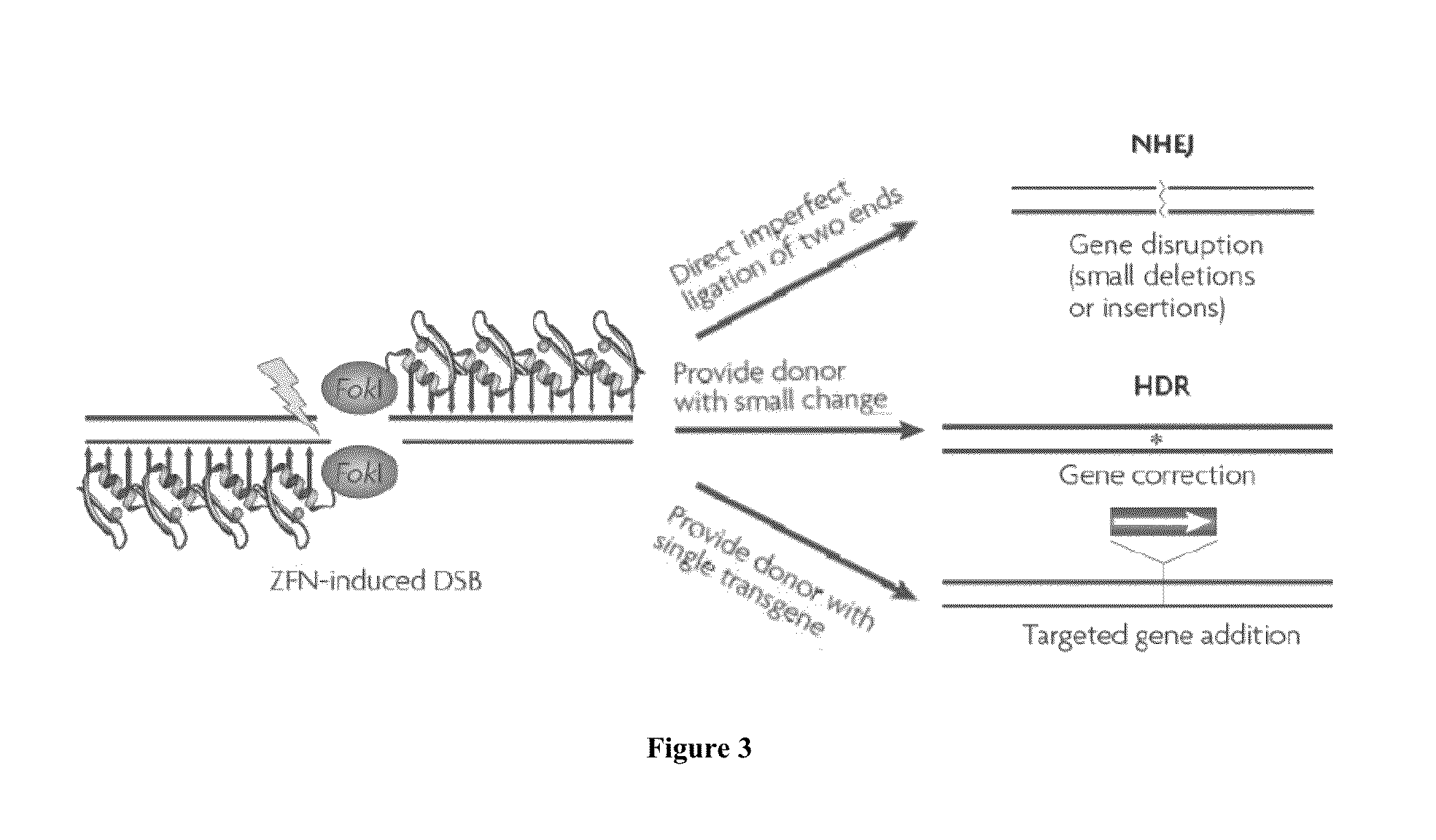
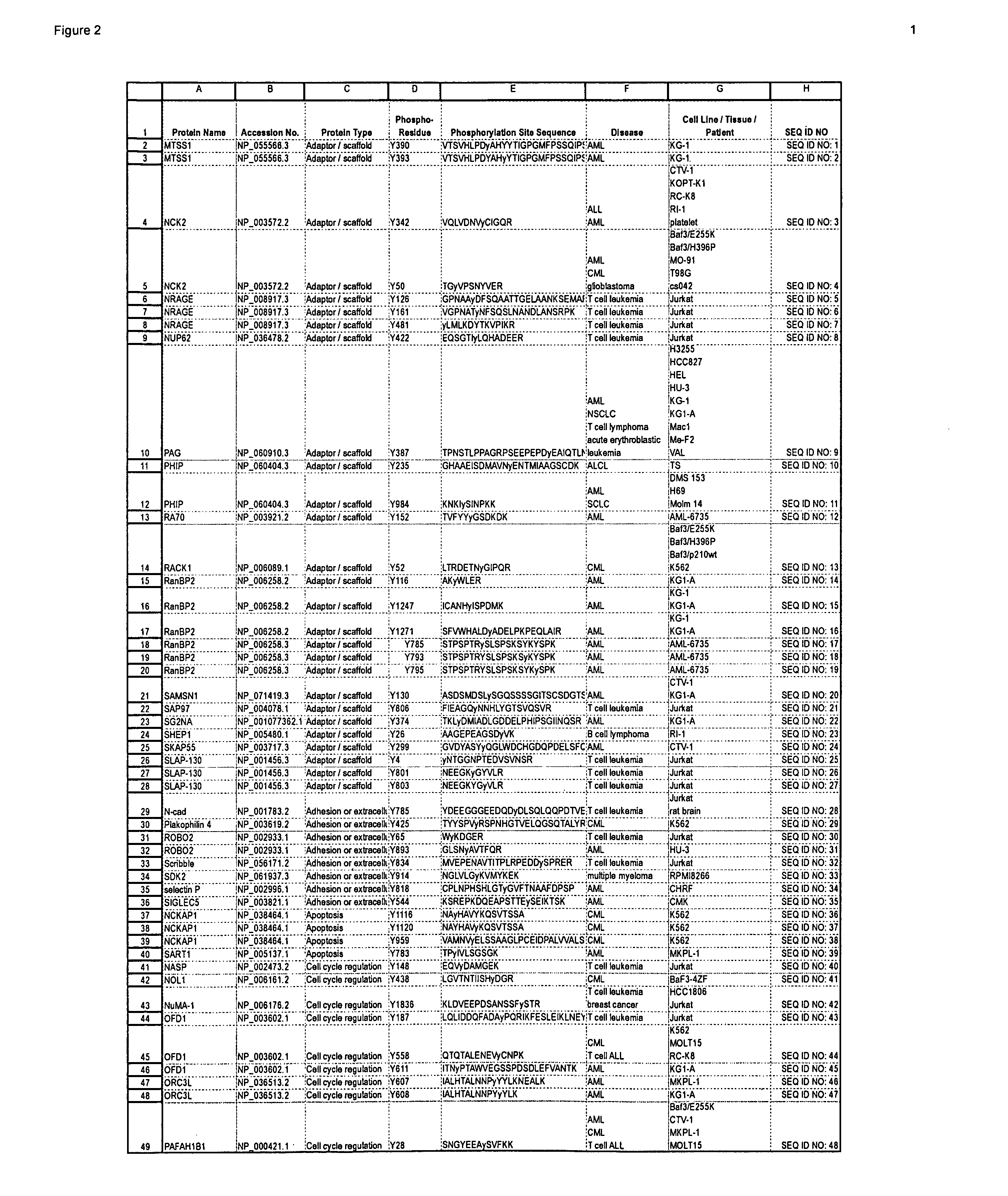
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
79 results about "Phosphorylation sites" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
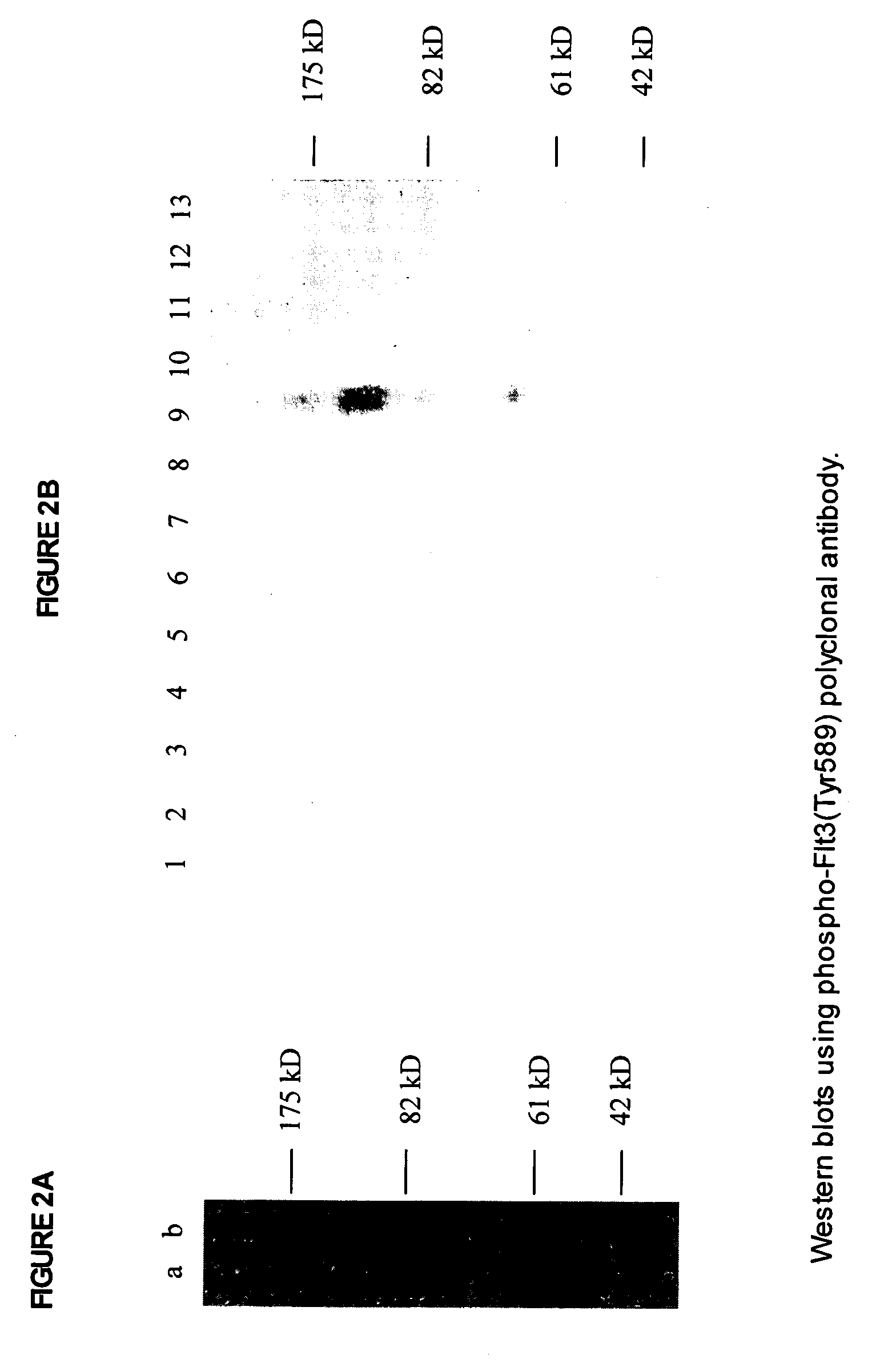
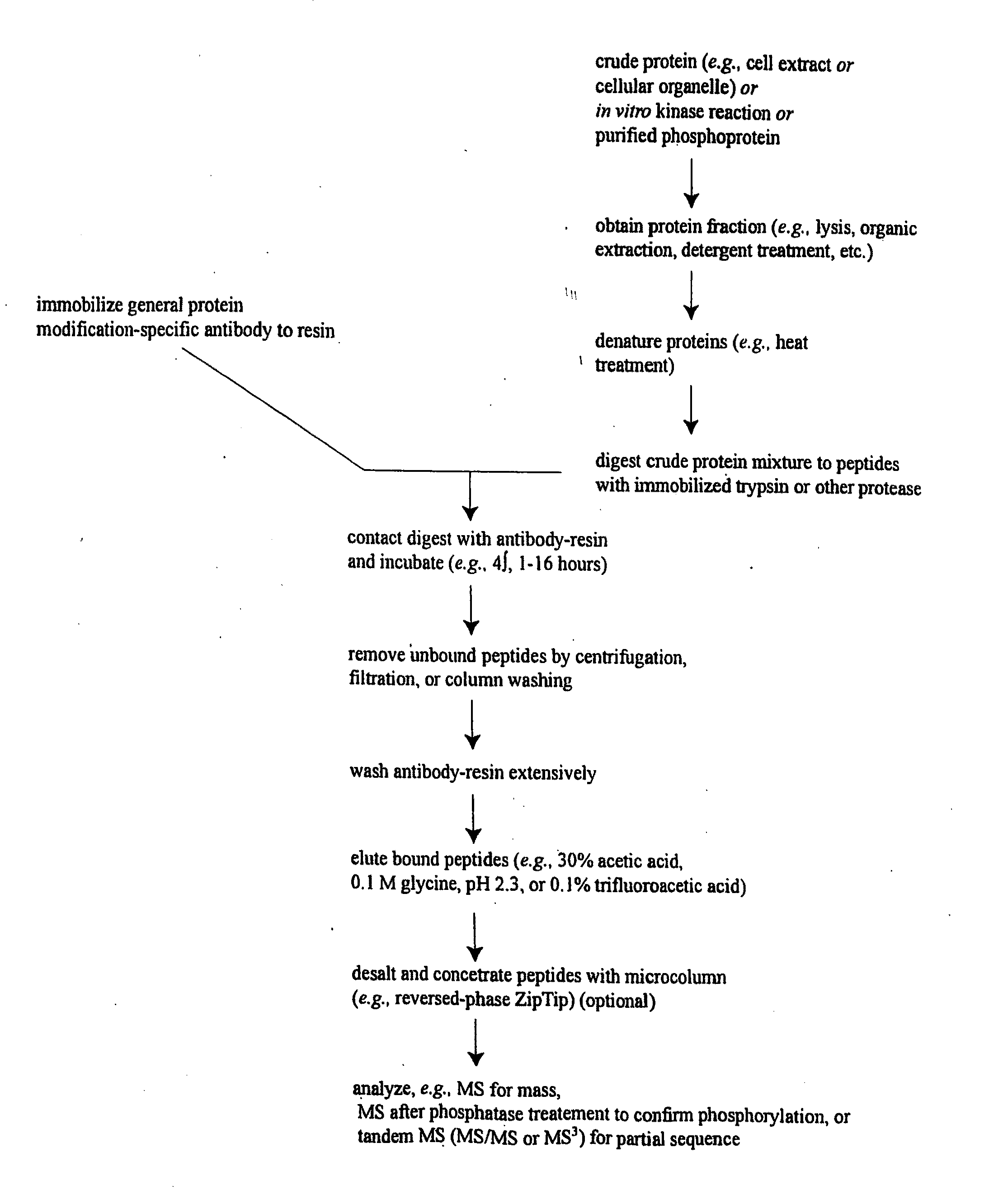
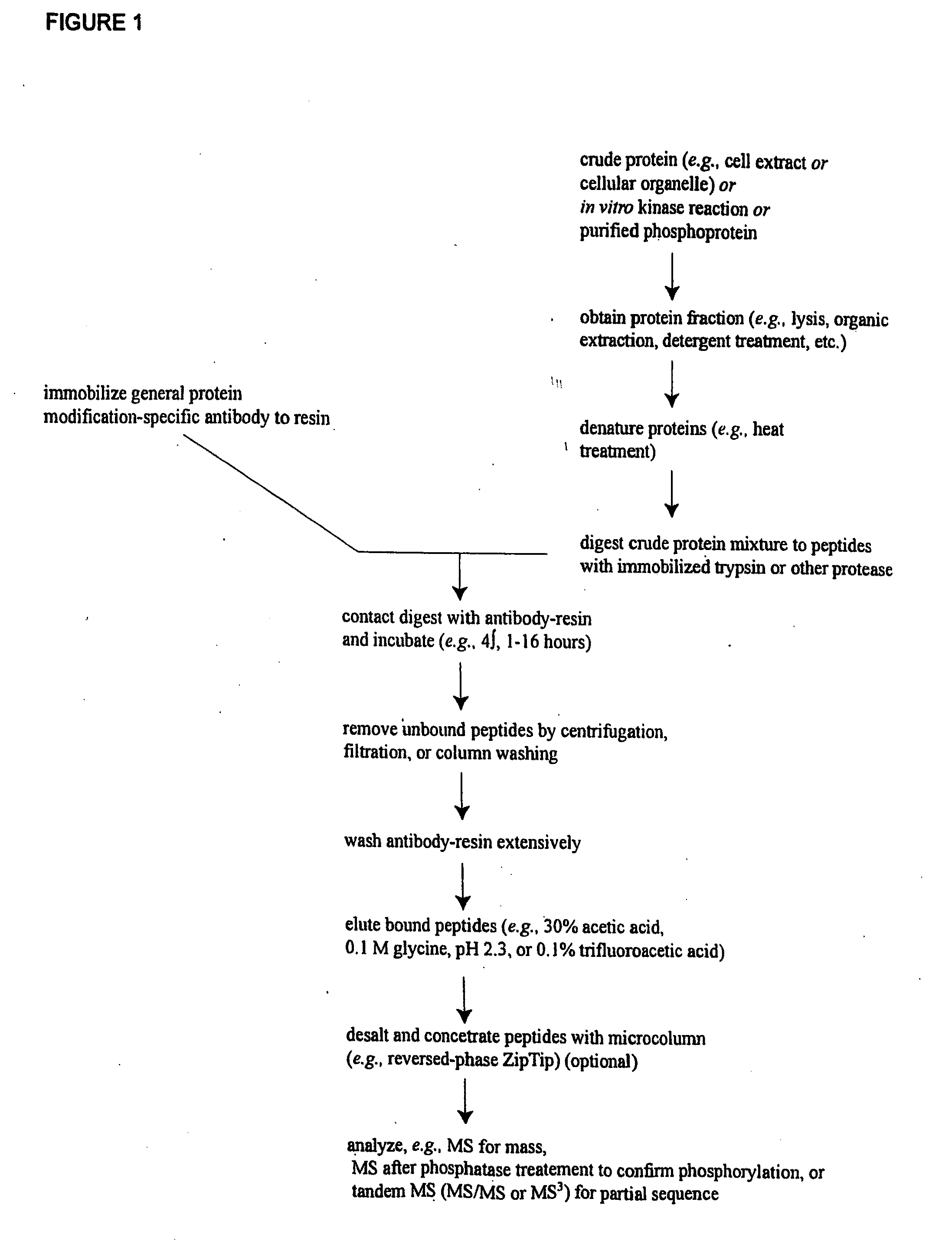
Phospho-specific antibodies to Flt3 and uses thereof
ActiveUS7183385B2Animal cellsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsTyrosinePhospho-Specific Antibodies
The invention discloses two newly-discovered Flt3 phosphorylation sites, tyrosine 589 (Tyr589) and tyrosine 591 (Tyr591) in the intracellular domain, and provides antibodies, both polyclonal and monoclonal, that selectively bind to Flt3 when phosphorylated at these novel sites. Also provided are assays utilizing these reagents, including methods for determining the phosphorylation of Flt3 in a biological sample, selecting a patient suitable for Flt3 inhibitor therapy, profiling Flt3 activation in a test tissue, and identifying a compound that modulates phosphorylation of Flt3 in a test tissue, by using a detectable reagent, such as the disclosed antibodies, that binds to Flt3 when phosphorylated at Tyr589 or Tyr591. The sample or test tissue may be taken from a subject suspected of having cancer, such as acute myelogenous leukemia (AML).
