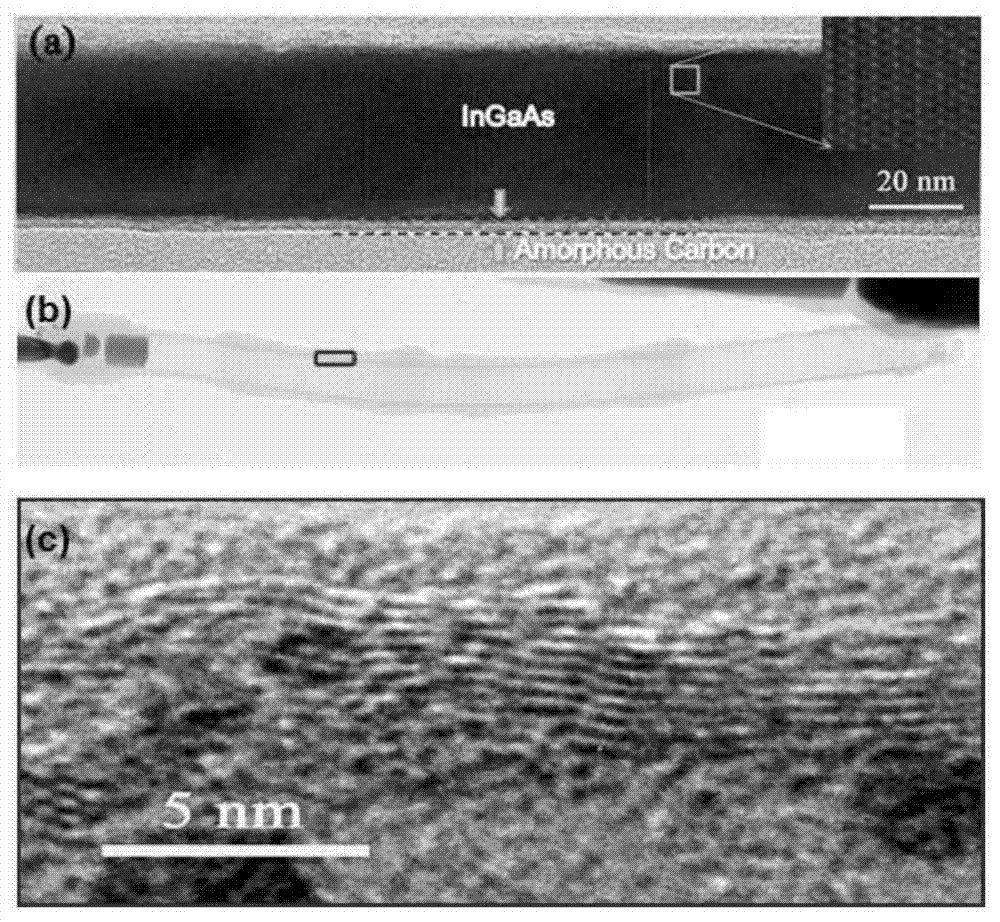
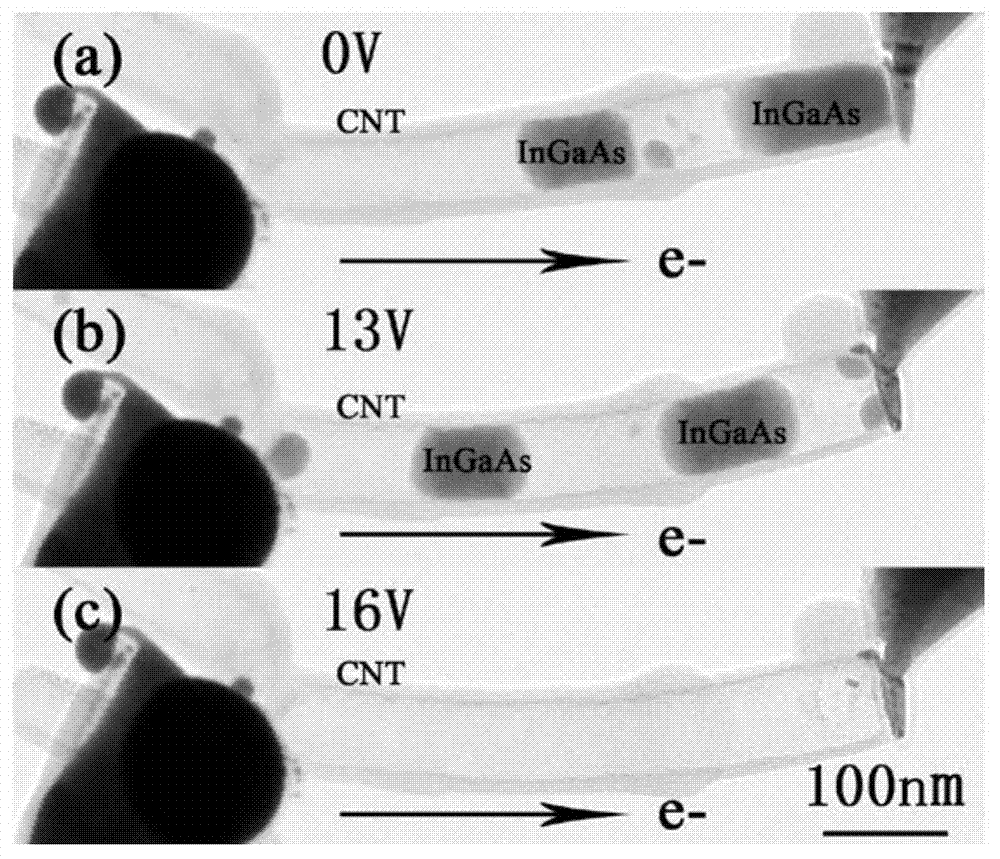
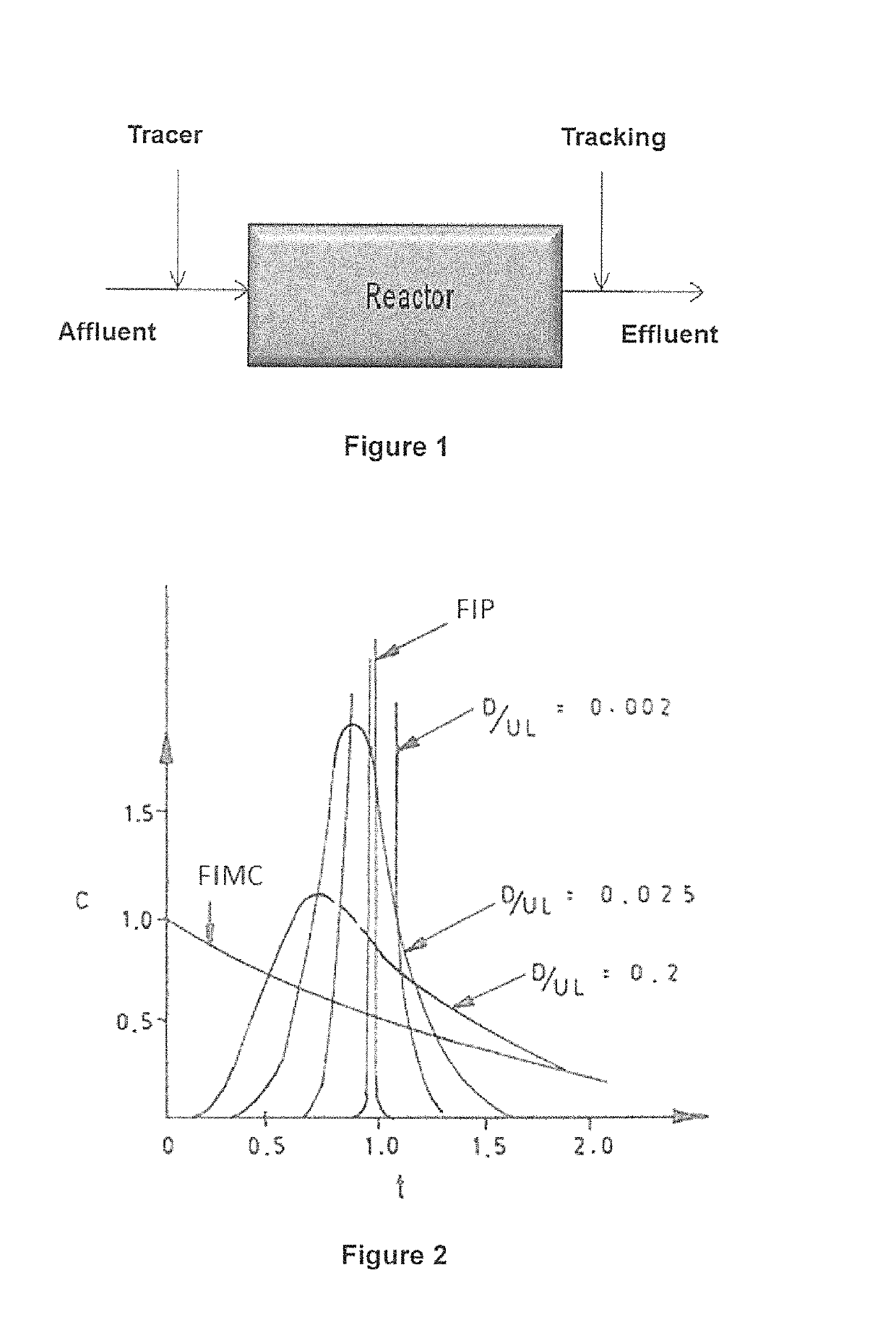
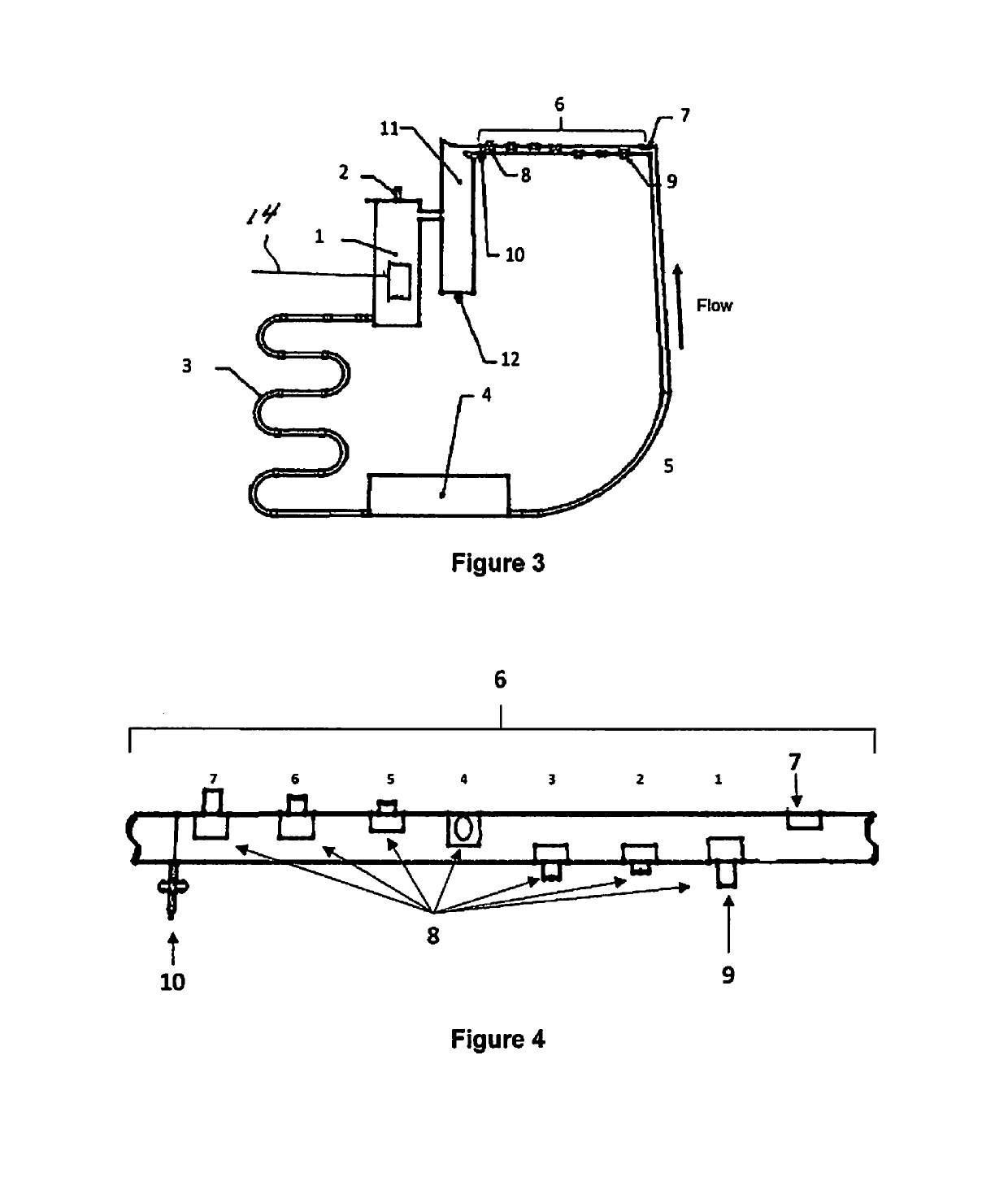
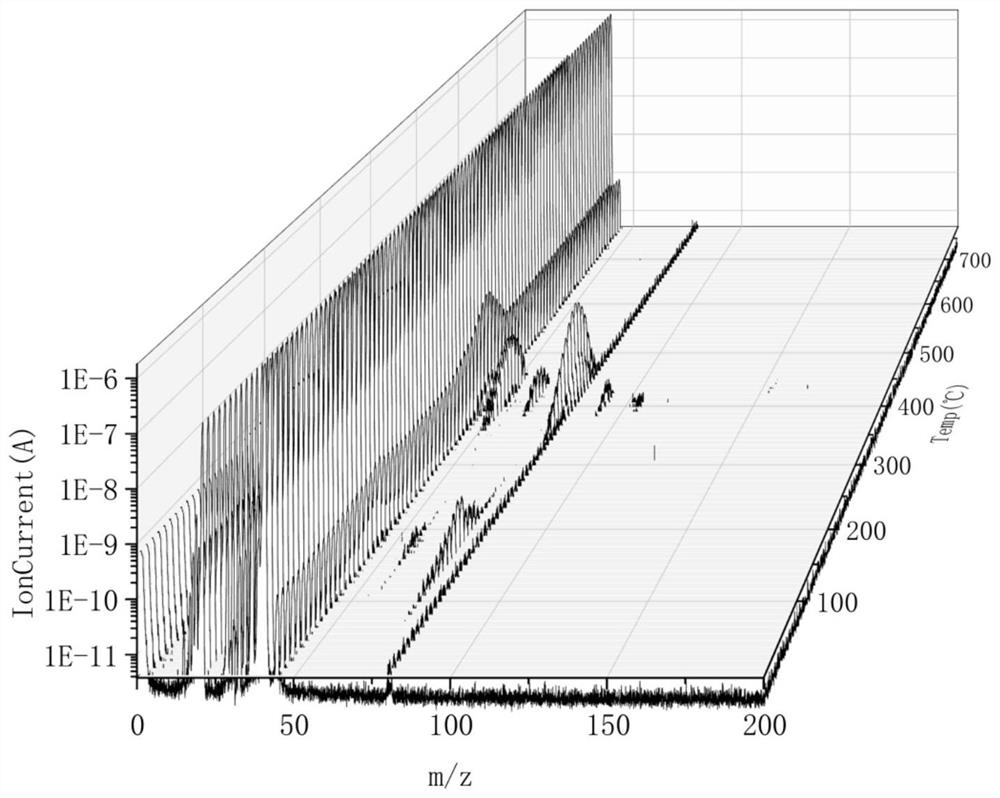
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
33 results about "In situ study" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
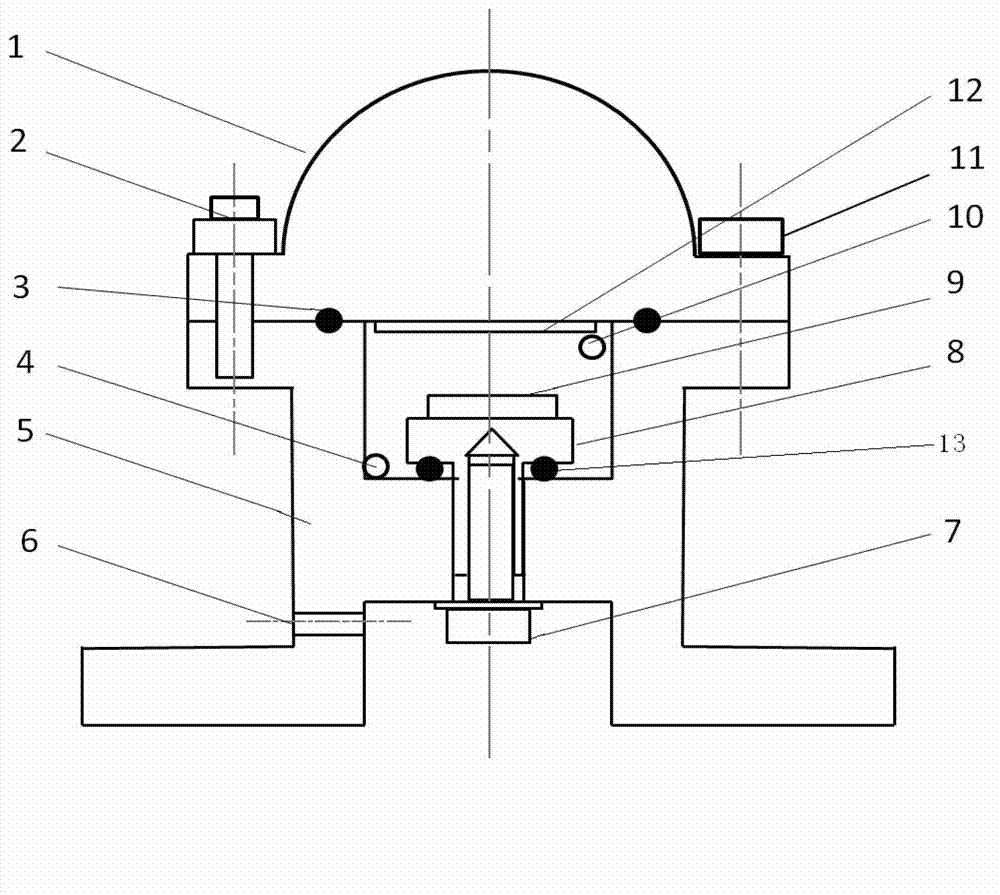
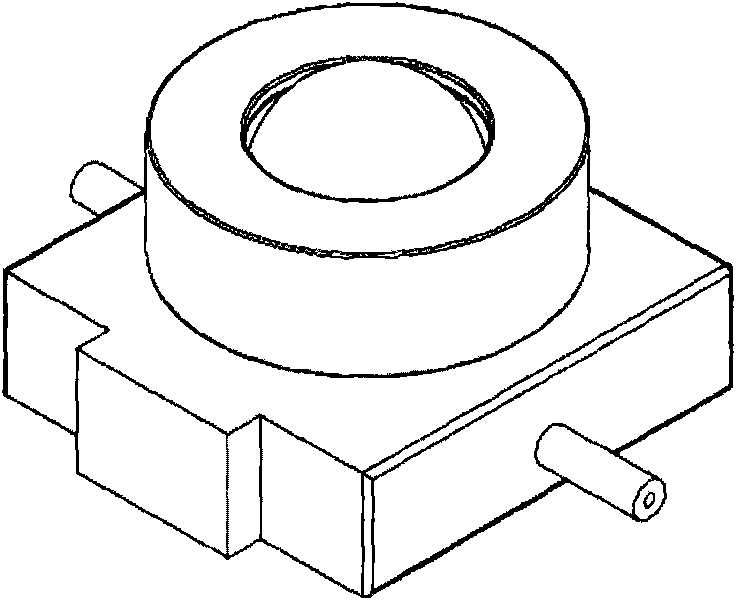
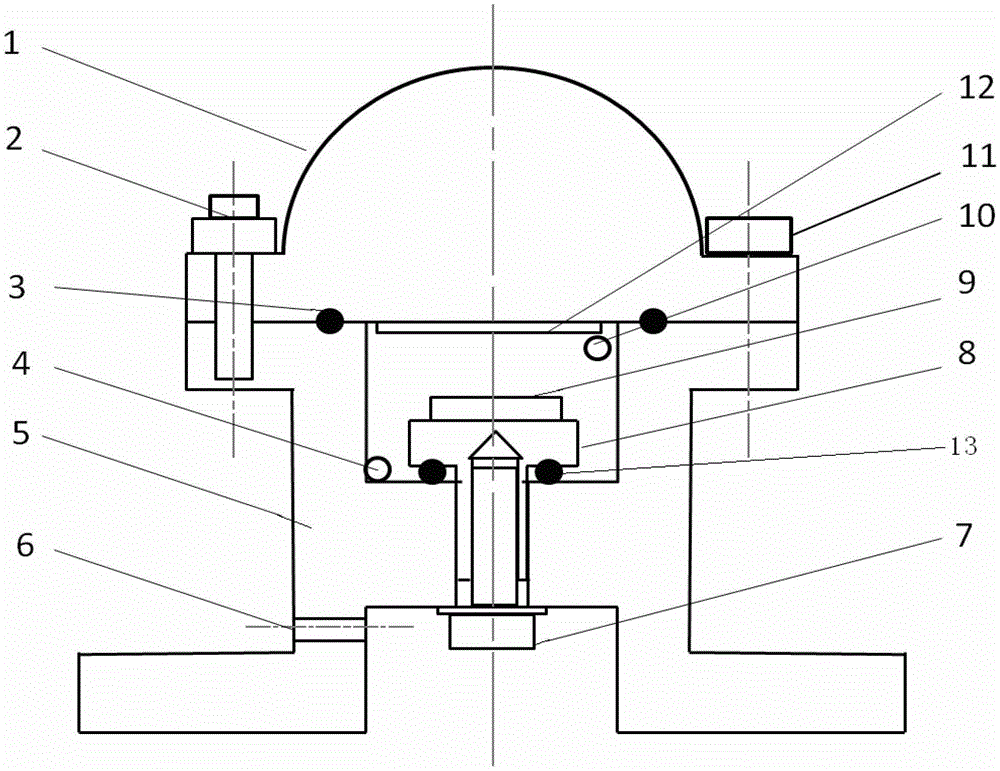
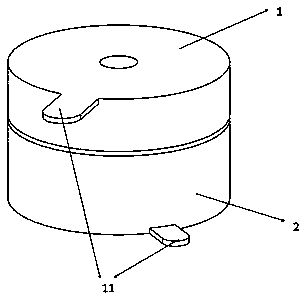
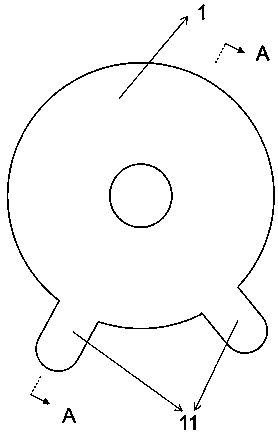
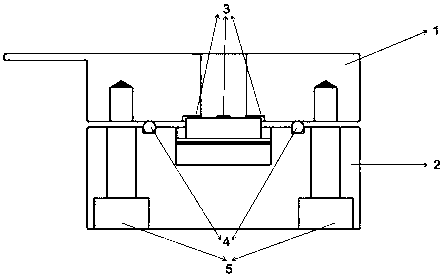
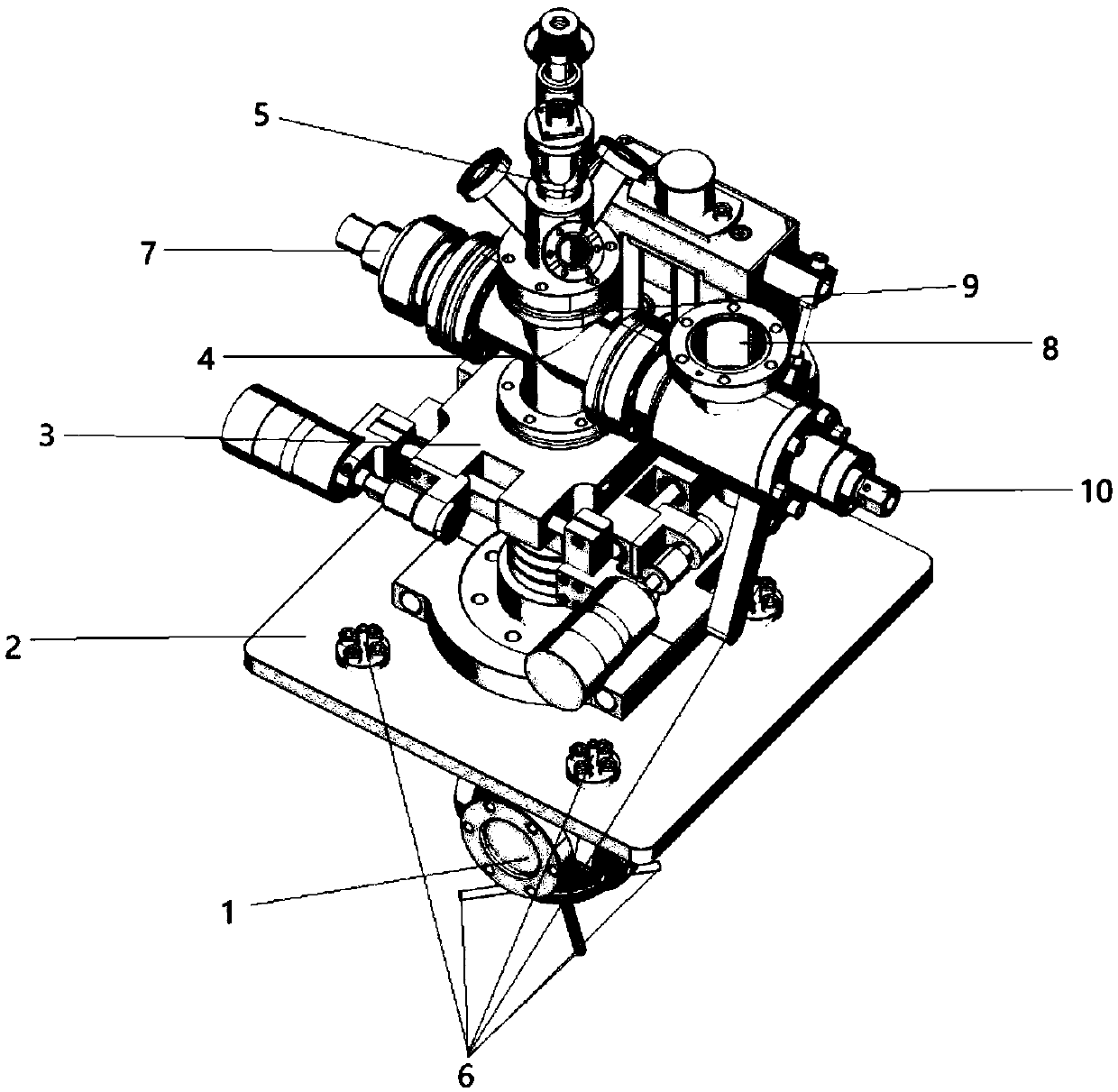
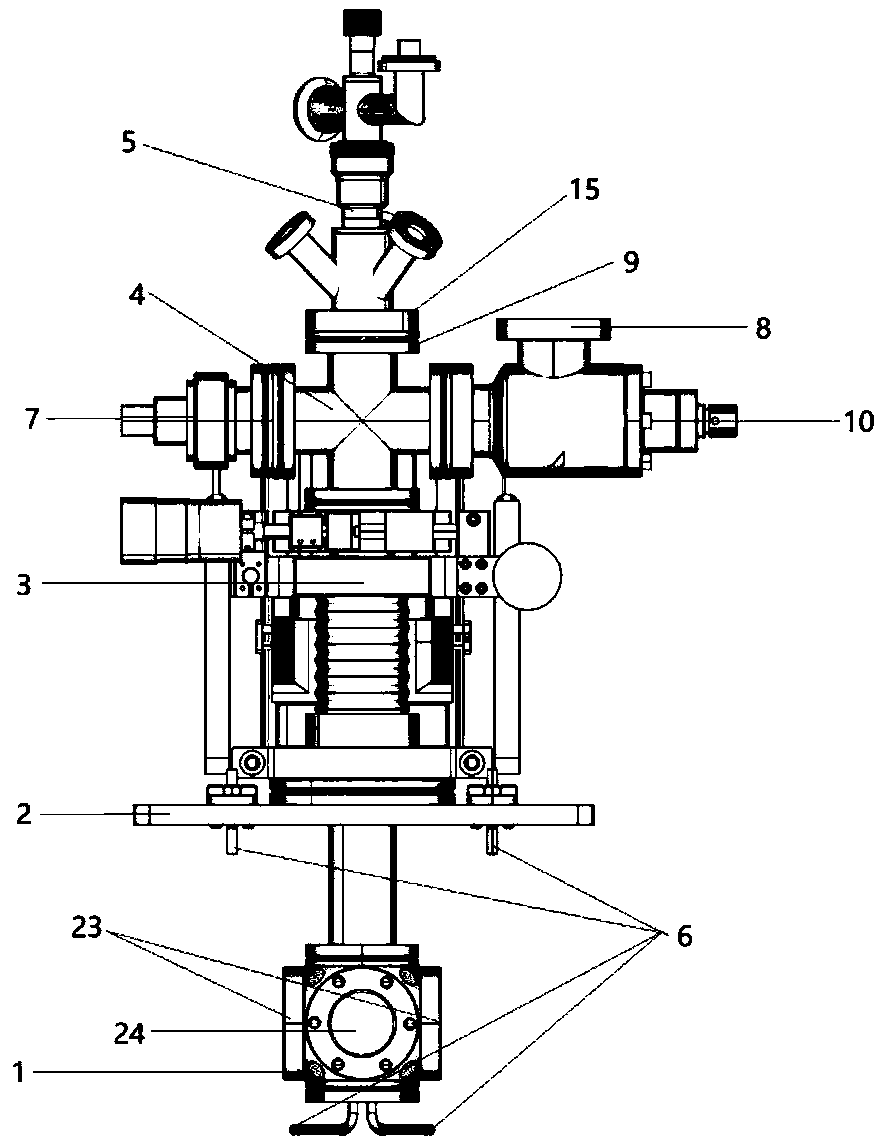
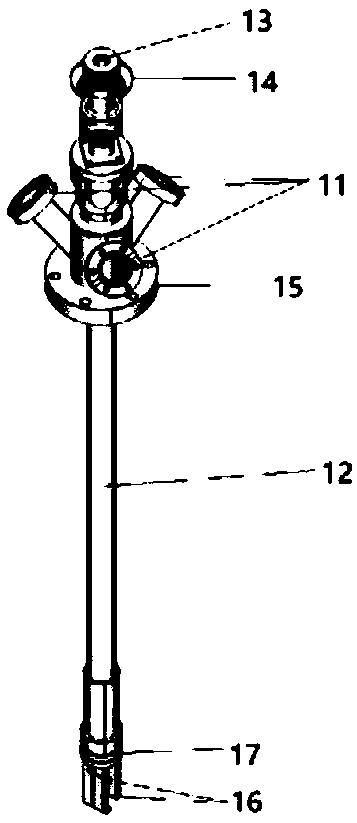
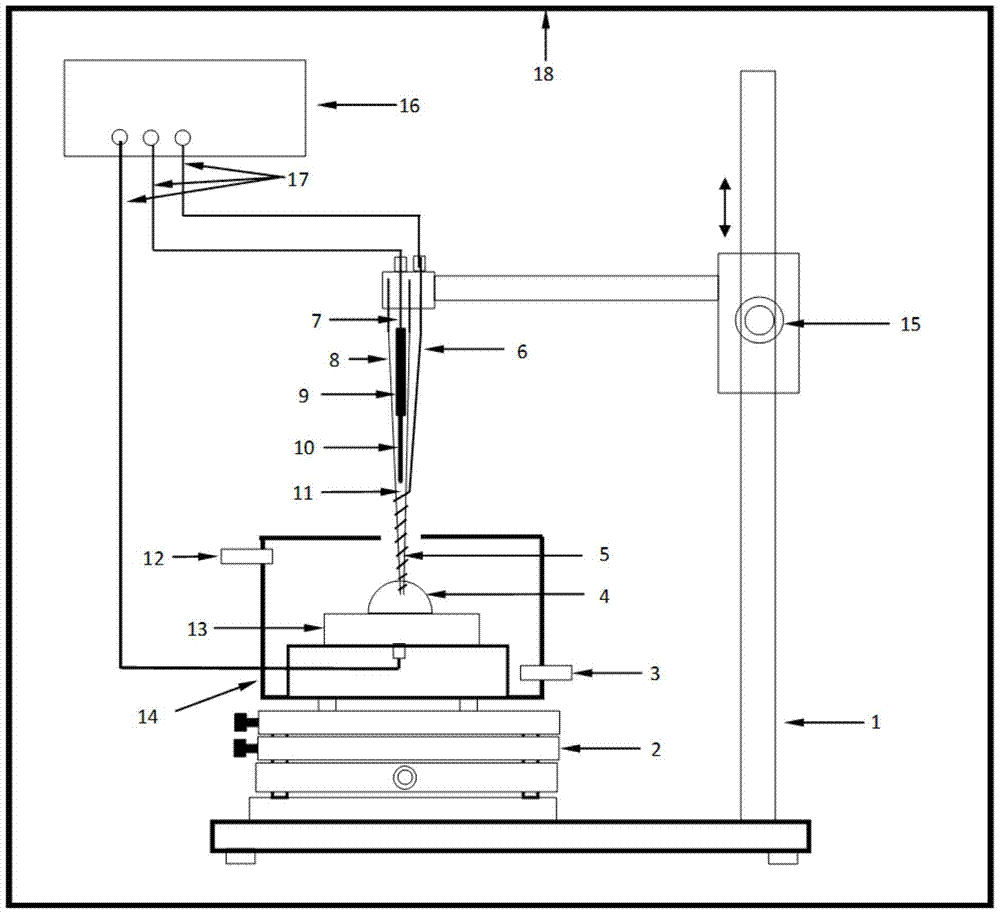
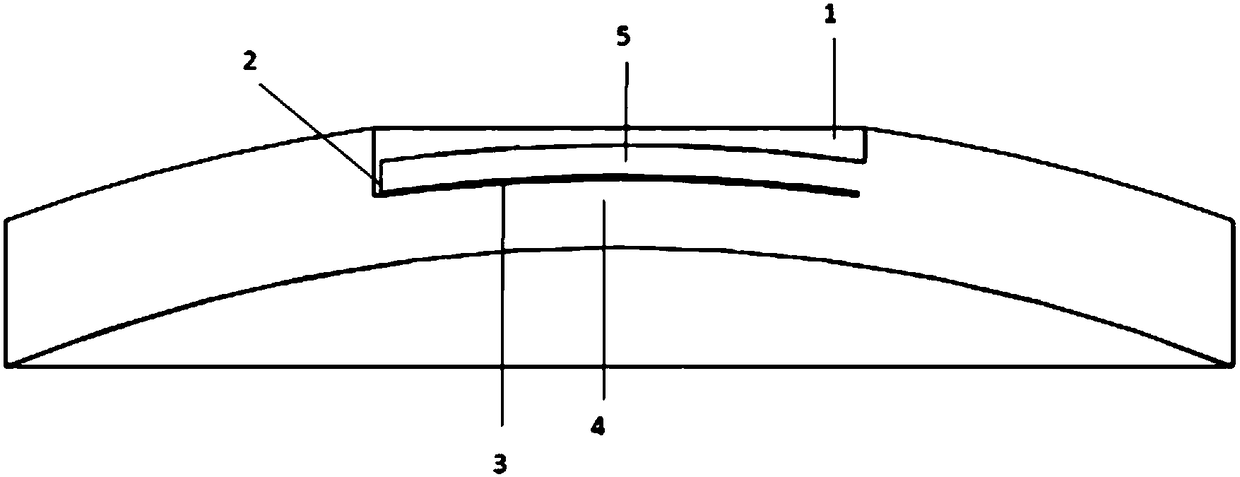
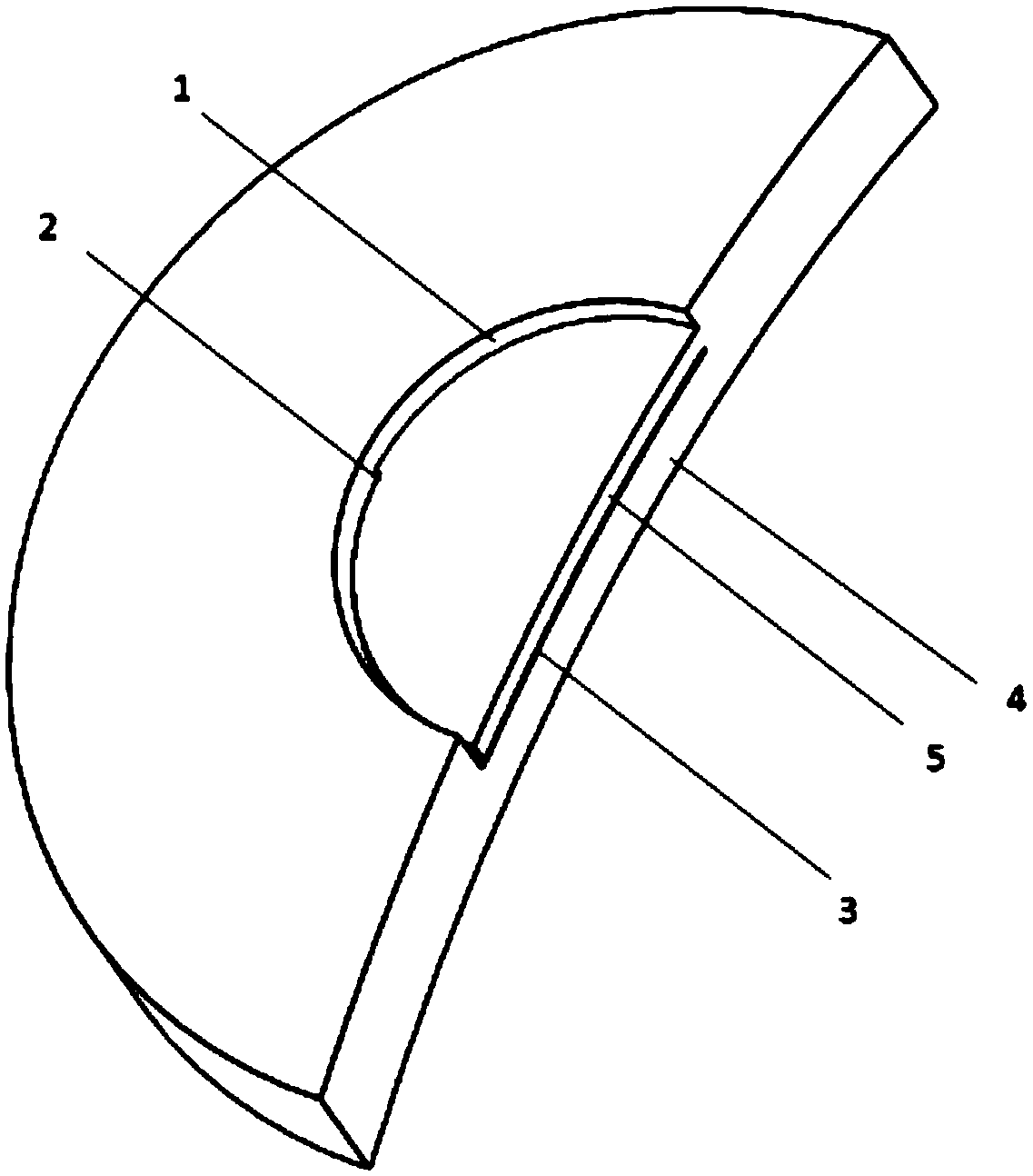
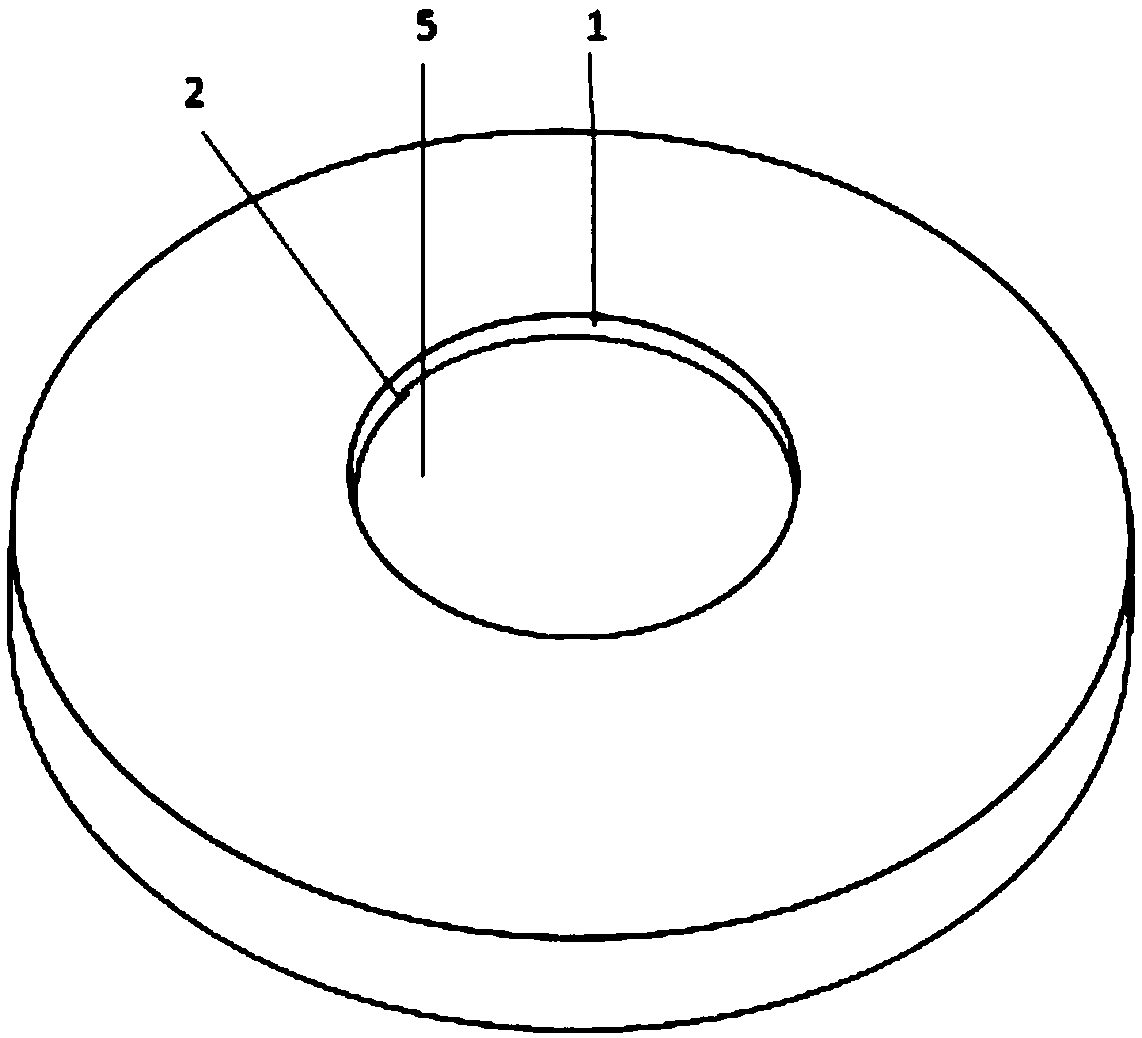
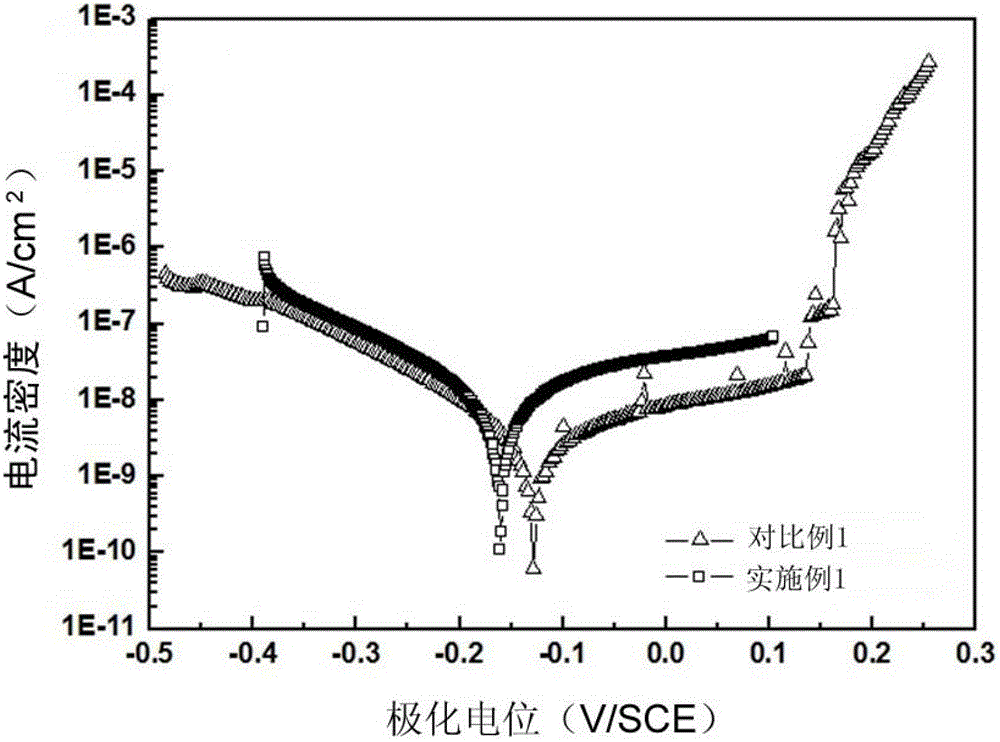
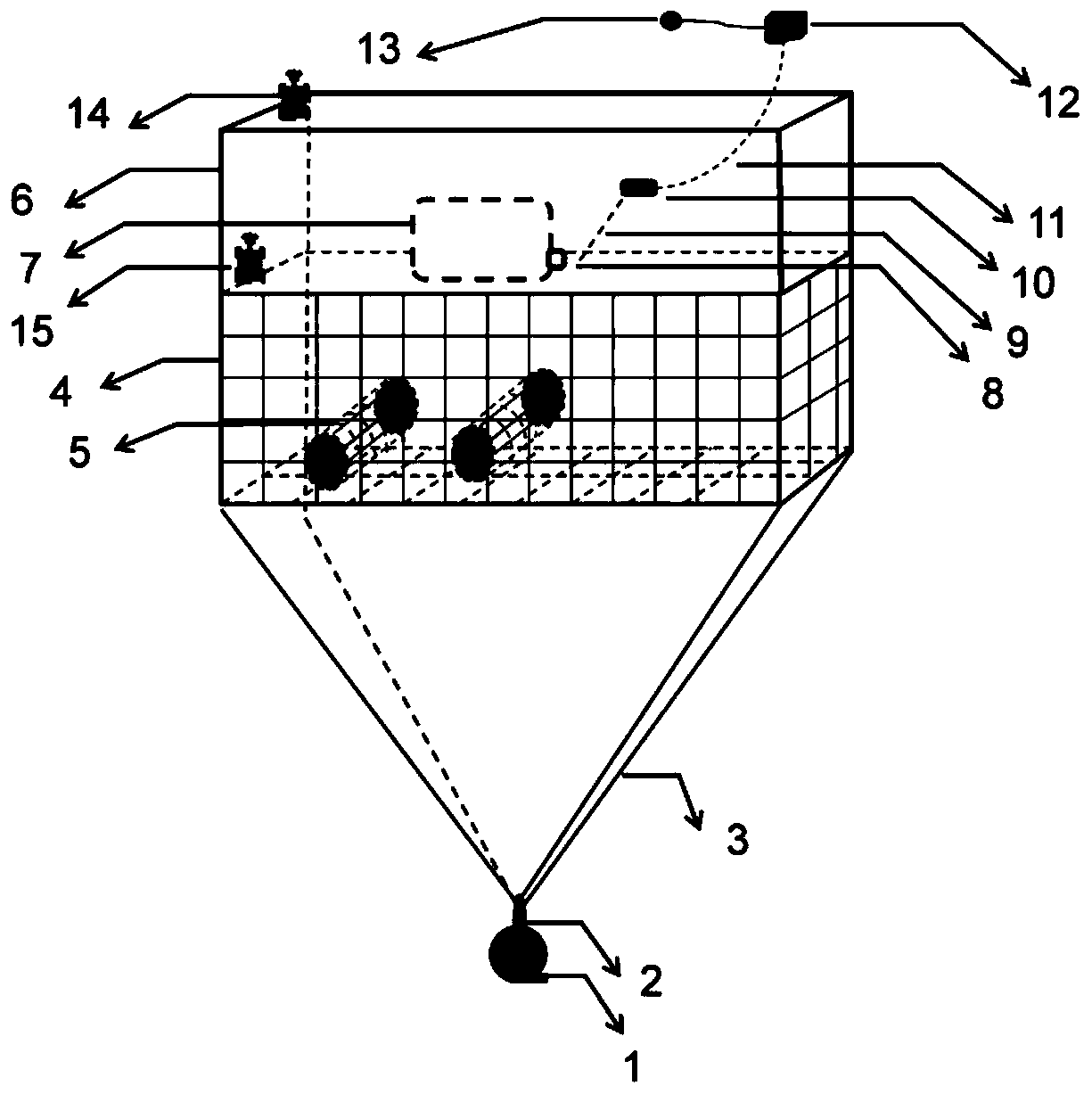
Electrochemical-optical combined in-situ study spectral cell
InactiveCN103033474AAvoid absorptionRealize joint useColor/spectral properties measurementsMaterial electrochemical variablesElectrochemical responseAdhesive
The invention discloses an electrochemical-optical combined in-situ study spectral cell. The electrochemical-optical combined in-situ study spectral cell comprises a cell body (5), a semi-cylindrical crystal light transmission window plate (1), a sample platform (8) and a reference electrode (9), wherein a layer of active substance film with the thickness at nanometer level is coated on the bottom plane of the semi-cylindrical crystal light transmission window plate (1) to be used as the a working electrode (12); a conducting line is led from the working electrode (12); the sample platform (8) is placed at the bottom part of the cell body (5) opposite to the working electrode (12); the reference electrode (9) is fixed relative to the working electrode (12) on the sample platform (8) by a conductive adhesive; and another conducting line is led from the reference electrode (9). By adopting the electrochemical-optical combined in-situ study spectral cell, spectral signals can be prevented from being absorbed by the solution; the real electrochemical reaction can be simulated; the electrochemical-optical combined in-situ spectral cell can be used in coupling with a spectrometer; the incident ray can be continuously adjusted from a smaller angle (15 degrees); and liquid in the cell body can flow so as to be exchanged.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
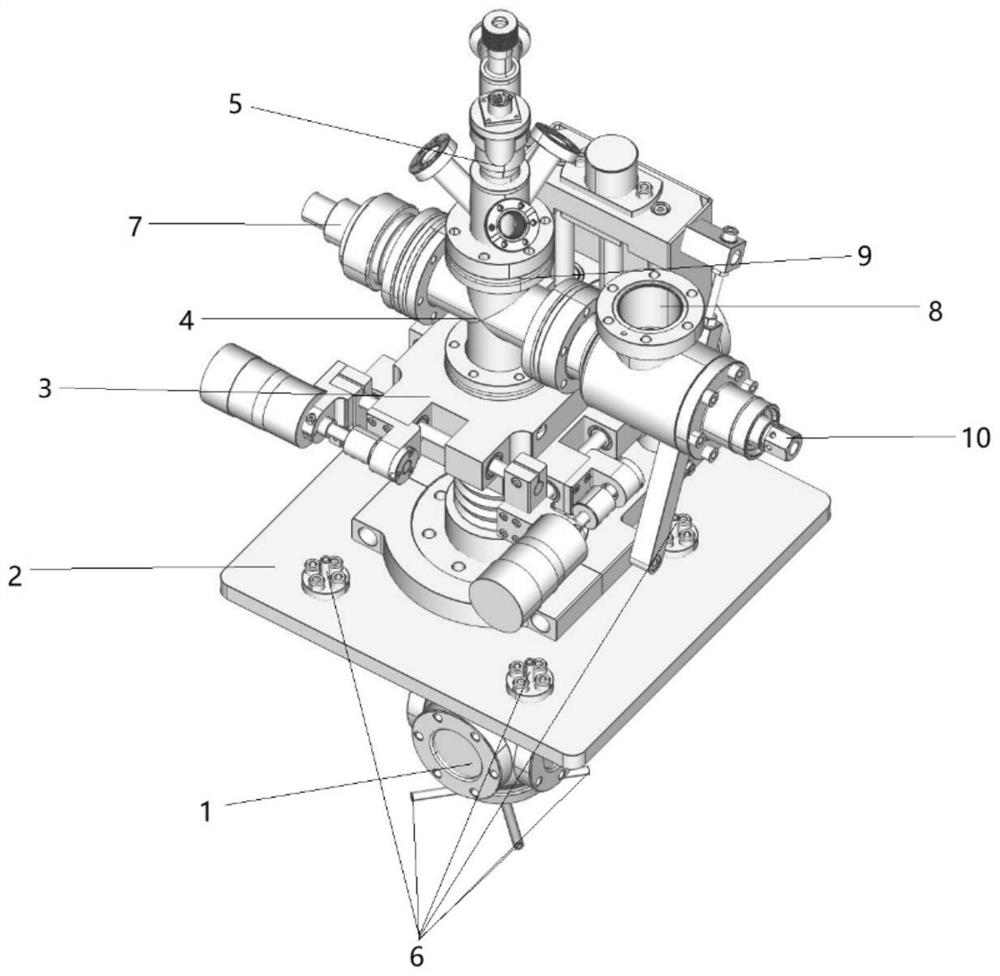
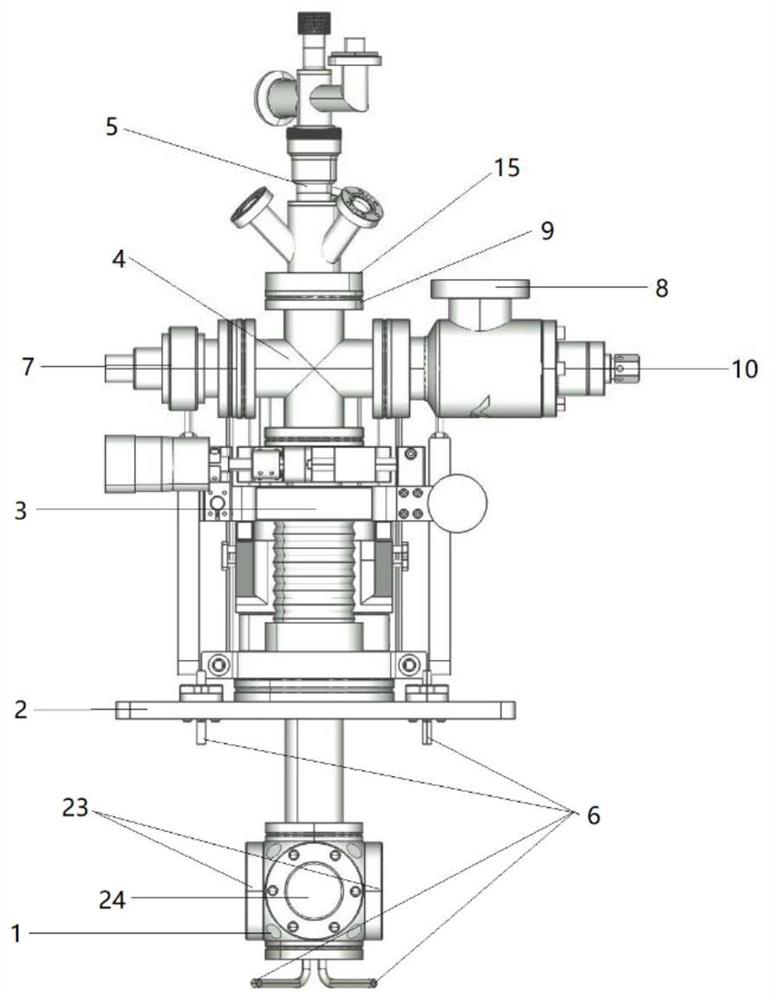
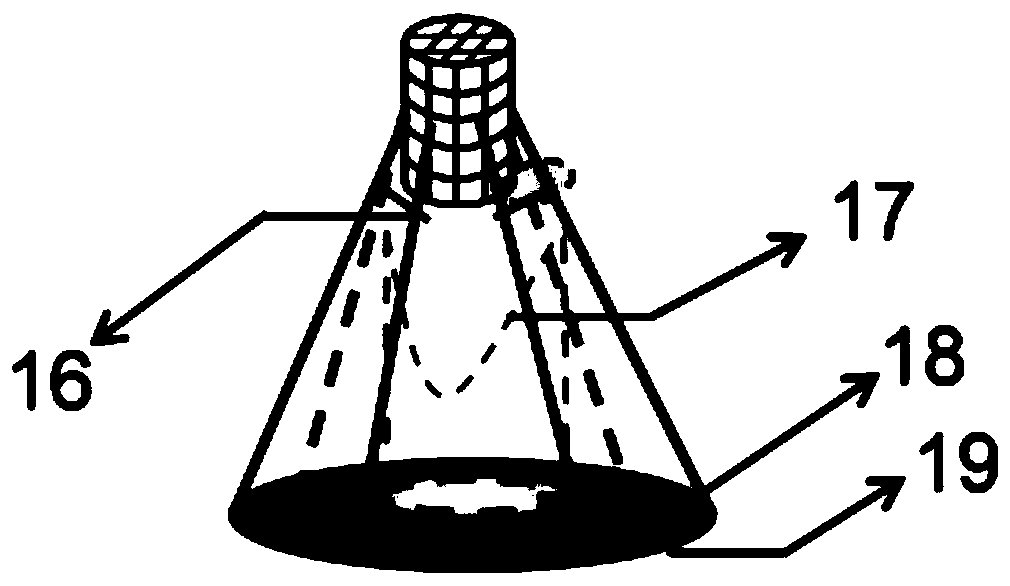
Apparatus for studying electrochemical behavior of material corrosion, and in-situ TEM method thereof
InactiveCN104007149ARealize Correspondence ObservationSmall working areaPreparing sample for investigationMaterial electrochemical variablesIn situ studyAluminium
