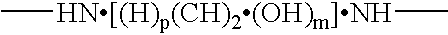Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
46 results about "Protein species" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Proteins are species -specific; that is, the proteins of one species differ from those of another species. They are also organ -specific; for instance, within a single organism, muscle proteins differ from those of the brain and liver.
Diagnosis of disease state using MRNA profiles in peripheral leukocytes
InactiveUS6190857B1High sensitivitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementWhite blood cellProstate cancer
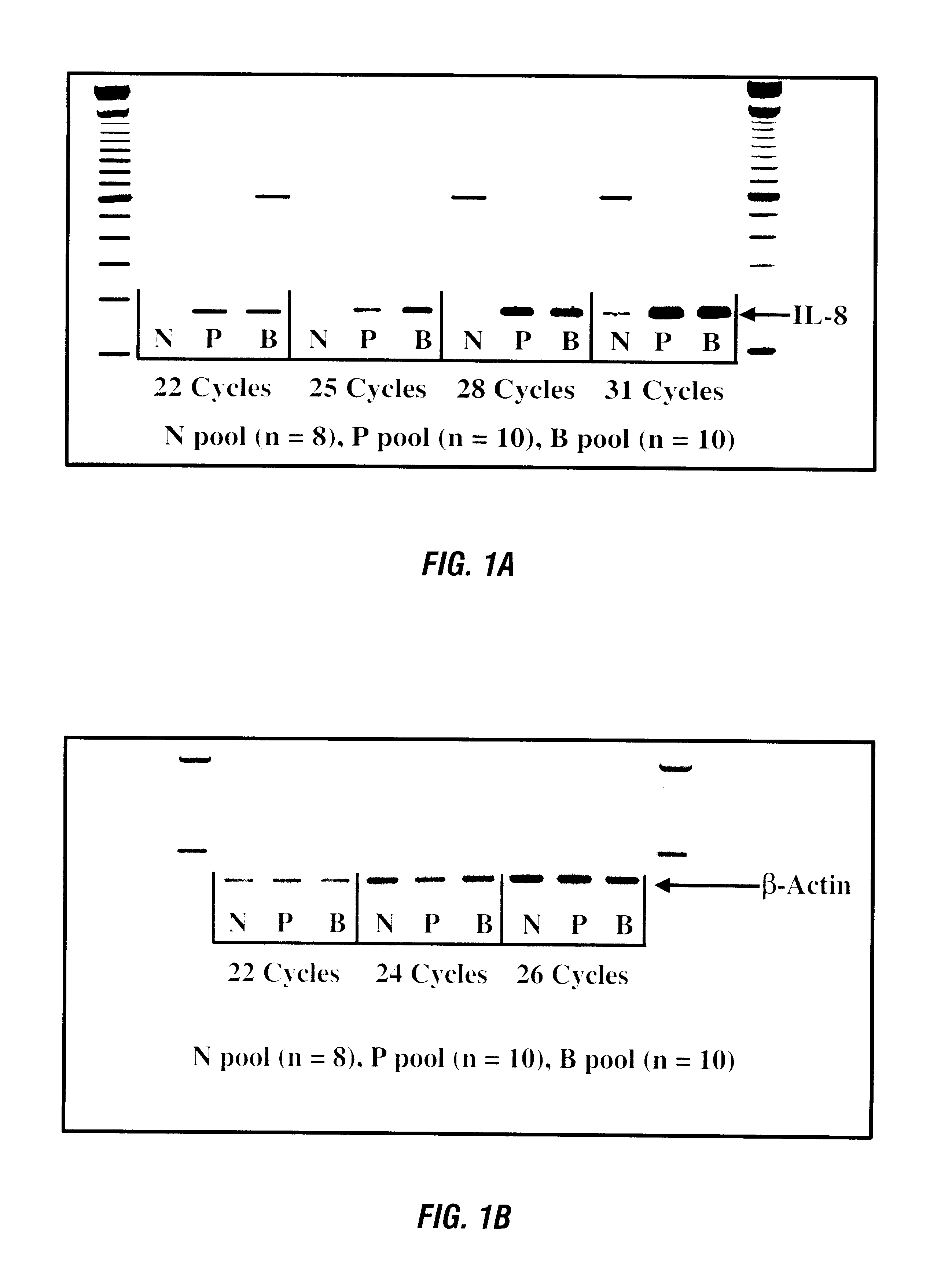
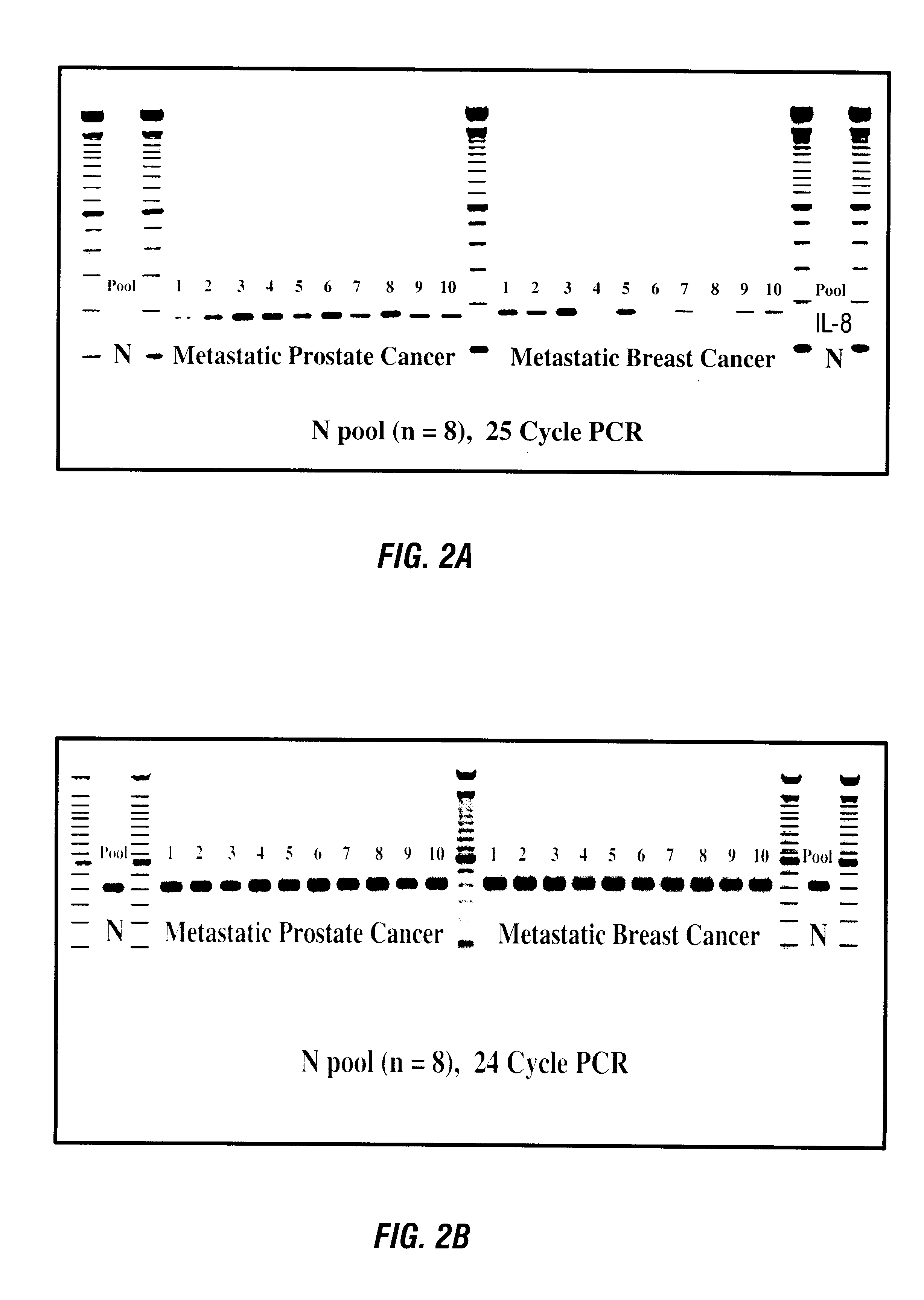
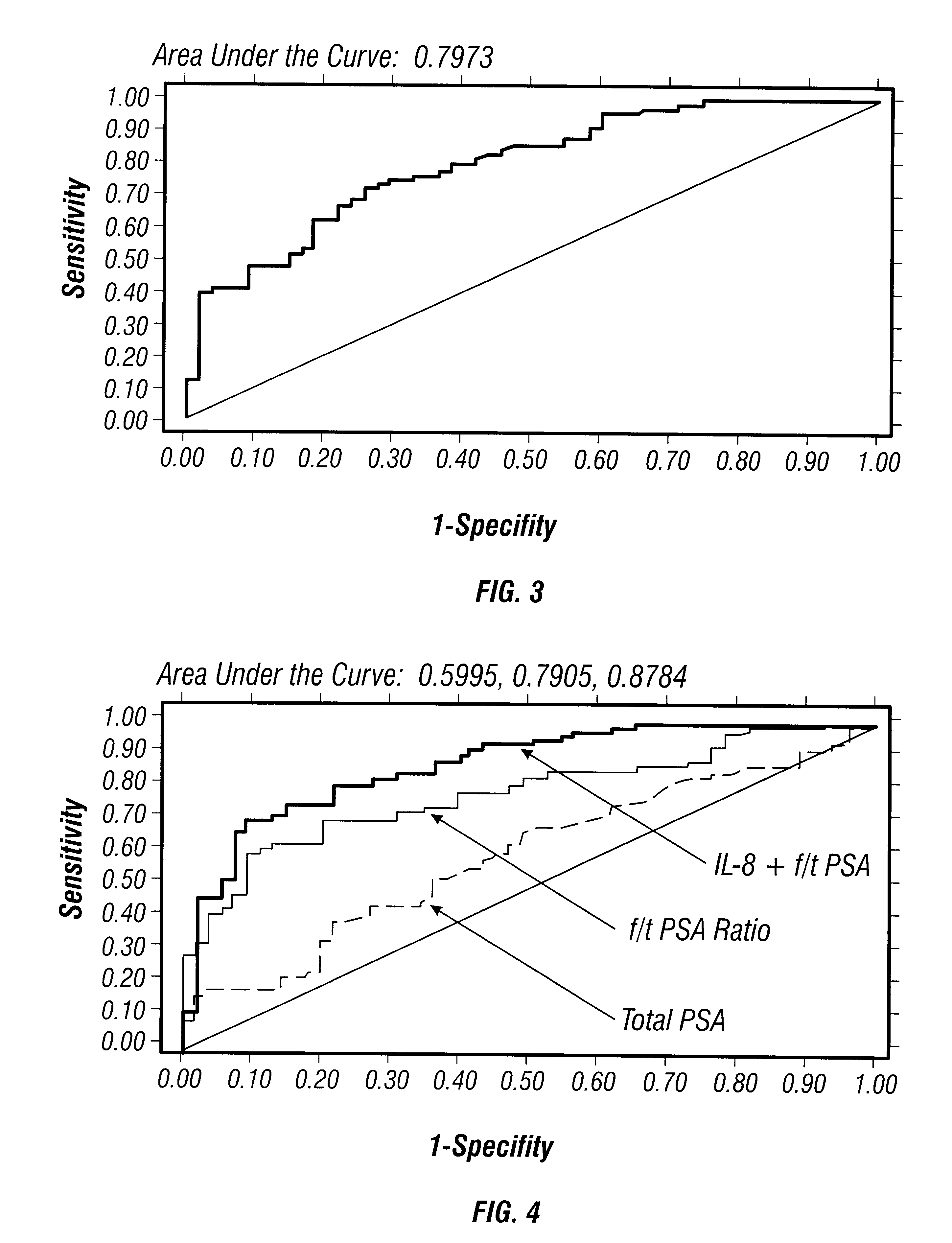
Disclosed are diagnostic techniques for the detection of human disease states that affect gene expression in peripheral leukocytes. The invention relates particularly to probes and methods for evaluating the presence of RNA species that are differentially expressed in the peripheral blood of individuals with such a disease state compared to normal healthy individuals. The invention further relates to methods for detection of protein species that are differentially expressed in the peripheral blood of individuals with such a disease state compared to normal healthy individuals. Genetic probes, antibody probes and methods useful in monitoring the progression and diagnosis of two specific disease states, prostatic cancer and breast cancer, are described.
