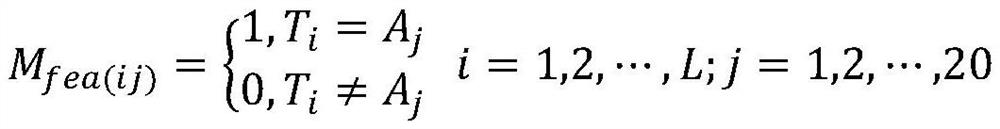Patents
Literature
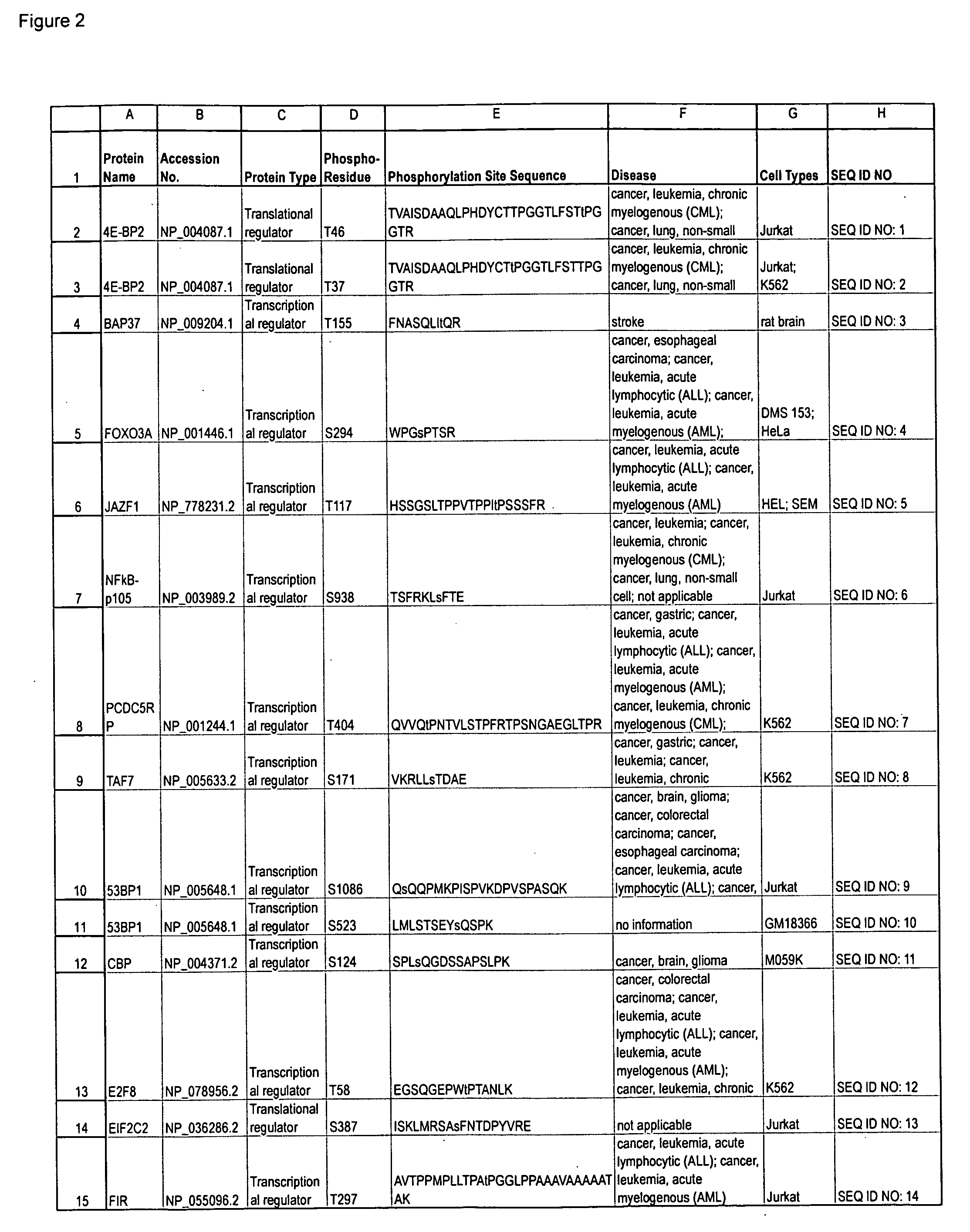
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
108 results about "Phosphorylation site" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
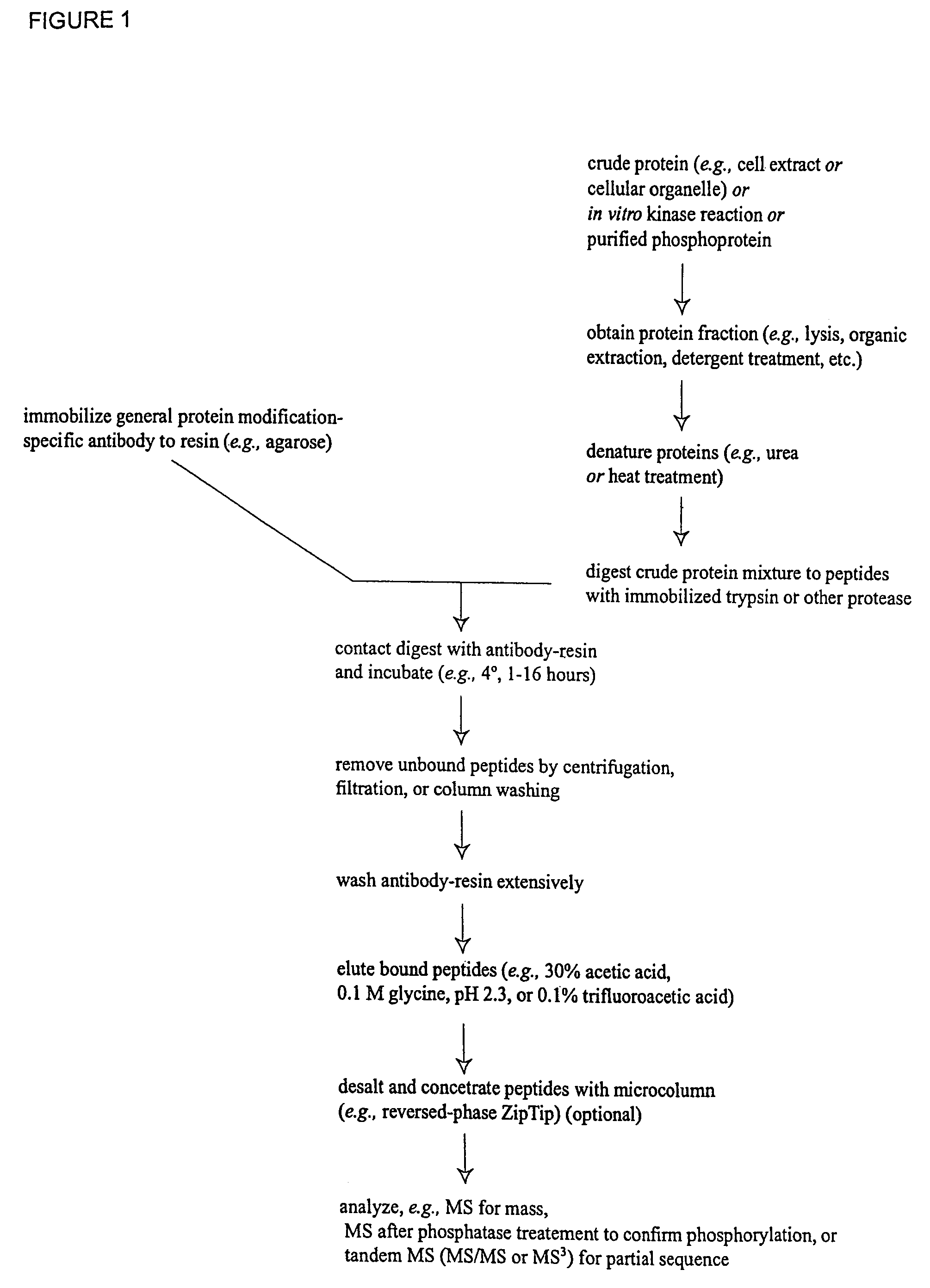
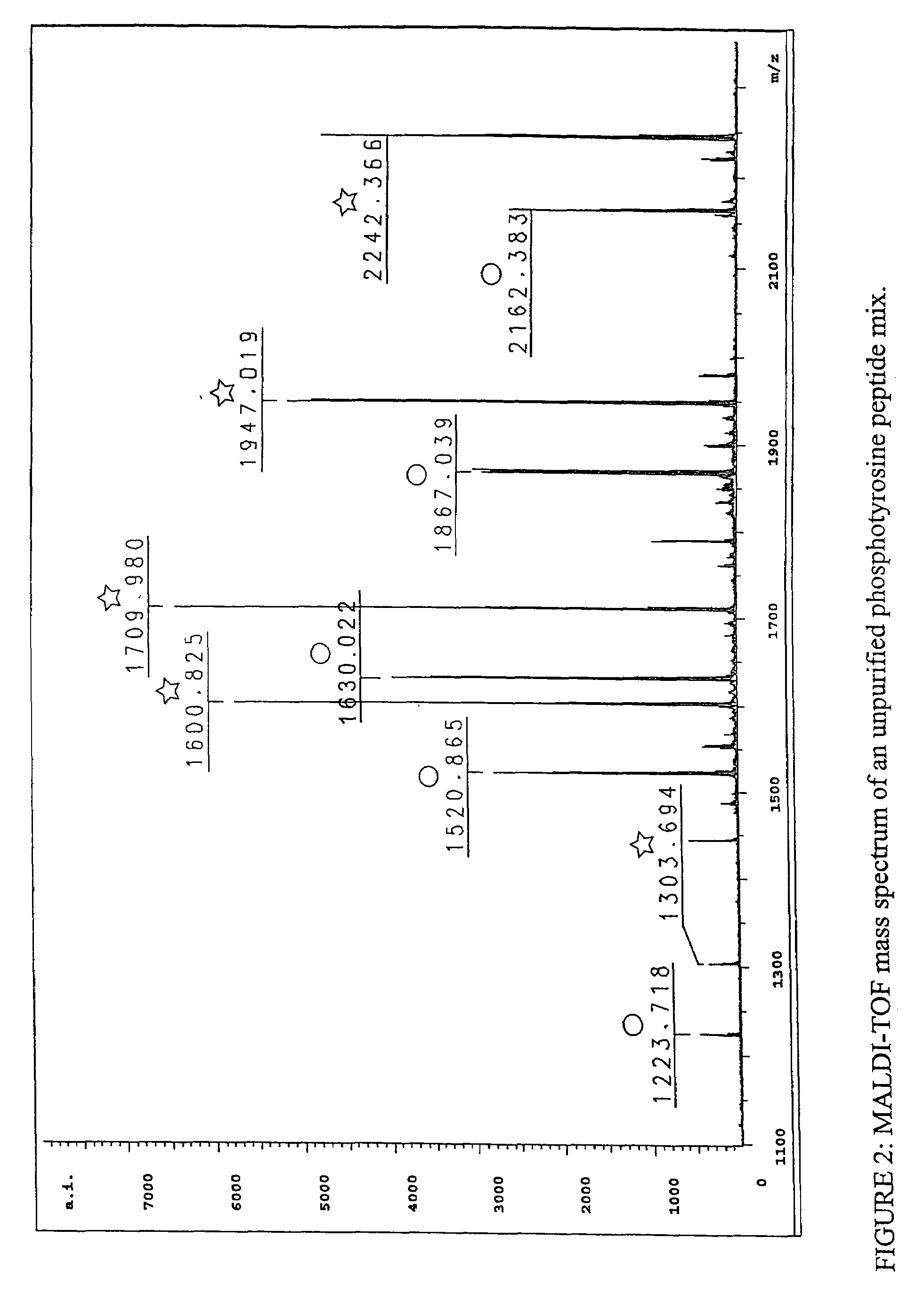
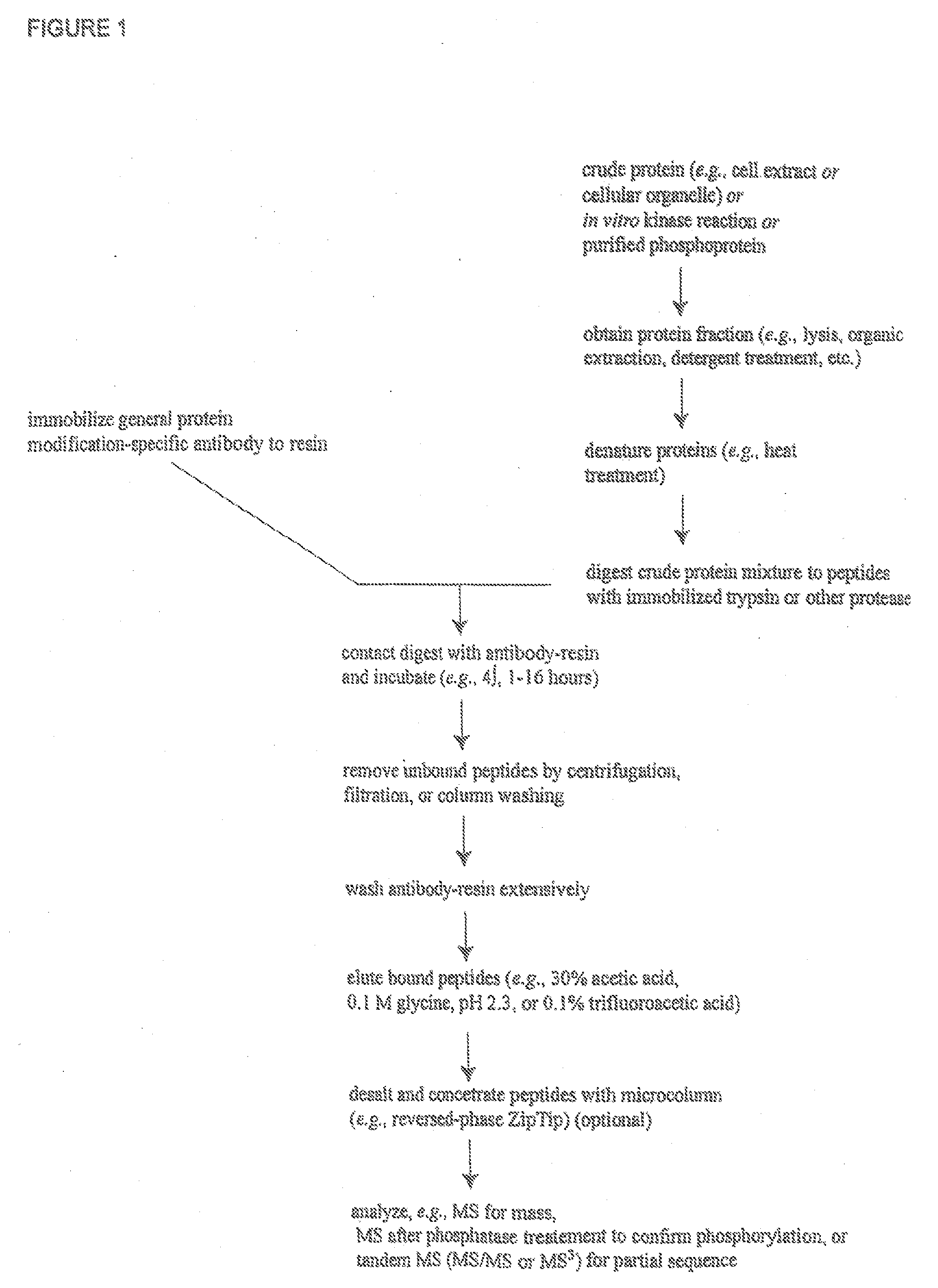
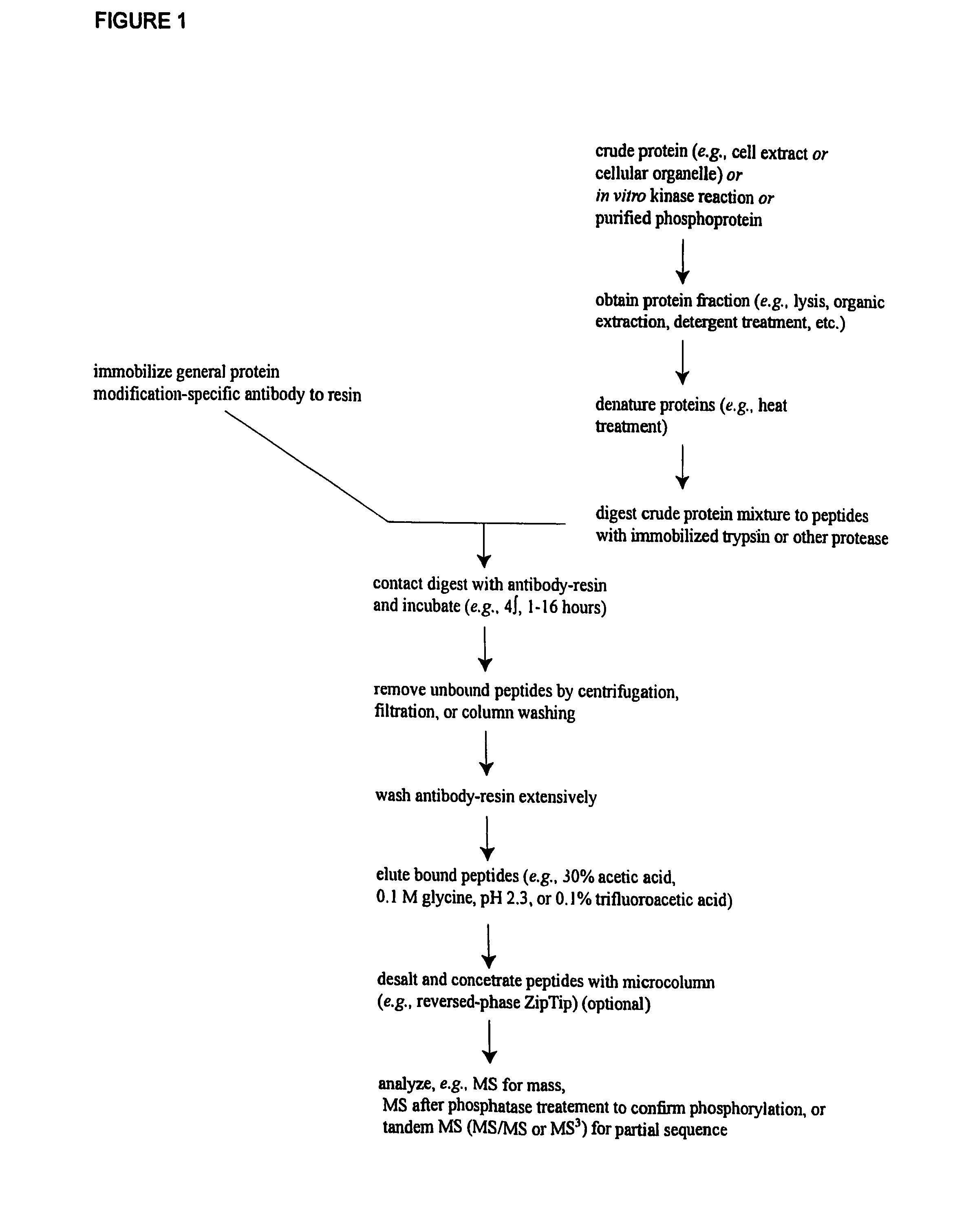
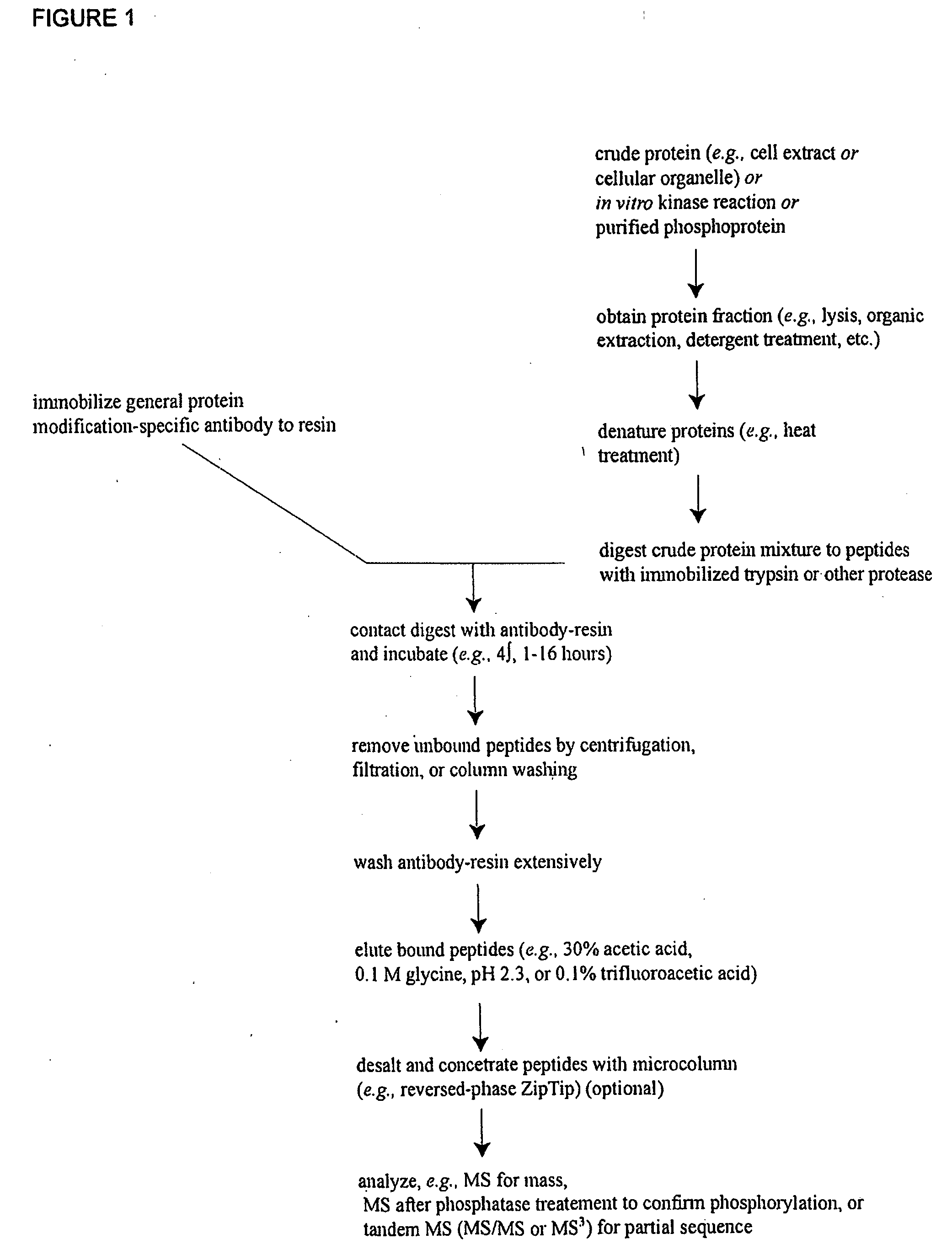
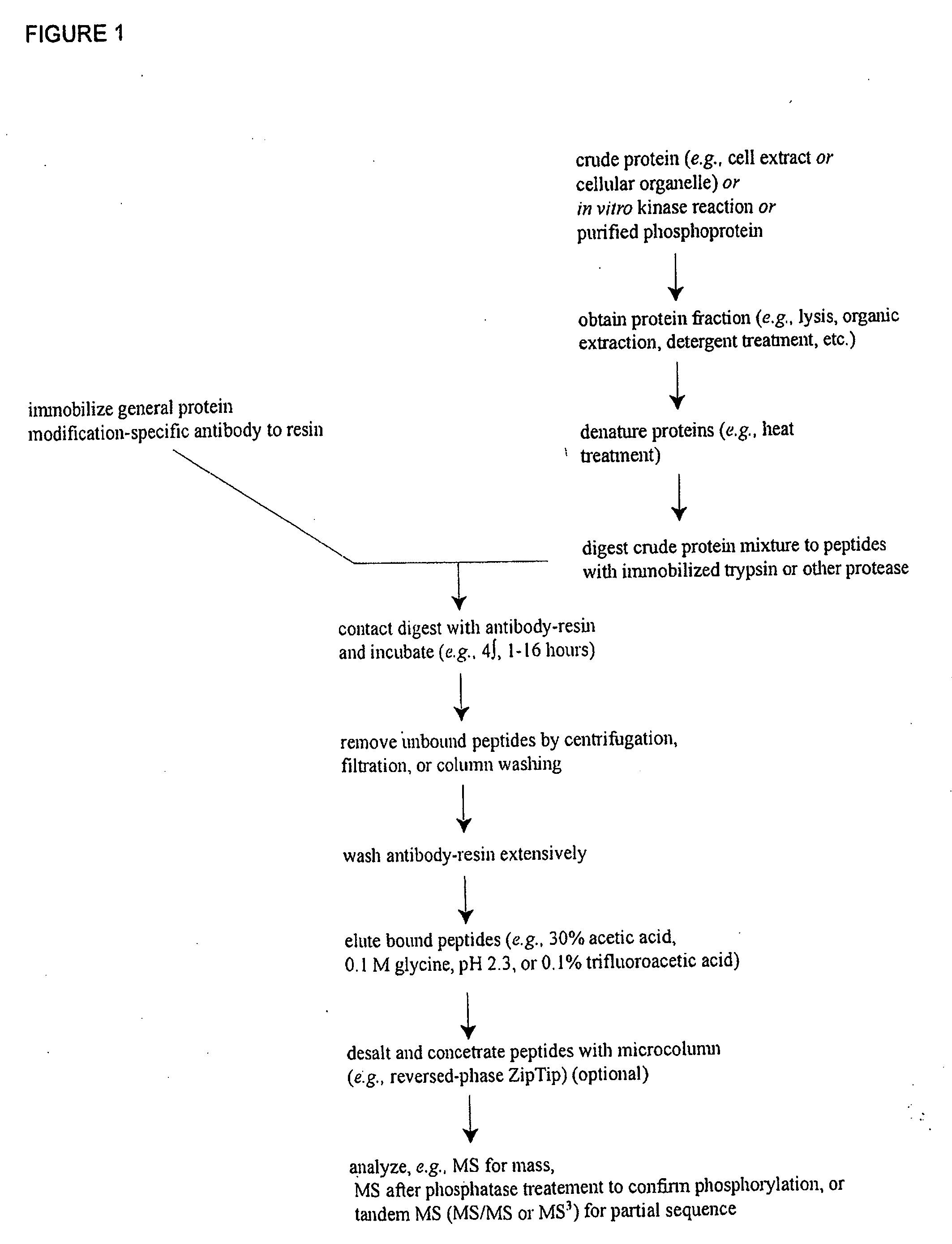
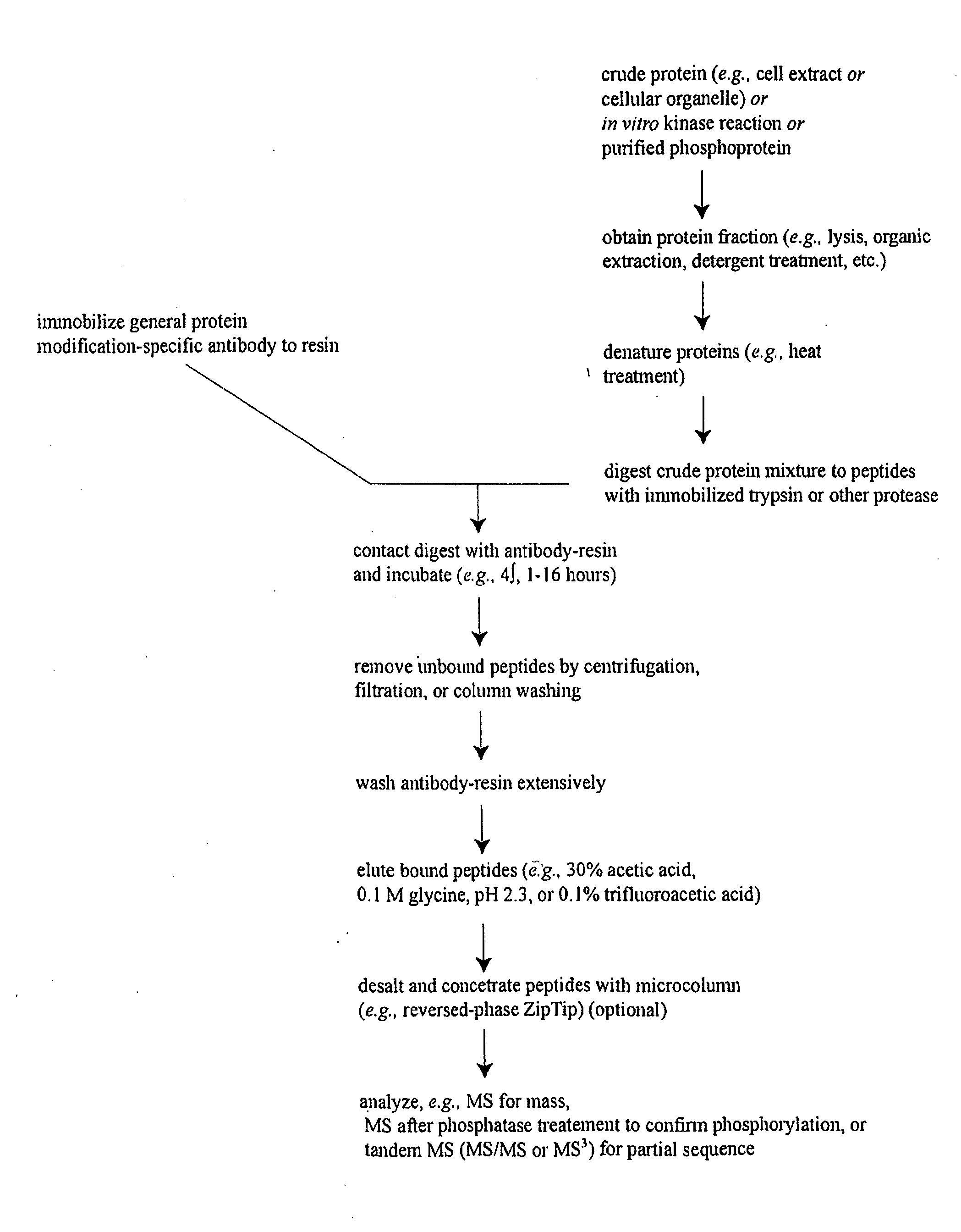
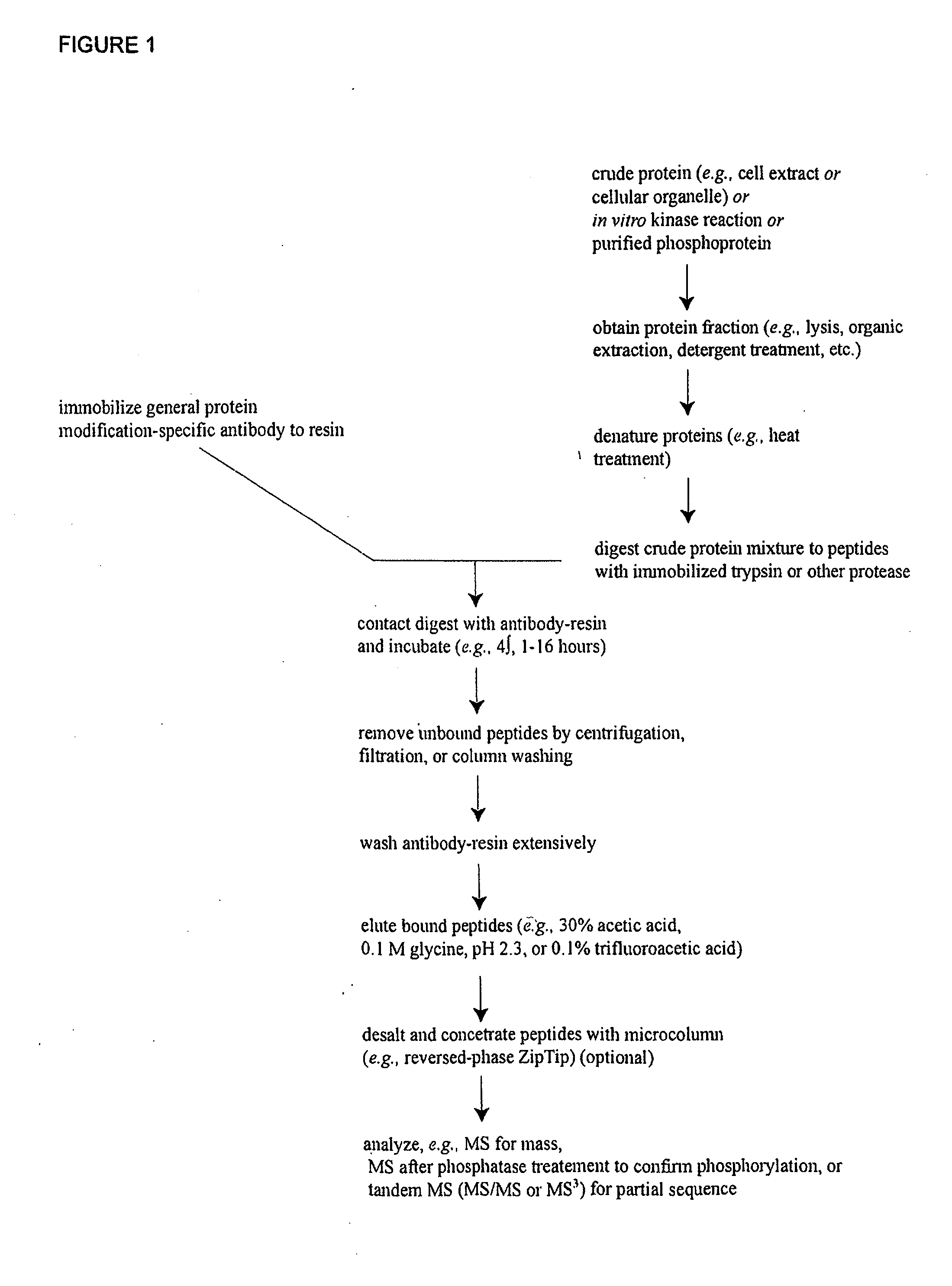
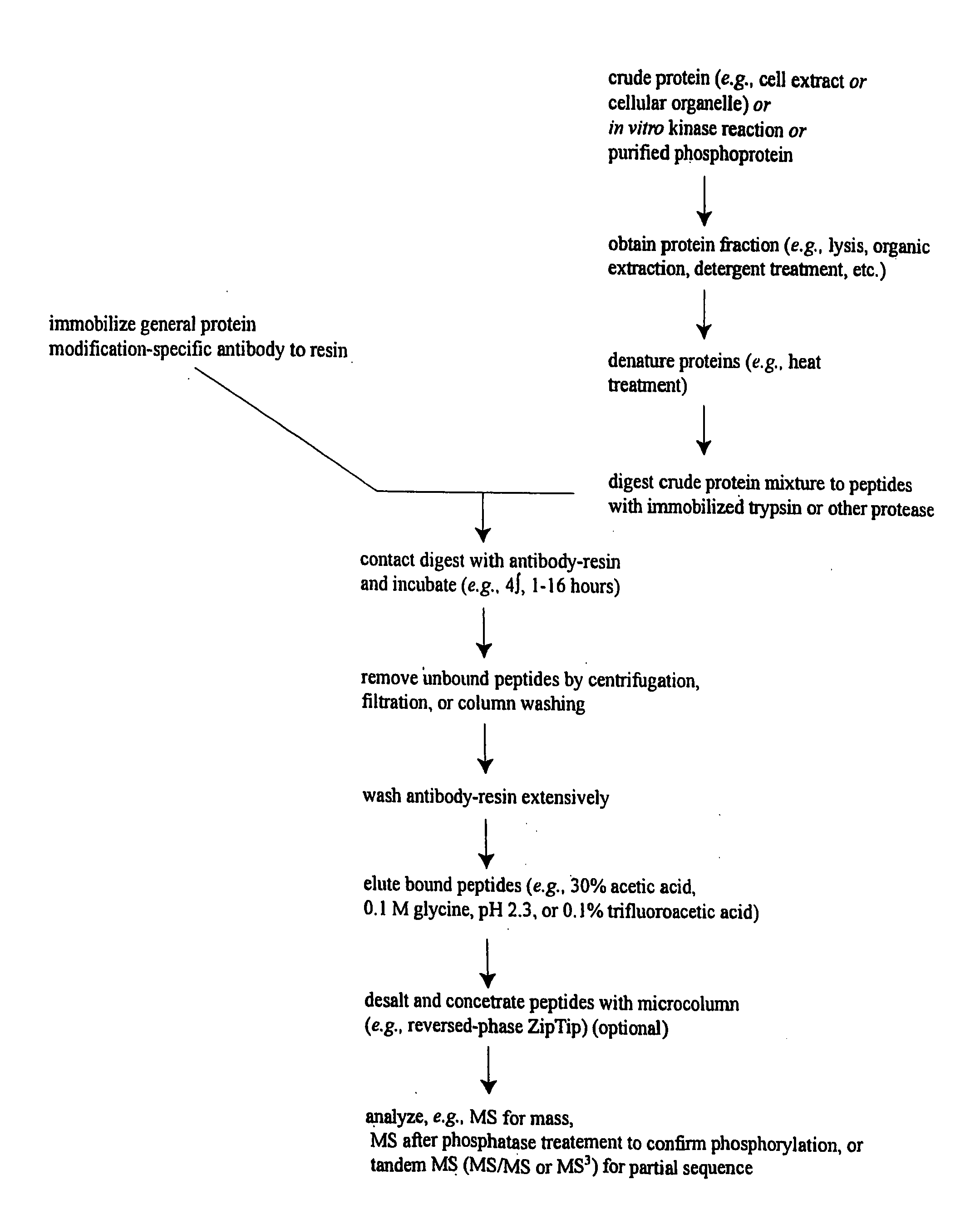
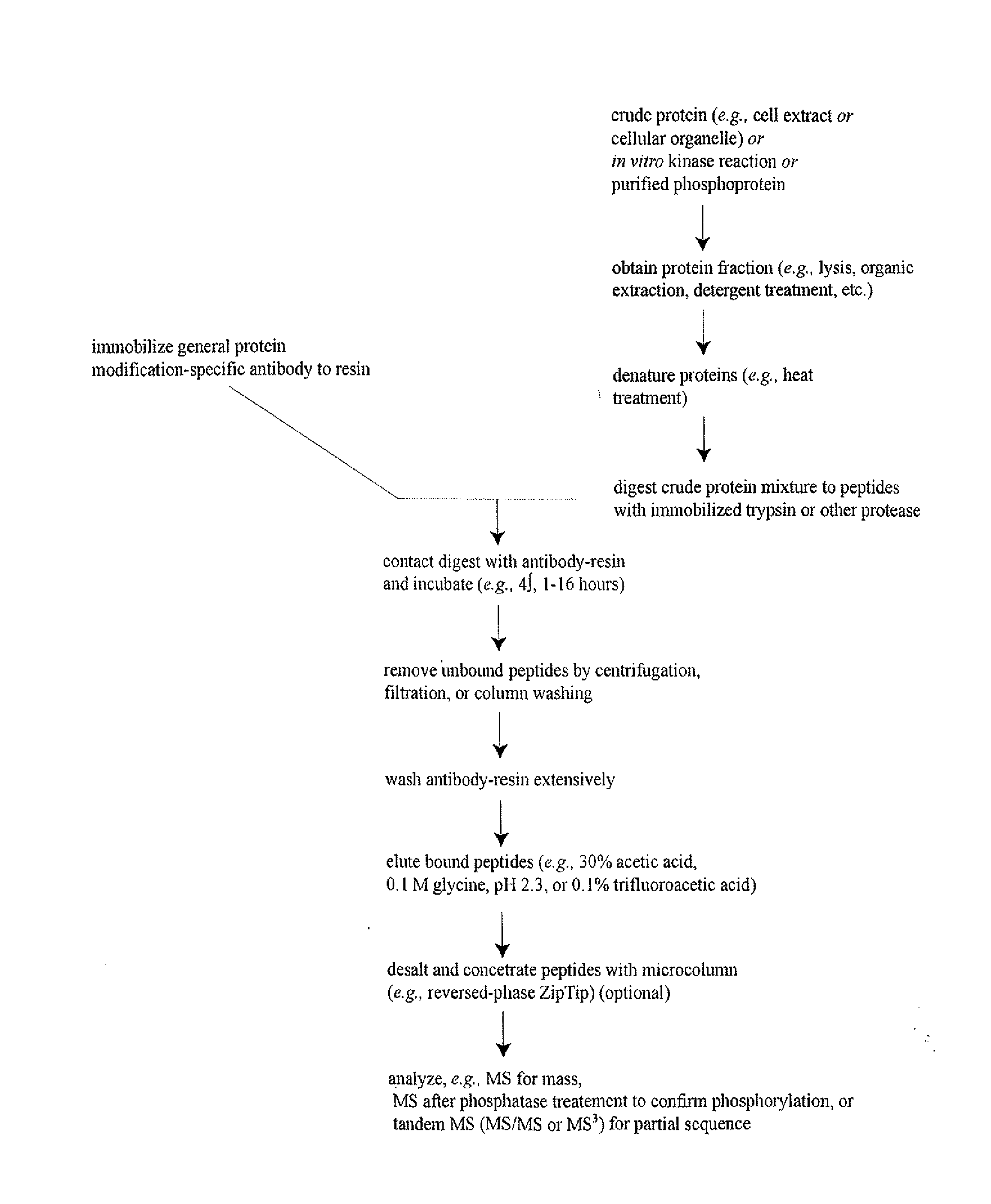
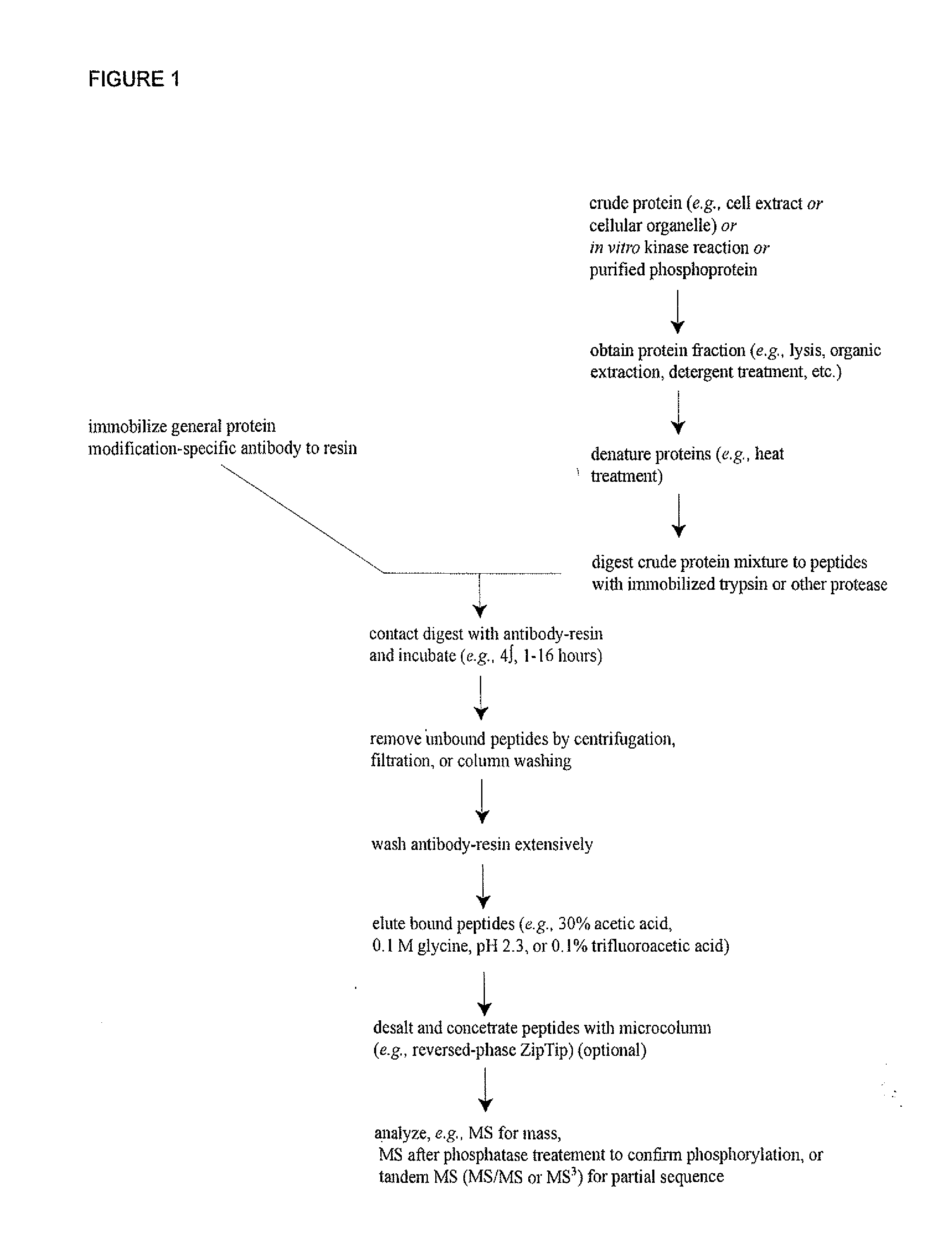
Immunoaffinity isolation of modified peptides from complex mixtures
InactiveUS7198896B2Rapid and efficient and direct isolationImprove automationIon-exchanger regenerationImmunoglobulinsBiological bodyPhosphorylation
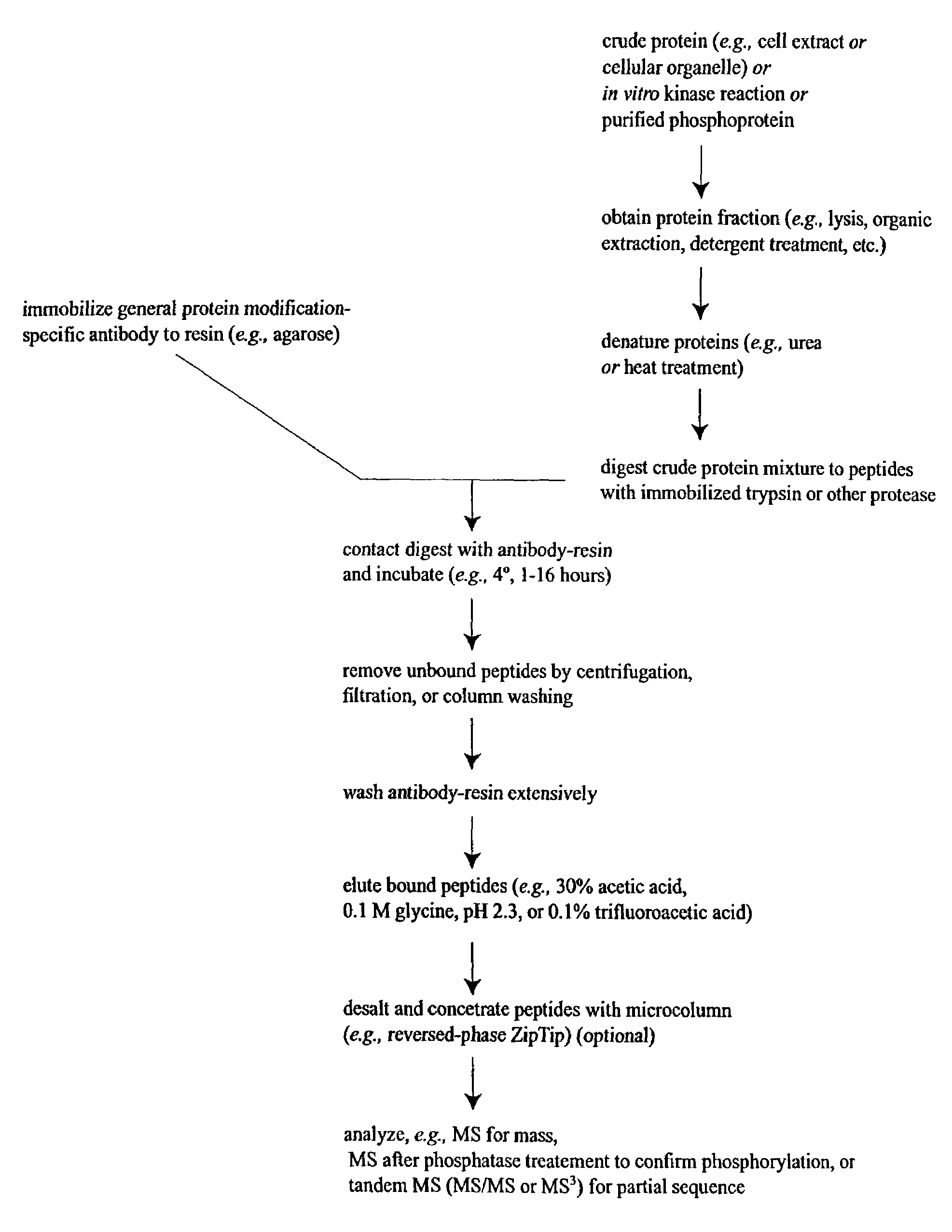
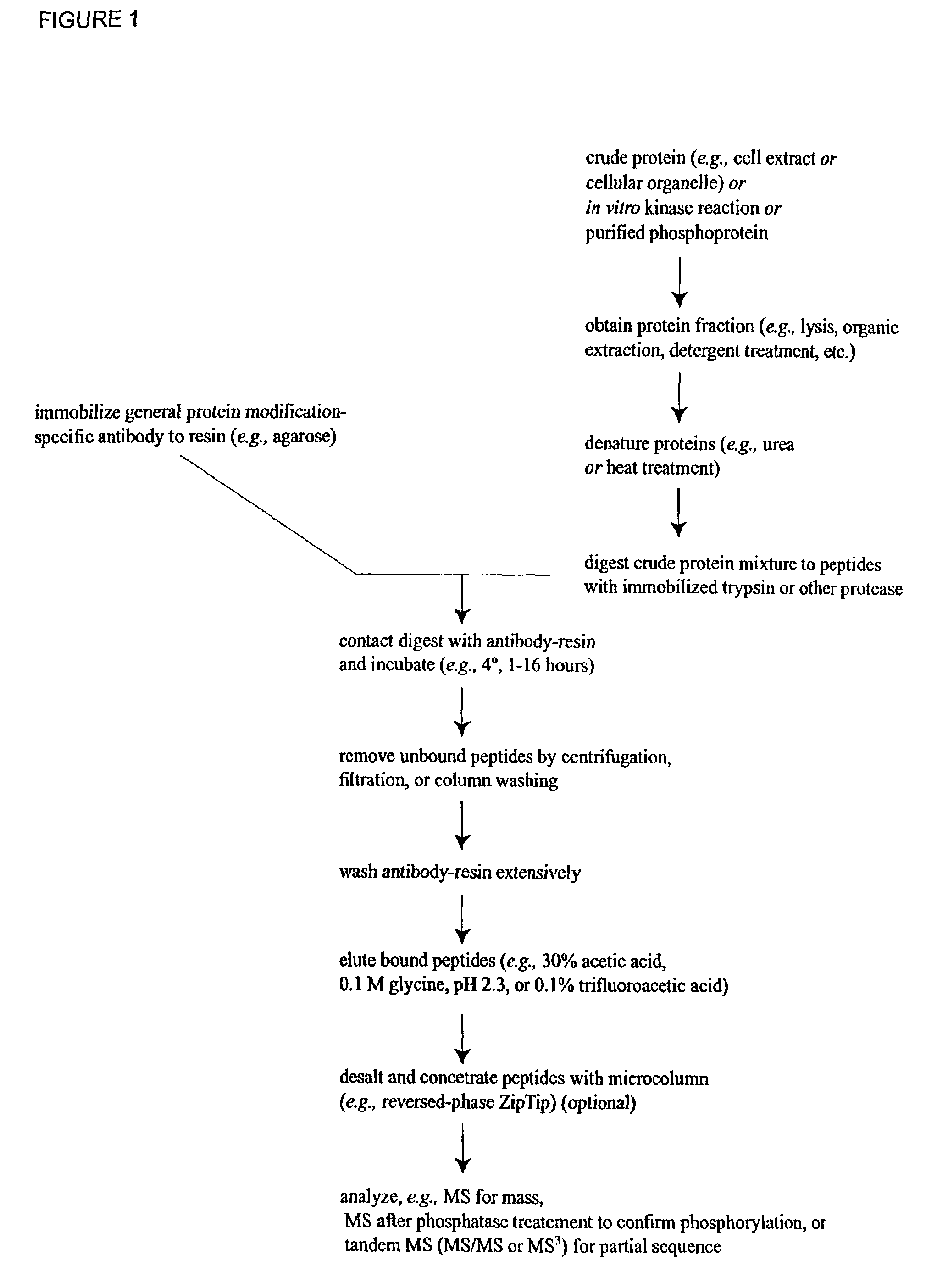
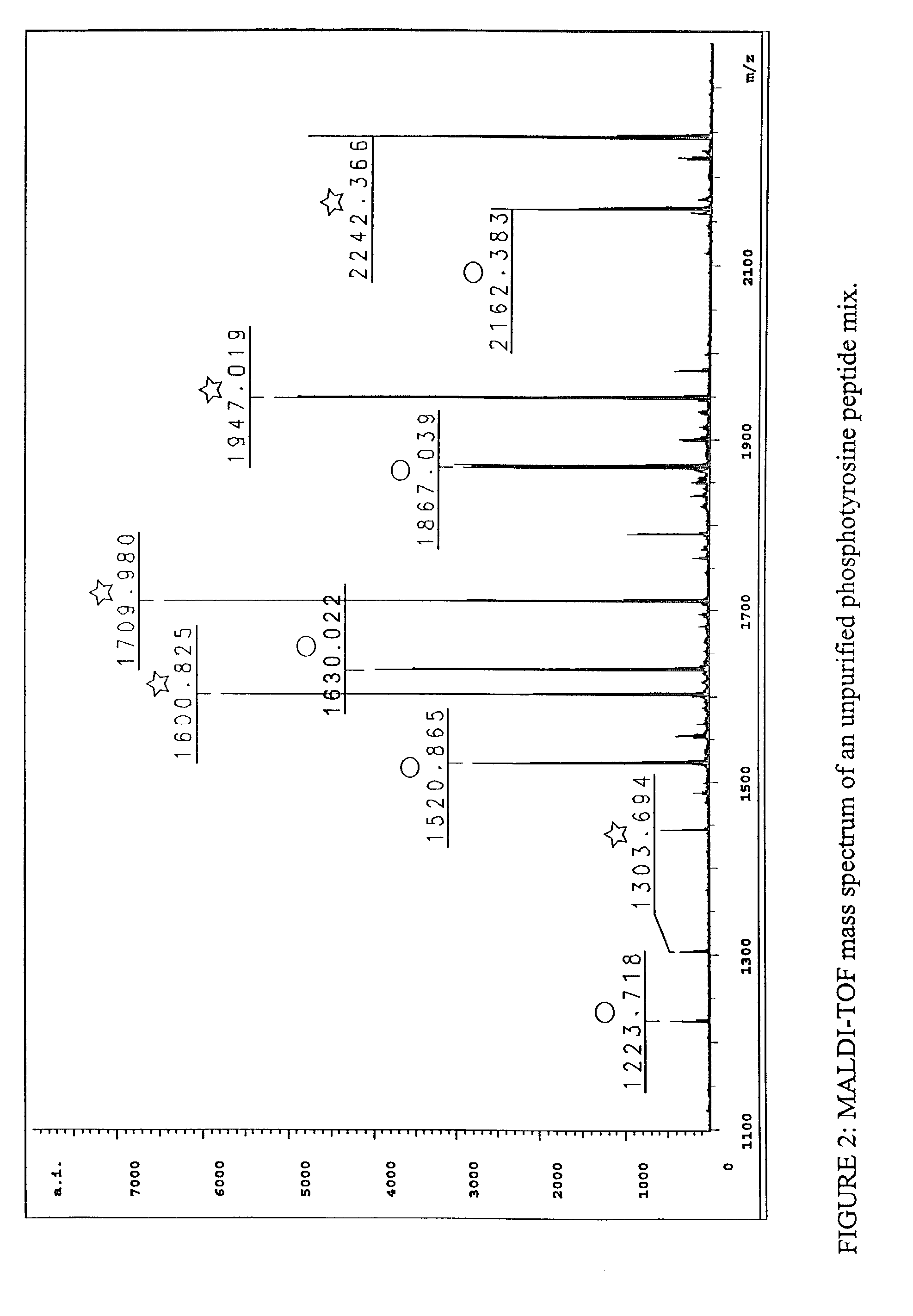
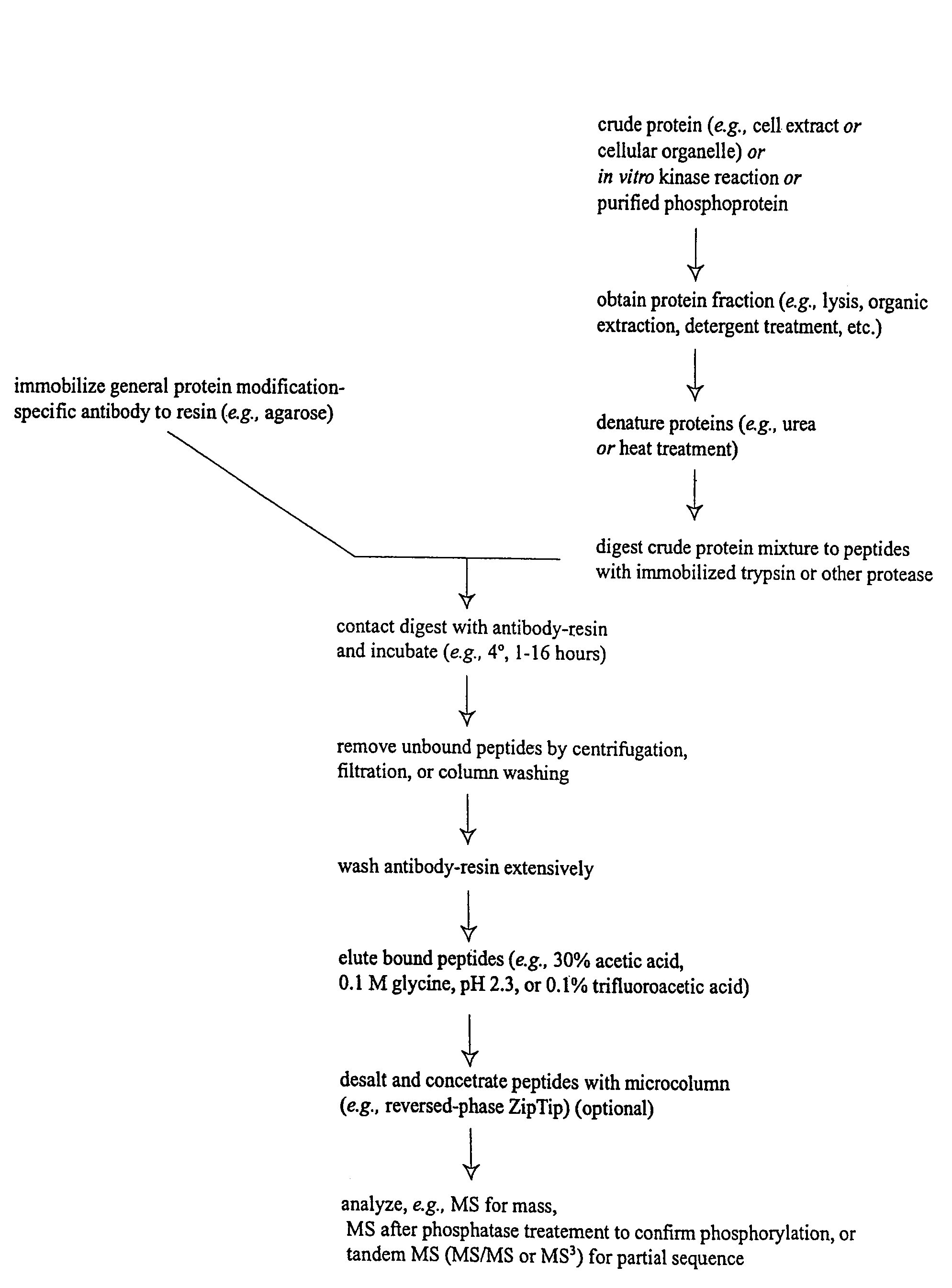
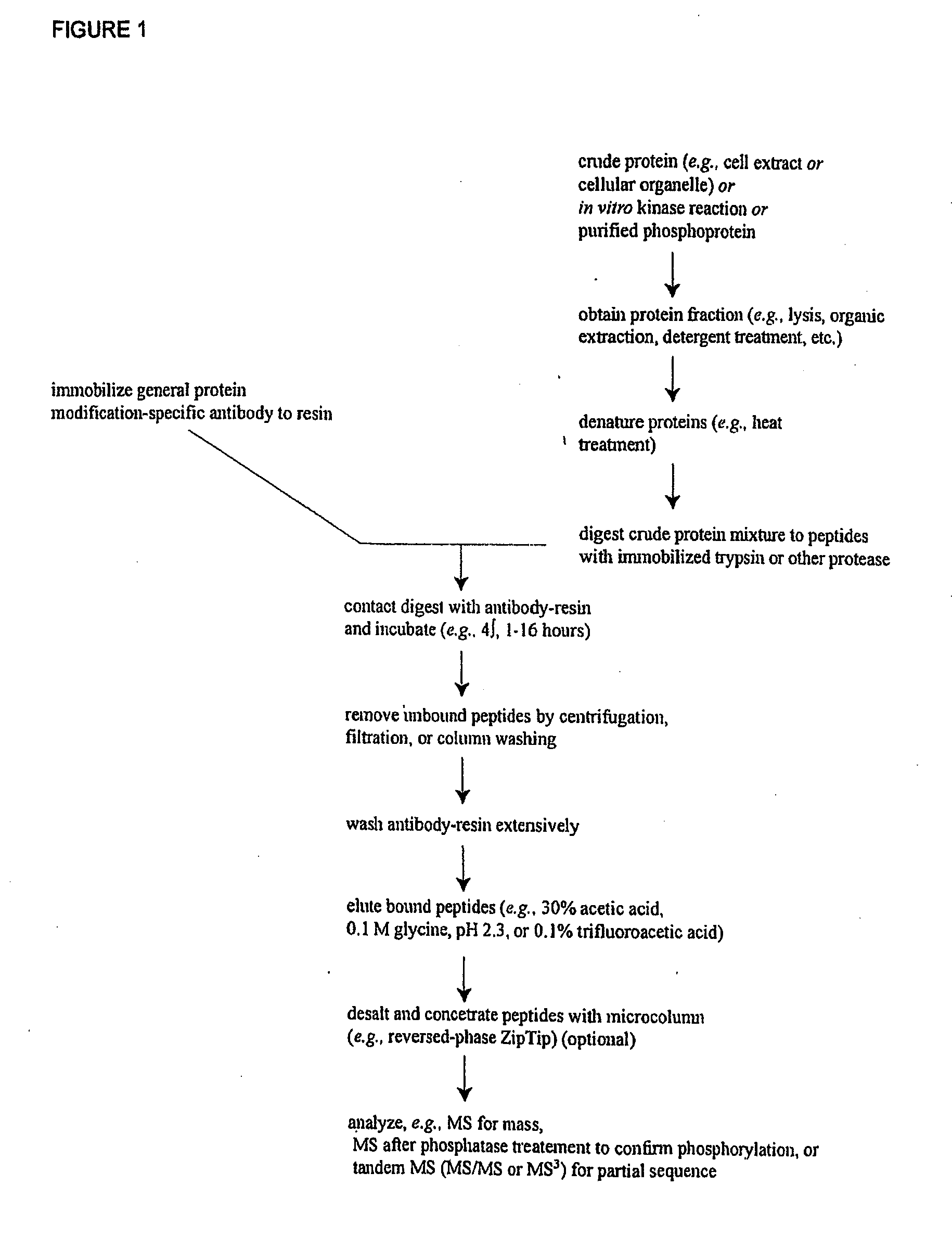
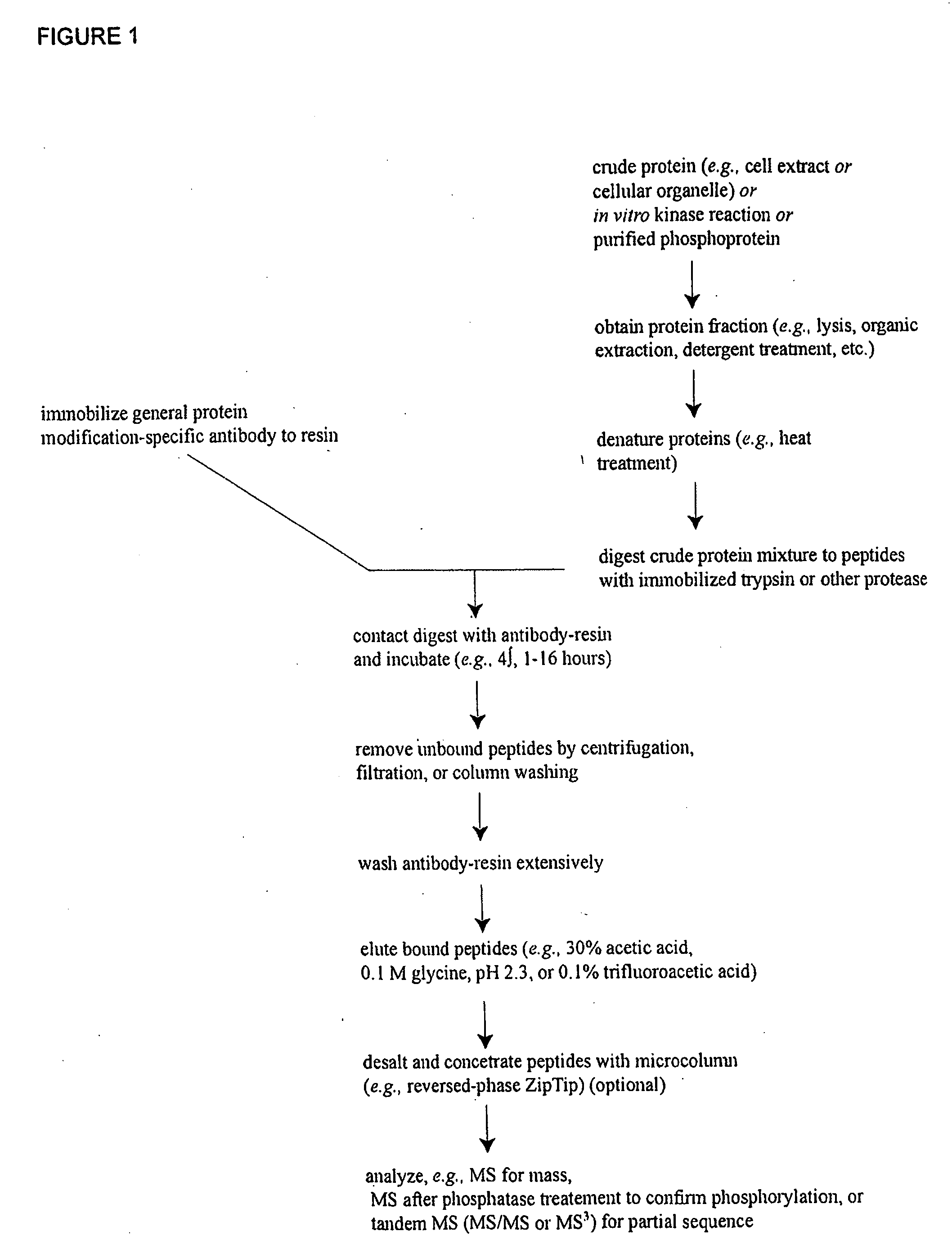
