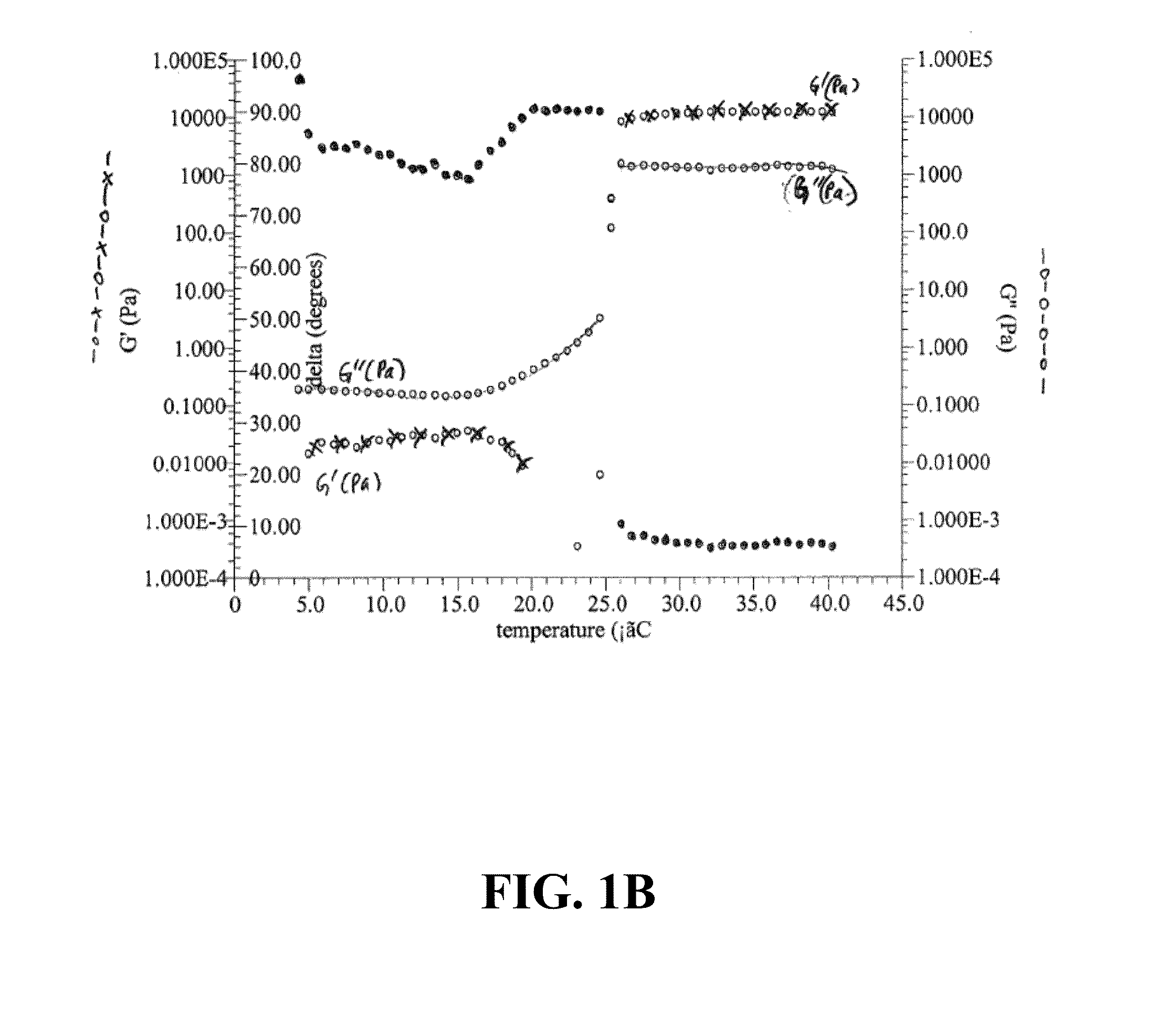
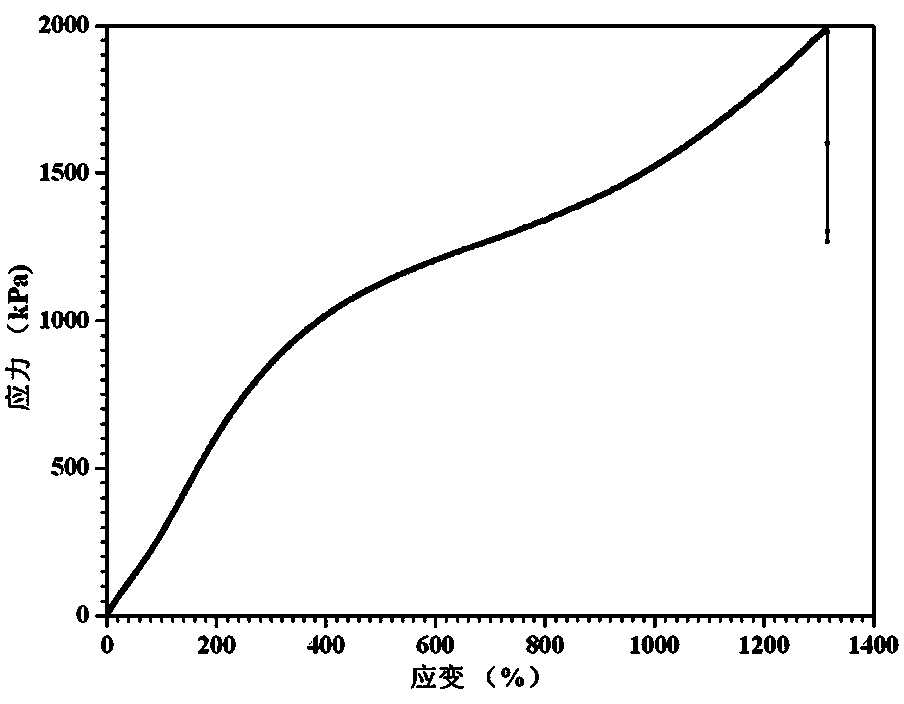
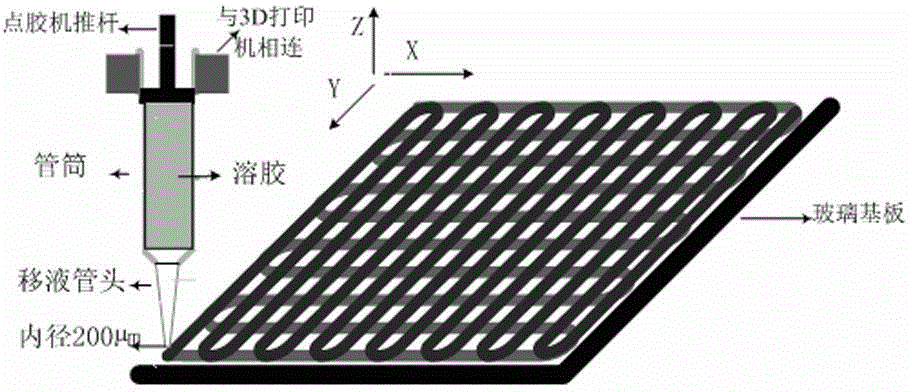
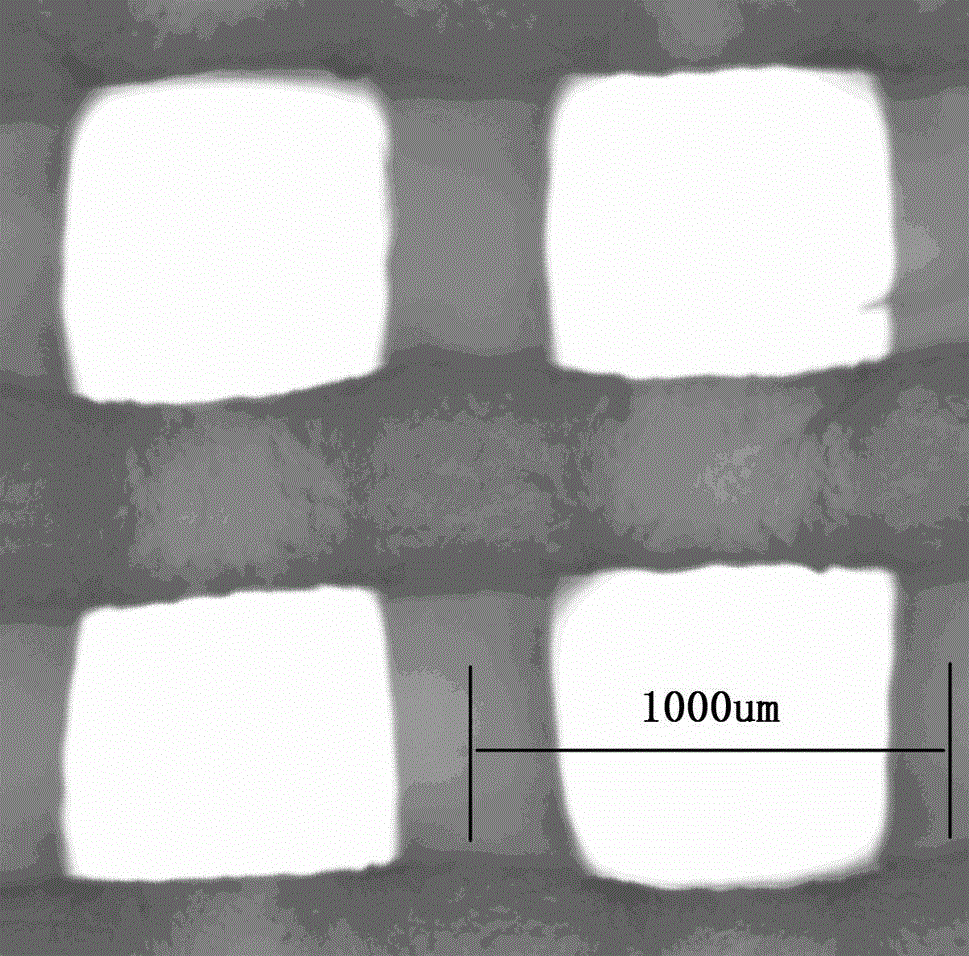
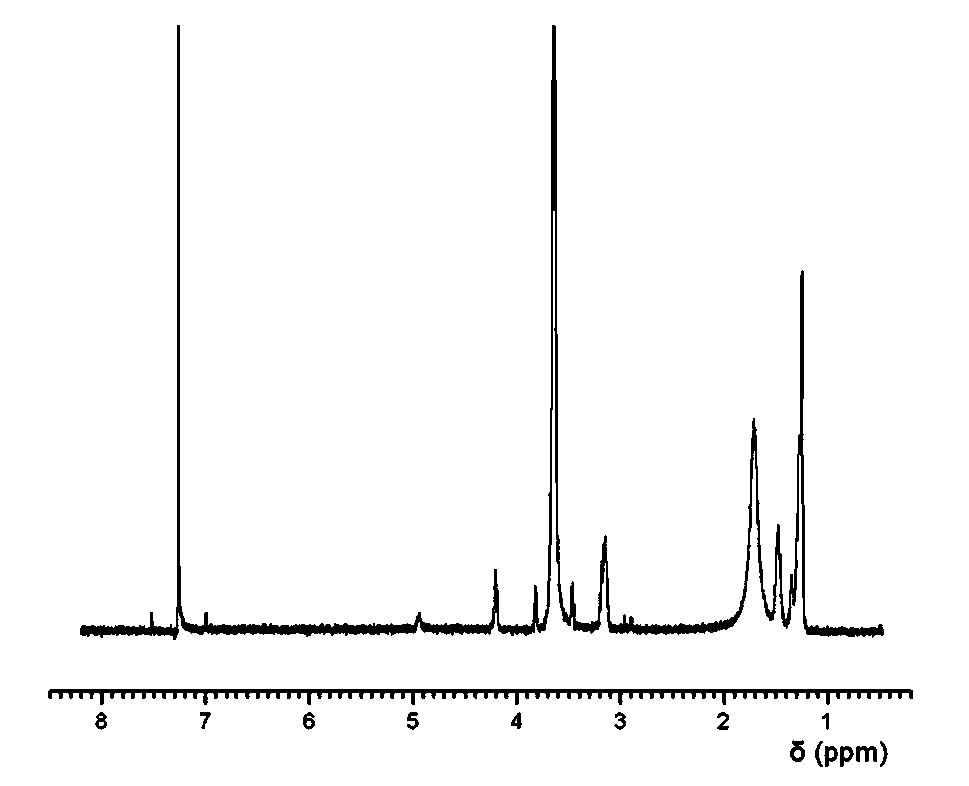
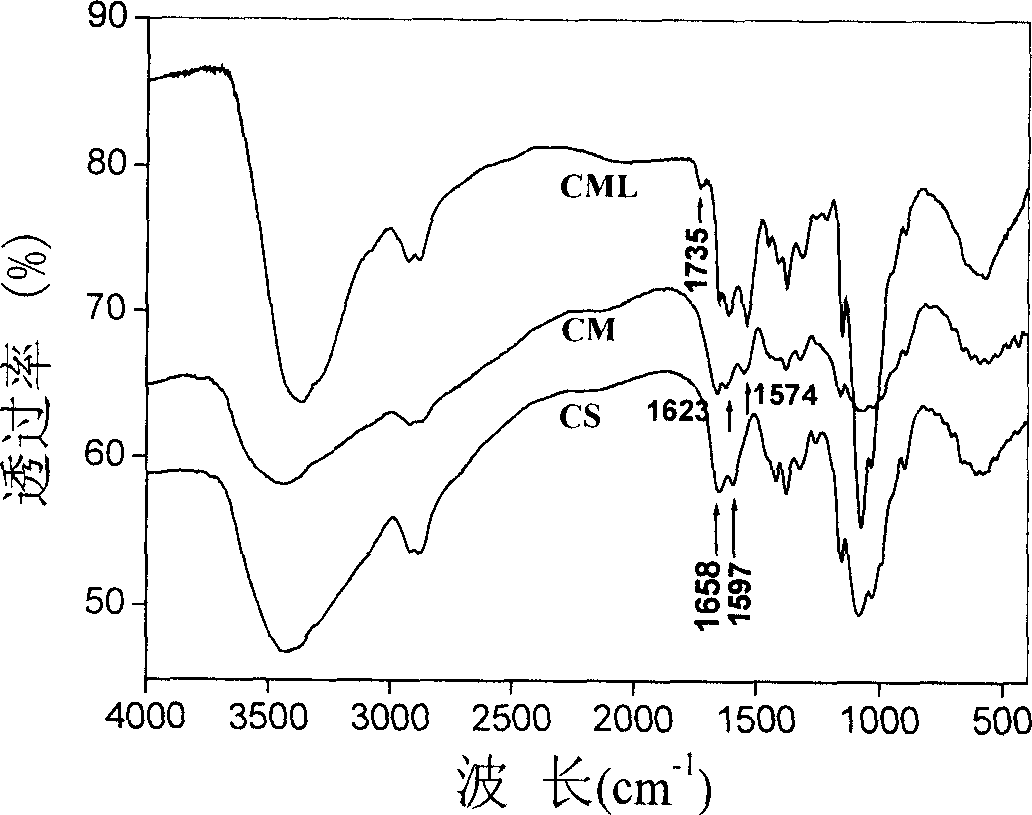
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
179 results about "Hydrogel scaffold" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Hybrid hydrogel scaffold compositions and methods of use
ActiveUS20130115196A1Reduce usageReduce scarsBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsHybrid materialMixed materials
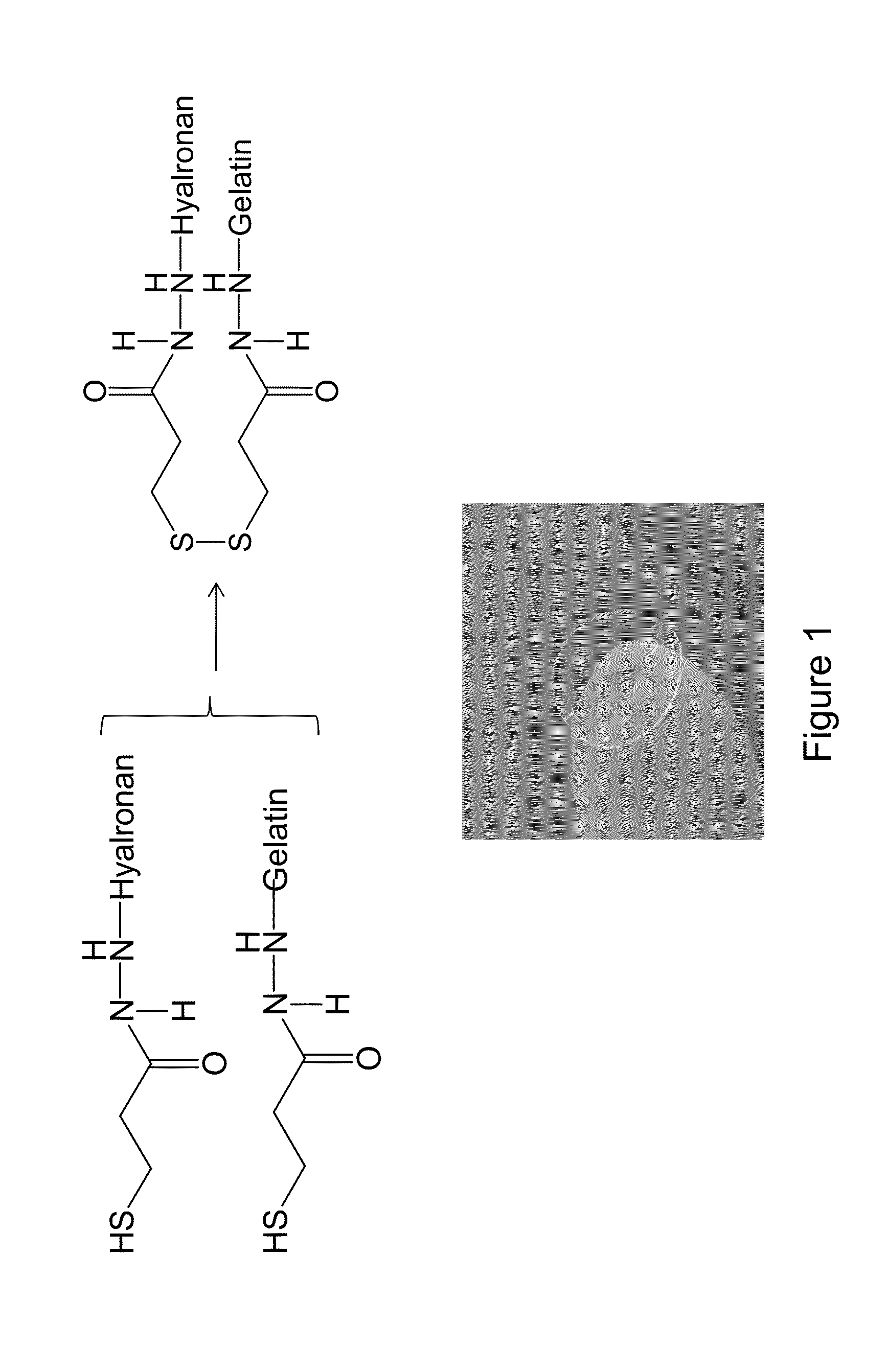
The present invention includes new hybrid hydrogel scaffolds comprised of a polyoxyethylene-polyoxypropylene (block) copolymer (a “poloxamer”) and a self-assembling peptide, which maintain the mechanical and bioactive properties of its individual constituents (as compared to when the individual constituents are scaffolds or hydrogels by themselves). The hydrogels of the invention can include a combination of materials from different origins or with different properties that provides a hybrid material that meets the multiple needs of a scaffold for tissue engineering.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD +1
Polyurethaneurea hydrogel and preparation methods therefor
InactiveCN103524697AHigh strengthProvides effective mechanical propertiesOrganic solventPolyethylene glycol
The invention relates to polyurethaneurea hydrogel and preparation methods therefor. The preparation methods comprise two preparation methods. The first preparation methods is as follows: diisocyanate and catalysts are added in a polyethylene glycol (PEG) organic solution for reaction, then diamine chain extender is added, and products are obtained in the organic solvent after precipitation, wherein, the molar ratio of PEG, diisocyanate and diamine is 1:2:1. The second preparation method is as follows: N,N'-dicarbonyl diimidazole is added in a PEG organic solution for reaction, then excess diamine chain extender is added, macromolecules with amidogens at two ends are obtained, finally, diisocyanate is added, and products are obtained in the organic solvent after precipitation, wherein, the molar ratio of PEG and diisocyanate is 1:2. The polyurethaneurea hydrogel has advantages of large elongation and high tensile strength, and has shape memory functions. The polyurethaneurea hydrogel has application prospects at aspects of biomedical hydrogel, tissue engineering, hydrogel support materials, biomedical devices with shape memory functions and the like.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Method for compounding aquo-gel to porous tissue engineering rack
InactiveCN1586636AImprove mechanical propertiesGood macroscopic plasticityHybrid cell preparationProsthesisBiocompatibility TestingCell growth
The present invention discloses the method of compounding aquogel into porous tissue engineering rack. Under sol state, aquogel is first led into porous rack, and the outer condition is altered to convert the sol into gel to obtain porous rack with compounded aquosol. According to requirement, the water sol may have cell growth factor for cell growth and differentiation may be added. The rack the present invention produces possesses the excellent mechanical performance of porous rack and the excellent biocompatibility of aquosol rack simultaneously. The present invention has wide application range, and is suitable for various porous rack with different structures and aquosols and various kinds of cell. The rack may be used widely in tissue engineering field.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for preparing high-strength double-network hydrogel stent by virtue of 3D printing
