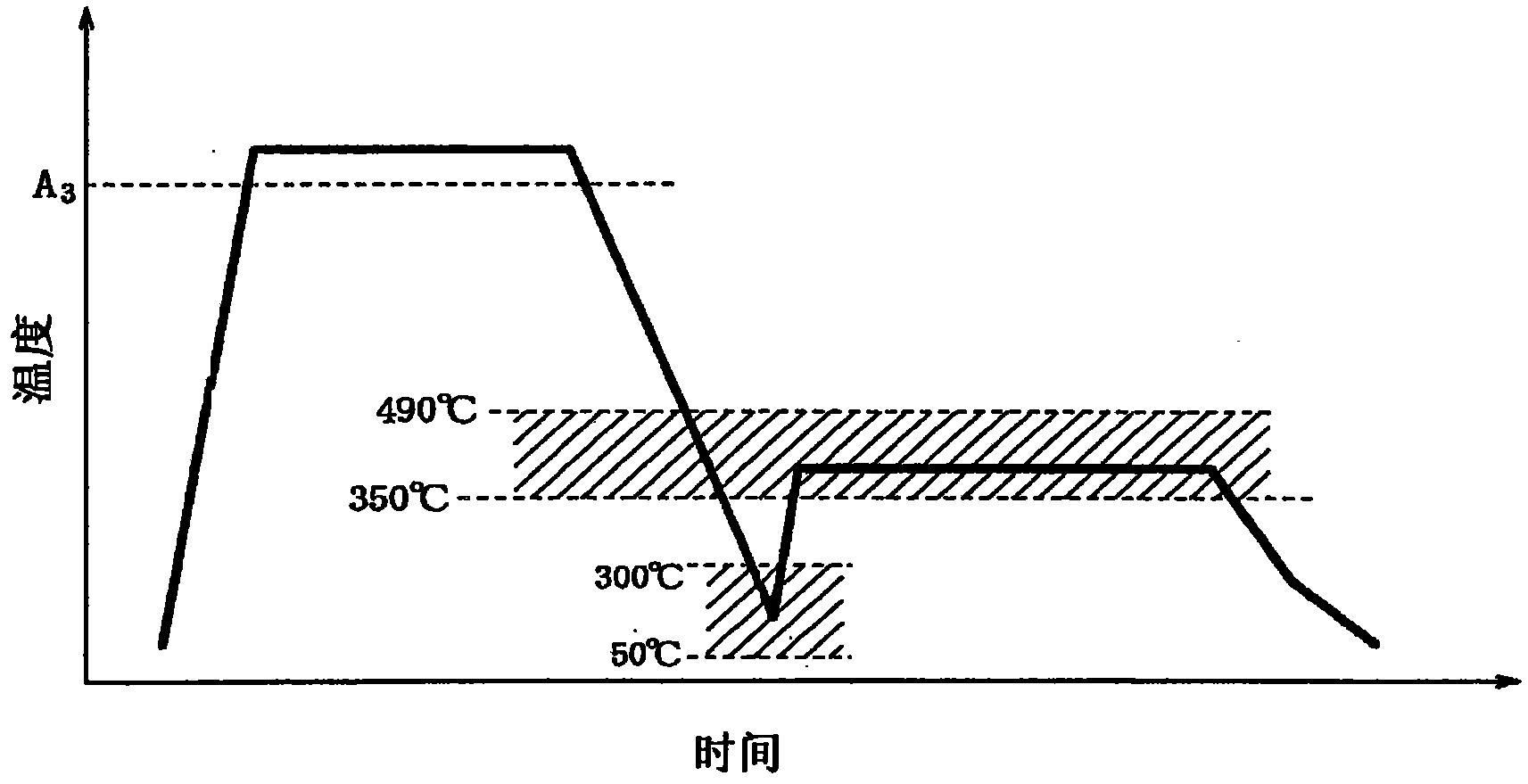
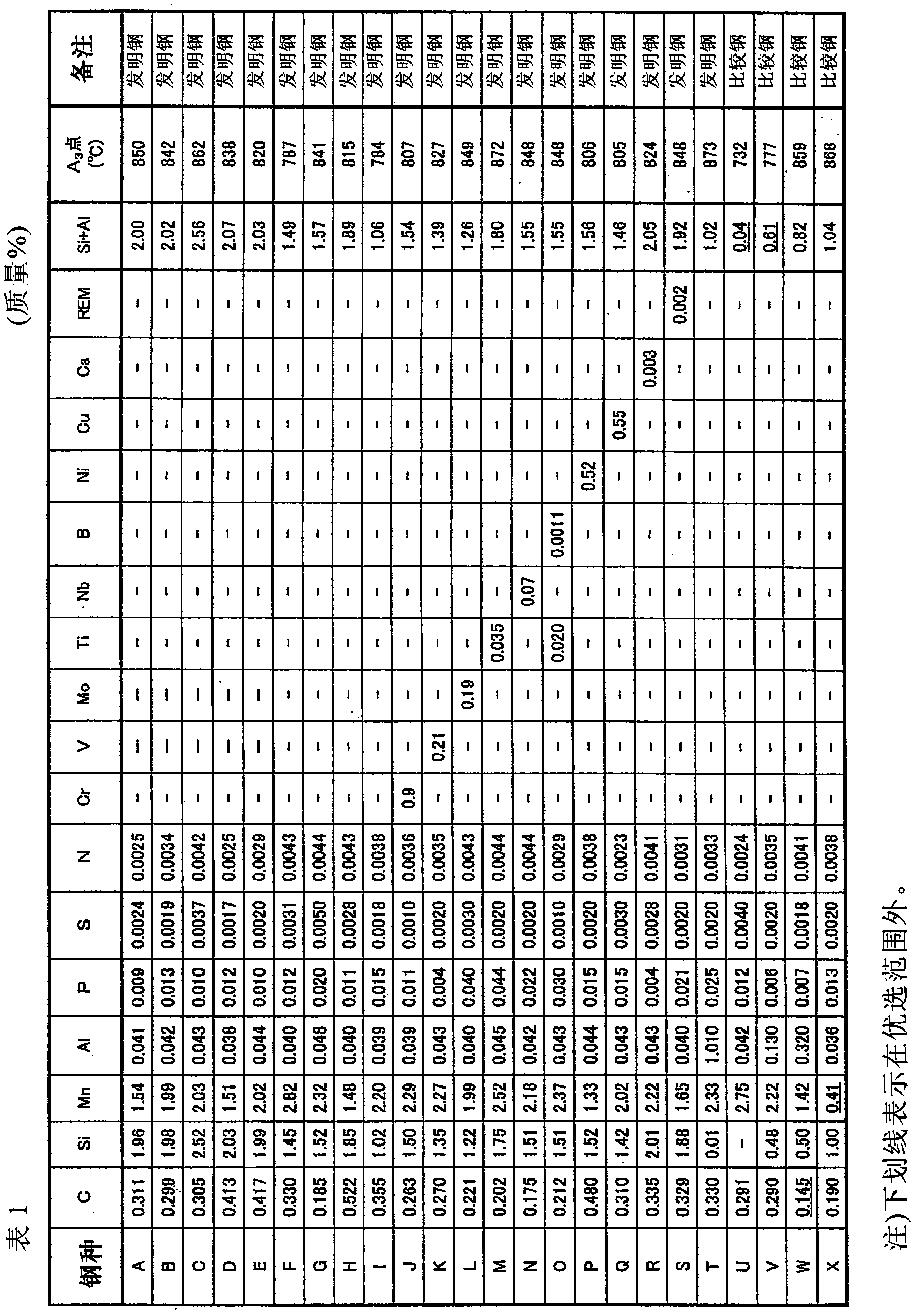
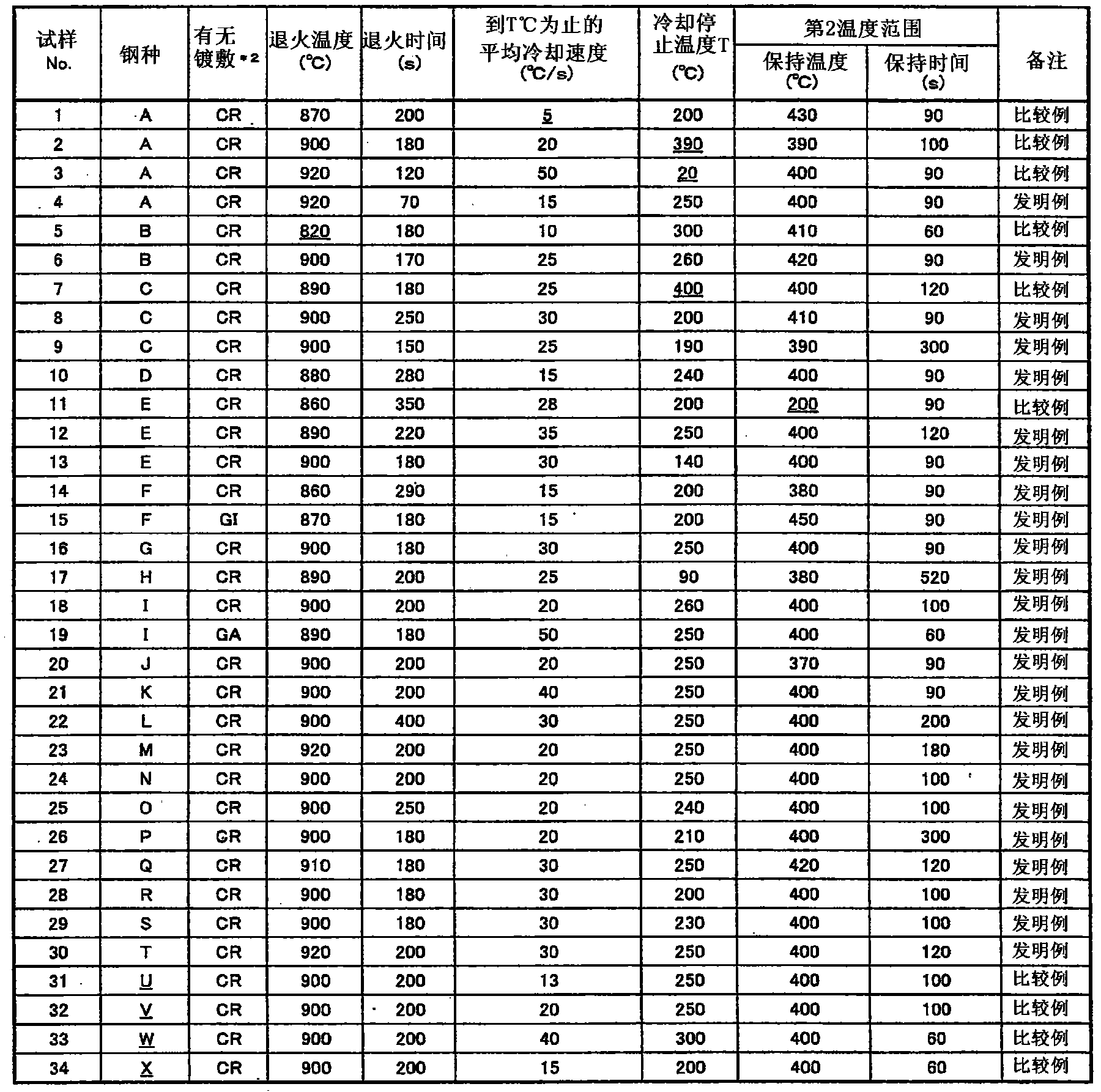
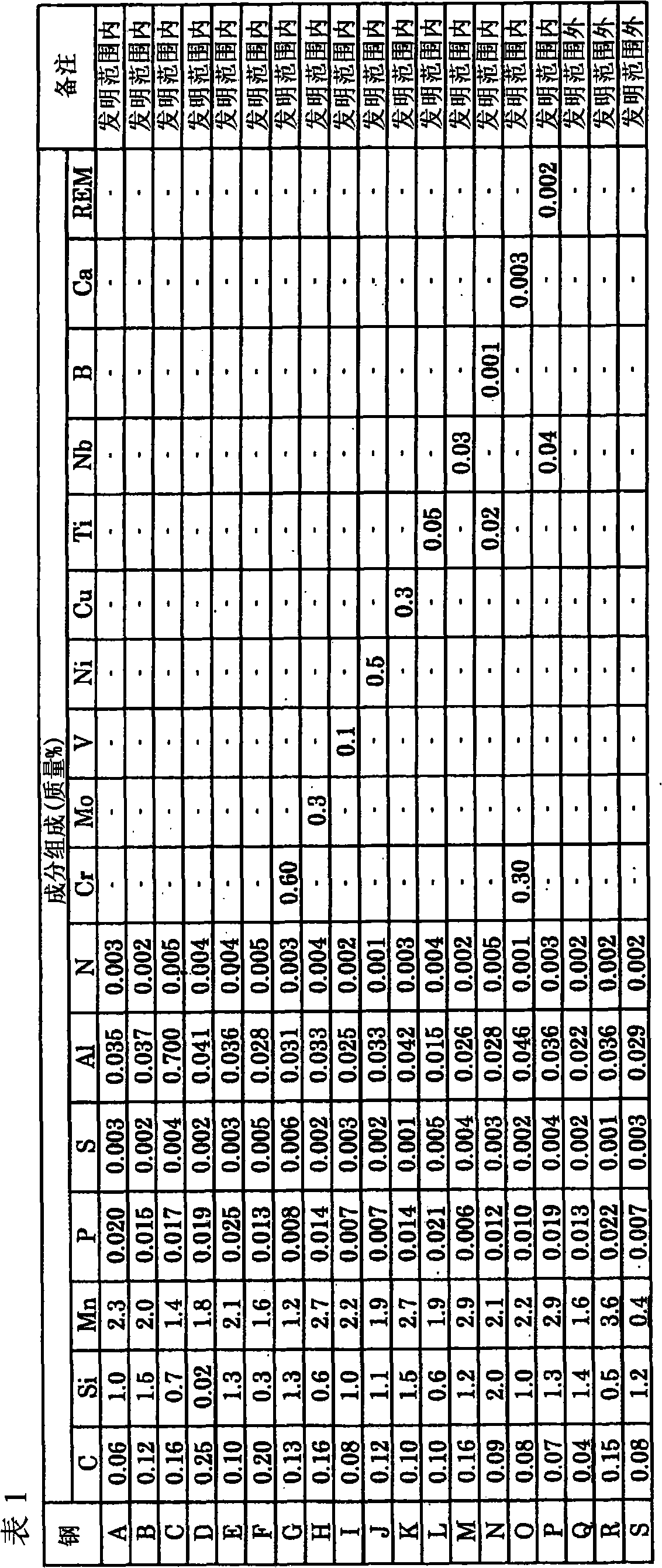
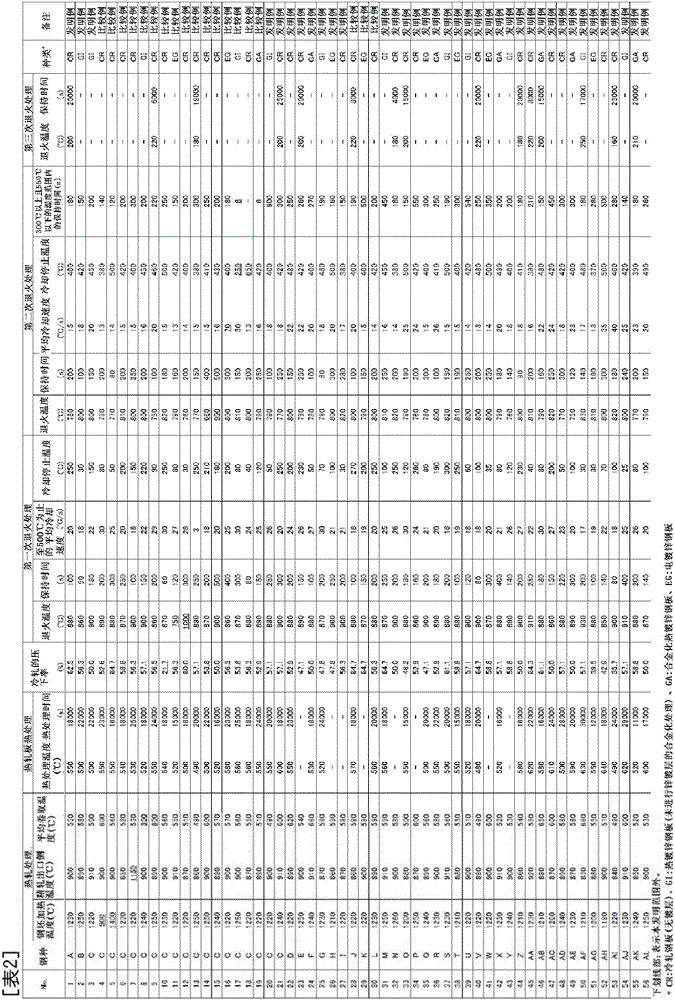
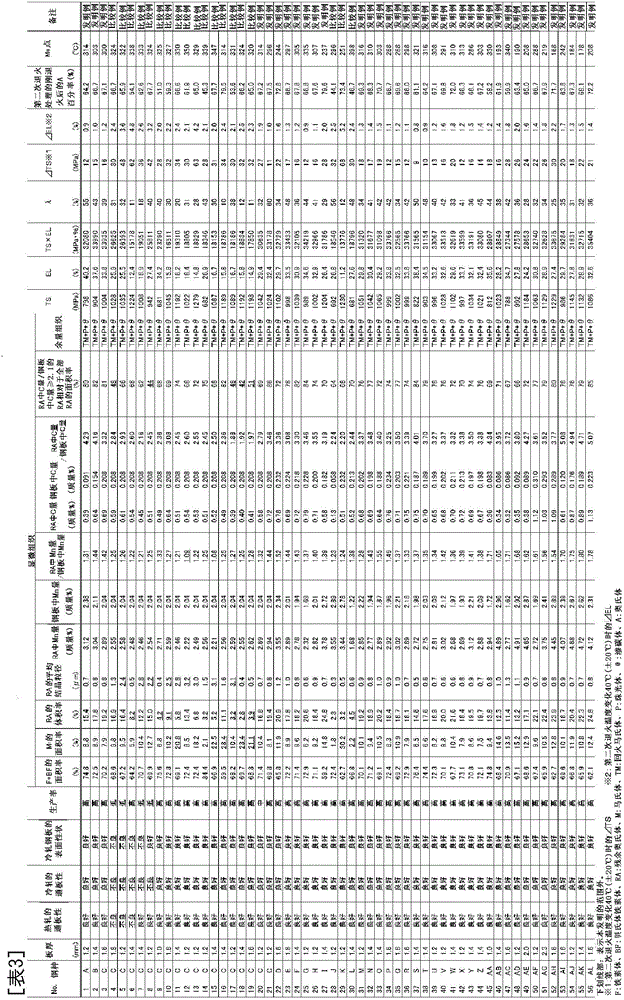
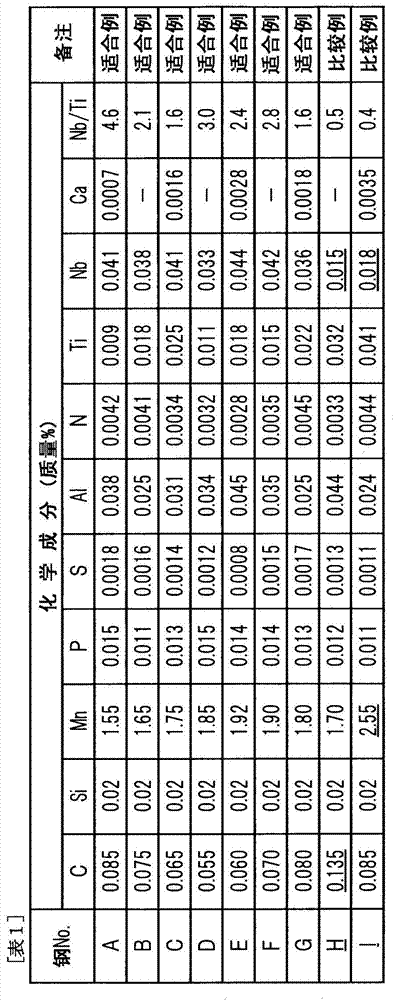
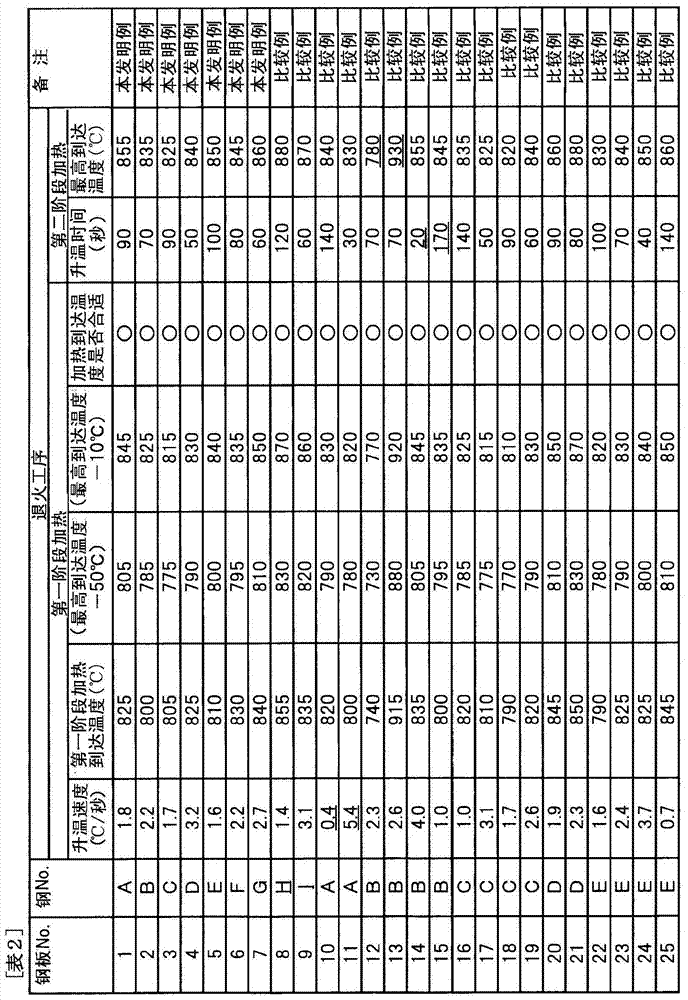
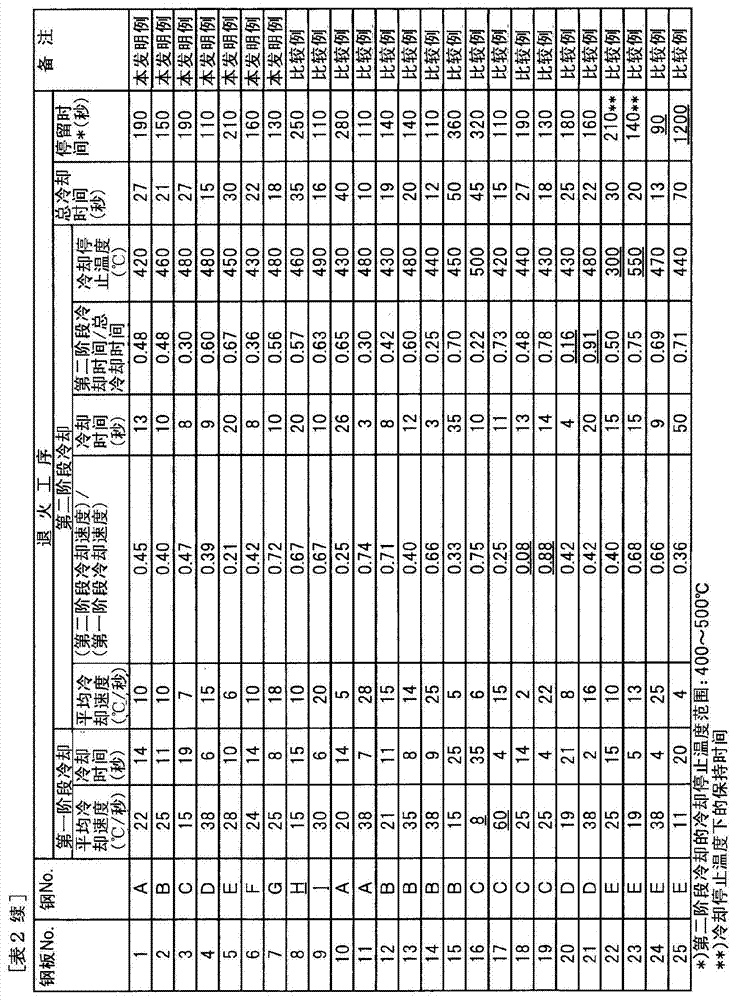
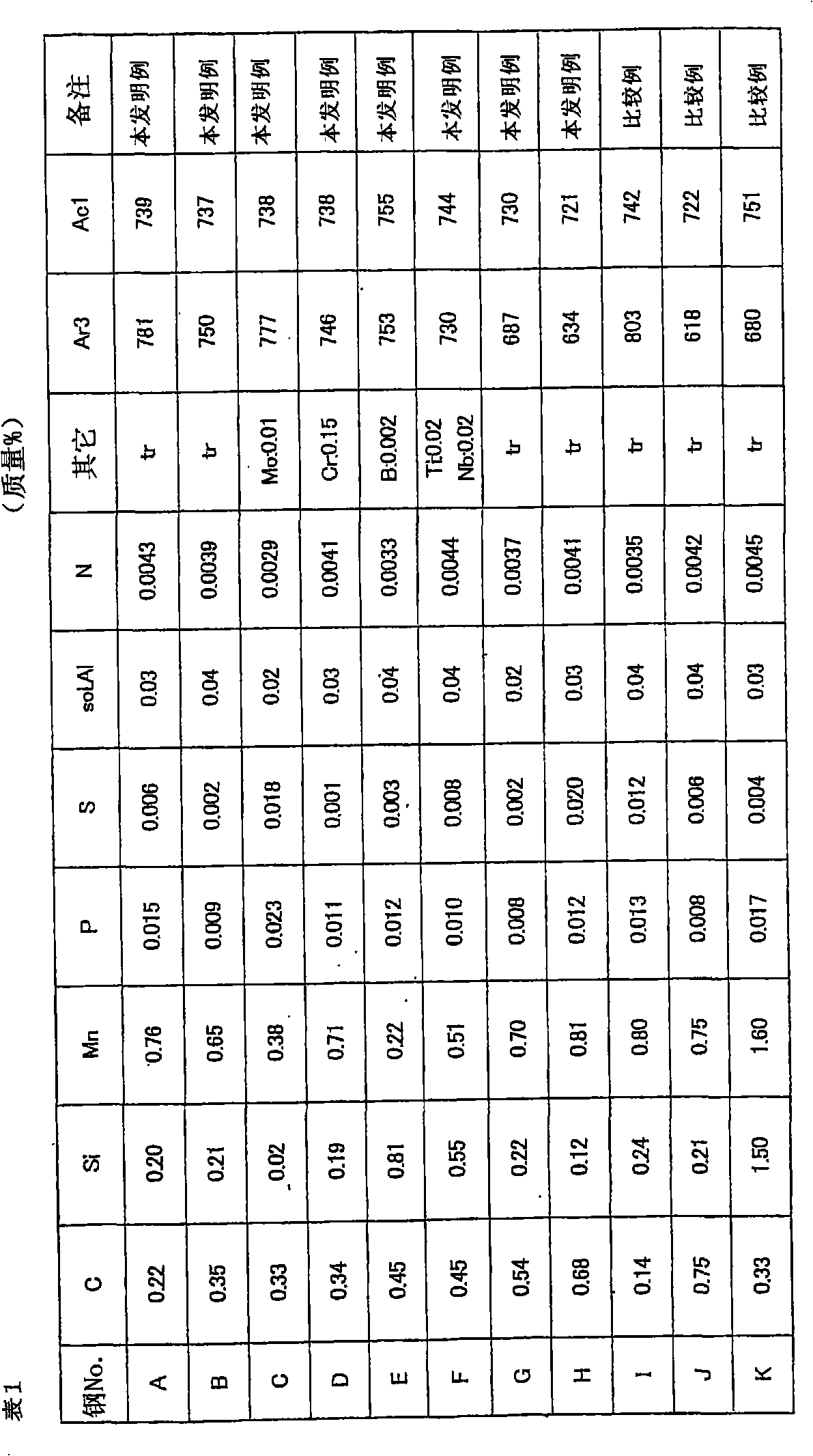
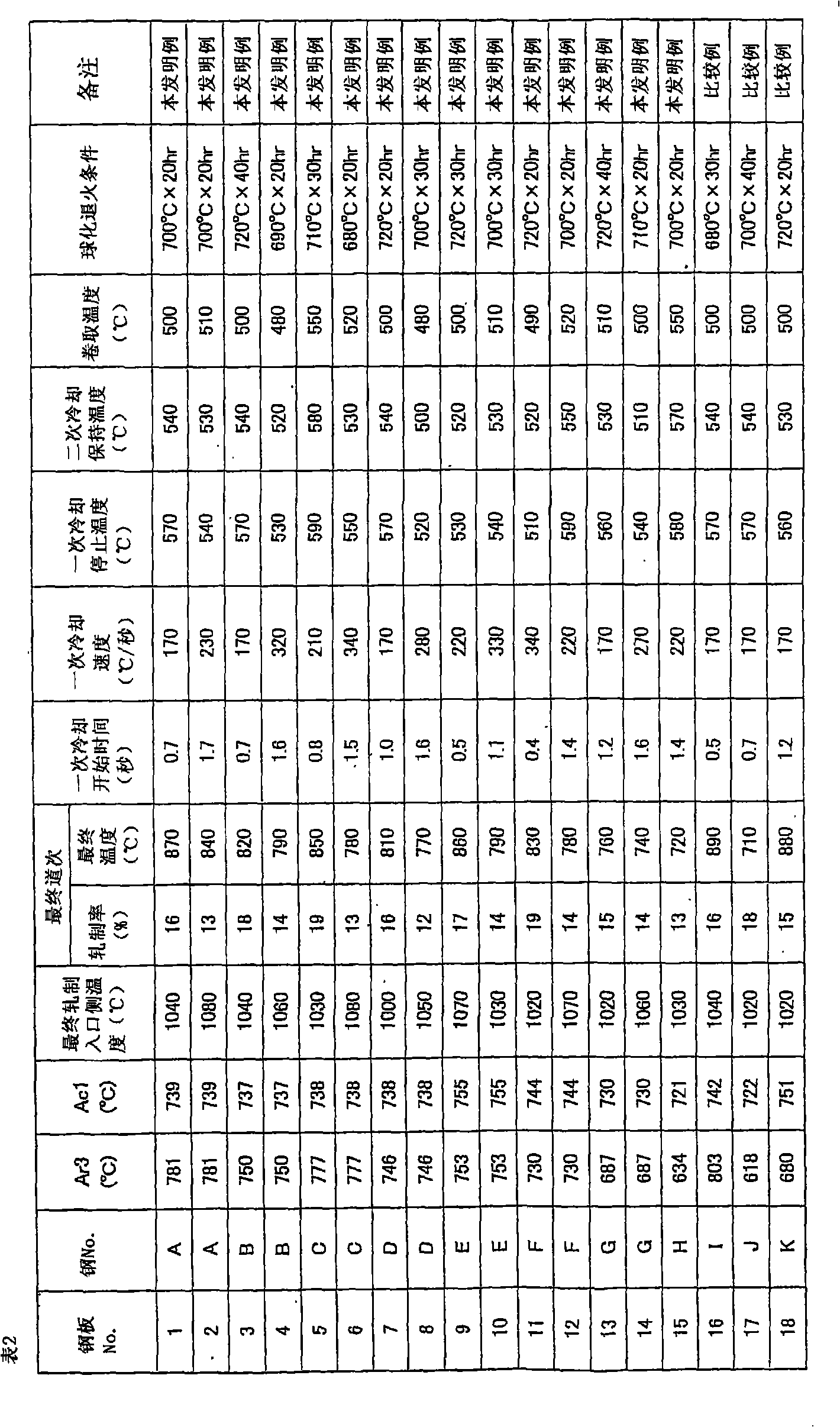
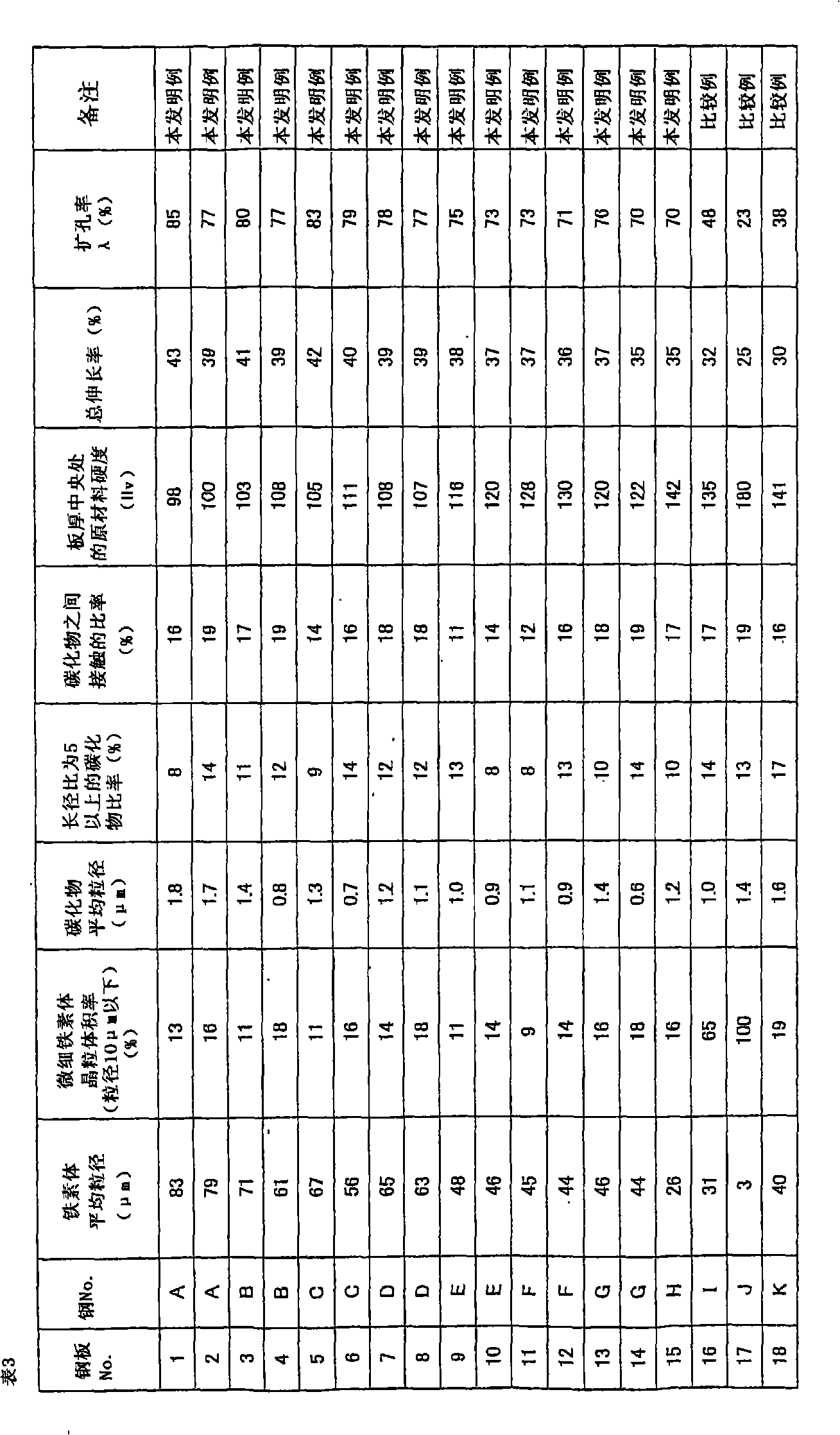
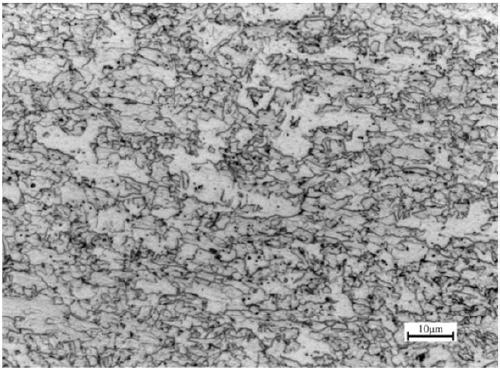
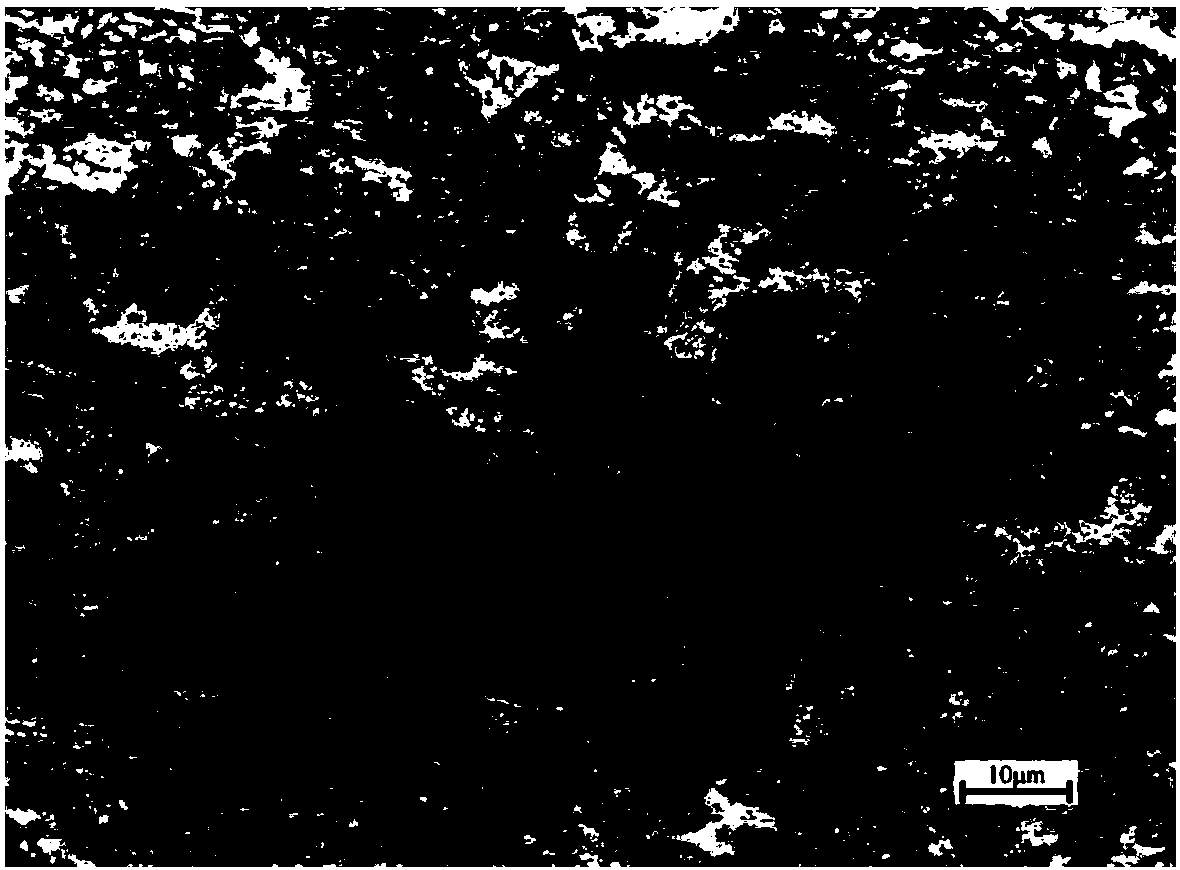
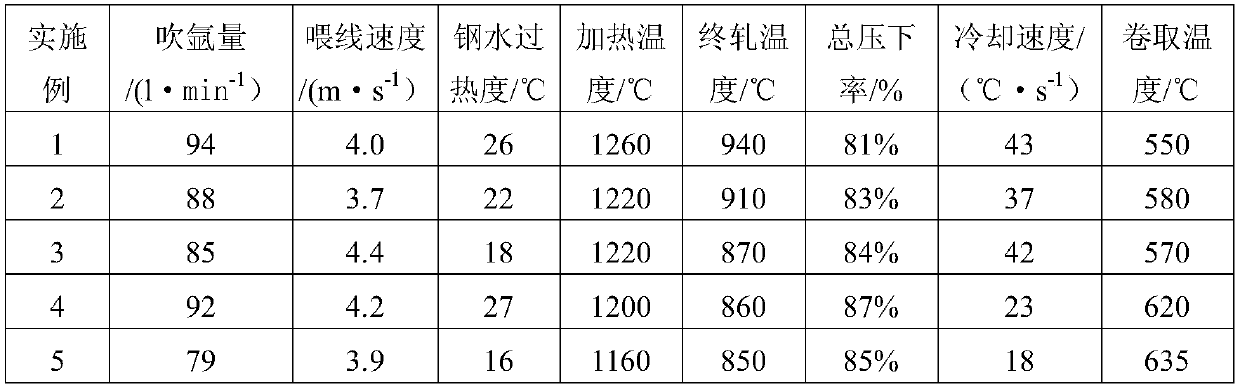
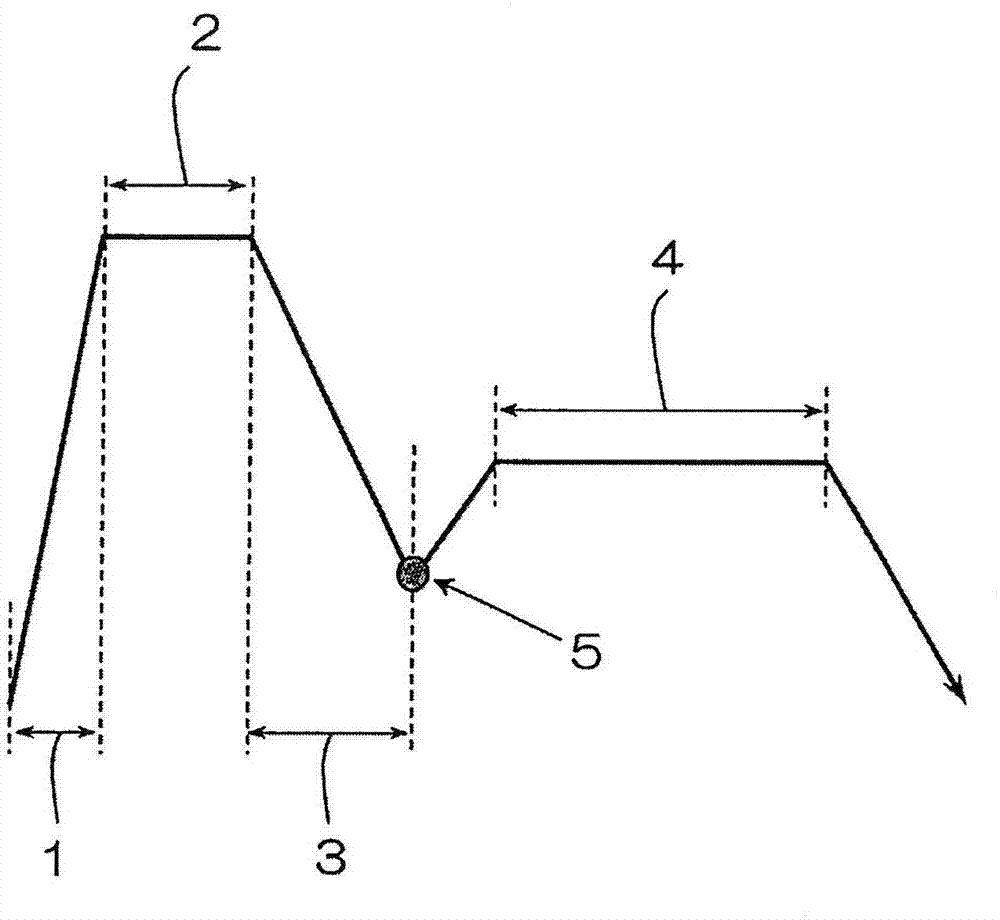
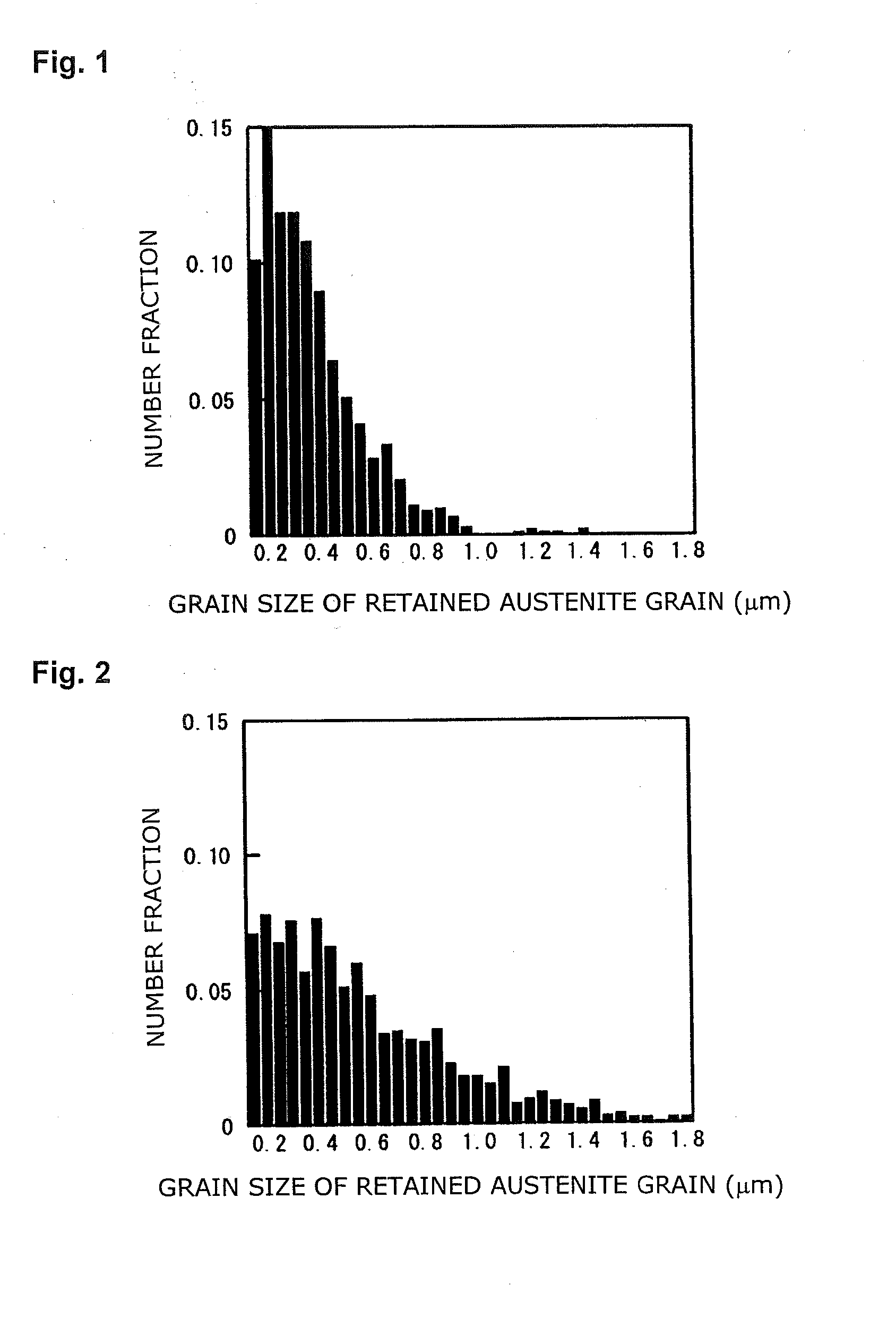
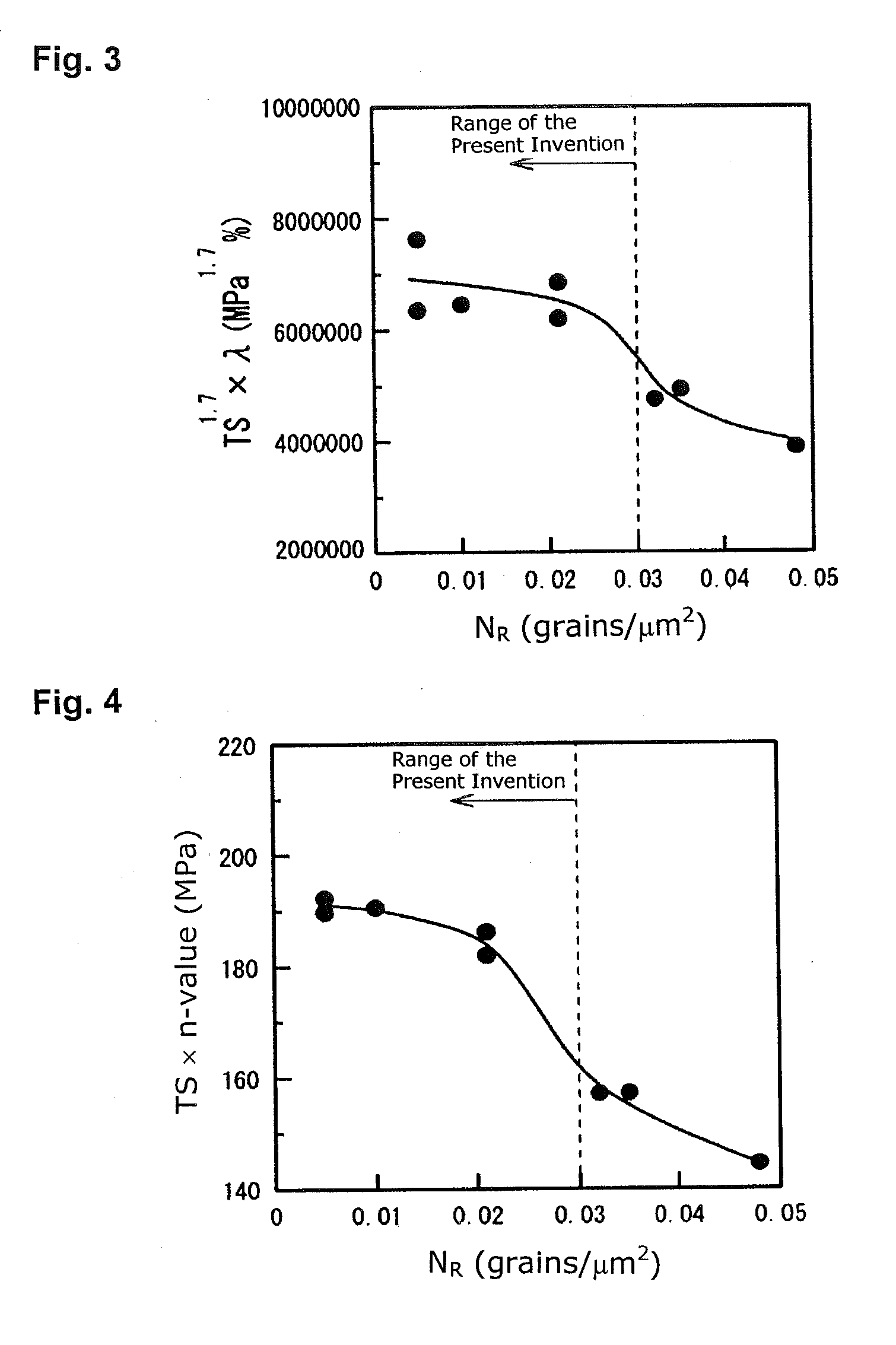
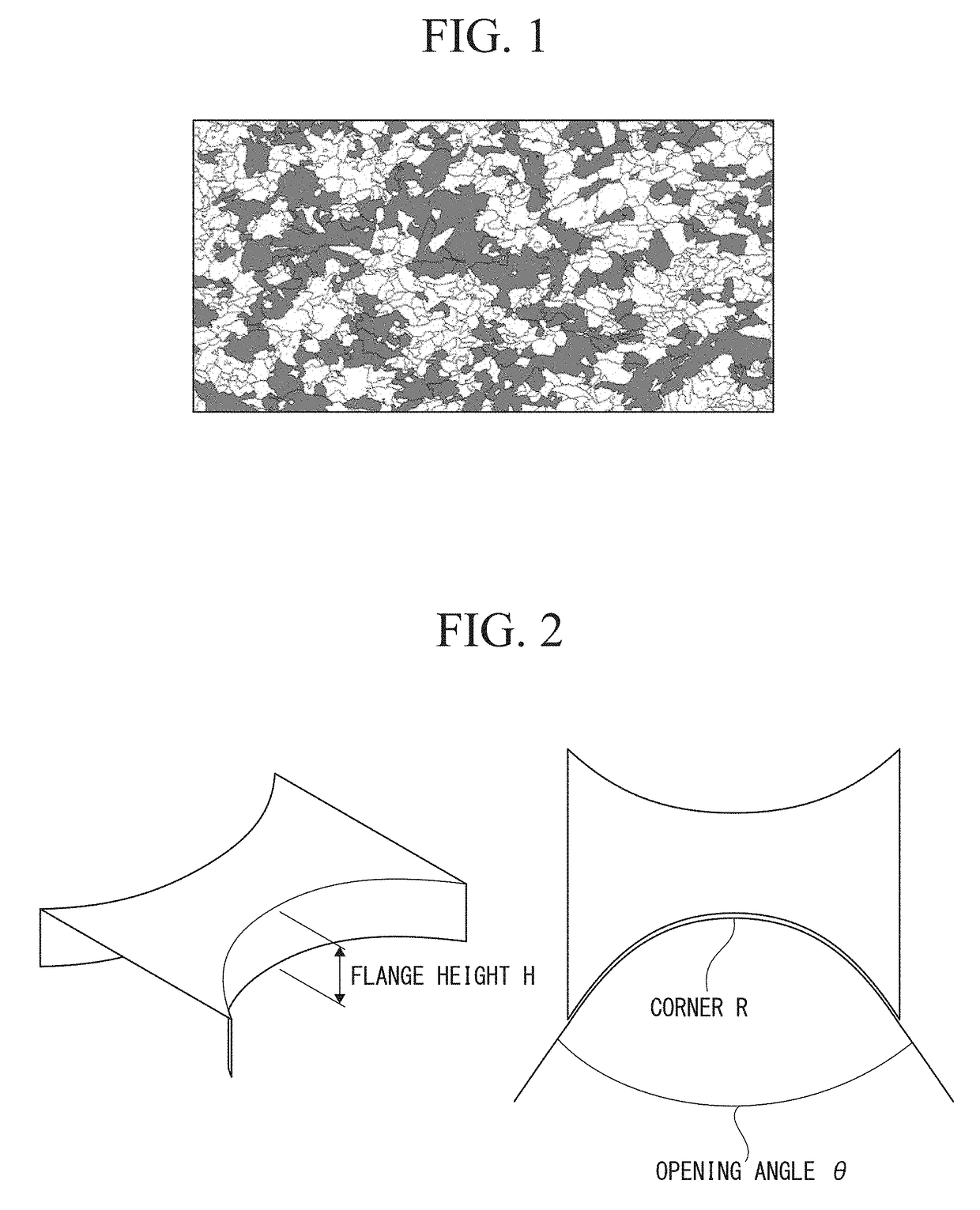
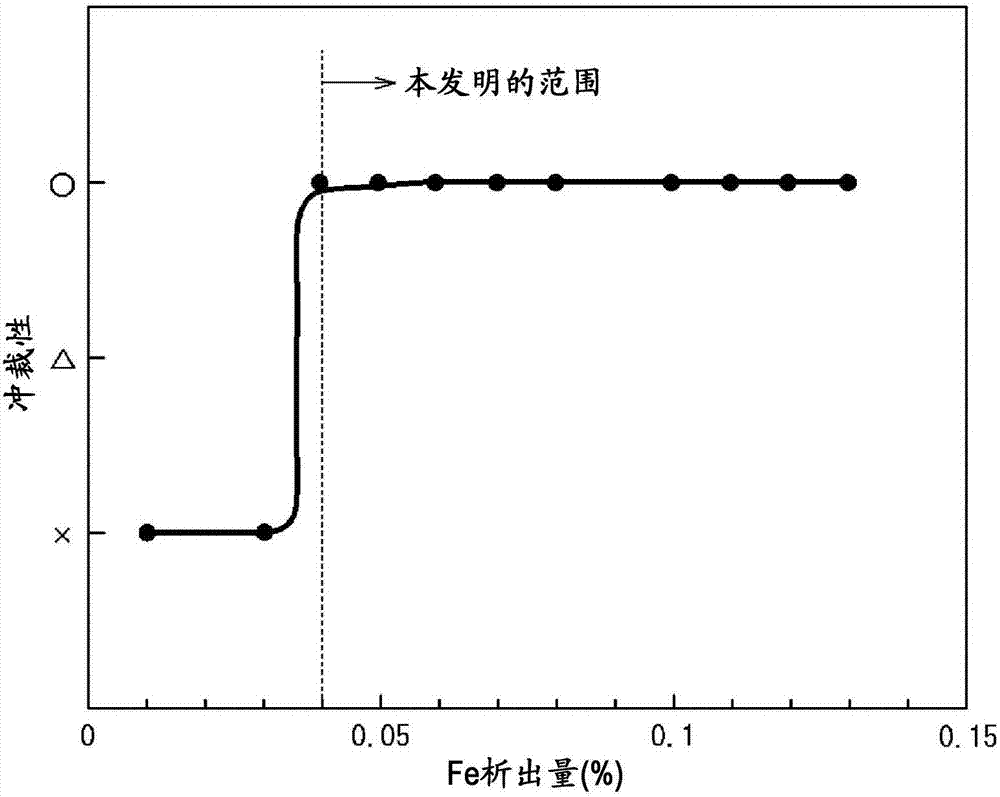
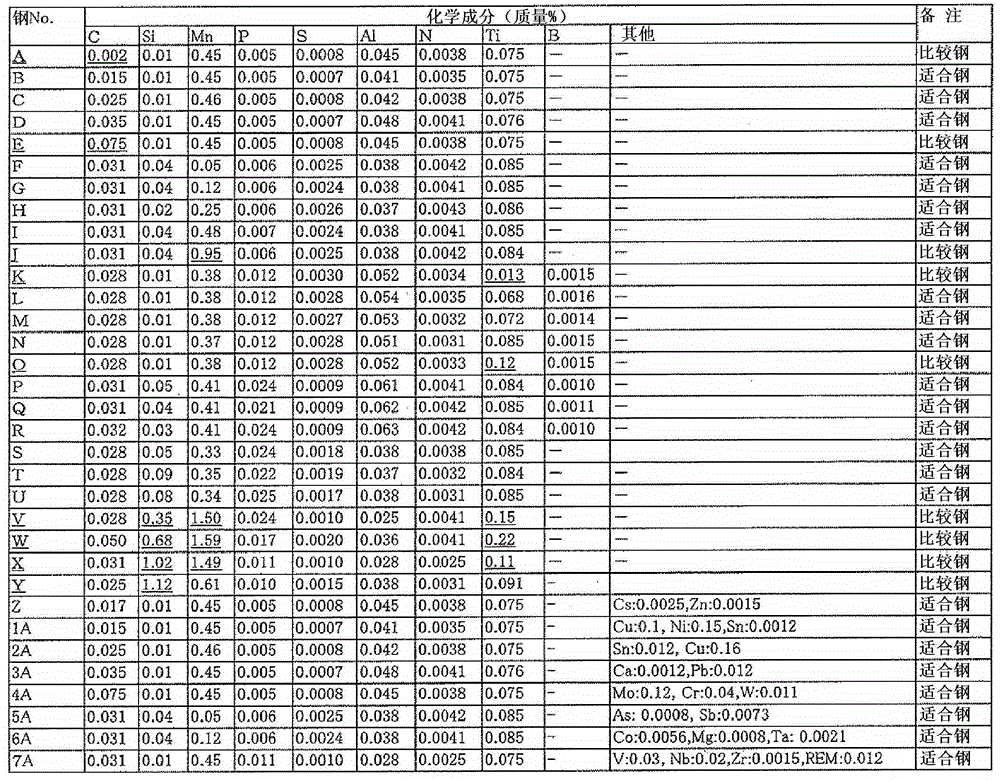
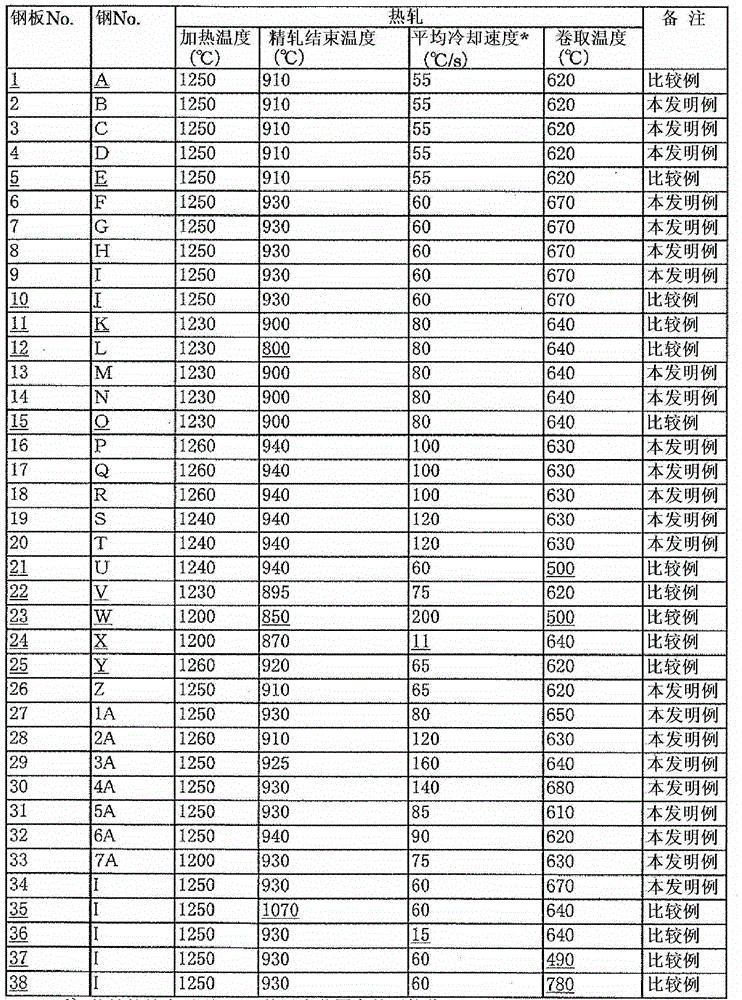
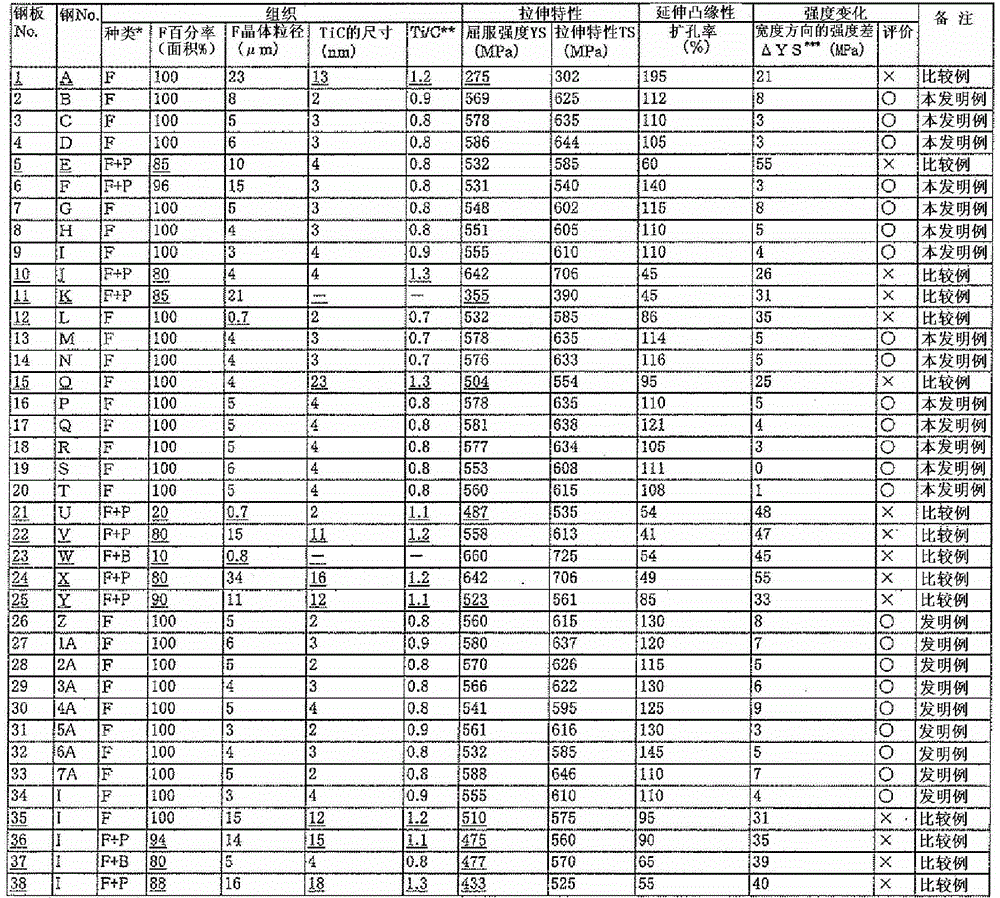
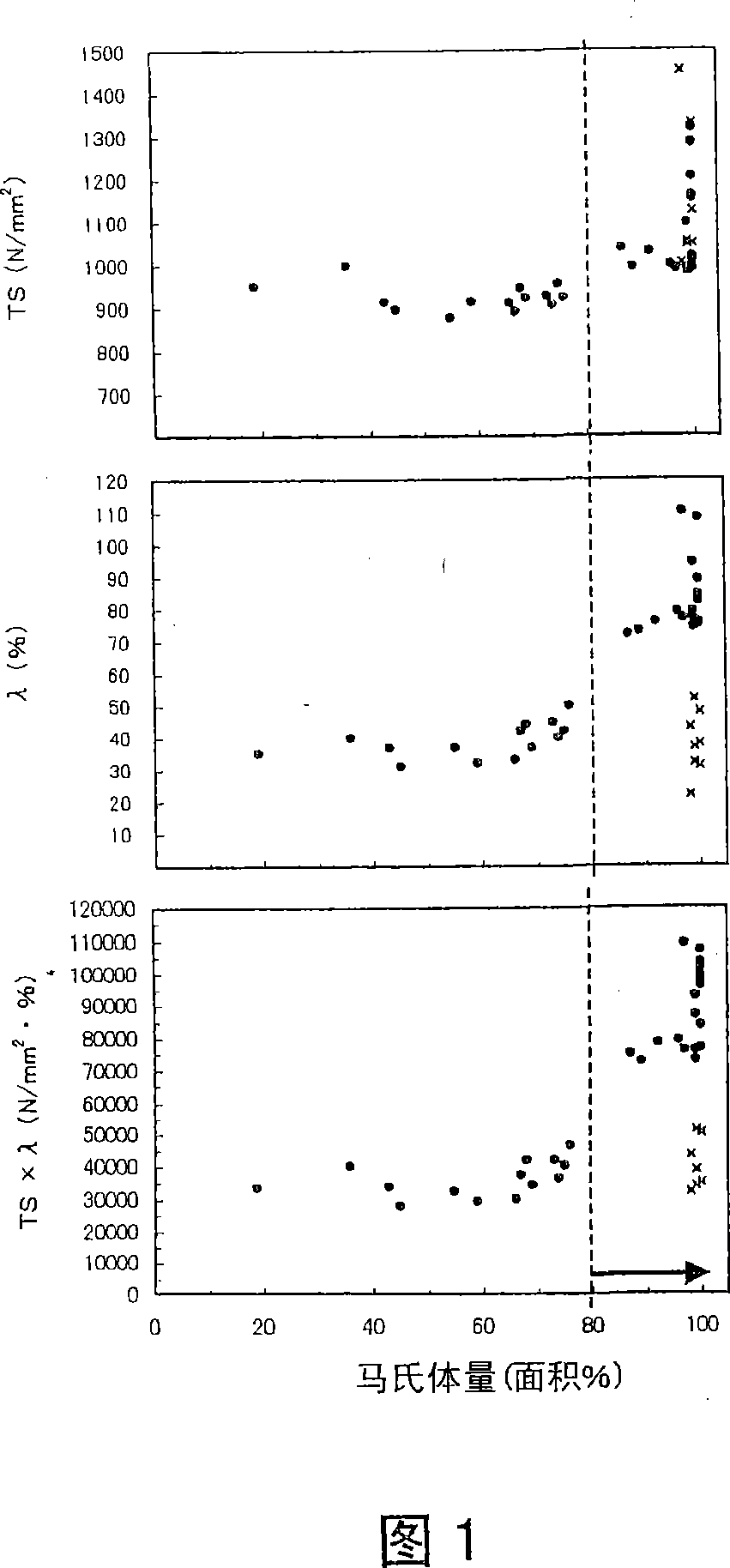
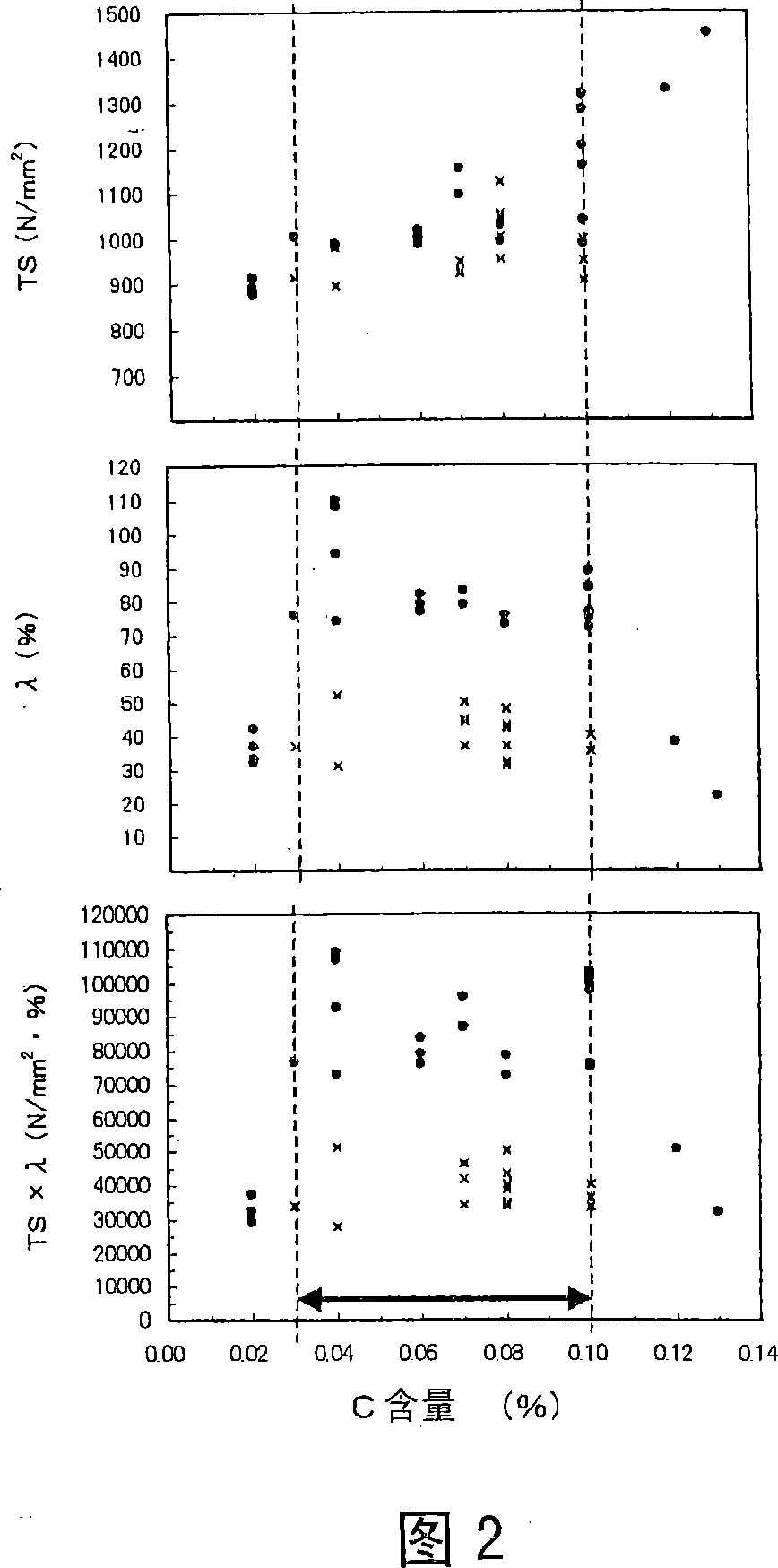
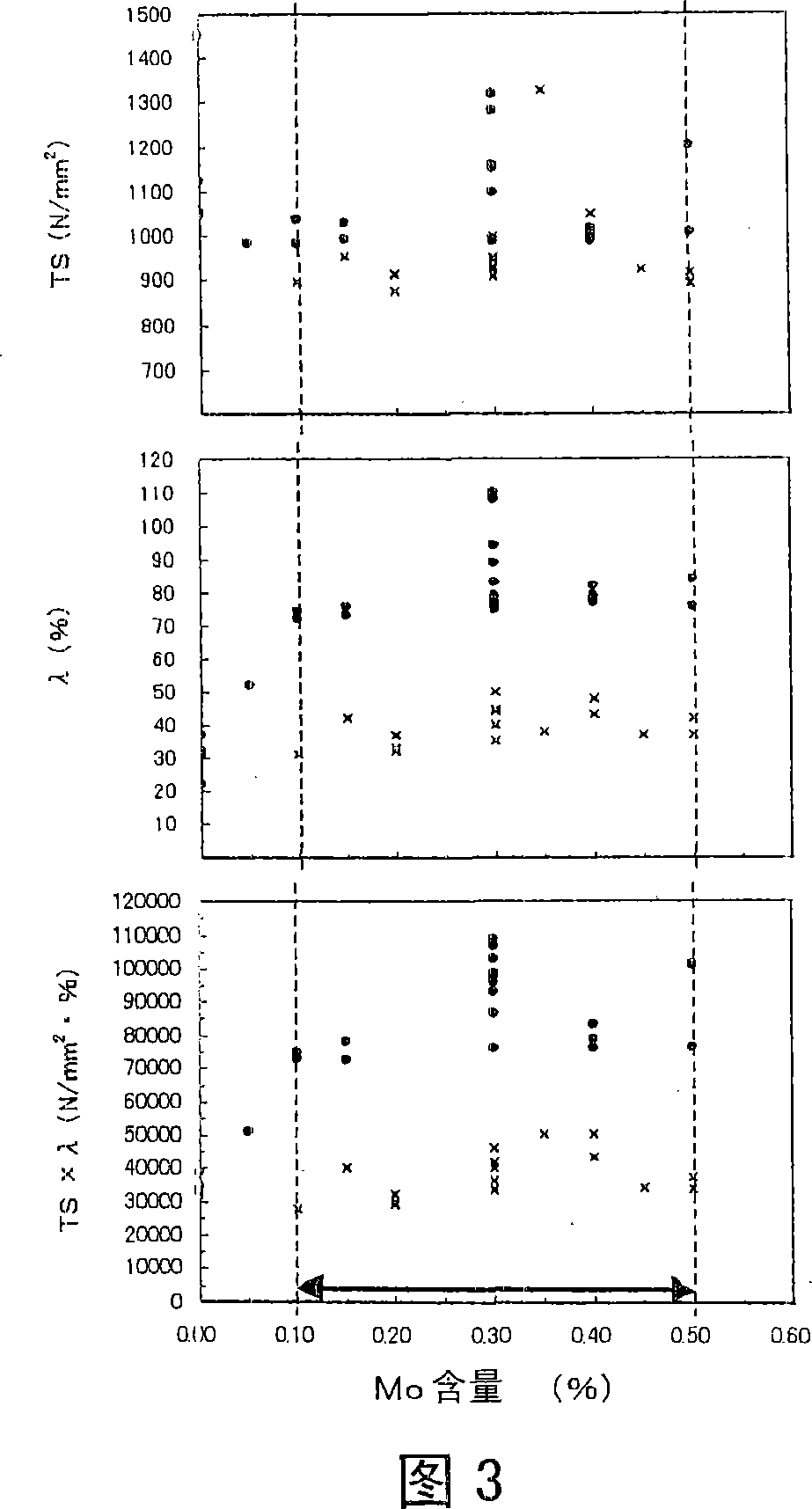
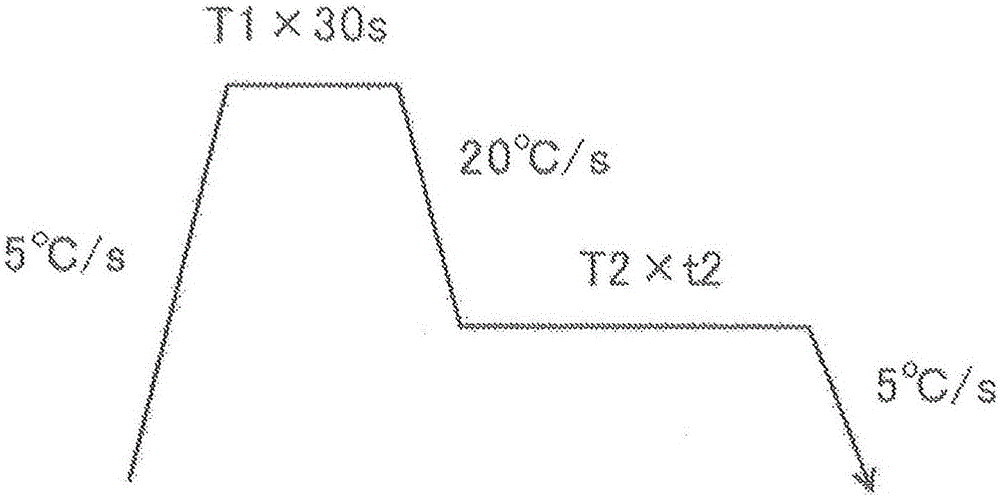
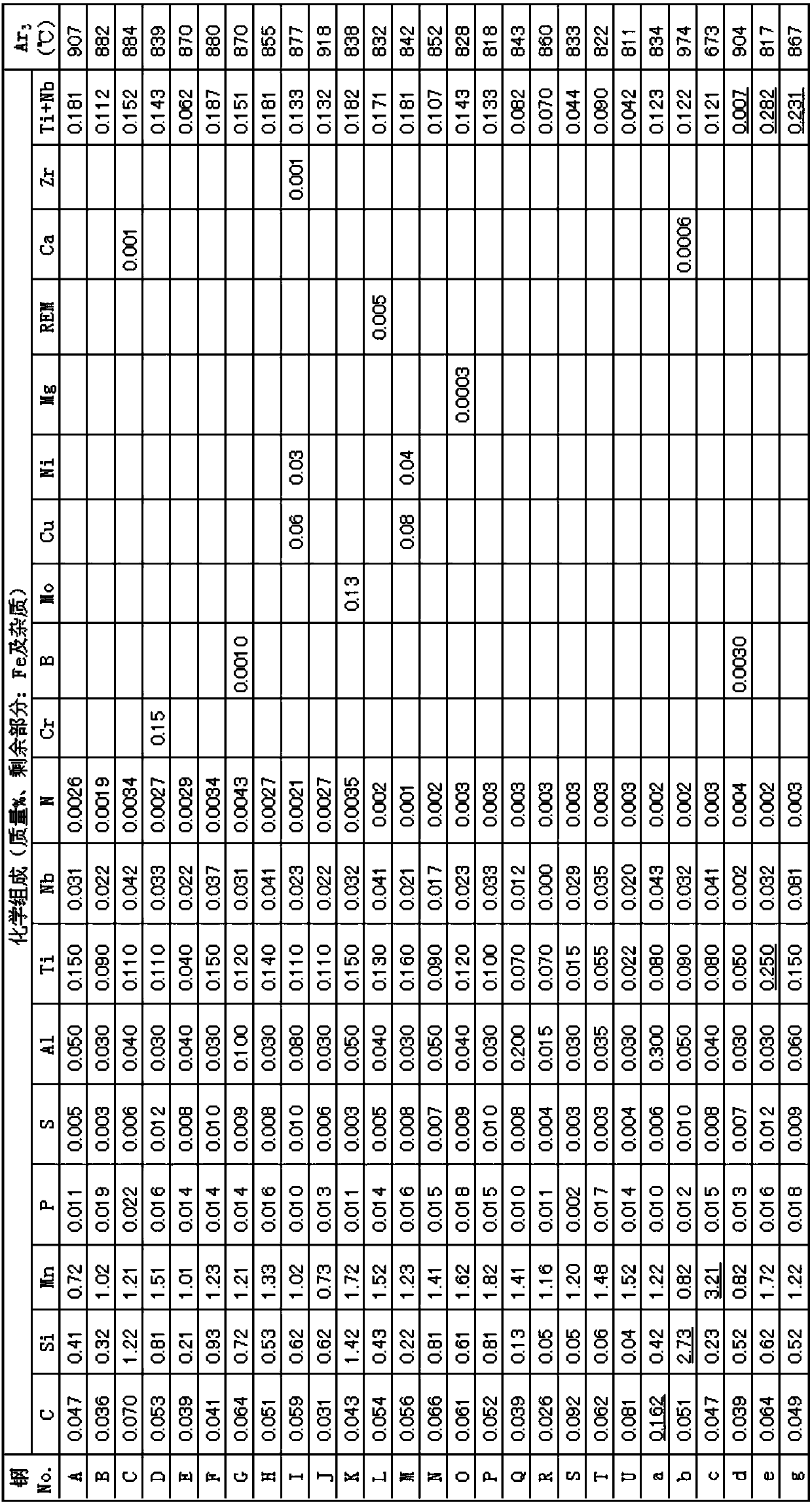
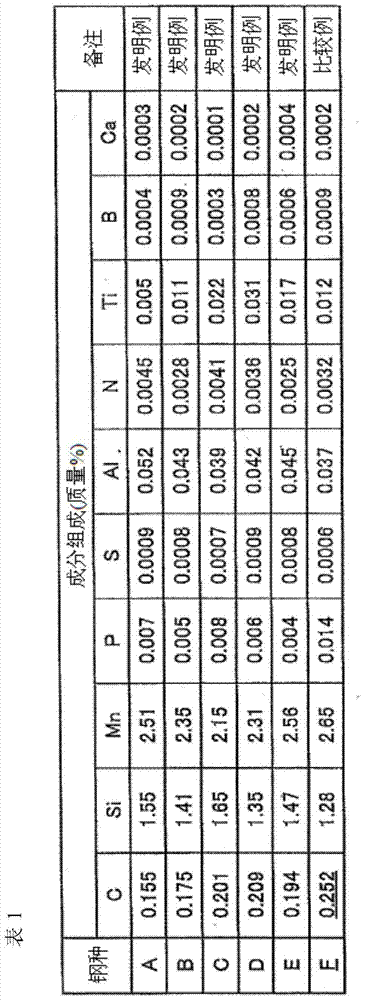
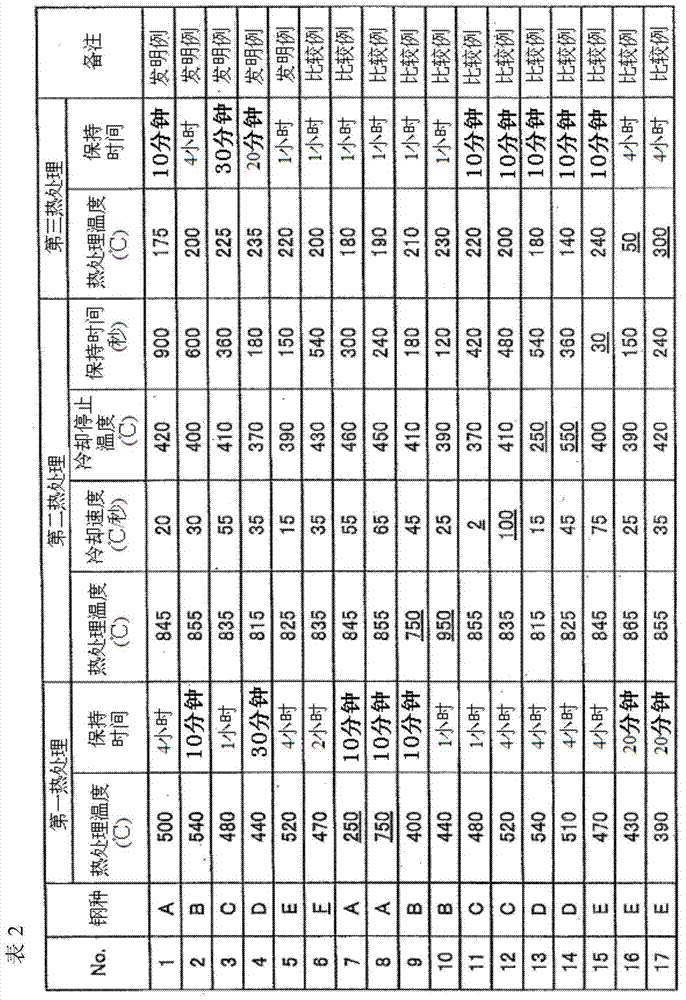
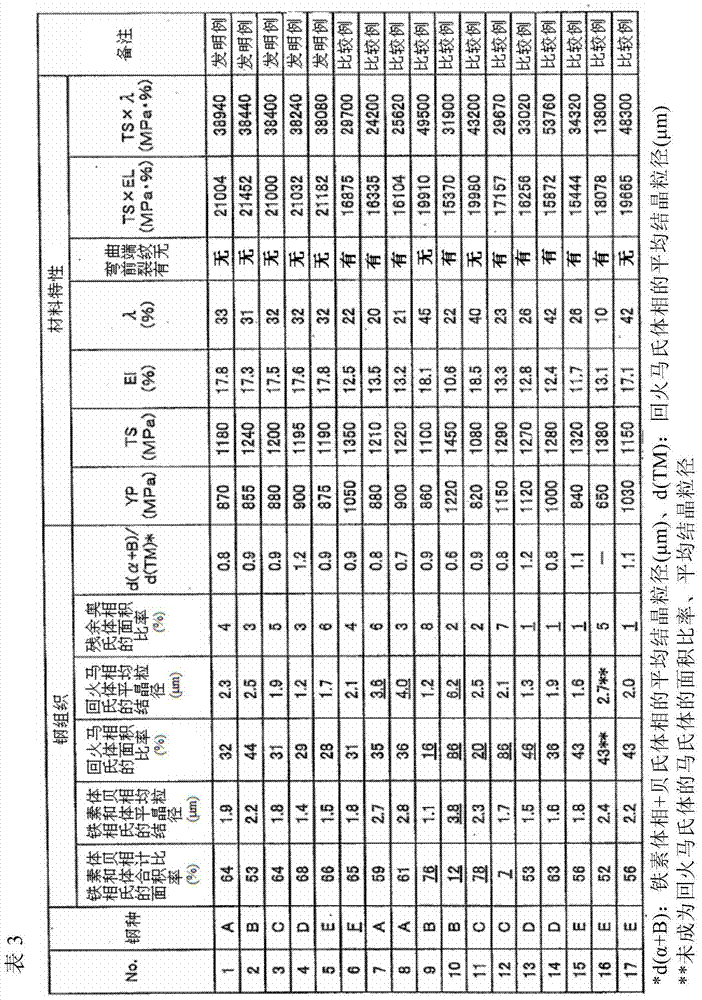
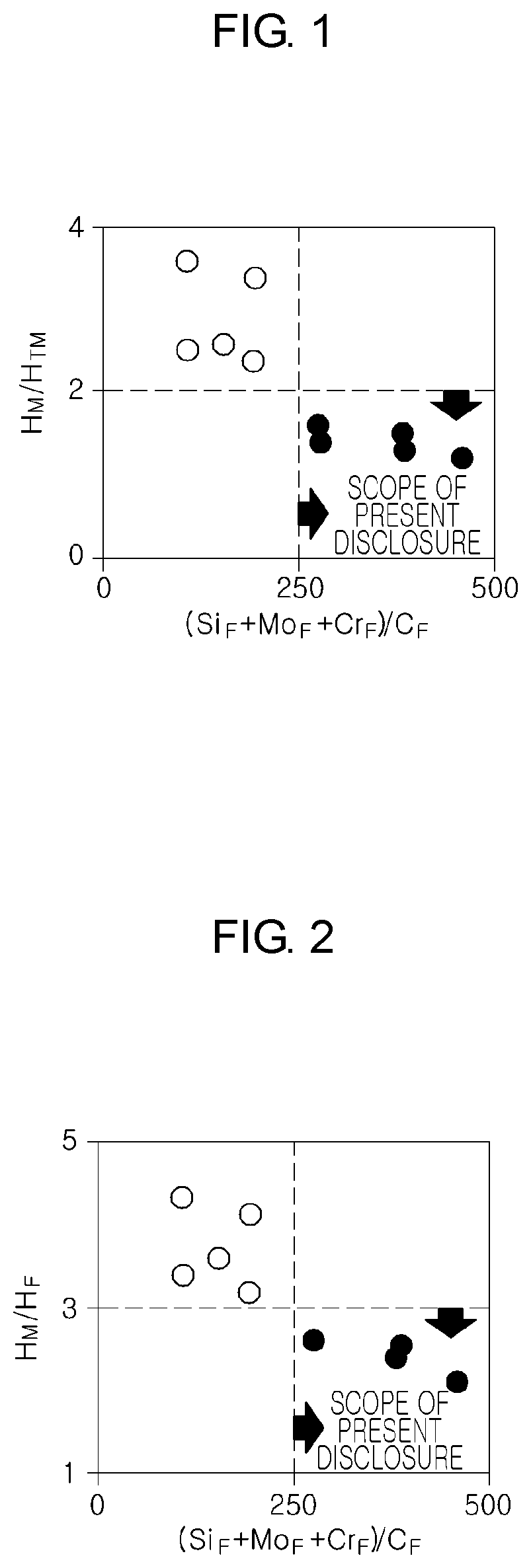
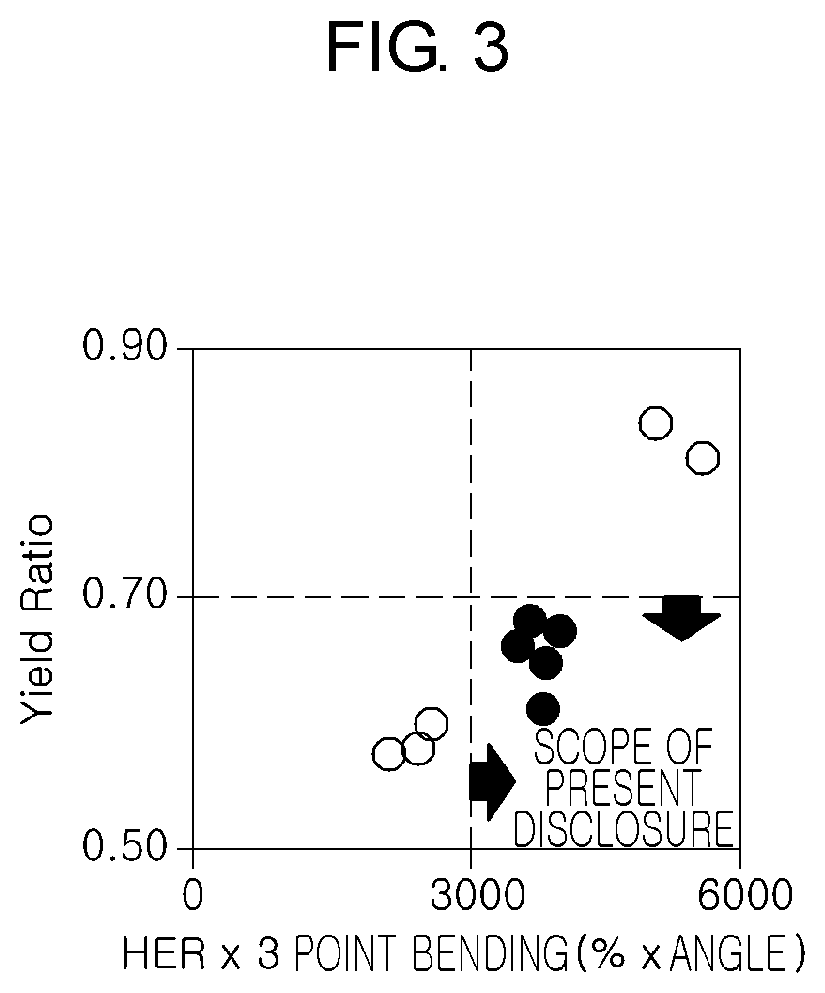
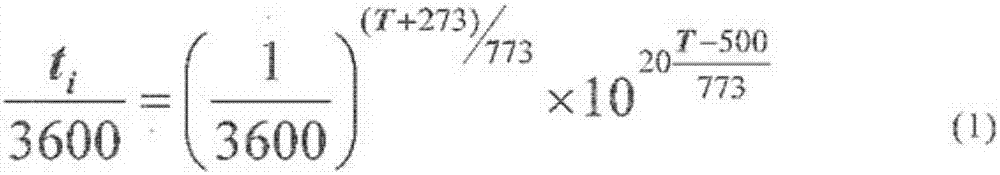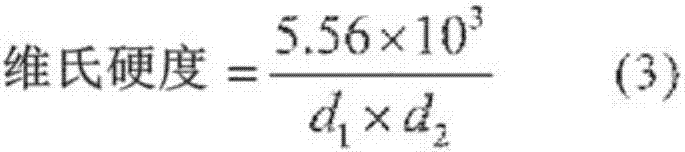Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
67results about How to "Excellent stretch flangeability" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
