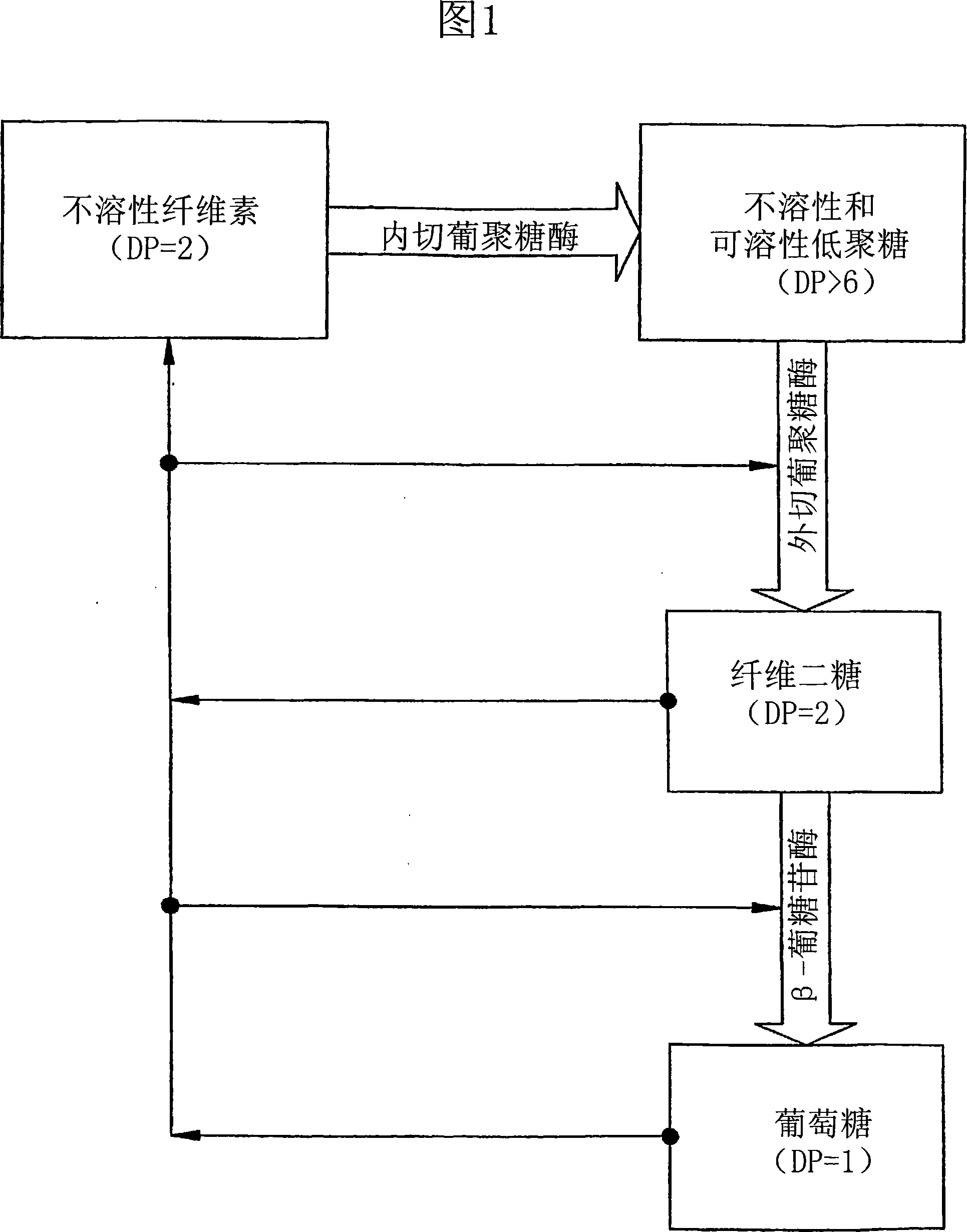
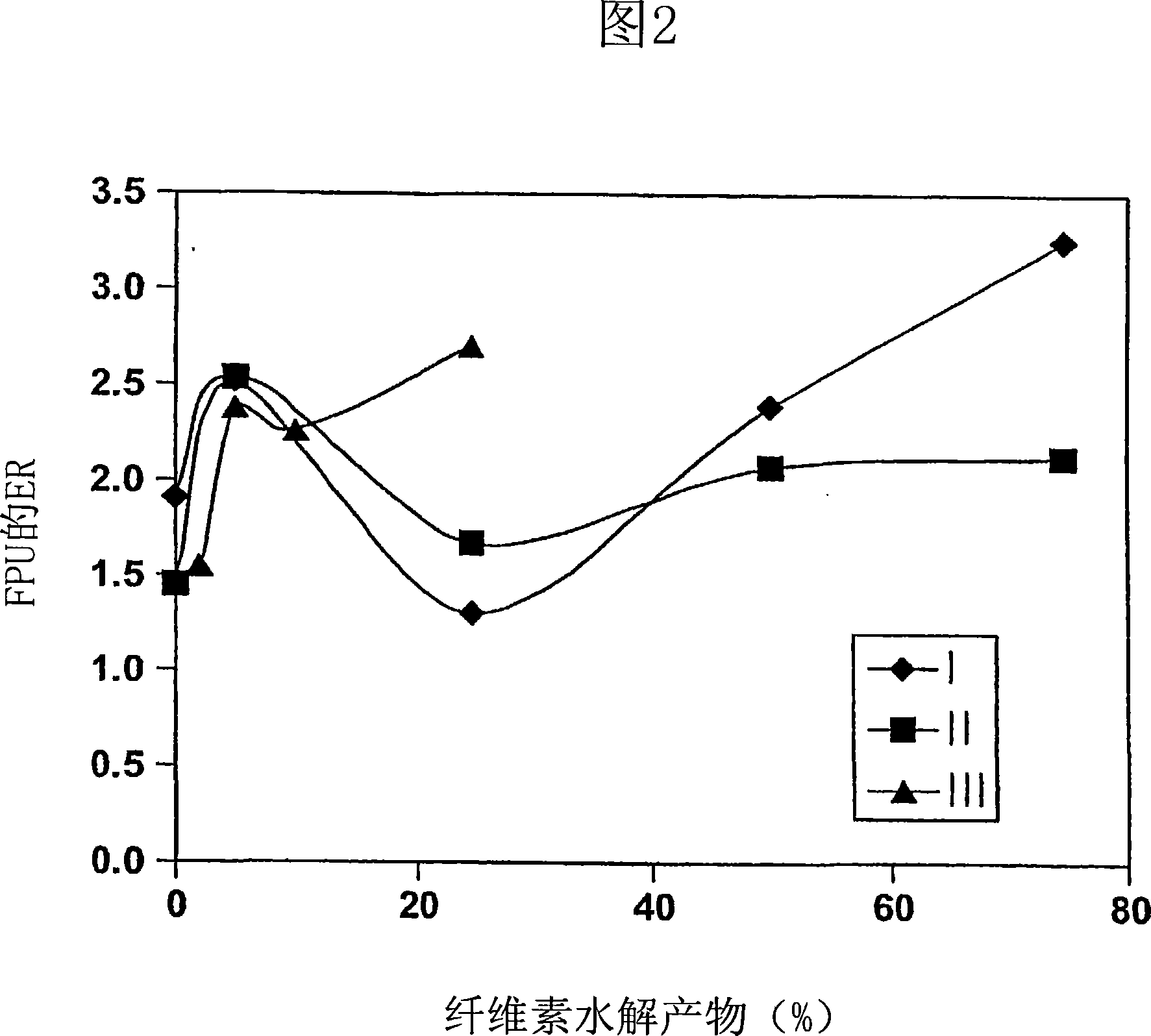
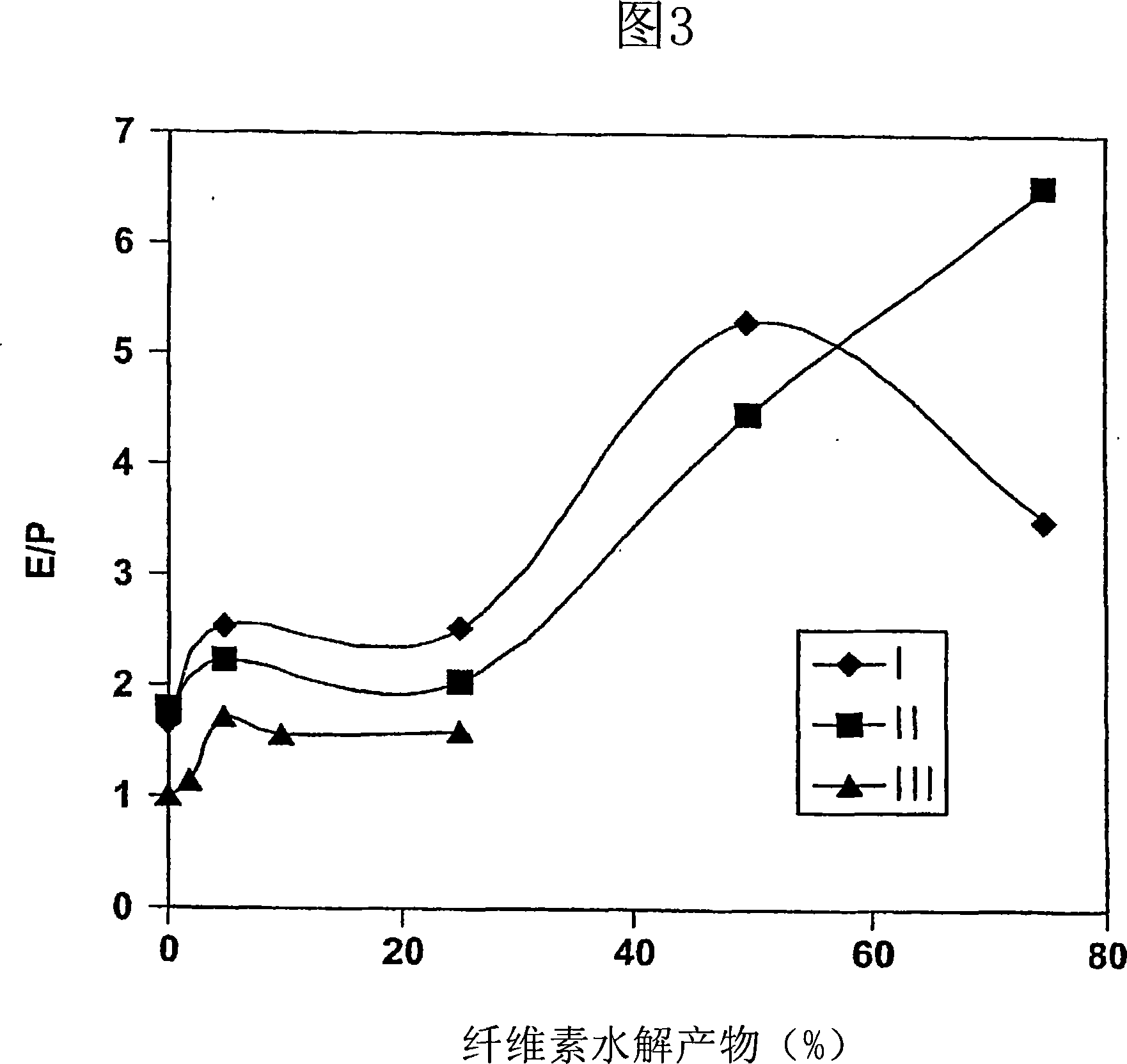
