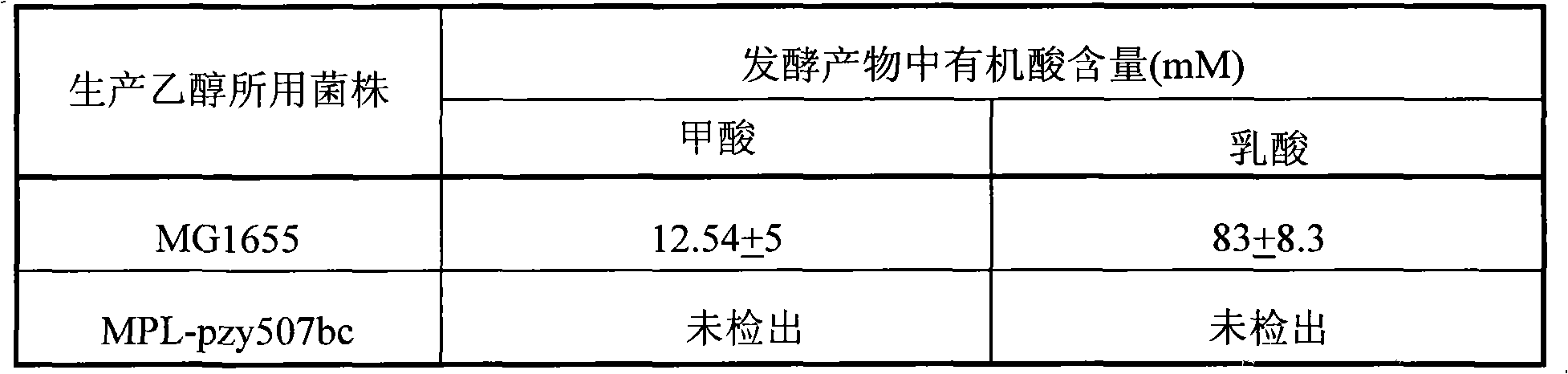
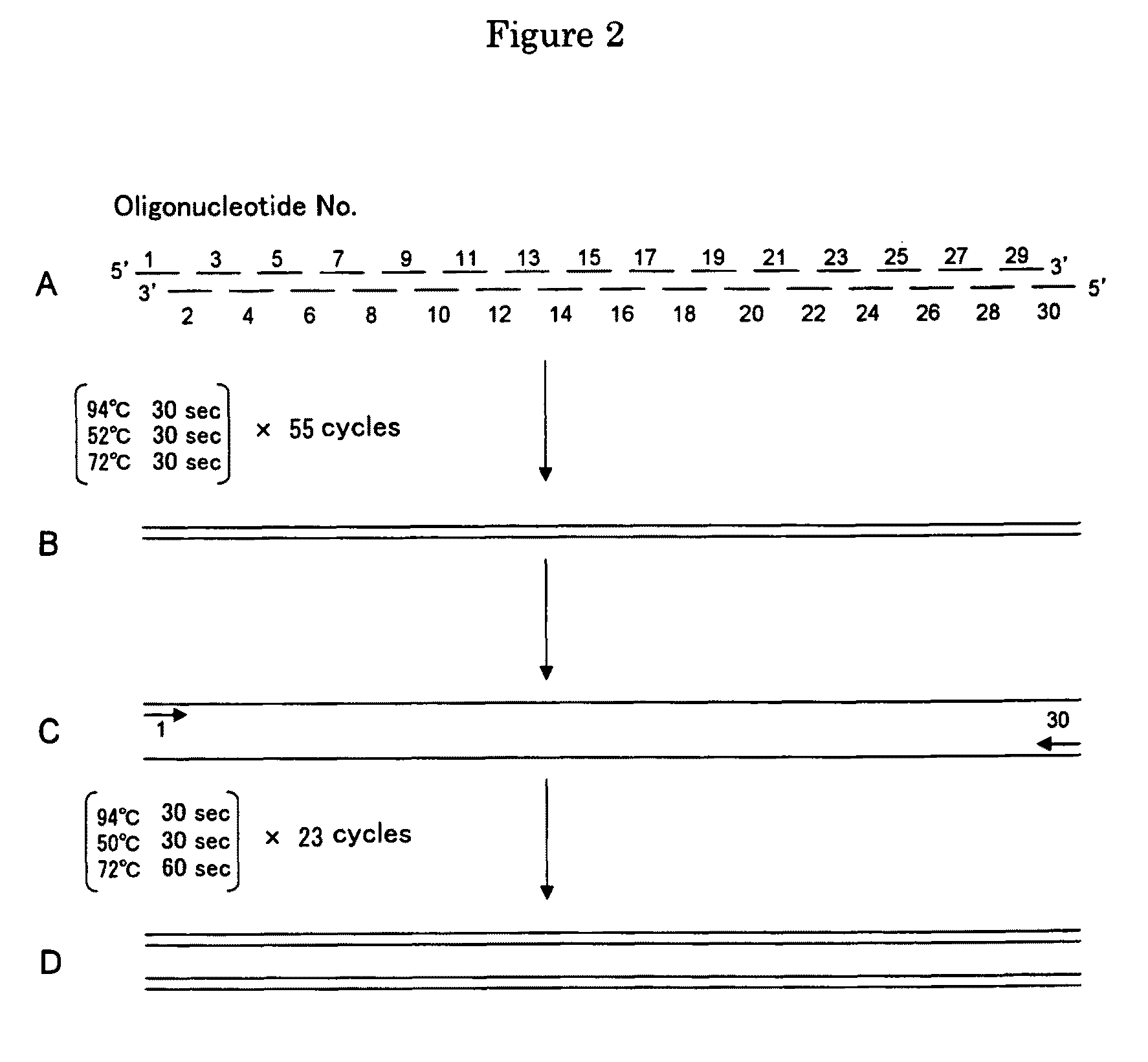
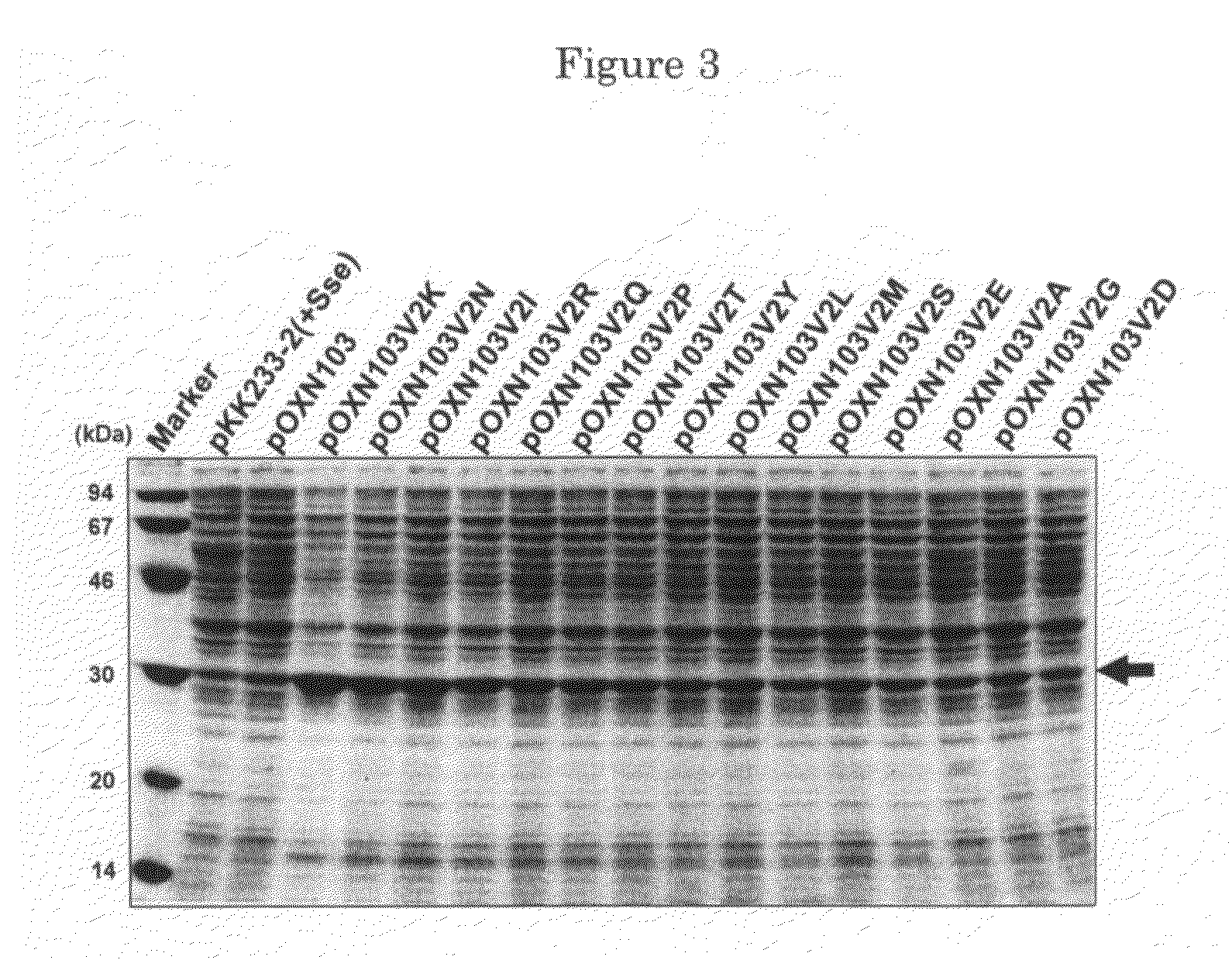
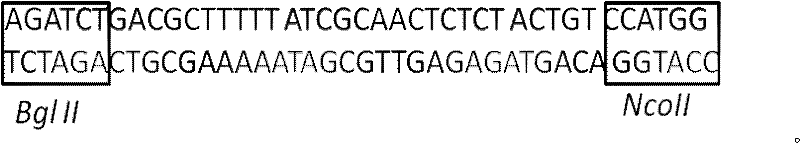Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
93 results about "Lyase Gene" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Lyase Genes encode Lyases, a class of enzymes that catalyze the hydration-dehydration cleavage of C-C, C-O, C-N, and other bonds by means other than hydrolysis or oxidation. (NCI)
XZ-A26 bacterial strain for producing L-alanine with high yield as well as construction method and application of XZ-A26 bacterial strain
Owner:ANHUI HUAHENG BIOTECH
Novel rumen bacteria variants and process for preparing succinic acid employing the same
ActiveUS20070054387A1High yieldBacteriaSugar derivativesHigh concentrationPhosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase
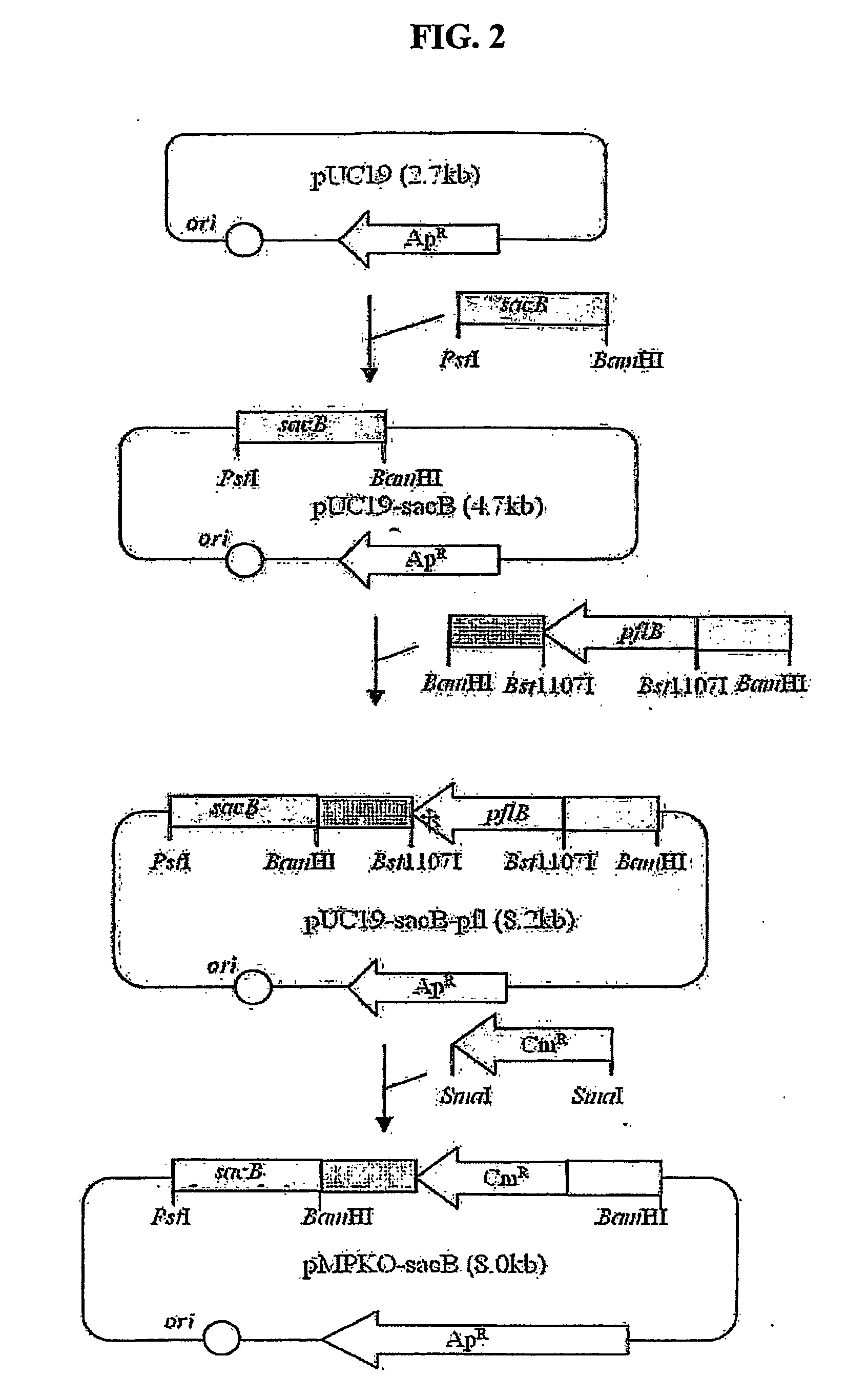
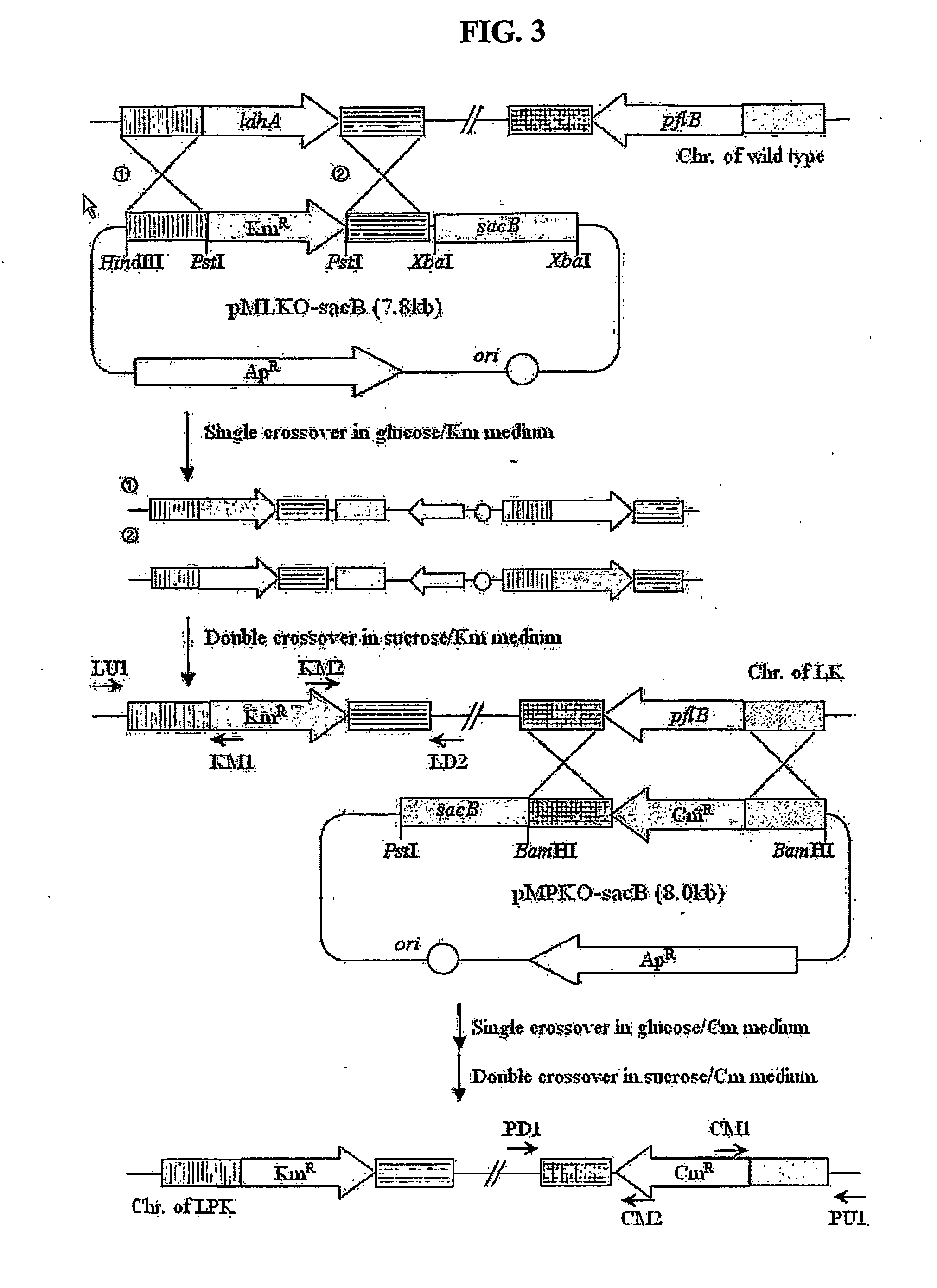
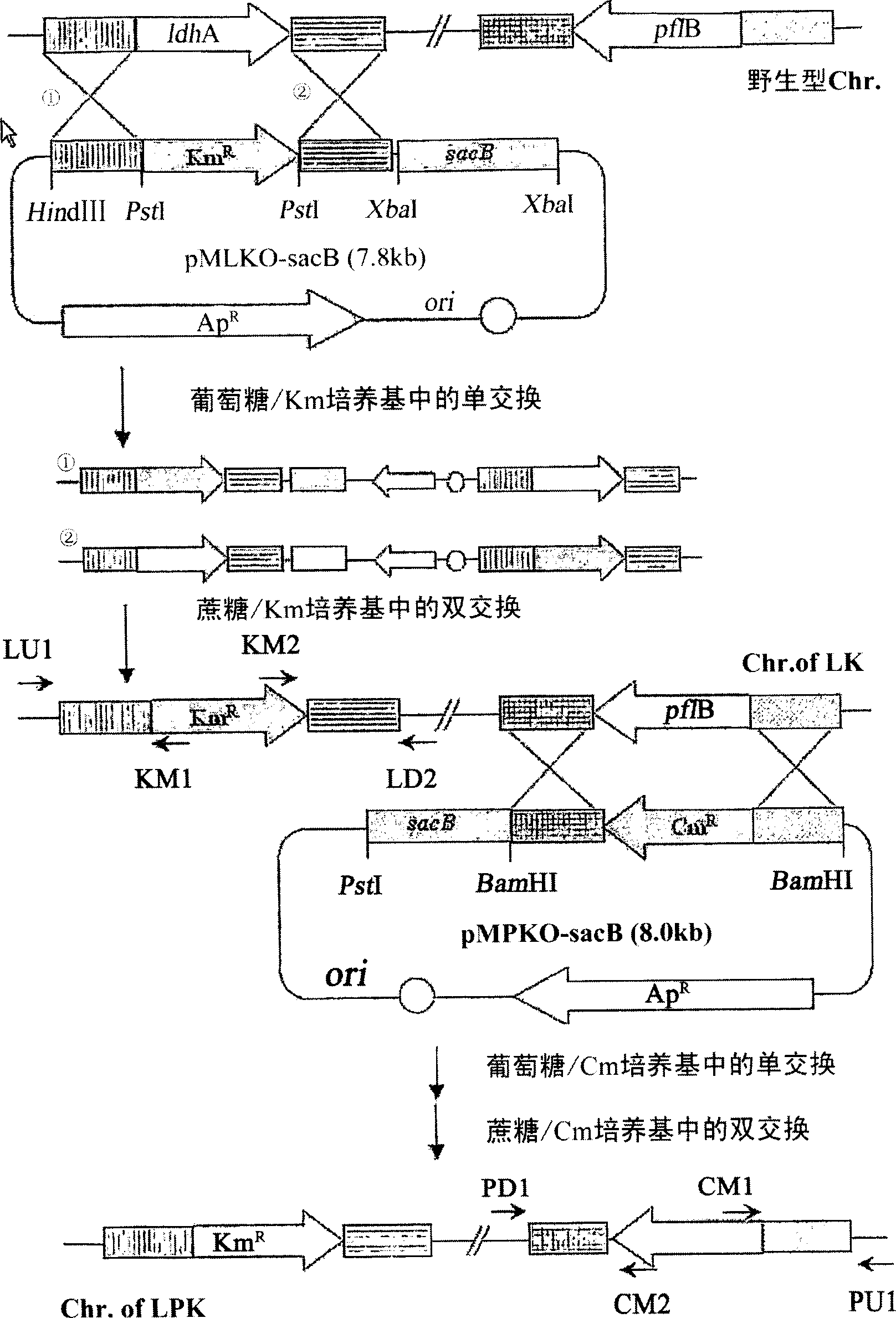
The present invention relates to novel rumen bacterial mutants resulted from the disruption of a lactate dehydrogenase gene (ldhA) and a pyruvate formate-lyase gene (pfl) (which are involved in the production of lactic acid, formic acid and acetic acid) from rumen bacteria; a novel bacterial mutant (Mannheimia sp. LPK7) having disruptions of a lactate dehydrogenase gene (ldhA), a pyruvate formate-lyase gene (pfl), a phosphotransacetylase gene (pta), and a acetate kinase gene (ackA); a novel bacterial mutant (Mannheimia sp. LPK4) having disruptions of a lactate dehydrogenase gene (ldhA), a pyruvate formate-lyase gene (pfl) and a phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase gene (ppc) involved in the immobilization of CO2 in a metabolic pathway of producing succinic acid; and a method for producing succinic acid, which is characterized by the culture of the above mutants in anaerobic conditions. The inventive bacterial mutants have the property of producing succinic acid at high concentration while producing little or no organic acids, as compared to the prior wild-type strains of producing various organic acids. Thus, the inventive bacterial mutants are useful as strains for the industrial production of succinic acid.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
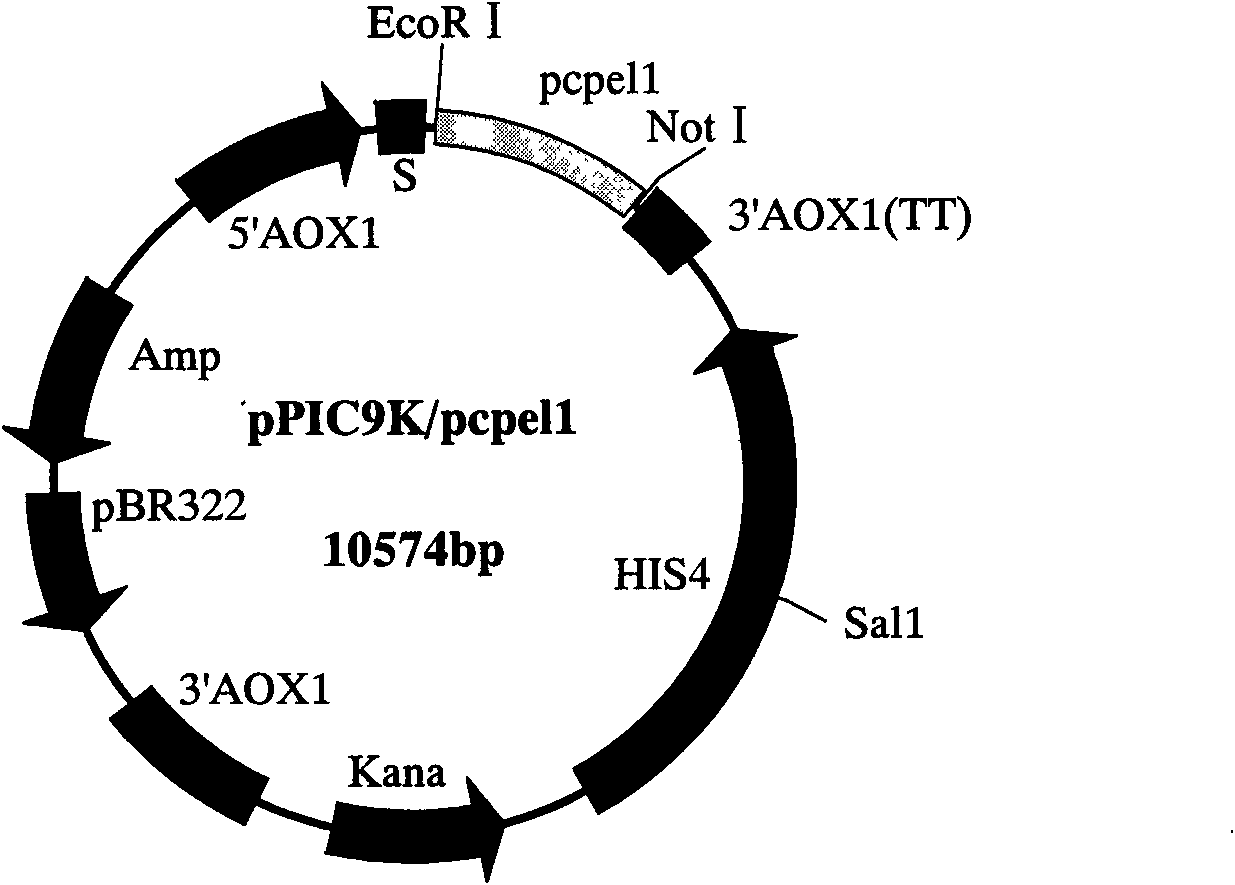
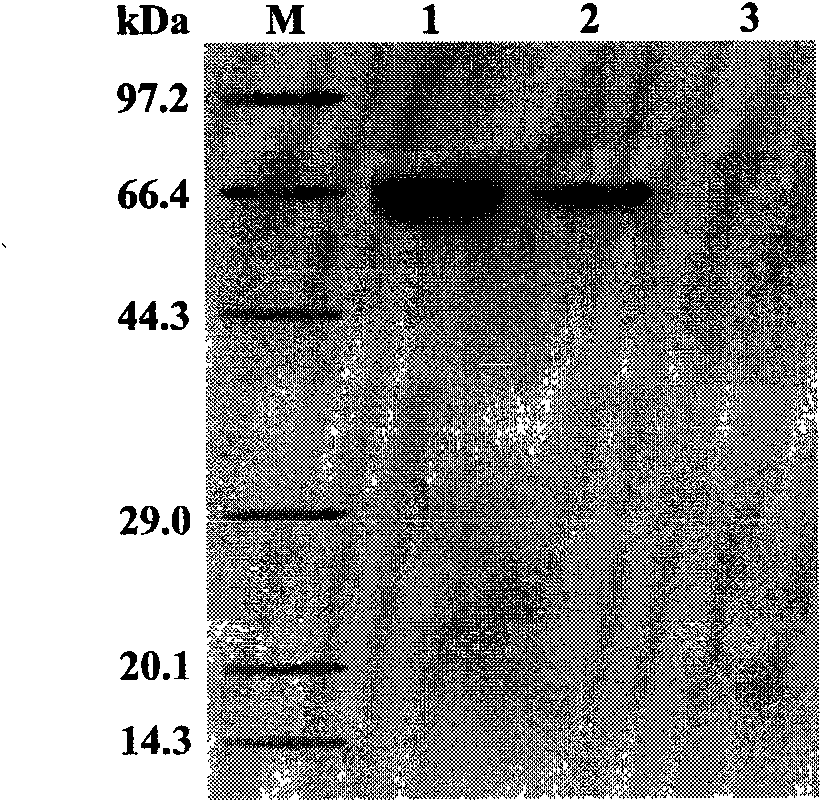
Phytophthora capsici pectate lyase (PL) Pcpel1 gene, protein preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN101638663AObvious symptomsSufficient technical reservesMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesCytochemistryPlant pathology
