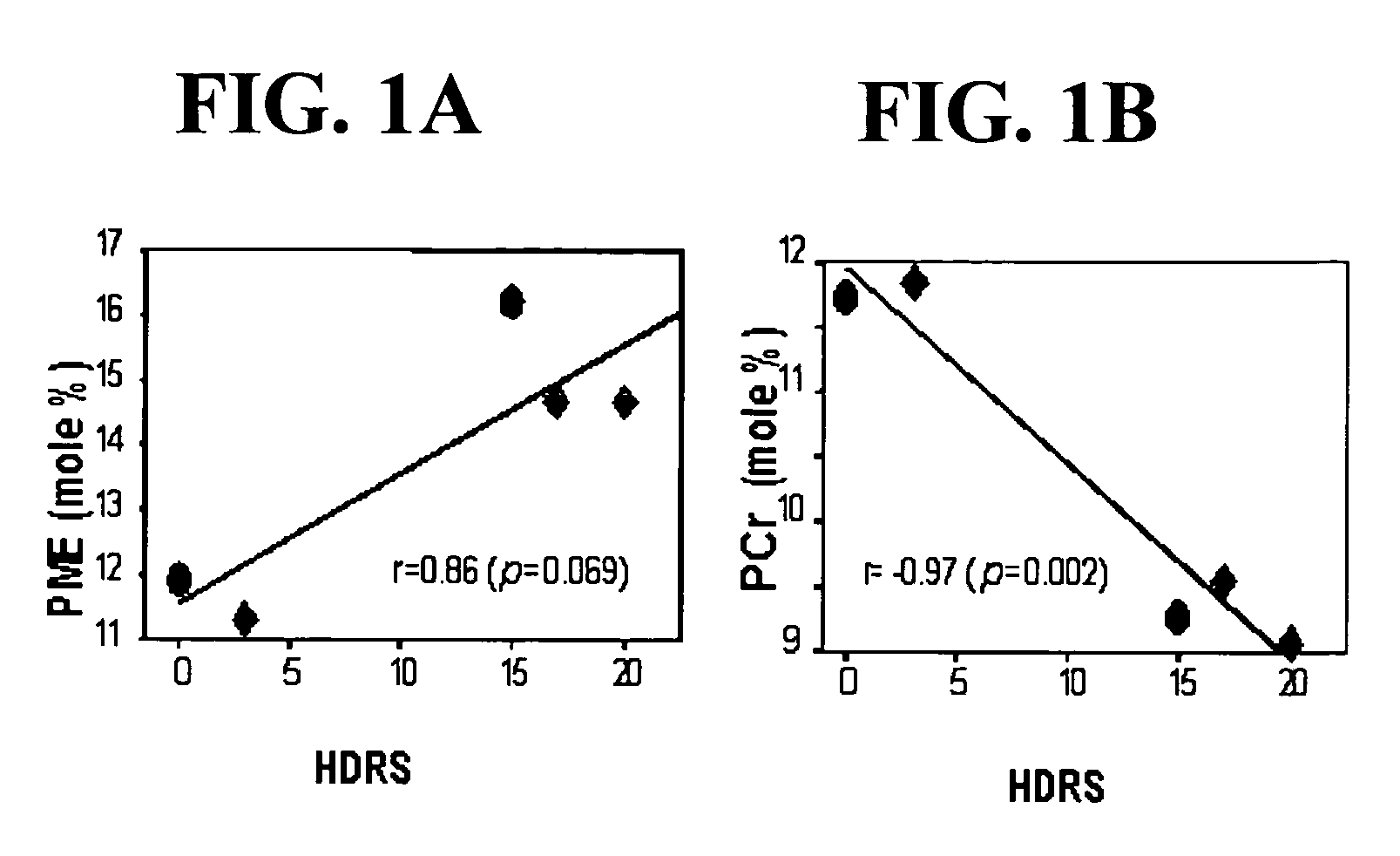
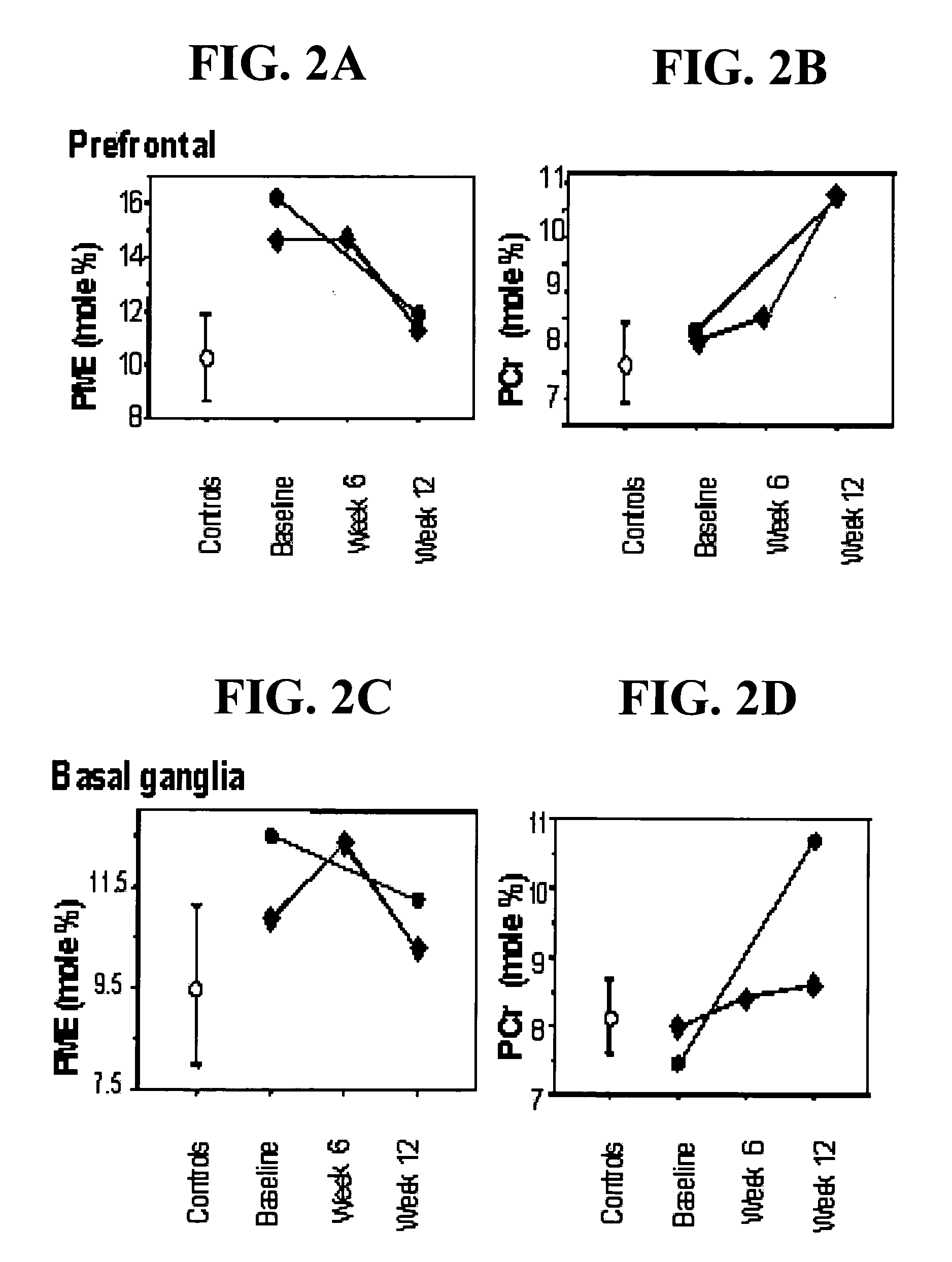
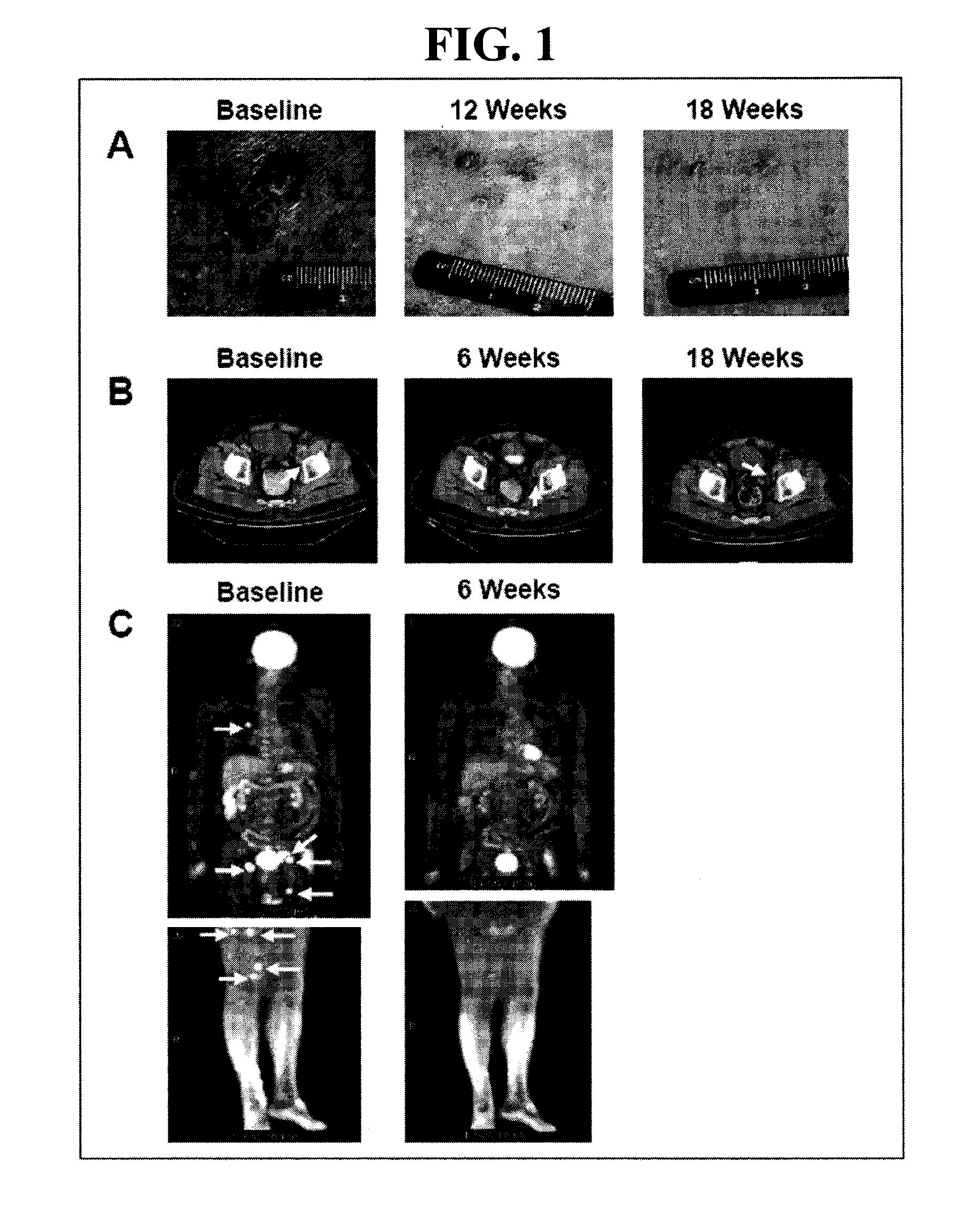
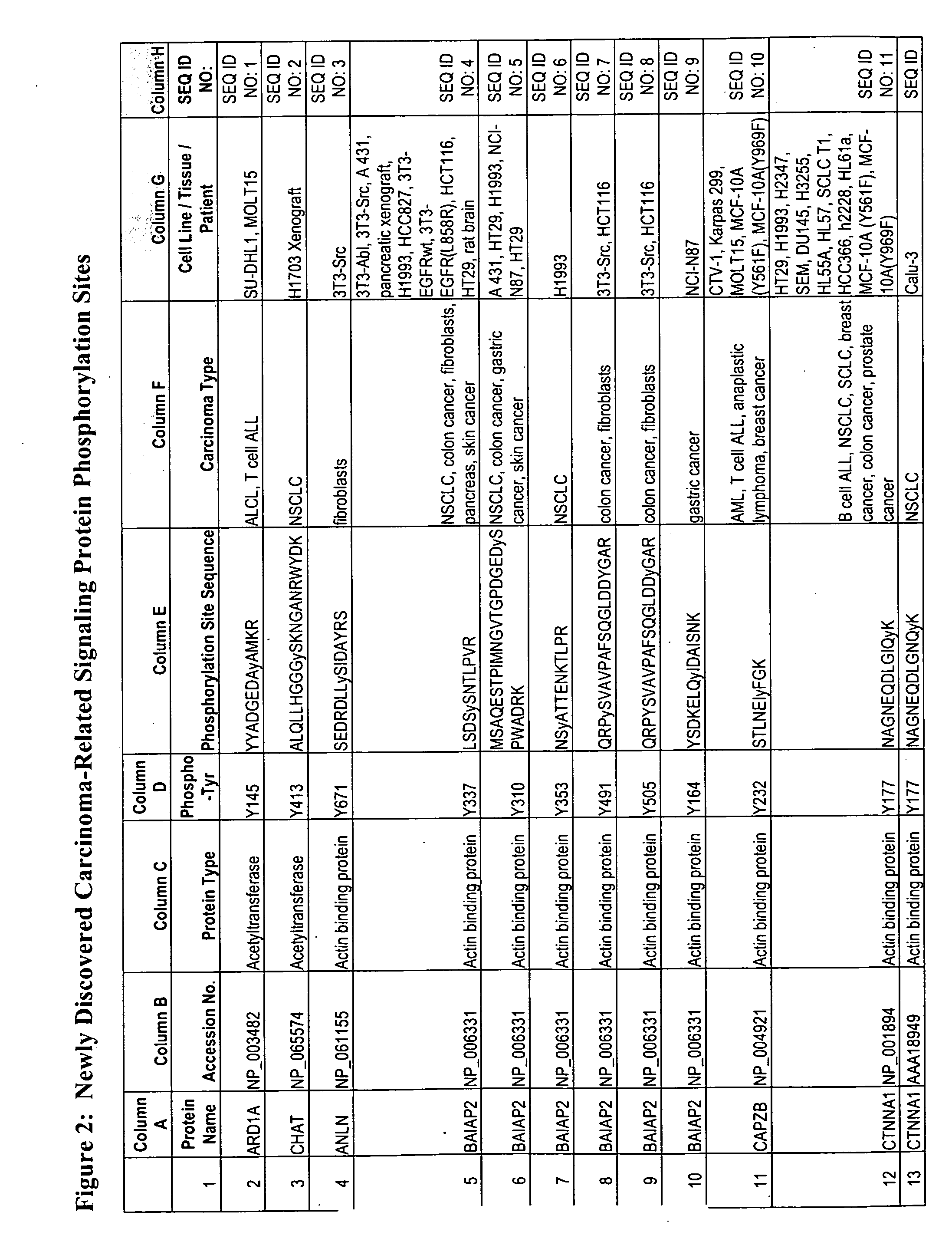
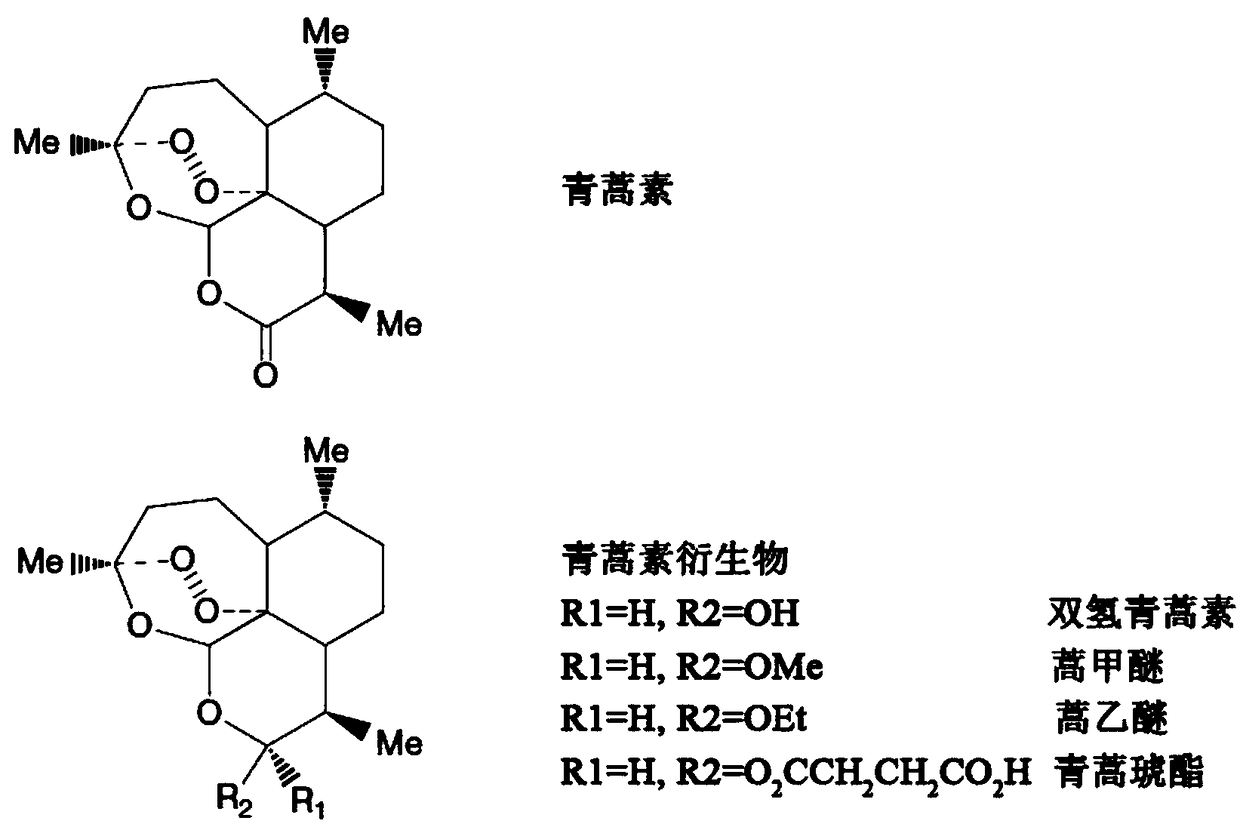
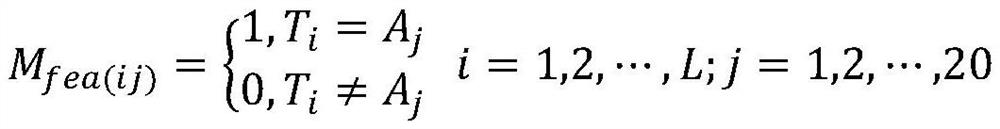Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
112 results about "Protein phosphorylation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Protein phosphorylation is a reversible post-translational modification of proteins in which an amino acid residue is phosphorylated by a protein kinase by the addition of a covalently bound phosphate group. Phosphorylation alters the structural conformation of a protein, causing it to become activated, deactivated, or modifying its function. Approximately 13000 human proteins have sites that are phosphorylated.