Owner:LAB OF AMERICA HLDG
Method for treating cancer using interference RNA
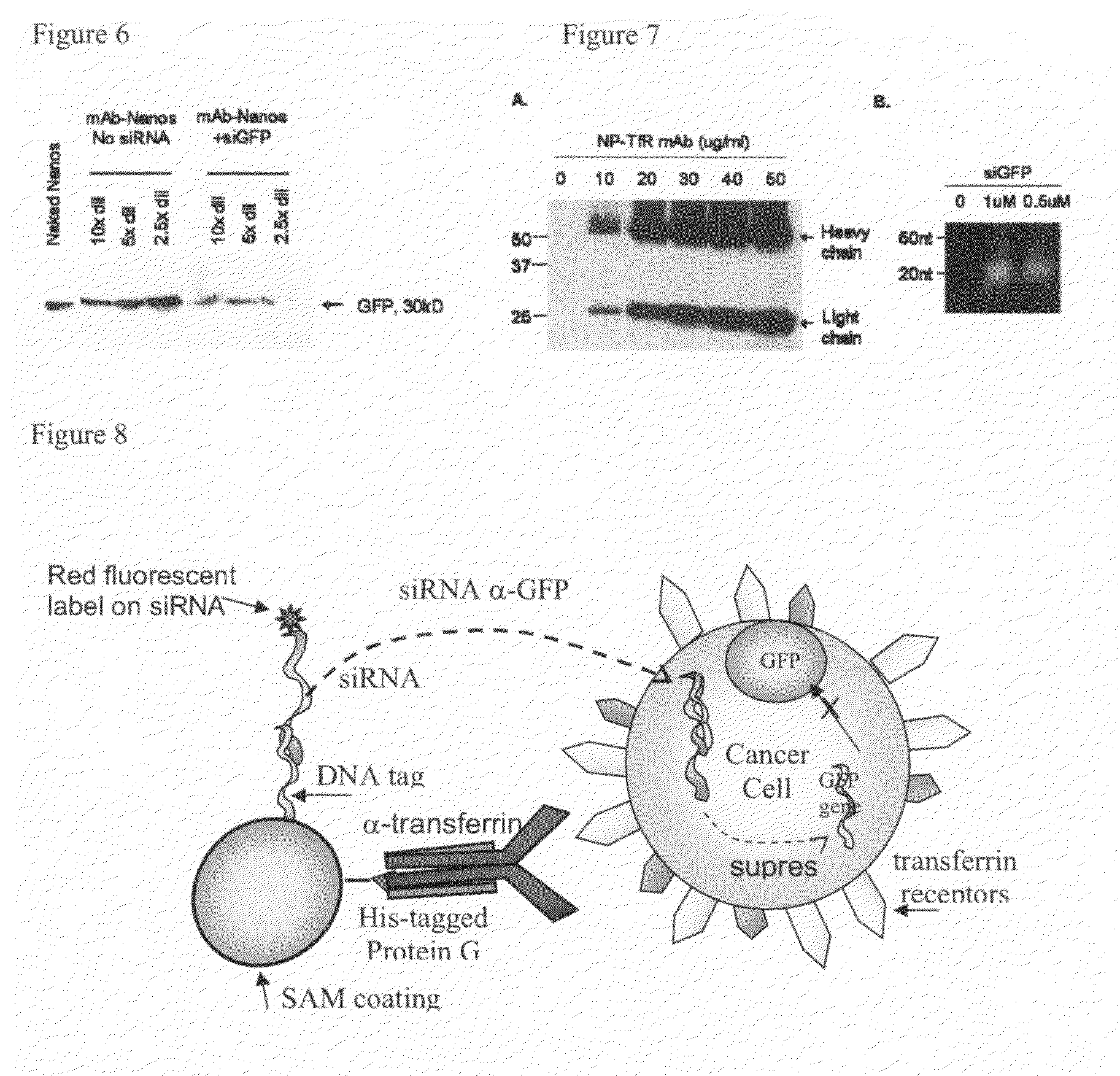
InactiveUS20090148535A1Facilitate communicationPowder deliverySpecial deliveryProtein targetColloidal nanoparticles
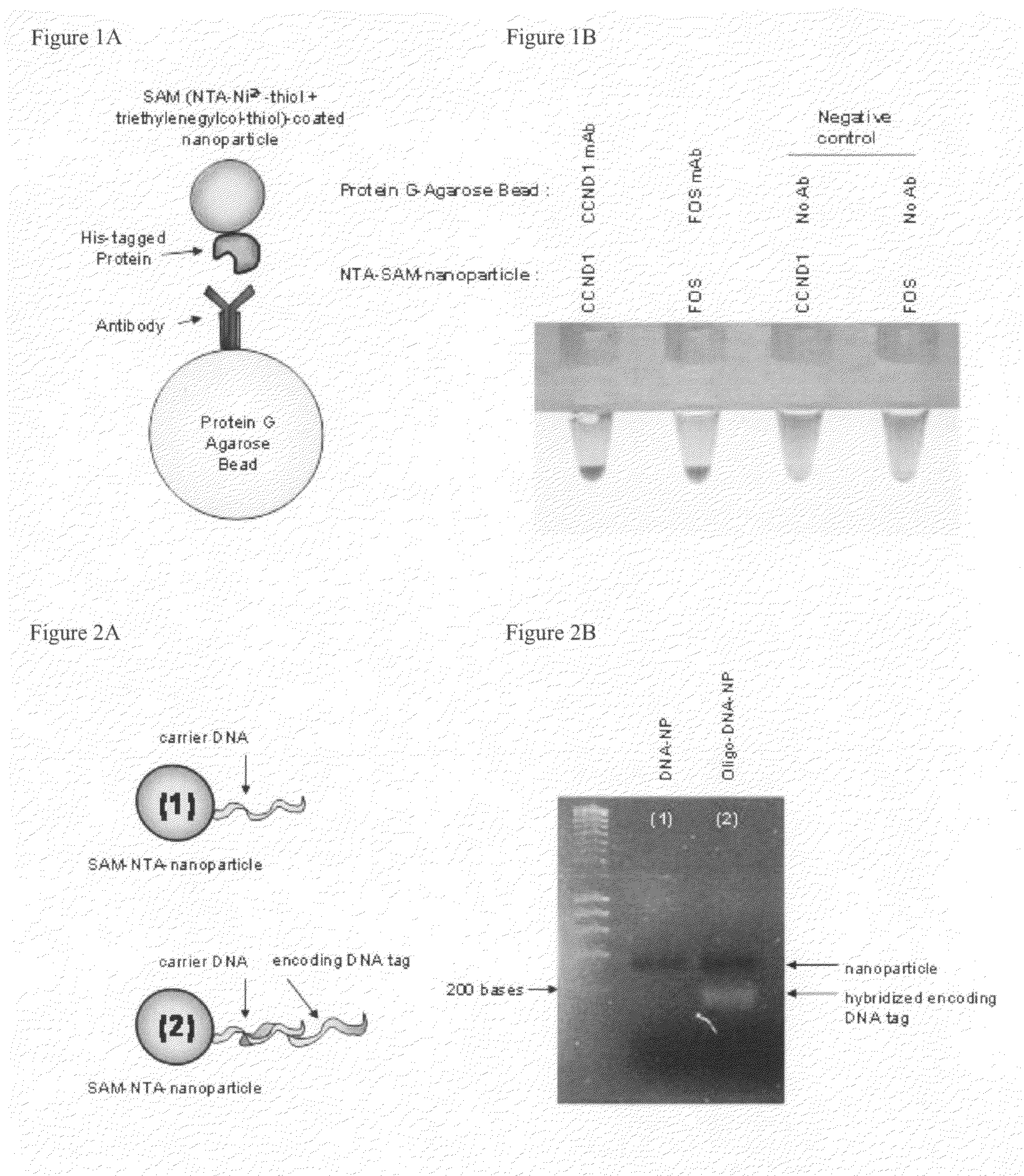
The present application discloses acolloidal nanoparticle that includes a therapeutic nucleic acid species and a targeting protein species attached via a coating on the nanoparticle that facilitates the specific attachment of both species.
Owner:MINERVA BIOTECH
Kit for in vitro synthesis of protein and preparation method
ActiveCN106978349ALow costEasy to operateMicroorganism lysisMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyFreeze-drying
The invention provides a preparation method of a yeast cell extracting solution, the yeast cell extracting solution and a method for synthesizing protein in an in vitro system by virtue of the yeast cell extracting solution, as well as a kit containing the yeast cell extracting solution. The kit, which is more convenient than a conventional method, is applicable to protein synthesis in the in vitro system; transformation, culture and crushing can be prevented; a great amount of using time and cost can be saved; various types of proteins can be expressed, and influence of protein toxicity can be prevented; and a plurality of protein complexes can be expressed, without the use of a high temperature at 37 