Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
2396 results about "X-ray tube" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
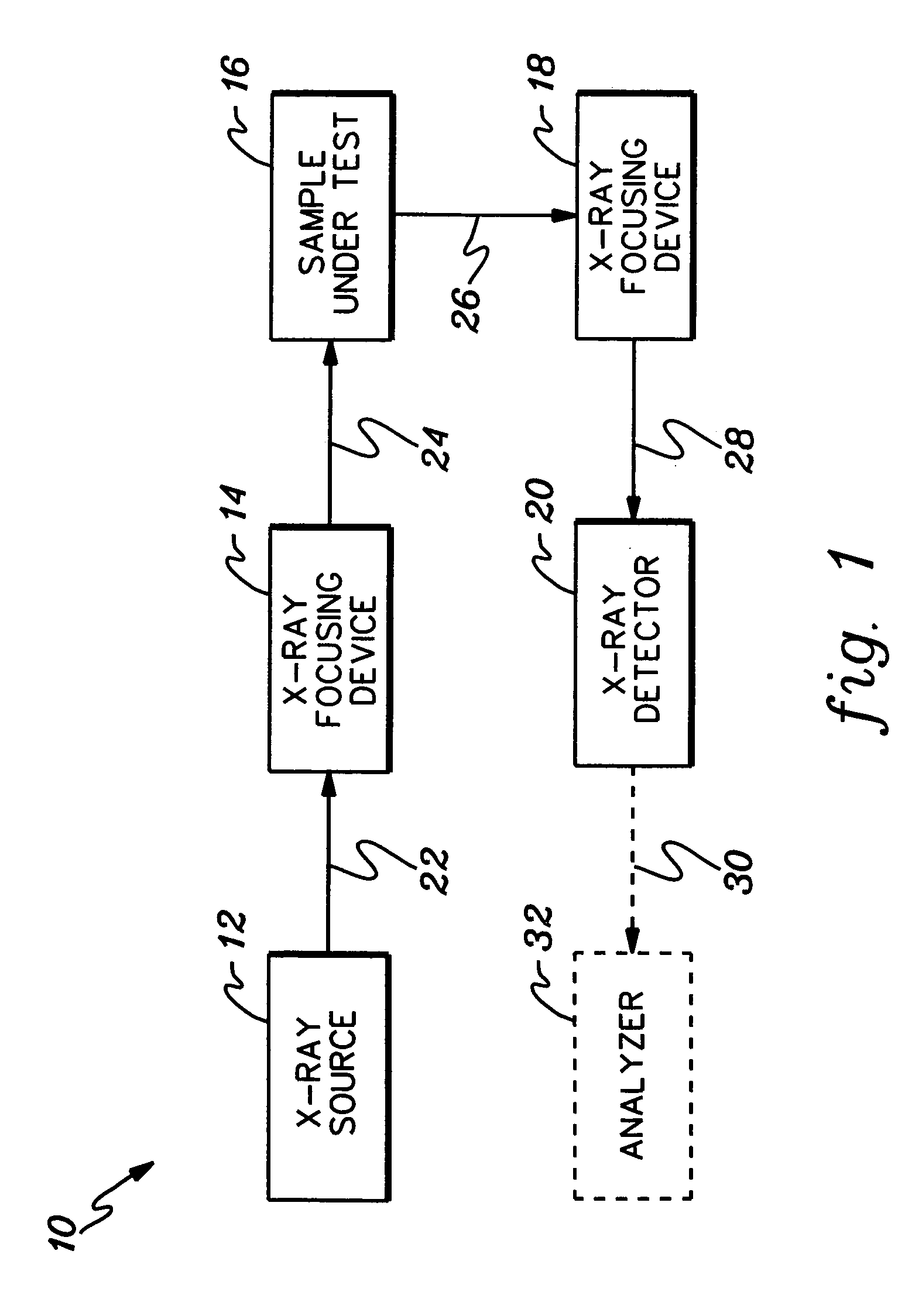
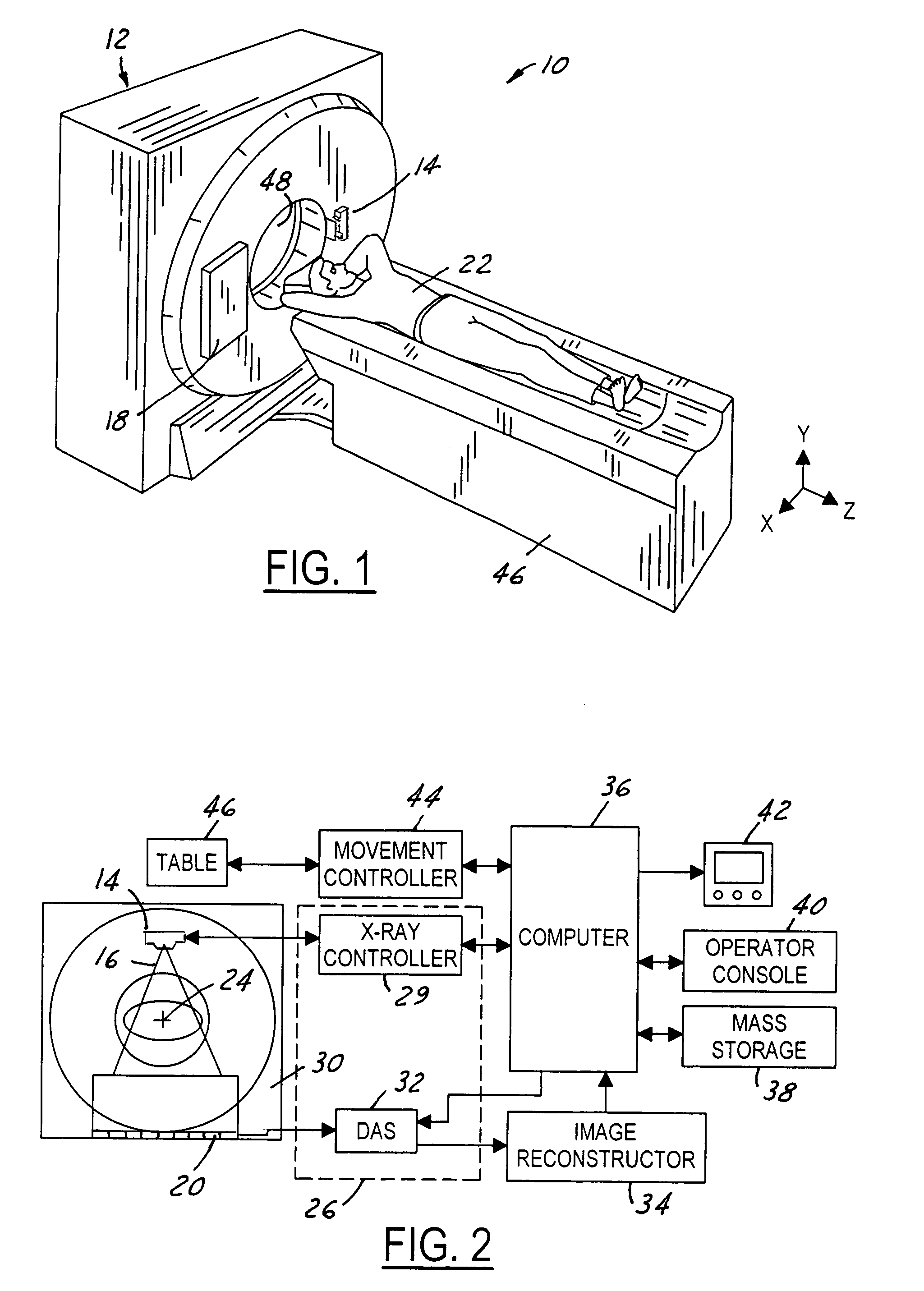
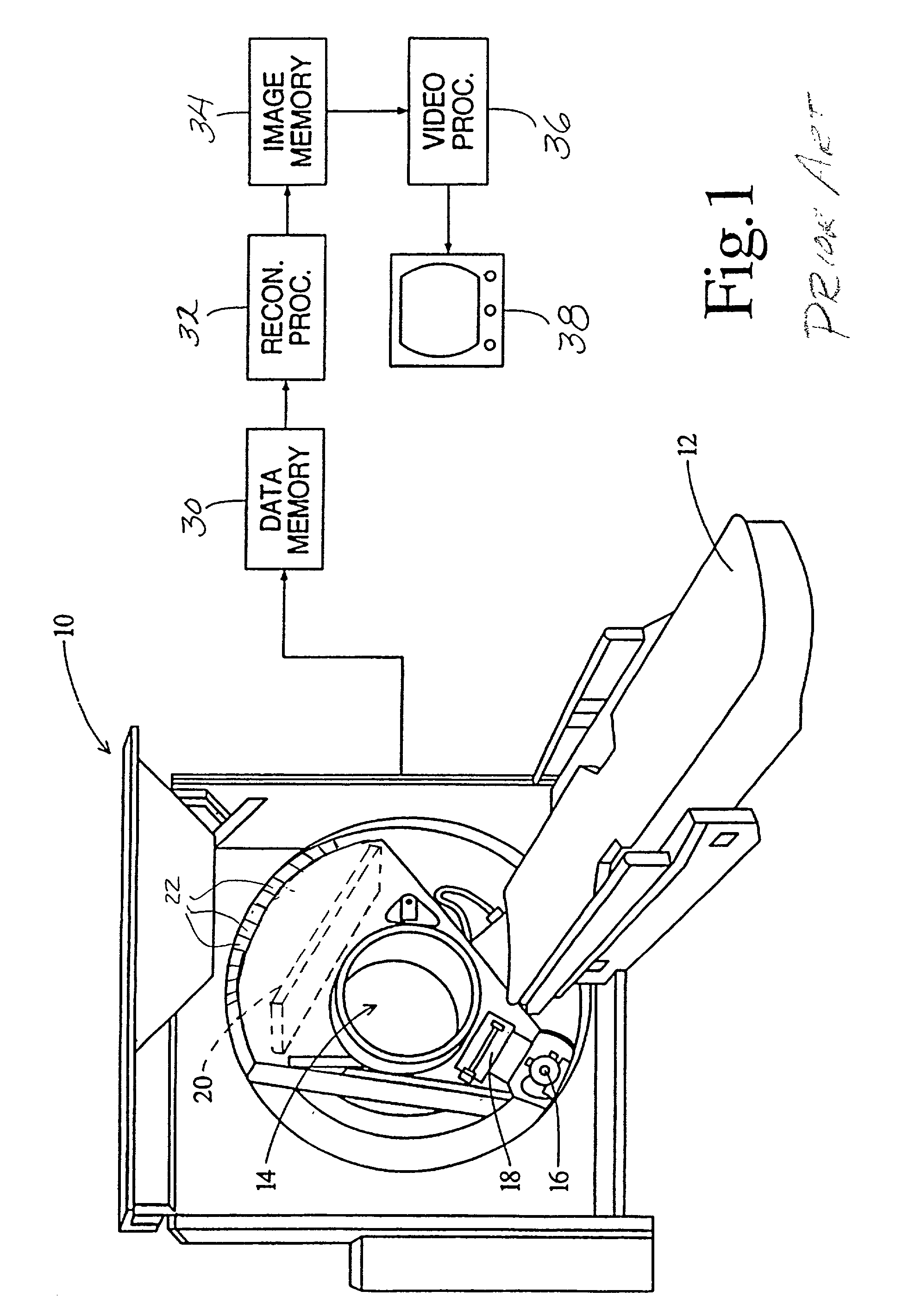
An X-ray tube is a vacuum tube that converts electrical input power into X-rays. The availability of this controllable source of X-rays created the field of radiography, the imaging of partly opaque objects with penetrating radiation. In contrast to other sources of ionizing radiation, X-rays are only produced as long as the X-ray tube is energized. X-ray tubes are also used in CT scanners, airport luggage scanners, X-ray crystallography, material and structure analysis, and for industrial inspection.
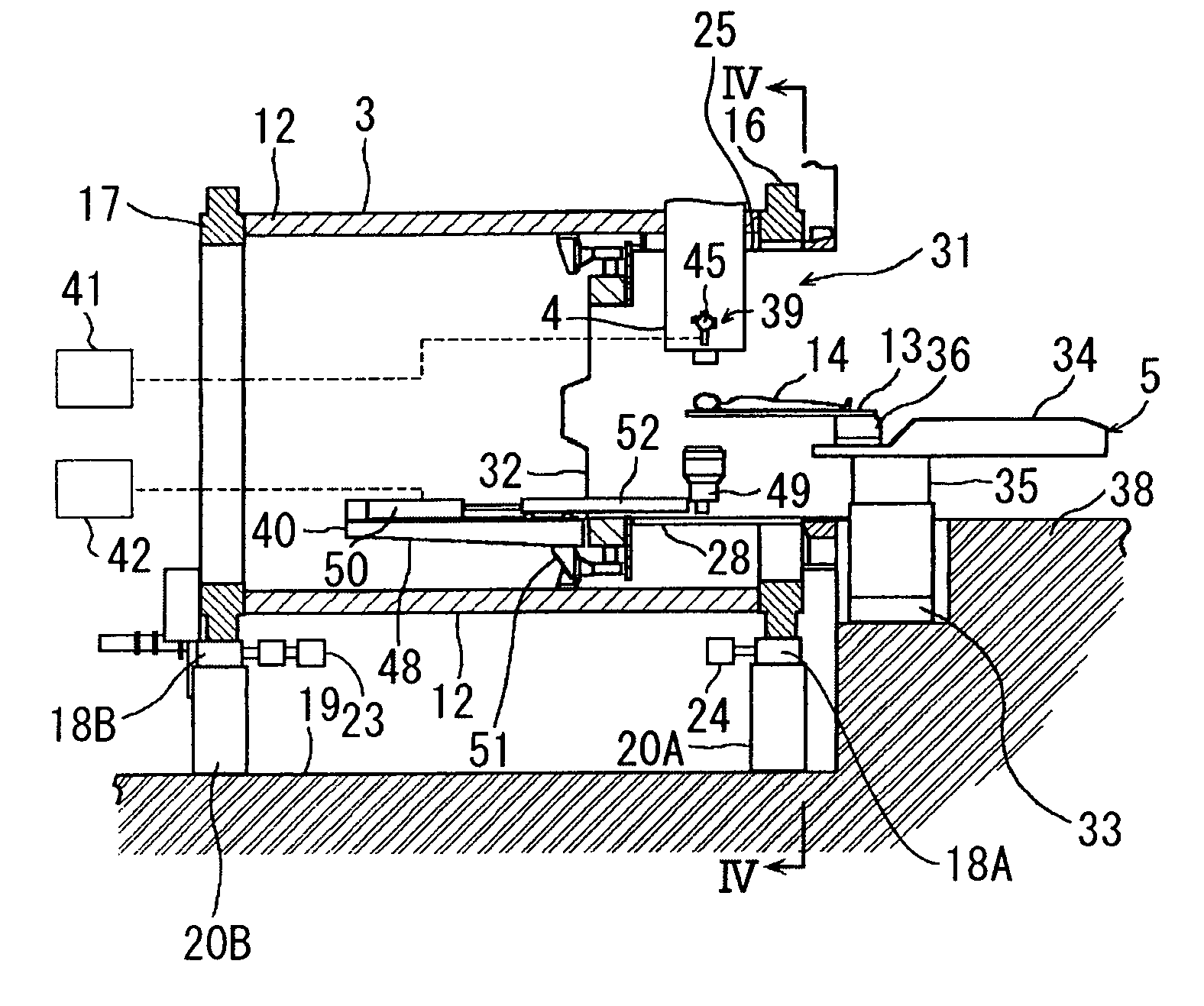
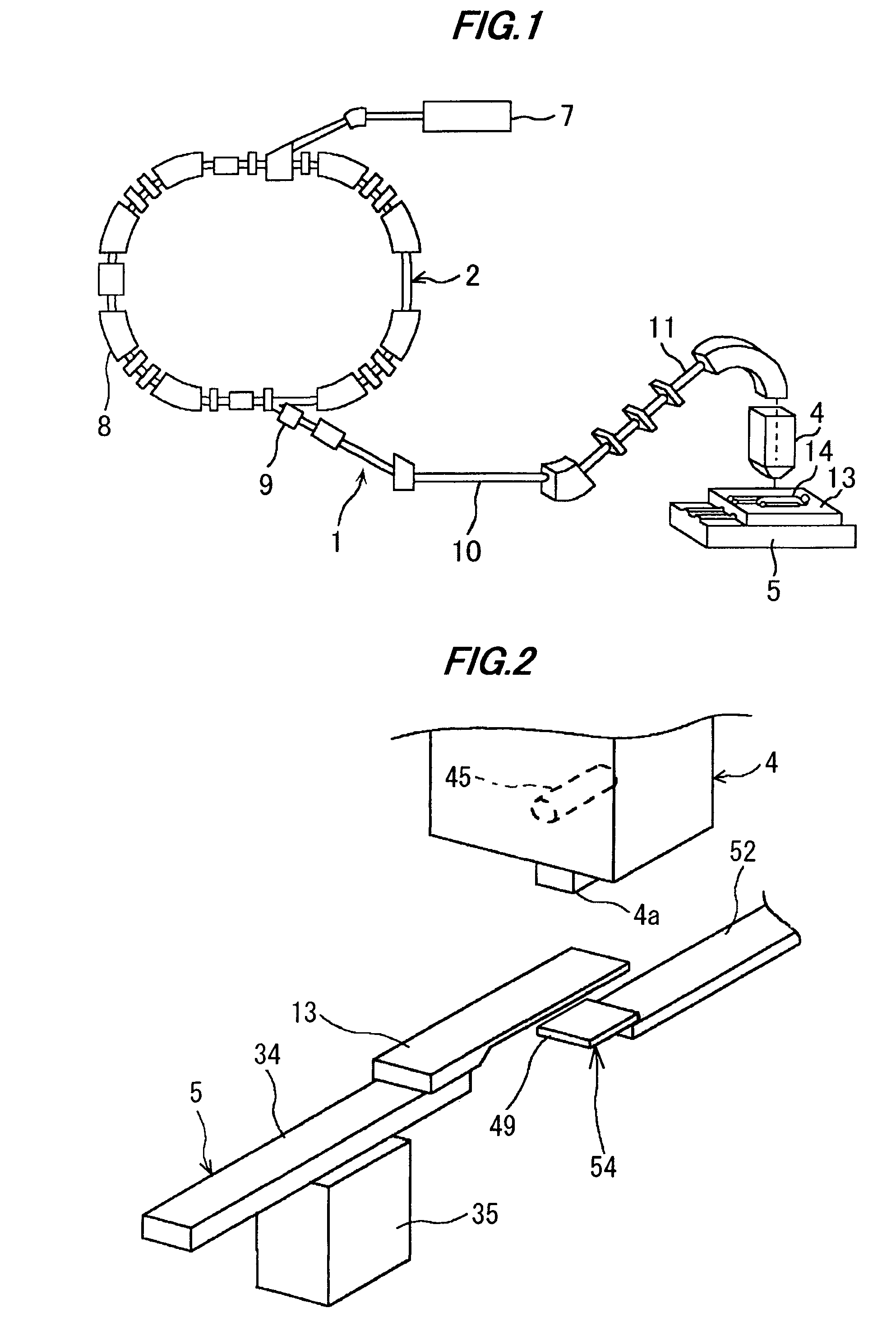
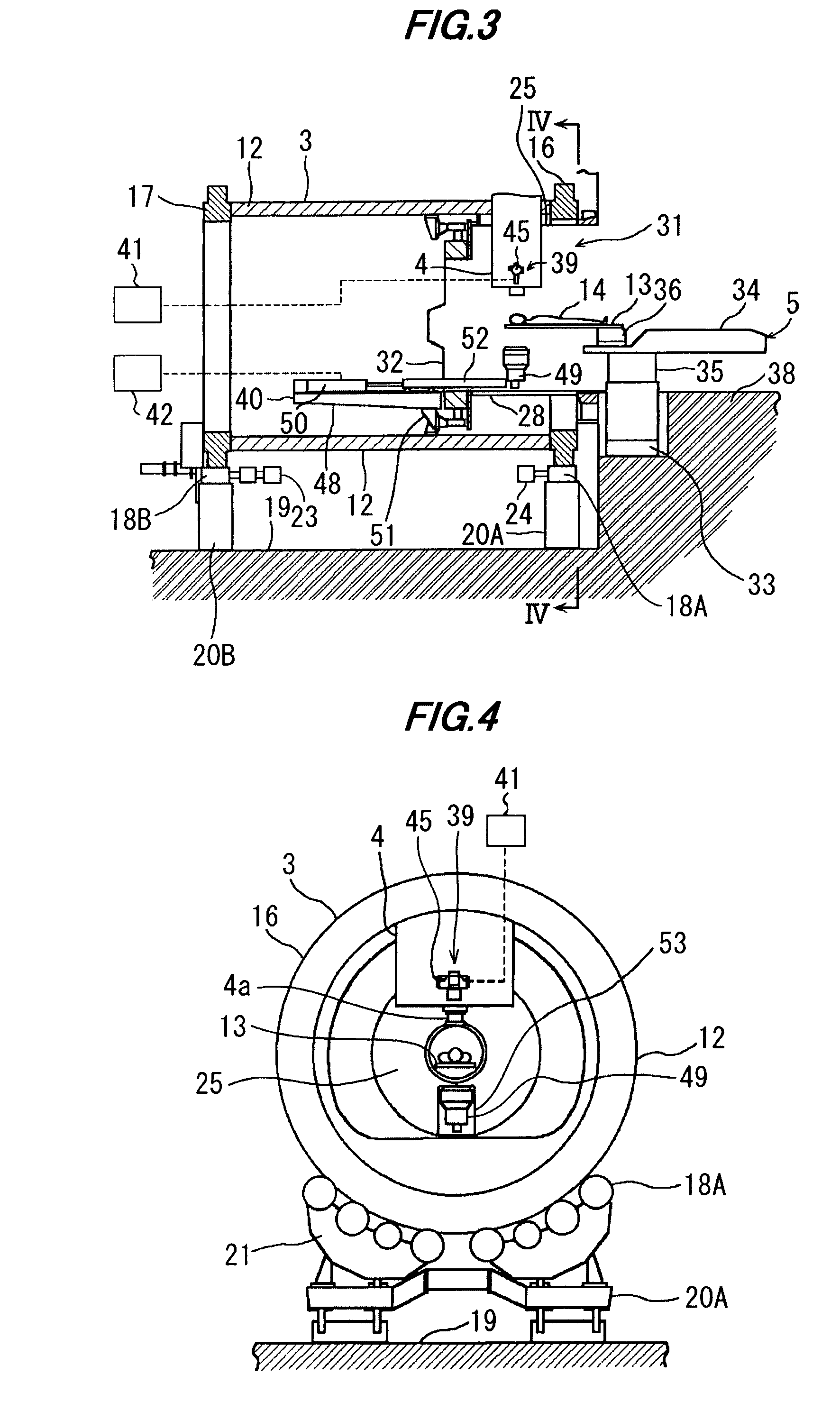
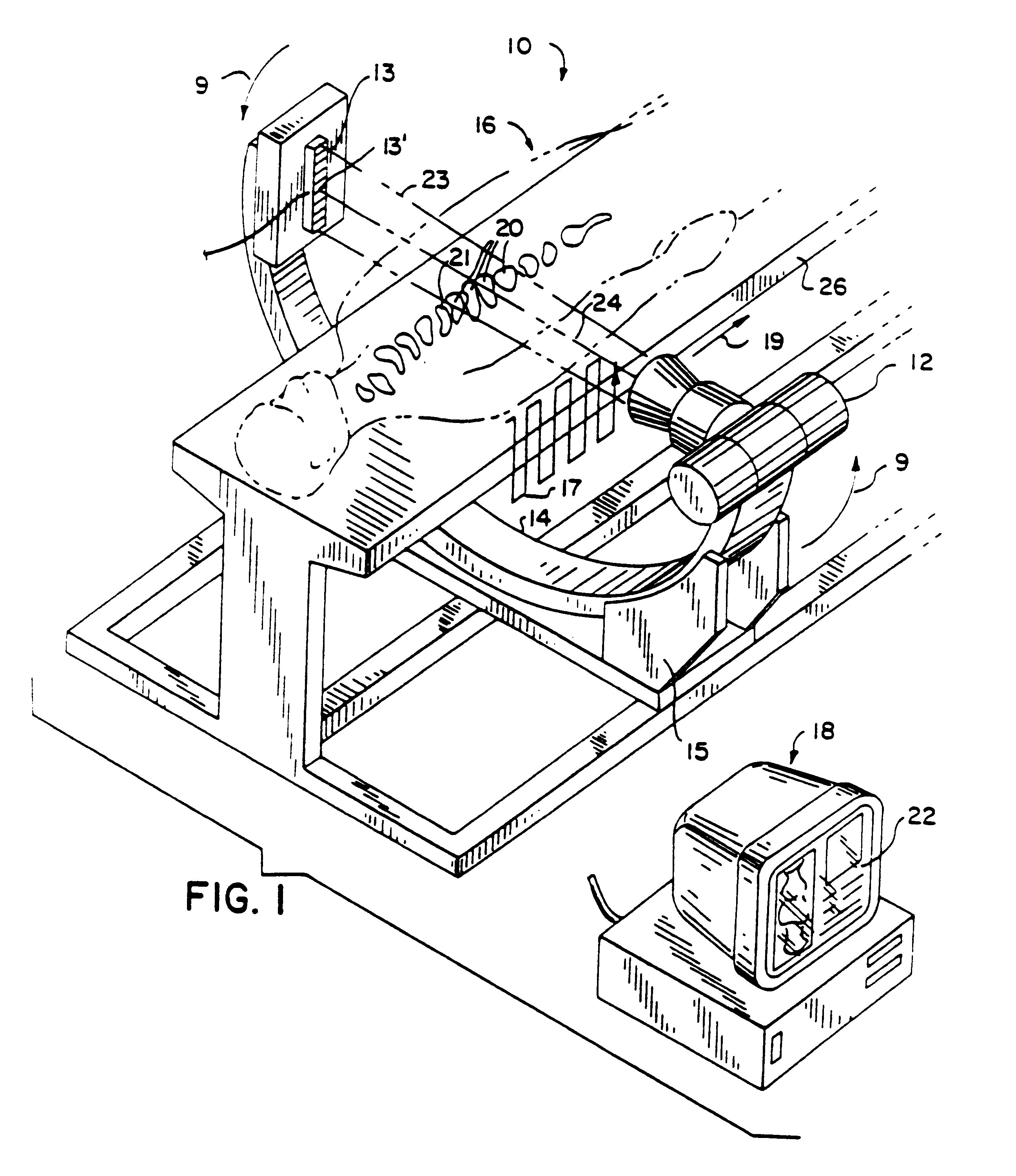
Ion beam therapy system and its couch positioning method
ActiveUS7193227B2Improve accuracyExtension of timeRadiation/particle handlingElectric discharge tubesIon beamX-ray
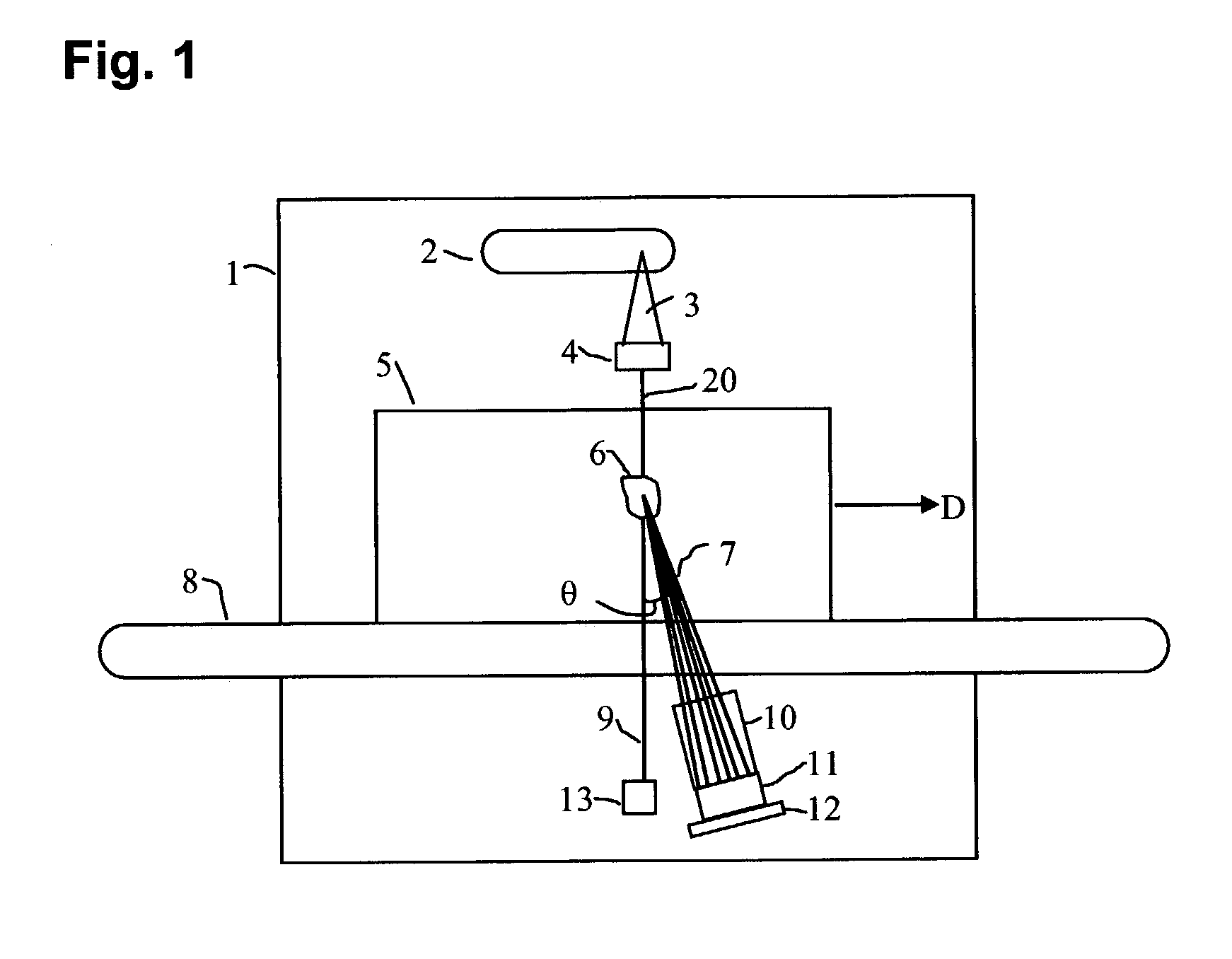
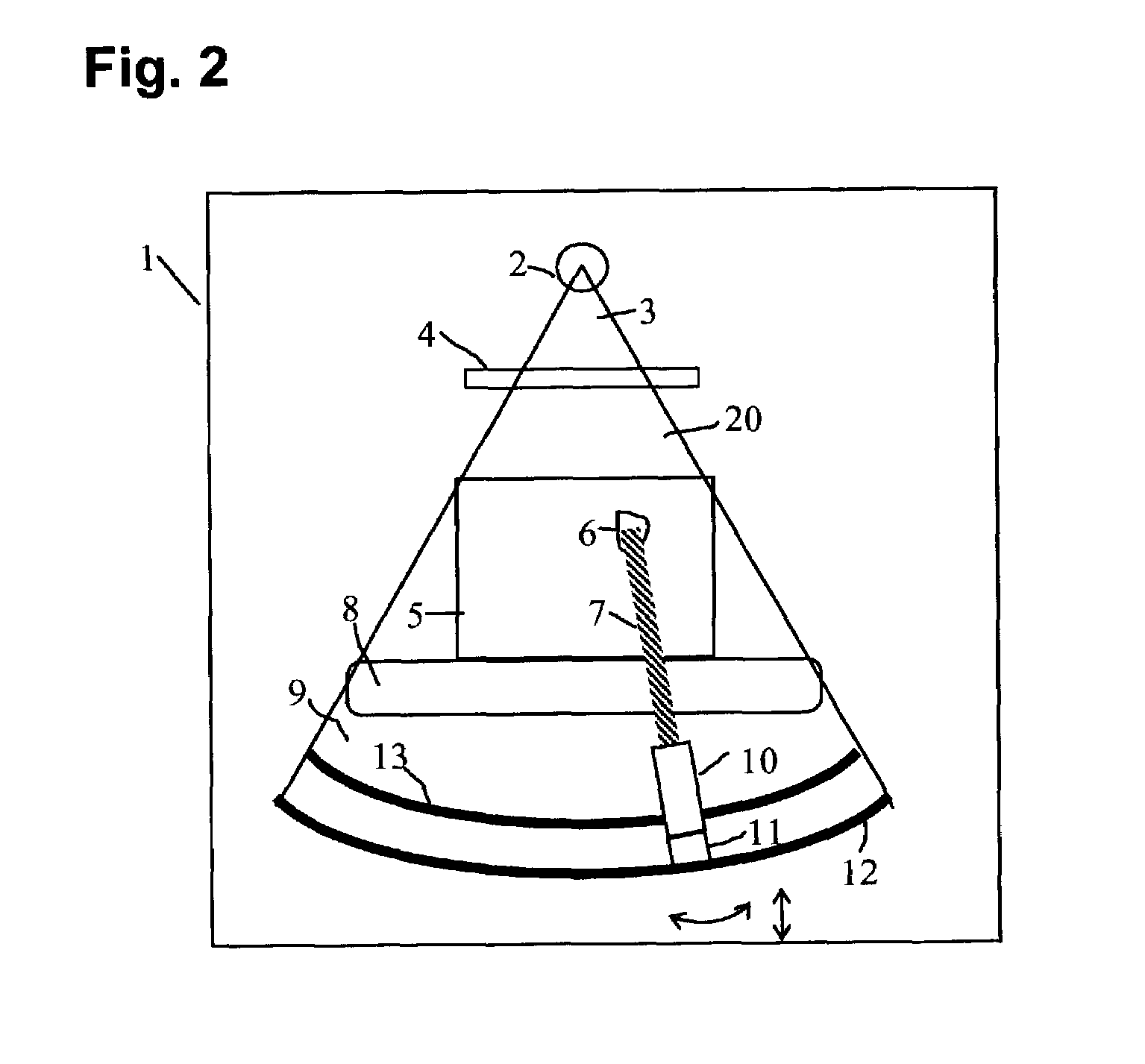
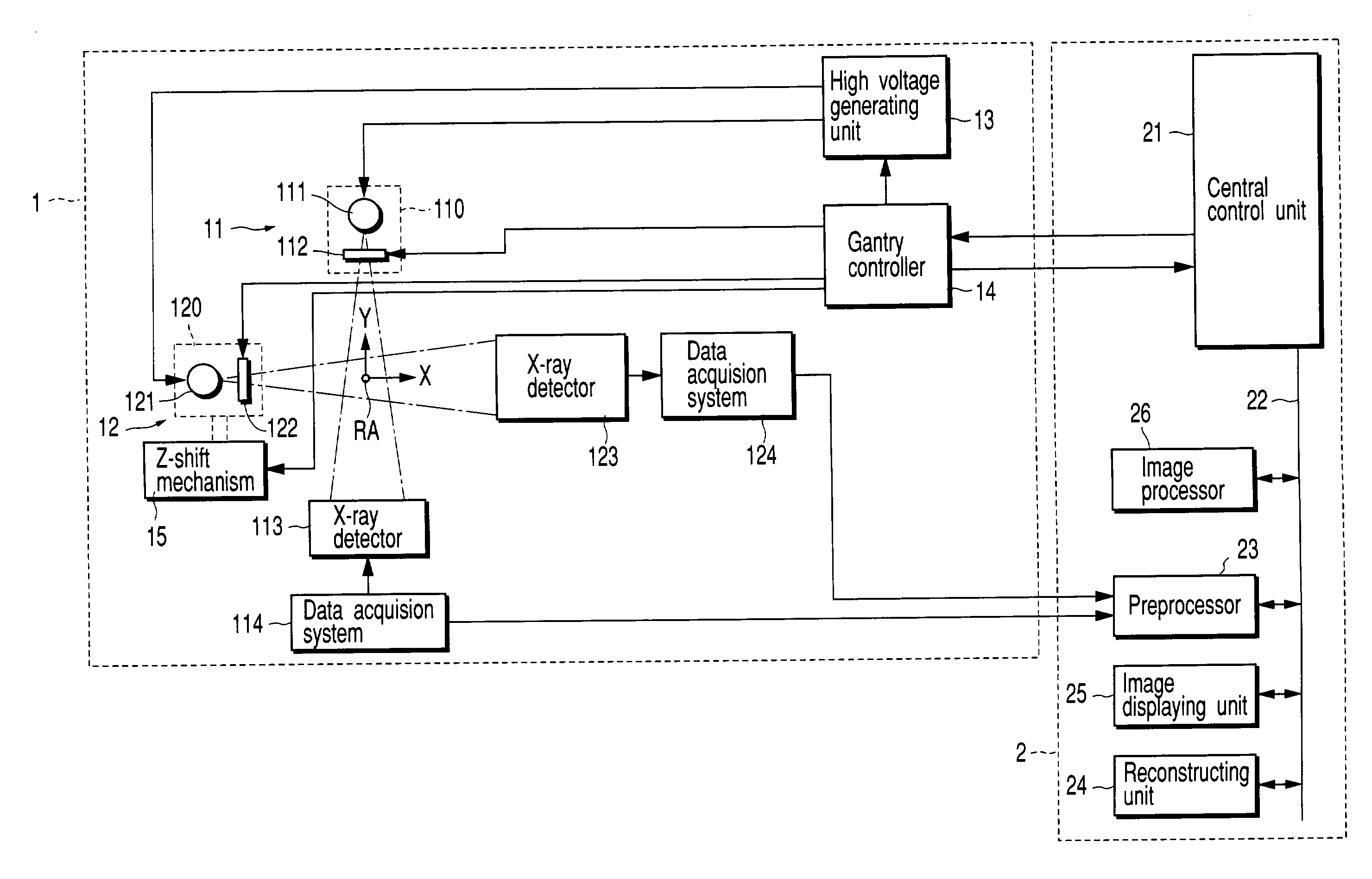
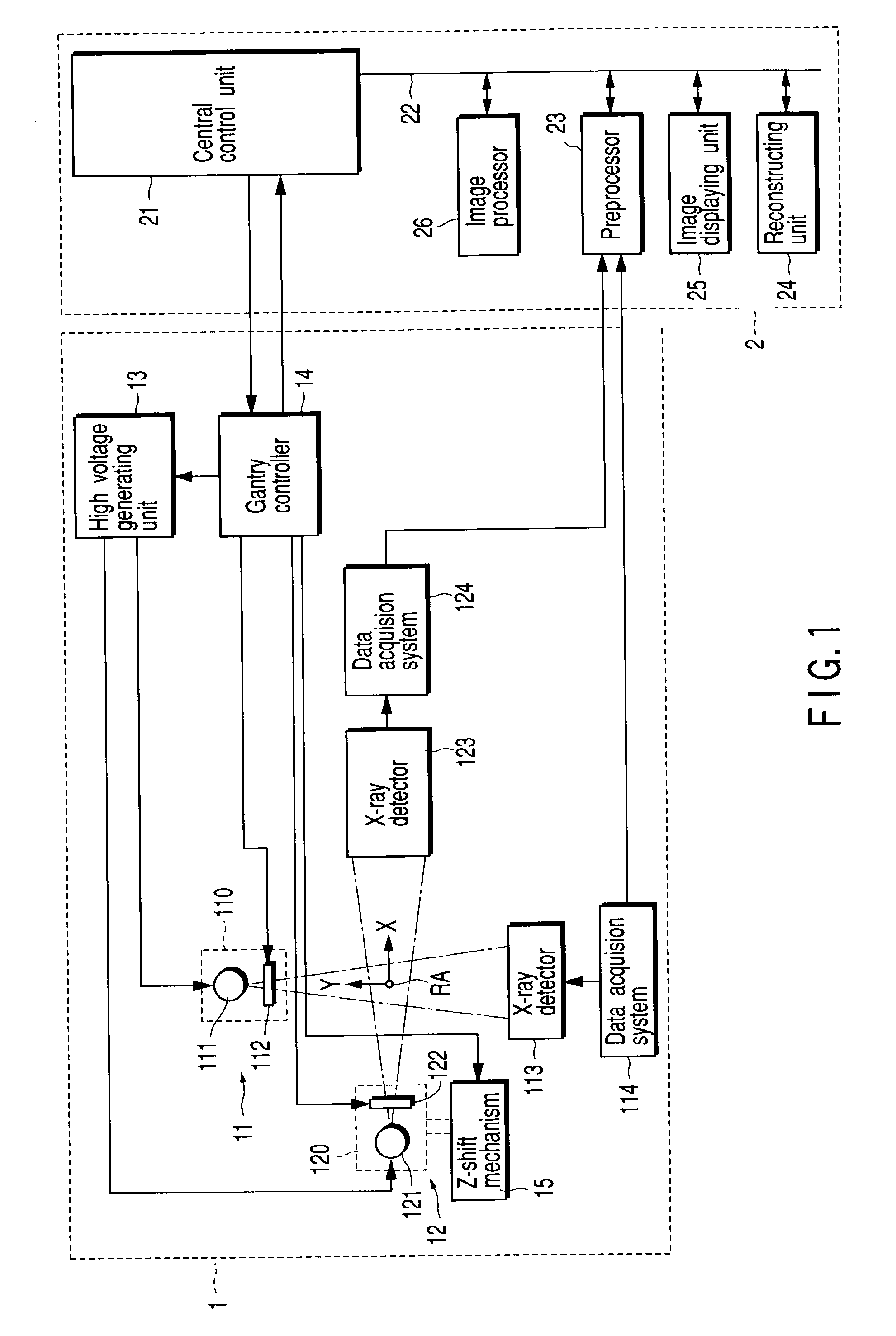
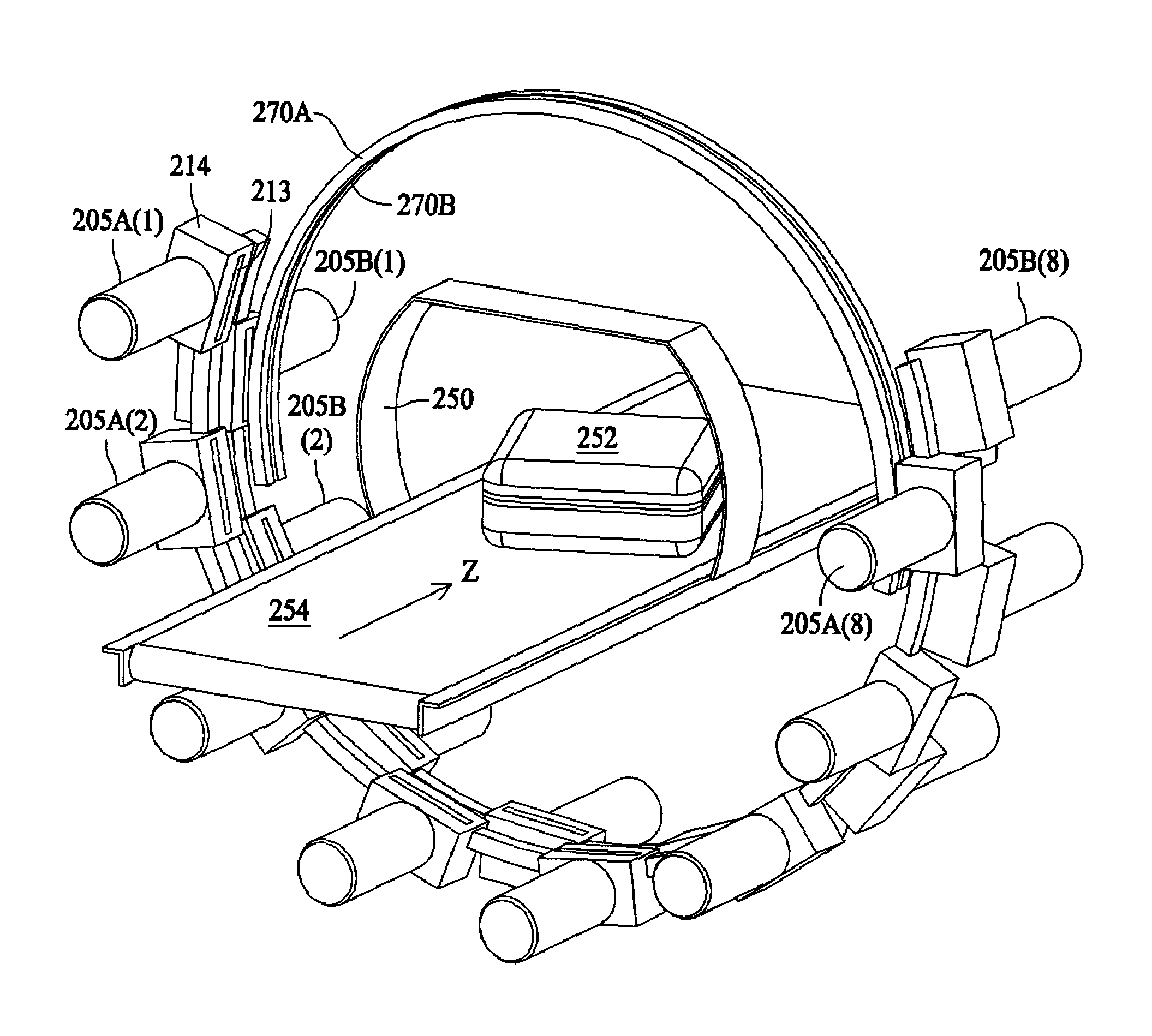
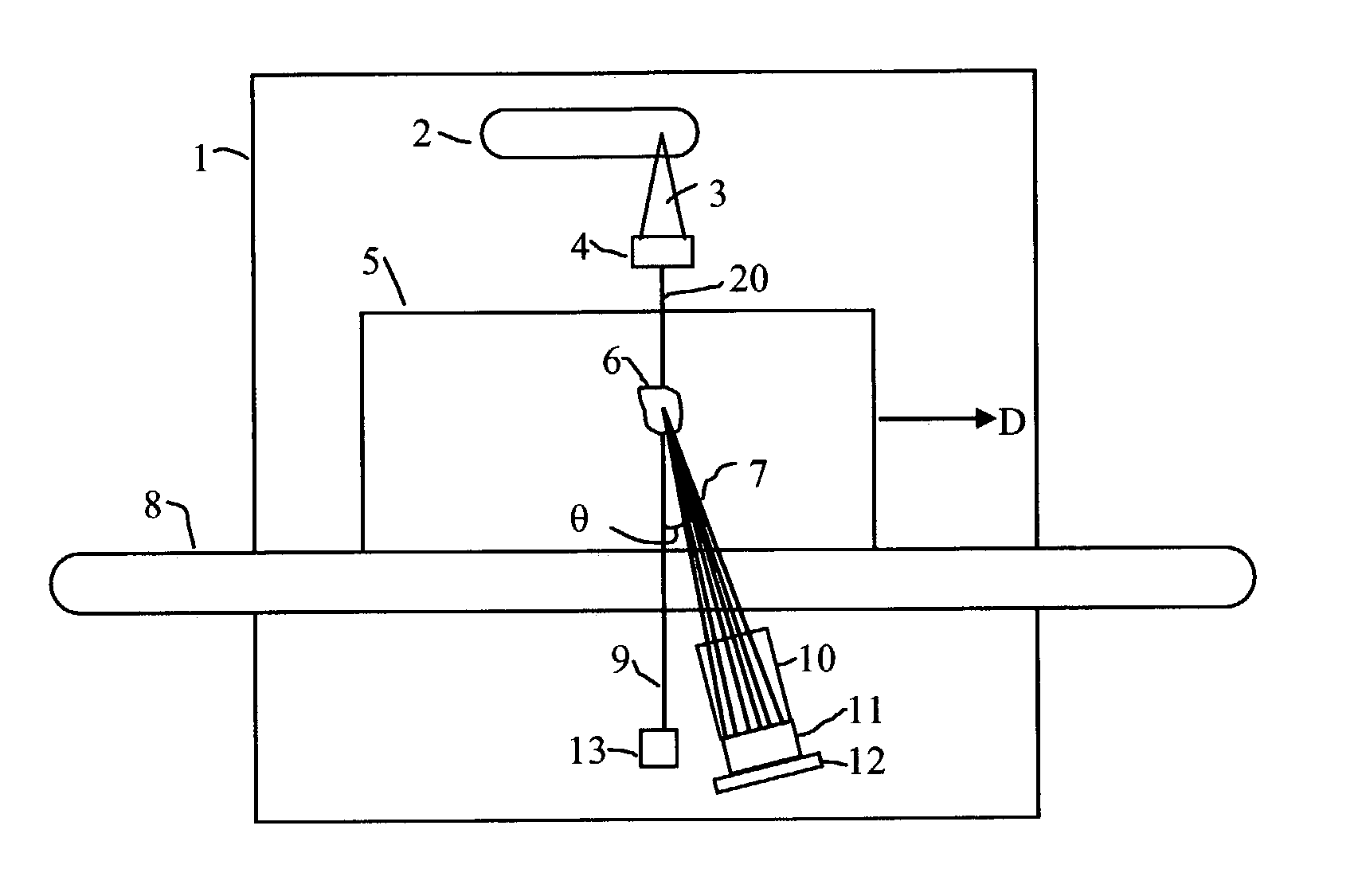
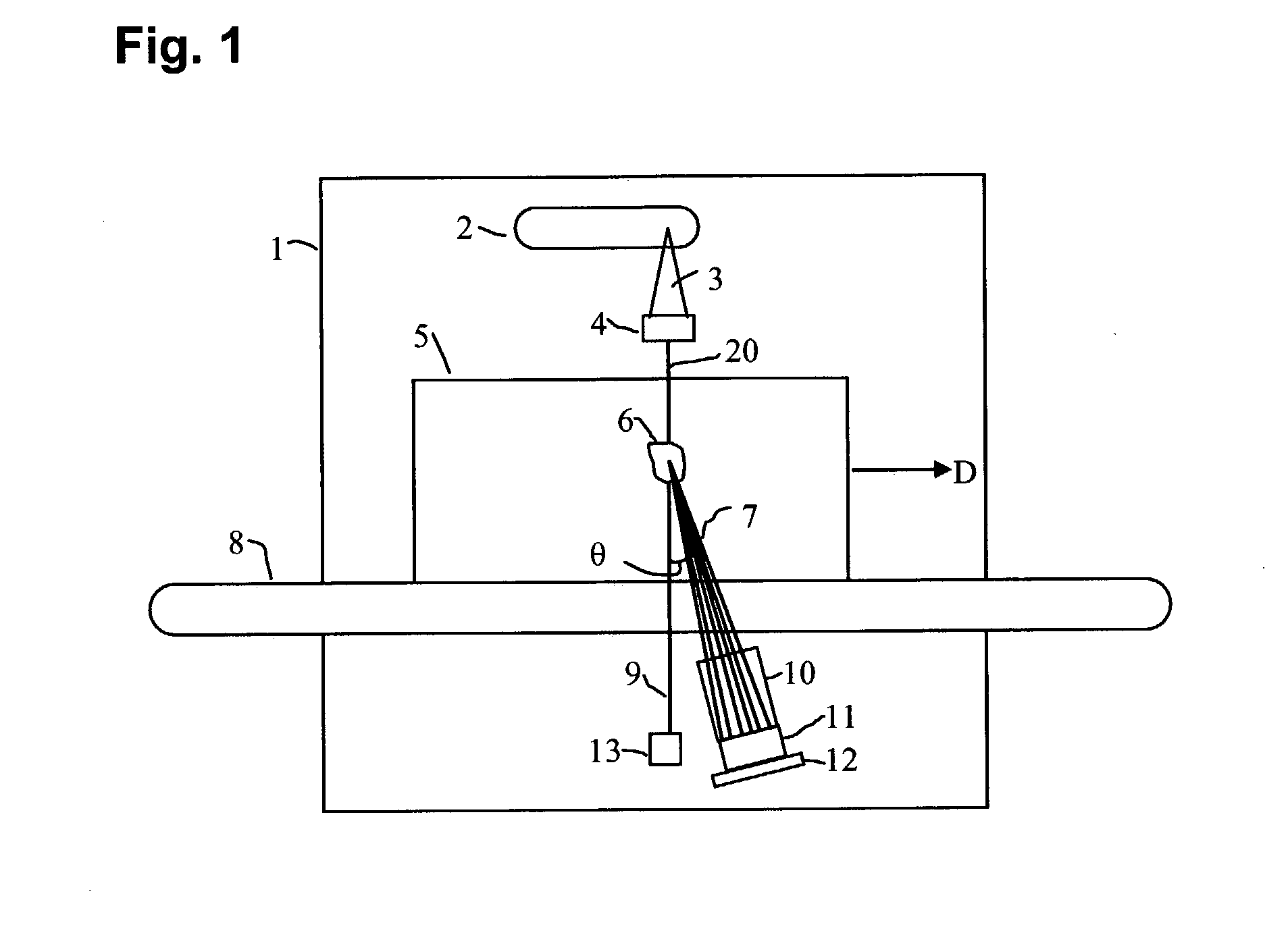
A therapy system using an ion beam, which can shorten the time required for positioning a couch (patient). The therapy system using the ion beam comprises a rotating gantry provided with an ion beam delivery unit including an X-ray tube. An X-ray detecting device having a plurality of X-ray detectors can be moved in the direction of a rotation axis of the rotating gantry. A couch on which a patient is lying is moved until a tumor substantially reaches an extension of an ion beam path in the irradiating unit. The X-ray tube is positioned on the ion beam path and the X-ray detecting device is positioned on the extension of the ion beam path. With rotation of the rotating gantry, both the X-ray tube emitting an X-ray and the X-ray detecting device revolve around the patient. The X-ray is emitted to the patient and detected by the X-ray detectors after penetrating the patient. Tomographic information of the patient is formed based on signals outputted from the X-ray detectors. Information for positioning the couch is generated by using the tomographic information.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST +1
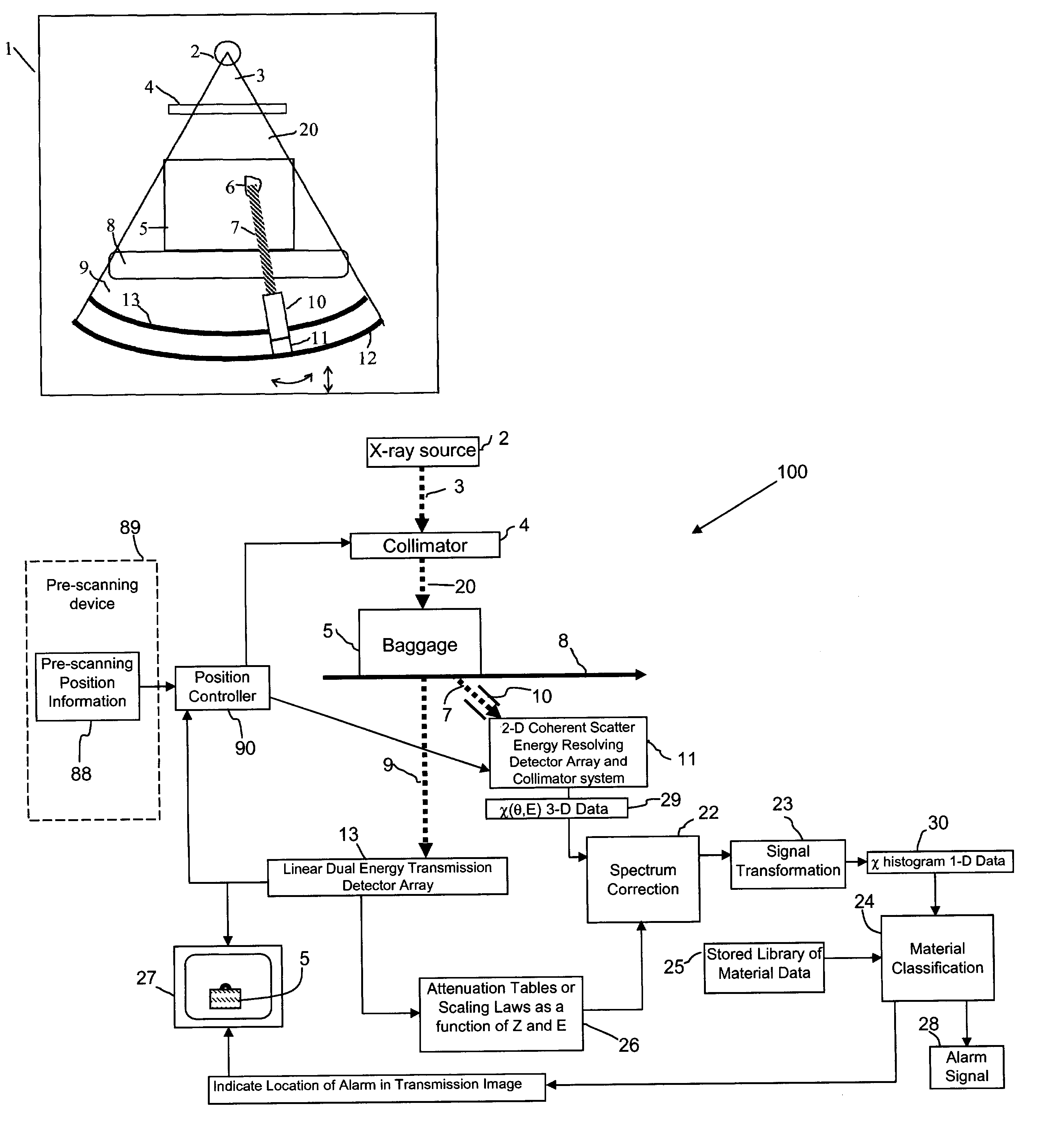
X-ray inspection system for detecting explosives and other contraband
InactiveUS7092485B2Rapidly and accurately discriminates among different substancesQuick checkUsing wave/particle radiation meansMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationX-rayExplosive material
A baggage scanning system and method employ combined angular and energy dispersive x-ray scanning to detect the presence of a contraband substance within an interrogation volume of a baggage item. The interrogation volume is illuminated with penetrating, polychromatic x-rays in a primary fan beam from a source such as a tungsten-anode x-ray tube. An energy-dependent absorption correction is determined from measurement of the attenuation of the fan beam at a plurality of different energies. Radiation coherently scattered by substances in the interrogation volume is detected by an energy-resolved x-ray detector operated at a plurality of scattering angles to form a plurality of scattering spectra. Each scattering spectrum is corrected for energy-dependent absorption and the corrected spectra are combined to produce a scattering pattern. The experimental scattering pattern is compared with reference patterns that uniquely characterize known contraband substances. The system and method can locate and identify a wide variety of contraband substances in an accurate, reliable manner. The system provides for automated screening, with the result that vagaries of human performance are virtually eliminated. False alarms and the need for hand inspection are reduced and detection efficacy is increased.