The invention discloses an apparatus for studying electrochemical behavior of material corrosion, and an in-situ TEM method thereof, and belongs to the research field of corrosion electrochemistry behaviors. The apparatus comprises an upper plastic shell, a lower plastic shell, a platinum sheet and an aluminium conductive wire. The upper plastic shell is provided with a hole having a diameter of 2 mm; an upper surface of the lower plastic shell is embedded with the platinum sheet; the platinum sheet is connected to one end of the aluminium conductive wire; the other end of the aluminium conductive wire extends to the outer part of the lower plastic shell; the platinum sheet is provided with a pad, a TEM sample and the upper plastic shell in sequence; and the TEM sample contacts with electrolyte out of the apparatus through the hole on the upper plastic shell. The TEM sample is encapsulated in to an electrode by using the apparatus; then test of an electrochemical curve is carried out in the electrolyte to obtain electrochemical information; and the sample after the test is observed and characterized by TEM. The method can realize in-situ study of structural evolution in an electrochemical corrosion process in small size, thereby realizing corresponding observation of the electrochemical information and the structural evolution.
Owner:INST OF METAL RESEARCH - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Gas-solid phase in-situ Raman reaction tank
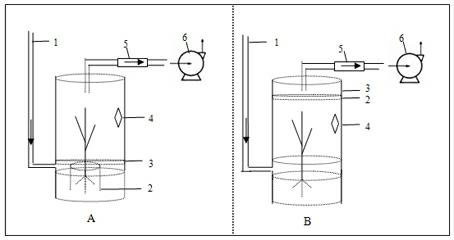
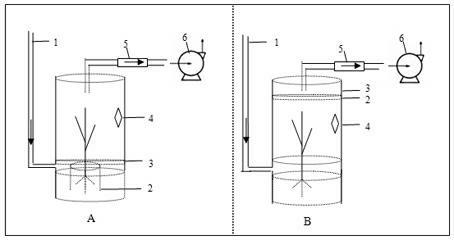
The invention belongs to the field of accessory research of spectroscopic technique application, and particularly provides a gas-solid phase in-situ Raman reaction tank which can be applied to the field of catalysis chemistry, materials, atmospheric chemistry and the like and in-situ research on heterogeneous process mechanism and dynamics. The in-situ reaction tank comprises a base, a detachable sample tank, a quartz glass cover, a sealing clamp sleeve, a hollow nut, an O-shaped ring groove and an air duct. The detachable sample pool can be a cylinder with a through hole at the center and made of stainless steel, PTFE materials or corundum. A heating device and a thermal couple can be embedded according to needs, thereby realizing temperature control and determination. The lower portion on the outer surface of the sample tank is provided with outer threads matching with inner threads which are arranged in the base and used for fixing the sample tank, thereby bringing convenience for filling and cleaning samples. The samples can be placed at a short focus of an ellipsoidal light collecting system of a Raman spectrometer, reaction gas entering a reaction cavity via the air duct sweeps over surfaces of the samples, and the Raman light spectrum during gas-solid reaction process can be acquired in situ.
Owner:RES CENT FOR ECO ENVIRONMENTAL SCI THE CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for preparing carbon nano tube through electron beam induced deposition
InactiveCN103693634APrecise length controlPrecise diameter controlMaterial nanotechnologyCarbon nanotubesNanowirePower flow