DEG C. In addition, as a raw material adopted by the invention, yeast cell is simple to cultivate, convenient to operate, rapid to propagate and relatively low in cost; a prepared yeast extract has a capacity of modifying translated protein, the yeast extract is suitable for large-scale preparation and has an advantage of industrial production; and the yeast cell extract, which is prepared into freeze-dried powder by virtue of a vacuum freeze-drying method and is preserved at low temperature or high temperature, is convenient to transport.
Owner:KANGMA SHANGHAI BIOTECH LTD
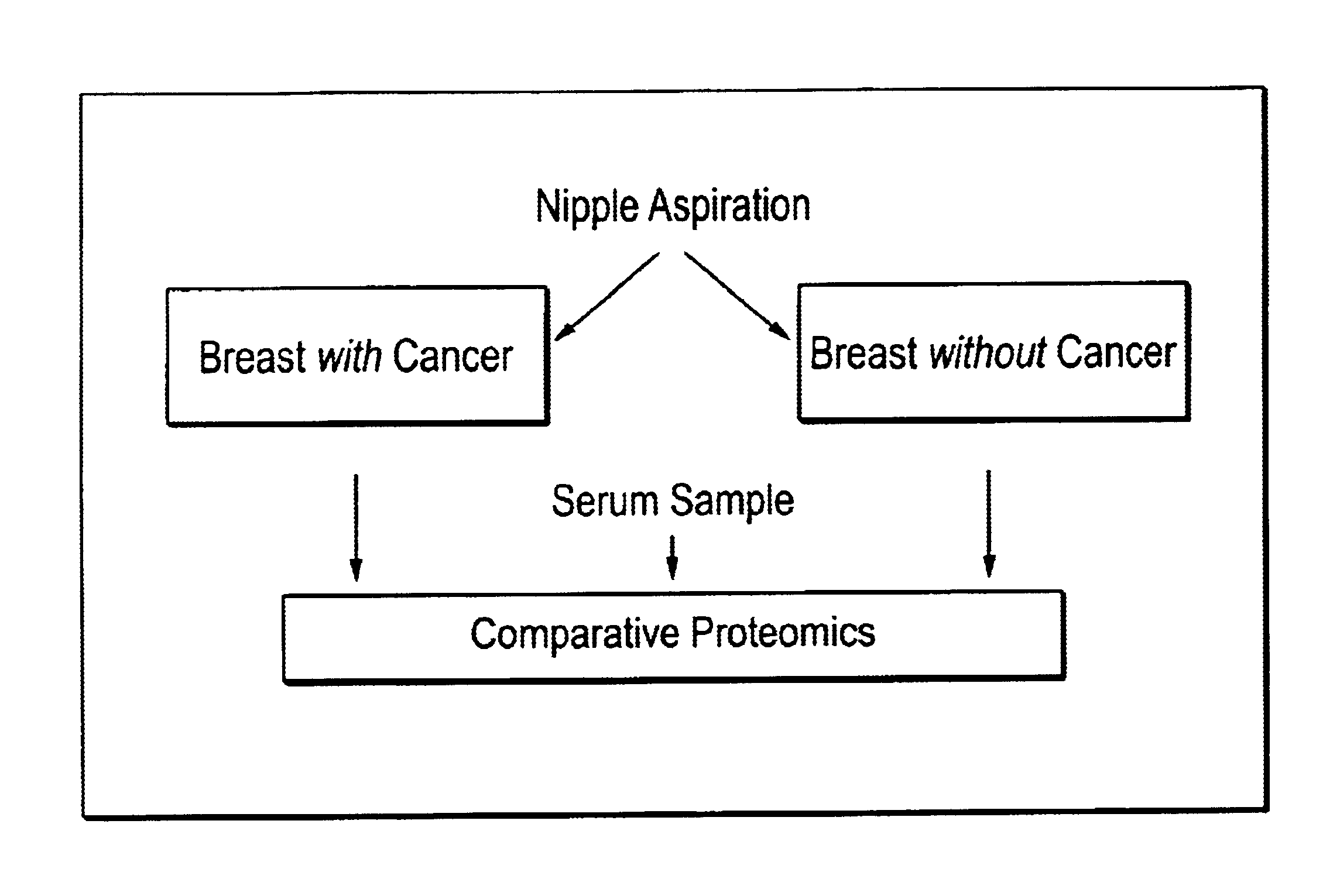
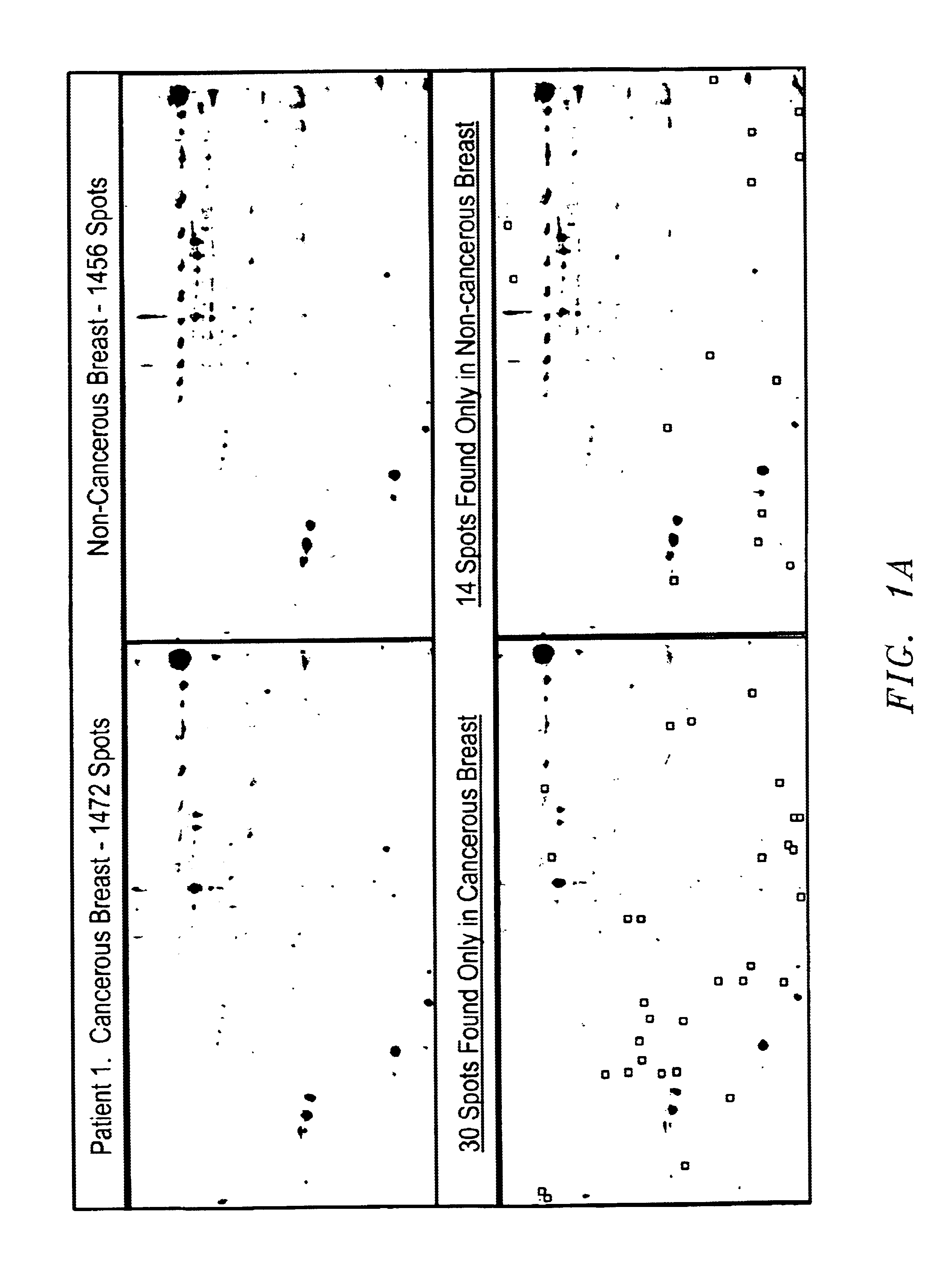
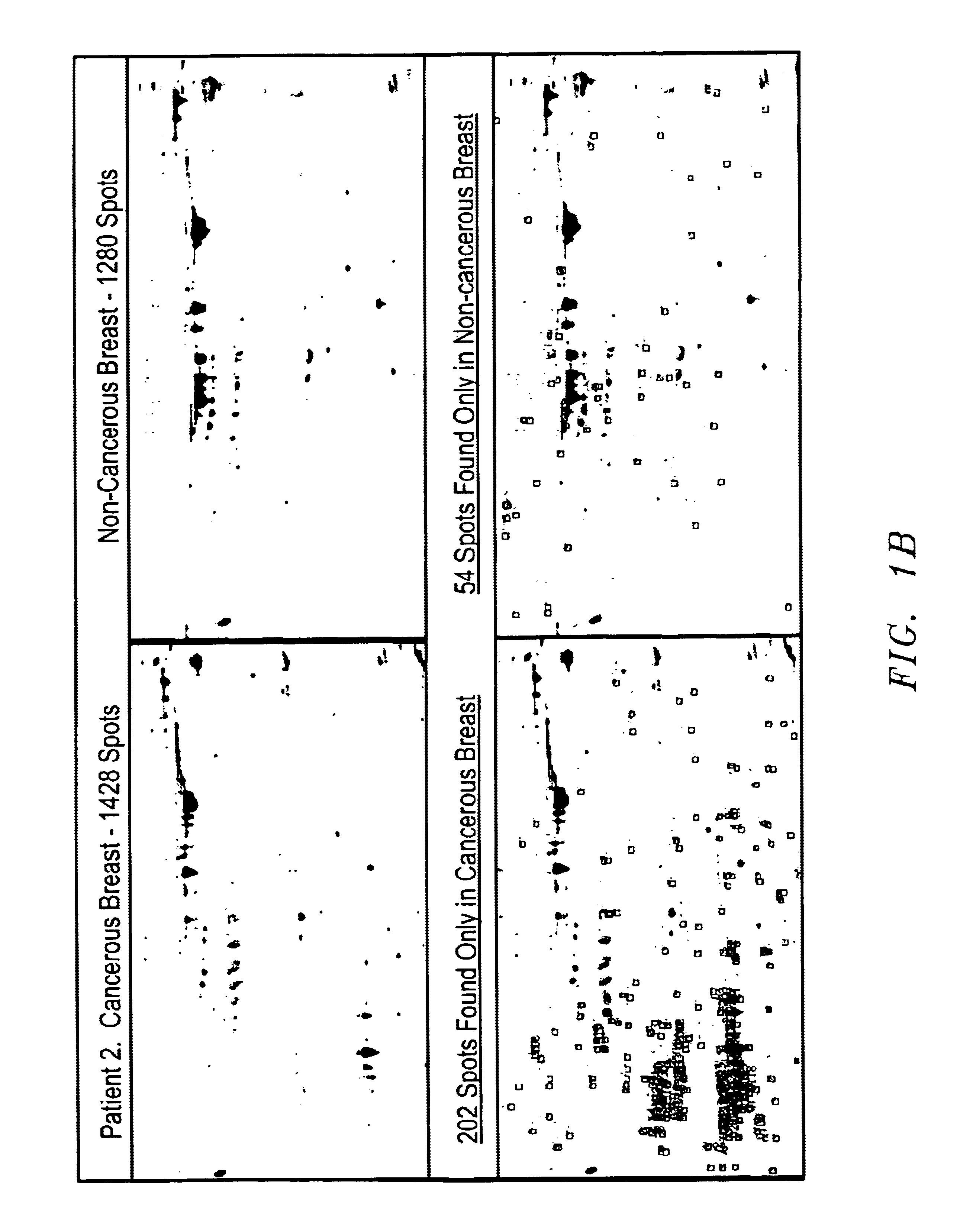
Methods and compositions for detection of breast cancer
Systematic comparisons of breast ductal fluid samples obtained by nipple aspiration from women with unilateral breast cancer revealed significant differences in ductal fluid protein expression between the breast with cancer and the breast without cancer in each patient. This study demonstrates that breast ductal fluid contains over 1000 separate protein species and suggests that ductal fluids from breast cancer patients may be useful for high-throughput biomarker discovery.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Chitosan-coated wires for biosensing
InactiveUS20110217785A1AnodisationMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological activationProtein species