Owner:CELL SIGNALING TECHNOLOGY
Kinase substrates with multiple phosphorylation sites
InactiveUS20060035302A1Facilitate in fluorescence of fluorescentFacilitates an increase in fluorescence of the fluorescent moietyPeptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescenceKinase substrate
Owner:APPL BIOSYSTEMS INC
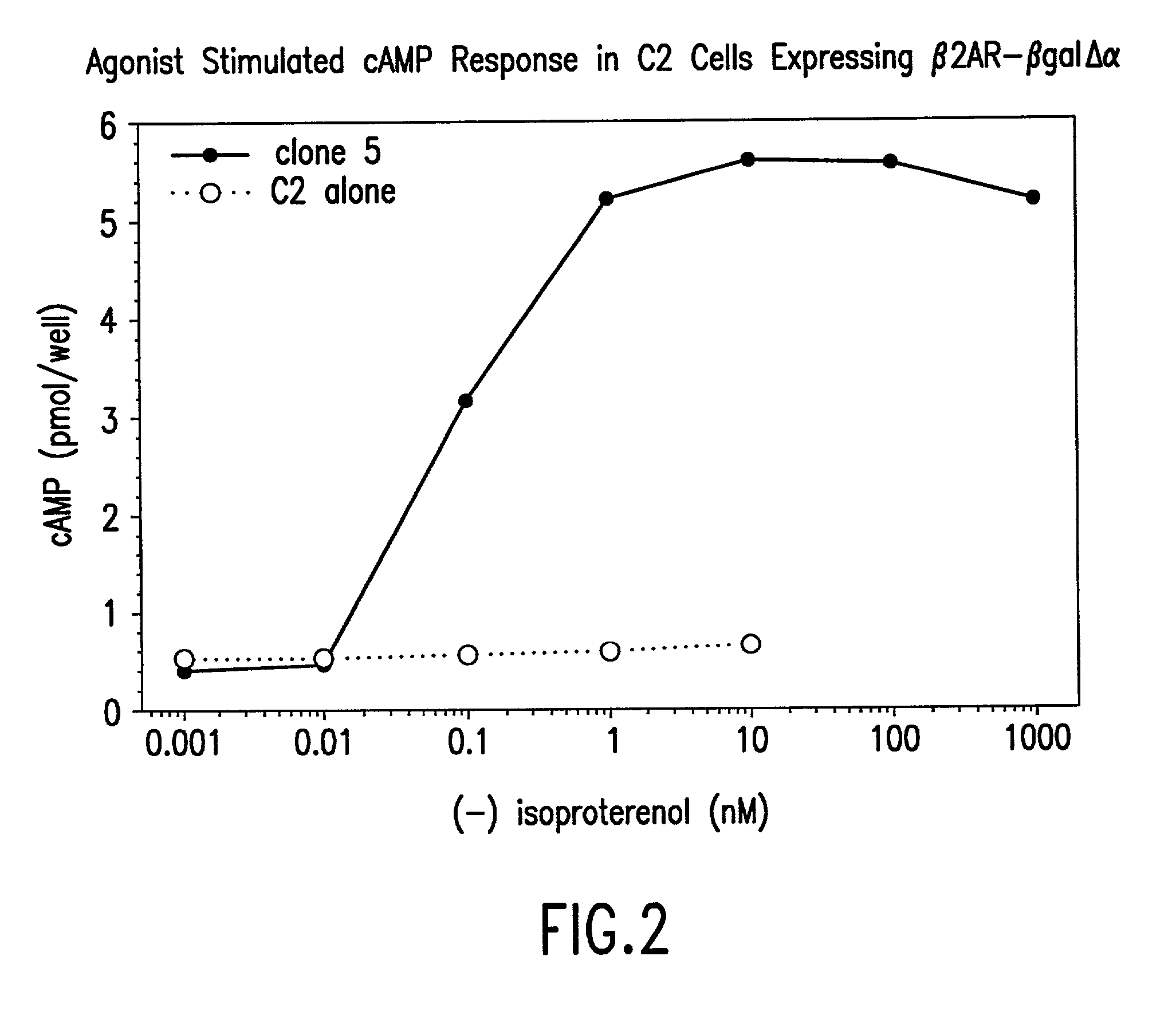
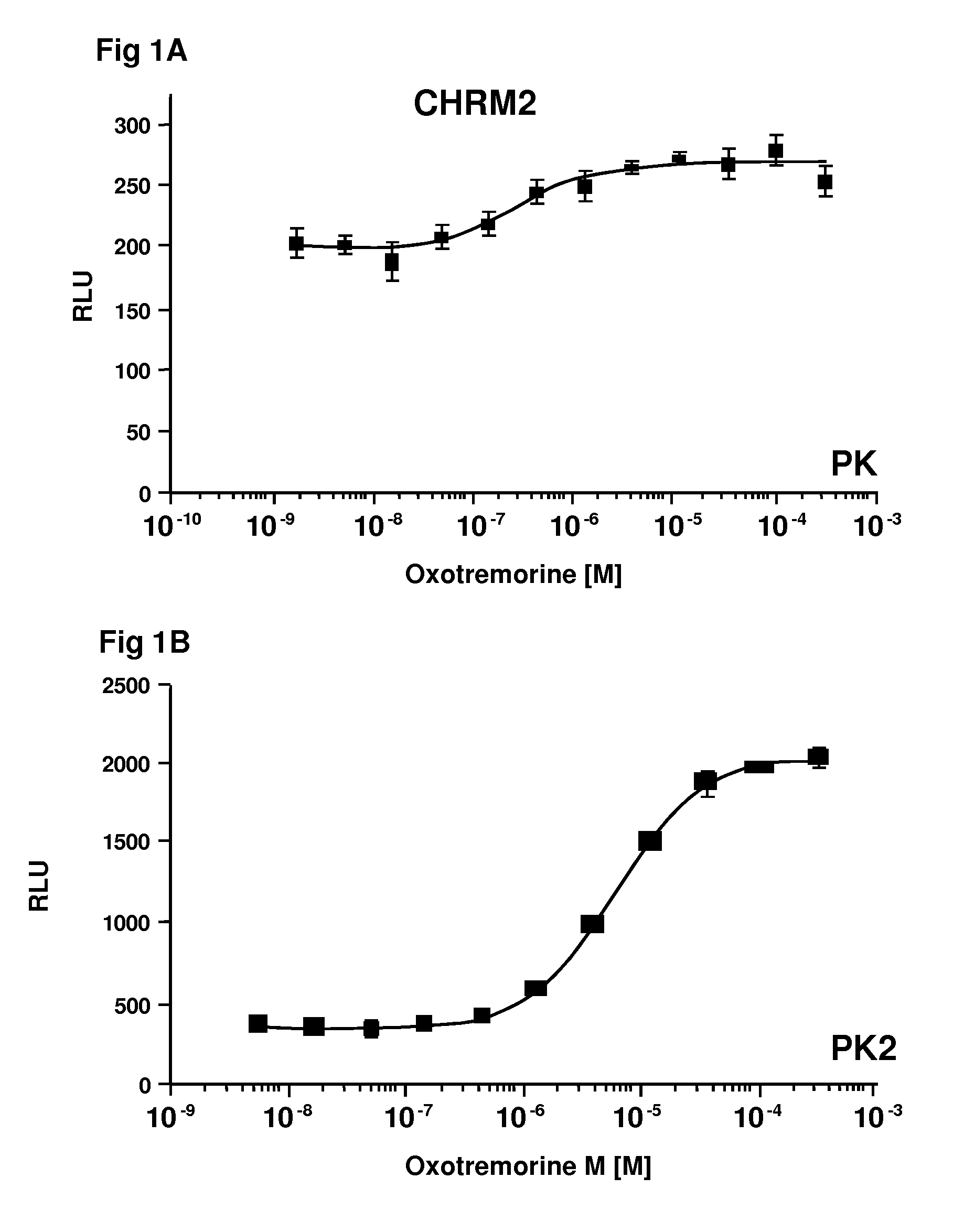
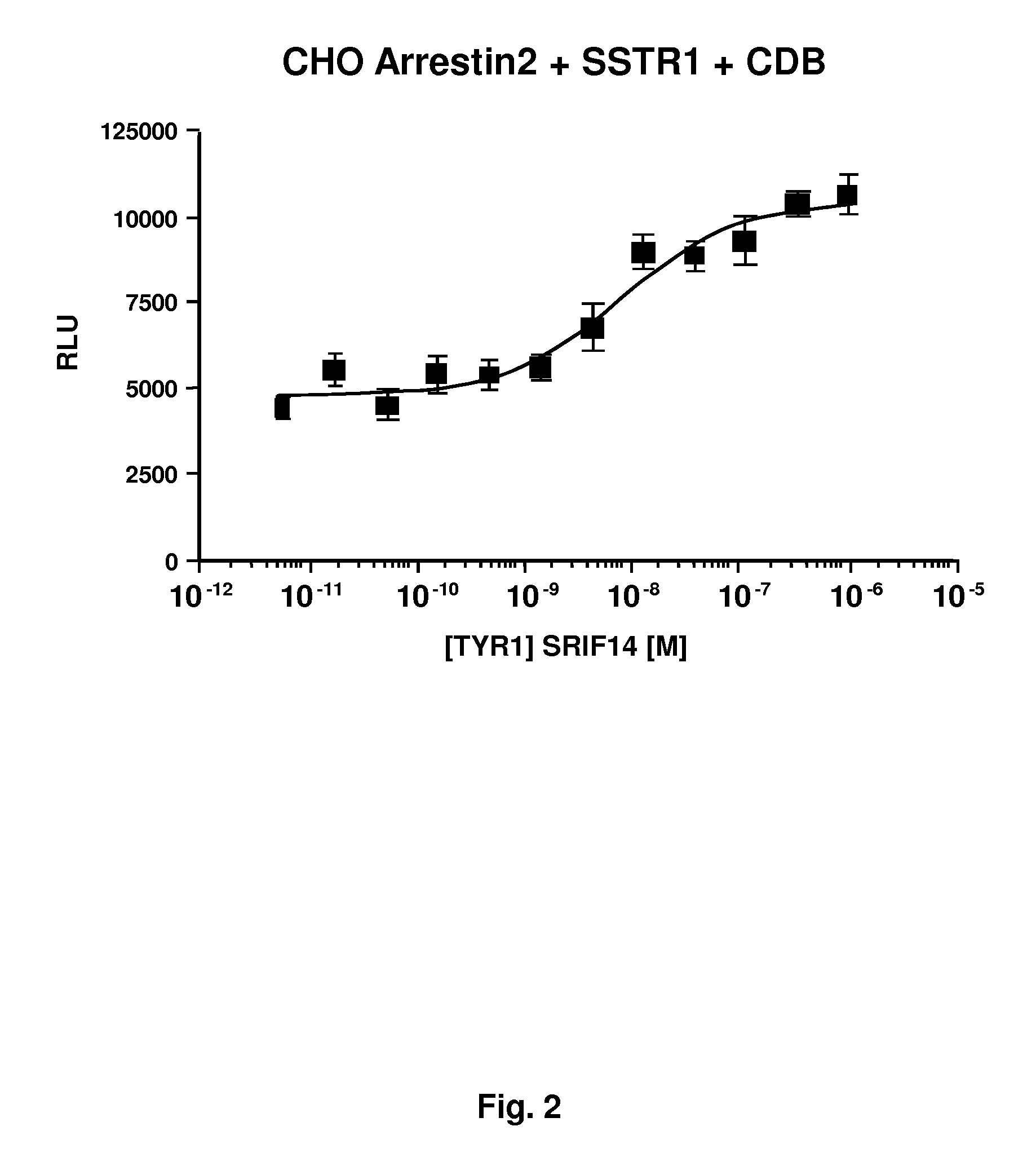
Systems for sensitive detection of G-protein coupled receptor and orphan receptor function using reporter enzyme mutant complementation
Methods for detecting G-protein coupled receptor (GPCR) activity; methods for assaying GPCR activity; and methods for screening for GPCR ligands, G-protein-coupled receptor kinase (GRK) activity, and compounds that interact with components of the GPCR regulatory process are described. Included are methods for expanding ICAST technologies for assaying GPCR activity with applications for ligand fishing, and agonist or antagonist screening. These methods include: engineering seronine / threonine phosphorylation sites into known or orphan GPCR open reading frames in order to increase the affinity of arrestin for the activated form of the GPCR or to increase the reside time of arrestin on the activated GPCR; engineering mutant arrestin proteins that bind to activated GPCRs in the absence of G-protein coupled receptor kinases which may be limiting; and engineering mutant super arrestin proteins that have an increased affinity for activated GPCRs with or without phosphorylation. These methods are intended to increase the robustness of the GPCR / ICAST technology in situations in which G-protein coupled receptor kinases are absent or limiting, or in which the GPCR is not efficiently down-regulated or is rapidly resensitized (thus having a labile interaction with arrestin). Included are also more specific methods for using ICAST complementary enzyme fragments to monitor GPCR homo- and hetero-dimerization with applications for drug lead discovery and ligand and function discovery for orphan GPCRs.
Owner:APPL BIOSYSTEMS INC
Phosphorylated fusion proteins
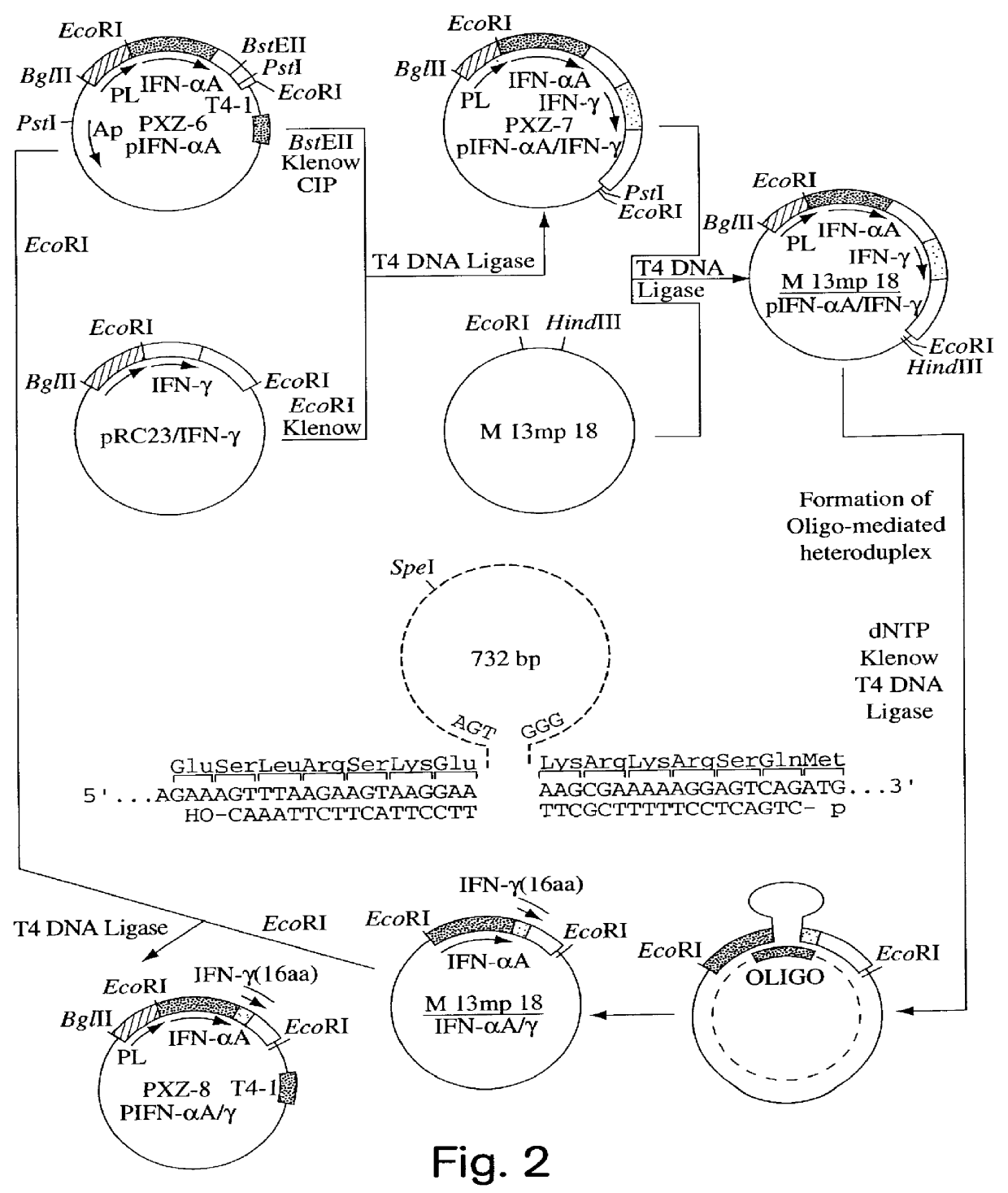
InactiveUS6150503AEnhanced radiationPhosphorylation reaction isBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsInterferonPhosphorylation site
Modified proteins, modified interferons alpha 's and beta 's, phosphorylated modified proteins and DNA sequences encoding the above, applications and uses thereof. Modified phosphorylated Hu-IFN- alpha -like proteins are provided which carry an identifiable label such as a radio-label. Corresponding phosphorylatable Hu-IFN- alpha -like proteins which contain a putative phosphorylation site. DNA sequences which encode a Hu-IFN- alpha -like protein and contain a sequence encoding a putative phosphorylatable site. Appropriate expression vectors are used to transform compatible host cells of various microorganisms, such as E. coli. Numerous uses for the phosphorylated proteins are disclosed.
