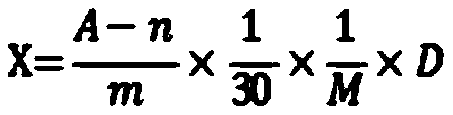Alginate lyase and gene and application thereof
A alginate lyase and gene technology, applied in the field of bioengineering, can solve problems such as difficulty in obtaining solubility, small molecular weight, cumbersome process, etc., and achieve good application prospects and mild reaction conditions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0013] Embodiment 1 Expression and purification of alginate lyase
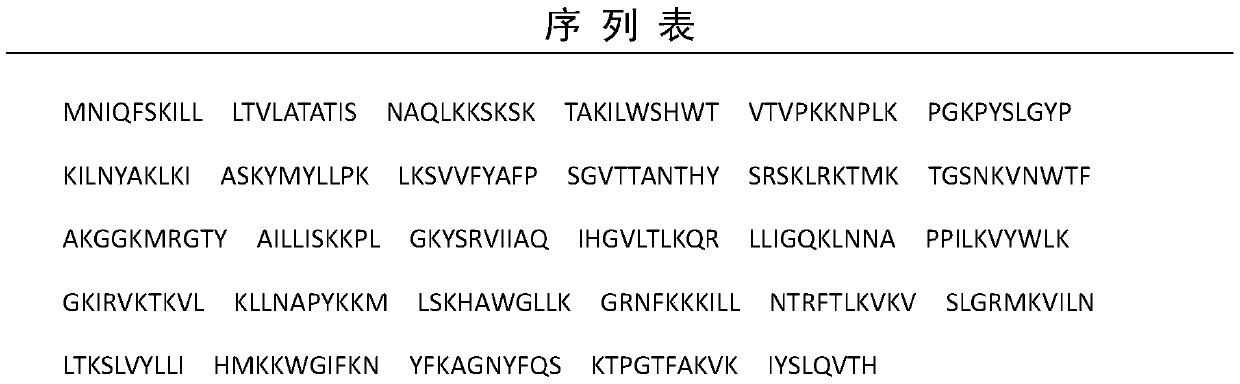
[0014] Carry out whole gene synthesis of SEQ ID NO: 1 according to conventional methods, connect to the prokaryotic expression vector pET-28a(+), and add a BamHI restriction site at the upstream of the gene, and a SacI restriction site at the downstream;
[0015] Transform the synthetic recombinant plasmid into Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) to obtain the genetically engineered bacteria BL21 / Alg3 producing Alg3;
[0016] The above-mentioned recombinant bacteria were inoculated into LB medium, cultured at 37°C to the logarithmic growth phase, then added IPTG to a final concentration of 0.1 mmol / L, and continued to be cultured overnight at 16°C for induction. The cells were collected by centrifugation, washed twice with saline, and a certain amount of buffer (50 mM Na 2 HP0 4 , 0.3M NaCl, pH8.0) to make a suspension of alginate lyase wet bacteria. Then ultrasonically destroy the bacteria in an ice-water bath (pow...
Embodiment 2
[0017] Enzyme activity detection of alginate lyase described in embodiment 2
[0018] Take 1ml of enzyme solution, add 1ml of 0.5% sodium alginate solution and 5ml of phosphate buffer solution with pH7.2, and bathe in constant temperature water at 40°C for 30min. The reducing sugar was used DNS method, the absorption wavelength was 540nm, the inactivated enzyme was used as a control, and the relative enzyme activity was calculated;
[0019] The alginate oligosaccharides produced by the degradation of sodium alginate by alginate lyase are reducing sugars. Enzyme activity is defined as: 1 μg of reducing sugar is released per gram of immobilized enzyme catalytic substrate per minute, which is an enzyme activity unit (U);
[0020]
[0021] Wherein, X is the enzyme activity (U / g) of the sample, A is the absorbance value at a wavelength of 540nm, the reaction time is 30min, M is the quality (g) of the enzyme added, and D is the dilution factor; m and n are reducing sugars respec...
Embodiment 3
[0022] Application of alginate lyase described in embodiment 3 in kelp degradation
[0023] Rinse the kelp with clean water, crush it with a pulverizer, and pass through a 60-mesh sieve to obtain dry powder; put the kelp powder into the enzymatic hydrolysis tank, add water 12 times the weight of the kelp powder, stir until fully suspended, and add 2% fiber by weight of the kelp powder Vegetase and 10% alginase crude enzyme solution, the ratio of the two enzymes is 1:2, stir evenly; adjust the pH to 5, hydrolyze at 55°C for 4 hours to obtain kelp hydrolyzate; hydrolyzate at 5000rpm Centrifuge for 20 minutes to separate the residue to obtain a soluble oligosaccharide supernatant; spray dry to obtain a dry powder of fucoidan oligosaccharide.
[0024] The obtained kelp hydrolyzed oligosaccharide is light yellow after drying, has good water solubility, a yield of 6%, simple operation, no pollution, no addition of chemical reagents, and has potential application value.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com