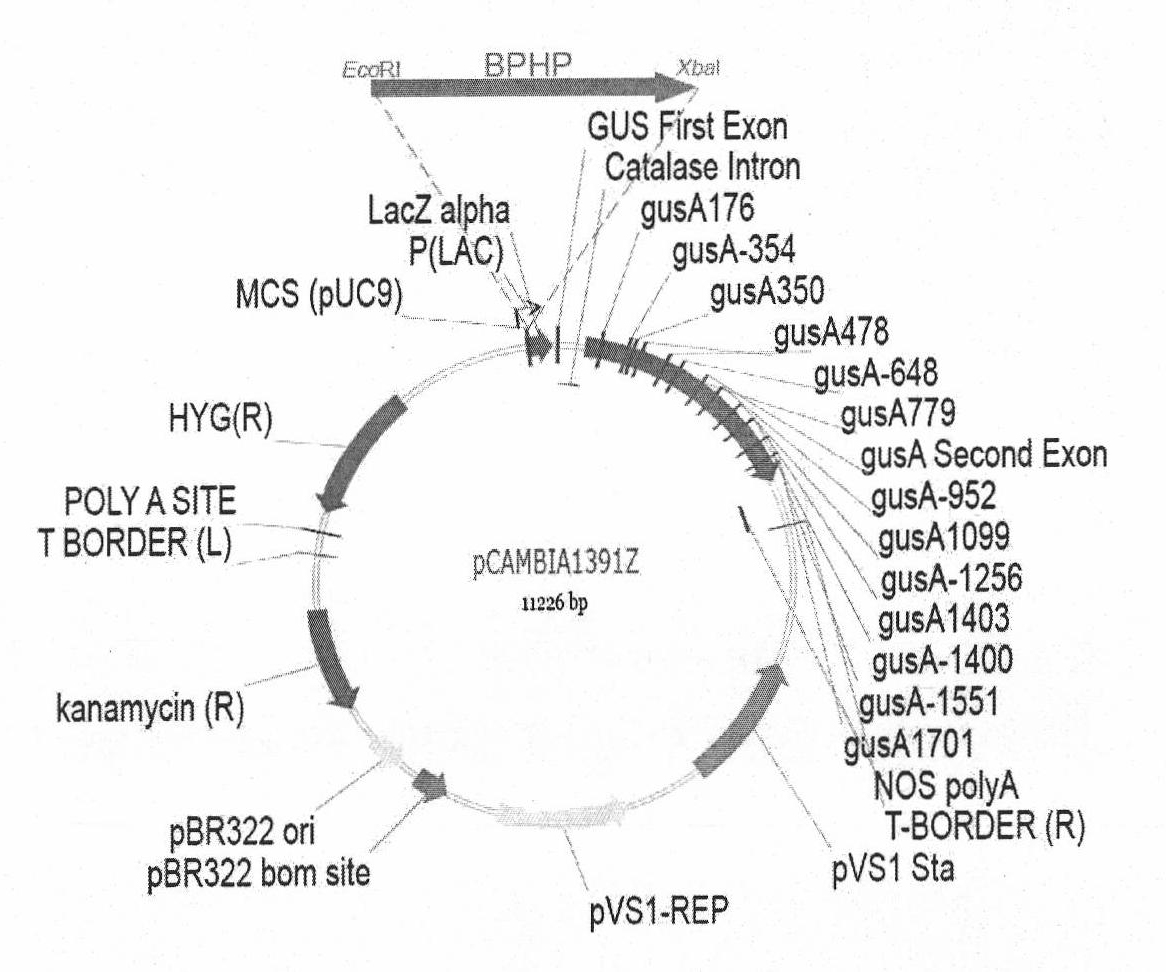
Induction-enhanced tissue specific promoter and application thereof
InactiveCN101792761AVector-based foreign material introductionDNA/RNA fragmentationVascular bundleCis-regulatory element
The invention relates to an induction-enhanced tissue specific promoter and application thereof, belonging to the technical field of plant genetic engineering. A promoter (BPHP, i.e. Bph14 promoter) for Oryza Sativa L. genes resistant to brown plant hoppers is separated from Oryza Sativa L. and is cloned. The promoter has a nucleotide sequence shown as SEQ ID No. 1, can control Oryza Sativa L. genes resistant to the brown plant hoppers to be specifically expressed in vascular bundle tissues and can be expressed in a way that the feeding induction of the brown plant hoppers is enhanced. The promoter contains BS1EGCCR cis-acting elements and can enable the genes to be specifically expressed in plant vascular bundle tissues. Moreover, the promoter has defense-related response cis-acting elements which can be combined with WRKY transcription factors, and the gene expression is increased when Oryza Sativa L. is fed by the brown plant hoppers or is infected by pathogenic bacteria. The promoter can be used as the promoter for the specific expression in the vascular bundle tissues and can be used as the brown plant hopper and pathogenic bacteria induction-enhanced promoter.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
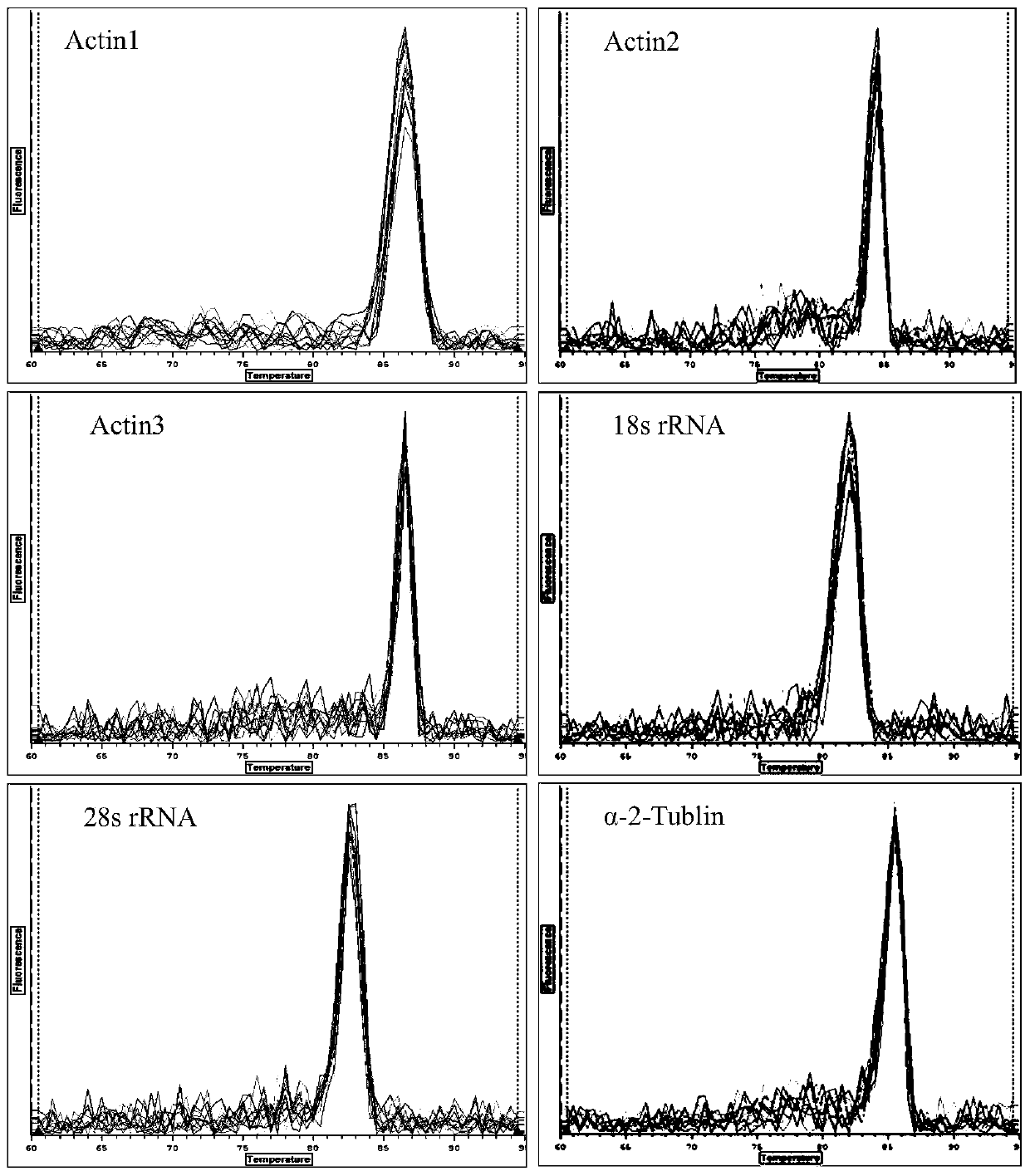
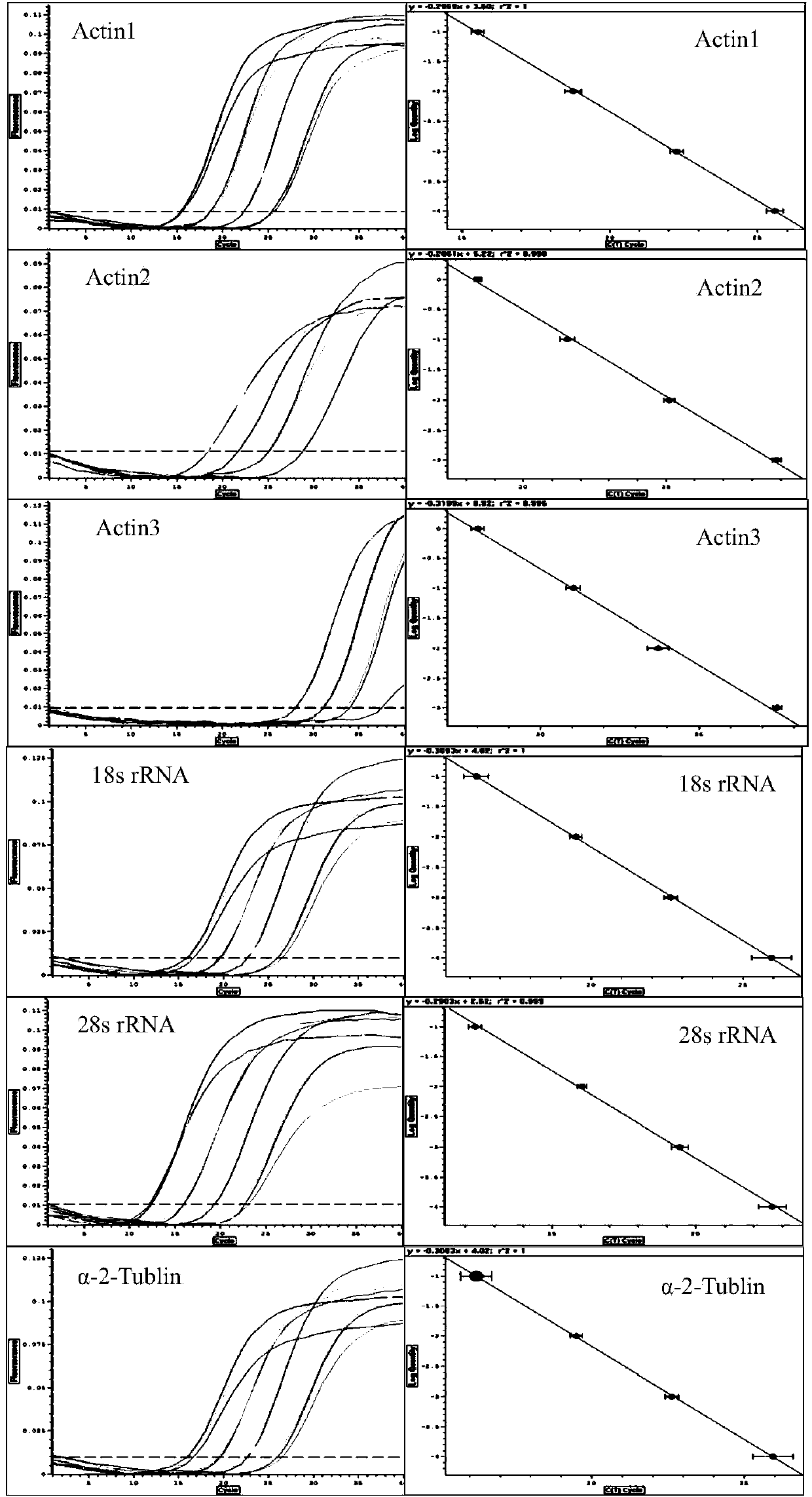
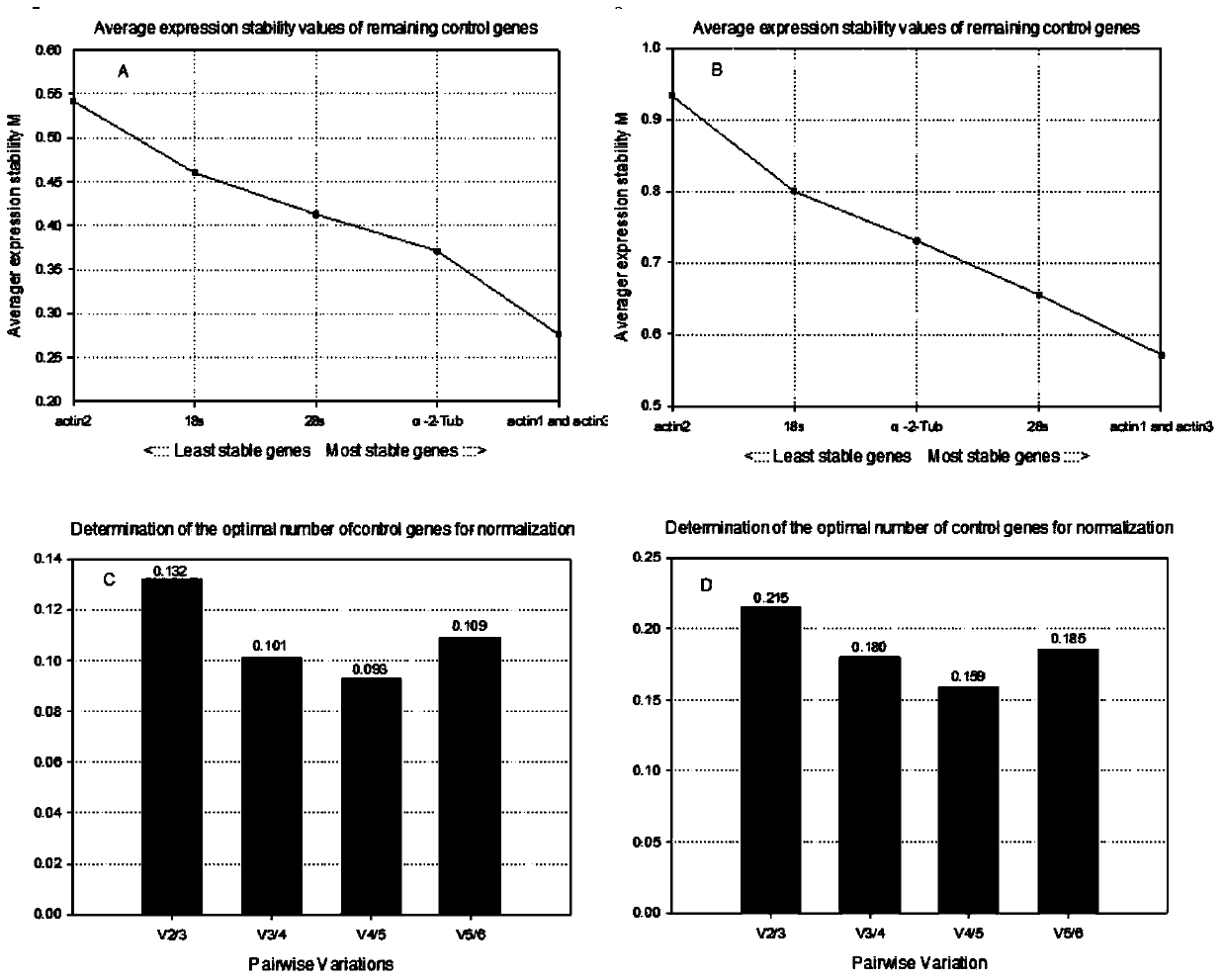
Screening method and applications of brown planthopper reference genes under high temperature stress
InactiveCN104178564ATroubleshoot screening issuesMicrobiological testing/measurementReference genesTemperature stress