InactiveCN104628936ANo collapseObvious collapse phenomenonAdditive manufacturing apparatusProsthesisCross-linkUltraviolet lights
The invention discloses a method for preparing a high-strength double-network hydrogel stent by virtue of 3D printing. The method comprises the following steps of adding a polymer monomer N, N-dimethyl acrylamide, an initiator, a crosslinking agent and sodium alginate (SA) into deionized water to form a solution and adding inorganic powder hydroxyapatite to obtain a sol; controlling and extruding the sol by a robot dispenser, and carrying out 3D printing molding to obtain a sol stent; placing the sol stent under ultraviolet light so that the monomer in the stent is subjected to photopolymerization and chemical cross-linking reaction to form a layer of chemically cross-linked network pre-molded hydrogel stent; immersing the pre-molded hydrogel stent into a CaCl2 aqueous solution so that SA in the stent is subjected to physical crosslinking to form a second layer of physically cross-linked network so as to obtain the hydrogel stent having physically and chemically cross-linked double-network. The hydrogel stent prepared by the method has higher mechanical strength and fine internal structure, and the three-dimensional morphology of the stent can be conveniently regulated and controlled to adapt to the complex application requirements of tissue engineering materials.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV OF TECH
Tissue engineering bone cartilage composite bracket and integrated photocuringable forming method thereof
InactiveCN102430151AHigh bonding strengthImprove stabilityProsthesisComputer Aided DesignCeramic brackets
The invention discloses a tissue engineering bone cartilage composite bracket and an integrated photocuringable forming method thereof. The tissue engineering bone cartilage composite bracket serves as a ceramic bracket, wherein the ceramic bracket is served as a bone-repair part, and a porous structure is arranged on the surface of the ceramic bracketbone-repair part of the porous structure; and the ceramic bracket is fixed on a supporting plate of a photocuringable quick forming machine. A laser scanning path is driven through a computer aided design (CAD) model; and laser directly exposes and cures a hydrogel bracket and a pure hydrogel bracket which contain a ceramic component onto the ceramic bracket sequentially to form a three-layer composite bracket. Therefore, quick and fine preparation of a three-dimensional composite bracket of bone cartilage-like tissue histomorphometry is realized; uncontrollable structures and low efficiency because of handwork in the preparation process of a traditional composite bracket are avoided; the preparation efficiency is improved; and a calcified cartilage-like layer bracket and a hydrogel cartilage bracket with subtle structures can be bonded and compounded on the surface of the ceramic bracket by means of a rivet and a two-phase material.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Preparation method of co-crosslinked double-network hydrogel support for promoting cartilage injury repair
ActiveCN107281550AImprove adhesionThe effect of promoting defect healingTissue regenerationProsthesisCartilage injuryDouble network