The invention provides a method for preparing a carbon nano tube through electron beam induced deposition. The method comprises the following steps of: withdrawing a single semiconductor nanowire; wrapping the surface with an amorphous carbon layer by the electron beam induced deposition technology so as to form a 'core-shell structure' with the nanowire and the amorphous carbon layer; loading a bias voltage; melting the nanowire and converting the amorphous carbon into stratified polycrystal under the effect of joule heat produced by current; and moving the molten nanowire out of the nano tube, thus obtaining a single carbon nano tube. With the adoption of the method, the length, diameter, wall thickness and other parameters of the carbon nano tube can be accurately controlled, the in-situ study can be performed for the formation process of the carbon nano tube, thus sufficient data can be provided for the study on the growth mechanism of the carbon nano tube; the method avoids inclusions and catalysts, so that the obtained carbon nano tube is relatively high in purity. The method can also be popularized to prepare carbon nano tube arrays.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Bioreactor for the in situ study of microbial biofilms inducing corrosion on metal surfaces
ActiveUS20170052165A1Avoid pollutionWeather/light/corrosion resistanceMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganismEngineering
A portable bioreactor is provided for the in situ study of mesophilic and thermophilic corrosion inducing microbial biofilms on metal surfaces used in any industry, such as oil, chemical, petrochemical, oil refining, food, metallurgical, paper. The bioreactor's configuration is a “batch” type for turbulent and piston-driven laminar flow, operating by cycles, with the continuous circulation of fluid. A culture medium, or industrial operation or production fluids containing microbiota is introduced into the load of the receiving body, thus the bioreactor is single phase. The bioreactor comprises a support section for corrosimetric test coupons that are in touch with the fluid under dynamic conditions, such as found in the fluid carrying pipelines, naturally promoting the formation of the microbial biofilm. The coupons are removed for analysis to follow the kinetics of microbial biofilm development. The operating conditions comprise a section having sufficient turbulence for the fluid to homogenize and maintain a temperature of 20 to 80° C. necessary for the mesophilic or thermophilic microorganism's growth. Salinity can be in the range 2 to 200 ppm (NaCl) and the pH range from 2 to 10; the bioreactor's operating conditions conform to the physicochemical characteristics of the fluid from the industry to be assessed.
Owner:INST MEXICANO DEL GASOLINEEO
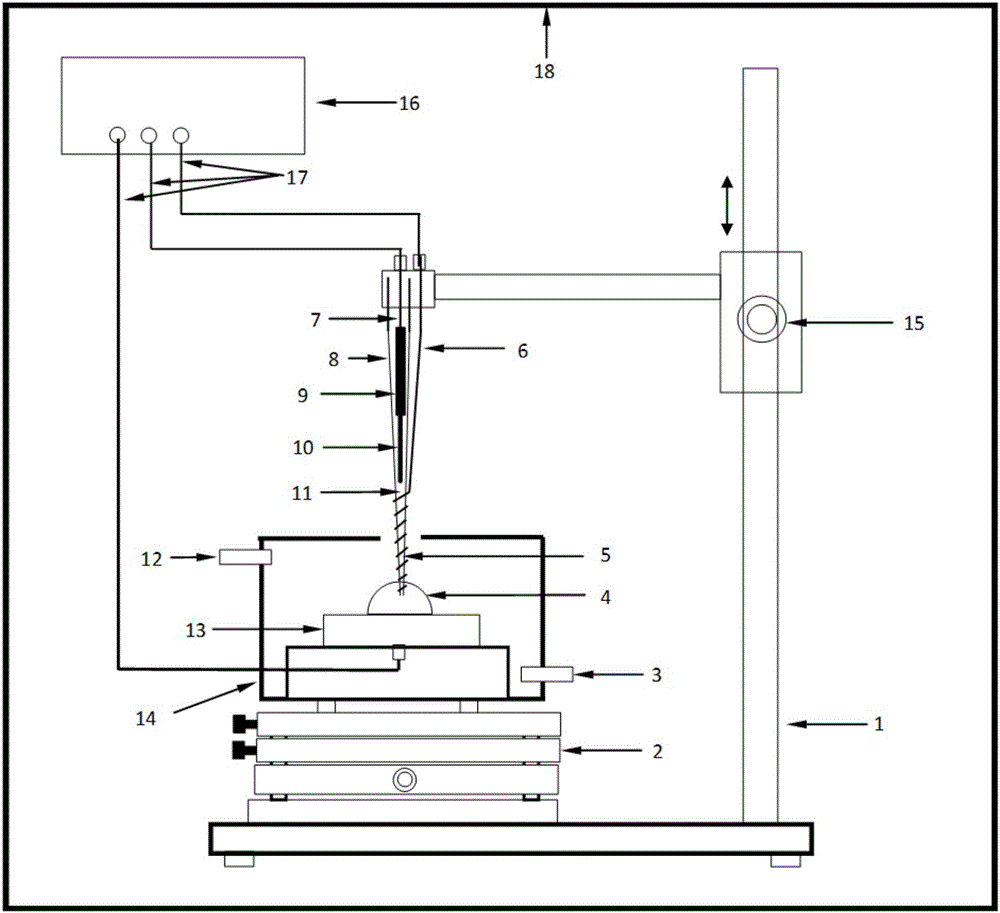
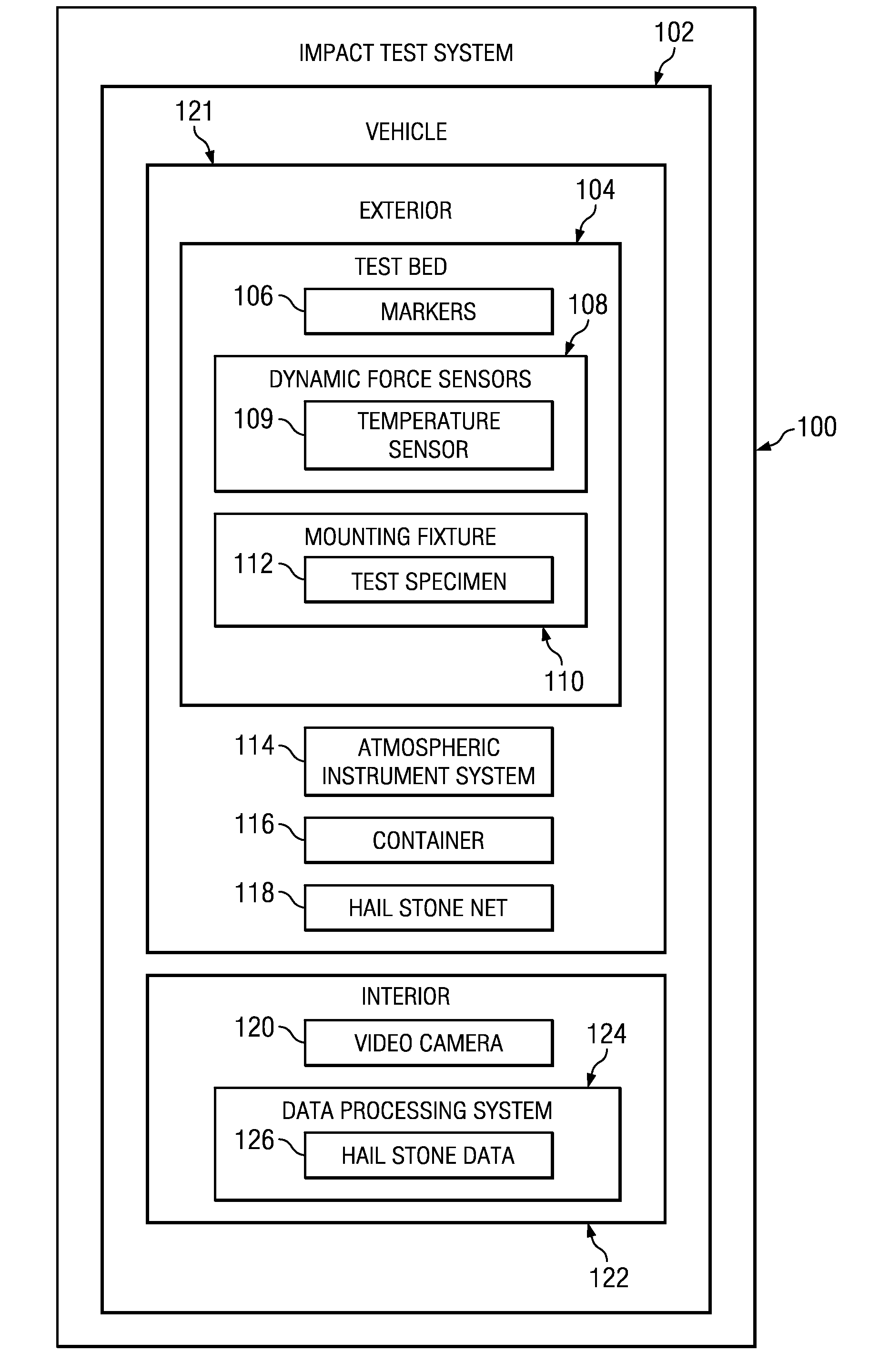
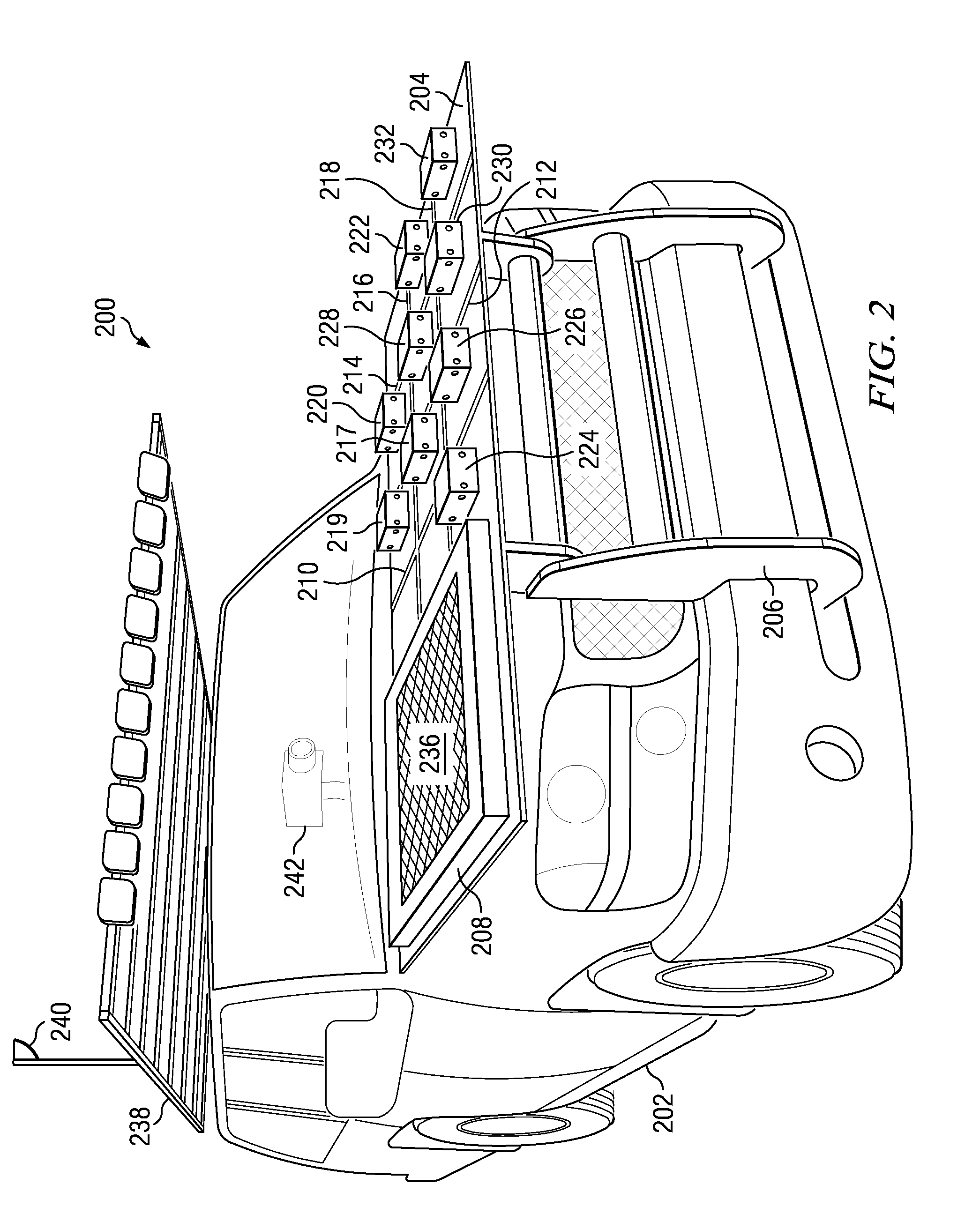
Test bed for in-situ studies
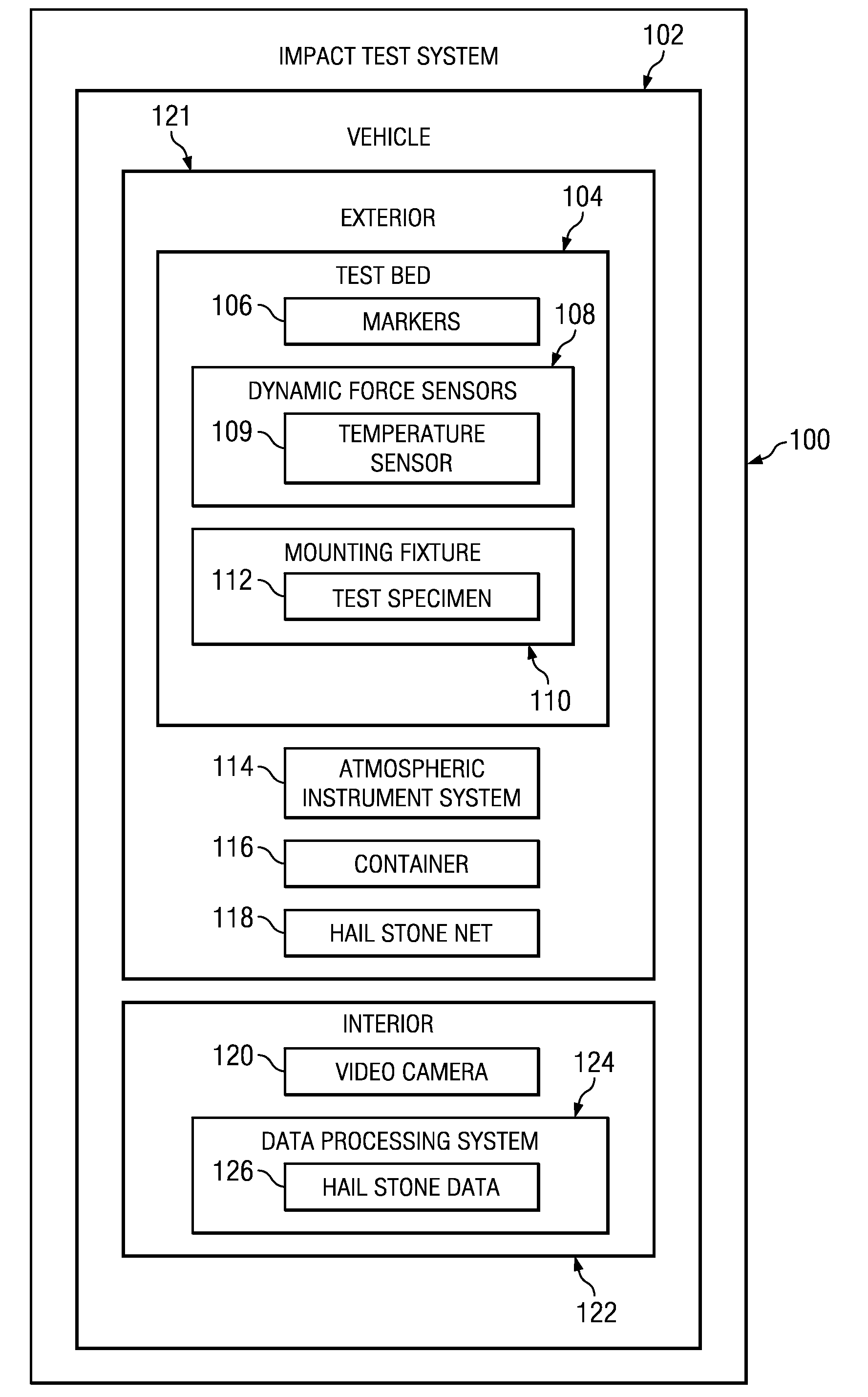
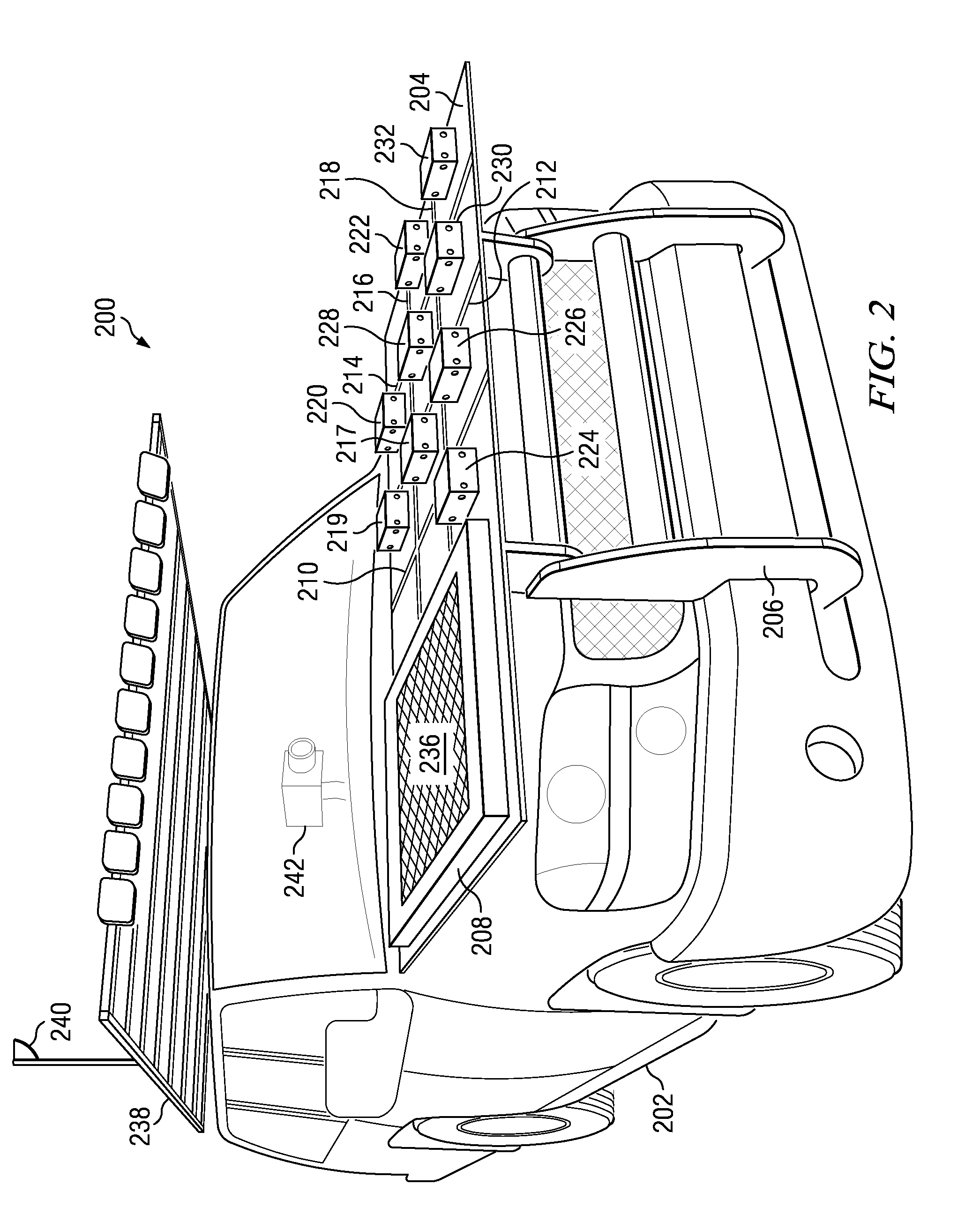
ActiveUS20090326822A1Rainfall/precipitation gaugesApparatus for force/torque/work measurementData processing systemIn situ study
