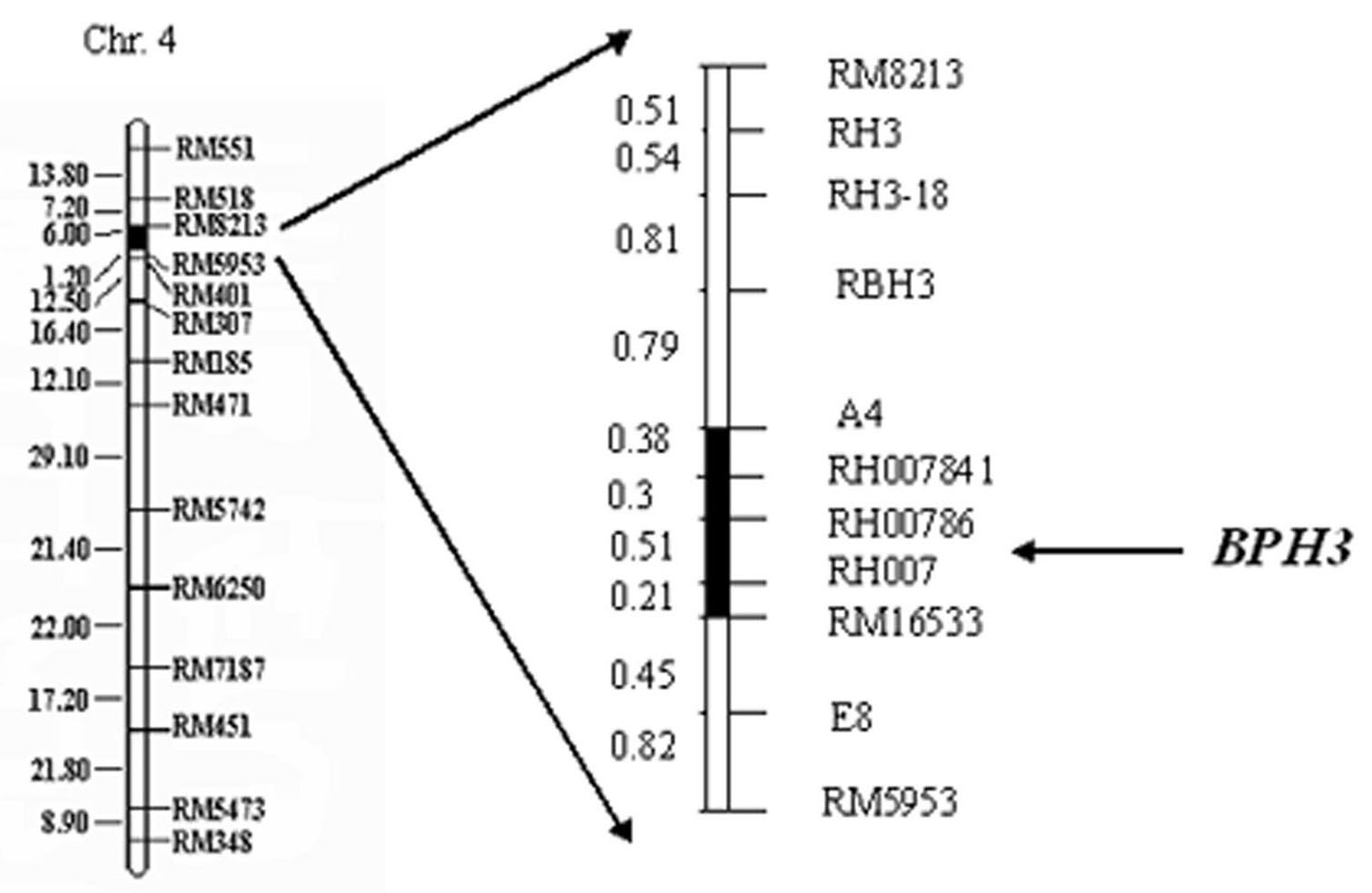
Molecular marker of anti-nilaparvata-lugens major gene Bph3 of rice
A brown planthopper resistance and molecular marker technology, applied in the field of molecular genetics, can solve problems such as difficult aggregation of insect-resistant genes, and achieve the effects of convenient identification, clear main gene location, and convenient and rapid detection.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0033] Studies have shown that BPH-resistant gene resources mainly exist in indica and wild rice species in Sri Lanka and India (Ikeda and Vaughau, 1991). Athwal et al. (1971) reported that Mudgo, CO22 and MTU15 carried the same brown planthopper resistance gene Bph-1, and ASD7 carried a recessive insect resistance gene bph-2. Athwal and Pathak (1972) reported that MGL2 contains the insect resistance gene Bph-1, and Ptb18 contains bph-2. Martinez and Khush (1974) reported that IR747B2-6 contained Bph-1, and R1154-243 and IR4-93 contained bph-2. Lakshiminarayana and Khush (1977) reported that the Sri Lankan insect-resistant variety Rathu Heenati is controlled by a dominant gene Bph-3 that segregates independently from Bph-1; while the variety Babawee is controlled by a recessive gene bph-4 that segregates independently from bph-2 . Sidhu and Khush (1978) reported that rice varieties carrying Bph-3 or bph-4 were resistant to all BPH biotypes. The Thai rice varieties Col.5 Tha...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com