The invention discloses a screening method of brown planthopper reference genes under high temperature stress. According to the screening method, fluorescent quantitative PCR studies are carried out through taking brown planthopper under no stress as a control material and brown planthoppers under the stress of different high temperatures as experimental materials; and quantitative PCR data of candidate reference genes are input to geNorm and BestKeeper softwares to be analyzed so as to screen the most suitable and most stably expressive reference gene-actin1 in the brown planthoppers under the high temperature stress and under no stress. On the basis, the expression pattern of an hsp90 gene of the brown planthopper under the high temperature stress is studied by the inventor through taking the brown planthopper at the high temperature as a sample, the heat shock protein gene hsp90 of the brown planthopper as a target gene and the screened actin1gene as the reference gene.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION GUANGXI ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
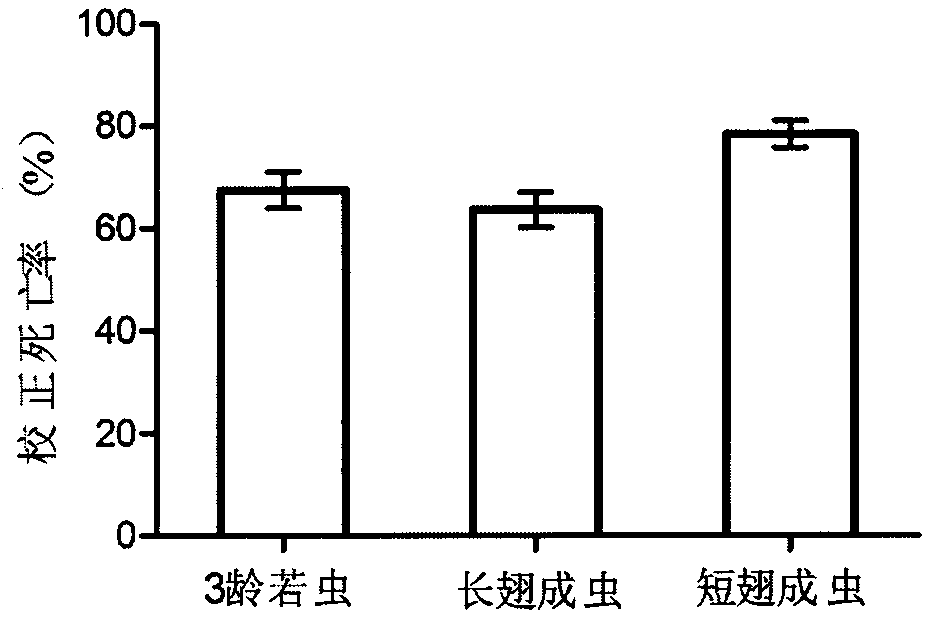
Serratia marcescens S-JS1 and application thereof
InactiveCN105331566AAvoid or reduce drug resistance problemsBiocideBacteriaMortality rateCulture bacteria
The invention relates to serratia marcescens S-JS1 and application of serratia marcescens S-JS1 in pest control. Serratia marcescens S-JS1 solid culture bacteria or bacterium suspension obtained through fermentation culture can both be applied to prevention and treatment of brown planthopper, beet armyworm and prodenia litura. After bacterium suspension of serratia marcescens S-JS1 is sprayed to brown planthopper, the result