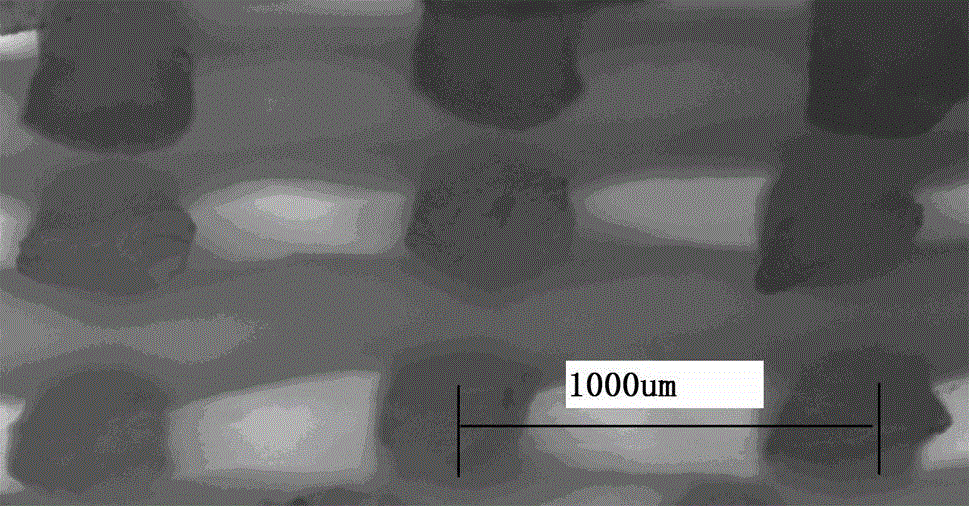
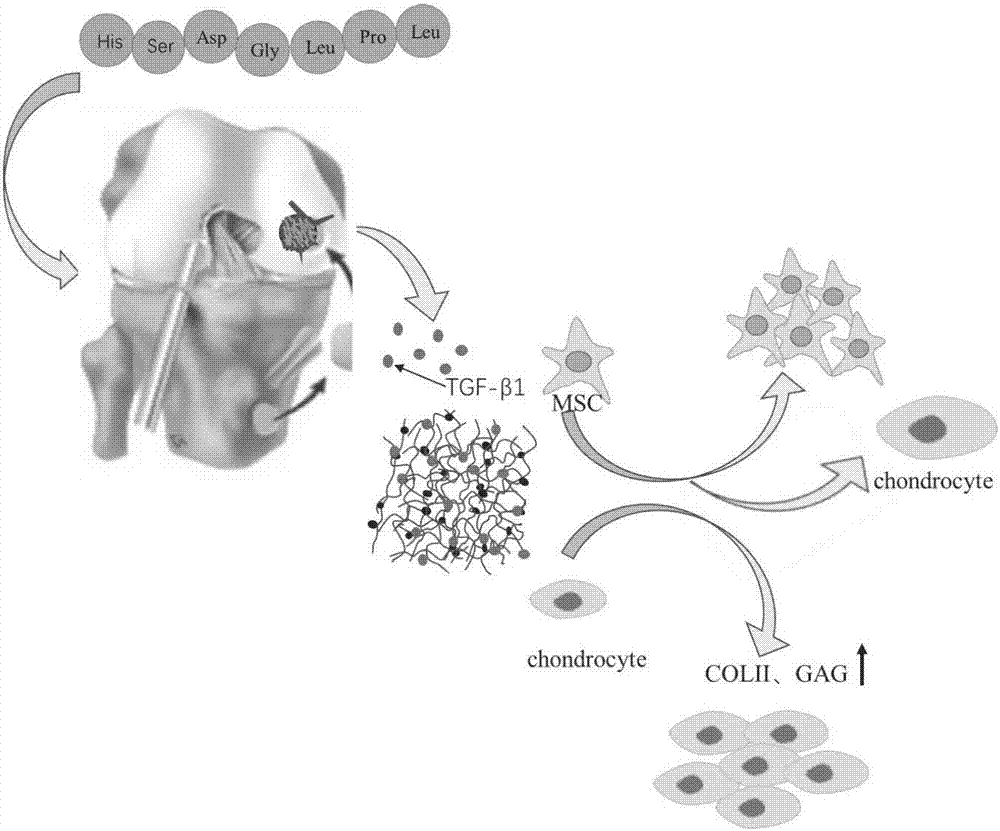
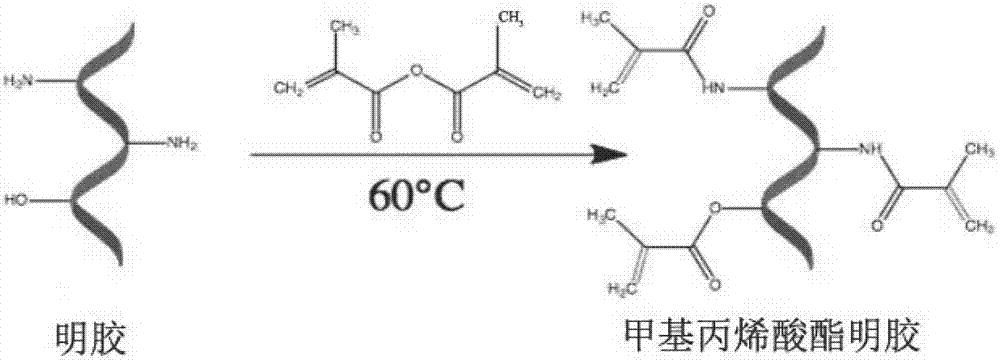
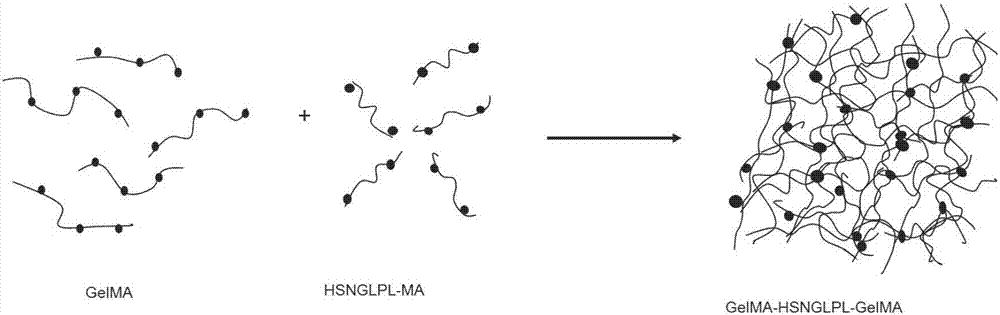
The invention belongs to the field of biomedical materials and particularly relates to a preparation method of a co-crosslinked double-network hydrogel support for promoting cartilage repair and growth. The method comprises the following steps of (1) preparation of GelMA; (2) preparation of a photo-crosslinked polypeptide; and (3) preparation of a hydrogel support, namely preparing the hydrogel support from the GelMA and the photo-crosslinked HSNGLPL under the action of a photoinitiator. The prepared hydrogel support has an obvious effect of promoting new cartilage generation and cartilage defect healing, and is capable of regulating cartilage matrix secretion of normal chondrocytes around the injured tissue, mesenchymal stem cell migration to the injured part and cartilage differentiation; by virtue of a porous structure of the hydrogel support, the HSNGLPL can be crosslinked to the surface of a porous support, endogenous TFG-beta is effectively adsorbed, the concentration of local TFG-beta beta1 is improved and the effects of the biological support in the orthopedics fields, such as a cartilage defect and a cartilage injury are achieved.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Mixed hydrogel with characteristics of temperature sensitivity and photosensitivity, and three-dimensional (3D) printing method using mixed hydrogel
ActiveCN107663377AGood printabilityExcellent temperature sensitive performanceAdditive manufacturing apparatusAdditive manufacturing with liquidsHydrogel scaffold3d printed
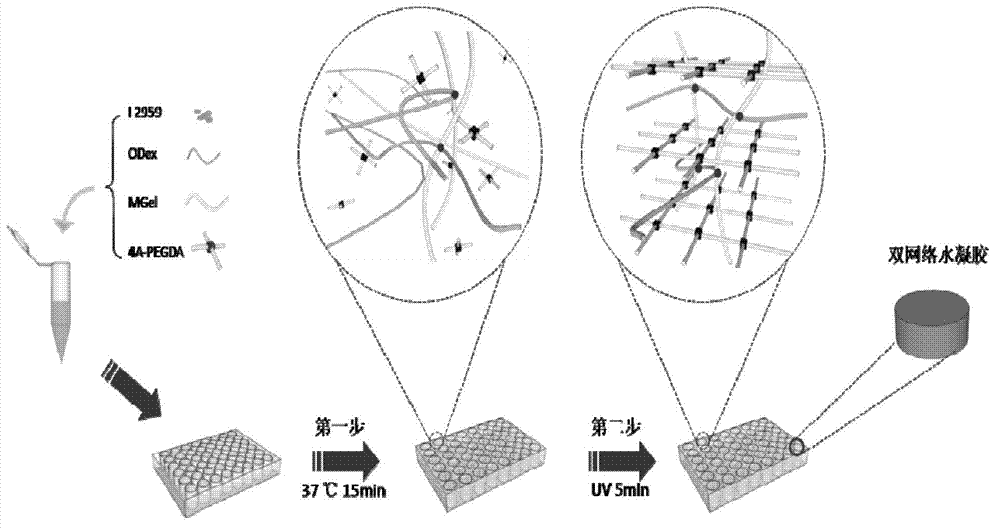
The invention discloses mixed hydrogel with characteristics of temperature sensitivity and photosensitivity. Every 100ml of the mixed hydrogel is prepared from the following components: 5-30g of methacrylamide-based gelatin, 0.1-10g of gelatin and 0.2-1g of a photoinitiator. The gelatin is added into the mixed hydrogel, so that the printability of low-concentration methacrylamide-based gelatin hydrogel can be improved, and the balance between the physical properties and biological functions of GelMA hydrogel can be well maintained. The invention also discloses a method for curing a 3D printedbiomimetic hydrogel scaffold by two steps of temperature sensitivity and photosensitivity; the method comprises the following steps: (1) putting the mixed hydrogel into a needle cylinder of a 3D printer; (2) extruding the mixed hydrogel in the needle cylinder onto a temperature control printing platform under the condition of preset printing parameters, and controlling the temperature of the temperature control printing platform so as to enable the mixed hydrogel to be preliminarily cured into a preset support structure; (3) carrying out ultraviolet irradiation on the preliminarily cured support structure to enable the support structure to be subjected to ultraviolet crosslinking and curing so as to form a bionic hydrogel support.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Preparation method of injectable double-cross-linked hydrogel for tissue engineering
ActiveCN102784414AAvoid moving aroundStrong mechanical propertiesProsthesisCross-linkBiocompatibility Testing