Owner:CONTROL SCREENING
X-ray computed tomography apparatus
InactiveUS6990175B2High positioning accuracyMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationHandling using diaphragms/collimetersSoft x rayBody axis
An X-ray computed tomography apparatus includes a first X-ray tube configured to generate X-rays with which a subject to be examined is irradiated, a first X-ray detector configured to detect X-rays transmitted through the subject, a second X-ray tube which generates X-rays with which a treatment target of the subject is irradiated, a rotating mechanism which rotates the first X-ray tube, the first X-ray detector, and the second X-ray tube around the subject, a reconstructing unit configured to reconstruct an image on the basis of data detected by the first X-ray detector, and a support mechanism which supports the second X-ray tube. The central axis of X-rays from the second X-ray tube tilts with respect to a body axis of the subject. This makes it possible to reduce the dose on a portion other than a treatment target.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
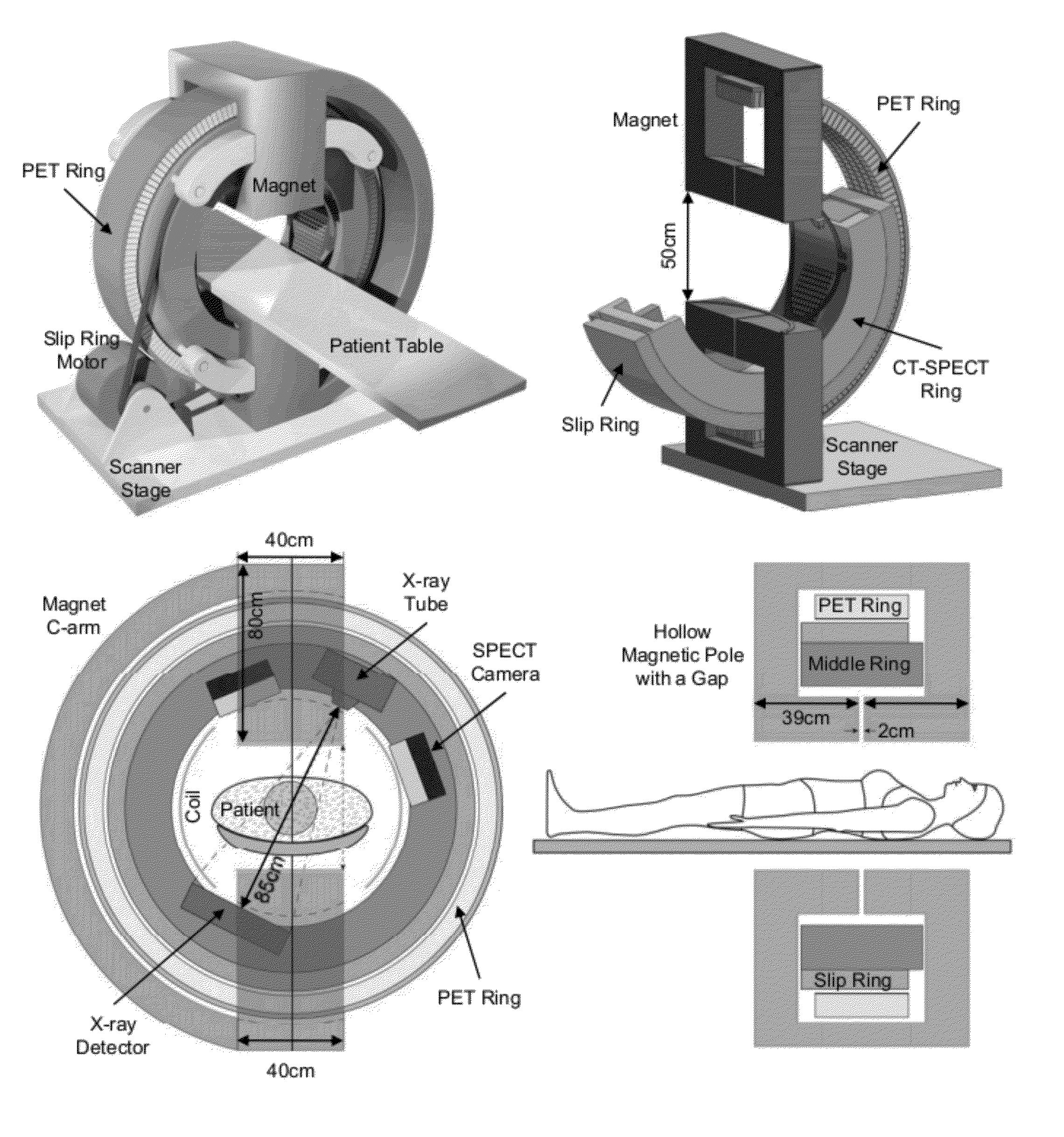
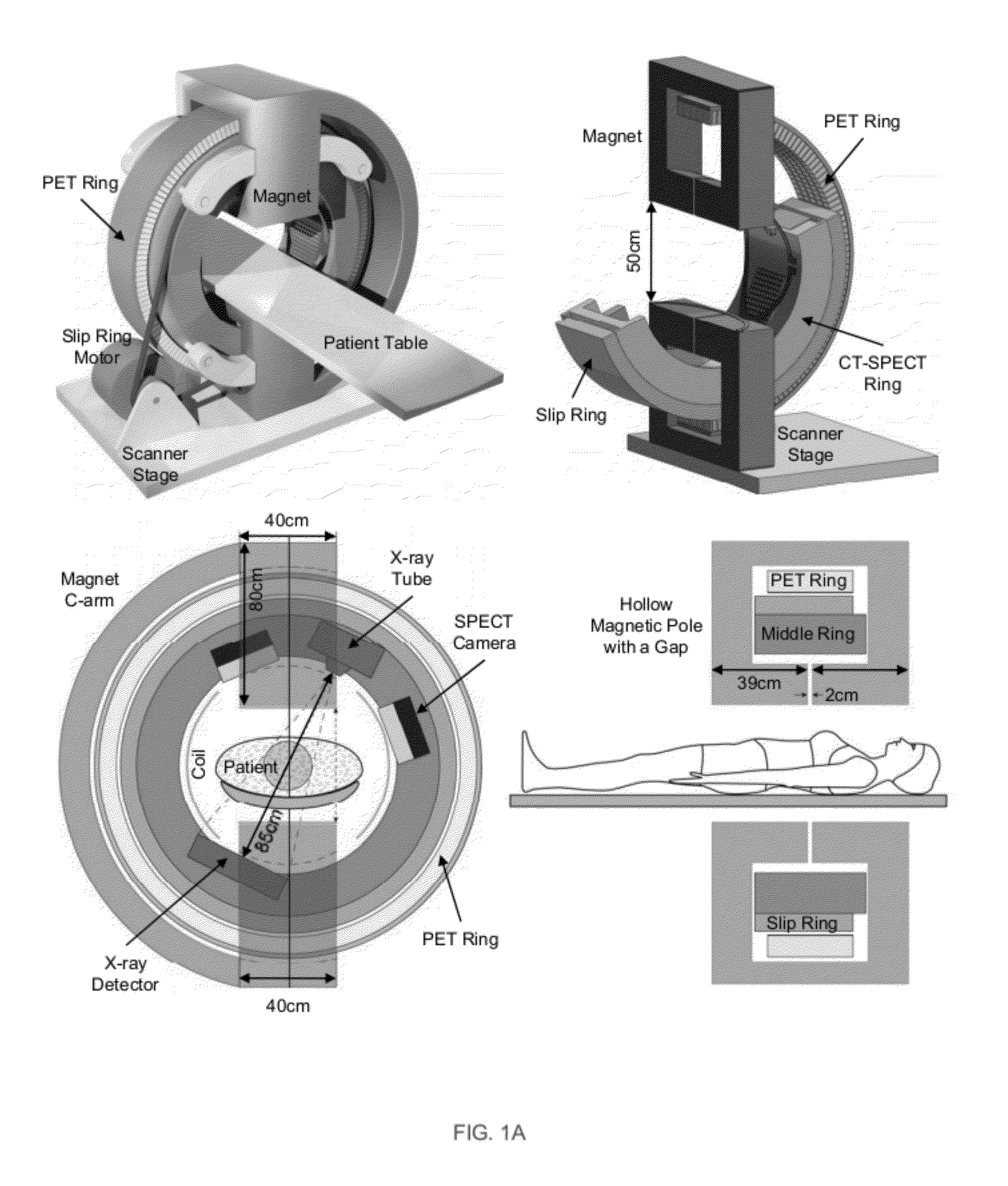
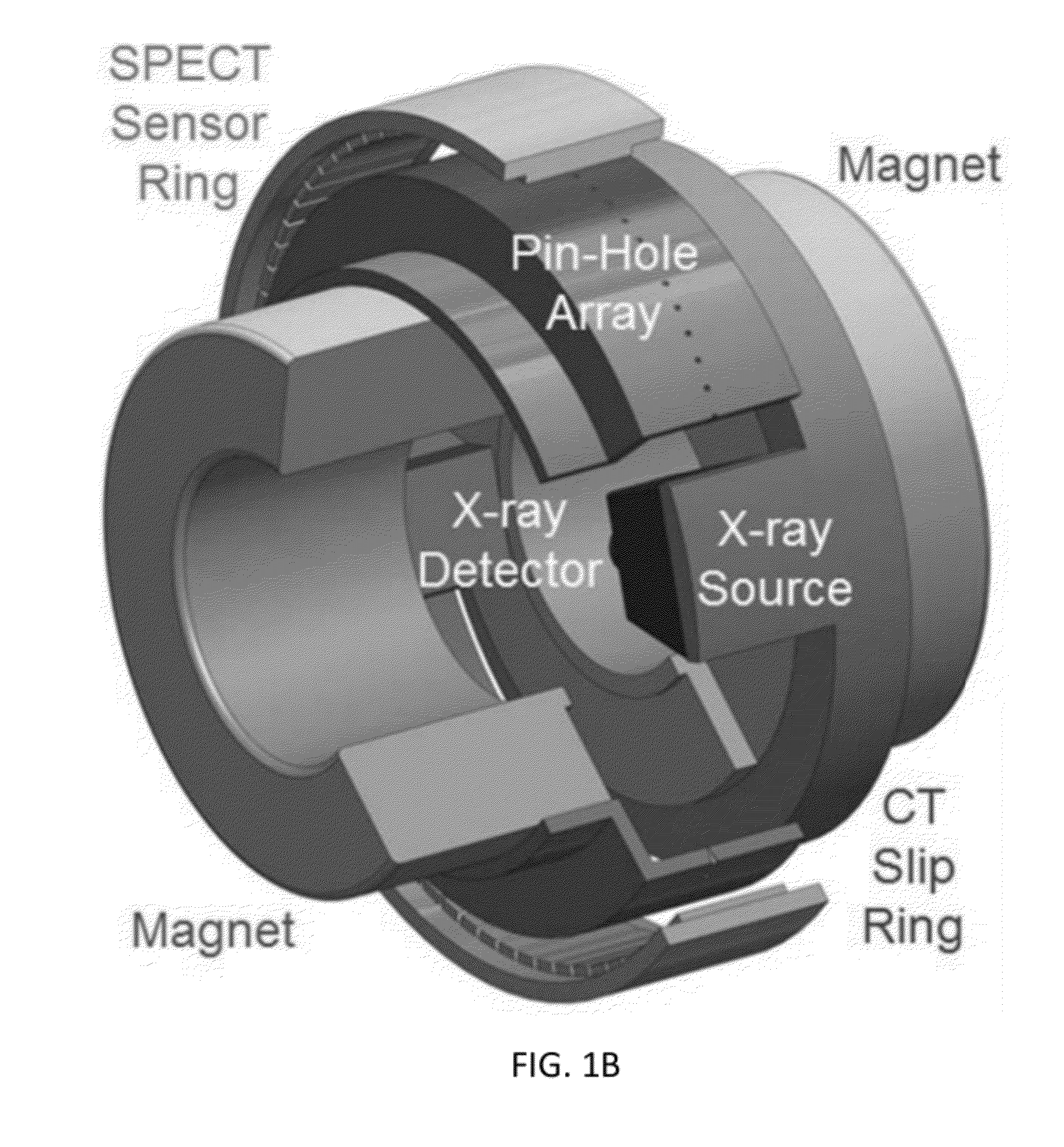
Omni-Tomographic Imaging for Interior Reconstruction using Simultaneous Data Acquisition from Multiple Imaging Modalities
InactiveUS20120265050A1Less importantLow costUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic Radiology ModalityModern medicine
Embodiments of the invention relate to omni-tomographic imaging or grand fusion imaging, i.e., large scale fusion of simultaneous data acquisition from multiple imaging modalities such as CT, MRI, PET, SPECT, US, and optical imaging. A preferred omni-tomography system of the invention comprises two or more imaging modalities operably configured for concurrent signal acquisition for performing ROI-targeted reconstruction and contained in a single gantry with a first inner ring as a permanent magnet; a second middle ring containing an x-ray tube, detector array, and a pair of SPECT detectors; and a third outer ring for containing PET crystals and electronics. Omni-tomography offers great synergy in vivo for diagnosis, intervention, and drug development, and can be made versatile and cost-effective, and as such is expected to become an unprecedented imaging platform for development of systems biology and modern medicine.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
Computed tomographic scanner using rastered x-ray tubes
ActiveUS7233644B1Reduce coolingReduced Power RequirementsRadiation/particle handlingX-ray apparatusComputing tomographyComputed tomography scanner
A high speed computed tomography x-ray scanner using a plurality of x-ray generators. Each x-ray generator is scanned along a source path that is a segment of the scanner's source path such that each point in the source path is scanned by at least one tube. X-ray generators and detectors can be arranged in different scan planes depending on the available hardware so that a complete and near planar scan of a moving object can be assembled and reconstructed into an image of the object.