High-strength steel plate and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN102149840AGood ductilityExcellent stretch flangeabilityHot-dipping/immersion processesFurnace typesSteel platesDuctility
Disclosed is a high-strength steel plate having superior ductility and stretch flangeability and a tensile strength (TS) of 980 MPa or higher, and having 0.17-0.73% C, 3.0% or less Si, 0.5-3.0 or less Mn, 0.1% or less P, 0.07% S, 3.0% or less Al, 0.010% or less N, and 0.7% or more Si + Al, an area ratio of martensite of 10-90% with respect to the entire steel plate composition, a residual austenite amount of 5-50%, and an area ratio of bainitic ferrite in the upper bainite of 5% or less with respect to the entire steel plate composition. Twenty-five percent or more of the aforementioned martensite is tempered martensite, and the total of the area ratio of the aforementioned martensite with respect to the entire steel plate composition, the aforementioned residual austenite amount and the area ratio of the aforementioned bainitic ferrite in the upper bainite with respect to the entire steel plate composition is 65% or more. The area ratio of polygonal ferrite with respect to the entire steel plate composition is 10% or less (including 0%), and the average amount of C in the aforementioned residual austenite is 0.70% or more.
Owner:JFE STEEL CORP
High-strength hot-dip zinc plated steel sheet excellent in workability and process for manufacturing the same
ActiveCN101821419AImprove balanceExcellent stretch flangeabilityHot-dipping/immersion processesFurnace typesSheet steelHigh intensity