shows that the correcting death rates of third-instar nymphs, long-wing adult insects and short-wing adult insects of brown planthopper can reach 67.47%, 63.58% and 78.28% within 5 days respectively through the bacterium suspension with concentration of 8*109 cfu / ml; after 100 micro litters of the strain fermentation liquid with concentration of 108 cfu / ml are added to feed blocks (1*1*1 cm), the correcting death rates of third-instar nymphs of beet armyworm and prodenia litura are 45.64% and 32.20% respectively five days after the nymphs eat the feed blocks; the correcting death rates of third-instar nymphs of beet armyworm and prodenia litura are 76.36% and 62.06% respectively 9 days after the nymphs eat the feed blocks.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
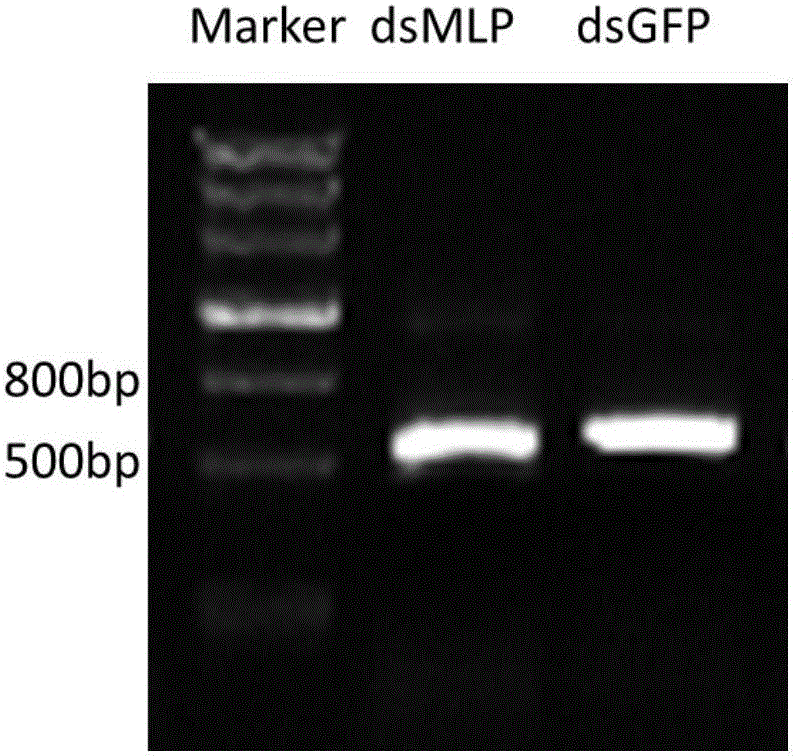
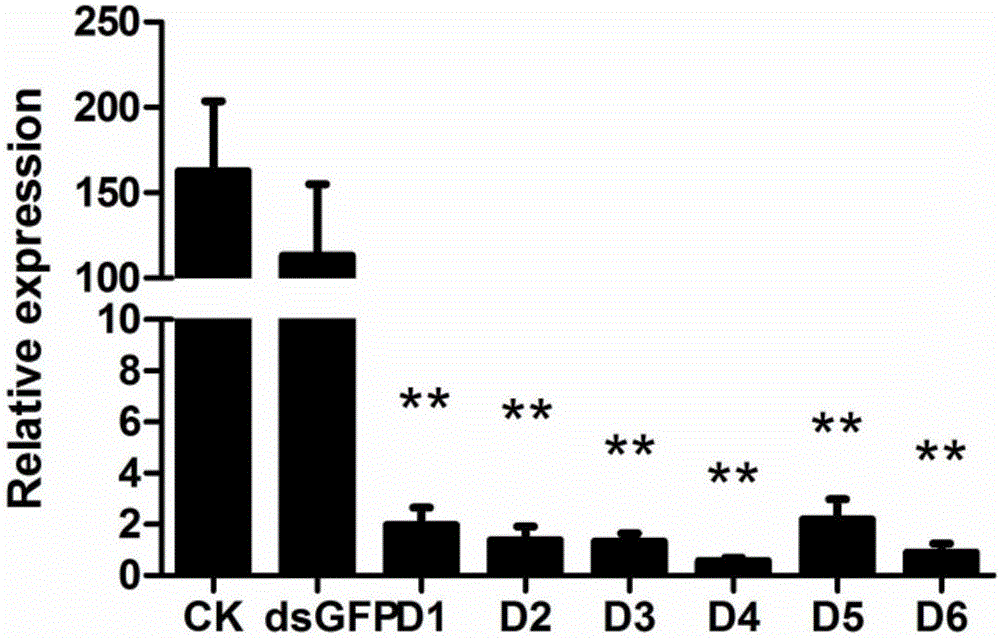
Brown planthopper N1MLP gene, encoded protein and application of brown planthopper NIMLP
ActiveCN106754948AFunctions that affect growth and developmentReduced survival rateBiocideAnimal repellantsBrown planthopperObserved Survival
The invention discloses a brown planthopper sialaden secretor gene N1MLP and an application OF brown planthopper NIMLP in paddy resisting against brown planthopper after the gene N1MLP is restrained. A complete cDNA sequence of the brown planthopper sialaden secretor gene N1MLP is shown as SEQ ID No.1; ds RNA of the N1MLP enters the brown planthopper in the manner of micro-injection, so that the N1MLP gene expression quantity is reduced, the feeding of the brown planthopper is affected and the survival rate of the brown planthopper is reduced; the ds RNA of the N1MLP is stably expressed in the paddy plant; after the brown planthopper eats the paddy, the N1MLP