Owner:MORPHO DETECTION INC
X-ray apparatus
ActiveUS7796728B2Improve performanceIncrease capacityHandling using diaphragms/collimetersComputerised tomographsTwo dimensional detectorX-ray
An investigative X-ray apparatus comprises a source of X-rays emitting a cone beam centred on a beam axis, a collimator to limit the extent of the beam, and a two-dimensional detector, the apparatus being mounted on a support which is rotatable about a rotation axis, the collimator having a first state in which the collimated beam is directed towards the rotation axis and the second state in which the collimated beam is offset from the rotation axis, the two-dimensional detector being movable accordingly, the beam axis being offset from the rotation axis by a lesser amount than the collimated beam in the second state. The X-ray source is no longer directed towards the isocentre as would normally be the case; the X-ray source is not orthogonal to the collimators. This is advantageous in that the entire field of the X-ray tube can be utilised. As a result, a lesser field is required of the X-ray tube and the choice of tube designs and capacities can be widened so as to optimise the performance of the X-ray tube in other aspects.
Owner:ELEKTA AB
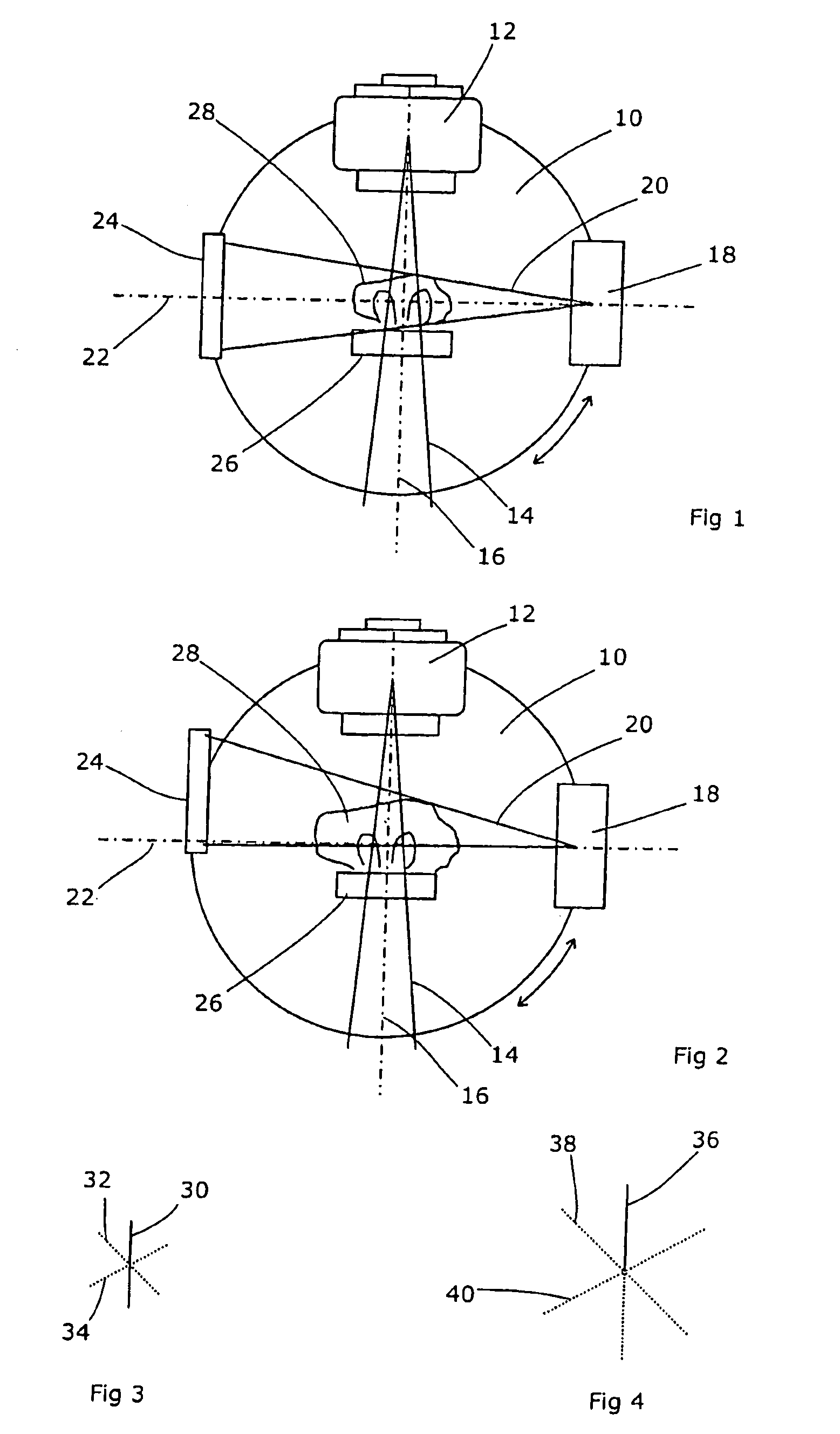
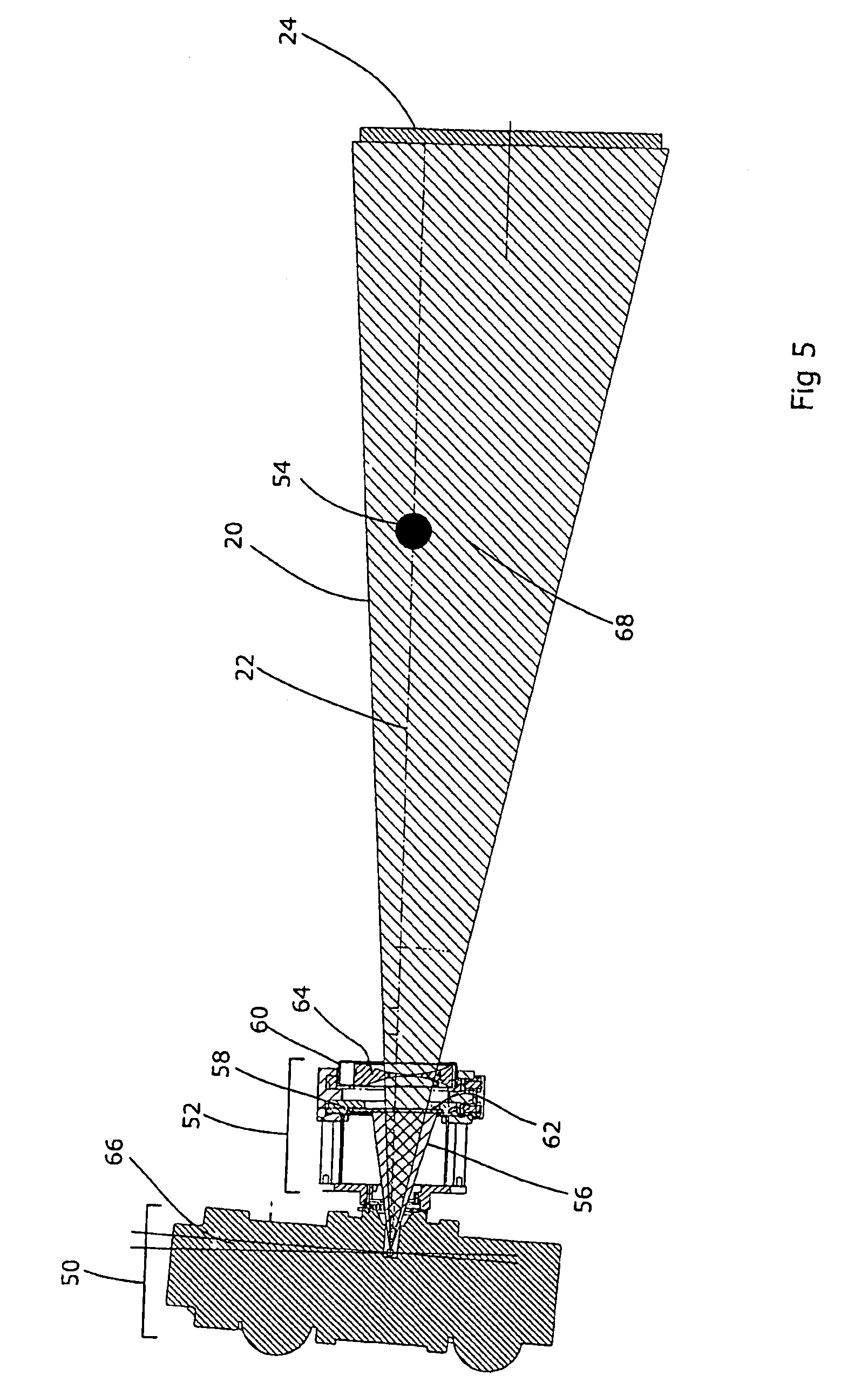
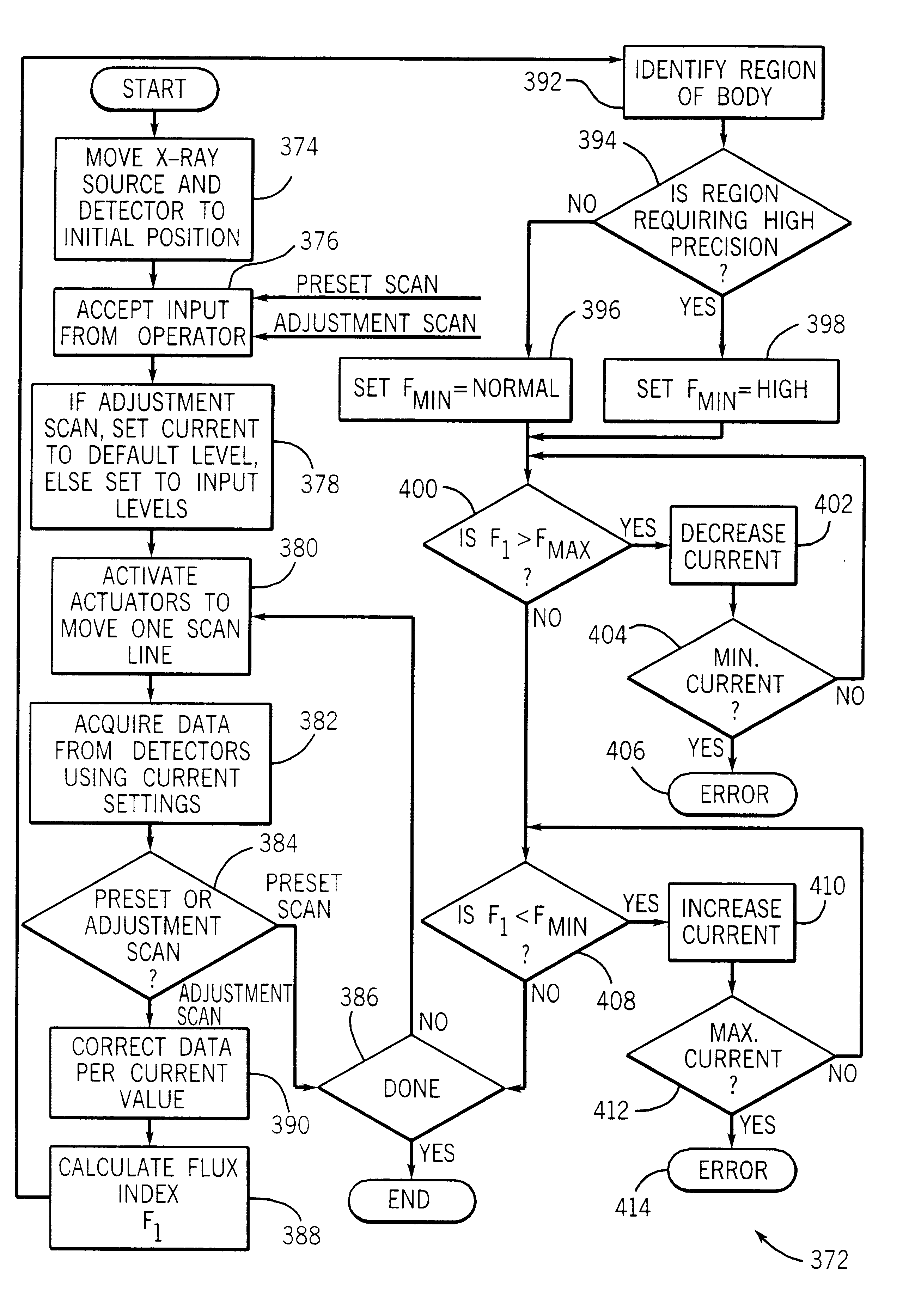
Scanning densitometry system with adjustable X-ray tube current
InactiveUS6438201B1Effectively continuous adjustmentEffective regulationImage enhancementImage analysisBone densityX-Ray Tube Current
A dual energy scanning densitometry system for imaging and measuring bone density maintains acceptable flux by adjusting the x-ray current or scan speed according to preceding scan line data. The amount of acceptable flux is maintained within limits modified by information about the region of the body being scanned so that different precisions may be maintained for different body regions. Scan speed and current may be controlled so that scan speed is maximized within the current limits. Essentially continuous flux control can be achieved.
Owner:LUNAR CORP
Method of and system for intravenous volume tomographic digital angiography imaging
InactiveUS6075836AQuality improvementEfficient contrastMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingCt scannersData acquisition
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
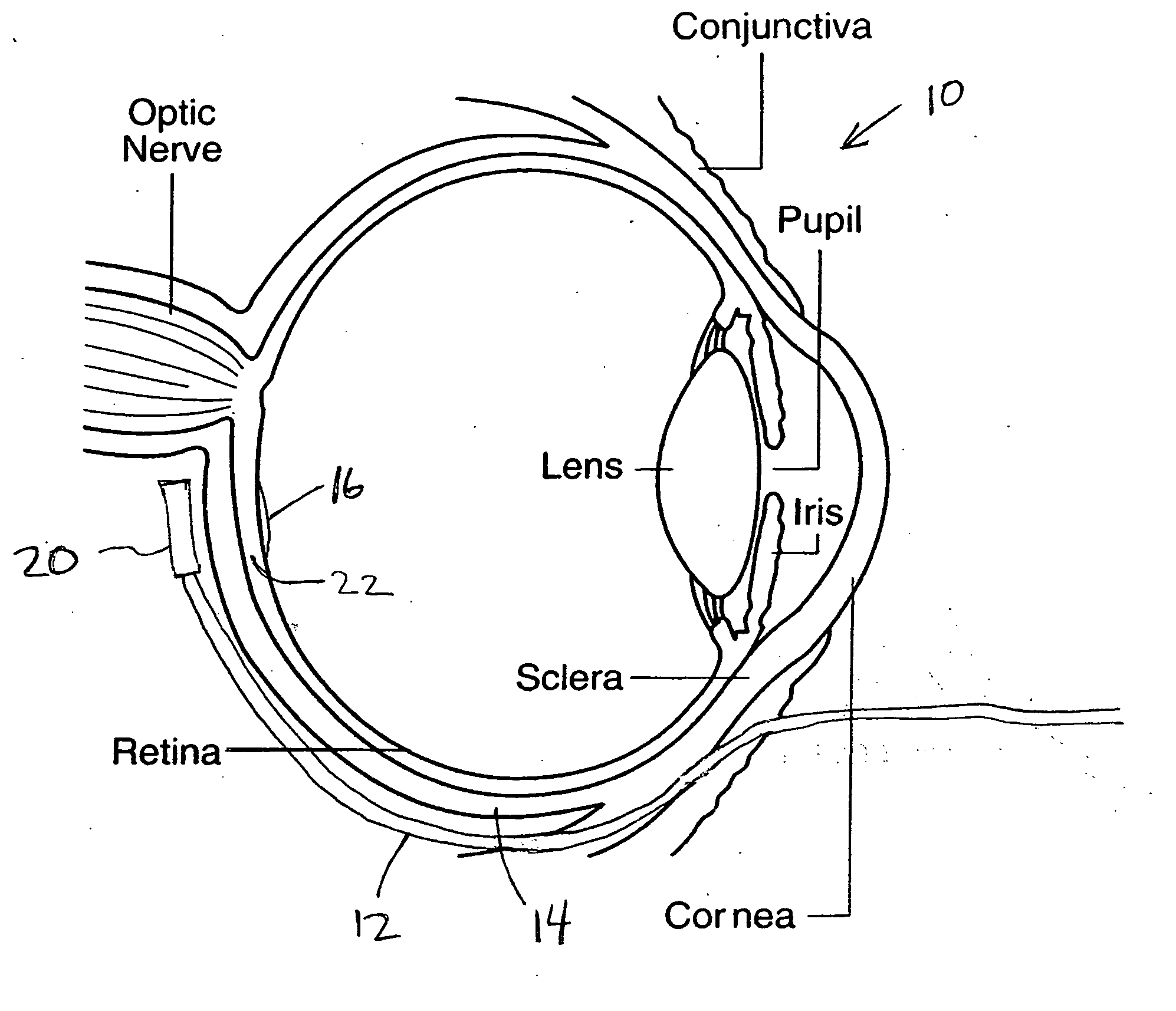
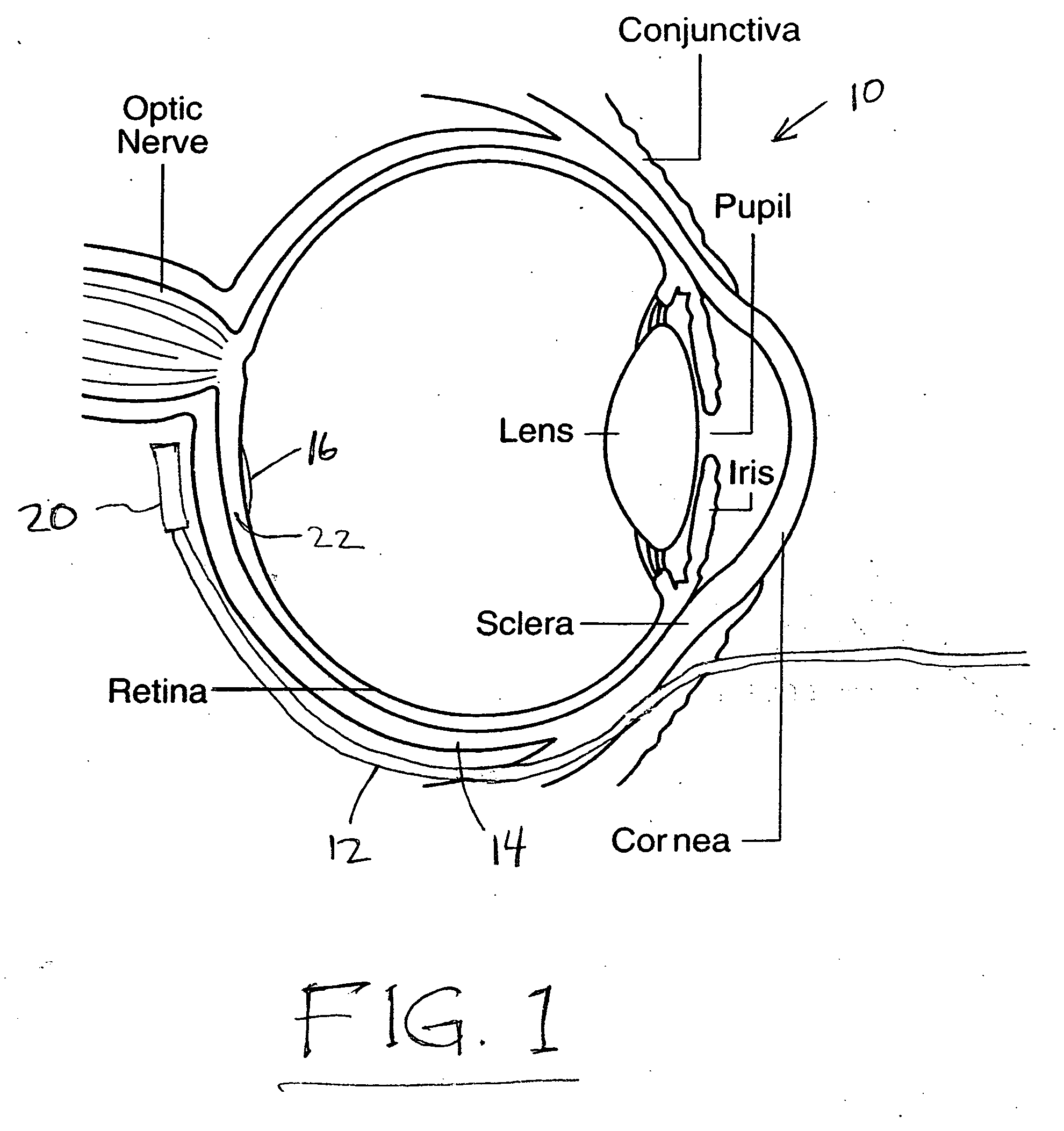
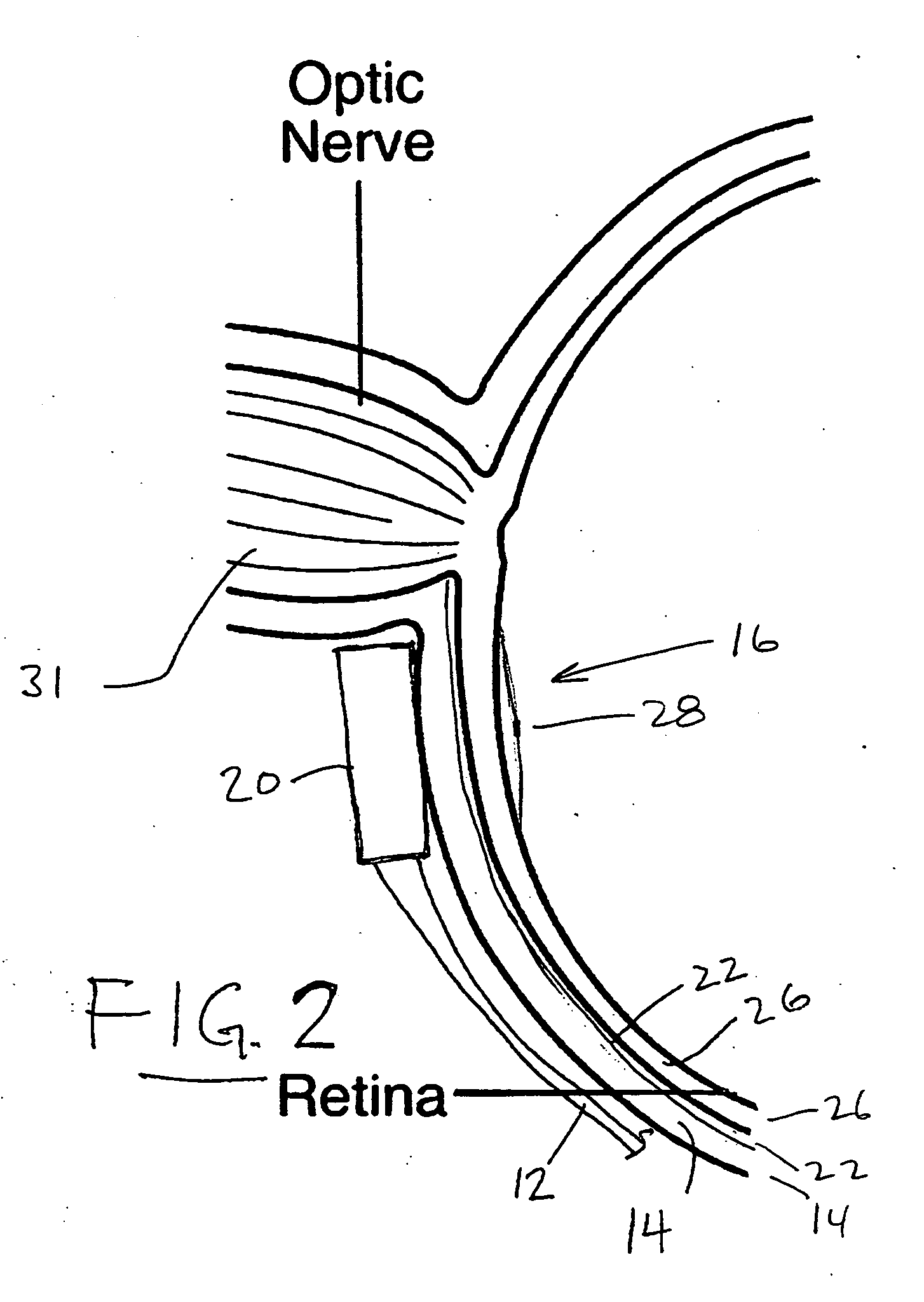
Treatment of age-related macular degeneration
Owner:XOFT INC +1
Method and apparatus for controlling electron beam current
InactiveUS7085351B2High emitted electron current densityHigh electron beam currentStatic indicating devicesNanoinformaticsHigh energyX-ray
An x-ray generating device includes a field emission cathode formed at least partially from a nanostructure-containing material having an emitted electron current density of at least 4 A / cm2. High energy conversion efficiency and compact design are achieved due to easy focusing of cold cathode emitted electrons and dramatic reduction of heating at the anode. In addition, by pulsing the field between the cathode and the gate or anode and focusing the electron beams at different anode materials, pulsed x-ray radiation with varying energy can be generated from a single device. Methods and apparatus for independent control of electron emission current and x-ray energy in x-ray tubes are also provided. The independent control can be accomplished by adjusting the distance between the cathode and anode. The independent control can also be accomplished by adjusting the temperature of the cathode. The independent control can also be accomplished by optical excitation of the cathode. The cathode can include field emissive materials such as carbon nanotubes.