The invention belongs to the technical field of biology and in particular provides a pectate lyase (PL) gene Pcpel1 which is cloned from phytophthora capsici and protein preparation technology thereof. Gene and protein levels prove that the gene is effectively involved in the process that the phytophthora capsici infects hot pepper hosts and results in occurrence of the course of diseases on hot pepper leaves. Plant pathology and cytochemistry technology further prove that after the protein coded by the gene is inoculated onto the hot pepper leaves, obvious withering and shrinking occur on theinoculated parts of the leaves and the cell walls on the affected parts of the leaves are obviously degraded, namely the gene code is an important protein related to the course of diseases or is possibly an important target pathogenic gene of a phytophthora capsici PL gene cluster. The invention provides important technical reserve for further developing phytophthora capsici molecule detection technology.
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Recombinant escherichia coli strain for producing beta-alanine as well as construction method and application thereof
ActiveCN103898035AHigh yieldSuitable for large-scale industrial productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliRecombinant escherichia coli
The invention discloses a recombinant escherichia coli strain (Escheerichiacoli) AHB-36 for producing beta-alanine, the preservation number is CCTCC M 2013629, the recombinant escherichia coli strain is a deficiency aspartic acid amino lyase gene and contains an aspartic acid-1-decarboxylase gene. The invention further aims at providing a construction method of the recombinant escherichia coli strain. The recombinant escherichia coli strain can be used for knocking off the aspartic acid amino lyase gene and preventing the escherichia coli from pyrolyzing the aspartic acid into fumaric acid, so that the aspartic acid is completely applied to production of beta-alanine, and meanwhile aspartic acid-1-decarboxylase is expressed in the recombinant escherichia coli strain, and thus the yield of beta-alanine is further increased.
Owner:ANHUI HUAHENG BIOTECH
Sodium alginate catenase gene algl and its preparation method and application
InactiveCN1514000AIncrease temperatureImprove stabilityBacteriaGenetic engineeringPolymannuronic acidEscherichia coli
