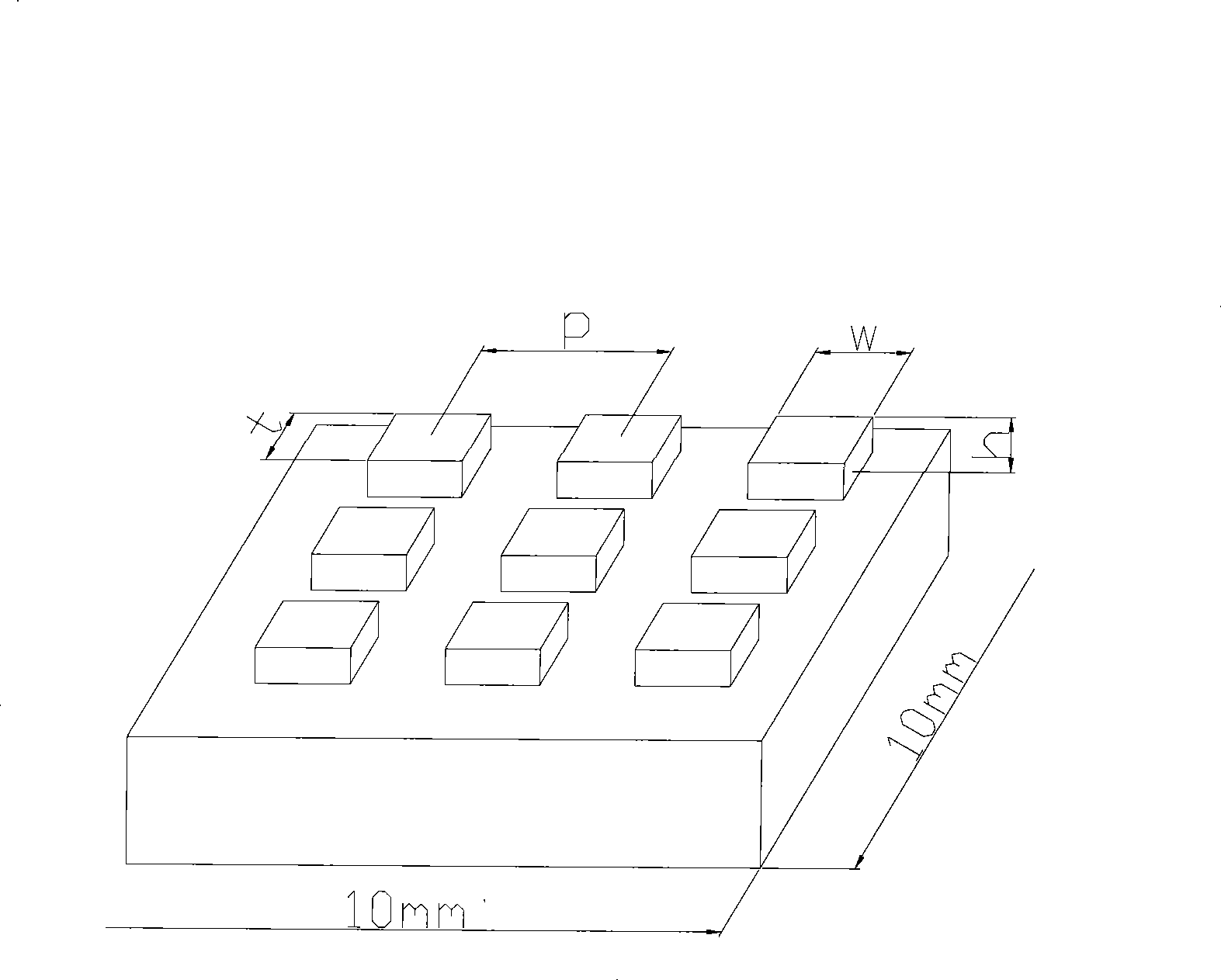Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
83 results about "Nucleate boiling" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
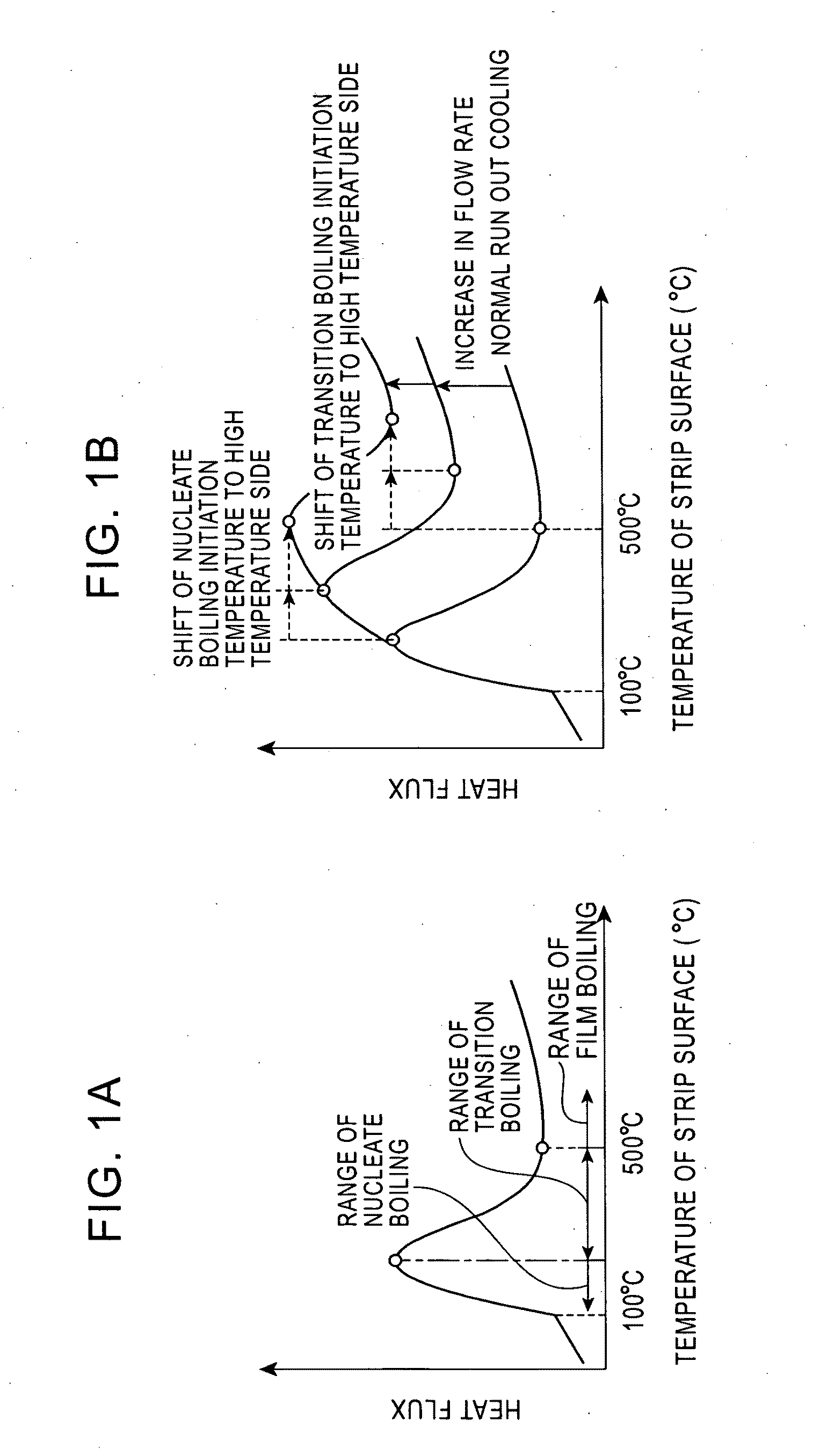
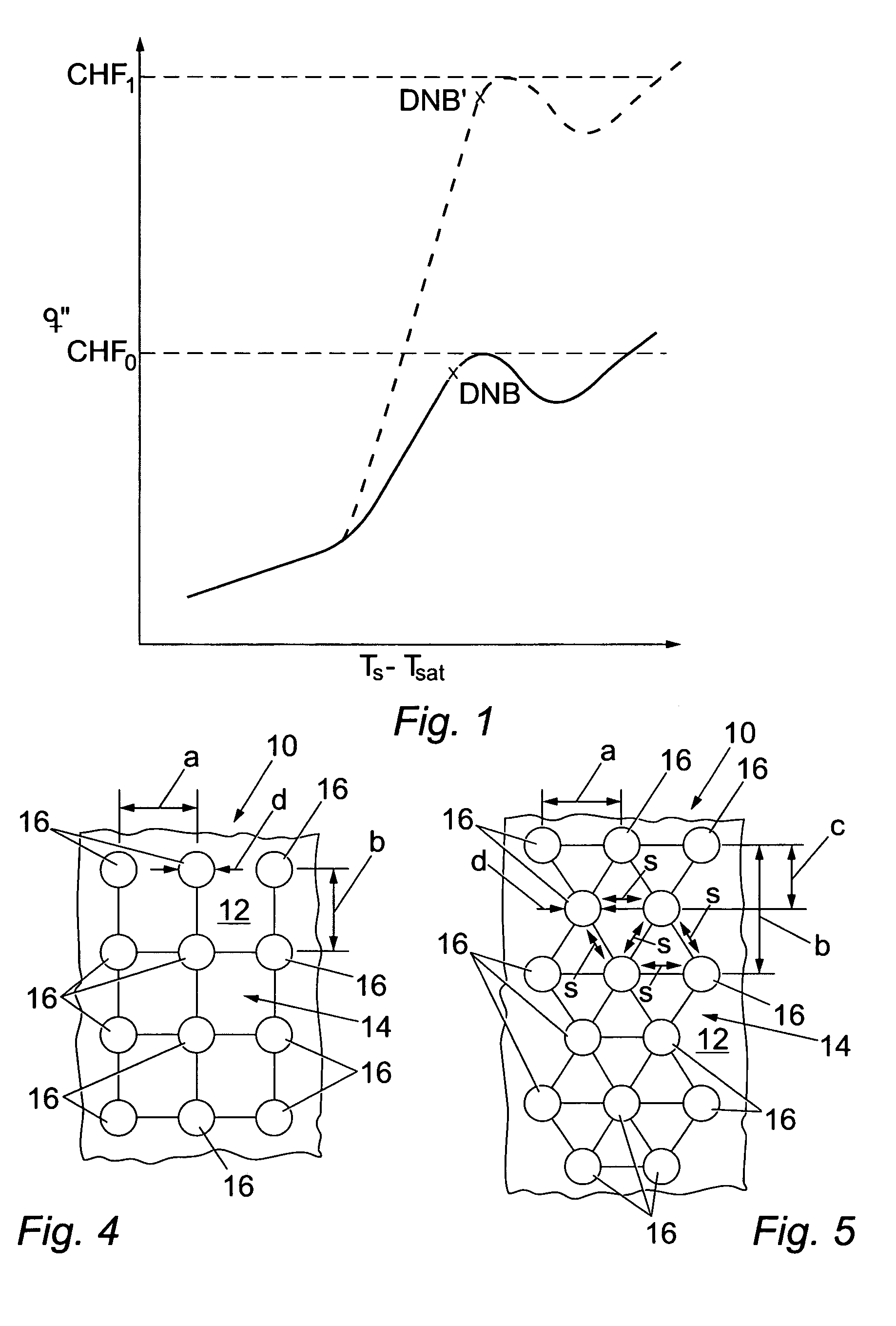
Nucleate boiling is a type of boiling that takes place when the surface temperature is hotter than the saturated fluid temperature by a certain amount but where the heat flux is below the critical heat flux. For water, as shown in the graph below, nucleate boiling occurs when the surface temperature is higher than the saturation temperature (TS) by between 10 °C (18 °F) to 30 °C (54 °F). The critical heat flux is the peak on the curve between nucleate boiling and transition boiling. The heat transfer from surface to liquid is greater than that in film boiling.