Owner:PESTKA BIOMEDICAL LAB
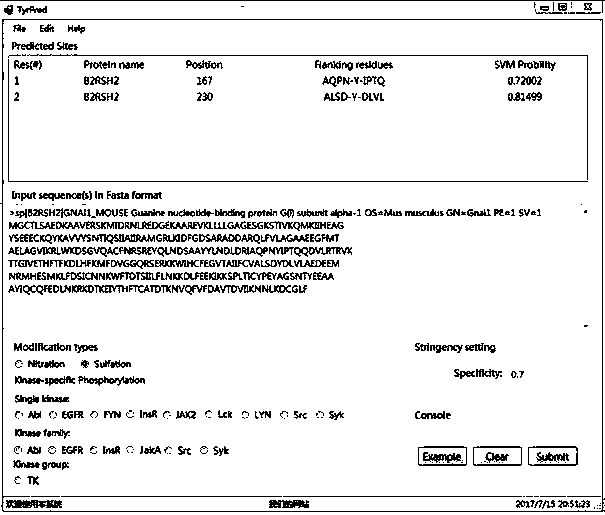
Prediction algorithm for recognizing tyrosine posttranslational modification sites
InactiveCN107463795AImprove predictive performanceImprove forecast qualityBiostatisticsProteomicsIntact proteinPrediction algorithms
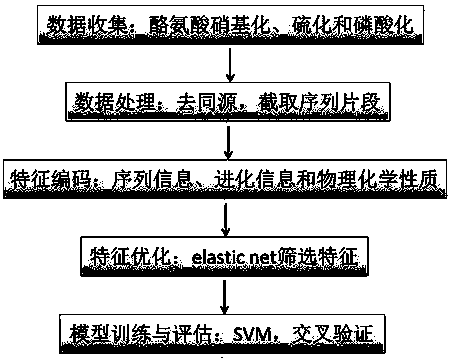
The invention discloses a prediction algorithm for recognizing tyrosine posttranslational modification sites. The algorithm comprises the steps of data collection, data processing, feature coding, feature optimization and model training and evaluation. The invention furthermore discloses application of the prediction algorithm. According to the algorithm, features of the tyrosine posttranslational modification sites are extracted comprehensively from the perspectives of protein sequence information, evolutional information and physical and chemical properties, Elastic Net is used as an optimization means to automatically select variables to screen multidimensional features, redundant information is removed, a prediction model of tyrosine nitration, sulfuration and phosphorylation sites is constructed in combination with an SVM, the prediction capability of the prediction model is improved, and the prediction quality of the tyrosine posttranslational modification sites is remarkably improved. Through a developed prediction software platform TyrPred, predictive analysis of nitration modification sites, sulfuration modification sites and phosphorylation modification sites of tyrosine on intact protein is realized, and a convenient, economical and rapid research tool and important reference are provided for research of tyrosine posttranslational modification.
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV
Multisite phosphorylated peptide (protein) recognizing compound and detection method, imaging method, alzheimer's disease diagnosing method and reagent kit using the same
ActiveUS20090233373A1High sensitivityNervous disorderNickel organic compoundsPhosphatePhosphoric acid
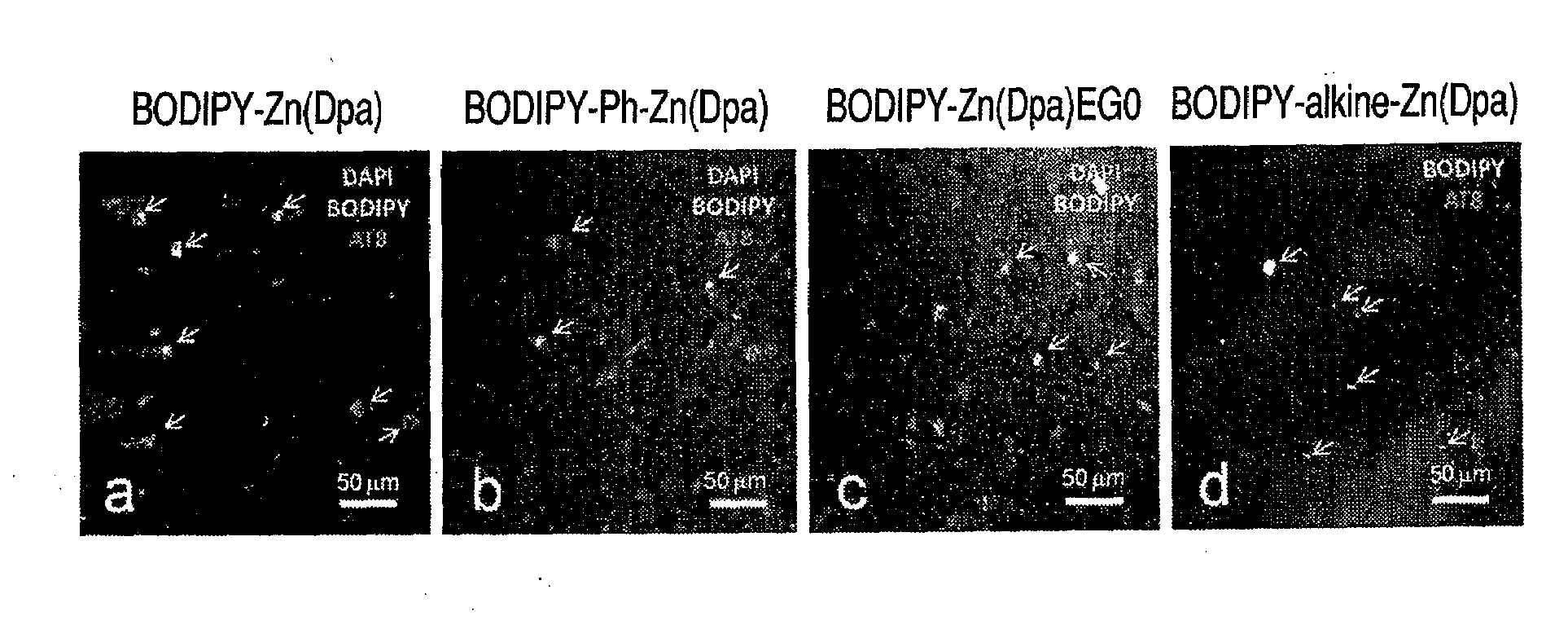
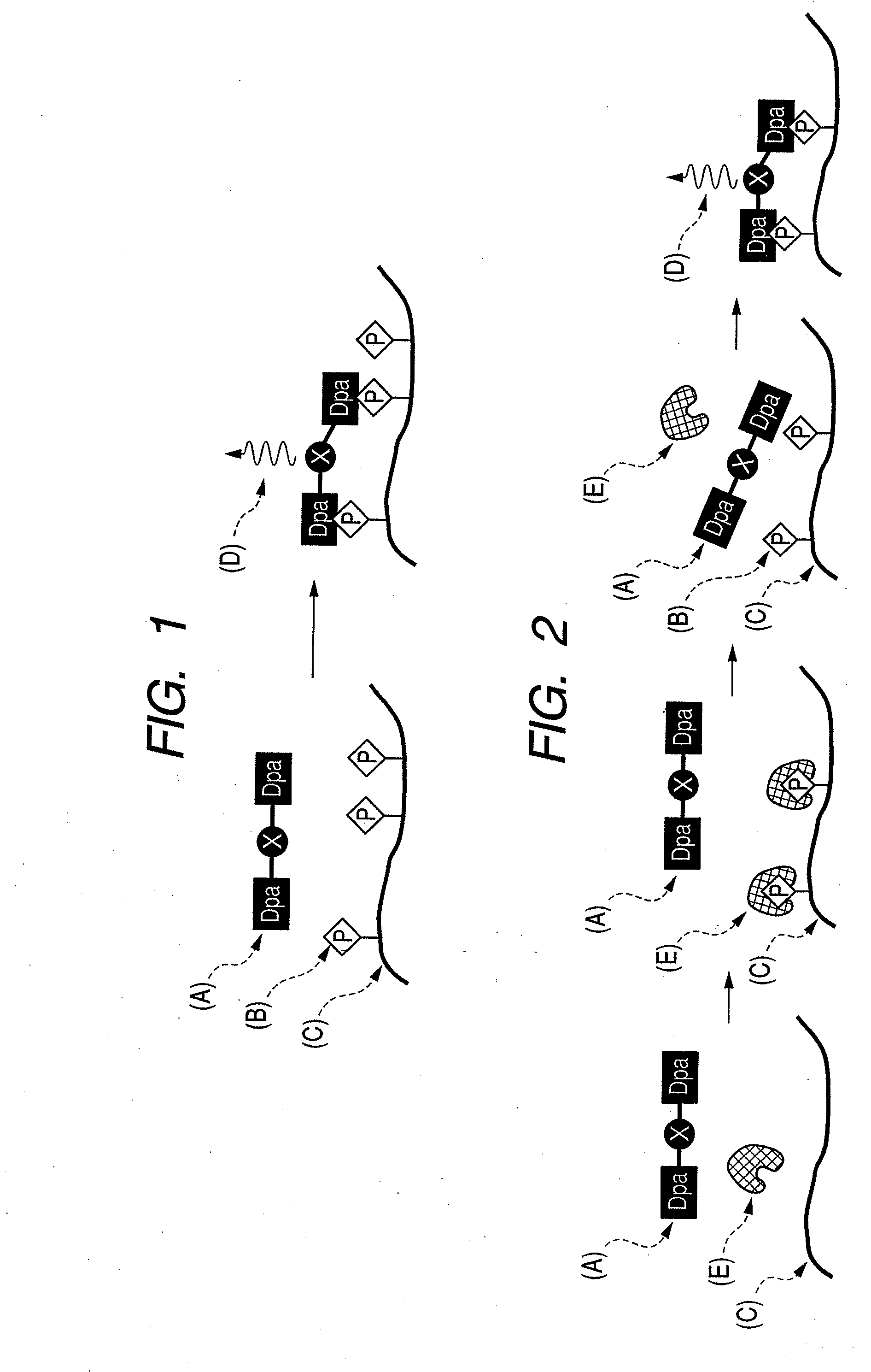
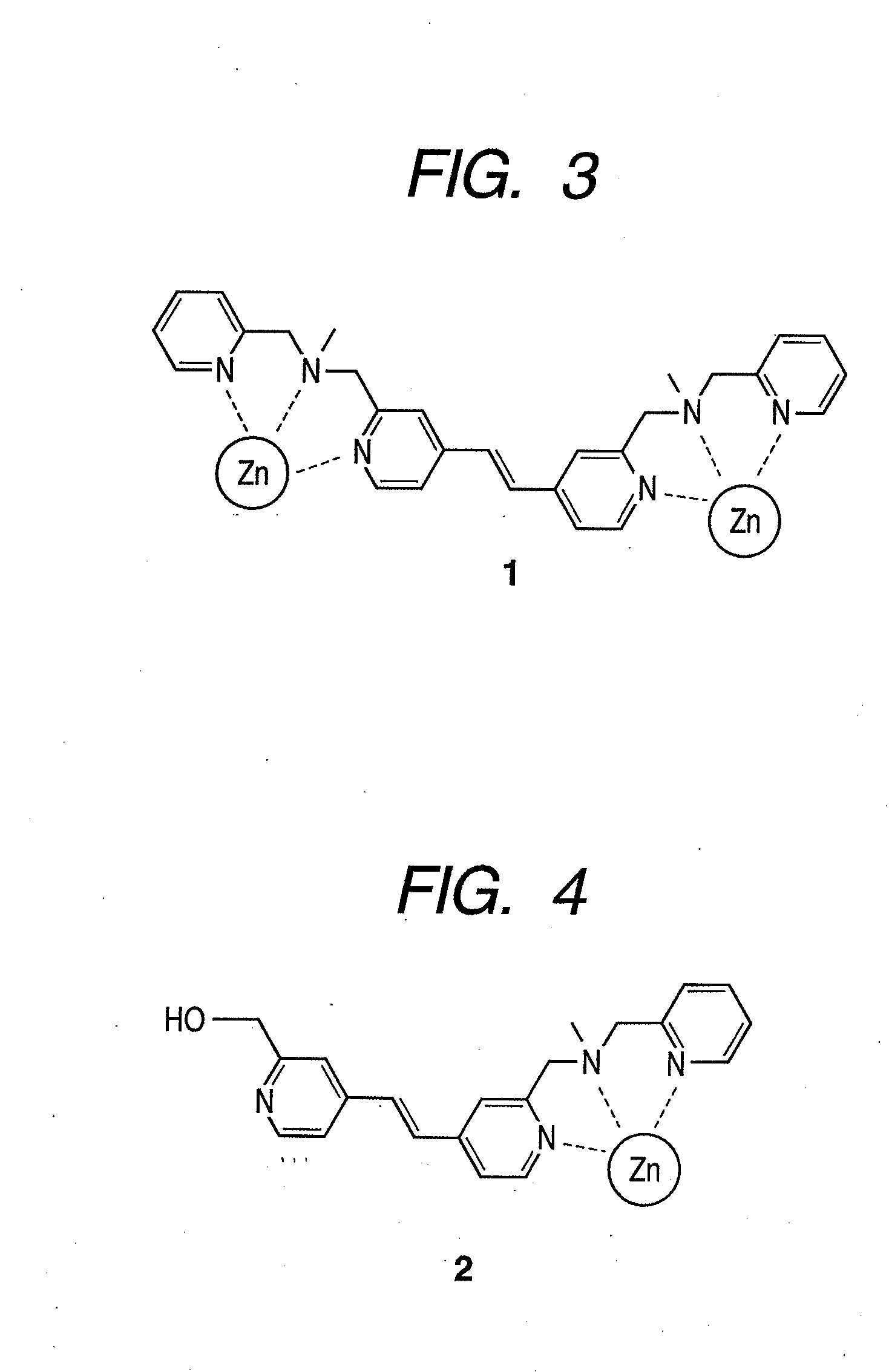
There are provided a novel compound which captures a multisite phosphorylated peptide or protein specifically to a phosphorylation site and a method for detecting a multisite phosphorylated peptide or protein using the same. In particular, there are provided a compound which specifically detects an excessively phosphorylated tau protein observed in the brain affected by Alzheimer's disease and a method for diagnosing Alzheimer's disease in vitro or in vivo using the compound. By bringing a metal complex compound having two dipicolylamine (Dpa) moieties and a spacer including a chromogenic or luminescent functional group or atom group into contact with a multisite phosphorylated peptide or protein, the compound recognizes the distance between phosphate groups and specifically binds to the peptide or the protein, and a multisite phosphorylated peptide or protein or a kinase activity is optically detected by measuring the change, or a multisite phosphorylated peptide or protein or kinase activity is imaged by an optical imaging method applying the change in the luminescence.