An impact test system for collecting hail storm data comprises a vehicle, a video recorder, a container, a plurality of dynamic force sensors, an atmospheric instrument system, a mounting fixture, and a data processing system. The plurality of dynamic force sensors is capable of detecting force generated by an impact of an object. The plurality of markers is capable of being used to determine an orientation of an incoming object. The mounting fixture is capable of holding a test specimen. The data processing system is capable of collecting data from the plurality of dynamic force sensors, the atmospheric instrument system, and the video recorder.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
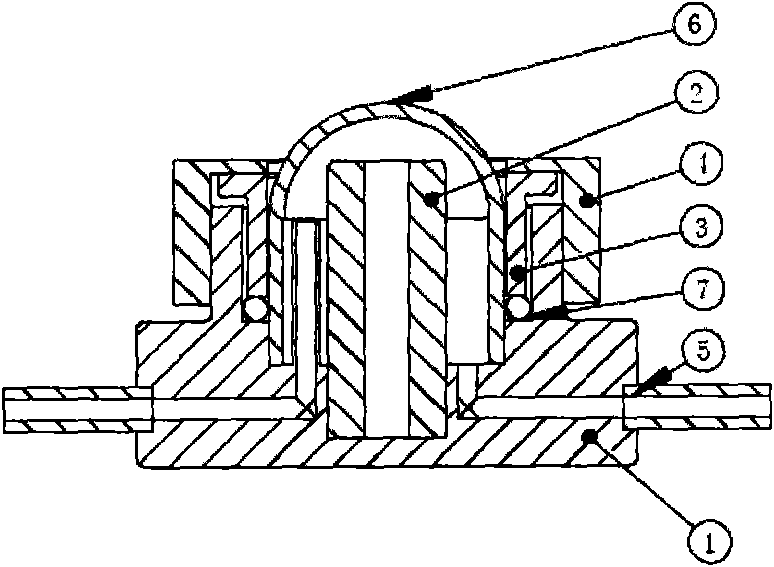
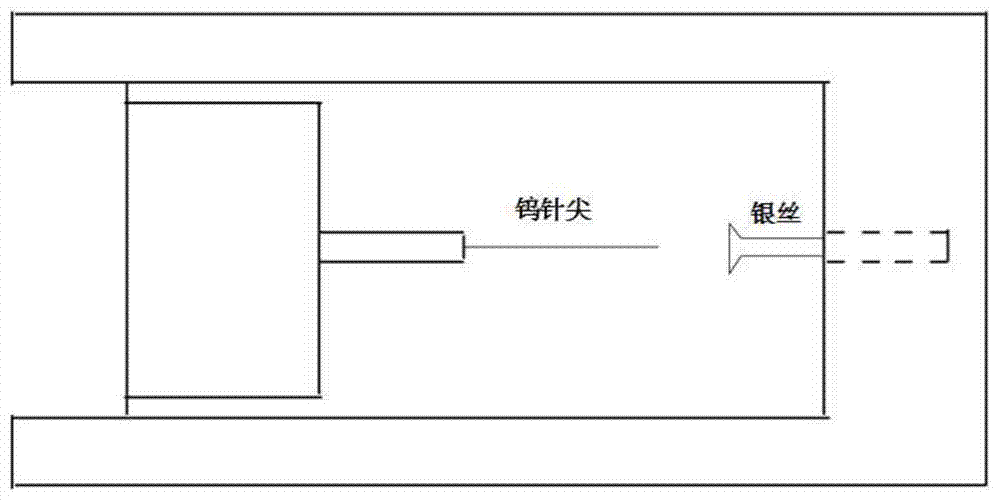
Electrode device for in-situ study of atmospheric corrosion process under liquid drops
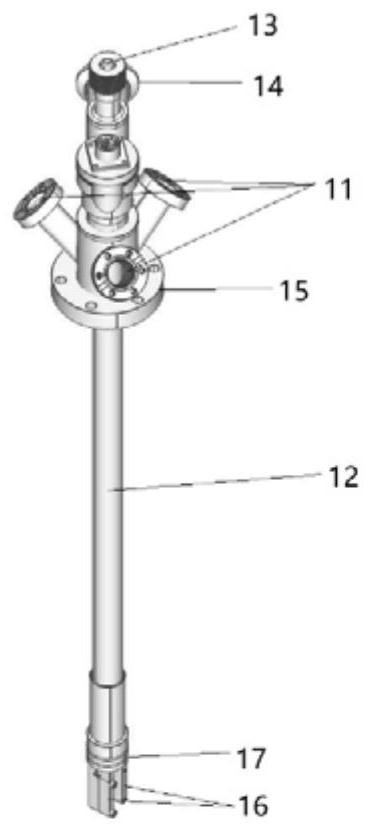
The invention relates to an electrode device for in-situ study of atmospheric corrosion process under liquid drops, and mainly solves the problems that in the prior art, the electrode device is complex in structure and high in price. The electrode device comprises an operating frame, a 3D operating table, a gas inlet, liquid drops, a capillary tube salt bridge of saturate KCl agar, a counter electrode, a silver wire, a glass tube, silica gel, silver chloride, a saturate KCl solution containing AgCl, a gas outlet, a working electrode, a test chamber, a rotary knob for adjusting upper and lower height, an electrochemical workstation, an outgoing line and a thermostat. Through the adoption of the electrode device for in-situ study of atmospheric corrosion process under liquid drops, the technical scheme well solves the problem, and the electrode device is applicable to in-situ study of atmospheric corrosion process under liquid drops.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP QINGDAO RES INST OF SAFETY ENG +1
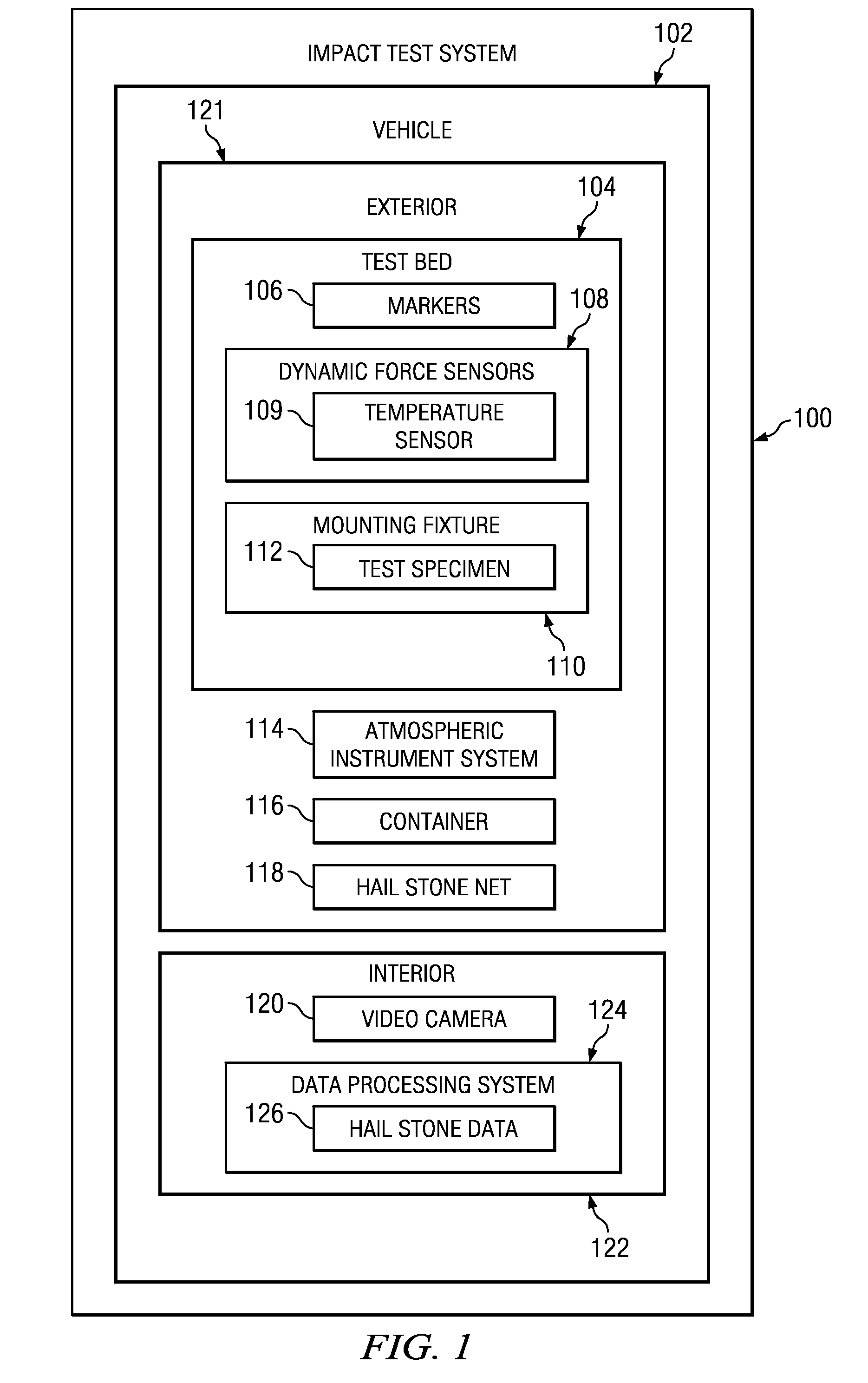
Test bed for in-situ studies
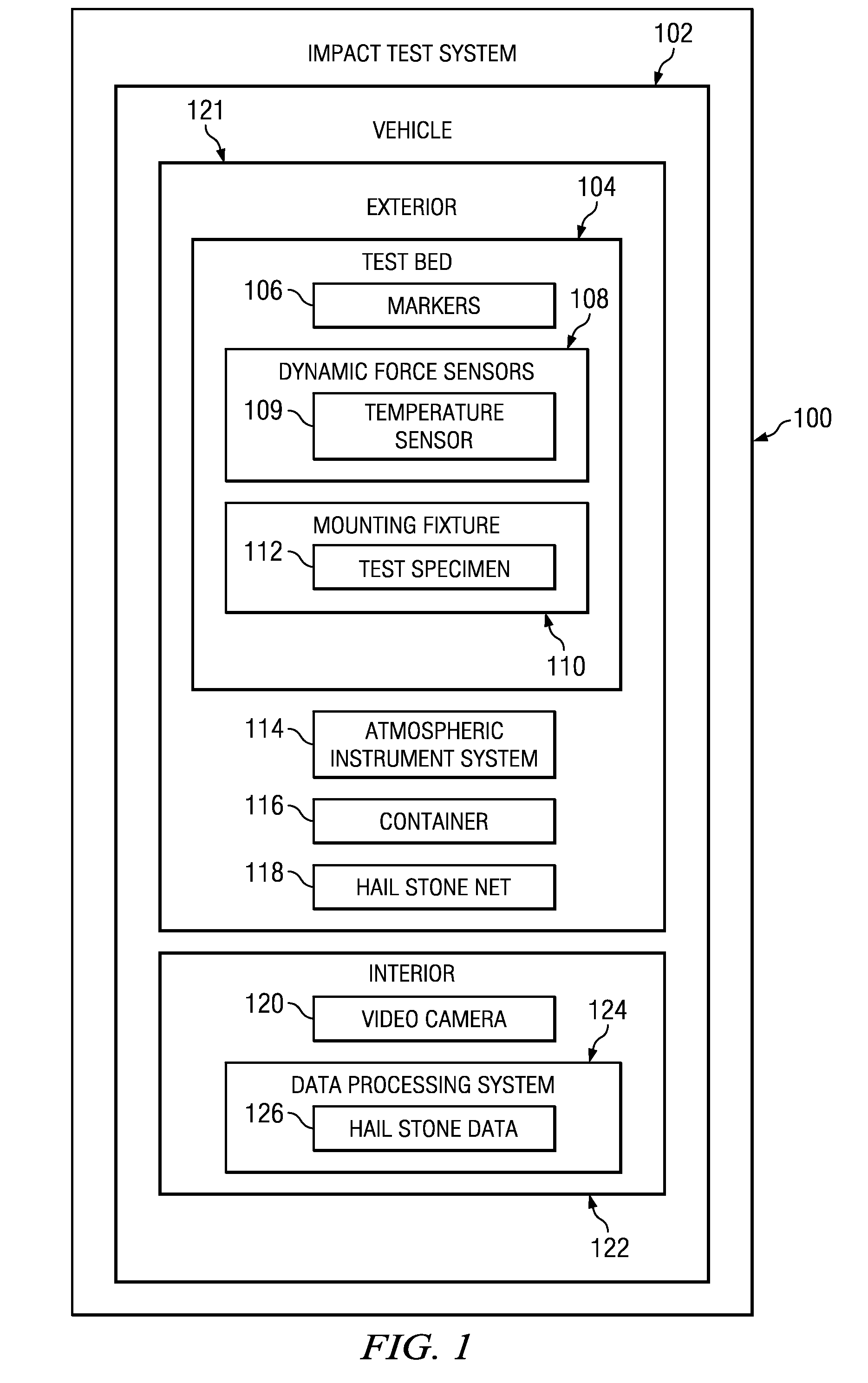
InactiveUS7945388B2Rainfall/precipitation gaugesApparatus for force/torque/work measurementData processing systemIn situ study
An impact test system for collecting hail storm data comprises a vehicle, a video recorder, a container, a plurality of dynamic force sensors, an atmospheric instrument system, a mounting fixture, and a data processing system. The plurality of dynamic force sensors is capable of detecting force generated by an impact of an object. The plurality of markers is capable of being used to determine an orientation of an incoming object. The mounting fixture is capable of holding a test specimen. The data processing system is capable of collecting data from the plurality of dynamic force sensors, the atmospheric instrument system, and the video recorder.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Electrochemical Optics Spectroscopic Cell for In Situ Research
InactiveCN103033474BAvoid absorptionRealize joint useColor/spectral properties measurementsMaterial electrochemical variablesElectrochemical responseAdhesive