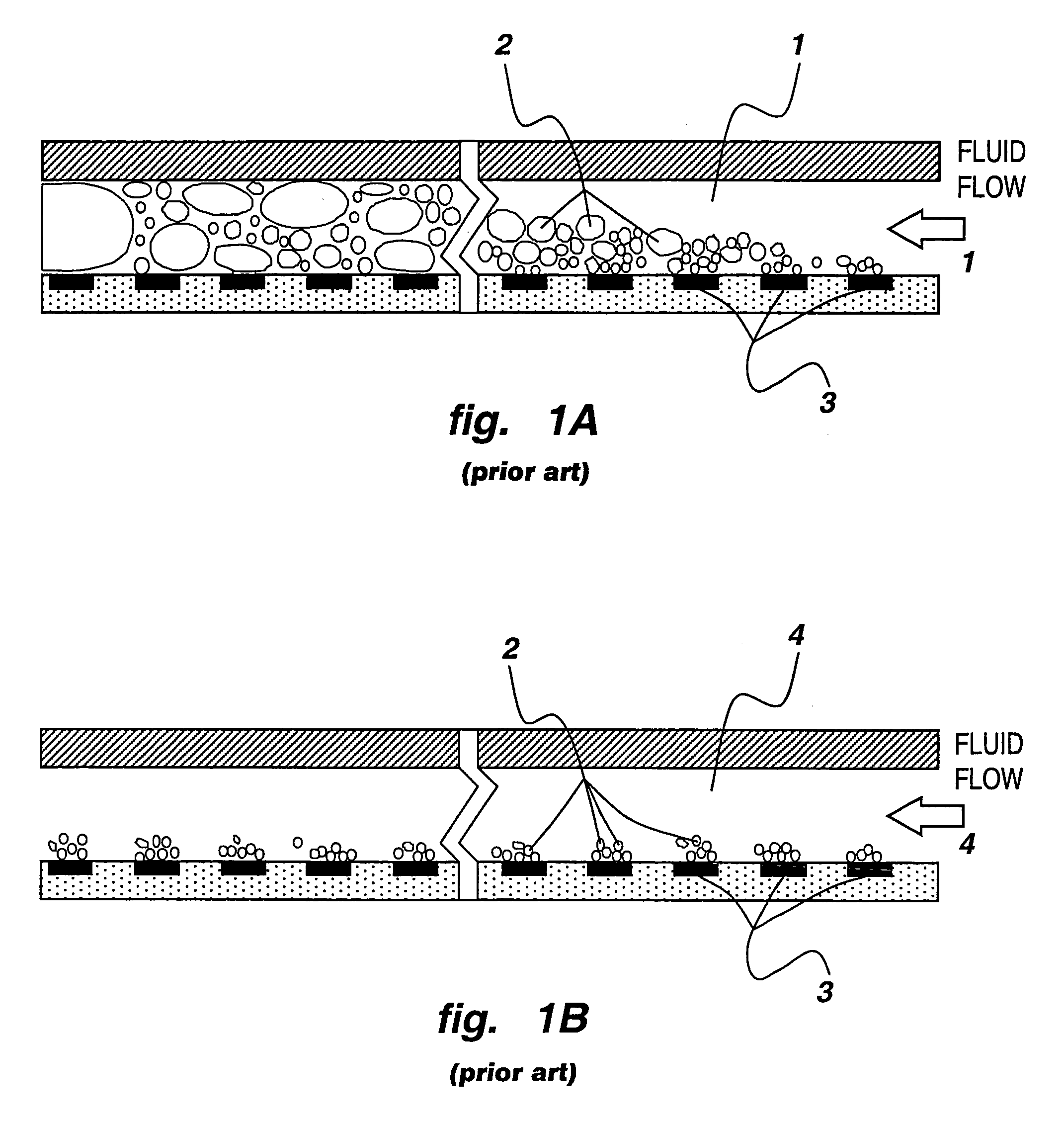
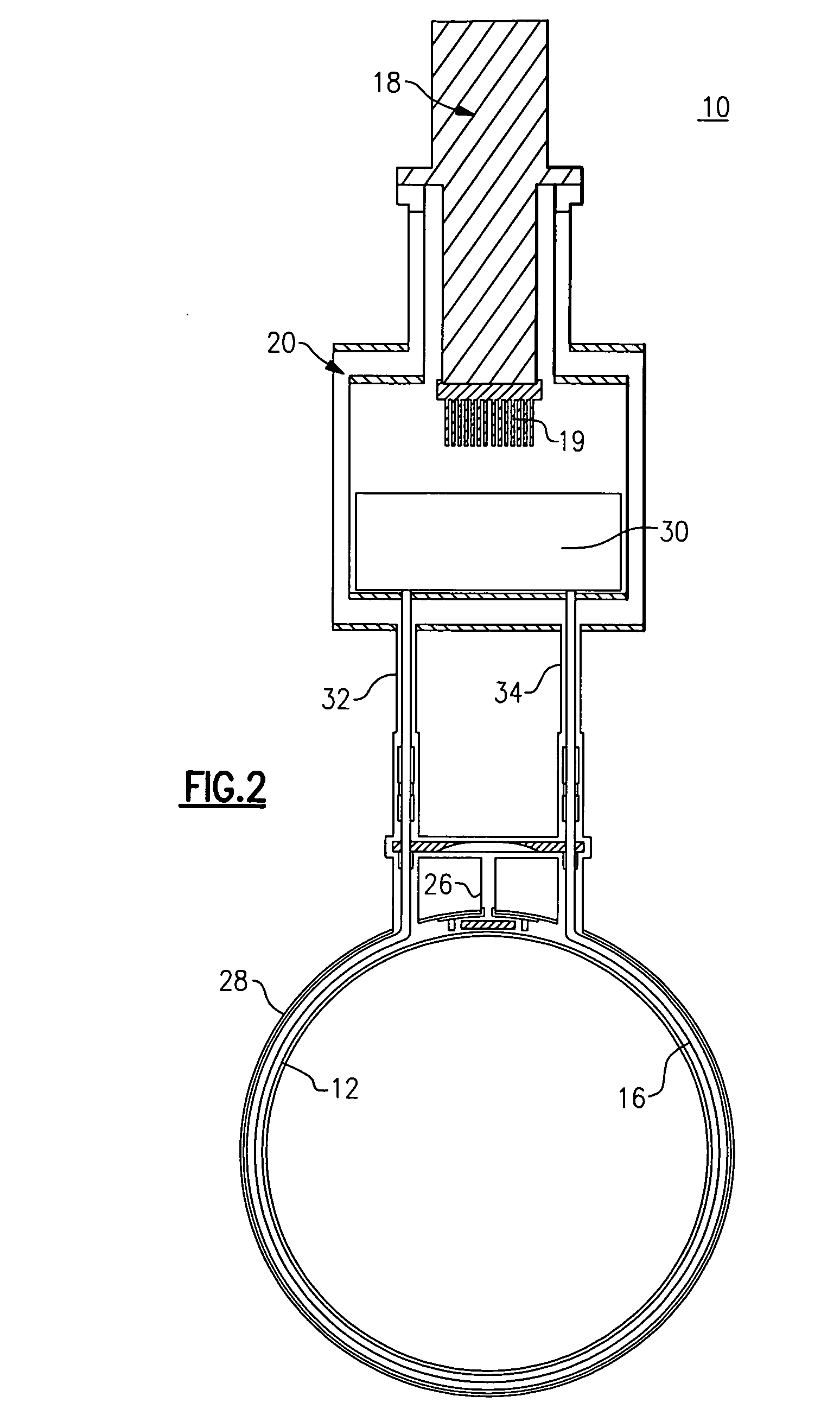
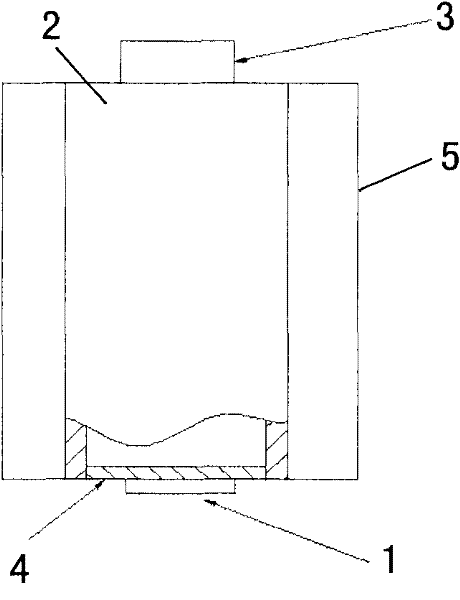
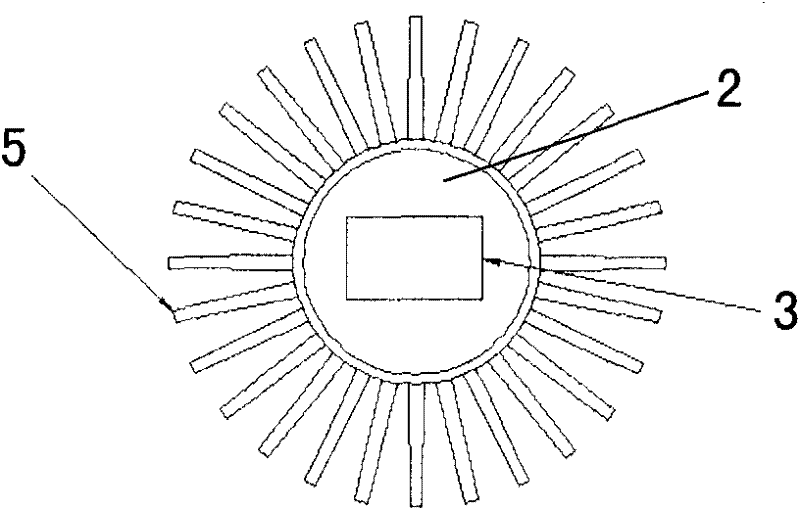
Apparatus for heat transfer and critical heat flux enhancement
InactiveUS7035104B2Increasing liquid velocityIncrease subcoolingSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesHigh fluxEngineering
An apparatus for cooling single and multiple high-flux and ultra-high-flux heat dissipating devices, comprising a liquid coolant module having a base plate and a cover plate defining therebetween a liquid coolant chamber with a liquid coolant inlet port and a liquid coolant outlet port in fluid communication with the liquid coolant chamber; at least one heat dissipating device mounted to the liquid coolant module; a multi-level-cooling-enhancement stud mounted upon each heat dissipating device and disposed within the liquid coolant module; and apparatus for inducing phase change nucleate boiling of a subcooled liquid coolant within the liquid coolant module to enhance its cooling performance.