An algin lyase gene algl able to code marine pseudomonads QDA is prepared from the QDA genome DNA library by cloning, and cna be used to prepare the recombinant algin lyase. It can degradate the homopolymannuronic acid to obtain algin oligose. Said recombinant algin lyase features high stability of temp and pH value, and activity, high expression level in colibacillus 24%, and low cost.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Ethanol fermentation engineering bacteria capable of reducing fermentation byproduct
InactiveCN101875912AReduce accumulationReduce contentBacteriaMutant preparationLactate dehydrogenaseEscherichia coli
The invention relates to an ethanol fermentation engineering bacteria capable of reducing a fermentation byproduct. The ethanol fermentation engineering bacteria is characterized in that a pyruvate formate-lyase gene and a lactate dehydrogenase gene of Escherichia coli are inactivated; and a Zymomonas mobilis gene is transferred into the Escherichia coli. When ethanol is produced by fermenting hexose and pentose with the engineering bacteria, lactic acid and formic acid are not produced and the byproduct is reduced, so that the ethanol productivity is improved.
Owner:THE INST OF BIOTECHNOLOGY OF THE CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
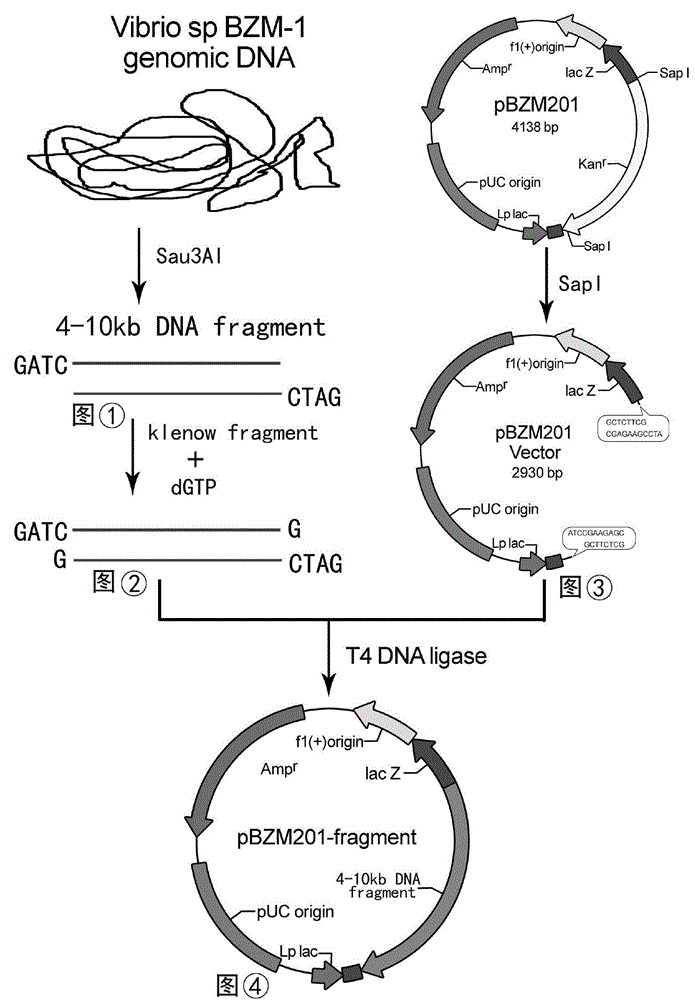
Gene of novel alginate endolyase, engineering bacterium and application
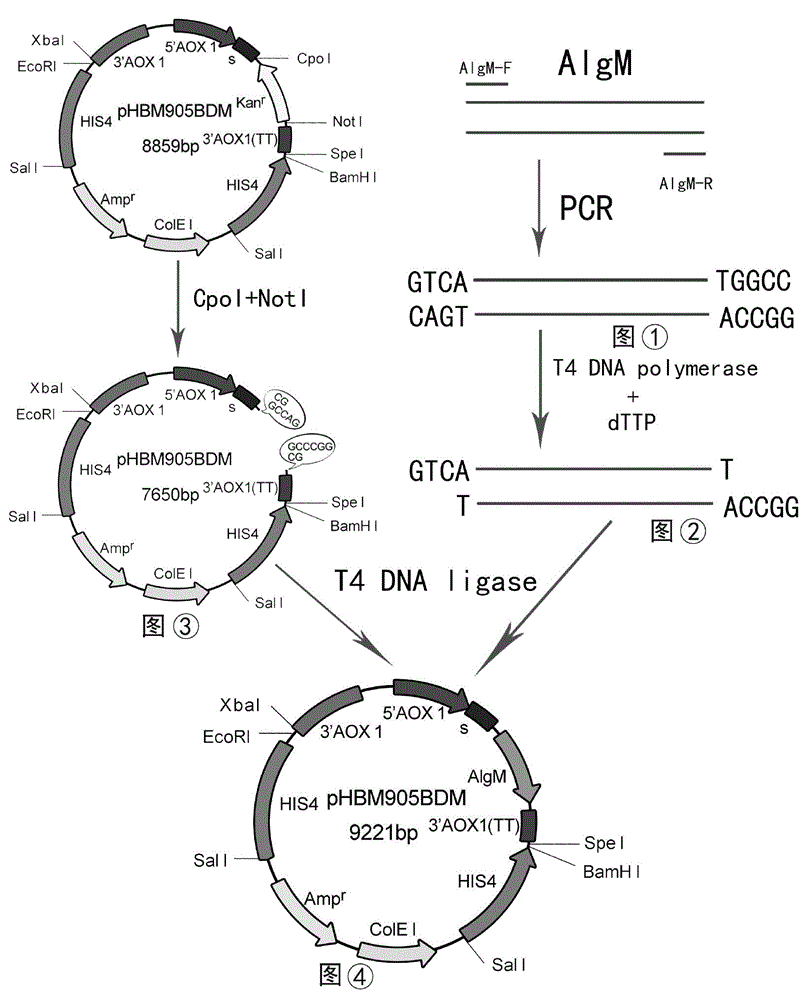
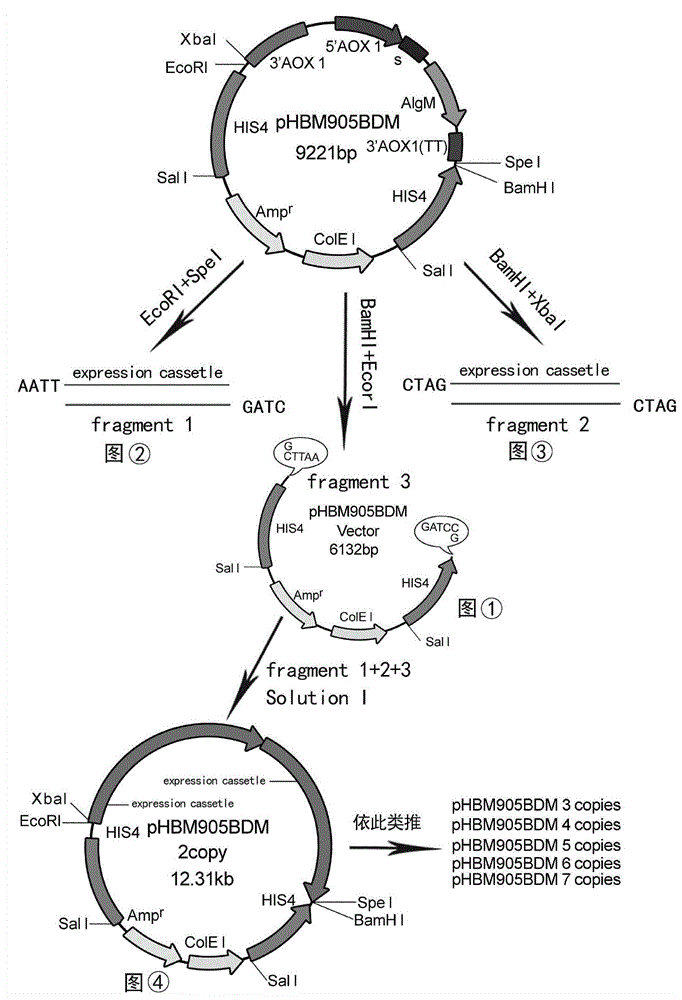
ActiveCN105154458AIncrease enzyme activityHigh purityFungiMicroorganism based processesCompetent cellAlginate lyase
The invention discloses recombinant alginate lyase, an engineering bacterium thereof and a method for preparing alginate oligosaccharide through hydrolysis. The method is characterized by screening an alginate lyase gene AlgM according to a strain Vibrio sp.BZM-1 newly isolated from seaweeds; constructing an expression vector pHBM905BDM-AlgM containing the gene, and converting pichia sp GS115 competent cells to obtain a single copy gene engineering bacterium; and constructing, culturing and verifying the multi-copy gene engineering bacterium to prepare recombinant alginate lyase through high-efficiency expression, and producing alginate oligosaccharide by hydrolyzing sodium alginate with alginate lyase. The recombinant alginate lyase gene engineering bacterium GS115 / AlgM4 (CCTCC No:M2015500) containing four copies has a higher expression level. The activity of recombinant alginate lyase is as high as 31000U / mL.