The invention discloses an electrochemical-optical combined in-situ study spectral cell. The electrochemical-optical combined in-situ study spectral cell comprises a cell body (5), a semi-cylindrical crystal light transmission window plate (1), a sample platform (8) and a reference electrode (9), wherein a layer of active substance film with the thickness at nanometer level is coated on the bottom plane of the semi-cylindrical crystal light transmission window plate (1) to be used as the a working electrode (12); a conducting line is led from the working electrode (12); the sample platform (8) is placed at the bottom part of the cell body (5) opposite to the working electrode (12); the reference electrode (9) is fixed relative to the working electrode (12) on the sample platform (8) by a conductive adhesive; and another conducting line is led from the reference electrode (9). By adopting the electrochemical-optical combined in-situ study spectral cell, spectral signals can be prevented from being absorbed by the solution; the real electrochemical reaction can be simulated; the electrochemical-optical combined in-situ spectral cell can be used in coupling with a spectrometer; the incident ray can be continuously adjusted from a smaller angle (15 degrees); and liquid in the cell body can flow so as to be exchanged.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Simulated battery device for in-situ detection of gas production of solid-state battery
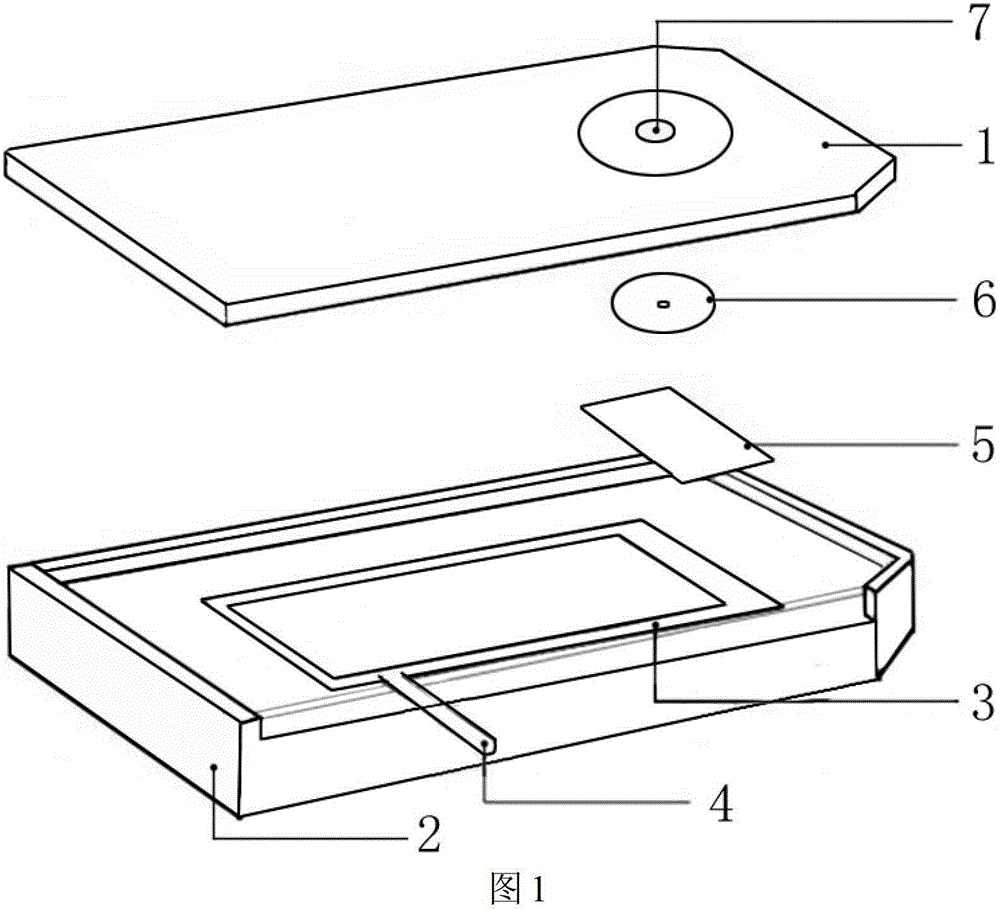
ActiveCN110954493AGuaranteed to workMeet different temperature requirementsMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansMaterial analysis by optical meansRubber ringEngineering
The invention provides a simulated battery device for in-situ detection of gas production of a solid-state battery. The device comprises an upper shell and a lower shell, wherein the pressure regulating mechanism, the battery module, the porous insulating film, the rubber ring and the gasket are positioned between the upper shell and the lower shell; wherein the lower shell is provided with a first groove and a second groove, the rubber ring is arranged in the first groove, the gasket is arranged in the second groove, the battery module is arranged on the gasket, the pressure adjusting mechanism is arranged on the battery module, the upper shell is arranged on the pressure adjusting mechanism, and the upper shell and the lower shell are connected and fixed through an insulating screw. Thesimulation battery device provided by the invention is combined with a mass spectrometer or an infrared spectrometer and the like, so that in-situ research on the gas production problem of the solid-state battery in the charging and discharging process is realized. The device provided by the invention has the advantages of small electrode chamber, capability of keeping higher vacuum degree and short response time, and can meet different temperature requirements during battery operation.
Owner:TIANMU LAKE INST OF ADVANCED ENERGY STORAGE TECH CO LTD +1