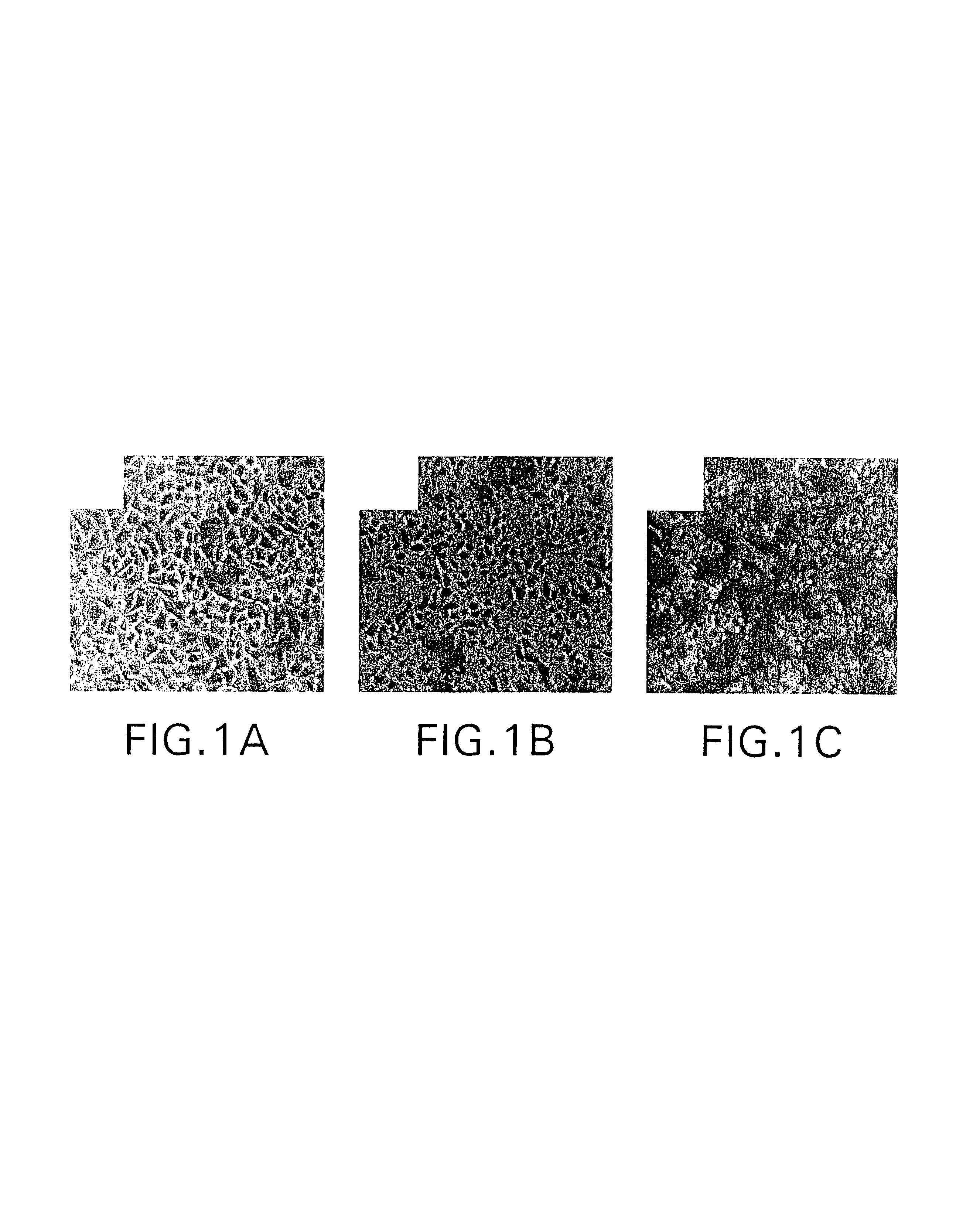
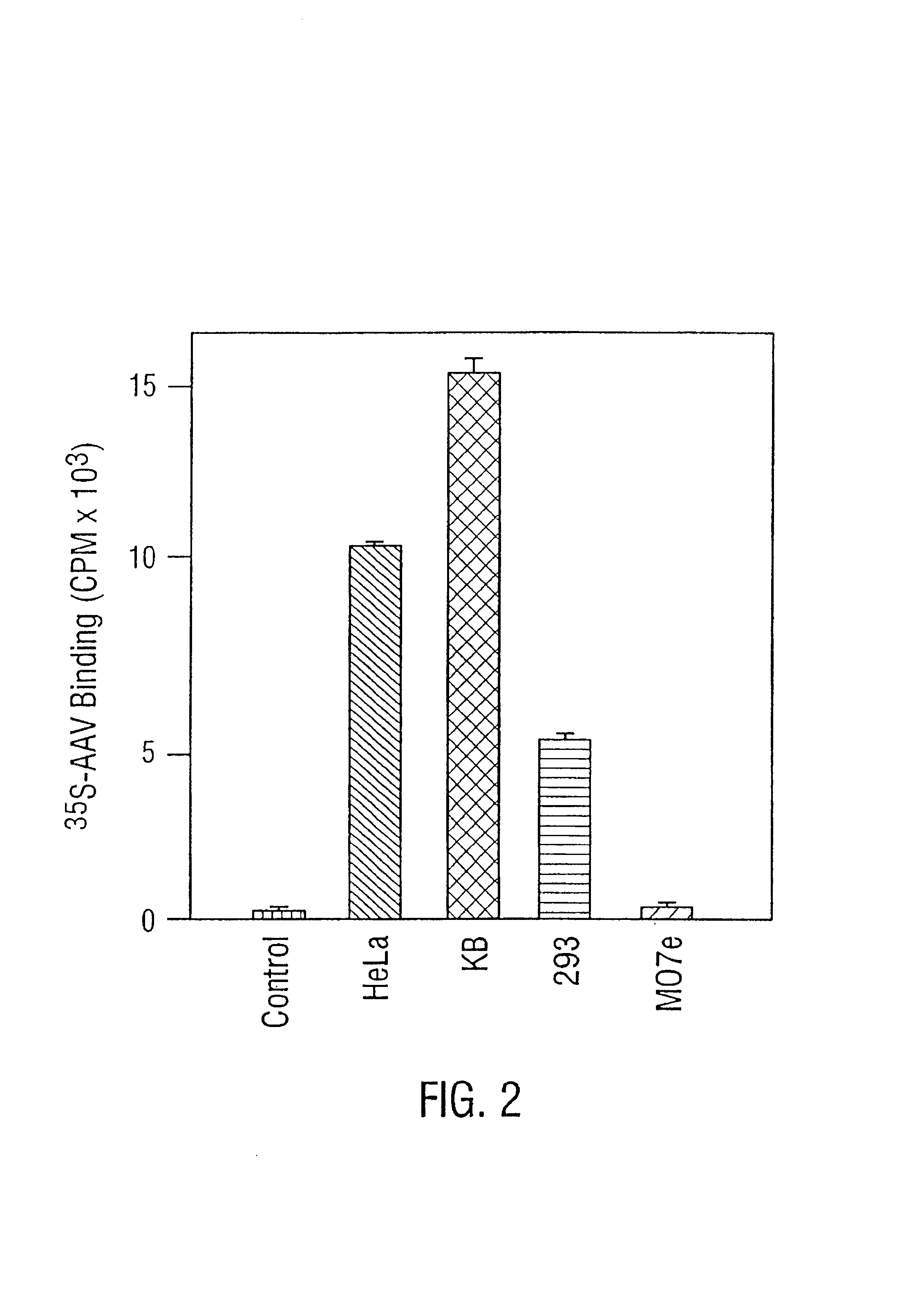
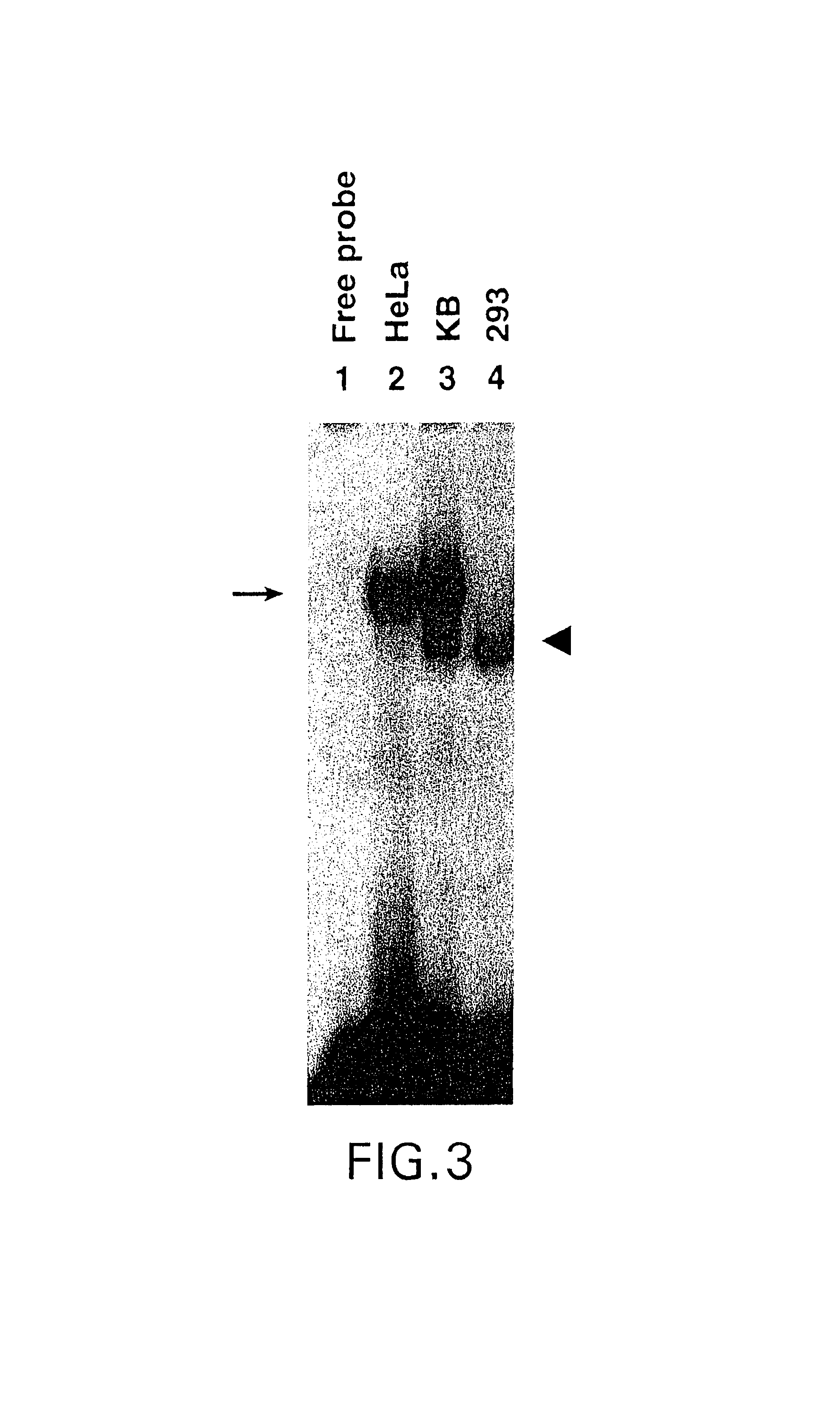
Role of tyrosine phosphorylation of a cellular protein in adeno-associated virus 2-mediated transgene expression
The present invention identifies a protein, designated the D-sequence-binding protein (D-BP), is phosphorylated at tyrosine residues and blocks AAV-mediated transgene expression in infected cells by inhibiting the leading strand viral DNA synthesis. More particularly, the present invention demonstrates that D-BP is phosphorylated by EGF-R protein tyrosine kinase. Methods of increasing transcription and promoting replication of transgenes exploiting this information are disclosed herein.
Owner:ADVANCED RES TECH INST
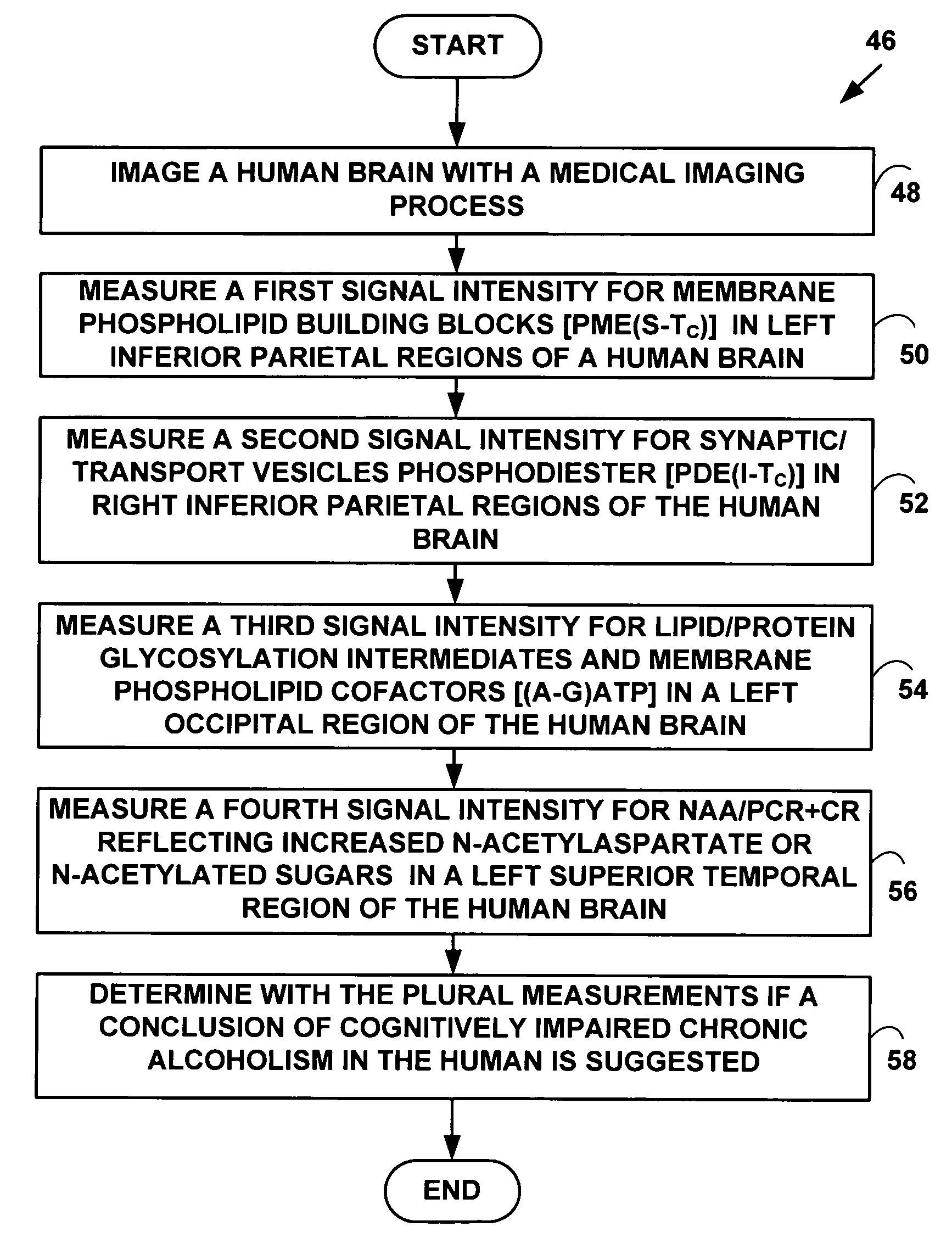
Method and system for diagnosis of neuropsychiatric disorders including chronic alcoholism
InactiveUS20060292547A1Neurological deficit scoreNavigation performance in was impairedBiocideMagnetic measurementsDiseaseLipid formation
Chronic alcoholism is a diverse and heterogeneous disorder that can be dichotomized into cognitively intact and cognitively impaired subgroups. At a molecular level, ethanol has been shown to have both acute and chronic effects on: Membrane biophysical properties, Membrane composition and metabolism, Protein phosphorylation, Lipid metabolic signaling, Lipoprotein transport of cholesterol. Actual molecular underpinnings are determined for cognitive impairment seen in some chronic alcoholism subjects including molecular / metabolic alterations of phospholipid and ganglioside metabolisms.
Owner:PETTEGREW JAY W +1
Method for classification of anti-psychotic drugs
The present invention provides a method for identifying an agent to be tested for an ability to treat a psychotic disorder in a patient in need of such treatment. The invention provides a method for screening candidate drugs for anti-psychotic drug activity, preferably atypical anti-psychotic activity, comprising contacting cells or tissues with a candidate drug, determining levels of phosphorylation of the intracellular signaling proteins, DARPP-32, ERK1, ERK2 and CREB, in said cells or tissues and determining the pattern of the levels of phosphorylation of the proteins. The pattern of the levels of phosphorylation of DARPP-32, ERK1, ERK2 and CREB is, in certain embodiments, compared with the pattern of the levels of phosphorylation of DARPP-32, ERK1, ERK2 and CREB in the presence of an atypical anti-psychotic drug.
Owner:THE ROCKEFELLER UNIV
c-KIT Phosphorylation in Cancer
InactiveUS20100143935A1Inhibit phosphorylationMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingProtein phosphorylationTreatment use
An antibody is disclosed for the detection of phosphorylated c-KIT. A method of diagnosing and monitoring cancers responsive to treatment using an anti-phospho-c-KIT antibody are also disclosed. A diagnostic kit is also provided for the detection and monitoring of cancers responsive to tyrosine phosphorylation inhibitor treatment.