Owner:BINZHOU MEDICAL COLLEGE
Alkaline pectate lyase producing gene engineering bacteria and construction and use thereof
InactiveCN102191212AIncrease productionShort fermentation timeBacteriaMicroorganism based processesHybrid proteinGenetic engineering
The invention discloses alkaline pectate lyase producing gene engineering bacteria and construction and use thereof and belongs to the field of genetic engineering. In the invention, the Escherichia coli pel engineering bacteria capable of secreting and expressing pectinase Pel in vitro with high efficiency are constructed from an industrial prospective by using a totally synthetic Aspergillus nidulans pel gene. The invention also provides a method for producing pectinase by using the engineering bacteria. When the engineering bacteria are used, the fermentation time is short, and at 37 DEG C, the total fermentation lasts for 6 hours, wherein the early fermentation lasts for 4 hours and post fermentation lasts for 6 hours; the enzyme active yield is as high as 400U / mL; in addition, the produced pectinase can be secreted in vitro directly, hybrid proteins are reduced, and the purification is easy. Therefore, the engineering bacteria have better industrial application prospect.
Owner:YANCHENG TEACHERS UNIV
Novel rumen bacteria variants and process for preparing succinic acid employing the same
The present invention relates to novel rumen bacterial mutants resulted from the disruption of a lactate dehydrogenase gene (ldhA) and a pyruvate formate-lyase gene (pfl) (which are involved in the production of lactic acid, formic acid and acetic acid) from rumen bacteria; a novel bacterial mutant (Mannheimia sp. LPK7) having disruptions of a lactate dehydrogenase gene (ldhA), a pyruvate formate-lyase gene (pfl), a phosphotransacetylase gene (pta), and a acetate kinase gene (ackA); a novel bacterial mutant (Mannheimia sp. LPK4) having disruptions of a lactate dehydrogenase gene (ldhA), a pyruvate formate-lyase gene (pfl) and a phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase gene (ppc) involved in the immobilization of CO2 in a metabolic pathway of producing succinic acid; and a method for producing succinic acid, which is characterized by the culture of the above mutants in anaerobic conditions. The inventive bacterial mutants have the property of producing succinic acid at high concentration while producing little or no organic acids, as compared to the prior wild-type strains of producing various organic acids. Thus, the inventive bacterial mutants are useful as strains for the industrial production of succinic acid.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
High-yield 3-Methionol saccharomyces cerevisiae engineering bacteria and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN103409331AIdentify key metabolic nodesOptimizing Fermentation MediumFungiMicroorganism based processesEnzyme GeneMetabolic network
The invention relates to high-yield 3-Methionol saccharomyces cerevisiae engineering bacteria and a preparation method and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of biological preparation of food flavors. According to the high-yield 3-Methionol saccharomyces cerevisiae engineering bacteria and the preparation method and application thereof, the engineering bacteria is designed and constructed through the coupling excessive expression of an aminotransferase gene (ARO9) and a decarboxylase gene (ARO10) and the knock-out of a methylthio lyase gene (CY3) in the anabolic pathway of Methionol by taking Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288c as an original strain; the expression of two key enzyme genes in a main synthetic pathway is enhanced, and the expression of the CY3 gene in a side reaction pathway is reduced or eliminated; the bred engineering bacteria (converter) is subjected to multiple-time passage and stable in inheritance, so that the metabolic network and metabolic pathway of the biological synthesis of the Methionol are optimized, and the metabolic flux and yield of the Methionol are obviously increased; a Methionol flavor prepared by fermenting and converting the engineering bacteria is single in structure and chirality and high in fragrance quality.
Owner:BEIJING TECHNOLOGY AND BUSINESS UNIVERSITY
Pectate lyases with increased thermostability and/or enzymatic activity
ActiveUS20100285569A1Improve enzymatic activityImprove thermal stabilityBacteriaPre-extraction tea treatmentXanthomonas campestrisEscherichia coli
Using site-directed mutagenesis to mutate the Xanthomonas campestris pectate lyase gene, variants of Xanthomonas campestris pectate lyase with improved thermostability and / or enzymatic activity have been expressed in Escherichia coli, and then isolated and purified. The mutant Xanthomonas campestris pectate lyases are more effective than the wild-type enzyme, also expressed in E. coli, in removing pectic compounds from natural hemp fiber.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
Co-expression system and construction method of polyvalent bacteriophage lyase genes, live vaccine of carrying system and preparation and application of live vaccine
InactiveCN104673821AEnables cheap scalingNo autolysisAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsMycobacterium smegmatisLatent tuberculosis
The invention discloses a co-expression system and construction method of polyvalent bacteriophage lyase genes, a live vaccine of a carrying system and preparation and application of the live vaccine. Eukaryotic expression plasmids are used as an expression vector, and LysinA, LysinB and Holin gene segments are directionally inserted into the plasmids to simultaneously express the co-expression system of the bacteriophage lyase genes of three kinds of targeted mycobacterium tuberculosis. Mycobacterium smegmatis with good targeting property of macrophages or genetically-modified recombinant BCG is used as a live vector, the co-expression system simultaneously carrying three kinds of genes is electrically transformed into the mycobacterium smegmatis or the genetically-modified recombinant BCG, and then the recombinant therapeutic tuberculosis live vaccine is obtained through expansion in vitro. The live vaccine has a good effect on the field of curing active tuberculosis or latent tuberculosis infection caused by proliferative mycobacterium tuberculosis, dormant mycobacterium tuberculosis and drug-resistant mycobacterium tuberculosis.
Owner:伊正君
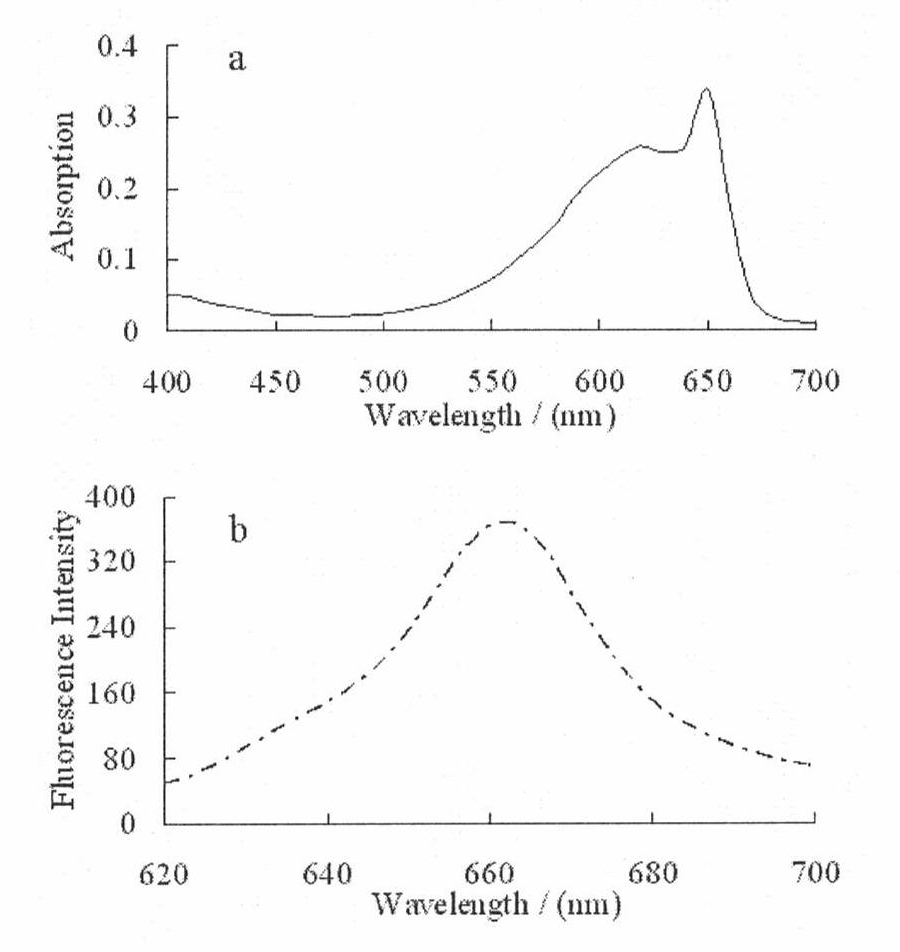
Method for preparing allophycocyanin tripolymer fluorescent protein
InactiveCN102094029AEasy to trainGrow fastAlgae/lichens peptidesFermentationBiotechnologyEnzyme Gene
The invention belongs to the field of fluorescent protein materials in biotechnology, and specifically relates to a method for preparing an allophycocyanin tripolymer fluorescent protein. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, cloning allophycocyanin alpha sub-gene apoprotein genes and phycobilin biosynthesis enzyme genes hol and pcyA into an expression vector; and secondly, cloning allophycocyanin beta sub-gene apoprotein genes and chromophore lyase genes cpcS and cpcU into another vector, using the two expression vectors to simultaneously transform Escherichia coli, and screening out an engineering bacterium simultaneously expressing the genes, thus obtaining the allophycocyanin tripolymer fluorescent protein. By using the Escherichia coli as the raw material instead of algae to produce the recombinant photo-activated protein, the Escherichia coli is easy to culture and grows fast, thereby greatly shortening the production cycle. Compared with algae, the cell wall of the Escherichia coli can be broken easily, energy can be saved in the purification process, and a high utilization rate can be achieved.