The invention provides a high-strength hot-dip zinc plated steel sheet which exhibits high TS-El balance, excellent stretch frangeability, excellent workability due to low YR, and excellent impact characteristics, and a process for manufacturing the same. A high-strength hot-dip zinc plated steel sheet excellent in workability and impact characteristics, having a composition which contains by mass C: 0.05 to 0.3%, Si: 0.01 to 2.5%, Mn: 0.5 to 3.5%, P: 0.003 to 0.100%, S: 0.02% or below, Al: 0.010 to 1.5%, and N: 0.007% or below and further contains at least one element selected from among Ti, Nb and V in a total amount of 0.01 to 0.2% with the balance being Fe and unavoidable impurities and a microstructure which comprises, in terms of area fraction, 20 to 87% of ferrite, 3 to 10% (in total) of martensite and retained austenite, and 10 to 60% of tempered martensite and in which the average grain diameter of the second phase consisting of the martensite, retained austenite, and tempered martensite is 3[mu]m or below.
Owner:JFE STEEL CORP
High-strength steel sheet and production method for same, and production method for high-strength galvanized steel sheet
InactiveCN107075627AImprove ductilityExcellent stretch flangeabilityHot-dipping/immersion processesFurnace typesSheet steelMartensite
The present invention provides a high-strength steel sheet having a tensile strength (TS) of at least 780 MPa, excellent ductility and stretch flangeability, and excellent material-quality stability, achieved by: having a specific component composition; the Mn volume divided by the B volume being not more than 2100; the steel structure having, in terms of area ratio, a total of ferrite and bainitic ferrite of 25-80%, and 3-20% martensite, and having, in terms of volume fraction, at least 10% retained austenite; the average crystalline particle diameter of the retained austenite being not more than 2[mu]m; the average Mn volume (mass%) in the retained austenite being at least 1.2 times the Mn volume (mass%) in the steel; and retained austenite aggregates, in which seven or more retained austenite crystal particles having the same orientation are grouped together, accounting for, in terms of area ratio, at least 60% of the total retained austenite.
Owner:JFE STEEL CORP
High strength hot rolled steel sheet and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS7527700B2High strengthHigh elongationFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesSheet steelHigh intensity
The present invention relates to a high strength hot rolled steel sheet consisting of 0.04 to 0.15% C, 1.5% or less Si, 0.5 to 1.6% Mn, 0.04% or less P, 0.005% or less S, 0.04% or less Al, 0.03 to 0.15% Ti, 0.03 to 0.5% Mo, by mass, and balance of Fe and inevitable impurities, and having a microstructure consisting of ferrite containing precipitates, second phase of bainite and / or martensite, and other phase, wherein the percentage of the ferrite containing precipitates is 40 to 95%, and the percentage of the other phase is 5% or less. For example, the high strength hot rolled steel sheet having a thickness of 1.4 