Owner:THE UNIV OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHAPEL HILL
Cone beam volume CT angiography imaging system and method
InactiveUS6298110B1Quality improvementEfficient contrastMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingCt scannersX-ray
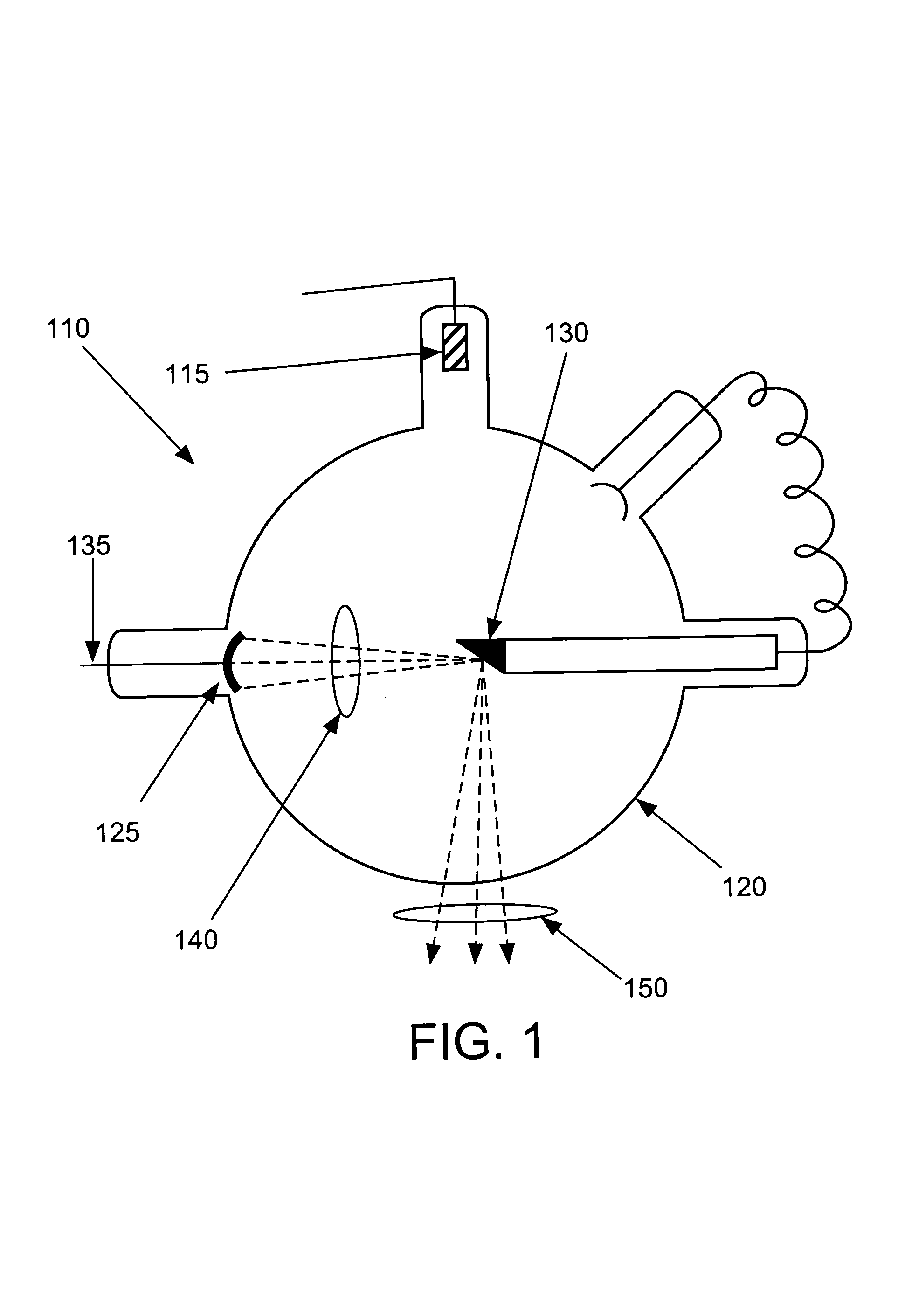
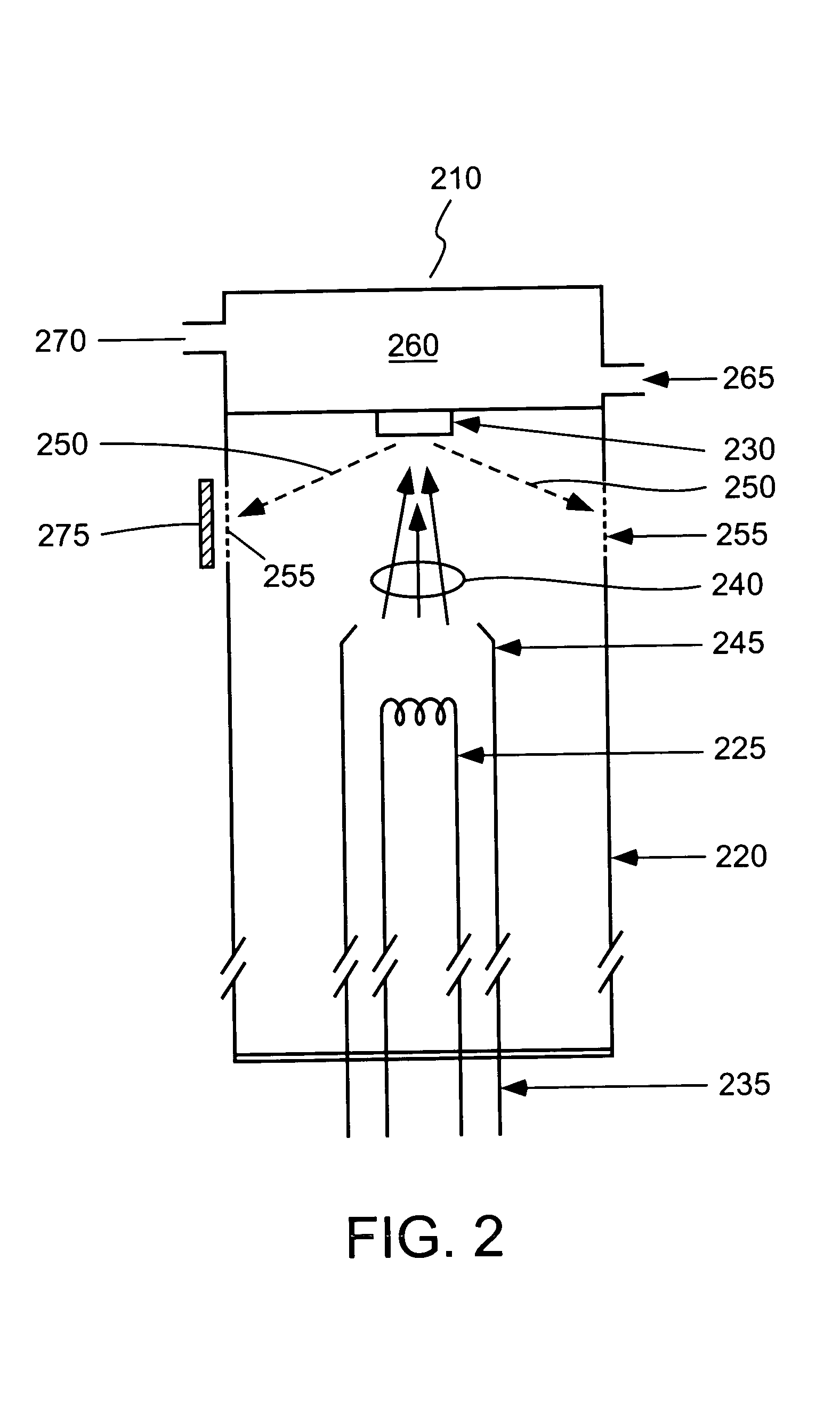
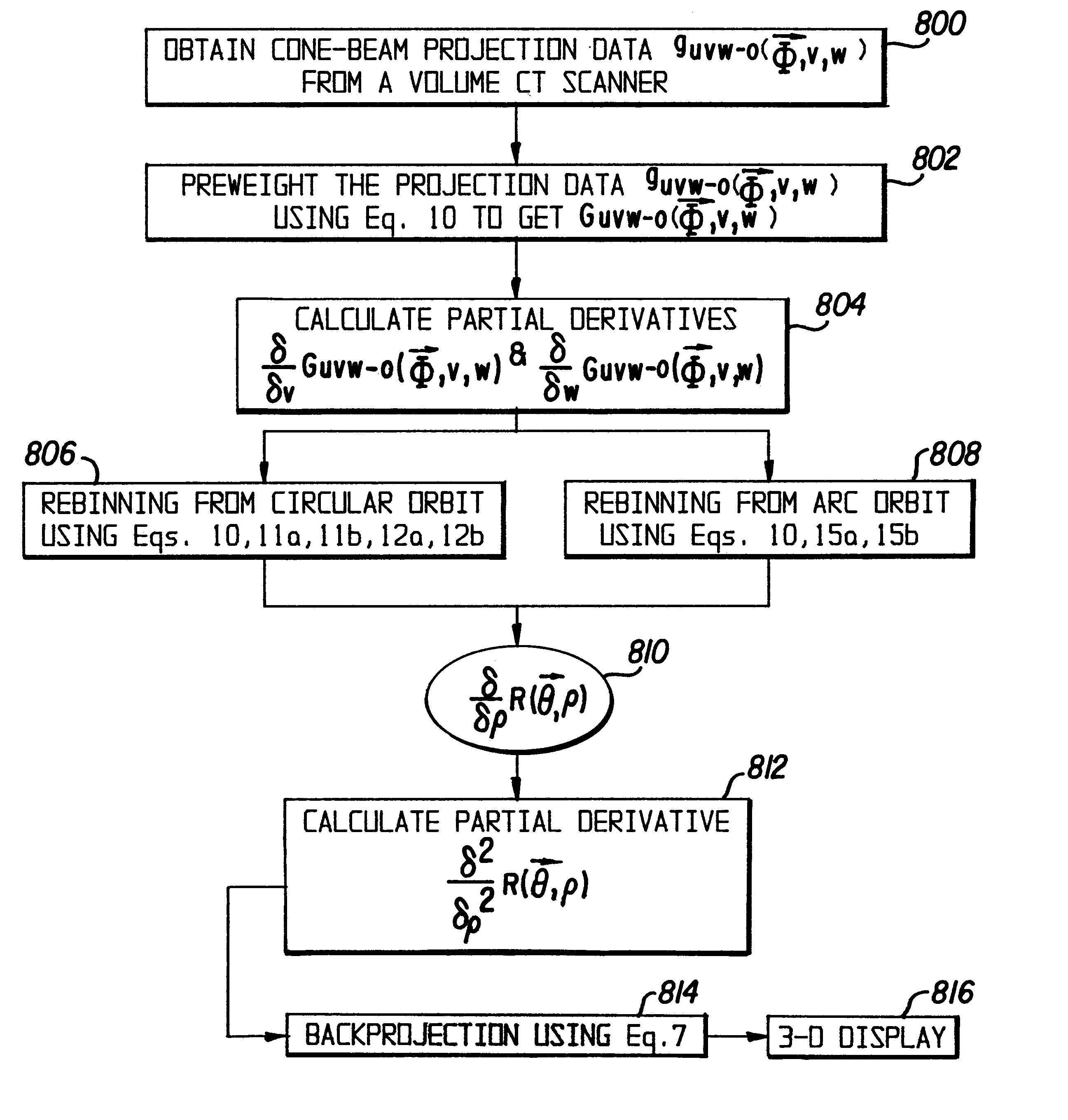
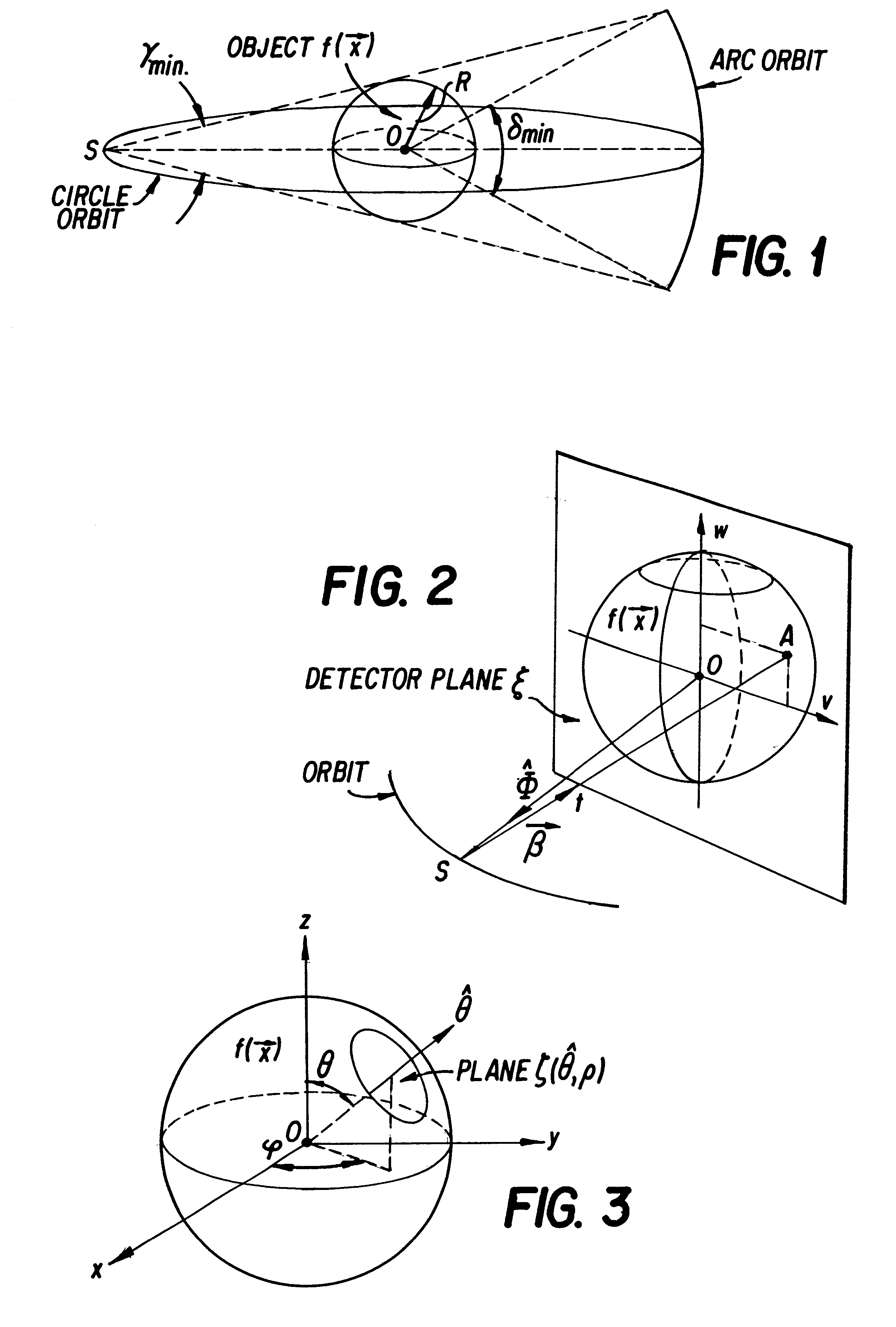
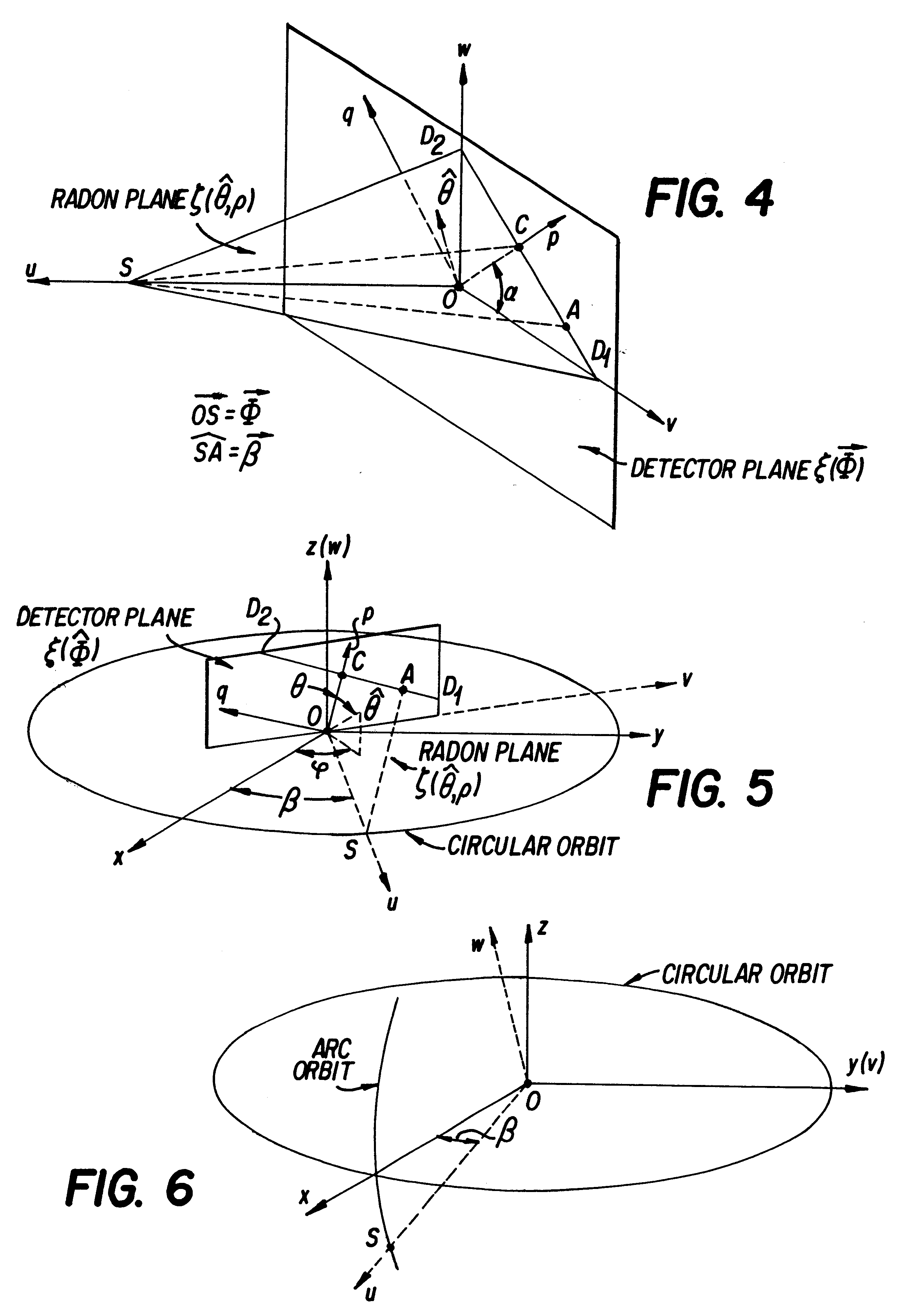
Only a single IV contrast injection with a short breathhold by the patient is needed for use with a volume CT scanner which uses a cone-beam x-ray source and a 2-D detector for fast volume scanning in order to provide true 3-D descriptions of vascular anatomy with more than 0.5 lp / mm isotropic resolution in the x, y and z directions is utilized in which one set of cone-beam projections is acquired while rotating the x-ray tube and detector on the CT gantry and then another set of projections is acquired while tilting the gantry by a small angle. The projection data is preweighted, partial derivatives are calculated and rebinned for both the circular orbit and arc orbit data The second partial derivative is then calculated and then the reconstructed 3-D images are obtained by backprojecting using the inverse Radon transform.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
X-ray inspection system for detecting explosives and other contraband
InactiveUS20060140340A1Improve accuracyImprove throughputUsing wave/particle radiation meansMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationX-rayExplosive material
A baggage scanning system and method employ combined angular and energy dispersive x-ray scanning to detect the presence of a contraband substance within an interrogation volume of a baggage item. The interrogation volume is illuminated with penetrating, polychromatic x-rays in a primary fan beam from a source such as a tungsten-anode x-ray tube. An energy-dependent absorption correction is determined from measurement of the attenuation of the fan beam at a plurality of different energies. Radiation coherently scattered by substances in the interrogation volume is detected by an energy-resolved x-ray detector operated at a plurality of scattering angles to form a plurality of scattering spectra. Each scattering spectrum is corrected for energy-dependent absorption and the corrected spectra are combined to produce a scattering pattern. The experimental scattering pattern is compared with reference patterns that uniquely characterize known contraband substances. The system and method can locate and identify a wide variety of contraband substances in an accurate, reliable manner. The system provides for automated screening, with the result that vagaries of human performance are virtually eliminated. False alarms and the need for hand inspection are reduced and detection efficacy is increased.
Owner:CONTROL SCREENING
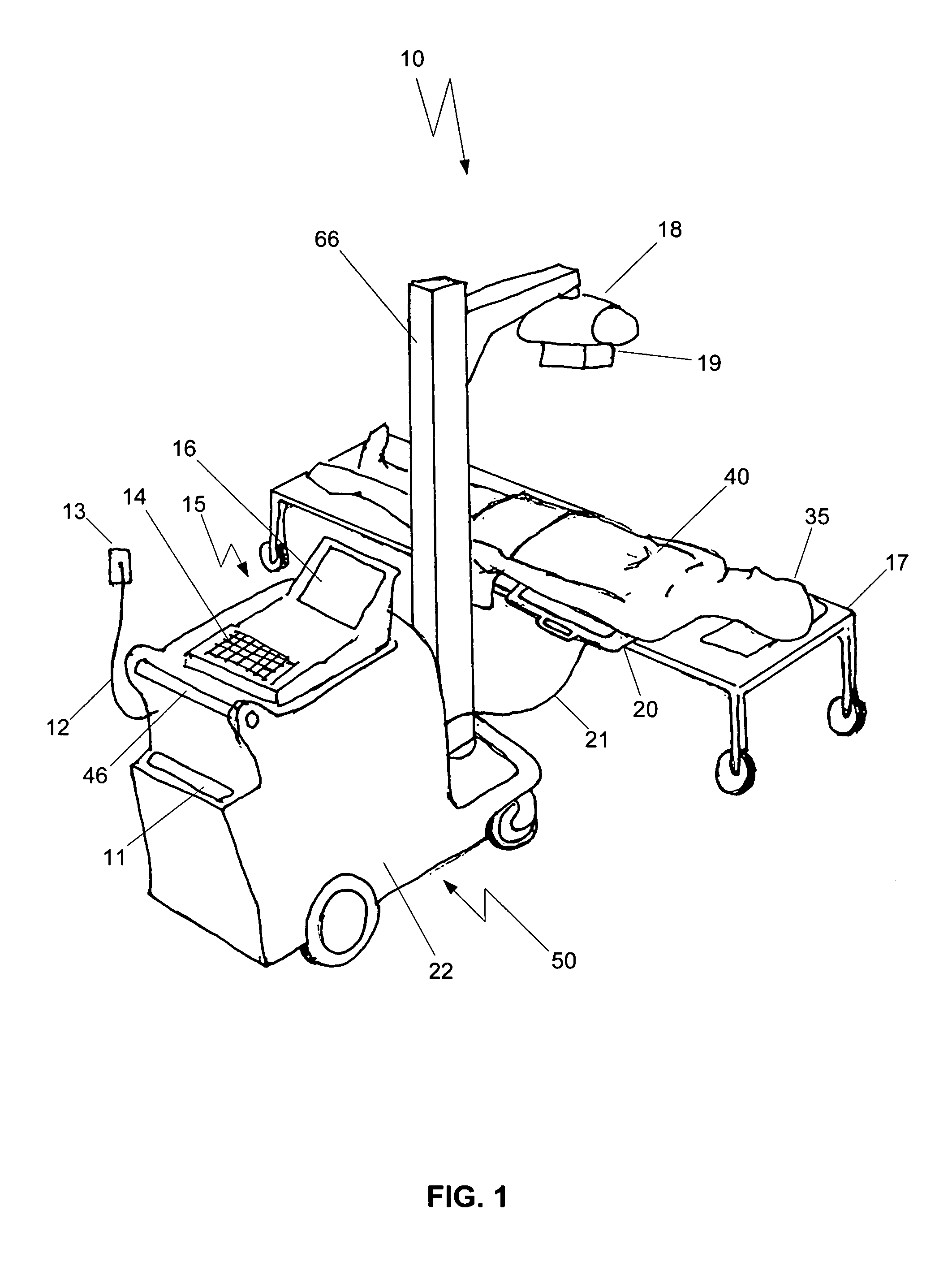
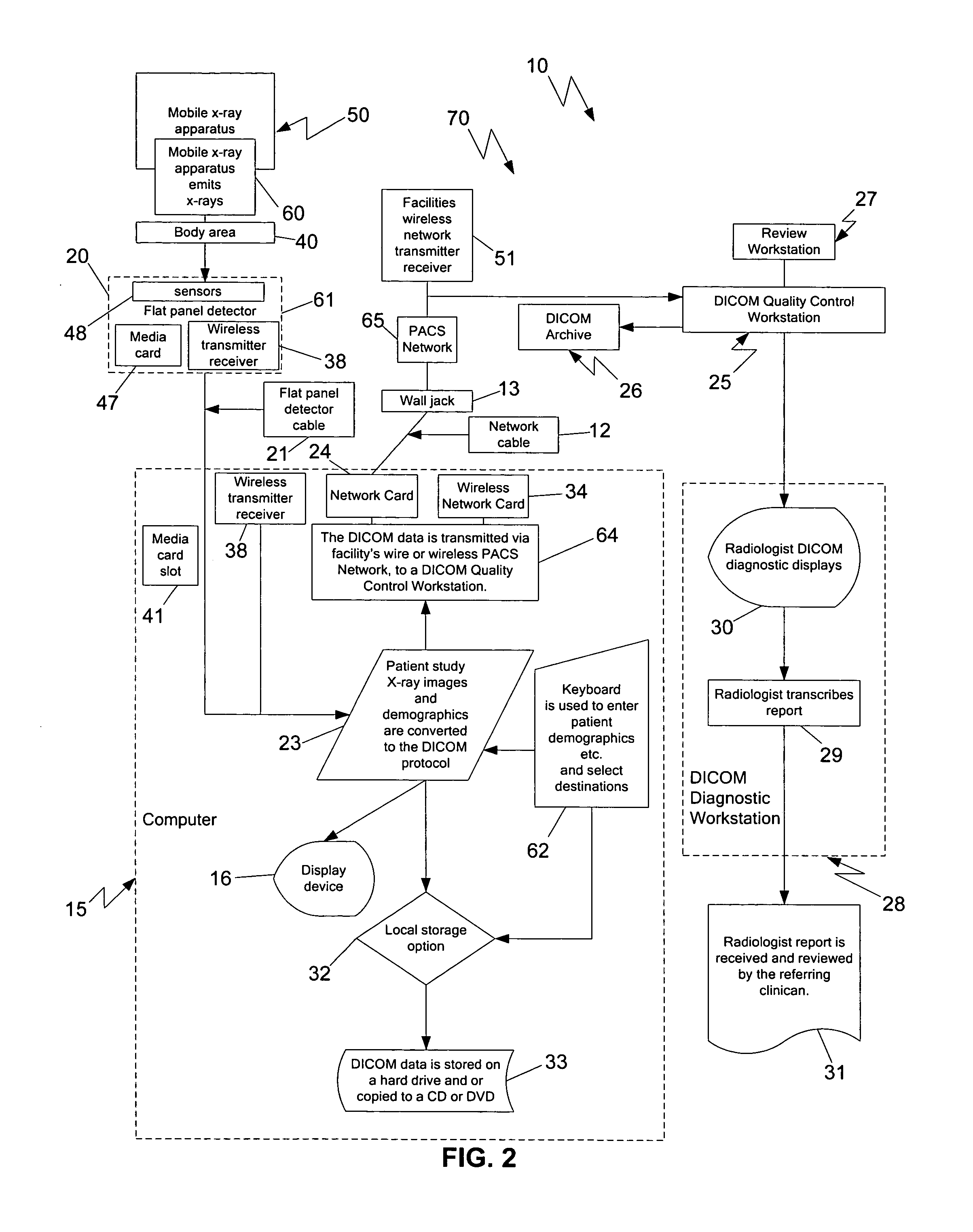
Mobile digital radiography x-ray apparatus and system
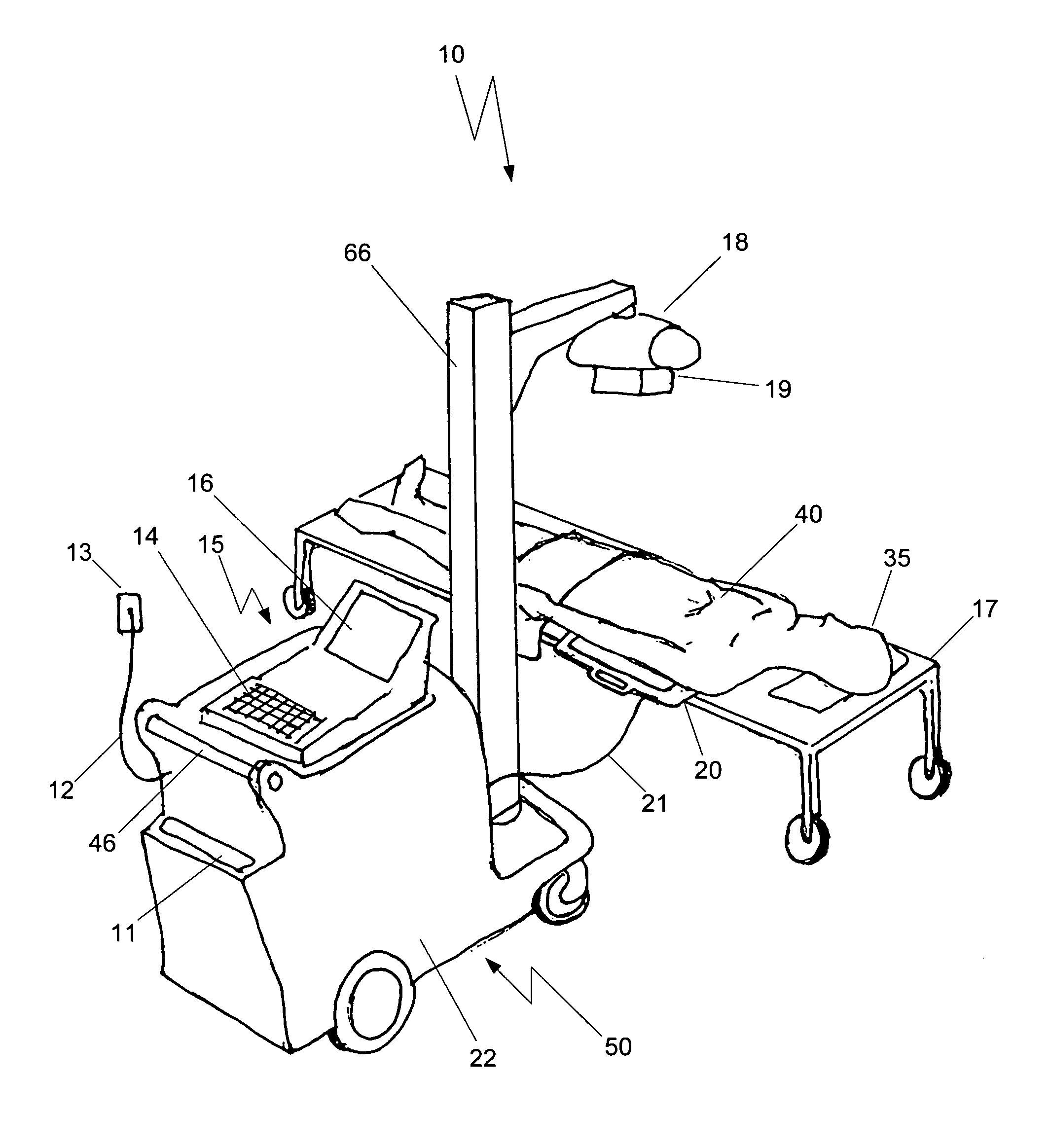
A mobile x-ray apparatus for generating a digital x-ray image and transmitting it to a remote site, includes: (a) a first computer; (b) a flat panel detector in communication with the first computer; and (c) an x-ray cart assembly removably supporting the first computer, which includes a cart with a battery charger and an x-ray machine in communication with the flat panel detector; wherein the mobile x-ray apparatus includes an x-ray tube extendible from the cart, and a mechanism for framing a target body area of a patient. Also included herein is a method of generating a digital x-ray image and forwarding it to a remote site using the mobile x-ray apparatus.
Owner:BROOKS JACK JEROME
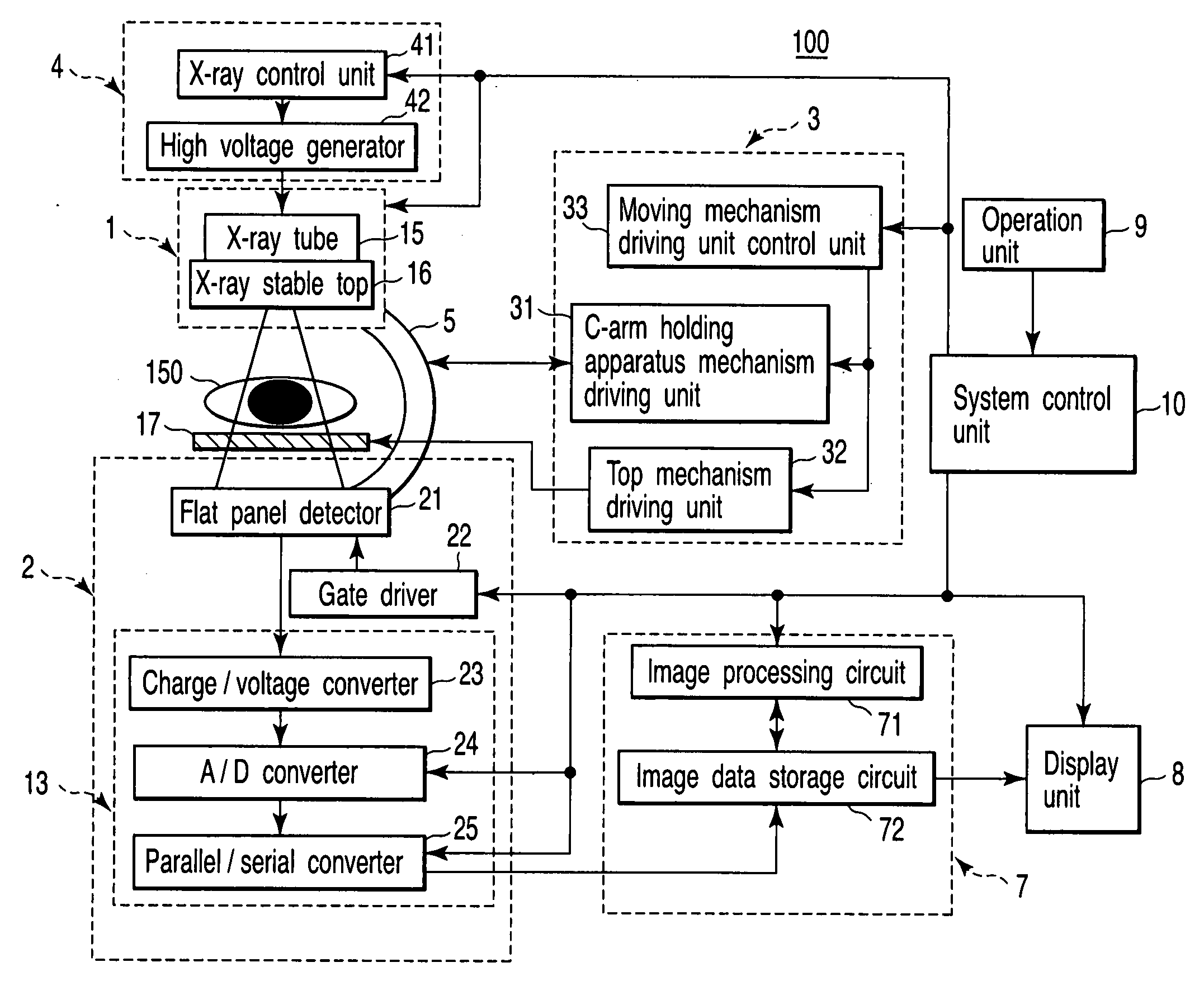
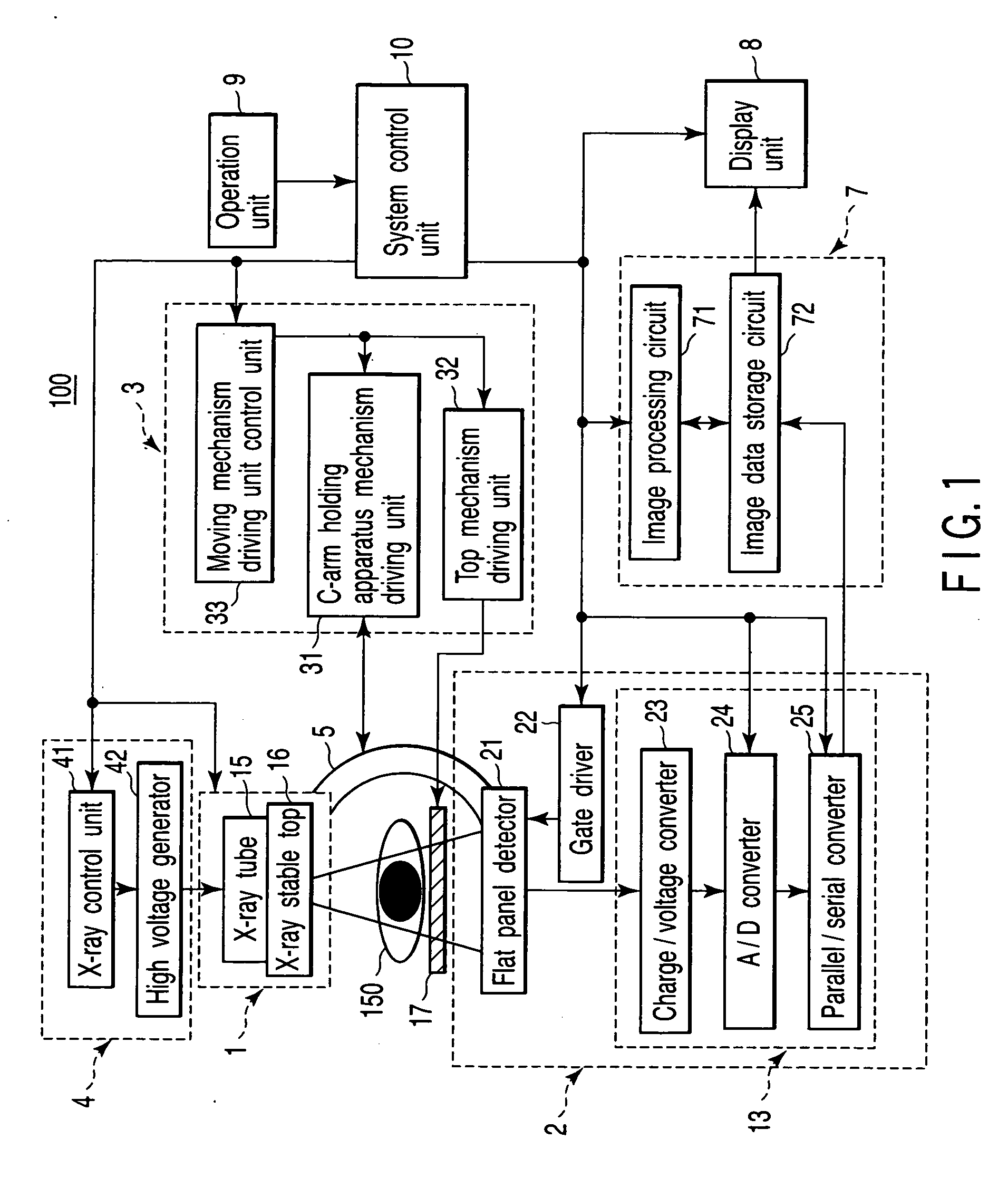
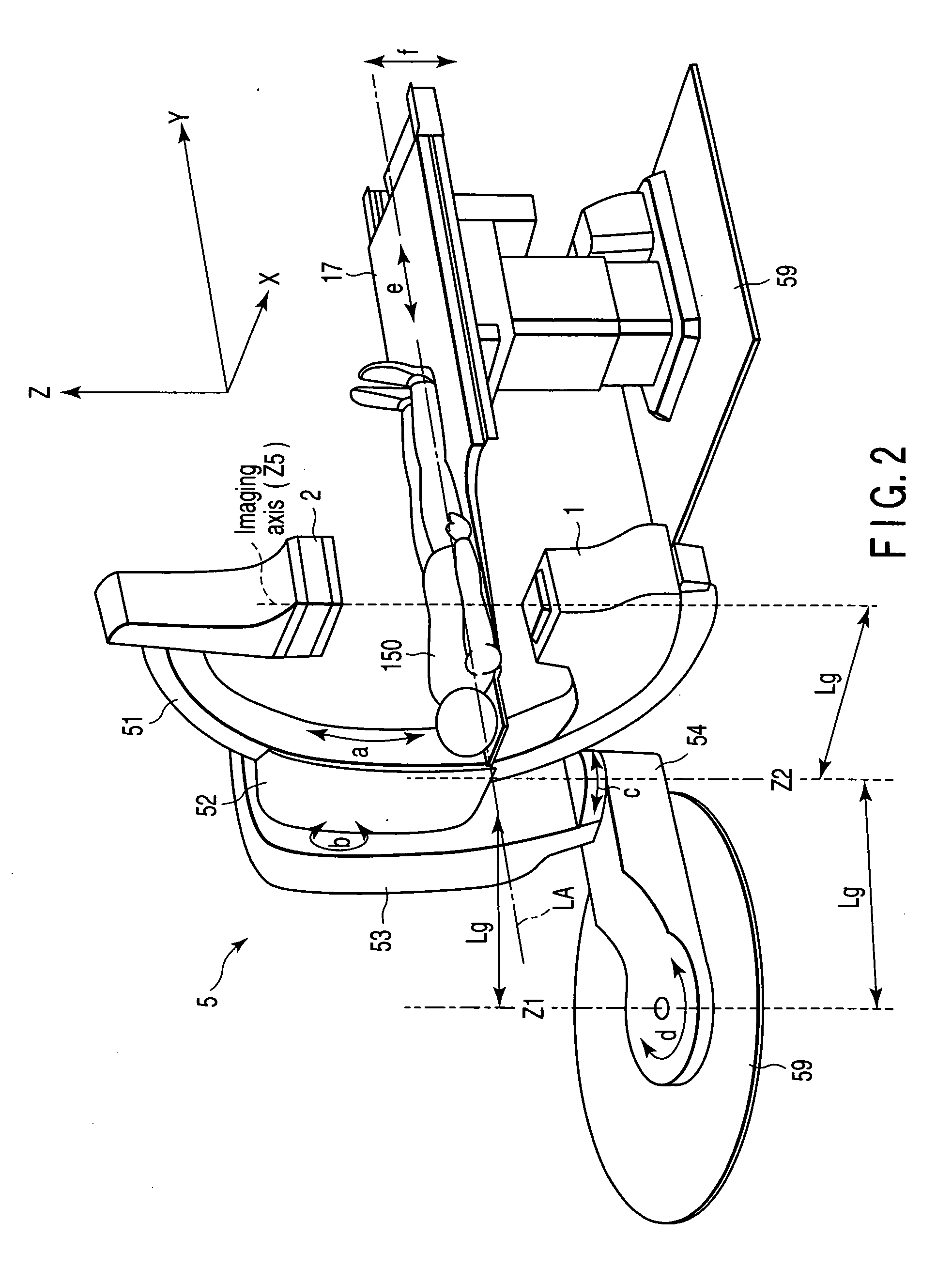
C-arm holding apparatus and X-ray diagnostic apparatus
An X-ray diagnostic apparatus includes a floor rotating arm which is installed at one end on a floor surface so as to be rotatable around a first rotation axis, a C-arm which is mounted on the other end of the floor rotating arm so as to be rotatable around a second rotation axis, an X-ray tube which is mounted on one end of the C-arm, an X-ray detector which is mounted on the other end of the C-arm, and a bed which has a table top provided to be movable along a longitudinal axis. The bed is placed such that the longitudinal axis is spaced apart from the first rotation axis by a predetermined distance.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
Compact high voltage x-ray source system and method for x-ray inspection applications
ActiveUS20090010393A1Reduce weightSmall sizeX-ray tube coolingX-ray tube vessels/containerX-rayHigh pressure
An x-ray system is disclosed that includes a bipolar x-ray tube. The bipolar x-ray tube includes two insulators that are separated by an intermediate electrode in an embodiment, wherein each insulator forms a portion of an outer wall of a vacuum envelope of the bipolar x-ray tube surrounding at least a portion of a path of an electron beam within the vacuum envelope. In further embodiments, the bipolar x-ray tube includes a first electrode at a positive high voltage potential with respect to a reference potential, a second electrode at a negative high voltage potential with respect to the reference potential, and an x-ray transmissive window that is at the positive high voltage potential.