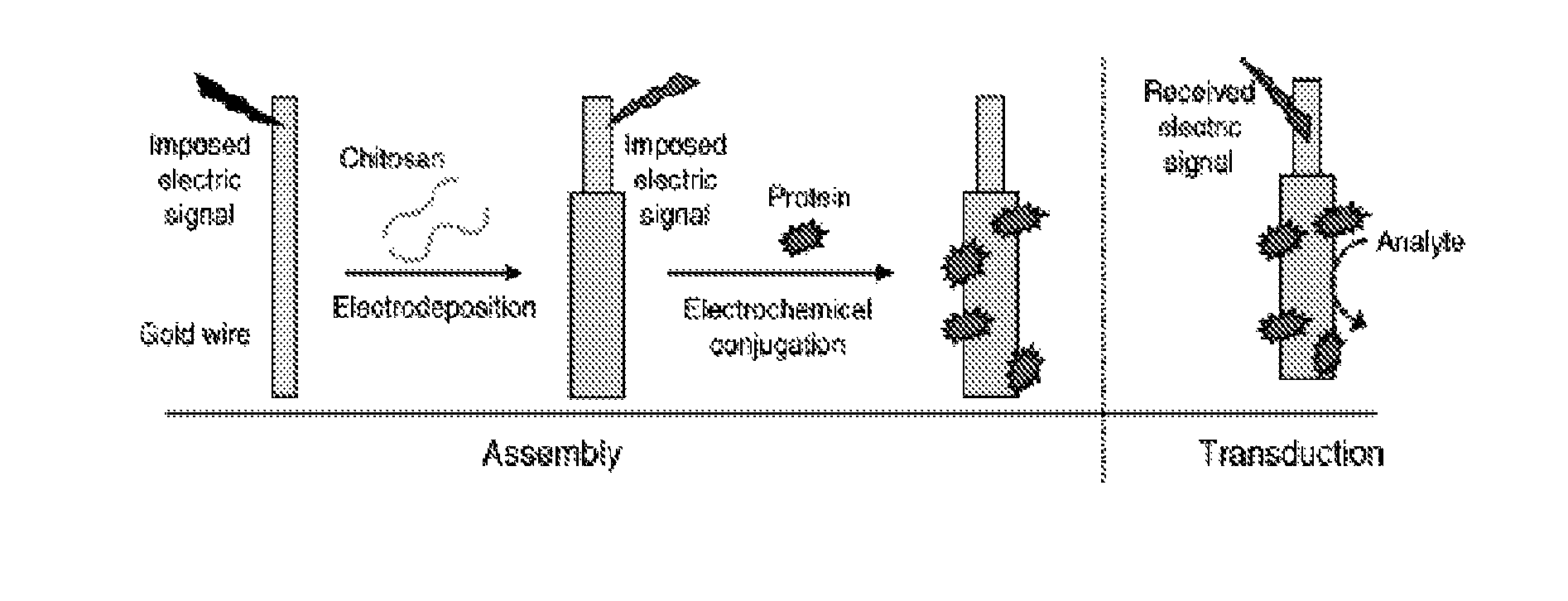
A method of forming a bioelectronic device including a protein on an electrically conductive substrate, by electro-depositing aminopolysaccharide chitosan on the substrate while applying a cathodic voltage to the substrate, to form an aminopolysaccharide chitosan film thereon, applying an anodic voltage to the substrate in the presence of NaCl to activate the aminopolysaccharide chitosan film so that it is reactive with protein. The method also optionally includes reacting the aminopolysaccharide film, after activation thereof, with the protein, so that the protein assembles on and is coupled to the substrate, thereby forming a bioelectronic device. The protein can include single or multiple protein species, and including biosensing proteins. Additional methods include biosensing of electrochemically active compounds either present in a sample or generated during a biological recognition event and devices useful in such methods. The resulting devices are useful as sensors in hand-held devices, textiles, garments and the like.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
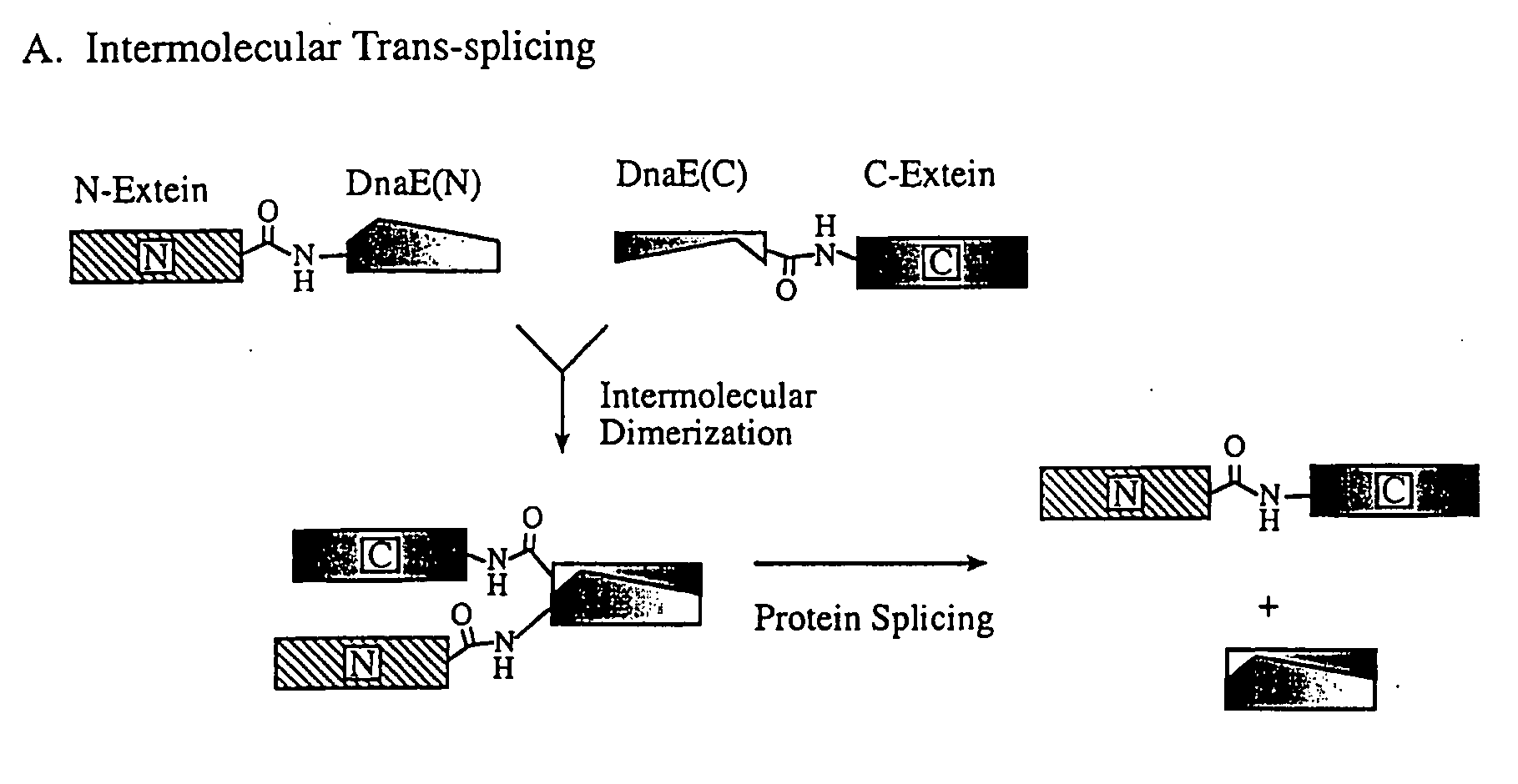
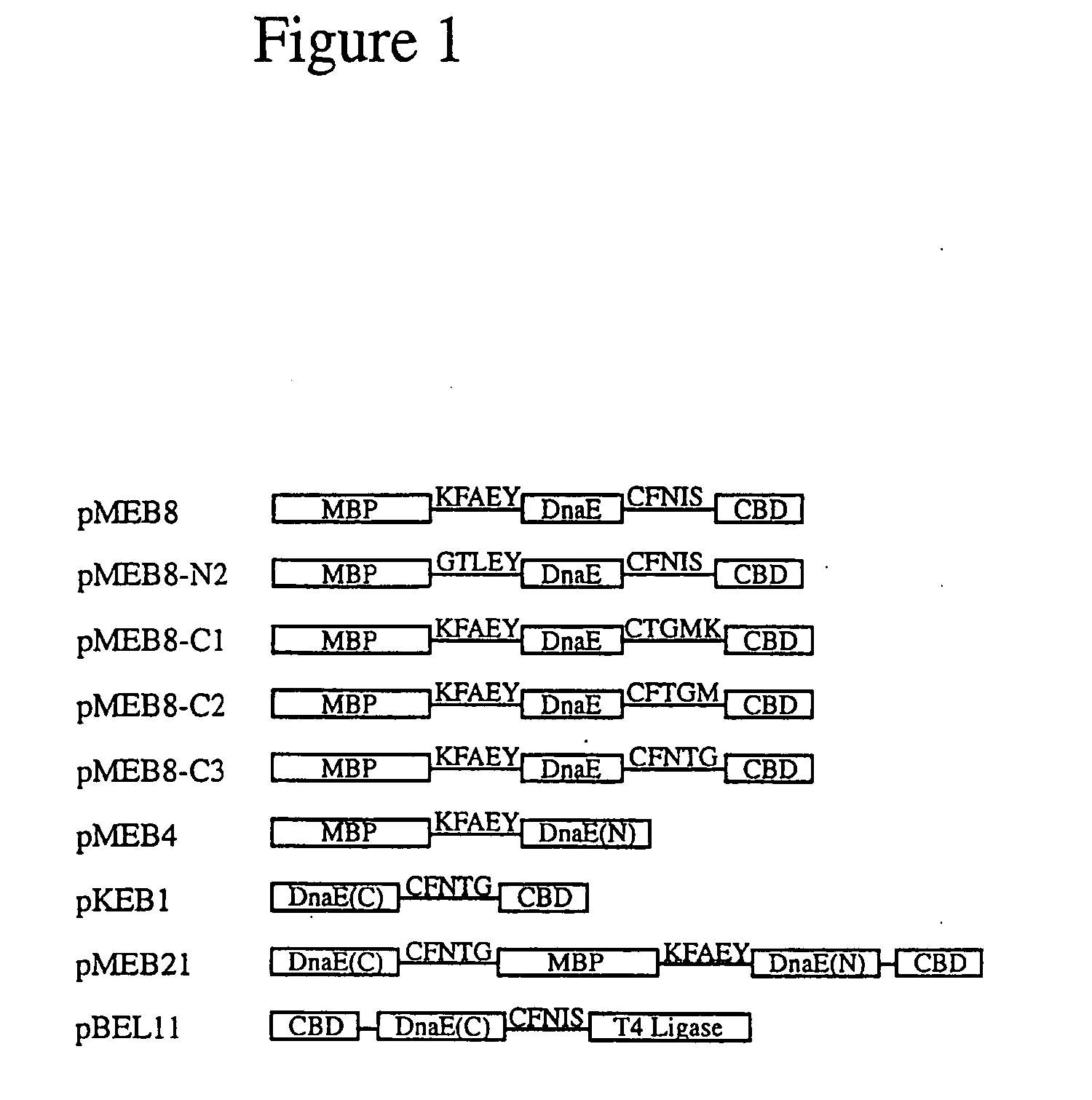
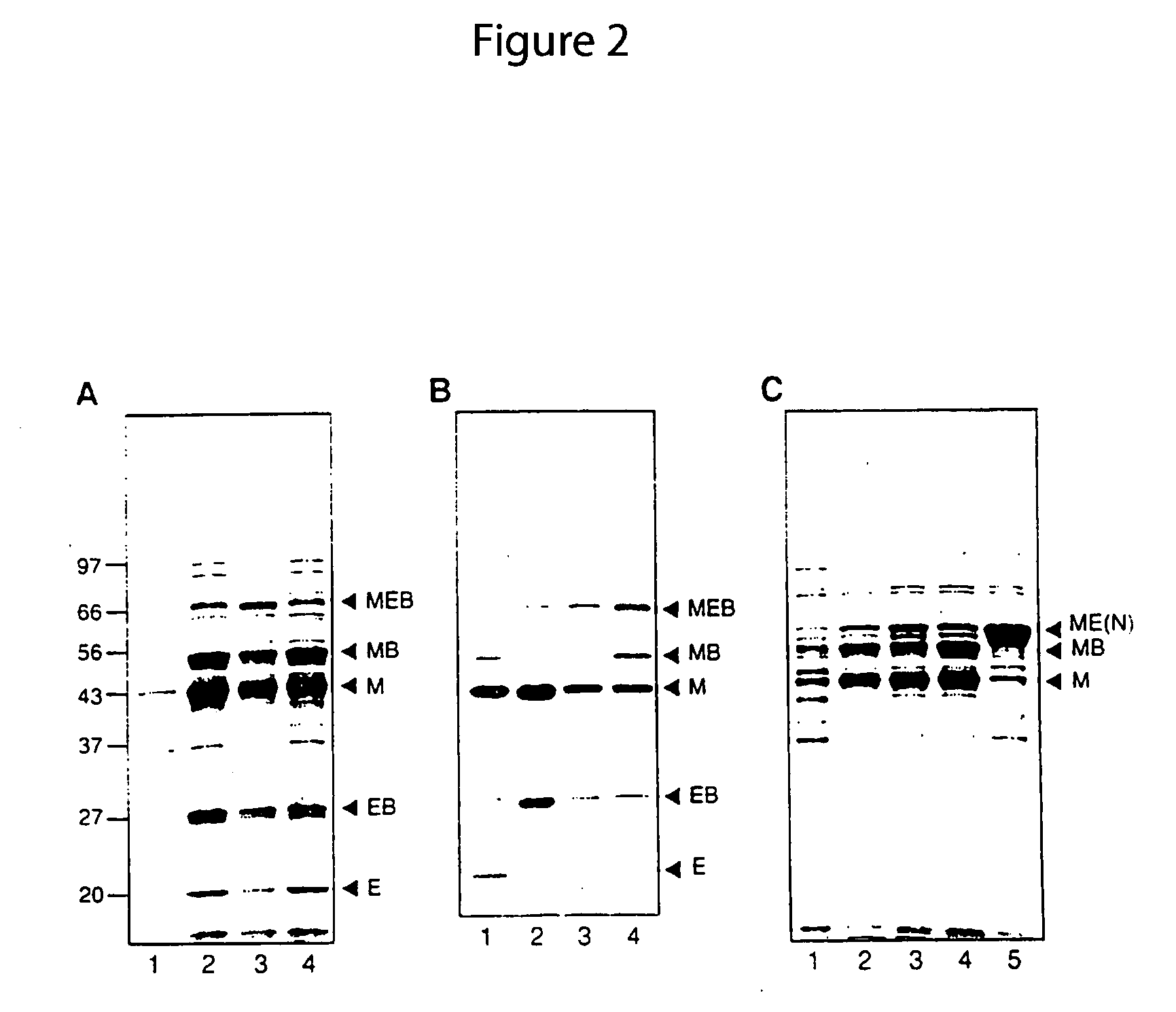
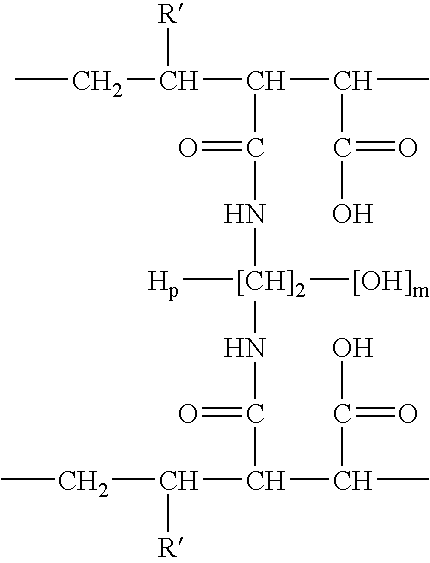
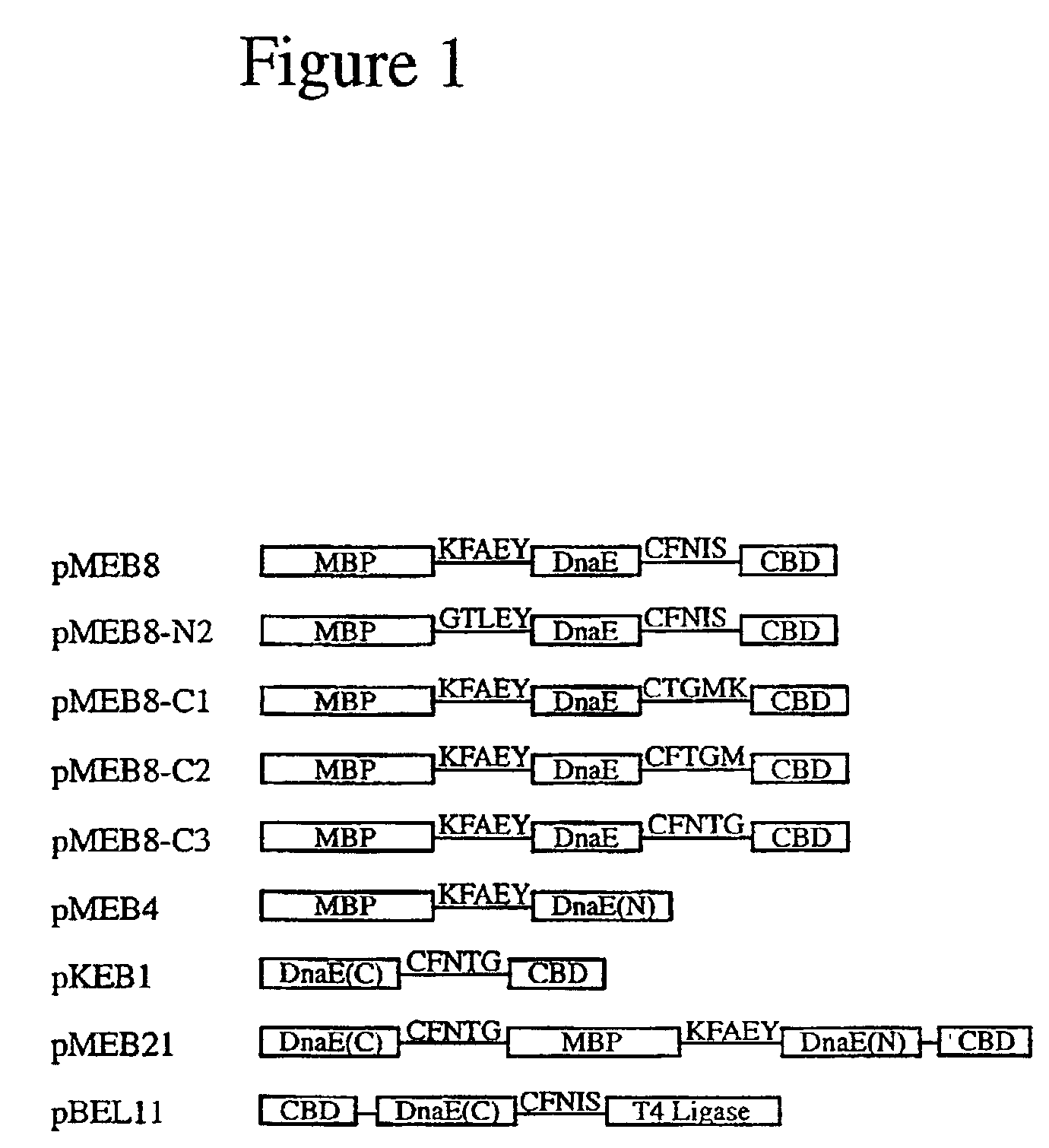
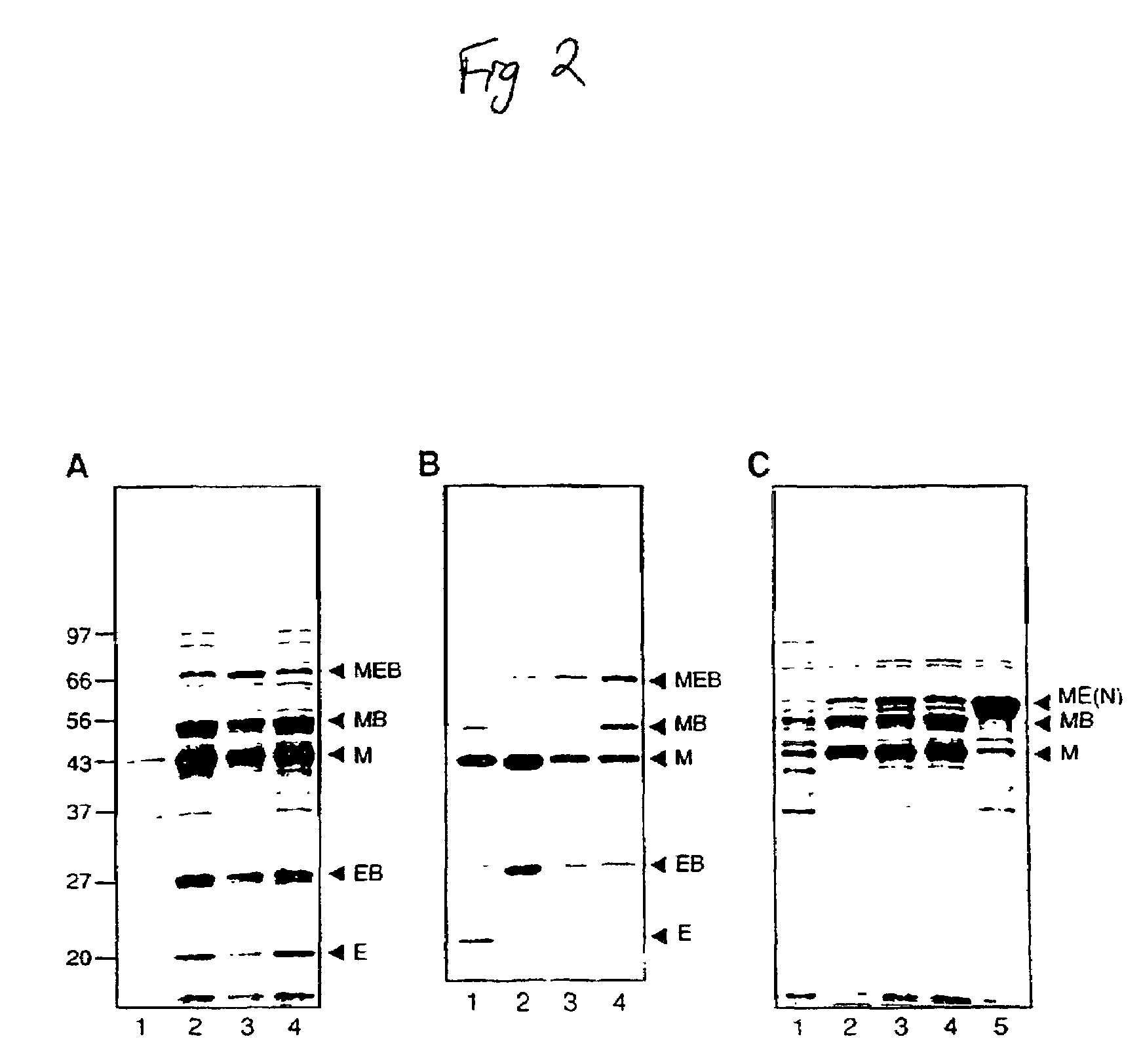
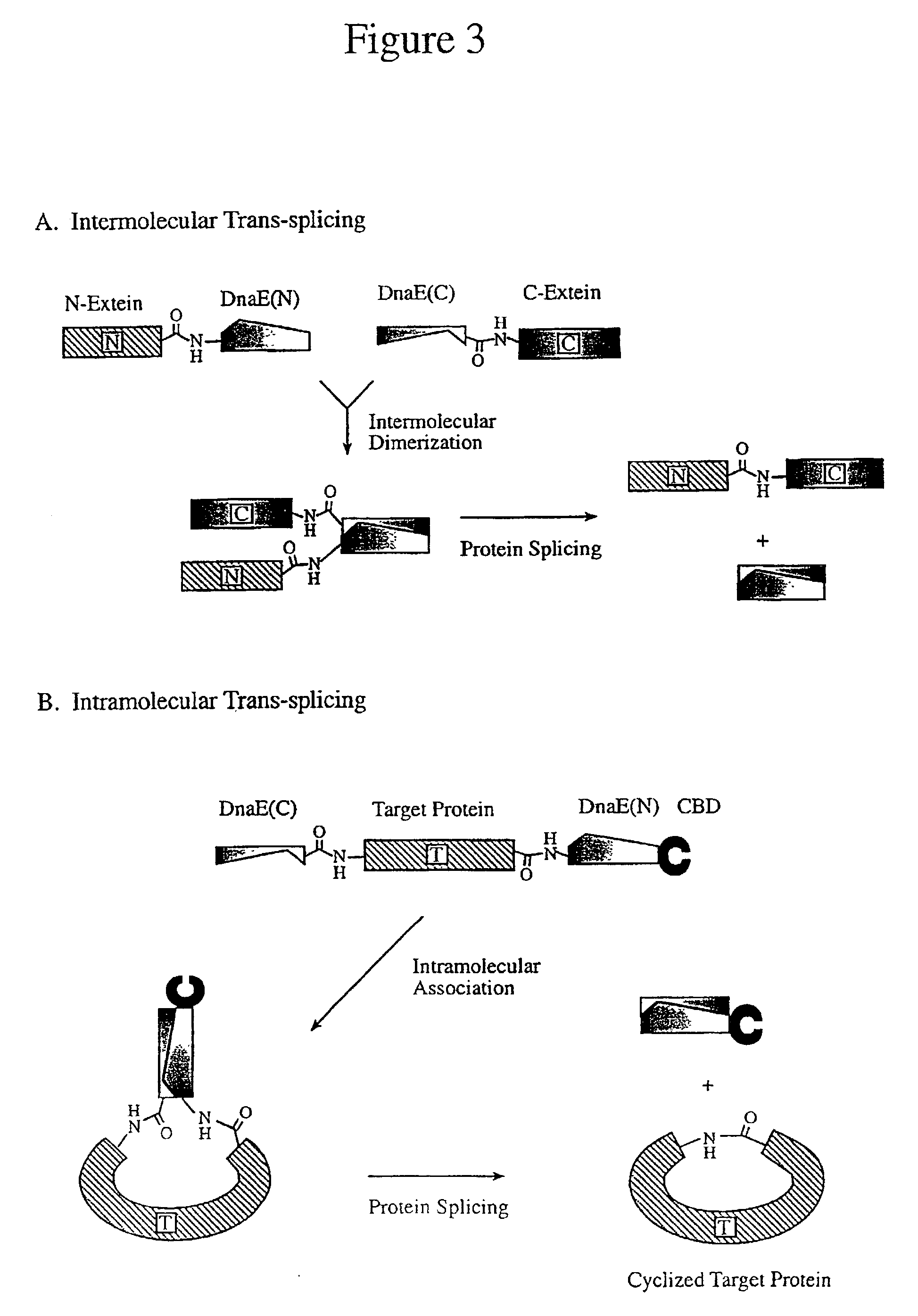