The invention provides methods for isolating a modified peptide from a complex mixture of peptides, the method comprising the steps of: (a) obtaining a proteinaceous preparation from an organism, wherein the preparation comprises modified peptides from two or more different proteins; (b) contacting the preparation with at least one immobilized modification-specific antibody; and (c) isolating at least one modified peptide specifically bound by the immobilized modification-specific antibody in step (b). The method may further comprise the step of (d) characterizing the modified peptide isolated in step (c) by mass spectrometry (MS), tandem mass spectrometry (MS—MS), and / or MS3 analysis, or the step of (e) utilizing a search program to substantially match the spectra obtained for the modified peptide during the characterization of step (d) with the spectra for a known peptide sequence, thereby identifying the parent protein(s) of the modified peptide. Also provided are an immunoaffinity isolation device comprising a modification-specific antibody, and antibodies against novel UFD1 and PTN6 phosphorylation sites.
Owner:CELL SIGNALING TECHNOLOGY
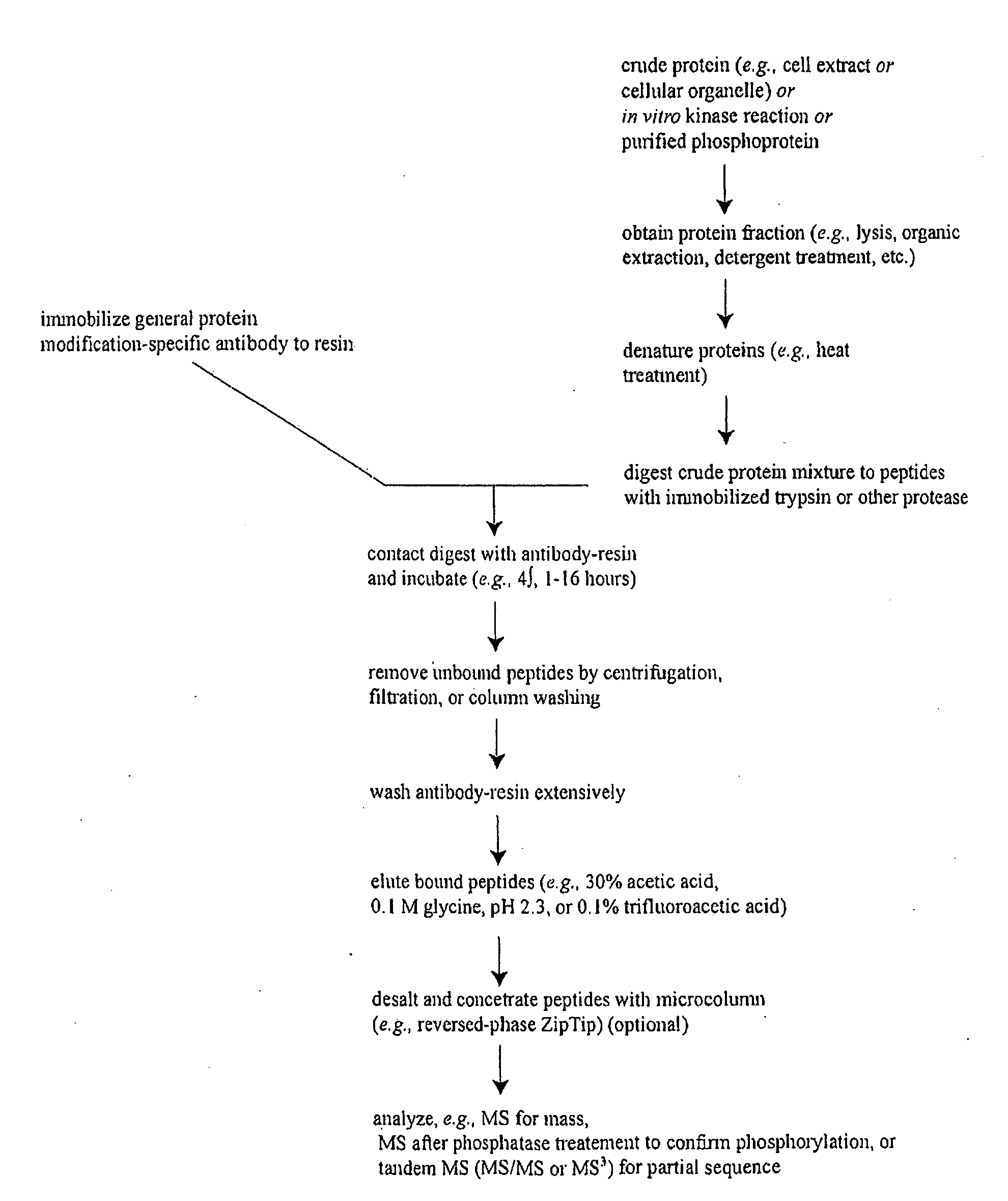
Immunoaffinity isolation of modified peptides from complex mixtures
InactiveUS7300753B2Rapid, efficient, and direct isolation (and subsequent characterization)Improve automationMicrobiological testing/measurementImmunoglobulins against animals/humansBiological bodyPhosphorylation
The invention provides methods for isolating a modified peptide from a complex mixture of peptides, the method comprising the steps of: (a) obtaining a proteinaceous preparation from an organism, wherein the preparation comprises modified peptides from two or more different proteins; (b) contacting the preparation with at least one immobilized modification-specific antibody; and (c) isolating at least one modified peptide specifically bound by the immobilized modification-specific antibody in step (b). The method may further comprise the step of (d) characterizing the modified peptide isolated in step (c) by mass spectrometry (MS), tandem mass spectrometry (MS—MS), and / or MS3 analysis, or the step of (e) utilizing a search program to substantially match the spectra obtained for the modified peptide during the characterization of step (d) with the spectra for a known peptide sequence, thereby identifying the parent protein(s) of the modified peptide. Also provided are an immunoaffinity isolation device comprising a modification-specific antibody, and antibodies against novel UFD1 and PTN6 phosphorylation sites.
