DNA element for high-throughput in vitro protein synthesis
A protein synthesis and exogenous protein technology, applied in the field of DNA elements, can solve the problems of increasing the time required for protein synthesis, limiting protein production, and low protein translation efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0089] In the present invention, the preparation method of the yeast cell extract is not limited, and a preferred preparation method includes the following steps:
[0090] (i) providing yeast cells;
[0091] (ii) washing the yeast cells to obtain washed yeast cells;
[0092] (iii) subjecting the washed yeast cells to destructive treatment to obtain crude yeast extract;
[0093] (iv) performing solid-liquid separation on the crude yeast extract to obtain the liquid part, which is the yeast cell extract.
[0094] In the present invention, the solid-liquid separation method is not particularly limited, and a preferred method is centrifugation.
[0095] In a preferred embodiment, said centrifugation is performed in a liquid state.
[0096] In the present invention, the centrifugation conditions are not particularly limited, and a preferred centrifugation condition is 5000-100000×g, preferably 8000-30000×g.
[0097] In the present invention, the centrifugation time is not parti...
Embodiment 1
[0166] Example 1: Kluyveromyces lactis-specific Kozak sequence analysis
[0167] 1.1 Determination of the specific Kozak sequence of Kluyveromyces lactis: According to the method for analyzing the specific Kozak sequence of Saccharomyces cerevisiae, the mRNA sequences of 107 genes of Kluyveromyces lactis were retrieved and collected, and the screened The 60-base sequence of the 5' end of the Kluyveromyces lactis mRNA translation initiation codon AUG and a codon sequence downstream of the 3' end were analyzed for the content of A, U, C and G, and it was unexpectedly found at the 5' end of AUG In terms of position, the proportion of adenine A is dominant, and a serine codon UCU is dominant at the 3' end of AUG, so that the specific Kozak sequence of Kluyveromyces lactis is preliminarily determined, named kl-Kozak sequence.
[0168] 1.2 Construction of yeast in vitro protein synthesis system plasmid containing Kl-Kozak sequence specific for K. lactis: In the original yeast in vi...
Embodiment 2
[0173] Example 2: Application of kl-Kozak sequence in yeast in vitro protein synthesis system
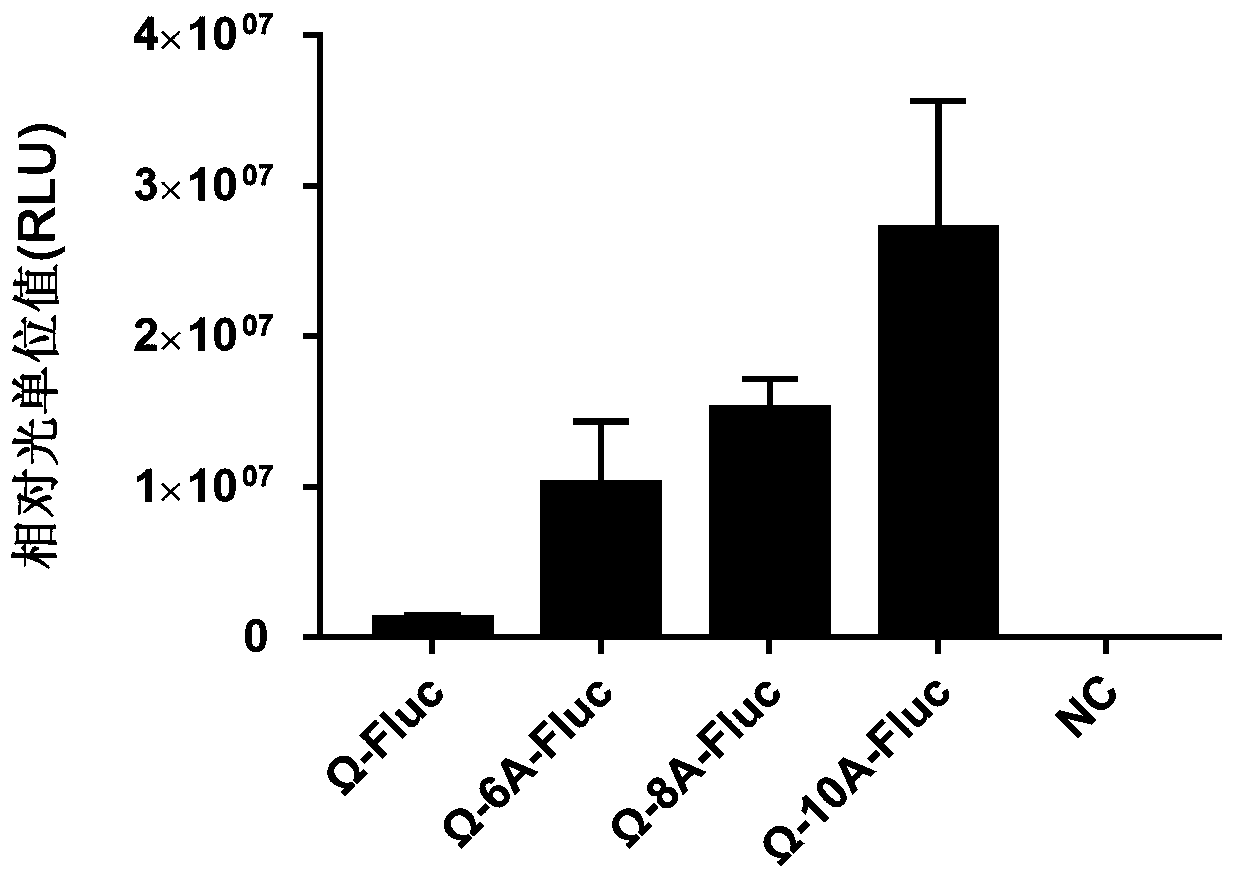
[0174] 2.1 Using the PCR method, and using primers T7_pET21a_F: CGCGAAATTAATACGACTCACTATAGG (SEQ ID NO.: 17) and T7ter_pET21a_R: TCCGGATATAGTTCCCTCCTTTCAG (SEQ ID NO.: 18) to convert the plasmids pKL-Ω-10A / 8A / 6A-Fluc and pKL-Ω- The fragments of Fluc including Ω-10A / 8A / 6A-Fluc and Ω-Fluc fragments located between the T7 transcription initiation sequence and termination sequence were amplified.
[0175] Purify and enrich the amplified DNA fragments by ethanol precipitation: add 1 / 10 volume of 3M sodium acetate (pH5.2) to the PCR product, and then add 2.5-3 times the volume (the volume is Add 95% ethanol (volume after sodium acetate) and incubate on ice for 15 min; centrifuge at a speed higher than 14000 g for 30 min at room temperature, discard the supernatant; wash with 70% ethanol, then centrifuge for 15 min, discard Discard the supernatant, dissolve the precipitate with ultrapure ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com