Owner:CANON KK
Method for quantifying phosphokinase activity on proteins
InactiveUS7888050B2Microbiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisProtein targetTyrosine
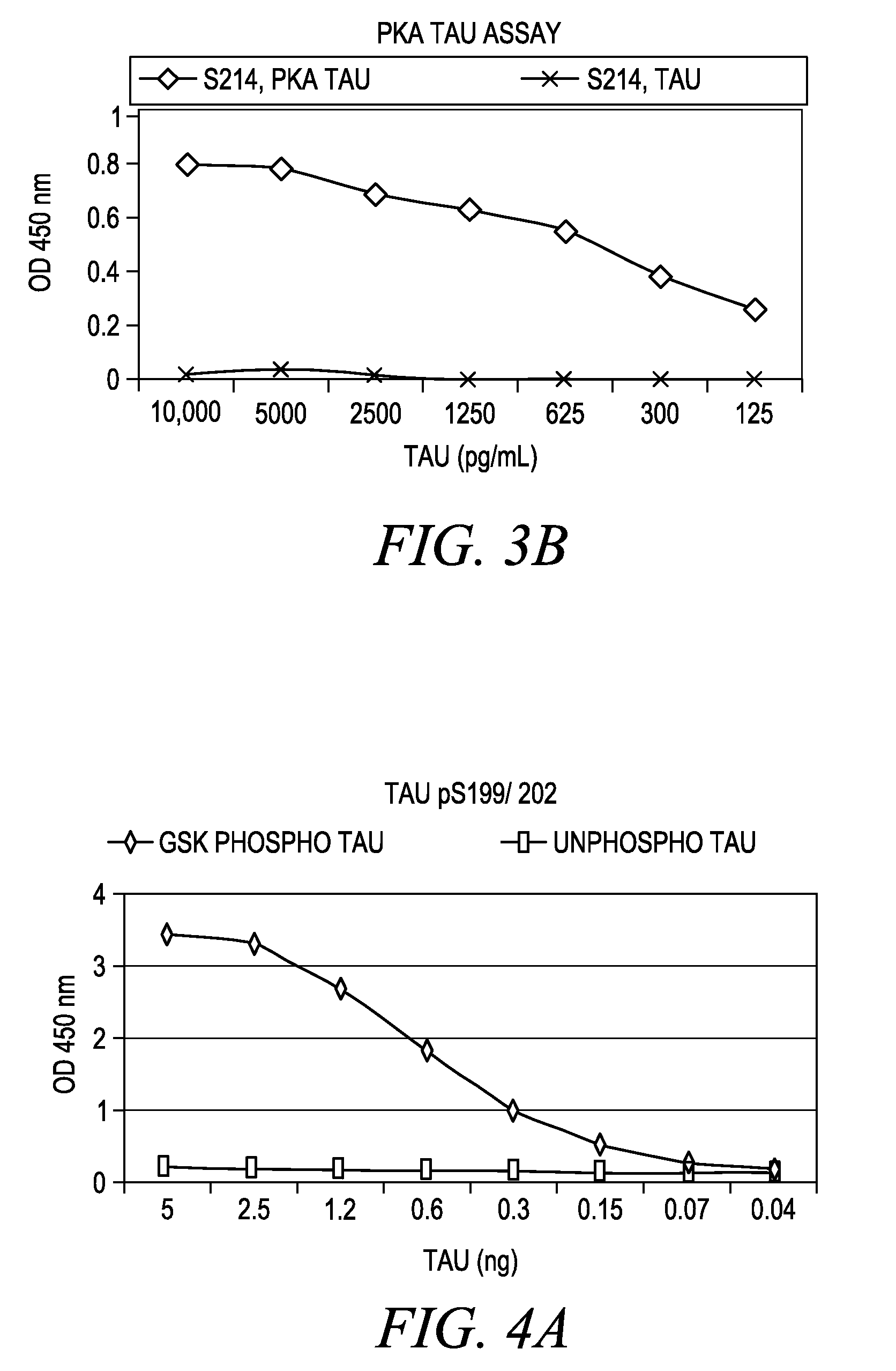
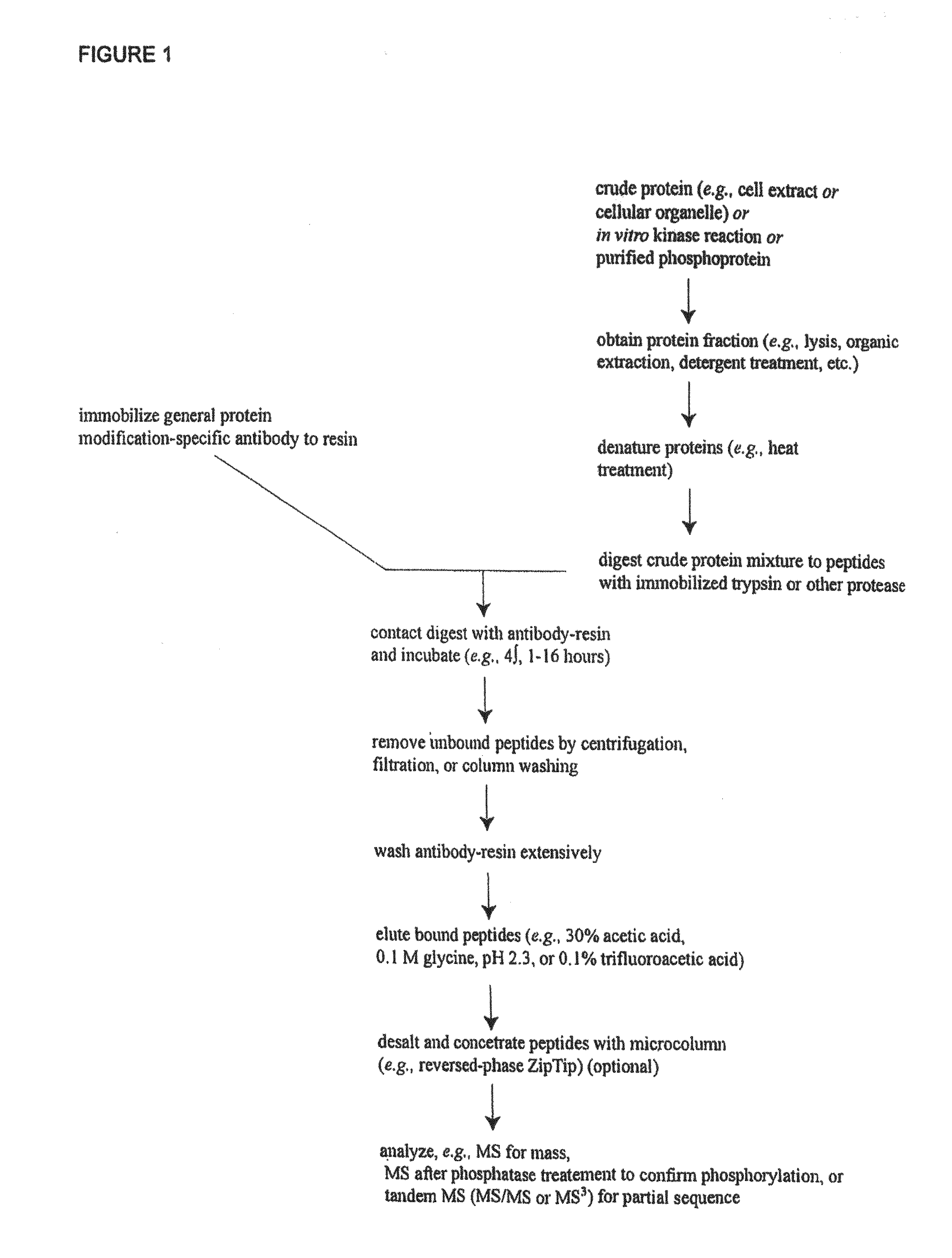
The invention involves a method for measuring phosphorylation of proteins at specific sites and, as such, is an indicator of the protein kinase activity of enzymes capable of phosphorylating those sites. The method involves the in vitro or in vivo phosphorylation of a target protein at a specific serine, threonine or tyrosine residue, subjecting that protein (non-phosphorylated) to reaction mixture containing all reagents, including phosphokinase which allow the creation of a phosphorylated form of protein. The phosphorylated protein is measured by contacting it with an antibody specific for the phosphorylation site(s). The invention includes antibodies useful in practicing the methods of the invention. The invention particularly relates to all proteins modified by phosphorylation and dephosphorylation as illustrated by Tau, Rb and EGFR proteins and antibodies specific for the site of phosphorylation of the Tau, Rb or EGFR proteins.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
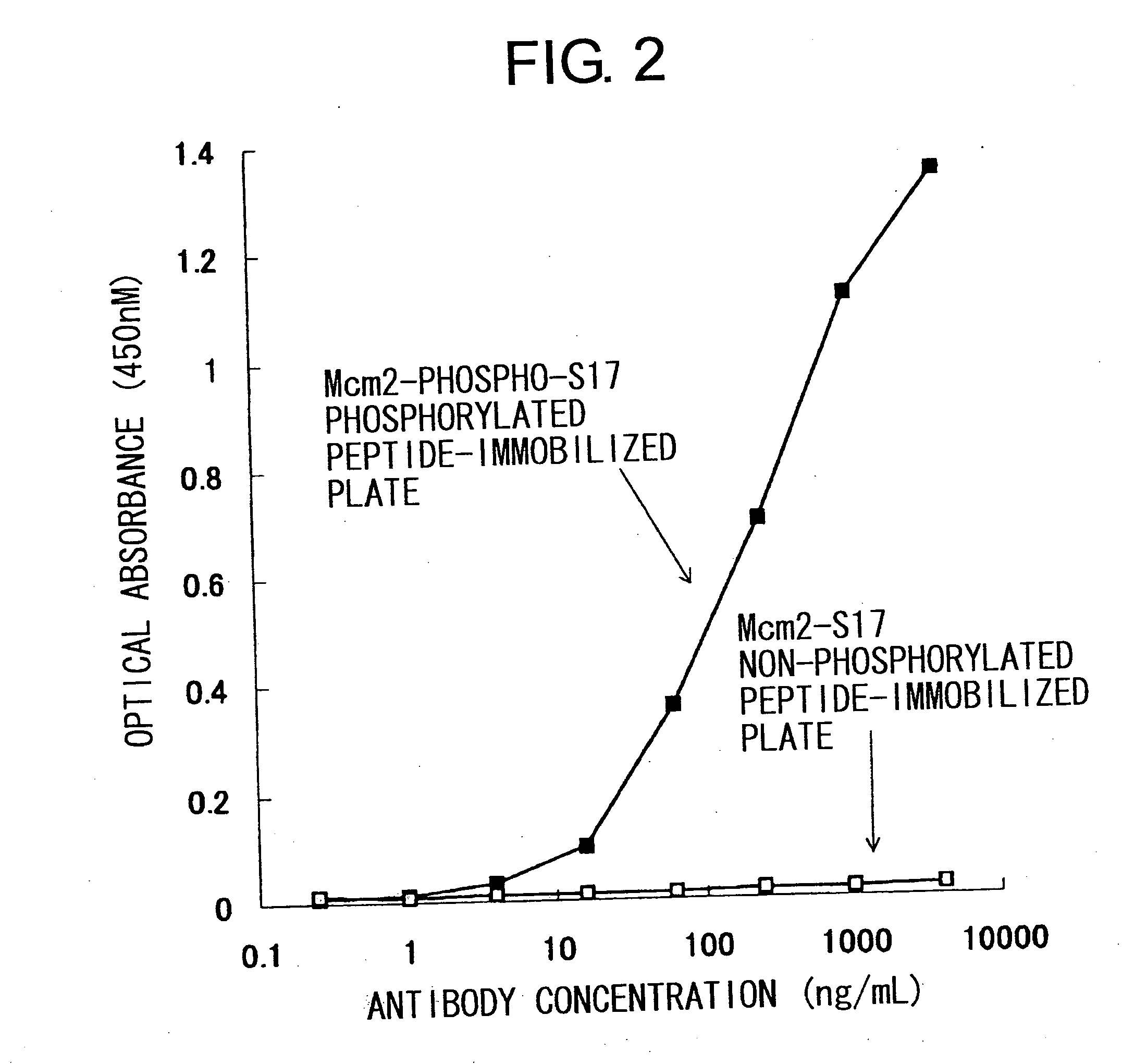
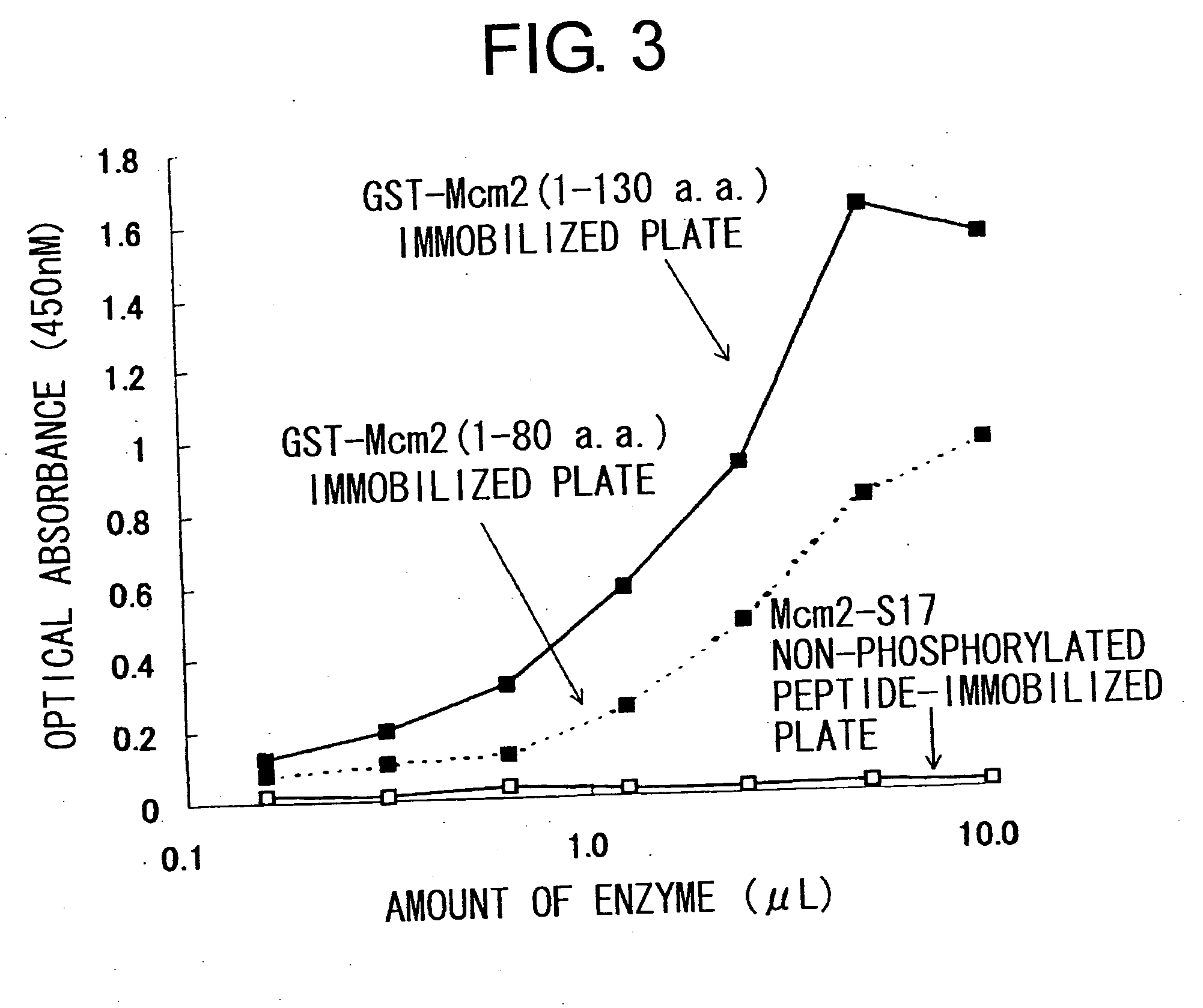
Cdc7-ask kinase complex, substrates of the kinase complex, antibody specific to the substrate, and method of screening compound capable of inhibiting cdc7-ask kinase using the same
InactiveUS20050250166A1Effective anticancer agentsCompound screeningApoptosis detectionAnticarcinogenPhosphorylation
The present invention provides methods for measuring the phosphorylation activity of Cdc7-ASK kinase complex by using as an indicator the level of phosphorylation at a phosphorylation site of MCM, which is a substrate of Cdc7-ASK kinase complex. The effects of test compounds on the phosphorylation activity of Cdc7-ASK kinase complex can also be evaluated based on these measurement methods. Compounds that inhibit this phosphorylation activity are useful as anti-cancer agents having superior specificity for cancer.
Owner:GINKGO BIOMEDICAL RES INST +2
Magnetic metal-organic framework nanosphere with multiple affinity sites as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN107486177AAchieve enrichmentHigh enrichment efficiencyOther chemical processesAlkali metal oxides/hydroxidesMetal-organic frameworkMagnetic response
The invention discloses a magnetic metal-organic framework nanosphere with multiple affinity sites as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The magnetic metal-organic framework nanosphere consists of a Fe3O4 magnetic sphere, a high-molecular polymer intermediate layer coating the surface of the magnetic sphere, a metal-organic framework growing on the high-molecular polymer intermediate layer and arginine grafted on the metal-organic framework. The magnetic metal-organic framework nanosphere disclosed by the invention takes the Fe3O4 magnetic sphere as a kernel and has good magnetic response performance; the metal-organic framework is introduced onto the surface of the magnetic sphere, and the organic ligand surface is modified through the arginine; as metal ions forming the metal-organic framework, a guanidyl on the arginine and the like can be taken as the multiple affinity sites for enriching phosphorylated polypeptides, the enrichment of the phosphorylated polypeptides for single-phosphorylation sites and multi-phosphorylation sites is achieved; the magnetic metal-organic framework nanosphere has high enrichment efficiency and has very important significance in studying the phosphorylation process of physiological behavioral proteins.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
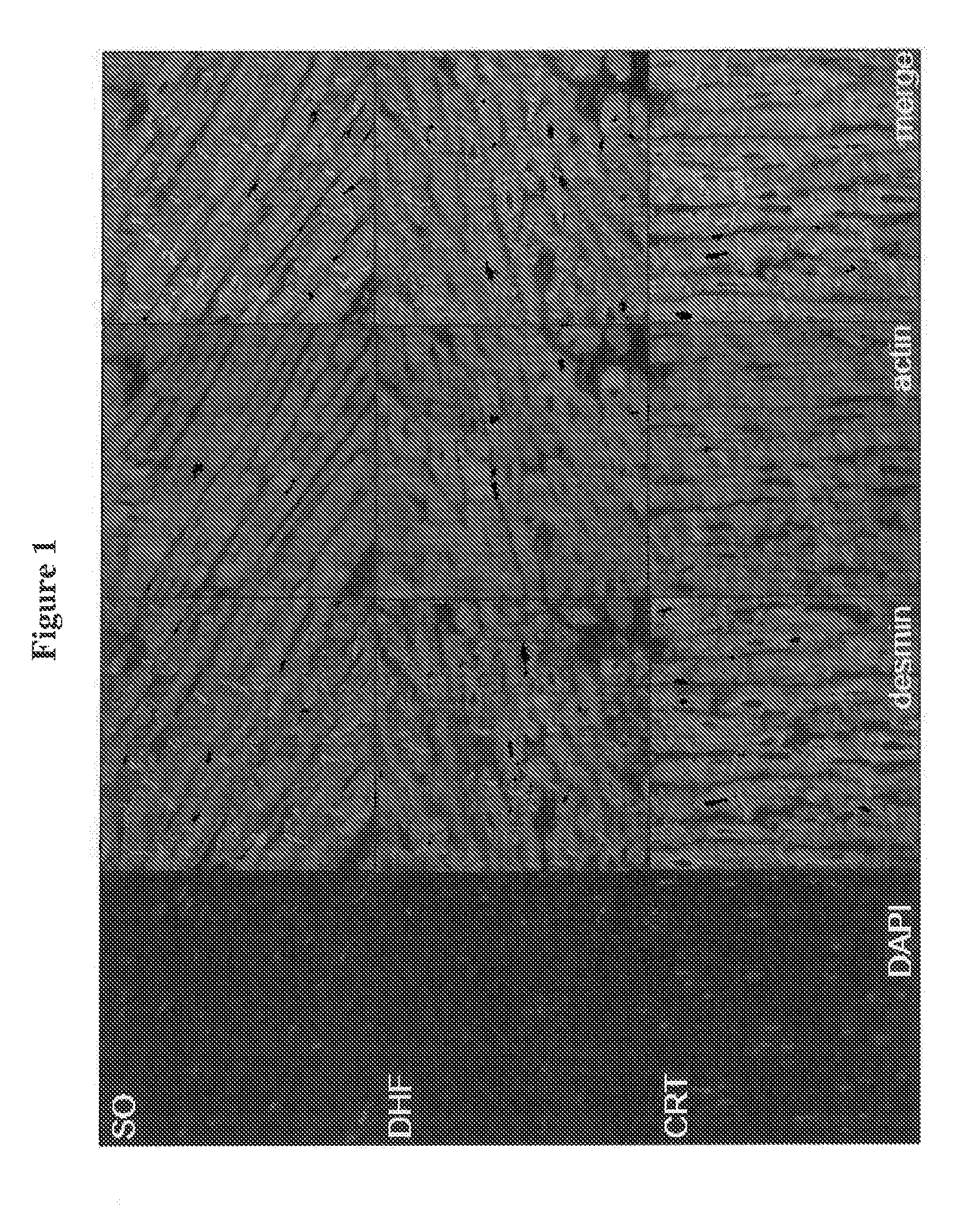
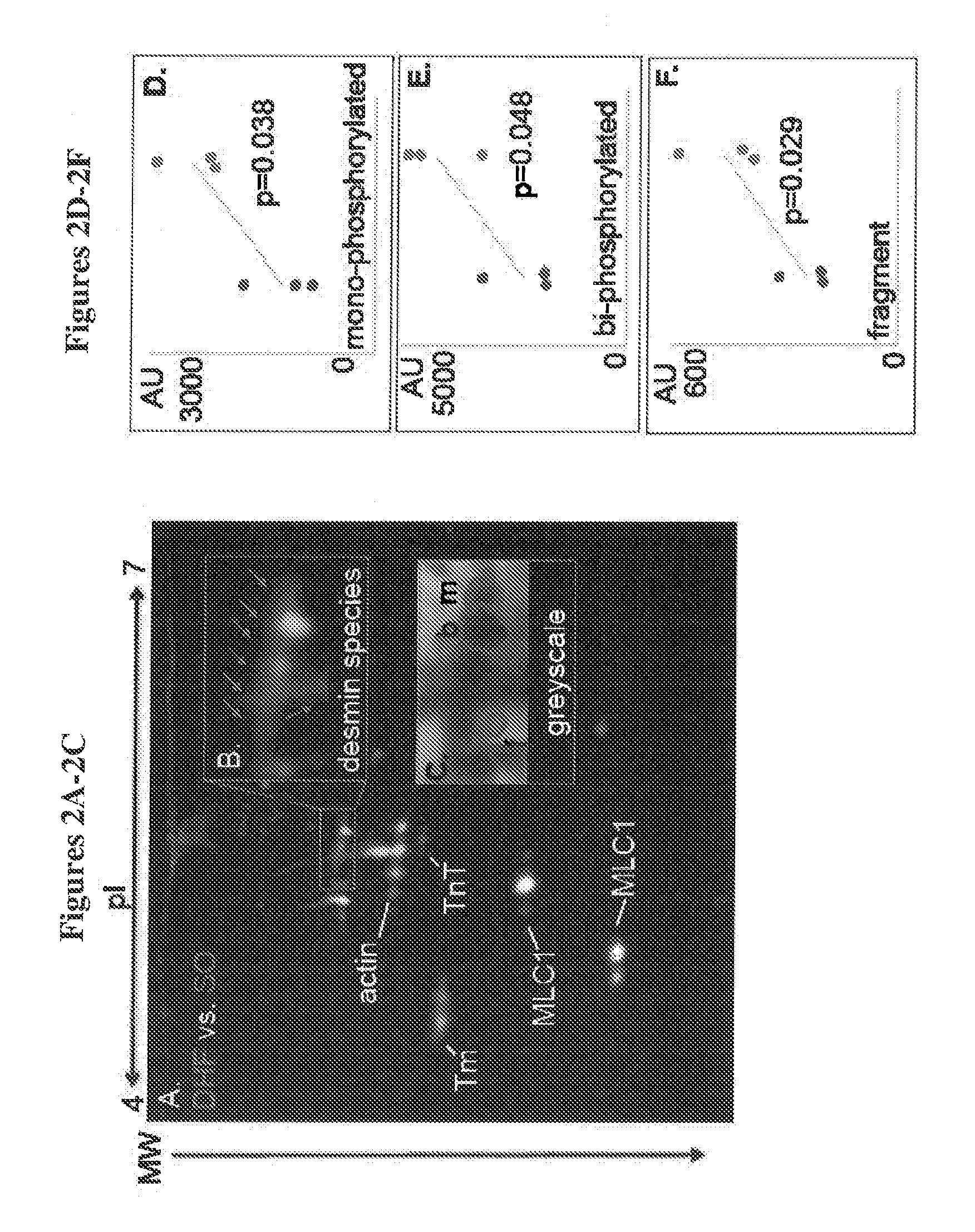
Novel desmin phosphorylation sites useful in diagnosis and intervention of cardiac disease
This invention relates to novel phosphorylation sites in the desmin protein that are associated with the onset of heart failure. The phosphorylation sites, i.e., Ser-27 and Ser-31, can be used as biomarkers for (i) identifying subjects at risk for the development of heart failure, (ii) treating subjects having a higher than normal level of the biomarker, and (iii) monitoring therapy of a subject at risk for the development of heart failure. Also described are antibodies, reagents, and kits for carrying out a method of the present invention.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Method for quantifying phosphokinase activity on proteins
InactiveUS20090104628A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisProtein targetTyrosine
The invention involves a method for measuring phosphorylation of proteins at specific sites and, as such, is an indicator of the protein kinase activity of enzymes capable of phosphorylating those sites. The method involves the in vitro or in vivo phosphorylation of a target protein at a specific serine, threonine or tyrosine residue, subjecting that protein (non-phosphorylated) to reaction mixture containing all reagents, including phosphokinase which allow the creation of a phosphorylated form of protein. The phosphorylated protein is measured by contacting it with an antibody specific for the phosphorylation site(s). The invention includes antibodies useful in practicing the methods of the invention. The invention particularly relates to all proteins modified by phosphorylation and dephosphorylation as illustrated by Tau, Rb and EGFR proteins and antibodies specific for the site of phosphorylation of the Tau, Rb or EGFR proteins.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Expression vectors for producing modified proteins
InactiveUS6514753B1Phosphorylation reaction isExtended shelf lifeBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsEscherichia coliMicroorganism
Modified proteins, modified interferons alpha's and beta's, phosphorylated modified proteins and DNA sequences encoding the above, applications and uses thereof. Modified phosphorylated Hu-IFN-alpha-like proteins are provided which carry an identifiable label such as a radio-label. Corresponding phosphorylatable Hu-IFN-alpha-like proteins which contain a putative phosphorylation site. DNA sequences which encode a Hu-IFN-alpha-like protein and contain a sequence encoding a putative phosphorylatable site. Appropriate expression vectors are used to transform compatible host cells of various microorganisms, such as E. coli. Numerous uses for the phosphorylated proteins are disclosed.