Temperature-controllable infrared in-situ reaction tank based on high vacuum condition from low temperature to high temperature
ActiveCN111272654AImprove accuracyMeet temperature requirementsMaterial analysis by optical meansVacuum pumpingOptical spectrometer
The invention relates to a temperature-controllable infrared in-situ reaction tank based on a high vacuum condition from a low temperature to a high temperature. The reaction tank consists of two parts, wherein one part is an infrared cavity main body part fixed on the infrared spectrometer and comprises a cubic cavity provided with a light inlet window and a light outlet window, a steel plate used for sealing a spectrograph, a gas path system, a vacuum pumping system joint, a cold head joint, a vacuum gauge port and a three-dimensional translation platform; and the other part is a detachablecold head part which is integrated with sample clamping and temperature adjustment and control. The in-situ tank can realize gas inlet, vacuum maintenance and accurate control from low temperature (110K) to high temperature (more than 1000K) under a high vacuum condition, so that gas adsorption and reaction of a powder sample and a film sample under different conditions can be researched in situ,and the influence of background atmosphere can be effectively eliminated.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
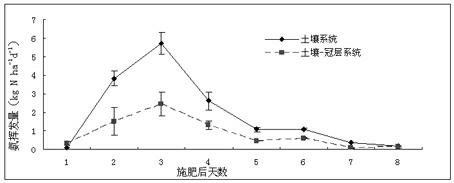
Device and monitoring method for in-situ research on ammonia exchange in crop canopy
InactiveCN102279179AOvercomes the inability to distinguish the contribution of plant canopies to ammonia emissions from farmlandGrowth does not affectMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorPhosphoric acidVacuum pump
The invention discloses a device for researching crop canopy ammonia exchange in situ at a farmland and a monitoring method. The device comprises an air-proof cultivation cover and a dilute acid carrier, wherein an air inlet pipe is arranged on the side wall, close to the zero depth, of the cultivation cover; an air exhaust hole is formed in the top of the cultivation cover; the air exhaust hole is connected with a vacuum pump; and brackets for fixing the dilute acid carrier are arranged at the ends, close to the zero depth and the air exhaust hole, in the cultivation cover respectively. The diameter and the height of a growth box of the device can be adjusted according to the size and the height of a monitored plant; and dilute acid for soaking sponge can be phosphoric acid, sulfuric acid and oxalic acid. By the device and the monitoring method, canopy ammonia exchange of farmland crops in a vigorous growing stage (particularly after fertilization) and ammonia emission of the farmland crops in a growing later stage can be researched; during monitoring, humiture in the cover is almost the same as the humiture in a natural environment, so mists in the cover are avoided and influence on growth of rice can be prevented; therefore, the repeatability of rice is high and the variation coefficient is generally less than or equal to 10 percent; and the device is easy to operate.