Owner:CELL SIGNALING TECHNOLOGY
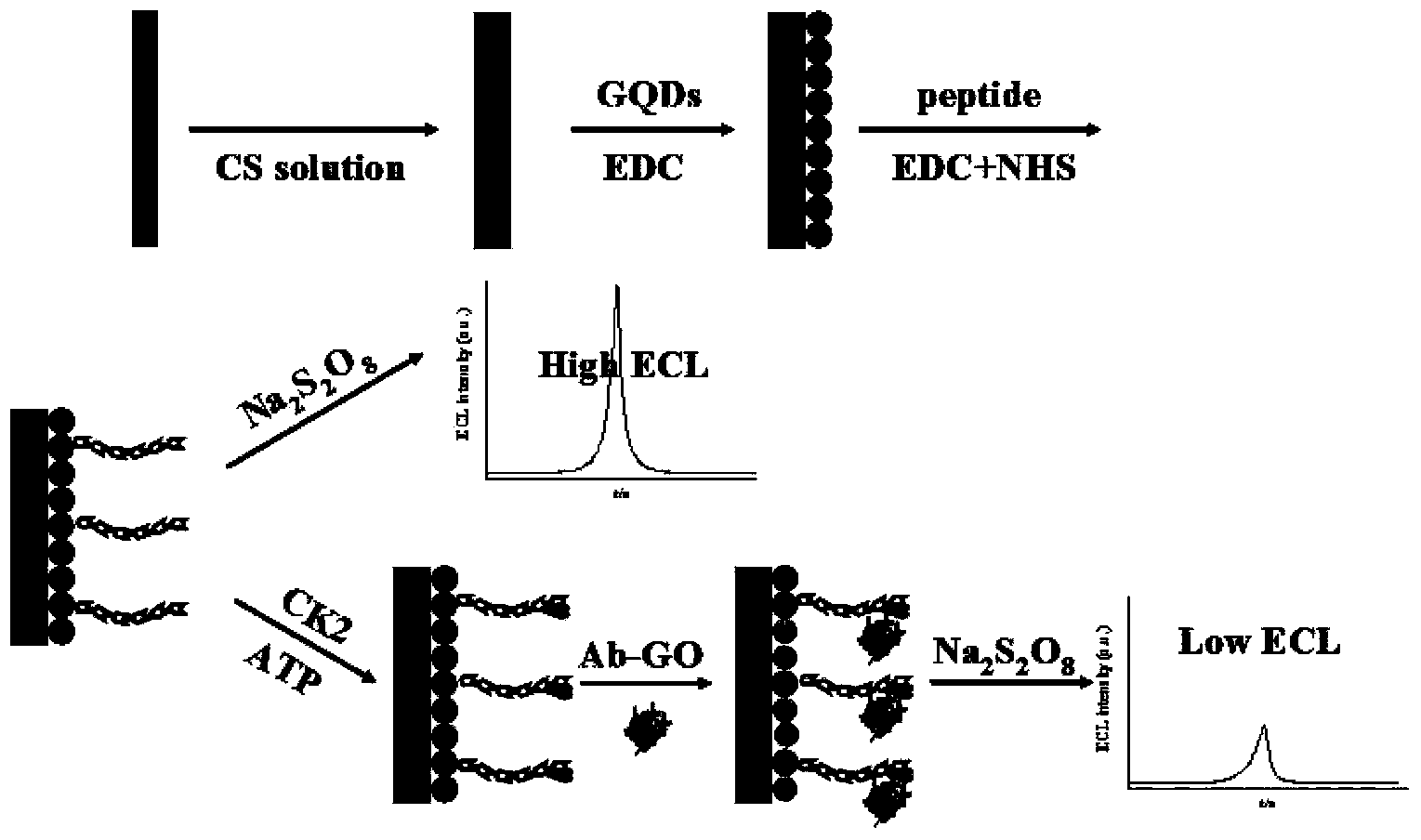
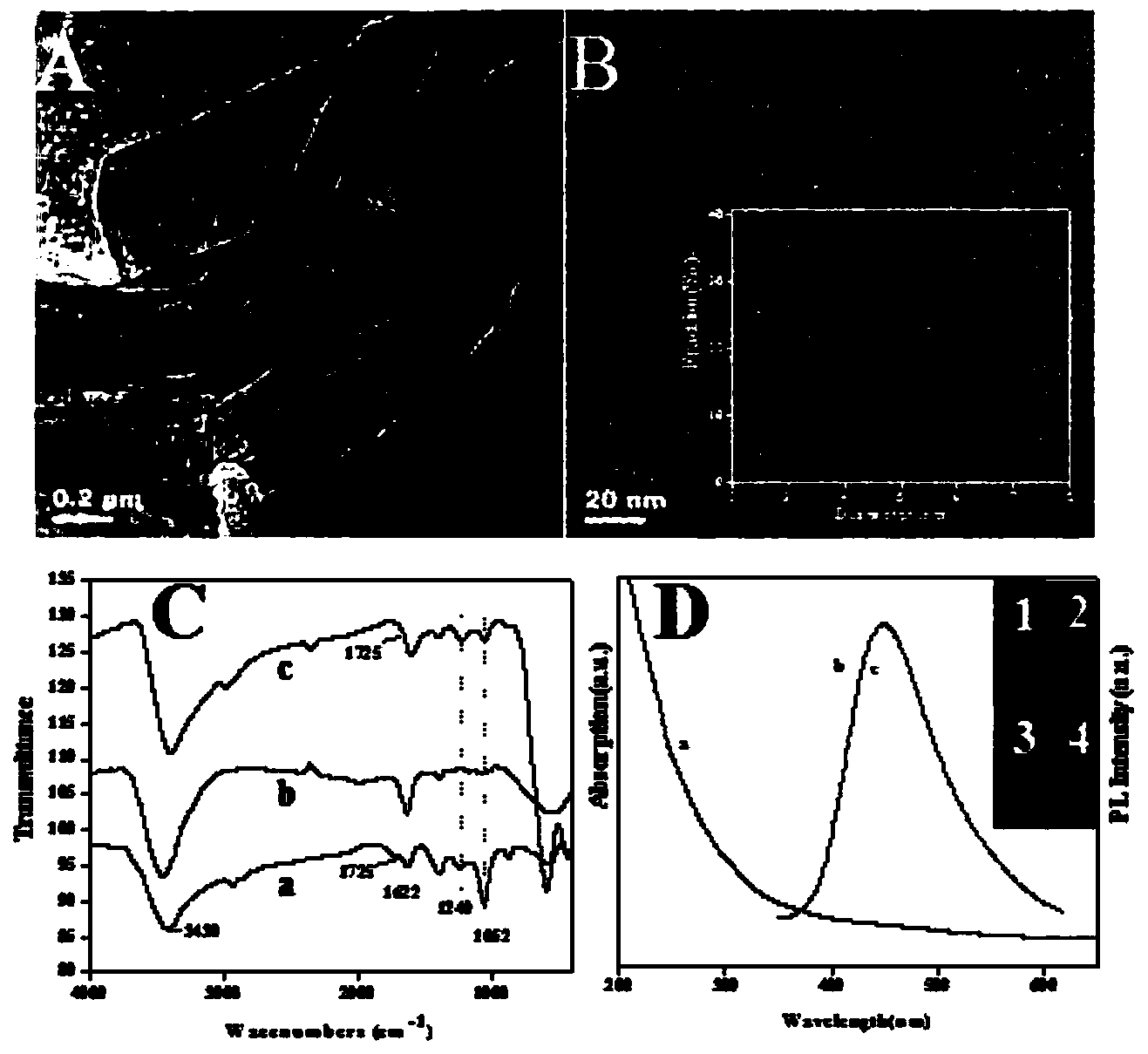
Sensor preparation method based on ECL-RET action between GO and GQDs and application on kinas detection
InactiveCN103512878AHigh sensitivityLow detection limitChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceGrapheneAntigenPhosphorylation
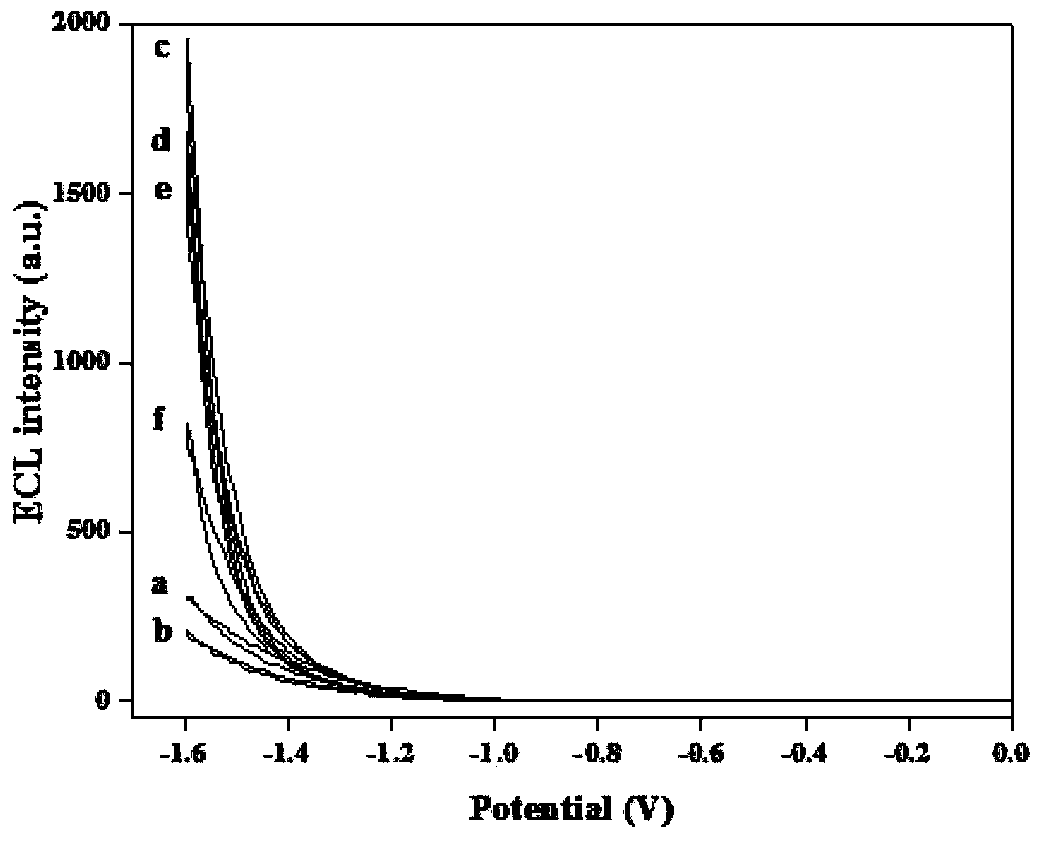
The invention discloses a sensor preparation method based on an ECL-RET action between GO and GQDs and an application on kinas detection, and belongs to the field of electrochemiluminescence (ECL). The preparation method comprises the following steps: coating chitosan on the surface of an electrode, and orderly assembling graphene quantum dots and polypeptides onto the surface of the electrode through a covalent interaction. Under the actions of protein kinase and triphosadenine, the polypeptides carry out phosphorylation reactions, through the specific recognition action between an antibody and an antigen, oxidized graphene conjugated with a phosphorylated antibody is assembled to the phosphorylated serine sites of the polypeptide, thus the distance between the oxidized graphene and the graphene quantum dots is narrowed down, so that the electrochemiluminescence (ECL) of graphene quantum dots is quenched. The larger the concentration of protein kinase is, the more phsophorylated sites are generated on the polypeptide modified electrode surface, the more oxidized graphene is assembled on a sensing interface, the stronger the electrochemiluminescence quenching effect of graphene quantum dots will be, and thus the high sensitive detection on protein kinase is achieved.
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV
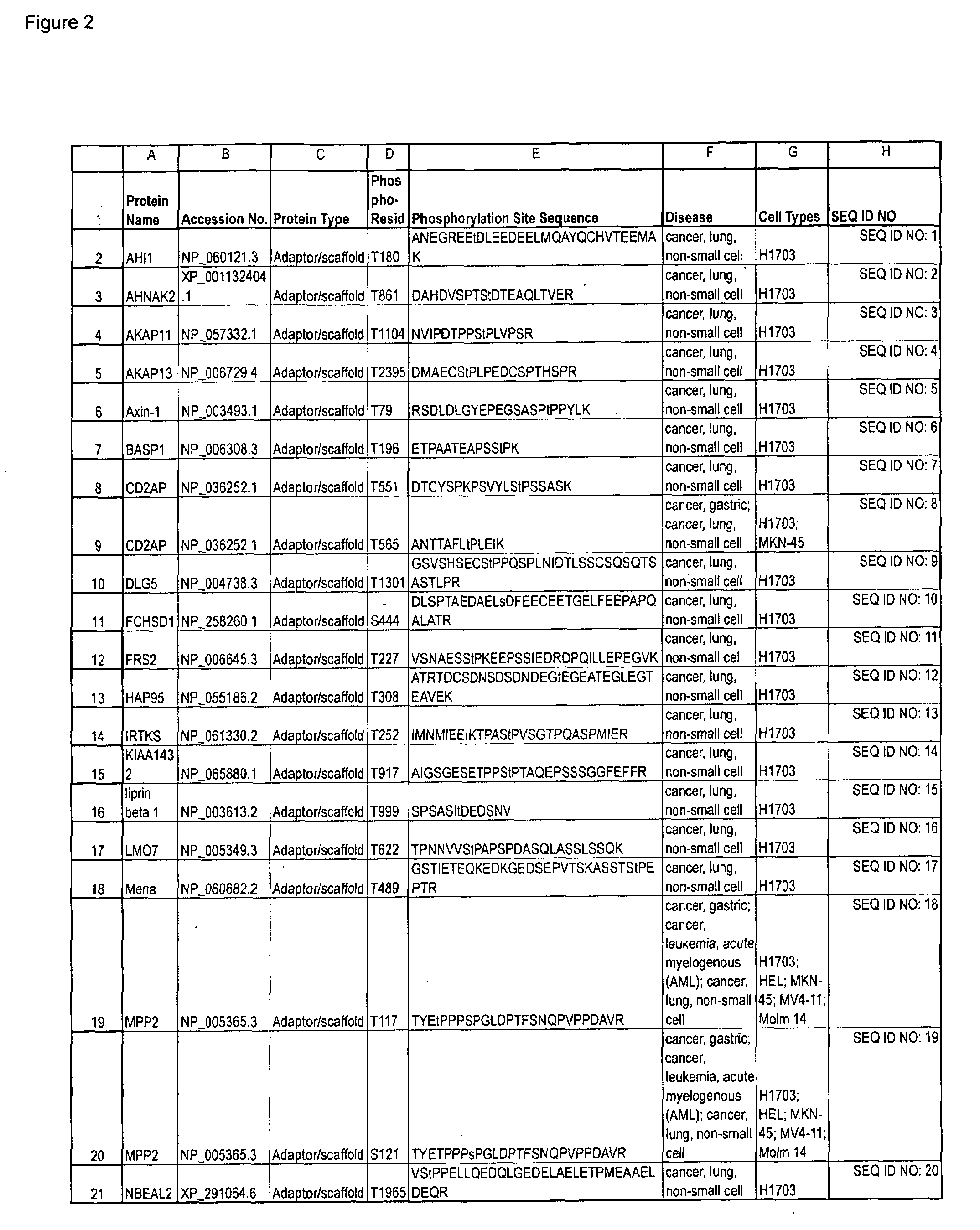
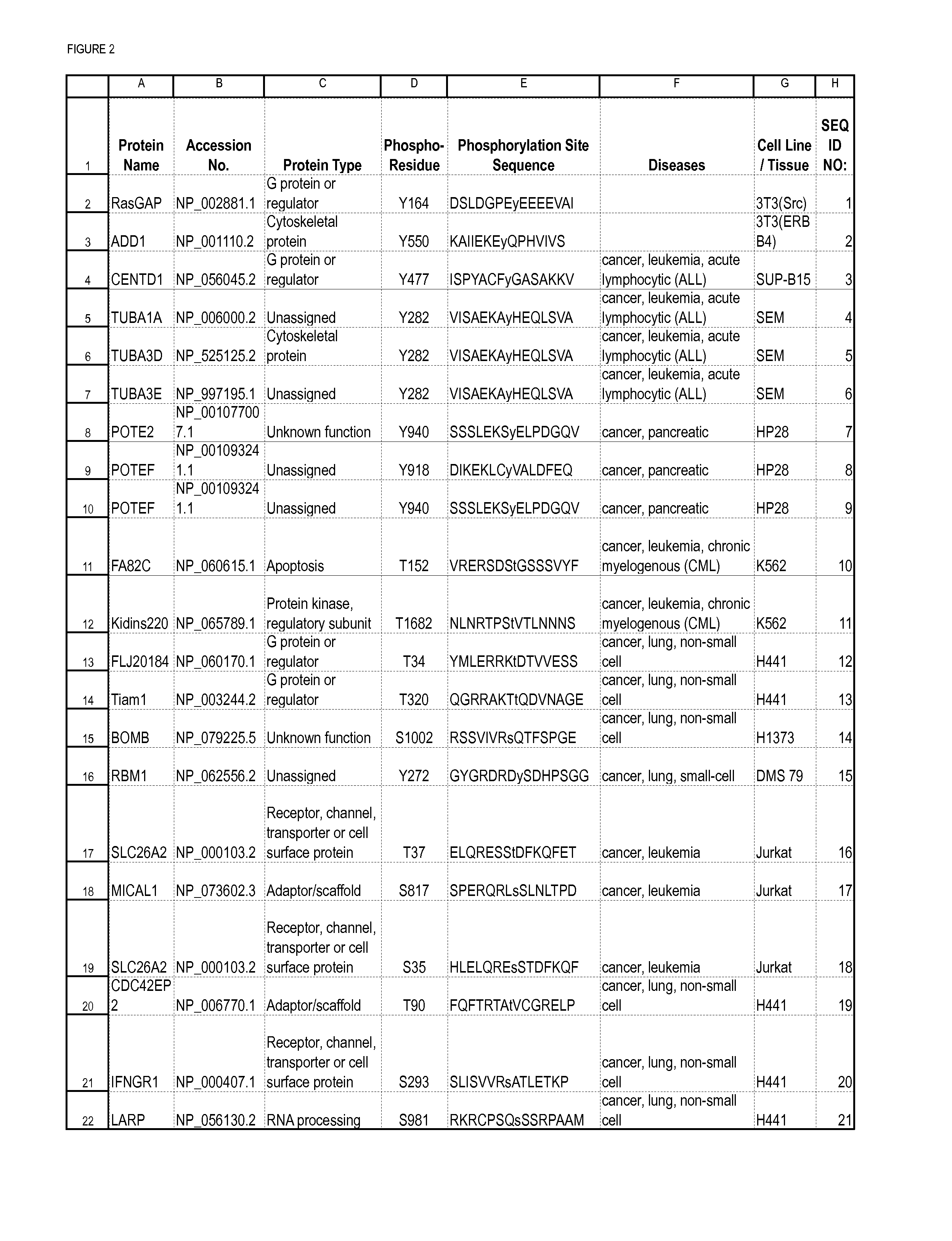
Serine and Threonine Phosphorylation Sites
InactiveUS20110059463A1Immunoglobulins against animals/humansBiological testingAntiendomysial antibodiesPhosphorylation
The invention discloses 726 novel phosphorylation sites identified in carcinoma and leukemia, peptides (including AQUA peptides) comprising a phosphorylation site of the invention, antibodies that specifically bind to a novel phosphorylation site of the invention, and diagnostic and therapeutic uses of the above.
Owner:CELL SIGNALING TECHNOLOGY
Tyrosine phosphorylation sites
ActiveUS7977462B2Immunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsFermentationTreatment usePhosphorylation site
The invention discloses 482 novel phosphorylation sites identified in carcinoma and / or leukemia, peptides (including AQUA peptides) comprising a phosphorylation site of the invention, antibodies specifically bind to a novel phosphorylation site of the invention, and diagnostic and therapeutic uses of the above.
Owner:CELL SIGNALING TECHNOLOGY
Reagents for the detection of protein phosphorylation in carcinoma signaling pathways
InactiveUS20090258442A1Immunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsFermentationPhospholipaseADAMTS Proteins
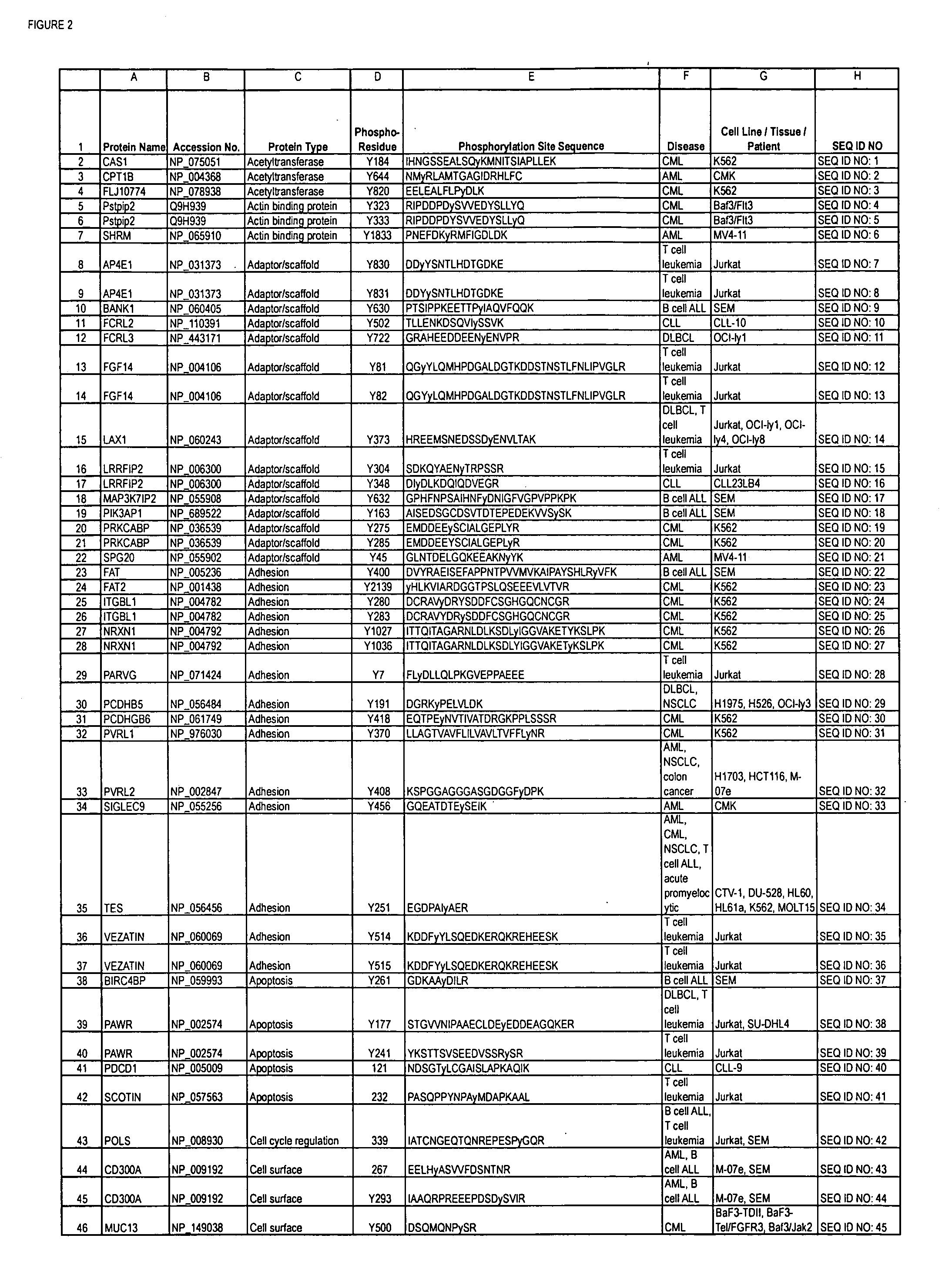
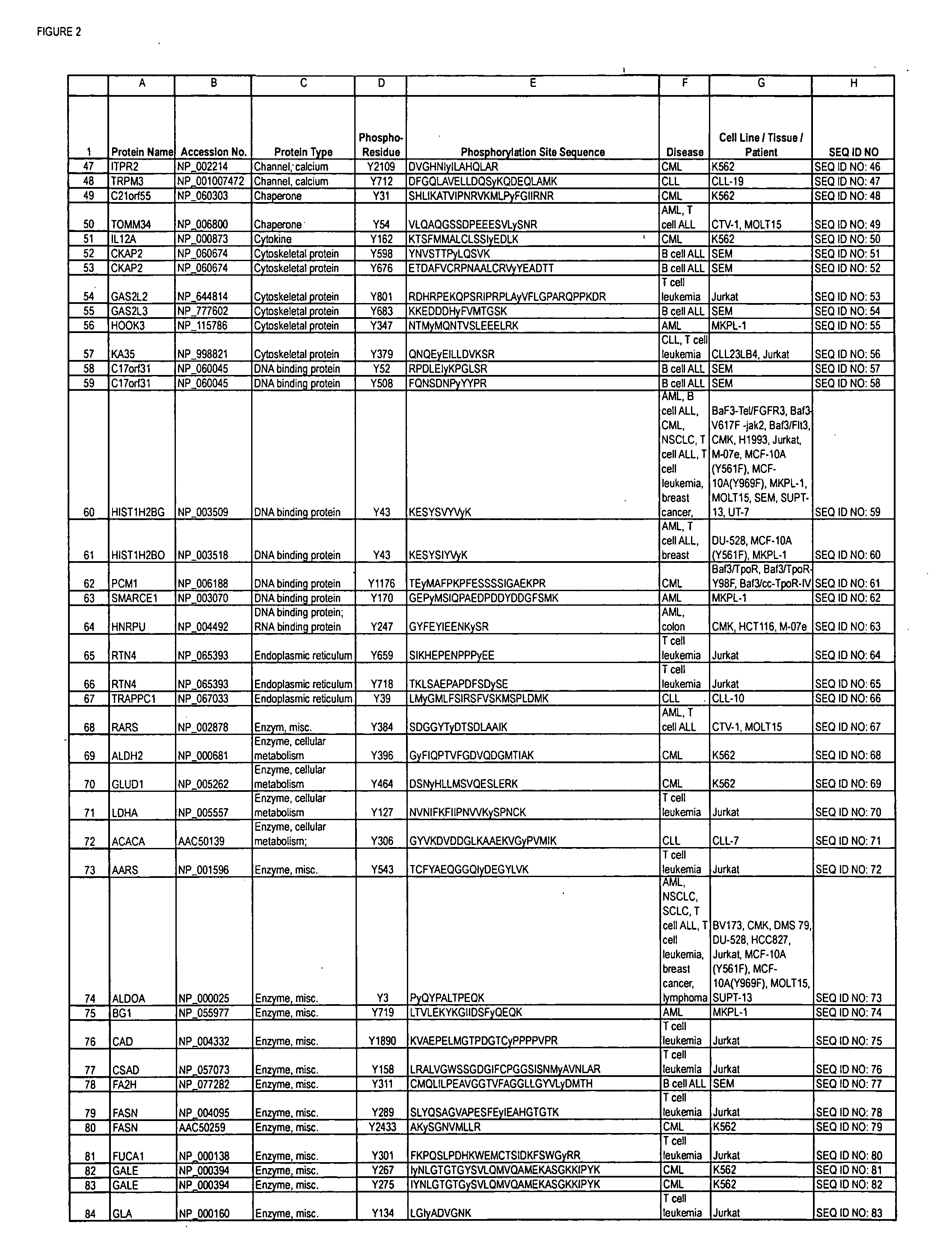
The invention discloses nearly 474 novel phosphorylation sites identified in signal transduction proteins and pathways underlying human carcinoma, and provides phosphorylation-site specific antibodies and heavy-isotope labeled peptides (AQUA peptides) for the selective detection and quantification of these phosphorylated sites / proteins, as well as methods of using the reagents for such purpose. Among the phosphorylation sites identified are sites occurring in the following protein types: Kinase, Adaptor / Scaffold proteins, Phosphatase, G protein Regulator / Guanine Nucleotide Exchange Factors / GTPase Activating Proteins, Cytoskeleton Proteins, DNA Binding Proteins, Phospholipase, Receptor Proteins, Enzymes, DNA Repair / Replication Proteins, Adhesion Proteins, and Proteases, as well as other protein types.