Owner:NEWTON SCI
Differential interference phase contrast X-ray imaging system
InactiveUS8073099B2High radiant fluxPhoton energy is highImaging devicesX-ray tube electrodesHigh energyPhotoconductive detector
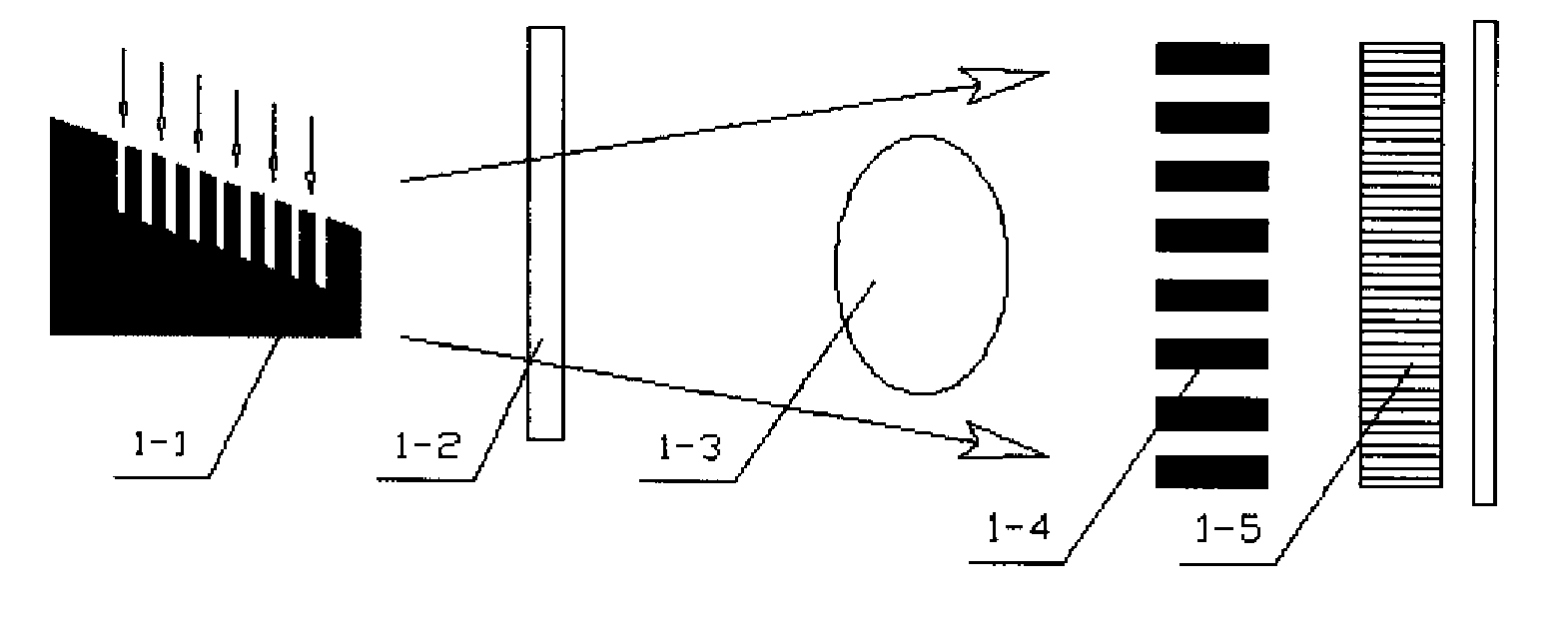
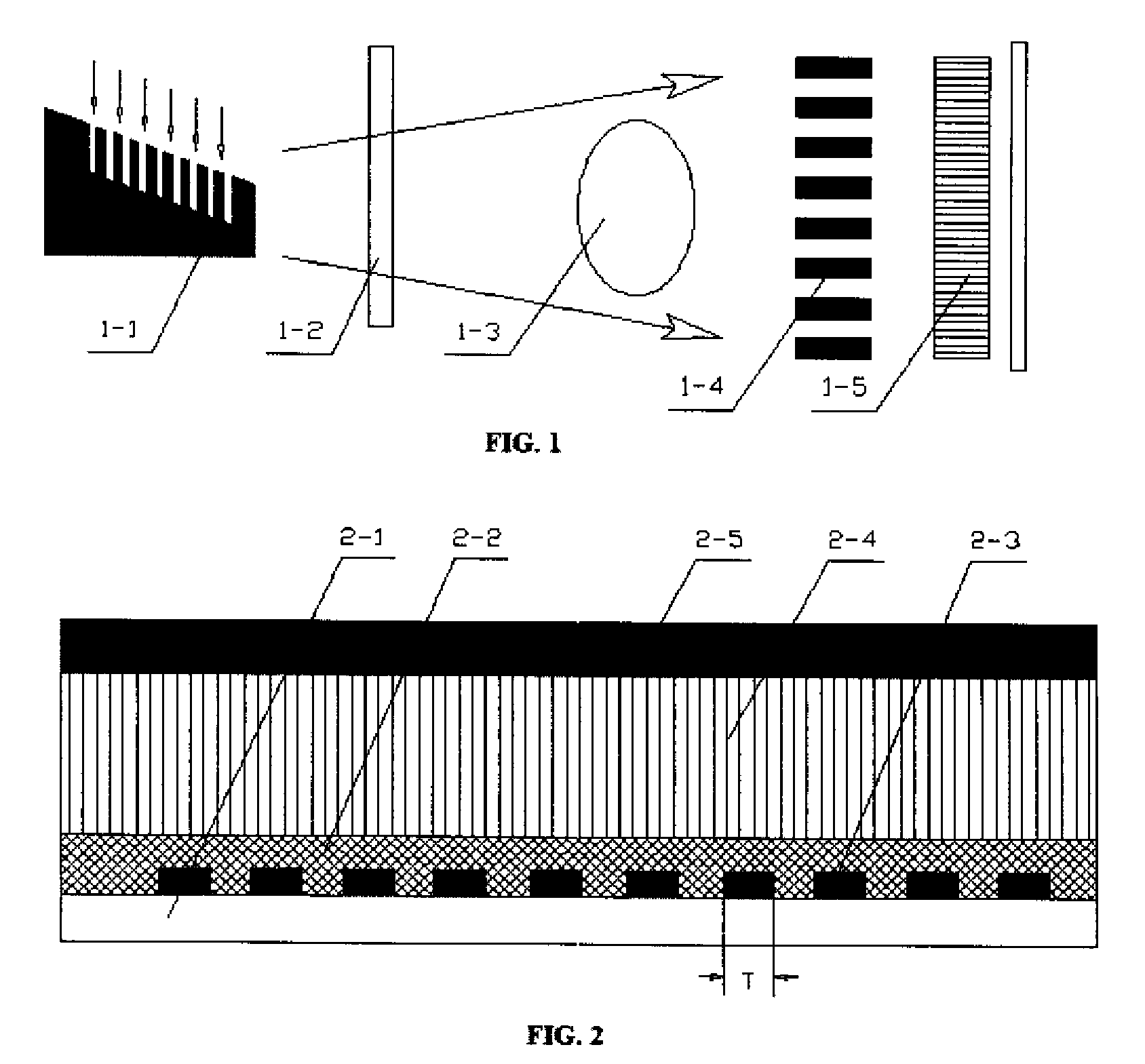
A differential phase-contrast X-ray imaging system is provided. Along the direction of X-ray propagation, the basic components are X-ray tube, filter, object platform, X-ray phase grating, and X-ray detector. The system provides: 1) X-ray beam from parallel-arranged source array with good coherence, high energy, and wider angles of divergence with 30-50 degree. 2) The novel X-ray detector adopted in present invention plays dual roles of conventional analyzer grating and conventional detector. The basic structure of the detector includes a set of parallel-arranged linear array X-ray scintillator screens, optical coupling system, an area array detector or parallel-arranged linear array X-ray photoconductive detector. In this case, relative parameters for scintillator screens or photoconductive detector correspond to phase grating and parallel-arranged line source array, which can provide the coherent X-rays with high energy.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
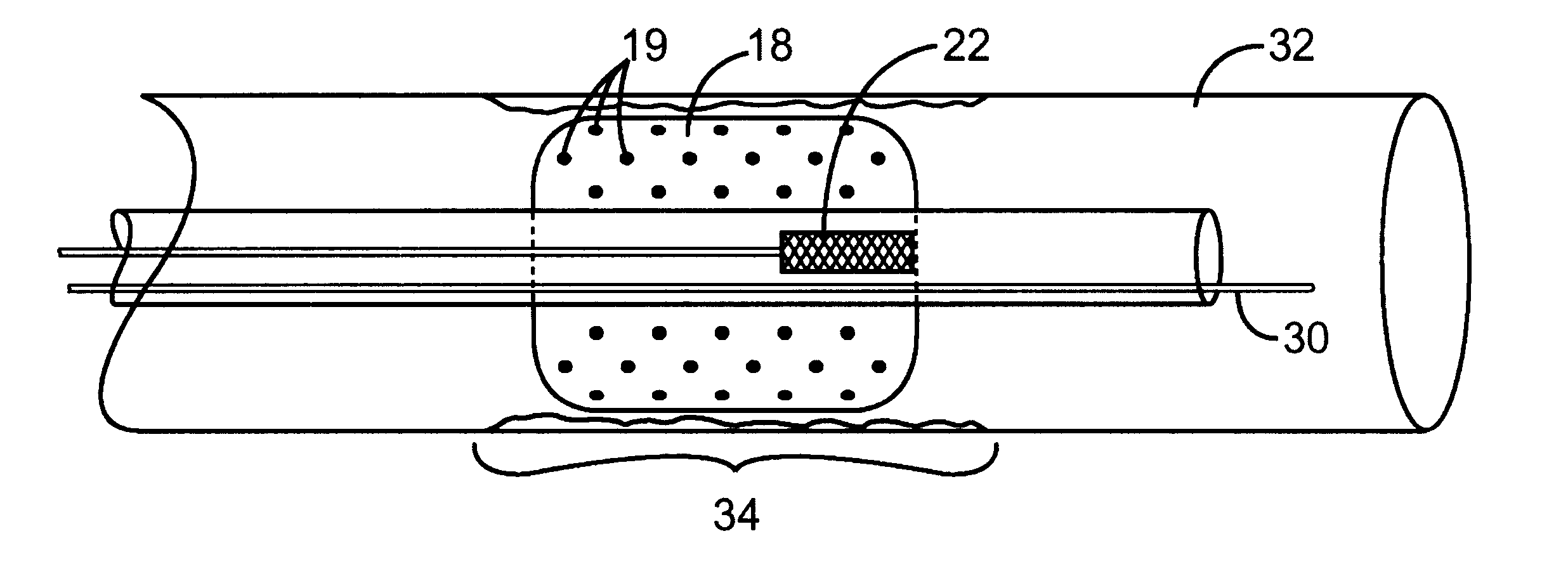
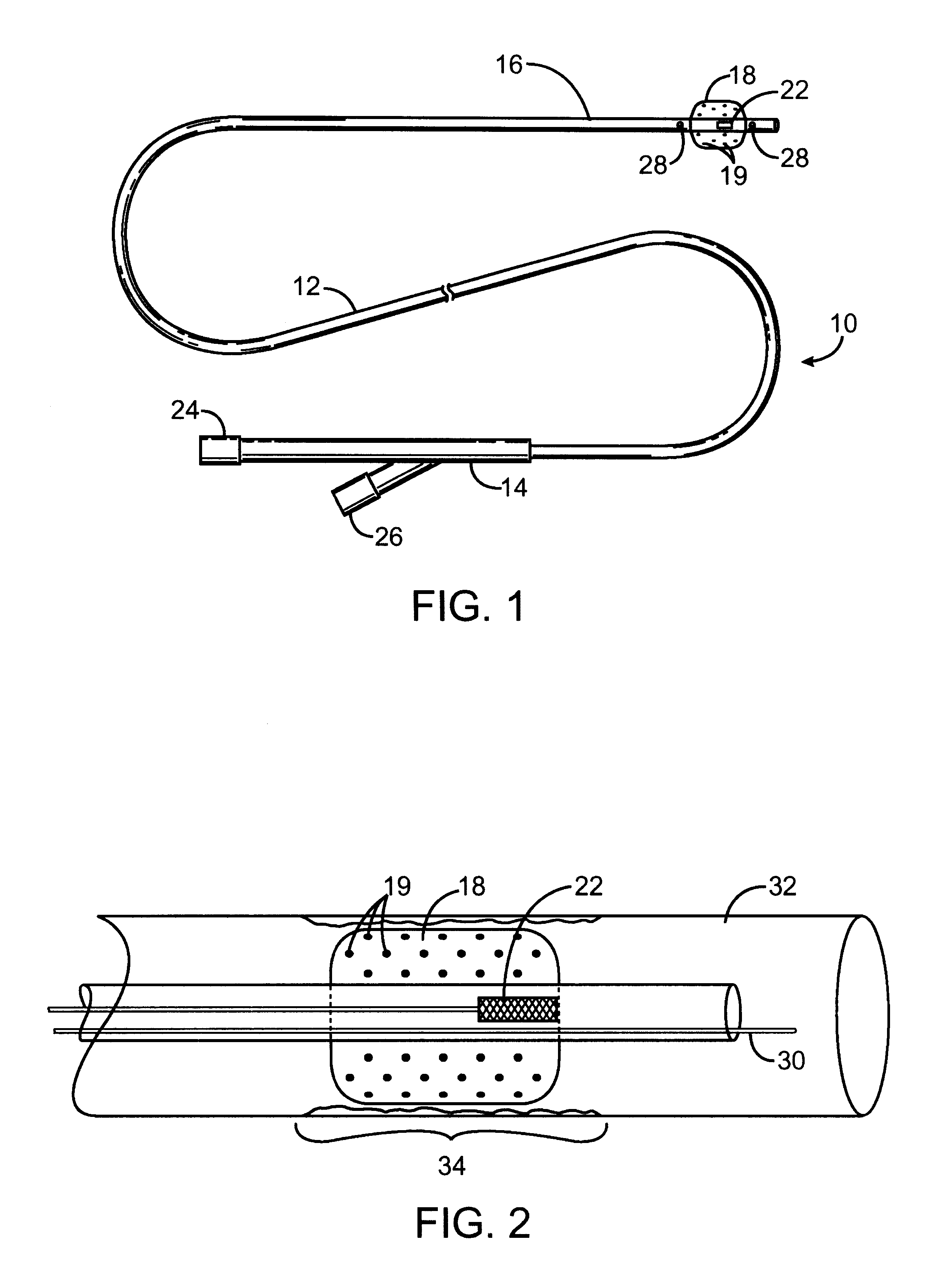
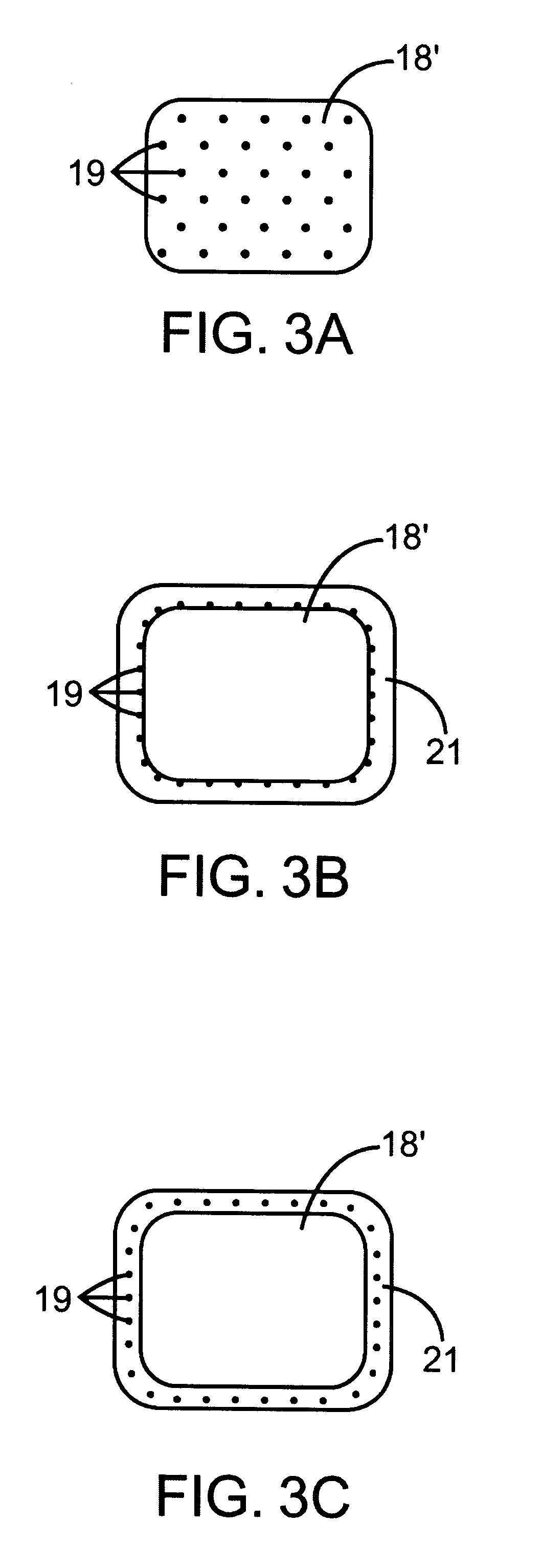
Combination x-ray radiation and drug delivery devices and methods for inhibiting hyperplasia
InactiveUS6537195B2Promote endothelializationReduced dosages/concentrationsStentsElectrotherapyInsertion stentPercent Diameter Stenosis
The present invention provides improved devices, methods, and kits for inhibiting restenosis and hyperplasia after intravascular intervention. In particular, the present invention provides controlled drug delivery in combination with x-ray radiation delivery to selected locations within a patient's vasculature to reduce and / or inhibit restenosis and hyperplasia rates with increased efficacy. In one embodiment, the combination radiation and agent delivery catheter for inhibiting hyperplasia comprises a catheter body having a proximal end and distal end, an x-ray tube coupleable to the catheter body for applying a radiation dose to a body lumen, and a porous material, matrix, membrane, barrier, coating, infusion lumen, stent, graft, or reservoir for releasing an agent to the body lumen.
Owner:XOFT INC +1
Method and device for cooling and electrically insulating a high-voltage, heat-generating component such as an x-ray tube for analyzing fluid streams
InactiveUS7110506B2Minimise currentCurrent lossElectrically conductive connectionsX-ray tube electrodesX-rayHigh pressure
Owner:S RAY OPTICAL SYST
Method and system of aligning x-ray detector for data acquisition
ActiveUS20060109958A1Precise alignmentPrecise positioningRadiation beam directing meansX-ray apparatusData acquisitionTransmitter
A method and system of aligning an x-ray detector and x-ray tube for data acquisition are presented. The x-ray detector and x-ray tube are equipped with transmitters and receivers designed to provide feedback relating to the orientation, spacing, and general position thereof. In this regard, a user can effectively and efficiently position the x-ray tube and x-ray detector relative to one another for data acquisition.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
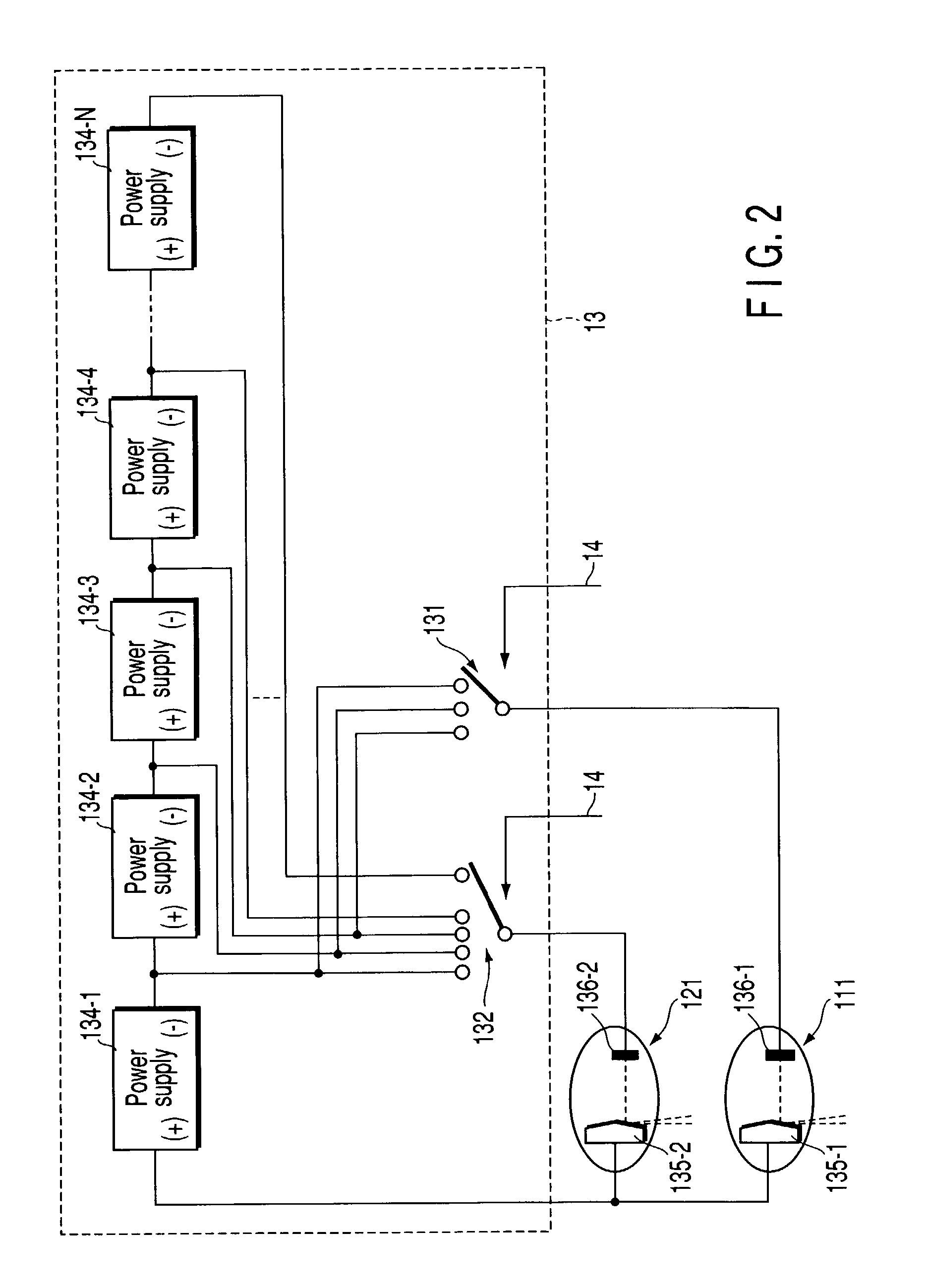
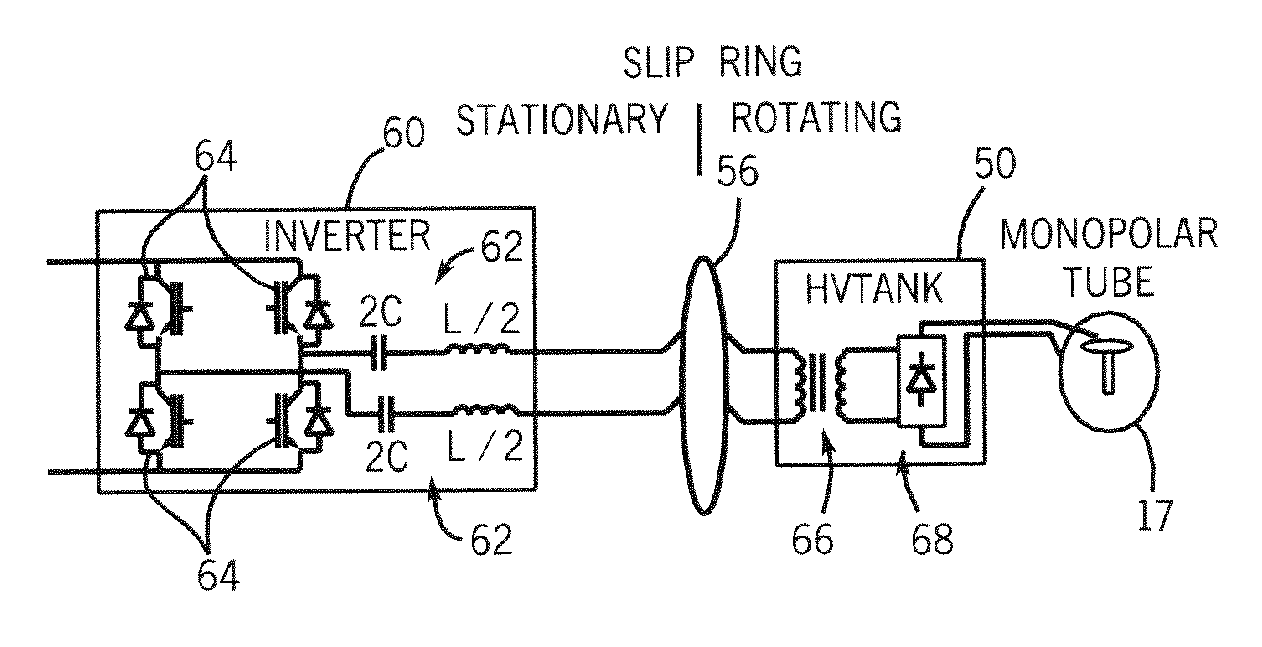
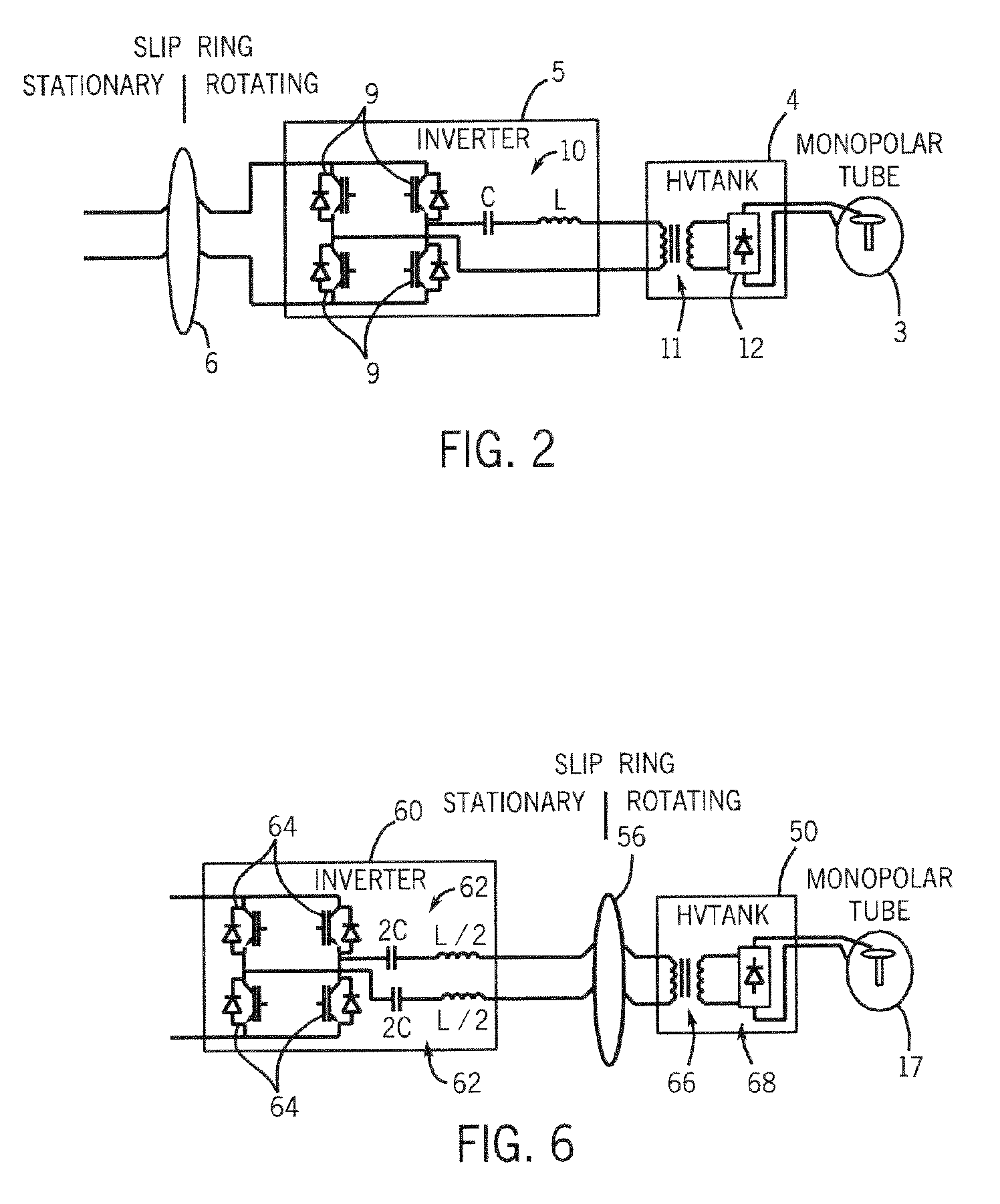
X-ray generator and slip ring for a CT system