mm shows a tensile strength of 780 MPa or higher, an elongation of 22% or higher elongation, and a hole expansion ratio of 60% or higher, thus the steel sheet is suitable for reinforcing members automobile cabin and crash worthiness members of automobile.
Owner:JFE STEEL CORP
Ultrahigh strength hot-rolled complex phase steel plate and production method thereof
ActiveCN109023036AReduce the difference in mechanical propertiesReduces sensitive points for crackingChemical compositionImpurity
The invention relates to an ultrahigh strength hot-rolled complex phase steel plate and a production method thereof. The ultrahigh strength hot-rolled complex phase steel plate comprises the followingchemical components of, by weight percentage, 0.05-0.15% of C, 0.1-0.8% of Si, 1.2-2.3% of Mn, no more than 0.012% of P, no more than 0.005% of S, 0.20-0.70% of Cr, 0.10-0.50% of Mo, 0.02-0.06% of Nb, 0.05-0.13% of Ti, 0.015-0.060% of Als and the balance Fe and inevitable impurities. The ultrahigh strength hot-rolled complex phase steel plate has the advantages that by controlling rolling and cooling, the effects of fine-grain strengthening, phase transformation strengthening and precipitation strengthening are comprehensively utilized, and the purposes that the high-strength performance of materials is maintained, the microhardness difference between two phases is reduced through precipitation strengthening, and the performance of chambering is improved are achieved.
Owner:ANGANG STEEL CO LTD
Hot-dip galvanized steel sheet with high tensile strength and superior processability and method for producing same