Owner:INST OF SOIL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Test device for in situ study of heavy metal dynamic adsorption reaction in water
ActiveCN108872278APromote research and developmentEfficient research and developmentMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationIn situ studyAdsorption reaction
The invention discloses a test device for in situ study of heavy metal dynamic adsorption reaction in water. The test device comprises a reactor, wherein an incidence window used for communicating outside environment with the inside of the reactor is formed in the reactor; the located surface of the incidence window is used as the front side of the reactor; an emergence window is arranged in the position, corresponding to the incidence window, at the back side of the reactor; a sealing film is arranged on the incidence window and the emergence window; a multidimensional regulation platform isarranged at the bottom of the reactor and can transversely move in the three directions X, Y and Z and can rotate in the horizontal direction; a feeding opening is formed in the top of the reactor; anelectromagnetic flat plate capable of turning and rotating is arranged inside the reactor. The device also comprises a capillary tube focusing lens; the capillary tube focusing lens is positioned atone side of the front side of the reactor. By using the device, the process of studying the dynamic adsorption process of the material on heavy metals in the solution by an in situ synchronous radiation QXAFS method can be achieved; the yield, the quality, the precision and the efficiency are improved.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY OF ARCHITECTURE
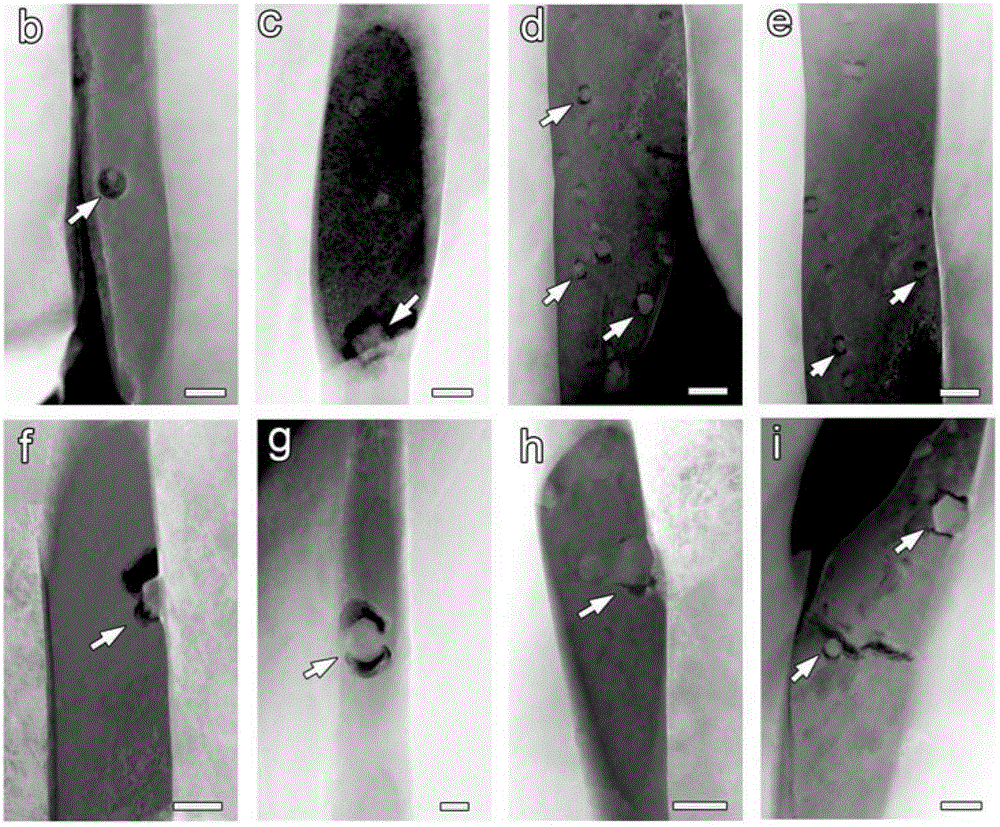
Method for in-situ study of amorphization mechanism of germanium-antimony-tellurium material under electron beam irradiation
InactiveCN110554060AAvoid molten stateUniversalPreparing sample for investigationMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationDirect observationTe element
The invention discloses a method for in-situ study of an amorphization mechanism of a germanium-antimony-tellurium material under electron beam irradiation. The method comprises the following steps: selecting a germanium-antimony-tellurium crystal thin film of which the surface is deposited on a carbon supporting film copper carrying net with a standard size of a transmission electron microscope;carrying out surface pretreatment on the prepared film sample by adopting a plasma cleaning technology, and carrying out plasma cleaning by selecting argon; placing a pretreated electron microscope sample in the transmission electron microscope, and searching an area which is smooth in surface, free of carbon deposition, pollution and damage and uniform in thickness in the thin film sample to serve as an irradiation area; setting irradiation parameters, and inducing the material to be gradually amorphized; and observing and recording the evolution process of the amorphous structure of the material in situ, and analyzing the amorphous phase change mechanism of the material. According to the method, the gradual amorphization of the germanium-antimony-tellurium material is realized through electron beam irradiation, and the structural evolution process of the material amorphization is directly observed and analyzed by virtue of the transmission electron microscope, so that the convenientresearch method and a reliable experimental basis are provided for exploring the amorphization mechanism of the germanium-antimony-tellurium material.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Transmission electron microscope technology for in-situ study of three-dimensional distribution structure of nanoparticles
ActiveCN110208168AImprove performancePrevent oxidationPreparing sample for investigationIndividual particle analysisConventional transmission electron microscopeCarbon fibers
The invention discloses a transmission electron microscope technology for in-situ study of a three-dimensional distribution structure of nanoparticles. The transmission electron microscope technologyis characterized by comprising the steps of: acquiring carbon nanofibers after carbonization treatment by adopting an electrospinning technique and thermal treatment; loading precursor salt of alloy on the carbon nanofibers; assembling a metal needle tip into a sample rod fixing end of a transmission electron microscope, the carbon nanofibers are loaded with a gold needle platform, and a gold needle is arranged on the movable end of a sample rod; the sample rod loaded with the metal needle tip and the gold needle is inserted into the transmission electron microscope, the height and position ofthe gold needle at the movable end of the sample rod are adjusted, such that the carbon nanofibers on the gold needle platform are in contact with the metal needle tip, a certain voltage is applied within certain instantaneous time, so that the precursor salt loaded on the carbon nanofibers on gold needle platform undergoes an instantaneous carbothermic reaction to form alloy nanoparticles, and the distribution variations and sintering situations of the alloy nanoparticles under the action of a current field are observed; and two-dimensional projection transmission electron microscope pictures are photographed, the electron microscope pictures are subjected to alignment, three-dimensional reconstruction and visualization by means of software.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Flexible Array Reference Electrode and Its Method for In-Situ Study of Metal Weld Corrosion
ActiveCN106066353BLow modulusGood high and low temperature resistanceMaterial electrochemical variablesHeat-affected zoneIn situ study
The invention discloses a flexible array reference electrode, and a method for in situ researches of the corrosion of a metal weld by using the electrode. The flexible array electrode is composed of a flexible substrate, an array electrode arranged on the surface of the flexible substrate, and a leading wire packaged in the flexible substrate and connected with the array electrode, the array electrode is formed by arranging Ag / AgCl micro-electrodes in an array manner, surface potentials of different micro-areas of the metal surface can be simultaneously obtained, and the flexible substrate with small modulus and flexible deformation is adopted to realize in situ and real time monitoring of the corrosion potential of abnormal complex surface of a metal weldment. The measurement method adopting the flexible array electrode as a reference electrode realizes in situ, lossless, convenient and sensitive detection of the corrosion potentials of the surface weld area, the thermal influence area and the base material area of the metal welding sample in order to observe the generation, development and extinction process of corrosion of different positions of the surface of the metal weldment, and the corrosion resistances of different welding modes in different environments are compared to realize onsite real time monitoring of the corrosion state of the metal weld in the service, so the method is especially suitable for long-term tracking monitoring of the service safety of metal weldments of automobiles, ships, engineering machines and aerospace.
Owner:厦门昕钢防腐工程科技有限公司 +1
Electrode device for in situ study of atmospheric corrosion process under liquid droplets
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP QINGDAO RES INST OF SAFETY ENG +1
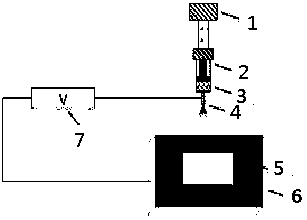
A method for in-situ measurement of sample magnetism
ActiveCN108490375BHigh resolutionReduce mechanical instabilityMagnetic property measurementsMagnetic field measurement using magneto-optic devicesImaging qualityPolarizer
The invention relates to the field of material surface magnetism measurement, and discloses an in-situ measurement method for sample magnetism. The in-situ measurement method adopts a measuring device, wherein the measuring device comprises a light source, an aspherical mirror I, an aspherical mirror II, a field diaphragm, a polarizer, an aspherical mirror III, a translucent reflector, an objective lens, a laser device, a sample, a sample platform, a substrate, a stepping motor, an inclined plane bench, an ejection pin, a magnet, slit diaphragms, a photoelectric detector I, a compensator, ananalyzer, an aspherical mirror IV and a photoelectric detector II. According to the in-situ measurement method, the illumination region on the sample does not need to be changed by means of the diaphragm slits, the Kerr sensitivity in different directions is measured, the mechanical instability in the experiment is reduced, incident light intensity in different directions are adjusted through adjusting the number and the duration of turned-on LED lamps, the intensity of incident light is adjusted in real time according to the acquired image quality so as to obtain an image with good resolution, and especially for some magnetic samples with complicated magnetization directions of magnetic domains, the magnetoelastic property of the sample can be studied in situ through adopting the method of applying stress to the back surface of the sample.
Owner:嘉兴诺恩医疗科技有限公司
A portable in-situ multi-field coupling loading device for neutron scattering
ActiveCN108459035BCompact structureMeet the needs of complex usage environmentsMaterial analysis using radiation diffractionNuclear engineeringNeutron scattering
The invention discloses a portable in-situ multi-field coupling loading device for neutron scattering. The device comprises a stress loading and testing assembly, a temperature loading assembly and amagnetic field loading assembly, wherein the stress loading and testing assembly comprises four parallel guide rods for supporting; a first fixing plate, a force sensor, a left clamp, a right clamp, aspring moving plate, a spring set, a second fixing plate and a stress loader are sequentially mounted on each guide rod from left to right; the temperature loading assembly comprises a left heating ring and a right heating ring which are correspondingly arranged on clamp heads of the left clamp and the right clamp; the magnetic field loading assembly comprises a support which his provided with two vertical arms, and the two vertical arms are correspondingly arranged at the front and back of a guide rod set. According to the device, the stress, temperature and magnetic field multi-field coupling loading is developed and achieved for the first time, and a foundation is provided to multi-site in-situ research of magnetic material type magnetic structures in evolving micromechanisms; and thedevice is applicable to different neutron source neutron scattering spectrometers.
Owner:INST OF HIGH ENERGY PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Living body in-situ study platform for tissue regeneration inducing mechanisms, and application method thereof
ActiveCN109444395AAchieve observationRealize evaluationDiagnostics using lightMicrobiological testing/measurementIn situ studyIn vivo
Disclosed are a living body in-situ study platform for tissue regeneration inducing mechanisms, and an application method thereof. The platform comprises a living rat cornea having a region from whichthe corneal epithelial cells are removed. A rat corneal stroma layer in the region has a rat corneal stroma layer graft and a rat corneal stroma layer planting bed, which are still connected after surface separation is formed by slicing from a set slit to the inner side. A to-be-studied tissue engineering material is put in a cavity formed between separation surfaces of the rat corneal stroma layer graft and the rat corneal stroma layer planting bed. The rat corneal stroma layer graft and the rat corneal stroma layer implanted bed are connected by a connecting material at the slit. The platform has the advantages that the interaction between the tissue engineering material and an organism can be well observed and evaluated through in-vivo microscope observation, tissue section observationand molecular biological analysis.
Owner:SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL TSINGHUA UNIV
A device for studying the electrochemical behavior of material corrosion and its in-situ TEM method
InactiveCN104007149BRealize Correspondence ObservationSmall working areaPreparing sample for investigationMaterial electrochemical variablesPlatinumKnowledge Field
Owner:INST OF METAL RESEARCH - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
A temperature-controllable infrared in-situ reaction cell based on high vacuum conditions from low temperature to high temperature
ActiveCN111272654BEliminate distractionsAvoid corrosionMaterial analysis by optical meansVacuum pumpingOptical spectrometer
The invention relates to a temperature-controllable infrared in-situ reaction pool based on high vacuum conditions from low temperature to high temperature. The device consists of two parts, one part is fixed on the main part of the infrared cavity of the infrared spectrometer, including a cubic cavity with a light entrance window and a light exit window, a steel plate for sealing the spectrometer, an air system, and a vacuum pumping system interface , cold head interface, vacuum gauge interface and three-dimensional translation stage, and the other part is a detachable cold head part that integrates sample clamping and temperature adjustment and control. The in-situ cell can achieve air intake and vacuum maintenance under high vacuum conditions, and precise control from low temperature (110K) to high temperature (above 1000K), so that the gas adsorption and reaction of powder samples and film samples under different conditions can be studied in situ and It can effectively eliminate the influence of background atmosphere.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
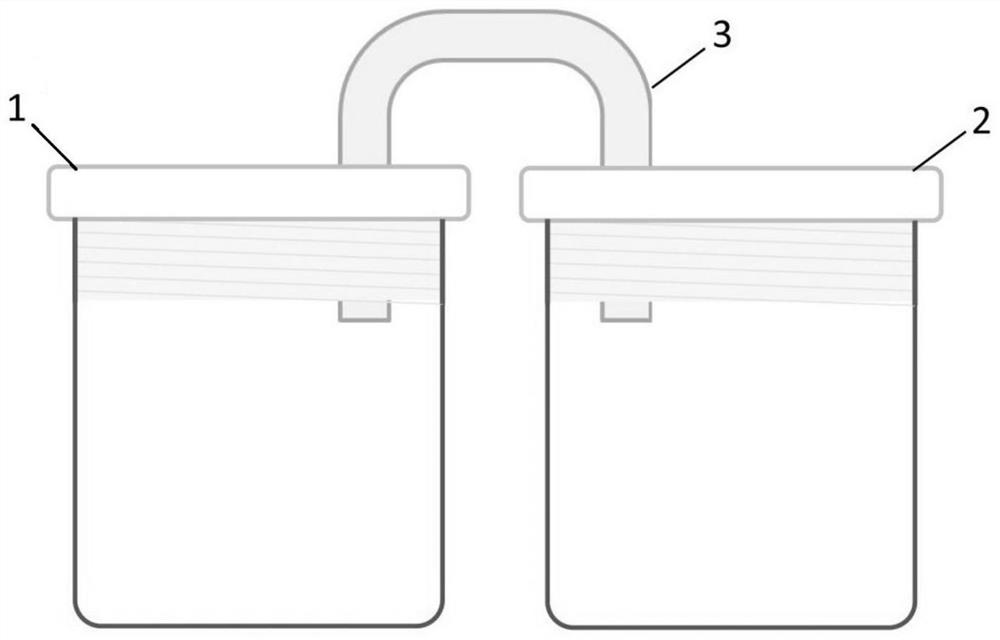
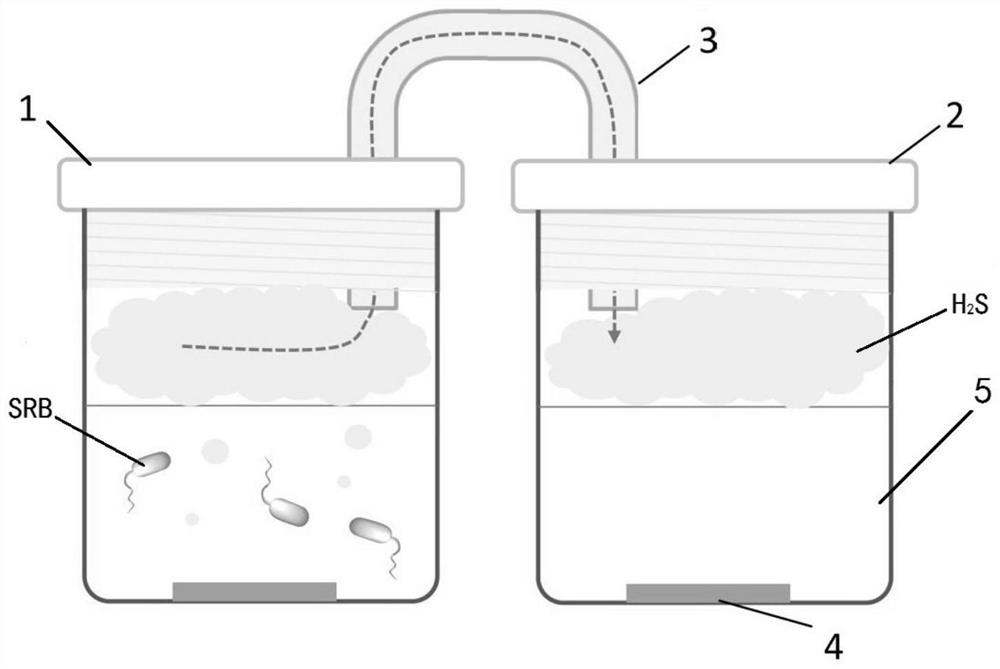
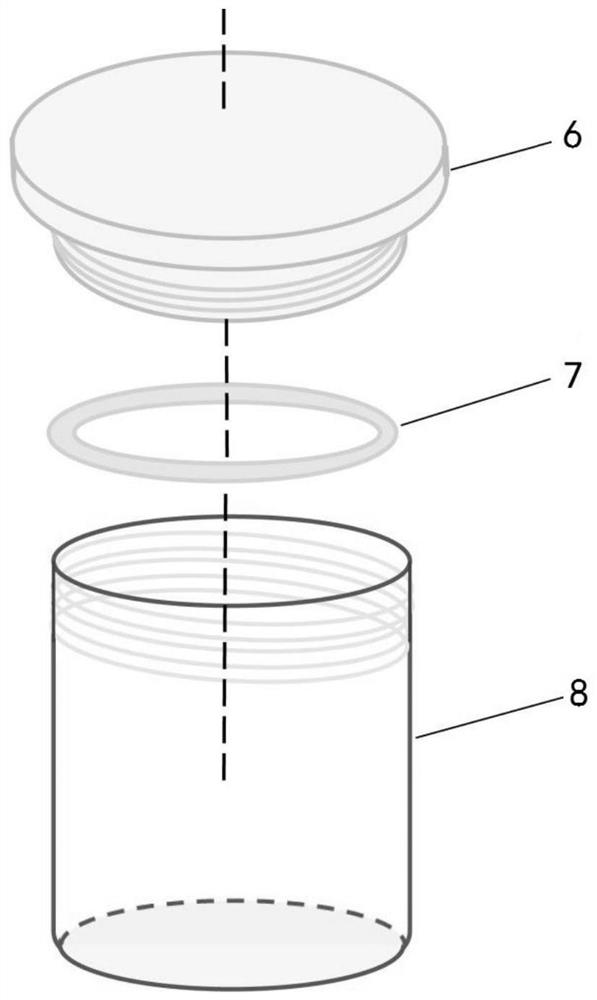
In-situ contrast experiment device and method for single-factor corrosion of gas in composite corrosion factors
PendingCN111855557AGuarantee authenticitySimplified experimental setupWeather/light/corrosion resistanceIn situ studyReaction system
The invention discloses an in-situ contrast experiment device for single-factor corrosion of gas in composite corrosion factors, which comprises a main chamber for composite corrosion and at least oneauxiliary chamber for single-factor corrosion of gas. The top of the main chamber is communicated with the top of the auxiliary chamber through a gas pipe. The invention further discloses an in-situcontrast experiment method for single-factor corrosion of gas in composite corrosion factors. Real-time in-situ research on the corrosion performance of each gas in a reaction system with corrosive gas on the material is realized at the same time, links of intermediate gas content measurement and the like are reduced, and the method has the characteristics of quickness and reliability.
Owner:GUANGDONG INST OF MICROBIOLOGY GUANGDONG DETECTION CENT OF MICROBIOLOGY
Bioreactor for the in situ study of microbial biofilms inducing corrosion on metal surfaces
ActiveUS10309951B2Avoid pollutionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsTest couponPetrochemical
A portable, single-phase bioreactor provides the in situ study of mesophilic and thermophilic corrosion inducing microbial biofilms on metal surfaces by oil, chemical, petrochemical, oil refining, food, metallurgical, paper fluids. The bioreactor is a batch-type for turbulent and piston-driven laminar flow, operated by cycles, with continuous circulation of the fluid. A culture medium or industrial or production fluid containing microbiota is introduced into a homogenizing container. The bioreactor includes a support section having removable corrosimetric test coupons that contact the fluid under dynamic conditions corresponding to fluid-carrying pipelines, and promote the formation of the microbial biofilm for analysis of the kinetics of microbial biofilm development. The bioreactor produces turbulence to homogenize the fluid and maintain a temperature of 20 to 80° C. for the microorganism growth. The fluid has a salinity of 2 to 200 ppm (NaCl) and a pH of 2 to 10.