InactiveUS6975698B2Radiation diagnosis data transmissionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationTransformerFuel tank
The present invention is directed to an apparatus for supplying power to a rotatable x-ray tube for generation of an x-ray beam for acquisition of CT data. The apparatus includes a slip ring to transfer power from a stationary inverter to a rotatable HV tank. The HV tank conditions the transferred power and creates a voltage potential across the x-ray tube for x-ray generation. The inverter has a single or pair of series resonant circuits connected either directly to the slip ring or indirectly through a transformer to limit frequency content and reduce common-mode component of the voltage and current waveforms carried by the slip ring as well as reduce power losses.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
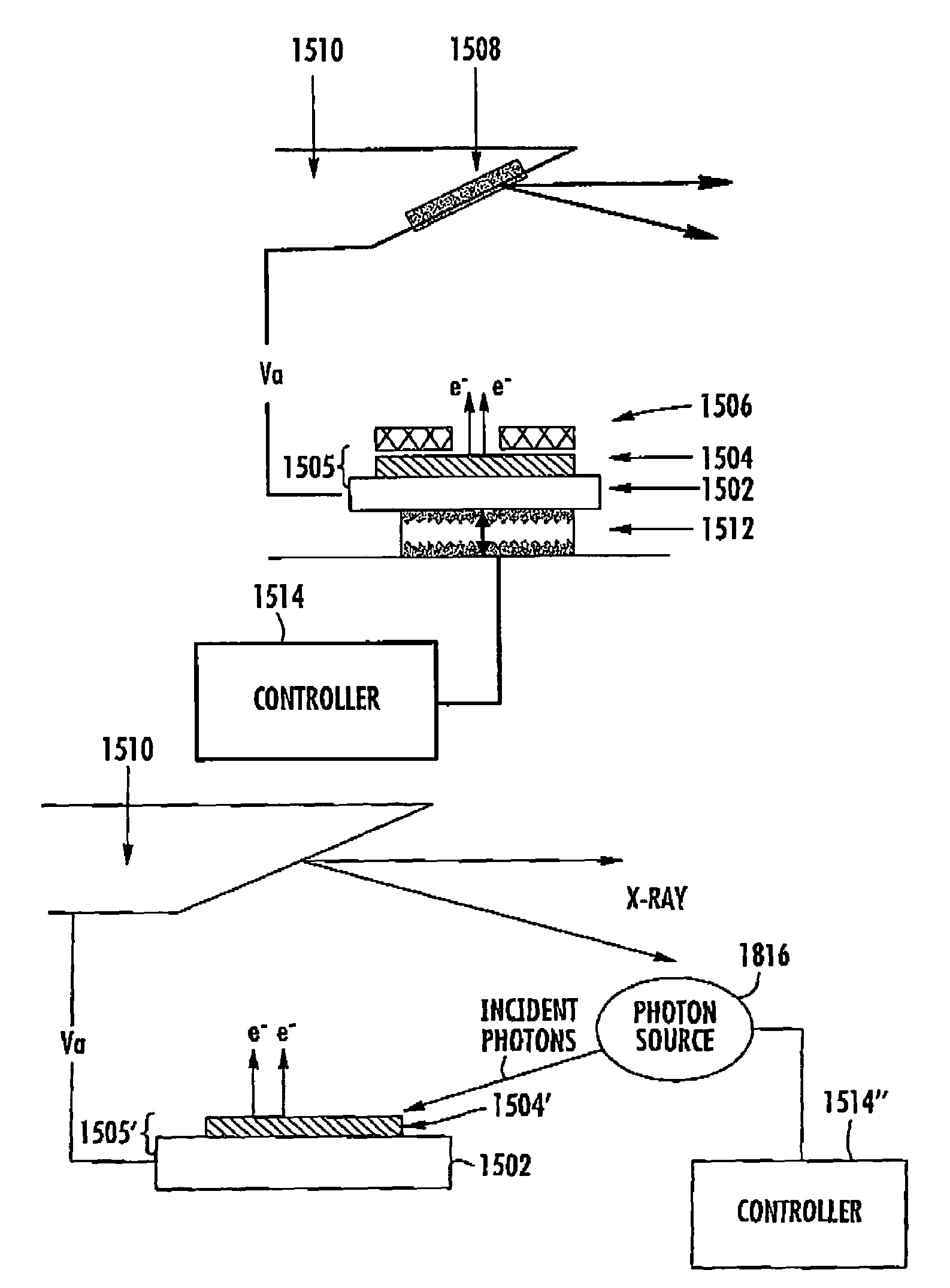
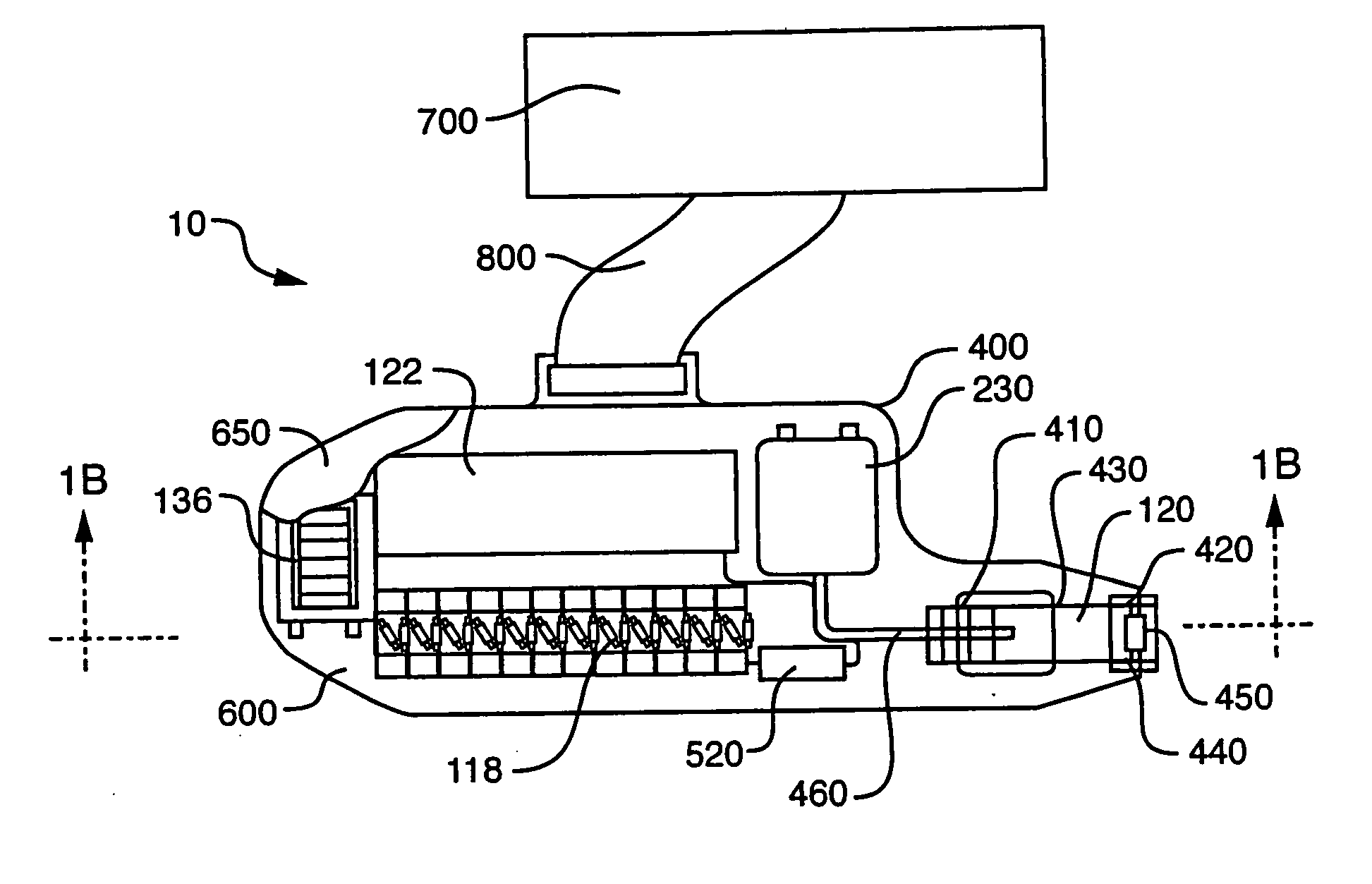
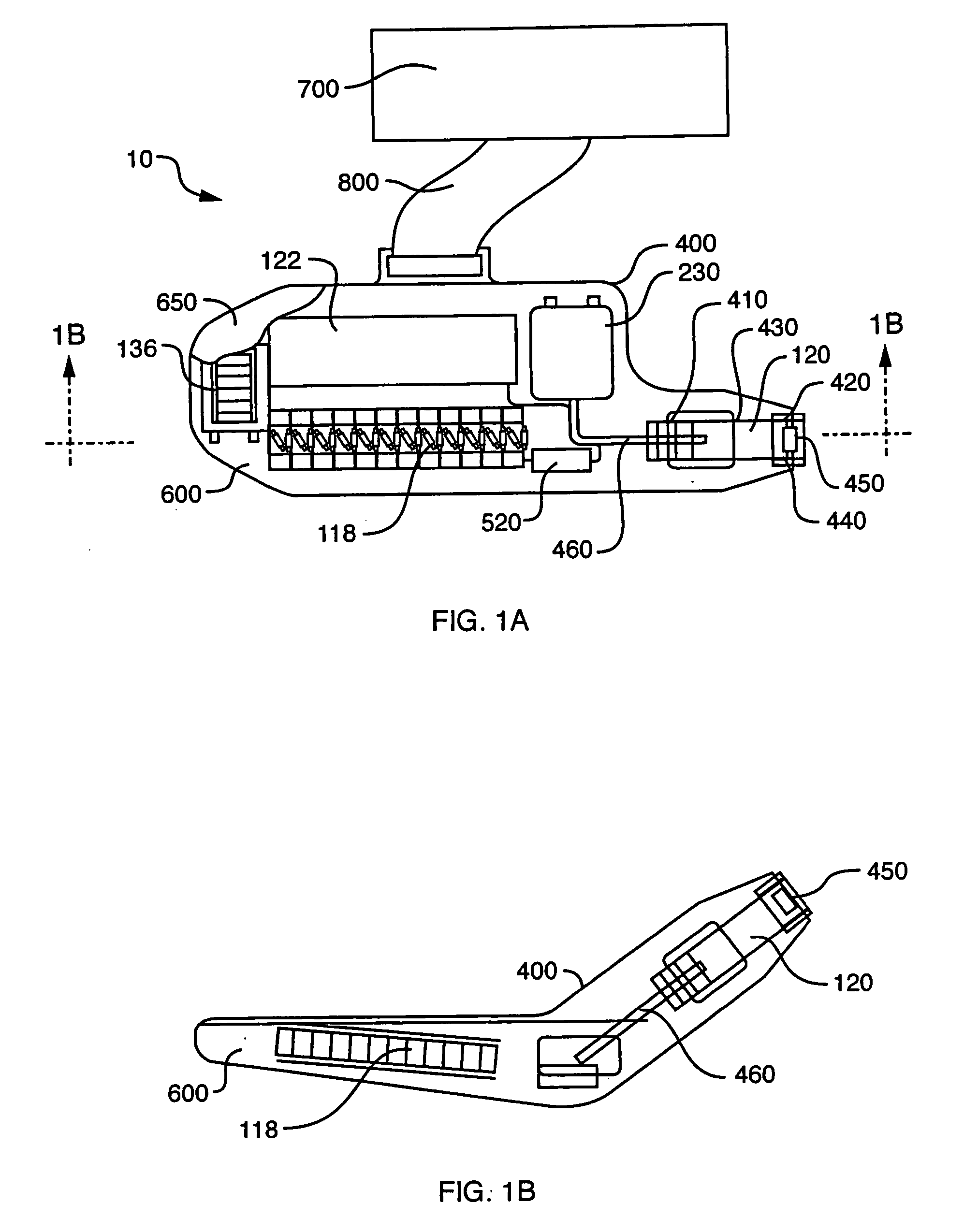
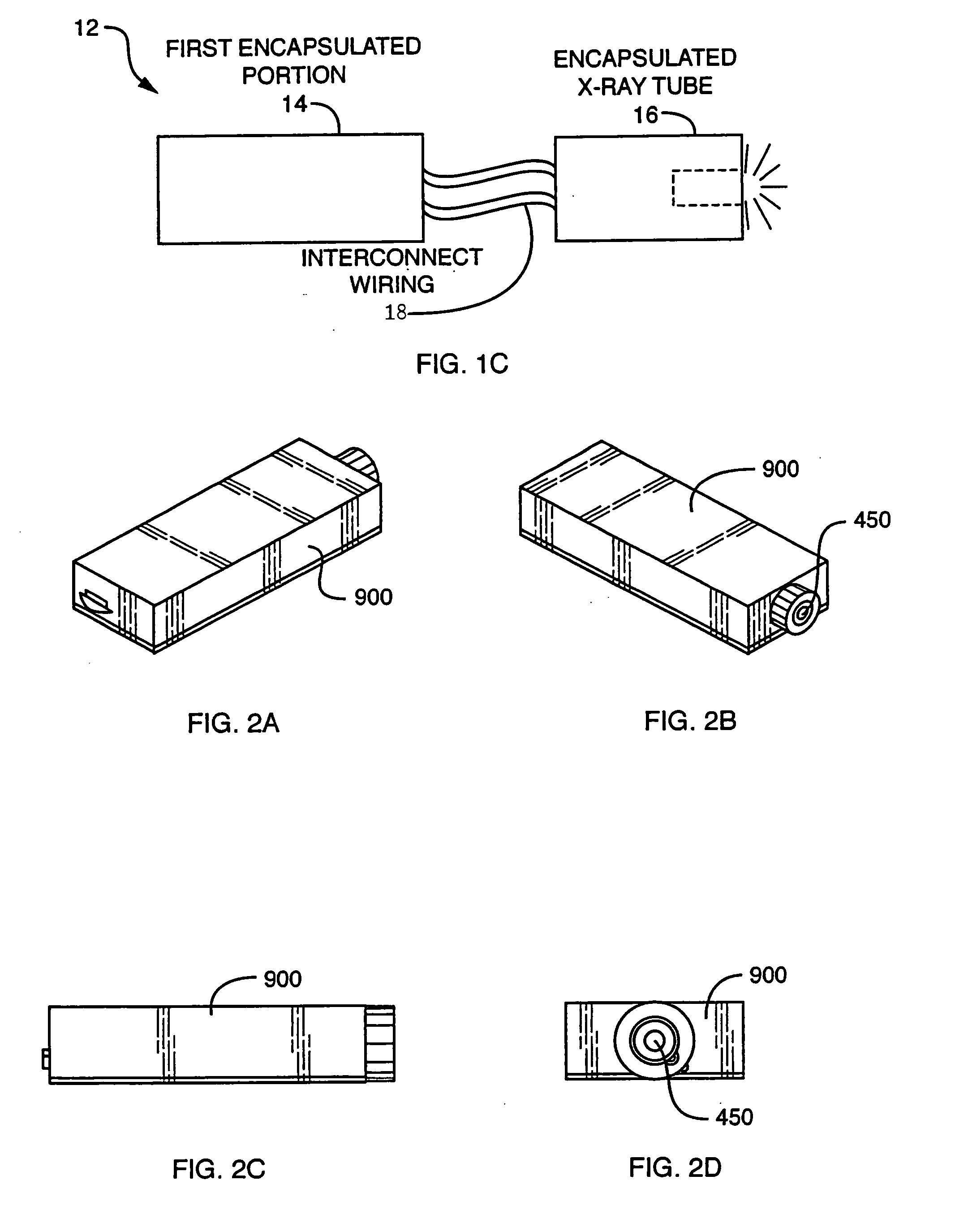
Integrated X-ray source module
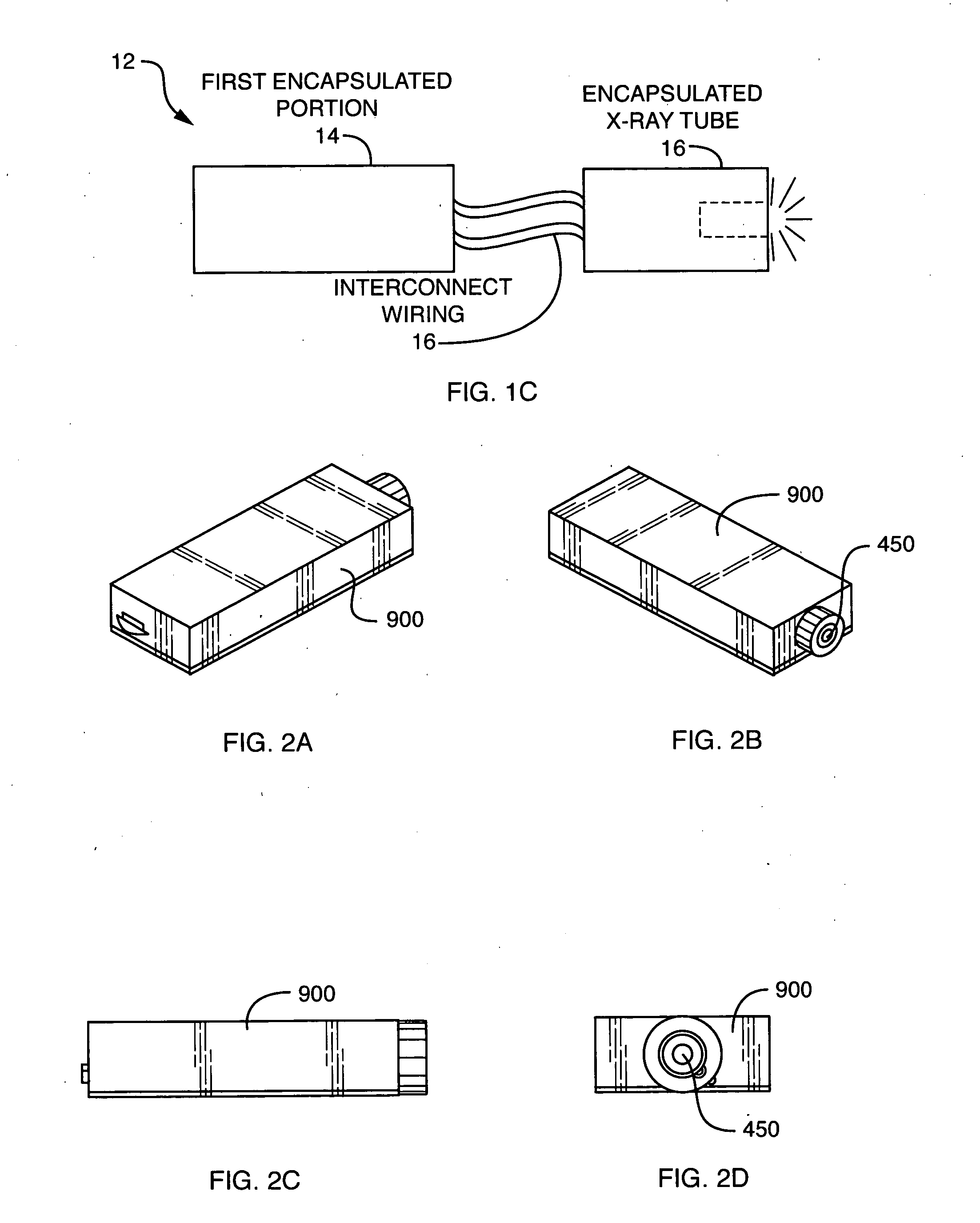
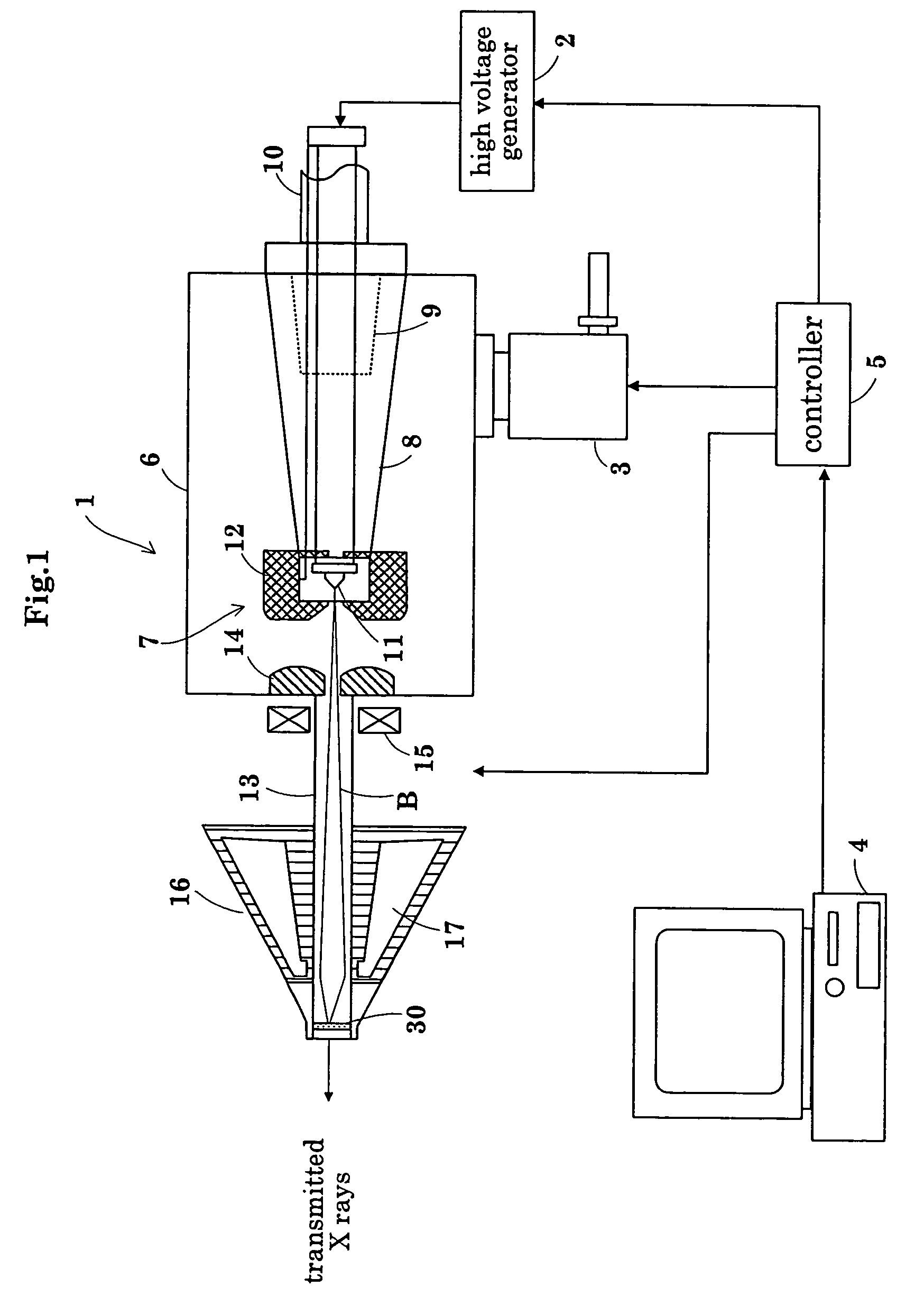
Described is a self-contained, small, lightweight, power-efficient and radiation-shielded module that includes a miniature vacuum X-ray tube emitting X-rays of a controlled intensity and defined spectrum. Feedback control circuits are used to monitor and maintain the beam current and voltage. The X-ray tube, high-voltage power supply, and the resonant converter are encapsulated in a solid high-voltage insulating material. The module can be configured into complex geometries and can be powered by commercially available small, compact, low-voltage batteries.
Owner:NEWTON SCI
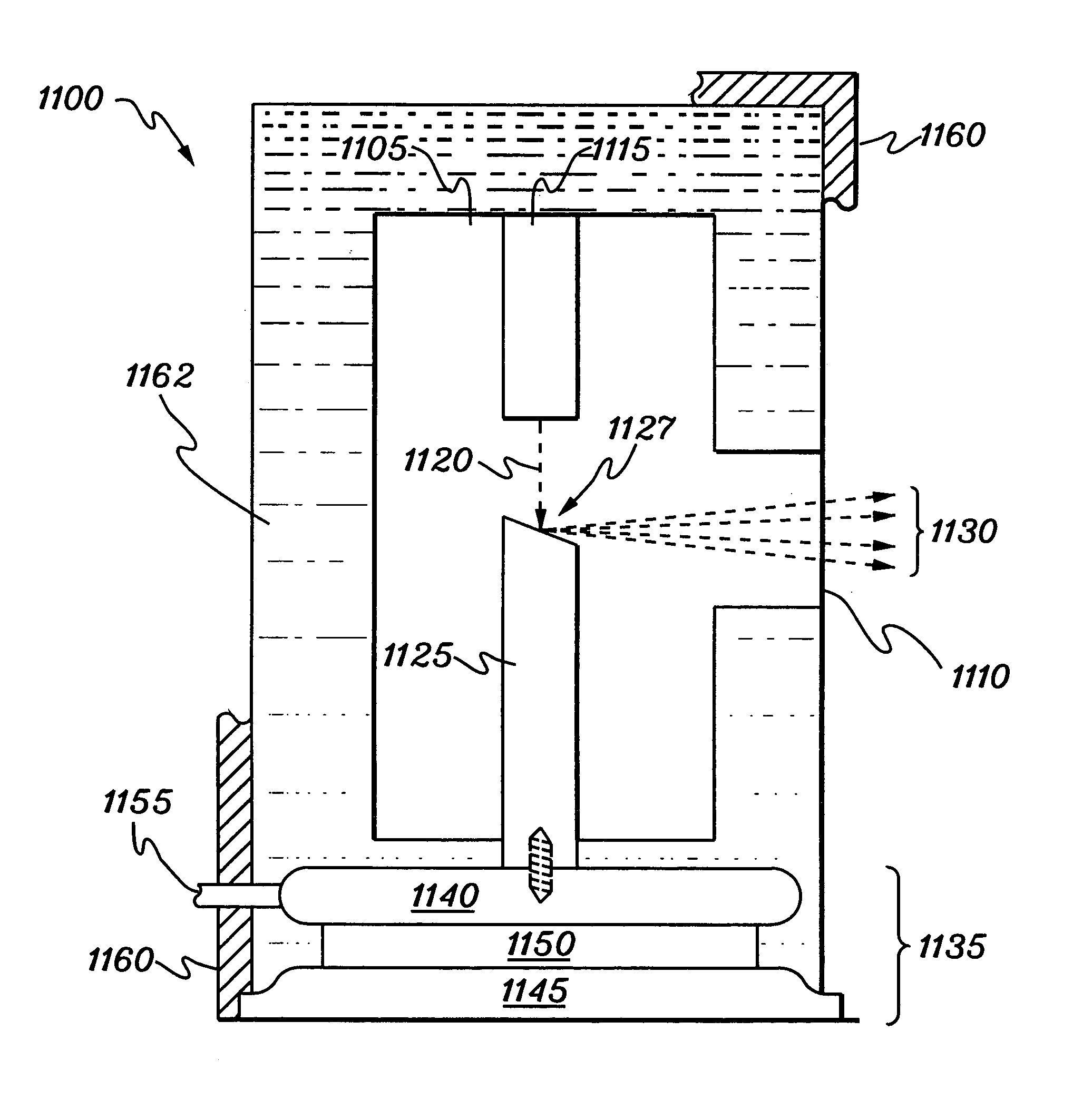
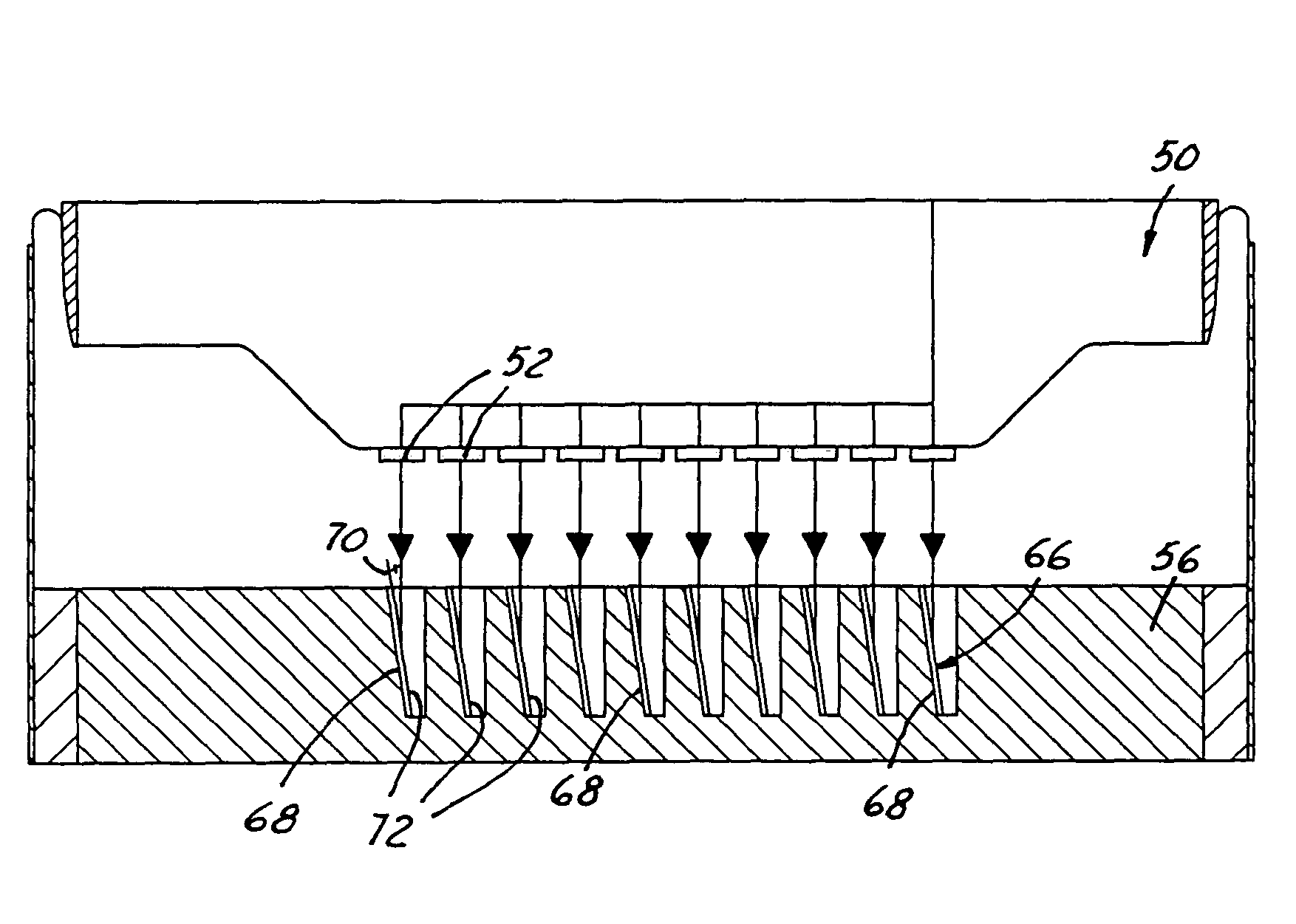
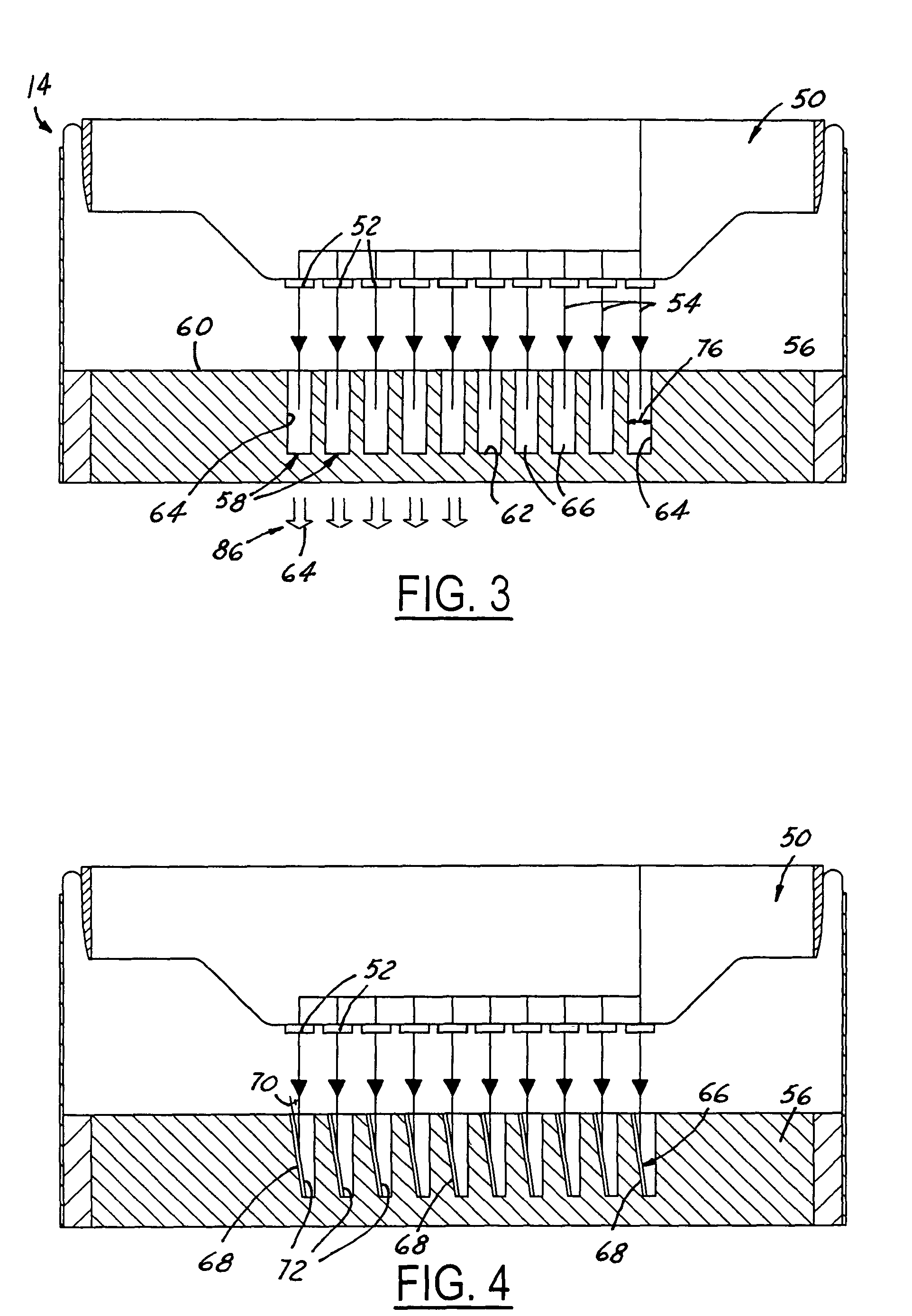
Notched transmission target for a multiple focal spot X-ray source
A flat panel x-ray tube assembly is provided comprising a cathode assembly including a plurality of emitter elements. An anode substrate is included having a substrate upper surface facing the plurality of emitter elements and a substrate lower surface. The substrate upper surface is positioned parallel to the plurality of emitter elements. A plurality of target wells are formed in the substrate upper surface. Each of the plurality of target wells comprises a first angled side surface positioned at an acute angle relative to the substrate upper surface. A plurality of first target elements is applied to each to one of the first angled side surfaces. The first target elements generate x-rays in a direction perpendicular to the plurality of emitter elements in response to electrons received from one of the plurality of emitter elements.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
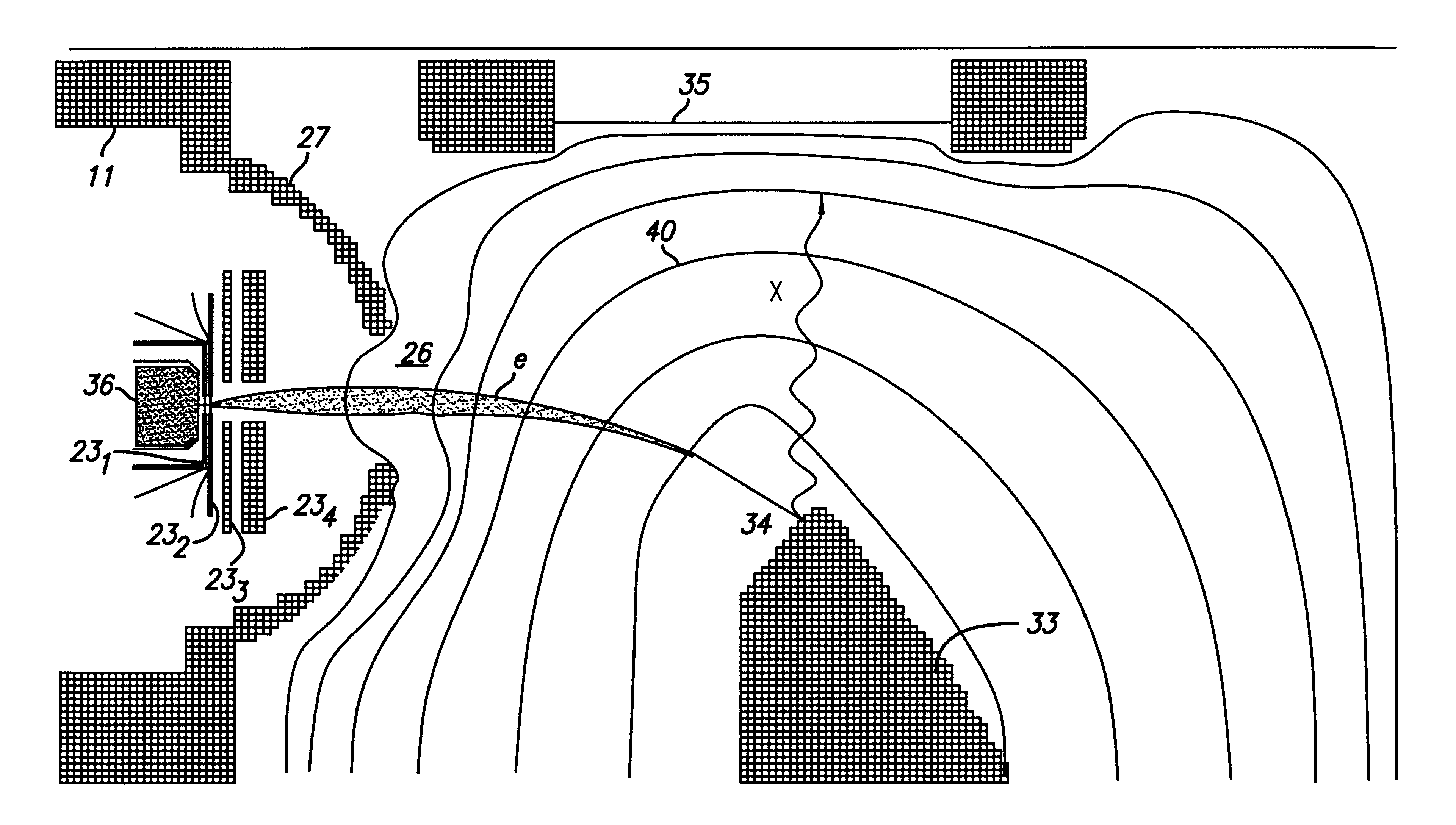
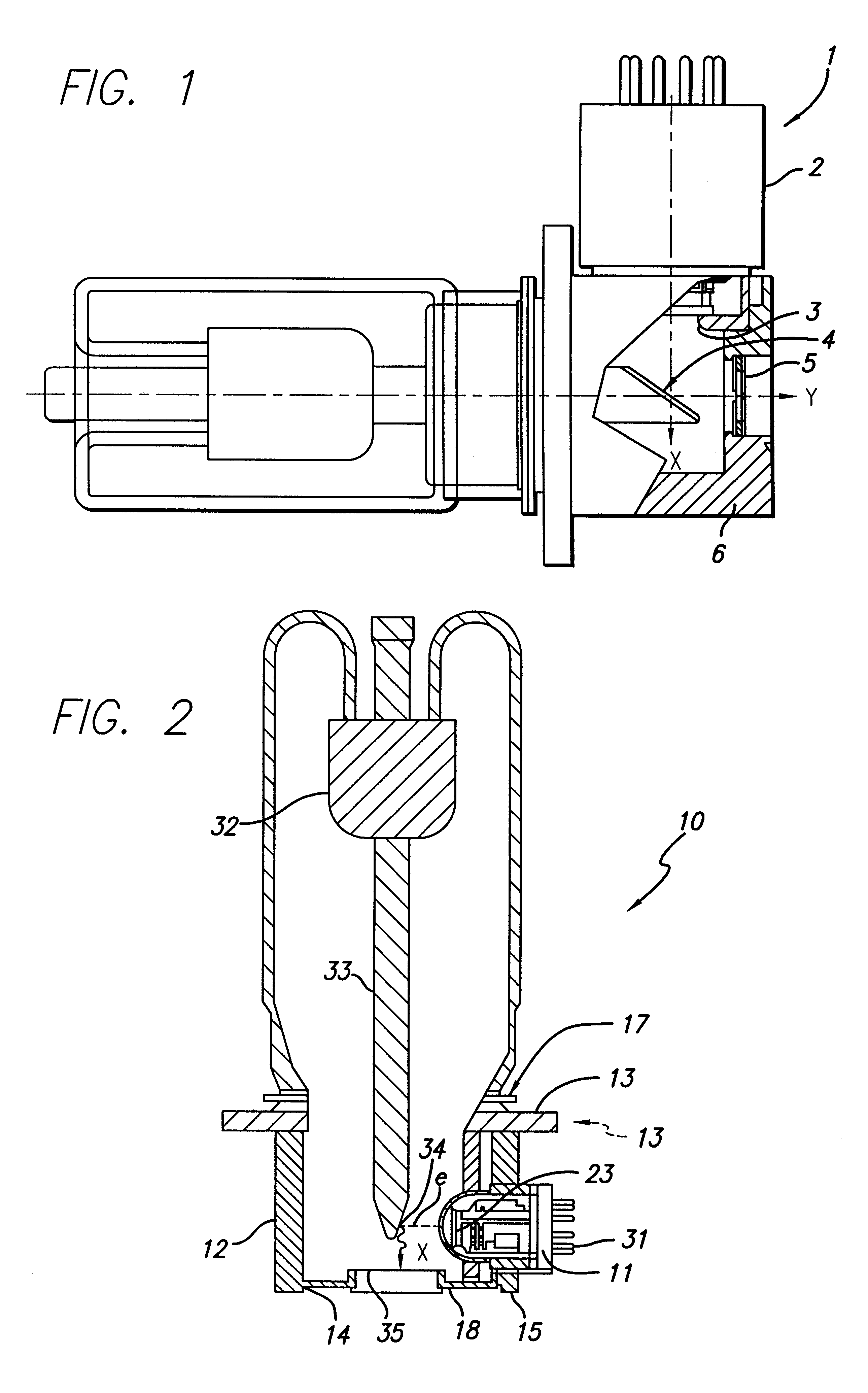
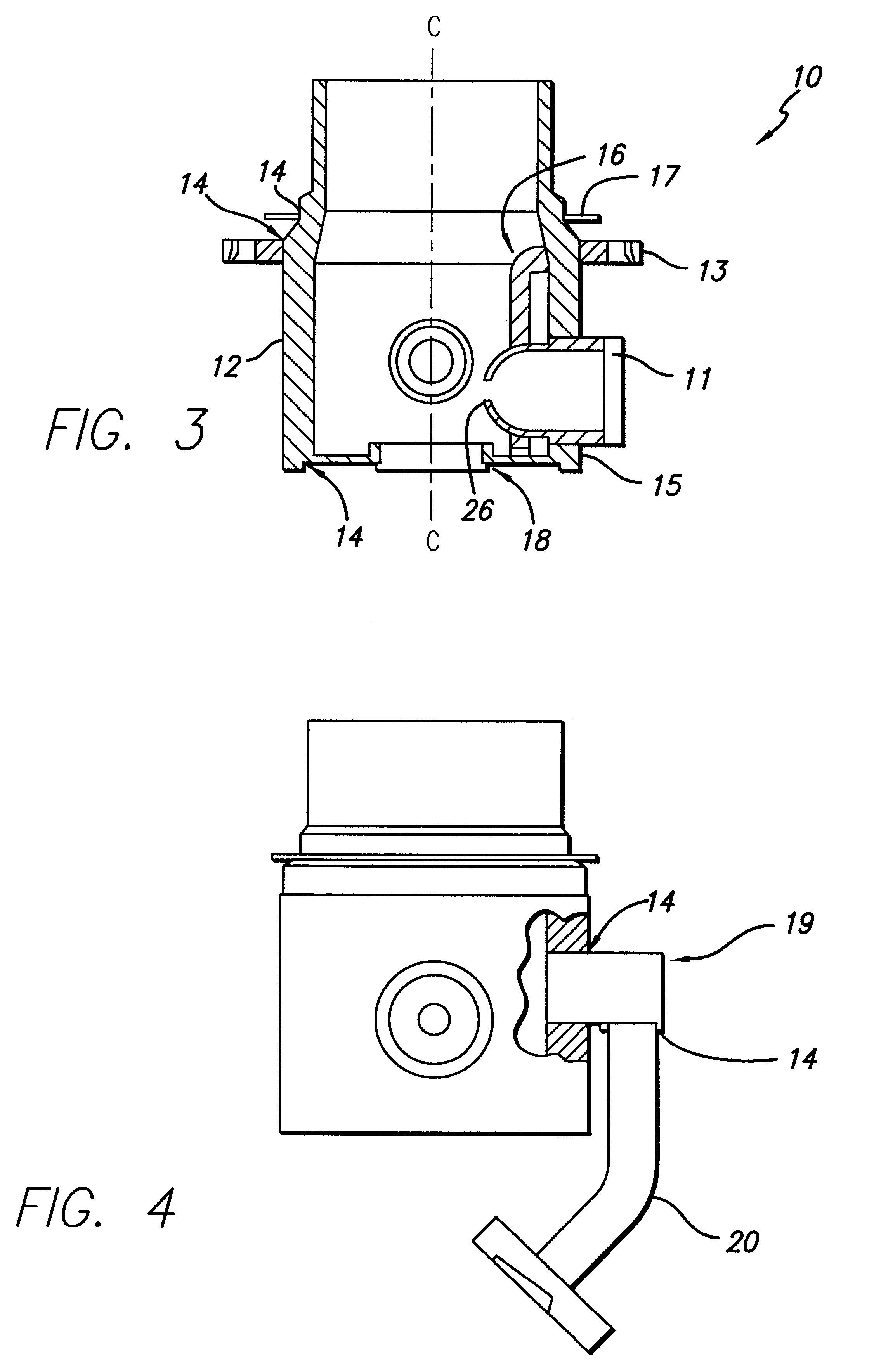
X-ray tube
InactiveUS6229876B1Enhances electron beam focusing capabilityLow possible surface fieldX-ray tube electrodesCathode ray concentrating/focusing/directingX-raySpherical shaped
An x-ray tube comprising an electron gun assembly having an electron gun container housing an electron generator for generating electrons in a first direction along a first axis. The beam of electrons impinges upon an anode which emits x-rays in response to the beam of electrons. The gun container is characterized by having a discharge end comprising a solid spherical shape.
Owner:KEVEX X RAY
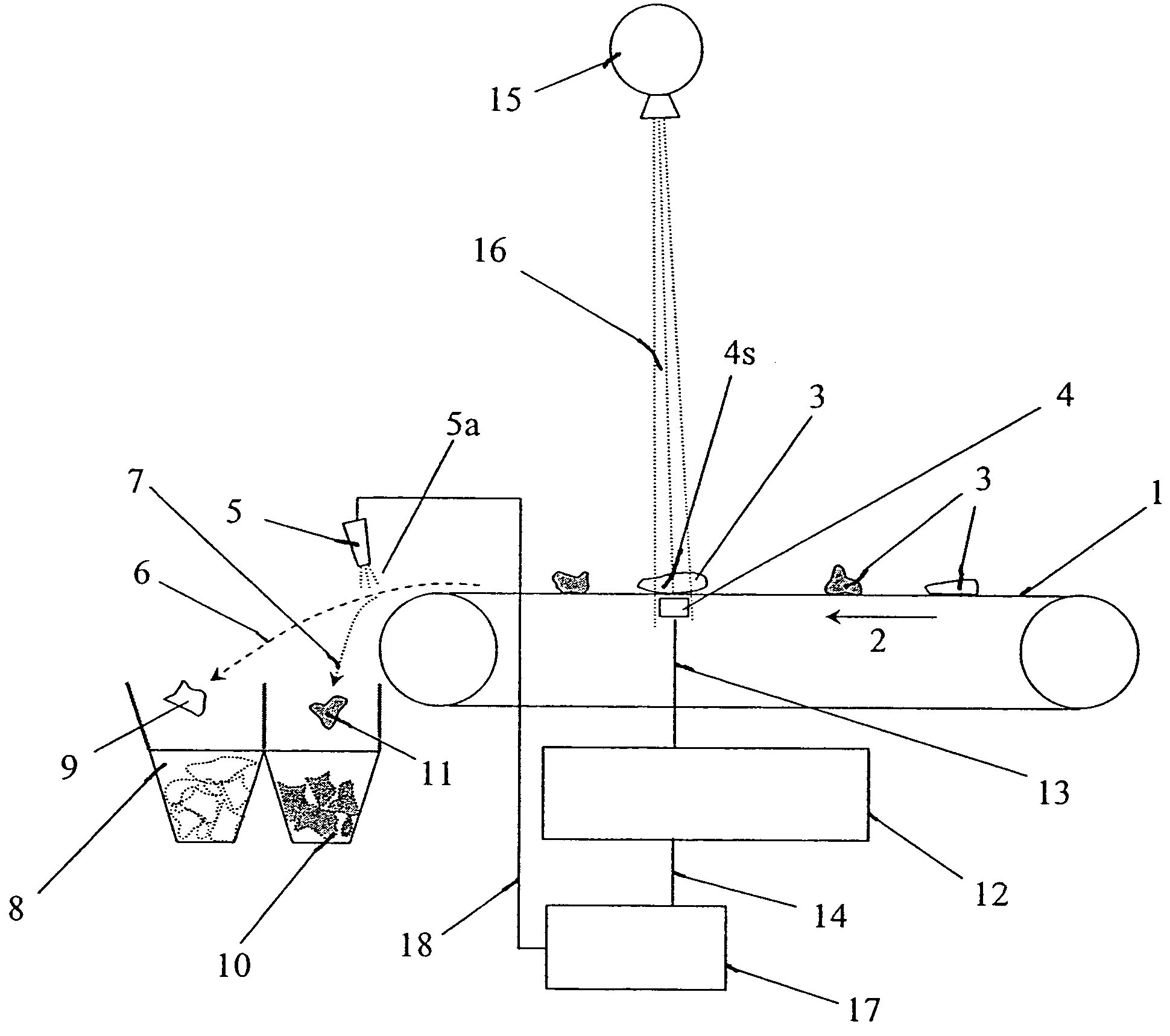
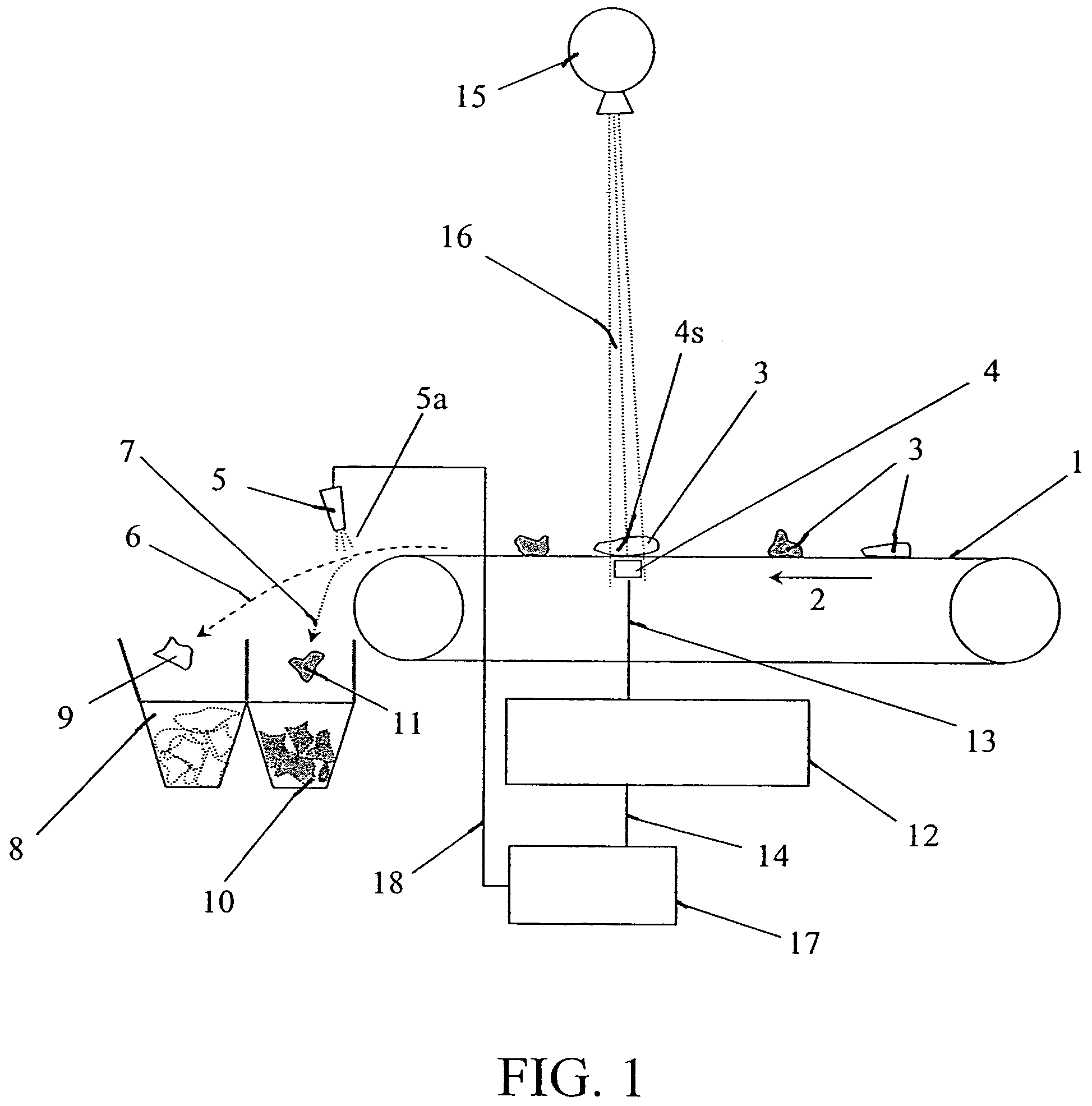
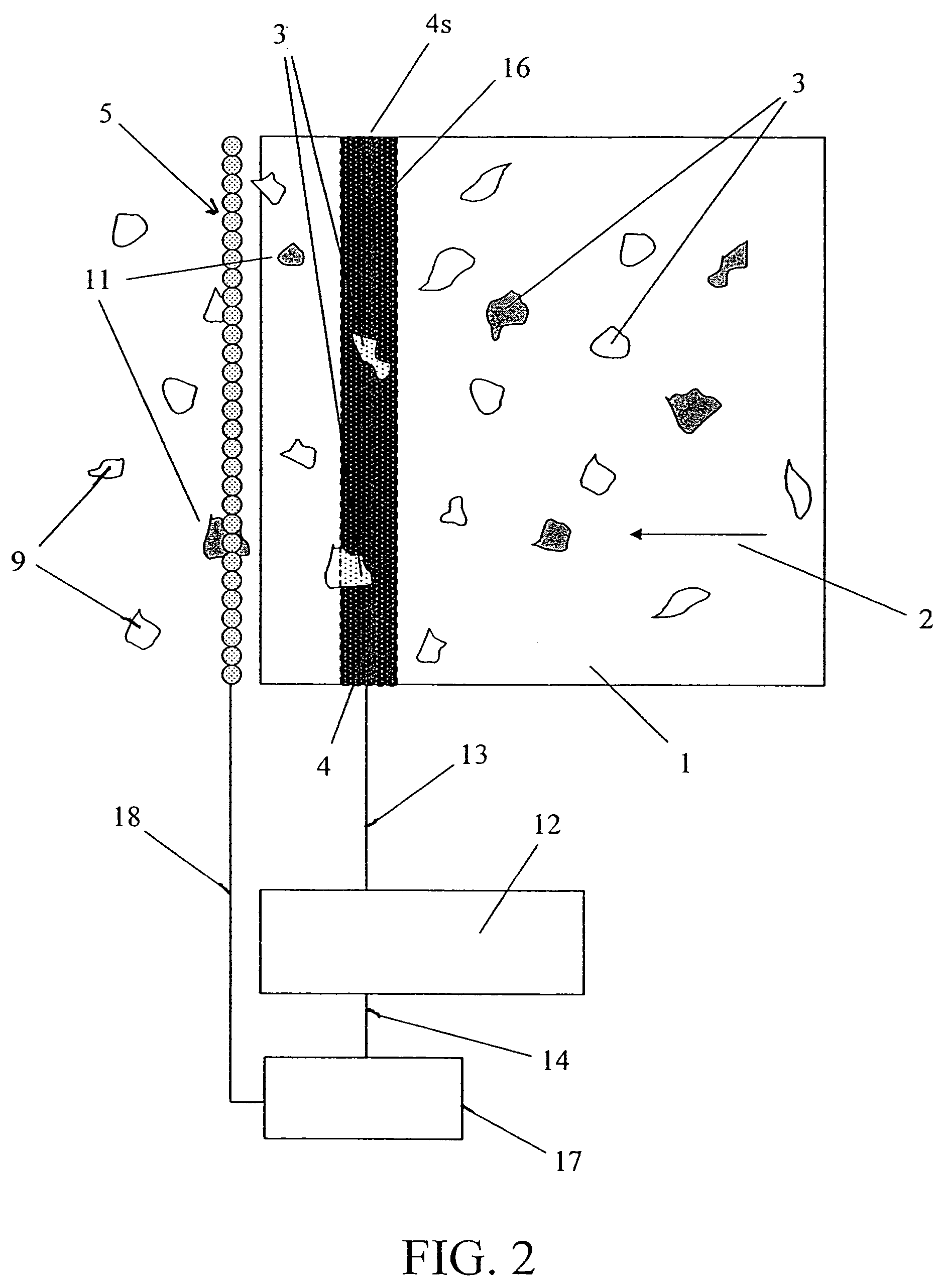
Method and apparatus for sorting materials according to relative composition