Method for producing circular or multimeric protein species in vivo or in vitro and related methods
InactiveUS20090035814A1Overcome disadvantagesOvercome problemsPeptide preparation methodsDepsipeptidesInteinProtein species
Owner:EVANS THOMAS C +1
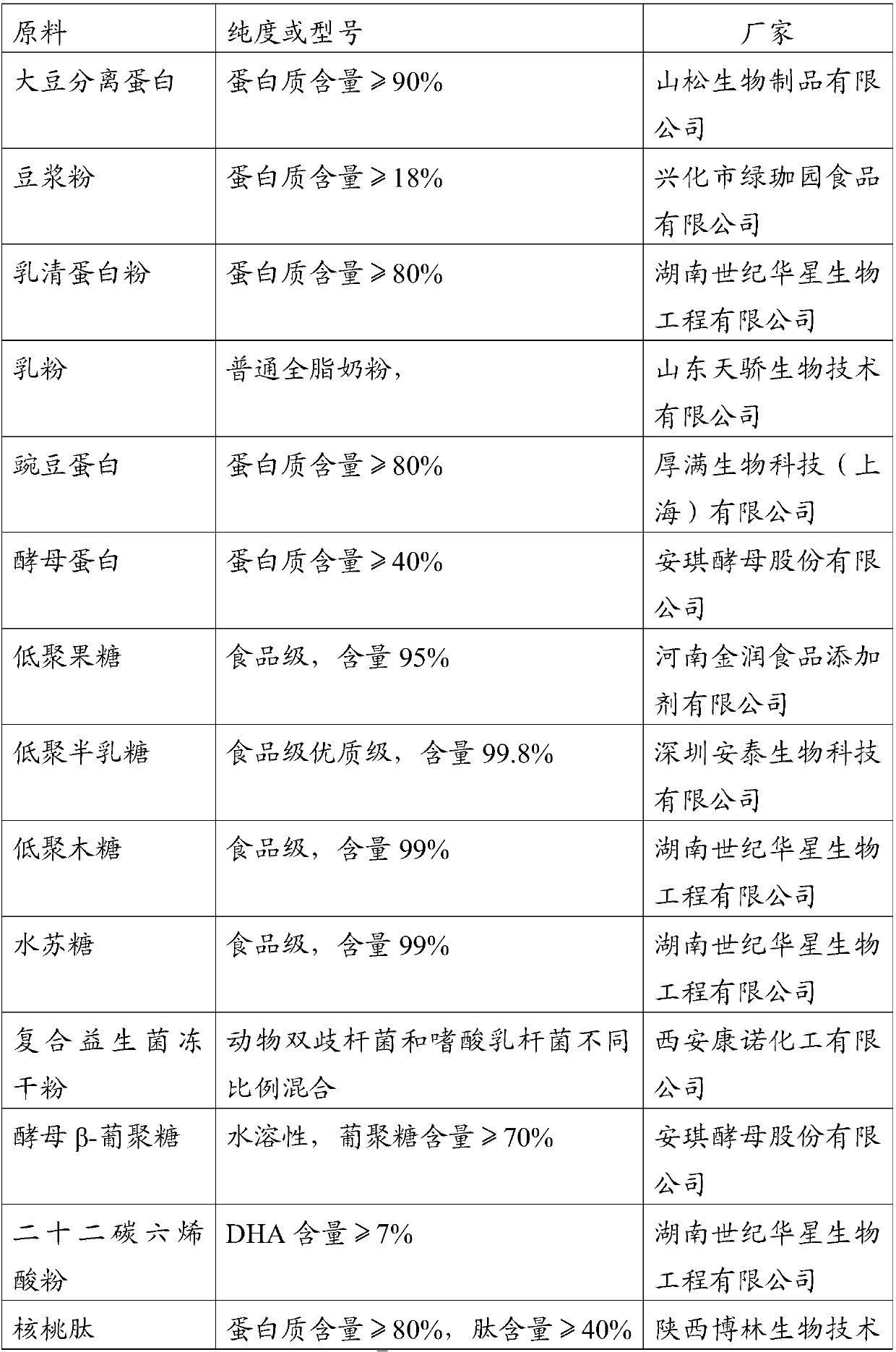
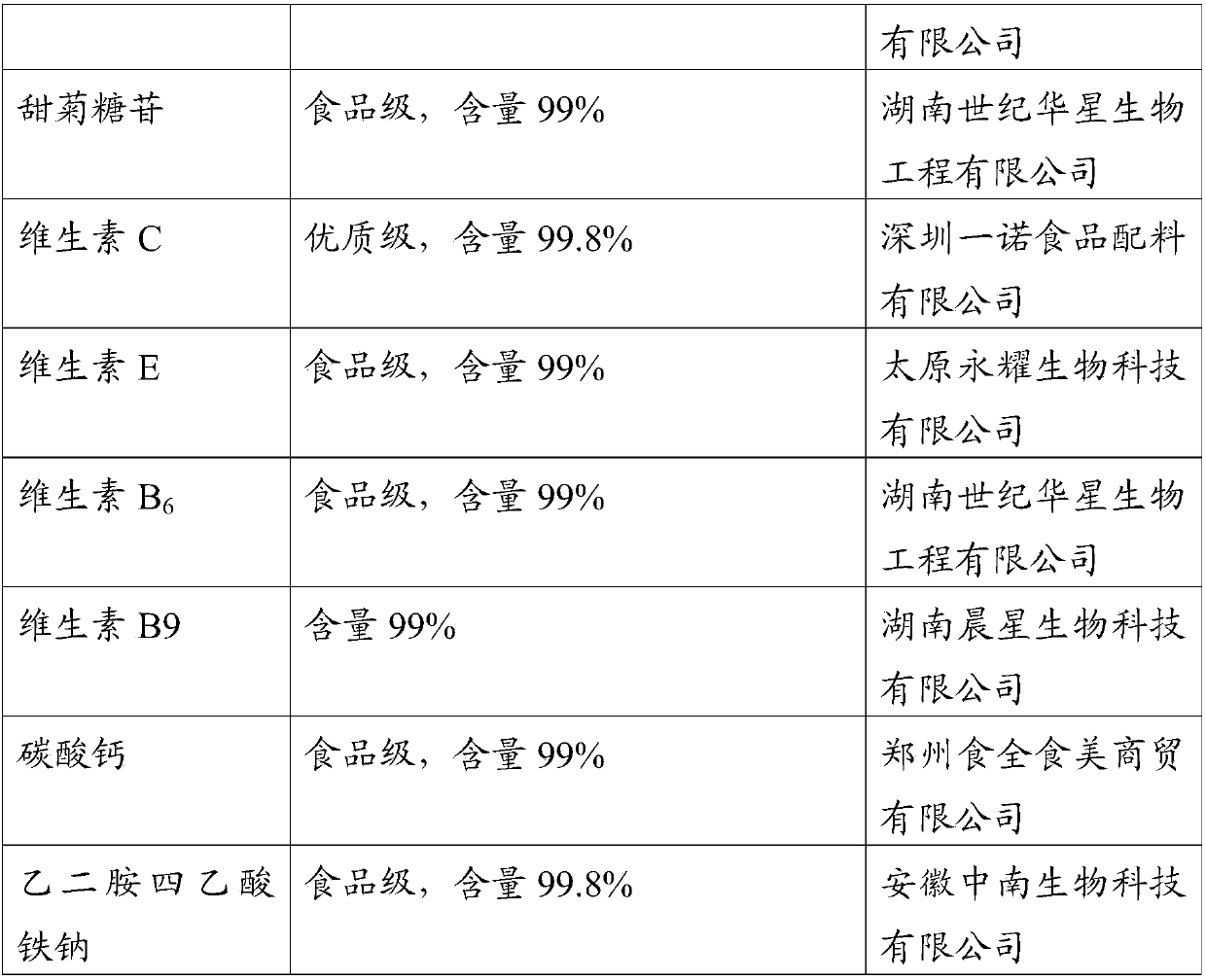
Protein-containing composition and food as well as preparation method and application of composition
PendingCN107752045ARich sourcesReasonable mix of typesVitamin food ingredientsYeast food ingredientsDocosahexaenoic acidYeast Proteins
The invention relates to protein-containing composition, in particular to protein-containing composition and food for pregnant women as well as a preparation method and an application of the composition. The composition is prepared from soy protein isolate, whey protein, pea protein, yeast protein and docosahexaenoic acid powder. The invention provides high-quality protein powder suitable for pregnant women, and protein is widely sourced and includes soy protein and pea protein which are vegetable protein, whey protein which is animal protein as well as yeast protein which is microbial protein. Compared with existing food for supplementing pregnant women with protein nutrition, the product has the advantages that matching of protein types is matched more reasonably, and more nutrients contributing to health keeping of pregnant women and fetuses exist in the composition.