Owner:MUDAWAR THERMAL SYST
Large surface area x-ray tube shield structure
InactiveUS6519318B1Effective coolingImprove heat transfer performanceX-ray tube electrodesX-ray tube vessels/containerElectron sourceCooling effect
An improved x-ray tube cooling system is disclosed. The system utilizes a shield structure that is connected between a cathode cylinder and an x-ray tube housing and is disposed between the electron source and the target anode. The shield includes a plurality of cooling fins to improve overall cooling of the x-ray tube and the shield so as to extend the life of the x-ray tube and related components. When immersed in a reservoir of coolant fluid, the fins facilitate improved heat transfer by convection from the shield to the to the coolant fluid. The cooling effect achieved with the cooling fins is further augmented by a convective cooling system provided by a plurality of fluid passageways formed within the shield, which are used to provide a fluid path to the coolant. In particular, a cooling unit takes fluid from the reservoir, cools the fluid, then circulates the cooled fluid through the fluid passageways. One or more depressions of "V" shaped cross section defined on the surfaces of the fluid passageways serve to facilitate nucleate boiling of the coolant in the passageway, and thereby materially increase the heat flux through the passageway to the coolant. Additionally, one or more extended surfaces disposed on the surfaces of the fluid passageways also facilitate a relative increase in the rate of heat transfer from the shield structure to the coolant. After flowing through the fluid passageway, the coolant is then discharged from the fluid passageways and directed over the cooling fins. In some embodiments, the fluid passageways are oriented so as to provide a greater heat transfer rate in certain sections of the shield than in other sections. Also disclosed is an improved braze joint for connecting the shield to the x-ray tube housing.
Owner:VAREX IMAGING CORP
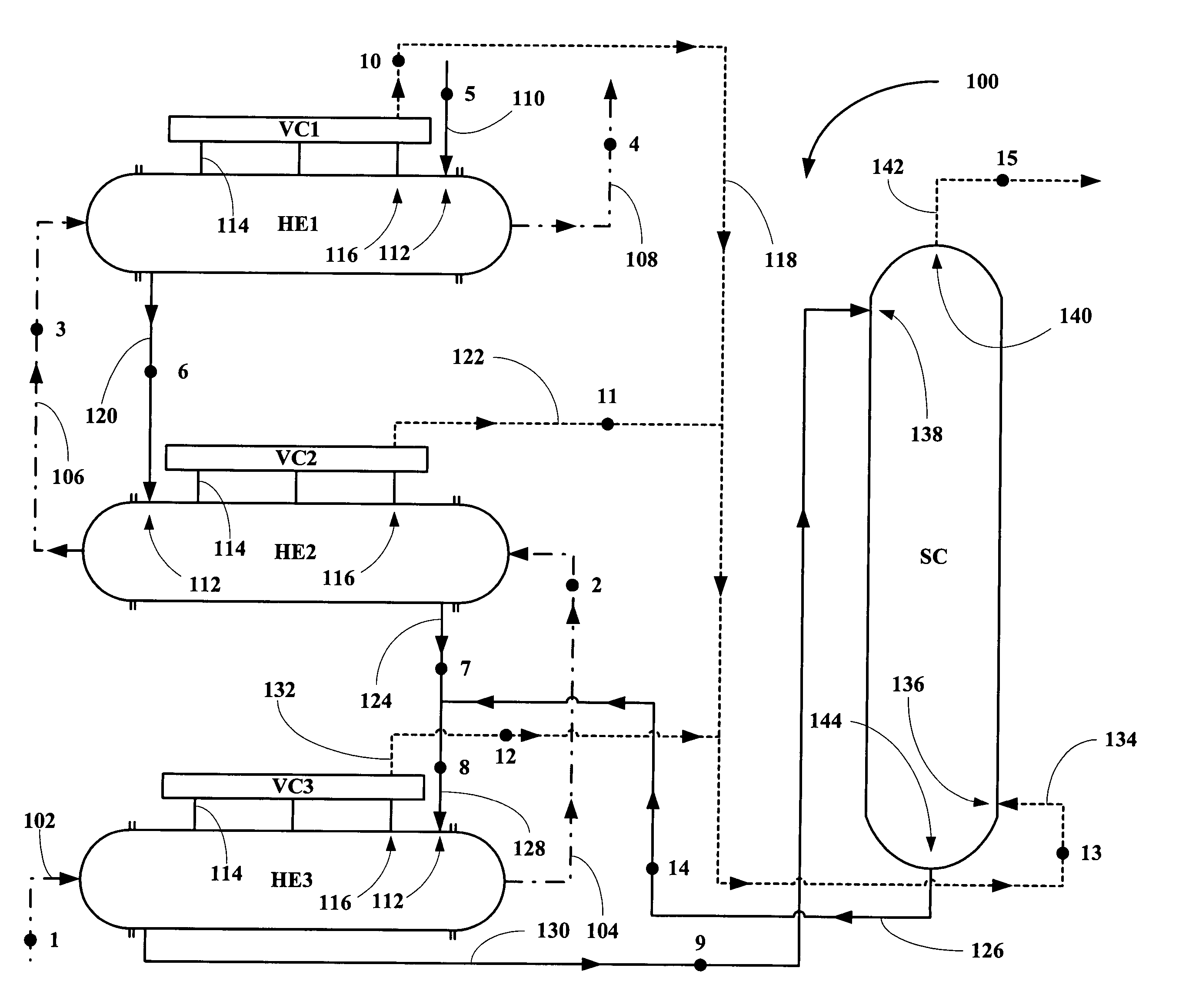
Process and apparatus for boiling and vaporizing multi-component fluids
Owner:KALINA POWER LTD
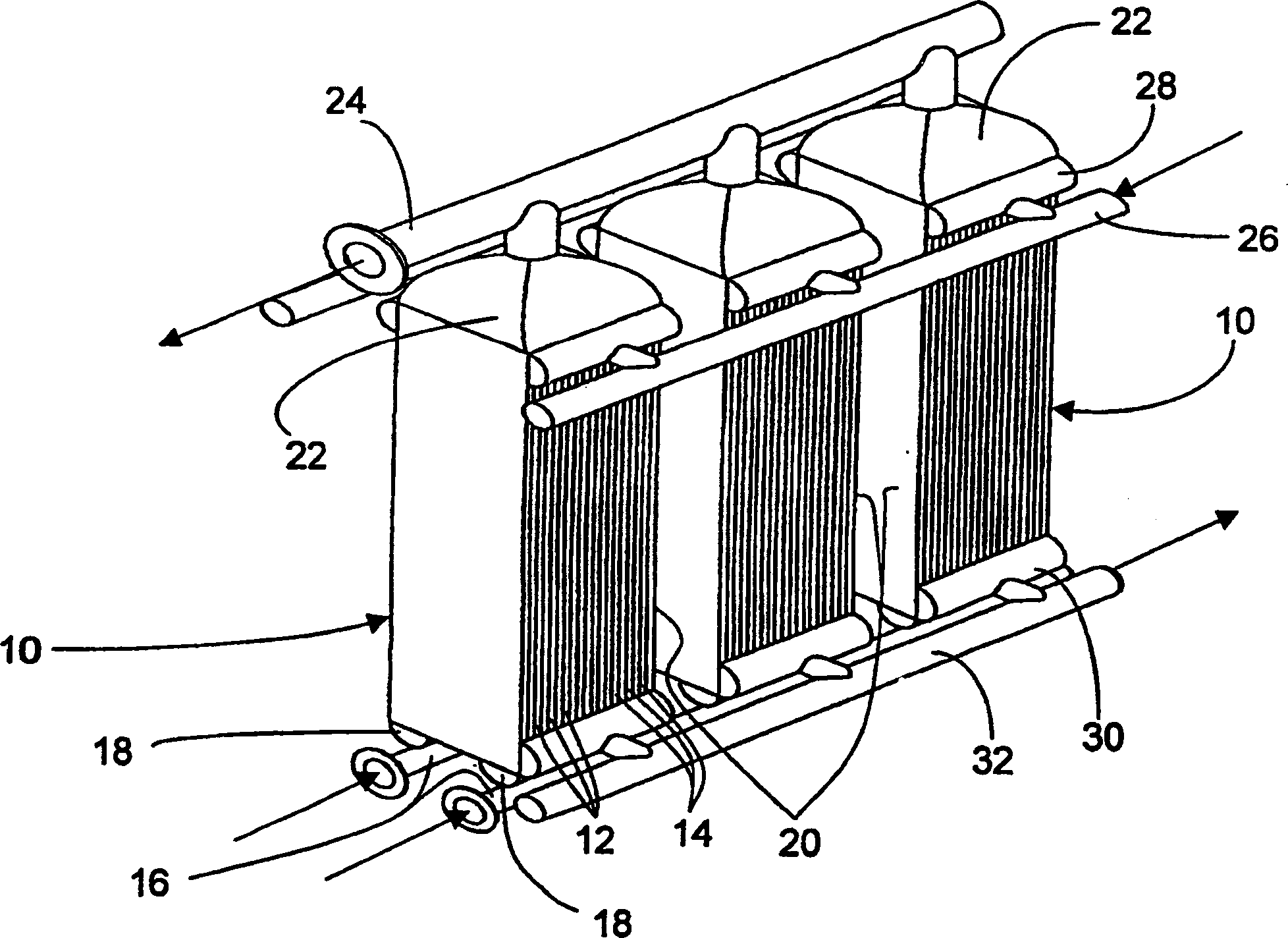
Internally finned tube having enhanced nucleation centers, heat exchangers, and methods of manufacture
Tubing having internal fins projecting inward from the tube wall, each fin having an external surface that includes multiple acute interior angles or crevices that may form nucleation boiling sites, heat exchangers comprising such tubing, and methods of making same. Acute angles, crevices, or elongated slits may be formed in the sides, center, or both, of the fins or between the fins and the tube wall, and convex rounded surfaces may be provided therebetween. Fins may be parallel to the tube centerline or helically wound. Tubing may be expanded with a bullet which may form an interference fit with external fins, may modify the fins to create more effective nucleate boiling cavities, or both.