ActiveCN102906295AEasy to processHigh elongationHot-dipping/immersion processesFurnace typesPhysical chemistryCarbide
Disclosed is a hot-dip galvanized steel sheet with high tensile strength that is provided with both strength and processability (elongation and stretch flangeability) and a method for producing the same. Specifically disclosed is a hot-dip galvanized steel sheet with high tensile strength that has tensile strength of 980 MPa or greater and superior processability. This hot-dip galvanized steel sheet has a composition containing 0.07 - 0.13% C, 0.3% or less Si, 0.5 - 2.0% Mn, 0.025% or less P, 0.005% or less S, 0.0060% or less N, 0.06% or less Al, 0.10 - 0.14% or less Ti, and 0.15 - 0.30% V (% by mass) such that S and N satisfy Ti >= 0.10 + (N / 14*48 + S / 32*48) and 0.8 <= (Ti / 48 + V / 51) / (C / 12) <= 1.2 (wherein C, Ti, V, S and N are the content for each element in % by mass). The composition further contains 0.04 - 0.1% V in solid solution and 0.05% or less Ti in solid solution, and the remainder is Fe and unavoidable impurities. The hot-dip galvanized steel sheet has a matrix that is 97% or more in areal proportion of the overall structure of the ferrite phase and a hot-dip galvanized coating or alloyed hot-dip galvanized coating on the surface of a hot-rolled steel sheet that has fine carbide that has an average particle diameter of less than 10 nm and contains Ti and V dispersed and precipitated, with a structure forming 0.007 or more in areal proportion of the overall structure of that fine carbide.