gene expression quantity is reduced, so that the brown planthopper weight is reduced and the survival rate of the brown planthopper is reduced. According to the invention, the N1MLP, of which the expression is restrained, has significance in researching the paddy resisting against brown planthopper and preventing and treating the brown planthopper in agricultural production.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Multi-effect flowable concentrate for seed coating
The present invention relates to a multi-effect flowable concentrate for seed coating, which comprises the effective ingredients of thiamethoxam and fludioxonil. The multi-effect flowable concentrate for seed coating of the present invention contains 1-55% of thiamethoxam, preferably 5-40%, and 1-65% of fludioxonil, preferably 5-40%. The multi-effect flowable concentrate for seed coating of the present invention can be used for seed coating, has characteristics of long duration, low toxicity and remarkable synergism, and can be applied to control of soil insects such as grub, mole cricket and wireworm in peanut, corn, wheat and rice, and control of insects with sucking mouth part, such as seedling aphide, brown planthopper, thrips, powdery mildew and leafhopper, and control of diseases of fusarium wilt, banded sclerotial blight, full rot, rice blast, powdery mildew and bacterial wilt.
Owner:SHANGDONG HAILIER CHEM
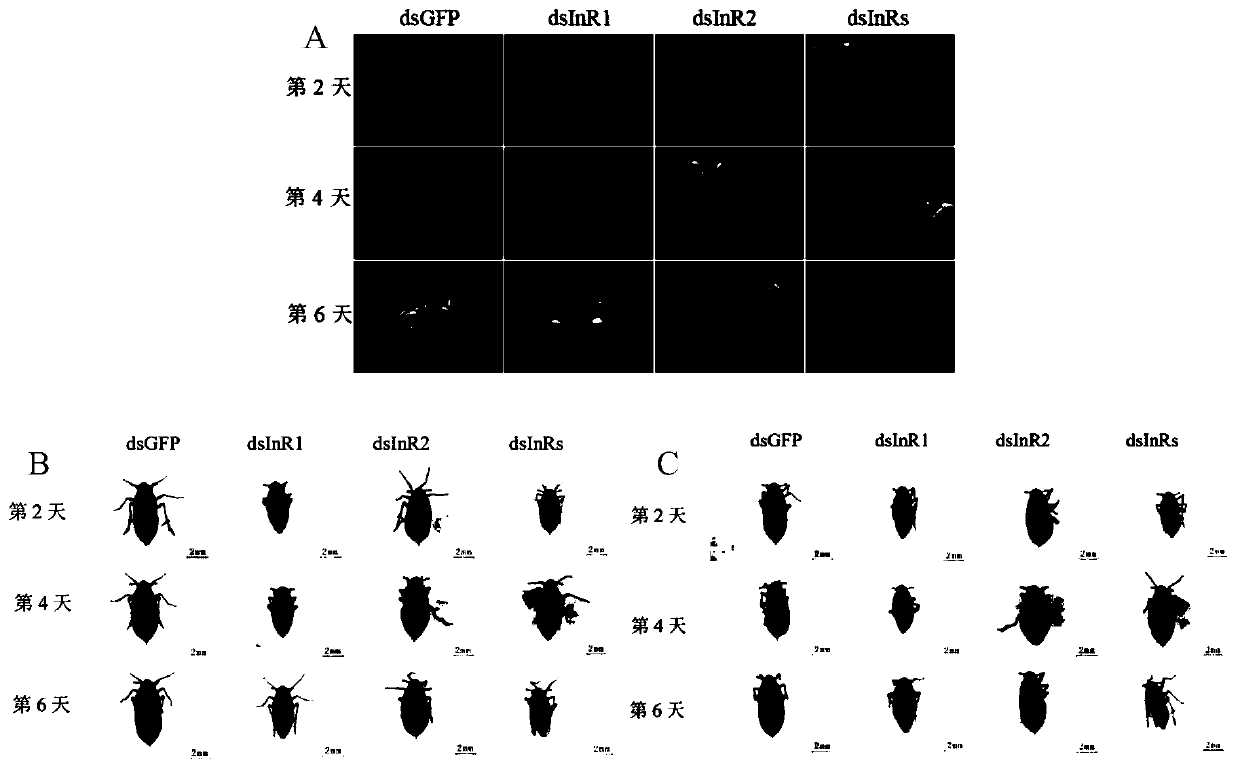
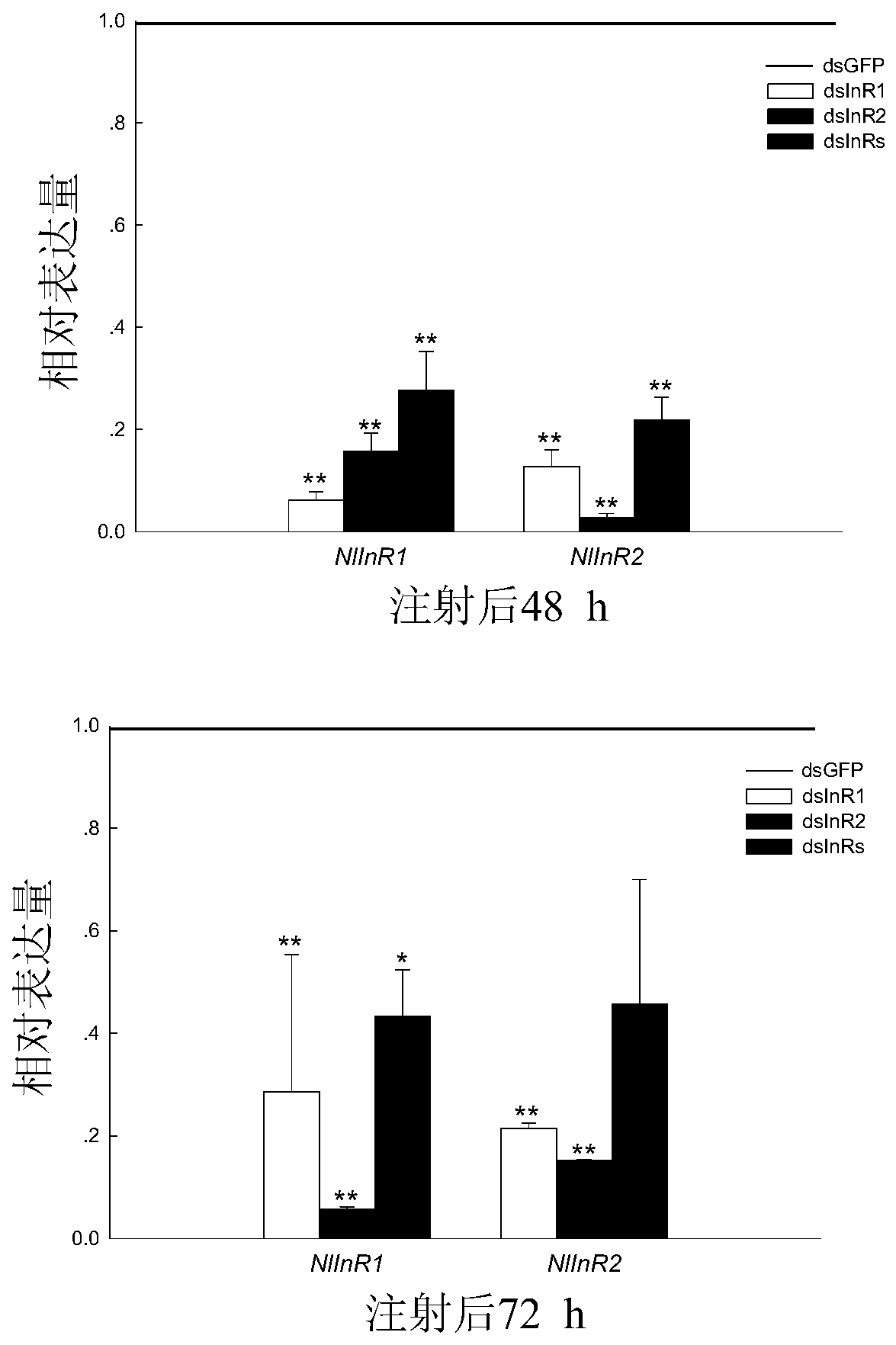
Application of NlInR gene of brown planthopper as target point in preparation of pesticide for preventing and treating brown planthopper
ActiveCN110066798ARealize prevention and controlInhibition of ontogenyBiocideAnimal repellantsBrown planthopperNucleotide