The invention relates to a preparation method of injectable double-cross-linked hydrogel for tissue engineering, which comprises the following steps that: an aqueous solution of aminated gelatin, an aqueous solution of aldehyde dextran, and an aqueous solution of terminated vinyl poly ethylene glycol are mixed according to a volume ratio of 4:4:3, then are cross-linked for 10-20 minutes at a temperature of 35 to 40 DED C, and finally are cross-linked for 3 to 8 minutes by ultraviolet irradiation. The preparation method provided by the invention has a simple operation process and mild implementation conditions; and the double-cross-linked hydrogel obtained by the invention is non-toxic and biodegradable, has good mechanical properties and biocompatibility, and can be used for injectable hydrogel scaffold in the tissue engineering.
Owner:烟台沃德麦克斯纳米科技有限公司
Preparation method of 3D printable iron ion double-crosslinked alginate-polyacrylamide acrylic acid high-performance hydrogel
ActiveCN108276522AImprove mechanical propertiesImprove fatigue resistanceAdditive manufacturing apparatusPorosityCross-link
The invention discloses a preparation method of 3D printable iron ion double-crosslinked alginate-polyacrylamide acrylic acid high-performance hydrogel. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, evenly mixing sodium alginate, acrylamide, acrylic acid and a photo-initiator; pre-molding by using a mould or a 3D printing way; illuminating by using an ultraviolet lamp so as to realize copolymerization between an AAc monomer and an AM monomer; after the polymerization is completed, soaking a hydrogel scaffold into an Fe3<+> solution to form ionic cross-linking; finally, soaking the productinto deionized water for balancing so as to remove the unreacted monomers. Two networks are both Fe3<+> cross-linked, so that a common cross-linking point exists between the two networks, and the hydrogel is enabled to have excellent performance. In addition, the sodium alginate has good natural high polymer with good biocompatibility, and the viscosity is adjusted by adding a small amount of adhesive in a sol state, so that the hydrogel has good anti-collapse and rapid gelation characteristics; the hydrogel can be prepared into high porosity hydrogel with various complex structures by usinga 3D printing technology.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV OF TECH
Method for reshaping and beautifying by using tissue engineering fat regeneration technology
The invention provides a method for reshaping and beautifying by using tissue engineering fat regeneration technology, which is applicable to plastic surgery and reshaping and beautifying and belongs to the field of tissue engineering. The method comprises the following technical routes: directly extracting mesenchyme matrix cells with multiple differentiation capabilities from fatty tissues of a patient, culturing and propagating the mesenchyme matrix cells in vitro, wrapping a specific amount of cells and other necessary components in a hydrogel stent material, and implanting the hydrogel stent material into the corresponding part in the body of the patient. The cells are grown into fatty tissues along with degradation and absorption of the stent material so as to perform regenerative repair on the soft tissue defect of the patient. The method has the advantages that the cells of the patient do not bring immunological rejection to the patient, and the regenerative repair effect is safe, natural and durable because the used hydrogel stent material is finally degraded and absorbed in the body of the patient.