Owner:INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Substitutional variants of hydroxynitrile lyase with high specific activity and methods of use
InactiveUS8030053B2High activitySugar derivativesBacteriaHydroxynitrile lyase activityHigh specific activity
An improved hydroxynitrile lyase characterized by having a mutation of substitution of at least one amino acid residue in the amino acid sequence of a wild-type hydroxynitrile lyase with another amino acid and by its hydroxynitrile lyase activity per transformant being higher than the hydroxynitrile lyase activity per transformant into which the wild-type hydroxynitrile lyase gene is introduced; and a method for producing a hydroxynitrile lyase, comprising expressing the improved hydroxynitrile lyase in a host and recovering the improved hydroxynitrile lyase from the resultant culture.
Owner:MITSUBISHI RAYON CO LTD
Multifunctional algal polysaccharide lyase gene and application thereof
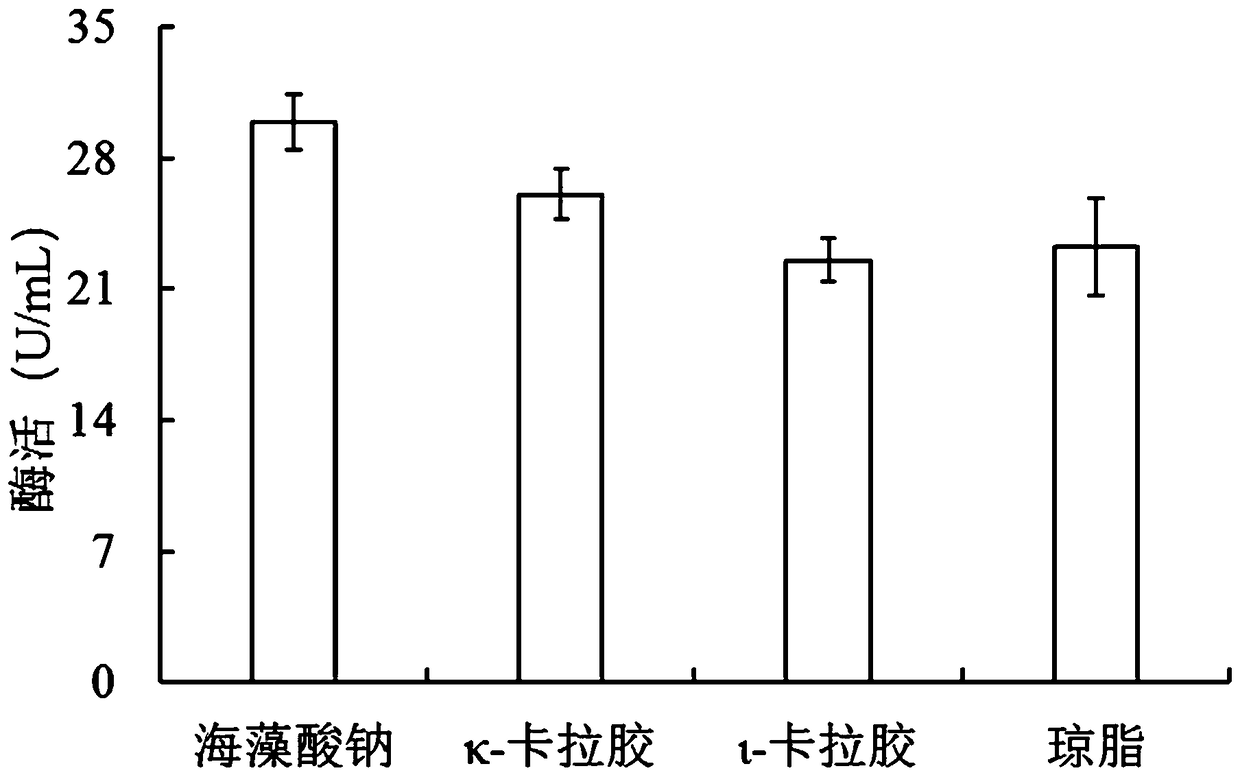
The invention discloses a multifunctional algal polysaccharide lyase gene, multifunctional algal polysaccharide lyase, a genetic engineering bacterium with the multifunctional algal polysaccharide lyase and a method for constructing the genetic engineering bacterium. Nucleotide and amino acid sequences of the multifunctional algal polysaccharide lyase are shown as SEQ ID NO.1 and SEQ ID NO.2. Themethod includes steps of firstly, utilizing DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) of genomes of marine bacteria as a template and amplifying multifunctional algal polysaccharide lyase gene sequences by the aidof primers; secondly, cloning the multifunctional algal polysaccharide lyase gene into plasmids to obtain recombinant vectors; thirdly, carrying out transformed cloning on the recombinant vectors in hosts; fourthly, carrying out transformed expression on the recombinant vectors in hosts to obtain the multifunctional algal polysaccharide lyase production genetic engineering bacterium. The multifunctional algal polysaccharide lyase gene, the multifunctional algal polysaccharide lyase, the genetic engineering bacterium and the method have the advantage that the multifunctional algal polysaccharide lyase is high in activity for sodium alginate, k-carrageenan, l-carrageenan and agar and can be widely used in the field of chemical engineering, agriculture, food and feed addition, medicines, algahereditary engineering and the like.
Owner:JIMEI UNIV
Preparation method for high-molecular-weight hyaluronic acid (HA), and engineering bacterium
ActiveCN103993031APrecise positioningDoes not affect functionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesStreptococcus zooepidemicusIntrinsic viscosity
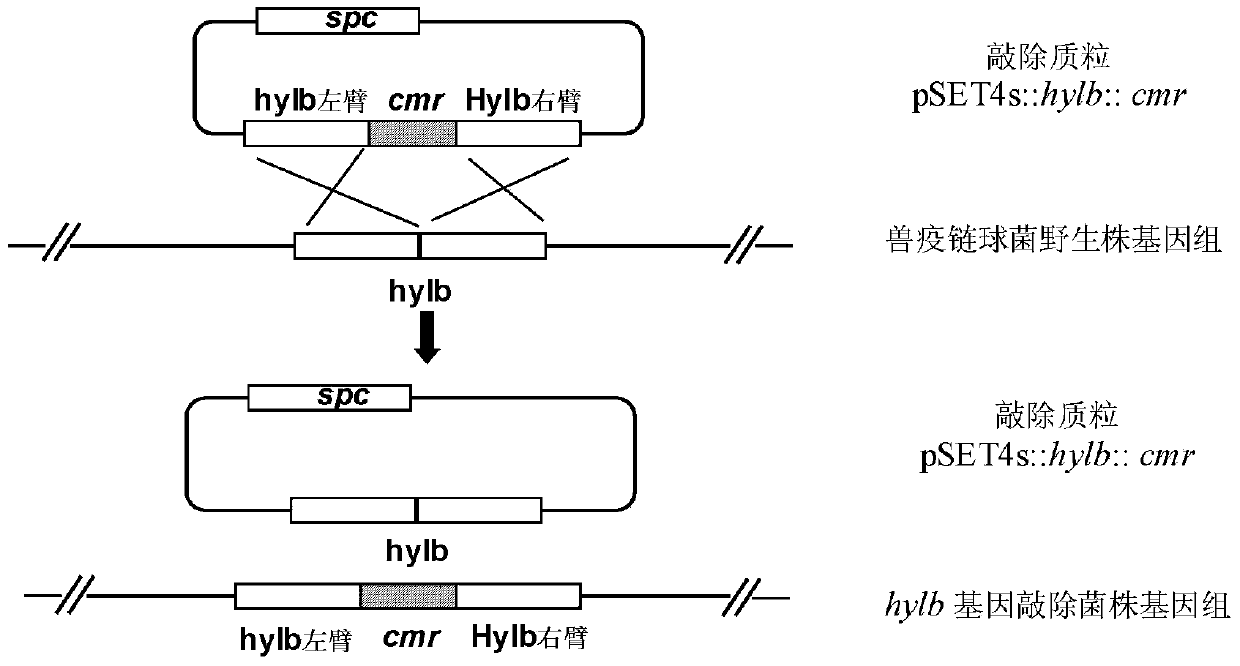
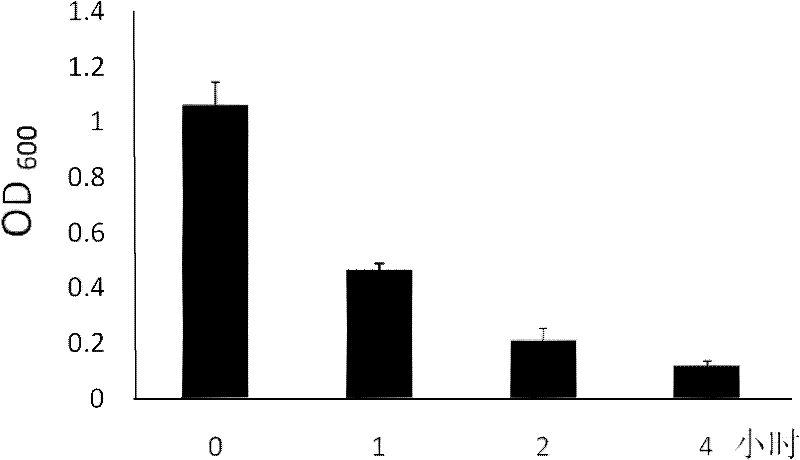
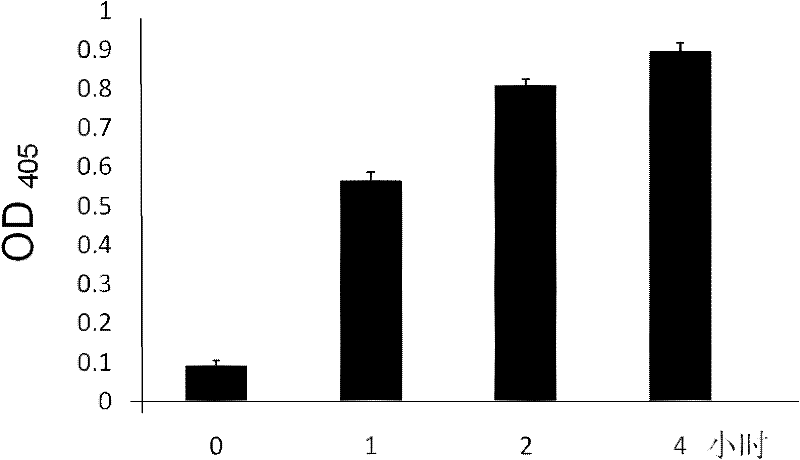
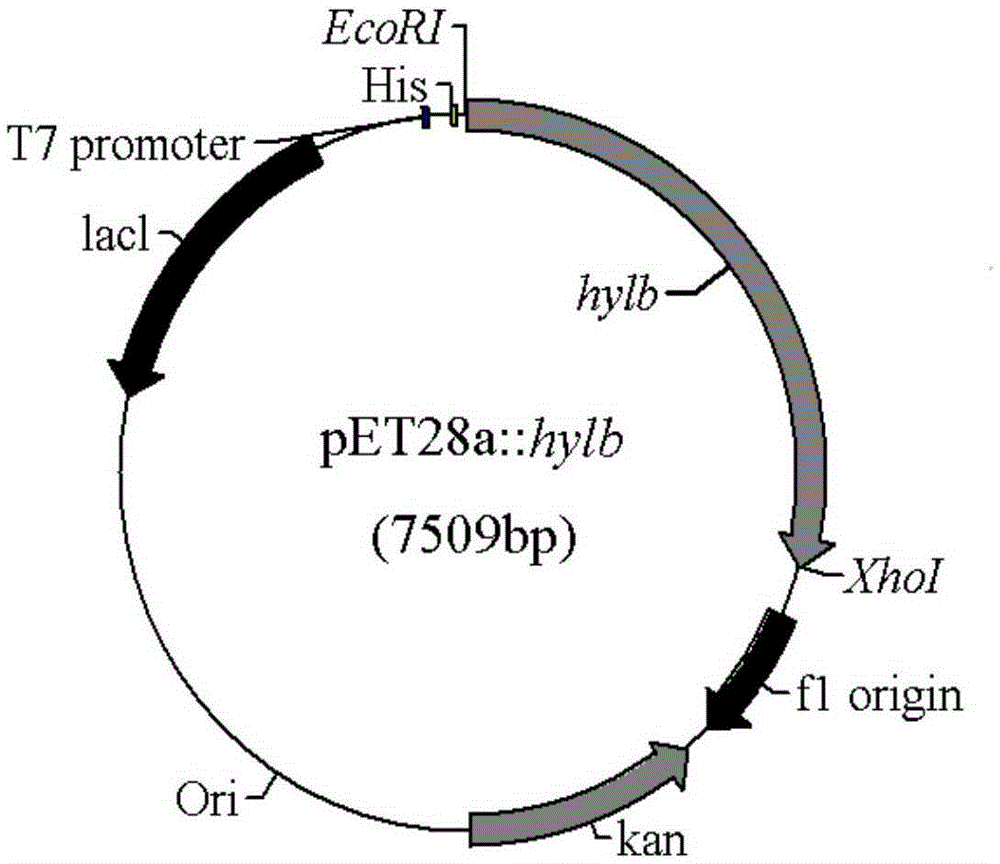
The invention relates to a preparation method for high-molecular-weight HA and an engineering bacterium. According to the method, a coding hyaluronic acid lyase gene (hylb) in the genome of Streptococcus zooepidemicus ATCC39920 is knocked out, and a hyaluronic acid lyase gene (hylb)-knocked out vector pSET4s:: hylb:: cmr is constructed. The method provided by the invention subjects a recombinant bacterium in which the hylb gene is knocked out to fermentation and analysis, the molecular weight of HA is measured by using an intrinsic viscosity process, and HA with a molecular weight of 3.9 * 10<6> Da is obtained.