Owner:APOCELL
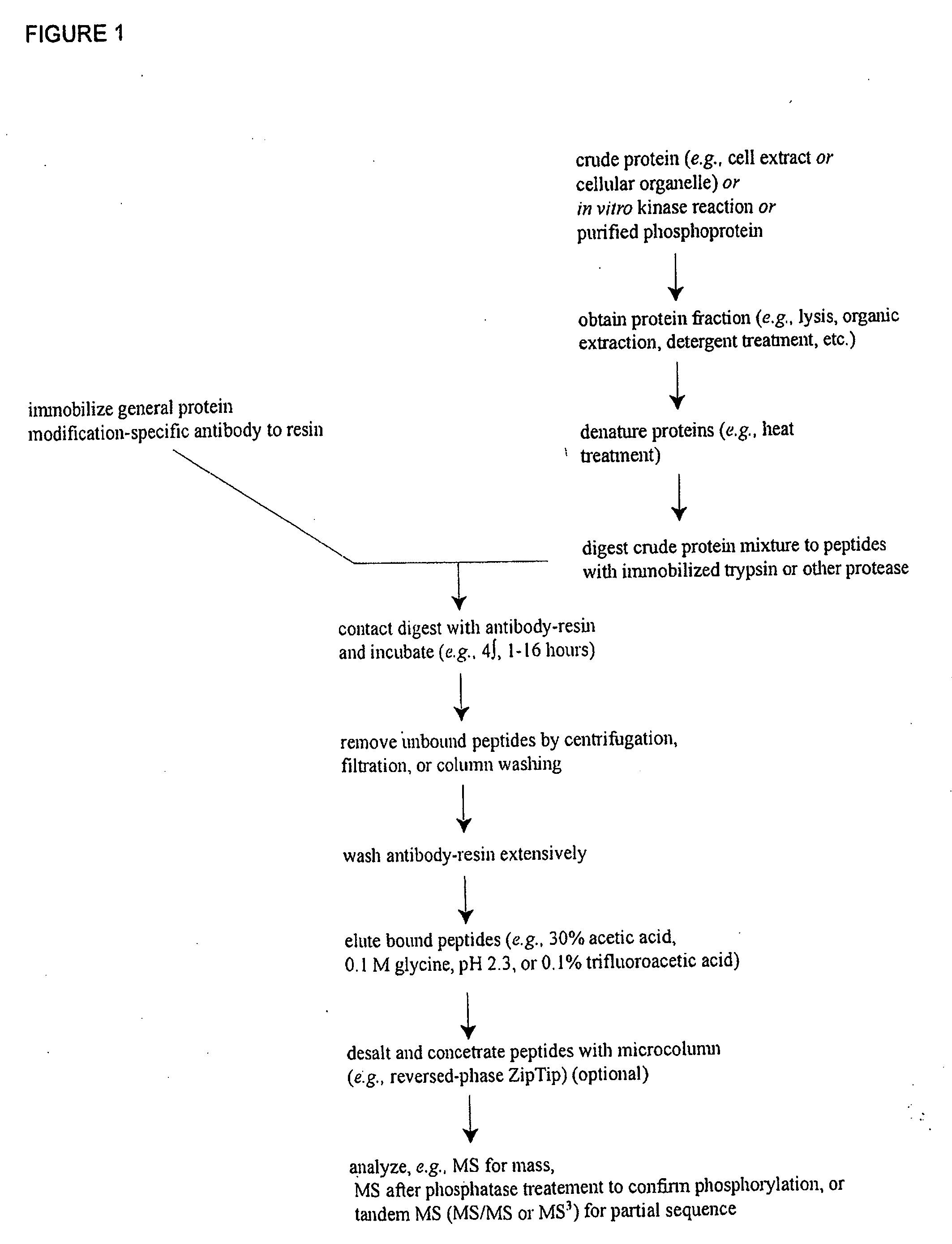
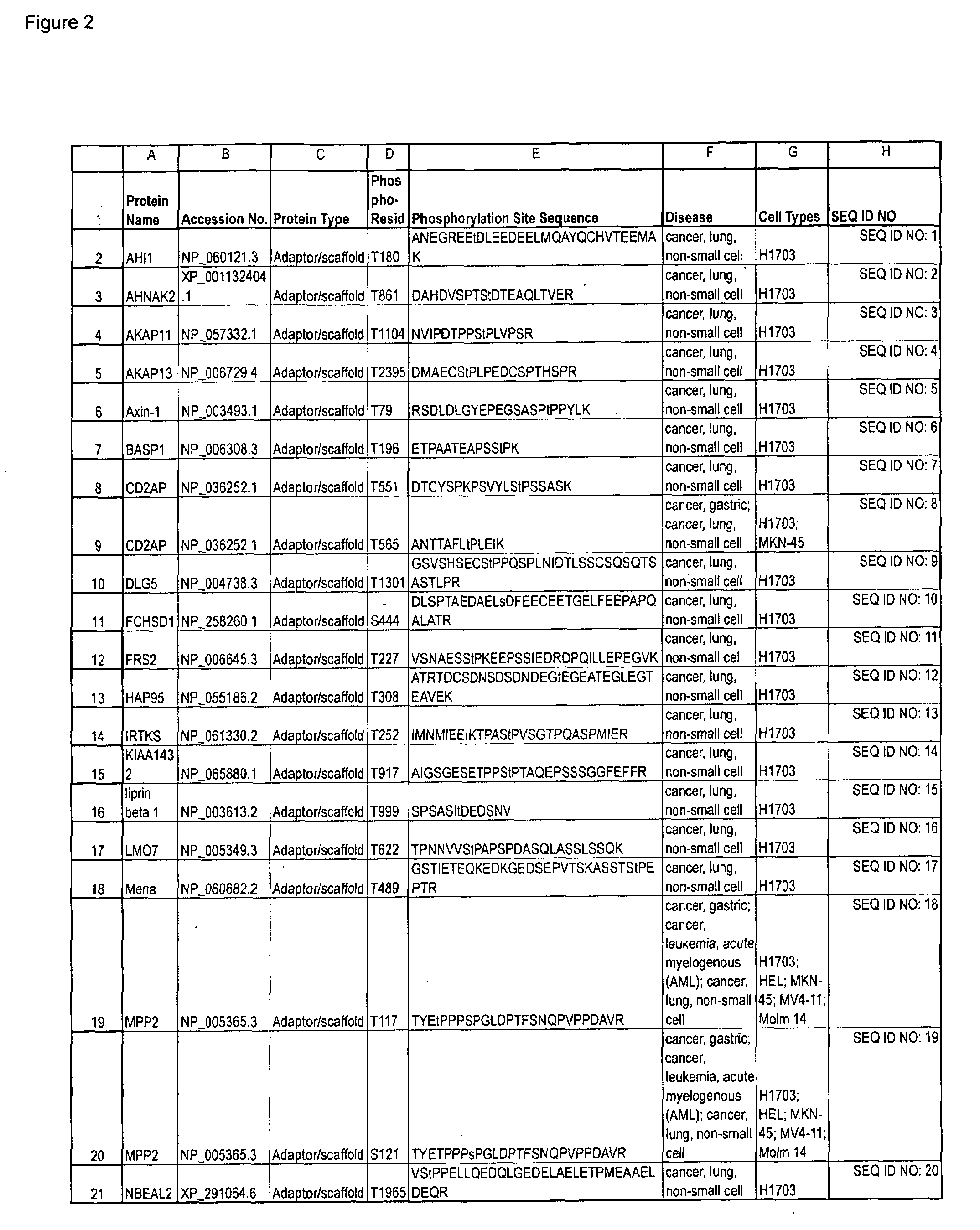
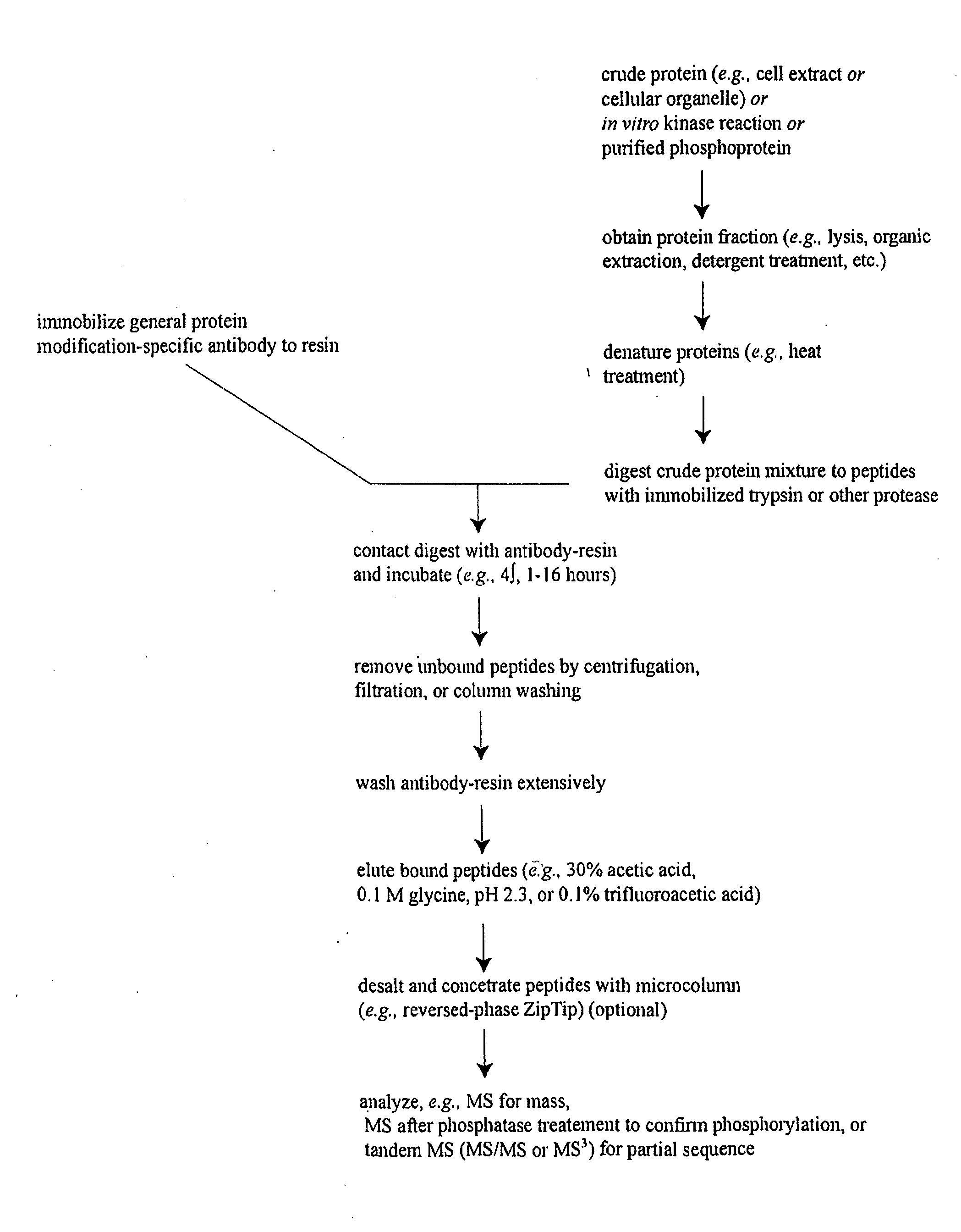
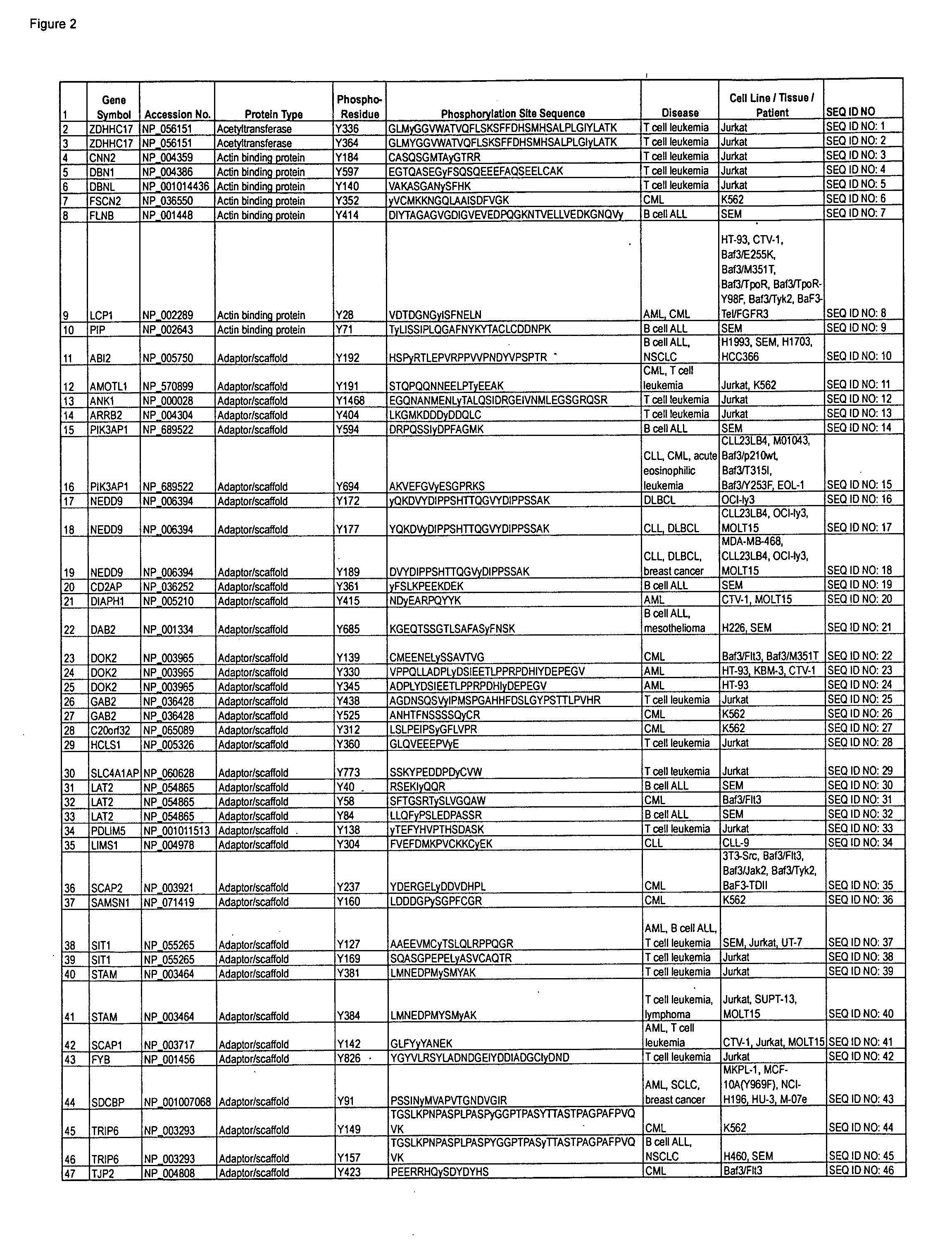
Reagents for the detection of protein phosphorylation in carcinoma signaling pathways
InactiveUS20090258442A1Immunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsFermentationPhospholipaseADAMTS Proteins
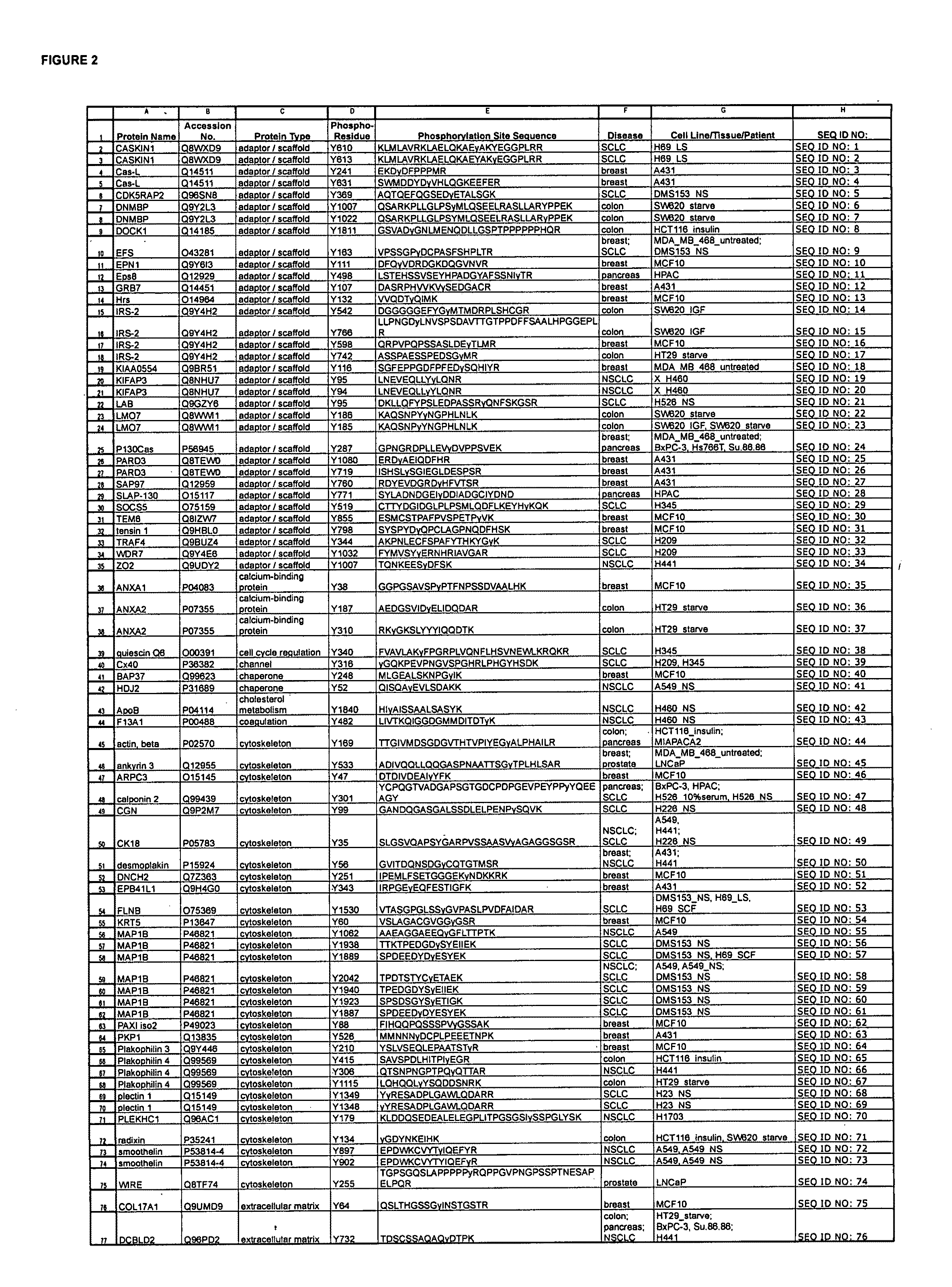
The invention discloses nearly 474 novel phosphorylation sites identified in signal transduction proteins and pathways underlying human carcinoma, and provides phosphorylation-site specific antibodies and heavy-isotope labeled peptides (AQUA peptides) for the selective detection and quantification of these phosphorylated sites / proteins, as well as methods of using the reagents for such purpose. Among the phosphorylation sites identified are sites occurring in the following protein types: Kinase, Adaptor / Scaffold proteins, Phosphatase, G protein Regulator / Guanine Nucleotide Exchange Factors / GTPase Activating Proteins, Cytoskeleton Proteins, DNA Binding Proteins, Phospholipase, Receptor Proteins, Enzymes, DNA Repair / Replication Proteins, Adhesion Proteins, and Proteases, as well as other protein types.
Owner:CELL SIGNALING TECHNOLOGY
Reagents for the detection of protein phosphorylation in Leukemia signaling pathways
ActiveUS20080248490A1Immunoglobulins against animals/humansBiological testingHuman leukemiaADAMTS Proteins
The invention discloses nearly 288 novel phosphorylation sites identified in signal transduction proteins and pathways underlying human Leukemia, and provides phosphorylation-site specific antibodies and heavy-isotope labeled peptides (AQUA peptides) for the selective detection and quantification of these phosphorylated sites / proteins, as well as methods of using the reagents for such purpose. Among the phosphorylation sites identified are sites occurring in the following protein types: Adaptor / Scaffold proteins, Cytoskeletal proteins, Cellular Metabolism enzymes, G Protein / GTPase Activating / Guanine Nucleotide Exchange Factor proteins, Immunoglobulin Superfamily proteins, Inhibitor proteins, Lipid Kinases, Nuclear DNA Repair / RNA Binding / Transcription proteins, Serine / Threonine Protein Kinases, Tyrosine Kinases, Protein Phosphatases, and Translation / Transporter proteins.
Owner:CELL SIGNALING TECHNOLOGY
Use of ursolic acid as colon tumor resistant medicament
InactiveCN101991579ABlock EGFR signaling pathwayOrganic active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsSide effectApoptosis
The invention relates to use of ursolic acid as a colon tumor resistant medicament. The ursolic acid has the effects of inhibiting colon cancer / tumor cell proliferation and inducing apoptosis. In naked mouse in vivo experiments, the ursolic acid can effectively inhibit the proliferation of colon cancer transplanted tumor and inhibit the generation of tumor blood vessels, and has no obvious toxic or side effect on mice. The ursolic acid has the effect of inhibiting EGFR / MAPK signal channel phosphorylation of colon cancer cells, and the key target of the ursolic acid is to inhibit ERK1 / 2 protein phosphorylation. The ursolic acid which is synergetic with oxaliplatin serving as a clinical first-line chemotherapy medicament of the colon cancer has better curative effect. The ursolic acid has better proliferation inhibiting effect on the colon cancer cells of K-RAS gene mutation. The use of the ursolic acid as the colon tumor resistant medicament provides a new thought for treating the colon tumor.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Modulation of protein methylation and phosphoprotein phosphate
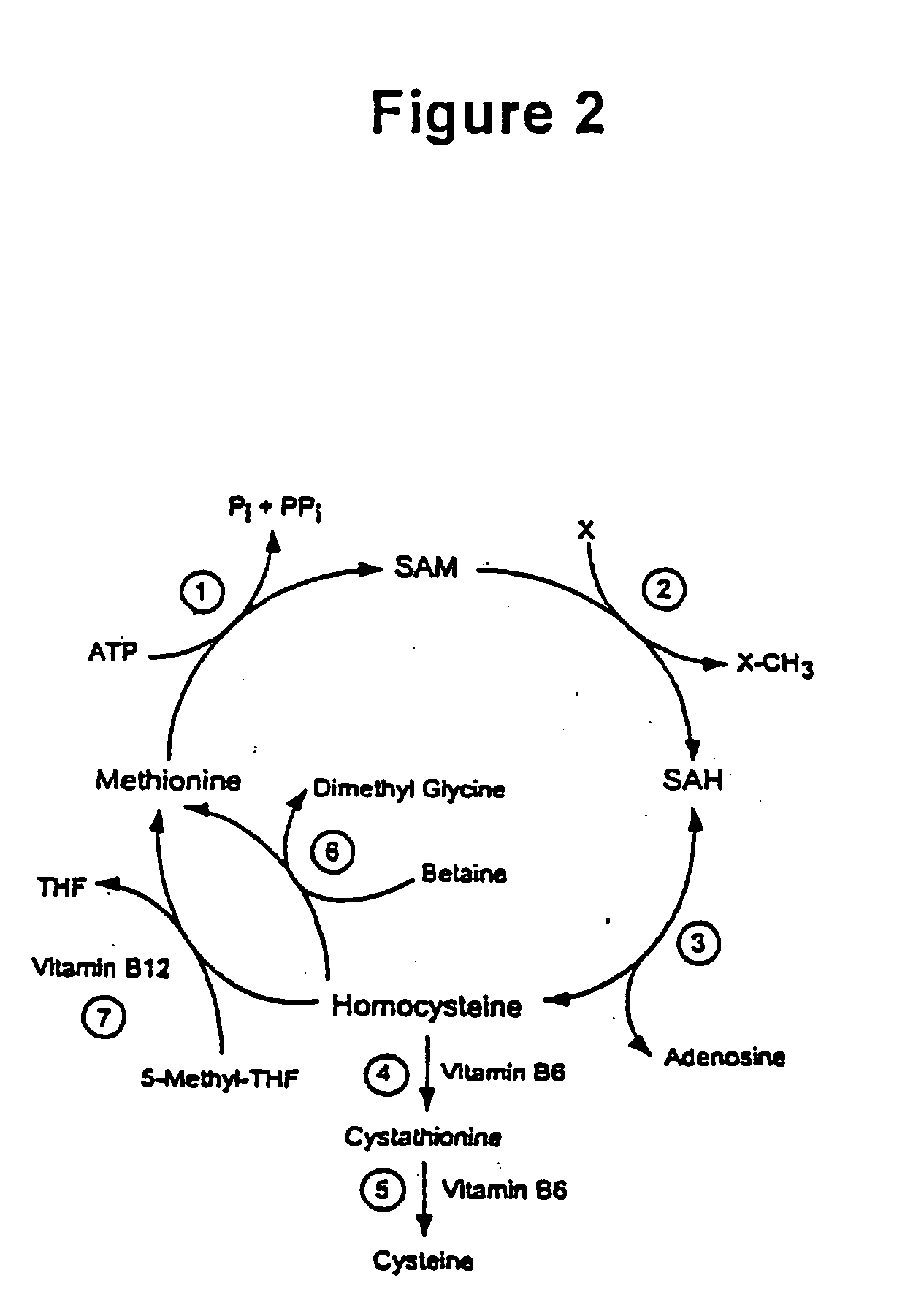
InactiveUS20070031909A1Reduces overall methylation rateReduction in methylation rateBiocideCompound screeningEtiologyPhosphate
The invention relates to methylated proteins that control protein phosphorylation, particularly phosphoesterases, such as PP2A. It relates to screening methods for determining agents that affect methylation of these proteins and thus also modulate the level of phosphorylation of phosphoproteins. It relates as well to the agents and to compositions comprising the agents. In a particular aspect in this regard the invention relates to agents that alter PP2A methylation and that thereby affect phosphorylation of phosphoproteins that play an important role in health or disease, such as the tau protein which is implicated in the etiology of Alzheimer's Disease. The invention further relates to diagnostic methods based on protein methylation levels, to compositions comprising agents for affecting methylation of proteins and for controlling the phosphate complement of phosphoproteins. Additionally, the invention relates to methods for administering the agents and compositions to affect methylation of proteins physiologically and to modulate the phosphate complement of phosphoproteins. Examples in this regard include agents and compositions that affect physiological activity of PP2A and alter the phosphate complement of phosphoproteins that are altered in disease.