The invention discloses application of a NlInR gene of brown planthopper as a target point in preparation of a pesticide for preventing and treating the brown planthopper, and provides dsRNA used forinhibiting expression of the NlInR gene, wherein the NlInR gene is composed of a NlInR1 gene and a NlInR2 gene; the nucleotide sequence of the NlInR1 gene is shown as SEQ ID NO.1; the nucleotide sequence of the NlInR2 gene is shown as SEQ ID NO.2. The effect of the NlInR gene in preventing and treating the brown planthopper is discovered for the first time, the dsRNA of the NlInR gene is obtainedthrough an RNAi technology, and after the NlInR gene is silenced through a micro-injection mode, the individual development and the ovarian development of the brown planthopper can be effectively inhibited, and the spawning amount is reduced, so that the propagation of the brown planthopper is inhibited, and the prevention and treatment of the brown planthopper are realized.
Owner:HANGZHOU NORMAL UNIVERSITY
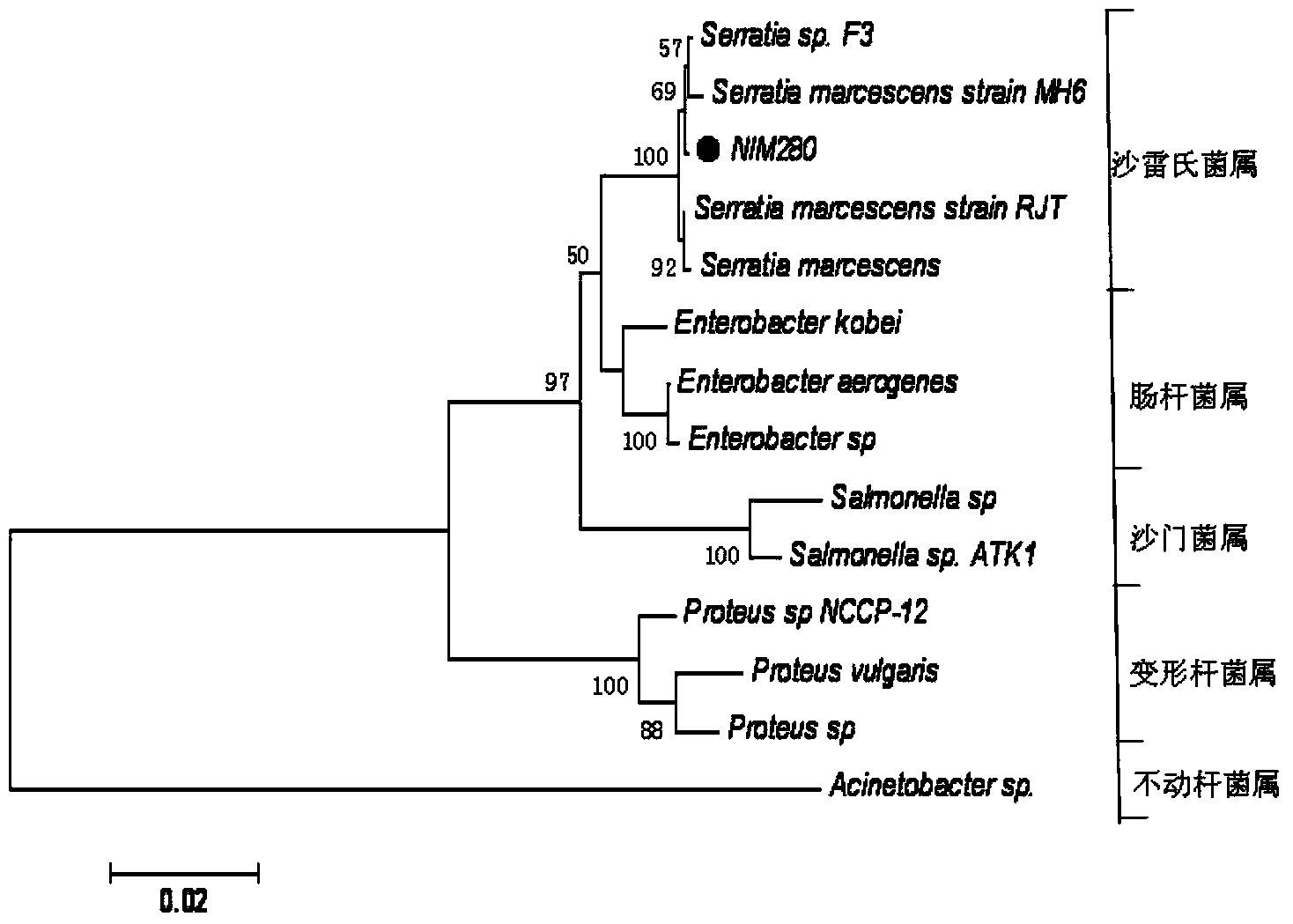
Serratia marcescens NlM280 and application thereof as insecticide
InactiveCN104109649ADoes not affect the pathogenic effectBiocideBacteriaBrown planthopperSerratia species
Owner:CHINA NAT RICE RES INST
Application of OsEXP10 gene in regulating rice growth and resisting nilaparvata lugens
The invention provides application of OsEXP10 gene in regulating rice growth and resisting nilaparvata lugens. Specifically, the invention finds an EXP10 gene or protein thereof unexpectedly for the first time. Analysis of the expression mode of the gene finds that increase or decrease of expression quantity or activity of EXP10 gene or protein thereof in plants (such as rice) can remarkably improve agronomic character of plants for the first time.