ActiveUS7564943B2Operate rapidly and accuratelyImprove throughputMaterial analysis by optical meansUsing wave/particle radiation meansX-rayDetector array
Disclosed herein is a metal sorting device including an X-ray tube, a dual energy detector array, a microprocessor, and an air ejector array. The device senses the presence of samples in the x-ray sensing region and initiates identifying and sorting the samples. After identifying and classifying the category of a sample, at a specific time, the device activates an array of air ejectors located at specific positions in order to place the sample in the proper collection bin.
Owner:SPECSTREETCARET
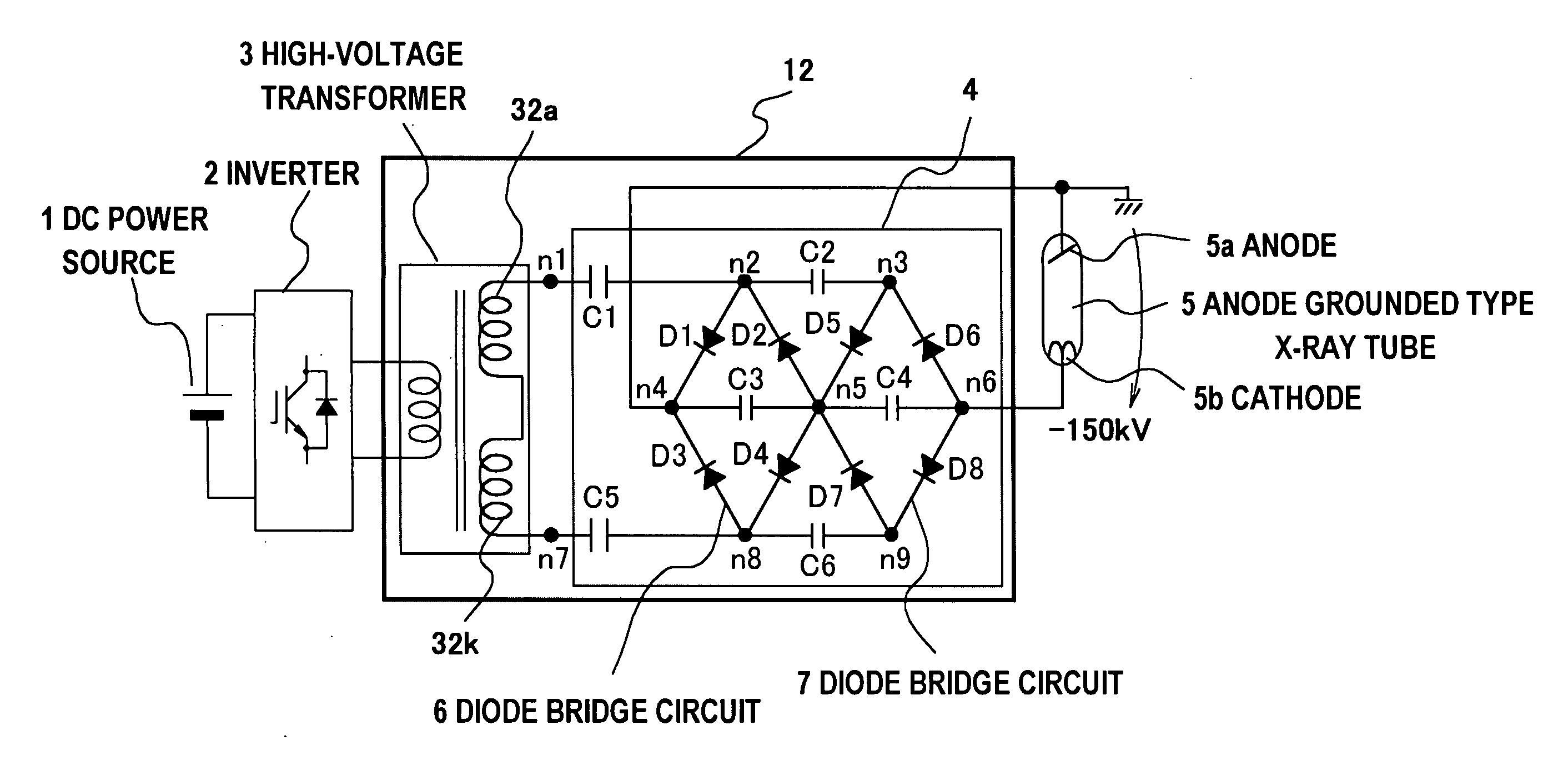
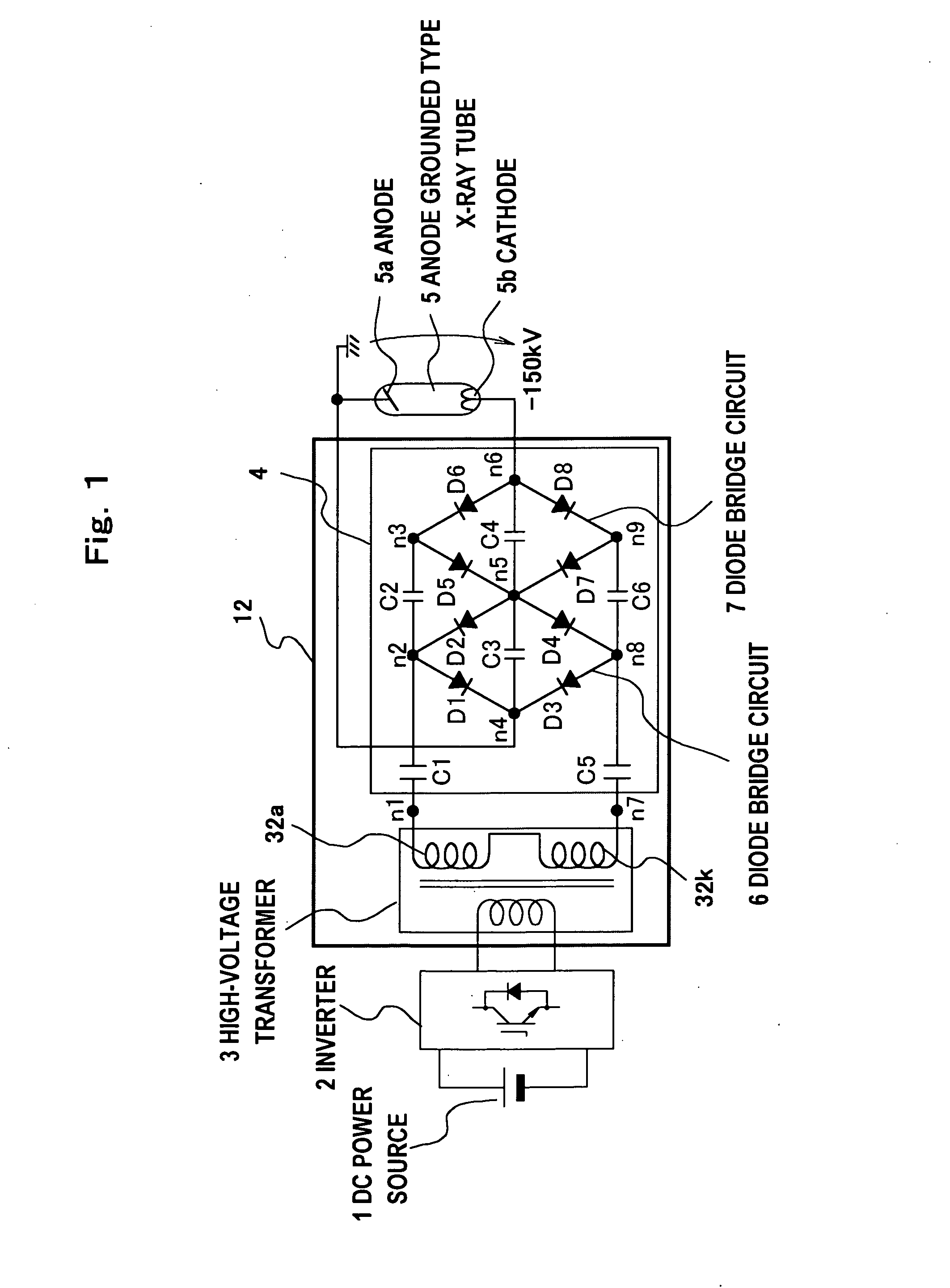
X-ray generation device
Between terminals of secondary windings in a high-voltage transformer (3), there are connected in parallel input side terminals of a plurality of diode full bridge circuits each via voltage maintaining means such as a capacitor maintaining a voltage peak value for a longer period than the cycle of an inverter (2). Between the input side terminals of the diode full bridge circuits, there are connected voltage maintaining means such as capacitors maintaining a voltage peak value for a longer period than the cycle of the inverter. Moreover, the output side terminals of the diode full bridges are connected in series via smoothing means such as almost equivalent smoothing capacitors and between the output side terminals, an anode grounding type X-ray tube (5) is connected. Thus, it is possible to realize a small-size and light-weight device at a reduced cost and reduce the ripple in the output voltage while using the anode grounding type X-ray tube.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
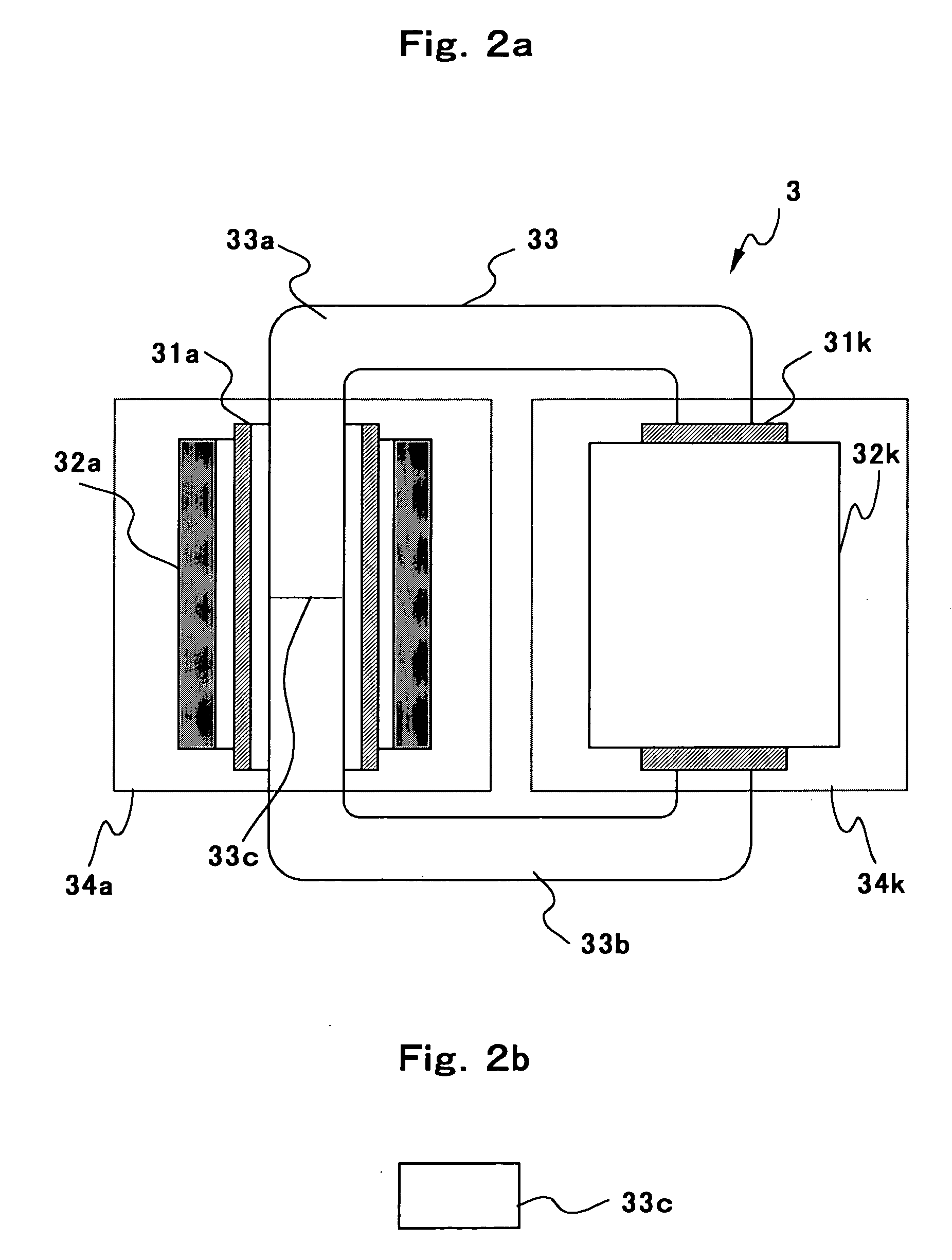
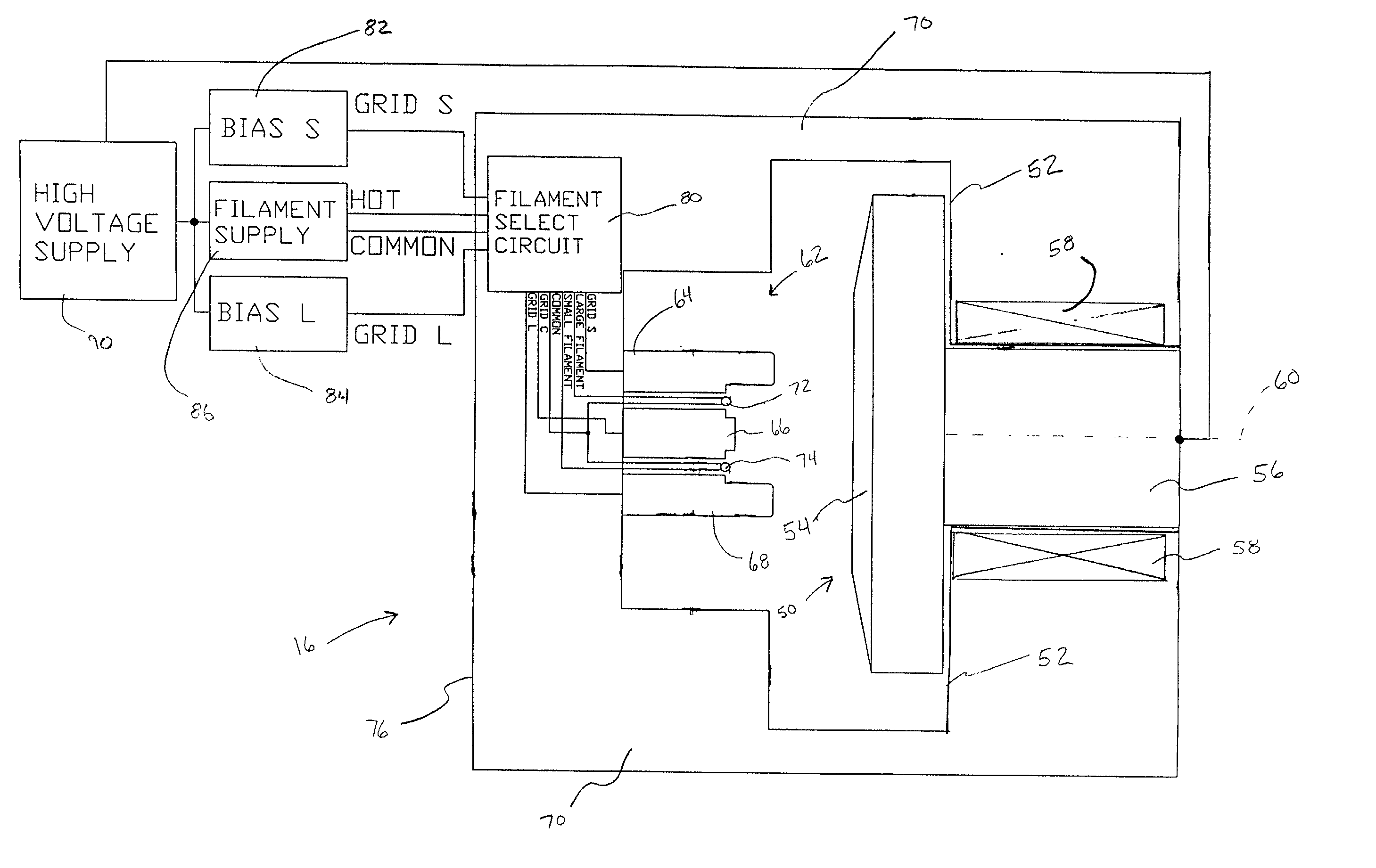
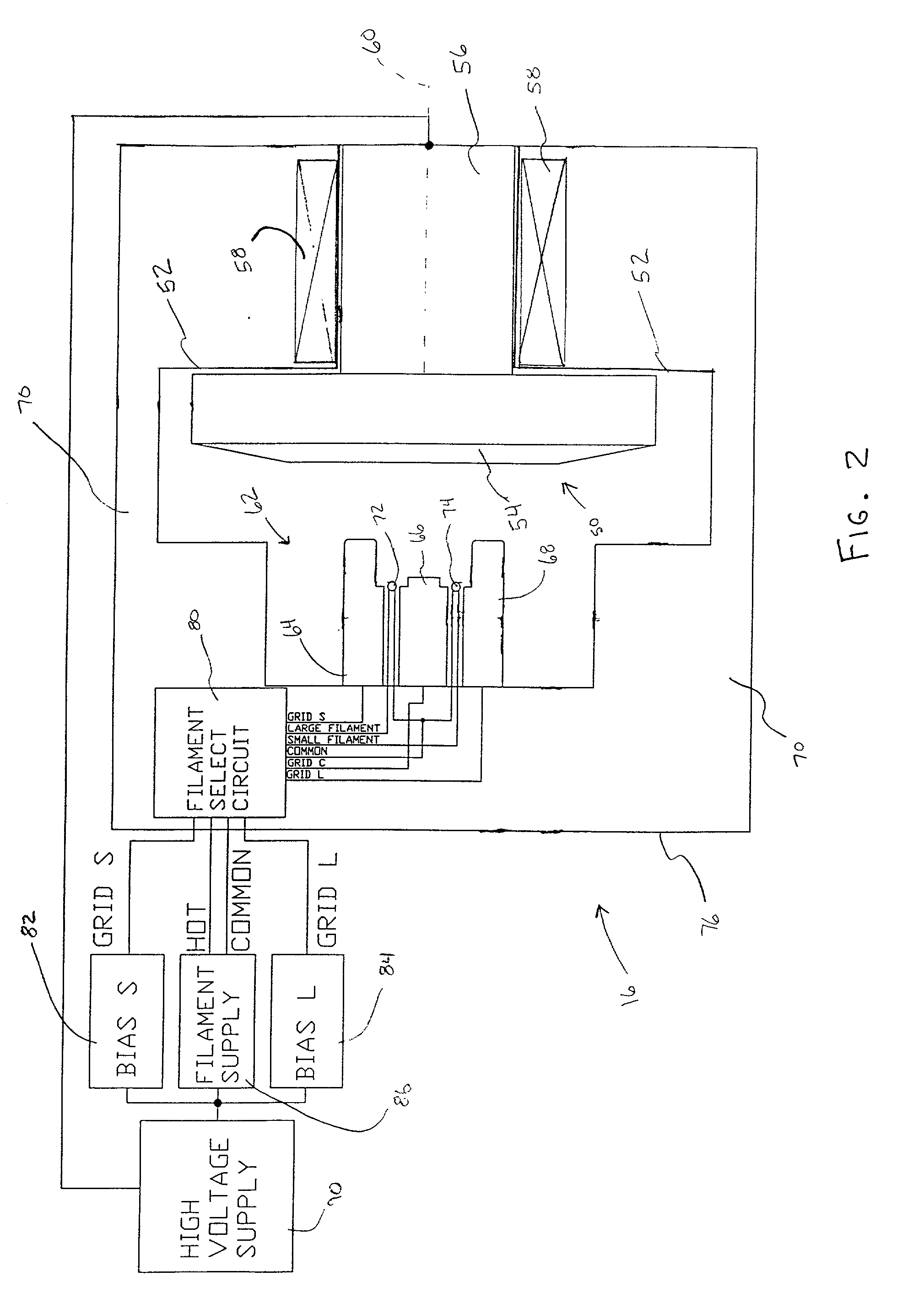
Dual filament, electrostatically controlled focal spot for x-ray tubes
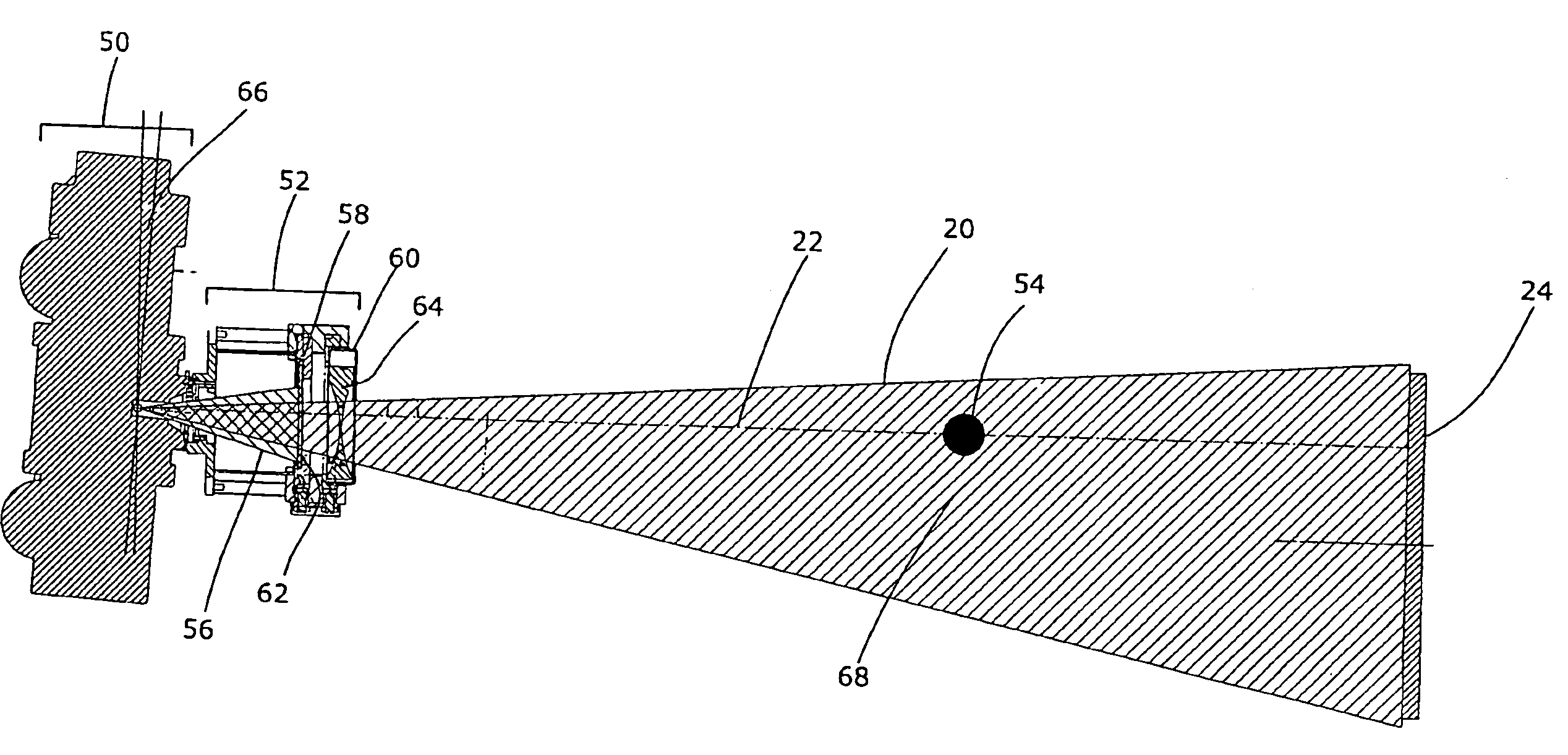
InactiveUS20020126798A1High x-ray fluxIncrease sampling densityX-ray tube electrodesCathode ray concentrating/focusing/directingX-rayVariable length
A dual filament x-ray tube assembly (16) includes an evacuated envelope (52) having an anode (54) disposed at a first end of the evacuated envelope (52) and a cathode assembly (62) disposed at a second end of the evacuated envelope (52). The cathode assembly includes a variable-length filament assembly (72, 74; 100) which emits electron beams for impingement on the anode (54) at focal spots having varying lengths. The cathode assembly (62) further includes a cathode cup (64, 66, 68; 110, 112) which is subdivided into a plurality of electrically insulated deflection electrodes (64, 66, 68; 110, 112). A filament select circuit (80) selectively and individually heats a portion of the variable-length filament assembly (72, 74). Electron beams emitted from the filament assembly (72, 74) are electrostatically focused and controlled by applying potentials to different ones of the deflection electrodes (64, 66, 68; 110, 112). The x-ray tube assembly (16) provides longer focal spots for thick-slice scanning applications and shorter focal spots for thin-slice scanning applications along with the benefit of electrostatic focusing and control.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV +1
X-ray tomogram imaging device
InactiveUS20150305696A1High resolutionImprove usabilityImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionSoft x rayX-ray
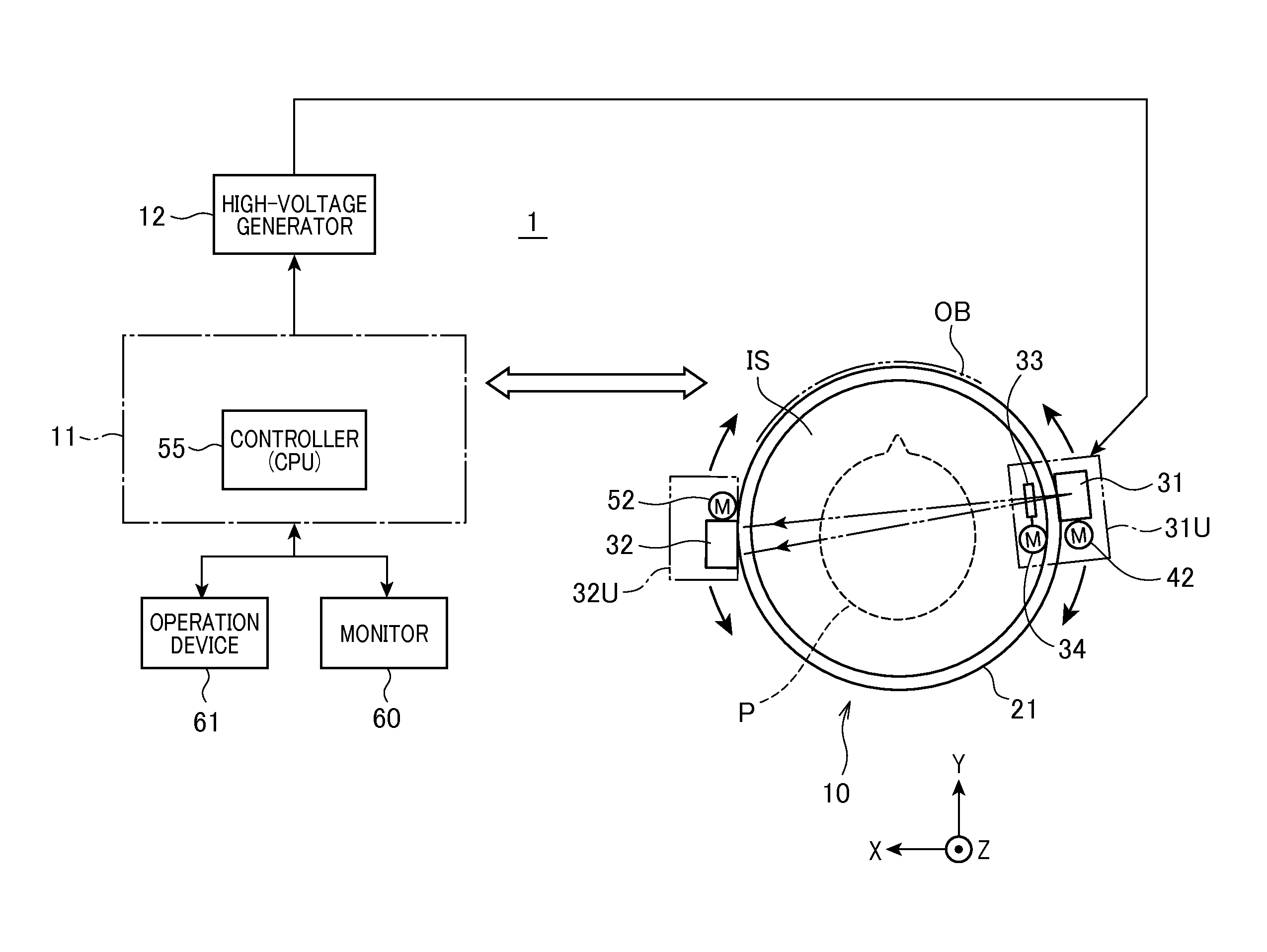
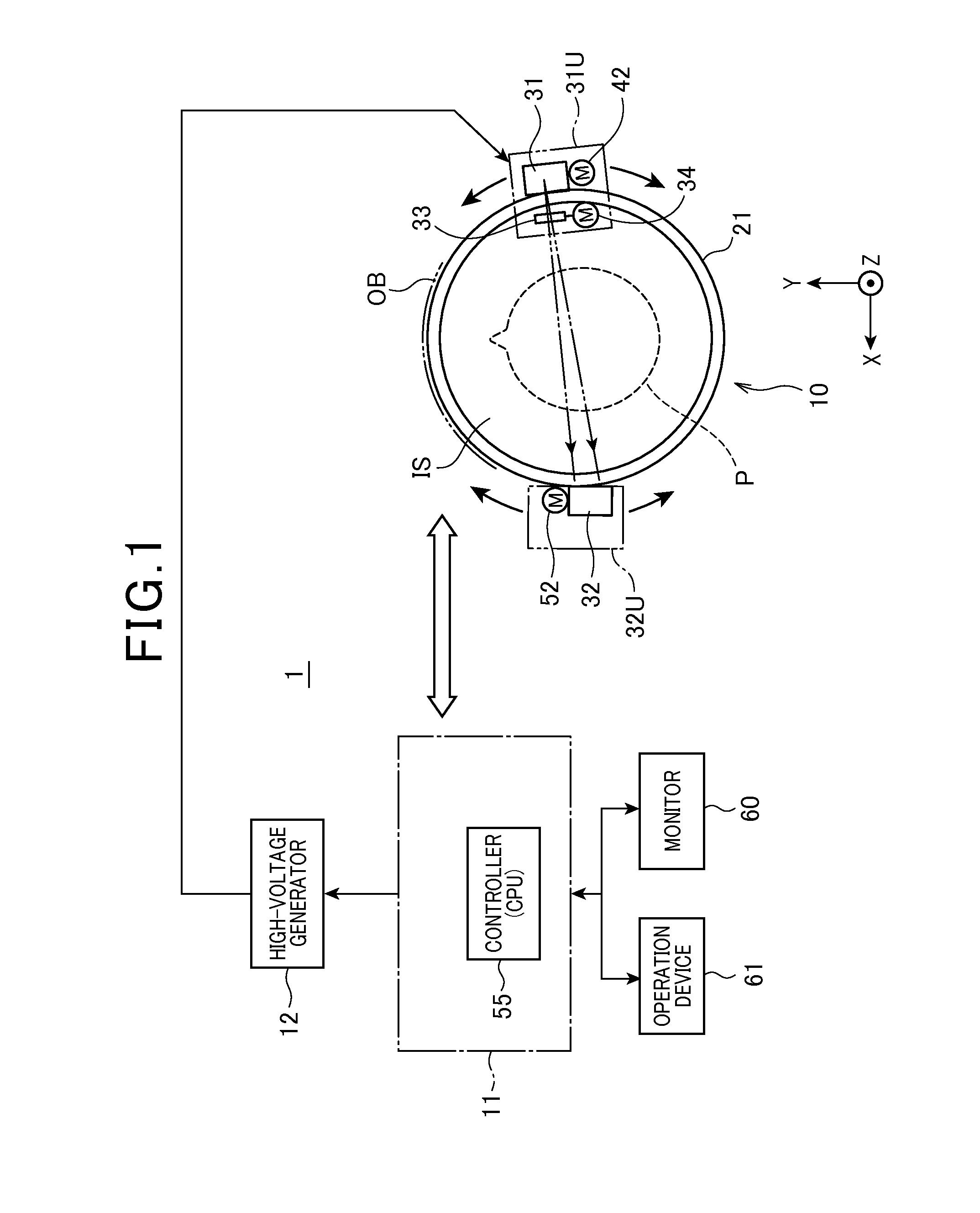