Owner:SIGNUM BIOSCIENCES INC +1
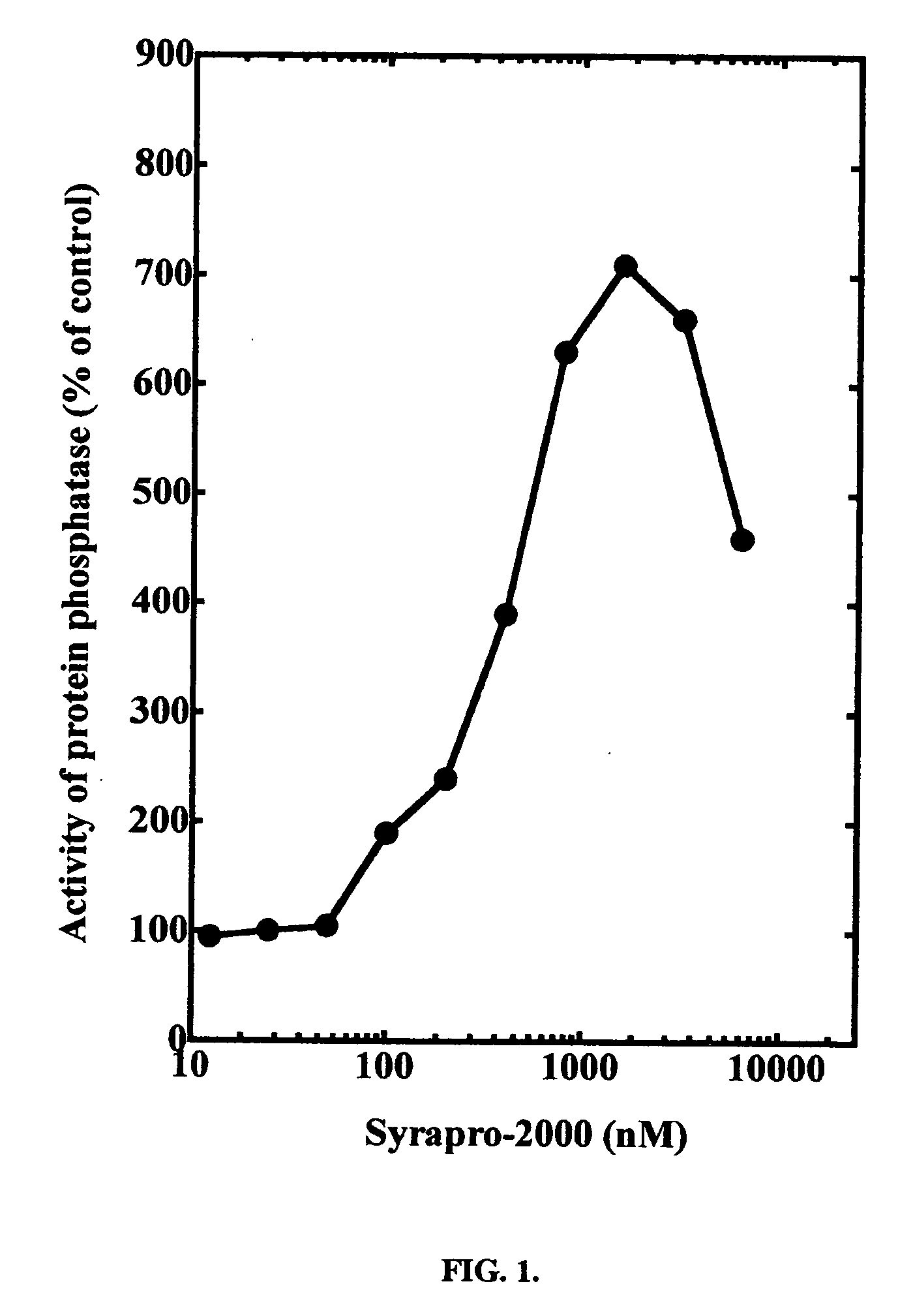
Preparation of a peptide compound (SYRAPRO-2000) and its use for the activation of protein phosphatase-2A1 enzyme
UndeterminedUS20060252683A1Prevent proliferationModulate activityNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsCancer cellProtein phosphorylation
This invention relates to the preparation of a peptide compound (SYRAPRO-2000), its use to activate protein phosphatase-2A enzymes for the dephosphorylation of proteins in vitro and in the cell and its use for inhibiting cell proliferation and induction of death of brain cancer cells and other cancer cells and therefore the treatment of proliferative disorder such as brain cancer and other forms of cancer. Drugs that target the enzymes of the protein phosphorylation / dephosphorylation apparatus of the cell are mostly inhibitor compounds. The present invention describes for the first time the use of an activating compound of a protein phosphatase to modulate the activity of a cell. In this invention, the peptide compound activator of protein phosphatase-2A1 (SYRAPRO-2000) is used to activate protein phosphatase-2A1, thereby causing inhibition of cell proliferation and induction of cell death of transformed T cells and brain cancer cells.
Owner:LIM TUNG HIN YOUNG
Reagents for the detection of protein phosphorylation in carcinoma signaling pathways
InactiveUS20090081659A1Microbiological testing/measurementImmunoglobulins against growth factorsProtein phosphorylationPhosphorylation site
The invention discloses 364 novel phosphorylation sites identified in carcinoma, peptides (including AQUA peptides) comprising a phosphorylation site of the invention, antibodies specifically bind to a novel phosphorylation site of the invention, and diagnostic and therapeutic uses of the above.
Owner:CELL SIGNALING TECHNOLOGY
Reagents for the detection of protein phosphorylation in leukemia signaling pathways
InactiveUS20090220991A1Animal cellsImmunoglobulins against animals/humansPhosphodiesteraseLipid kinases
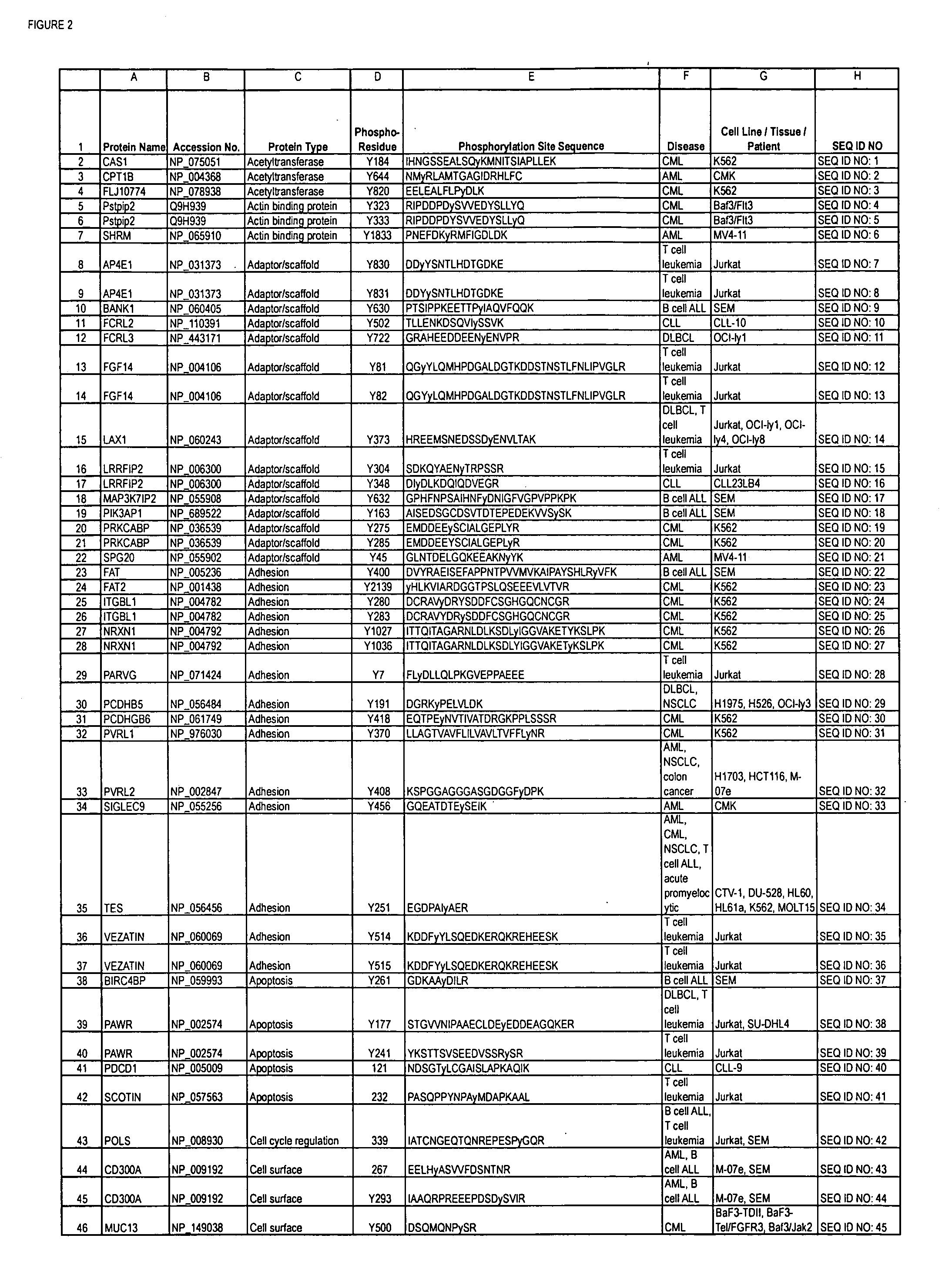
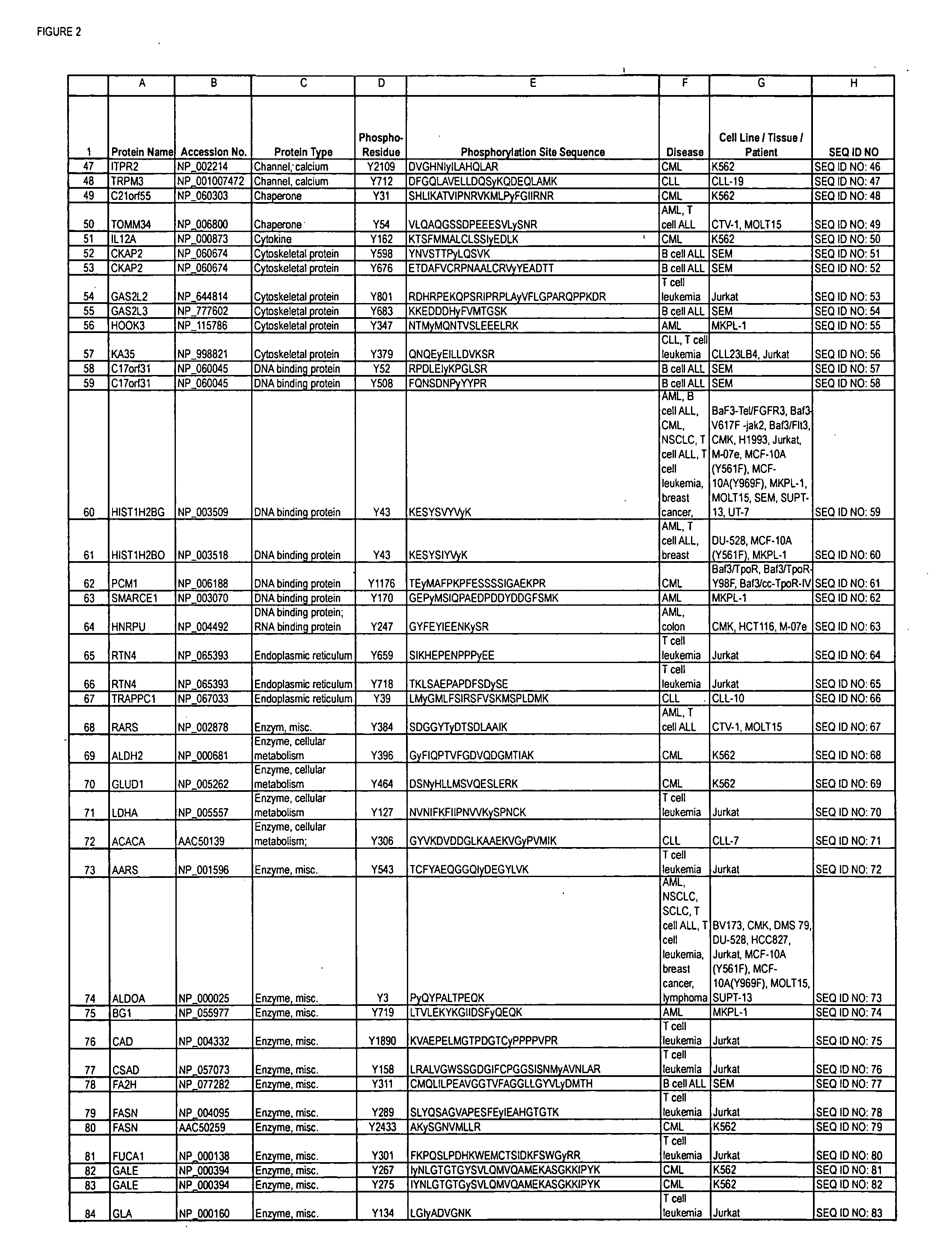
The invention discloses nearly 480 novel phosphorylation sites identified in signal transduction proteins and pathways underlying human Leukemia, and provides phosphorylation site specific antibodies and heavy-isotope labeled peptides (AQUA peptides) for the selective detection and quantification of these phosphorylated sites / proteins, as well as methods of using the reagents for such purpose. Among the phosphorylation sites identified are sites occurring in the following protein types: adaptor / scaffold proteins, acetyltransferases, actin binding proteins, adhesion proteins, apoptosis proteins, calcium-binding proteins, cell cycle regulation proteins, cell surface proteins, channel proteins, chaperone proteins, contractile proteins, cytokine proteins, cytoskeletal proteins, G protein regulators and GTPase activating proteins, guanine nucleotide exchange factors, helicase proteins, immunoglobulin superfamily proteins, inhibitor proteins, protein kinases, lipid kinases, ligases, lipid binding proteins, methytransferases, motor proteins, oxidoreductases, phosphotases, phosphodiesterases, phospholipases, proteases, receptor proteins, trascription factors, transferases, translation / transporter proteins, and ubiquitin conjugating system proteins.
Owner:CELL SIGNALING TECHNOLOGY
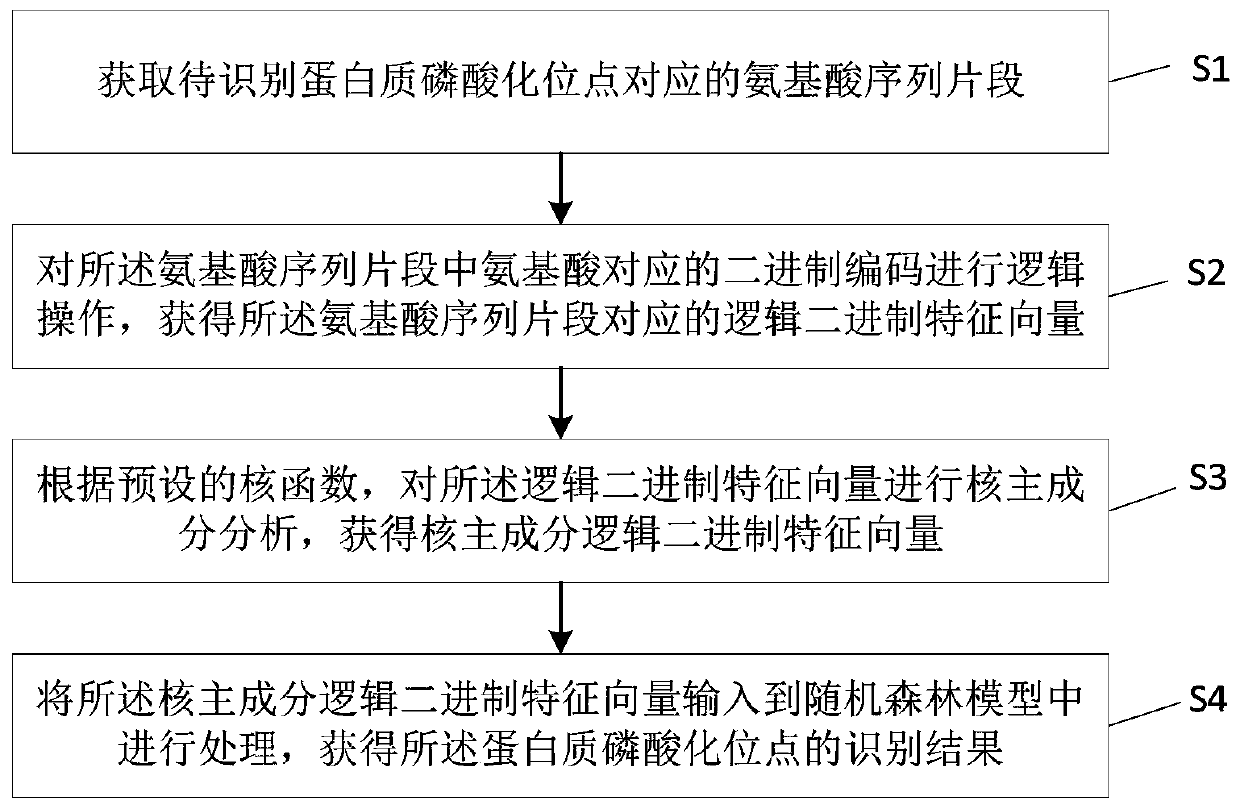
Protein phosphorylation site recognition method, system and device and storage medium
ActiveCN110349628AAccurate identificationImprove developmentArtificial lifeSequence analysisDiseaseFeature vector
The invention discloses a protein phosphorylation site identification method, system and device and a storage medium. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring an amino acid sequence fragment of a protein phosphorylation site to be identified; performing logic operation on binary codes of amino acids in the amino acid sequence fragment to obtain logic binary feature vectors of the aminoacid sequence fragment; performing kernel principal component analysis on the logic binary feature vector according to a preset kernel function to obtain a kernel principal component logic binary feature vector; and inputting the kernel principal component logic binary feature vector into a random forest model for processing to obtain an identification result of the protein phosphorylation site. Based on theoretical calculation of the random forest model, the method can achieve the quick and accurate recognition of the information of a large number of protein phosphorylation sites, is low in cost, facilitates the development of phosphorylation mechanism and phosphorylation and disease relation research, and is widely applied to the field of protein phosphorylation site recognition.