Owner:CELL SIGNALING TECHNOLOGY
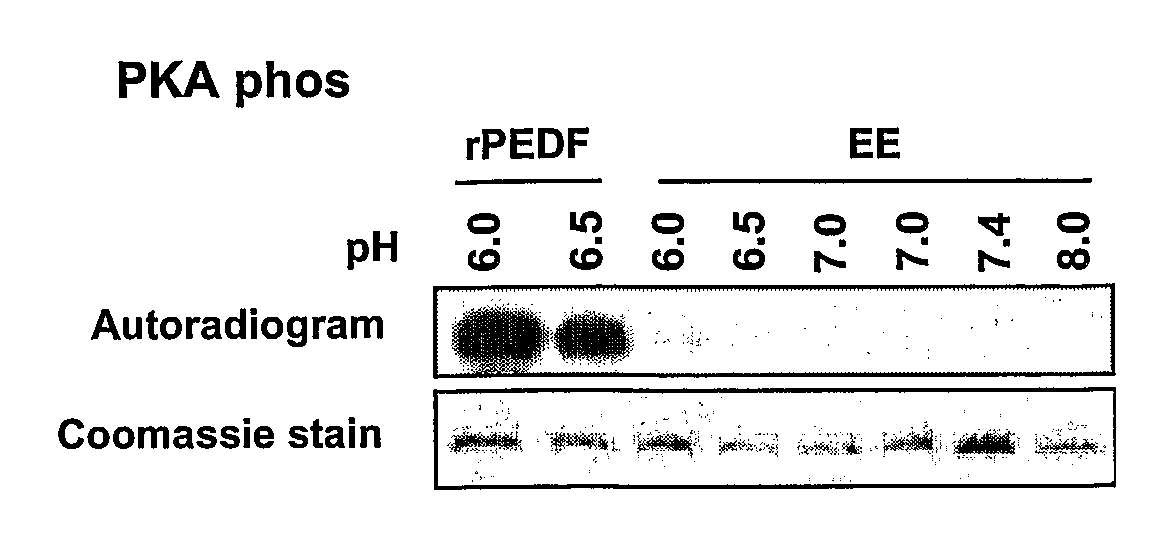
Variants of Pigment Epithelium Derived Factor and Uses Thereof
InactiveUS20080274967A1Negligible neurotrophic activityGood anti-angiogenic activityOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderPIGMENT EPITHELIUM-DERIVED FACTORPhosphorylation
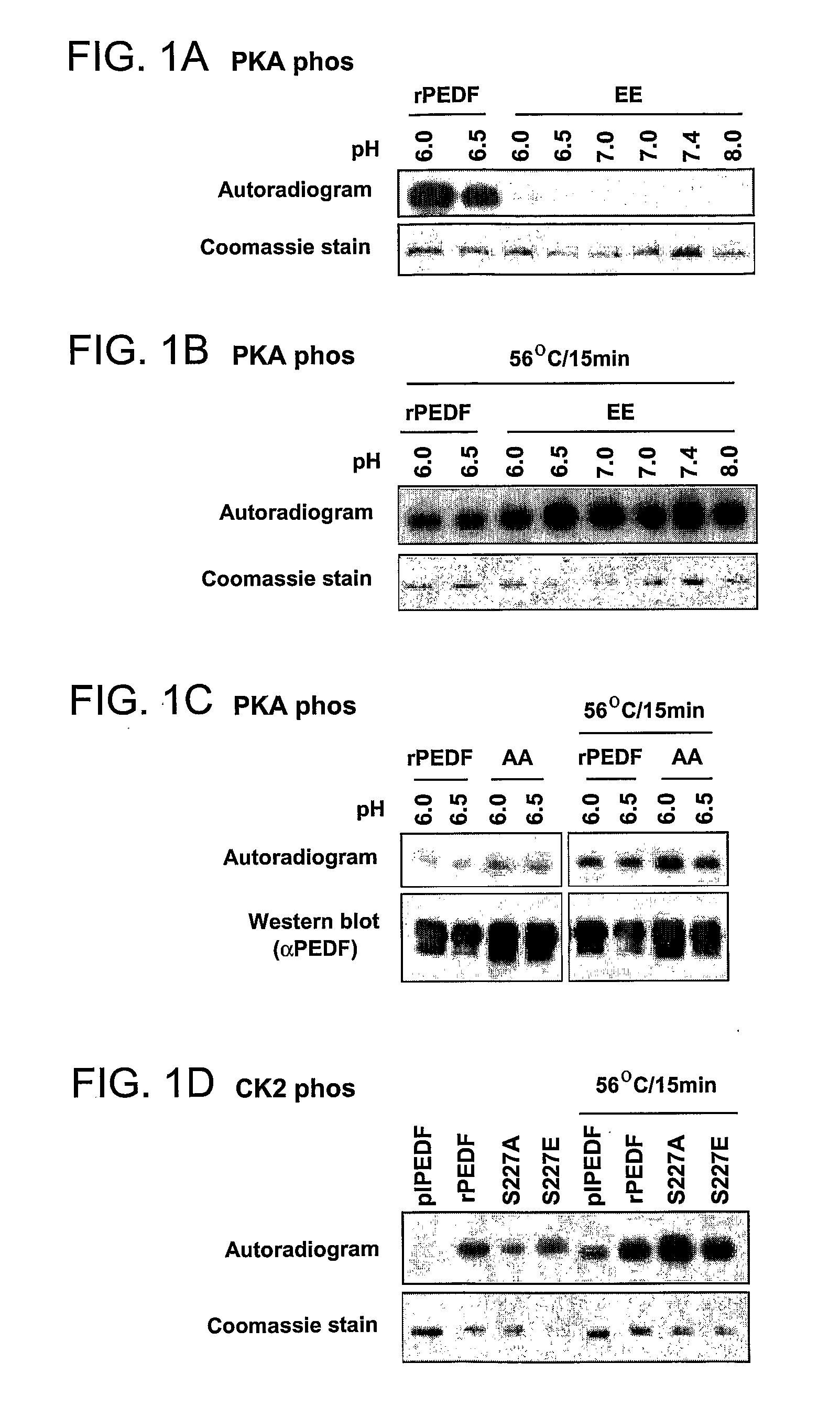
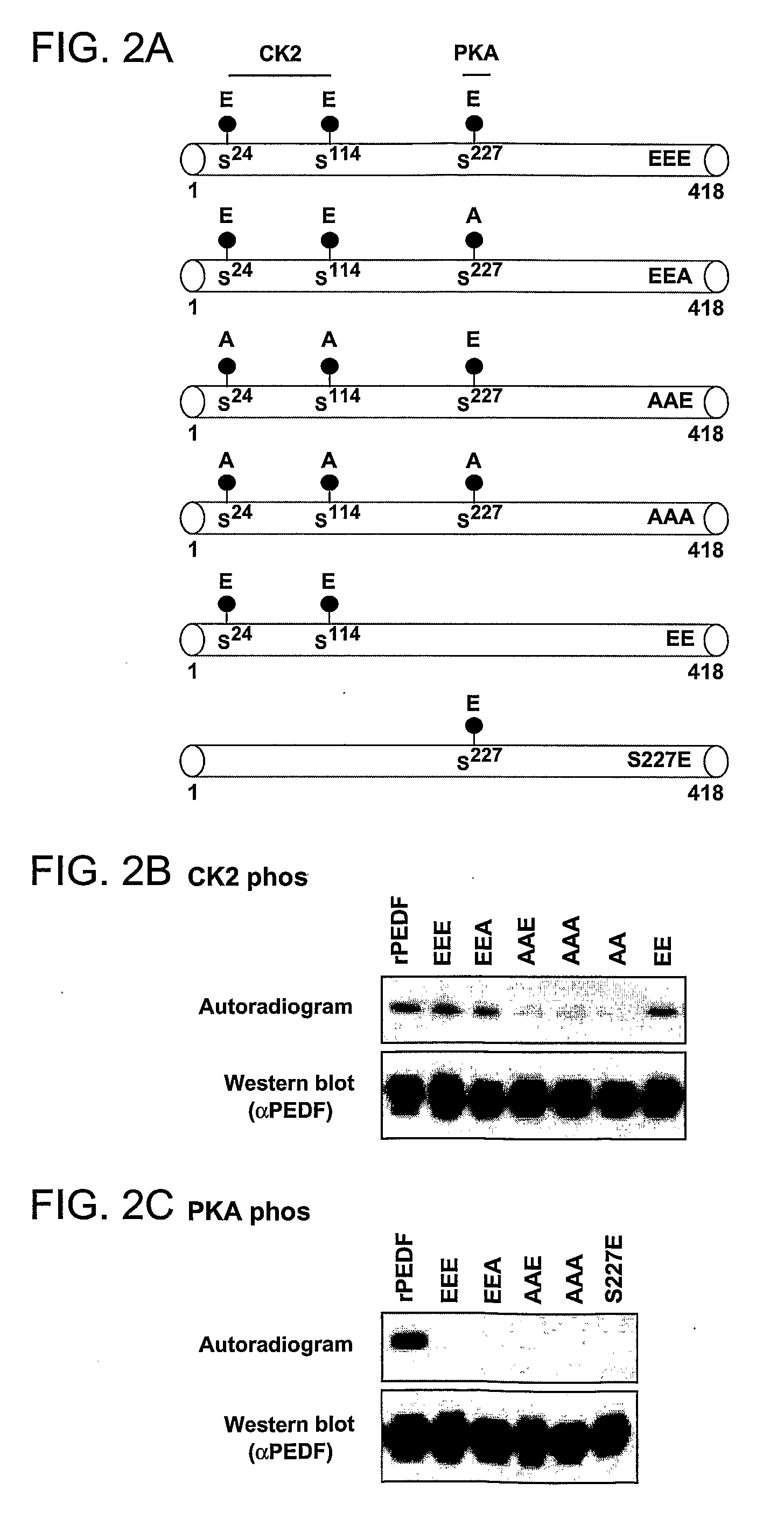
The present invention relates to anti-angiogenic variants of pigment epithelium derived factor (PEDF) comprising a plurality of altered phosphorylation sites, polynucleotides encoding same and uses thereof. In particular, the PEDF variants of the present invention provide superior anti-angiogenic activity and high neurotrophic activity and are useful in treating diseases associated with neovascularization and with neurodegenerative conditions.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
Method for quantifying phosphokinase activity on proteins
InactiveUS20090104628A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisProtein targetTyrosine
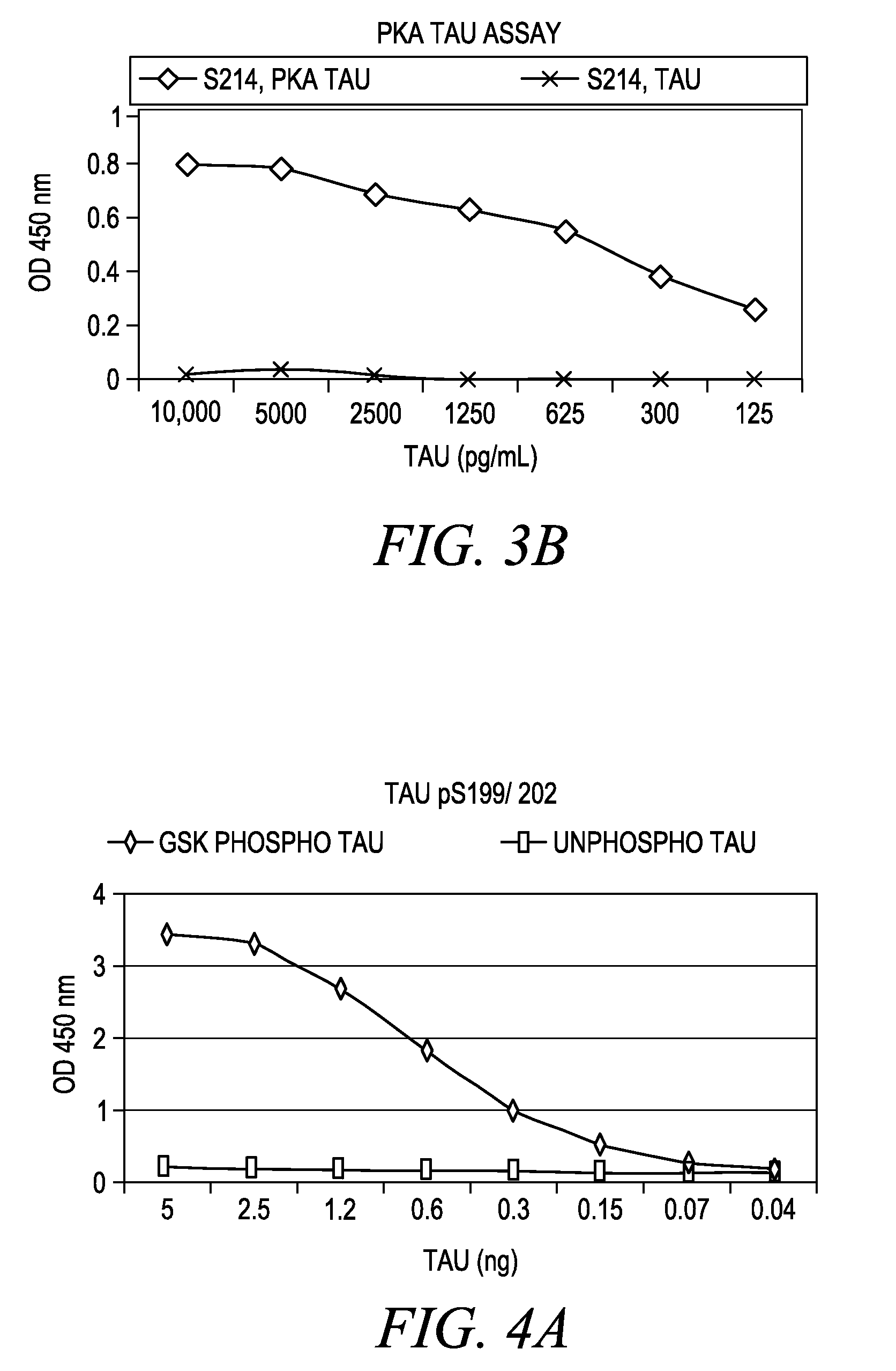
The invention involves a method for measuring phosphorylation of proteins at specific sites and, as such, is an indicator of the protein kinase activity of enzymes capable of phosphorylating those sites. The method involves the in vitro or in vivo phosphorylation of a target protein at a specific serine, threonine or tyrosine residue, subjecting that protein (non-phosphorylated) to reaction mixture containing all reagents, including phosphokinase which allow the creation of a phosphorylated form of protein. The phosphorylated protein is measured by contacting it with an antibody specific for the phosphorylation site(s). The invention includes antibodies useful in practicing the methods of the invention. The invention particularly relates to all proteins modified by phosphorylation and dephosphorylation as illustrated by Tau, Rb and EGFR proteins and antibodies specific for the site of phosphorylation of the Tau, Rb or EGFR proteins.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Applications of ZrO2 in the process for concentrating and purifying phosphorylated peptides
InactiveCN101284864ALarge specific surface areaHigh selectivityPeptide preparation methodsPhosphopeptidePhosphorylation site
The invention relates to the enrichment and purification of phosphopeptide in phosphoproteome, in particular to the application of ZrO2 in the enrichment and purification of phosphopeptide. ZrO2 nano material shows high specificity, selectivity, binding capacity and sensitivity at a phosphopeptide section; meanwhile, the affinity of the ZrO2 nano material to the specificity of phosphopeptide ensures that the material can be used in phosphoproteome during protein post-translational modification. Due to the specificity combination of ZrO2 with the phosphopeptide section in complex proteolysis sample, large-scale identification of phosphorylated protein and determination of phosphorylation sites can be realized through combining with MALDI-TOF MS and nano-LC MS / MS.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Reagents for the detection of protein phosphorylation in signaling pathways
InactiveUS20100009463A1Animal cellsIsotope introduction to peptides/proteinsCell Surface ProteinsPhosphorylation
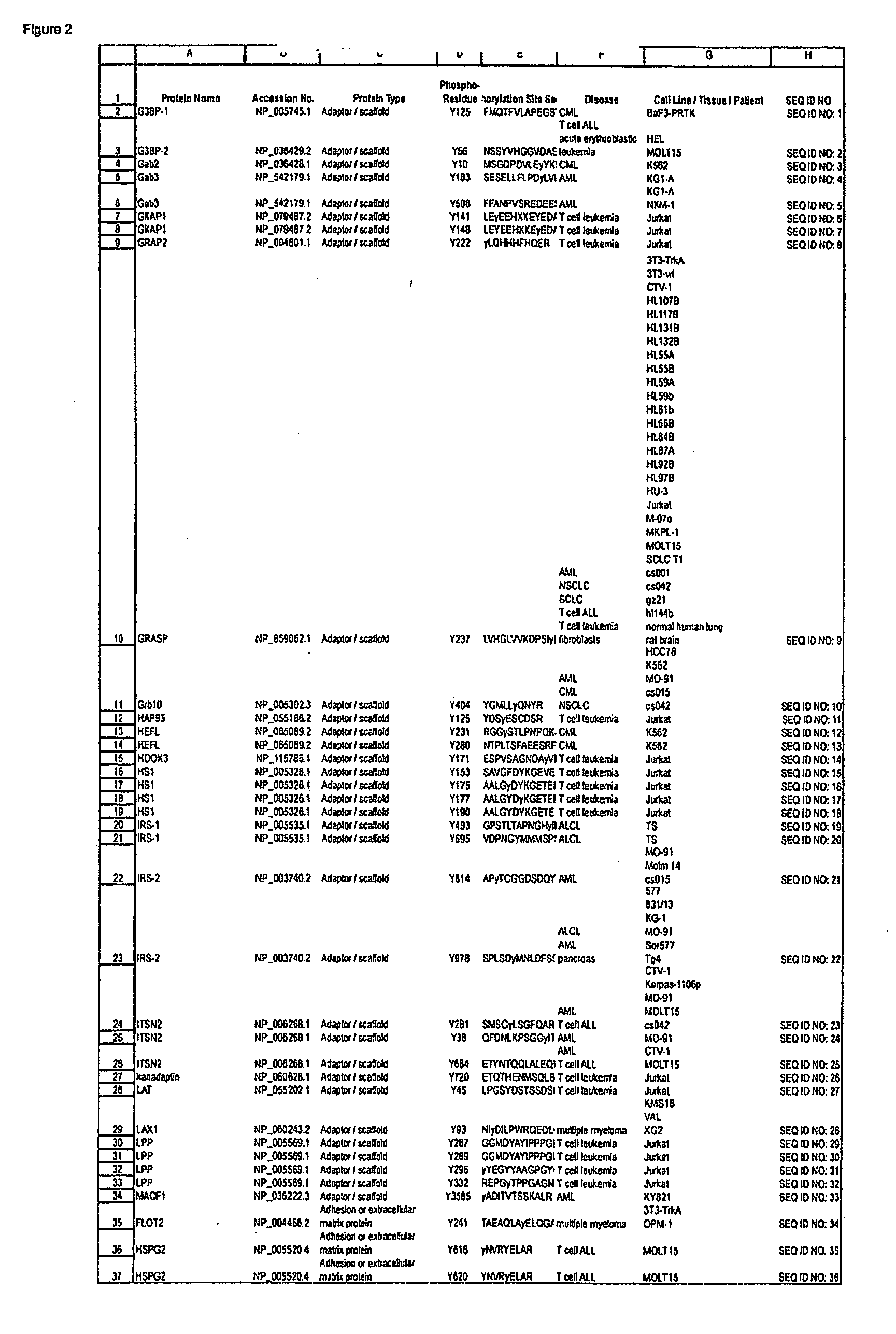
The invention discloses novel phosphorylation sites identified in signal transduction proteins and pathways, and provides phosphorylation-site specific antibodies and heavy-isotope labeled peptides (AQUA peptides) for the selective detection and quantification of these phosphorylated sites / proteins, as well as methods of using the reagents for such purpose. Among the phosphorylation sites identified are sites occurring in the following protein types: adaptor / scaffold proteins, adhesion / extracellular matrix protein, apoptosis proteins, calcium binding proteins, cell cycle regulation proteins, chaperone proteins, chromatin, DNA binding / repair / replication proteins, cytoskeletal proteins, endoplasmic reticulum or golgi proteins, enzyme proteins, G / regulator proteins, inhibitor proteins, motor / contractile proteins, phosphatase, protease, Ser / Thr protein kinases, protein kinase (Tyr)s, receptor / channel / cell surface proteins, RNA binding proteins, transcriptional regulators, tumor suppressor proteins, ubiquitan conjugating system proteins and proteins of unknown function.
Owner:CELL SIGNALING TECHNOLOGY
Agents for prophylaxis or treatment of neurological related diseases and conditions
InactiveUS20080306007A1Reduce the binding forceNervous disorderHydrolasesCell vesiclePhosphorylation
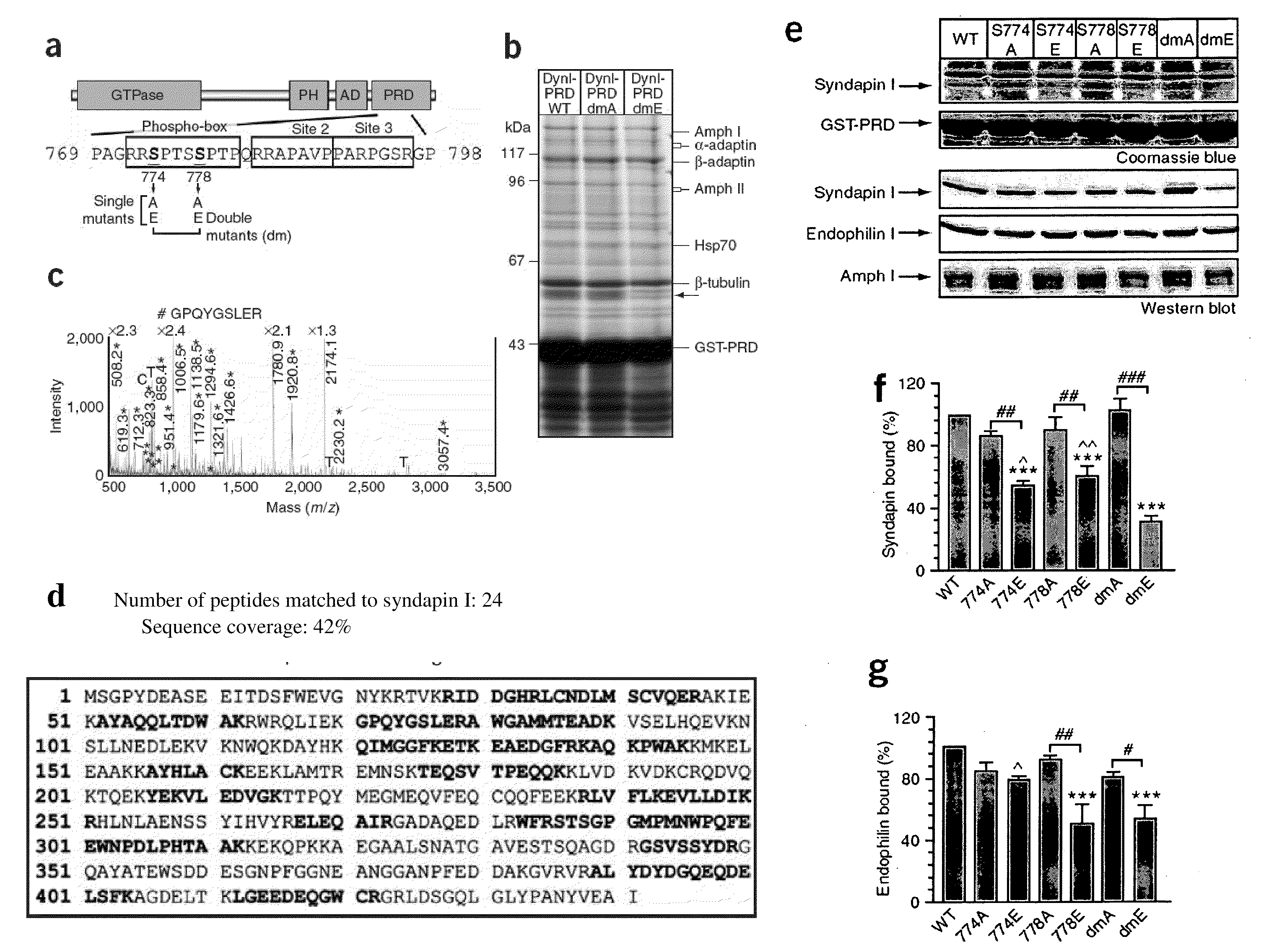
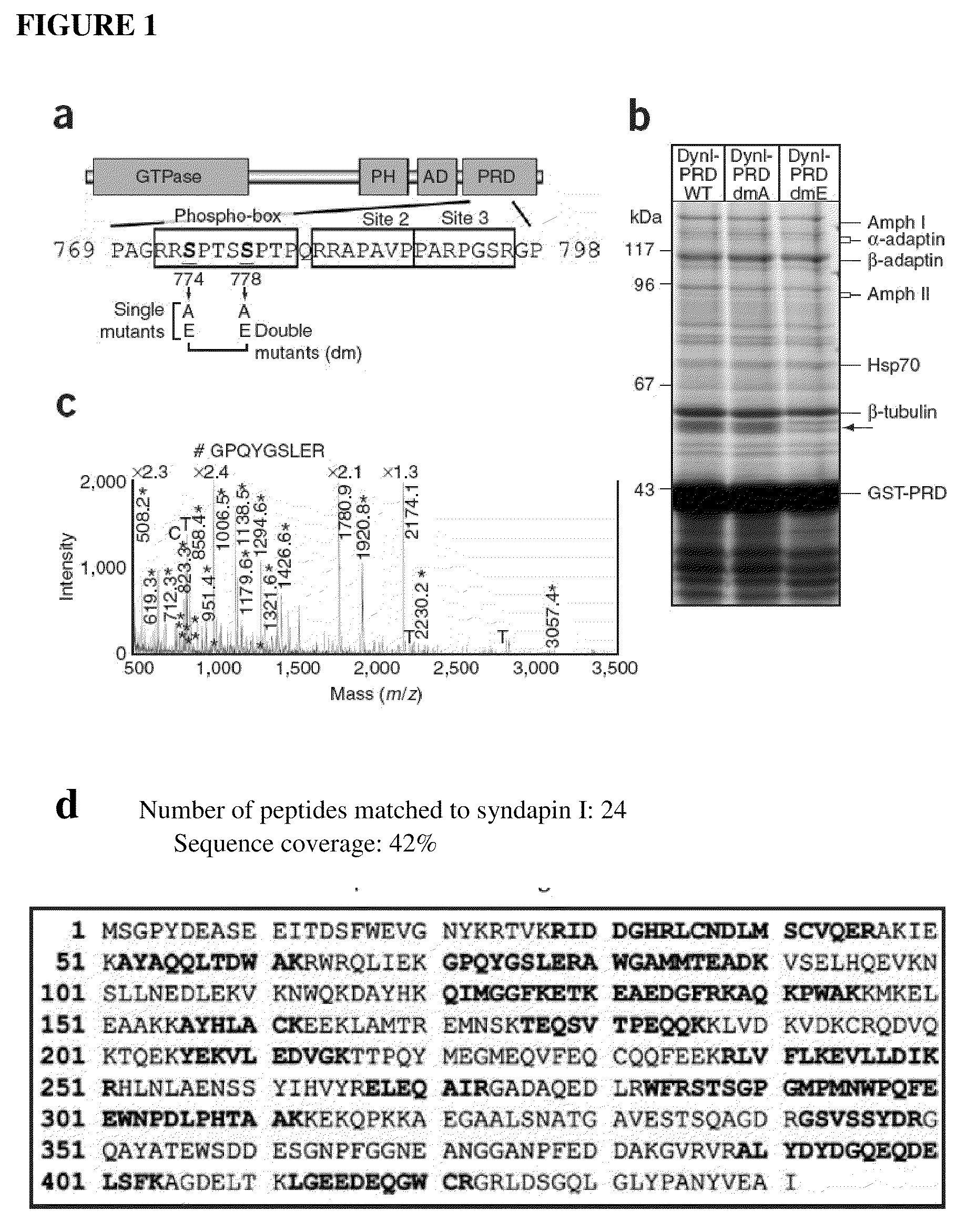
Inhibitors of syndapin I binding to dynamin I (DynI) are provided. Examples include mimetics of a region of DynI including the serine residues S774 and S778 or phosphorylatable amino acids in homologous positions. Typically, the mimetics exclude or do not imitate at least one phosphorylation site provided by the serine residues or phosphorylatable amino acids. Peptide fragment inhibitors comprising or consisting of this region of DynI are also described. The inhibitors have application in the prophylaxis or treatment of neurological diseases or conditions. The inhibitors can also be used to inhibit neuronal cell vesicle trafficking and synaptic signal transmission.