Owner:王影
Method for preparing polyving akohol/nanosized silica composite hydrogel scaffold through 3D printing
The invention discloses a method for preparing a polyving akohol / nanosized silica composite hydrogel scaffold through 3D printing. The method comprises the steps that firstly, polyving akohol (PVA) resin with the mass concentration of 8-12% is added into deionized water to be stirred and dispersed, and is completely decomposed in a thermostatic waterbath of 90 DEG C to 95 DEG C to obtain a PVA solution; the obtained PVA solution is slowly added into inorganic nano silicon oxide (SiO2), and is evenly stirred to obtain mixed collosol with the thixotropic property, wherein the mass ratio of the nano SiO2 to the PVA is (0.5-1):1; then, a robot dispenser is utilized for extruding the mixing collosol, and through 3D printing forming, a collosol scaffold sample is obtained; and finally, the sample is placed in a freezing chamber at the temperature of minus 20 DEG C to minus 40 DEG C to be frozen for 20 hours to 22 hours, after the sample is taken out of the chamber, the sample is unfrozen and melted for 2 hours to 4 hours at the room temperature, and the hydrogel scaffold of a controllable fine structure is obtained. The method can conveniently and rapidly prepare the biological scaffold, and controllability of a support structure and inner pores is achieved, so that the method adapts to needs of different application occasions.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV OF TECH
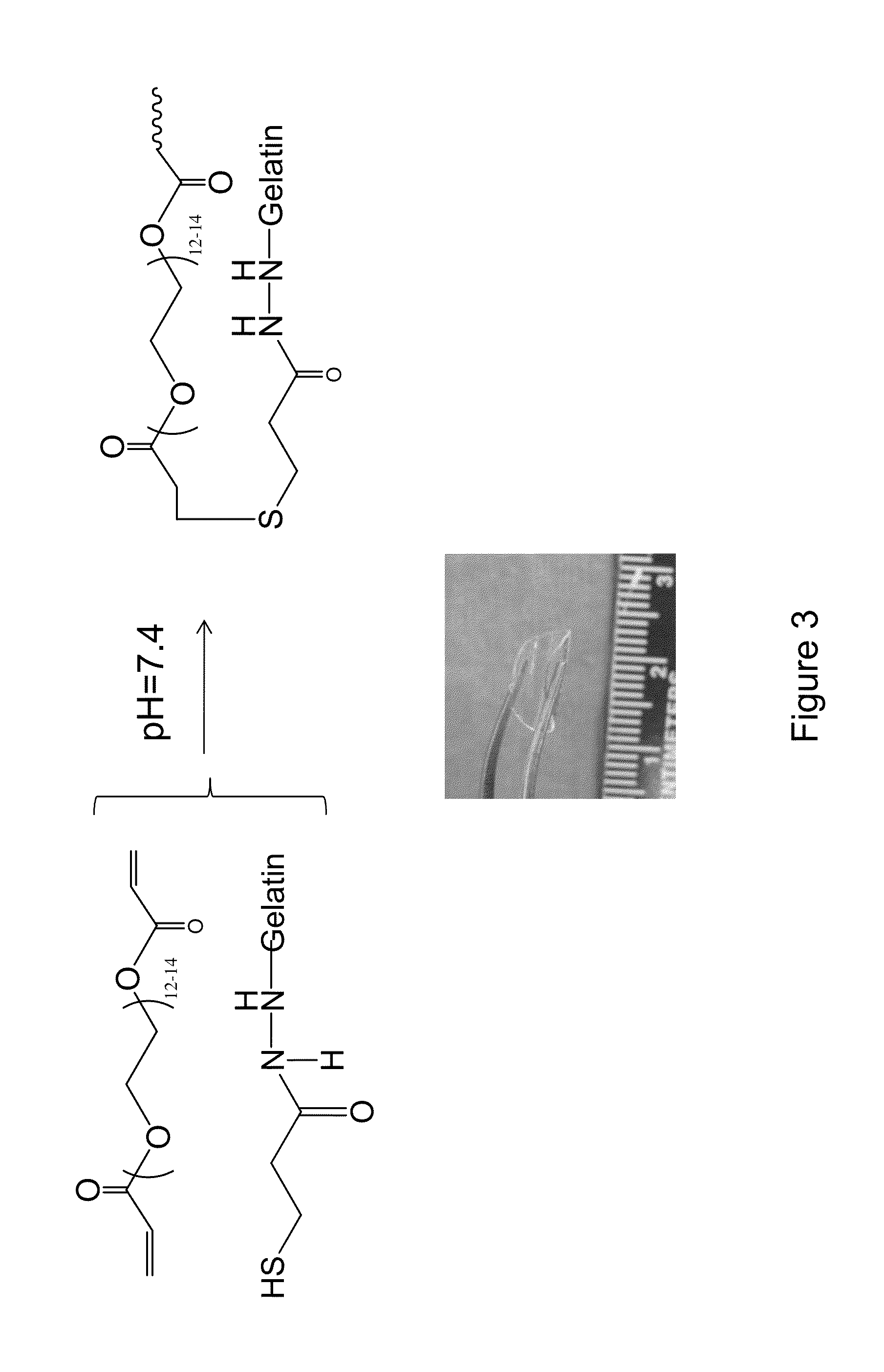
Fabrication of gelatin hydrogel sheet for the transplantation of corneal endothelium
The invention provides a corneal endothelial composition comprising a transparent hydrogel scaffold and a single layer of cultured corneal endothelial cells on the surface of the scaffold. The hydrogel scaffold I comprised of at least one biopolymer, preferably gelatin. Also provided are methods of making a corneal endothelial scaffold
Owner:WAKE FOREST UNIV HEALTH SCI INC
3D printing method of sodium alginate/polyvinyl chloride all-physically-crosslinked double-network hydrogel scaffold
ActiveCN106178106AGood biocompatibilityHigh strengthAdditive manufacturing apparatusTissue regenerationPolyvinyl alcoholPolyvinyl chloride
The invention discloses a 3D printing method of a sodium alginate / polyvinyl chloride all-physically-crosslinked double-network hydrogel scaffold. According to the technical scheme, the method comprises adding a mixed solution of SA / PVA into gaseous silica to produce thixotropic sol, using an obtained product as a printing material to produce a sol scaffold by 3D printing, freezing the sol scaffold to initiate polymerization of polymer PVA (polyvinyl acetate), fully crosslinking into a single network to produce a preformed gel scaffold, removing to thaw at room temperature, and soaking the preformed gel scaffold in CaCl2 aqueous solution so that SA is fully crosslinked into another gel network to produce the hydrogel scaffold. The method is simple, the production process is short, controlling is simple, production cost is low, the scaffold has good reliability, and the 3D printing method of the sodium alginate / polyvinyl chloride all-physically-crosslinked double-network hydrogel scaffold produces the hydrogel scaffold that is nontoxic, good in mechanical property, high in water absorption and good in biocompatibility.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV OF TECH
Optimal control system and method for three-dimensional bio-printing aquogel supports
ActiveCN105479751AGood repeatabilityEasy for mass customizationAdditive manufacturing apparatusNon destructiveOptimal control system
The invention discloses an optimal control system and method for three-dimensional bio-printing aquogel supports. The system comprises a quantitative visualization device for the three-dimensional bio-printing aquogel supports based on optical coherence tomography scanning and three-dimensional bio-printing equipment; the visualization device comprises a light source, a low-coherence interference module, a sample scanning module, an interference signal detecting module and a computer. According to the method, the quantitative structure characteristics of the three-dimensional bio-printing aquogel supports are obtained through the OCT technology, the designing and the printing of the supports are fed back on the basis of the results of the quantitative structure characteristics, and the stability and the controllability of three-dimensional manufacturing of the supports are improved by lowering the difference between the designing and the printing through iteration. According to the invention, the requirements of optimal control of three-dimensional bio-printing aquogel for high resolution and wide-range and three-dimensional fast scanning can be met, non-destructive and non-intrusive fast imaging of the whole supports can be realized through the OCT technology, and the information of the whole supports and local shape features of space is quantitatively analyzed based on the algorithm automatically selecting object regions.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
Core-shell capsules
InactiveUS20140106032A1Environmental lossImprove mechanical stabilityEssential-oils/perfumesGaseous substancesCross-linkHydrogel scaffold
The invention provides a process for preparing a core-shell capsule comprising the steps of (i) mixing a solid active ingredient and / or an oily liquid active ingredient with a polymeric material capable of forming a hydrogel shell around the active ingredient(s), (ii) forming a shell comprising a hydrogel scaffold formed of a polymeric lattice around the core, (iii) optionally cross-linking the polymeric lattice; and (iv) contacting the optionally cross-linked core-shell hydrogel shell with a liquid silica precursor so as to cause precipitation of silica within the scaffold structure thereby forming a composite shell of silica interspersed between the polymeric lattice.