Owner:GUANGDONG PHARMA UNIV +1
Magnetic nano composite material for multimode peptide fragment enrichment and preparation method and application thereof
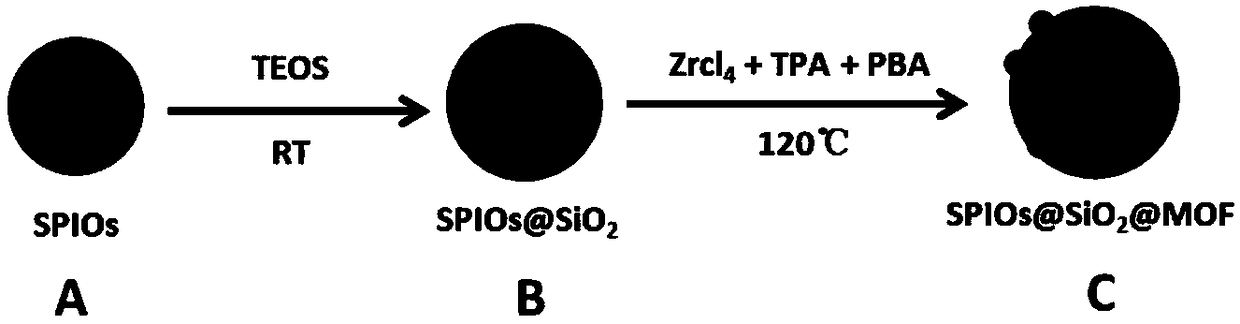
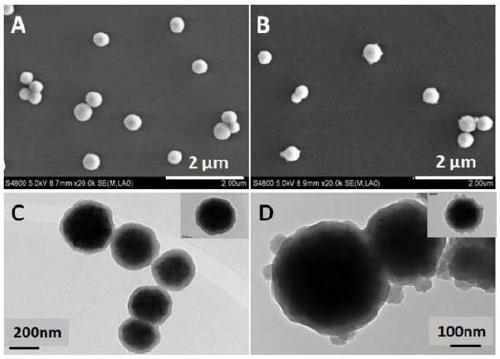
ActiveCN109433158AUniform particle sizeSolve reunionOther chemical processesPeptide preparation methodsGlycopeptideProtein phosphorylation
The invention discloses a magnetic nano composite material for multimode peptide fragment enrichment and a preparation method and application thereof. The magnetic nano composite material is composedof Fe3O4 magnetic sphere, a SiO layer coating the surface of the Fe3O4 magnetic sphere and a metal-organic frame layer growing on the SiO2 layer, the metal-organic frame layer is formed by metal ion Zr4+ and two organic ligands through coordination, and the organic ligands are terephthalic acid and phenylenebisboronic acid. The magnetic nano composite material takes the Fe3O4 magnetic sphere as acore, thereby having good magnetic response performance, and takes Zr4+ as an affine site of phosphorylated polypeptide and boric acid group on terephthalic acid as an affine site of glycopeptide, thereby being capable of realizing gathering of the phosphorylated polypeptide and gathering of the glycopeptides, high in gathering efficiency, of very important significance in studying physiological behavior protein phosphorylation and glycosylation and good in application prospect.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
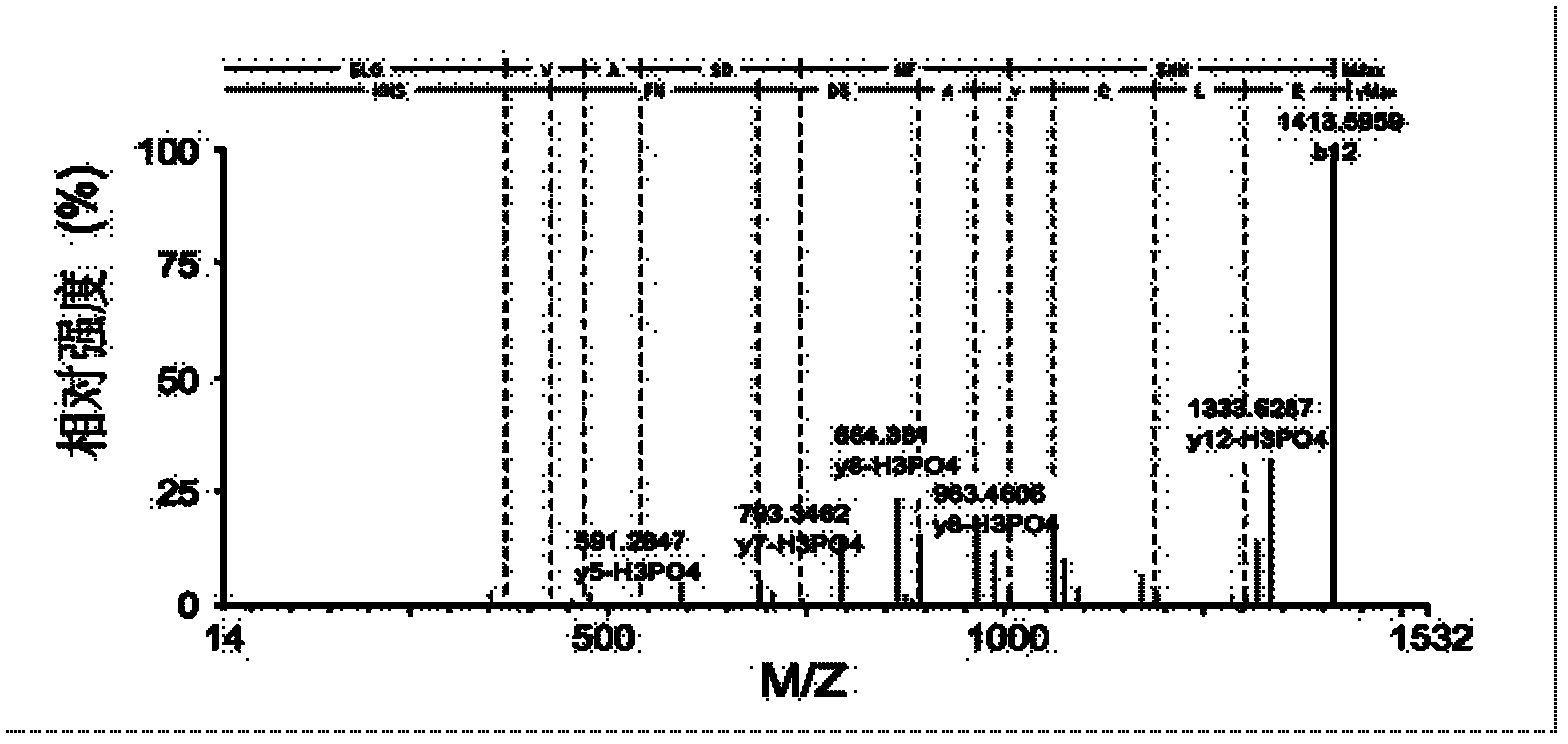
Method for relative quantitative analysis of protein phosphorylation modification level
InactiveCN103163010AHigh sensitivityImprove accuracyComponent separationPreparing sample for investigationStable Isotope LabelingProtein phosphorylation
The invention provides an isotope label-free method for relative quantitative analysis of a protein phosphorylation modification level. The method comprises: conducting enzymolysis on protein to make it into peptide fragments, making use of a data-independent MS / MS technique to determine peptide fragments with phosphorylation sites, and utilizing a label-free quantitation technique to carry out relative quantitative analysis on the peptide fragments with phosphorylation sites. Compared with the existing methods combining data-dependent MS / MS analysis and stable isotope-labeling technologies, the method does not need an isotope labeling reagent, thus having the advantages of reducing the experiment cost and operation complexity.
Owner:TIANJIN INT JOINT ACADEMY OF BIOTECH & MEDICINE +1
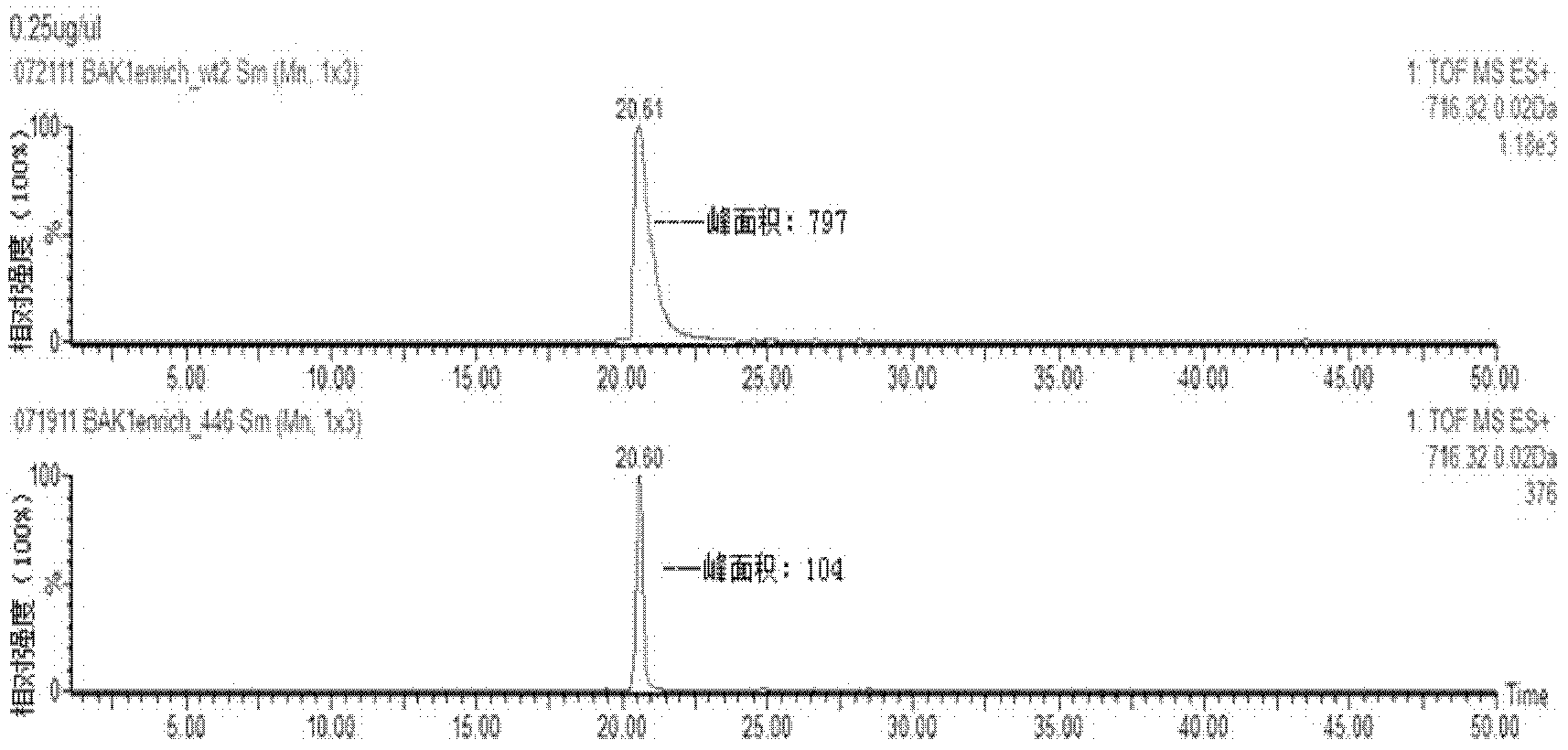
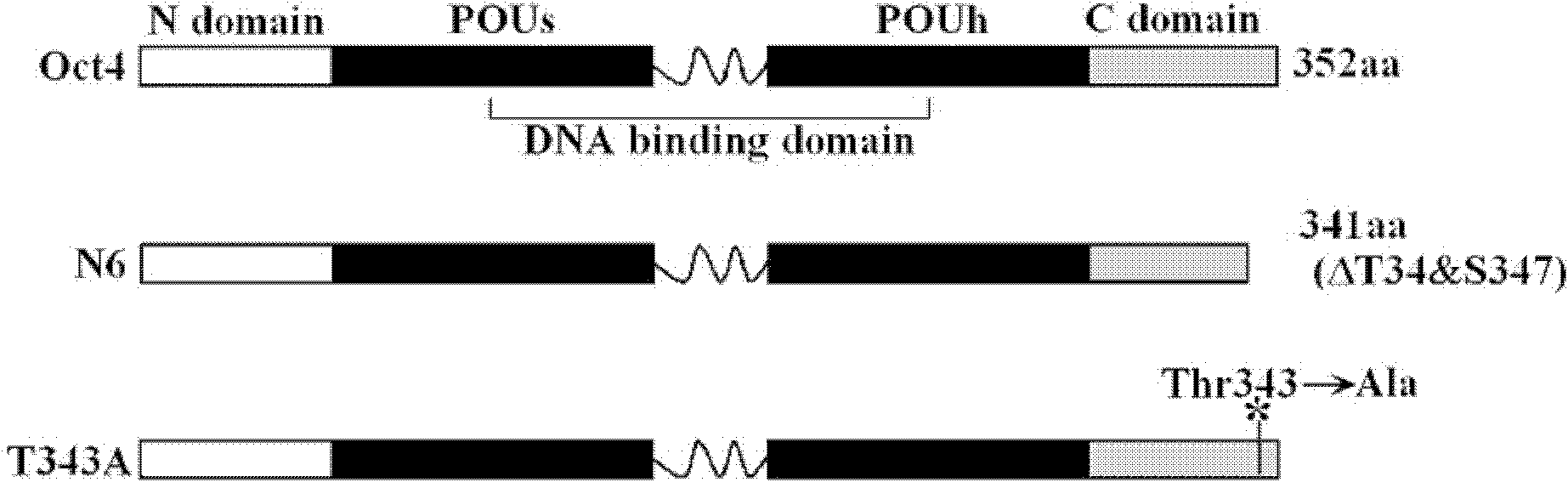
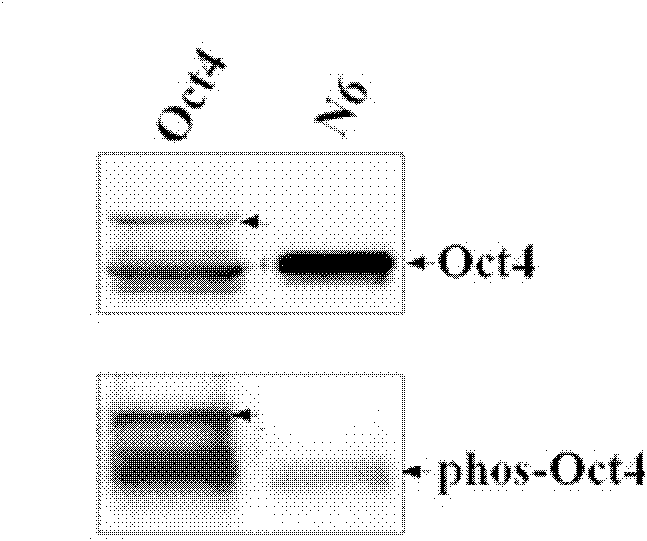
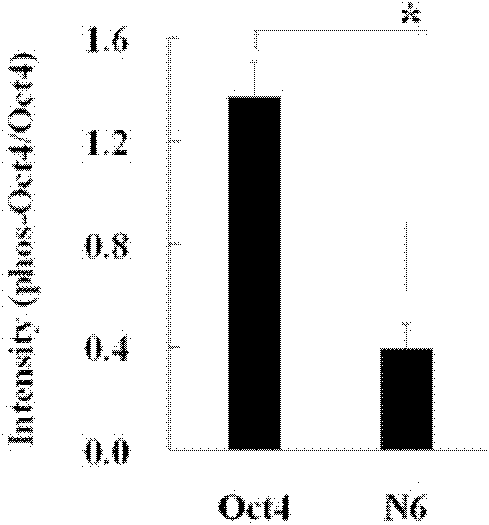
Anti-phosphorylation Oct4 protein antibody and its application
InactiveCN102731653ADecreased ability to positively regulateImmunoglobulins against animals/humansBiological testingSOX2Threonine
The invention relates to Oct4 protein phosphorylation sites and an anti-phosphorylation Oct4 protein antibody, concretely relates to Oct4 protein 343rd site phosphorylation and an antibody aimed at Oct4 protein 343rd site phosphorylation. The antibody is a monoclonal antibody or a polyclonal antibody. The invention also relates to an application of the antibody used for detecting phosphorylation of Oct4 protein 343rd site threonine. When the Oct4 protein 343rd site threonine is subjected to phosphorylation, the positive regulation and control capability of Oct4 protein on downstream genes Nanong and Sox2 is decreased, thereby the capability for keeping self-replicating type stem cells and pluripotent differentiation is lost. The application of the invention comprises the application of the antibody in detection of stem cells proliferation, cell differentiation, stem cell pluripotency and stem cells self-replicating capability.
Owner:李凌松 +1
Reagents for the Detection of Protein Phosphorylation in Carcinoma Signaling Pathways
InactiveUS20110105732A1Immunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsFermentationADAMTS ProteinsProtein phosphorylation
The invention discloses 214 novel phosphorylation sites identified in signal transduction proteins and pathways underlying human carcinoma, and provides phosphorylation-site specific antibodies and heavy-isotope labeled peptides (AQUA peptides) for the selective detection and quantification of these phosphorylated sites / proteins, as well as methods of using the reagents for such purpose. Among the phosphorylation sites identified are sites occurring in the following protein types: Adaptor / Scaffold proteins, Cytoskeleton proteins, GTP Signaling proteins, Kinases, Metabolism proteins, Phosphatases / Phospho-diesterases / Proteases, Receptor proteins, RNA Processing proteins, Transcription proteins, Translation proteins, Transporter proteins, and Ubitquitin proteins, as well as other protein types.
Owner:CELL SIGNALING TECHNOLOGY
Bad phosphorylation determines ovarian cancer chemo-sensitivity and patient survival
Despite initial sensitivity BAD-protein phosphorylation were evaluated in patient samples and cell lines as determinants of chemo-sensitivity and / or clinical outcome, and as therapeutic targets. Induced in-vitro OVCA cisplatin-resistance was associated with BAD-pathway expression. Expression of the pathway was also associated with resistance of 7 different cancers cell-types to 8 chemotherapeutic agents. Phosphorylation of the BAD-protein was associated with platinum-resistance in OVCA cells and primary OVCA specimens, and also overall patient survival. Targeted modulation of BAD-phosphorylation levels influenced cisplatin-sensitivity. A 47-gene BAD-pathway signature was associated in-vitro phospho-BAD levels and with survival of 838 patients with ovarian, breast, colon, and brain cancer. The survival advantage associated with both BAD-phosphorylation and also the BAD-pathway signature was independent of surgical cytoreductive status. The BAD apoptosis pathway influences human cancer chemo-sensitivity and overall survival. The pathway is useful as a biomarker of therapeutic response, patient survival, and therapeutic target.
Owner:H LEE MOFFITT CANCER CENT & RES INST INC
Reagents for the detection of protein phosphorylation in carcinoma signaling pathways
InactiveUS20090099340A1Immunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsFermentationADAMTS ProteinsProtein phosphorylation
The invention discloses 214 novel phosphorylation sites identified in signal transduction proteins and pathways underlying human carcinoma, and provides phosphorylation-site specific antibodies and heavy-isotope labeled peptides (AQUA peptides) for the selective detection and quantification of these phosphorylated sites / proteins, as well as methods of using the reagents for such purpose. Among the phosphorylation sites identified are sites occurring in the following protein types: Adaptor / Scaffold proteins, Cytoskeleton proteins, GTP Signaling proteins, Kinases, Metabolism proteins, Phosphatases / Phospho-diesterases / Proteases, Receptor proteins, RNA Processing proteins, Transcription proteins, Translation proteins, Transporter proteins, and Ubitquitin proteins, as well as other protein types.
Owner:CELL SIGNALING TECHNOLOGY
Method for calculating and identifying protein kinase phosphorylation specific sites
InactiveCN101710365ALarge amount of informationStrong representation abilitySpecial data processing applicationsPrincipal component analysisValidation methods
The invention discloses a method for calculating and identifying protein kinase phosphorylation specific sites, which is characterized in that, the method comprises the following steps: a) establishing a new protein sequence structure characterization method-amino acid three-dimensional character scoring based on the active ingredient analysis method; b) using the amino acid three-dimensional character scoring for characterizing the structure features of the protein kinase phosphorylation specific sites; c) using a Fisher criterion scoring method for selecting parameters which are closely related to the features of the protein kinase phosphorylation specific sites; and d) and establishing a protein kinase phosphorylation specific site identification model by a radial basis kernel support vector machine, carrying out the self-replacement verification respectively, and using the retaining 1 / 10 cross-verification and the external verification for verifying the predictive capability of the method. The method can be used for the identification of the protein kinase phosphorylation specific sites, explore the protein phosphorylation rules under physiological and pathological states, further elaborate the nature of life and the disease pathogenesis and provide the important support for developing new drugs.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Reagents for the detection of protein phosphorylation in signaling pathways
InactiveUS20100159477A1Peptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementGolgi componentCell Surface Proteins
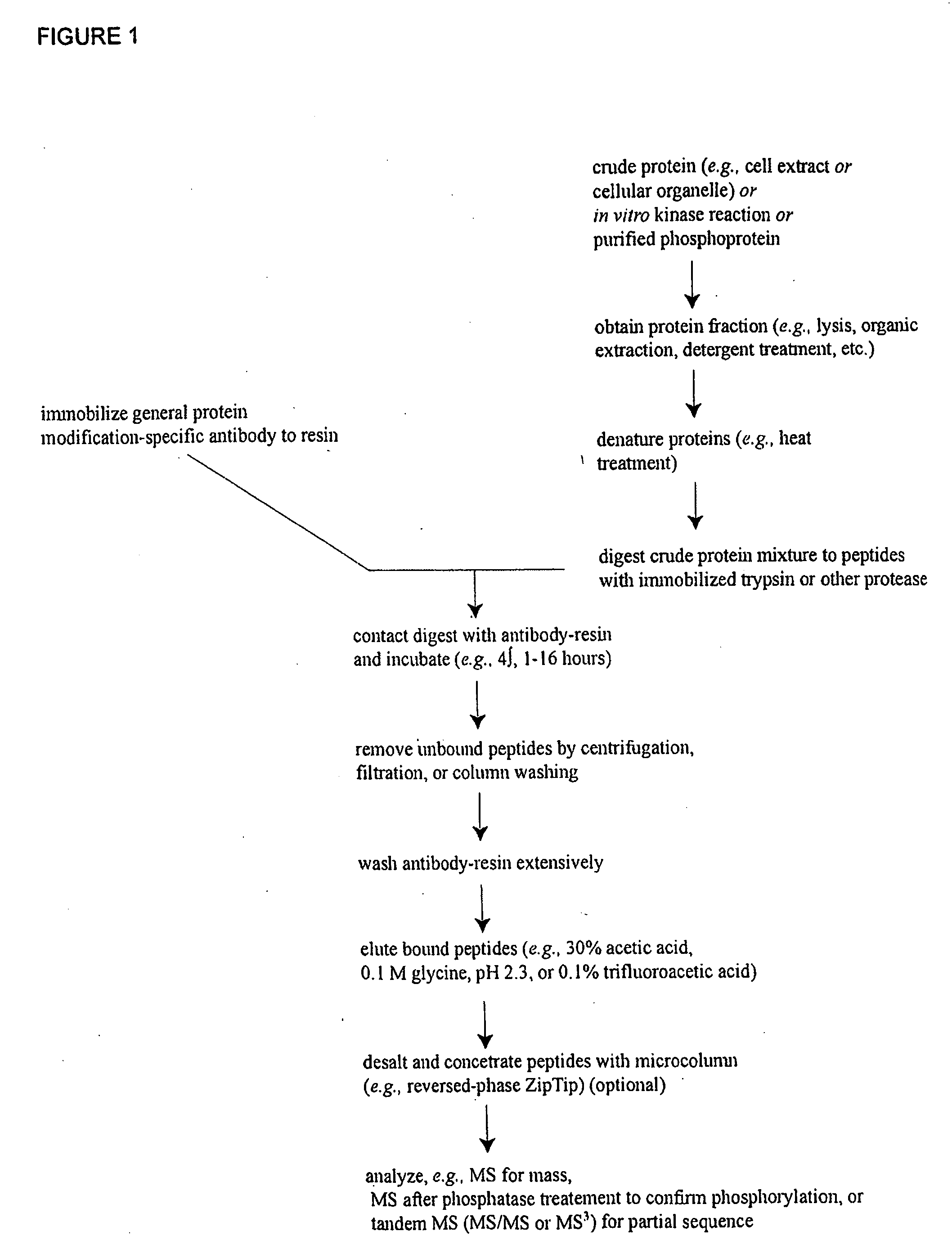
The invention discloses novel phosphorylation sites identified in signal transduction proteins and pathways, and provides phosphorylation-site specific antibodies and heavy-isotope labeled peptides (AQUA peptides) for the selective detection and quantification of these phosphorylated sites / proteins, as well as methods of using the reagents for such purpose. Among the phosphorylation sites identified are sites occurring in the following protein types: adaptor / scaffold proteins, adhesion / extracellular matrix protein, apoptosis proteins, calcium binding proteins, cell cycle regulation proteins, chaperone proteins, chromatin, DNA binding / repair / replication proteins, cytoskeletal proteins, endoplasmic reticulum or golgi proteins, enzyme proteins, G / regulator proteins, inhibitor proteins, motor / contractile proteins, phosphatase, protease, Ser / Thr protein kinases, Protein kinase (Tyr)s, receptor / channel / cell suface proteins, RNA binding proteins, transcriptional regulators, tumor suppressor proteins, ubiquitan conjugating system proteins and proteins of unknown function.