Owner:NORDYNE
Process and apparatus for boiling add vaporizing multi-component fluids
InactiveUS20060165394A1Various ingredientsIncrease temperatureSteam generation using steam absorptionGaseous substancesWorking fluidProcess engineering
A new boiler or heat transfer apparatus is disclosed for use with multi-component working fluids which includes a vapor removal apparatus designed to maintain a substantial compositional identity between the boiling liquid and its vapor along a length of the apparatus resulting in the maintenance of substantially nucleate boiling along the entire length of the apparatus. Systems incorporating the apparatus and methods for making and using the apparatus are also disclosed.
Owner:KALEX LLC
High temperature superconducting magnet
A high temperature superconducting (HTS) magnet coil disposed within a cryostat is configured with a thermo-siphon cooling system containing a liquid cryogen. The cooling system is configured to indirectly conduction cool the HTS magnet coil by nucleate boiling of the liquid cryogen that is circulated by the thermo-siphon in a cooling tube attached to a heat exchanger bonded to the outside surface of the HTS magnet coil. A supply dewar is configured with a re-condenser cryocooler coldhead to recondense boiloff vapors generated during the nucleate boiling process.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
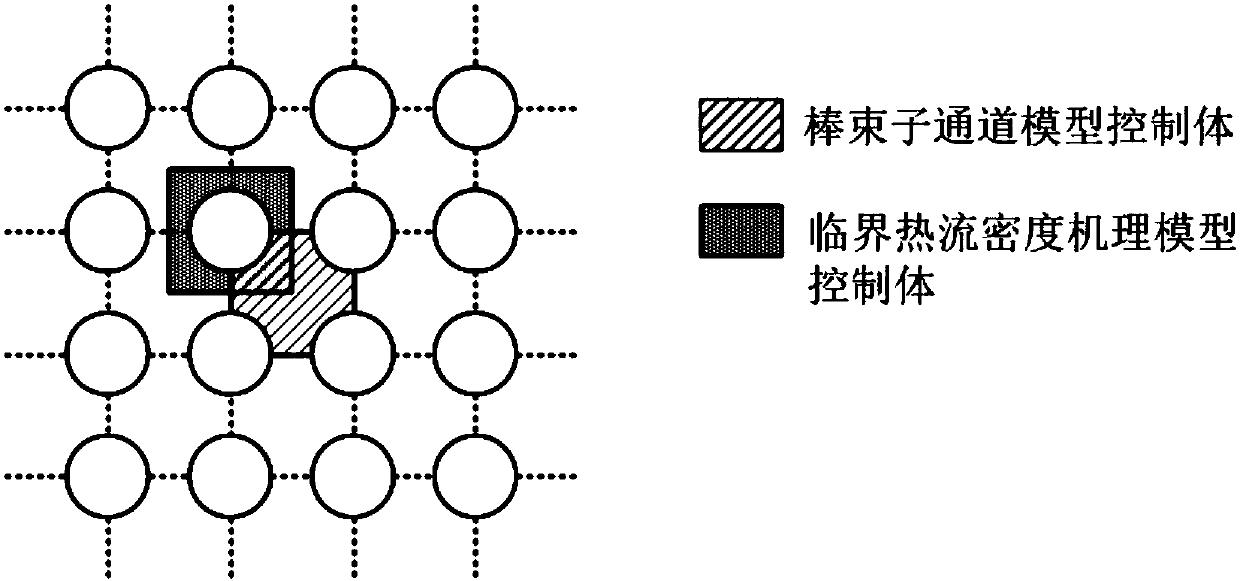
Coupling analysis method of rod cluster subchannel and critical heat flux mechanism model
InactiveCN107895095AAccurate calculationCritical heat flux facilitates subsequent analysisGeometric CADSpecial data processing applicationsStable stateThermodynamics
The invention relates to a coupling analysis method of a rod cluster subchannel and a critical heat flux mechanism model. The coupling analysis method comprises the following steps: firstly, setting the average heat flux qo of rod cluster channels, and calculating thermo-hydraulic parameters in the channels by adopting a subchannel analysis method; secondly, when the thermo-hydraulic parameters obtained through calculation in the step 1 reach a stable state, correcting and converting the obtained subchannel thermo-hydraulic parameters into a control volume of the critical heat flux mechanism model, judging a critical heat flux occurrence type, calling a departure nucleate boiling type or dry type critical heat flux mechanism model, and solving critical heat flux qCHF; and thirdly, judgingwhether critical heat flux can occur in the hottest channel, if conditions are not met, returning to the step 1 and modifying the preset average heat flux qo of the channels, and repeating the step 1and the step 2 until the conditions are met. The coupling analysis method provided by the invention has the advantages that the critical heat flux in the rod cluster subchannel can be effectively predicted, data dependency is reduced, application range is widened, and the coupling analysis method provided by the invention is significant on design and safety analysis of a reactor.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Method for cooling hot strip
ActiveUS20100192658A1Reduce temperature changesAvoid instabilityShaping toolsTemperature control deviceThermal instabilityWater flow
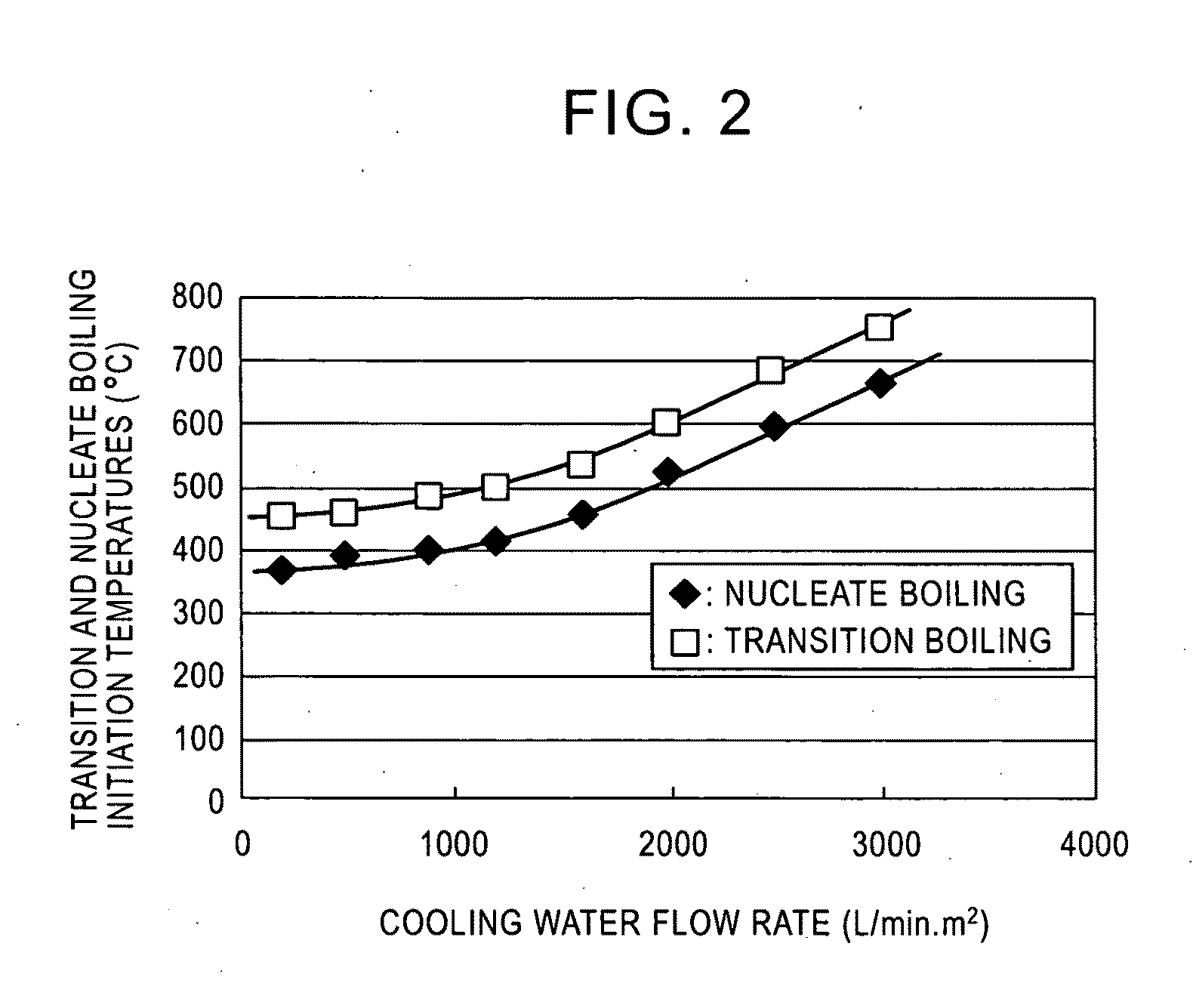
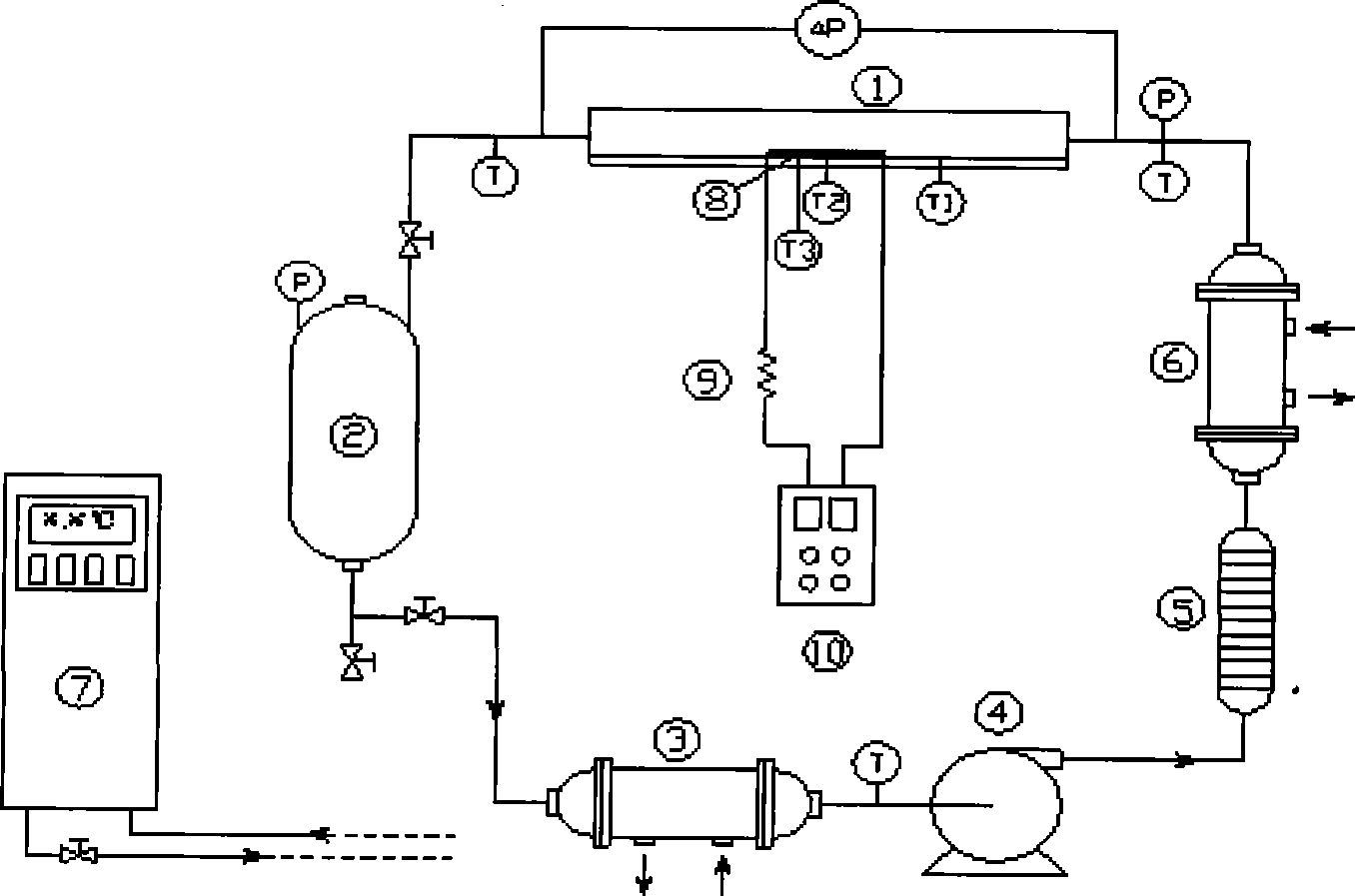
A method for cooling a hot strip with less facilities and processing costs in which the temperature variation of a strip after cooling is controlled to be small and a cooling end temperature can be precisely controlled particularly when the hot strip is cooled to the temperature range of 500° C. or less is provided. The method for cooling a hot strip, which is obtained after a hot rolling process, by bringing cooling water into contact with the hot strip, includes a first cooling step and a subsequent second cooling step. In this method, cooling is stopped at a strip temperature that is higher than a transition boiling initiation temperature in the first cooling step, and the cooling is conducted using the cooling water having a water flow rate that causes nucleate boiling in the subsequent second cooling step. Entering the temperature range of transition boiling can be completely prevented to avoid thermal instability in cooling resulting from the transition boiling, and the temperature variation of the strip after cooling is controlled to be small while the cooling end temperature can be precisely controlled.