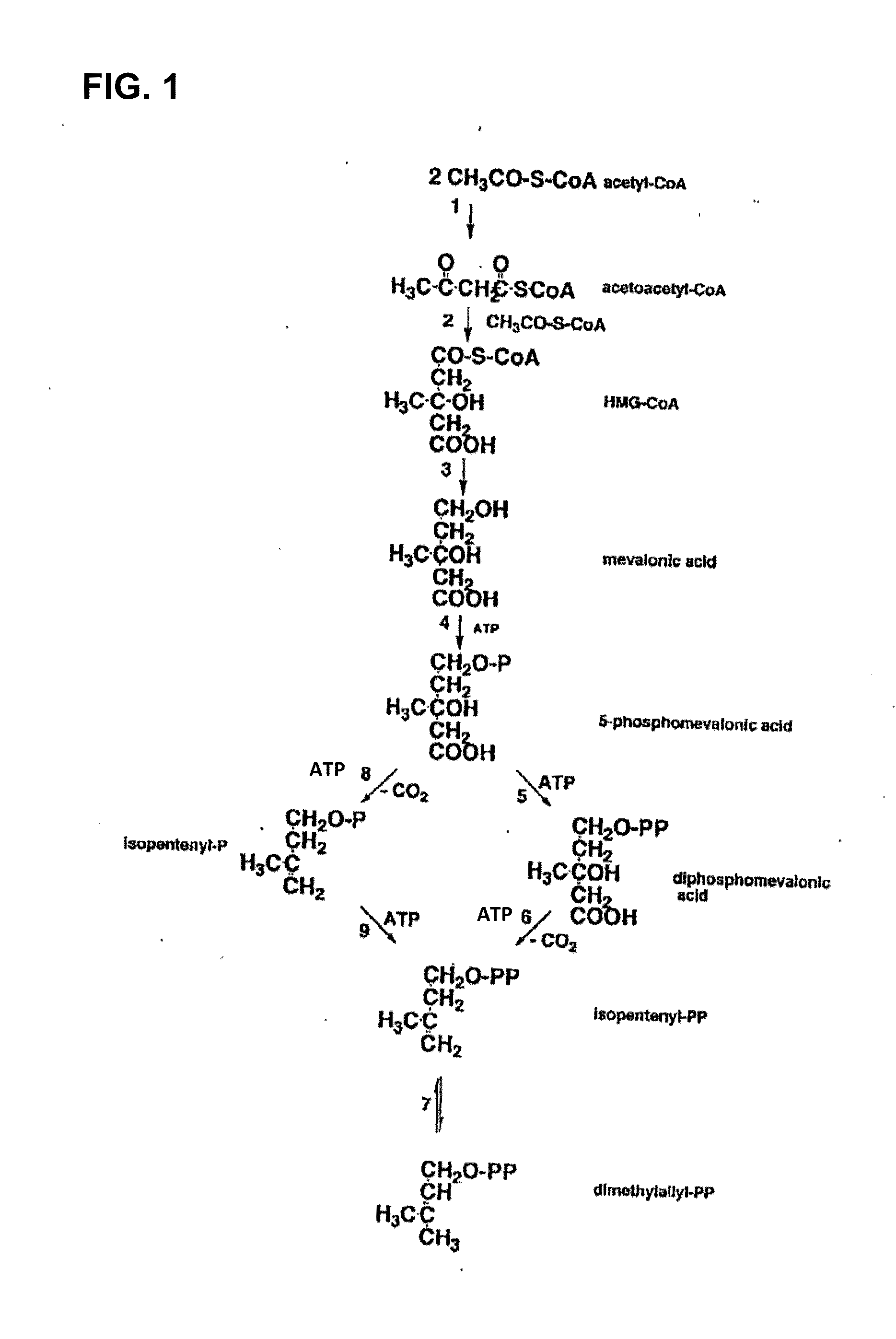
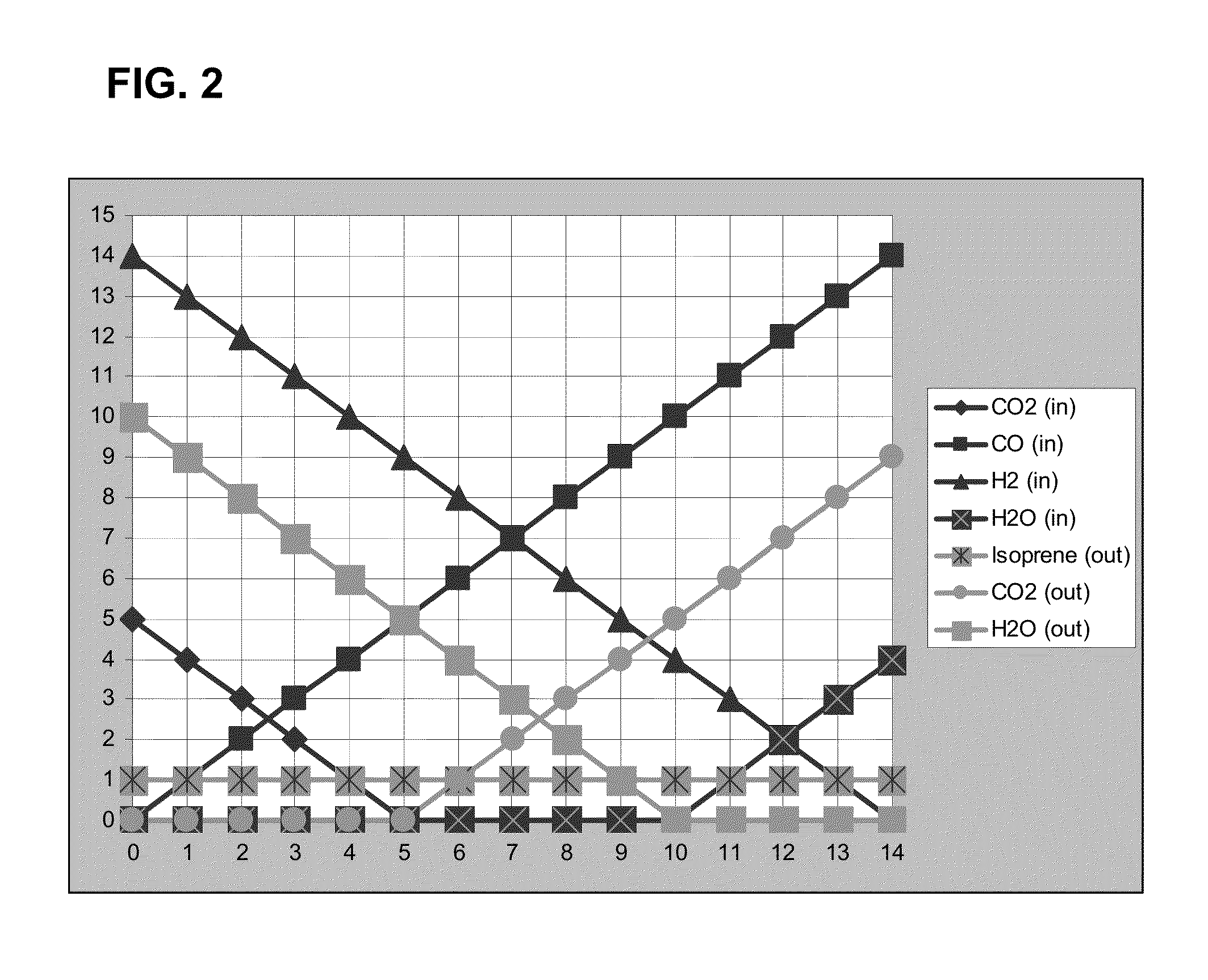
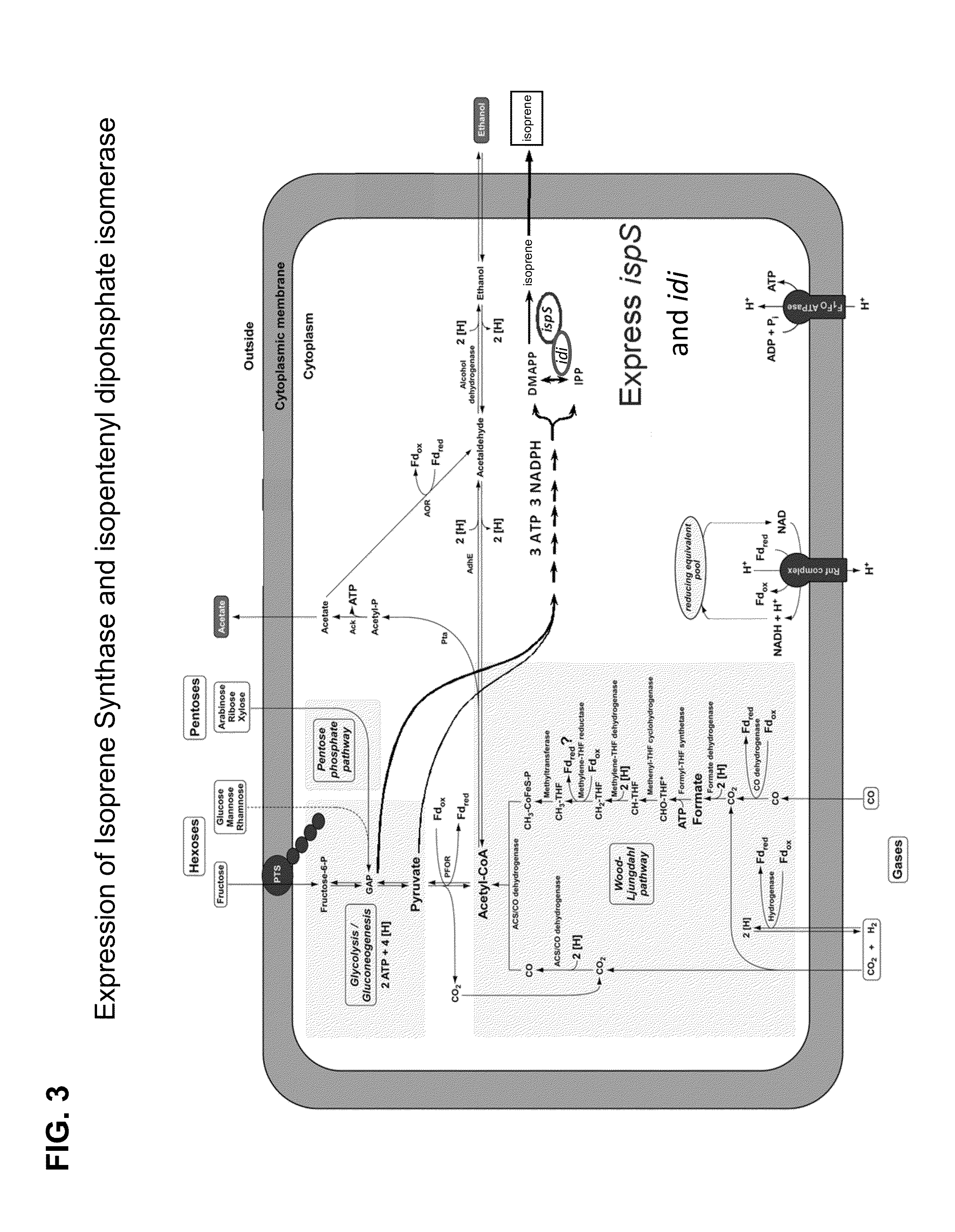
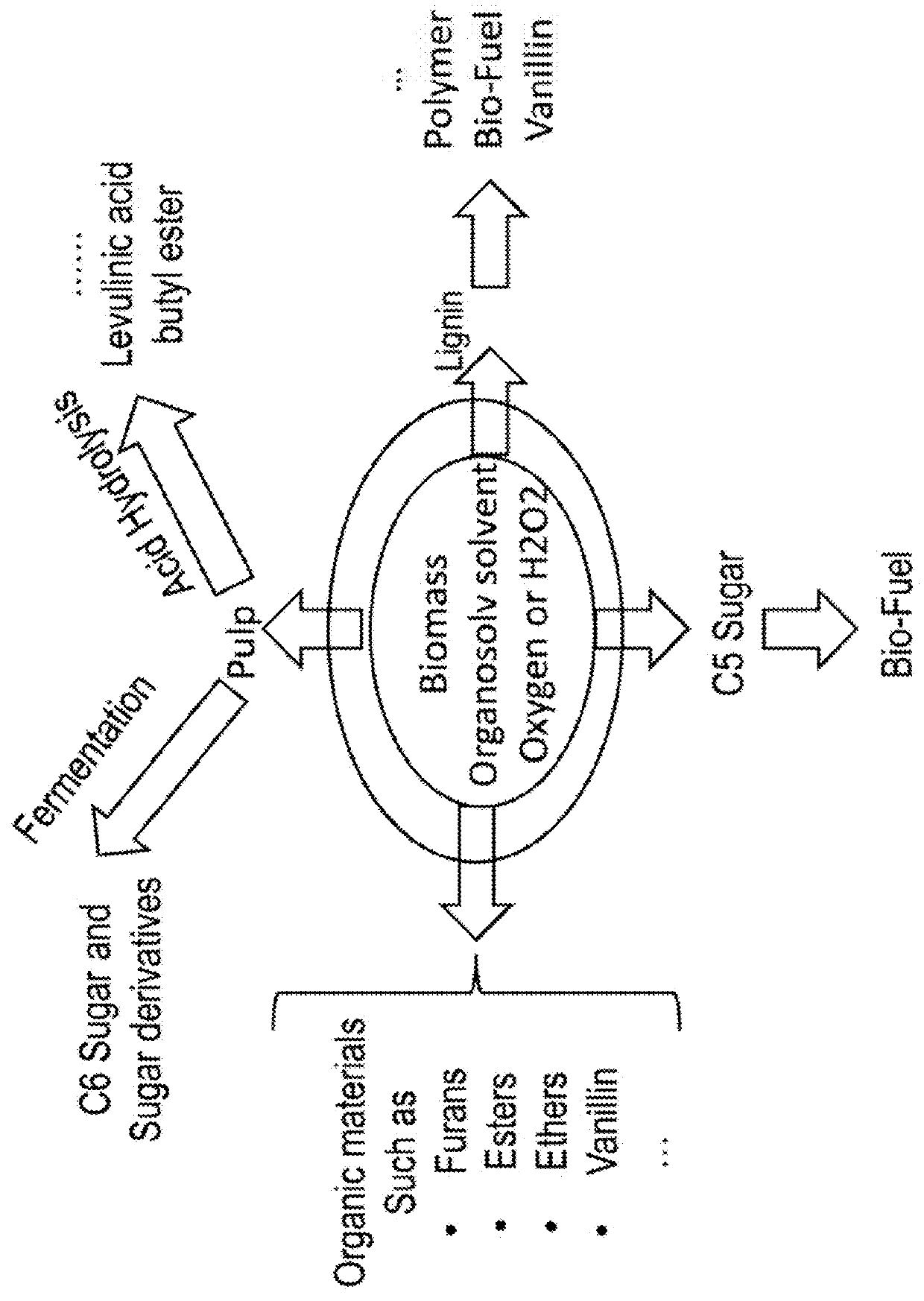