Owner:CELL SIGNALING TECHNOLOGY
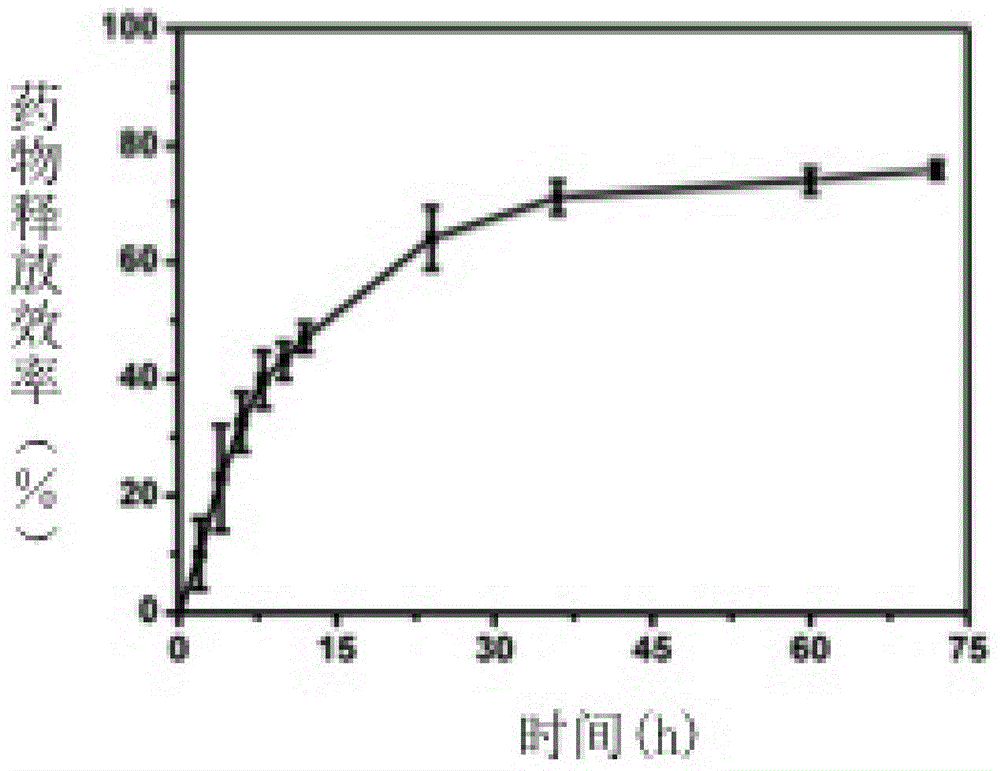
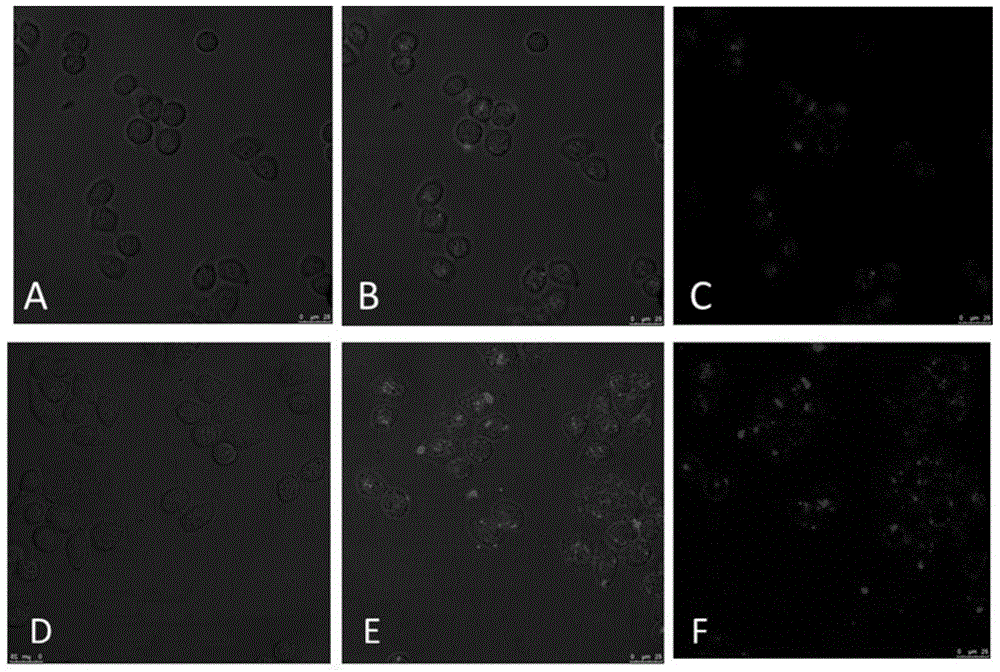
Targeted EGFR (epidermal growth factor receptor) modified platinum drug supported albumin nanoparticle as well as preparation and application thereof
ActiveCN104606127ASimple preparation processImprove stabilityHeavy metal active ingredientsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismToxicity reductionSide effect
The invention belongs to the field of a medicinal preparation, and relates to an EGFR (epidermal growth factor receptor) modified platinum drug albumin nano preparation with a target tumor cell identification function. According to the invention, albumin is used for supporting platinum drugs, medical PEG (polyethylene glycol) is taken as a dispersing and cross-linking agent, and amination EGFR aptamer is taken as a target modifying molecule, so that the soluble albumin nano (Apt-PtNPs) preparation is prepared. The nanoparticle can be specifically combined with the EGFR on the surface of the tumor cell and has a cell endocytosis function, so that the toxic and side effects of the platinum drugs can be reduced, the purposes of toxicity reduction and efficacy enhancement are achieved, EGFR expression can be inhibited by prompting EGFR protein phosphorylation, and the anti-tumor effect of the nanoparticle in combination of the platinum drugs is achieved; the nanoparticle can be used for preparing the anti-tumor drugs, and particularly, the treatment research of the nanoparticle in the aspects of cervical cancer and ovarian cancer proves that the nanoparticle is good in targeting and good in killing effect and has good application prospect in gene therapy of tumors and combined treatment by chemotherapeutic drugs.
Owner:上海纳奥生物科技有限公司
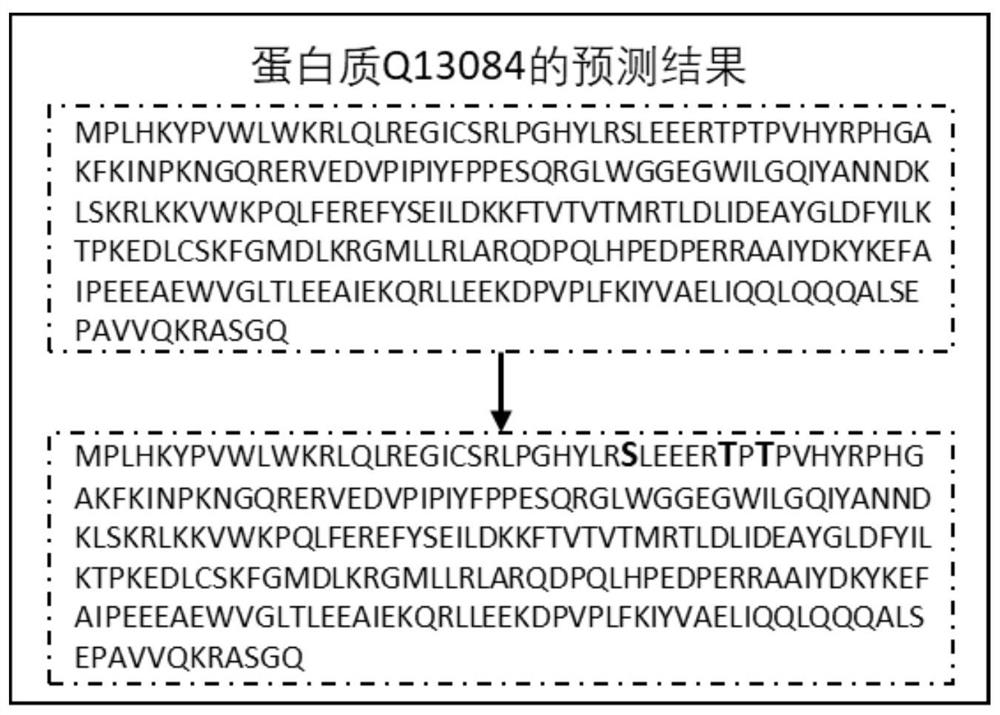
Protein phosphorylation site prediction method based on inner product self-attention neural network
PendingCN113096722AReduce computational costImprove forecast accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesProtein phosphorylationData mining
The invention relates to a protein phosphorylation site prediction method based on an inner product self-attention neural network. The method comprises the steps that: firstly, a protein sequence which has an quantityL of amino acid residues and is to be subjected to phosphorylation site prediction is input, and the protein sequence is converted into an L * 20 feature matrix Mfea through one-hot coding expression forms of 20 common amino acids; then, for each residue of the protein, a characteristic matrix M with the size of w * 20 is acquired by using a sliding window according to the Mfea; protein sequences of known phosphorylation site tags are obtained from a database to construct a training set; a neural network framework is built, the network is trained by using the training set, and a prediction model is obtained; and finally, the feature matrix of the protein sequence residues to be predicted is input into the trained model, and whether target residues in the protein sequence are phosphorylation sites or not is predicted according to a probability value output by the model. The method is low in calculation cost and high in prediction accuracy.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Stabilization method for biological samples by combination of heating and chemical fixation
ActiveUS20120122150A1Efficient heatingReduce acquisition timePreparing sample for investigationArtificial cell constructsPost translationalProtein phosphorylation
The present invention provides methods for stabilizing a biological sample for analysis. The invention more particularly provides methods combining heat treatment and chemical fixation of biological samples in order to maintain protein primary structure and post-translational modifications, such as protein phosphorylations.
Owner:DENATOR +1
Method and system for diagnosis of neuropsychiatric disorders including chronic alcoholism
Chronic alcoholism is a diverse and heterogeneous disorder that can be dichotomized into cognitively intact and cognitively impaired subgroups. At a molecular level, ethanol has been shown to have both acute and chronic effects on: Membrane biophysical properties, Membrane composition and metabolism, Protein phosphorylation, Lipid metabolic signaling, Lipoprotein transport of cholesterol. Actual molecular underpinnings are determined for cognitive impairment seen in some chronic alcoholism subjects including molecular / metabolic alterations of phospholipid and ganglioside metabolisms.
Owner:PETTEGREW JAY W +1
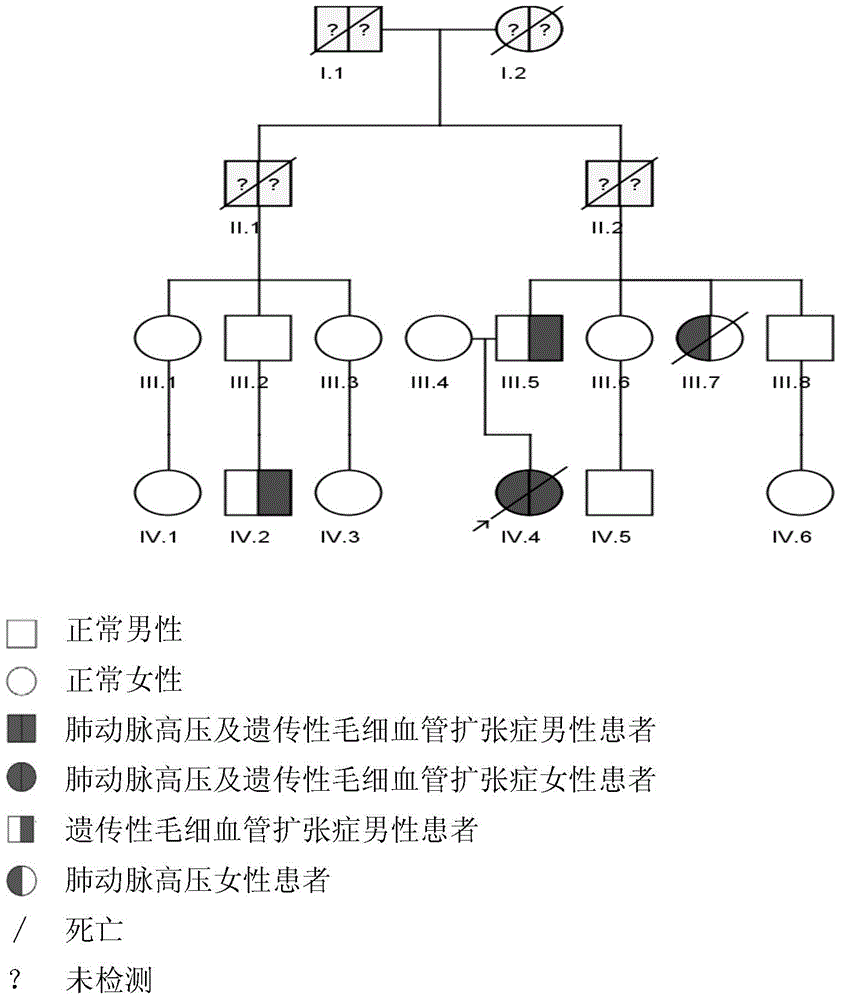
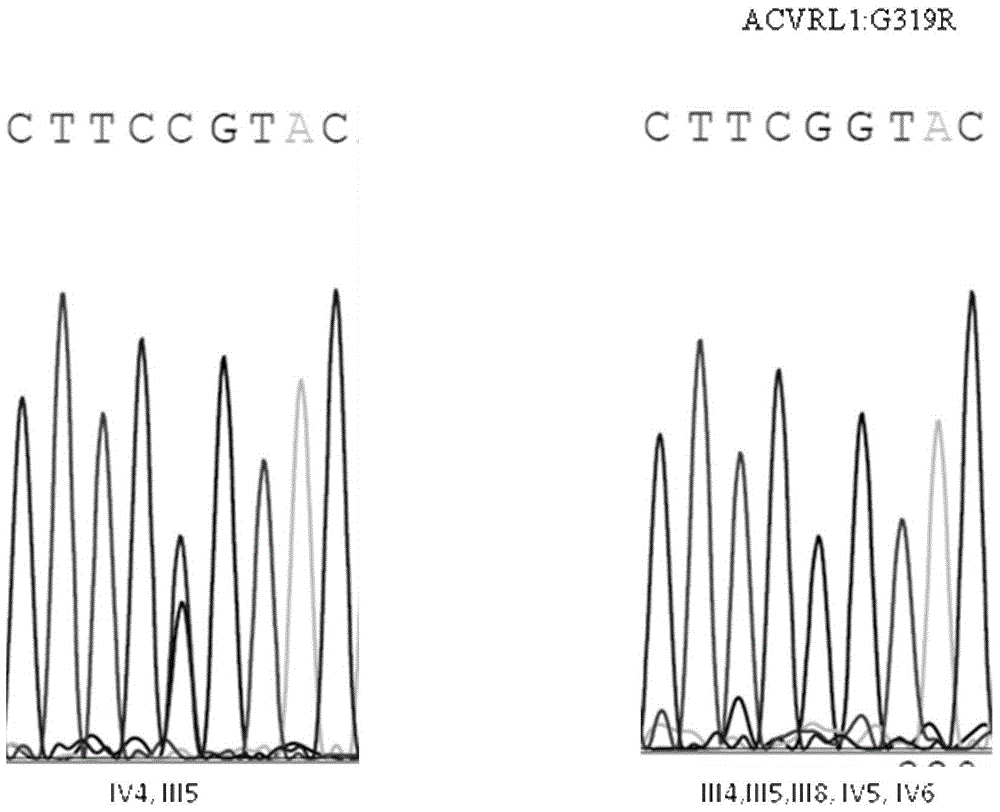
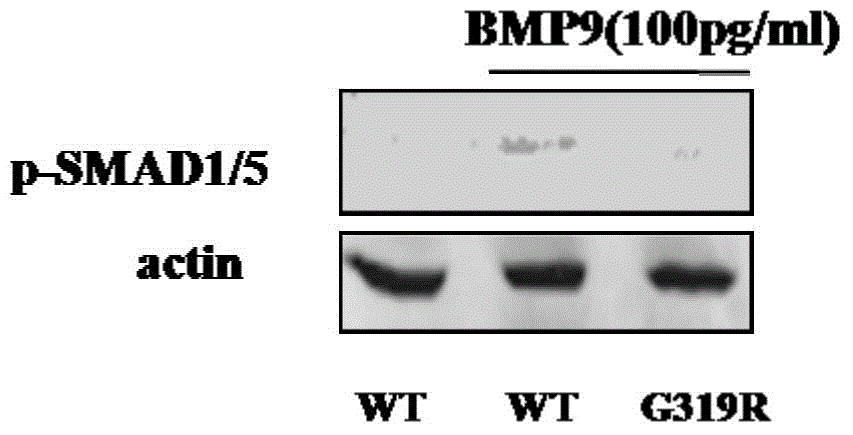
Pulmonary hypertension virulence gene ACVRL1 mutation site and application thereof
ActiveCN104650214AIncrease transcriptional activityReduce phosphorylationFungiBacteriaNucleotideProtein phosphorylation
The invention discloses a pulmonary hypertension virulence gene ACVRL1 mutation site and an application thereof. The amino acid sequence of a protein provided by the invention is sequence 4. The DNA molecule of the protein is coded and the nucleotide sequence of the DNA molecule is sequence 2. The experiment shows that the novel ACVRL1 gene mutation site is related to the pulmonary hypertension, by means of detecting whether the novel gene mutation site is the mutation site, whether the sample to be tested suffers from pulmonary hypertension can be predicted; and the novel gene mutation site can be used as a target for treating the pulmonary hypertension, and a new therapy pathway for researching the pulmonary hypertension drugs can be provided. The cell experiment verifies that the ACVRL1 gene mutation site is capable of reducing the SMAD1 and SMAD5 protein phosphorylation and / or increasing the BMP transcriptional activity in the cell.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF HEART LUNG & BLOOD VESSEL DISEASES
Reagents for the detection of protein phosphorylation in anaplastic large cell lymphoma signaling pathways
The invention discloses 211 novel phosphorylation sites identified in signal transduction proteins and pathways underlying Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma (ALCL) involving the ALK-NPM translocation / fusion, and provides phosphorylation-site specific antibodies and heavy-isotope labeled peptides (AQUA peptides) for the selective detection and quantification of these phosphorylated sites / proteins, as well as methods of using the reagents for such purpose. Among the phosphorylation sites identified are sites occurring in the following protein types: Protein Kinases (including Receptor Tyrosine Kinases), Adaptor / Scaffold Proteins, Cellular Metabolism or Miscellaneous Enzymes, Oxidoreductases, Transcription Factors, Cytoskeletal Proteins, Translation Initiation Complexes, RNA Binding Proteins, Proteases, Acetyltransferases, G protein regulators / GTPases, Helicases, Apoptosis / Cell Cycle Regulation proteins, and Hydrolases.