Owner:JFE STEEL CORP
Boiling enhanced heat exchange structure of chips and fabrication method thereof
InactiveCN101447466AReduce thermal shockExtend your lifeSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSputteringBubble nucleation
The invention relates to a high heat flux density boiling enhanced heat exchange technology, in particular to amicroelectronic chip high efficiency cooling technology with a high heat flux density, particularly the boiling enhanced heat exchange structure of chips and the fabrication method thereof, which is characterized in that a plurality of lug bosses with a column structure are corroded on the surface of a chip; a SiO2 layer is splashed on the surface of the chip with the lug bosses; and the SiO2 layer is corroded to form a porous structure. The boiling enhanced heat exchange structure of chips can provide sufficient bubble nucleation number and a larger effective heat exchange area under the circumstance of a lower wall surface superheat degree, thereby solving the problem that the thermal shock of the chip exists from incipient boiling to nucleate boiling, and meanwhile, improving critical heat flux density remarkably to ensure the effective heat exchange of a high heat flux density electronic device.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Nucleate boiling cooling system and method
Owner:DEERE & CO
Heat exchanger with surface-treated substrate
An organic rankine cycle system for recovering and utilizing waste heat from a waste heat source by using a closed circuit of a working fluid is provided. The organic rankine cycle system includes at least one evaporator. The evaporator further includes a surface-treated substrate for promoting nucleate boiling of the working fluid thereby limiting the temperature of the working fluid below a predetermined temperature. The evaporator is further configured to vaporize the working fluid by utilizing the waste heat from the waste heat source.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
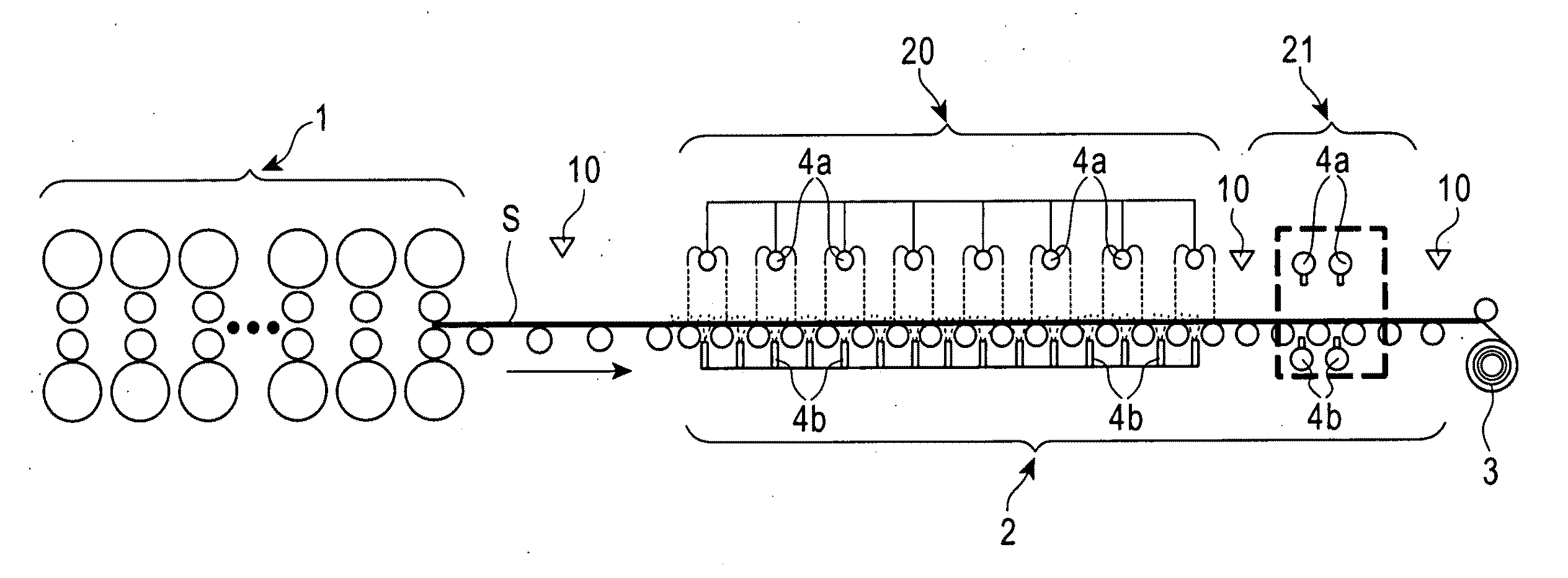
Boil Cooling Method, Boil Cooling Apparatus, Flow Channel Structure, and Applied Technology Field Thereof
InactiveUS20080104970A1Devising downsizing/weight-savingSave energySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsEvaporators/condensersEngineeringCooling fluid
In the process of boil cooling, boil cooling by nucleate boiling in a temperature area wherein transition boiling may occur is enabled to a larger cooling area.A boil cooling method of the present invention forms, with a surface of an object to be cooled ob or a surface of a heating member in close contact with the surface of the object to be cooled made to serve as a cooling surface, a main flow channel 10A and a sub-flow channel 10B for a cooling liquid from the side of the cooling surface in the above-described order, arranges a plurality of nozzles NZ penetrating a partition wall 10C separating the sub-flow channel 10B and the main flow channel 10A and protruding into the main flow channel 10A in a flow channel direction of the main flow channel, causes tip end parts of individual nozzles NZ to be in the vicinity of or in contact with the cooling surface, causes a cooling liquid 21 to circulate to the main flow channel 10A and the sub-flow channel 10B, and cools the cooling surface by boiling of the cooling liquid flowing through the main flow channel 10A, and at the same time, supplies the cooling liquid at the side of the sub-flow channel 10B from the side of the sub-flow channel 10B through each of the nozzles NZ to the vicinity of the cooling surface, and cools the cooling liquid in the main flow channel.