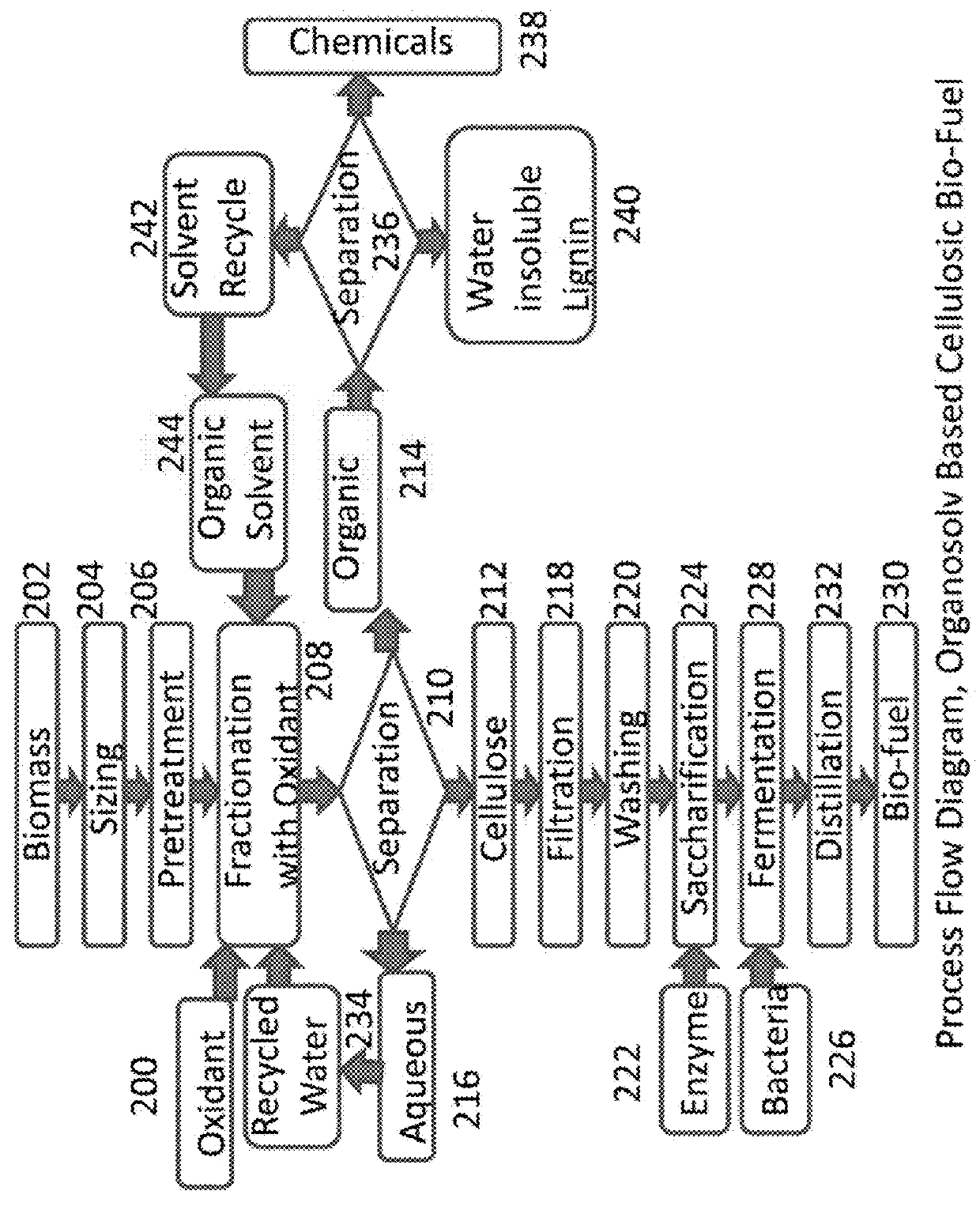
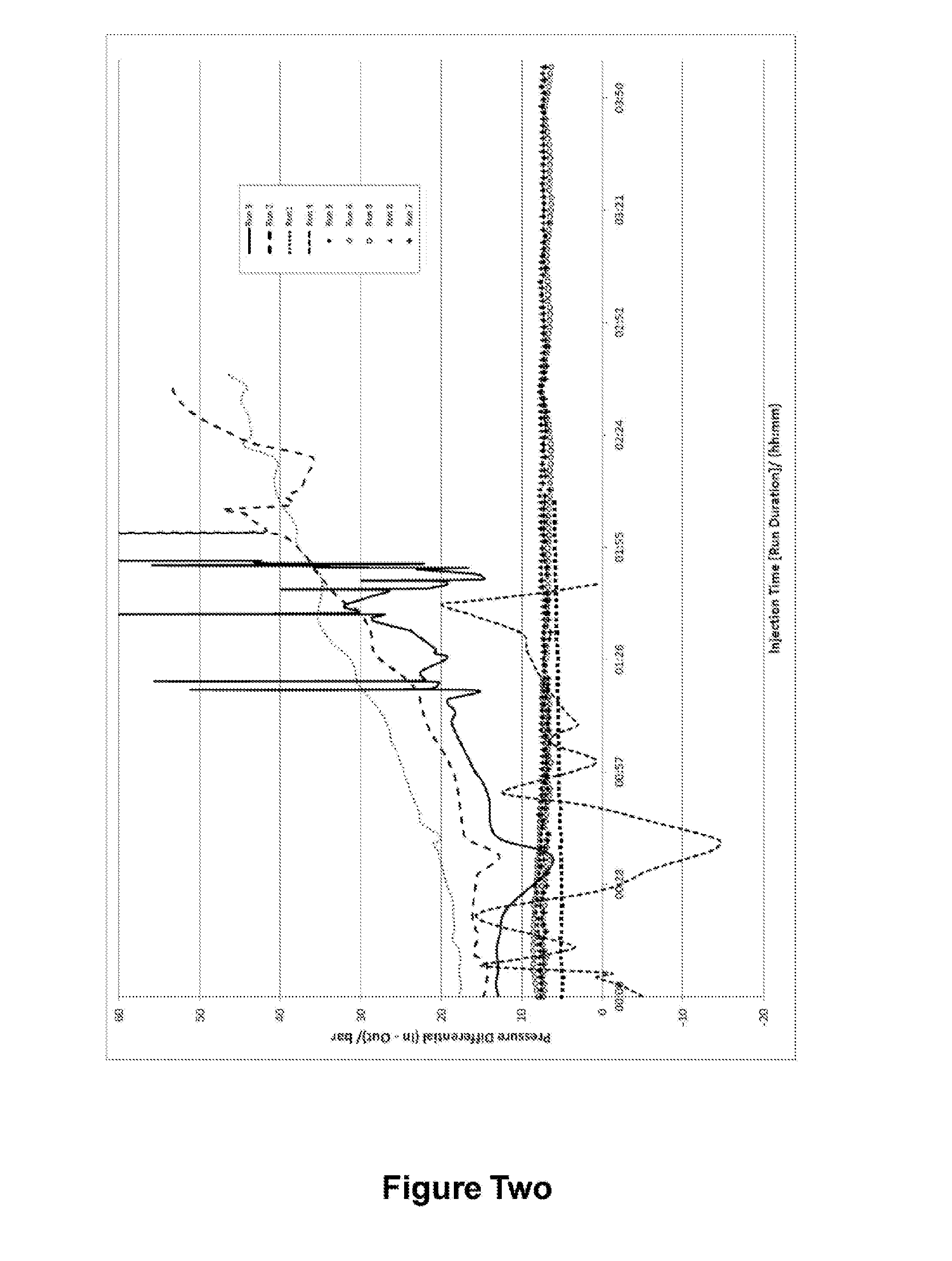
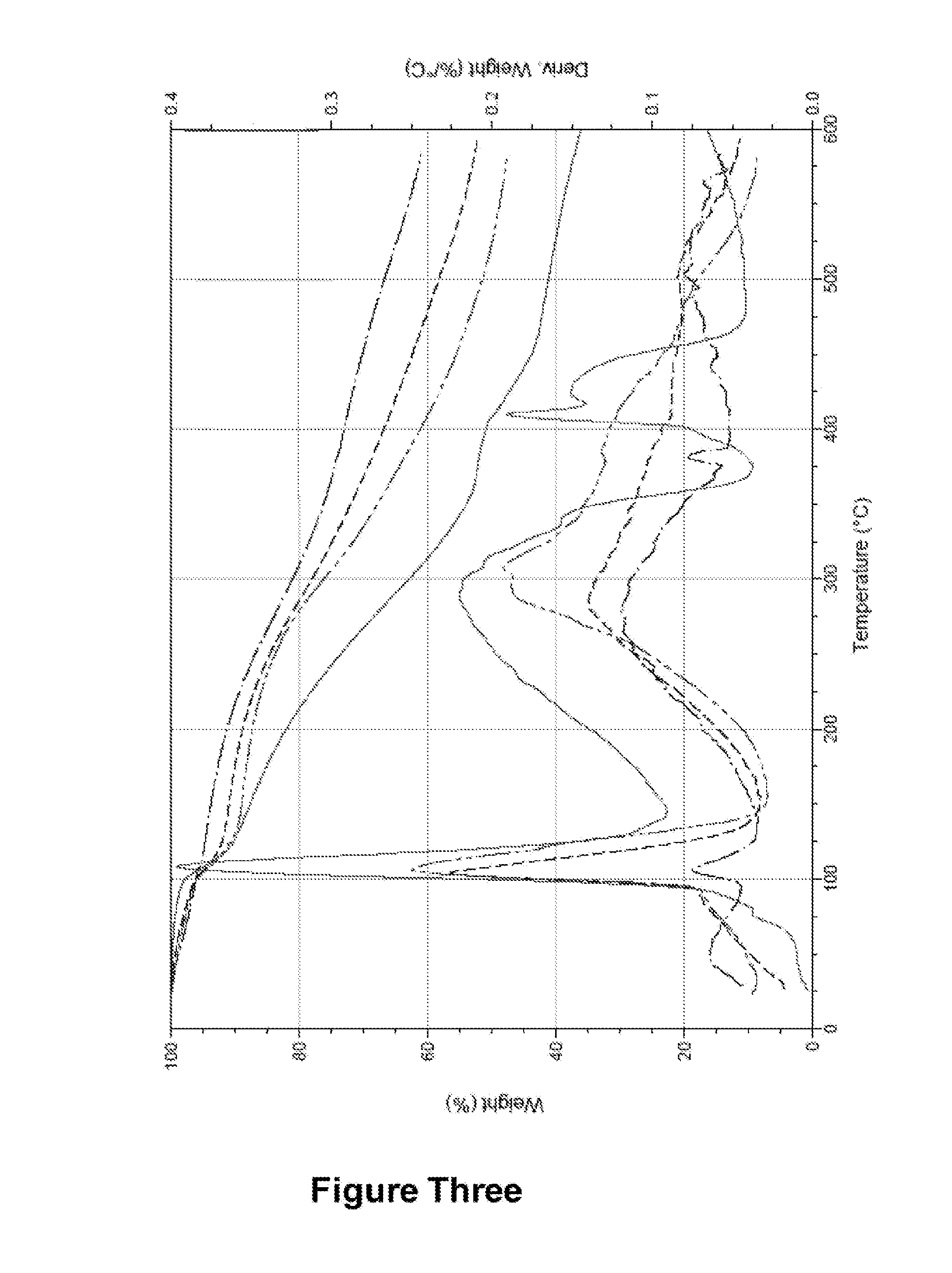