Owner:CHILDRENS MEDICAL RES INST +2
Reagents for the detection of protein phosphorylation in Leukemia signaling pathways
ActiveUS20080248490A1Immunoglobulins against animals/humansBiological testingHuman leukemiaADAMTS Proteins
The invention discloses nearly 288 novel phosphorylation sites identified in signal transduction proteins and pathways underlying human Leukemia, and provides phosphorylation-site specific antibodies and heavy-isotope labeled peptides (AQUA peptides) for the selective detection and quantification of these phosphorylated sites / proteins, as well as methods of using the reagents for such purpose. Among the phosphorylation sites identified are sites occurring in the following protein types: Adaptor / Scaffold proteins, Cytoskeletal proteins, Cellular Metabolism enzymes, G Protein / GTPase Activating / Guanine Nucleotide Exchange Factor proteins, Immunoglobulin Superfamily proteins, Inhibitor proteins, Lipid Kinases, Nuclear DNA Repair / RNA Binding / Transcription proteins, Serine / Threonine Protein Kinases, Tyrosine Kinases, Protein Phosphatases, and Translation / Transporter proteins.
Owner:CELL SIGNALING TECHNOLOGY
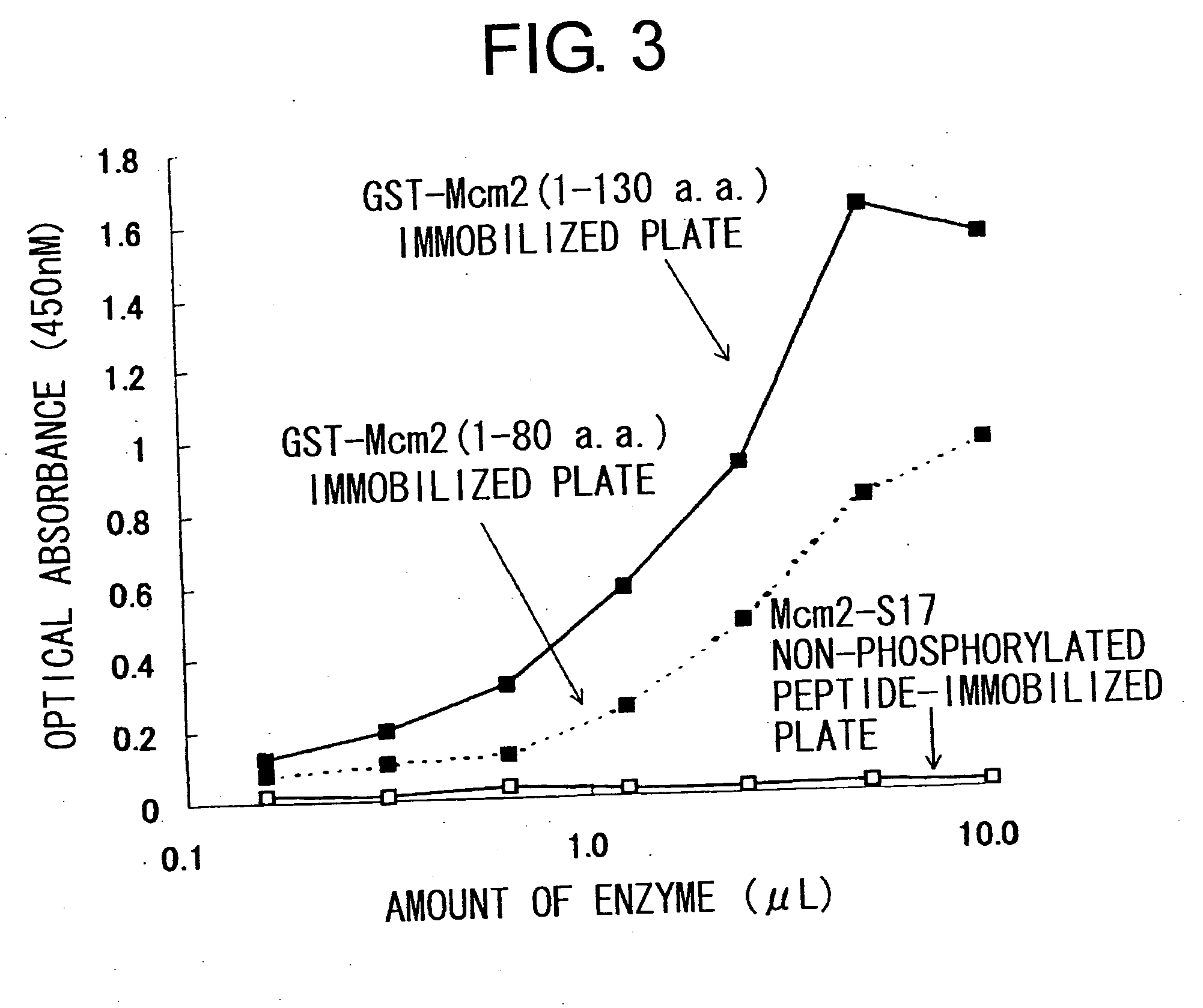
Cdc7-ask kinase complex, substrates of the kinase complex, antibody specific to the substrate, and method of screening compound capable of inhibiting cdc7-ask kinase using the same
InactiveUS20050250166A1Effective anticancer agentsCompound screeningApoptosis detectionAnticarcinogenPhosphorylation
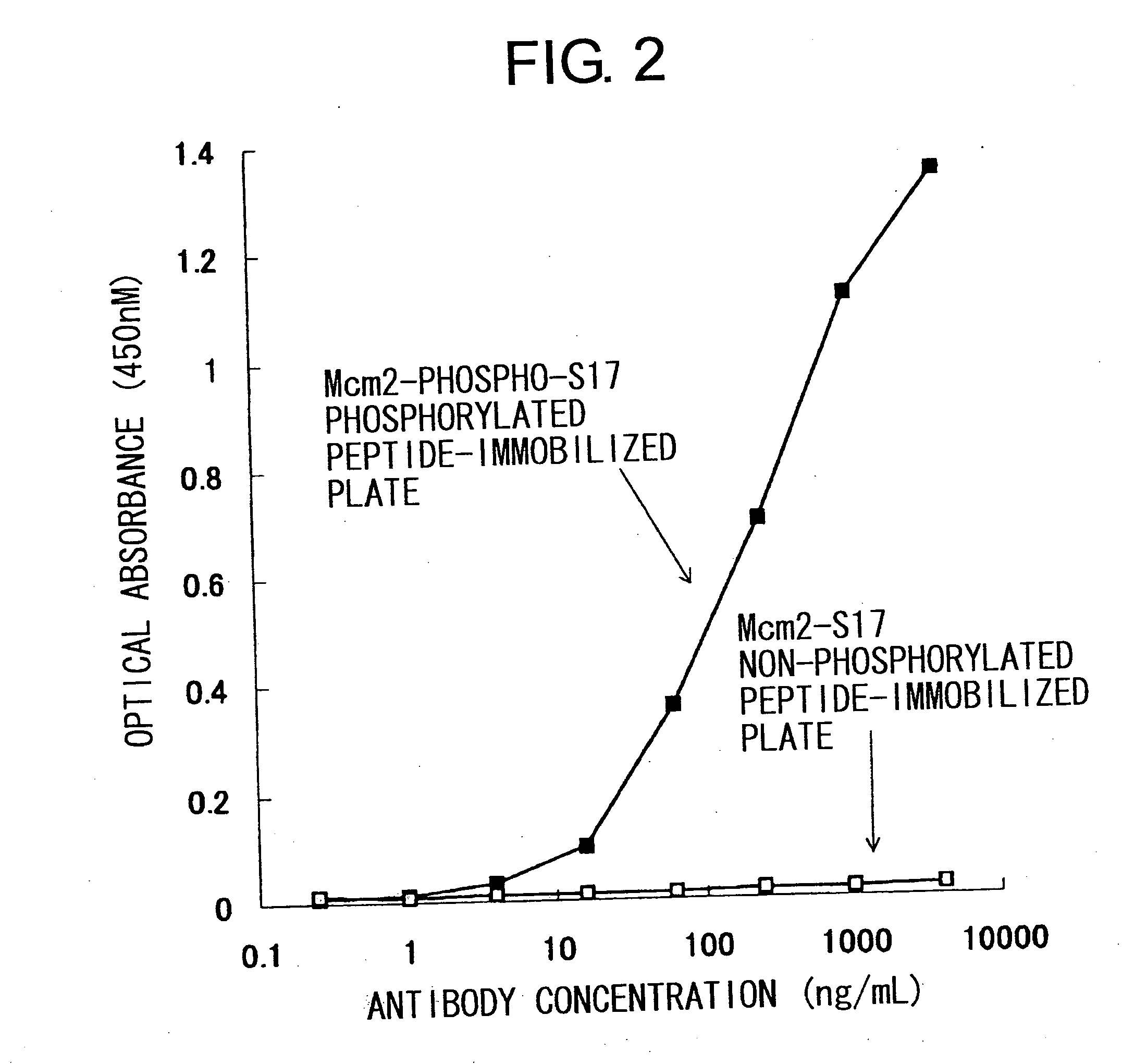
The present invention provides methods for measuring the phosphorylation activity of Cdc7-ASK kinase complex by using as an indicator the level of phosphorylation at a phosphorylation site of MCM, which is a substrate of Cdc7-ASK kinase complex. The effects of test compounds on the phosphorylation activity of Cdc7-ASK kinase complex can also be evaluated based on these measurement methods. Compounds that inhibit this phosphorylation activity are useful as anti-cancer agents having superior specificity for cancer.
Owner:GINKGO BIOMEDICAL RES INST +2
Tyrosine phosphorylation sites
InactiveUS20090325189A1Immunoglobulins against animals/humansBiological testingTreatment usePhosphorylation site
The invention discloses 443 novel phosphorylation sites identified in leukemia, peptides (including AQUA peptides) comprising a phosphorylation site of the invention, antibodies specifically bind to a novel phosphorylation site of the invention, and diagnostic and therapeutic uses of the above.
Owner:CELL SIGNALING TECHNOLOGY
Serine and threoninephosphorylation sites
InactiveUS20090068684A1Immunoglobulins against animals/humansDisease diagnosisPhosphorylationThreonine Phosphorylation Site
The invention discloses 345 novel phosphorylation sites identified in carcinoma and leukemia, peptides (including AQUA peptides) comprising a phosphorylation site of the invention, antibodies specifically bind to a novel phosphorylation site of the invention, and diagnostic and therapeutic uses of the above.
Owner:CELL SIGNALING TECHNOLOGY
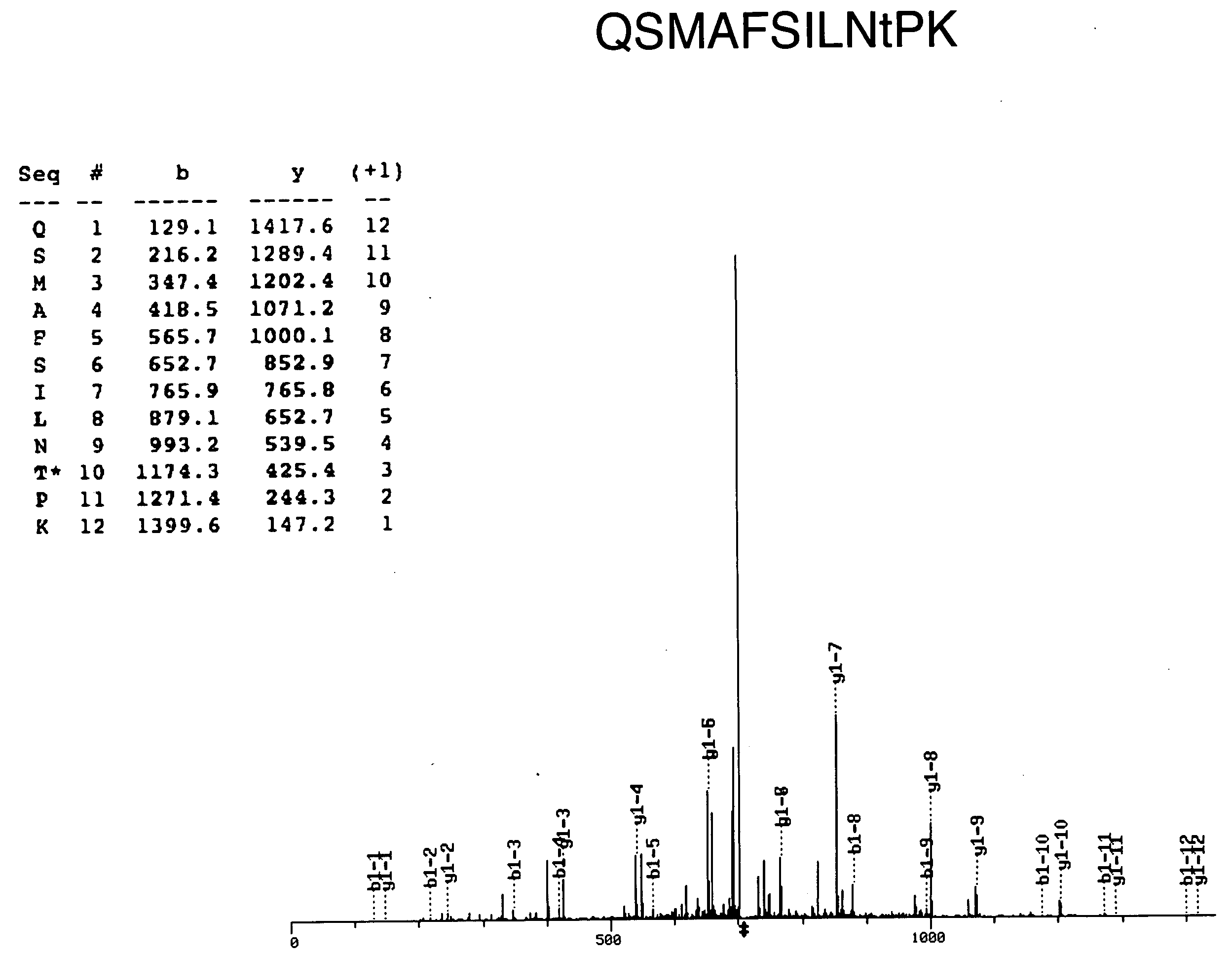
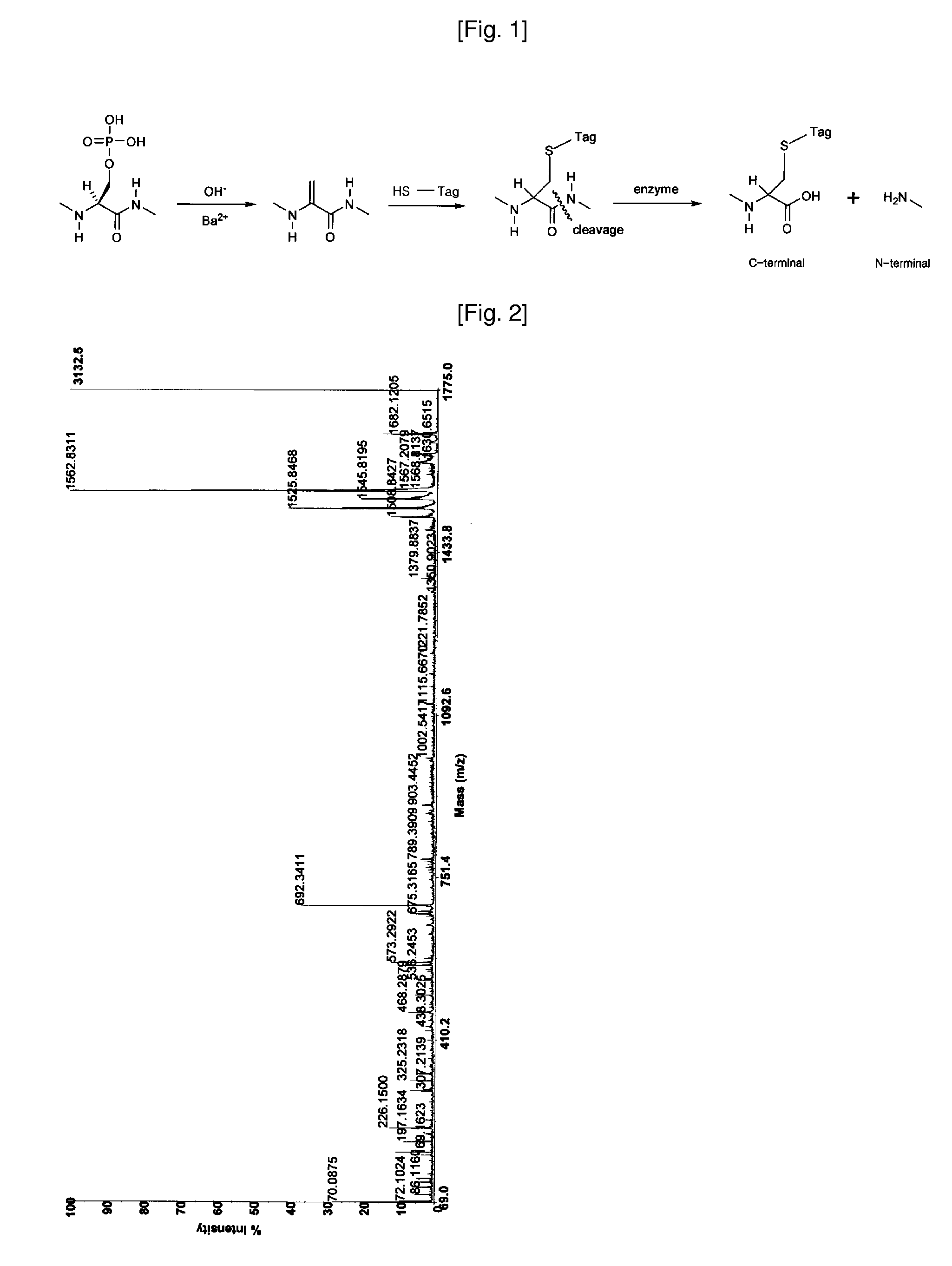
In-gel tagging and in-gel digestion for phosphoproteins analysis and phosphorylation site identification
The present invention relates to a method for phosphorylation site-specific labeling of phosphoproteome with a site-specific tagging reagent and analyzing of the resulting labeled one, more especially, a method for in-situ tagging of phosphorylation sites of phosphoproteins retained in polymeric gel with a nucleophilic tagging reagent. It also relates a method for generating new proteolytic cleavable sites at formerly phosphorylation sites by a proper choice of a nucleophilic tagging reagent. It also relates to a method for phosphopeptides analysis and phosphorylation site identification by in-gel digestion of the previously in-gel tagged proteins and subsequent mass analysis of the resulting peptides. The invention provides in-gel chemical tagging method for phosphoaminoacid residue of phosphoproteins retained in polymeric gel matrix. Phosphoprotein can be immobilized into gel matrix by a variety of methods such as gel electrophoresis. The immobilized phosphoproteins are retained in gel matrix during tagging reaction to phosphorylated aminoacid residue of phosphoproteins, and the resulting tagged proteins are also retained in gel matrix till following purification steps like washing of the tagging reagents are accomplished. The tagged proteins is digested by protease, and the resulting digested peptides is released from gel into solution and applied for peptide mass analysis.
Owner:KOREA BASIC SCI INST
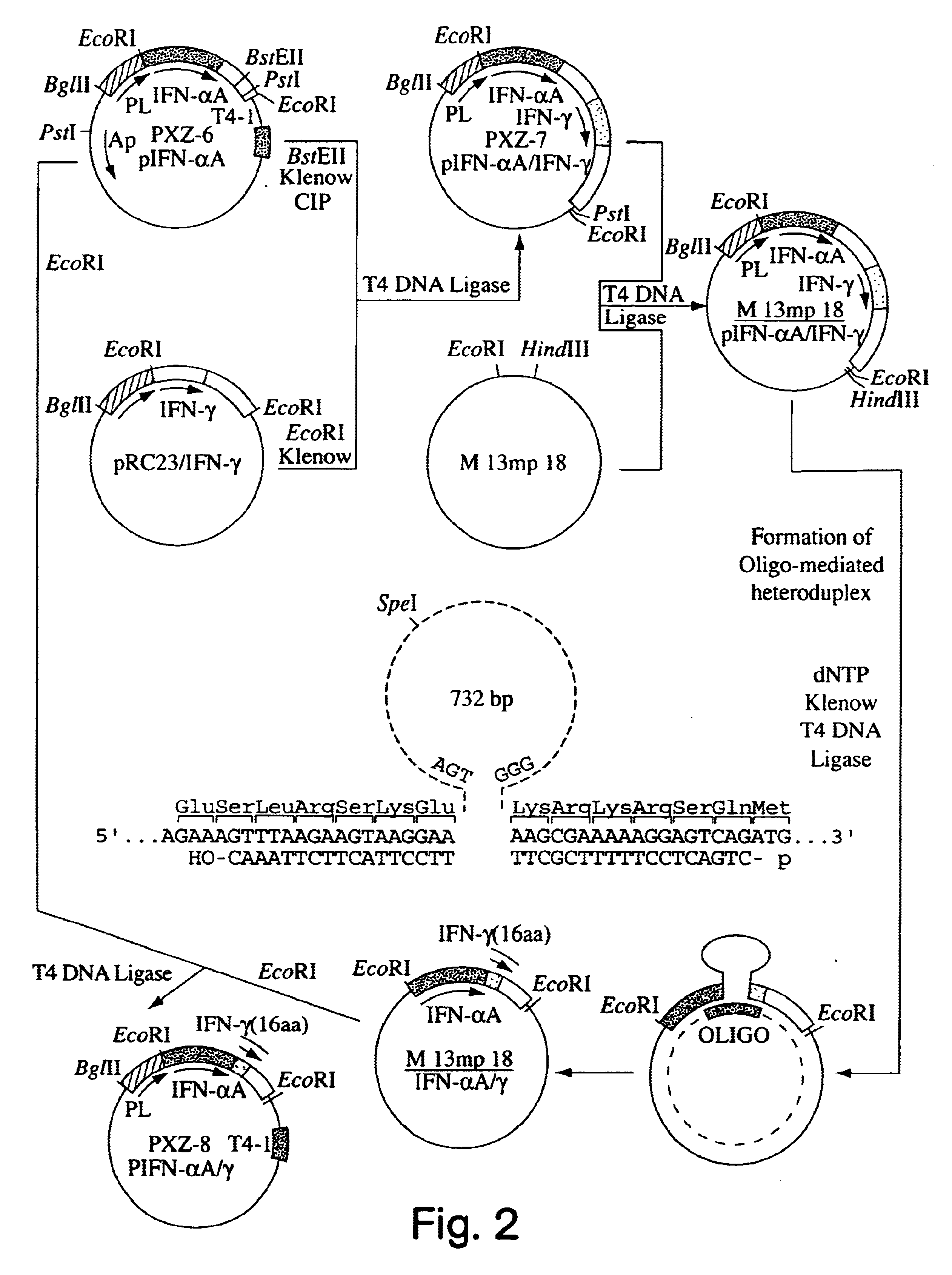
Expression vectors for producing modified proteins
InactiveUS6514753B1Phosphorylation reaction isExtended shelf lifeBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsEscherichia coliMicroorganism
Modified proteins, modified interferons alpha's and beta's, phosphorylated modified proteins and DNA sequences encoding the above, applications and uses thereof. Modified phosphorylated Hu-IFN-alpha-like proteins are provided which carry an identifiable label such as a radio-label. Corresponding phosphorylatable Hu-IFN-alpha-like proteins which contain a putative phosphorylation site. DNA sequences which encode a Hu-IFN-alpha-like protein and contain a sequence encoding a putative phosphorylatable site. Appropriate expression vectors are used to transform compatible host cells of various microorganisms, such as E. coli. Numerous uses for the phosphorylated proteins are disclosed.