Owner:CELL SIGNALING TECHNOLOGY
Application of composition of artemisinin or derivative thereof and EGFR-TKI targeted drug
InactiveCN109432086AGood synergyOrganic active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsDihydroartemisininProtein phosphorylation
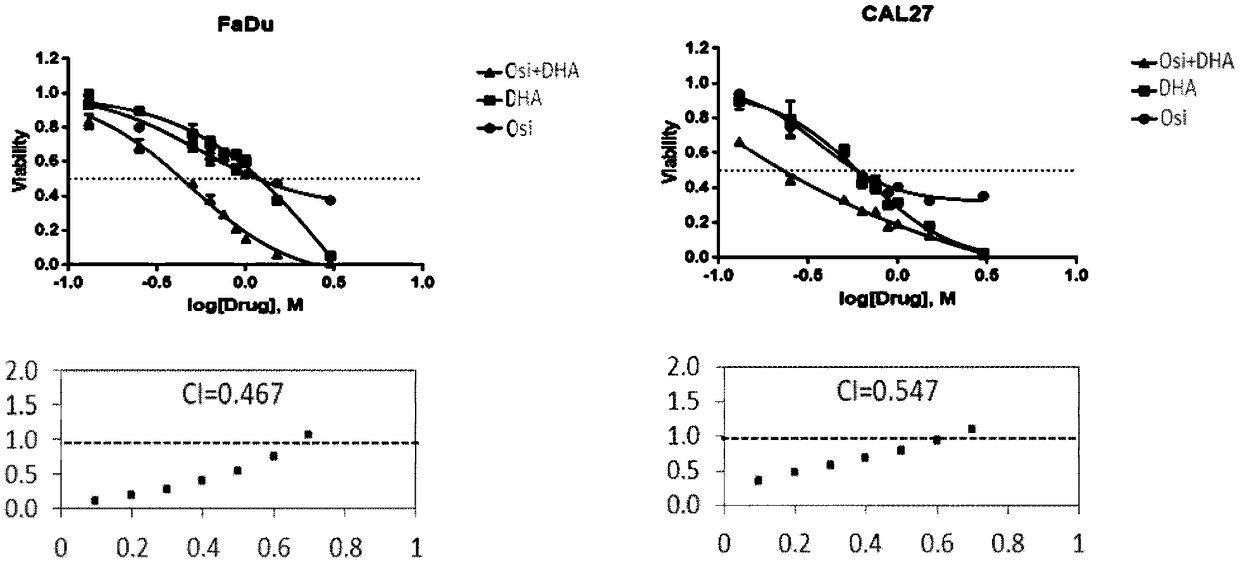
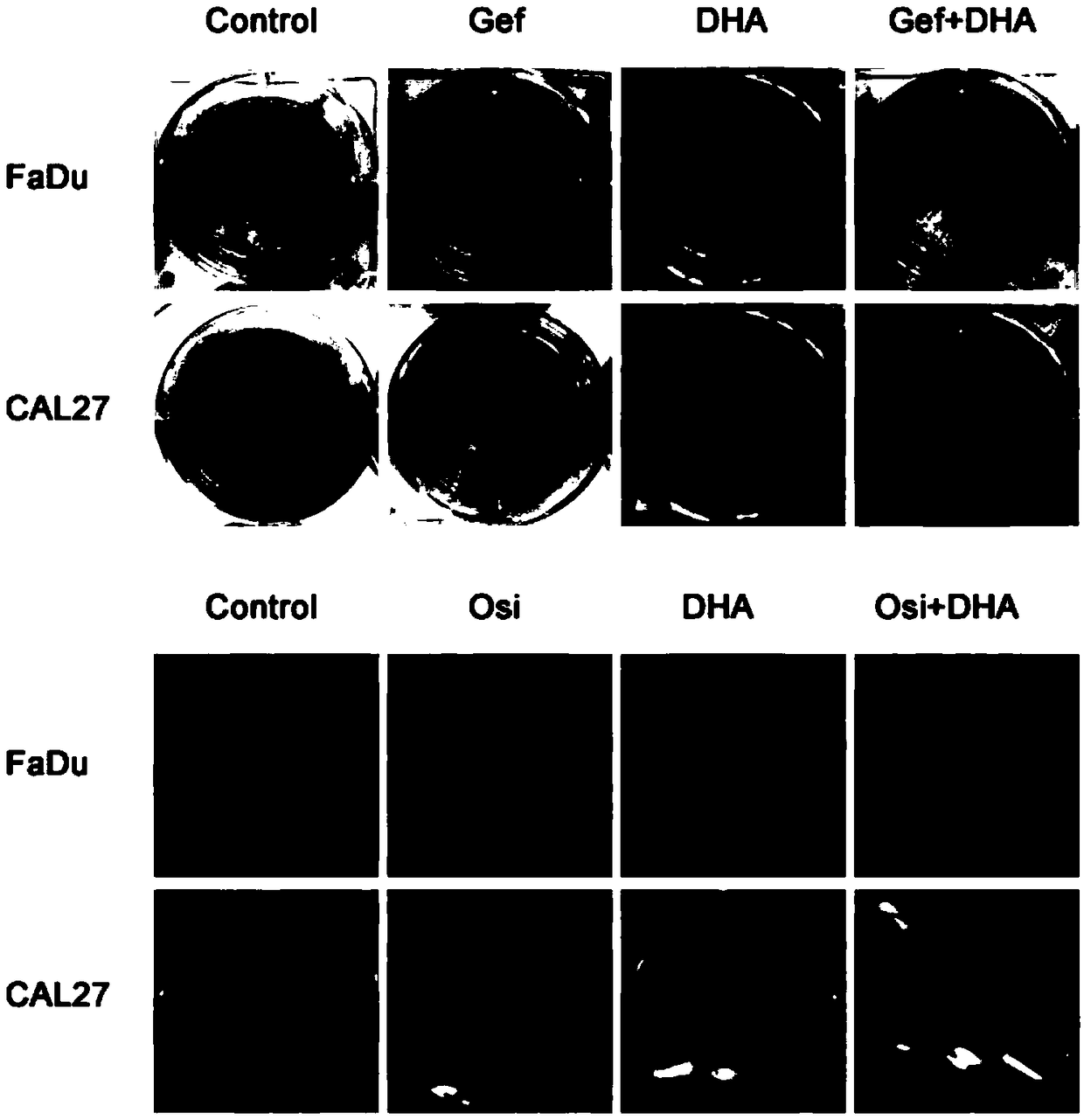
The invention discloses application of a composition of artemisinin or a derivative thereof and an EGFR-TKI targeted drug in preparation of drugs for treating tumors of the head and neck. Experimentsprove that the artemisinin and the derivative (such as dihydroartemisinin) thereof can reverse drug resistance of the tumors of the head and neck to the targeted drug, and when the artemisinin and thederivative thereof are combined to the target drug to treat the tumors of the head and neck, a remarkable synergistic effect is achieved. Through experiments, it proves that the artemisinin and the derivative such as dihydroartemisinin thereof can inhibit protein phosphorylation such as STAT3, paxillin and FAK, by the activity, the effect of resisting the tumors of the head and neck of the targeted drug (such as osimertinib as an EGFR inhibitor) is enhanced, and pharmacological basis is provided for developing new application of artemisinins drugs.
Owner:JIANGSU PROVINCE INST OF TRADITIONAL CHINESE MEDICINE
Reagents for the detection of protein phosphorylation in anaplastic large cell lymphoma signaling pathways
InactiveUS20100173322A1Immunoglobulins against animals/humansBiological testingProtein phosphorylationSpecific antibody
Owner:CELL SIGNALING TECHNOLOGY
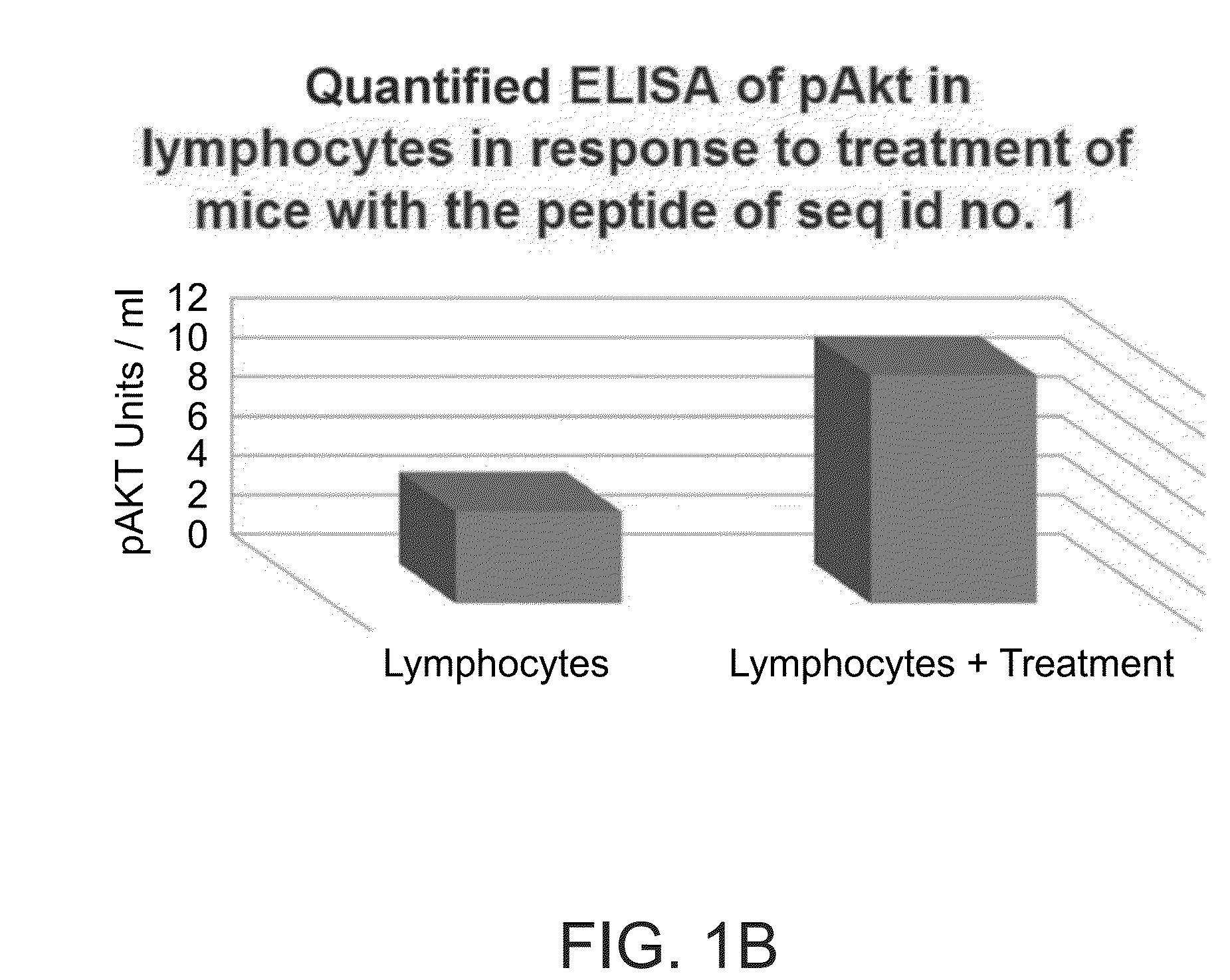