Owner:ANGEL NUTRITECH CO LTD
Compositions and methods for proteomic investigations
Abstract of the Disclosure The present invention provides a variety of related proteomics analytical modalities that are open-ended, rapid, convenient and suitable for implementation in a high throughput parallel assay system. Specificity-determining compositions and methods are disclosed for use in proteomics. These compositions and methods provide a protein resolved from other protein species contained in a sample fluid, in its native, biologically functional conformation. The present invention provides a specificity-determining substrate that forms a complex with a protein molecule in a homogenous fashion. The specificity-determining substrate includes a specificity-determining ligand bound to a support, wherein optionally the substrate further includes a spacer bound between the ligand and the support. In addition a complex is provided that includes a specificity-determining substrate and a protein molecule. Furthermore, an array including a plurality of loci is provided, in which each locus includes a specificity-determining substrate of the invention. These substrates, complexes and arrays may be employed in a method of resolving a first protein from a fluid including one or more species of native, biologically active protein molecules, wherein the first protein retains its native structure and its biological activity; in a method of purifying one or more first proteins from a fluid including one or more species of native, biologically active protein molecules, wherein the purified first protein retains its native structure and its biological activity; in a method of characterizing one or more proteins in a fluid including one or more species of protein molecule; and in a method of identifying one or more proteins in a sample fluid wherein the concentration of the one or more proteins in the sample fluid differs from the concentration of the one or more proteins in a reference fluid.
Owner:ROY SWAPAN +2
Protein powder for enhancing immunity
ActiveCN106174598AGood dispersionUniform and stable dispersionSugar food ingredientsFood ingredient functionsSide effectSodium Caseinate
The invention belongs to the field of healthcare foods, and particularly relates to protein powder for enhancing the immunity. The protein powder comprises plant proteins, animal proteins, phospholipid and additives. The additives comprise hydrogenated soybean oil, glucose syrup, sodium caseinate, sodium stearyl lactate and silicon dioxide, and the animal proteins and the phospholipid in the protein powder need to be proportionally prepared. The protein powder has the advantages that the protein powder simultaneously contains the animal proteins and the plant proteins, accordingly, the variety of the proteins can be increased, human bodies can advantageously absorb the protein powder, and the immunity of the human bodies can be advantageously enhanced; the phospholipid and the animal proteins are prepared according to certain proportions, accordingly, harm such as high blood lipid and high cholesterol due to excessive consumption of the animal proteins can be prevented, the protein powder is free of side effect, and people can safely and conveniently eat the protein powder.
Owner:HAINAN ZHENGKANG PHARMA
Method for establishing quantitative reference range of healthy human urine proteome and database of healthy human urine proteome
ActiveCN108334752AEliminate distractionsSpecial data processing applicationsBioinformaticsData setLibrary searching
The invention discloses a method for establishing a quantitative reference range of a healthy human urine proteome and a database of a healthy human urine proteome. The method comprises the steps thata statistical quantity of healthy human urine samples are made into urine protein samples, protein species and quantification of each protein are determined by mass spectrometric detection, library searching and quantification to form urine proteome data, different urine proteome data is collected into different urine proteome sub-data sets and total data sets, and the quantitative reference range of the healthy human urine proteome is obtained by the data calculation of the data sets. The established quantitative reference range of the human urine protein in the healthy human urine proteomedatabase can better exclude interference from physiological fluctuations and inter-individual differential protein in the discovery of urine protein biomarkers.
Owner:北京松果天目健康管理有限公司
Microfabricated chip and method of use
ActiveUS7497937B2Easy to analyzeSludge treatmentVolume/mass flow measurementElectrophoresisProtein species
A multiplexed, absorbance-based microfabricated chip electrophoresis system, microfabricated chip, and method of use are included for the detection and identification of protein species. The microfabricated chip electrophoresis system capable of analyzing multiple samples simultaneously. The system uses a microfabricated chip having a sample chamber for first dimension separation of a sample, a first planar array of channels for second dimension separation of the sample approximately perpendicular the sample chamber, and a barrier separating the sample chamber from the first planar array of channels during the first dimension separation. In use, the sample is placed into a sample chamber, a barrier is established around the sample chamber, the sample is isoelectric focused within the sample chamber, the barrier is then removed, and the sample separated in the first array of channels by molecular weight.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Mass spectrometric immunoassay analysis of specific proteins and variants present in various biological fluids
InactiveUS7396687B2Adequate quantitative dynamic range and accuracy and linearityMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingProtein targetMass spectrometric immunoassay
Presented herein is the construction of pipettor tips (termed MSIA-Tips) containing porous solid supports that are constructed, covalently derivatized with affinity ligand, and used to extract specific proteins and their variants from various biological fluids by repeatedly flowing the fluids through the MSIA-Tips. A second protein species (a mass-shifted variant of the targeted protein doped into the samples at a constant concentration) is co-extracted with the endogenous protein and variants and is used as a quantitative internal reference standard (IRS). Nonspecifcally bound compounds are rinsed from the MSIA-Tip using a series of buffer and water rinses, after which the wild type protein, protein variants and the IRS are eluted from the MSIA-Tips directly onto a target in preparation for analysis such as MALDI-TOF. Mass spectrometry of the eluted sample then follows with the retained proteins identified via accurate molecular mass determination. Protein and variant levels are determined via a quantitative method in which the protein / variant signals are normalized to the signal of the IRS and the values compared to a working curve constructed from samples containing known concentrations of the protein or variants.
Owner:INTRINSIC BIOPROBES
Method for producing circular or multimeric protein species in vivo or in vitro and related methods
Owner:NEW ENGLAND BIOLABS
Cast-to-shape electrokinetic trapping medium
InactiveUS7052608B2Improve structural stabilityElectrolysis componentsIon-exchanger regenerationChemical physicsTrapping
A three-dimensional microporous polymer network material, or monolith, cast-to-shape in a microchannel. The polymer monolith, produced by a phase separation process, is capable of trapping and retaining charged protein species from a mixture of charged and uncharged species under the influence of an applied electric field. The retained charged protein species are released from the porous polymer monolith by a pressure driven flow in the substantial absence of the electric field. The pressure driven flow is independent of direction and thus neither means to reverse fluid flow nor a multi-directional flow field is required, a single flow through the porous polymer monolith can be employed, in contrast to prior art systems. The monolithic polymer material produced by the invention can function as a chromatographic medium. Moreover, by virtue of its ability to retain charged protein species and quantitatively release the retained species the porous polymer monolith can serve as a means for concentrating charged protein species from, for example, a dilute solution.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC
Retinol formulations and methods for their use
A composition for the treatment of skin comprises a non-emulsified, aqueous suspension of retinol. The composition may further include at least one protein species, and some proteins used in the composition include collagen and elastin. The composition may also include hyaluronic acid. The composition may also include one or more of tocopheryl acetate, propylene glycol, and linseed extract. Also disclosed are methods for making the composition and use of the composition for the treatment of skin.
Owner:MILLSTEIN ELLIOTT
Fig soy sauce
ActiveCN107647371AFull of nutritionRich in nutrientsYeast food ingredientsFood ingredient as flavour affecting agentFiberFicus erecta
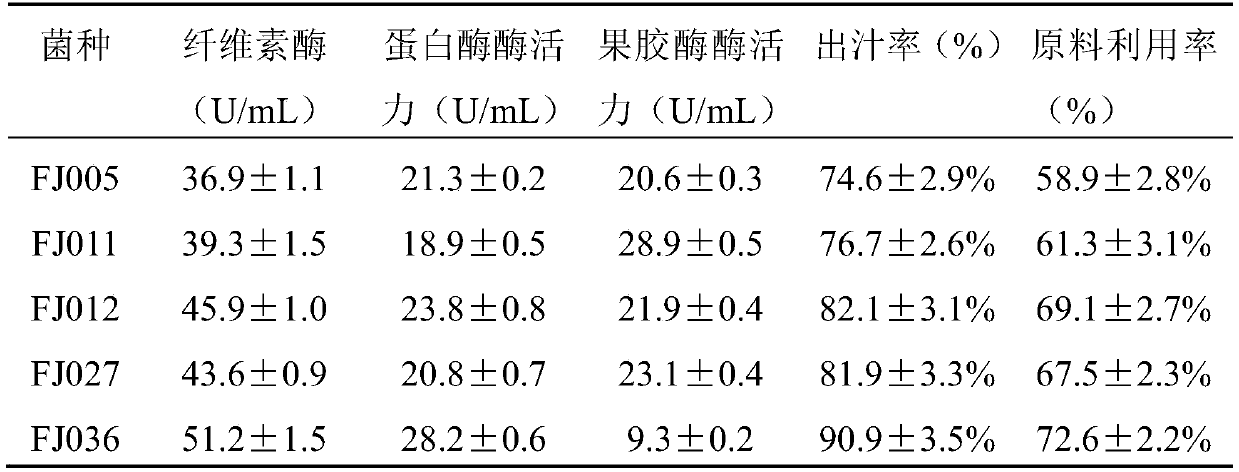
The invention provides a fig soy sauce. The fig soy sauce has nutrient components of figs, is bright in color and glossy, has rich sauce fragrance and ester fragrance and faint fig fragrance, is fresh, delicious and mellow in flavor, fresh, sweet and palatable, unique in style and rich in nutrition, and provides a new variety for soy sauce families. Compared with a conventional high-salt liquid soy sauce, the fig soy sauce has the advantages that the figs are added, so that the kinds of protein are increased, more carbohydrate and more vitamins are increased, and growth and metabolism of various microorganisms are facilitated; besides, cancer resisting components in the figs are added, and fig slurry is subjected to enzymolysis of aspergillus FJ036, so that components of protein, fibers and the like in the figs can be fully utilized, and the utilization effect of fig components can be effectively improved.