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
97 results about "Bio products" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Multiuse reactors and related methods
InactiveUS20120231504A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsPeptide/protein ingredientsUnit operationProduct gas
Owner:THERAPEUTIC PROTEINS INT
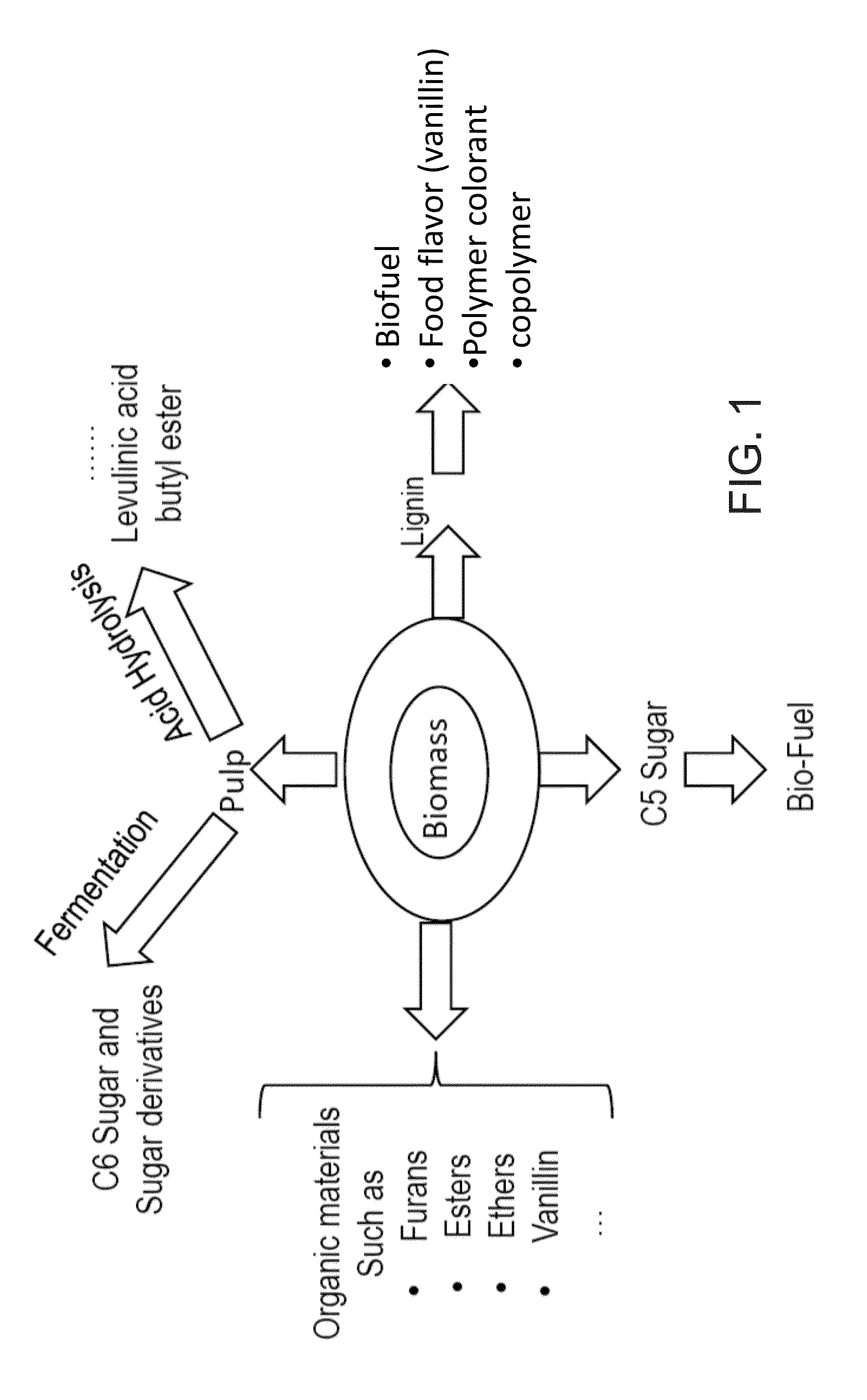
System and method for extraction of chemicals from lignocellulosic materials