Owner:PESTKA BIOMEDICAL LAB
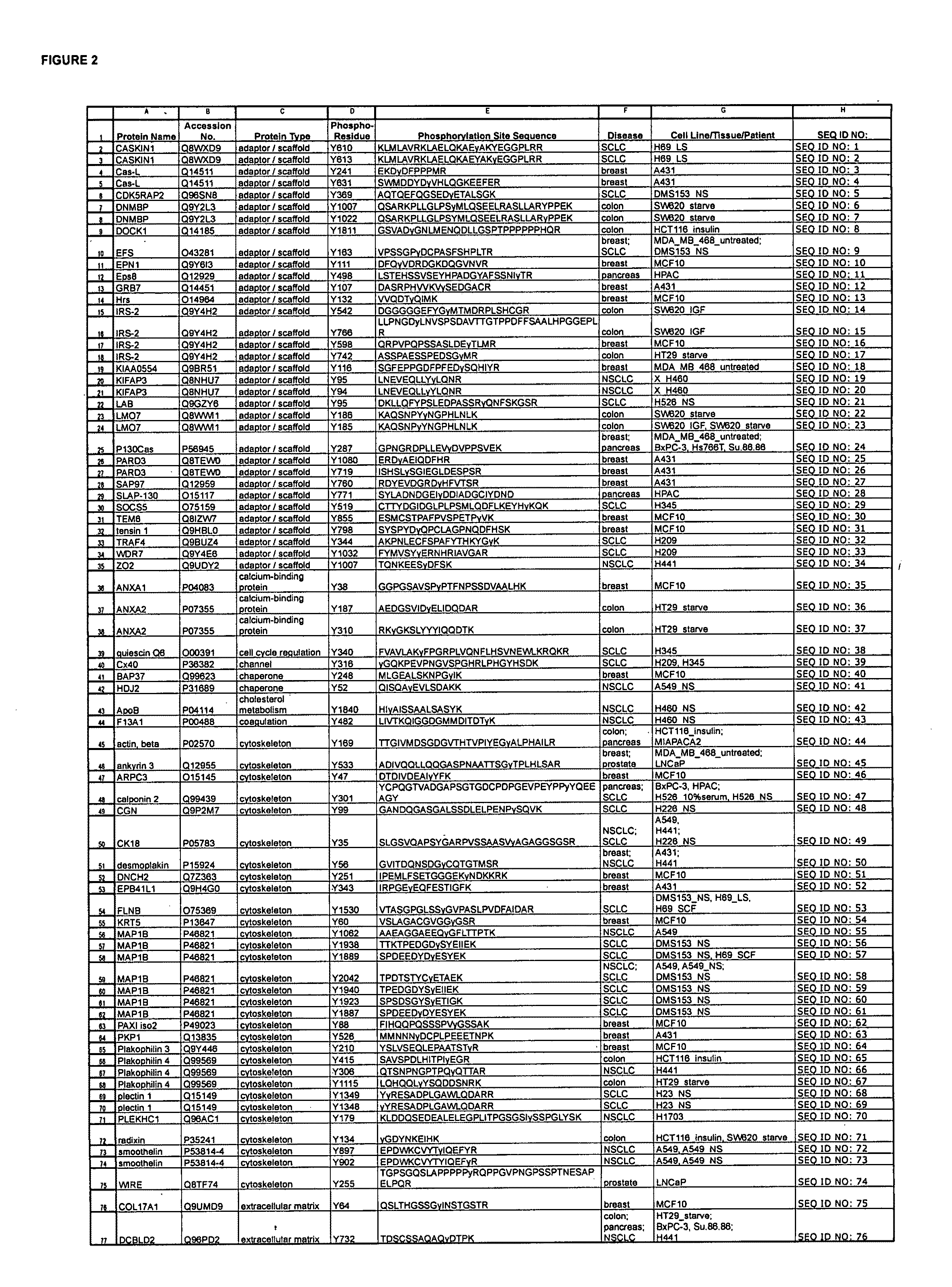
Tyrosine Phosphorylation Sites
InactiveUS20100129928A1Immunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsBiological testingPeptideAntibody
The invention discloses 347 novel phosphorylation sites identified in carcinoma, peptides (including AQUA peptides) comprising a phosphorylation site of the invention, antibodies specifically bind to a novel phosphorylation site of the invention, and diagnostic and therapeutic uses of the above.
Owner:CELL SIGNALING TECHNOLOGY
Modified G-protein coupled receptors
InactiveUS7214496B2High affinityImprove performanceCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsSugar derivativesCarboxyl radicalReceptor
The present invention relates to modified G-protein coupled receptors (GPCRs). The modified GPCRs of the present invention include GPCRs that have been modified to have carboxyl terminal tails comprising one or more sites of phosphorylation, preferably one or more clusters of phosphorylation sites. The modified GPCRs of the present invention may comprise a retained portion of a carboxyl-terminus region from a first GPCR fused to a polypeptide, wherein the polypeptide comprises the one or more clusters of phosphorylation. The present invention also relates to methods of screening compounds and sample solutions for GPCR activity using the modified GPCRs.
Owner:DUKE UNIV
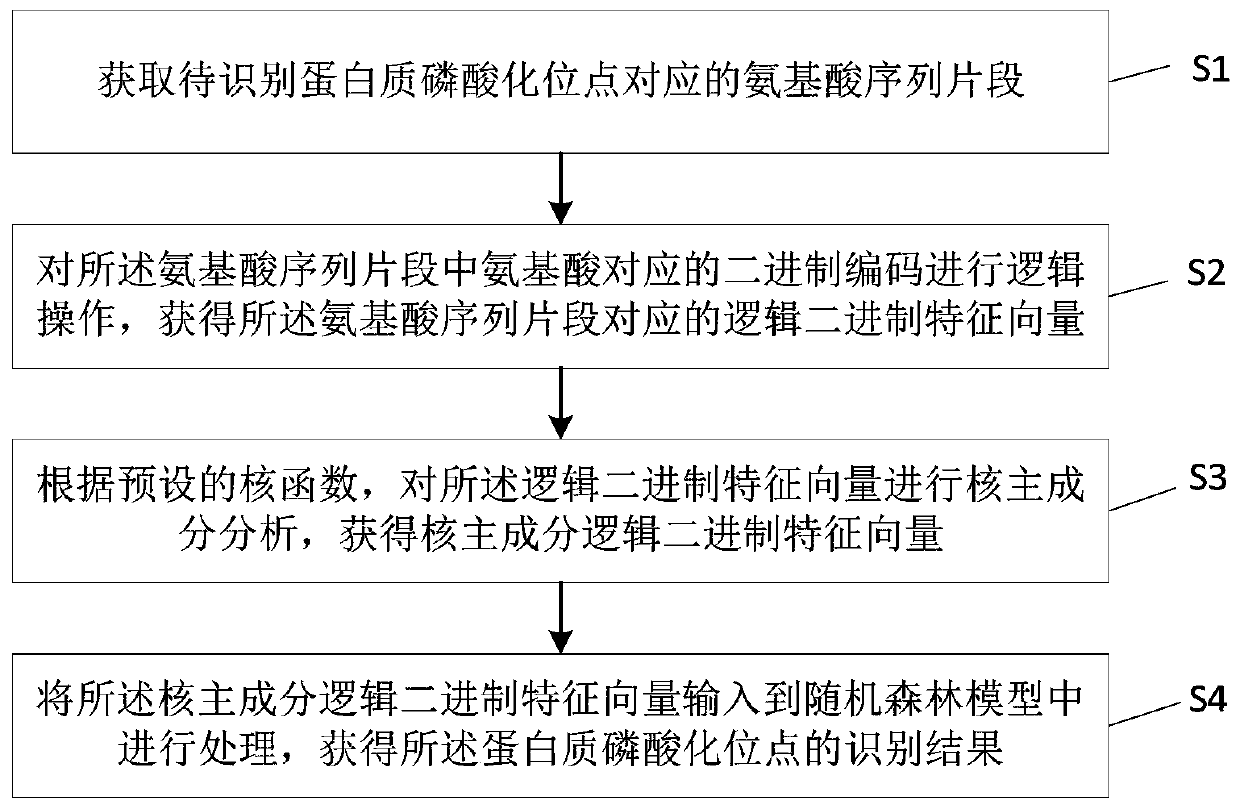
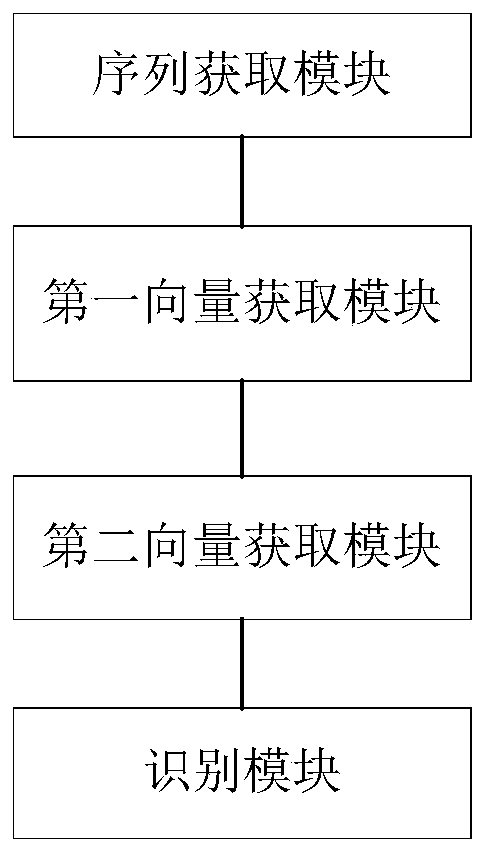
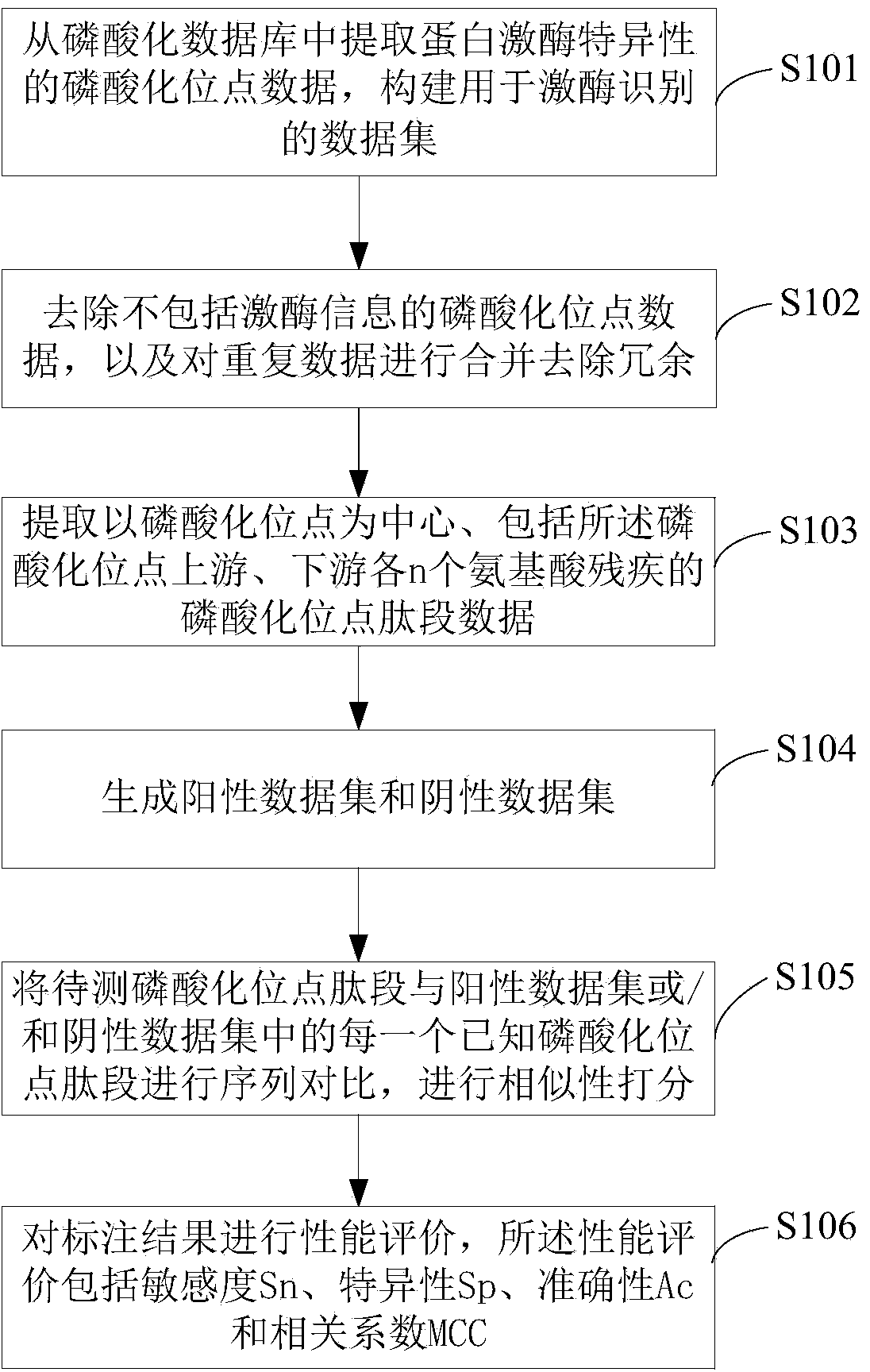
Protein phosphorylation site recognition method, system and device and storage medium
ActiveCN110349628AAccurate identificationImprove developmentArtificial lifeSequence analysisDiseaseFeature vector
The invention discloses a protein phosphorylation site identification method, system and device and a storage medium. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring an amino acid sequence fragment of a protein phosphorylation site to be identified; performing logic operation on binary codes of amino acids in the amino acid sequence fragment to obtain logic binary feature vectors of the aminoacid sequence fragment; performing kernel principal component analysis on the logic binary feature vector according to a preset kernel function to obtain a kernel principal component logic binary feature vector; and inputting the kernel principal component logic binary feature vector into a random forest model for processing to obtain an identification result of the protein phosphorylation site. Based on theoretical calculation of the random forest model, the method can achieve the quick and accurate recognition of the information of a large number of protein phosphorylation sites, is low in cost, facilitates the development of phosphorylation mechanism and phosphorylation and disease relation research, and is widely applied to the field of protein phosphorylation site recognition.