Owner:INST MEXICANO DEL GASOLINEEO
Preparation method of porous carbon photo-thermal material with specific morphology and multi-fractal structure
InactiveCN113307245AImprove performanceCarbon preparation/purificationPorous carbonMetal-organic framework
The invention relates to a preparation method of a porous carbon photo-thermal material with specific morphology and a multi-fractal structure, and belongs to the technical field of seawater desalination. The method comprises the following steps: 1, preparing a metal organic framework material MOFs to be tested; 2, carrying out a thermogravimetric-mass spectrometry test and an in-situ infrared test on the MOFs; 3, recording mass spectrum information of gas byproducts during pyrolysis of the MOFs; 4, according to the in-situ infrared test result of the MOFs, analyzing the change of functional groups in the pyrolysis process of the MOFs; 5, confirming the pyrolysis mechanism of the MOFs according to mass spectrum information and functional group information; 6, carrying out a designed carbonization experiment on the MOFs according to a pyrolysis mechanism; and 7, carrying out photo-thermal performance test and seawater desalination experiment on the carbonized product of MOFs. According to the method, the pyrolysis mechanism of MOFs is researched in situ, a carbonized product with expected morphology can be designed and synthesized, and finally the porous carbon material with excellent photo-thermal performance can be prepared.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Method for preparing carbon nanotubes by electron beam induced deposition
InactiveCN103693634BPrecise length controlControl wall thicknessMaterial nanotechnologyCarbon nanotubesNanowireCarbon nanotube
The invention provides a method for preparing a carbon nano tube through electron beam induced deposition. The method comprises the following steps of: withdrawing a single semiconductor nanowire; wrapping the surface with an amorphous carbon layer by the electron beam induced deposition technology so as to form a 'core-shell structure' with the nanowire and the amorphous carbon layer; loading a bias voltage; melting the nanowire and converting the amorphous carbon into stratified polycrystal under the effect of joule heat produced by current; and moving the molten nanowire out of the nano tube, thus obtaining a single carbon nano tube. With the adoption of the method, the length, diameter, wall thickness and other parameters of the carbon nano tube can be accurately controlled, the in-situ study can be performed for the formation process of the carbon nano tube, thus sufficient data can be provided for the study on the growth mechanism of the carbon nano tube; the method avoids inclusions and catalysts, so that the obtained carbon nano tube is relatively high in purity. The method can also be popularized to prepare carbon nano tube arrays.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
A method for modifying gold chips in situ with cellulase
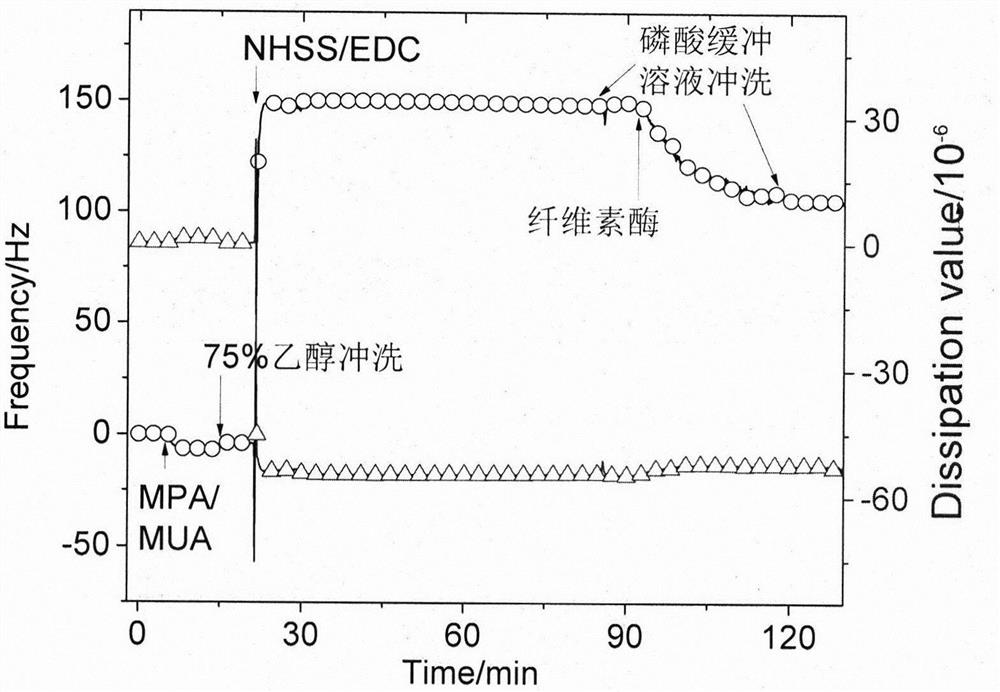
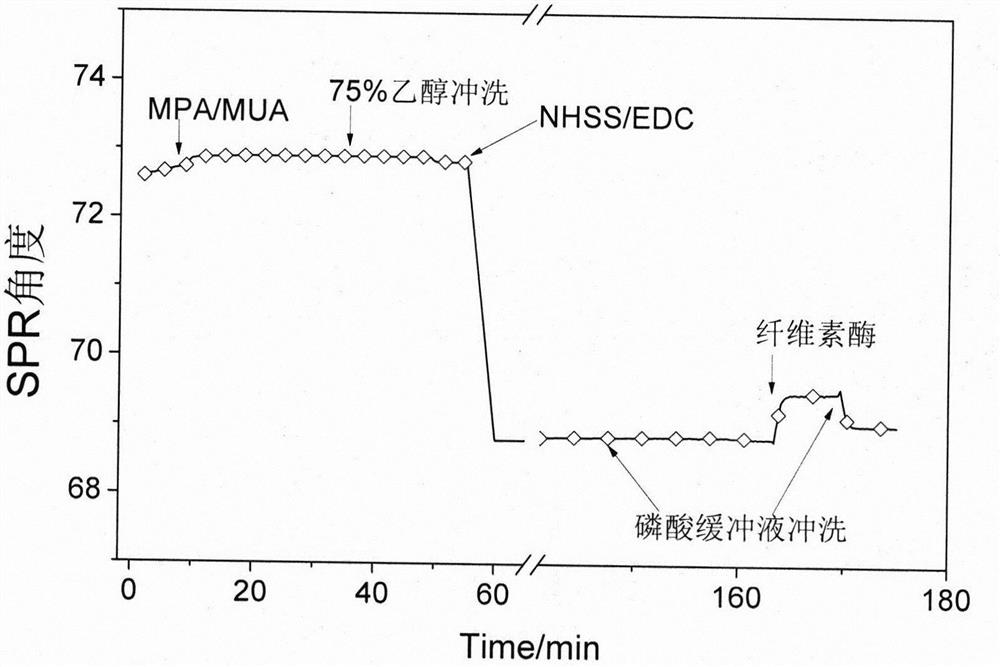
ActiveCN109239182BAnalysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesMaterial analysis by optical meansQuartz crystal microbalancePhysical chemistry
The invention relates to a method for modifying a gold chip in situ with cellulase. Quartz crystal microbalance (QCM) and surface plasmon resonance (SPR) technologies are important tools for real-time and in-situ research on the adsorption of biomacromolecules on solid interfaces. ) and the energy dissipation value of the adsorbed layer (corresponding to the structure of the thin film on the sensor), the latter only studying the change of "dry matter". The traditional method of studying cellulase and substrate is to immobilize the substrate on a QCM or SPR chip, and then pass cellulase as the mobile phase to study the interaction between the two. The present invention combines cellulase with a gold chip by in-situ modification method, constructs a cellulase film with a uniform surface, and broadens the application range of QCM or SPR to study the interaction between cellulase and other macromolecules in the system .
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
Device for in-situ study of wetland rhizosphere effect
PendingCN112014544AAvoid punctureGuaranteed CorrosionEarth material testingTesting plants/treesMicroorganismSoil science
The invention discloses a device for in-situ study of wetland rhizosphere effect. A main body of the device is a PVC long pipe, a top cover is arranged at the top end of the device in a matched mode,a plurality of top cover penetrating holes are formed in the top cover, and a bottom cover is arranged at the bottom end of the device in a matched mode; a drain hole is formed in the upper part of the pipe wall and is provided with a rubber plug; a plurality of pipe wall through holes are formed in the lower part of the pipe wall; the PVC long pipe is arranged in soil, the upper part is exposed out of the ground surface, and the lower part is buried in underground soil; the two PVC long pipes are arranged in a combined mode, wherein the portion, provided with the pipe wall penetrating holes,of one PVC long pipe is wrapped by a wrapping layer for preventing plant root systems from penetrating through and permeating water and used for measuring the rhizosphere effect, and the other PVC long pipe is not provided with a wrapping layer and used for measuring the non-rhizosphere effect. The device is simple in structure, low in cost and wide in applicability, can be directly used for fieldin-situ detection, and can also be matched with other field instruments and equipment for long-term monitoring; and a stable in-situ environment can be maintained, so that the influence of manual operation on a microbial experiment result is reduced.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Experimental device and application method for in situ study of seawater microplastic niche
ActiveCN107957490BGuaranteed certaintyEnsure consistencyMaterial testing goodsExperimental laboratoryCollection system
The invention provides an experimental device for an in-situ research of an ecological niche of seawater micro-plastic and an application method, and belongs to the field of marine environments. The experimental device comprises an anchoring system, a bearing system, a ballasting system and a collection system, wherein the anchoring system is connected with the bearing system; the ballasting system is connected above the bearing system; the collection system is used for collecting an obtained sample. According to the experimental device provided by the invention, experimental conditions consistent to environment parameters including natural seawater water temperature, salinity, pH (Potential of Hydrogen), nutrient salt and the like are created to carry out an in-situ experiment; the disadvantages of uncertainty and complexity of investigating and collecting materials, shapes and sizes of the micro-plastic on the scene, and difficulty in recovering a real marine environment under laboratory conditions are overcome. Meanwhile, the ballasting system in the device realizes automatic upward floating and sinking of the bearing system, and a sample is convenient to feed and collect. Furthermore, the collection system has good shipboard operation coordination performance and is rapid in collection; the application of the device provided by the invention provides important guarantees for analyzing structure characteristics of the ecological niche of the micro-plastic and correlation with environment factors.
Owner:YELLOW SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERIES SCI
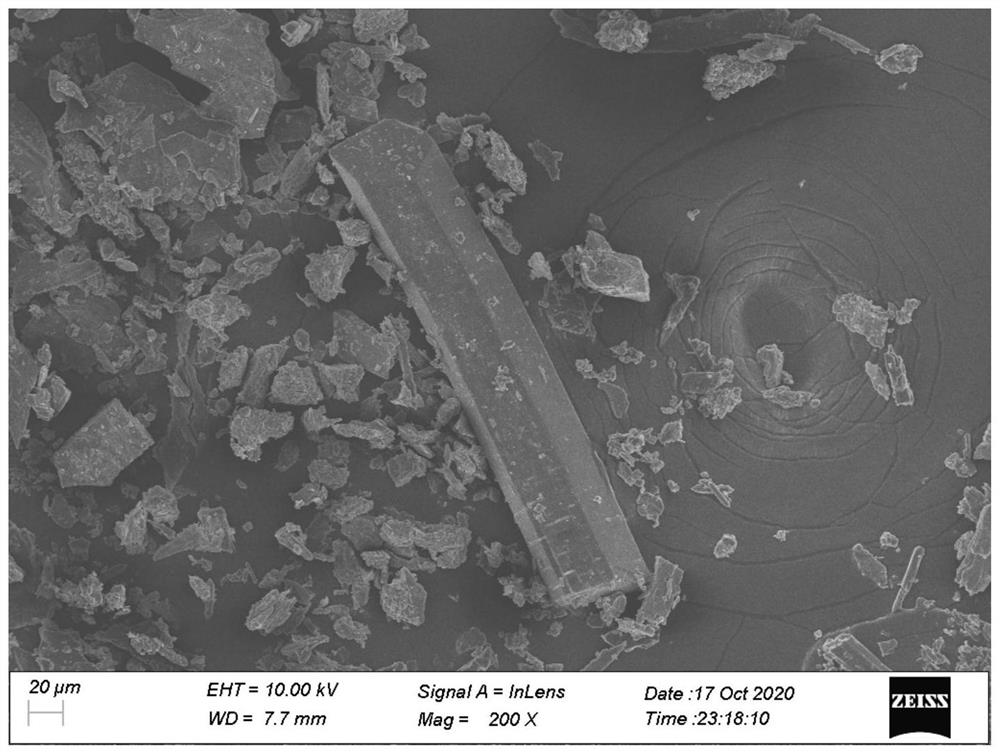
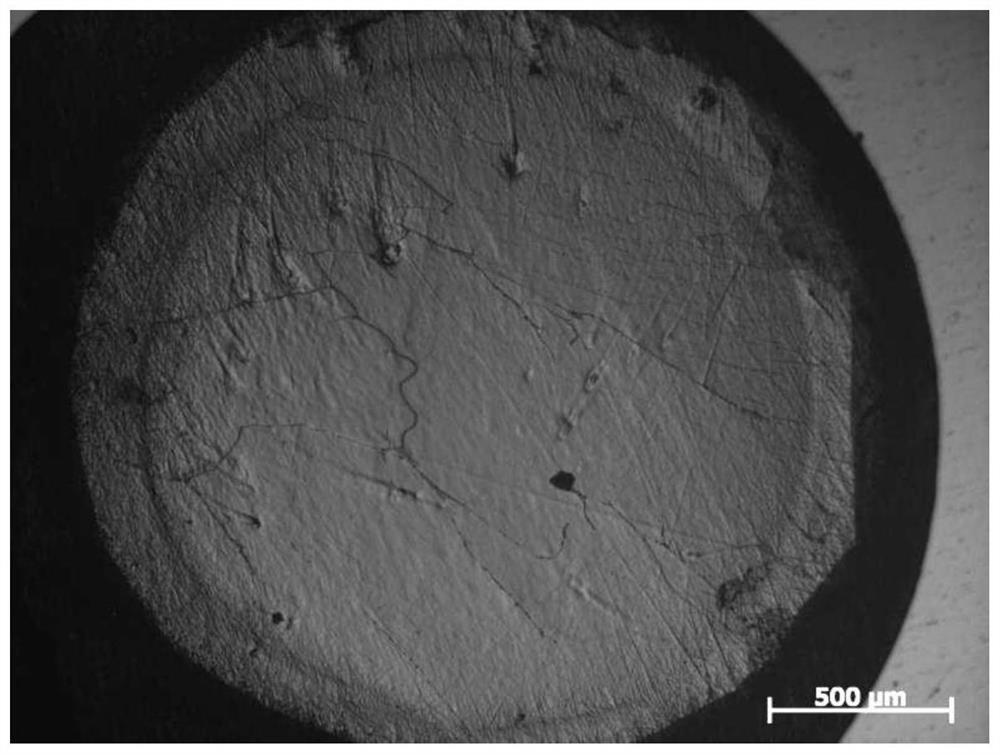
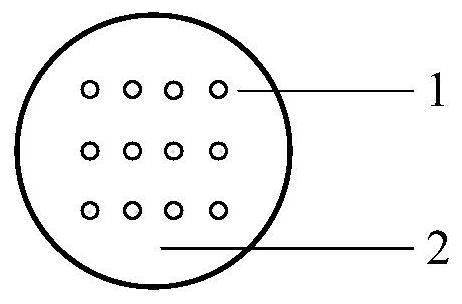
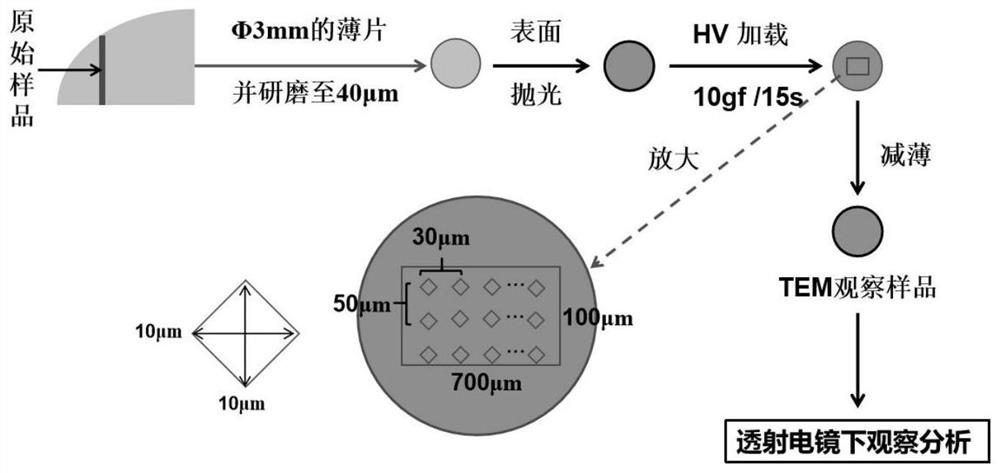
Sample preparation method for in-situ observation of dislocation slip traces by transmission electron microscope
InactiveCN112577797AAccurately determine the directionExact sizeMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationPreparing sample for investigationElectron microscopeIn situ study
The invention relates to a sample preparation method for observation and analysis by a transmission electron microscope, in particular to a sample preparation method for in-situ observation of dislocation slip traces by the transmission electron microscope. The sample preparation method comprises the following steps: cutting and processing a sample; polishing the surface; loading the Vickers hardness; and thinning and carrying out subsequent observation and analysis. The sample is relatively simple to prepare, and high-precision instruments and equipment are not needed; by adopting the methodprovided by the invention, the direction and size of the loading force can be accurately determined, and the characteristics of the slip trace near the indentation are determined in situ. By means ofthe transmission electron microscope, the dislocation slip trace characteristics can be observed, and the dislocation slip trace characteristics of the material under the action of an external load can be observed and analyzed in situ through indentation positioning, so that the purpose of in-situ research on the microscopic deformation of the material is achieved.
Owner:INST OF METAL RESEARCH - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com