Owner:QINGDAO DENGTA FLAVOUR IND
Enhanced protein separation and analysis
InactiveUS20040107057A1Easy to analyzeHigh proportionBiocideNervous disorderProtein profilingMode of action
Methods for enhancing separation and analysis of biological molecules, particularly proteins, and for characterizing tissue, cell, and subcellular (e.g., organelle) expressed protein profiles (proteomes or protein fingerprints) are disclosed. Multi-dimensional diagrams that illustrate the characteristics of the proteins in a sample, based at least in part on interactions between proteins in the system can be produced. In certain embodiments, the diagrams are three-dimensional and incorporate information on protein-protein interactions, protein charge, and protein size for substantially all of the protein species in the sample. Also described are methods of using the provided multi-dimensional diagrams to detect changes in biological systems that are for instance due to disease, drug treatment, environmental condition, and so forth. Methods are provided for correlating changes in three-dimensional proteomic diagrams to disease diagnosis and prognosis, toxicology, therapeutic compound (e.g., drug or hormone) efficacy and mode of action, and drug design.
Owner:STATE OF OREGON ACTING BY & THROUGH THE OREGON STATE BOARD OF HIGHER EDUCATION ON BEHALF OF THE OREGON HEALTH SCI UNIV +1
Method for preparing fodder by utilizing shrimp leftovers
The invention provides a method for preparing a fodder by utilizing shrimp leftovers. The method comprises the following steps: 1) preprocessing; 2) activating; 3) primarily fermenting; 4) preparing compound albumen powder; and 5) preparing the fodder. The method has the beneficial effects that the strong acid production capacity and enzyme production capacity of lactobacillus bulgaricus and bacillus subtilis are utilized to treat the shrimp leftovers under the assistance of additive 1; protein and calcium carbonate are removed from the shrimp shells; according to the method, the protein extraction rate is high and the decalcification rate of the shrimp shells is high; the bacillus subtilis is compounded into alpha-amylase and protease which can degrade the vegetable protein and decompose the vegetable protein inhibitors; the vegetable protein in bean pulp is decomposed into quickly absorbed and digested small molecular weight protein and amino acid, the protein category is enriched and the fodder nutrition is more complete; and the preparation method is simple in operation, high in protection extraction rate, high in activity of extracted protein and high in economic benefit.
Owner:ZHEJIANG OCEAN UNIV
Method for extracting xyloglucan from tamarind seeds
The invention discloses a method for extracting xyloglucan from tamarind seeds, and belongs to the technical field of plant polysaccharide extraction. According to the diversity of protein types in tamarind seeds and the characteristics of acid resistance, salt resistance and heat resistance of tamarind xyloglucan, the tamarind seeds are pretreated to obtain tamarind polysaccharide coarse powder, and then protein in polysaccharide is removed through acid treatment and alkali treatment in sequence in combination with activated carbon adsorption. And dialyzing under a sterile condition to finally prepare the ultra-pure tamarind xyloglucan with low protein content and low bacterial endotoxin content. Compared with an existing water extraction and alcohol precipitation method and an organic acid extraction method for extracting tamarind xyloglucan, the polysaccharide prepared through the method has the advantages of being good in solubility, high in purity and the like, application of the tamarind xyloglucan in the field of biological medicine is greatly promoted, alcohol is not needed to serve as a settling agent, procedures are reduced, and cost is reduced.
Owner:QINGDAO CHENLAND MARINE BIOTECH CO LTD
Method for screening biomarkers of ionizing radiation as well as application of SZT2 protein determined by method
InactiveCN105803049AMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingScreening methodMolecular biomarker
Owner:CHINA INST FOR RADIATION PROTECTION
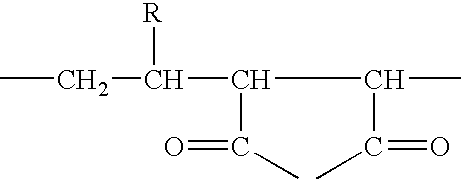
Soybean protein gel, preparation method and applications thereof
InactiveCN103734453ARich varietyImprove crispnessVegetable proteins working-upPROTEIN S HEERLENProtein species
The invention discloses a soybean protein gel, a preparation method and applications thereof. The soybean protein gel is composed of the following raw materials in parts by weight: 0.5 to 1.5 parts of isolated soybean protein powder and 3.5 to 7 parts of ice water. The soybean protein gel is mainly prepared from isolated soybean protein powder and ice water; in the preparation method of the soybean protein gel, the isolated soybean protein powder is subjected to a pretreatment and is converted into protein gel before the isolated soybean protein powder is added into the product; thus the characteristics of the isolated soybean protein gel can be more fully exerted than directly adding the isolated soybean protein powder; the crispy degree and elasticity of pills are increased, the taste and the product quality are improved, the cost is reduced at the same time, plant protein is added to increase the protein content and enrich the protein species, so the product is benefit for human health.
Owner:SHANDONG HUIFA FOODS
Soy sauce prepared from plum
The invention provides a soy sauce prepared from plum. The prepared soy sauce has strong sauce fragrance, ester flavor and plum fragrance; the soy sauce has delicious and mellow flavor, fresh and sweet taste, palatable flavor, light salty taste, unique style and abundant nutrition; a new variety of soy sauce is added. Compared with the traditional high-salt rare soy sauce, the soy sauce prepared from plum has the advantages that the addition of plum is capable of increasing the variety of proteins and increasing more saccharides and vitamins and is beneficial to growth and metabolism of various microorganisms; nutritional ingredients in plum are added into the soy sauce; under the enzymolysis effect of aspergillus FJ036 and pectinase, ingredients, such as protein, fiber and pectin in plumslurry can be fully utilized, and the utilization effect of plum ingredients is effectively promoted; due to the usage of ester-generating brewer's yeast and lactobacillus, more organic acids, alcohols and esters can be generated, and total ester content and fragrance of soy sauce can be further increased.
Owner:QINGDAO DENGTA FLAVOUR IND
Application of RNA Interference Targeting dhfr Gene, to Cell for Producing Secretory Protein
Biological materials are applied to a CHO cell or the like for enhancing production of a species of protein. The biological materials includes an expression vector and a silencing vector, the expression vector including a dhfr gene of a species of mammal and a gene encoding the species of protein, the silencing vector including a DNA fragment for inducing a RNA interference in the CHO cell to reduce expressions of both exogenous dhfr gene and endogenous dhfr gene after the biological material is applied to the CHO cell, and the CHO cell is thus not limited to dhfr gene deficient type. The DNA fragment consists of nucleotides characterizing a segment of a dhfr gene of the CHO cell and a segment of a dhfr gene of the species of mammal.
Owner:NATIONAL TSING HUA UNIVERSITY
Chitosan-coated wires for biosensing
InactiveUS8562809B2Surface reaction electrolytic coatingElectrolytic organic material coatingProtein speciesHand held devices
A method of forming a bioelectronic device including a protein on an electrically conductive substrate, by electrodepositing aminopolysaccharide chitosan on the substrate while applying a cathodic voltage to the substrate, to form an aminopolysaccharide chitosan film thereon, applying an anodic voltage to the substrate in the presence of NaCl to activate the aminopolysaccharide chitosan film so that it is reactive with protein. The method also optionally includes reacting the aminopolysaccharide film, after activation thereof, with the protein, so that the protein assembles on and is coupled to the substrate, thereby forming a bioelectronic device. The protein can include single or multiple protein species, and including biosensing proteins. Additional methods include biosensing of electrochemically active compounds either present in a sample or generated during a biological recognition event and devices useful in such methods. The resulting devices are useful as sensors in hand-held devices, textiles, garments and the like.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
Processing method of highly-flavored liquor
ActiveCN104450383AGreat tasteUniform infiltrationAlcoholic beverage preparationMicroorganismBiotechnology
The invention relates to a processing method of highly-flavored liquor. The processing method comprises the following steps: (1) crushing selected sorghum, corn, rice and sticky rice with full particles into 40 meshes of particles by using a crusher and uniformly mixing the mixed particles; (2) wetting the raw materials; (3) pasting the raw materials; (4) putting the raw materials into a pit and sealing by using pit mud to ferment for above 6 months; (5) distilling the fermented raw materials to take out liquor, selecting a liquor jar of 50-65 degrees to age for 3-5 years, blending and obtaining the finished liquor. The processing method has the benefits that as the sorghum, corn, rice and sticky rice are used as the processing raw materials, protein varieties in the raw materials are mutually complementary, so that the growth and the fermentation of microorganisms are promoted; the raw materials processed by using the method can be uniformly wetted; as the raw materials are fully wetted, the complete pasting of the raw materials is facilitated, the utilization rate of the raw materials is improved, and the mouth feeling of the processed liquor is improved.
Owner:ANHUI WANGJIABA WINE
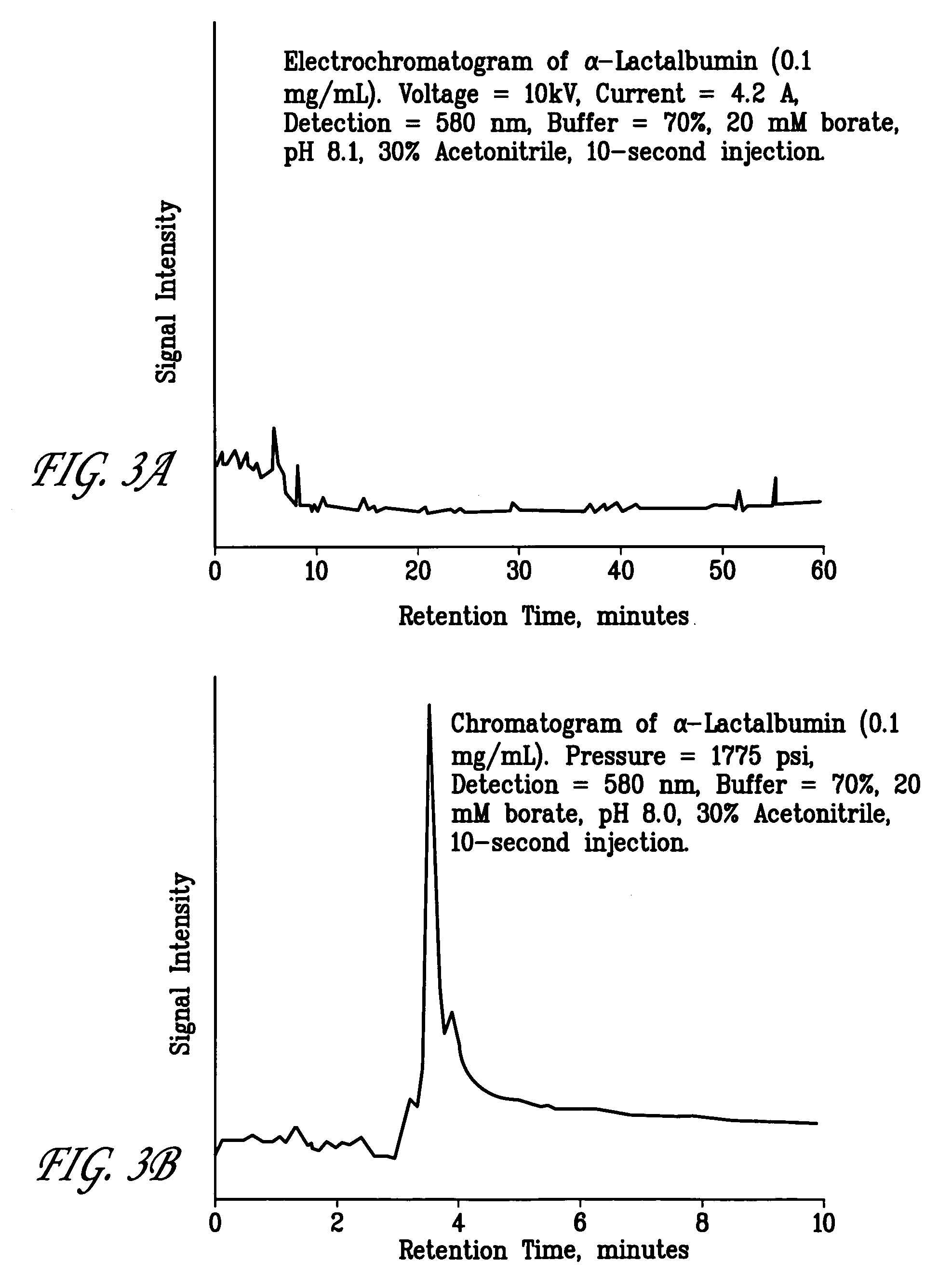
Methods, compositions, and kits for protein crystallization
InactiveUS20050202405A1Reduce solubilityPromote crystallizationFrom normal temperature solutionsElectrolysis componentsElectrophoresisProtein insertion
The present invention provides methods, compositions, and kits for protein crystallization. The present invention involves electrophoretically focusing at least a first protein species within a matrix comprising at least 2 regions of different pH, the protein being present in amount sufficient to permit crystallization within said pH gradient.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Fermentation and detoxification method of tea seed cake
InactiveCN107691985AThorough detoxificationAnti-virus to ensureFood processingAnimal feeding stuffNon toxicityProduct processing
The present invention mainly relates to the technical field of agricultural and sideline product processing, and discloses a fermentation and detoxification method of tea seed cake. The method comprises the following steps: crushing, primary fermenting, secondary fermenting, drying and packaging. The method is simple and convenient for large scale operations, does not need heating, is safe and environmentally protective, saves energy, enables the tea seed cake to be completely detoxified, significantly reduces tea saponin residue amount to be as low as 0.03%, ensures safety and non-toxicity, avoids harms on animals, increases added values of the tea seed cake and sesame seed meal, and improves economic income by 9.6%. The sesame seed meal is added into the tea seed cake, and sesamin in thesesame seed meal neutralizes the tea saponin, reduces the content of the tea saponin, balances protein species, promotes microorganism proliferation and speeds up fermentation processes.