Owner:GUANGDONG PHARMA UNIV +1
GPCR Arrestin Assays
InactiveUS20100120063A1Improve bindingEnhance arrestin bindingMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisSmall fragmentLarge fragment
Sensitive assays for candidate compounds affecting GPCR activity are provided using a cell containing fusion proteins comprising a first fusion protein comprising (a) a target GPCR fused to a small fragment of β-galactosidase through a linker comprising a phosphorylation site or (b) a GPCR or a protein of interest, where the GPCR and protein of interest form a complex and one of them is fused to the small fragment of β-galactosidase; and a second fusion protein comprising arrestin fused to a large fragment of β-galactosidase. In (a), the affinity of the small and large fragments is optimized based on the background to signal ratio and the absolute signal observed. The assay is performed using a β-galactosidase substrate that provides a detectable optical signal.
Owner:DISCOVERYX CORP
Method for relative quantitative analysis of protein phosphorylation modification level
InactiveCN103163010AHigh sensitivityImprove accuracyComponent separationPreparing sample for investigationStable Isotope LabelingProtein phosphorylation
The invention provides an isotope label-free method for relative quantitative analysis of a protein phosphorylation modification level. The method comprises: conducting enzymolysis on protein to make it into peptide fragments, making use of a data-independent MS / MS technique to determine peptide fragments with phosphorylation sites, and utilizing a label-free quantitation technique to carry out relative quantitative analysis on the peptide fragments with phosphorylation sites. Compared with the existing methods combining data-dependent MS / MS analysis and stable isotope-labeling technologies, the method does not need an isotope labeling reagent, thus having the advantages of reducing the experiment cost and operation complexity.
Owner:TIANJIN INT JOINT ACADEMY OF BIOTECH & MEDICINE +1
Reagents for the Detection of Protein Phosphorylation in Carcinoma Signaling Pathways
InactiveUS20110105732A1Immunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsFermentationADAMTS ProteinsProtein phosphorylation
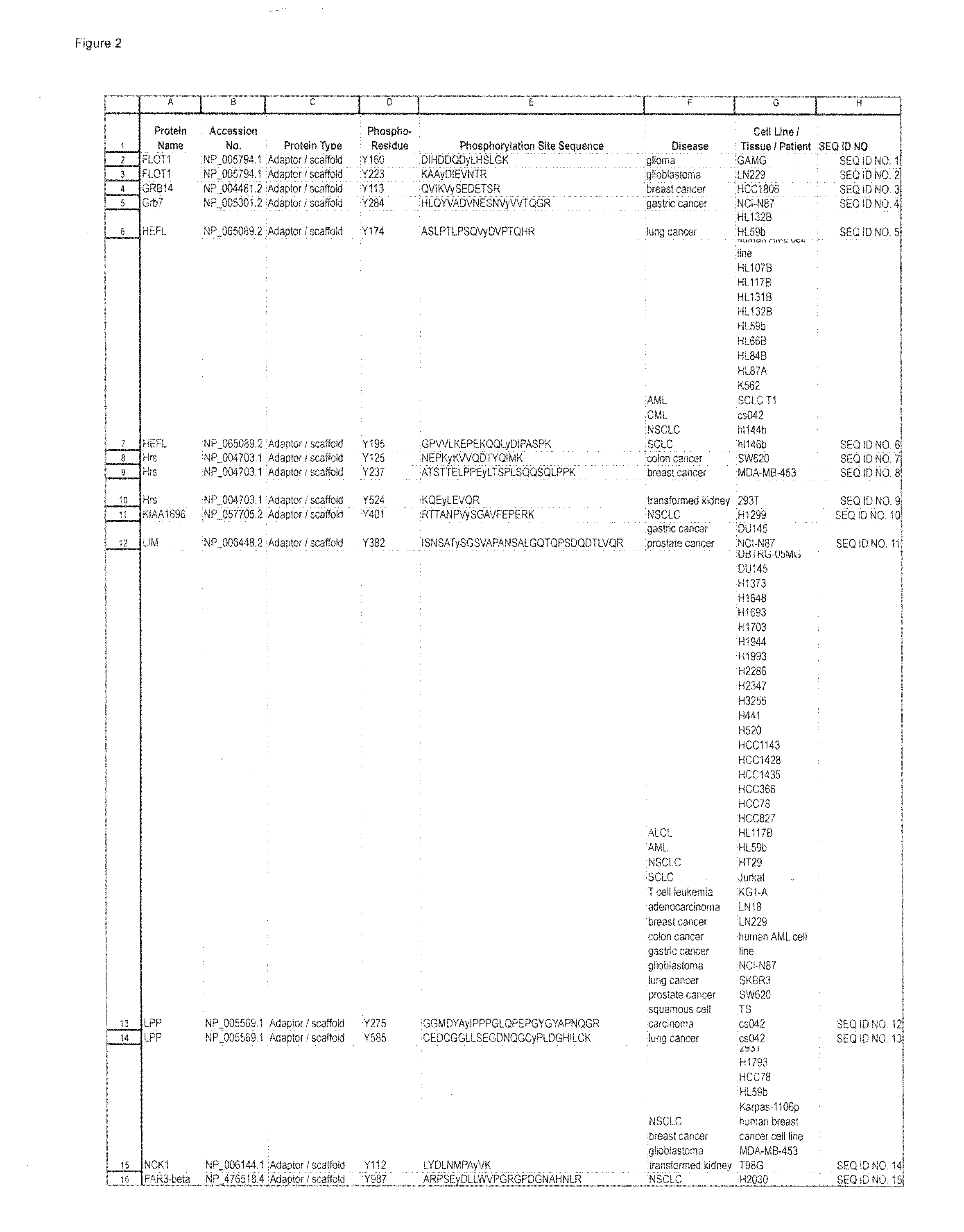
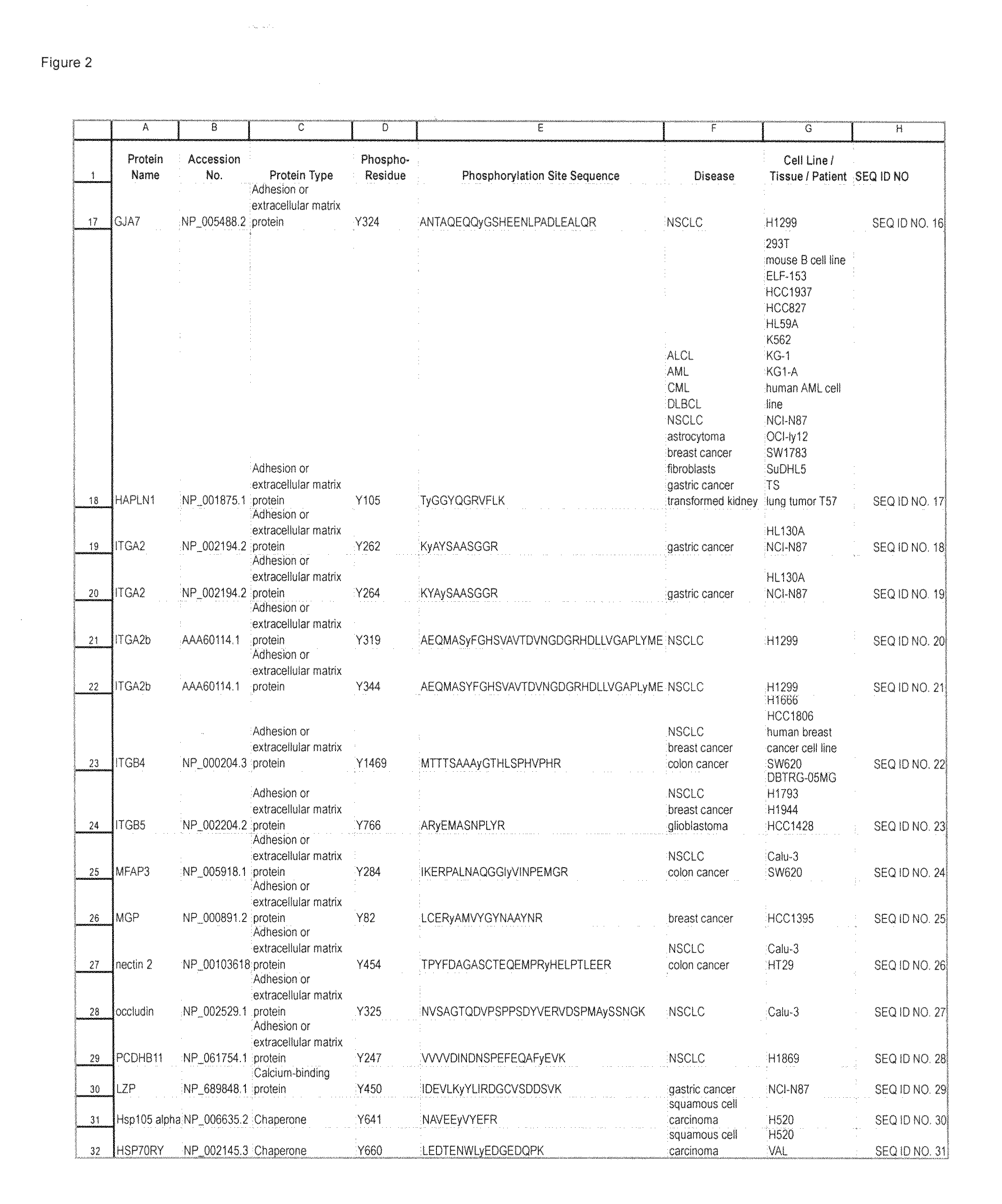
The invention discloses 214 novel phosphorylation sites identified in signal transduction proteins and pathways underlying human carcinoma, and provides phosphorylation-site specific antibodies and heavy-isotope labeled peptides (AQUA peptides) for the selective detection and quantification of these phosphorylated sites / proteins, as well as methods of using the reagents for such purpose. Among the phosphorylation sites identified are sites occurring in the following protein types: Adaptor / Scaffold proteins, Cytoskeleton proteins, GTP Signaling proteins, Kinases, Metabolism proteins, Phosphatases / Phospho-diesterases / Proteases, Receptor proteins, RNA Processing proteins, Transcription proteins, Translation proteins, Transporter proteins, and Ubitquitin proteins, as well as other protein types.
Owner:CELL SIGNALING TECHNOLOGY
Protein kinase specificity prediction method and device based on nearest neighbor algorithm
InactiveCN103745135AImprove accuracyHigh sensitivitySpecial data processing applicationsNear neighborTrue positive rate
The invention relates to the technical field of protein modification site identification, in particular to a protein kinase specificity prediction method and device based on a nearest neighbor algorithm. According to the prediction method, amino acid information on the upstream and the downstream of a phosphorylation site is fully utilized, and the accuracy of prediction is increased. According to the protein kinase specificity prediction method, an amino acid permutation matrix is used for scoring the similarity of a phosphorylation site peptide fragment to be detected and a known phosphorylation site peptide fragment, the phosphorylation site peptide fragment to be detected is marked to be the highest scored known phosphorylation site peptide fragment, and the sensitivity and the specificity of prediction are improved.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH
Saccharomyces cerevisiae engineering bacteria with low-yielding ethyl carbamate, and building method and application of saccharomyces cerevisiae engineering bacteria
InactiveCN103571765AImprove utilizationReduce formationFungiMicroorganism based processesAdditive ingredientBacterial strain
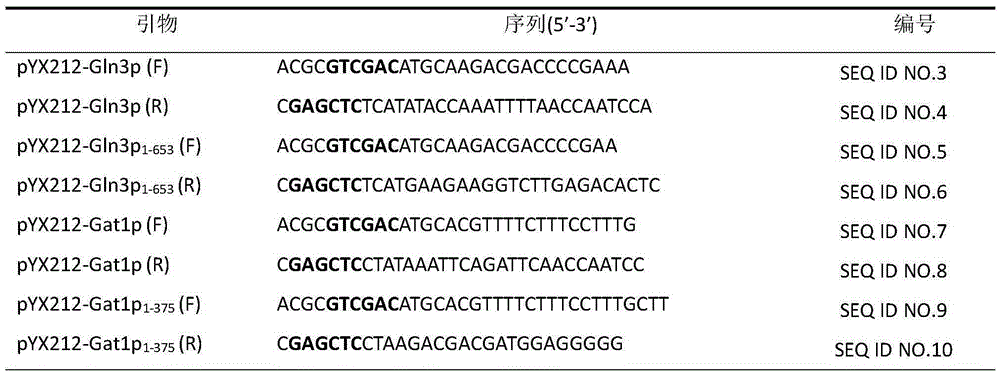