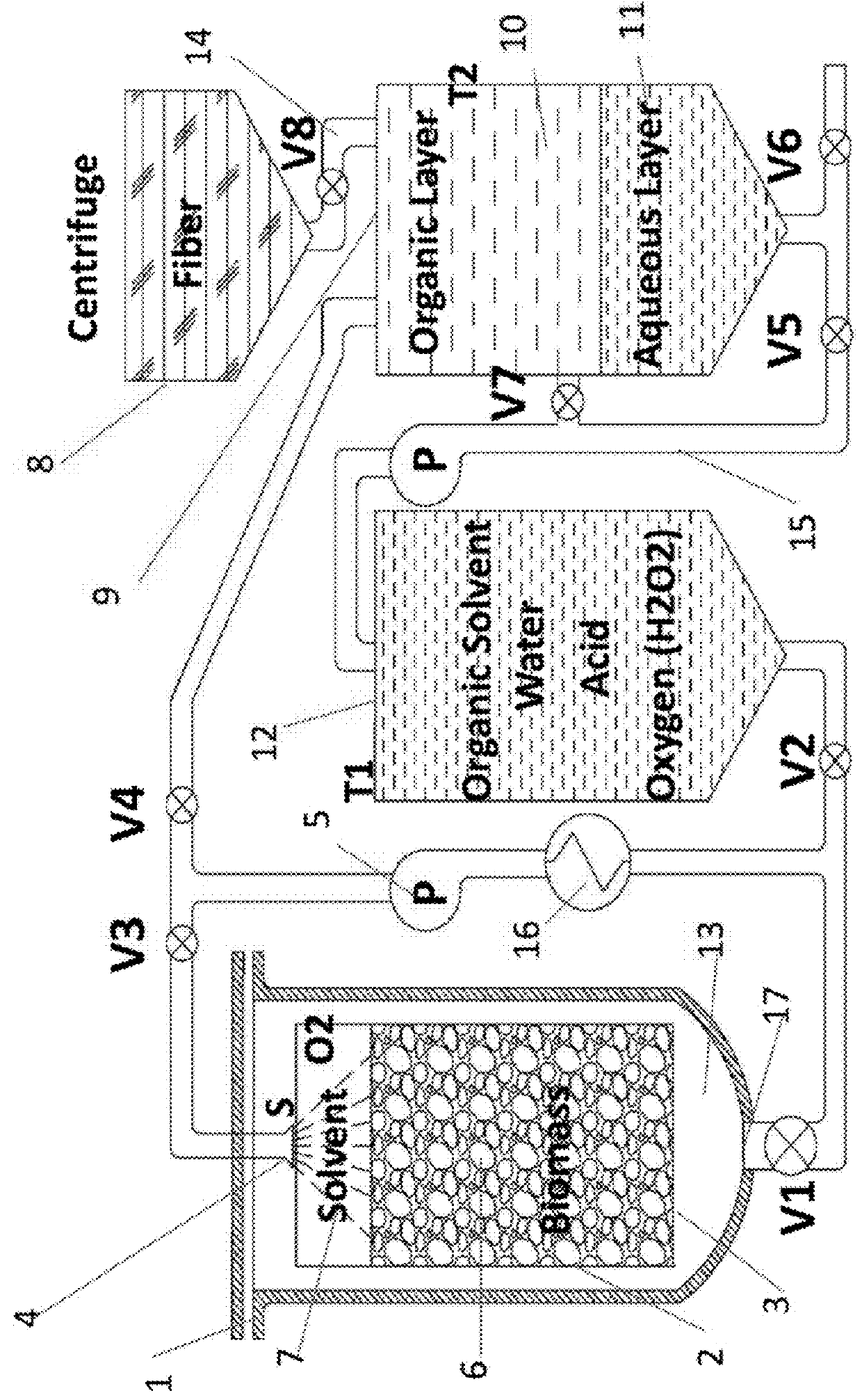
ActiveUS20140227161A1Oxygen-containing compound preparationOrganic compound preparationFuranCellulose