Owner:PESTKA BIOMEDICAL LAB
Phosphorylated polypeptides and uses related thereto
InactiveUS7129331B2Time-consuming to improveImprovement inefficient trial-and-error approachPeptide/protein ingredientsPeptide preparation methodsDiseaseHeterologous
Methods to generate modified polypeptides, modified antibodies, stably phosphorylated modified polypeptides, stably phosphorylated modified antibodies, polynucleotide sequences encoding the polypeptides, and uses thereof are provided. A computer-aided molecular modeling method is also provided to generate modified phosphorylatable polypeptides, particularly monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) for use in the diagnosis and treatment of cancers and other diseases. The corresponding MAbs contain heterologous recognition sites for polypeptide kinases and can be labeled by an identifiable label, such as radio-isotope 32P. The phosphate group(s) attached to the phosphorylated polypeptide is unusually stable due to engineered intramolecular interactions between the phosphate group and its neighbouring groups. Polynucleotide sequences which encode a monoclonal antibody containing sequences encoding a putative phosphorylation site, and methods for analyzing the biochemical properties of a polypeptide by using molecular modeling tools, are also disclosed.
Owner:PESTKA BIOMEDICAL LAB
Phosphatase inhibitor protein-1 as a regulator of cardiac function
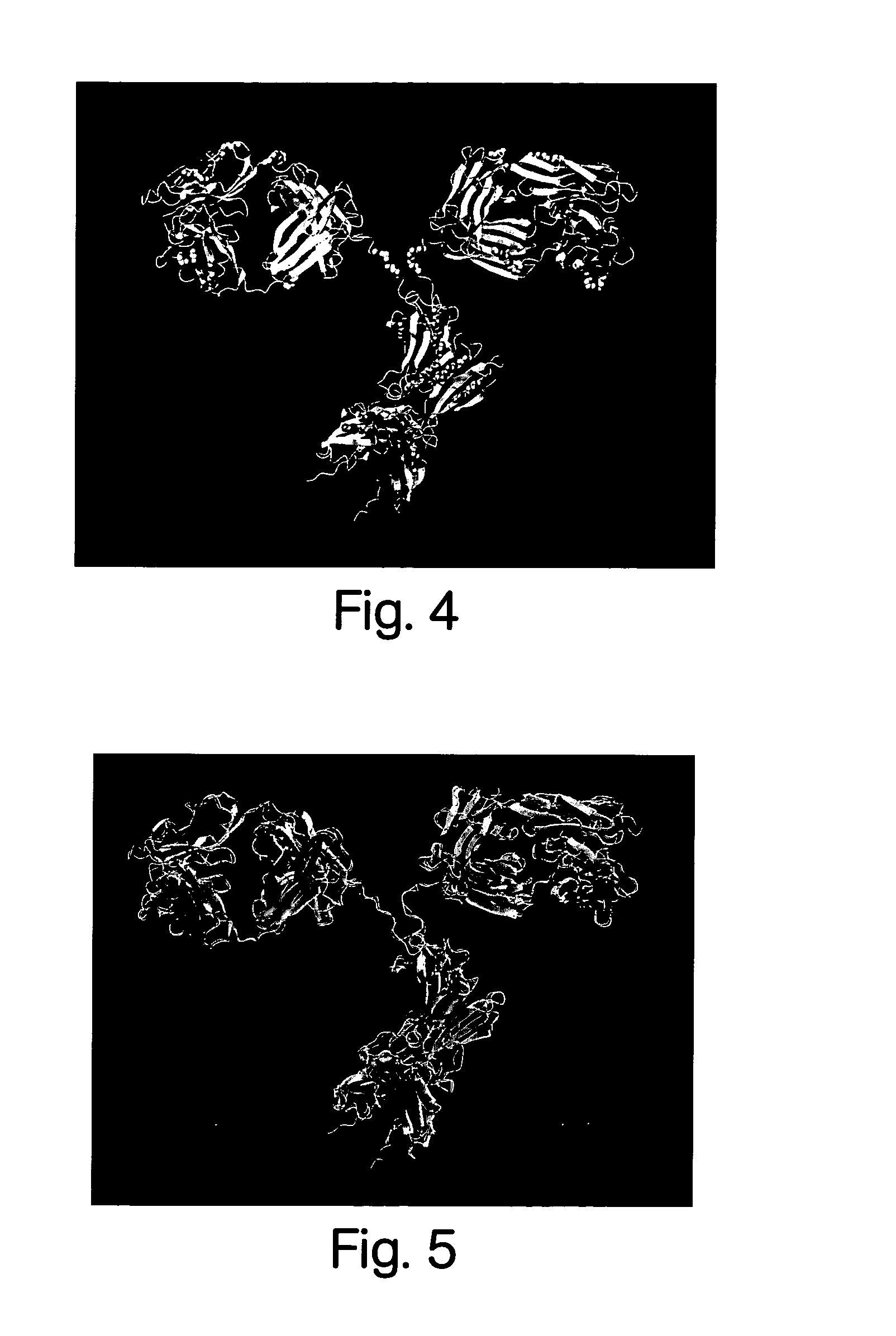
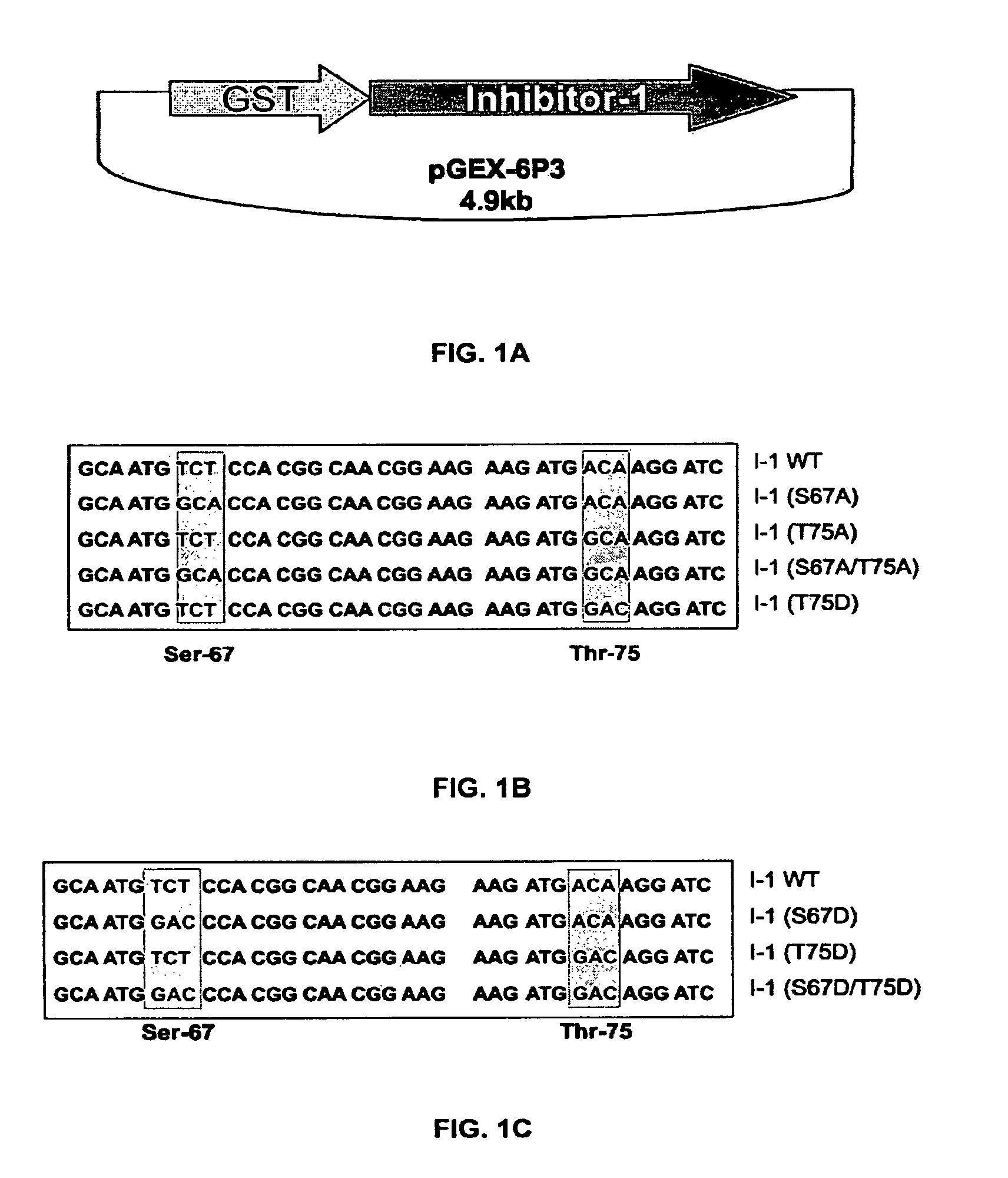
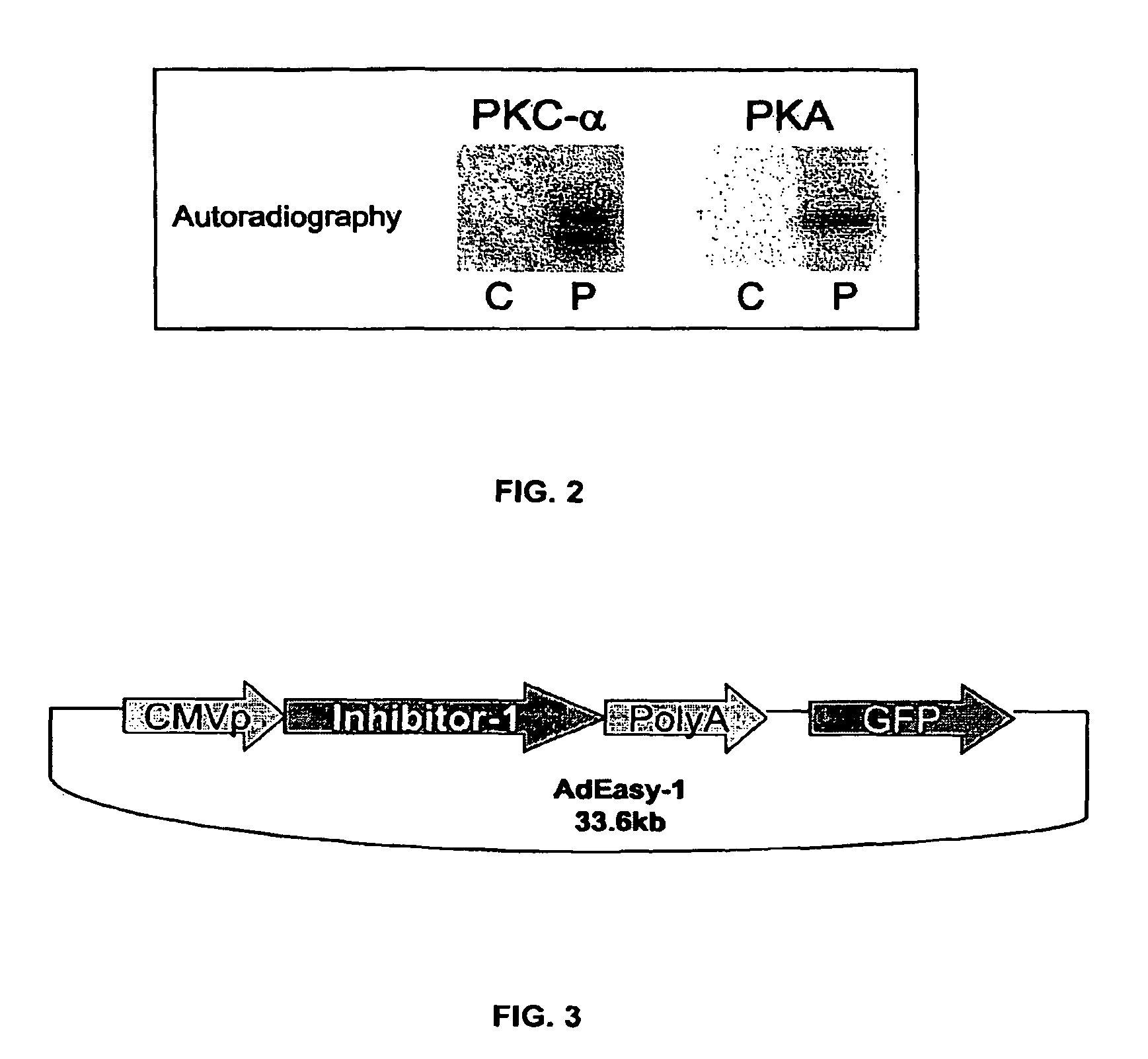
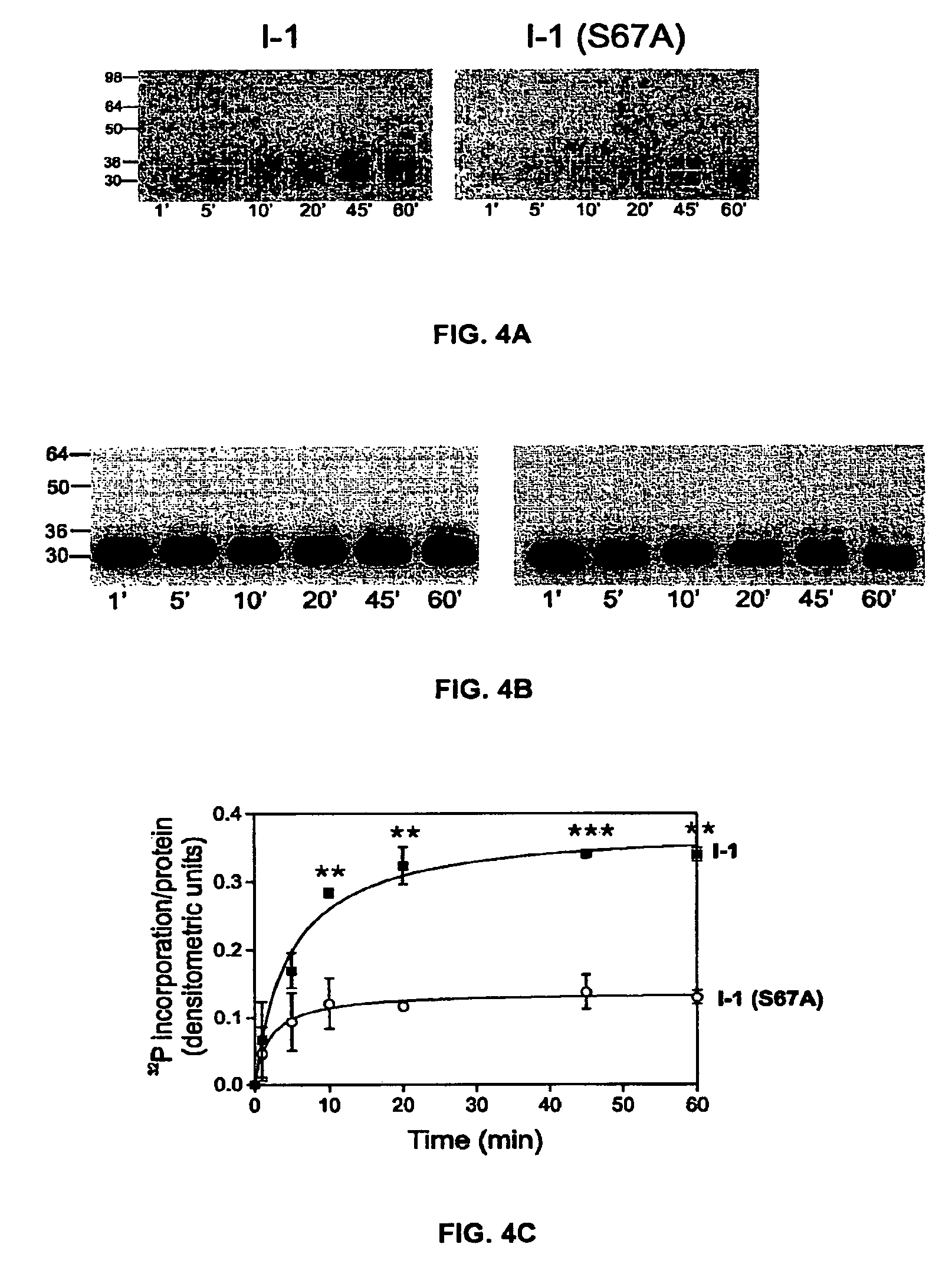
The present invention relates to novel nucleic acids which encode novel mutant forms of Inhibitor Protein-1 (1-1). In particular, the 1-1 mutant forms comprise altered phosphorylation sites of PKC-α. In addition, the present invention relates to methods of regulating cardiac contractility and function, and for treatment of cardio myopathy and heart failure, which employ the novel nucleic acids and polypeptides. Vectors comprising the novel nucleic acids, Antibodies to the novel proteins, and diagnostic and screening methods associated therewith, are also provided.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CINCINNATI
Tyrosine phosphorylation sites
InactiveUS20090305297A1Microbiological testing/measurementImmunoglobulins against animals/humansPhosphorylation siteLeukemia
The invention discloses 397 novel phosphorylation sites identified in carcinoma and / or leukemia, peptides (including AQUA peptides) comprising a phosphorylation site of the invention, antibodies specifically bind to a novel phosphorylation site of the invention, and diagnostic and therapeutic uses of the above.
Owner:CELL SIGNALING TECHNOLOGY
Reagents for the detection of protein phosphorylation in carcinoma signaling pathways
InactiveUS20090081659A1Microbiological testing/measurementImmunoglobulins against growth factorsProtein phosphorylationPhosphorylation site
The invention discloses 364 novel phosphorylation sites identified in carcinoma, peptides (including AQUA peptides) comprising a phosphorylation site of the invention, antibodies specifically bind to a novel phosphorylation site of the invention, and diagnostic and therapeutic uses of the above.
Owner:CELL SIGNALING TECHNOLOGY
Reagents for the detection of protein phosphorylation in leukemia signaling pathways
InactiveUS20090220991A1Animal cellsImmunoglobulins against animals/humansPhosphodiesteraseLipid kinases
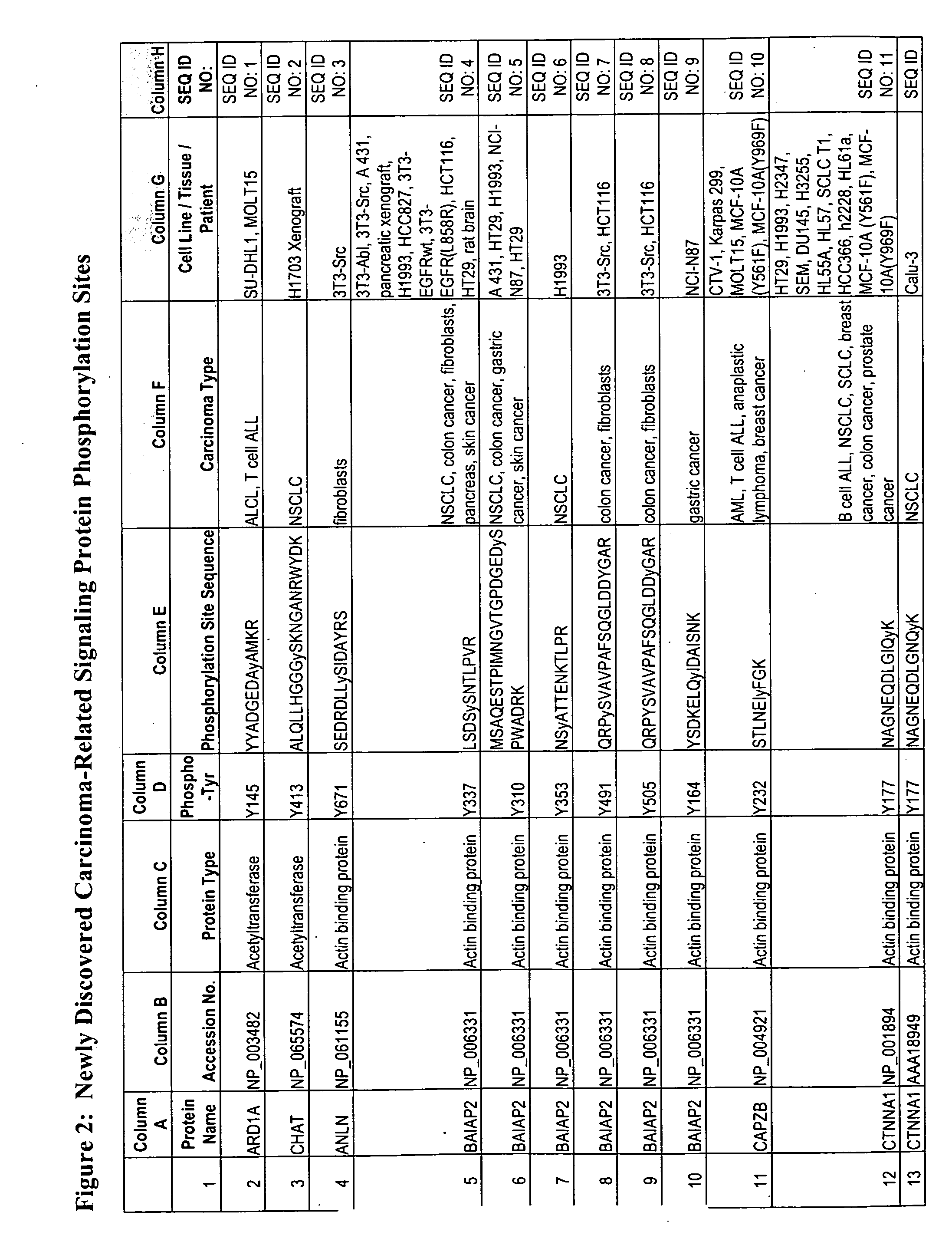
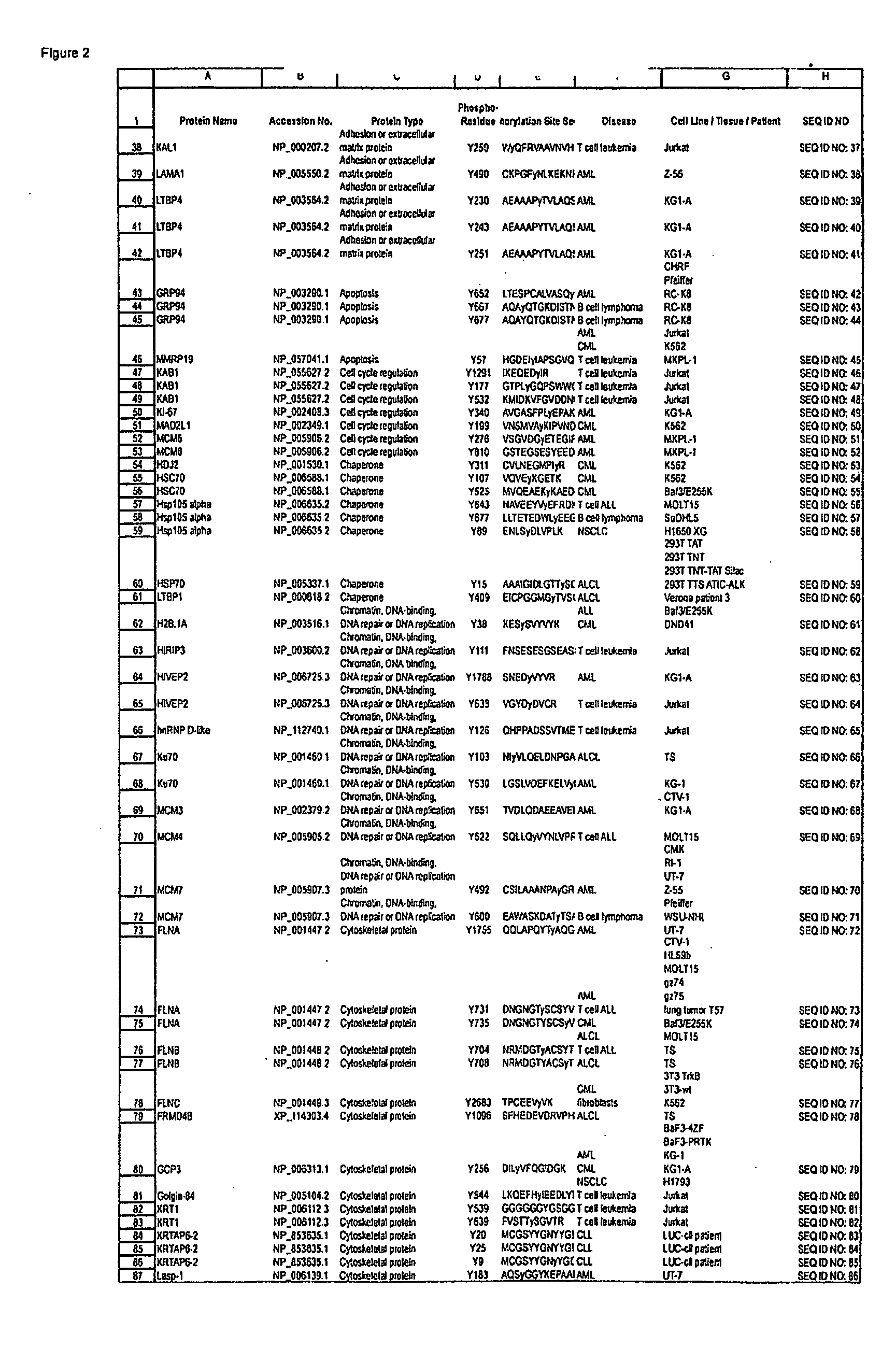
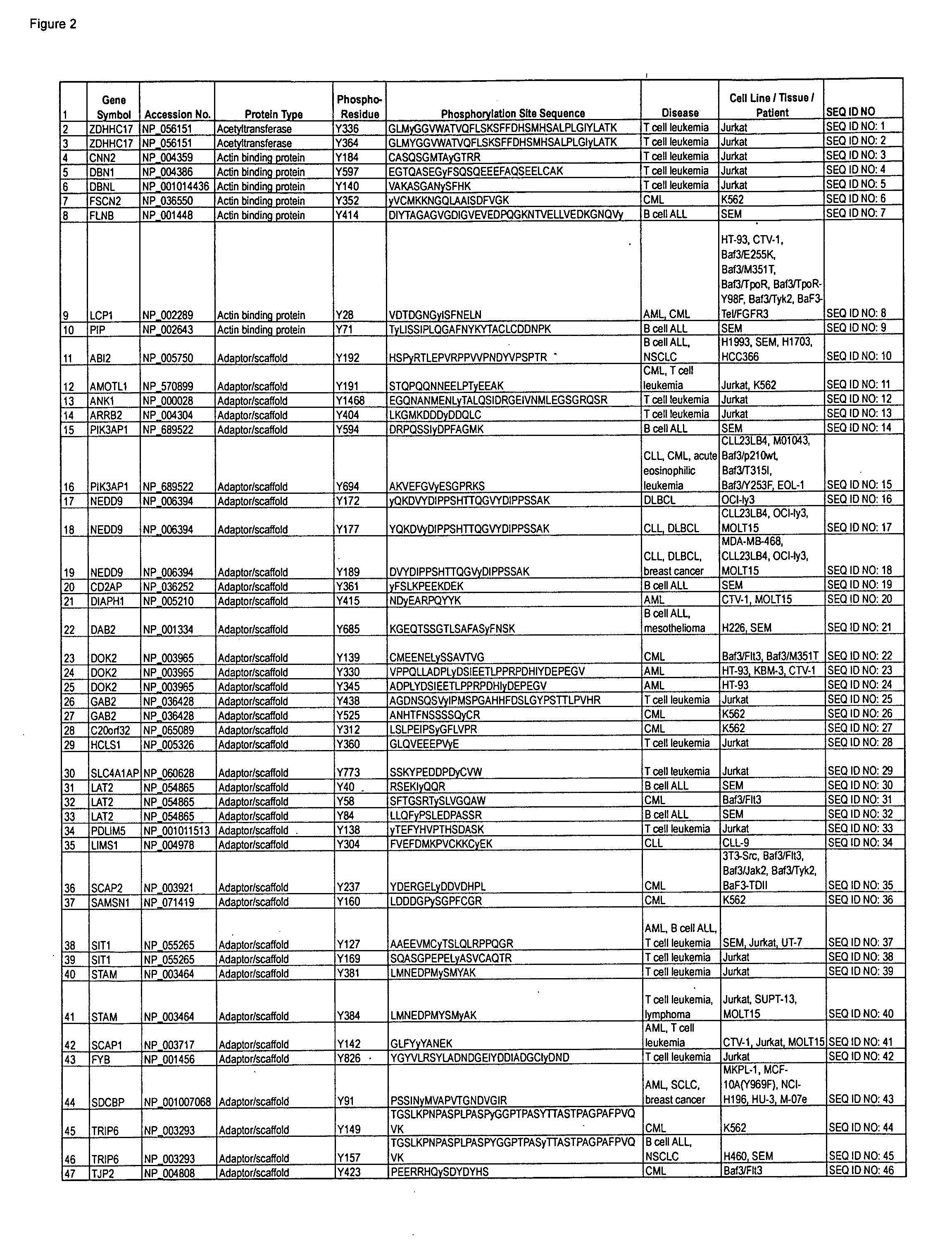
The invention discloses nearly 480 novel phosphorylation sites identified in signal transduction proteins and pathways underlying human Leukemia, and provides phosphorylation site specific antibodies and heavy-isotope labeled peptides (AQUA peptides) for the selective detection and quantification of these phosphorylated sites / proteins, as well as methods of using the reagents for such purpose. Among the phosphorylation sites identified are sites occurring in the following protein types: adaptor / scaffold proteins, acetyltransferases, actin binding proteins, adhesion proteins, apoptosis proteins, calcium-binding proteins, cell cycle regulation proteins, cell surface proteins, channel proteins, chaperone proteins, contractile proteins, cytokine proteins, cytoskeletal proteins, G protein regulators and GTPase activating proteins, guanine nucleotide exchange factors, helicase proteins, immunoglobulin superfamily proteins, inhibitor proteins, protein kinases, lipid kinases, ligases, lipid binding proteins, methytransferases, motor proteins, oxidoreductases, phosphotases, phosphodiesterases, phospholipases, proteases, receptor proteins, trascription factors, transferases, translation / transporter proteins, and ubiquitin conjugating system proteins.