Owner:FIRMENICH SA
Preparation method of multifunctional layered joint cartilage support
InactiveCN108355174ARealize regulationReduce rejectionAdditive manufacturing apparatusTissue regenerationCartilage cellsOsteoblast
The invention provides a preparation method of a multifunctional layered joint cartilage support. The multifunctional layered joint cartilage support capable of simulating the biological property andthe mechanical property of natural cartilage is prepared by taking hydrogel as a support material, taking mesenchymal stem cells, cartilage cells and osteoblasts as inducing and developing objects andby adopting a 3D printing technology. The multifunctional layered joint cartilage support can accurately simulate the internal tissue form and the contour of each layer of the natural cartilage and can realize that different layers have different mechanical and biological characteristics. The prepared artificial cartilage support cells are derived from patients, the support serves as a degradablehydrogel material and the rejection reaction after implantation is greatly reduced. Various nutritional substances and growth factors are mixed in the hydrogel support, so that the sustained releaseeffect can be achieved and regulation and control of the growth and development of the artificial cartilage can be realized.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
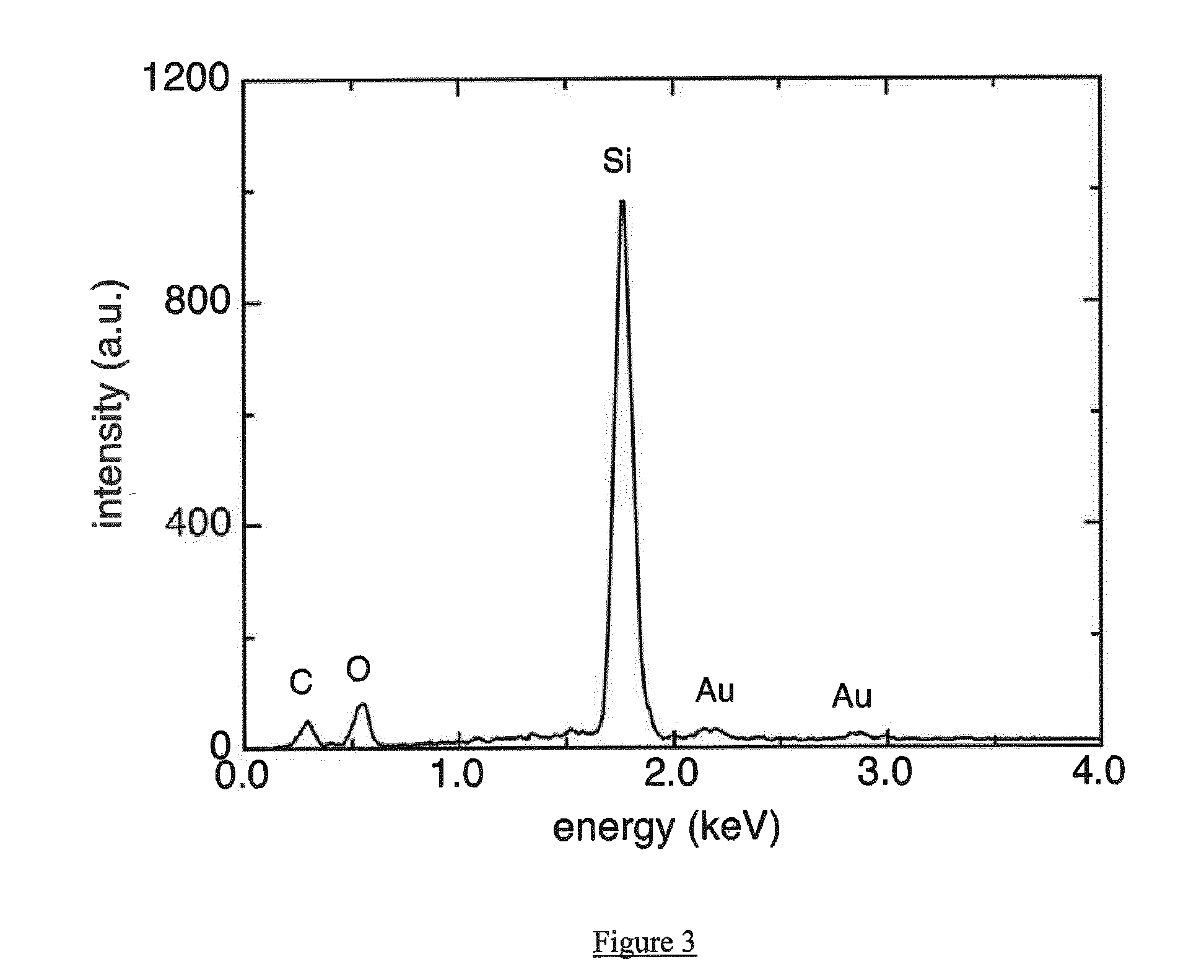
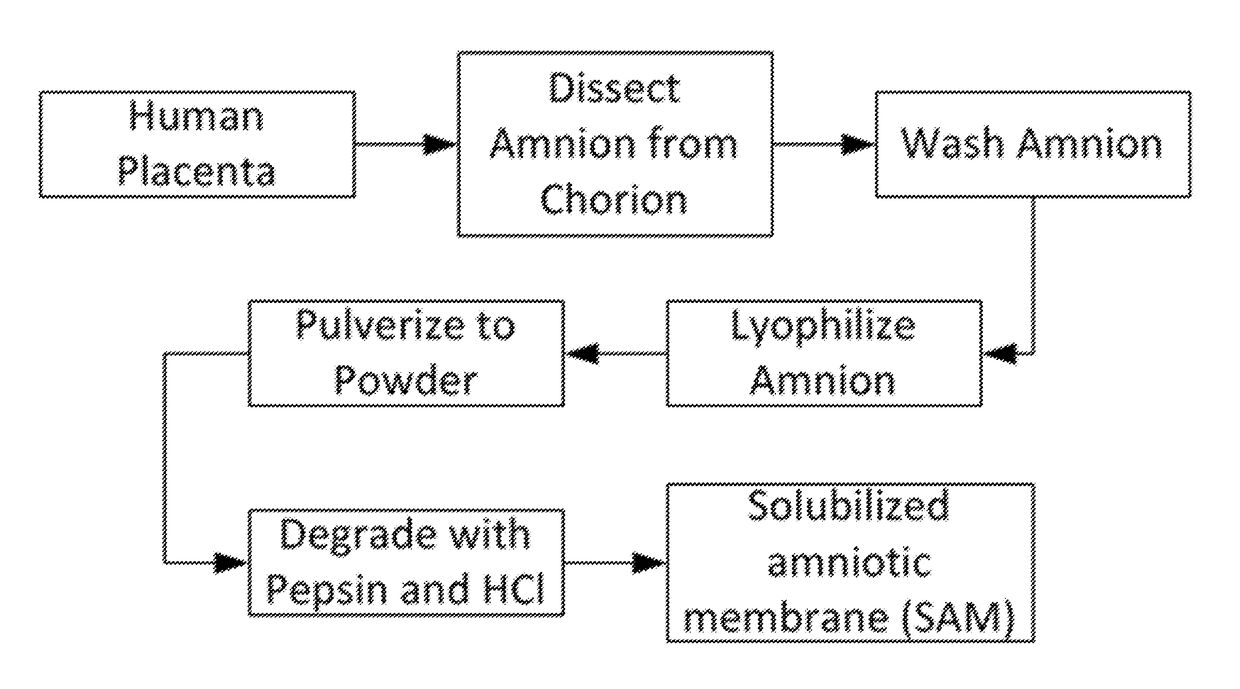
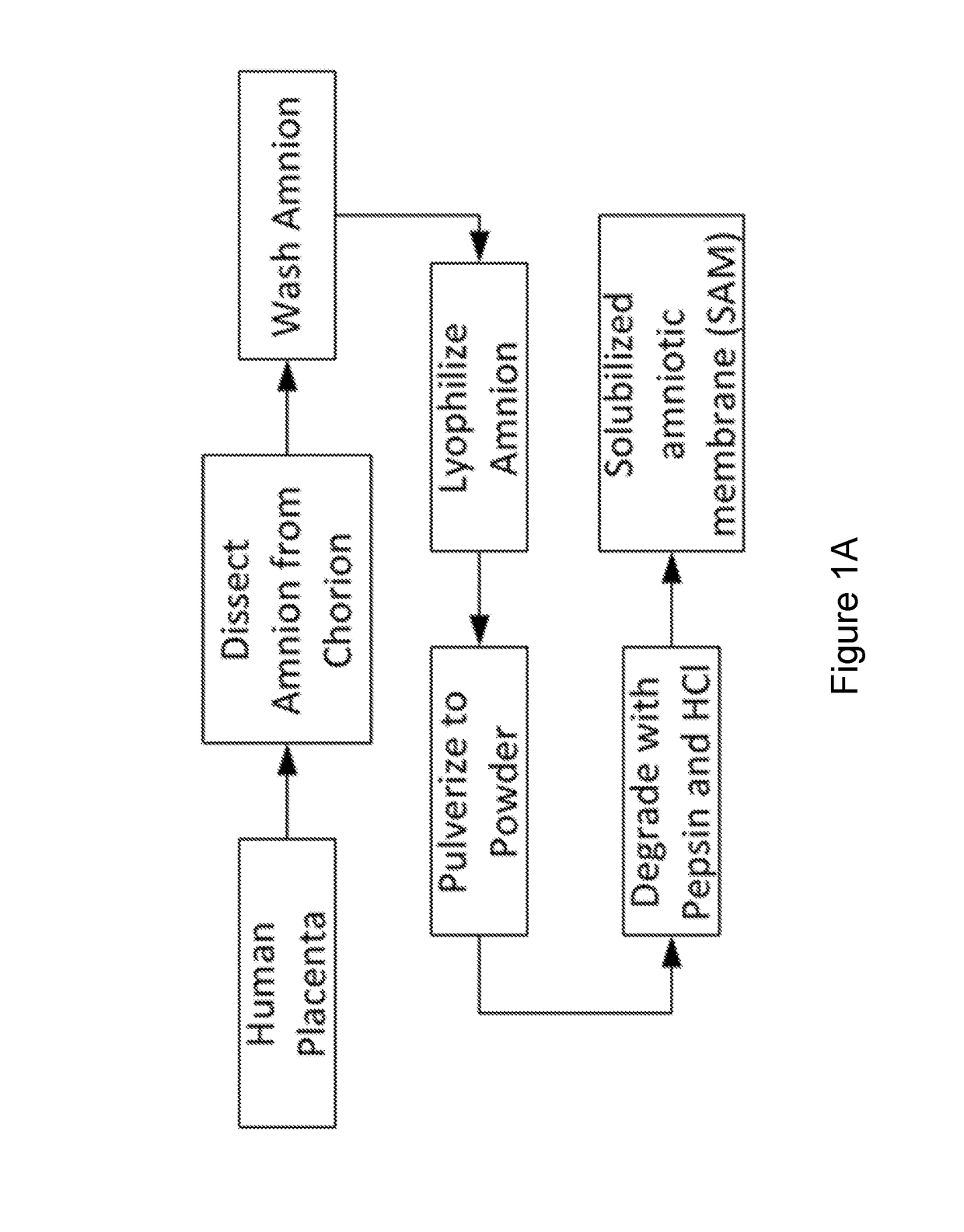
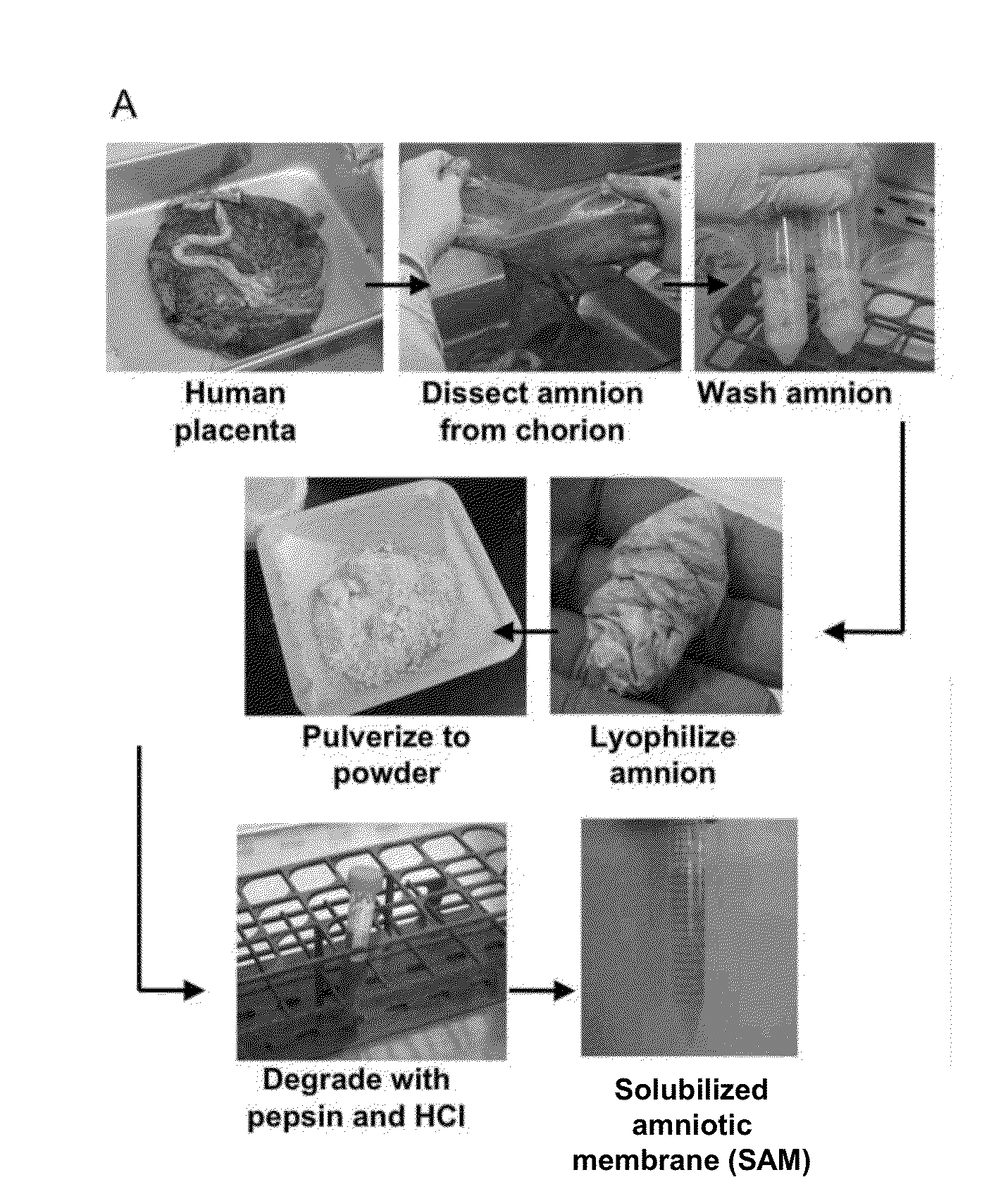
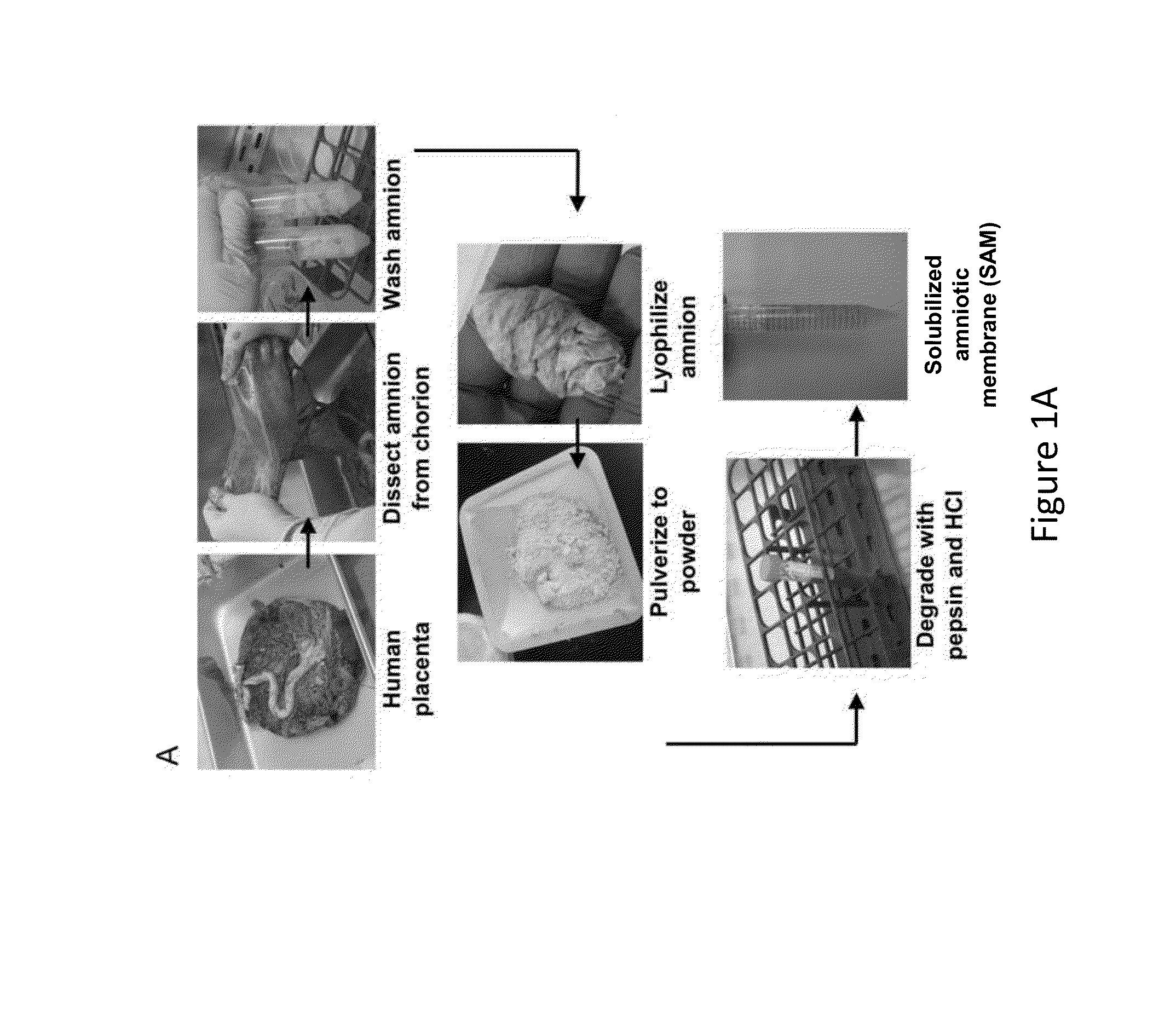
Amniotic membrane hydrogel and methods of making
ActiveUS10016464B2Mammal material medical ingredientsCell culture supports/coatingCell-Extracellular MatrixCell free