Owner:TOKYO UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE
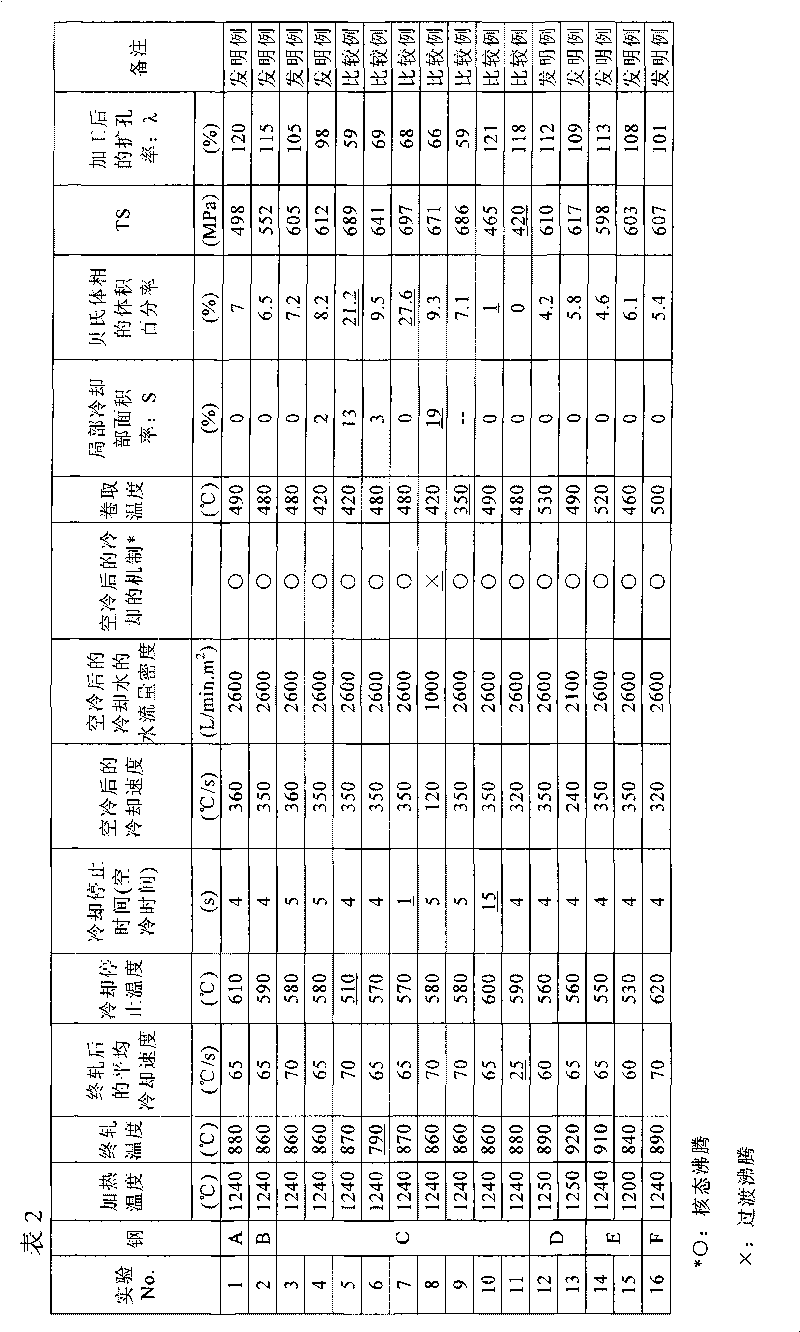
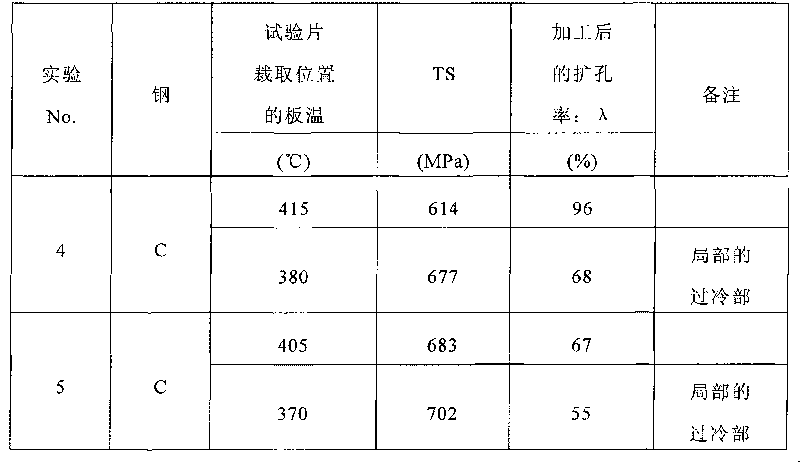
Process for manufacturing high-strength hot-rolled steel sheet
ActiveCN101755062AExcellent stretch flangeabilityFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesSheet steelHigh intensity
The invention provides a process for manufacturing a high -strength steel sheet which has a strength of 490MPa or above and excellent stretch flange formability with a hole enlargement ratio of 80% or above after 10% working and which is reduced in the local property variation in a coil. A process for manufacturing a high-strength hot-rolled steel sheet, characterized by heating a billet which contains by mass C: 0.05 to 0.15%, Si: 0.1 to 1.5%, Mn: 0.5 to 2.0%, P: 0.06% or below, S: 0.005% or below, and Al: 0.10% or below with the balance consisting of Fe and unavoidable impurities to 1150 to 1300 DEG C, subjecting the resulting billet to hot rolling with a finishing temperature of 800 to 1000 DEG C, cooling the obtained sheet at an average cooling rate of 30 DEG C / s or above to a cooling stop temperature of 525 to 625 DEG C, stopping the cooling of the sheet for 3 to 10seconds, cooling the resulting sheet by such a cooling method as to cause nucleate boiling, and then coiling the sheet at 400 to 550 DEG C.
Owner:JFE STEEL CORP
Liquid/coolant system including boiling sensor
Coolant systems, for power sources (e.g. internal combustion engines, fuel cells, and nuclear reactors) or microprocessors for example, are beneficially operated with coolant in a nucleate boiling state, but transitions to damaging film boiling are then possible. The disclosed coolant system includes a sensor, such as a thermocouple or thermistor, that provides a signal representative of fluctuations in the temperature at a heated surface. The signal also includes at least one parameter. A controller processes the signal to determine changes in the parameter of the signal and / or to determine the state of the coolant and can responsively change the coolant flow to avoid undesirable coolant states. For example, coolant flow can be changed by changing the output of a coolant pump. The controller can change coolant flow automatically, or a signal can be provided to an operator that an undesirable coolant state change is imminent or has occurred, thereby allowing operator intervention. The system may also be used with liquids other than coolant.
Owner:PERKINS ENGINES
Cavity-type light emitting diode lamp
InactiveCN102235615AThe overall thickness is thinReduce heat transfer resistancePoint-like light sourceElectric circuit arrangementsLED lampLight-emitting diode
The invention relates to a cavity-type light emitting diode lamp. A cooler is an enclosed metal cavity which is internally filled with a liquid working medium with latent heat of vaporization; a microgroove group metal plate is arranged on the cavity wall of the side or bottom of the metal cavity, and the periphery of the metal cavity is fixedly connected to the cavity wall of the metal cavity in a sealing mode; the back side of the metal cavity is provided with a microgroove group which is sealed in the cavity inward, and the frontage of the metal cavity is outward; the microgroove group is provided with a plurality of open-type microgroove channels, thus an open-type microgroove group is formed; an LED (light emitting diode) chip is encapsuled on the frontage of the metal plate, the light emitting surface of the chip is outward, the outer surface of the cavity wall at the top of the metal cavity is fixedly connected with a power supply, and the chip is electrically connected with a power supply; and the outer side wall of the cooler, except for the microgroove metal plate, is provided with fins. When the lamp works, the heat transfer process is intensified by high-strength minuteness scale composite phase-change of nucleate boiling of the liquid working medium, the liquid working medium is changes into steam, and the heat is taken away, expands on the surface of the metal cavity, and is released into the environment through the fins. The problems of insufficient heat radiation, over-heavy weight and overlarge volume of the existing LED lamp chip are solved.