Owner:安徽省霍山县中绿农林开发有限公司
Method for detecting diagnostic marker of follicular thyroid carcinoma using expression level of aminoacyl-trna synthetase-related protein
InactiveCN109844535ASimple and accurate diagnosisHigh sensitivityBiological testingTrue positive rateProtein species
Owner:MEDICINAL BIOCONVERGENCE RES CENT +2
Squid protein powder and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a squid protein powder and a preparation method, which is characterized in that it consists of the following raw materials and mass fractions: 35-50 parts of Peruvian squid extract, 90-100 parts of soybean protein isolate, and 25-30 parts of spirulina extract , 10‑12 parts of stachyose, 5‑8 parts of soft white sugar, 0.1‑0.3 parts of citric acid, 3‑5 parts of dextrin, and 10‑15 parts of sodium bicarbonate. The product of the invention is rich in proteins, amino acids, vitamins, minerals and peptides, has high nutritional value, can be taken directly or processed into health care products, leisure foods and other products as raw materials, thereby increasing the use value of the Peruvian squid.
Owner:山东麦可欣餐饮管理有限公司
Linear high-throughput proteomics
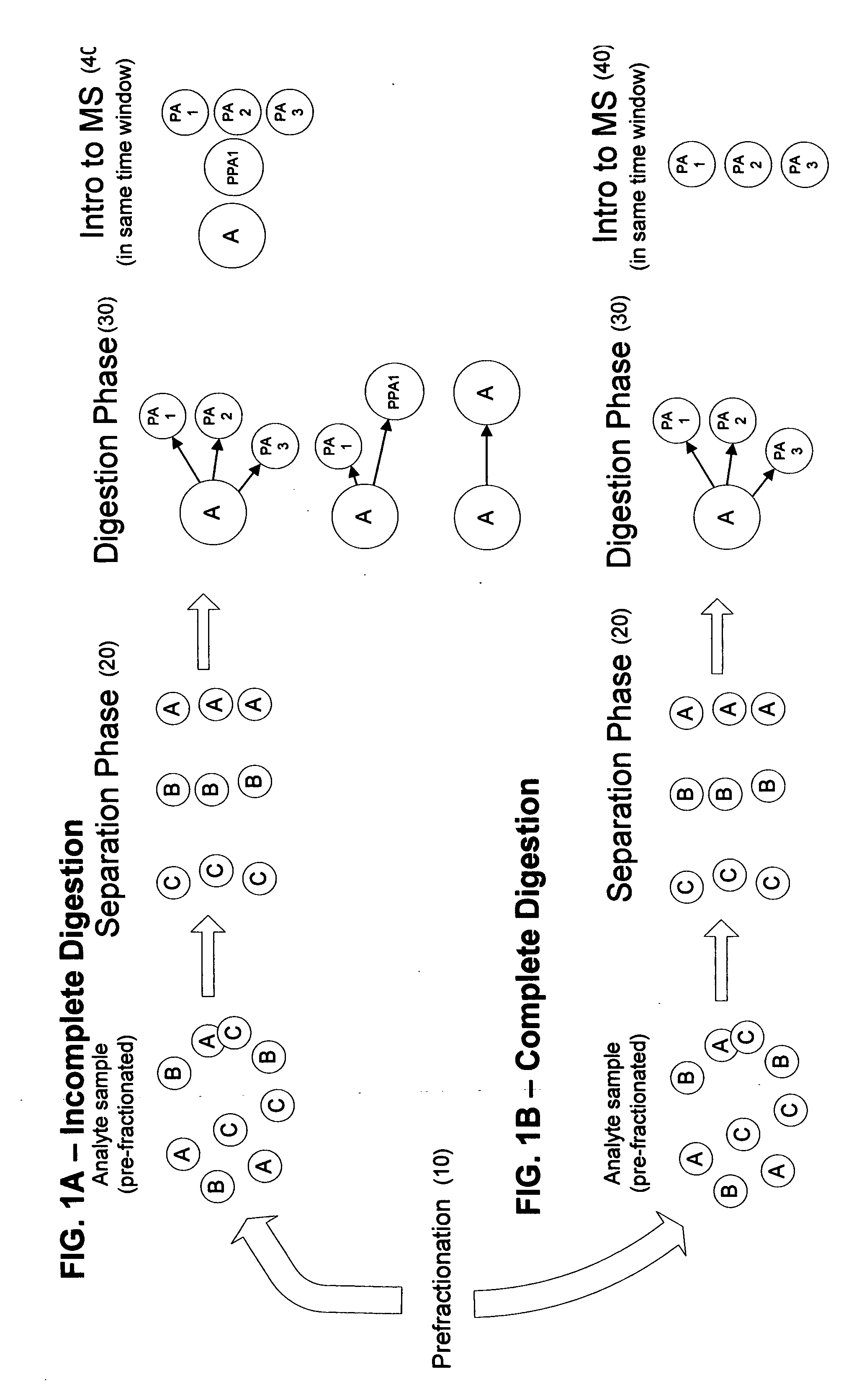
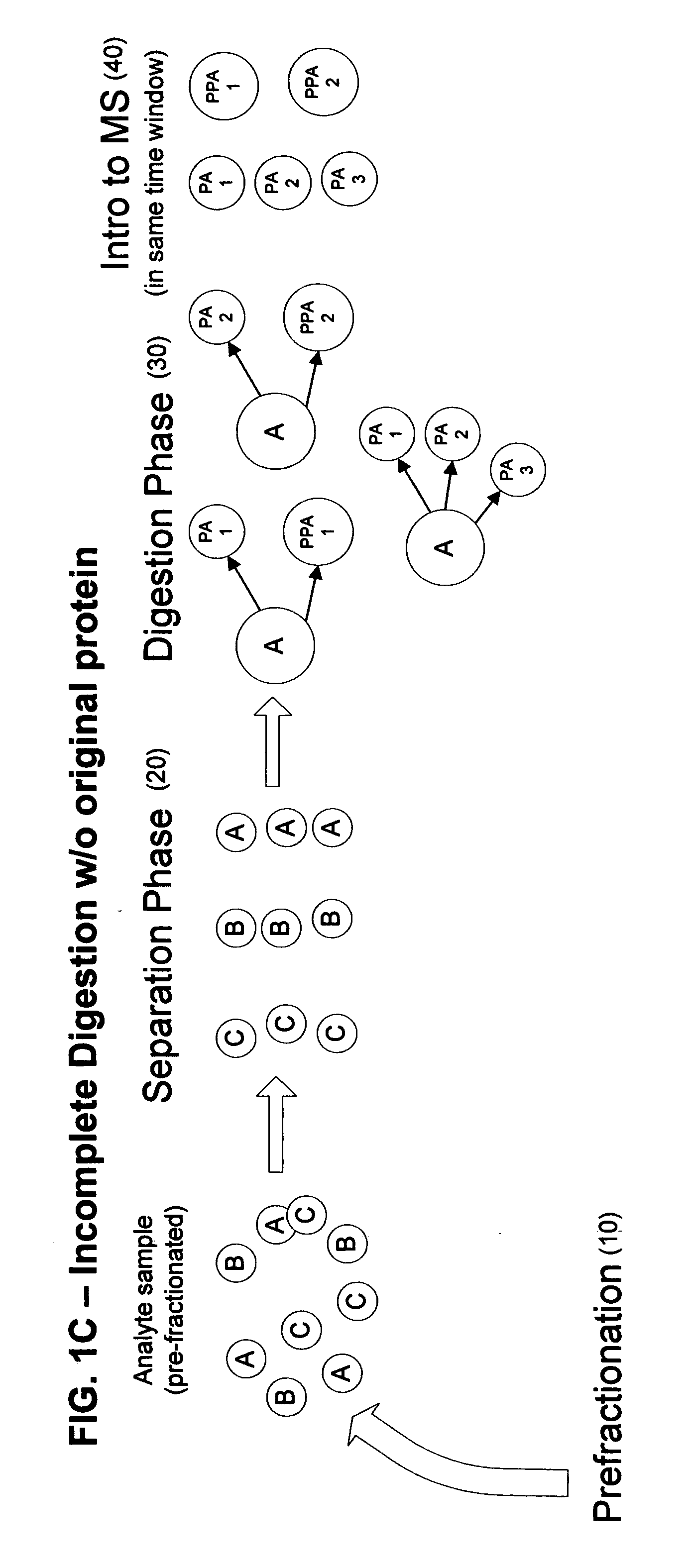
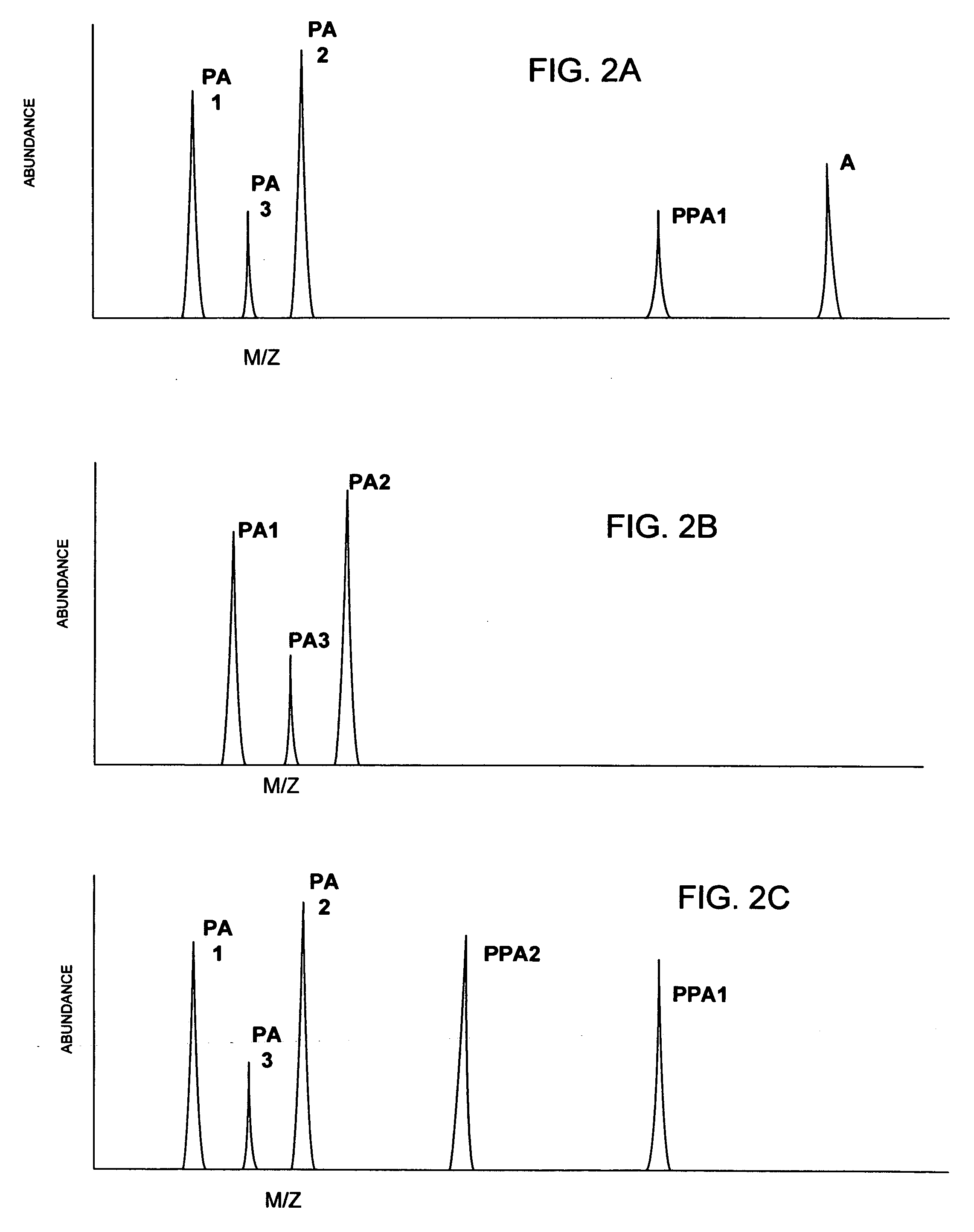
ActiveUS20080014603A1Elucidation facilitatedEasy to identifyComponent separationSamples introduction/extractionProtein speciesBiology
A method of analyzing a sample comprising multiple protein species is provided. The proteins are separated by species such that the multiple protein species emerge in a sequential order and are then digested in the sequential order in which they emerge from the separation process. The digested proteins are introduced into a mass spectrometer in the same sequential order so that, within a given time window, the digested proteins introduced into the mass spectrometer are covariant.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com