Use of akt phosphorylation as a biomarker for prognosing neurodegenerative diseases and treating same
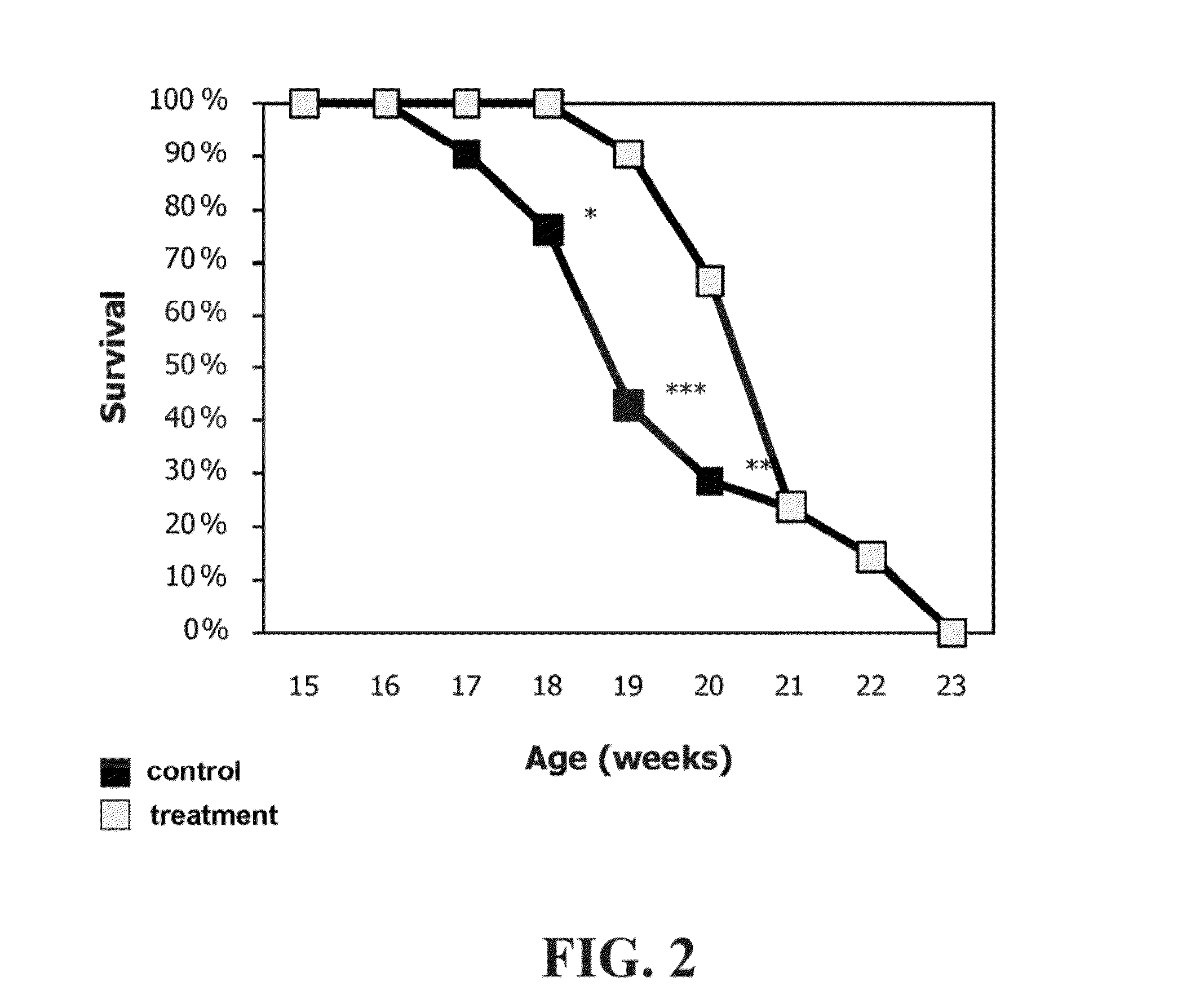
InactiveUS20140088017A1Improve survivalExtend your lifeOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderAmyotrophic lateral sclerosisProtein phosphorylation
The present invention relates to uses of a peptide comprising an amino acid sequence selected from the group consisting of SEQ ID NO: 1, SEQ ID NO: 2, analogues and derivatives thereof, for the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases, such as amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). The present invention further provides a method for assessing responsiveness to treatment with the peptide of the invention. In addition, the present invention relates to prognosis of ALS progression, using Akt and phosphorylated Akt as biomarkers.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD +1
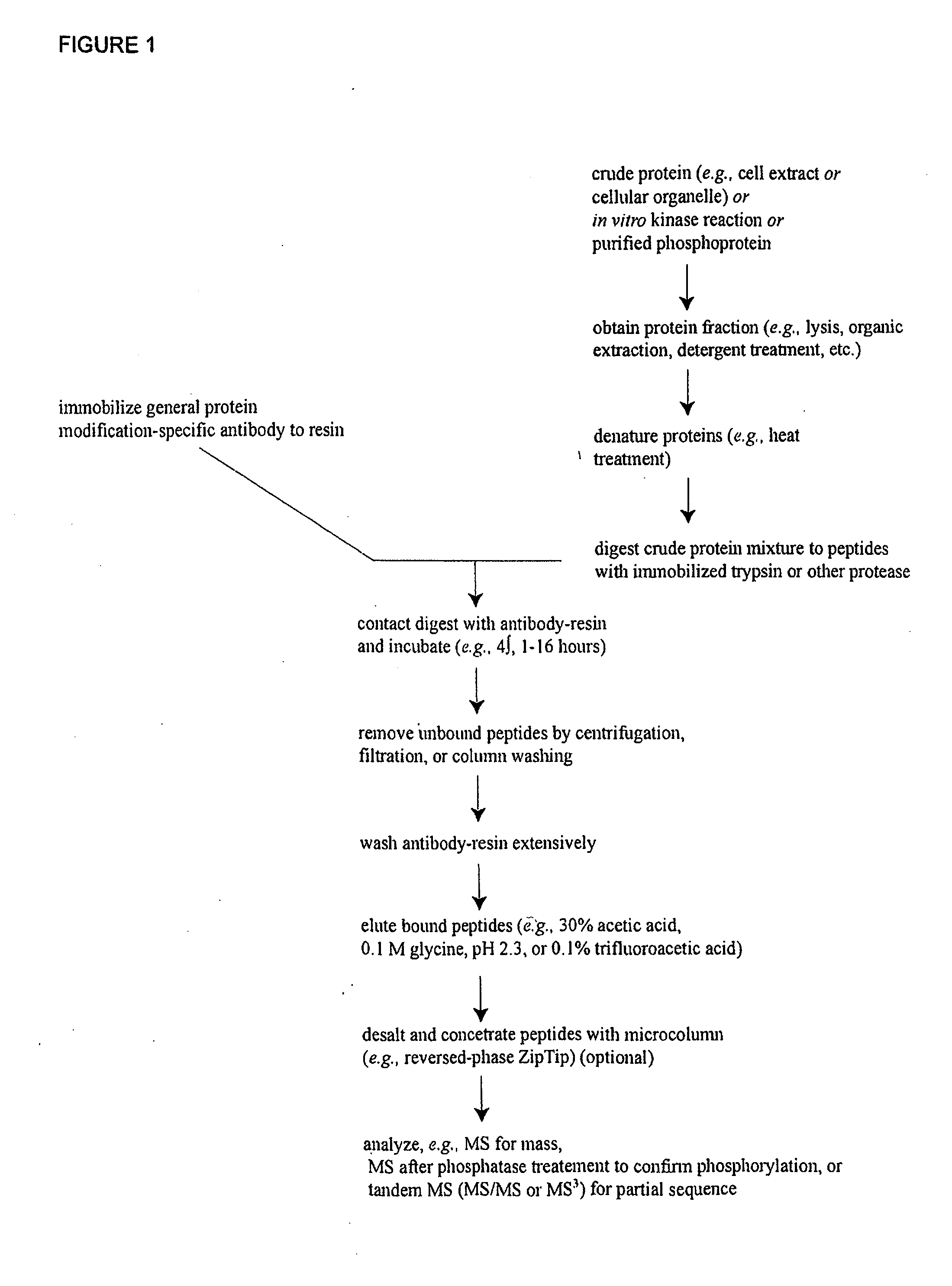
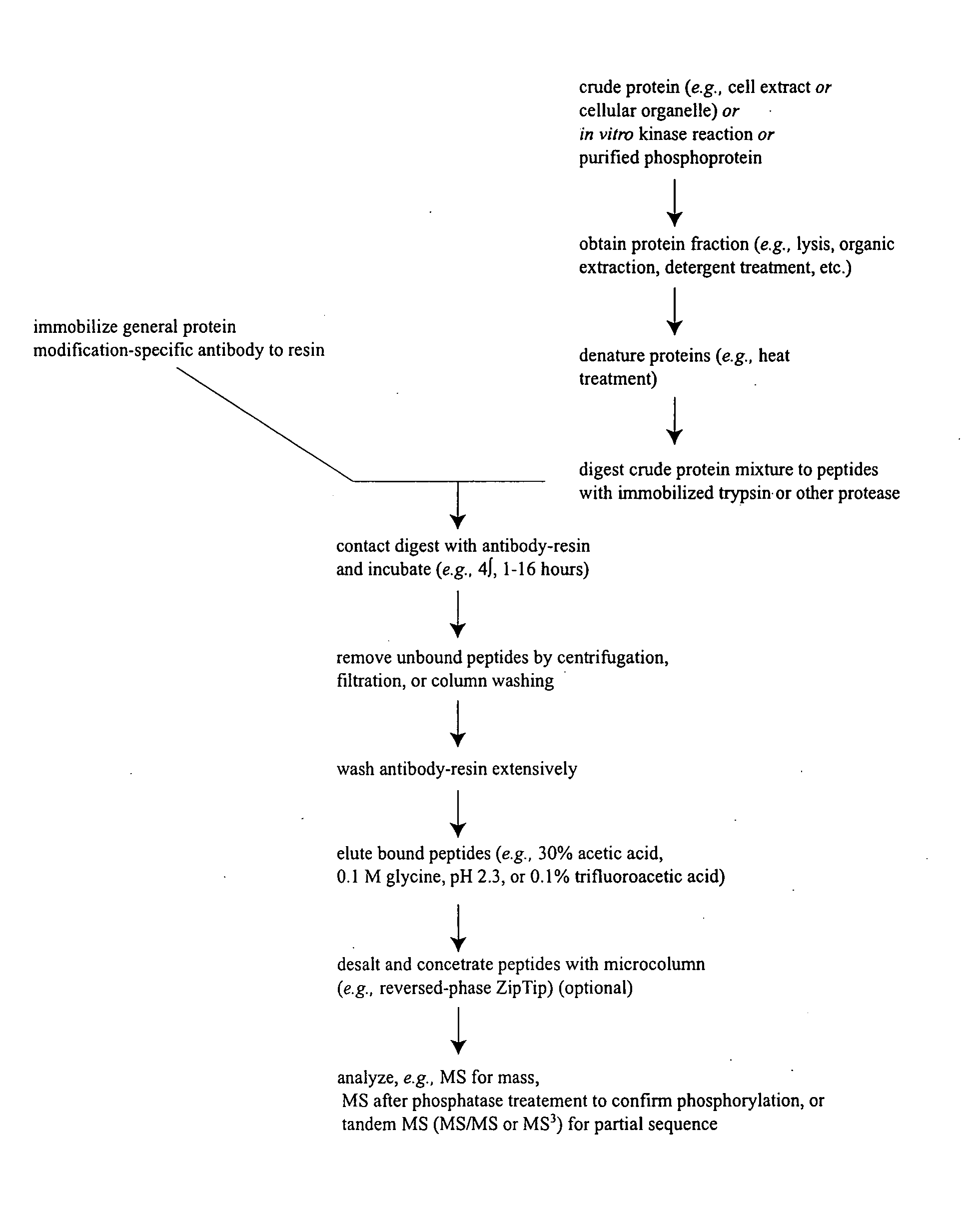
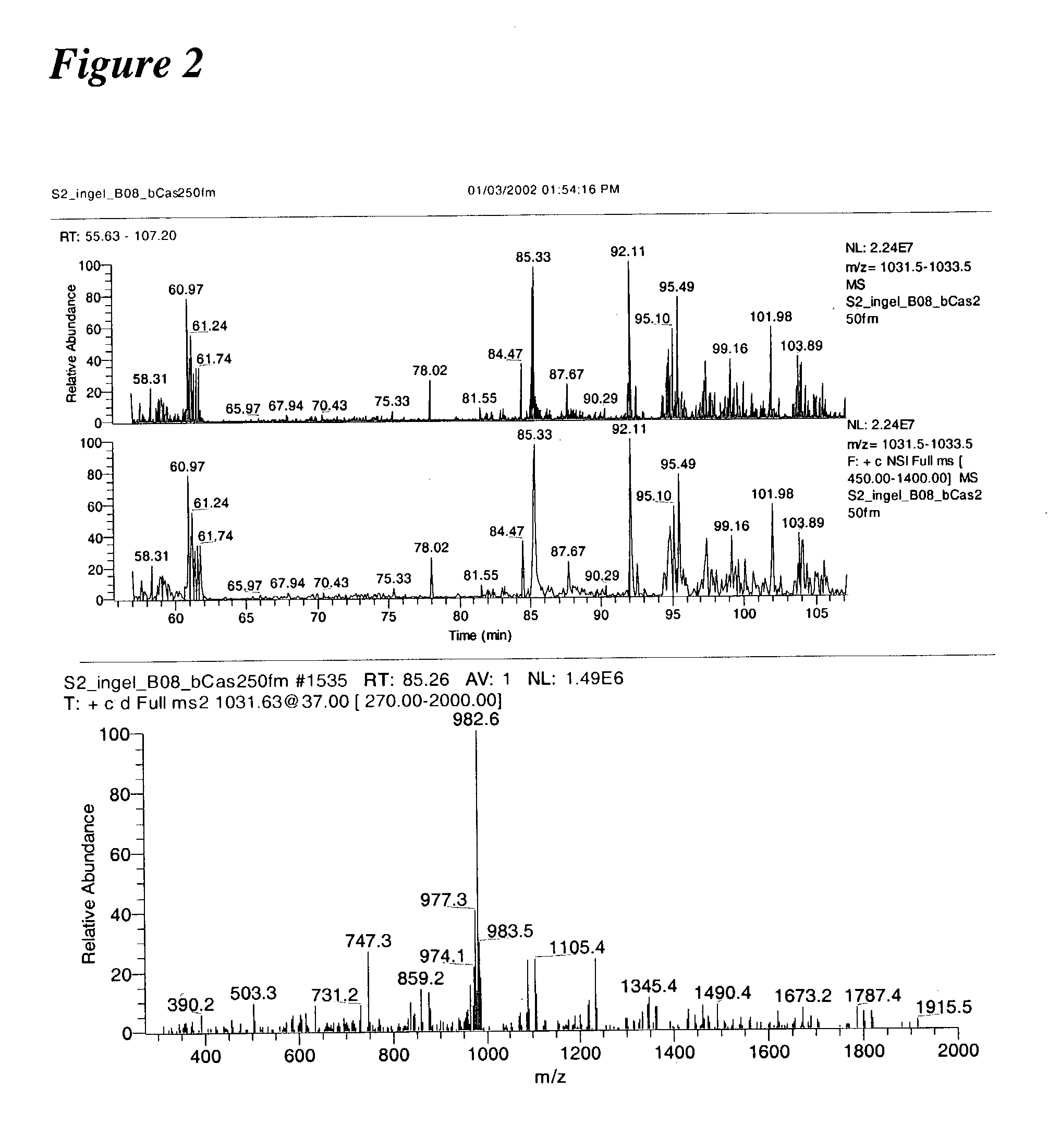
Systems and methods for the analysis of protein phosphorylation
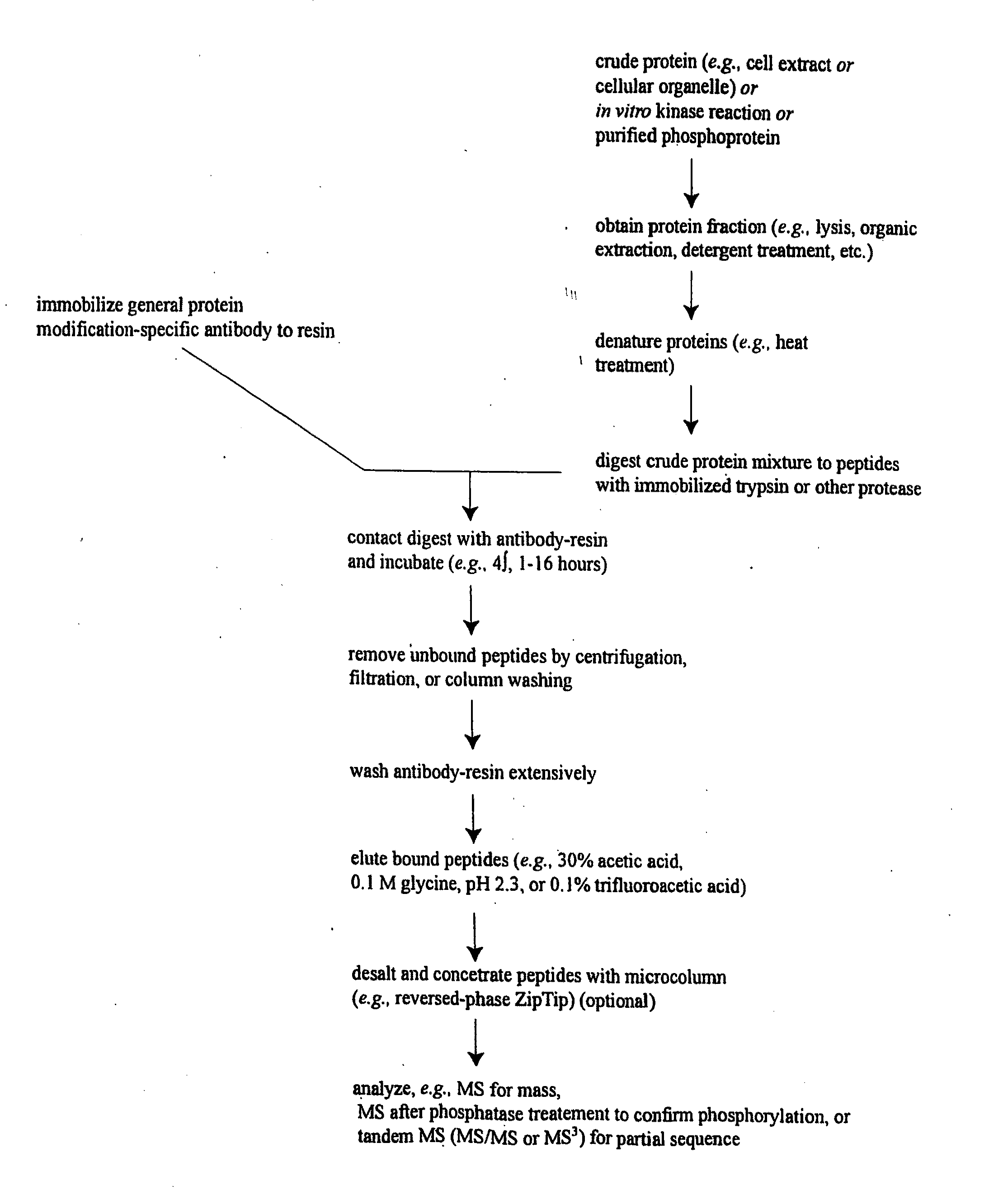
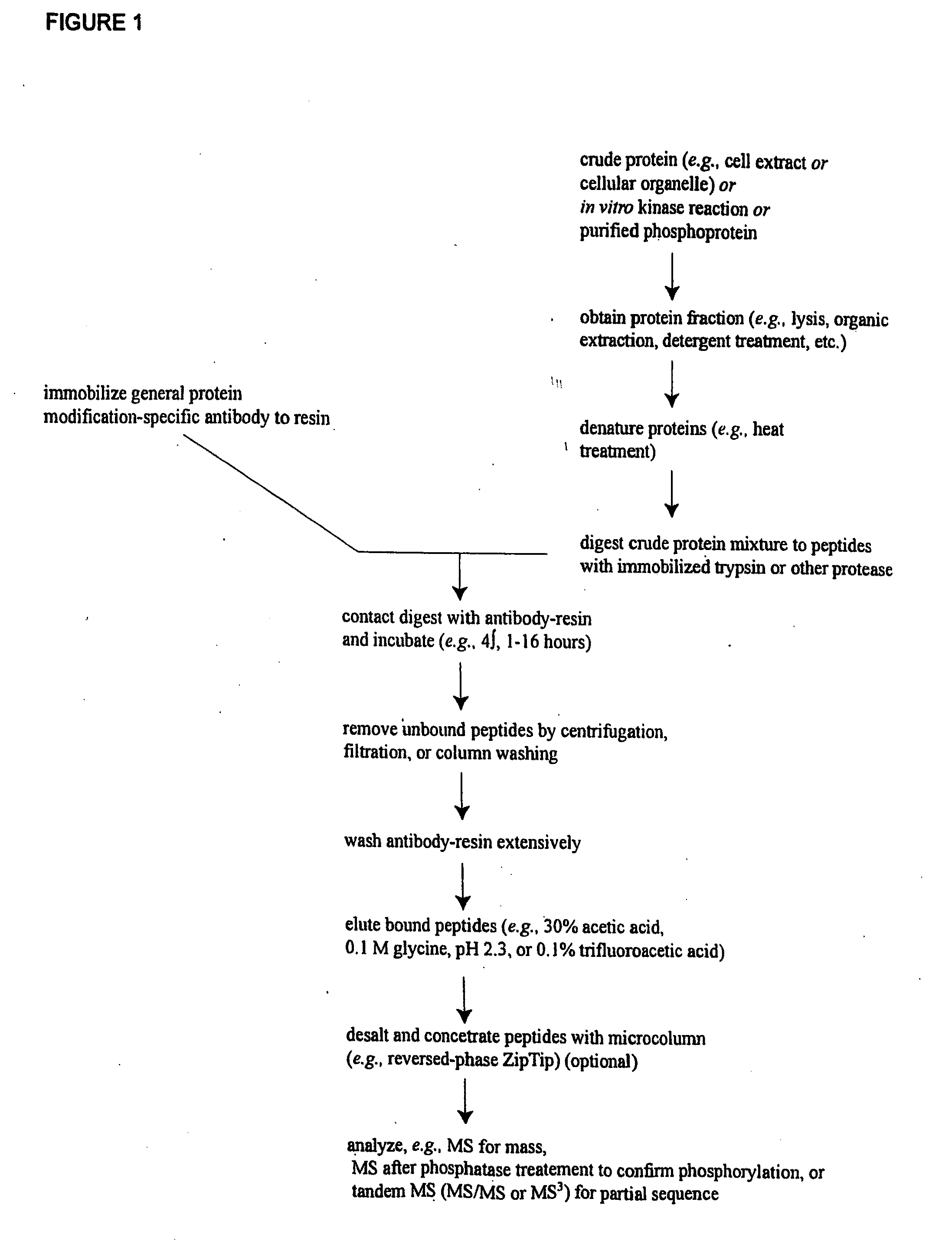
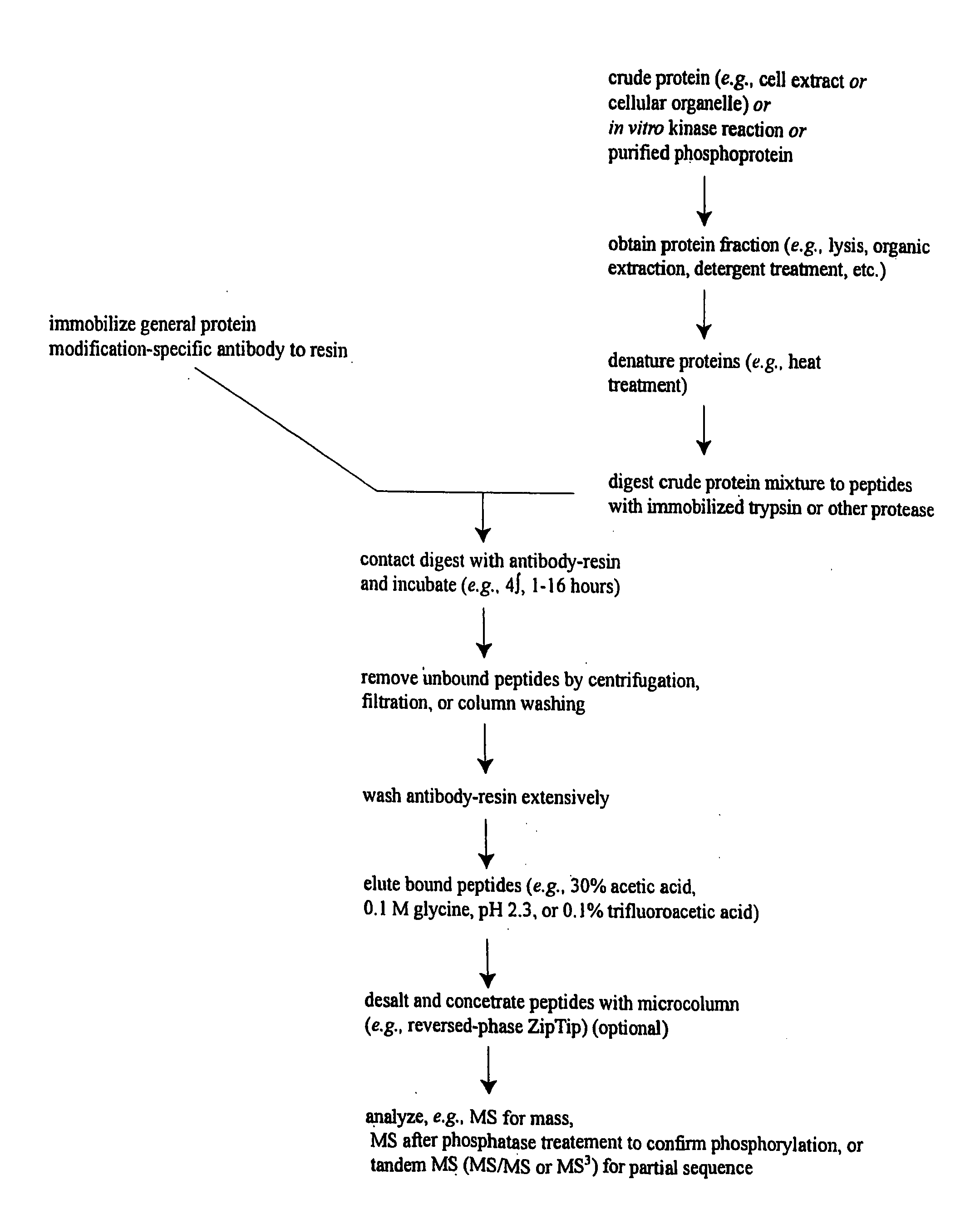
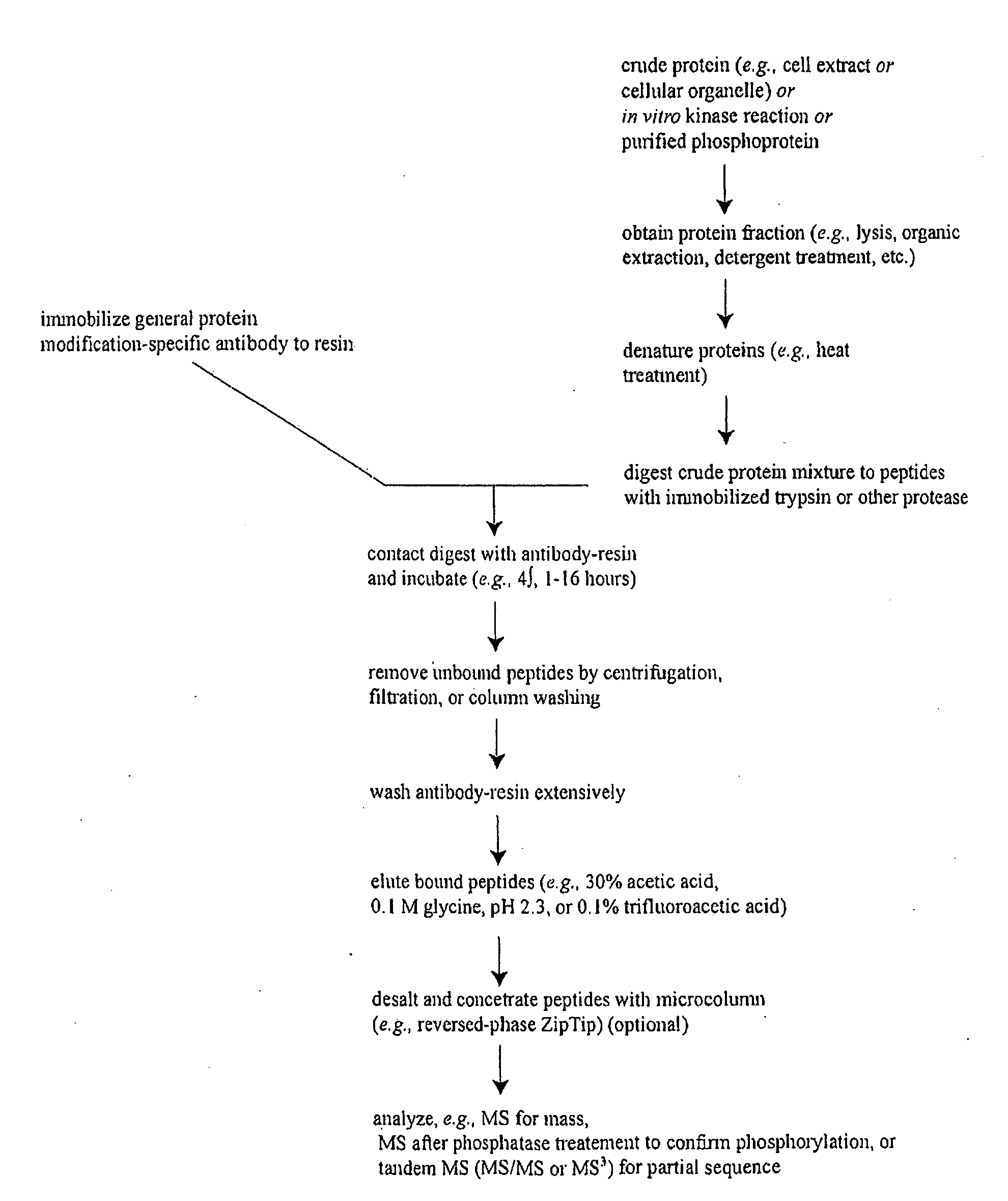
InactiveUS20030224967A1Organic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsMass Spectrometry-Mass SpectrometryProtein phosphorylation
Methods and systems of applying mass spectrometry to the analysis of peptides and amino acids, especially in the proteome setting. More particularly, the invention relates to a mass spectrometry-based method for detection of amino acid phosphorylation.
Owner:PROTANA +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com