Molecular marker of major gene Bph6 resistant to brown planthopper and application thereof
A technology of anti-BPH and main gene, applied in the field of molecular genetics, can solve the problems of complex insect resistance identification, difficulty in effectively introducing and aggregating insect resistance genes, etc., and achieve the effects of convenient identification, shortened breeding cycle, and clear selection targets
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
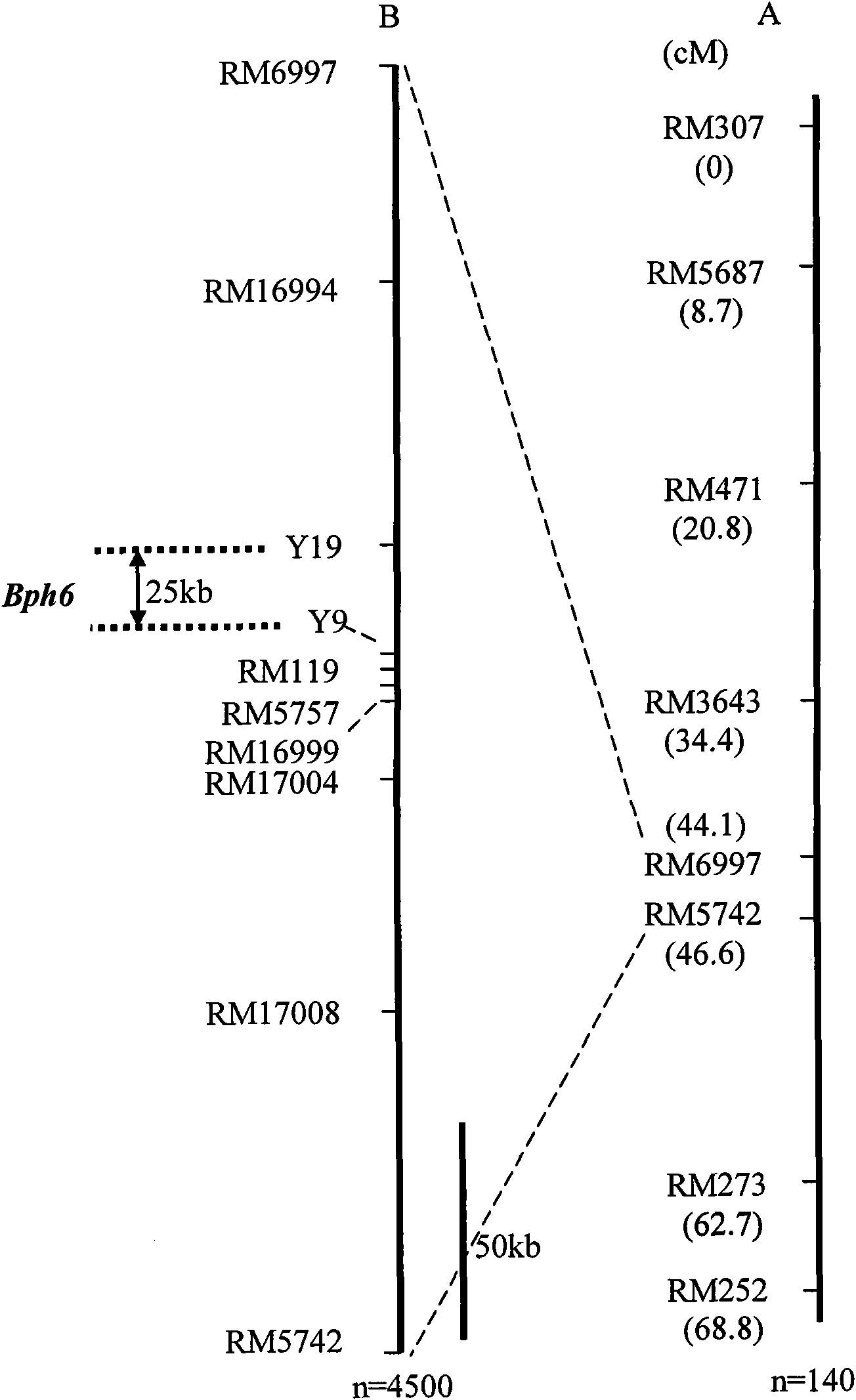
[0046] (1) 9311 / Swarnalata F 2 Population construction and phenotyping
[0047] (1) In 1988, Kabir & Khush first identified the brown planthopper-resistant rice variety Swarnalata Bangladesh population using classical genetic analysis methods, and was controlled by a pair of dominant genes, so the brown planthopper-resistant gene was named Bph6 (Kabir & Khush.1988 Genetic analysis of resistance to brown planthopper in rice, Oryza sativa L. Plant Breeding 100, 54-58). The rice varieties come from the germplasm resource bank of the Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, and Swarnalata comes from the rice germplasm resource bank of the International Rice Research Institute. Insect resistance identification experiments showed that Swarnalata has high resistance to the brown planthopper population in my country. In order to find simple and effective molecular markers that are closely linked to Bph6, the present invention uses the insect-susceptible variety 9311 as the female p...
Embodiment 2
[0072] Example 2 Verification of Molecular Markers
[0073] 1. Materials and methods
[0074] 1.1 Materials
[0075] Negative varieties: 10, susceptible varieties 9311, Nipponbare, Taichung Local No. 1, 7 non-resistant materials in the 9311XSwarnalata breeding combination.
[0076] Positive cultivars: 9 non-resistance materials in the breeding combination of the highly resistant cultivar Swarnalata and 9311 X Swarnalata.
[0077] Molecular marker primers: RM16994, Y19, Y9, RM119, RM5757, RM16999, RM17004, RM17008.
[0078] 1.2 Method
[0079] Genomic DNA of rice sample was extracted by CTAB extraction method (method is the same as in Example 1). Sample DNA was amplified with primers RM16994, Y19, Y9, RM119, RM5757, RM16999, RM17004, RM17008, respectively. The reaction system included 0.10 μM primers, 250 μM dNTPs, 1× PCR reaction buffer (50 mM KCl, 10 mM Tris-HCl pH8.3, 1.5 mM MgCl 2 ), 100ng of DNA template, 1UTaq enzyme. The reaction program was: 94°C pre-denaturation...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com