Owner:INST OF ENGINEERING THERMOPHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
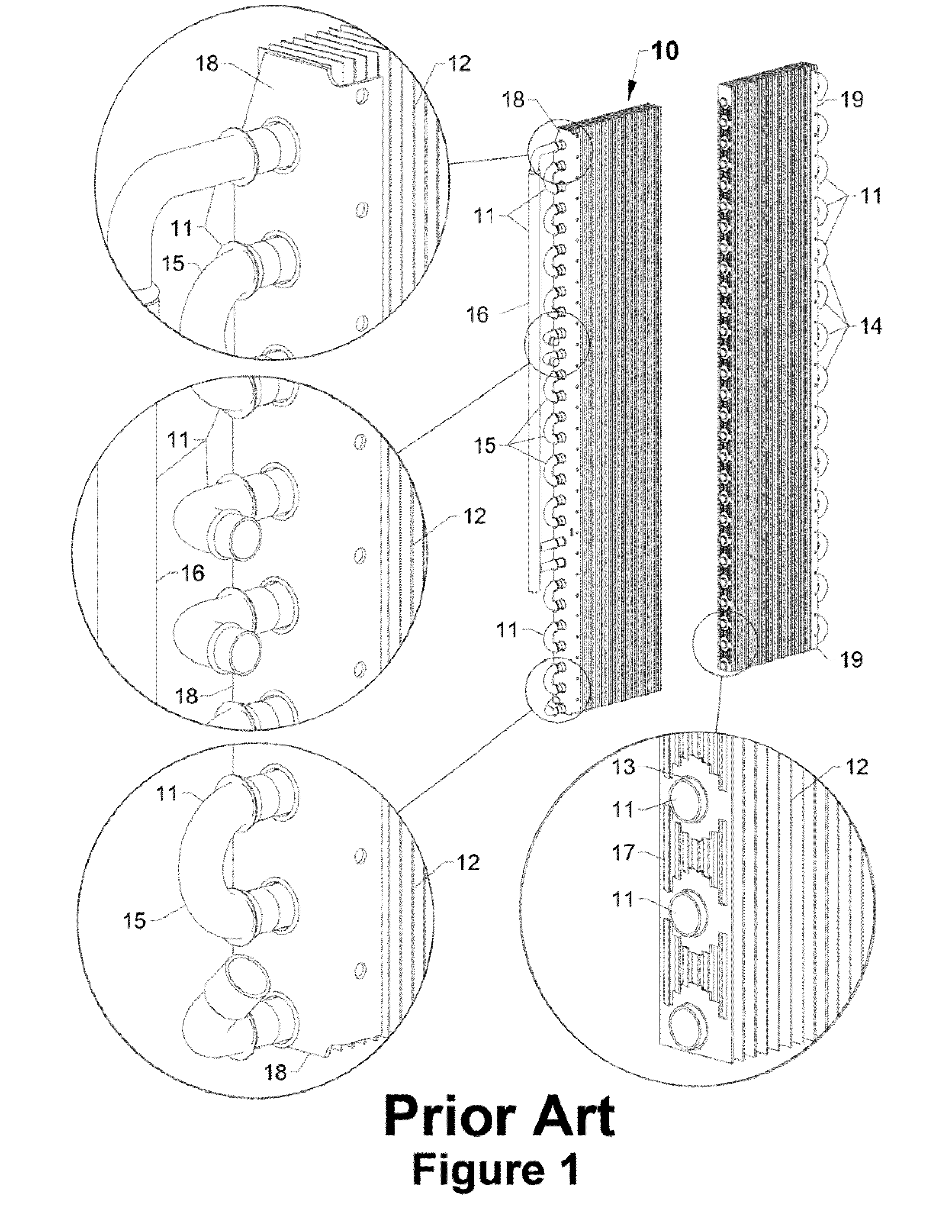
Method for making brazed aluminum heat exchanger and apparatus
InactiveUS20110139417A1Enhance layeringImprove heat transfer performanceSolidificationLiquefactionMetal particleHigh intensity
Disclosed is a heat exchanger comprising a boiling passage and cooling passage defined by opposite sides of metal walls. The heat exchanger is made with high strength alloys of aluminum that have improved creep resistance that maintain tensile strength and yield strength after use in this invention. Layers of brazing material between the metal walls and a spacer member bond components of the heat exchanger together. An enhanced boiling layer (EBL) comprising metal particles bonded to each other and to a boiling side of the metal wall provides nucleate boiling pores to improve heat transfer. The EBL has a melting temperature that is higher than the melting temperature of the brazing material. Also disclosed is a process for assembling the heat exchanger.
Owner:UOP LLC
Method for making brazed heat exchanger and apparatus
InactiveCN1813166AWithout compromising thermal conductivitySolidificationLiquefactionMetal particleMelt temperature
Disclosed is a heat exchanger comprising a boiling passage and cooling passage defined by opposite sides of metal walls. Layers of brazing material between the metal walls and a spacer member bond components of the heat exchanger together. An enhanced boiling layer (EBL) comprising metal particles bonded to each other and to a boiling side of the metal wall provides nucleate boiling pores to improve heat transfer. The EBL has a melting temperature that is higher than the melting temperature of the brazing material. Also disclosed is a process for assembling the heat exchanger.
Owner:UOP LLC
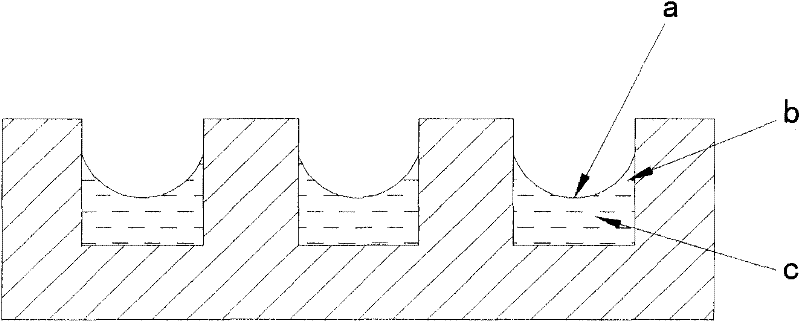
Metal plate for heat exchange and method for manufacturing metal plate for heat exchange
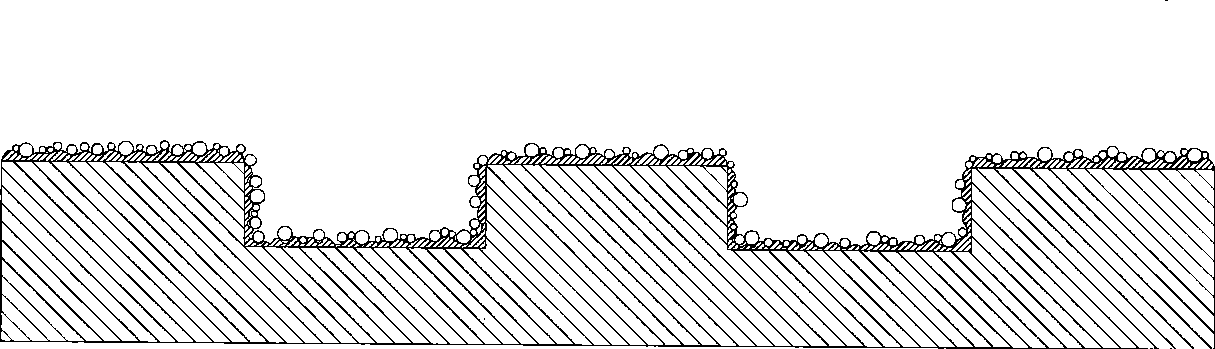
ActiveUS20120077055A1Facilitates nucleate boilingImprove thermal conductivityLayered productsDomestic articlesMaterials scienceMetal
The present invention provides a metal plate for heat exchange which facilitates nucleate boiling and is extremely excellent in heat conductivity. In the metal plate for heat exchange of the present invention, a recess part 2 having a depth of 5 μm or more and 10% or less of a plate thickness of the metal plate is formed. A crevasse part 7 is formed at least at a bottom corner 6 of the recess part 2. The crevasse part 7 is formed by cutting away the bottom corner 6 of the recess part 2 in the thickness direction. An angle θ formed by one cut-away surface and the other cut-away surface is 90 degrees or less. In addition, the crevasse part 7 is formed by cutting away a crystal grain 9. The recess part 2 is formed on the surface of the metal plate 1 by pressing a working part 14 formed on a surface of a working roll 12 against the surface of the metal plate 1 being carried.
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD
Fuel assembly and fuel rod capable of improving reactor security of fuel assembly
ActiveCN105469838AImprove securityReduce heat fluxFuel elementsNuclear energy generationReactor safetyNormal conditions
The invention relates to a fuel assembly and a fuel rod capable of improving reactor security of the fuel assembly. The fuel assembly comprises an integrated fuel rod body containing a nuclear fuel component; an axial perforative through hole is formed in the middle part of the fuel rod body. The through hole of the fuel rod provided by the invention can remarkably add the heat transfer area, reduce heat flux within a unit area of the fuel rod under the condition of constant reactor capability, and lower the probability of generating departure nucleate boiling; meanwhile the temperature of the center area of the fuel rod can be greatly lowered, thus the safety margin of the fuel rod under normal condition and accident condition of the reactor is greatly increased.