Owner:JIANGSU HEVI BIOTECH CO LTD
Recombinant strain expressing organophosphorus hydrolase, complex enzyme preparation technology, complex enzyme preparation and fruit and vegetable detergent
InactiveCN102199550AEasy to operateAvoid the influence of expressed enzyme activityFungiBacteriaPesticide degradationHydrolase
The invention relates to a recombinant strain expressing organophosphorus hydrolase, a complex enzyme preparation technology, a complex enzyme preparation and a fruit and vegetable detergent, wherein the recombinant strain comprises a controllable lyase gene. The complex enzyme preparation technology comprises the following steps: culturing the recombinant strain expressing organophosphorus hydrolase, adding proper start-up condition induced expression lyase; and using the obtained culture solution to prepare the complex enzyme preparation. The recombinant strain expressing organophosphorus hydrolase is cultured and the expression of lyase lysed cells is induced, thus the possible influences of complicated mechanical and chemical pyrolysis methods on the expression of enzyme activity can be avoided and the cheap industrialized production is convenient to realize. The complex enzyme preparation produced on the basis of the preparation technology has organophosphorus hydrolase and cell lyase simultaneously, has the double functions of pesticide degradation and sterilization and can be used in the development of the new fruit and vegetable detergent.
Owner:SHENZHEN SYDSCI TECH
Alginate lyase and gene and application thereof
InactiveCN109777817ANothing producedMild reaction conditionsBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliBiotechnology
The invention discloses an alginate lyase and a gene and application thereof. The nucleic acid sequence of the alginate lyase gene is shown as SEQ ID NO:1; the amino acid sequence of the alginate lyase Alg3 encoded according to a nucleotide sequence is shown as SEQ ID N0:2. The invention also discloses a technical method for transforming a gene engineering strain of the alginate lyase gene into Escherichia coli by means of genetic engineering. The alginate lyase is prepared by connecting the alginate lyase gene with a vector, constructing tecombinant expression plasmid and transforming the Escherichia coli. The alginate lyase can specifically degrade sodium alginate to produce alginate oligosaccharide and can be used together with cellulase for hydrolyzing kelp to produce a water-soluble oligosaccharide product. Therefore, the alginate lyase can be used for preparation of alginate oligosaccharide; moreover, reaction conditions are mild, consumption of energy is low, no pollutants are produced, and the alginate lyase has an important industrial application value.
Owner:青岛海大生物集团股份有限公司
Kluyvera intermedia tyrosine phenol-lyase mutant and application thereof
ActiveCN110331153ASimple processEasy to operateBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliRandom mutation
The invention discloses a kluyvera intermedia tyrosine phenol-lyase mutant and an application thereof. A tyrosine phenol-lyase gene from the kluyvera intermedia is cloned, random mutation is conductedon the tyrosine phenol-lyase gene, and the mutated gene is expressed in escherichia coli to obtain an engineering bacterium YW021 of which the enzyme activity is greatly improved. The maximum concentration of levodopa synthesized by the engineering bacterium YW021 provided by the invention is as high as 150g / L which is improved by about 30% than that of a wild type, and the conversion rate of zymolyte catechol is 99.9% or more.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH +1
Method for preparing fluorescent magnetic nanoparticles with streptavidin combination function
InactiveCN102010872AGood water solubilitySmall side effectsInorganic material magnetismAlgae/lichens peptidesEscherichia coliFluorescence
The invention belongs to the technical field of nano materials and particularly relates to a method for preparing fluorescent magnetic nanoparticles with streptavidin combination function. The method comprises the following specific steps of: respectively connecting a Strep II label gene to N ends of alpha and beta sub-gene apoprotein genes to obtain Strep II-apcA and Strep II-apcB gene segments; embedding the Strep II-apcA gene segment to the downstream of a 6*His gene, and cloning to one expression vector together with a phycobilin biosynthetic enzyme gene; embedding the Strep II-apcB gene segment to the downstream of the 6*his gene, cloning to another vector together with a chromphore lyase gene, simultaneously converting the two expression vectors into escherichia coli, screening engineering bacteria, separating and purifying the engineering bacteria by protein, and oscillating and mixing the purified double-label recombinant APC fluorescent protein and zinc ion modified superparamagnetism silicon shell nanoparticles to obtain the fluorescent magnetic nanoparticles with the streptavidin combination function. The obtained double-label recombinant protein can biologically combine streptavidin without being modified chemically.
Owner:INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
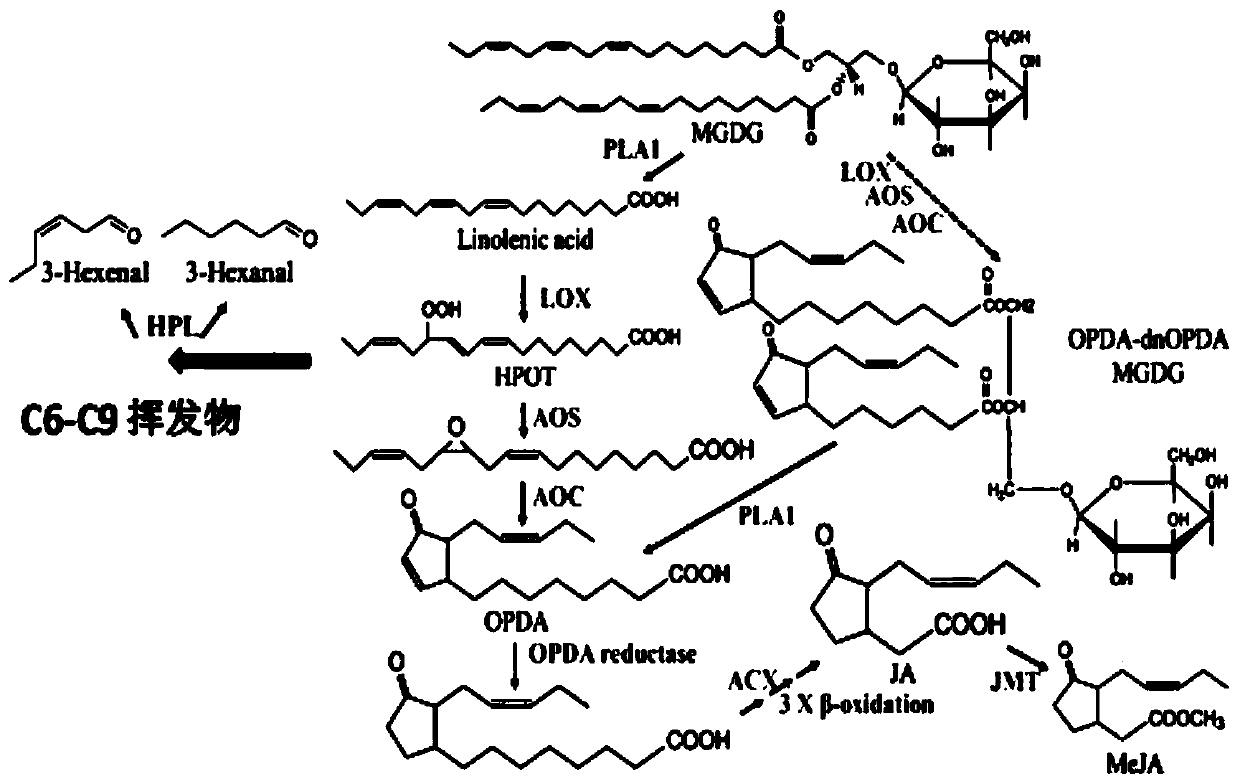
Lipid hydroperoxide lyase, as well as gene and application thereof
ActiveCN110724696AIncrease contentMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationHydroperoxide lyaseNucleotide
The invention discloses lipid hydroperoxide lyase, as well as a gene and application thereof. The gene has a nucleotide sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO.1, or has a nucleotide sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO.3. The lyase gene provided by the invention can regulate and control the contents of volatile matters and jasmonic acid matters in plants, and participates in a tea leaf processing process; the expression of the lyase gene is used for improving the generation of the grass-flavor C6-C9 volatility in the plants; and the inhibition of the lyase gene is used for improving the contents of jasmonicacid premise matters and the jasmonic acid matters.