Owner:CELL SIGNALING TECHNOLOGY
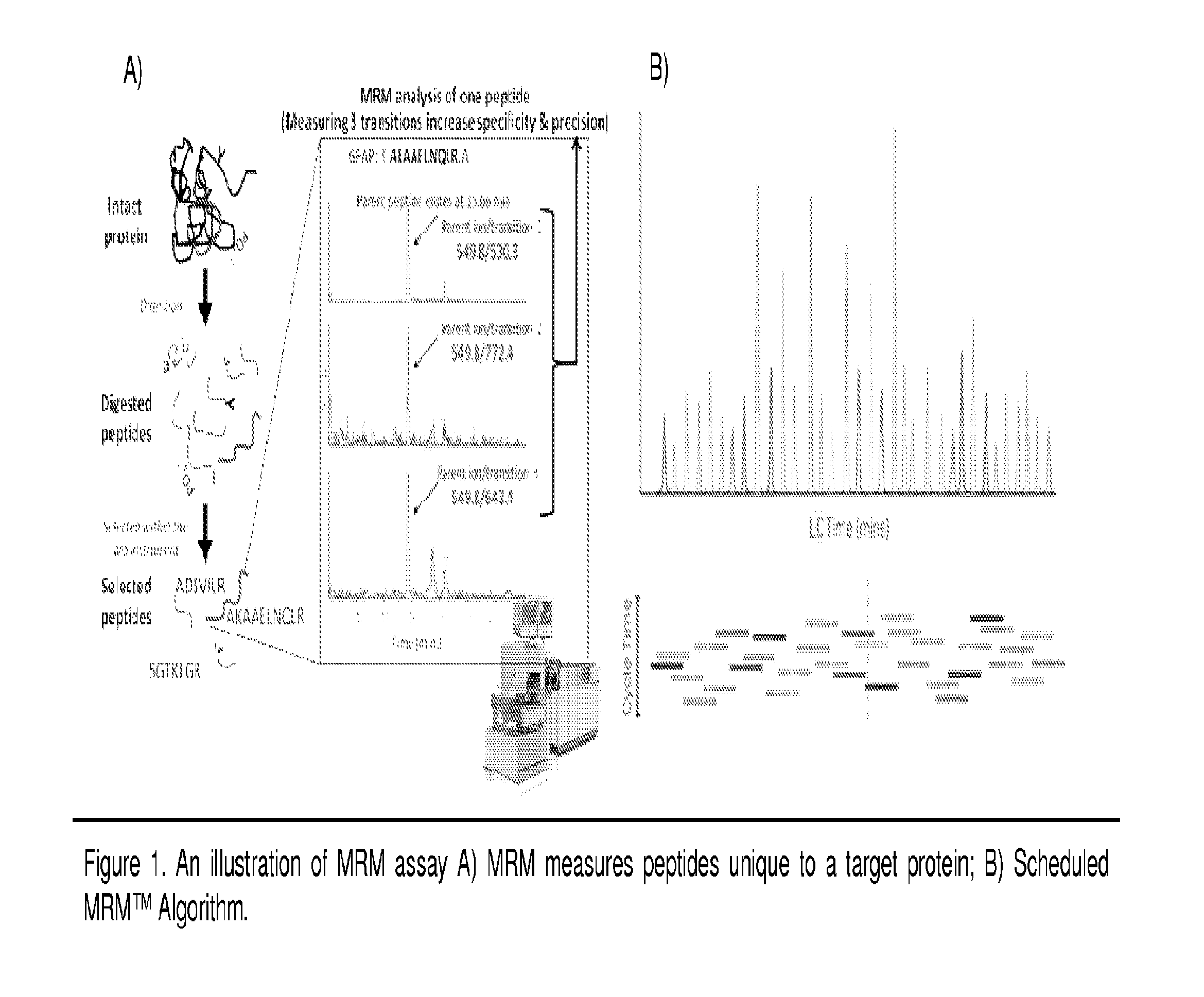
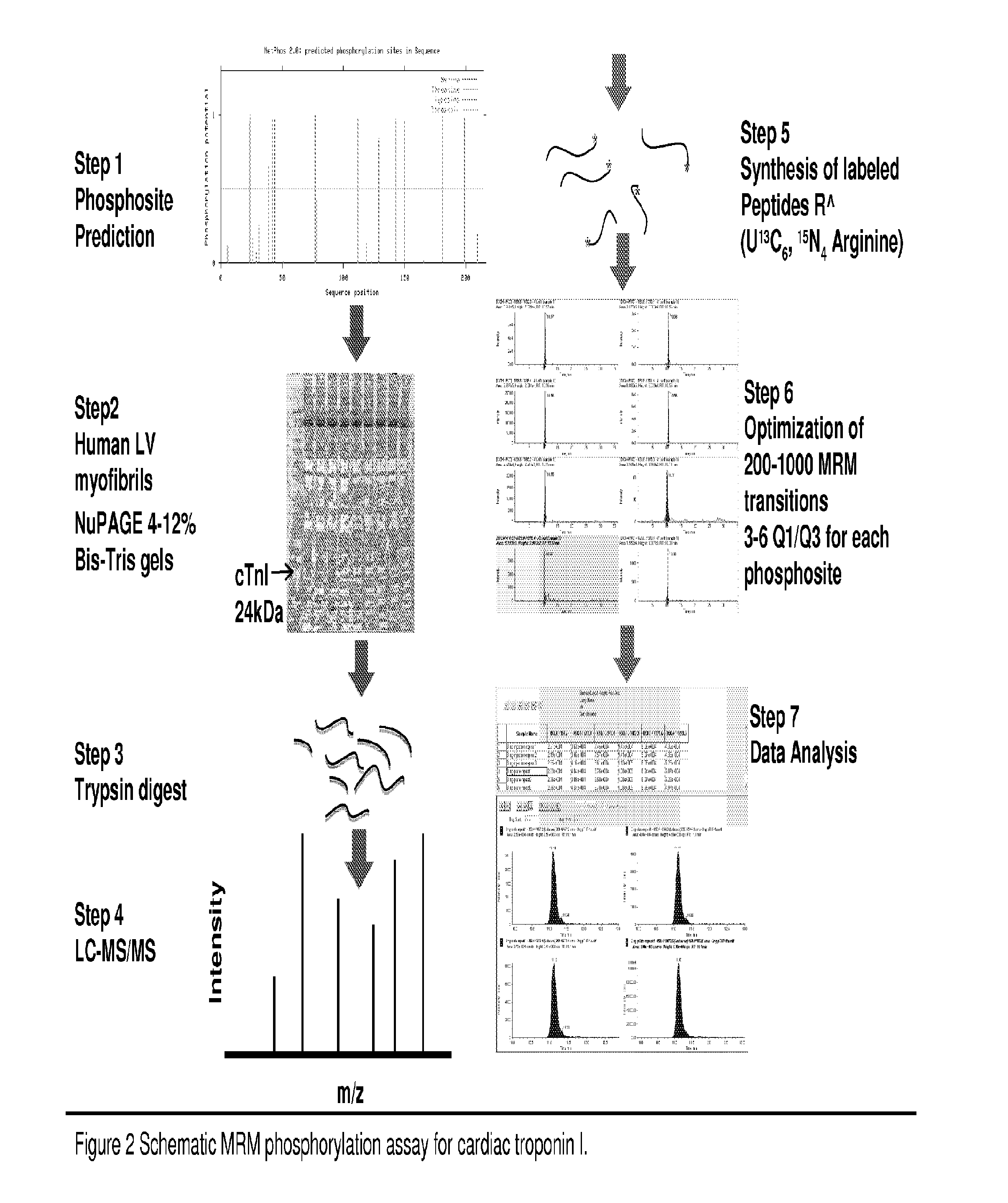
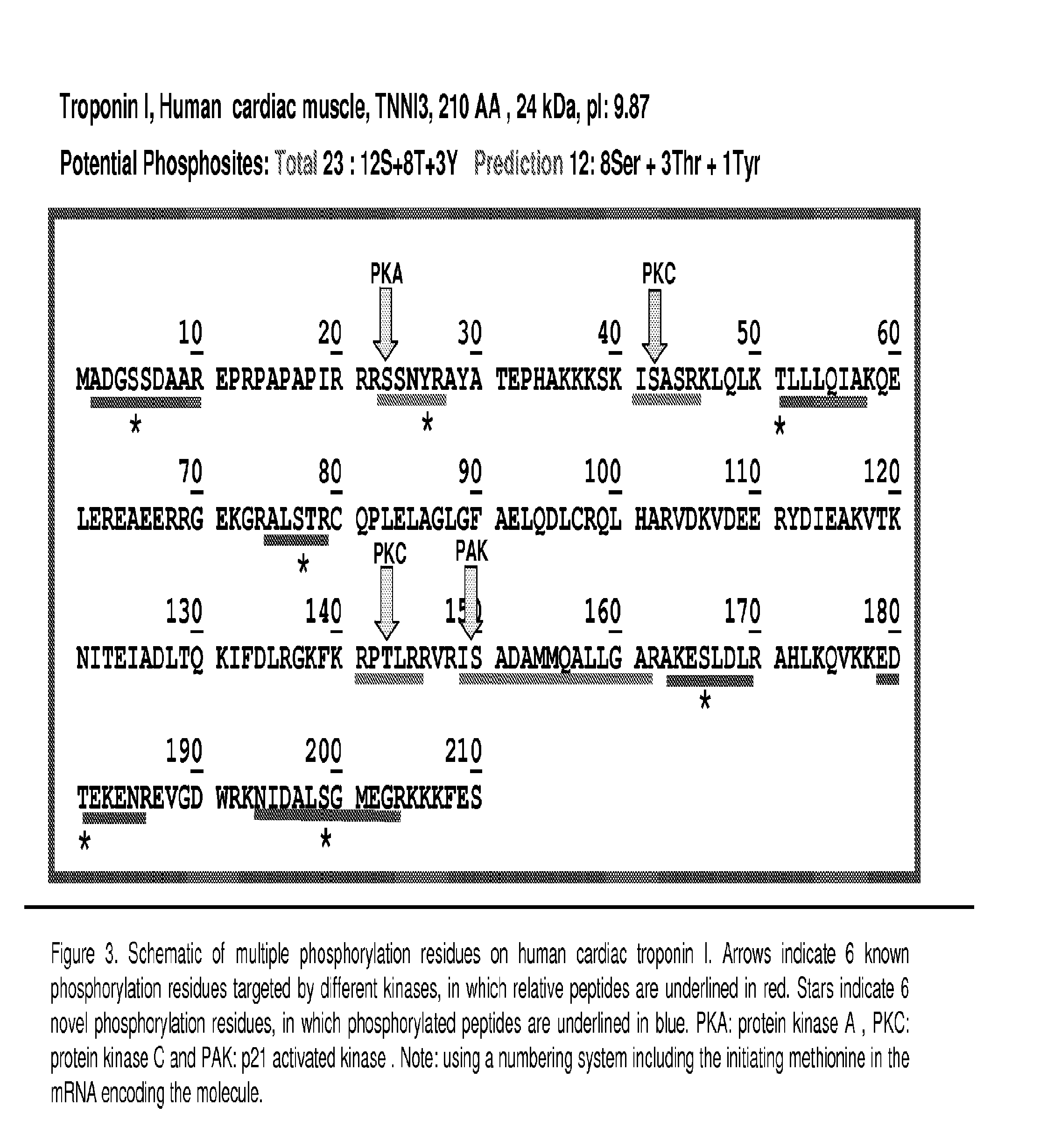
Novel Phosphorylation of Cardiac Troponin I as a Monitor for Cardiac Injury
ActiveUS20130101606A1Immunoglobulins against animals/humansAntibody ingredientsPhosphorylationThreonine
This invention relates to novel phosphorylation sites in cardiac Troponin I that are associated with the onset of heart failure. The phosphorylation sites, i.e., serine 5, tyrosine 26, threonine 51, serine 166, threonine 181 and / or serine 199, can be used as biomarkers for (i) identifying subjects at risk for the development of heart failure, (ii) treating subjects having a higher than normal level of the biomarker, and (iii) monitoring therapy of a subject at risk for the development of heart failure. Also described are antibodies, reagents, and kits for carrying out a method of the present invention.
Owner:CEDARS SINAI MEDICAL CENT +1
Reagents for the detection of protein phosphorylation in carcinoma signaling pathways
InactiveUS20090099340A1Immunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsFermentationADAMTS ProteinsProtein phosphorylation
The invention discloses 214 novel phosphorylation sites identified in signal transduction proteins and pathways underlying human carcinoma, and provides phosphorylation-site specific antibodies and heavy-isotope labeled peptides (AQUA peptides) for the selective detection and quantification of these phosphorylated sites / proteins, as well as methods of using the reagents for such purpose. Among the phosphorylation sites identified are sites occurring in the following protein types: Adaptor / Scaffold proteins, Cytoskeleton proteins, GTP Signaling proteins, Kinases, Metabolism proteins, Phosphatases / Phospho-diesterases / Proteases, Receptor proteins, RNA Processing proteins, Transcription proteins, Translation proteins, Transporter proteins, and Ubitquitin proteins, as well as other protein types.
Owner:CELL SIGNALING TECHNOLOGY
Reagents for the detection of protein phosphorylation in signaling pathways
InactiveUS20100159477A1Peptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementGolgi componentCell Surface Proteins
The invention discloses novel phosphorylation sites identified in signal transduction proteins and pathways, and provides phosphorylation-site specific antibodies and heavy-isotope labeled peptides (AQUA peptides) for the selective detection and quantification of these phosphorylated sites / proteins, as well as methods of using the reagents for such purpose. Among the phosphorylation sites identified are sites occurring in the following protein types: adaptor / scaffold proteins, adhesion / extracellular matrix protein, apoptosis proteins, calcium binding proteins, cell cycle regulation proteins, chaperone proteins, chromatin, DNA binding / repair / replication proteins, cytoskeletal proteins, endoplasmic reticulum or golgi proteins, enzyme proteins, G / regulator proteins, inhibitor proteins, motor / contractile proteins, phosphatase, protease, Ser / Thr protein kinases, Protein kinase (Tyr)s, receptor / channel / cell suface proteins, RNA binding proteins, transcriptional regulators, tumor suppressor proteins, ubiquitan conjugating system proteins and proteins of unknown function.
Owner:CELL SIGNALING TECHNOLOGY
Gene for identifying individuals with familial dysautonomia
InactiveUS7388093B2Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementAutonomic bladder dysfunctionPhosphorylation
This invention relates to methods and compositions useful for detecting mutations which cause Familial Dysautonomia. Familial dysautonomia (FD; Riley-Day syndrome), an Ashkenazi Jewish disorder, is the best known and most frequent of a group of congenital sensory neuropathies and is characterized by widespread sensory and variable autonomic dysfunction. Previously, we mapped the FD gene, DYS, to a 0.5 cM region of chromosome 9q31 and showed that the ethnic bias is due to a founder effect, with >99.5% of disease alleles sharing a common ancestral haplotype. To investigate the molecular basis of FD, we sequenced the minimal candidate region and cloned and characterized its 5 genes. One of these, IKBKAP, harbors two mutations that can cause FD. The major haplotype mutation is located in the donor splice site of intron 20. This mutation can result in skipping of exon 20 in the mRNA from FD patients, although they continue to express varying levels of wild-type message in a tissue-specific manner. RNA isolated from patient lymphoblasts is primarily wild-type, whereas only the deleted message is seen in RNA isolated from brain. The mutation associated with the minor haplotype in four patients is a missense (R696P) mutation in exon 19 that is predicted to disrupt a potential phosphorylation site. Our findings indicate that almost all cases of FD are caused by an unusual splice defect that displays tissue-specific expression; and they also provide the basis for rapid carrier screening in the Ashkenazi Jewish population.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Phosphorylated fusion proteins
InactiveUS6747131B1Enhanced radiationPhosphorylation reaction isBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsEscherichia coliPhosphorylation
Modified proteins, modified interferons alpha's and beta's, phosphorylated modified proteins and DNA sequences encoding the above, applications and uses thereof. Modified phosphorylated Hu-IFN-alpha-like proteins are provided which carry an identifiable label such as a radio-label. Corresponding phosphorylatable Hu-IFN-alpha-like proteins which contain a putative phosphorylation site. DNA sequences which encode a Hu-IFN-alpha-like protein and contain a sequence encoding a putative phosphorylatable site. Appropriate expression vectors are used to transform compatible host cells of various microorganisms, such as E. coli. Numerous uses for the phosphorylated proteins are disclosed.
Owner:PESTKA BIOMEDICAL LAB
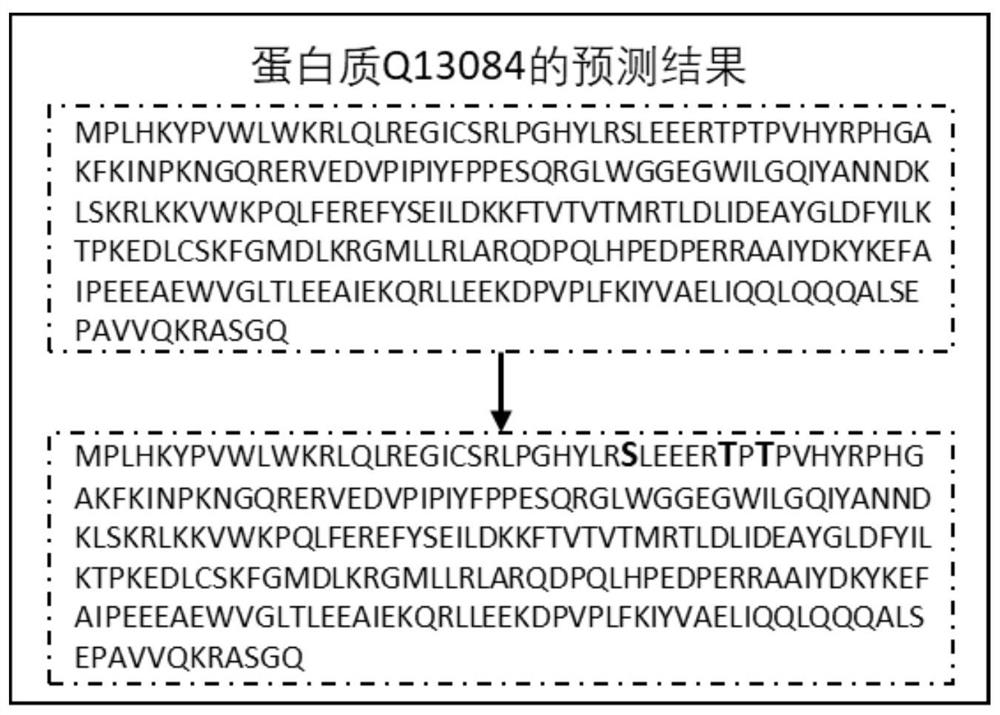
Protein phosphorylation site prediction method based on inner product self-attention neural network
PendingCN113096722AReduce computational costImprove forecast accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesProtein phosphorylationData mining
The invention relates to a protein phosphorylation site prediction method based on an inner product self-attention neural network. The method comprises the steps that: firstly, a protein sequence which has an quantityL of amino acid residues and is to be subjected to phosphorylation site prediction is input, and the protein sequence is converted into an L * 20 feature matrix Mfea through one-hot coding expression forms of 20 common amino acids; then, for each residue of the protein, a characteristic matrix M with the size of w * 20 is acquired by using a sliding window according to the Mfea; protein sequences of known phosphorylation site tags are obtained from a database to construct a training set; a neural network framework is built, the network is trained by using the training set, and a prediction model is obtained; and finally, the feature matrix of the protein sequence residues to be predicted is input into the trained model, and whether target residues in the protein sequence are phosphorylation sites or not is predicted according to a probability value output by the model. The method is low in calculation cost and high in prediction accuracy.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Phospho-specific antibodies to flt3 (tyr969) and uses thereof
InactiveUS20100093008A1Microbiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisPhosphoric acidPhospho-Specific Antibodies
The invention discloses a newly discovered Flt3 phosphorylation site, tyrosine 969 (Tyr969) in the intracellular domain, and provides reagents, including polyclonal and monoclonal antibodies, that selectively bind to Flt3 when phosphorylated at this site. Also provided are assays utilizing this reagent, including methods for determining the phosphorylation of Flt3 in a biological sample, selecting a patient suitable for Flt3 inhibitor therapy, profiling Flt3 activation in a test tissue, and identifying a compound that modulates phosphorylation of Flt3 in a test tissue, by using a detectable reagent, such as the disclosed antibody, that binds to Flt3 only when phosphorylated at Tyr969. The sample or test tissue may be taken from a subject suspected of having cancer, such as acute myelogenous leukemia (AML).
Owner:CELL SIGNALING TECHNOLOGY
Serine, Threonine, and Tyrosine Phosphorylation Sites
The invention discloses 990 novel phosphorylation sites identified in carcinoma and leukemia, peptides (including AQUA peptides) comprising a phosphorylation site of the invention, antibodies specifically bind to a novel phosphorylation site of the invention, and diagnostic and therapeutic uses of the above.
Owner:CELL SIGNALING TECHNOLOGY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com