The invention discloses saccharomyces cerevisiae engineering bacteria with low-yielding ethyl carbamate. A regulatory factor G1n3p in saccharomyces cerevisiae is transformed through engineering bacteria. The concrete strategy is that a phosphorylation site on a G1n3p nuclear localization sequence is subjected to mutation to form three phosphorylation sites on the G1n3p nuclear localization sequence; the three phosphorylation sites respectively are the 344th, 347th and 355th serine. In order to obtain a better technical effect, a nuclear localization regulatory region of combining G1n3p with an upstream regulatory factor can be further removed; the G1n3p of a regulatory sequence at the tail end of C is removed by truncated expression, wherein an expression sequence is 1-653. The EC yield of the engineering bacteria disclosed by the invention is reduced by 62% by detection of a yellow rice wine simulation system. In addition, the content of main ingredients is not significantly changed, and the fermentation characteristics and the growth characteristics of a bacterial strain are not affected after the content of other ingredients in a fermentation liquor after fermentation is detected.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
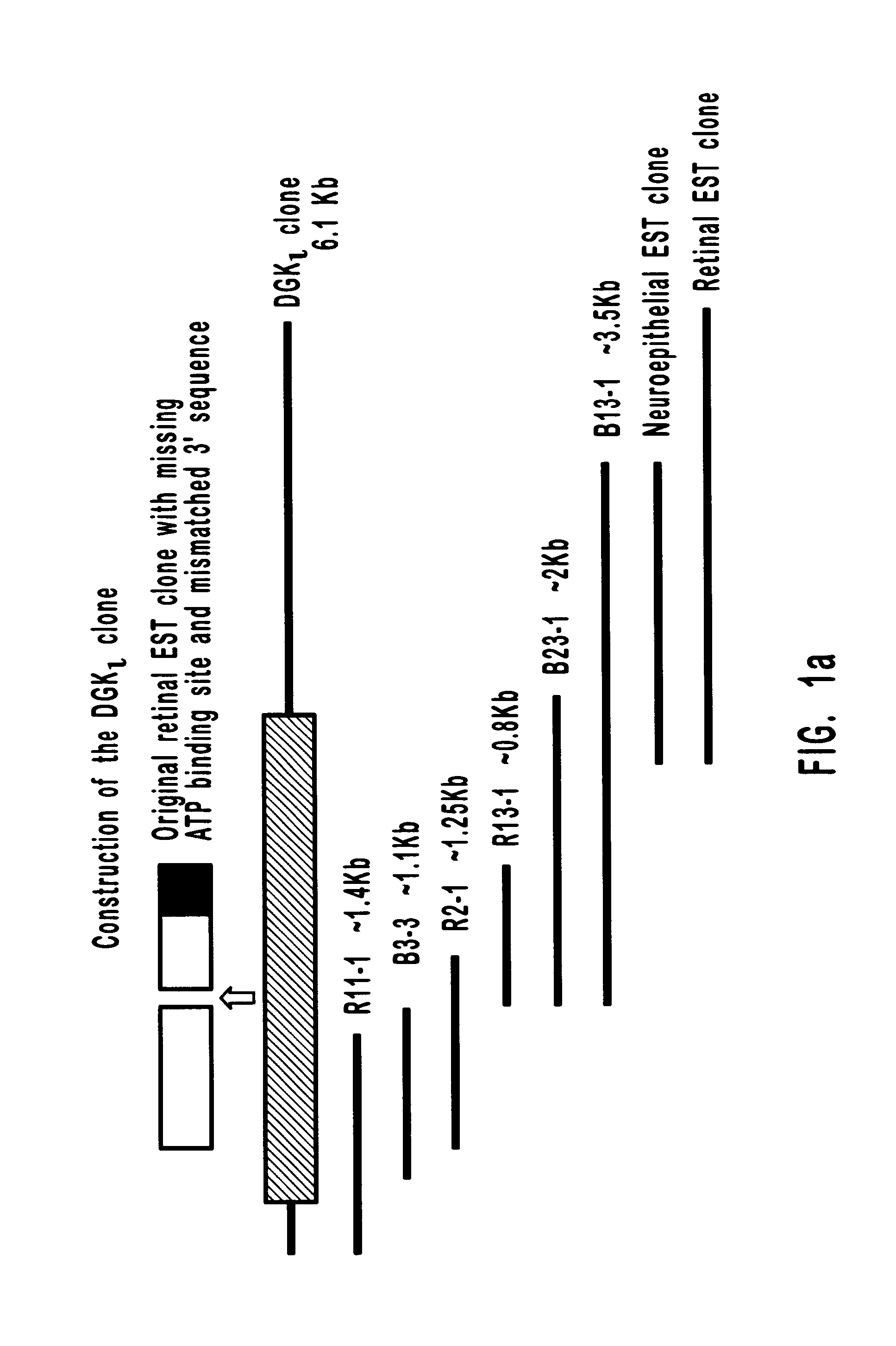
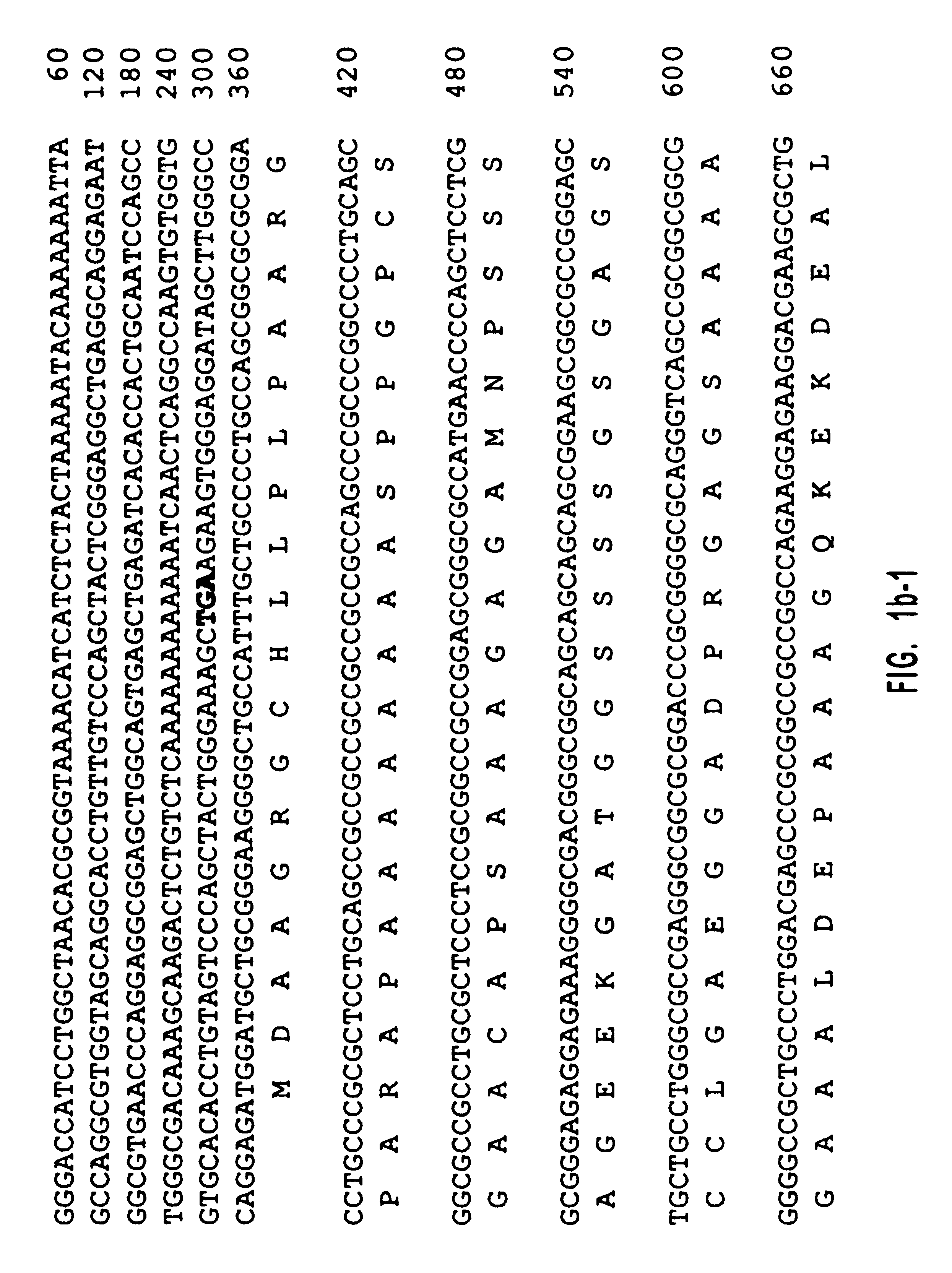
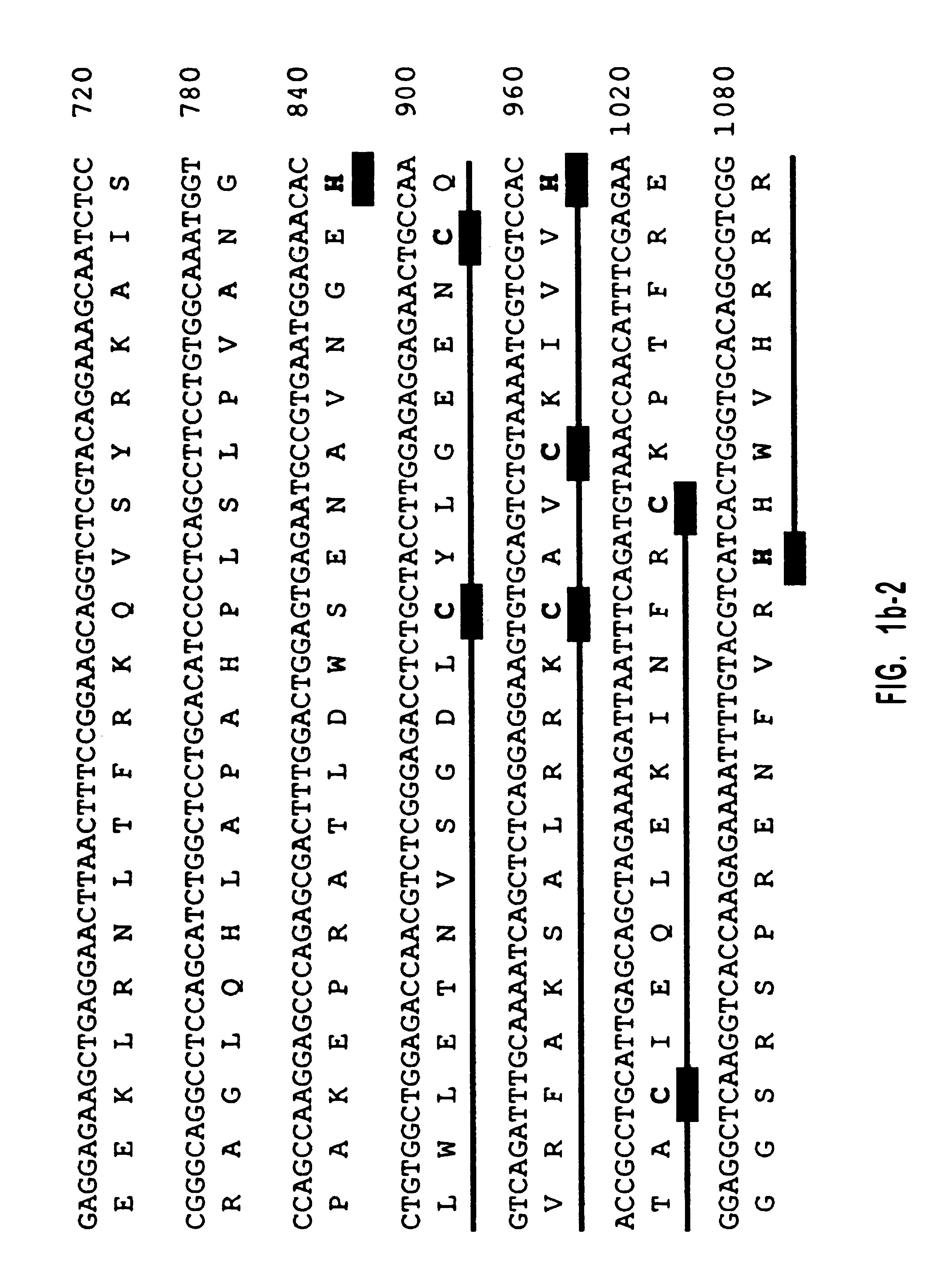
Human diacylglycerol kinase iota
Diacylglycerol (DAG) plays a central role in both the synthesis of complex lipids and in intracellular signaling; diacylglycerol kinase (DGK) catalyzes the phosphorylation of DAG, which yields phosphatidic acid. A family of DGKs has been identified in multicellular organisms over the past few years, but the physiological function(s) of this diversity is not clear. One clue has come from the Drosophila DGK2, rdgA, since mutations in this gene cause retinal degeneration. The present invention relates to a novel DGK, designated DGKι, which was isolated from human retina and brain libraries. DGKι contains two cysteine-rich repeats, a region similar to the phosphorylation site domain of MARCKS, a conserved catalytic domain, and four ankyrin repeats at its C-terminus. By primary structure, DGKι is most similar to human DGKζ and Drosophila rdgA. A>12 kb mRNA for DGKι was detected only in brain and retina among the tissues examined. In cells transfected with the DGKι cDNA, an approximately 130 kDa protein was detected by immunoassay, and activity assays demonstrated that it encodes a functional DAG kinase. The protein was found to be in both the cytoplasm and nucleus, with this localization controlled by PKC isoforms alpha and gamma. The gene encoding DGKι was localized to human chromosome 7q32.3-33, which is known to be a locus for an inherited form of retinitis pigmentosa. These results have defined a novel isoform of DAG kinase, which may have important cellular functions in the retina and brain.
Owner:THE UNIV OF UTAH
Tyrosine, Serine, And Threonine Phosphorylation Sites
The invention discloses 94 novel phosphorylation sites identified in carcinoma and leukemia, peptides (including AQUA peptides) comprising a phosphorylation site of the invention, antibodies that specifically bind to a novel phosphorylation site of the invention, and diagnostic and therapeutic uses of the above.
Owner:CELL SIGNALING TECHNOLOGY
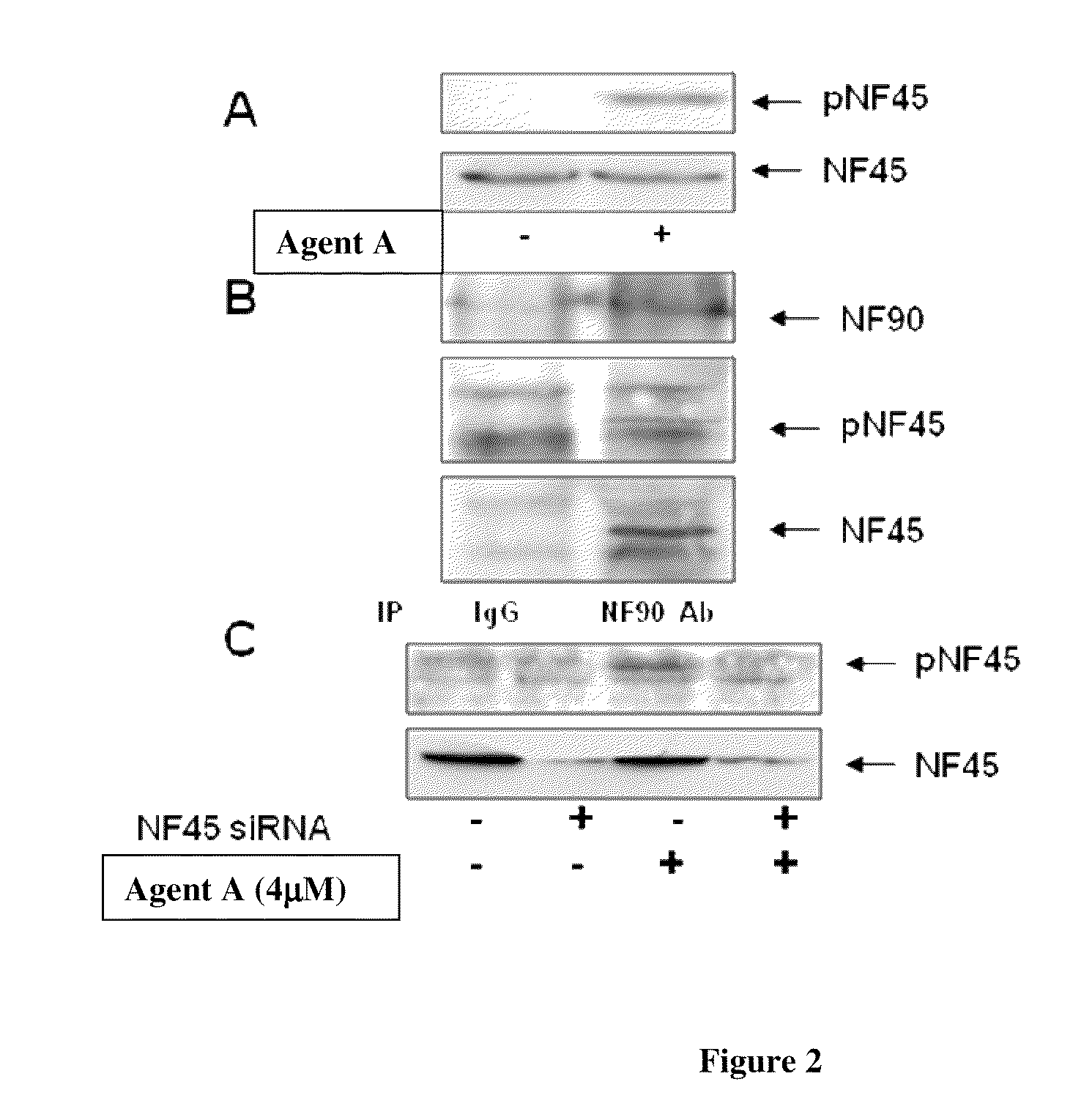
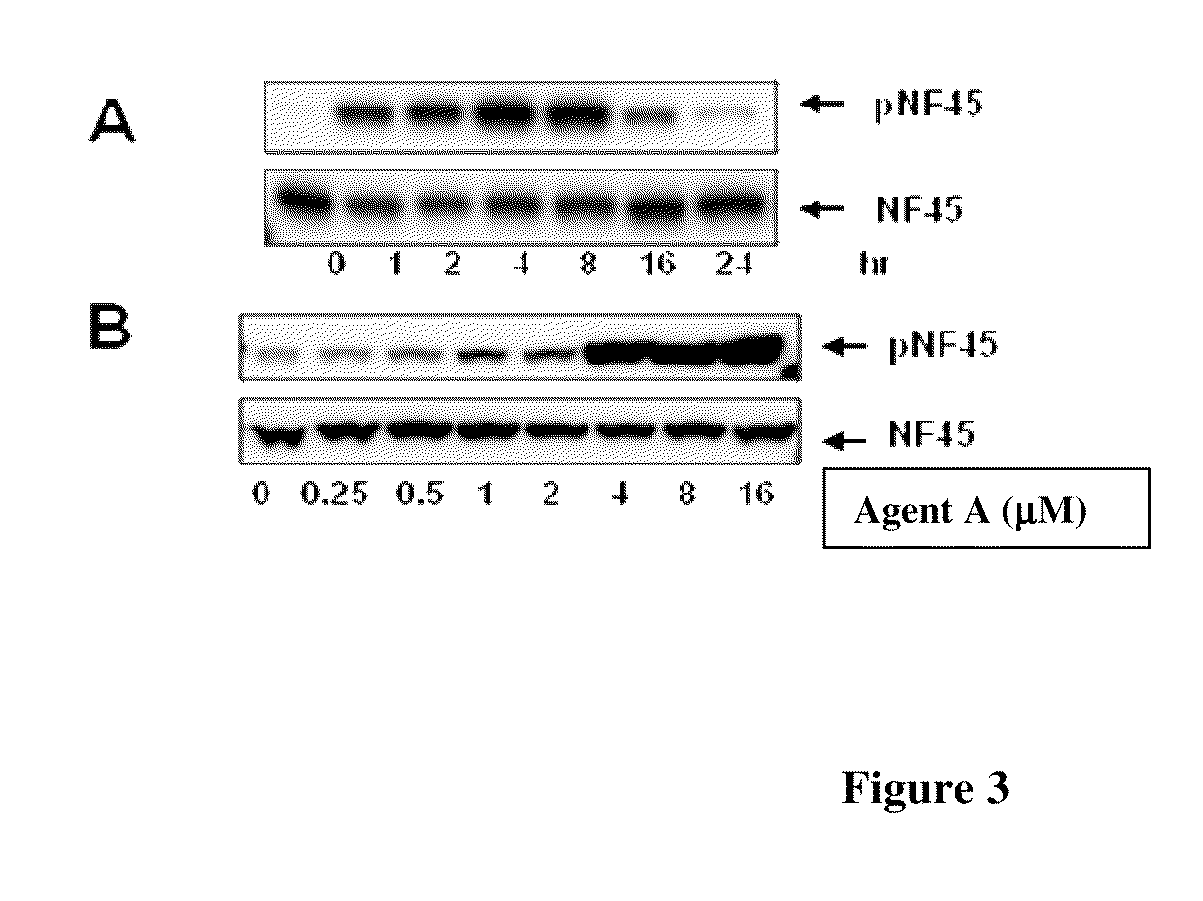
Phosphorylated NF45 Biomarkers, Antibodies And Methods Of Using Same
InactiveUS20120021432A1Peptide/protein ingredientsImmunoglobulins against animals/humansAntigen bindingSpecific antibody
The present invention relates to isolated phosphorylated NF45 peptides and isolated phosphorylation site-specific antibody or antigen-binding portion thereof that specifically binds a phosphorylated NF45 protein. The present invention also relates to methods of utilizing these antibodies to determine the therapeutic efficacy of a candidate compound and methods for screening for candidate compounds that increase the phosphorylation of NF45 protein in a cell.
Owner:ARQULE INC
Reagents for the detection of protein phosphorylation in anaplastic large cell lymphoma signaling pathways
The invention discloses 211 novel phosphorylation sites identified in signal transduction proteins and pathways underlying Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma (ALCL) involving the ALK-NPM translocation / fusion, and provides phosphorylation-site specific antibodies and heavy-isotope labeled peptides (AQUA peptides) for the selective detection and quantification of these phosphorylated sites / proteins, as well as methods of using the reagents for such purpose. Among the phosphorylation sites identified are sites occurring in the following protein types: Protein Kinases (including Receptor Tyrosine Kinases), Adaptor / Scaffold Proteins, Cellular Metabolism or Miscellaneous Enzymes, Oxidoreductases, Transcription Factors, Cytoskeletal Proteins, Translation Initiation Complexes, RNA Binding Proteins, Proteases, Acetyltransferases, G protein regulators / GTPases, Helicases, Apoptosis / Cell Cycle Regulation proteins, and Hydrolases.