Owner:ANHUI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
XZ-A26 bacterial strain for producing L-alanine with high yield as well as construction method and application of XZ-A26 bacterial strain
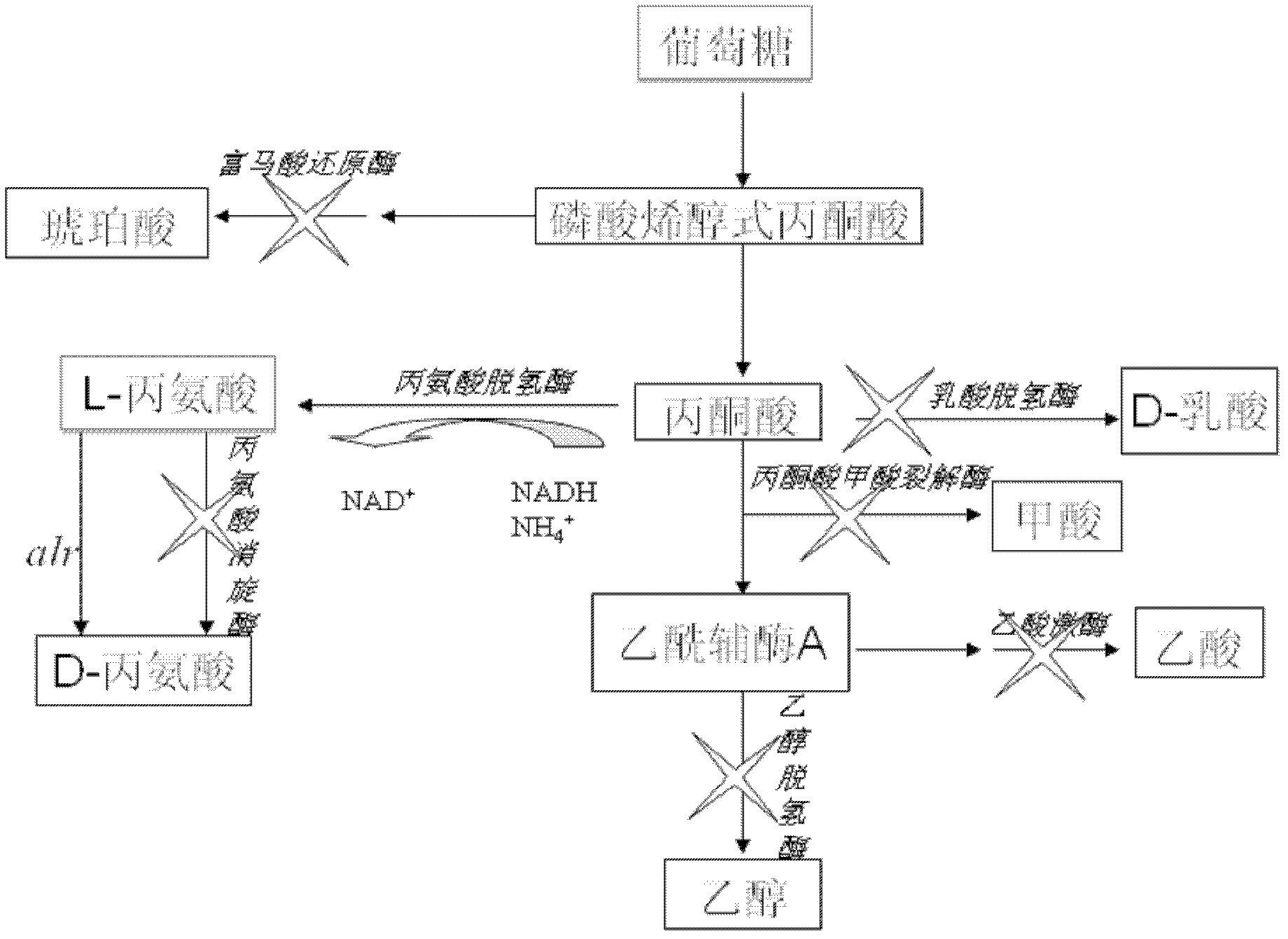
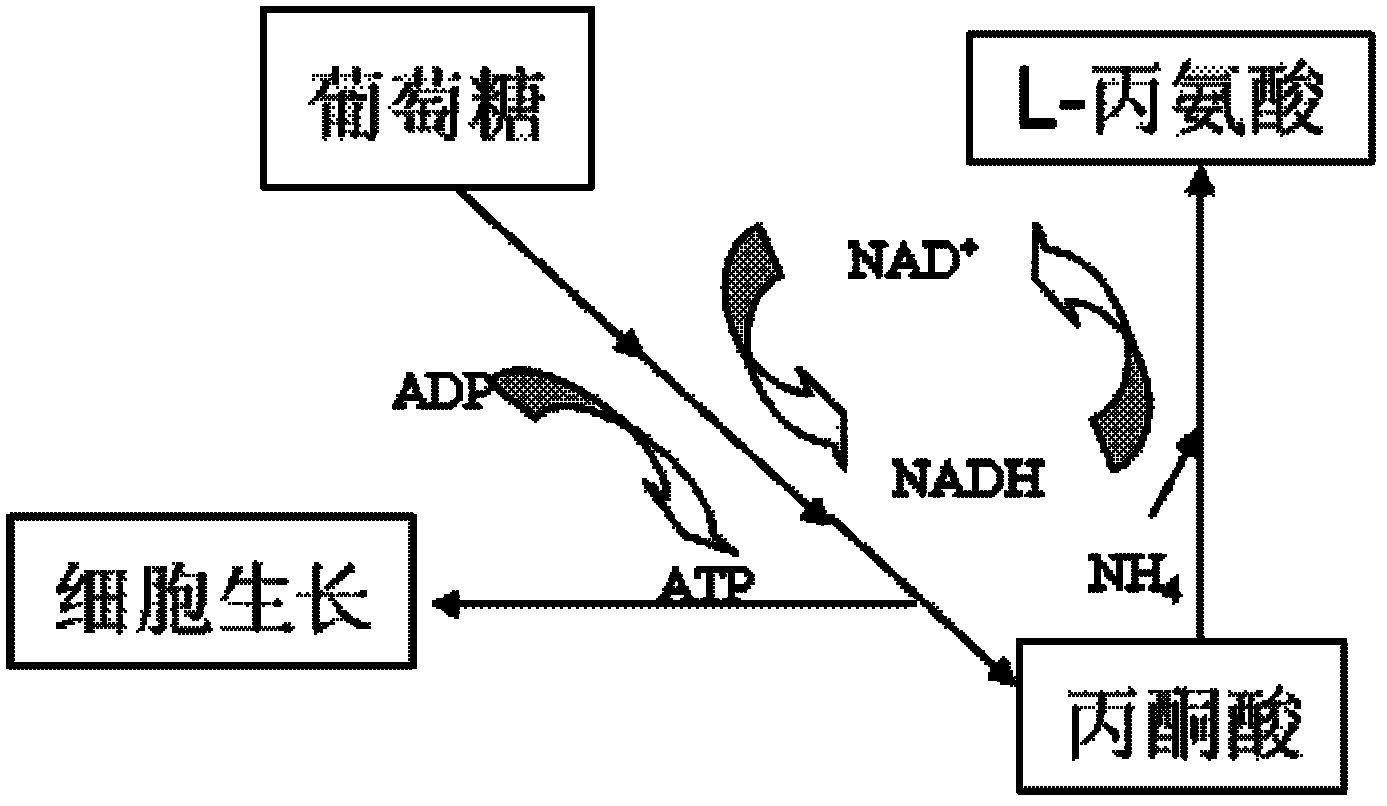
The invention discloses an XZ-A26 bacterial strain for producing L-alanine with high yield, wherein the preservation number is CGMCC No.4036. The XZ-A26 bacterial strain has the ability of fermenting to produce high-concentration L-alanine and is genetic engineering bacteria prepared by integrating the L-alanine dehydrogenase gene on Escherichia Coli chromosome of a lipase gene from Geobacillus Stearothermophilus at the lactic dehydrogenase of Escherichia coli ATCC 8739 chromosome, then sequentially removing a pyruvate formate-lyase gene, an ethanol dehydrogenase gene, an acetokinase gene, a fumarate reductase gene and an alanine racemase gene of the escherichia coli chromosome and then continuously subculturing in a fermentation tank. The invention also relates to a construction method of the bacterial strain and the application of the bacterial strain in preparing the L-alanine. According to the metabolic engineering method, the escherichia coli CGMCC No.4036 capable of fermenting to produce the high-concentration L-alanineis constructed, and the yield of the L-alanine produced by fermenting the bacterial strain is as high as 115g / L. The invention is suitable for the industrial production of L-alanine.
Owner:ANHUI HUAHENG BIOTECH
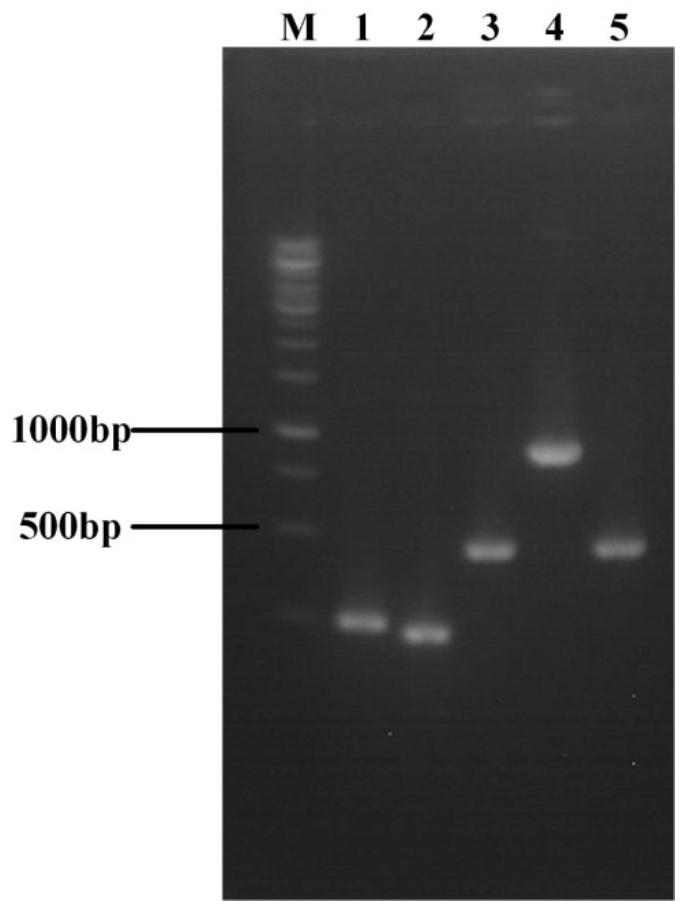
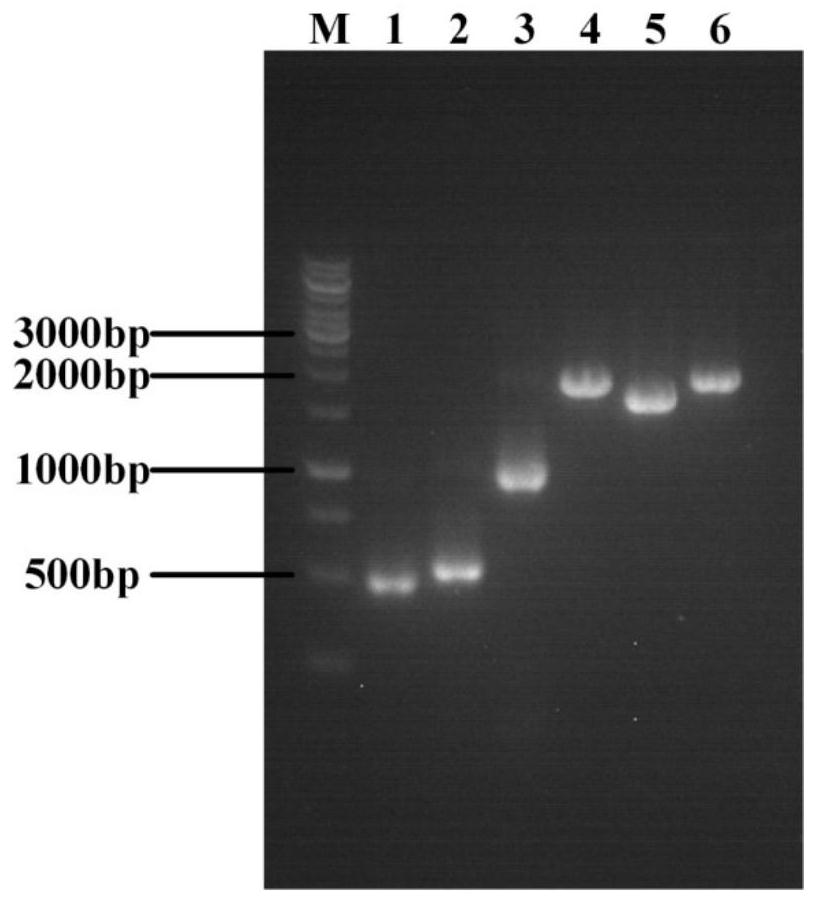
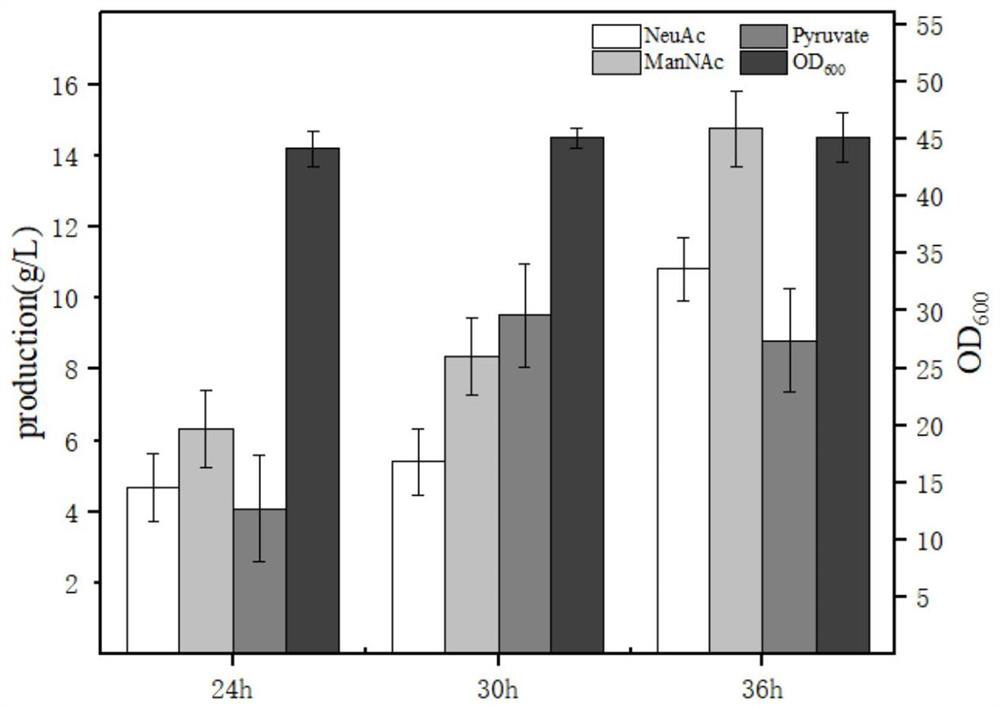
Engineering strain for xylose-induced production of N-acetylneuraminic acid and application of engineering strain
The invention belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering and particularly relates to construction and application of a genetic engineering strain for xylose-induced production of N-acetylneuraminic acid. According to the construction and the application, a N-acetylglucosamine synthesis way is integrated with a genome, a N-acetylglucosamine 2-epimerase gene bAGE and a N-acetylneuraminicacid lyase gene shNAL are introduced, a N-acetylneuraminic acid synthesis way is constructed, and a key gene nanTEK of a catabolism way of the N-acetylneuraminic acid synthesis way is knocked out. Meanwhile, metabolic ways of precursor substances required for synthesizing the N-acetylneuraminic acid are subjected to multicopy strengthening, and part of bypath metabolic ways are subjected to knockout, so that the N-acetylneuraminic acid high yielding strain is obtained. In case of shake-flask fermentation for 36h, the yield of the N-acetylneuraminic acid can reach 10.8g / L to the maximum, the production intensity can reach 0.3g / (L*h) which is the maximum value reported at present, and thus, the engineering strain has an important industrial application value.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Enterobacteria recombinant strain and use thereof
InactiveCN101348775BLess quantityImprove conversion rateBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyKlebsiella oxytoca
The invention discloses a recombination strain for an enterobacterium and application of the recombination strain for the enterobacterium. The recombination strain provided by the invention is a recombination strain obtained after deactivation of a pyruvate formate-lyase gene in the enterobacterium. As shown by experiments, the amount of by-product CO2 produced during the fermentation process of the recombination strain is obviously reduced and the amount of target products is obviously improved compared with the control. For example, the amount of lactic acid, the amount of succinic acid and the amount of 2, 3-butanediol produced by fermentation of klebsiella oxytoca are respectively improved by 30 percent, 9 percent and 23 percent compared with the control, and the amount of the CO2 produced is only 8.04 percent compared with the control. The recombination strain helps to release the pressure of the greenhouse effect, has important function in the actual industrial production,not only can greatly reduce the yield of the CO2, but also can improve the conversion rate of converting substrates into products, and has wide application prospect.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Escherichia coli for synthesis of propane through pathway of valine and establishing method of escherichia coli
InactiveCN105296410ADecreased aldehyde reductase activityDoes not affect normal growthBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliFormate
The invention discloses escherichia coli for synthesis of propane through the pathway of valine and an establishing method of the escherichia coli, and belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering. According to the escherichia coli, nine sorts of aldose reductase genes, a lactic dehydrogenase gene, a fumarate reductase gene, a formate-lyase gene and an overall transcription factor gene are eliminated. Meanwhile, overexpression of an acetolactate synthetase gene, a ketol-acid reductoisomerase gene, a DHAD gene, a 2-ketoacid decarboxylase gene and an aldehyde deformylating oxygenase gene is achieved. The invention provides the establishing method of the escherichia coli at the same time. Through overexpression of the propane synthesis pathway in an improved strain, the strain successfully achieves biosynthesis of propane.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Preparation method and application of small molecular weight hyaluronic acid, and hyaluronate lyase genetic vector and engineering bacteria
InactiveCN105274127AIncrease enzyme activityMolecular weight controllableBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliStreptococcus zooepidemicus