The present invention provides compositions and methods for wound healing and tissue regeneration. The compositions of the present invention comprise amniotic membrane of the placenta. In certain embodiments, the composition comprises amniotic membrane powder or solubilized amniotic membrane (SAM). In some aspects, the composition is cell-free and rich in cytokines, extracellular matrix proteins, and other components that improve tissue regeneration. In one aspect, the composition is a hydrogel scaffold that comprises amniotic membrane. The present invention reduces contraction and improves blood vessel development in regenerating tissue.
Owner:WAKE FOREST UNIV HEALTH SCI INC
Amniotic Membrane Hydrogel and Methods of Making
ActiveUS20140348940A1Mammal material medical ingredientsCell culture supports/coatingCell-Extracellular MatrixRegeneration tissue
Owner:WAKE FOREST UNIV HEALTH SCI INC
Bone-repairing hydrogel stent and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN108815574AGuaranteed porosityHigh porosityAdditive manufacturing apparatusPharmaceutical delivery mechanismPorosityHydrogel scaffold
The invention provides a bone-repairing hydrogel stent and a preparation method thereof. The bone-repairing hydrogel stent comprises a polymer gel carrier and mineralized nano bone particles. The polymer gel carrier comprises polymer gel and matrix metalloprotease responding peptide chains. The matrix metalloprotease responding peptide chains are directly crosslinked to the polymer gel. The bone-repairing hydrogel stent is prepared by 3D printing under the irradiation of UV rays. Furthermore, the invention also relates to a preparation method of the bone-repairing hydrogel stent. The providedbone-repairing hydrogel stent has the advantages of high porosity and mechanical strength, and can intelligently response to mesenchymal stem cells or bone cell systems, promote tissue growth, and induce bone healing. Moreover, the preparation technology is simple, and once moulding can be realized.