Owner:CAS CENT FOR EXCELLENCE IN MOLECULAR PLANT SCI
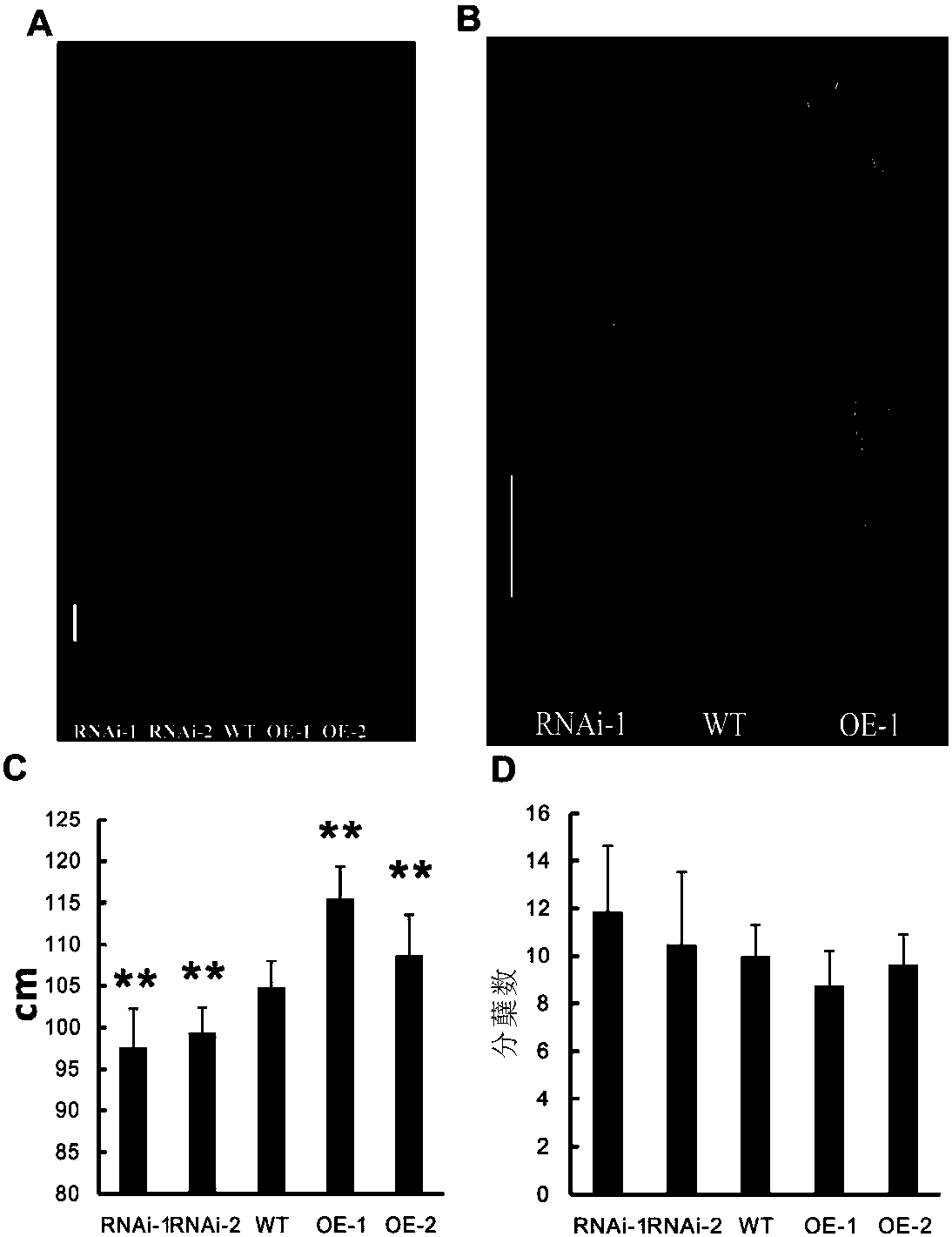
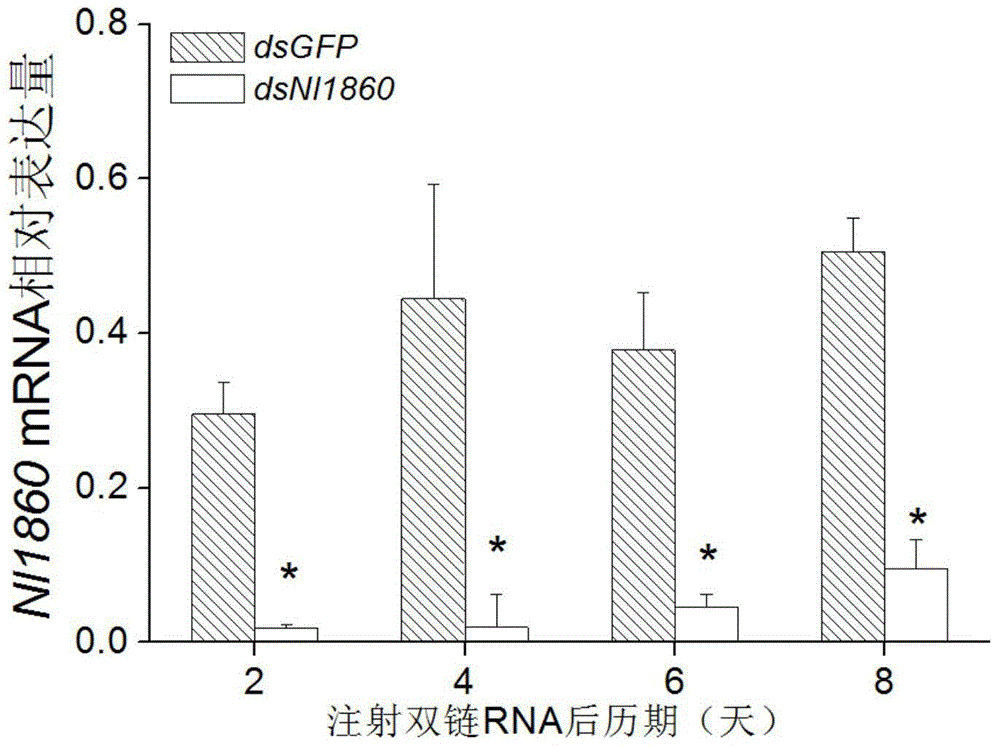
Brown planthopper gene Nl1860 as well as encoding product and application thereof
InactiveCN103820460AGood insect resistanceFermentationGenetic engineeringGenetically modified riceNucleotide
The invention discloses a brown planthopper gene Nl1860 as well as an encoding product and application thereof. The gene Nl1860 has the DNA sequence shown in SEQ ID No. 1. The DNA sequence is composed of 1454 nucleotide bases and contains a complete encoding frame composed of 1386 nucleotides, and the coded proteins contain a protein containing 461 amino acid residues. Research finds that the gene is related to the feeding, survival and egg laying amount of brown planthopper. An RNAi vector for the Nl1860 is constructed and then is transferred into rice to express dsRNA of the gene Nl1860 in the transgenic rice body, so as to achieve the purpose of improving the resistance to brown planthopper of rice. The brown planthopper gene Nl1860 can be widely applied to crop breeding, particularly breeding of insect-resistant rice.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Isolation and expression pattern identification of brown planthopper infestation inducible rice promoter zone
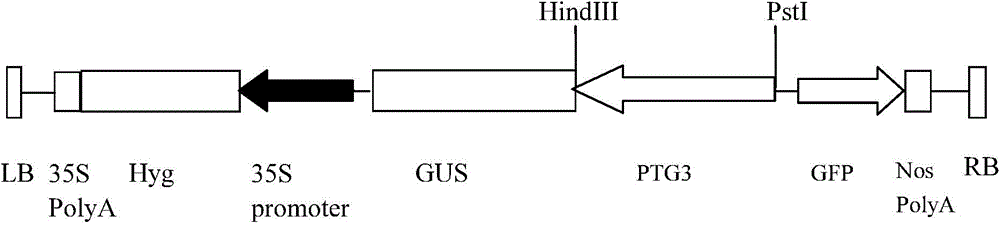
InactiveCN105861501AVector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsGenetically modified riceStaining
The present invention belongs to the technical field of plant genetic engineering, and in particular to isolation and expression pattern identification of a brown planthopper infestation inducible rice promoter. The invention is as below: screening to obtain a gene with specific expression in rice green tissue and expression level in up-regulation by the brown planthopper infestation; isolating a promoter zone of the gene from rice genome by a PCR method, naming the promoter as PTG3 with a nucleotide sequence shown as SEQ ID NO: 1; constructing a fusion expression gene by using PTG3 with a GUS reporter gene, and transforming a rice Zhonghua 11 by an Agrobacterium-mediated method; and conducting GUS tissue chemical staining and quantitative RT-PCR detection on the obtained transgenic rice seedling before and after inoculation of brown planthopper. The invention determines that PTG3 promoter can significantly increase the expression level of the downstream gene under the brown planthopper infestation conditions, and the characteristic has potential application value in rice insect-resistant gene engineering breeding.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Brown planthopper and whitebacked planthopper repellent as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN106689239AObvious antifeedant effectIncrease contactBiocideDead plant preservationPlanthopperPollution
The invention discloses a brown planthopper and whitebacked planthopper repellent as well as a preparation method and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of agricultural production. The repellent comprises the following components: cinnamon essential oil, notopterygium incisum essential oil, citronella essential oil, eucalyptus oil essential oil, zanthoxylum essential oil, high lipid film and Tween-80. The repellent provided by the invention has the advantage of high safety, has two functions of protection and insect expelling, and is simple in preparation method and convenient to use; the repellent provided by the invention is prepared from natural plant essential oils, is safe and harmless to rice seedlings, repels feeding of adults and nymphs of brown planthopper and whitebacked planthopper and spawning of female adults so as to effectively reduce damage and population quantity of brown planthopper and whitebacked planthopper, does not repel a predator spider, and has advantages of low cost, high efficiency, environmental friendliness, safety for human and animals and the like; the repellent provided by the invention has a broad industrialization prospect, is particularly suitable for use in pollution-free production of rice, and has broad economic, social and ecological benefits.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Botanical synergistic compound pesticide