Owner:CELL SIGNALING TECHNOLOGY
Kinase substrate sensor
ActiveUS20140030746A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioSolve the real problemAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsMicrobiological testing/measurementKinase substrateCytoplasmic protein
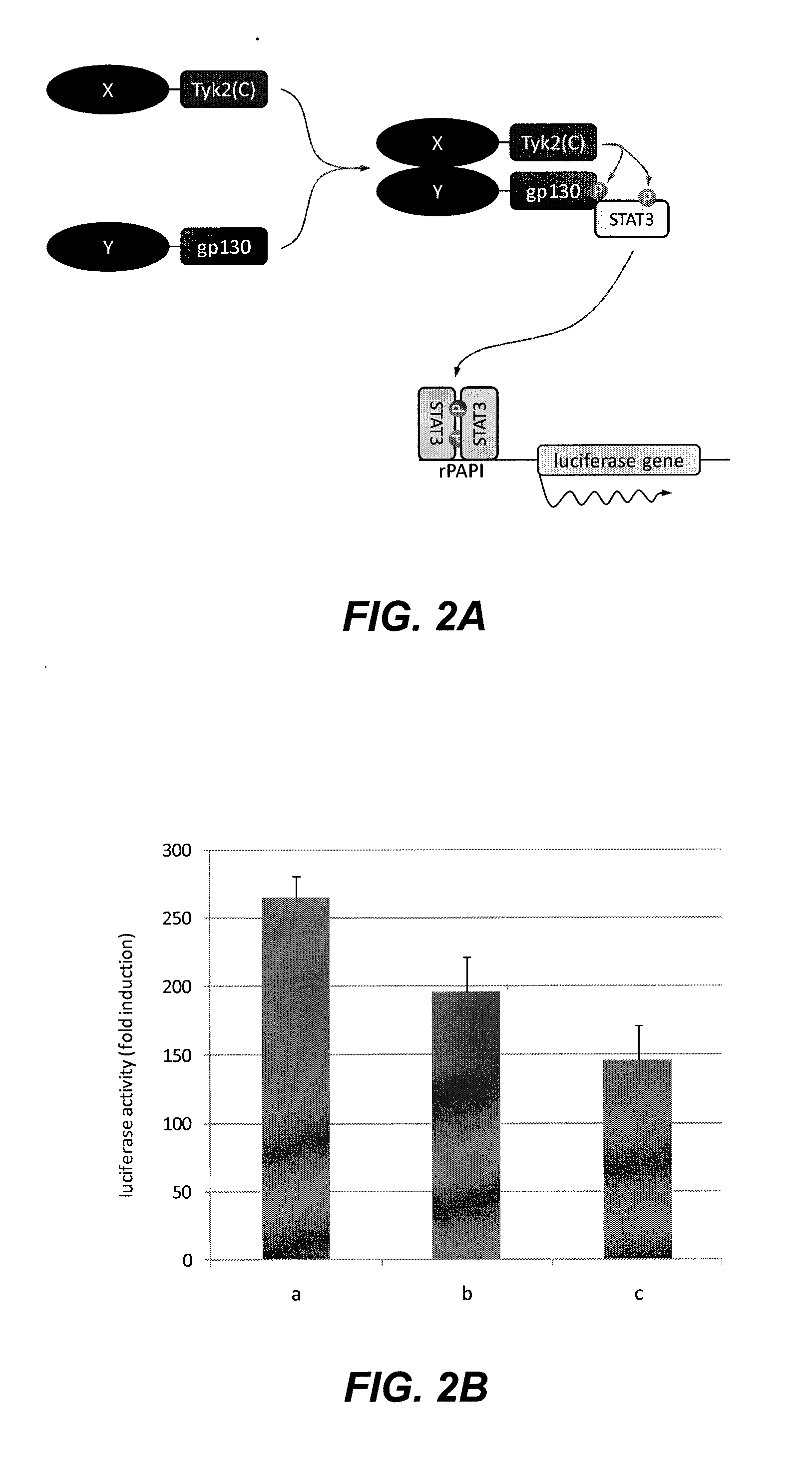
The disclosure relates to a cytoplasmic protein complex comprising: (a) a first recombinant fusion protein comprising a kinase, fused to a first interaction polypeptide; and (b) a second recombinant fusion protein comprising a domain comprising a reporter phosphorylation site, whereby the domain is fused to a second interaction polypeptide. The disclosure relates further to a method to detect compound-compound-interaction using the cytoplasmic protein complex, and to cells comprising such cytoplasmic protein complex.
Owner:VLAAMS INTERUNIVERSITAIR INST VOOR BIOTECHNOLOGIE VZW +1
Reagents for the detection of protein phosphorylation in anaplastic large cell lymphoma signaling pathways
InactiveUS20100173322A1Immunoglobulins against animals/humansBiological testingProtein phosphorylationSpecific antibody
Owner:CELL SIGNALING TECHNOLOGY
Method with function of reducing accumulation of ethyl carbamate in rice wine fermentation
InactiveCN105273918AMeet production requirementsReduce contentFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyMicrobial genetics
The invention belongs to the field of microbial genetics and molecular biology and discloses a method with a function of reducing accumulation of ethyl carbamate in rice wine fermentation. Genetically engineered bacteria modified by nitrogen catabolite repression regulation factors are adopted for rice wine fermentation, and engineered saccharomyces cerevisiae eliminates nuclear localization regulatory sequences of the regulation factors Gln3p and Gat1p and mutates phosphorylation sites of the nuclear localization sequences. In a simulated rice wine fermentation system, compared with rice wine with wild strains for fermentation, rice wine fermented with the genetically engineered bacteria has the advantages that contents of carbamide and ethyl carbamate in the rice wine are decreased by 63% and 72% respectively, the content of the ethyl carbamate in the rice wine is decreased to about 55.53 microgram / L, and contents of major nutrient substances and characteristic flavor substances are less in difference. Therefore, the method has a huge potential of application to rice wine production.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
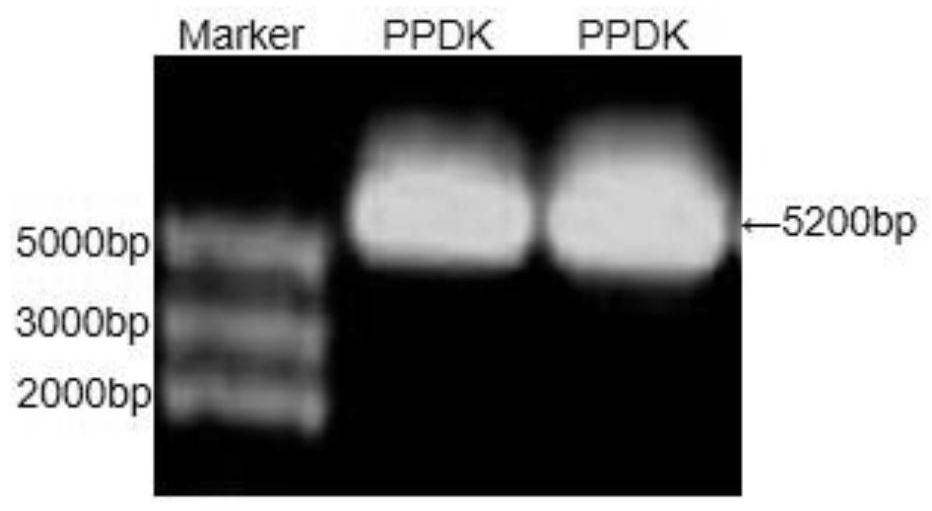
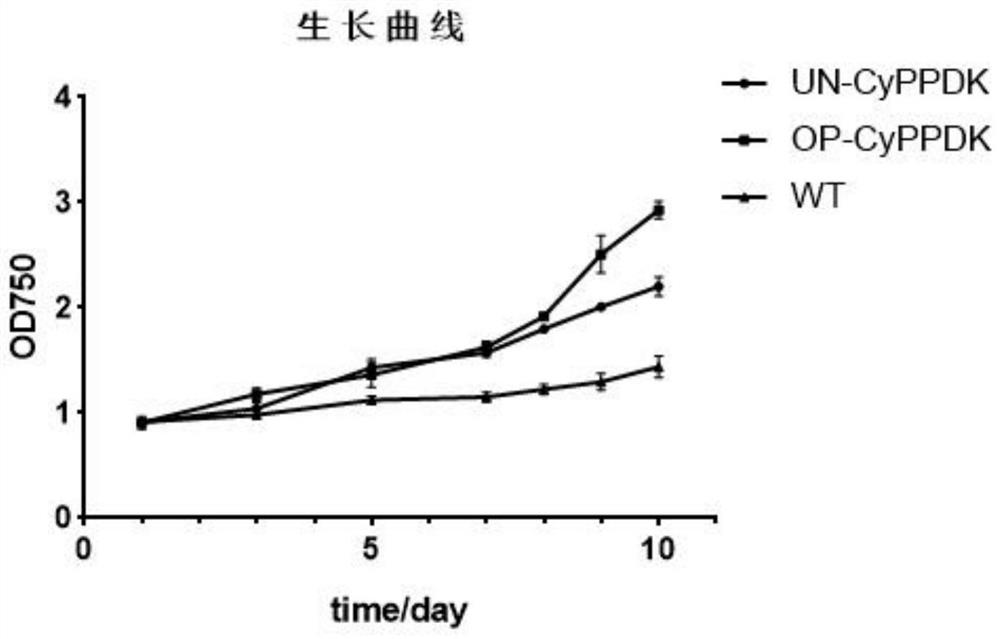
Method for producing fucoxanthin by using mutant strain for expressing exogenous pyruvate phosphate dikinase in phaeodactylum tricornutum
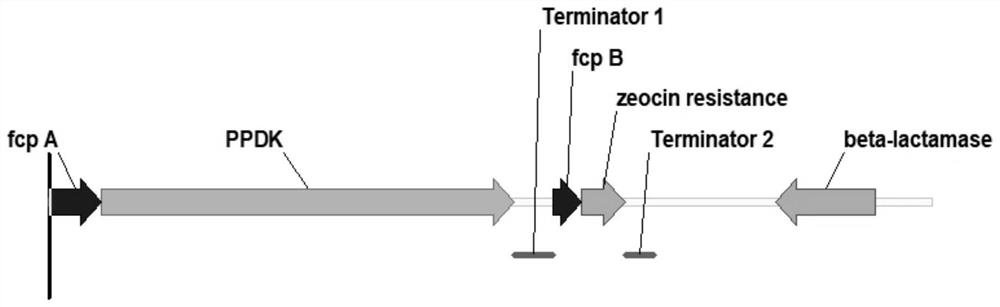
ActiveCN112695047AIncrease growth rateIncrease productionUnicellular algaeTransferasesBiotechnologyFucoxanthin
The invention provides a method for producing fucoxanthin by using a mutant strain for expressing exogenous pyruvate phosphate dikinase in phaeodactylum tricornutum, and particularly relates to algae preference codon optimization on an original CyPPDK gene to obtain a new CyPPDK gene with a nucleotide sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO.7; the constructed shuttle expression vector is named as pPha-fcp-PPDK; and the obtained new gene is introduced into a host algae cell phaeodactylum tricornutum cell in an electric transformation manner, and a transformant is screened to obtain a phaeodactylum tricornutum transgenic algae strain for overexpression of pyruvate phosphate dikinase. Compared with an unoptimized transformant, the optimized transformant for phosphorylation sites of the CyPPDK gene has the advantages that the biomass accumulation is improved by 33.3%, the content of EPA in grease is improved by 11.5%, and the fucoxanthin yield is improved by 21.2%.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
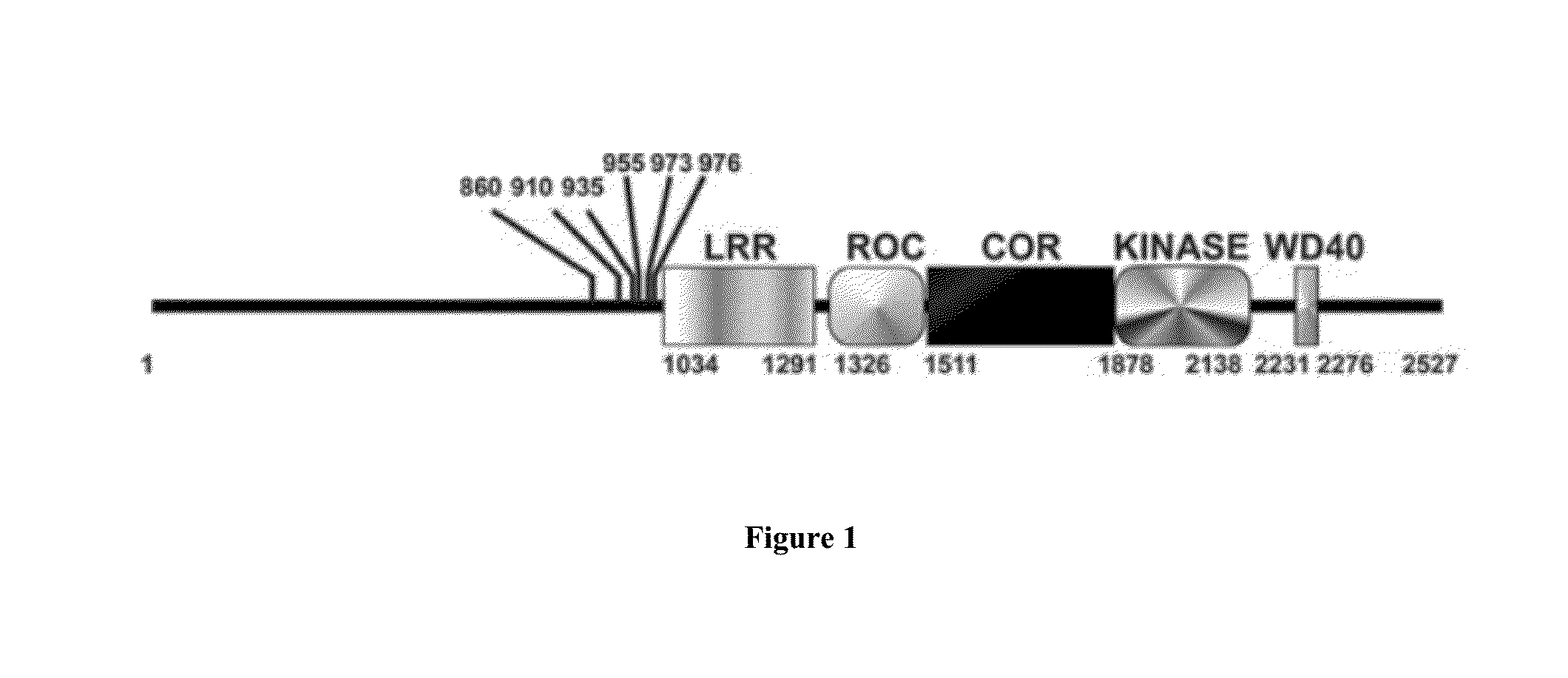
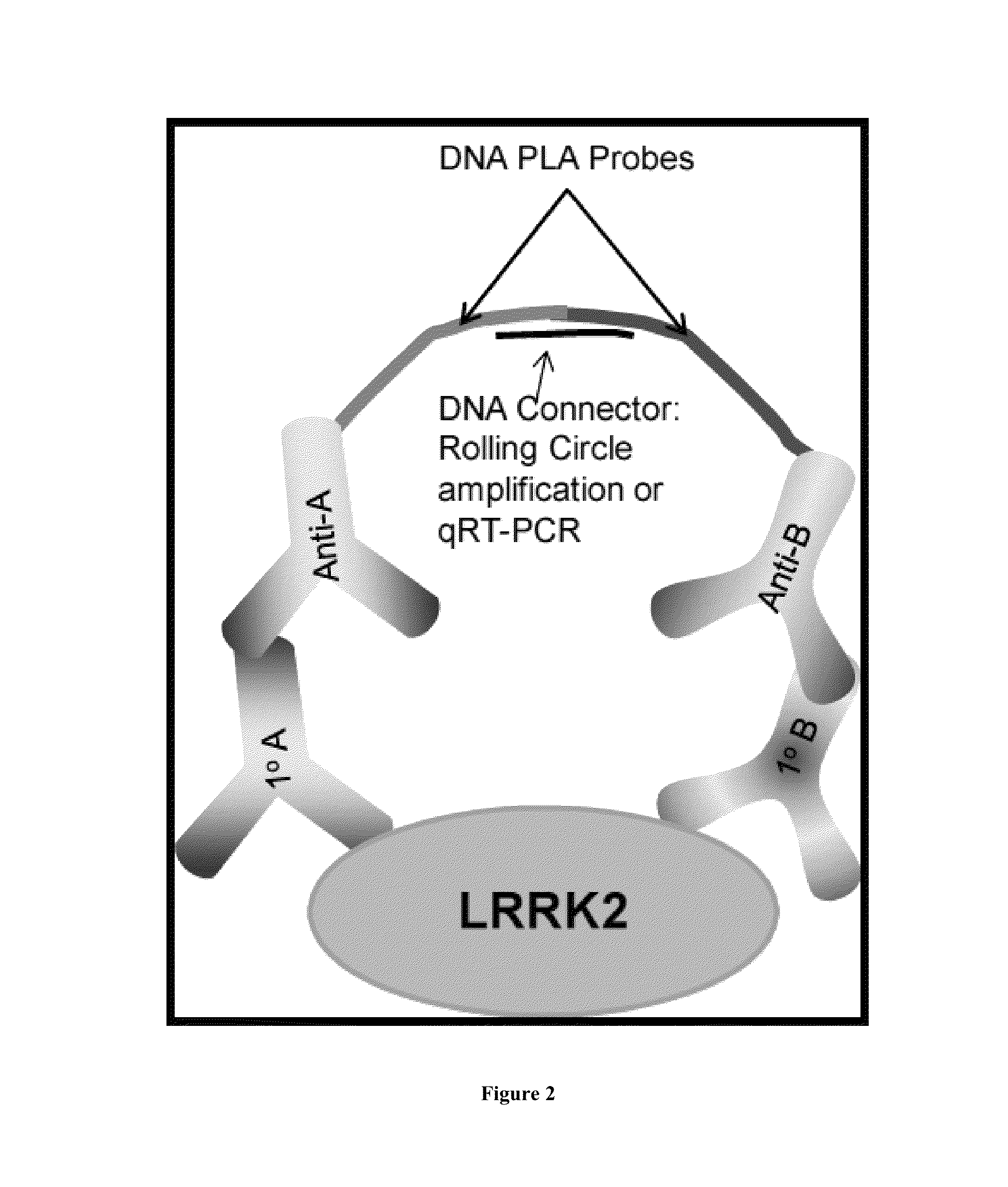
Assay to determine LRRK2 activity in parkinson's disease
Disclosed are novel phosphorylation sites identified in LRRK2 and associated with Parkinson's Disease, antibodies that specifically bind to the novel phosphorylation sites, and laboratory and clinical uses thereof.
Owner:TYLER MEDICAL RES LLC
Reagents for the detection of protein phosphorylation in signaling pathways
ActiveUS7999080B2Microbiological testing/measurementImmunoglobulins against animals/humansCell Surface ProteinsSignalling pathways
The invention discloses novel phosphorylation sites identified in signal transduction proteins and pathways, and provides phosphorylation-site specific antibodies and heavy-isotope labeled peptides (AQUA peptides) for the selective detection and quantification of these phosphorylated sites / proteins, as well as methods of using the reagents for such purpose. Among the phosphorylation sites identified are sites occurring in the following protein types: adaptor / scaffold proteins, adhesion / extracellular matrix protein, apoptosis proteins, calcium binding proteins, cell cycle regulation proteins, chaperone proteins, chromatin, DNA binding / repair / replication proteins, cytoskeletal proteins, endoplasmic reticulum or golgi proteins, enzyme proteins, G / regulator proteins, inhibitor proteins, motor / contractile proteins, phosphatase, protease, Ser / Thr protein kinases, Protein kinase (Tyr)s, receptor / channel / cell surface proteins, RNA binding proteins, transcriptional regulators, tumor suppressor proteins, ubiquitan conjugating system proteins and proteins of unknown function.
Owner:CELL SIGNALING TECHNOLOGY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com