The invention provides a preparation method and application of small molecular weight hyaluronic acid, and a hyaluronate lyase genetic vector and engineering bacteria. An expression vector successfully constructed is converted to Escherichia coli BL21 (DE3) by: cloning part of fragments encoding hyaluronate lyase gene (hylb) in genome of Streptococcus zooepidemicus ATCC 39920 and constructing the expression carrier pET 28a:hylb, and high-activity soluble hyaluronate lyase is obtained by the induced expression of Escherichia coli. Specific enzyme activity of purified liquid of the lyase is 4655 U / mg (equivalently 4.655*107 IU / mg) that is measured by N-acetyl-glucosamine (NAG) measurement. The small molecular weight hyaluronic acid is prepared by controlling the enzyme content and reaction conditions to degrade large molecular weight hyaluronic acid, the molecular weight of the hyaluronic acid is measured by means of an intrinsic viscosity method and agarose gel electrophoresis, and the obtained molecular weight is that of small molecular weight hyaluronic acid of 6000Da level, an infrared spectrogram of which is consistent with standard atlas in national pharmacopoeia.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Preparation method and application of alginatelyase OalC6
The invention discloses exo-alginatelyase, a coding gene thereof and an application of the exo-alginatelyase. A novel alginatelyase gene is cloned from marine bacterium Cellulophaga sp. SY116, has thesize of 2328 bp, encodes 775 amino acids and belongs to the family of polysaccharide lyase PL-6. The gene can be expressed and purified in Escherichia coli to obtain recombinant OalC6, and the molecular weight of the gene is about 85.9 kDa. The exo-alginatelyase is active to sodium alginate and alginate oligosaccharide and preferential to guluronic acid fragment (polyG). The exo-alginatelyase haspotential application values in terms of production of bioethanol and development of new energy.
Owner:QINGDAO UNIV
Bacteria-cracking preparation for effectively cracking escherichia coli as well as cracking method and application thereof
InactiveCN102703491AEfficient crackingSpecific lysisAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsEscherichia coliSodium acetate
The invention discloses a bacteria-cracking preparation for effectively cracking escherichia coli as well as a cracking method and an application thereof. The bacteria-cracking preparation is prepared by the following steps of: designing a primer; using PCR (polymerase chain reaction) to amplify catenase gene in lysogenic escherichia coli for inducing lytic phage to obtain a target segment; connecting the target segment with pET-28a(+) carrier to obtain recombinant expression plasmid; introducing the recombinant expression plasmid to escherichia coli BL21(DE3) to express, thus obtaining positive transformant; expressing the recombinant fusion protein by induction; performing purification and induction to obtain purified recombinant protein, and screening the recombinant expression protein with cracking activity to obtain the bacteria-cracking preparation. The cracking method comprises the step of adopting 0.8% of beta-mercaptoethanol or 10mM of cysteine as reducing agent at pH of 8.0 and temperature of 37 DEG C, and 20mM of sodium acetate buffer liquid at pH of 5.2. The bacteria-cracking preparation obtained by the method provided by the invention has strong cracking specificity and high cracking efficiency for various serotype escherichia coli, and can effectively kill the escherichia coli.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Enterobacteria recombinant strain and use thereof
InactiveCN101348775ALess quantityImprove conversion rateBacteriaMicroorganism based processesKlebsiella oxytocaEnterobacter
The invention discloses a recombination strain for an enterobacterium and application of the recombination strain for the enterobacterium. The recombination strain provided by the invention is a recombination strain obtained after deactivation of a pyruvate formate-lyase gene in the enterobacterium. As shown by experiments, the amount of by-product CO2 produced during the fermentation process of the recombination strain is obviously reduced and the amount of target products is obviously improved compared with the prior art. For example, the amount of lactic acid, the amount of succinic acid and the amount of 2, 3-butanediol produced by fermentation of klebsiella oxytoca are respectively improved by 30 percent, 9 percent and 23 percent compared with the prior art, and the amount of the CO2 produced is only 8.04 percent compared with the prior art. The recombination strain helps to release the pressure of the greenhouse effect, has important function in the actual industrial production, not only can greatly reduce the yield of the CO2 but also can improve the conversion rate of converting substrates into products, and has wide application prospect.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
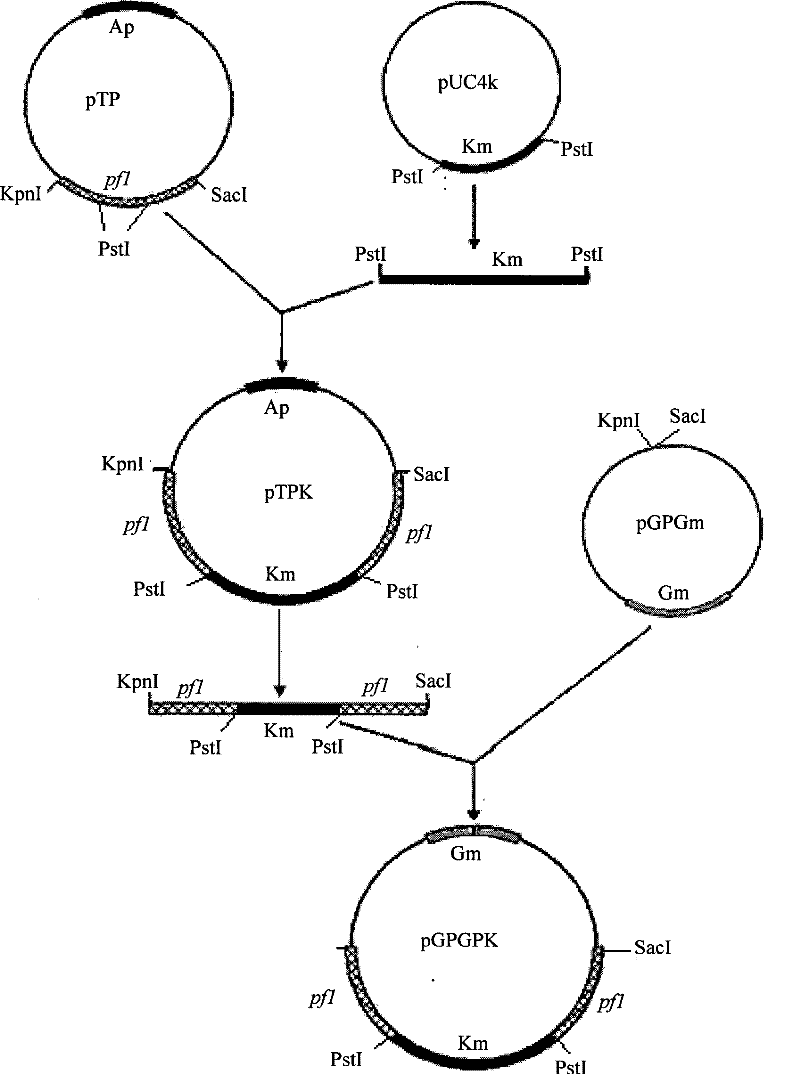
Engineering bacteria for knocking out pyruvate formate-lyase genes and application of engineering bacteria
ActiveCN104498523AReduce metabolic shunt effectReduce synthesisBacteriaMicroorganism based processes1,3-PropanediolPropanediol
The invention discloses engineering bacteria for knocking out pyruvate formate-lyase genes and an application of the engineering bacteria. The pyruvate formate-lyase (flpB) genes in a wild-type strain for producing 1,3-propanediol are knocked out by utilizing a gene homologous recombination and gene insertional inactivation method, so that the gene engineering bacteria with blocked metabolic pathways of methanoic acid can be obtained. The engineering bacteria are used for fermenting production of 1,3-propanediol, and the synthesis of the byproduct methanoic acid is greatly reduced, so that the toxicity effect of the methanoic acid for cells can be reduced, and the concentration, production intensity and substrate conversion rate of the 1,3-propanediol can be improved. The experiment shows that when the engineering bacteria are fermented for 32h in a conventional method, the synthesis amount of the methanoic acid is reduced by more than 90 percent, and the concentration of the 1, 3-propanediol can reach more than 72g / L. By adopting the engineering bacteria, the progress of the technology for producing the 1,3-propanediol in the microorganism fermentation method can be promoted, and the application value can be realized.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA SEA INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com