InactiveCN103609597AEasy to degradeLower resistanceBiocideMolluscicidesIlex cornutaBrown planthopper
The invention discloses a botanical synergistic compound pesticide. The botanical synergistic compound pesticide consists of ginkgo leaf methanol extract as an insecticidal agent, Chinese holly methanol extract as a synergist and an emulsion in water prepared by mixing other auxiliaries. The botanical synergistic compound pesticide is free from any chemical component, low-toxic to human and animals, and environment-friendly; and the botanical synergistic compound pesticide can prevent and control brown planthopper, small brown planthopper, bemisia tabaci, aphid, citrus fruit fly, ampullaria gigas, wiggler and other insects.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
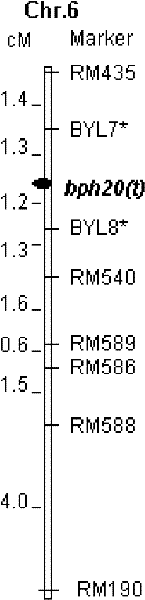
SSR marker BYL8 of brown planthopper resistant genetic locus bph20(t)
InactiveCN102199596AImprove breeding efficiencyReduce lossMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationResistant genesBrown planthopper
The invention provides a molecule marker of brown planthopper resistant gene. According to the present invention, through the hybridization and backcrossing of a resistant parent RBPH54 and a susceptible variety TN1, progenies are obtained. Through respective resistance identifications and molecule genetic linkage analysis of the progeny strains, a brown planthopper resistant major recessive genebph20(t) is obtained. Two nearest molecule markers linked beside bph20(t) are BYL7 and BYL8, which are self-developed SSR markers. The distances from the markers to bph20(t) are 1.3cM and 1.2 cM. With molecule markers linked to the brown planthopper resistant gene, the detection can be carried out to detect whether the pest resistant variety RBPH54 or the derivative varieties (systems) of RBPH54 contain the pest resistant genetic locus. Therefore, the selection of brown planthopper resistant paddy varieties or paddy qualities can be substantially improved in efficiency.
Owner:GUANGXI ZHUANG AUTONOMOUS REGION ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method for preventing and controlling brown planthopper by using harpactor fuscipes
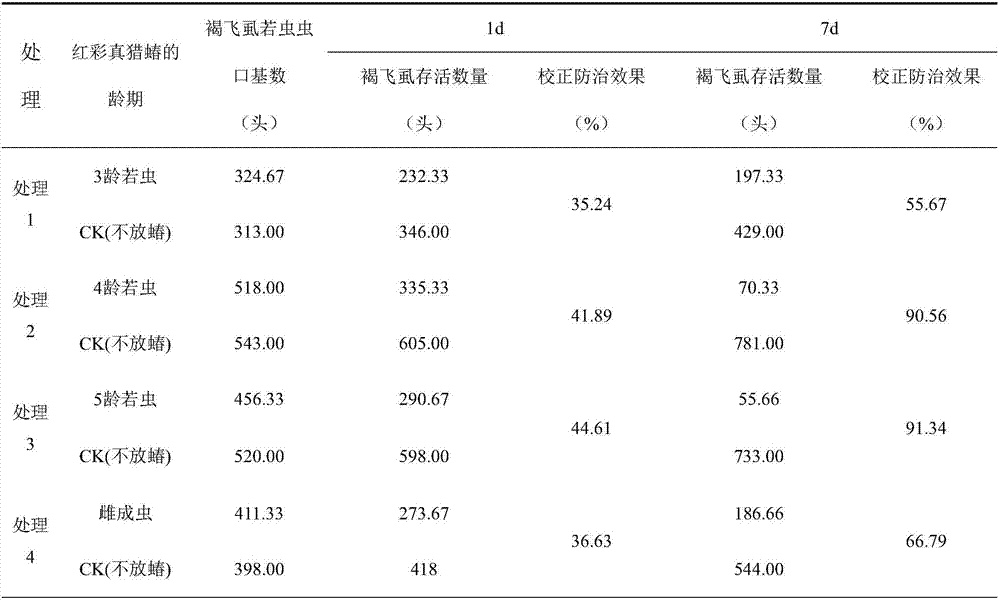
ActiveCN107278741AControl hazardsResidue reductionPlant protectionRice cultivationEcological environmentFood safety
The invention discloses a method for preventing and controlling brown planthopper by using harpactor fuscipes. The method comprises the following steps: step one, sampling the brown planthopper in a target rice field by using a five-point sampling method and identifying the age of the brown planthopper; step two, counting the density of the brown planthopper at the age of 2-3 in the target rice field by using an investigation and sampling method; and step three, prevention and control operation: draining accumulated water of the target rice field, and releasing nymphs at the age of 4 and nymphs at the age of 5 of the harpactor fuscipes at single times, wherein the number ratio of the nymphs at the age of 4 and the nymphs at the age of 5 of the harpactor fuscipes to the brown planthopper at the age of 2-3 is 2: 1.5-2: 60. The user amount of chemical pesticide on rice is reduced, pesticide residue of the rice field is reduced, the ecological environment of a farmland is protected, and reliable technical guarantee is provided for food safety.