Owner:深圳市晶莱新材料科技有限公司
Application of polyurethane urea hydrogel with shape memory function
ActiveCN103539919AProvides effective mechanical propertiesEasy processing and applicationTemperature responsePolyethylene glycol
The invention relates to an application of a polyurethane urea hydrogel with a shape memory function. The polyurethane urea hydrogel is a copolymer of polyethylene glycol, diisocyanate and diamine. The polyurethane urea hydrogel provided by the invention has a temperature response shape memory function and a water response shape memory function at room temperature, and is capable of realizing deformation generation, fixation and restoration under the conditions of room temperature and water medium by means of good tensile properties of the prepared hydrogel and crystalline phase transformation of PEG (Polyethylene Glycol) in the process of dehydration crystallization and water-absorption decrystallization. The polyurethane hydrogel also has the characteristics of large elongation rate and high tensile strength and has application prospects in biomedical hydrogels, tissue engineering, hydrogel bracket materials and biomedical devices endowed with the shape memory function.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Myocardial patch and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105749350AGood mechanical propertiesGood restorativeTissue regenerationProsthesisGramNormal growth
The invention relates to a myocardial patch and a preparation method thereof and discloses a hydrogel scaffold.The hydrogel scaffold is prepared according to a method including steps: (1) using gelatin for preparing a gelatin solution with the concentration being 4-10%w / v, then preparing a transglutaminase solution, adding the transglutaminase solution into the gelatin solution according to a proportion that per gram of gelatin is added with not less than 5U of transglutaminase, and well mixing to obtain a hydrogel solution; (2) adding cells into the hydrogel solution, well mixing to obtain a hydrogel solution containing the cells, and gelatinizing to obtain the hydrogel scaffold.The hydrogel scaffold is excellent in mechanical property, cell growth normality is guaranteed, and body injuries can be effectively repaired.The myocardial patch prepared from the hydrogel scaffold is 2-4mm in thickness and convenient for surgical suture, and normality in growth of compound cells is ensured.Furthermore, the myocardial patch is excellently effective in myocardia repair and has a promising clinical application prospect.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Method for preparing injectable chitosan hydrogen for tissue engineering
InactiveCN1799645ASimple operation processMild implementation conditionsCoatingsProsthesisSolubilityDouble bond
The invention discloses a method for preparing an injection chitose aqueous gel used in tissue engineering, grafting the methacrylic acid and lactic acid onto the chitose molecular chain in order with carbodiimide condensation method, the got chitose derivative possesses the polymerized carbon-to-carbon unsaturated bond and water solubility. Employing the redox initiating system of ammonium peroxodisulfate and tetramethylethylenediamine to make the chitose derivative form into chitose aqueous gel through double bond cross-linking. The chitose aqueous gel is non toxic, biodegradable and biological compatibility. The process of the invention is simple and can be used for injection aqueous gel cradle in the tissue engineering.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Preparation method of living cell based complex three-dimensional microchannel porous support
A preparation method of a living cell based complex three-dimensional microchannel porous support. The method comprises steps of: first, preparing two parts of hydrogel collosol with different hydrogel monomer concentrations; then preparing two mixed liquors containing the hydrogel collosol and cell culture solution; putting the two mixed liquors into two sets of different injectors of a cell printer; then printing the mixed liquors on a petri dish surface until formation of a required three-dimensional cell-laden hydrogel support; cultivating the cell-laden hydrogel support in an incubator; then soaking the cell-laden hydrogel support in lauryl sodium sulfate to complete split and kill the cells; flushing with Dulbecco's phosphate-buffered saline and deionized water successively; finally obtaining the three-dimensional porous hydrogel support with complex microchannels. According to the invention, living cells are employed as a porogenic agent; size and density of the holes are controlled through controlling of the cell concentration and culture conditions; distribution of the holes is controlled through controlling of a printing platform; and a complex and controllable microchannel structure is formed in the hydrogel support.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Biological ink and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN110801532AAvoid harmMild reaction conditionsAdditive manufacturing apparatusProsthesisCross linkerHydrogel scaffold
The invention discloses a biological ink used for 3D biological printing and a preparation method thereof. The biological ink comprises the following components in percentage by mass: 8%-20% of a hydrophilic polymer with the crosslinking function, 10-20% of a water-soluble enzyme with the crosslinking function, 0.1%-1% of bacterial cellulose, and the balance a sterile PBS solution. The biologicalink can be used for 3D printing after mixed with cells, and the shear thinning properties of the used materials make the biological ink have the characteristics of self-supporting after extrusion. Theused materials have good cell compatibility, the enzyme crosslinking agent forms a hydrogel at physiological temperature (about 37 DEG C), the reaction conditions are mild, the cells are not damaged,a hydrogel support has relatively good stability in a culture medium, and thereby cell proliferation can be supported.
Owner:RENMIN UNIVERSITY OF CHINA
Human tumor invasion and metastasis histioid in vitro three-dimensional model and construction and evaluation thereof
InactiveCN103160468AKeep aliveSimulation excellentMicrobiological testing/measurementTumor/cancer cellsHuman tumorHydrogel scaffold
The invention discloses an in vitro model simulating human tumor metastasis. Cells in the model have a tumor high metastasis character. The model is constructed by building of a micro spherical hydrogel support frame by tumor high metastasis cells, building of a tumor cell in vitro metastasis model and identifying of the constructed tumor cell in vitro metastasis model. The model can grow in a three-dimensional culturing cell in a clustering mode, and tumor cell biological behaviors in metastasis can be detected. The model has important value in studying of a clinical tumor metastasis mechanism and controlling of screening of metastasis medicine and can be taken as a technical platform for manufacturing anti-tumor metastasis gene vaccines and building screening of anti-tumor metastasis medicine.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Intelligent hydroxybutyl chitosan hydrogel stent based on 3D printing technology and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses an intelligent hydroxybutyl chitosan hydrogel stent based on the 3D printing technology and a preparation method of the intelligent hydroxybutyl chitosan hydrogel stent based on the 3D printing technology. The intelligent hydrogel, thermo-sensitive hydroxybutyl chitosan, which is of a single system and has high responsiveness to temperature and ion strength is adopted, the feature that sol-gel phase change is caused by the temperature and the ion strength of the thermo-sensitive hydroxybutyl chitosan is utilized, and the formed hydrogel stent is obtained through adjustment and control over the temperature and 3D printing parameters; then, through inorganic-salt-induced phase change, the hydrogel stent is evenly shrunk, and the mechanical strength and the precision of the hydrogel stent are further improved. The intelligent hydroxybutyl chitosan hydrogel stent based on the 3D printing technology overcomes the defects that 3D printing hydrogel is generally poor in formability, low in mechanical strength, low in precision and the like. Compared with existing common methods of adopting photosensitizer, complex-system hydrogel and the like, the intelligent hydroxybutyl chitosan hydrogel stent based on the 3D printing technology does not need introducing of any photosensitizer or cross-linking agent, is simple in system and gentle in technology; and the prepared 3D stent has high mechanical strength and is provided with a precise internal structure, and the prepared 3D stent can be widely applied to tissue engineering and tissue repair of the cartilage, the skin, the vessel, the nerve, the myocardium and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI QISHENG BIOLOGICAL PREPARATION CO LTD
Preparation method of hydrogel scaffold for amplifying human iPS (induced pluripotent stem) cells without differentiating
InactiveCN102382797AClear chemical structurePhysicochemically stableArtificially induced pluripotent cellsNon-embryonic pluripotent stem cellsChemical structureSynthetic Polymeric Macromolecules
The invention provides a preparation method of a hydrogel scaffold for amplifying human iPS (induced pluripotent stem) cells without differentiating. The prepared hydrogel cell scaffold takes synthetic polymer hydrogel as a cell culture scaffold under conditions of not modifying any protein extracted from an animal body or relating to any trophocyte, and is an ideal biological material for safelyculturing human pluripotent stem cells with the advantages of definite chemical structure of synthetic polymer hydrogel, stable physicochemical performance, easiness in regulation and control, no foreign body infection, easiness in sterilization and low price. Therefore, a soft material culture system, which can safely, simply and conveniently amplify human iPS cells without differentiating, can be established.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Vascularized full-thickness tissue-engineered skin layer-by-layer assembled by hydrogel, nanofiber scaffolds and skin cells and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN109529123AImprove adhesionPromote growthSkin implantsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismFiberCell layer
The invention discloses a vascularized full-thickness tissue-engineered skin layer-by-layer assembled by hydrogel, nanofiber scaffolds and skin cells and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the technical fields of macromolecule materials and biomedical materials. Artificial tissue engineered skin consists of an epidermal layer and a corium layer, wherein the epidermal layer is formed by alternately stacking nanofiber scaffolds located above the corium layer with seed cells. The corium layer consists of lower-layer nanofiber scaffolds, upper-layer hydrogel scaffolds and three kinds ofseed cells, and the seed cells are distributed on the surface of the nanofiber scaffolds, inside the hydrogel and on the surface of the hydrogel. The vascularized full-thickness tissue-engineered skinis prepared by combination of an electrospinning technology and a macromolecular complexation technology with a fiber / cell layer-gel layer-fiber / cell layer-by-layer self-assembly technology. The artificial tissue-engineered skin with biological function can be used for regeneration and repair of various tissues, especially for wound healing, angiogenesis, scar formation reduction and the like.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Method of preparing highly branched polysaccharide-fibroin hydrogel bracket
InactiveCN104548200APromote swellingImprove mechanical propertiesAerosol deliveryOintment deliveryPolymer sciencePleurotus tuber-regium
The invention discloses a method of preparing a highly branched polysaccharide-fibroin hydrogel bracket and belongs to the technical field of natural polymer materials. The method comprises the following steps: dispersing highly branched polysaccharide of pleurotus tuber-regium into NaOH and isopropanol, carrying out reaction with chloroacetic acid at the temperature of 60 DEG C, carrying out reaction, cooling, neutralization, dialysis and freeze drying to obtain carboxymethyl highly branched polysaccharide, dissolving the obtained carboxymethyl polysaccharide into a phosphoric acid buffer salt solution with a pH value to be 7.4, carrying out activation on 1-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)-3-ethyl carbodiimide hydrochloride and N-hydroxysuccinimide for 15 minutes to 4 hours, and carrying out crosslinking reaction on an activated product and a fibroin solution for 6-48h at the temperature of 4-37 DEG C to obtain the highly branched polysaccharide-fibroin hydrogel bracket. The method is simple in operation and rich in raw material source; in addition, the prepared bracket material has the drug controlled release property and biocompatibility and is good in mechanical property; the highly branched polysaccharide-fibroin hydrogel bracket can be used for preparing an artificial tissue bracket.
Owner:WUHAN TEXTILE UNIV
Biomimetic electronic skin medical stent material with self-repairing function and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN111825859AImprove adhesionPromote growthPharmaceutical delivery mechanismDomestic articlesPolystyreneBiocompatibility
The invention relates to the field of gelatin-based biomedical materials, in particular to a preparation method and application of a bionic electronic skin medical stent with a self-repairing function. The method is characterized in that gelatin extracted from an acellular fetal calfskin dermal matrix with good biological safety is used as a raw material; then, conducting polymer poly (3, 4-ethylenedioxythiophene) with good biocompatibility is used; compounding a polystyrene sulfonate (PEDOT: PSS) solution with self-made acidified carbon nanotubes (H-MWCNTs); the hydrogel stent with a multifunctional three-dimensional network space structure is obtained through crosslinking of 1-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)-3-ethylcarbodiimide hydrochloride (EDC), and the hydrogel is good in biocompatibility and high in mechanical strength, has both self-repairing performance and tissue regeneration inducing repairing performance and can be widely applied to skin wound repairing treatment.
Owner:SHAANXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com