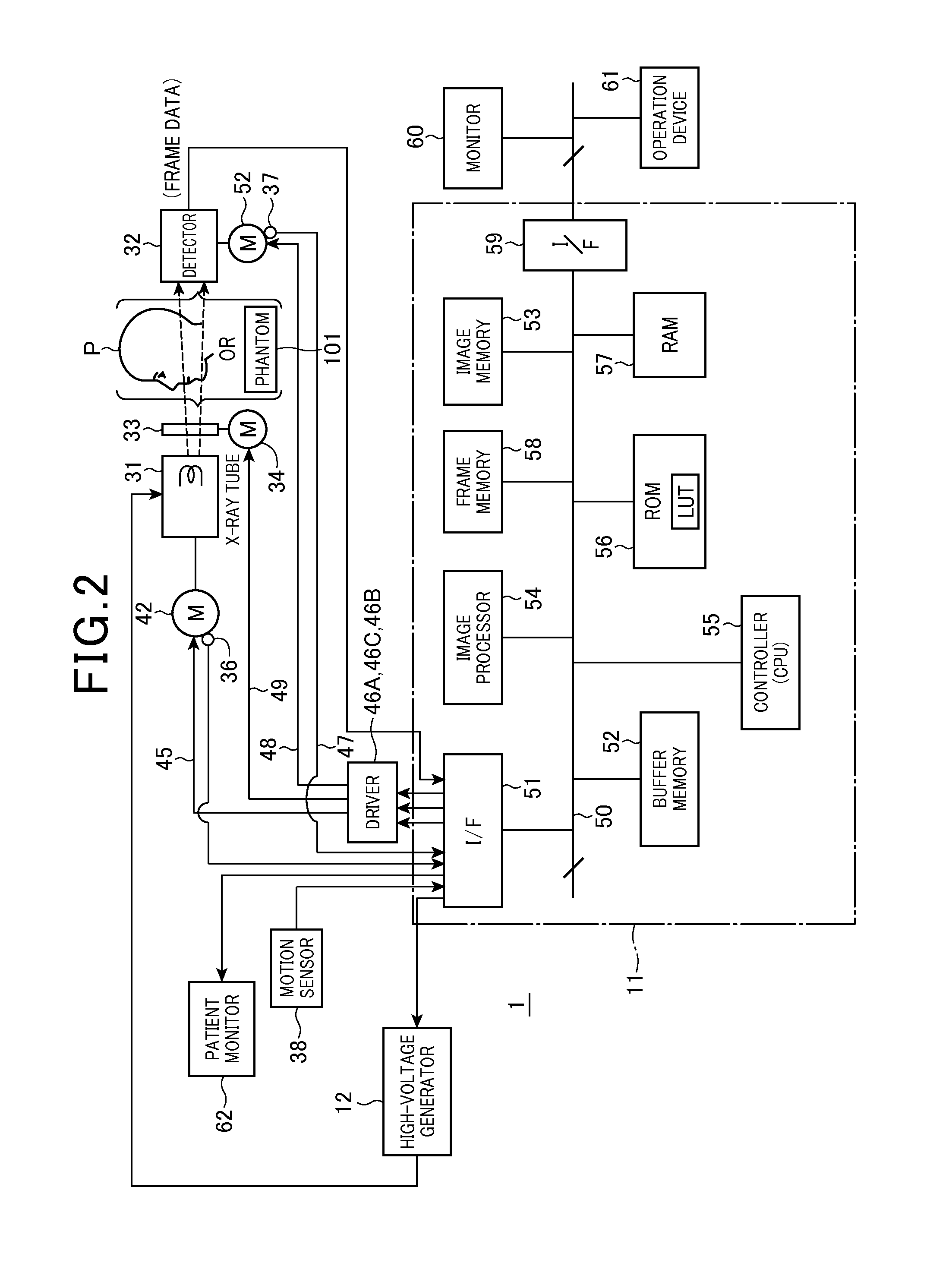
An X-ray tomographic imaging apparatus includes an X-ray and a direct conversion type of detector. The X-ray tube and the detector are supported by the support means so as to be rotatable along curved orbits mutually independently. Under instructions from a computer, scans and image reconstruction are performed. The X-ray tube and the detector are moved along the orbits mutually independently so that X-ray beams are always transmitted through a desired tomographic plane of an object at desired angles. Acquired frame data are used to produce a panoramic image of the plane, while the frame data and the panoramic image are used to produce a tomographic image in which structural components of the object are optically focused and distortions caused due to differences in X-ray paths are suppressed. The apparatus can be used as devices for dental, medical diagnosis and nondestructive inspection, and can have a CT imaging function.
Owner:TAKARA TELESYST
X-ray computed tomographic imaging apparatus
InactiveUS6990170B2Prevent irradiationAvoid omissionsReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationHelical scanData reconstruction
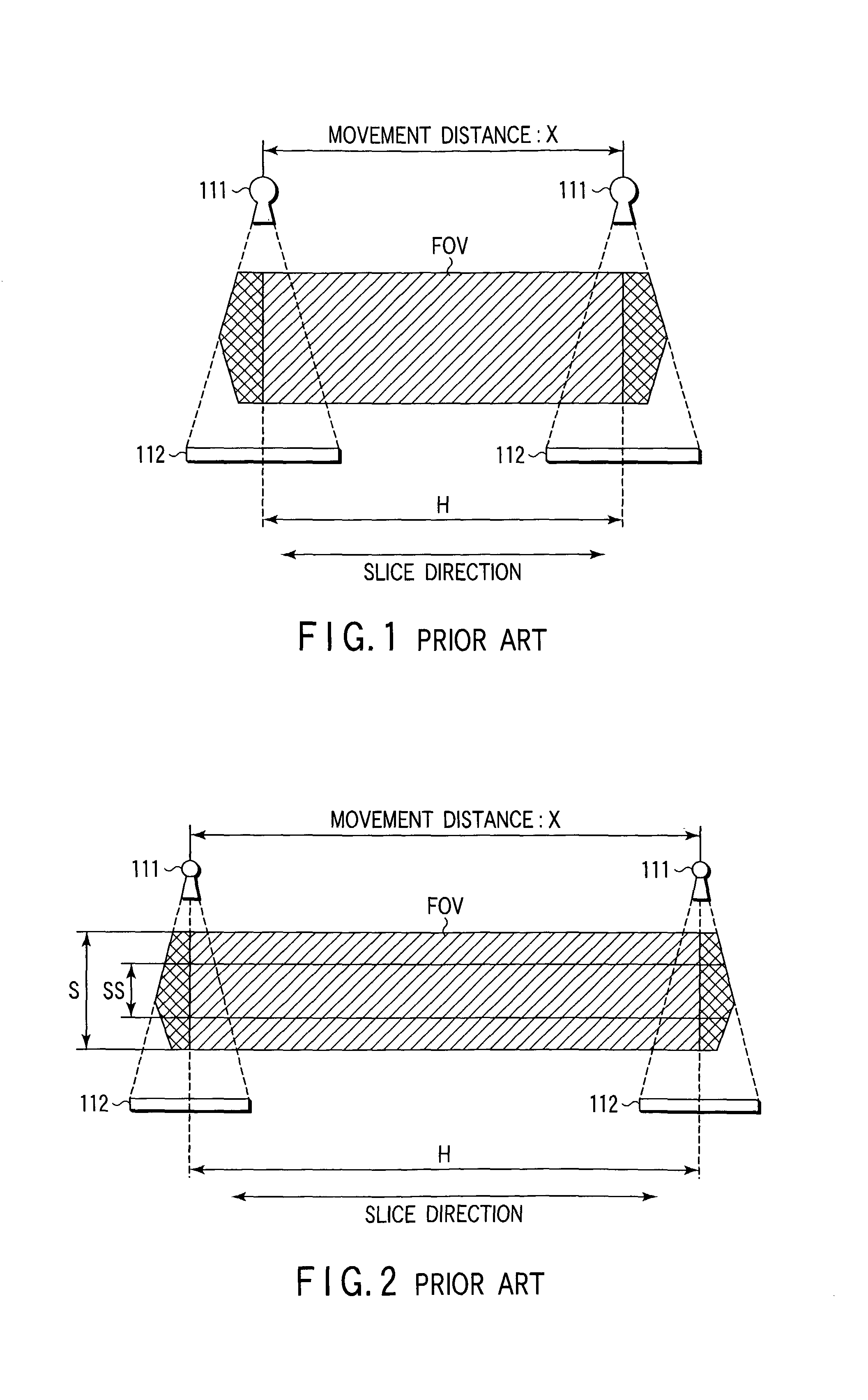
An X-ray computed tomography apparatus includes a cone beam X-ray tube, an X-ray detector, a rotating mechanism for supporting the X-ray tube and X-ray detector, a moving mechanism for moving the object in the slice direction, a control unit for controlling the rotating mechanism and moving mechanism to execute helical scan operation and move relative to the object, an input device for setting a substantially cylindrical reconstruction area, and an image reconstructing unit for reconstructing image data within the set reconstruction area based on the output of the detector. The apparatus also includes a movement distance determining unit for determining the movement distance of the X-ray tube and X-ray detector relative to the object on the basis of the radius of the set reconstruction area as well as its height.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC +1
X-ray generating apparatus
InactiveUS7215741B2Precise positioningProlong lifeX-ray tube anode coolingX-ray tube electrodesTarget surfaceEvaporation
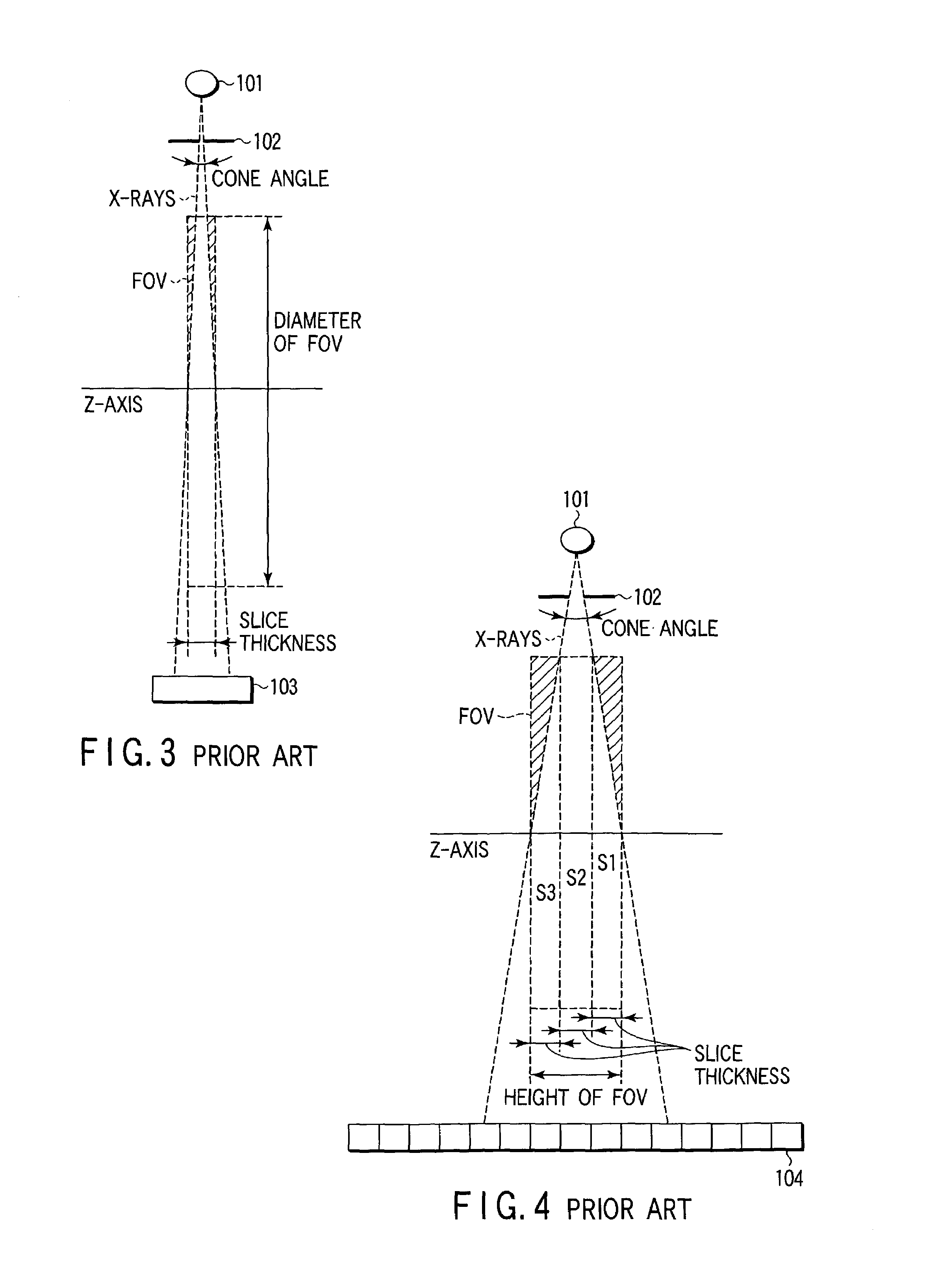
This invention relates to a microfocus X-ray tube having a heat-dissipation solid formed on the target adhesively. Specifically, the heat-dissipation solid defining an opening is formed on the target surface irradiated with an electron beam. Heat generated adjacent the target surface by impingement of an electron beam having passed through the opening is promptly distributed by heat conduction through the surface solid. The heat-dissipation solid contributes to lowering of a surface temperature of the target layer with which the electron beam collides, and a reduction of evaporation of a material forming the target, thereby extending an X-ray generating time.
Owner:SHIMADZU CORP
Integrated X-ray source module
Described is a self-contained, small, lightweight, power-efficient and radiation-shielded module that includes a miniature vacuum X-ray tube emitting X-rays of a controlled intensity and defined spectrum. Feedback control circuits are used to monitor and maintain the beam current and voltage. The X-ray tube, high-voltage power supply, and the resonant converter are encapsulated in a solid high-voltage insulating material. The module can be configured into complex geometries and can be powered by commercially available small, compact, low-voltage batteries.
Owner:NEWTON SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com