Owner:ZHONGKAI UNIV OF AGRI & ENG +1
Mixed formula preparation for controlling nilaparvata lugens stal
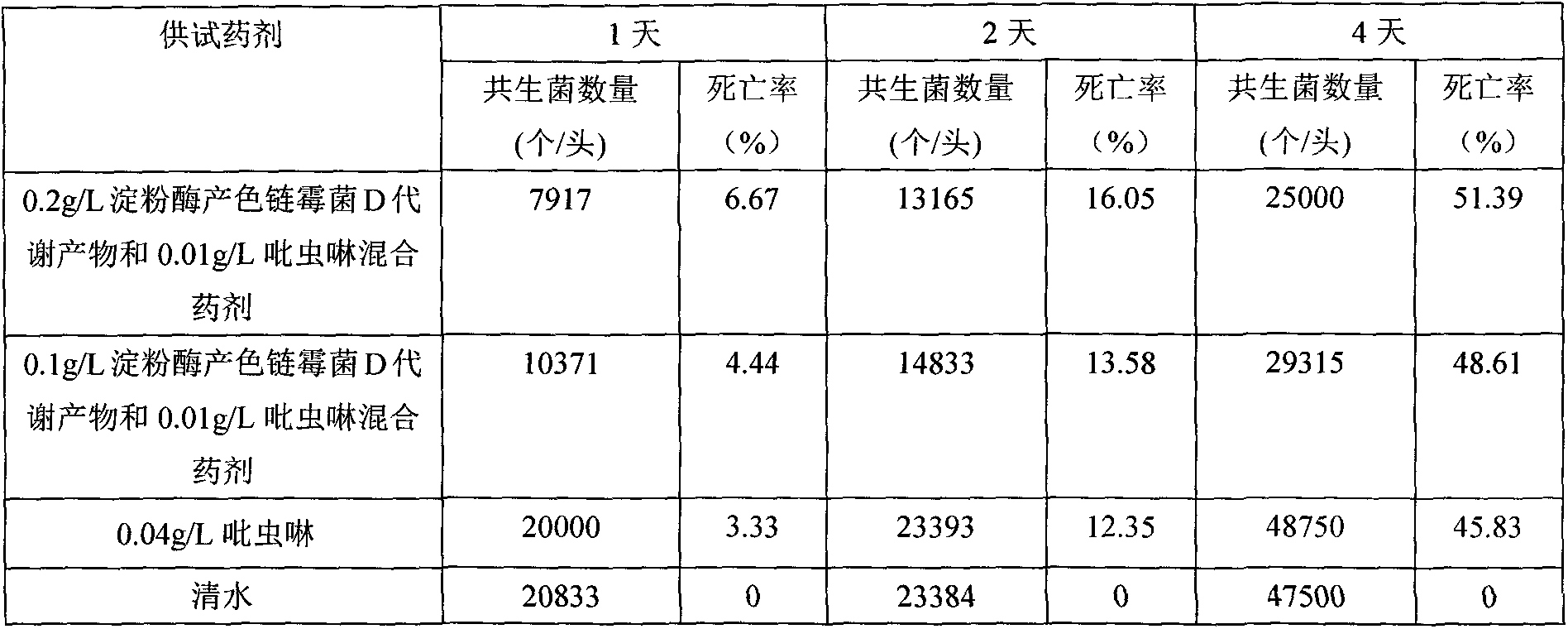
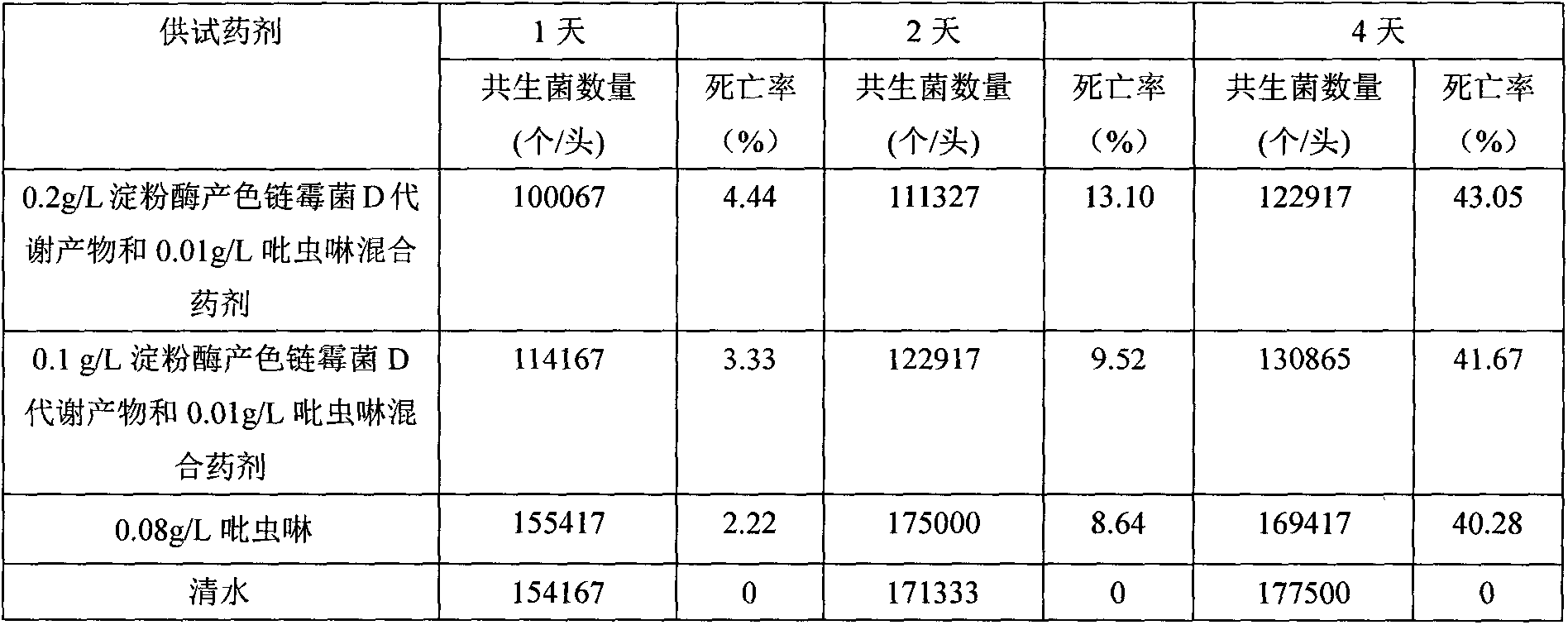
The invention relates to the technical field of microorganisms, particularly to a Streptomyces diastatochromogenes D metabolite and imidacloprid mixed formula preparation. Streptomycesdiastatochromogenes is named Streptomycesdiastatochromogenes D. The strain is preserved in the CGMCC (China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center) of the China Committee for Culture Collection of Microorganisms on May25th, 2007 with the preservation register number of CGMCC No.2060. Metabolites capable of inhibiting nilaparvatalugensstal yeast symobiotic bacteria can be obtained through fermentation and extraction of the Streptomyces diastatochromogenes D. The most significant characteristic of the preparation is that the Streptomyces diastatochromogenes D metabolites and conventional insecticide imidacloprid are mixed in a certain proportion to prepare a new formula, after the mixed formula is used for controlling nilaparvata lugens stal, the usage amount of insecticides can be reduced obviously, the control effect on the nilaparvata lugens stal can be effectively improved, and the development of the drug resistance of the nilaparvata lugens stal can be delayed.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com