Owner:JFE STEEL CORP
High-strength steel sheet and production method for same, and production method for high-strength galvanized steel sheet
ActiveCN106574341AImprove ductilityExcellent stretch flangeabilityHot-dipping/immersion processesFurnace typesMartensiteAustenite
The present invention provides a high-strength steel sheet having a tensile strength (TS) of at least 780 MPa, excellent ductility and stretch flangeability, and excellent material-quality stability, achieved by: having a specific component composition; the steel structure having, in terms of area ratio, a total of ferrite and bainitic ferrite of 25-80%, and 3-20% martensite, and having, in terms of volume fraction, at least 10% retained austenite; the average crystalline particle diameter of the retained austenite being not more than 2[mu]m; the average Mn volume (mass%) in the retained austenite being at least 1.2 times the Mn volume (mass%) in the steel; and the area ratio of retained austenite that has an average C volume (mass%) of at least 2.1 times the C volume (mass%) of the steel being at least 60% of the area ratio of the total retained austenite.
Owner:JFE STEEL CORP
High-strength cold-rolled steel sheet having excellent stretch flange properties, and process for production thereof
ActiveCN103080357AStable and cheap to manufactureExcellent stretch flangeabilityFurnace typesProcess efficiency improvementSheet steelChemical composition
The present invention provides: a high-strength cold-rolled steel sheet which has excellent stretch flange properties, and which has a chemical composition comprising, in mass%, 0.050-0.090% of C:, 0.05% or less of Si, 1.5-2.0% of Mn, 0.030% or less of P, 0.0050% or less of S, 0.005-0.1% of Al, 0.01% or less of N, 0.005-0.050% of Ti, 0.020-0.080% of Nb and a remainder made up by Fe and unavoidable impurities, has a tissue composed of, in vol%, 50-77% of a ferrite phase, 20-50% of a bainite phase, 2-10% of a martensite phase and 1-5% of a residual austenite phase, and has such high strength that the tensile strength (TS) is 590 MPa or more, a strength-elongation balance (TSEl) of 16000 MPa% or more and a strength-(hole expanding ratio) balance (TS[lambda]) of 40000 MPa% or more; and a process for producing the high-strength cold-rolled steel sheet.
Owner:JFE STEEL CORP
Hot-rolled ultra soft high-carbon steel plate and process for production thereof
ActiveCN101410544AImprove ductilityExcellent stretch flangeabilityFurnace typesMetal rolling arrangementsMean diameterSheet steel
An ultra soft high carbon hot-rolled steel sheet having excellent workability. The steel sheet is a high carbon hot-rolled steel sheet containing 0.2 to 0.7% C, and has a structure in which mean grain size of ferrite is 20 [mu]m or larger, the volume percentage of ferrite grains having 10 [mu]m or smaller size is 20% or less, mean diameter of carbide is in a range from 0.10 [mu]m to smaller than 2.0 [mu]m, the percentage, of carbide grains having 5 or more of aspect ratio is 15% or less, and the contact ratio of carbide is 20% or less. The steel sheet is manufactured by the steps of: rough-rolling the steel; finish-rolling the rough-rolled steel sheet at a temperature of 1100 DEG C or below at inlet of finish rolling, a reduction in thickness of 12% or more at the final pass, and a finishing temperature of (Ar3 - 10) DEG C or above; primary-cooling the finish-rolled steel sheet to a cooling-stop temperature of 600 DEG C or below within 1.8 seconds after the finish rolling at a cooling rate of higher than 120 DEG C / sec; secondary-cooling the primary-cooled steel sheet to hold the steel sheet at a temperature of 600 DEG C or below; coiling the secondary-cooled steel sheet at a temperature of 580 DEG C or below; pickling the coiled steel sheet; and spheroidizing-annealing the pickled steel sheet by the box annealing method at a temperature in a range from 680 DEG C to Ac1 transformation point.
Owner:JFE STEEL CORP
Process for manufacturing high-strength hot-rolled steel sheet
ActiveCN101755062AExcellent stretch flangeabilityFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesSheet steelHigh intensity
The invention provides a process for manufacturing a high -strength steel sheet which has a strength of 490MPa or above and excellent stretch flange formability with a hole enlargement ratio of 80% or above after 10% working and which is reduced in the local property variation in a coil. A process for manufacturing a high-strength hot-rolled steel sheet, characterized by heating a billet which contains by mass C: 0.05 to 0.15%, Si: 0.1 to 1.5%, Mn: 0.5 to 2.0%, P: 0.06% or below, S: 0.005% or below, and Al: 0.10% or below with the balance consisting of Fe and unavoidable impurities to 1150 to 1300 DEG C, subjecting the resulting billet to hot rolling with a finishing temperature of 800 to 1000 DEG C, cooling the obtained sheet at an average cooling rate of 30 DEG C / s or above to a cooling stop temperature of 525 to 625 DEG C, stopping the cooling of the sheet for 3 to 10seconds, cooling the resulting sheet by such a cooling method as to cause nucleate boiling, and then coiling the sheet at 400 to 550 DEG C.
Owner:JFE STEEL CORP
High strength steel sheet having excellent stretch flangeability
ActiveUS7468109B2High strengthExcellent stretch-flangeabilityFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesTRIP steelHigh intensity
Disclosed is a steel sheet including 0.10 to 0.20 mass % of C, 0.8 to 2.5 mass % of Si, 1.5 to 2.5 mass % of Mn, and 0.01 to 0.10 mass % of Al, wherein P is limited to less than 0.1 mass %, and S is limited to less than 0.002 mass % and more than 0 mass %, and the structure includes bainitic ferrite and residual austenite such that area percentage of the bainitic ferrite in relation to the entire structure is at least 70%, area percentage of the residual austenite is 2 to 20%, and total area percentage of polygonal ferrite and quasi-polygonal ferrite is up to 15%, and proportion of the residual austenite having an average particle size of up to 5 μm in the residual austenite is at least 60%. The steel sheet is a TRIP steel sheet which has bainitic ferrite as its matrix, and it has a tensile strength (TS) of at least 980 MPa as well as an excellent stretch flangeability.
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD
High strength steel sheet having excellent stretch flangeability
ActiveUS20080023112A1High strengthExcellent stretch-flangeabilityFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesTRIP steelHigh intensity
Disclosed is a steel sheet including 0.10 to 0.20 mass % of C, 0.8 to 2.5 mass % of Si, 1.5 to 2.5 mass % of Mn, and 0.01 to 0.10 mass % of Al, wherein P is limited to less than 0.1 mass %, and S is limited to less than 0.002 mass % and more than 0.1 mass %, and the structure includes bainitic ferrite and residual austenite such that area percentage of the bainitic ferrite in relation to the entire structure is at least 70%, area percentage of the residual austenite is 2 to 20%, and total area percentage of polygonal ferrite and quasi-polygonal ferrite is up to 15%, and proportion of the residual austenite having an average particle size of up to 5 μm in the residual austenite is at least 60%. The steel sheet is a TRIP steel sheet which has bainitic ferrite as its matrix, and it has a tensile strength (TS) of at least 980 MPa as well as an excellent stretch flangeability.
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD
Single-ferrite-precipitated steel plate with high strength and high pore-expansion property and preparation method for same
The invention discloses a single-ferrite-precipitated steel plate with high strength and a high pore-expansion property and a preparation method for the same. Steel comprises 0.05%-0.12% of C, 0.1%-0.7% of Si, 0.8%-2.2% of Mn, 0.05%-0.10% of Ti, less than 0.035% of P, less than 0.035% of S, 0.015%-0.060% of Als, 0.0015%-0.0050% of Ca, less than 0.0050% of Mg and less than 0.005% of N, at least oneof ingredients including 0.15%-0.3% of Cr and 0.05%-0.3% of Mo, at least one of ingredients including 0.02%-0.06% of Nb and 0.05%-0.25% of V as well as the balance being Fe and inevitable impurities.The linear speed of Si-Ca feeding is more than or equal to 3.5m / s, and a superheat degree of the molten steel is less than or equal to 30 DEG C; and the heating temperature of a casting blank is 1150-1250 DEG C, the multi-pass rolling total reduction rate is more than or equal to 80%, the final rolling temperature of hot rolling is 850-950 DEG C, the after-rolling cooling rate is 15-45 DEG C / s, and the rolling temperature is 550-650 DEG C. The finished steel plate has the good pore-expansion property.
Owner:ANGANG STEEL CO LTD
High-strength cold-rolled steel sheet having excellent workability and collision characteristics and having tensile strength of 980 MPa or more, and method for producing same
ActiveCN107429370AExcellent stretch flangeabilityEasy to processHot-dipping/immersion processesFurnace typesHigh intensityUltimate tensile strength
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD
Hot-dip galvanized cold-rolled steel sheet and process for producing same
ActiveUS20140212686A1Improve stabilityImprove workabilityHot-dipping/immersion processesFurnace typesAustenite grainGalvanization
A hot-dip galvanized cold-rolled steel sheet has a tensile strength of 750 MPa or higher, a composition consisting, in mass percent, of C: more than 0.10% and less than 0.25%, Si: more than 0.50% and less than 2.0%, Mn: more than 1.50% and 3.0% or less, and optionally containing one or more types of Ti, Nb, V, Cr, Mo, B, Ca, Mg, REM, and Bi, P: less than 0.050%, S: 0.010% or less, sol. Al: 0.50% or less, and N: 0.010% or less, and a main phase as a low-temperature transformation product and a second phase as retained austenite. The retained austenite volume fraction is more than 4.0% and less than 25.0% of the whole structure, and has an average grain size of less than 0.80 □m. A number density of retained austenite grains having a grain size of 1.2 □m or more is 3.0□10−2 / □m2 or less.
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP
Steel sheet and plated steel sheet
ActiveUS20190226061A1High strengthExcellent stretch-flangeabilityHot-dipping/immersion processesFurnace typesChemical compositionCarbide
A steel sheet has a specific chemical composition and has a structure represented by, by area ratio, ferrite: 30 to 95%, and bainite: 5 to 70%. When a region that is surrounded by a grain boundary having a misorientation of 15° or more and has a circle-equivalent diameter of 0.3 μm or more is defined as a crystal grain, the proportion of crystal grains each having an intragranular misorientation of 5 to 14° to all crystal grains is 20 to 100% by area ratio. An average aspect ratio of ellipses equivalent to the crystal grains is 5 or less. An average distribution density of the total of Ti-based carbides and Nb-based carbides each having a grain size of 20 nm or more on ferrite grain boundaries is 10 carbides / μm or less.
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP
Cold-rolled steel sheet
ActiveUS20140241933A1Improve stabilityImprove workabilityFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesAustenite grainChemical composition
A high-strength cold-rolled steel sheet excellent in ductility, work hardenability, and stretch flangeability, and having tensile strength of 780 MPa or more includes: a chemical composition containing, in mass percent, C: more than 0.020% to less than 0.30%, Si: more than 0.10% to 3.00% or less, Mn: more than 1.00% to 3.50% or less; and metallurgical structure whose main phase is a low-temperature transformation product, and whose secondary phase contains retained austenite. The retained austenite has a volume fraction relative to overall structure of more than 4.0% to less than 25.0% and an average grain size of less than 0.80 μm, and of the retained austenite, the number density of retained austenite grains whose grain size is 1.2 μm or more is 3.0×10−2 grains / μm2 or less.
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP
Hot-rolled steel sheet
ActiveUS20180037967A1Excellent stretch-flangeabilityHigh strengthFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesChemical compositionGrain boundary
A hot-rolled steel sheet includes a predetermined chemical composition, and a structure which includes, by area ratio, a ferrite in a range of 5% to 60% and a bainite in a range of 30% to 95%, in which in the structure, in a case where a boundary having an orientation difference of equal to or greater than 15° is defined as a grain boundary, and an area which is surrounded by the grain boundary and has an equivalent circle diameter of equal to or greater than 0.3 μm is defined as a grain, the ratio of the grains having an intragranular orientation difference in a range of 5° to 14° is, by area ratio, in a range of 20% to 100%.
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP
Low-yield-ratio high-strength cold-rolled steel sheet and method for manufacturing same
ActiveCN104870676AHigh elongationExcellent stretch flangeabilityFurnace typesMetal rolling arrangementsChemical compositionYield ratio
Provided are: a high-strength steel sheet having excellent stretchability and stretch flangeability, and a low yield ratio; and a method for manufacturing the high-strength steel sheet. A low-yield-ratio high-strength cold-rolled steel sheet having a chemical composition containing, by mass, 0.05 to 0.10% of C, 0.6 to 1.3% of Si, 1.4 to 2.2% of Mn, 0.08% or less of P, 0.010% or less of S, 0.01 to 0.08% of Al, and 0.010% or less of N, with the remainder made up by Fe and unavoidable impurities. The low-yield-ratio high-strength cold-rolled steel sheet has a microstructure in which the average crystal grain size of ferrite is equal to or smaller than 15 μm, the volume fraction of ferrite is equal to or greater than 70%, the volume fraction of bainite is equal to or greater than 3%, the volume fraction of residual austenite is 4 to 7%, the average crystal grain size of martensite is equal to or smaller than 5 μm, and the volume fraction of martensite is 1 to 6%. The average C concentration (mass%) in the residual austenite is 0.30 to 0.70%. The steel sheet characteristics are such that the yield ratio is equal to or less than 64% and the tensile strength is equal to or greater than 590 MPa.