Owner:CHINA NUCLEAR POWER TECH RES INST CO LTD +2
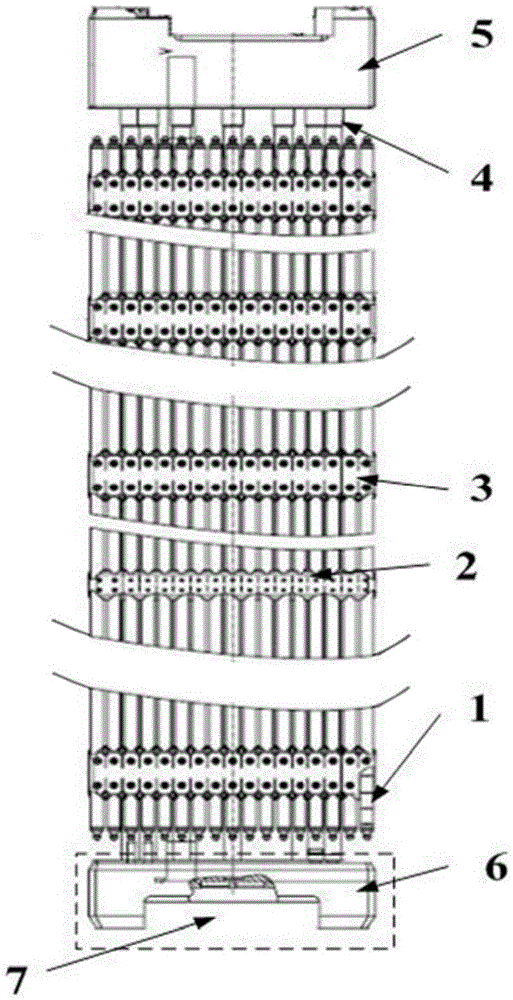
Slot-nanometer flower composite capillary core structure and fabrication method thereof
InactiveCN107660102AIncrease the lengthImprove wettabilityCooling/ventilation/heating modificationsCopper oxideImpurity
The invention discloses a slot-nanometer flower composite capillary core structure and a fabrication method thereof. In a composite-structure capillary core, a slot structure is arranged on a copper-based surface, and a micro nanometer flower-shaped copper oxide layer is grown on a surface of a slot. The preparation of the composite-structure capillary core comprises the steps of performing linearcutting on a copper surface, and fabricating the slot structure on the copper surface; placing the copper surface after linear cutting in acetone and dilute sulphuric acid for ultrasonic washing to remove impurity and an oxide on the copper surface; placing the copper surface in an oxidization agent, and performing reaction at 50-80 DEG C for 30-90 minutes; and fully cleaning the copper surface with deionized water, and performing reaction at 150-200 DEG C for 18-36 hours to generate uniform and micro nanometer flower-shaped copper oxide. With the slot-nanometer flower composite-structure capillary core fabricated by the method, the backflowing capillary force of a working medium can be effectively improved, the wetting area is expanded, relatively many nucleate boiling activate holes areprovided, and nucleate boiling heat exchange is improved; and when the slot-nanometer flower composite-structure capillary core is applied to a flat heat pipe, the flowing and heat exchange characteristic of the working medium can be substantially improved, and the performance of the flat heat pipe is improved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Micro-nano structure array heat dissipation surface and preparation method thereof
PendingCN108346633AEnhanced ability to rewet dry surfacesPromote wettingMaterial nanotechnologySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsMicro nanoHeat conducting
The invention discloses a micro-nano structure array heat dissipation surface and a preparation method thereof. The heat dissipation surface comprises a heat dissipation substrate and an array structure which is constructed on the surface of the heat dissipation substrate and formed by cones composed of a fluorine-containing polymer and heat conducting particles. The heat dissipation surface can greatly increase the effective heat exchange area, the surface roughness and the heat conducting coefficient, facilitates the transfer of heat to a fluorine-containing working medium, facilitates nucleate boiling of the fluorine-containing working medium, can strengthens a wetting ability of the fluorine-containing working medium for the heat dissipation surface, improves the critical heat flux density and plays a role of strengthening phase change heat transfer. The preparation method comprises the steps of uniformly stirring and mixing a fluorine-containing polymer emulsion, the heat conducting particles, a solvent, an auxiliary and the like to obtain slurry, printing the slurry on the surface of the heat dissipation substrate through a silk-screen printing process, drying to remove the solvent, then performing thermal treatment in the protective atmosphere, enabling the fluorine-containing polymer resin to be solidified on the surface of the heat dissipation substrate, and obtaininga heat dissipation surface with a micro-nano structure array. The preparation steps are easy and easy to implement, and scale production is easy to be realized.
Owner:CHINA EPRI ELECTRIC POWER ENG CO LTD +1
Cooling arrangement and method with selected surfaces configured to inhibit changes in boiling state
InactiveUS7028763B2High heat fluxLiquid coolingCoolant flow controlInternal combustion engineNucleation
Heat transfer in coolant circuits, as in an internal combustion engine for example, can be beneficially enhanced by maintaining the coolant in a nucleate boiling state, but undesirable transitions to a film boiling state are then possible. The disclosed coolant circuit has selected surface(s) that have a tendency to experience high heat flux in comparison to adjacent surfaces in the coolant circuit. These surfaces are provided with a surface configuration, such as a matrix of nucleation cavities, which has a tendency to inhibit a change in boiling state. The surface configuration can be provided on the parent coolant circuit surface or on a surface of an insert positioned in the coolant circuit. Thus, transitions to film boiling can be effectively avoided at locations in the coolant circuit that are susceptible to such transitions.
Owner:PERKINS ENGINES
Nucleate boiling cooling system
A cooling system for a liquid cooled internal combustion engine having coolant passages and a heat exchanger selected to operate the engine cooling system in the region of nucleate boiling. A sensor detects the presence of nucleate boiling and a variable volume chamber has a flexible diaphragm urged on one side by controlled air pressure and responsive to the sensor maintain the coolant system pressure at a level maintaining optimum nucleate boiling to increase heat flux from the engine and reduce overall size of the system.
Owner:DEERE & CO
Monitoring and alarming device for departure from nucleate boiling ratio (DNBR) of reactor core of pressurized water reactor
InactiveCN103065433AAccurate DNB early warningTimely DNB early warningNuclear energy generationNuclear monitoringFault tolerancePressurized water reactor
The invention discloses a monitoring and alarming device for a departure from nucleate boiling ratio (DNBR) of a reactor core of a pressurized water reactor. Relevant factors which are detected by a detector is conducted through data preprocessing and a DNBR data base is obtained, and meanwhile, a DNBR nonlinear computational model which is trained by a cloud adaptive support vector machine is adopted to calculate a DNBR value, an output module displays the DNBR value, a differentiating signal is transmitted to a DNBR alarming controller to trigger alarming through a signal transmission device in a manual or intelligent mode, a DNBR alarming signal is fed back to the data base, a disaster signal which needs to be alarmed is transmitted to an alarming system, and relevant people conduct urgent elimination measurements on DNBR occurrence conditions inside the reactor core of the pressurized water reactor. The monitoring and alarming device for the DNBR has self-learning ability, continuously improves a DNBR computational model, and utilizing a central processing unit system to conduct real-time processing. The monitoring and alarming device for the DNBR is rapid in reaction speed, high in fault tolerance, capable of monitoring and forecasting changes of the DNBR inside the reactor core of the pressurized water reactor accurately and rapidly.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Online monitoring method for scaling thickness on surface of electric heating element of electric boiler
ActiveCN108507521AAccurate online monitoringAccurate monitoringMeasurement devicesElectricityHeat flow
The invention relates to an online monitoring method for the scaling thickness on the surface of an electric heating element of an electric boiler, which is characterized by comprising the steps of data acquisition of the electric boiler, calculation for the non-scaling surface temperature of the heating element of the electric boiler, calculation for the average scaling thickness of the electricheating element of the electric boiler, determination for the scaling thickness of different parts of the electric heating element of the electric boiler and the like. The heat flux density on the surface of the electric heating element immersed in the water during the operation of the electric boiler is determined according to the measured water level of the electric boiler and the actual heat exchange capacity of a working medium together, thus the temperature of the non-scaling surface of the electric heating element of the electric boiler is calculated according to a dimensionless correlation formula, which is organized by Rohsenow, of saturated nucleate boiling, then the average scaling thickness of the heating element of the electric boiler is obtained, and the scaling thickness of different parts of the electric heating element of the electric boiler is obtained according to a correction coefficient for the scaling thickness of different parts of the electric heating element, thereby achieving online accurate monitoring for the scaling thickness on the surface of the electric heating element of the electric boiler, and solving a problem that accurate online monitoring cannotbe performed on the scaling thickness of the electric heating element of the electric boiler.
Owner:JILIN ELECTRIC POWER RES INST LTD +2
Variable spray injector with nucleate boiling heat exchanger
InactiveUS9074566B2Maximizes timeConduction maximizedLiquid surface applicatorsSpray nozzlesNuclear engineeringInduction heater
A heat exchanger, internal to an injector for a variable spray fuel injection system, uses nucleate boiling to maximize the heat flux from the heated metal to the fuel, wherein the nucleate boiling occurs along a control surface characterized by features conducive to generating detaching bubbles to transfer heat energy in a vapor flux. The source of heat flux may be an induction heater coil magnetically coupled to an appropriate loss component so that fuel inside a fuel component is heated to a desired temperature.
Owner:VITESCO TECH USA LLC
Process and apparatus for boiling and vaporizing multi-component fluids
A new boiler or heat transfer apparatus is disclosed for use with multi-component working fluids which includes a vapor removal apparatus designed to maintain a substantial compositional identity between the boiling liquid and its vapor along a length of the apparatus resulting in the maintenance of substantially nucleate boiling along the entire length of the apparatus. Systems incorporating the apparatus and methods for making and using the apparatus are also disclosed.
Owner:KALINA POWER LTD
Tunable nucleate boiling using electric fields and ionic surfactants
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Fuel pellet and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN106448749AReduce the temperatureReduce loadFuel elementsNuclear energy generationSolid structureEngineering
The invention discloses a fuel pellet and a preparation method thereof. The fuel pellet comprises a first fissible part and a second fissible part filling the inner side of the first fissible part, wherein raw materials of the second fissible part comprise a fissible material and additives, and a high-thermal-conductivity area is formed by the second fissible part. Under the condition that life cycle of nuclear fuel is not influenced obviously, the high-thermal-conductivity area is formed by the second fissible part by the aid of the additives, and the center temperature of the pellet can be reduced under the condition of the same heating power; the loading quantity of the fissible material in the pellet area can be properly reduced in the presence of the additives, then the fission density is reduced, the center temperature of the pellet can be reduced finally, and the thermal margin of a reactor is increased. The second fissible part is arranged in the first fissible part, so that the whole fuel pellet is enabled to be in a solid structure, the strength of the fuel pellet is higher than that of a fuel pellet with a hollow structure, and the pellet is prevented from cracking after bearing high stress; an inner passage with smaller MDNBR (minimum departure from nucleate boiling ratio) does not exist, and DNB is avoided more easily.
Owner:CHINA NUCLEAR POWER TECH RES INST CO LTD +3
Passive dual-phase cooling for fuel cell assemblies
A cooling apparatus for a fuel cell assembly includes a heat transfer fluid and at least one fluid flow field plate configured to facilitate essentially passive, two-phase cooling for an membrane electrode assembly (MEA) as the MEA is subject to changes in heat flux to the heat transfer fluid from about 0 W / cm<2> to about 1.5 W / cm<2>. The flow field plate includes fluid flow channels that have a channel depth, a channel spacing, a channel length, and a channel width, which are dimensioned to promote nucleated boiling of the heat transfer fluid below a critical heat flux and to prevent dryout as the heat transfer fluid passes along the length of the channels. The channels may include coatings and / or features, such as microporous or nanostructured coatings, that extend the critical heat flux and preclude dryout at the distal sections of the fluid flow channels.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com