Owner:JFE STEEL CORP
High strength steel sheet and manufacturing method therefor
ActiveCN107406937AHigh tensile strengthHigh strengthFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesUltimate tensile strengthArea ratio
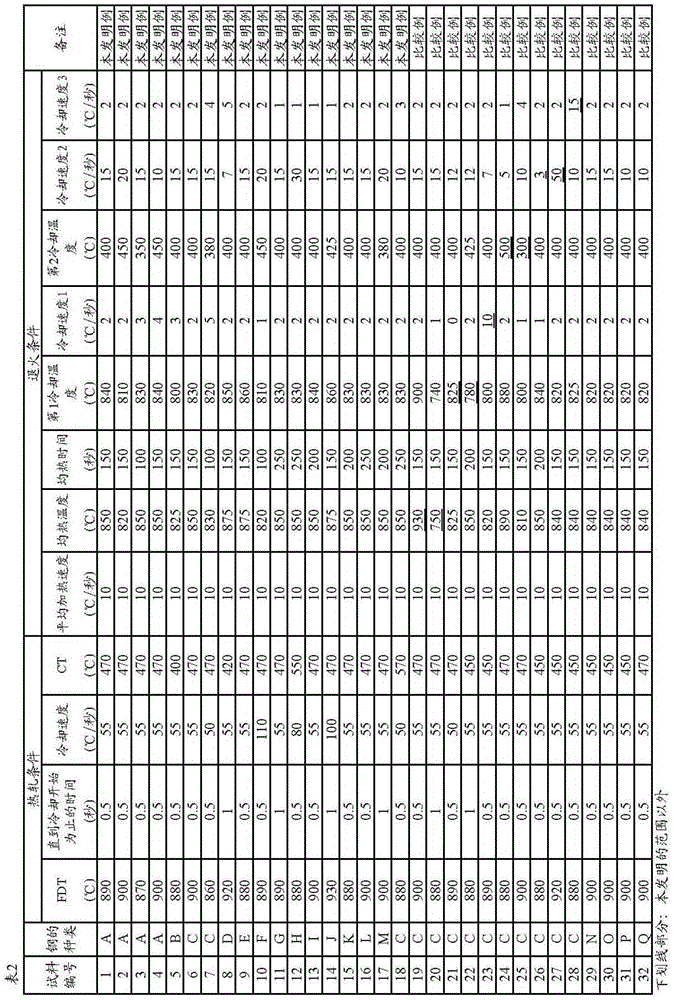
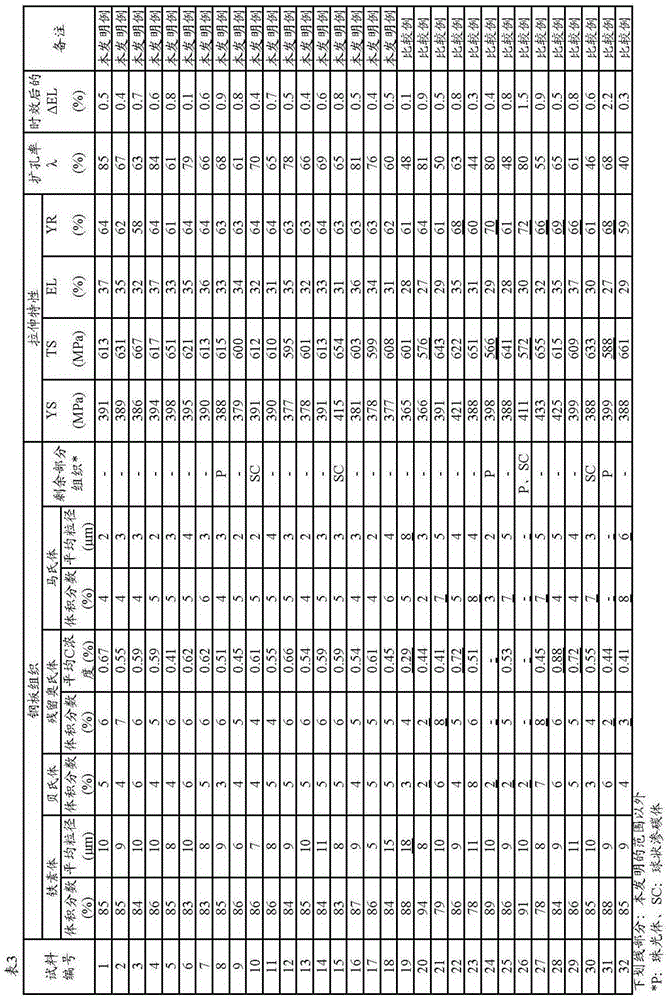
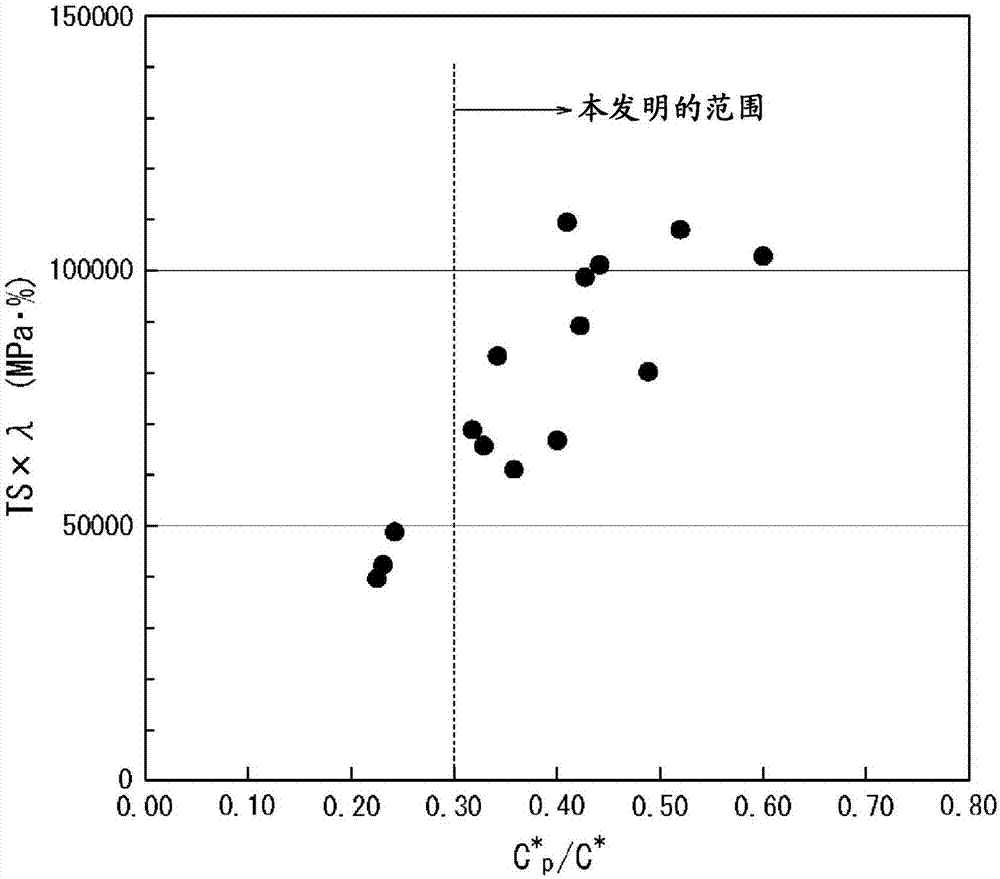
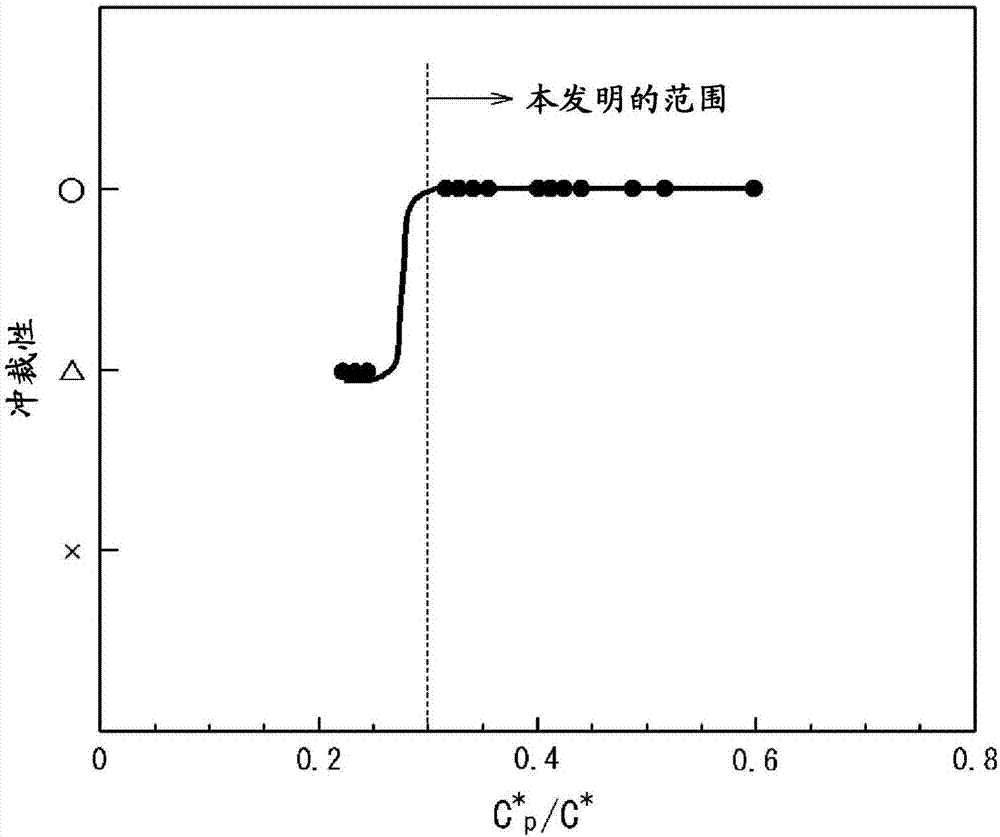
The purpose of the present invention is to provide: a high strength steel sheet that has high strength such that tensile strength is at least 780 MPa, and excellent blanking quality combined with stretch-flangeability; and a manufacturing method therefor. Provided is a high strength steel sheet wherein: the steel sheet contains, in mass%, C: 0.05-0.30%, Si: 0.6-2.0%, Mn 1.3-3.0%, P: not more than 0.10%, S: not more than 0.030%, Al: not more than 2.0%, N: not more than 0.010%, and one or more of Ti, Nb and V: 0.01-1.0% each, the balance being obtained from iron and unavoidable impurities; the steel sheet comprises at least 50% area ratio of ferrite structure; the amount of Fe deposited is at least 0.04 mass%; the steel sheet contains a deposit in which the particle diameter is less than 20 nm; and C* defined by expression (1) and C*p defined by expression (2) satisfy the conditions in expressions (3)-(5). C*=([Ti] / 48+[Nb] / 93+[V] / 51+[Mo] / 96+[Ta] / 181+[W] / 184) * 12... (1) C*p=([Ti]p / 48+[Nb]p / 93+[V]p / 51+[Mo]p / 96+[Ta]p / 181+[W]p / 184)*12... (2) C* >= 0.035... (3) -0.015 <=[C]-C* <= 0.03... (4) C*p / C* >=0.3... (5)
Owner:JFE STEEL CORP
High-strength hot-rolled steel sheet and manufacturing method therefor
ActiveCN104024460ALittle change in mechanical propertiesExcellent stretch flangeabilityFurnace typesThin material handlingMean diameterManganese
Provided is a high-strength hot-rolled steel sheet that exhibits little inter-coil variability in mechanical properties and excellent stretch flangeability. By mass, said steel sheet contains more than 0.010% and no more than 0.06% carbon, up to 0.3% silicon, up to 0.8% manganese, up to 0.03% phosphorus, up to 0.02% sulfur, up to 0.1% aluminum, up to 0.01% nitrogen, and 0.05-0.10% titanium, with the remainder comprising iron and unavoidable impurities. The amounts of silicon and manganese are minimized, the amount of segregation and the like is reduced, and strength variation due to inter-coil position differences is decreased. The structure of the steel sheet is such that the area fraction of a ferrite phase is at least 95%, the mean diameter of ferrite crystal grains is at least 1 [mu]m, and TiC with a mean grain diameter of at most 7 nm is dispersed inside the ferrite crystal grains. This results in a high-strength hot-rolled steel sheet that maintains a yield strength of at least 530 MPa.
Owner:JFE STEEL CORP
High strength hot rolled steel sheet having excellent stretch flangeability and its production method
InactiveCN101078089AHigh strengthGuaranteed tensile strengthTemperature control deviceHeat treatment process controlSheet steelChemical composition
Disclosed is a hot rolled steel sheet in which it includes a steel having a chemical composition of 0.03 to 0.10% (the percent hereinafter representing % by mass) of C, 0.2 to 2.0% of Si, 0.5 to 2.5% of Mn, 0.02 to 0.10% of Al, 0.2 to 1.5% of Cr, 0.1 to 0.5% of Mo, and the residue of iron and inevitable contaminants, and in this steel sheet, at least 80% by area in longitudinal cross section has a martensitic structure. As a consequence, a high strength hot rolled steel sheet having a tensile strength of the level as high as 980 MPa or higher simultaneously with an excellent forming workability, and in particular, excellent stretch flangeability is provided at a relatively low cost.
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD
High-strength cold-rolled steel sheet, high-strength hot-dip galvanized steel sheet, and high-strength hot-dip galvannealed steel sheet having excellent ductility, stretch-flangeability, and weldability
ActiveCN106103774AHigh tensile strengthHigh strengthHot-dipping/immersion processesFurnace typesChemical compositionUltimate tensile strength
Provided is a high-strength cold-rolled steel sheet having excellent ductility and stretch-flangeability as well as weldability at a range in which the tensile strength is at least 980 MPa and the 0.2% yield strength is at least 700 MPa. In this high-strength cold-rolled steel sheet, the chemical composition is adjusted as appropriate, and the area ratio of the belowmentioned metal structure at a position of 1 / 4 sheet thickness in the steel sheet satisfies the following: at least 30 area% of tempered martensite; 15-70 area%, inclusive, of bainite; at least 90 total area% of tempered martensite and bainite; 0-5 area%, inclusive, of ferrite; and 0-4 area%, inclusive, of retained austenite. The high-strength cold-rolled steel sheet has excellent ductility, stretch-flangeability, and weldability, and has a tensile strength of at least 980 MPa and a 0.2% yield strength of at least 700 MPa.
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD
Steel sheet and plated steel sheet
ActiveUS20190241996A1High strengthExcellent stretch-flangeabilityHot-dipping/immersion processesFurnace typesChemical compositionNumber density
A steel sheet has a specific chemical composition and has a structure represented by, by area ratio, ferrite: 0 to 30%, and bainite: 70 to 100%. When a region that is surrounded by a grain boundary having a misorientation of 15° or more and has a circle-equivalent diameter of 0.3 μm or more is defined as a crystal grain, the proportion of crystal grains each having an intragranular misorientation of 5 to 14° to all crystal grains is 20 to 100% by area ratio. A grain boundary number density of solid-solution C or a grain boundary number density of the total of solid-solution C and solid-solution B is 1 piece / nm2 or more and 4.5 pieces / nm2 or less. An average grain size of cementite precipitated at grain boundaries is 2 μm or less.
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP
Steel sheet and plated steel sheet
PendingCN109563580AHigh strengthExcellent stretch flangeabilityHot-dipping/immersion processesFurnace typesChemical compositionCarbide
This steel sheet has a specific chemical composition and is provided with a structure represented by, in terms of area ratio, 30-95% ferrite and 5-70% bainite. When a crystal grain is defined as a region which is surrounded by grain boundaries having a misorientation of 15D or higher and for which the equivalent circle diameter is 0.3 Mum or larger, the proportion of crystal grains having an intragranular misorientation of 5-14D relative to all of the crystal grains is 20-100% in terms of area ratio. The average aspect ratio of ellipses equivalent to the crystal grains is 5 or lower. The average distribution density of the total of Ti carbides and Nb carbides having a particle size of 20 nm or larger in the ferrite grain boundaries is 10 particles / Mum or lower.
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP
Steel sheet and plated steel sheet
ActiveCN109642279AImprove toleranceImprove surface propertiesHot-dipping/immersion processesFurnace typesChemical compositionSolid solution
This steel sheet has a specific chemical composition and is provided with a structure represented by, in terms of area ratio, 0 - 30% ferrite and 70 - 100% bainite. When a crystal grain is defined asa region which is surrounded by grain boundaries having a misorientation of 15 DEG or higher and for which the equivalent circle diameter is 0.3 mu m or larger, the proportion of crystal grains havingan intragranular misorientation of 5 - 14 DEG relative to all of the crystal grains is 20 - 100% in terms of area ratio. The grain boundary number density of a solid solution of C, or the total grainboundary number density of a solid solution of C and a solid solution of B is 1 particle / nm<2> to 4.5 particles / nm<2> inclusive. The average particle size of cementite precipitated in the grain boundaries is no larger than 2 mu m.
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP
Steel sheet, coated steel sheet, method for producing hot-rolled steel sheet, method for producing full hard cold-rolled steel sheet, method for producing steel sheet, and method for producing coated steel sheet
ActiveUS20200299797A1High tensile strengthExcellent stretch-flangeabilityHot-dipping/immersion processesFurnace typesCarbideMartensite
Provided are a coated steel sheet and so forth, the coated steel sheet having a tensile strength of 590 MPa or more and good stretch-flangeability. The coated steel sheet includes a specific component composition, in which the area fraction of a ferrite phase is 80% or more and 98% or less, the area fraction of a martensite phase of 2% or more and 15% or less, ferrite grains have an average thickness of 3.0 μm or less in the sheet-thickness direction, the martensite phase has an average grain size of 2.0 μm or less, and a Nb-containing carbide precipitated in the ferrite grains has an average grain size of 8 nm or less, and in which the steel sheet has a tensile strength of 590 MPa or more.
Owner:JFE STEEL CORP
High-strength cold-rolled steel sheet and method for manufacturing same
ActiveCN104736736AHigh elongationExcellent stretch flangeabilityFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesChemical compositionImpurity
Provided are: a high-strength cold-rolled steel sheet having excellent ductility, stretch-flangeability and bendability; and a method for manufacturing the high-strength cold-rolled steel sheet. A high-strength cold-rolled steel sheet having the following chemical composition, in mass%: 0.12 to 0.22% of C; 0.8 to 1.8% of Si; 1.8 to 2.8% of Mn; 0.020% or less of P; 0.0040% or less of S; 0.005 to 0.08% of Al; 0.008% or less of N; 0.001 to 0.040% of Ti; 0.0001 to 0.0020% of B; and 0.0001 to 0.0020% of Ca; with the remainder made up by Fe and unavoidable impurities. The high-strength cold-rolled steel sheet has such a structure that the total area ratio of a ferrite phase and a bainite phase is 50 to 70%, the average crystal particle diameter of the ferrite phase and the bainite phase is 1 to 3 μm, the area ratio of a tempered martensite phase is 25 to 45%, the average crystal particle diameter of the tempered martensite phase is 1 to 3 μm, and the area ratio of a retained austenite phase is 2 to 10%.
Owner:JFE STEEL CORP
High-strength steel sheet and method for producing same
ActiveCN107406938AExcellent stretch flangeabilityConducive to lightweightHot-dipping/immersion processesFurnace typesElement compositionUltimate tensile strength
Provided is a high-strength steel sheet having: an element composition that includes, in mass%, C: 0.09-0.17% of C, Si: 0.6-1.7% of Si, 3.5% or less of Mn, 0.03% or less of P, 0.005% or less of S, 0.08% or less of Al, 0.006% or less of N, 0.05% or less of Ti, and 0.0002-0.0030% of B, the balance being Fe and unavoidable impurities; and a steel sheet structure that includes, in area percentage, less than 20% (including 0%) of a ferrite phase, 75% or more (including 100%) of a tempered martensite phase, 10% or less (including 0%) of a non-tempered martensite phase, and less than 5% (including 0%) of a residual austenite phase, the Vickers hardness of the tempered martensite phase being 280-340, and the tensile strength of the sheet being 950-1,120 MPa.
Owner:JFE STEEL CORP
High tensile strength steel having excellent bendability and stretch-flangeability and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveUS20200087762A1Improve bendabilityExcellent stretch-flangeabilityHot-dipping/immersion processesFurnace typesStructural componentDuctility
Provided is a high tensile strength steel having a tensile strength of 780 MPa grade or higher which is used for structural members of automobiles, and more specifically relates to high tensile strength steel having excellent bendability and stretch-flangeability while still satisfying characteristics of DP steels of low yield ratio and high ductility, and to a manufacturing method thereof.
Owner:POHANG IRON & STEEL CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com