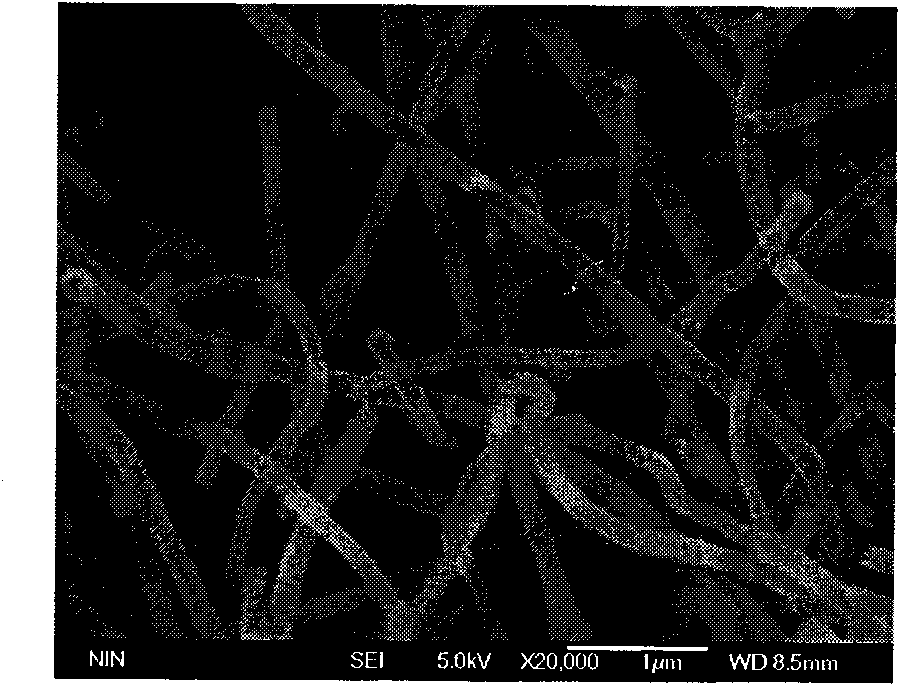
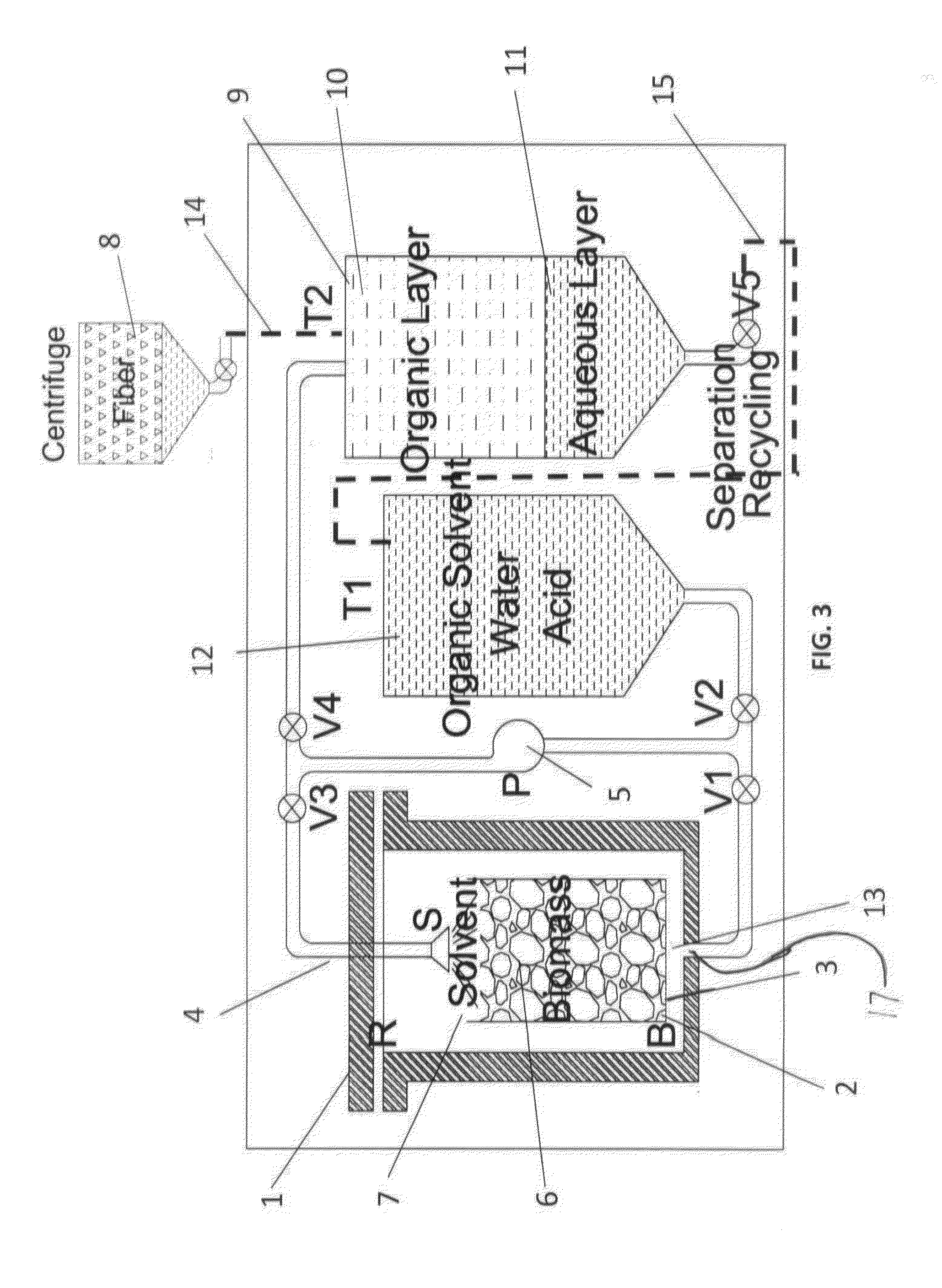
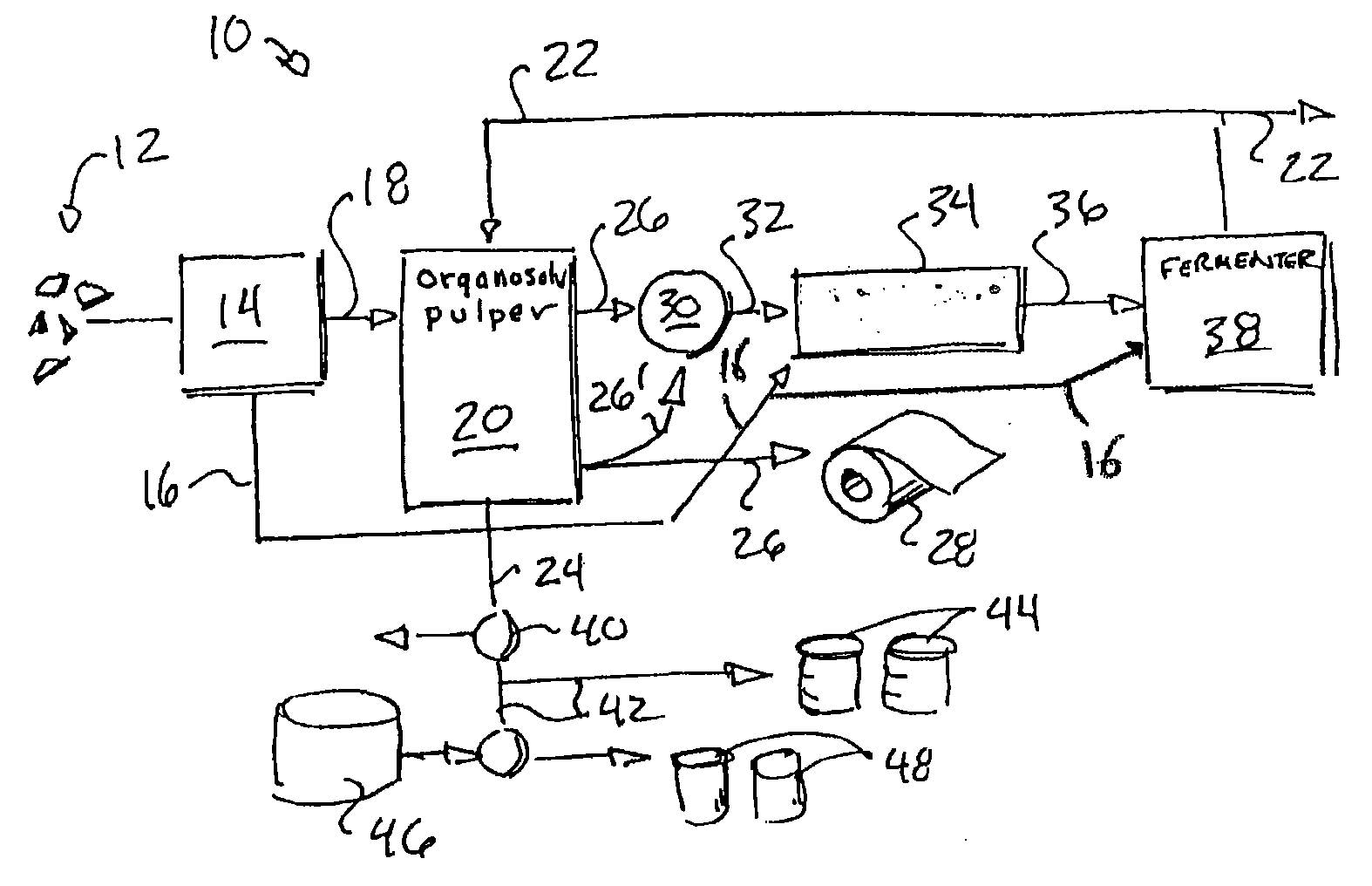
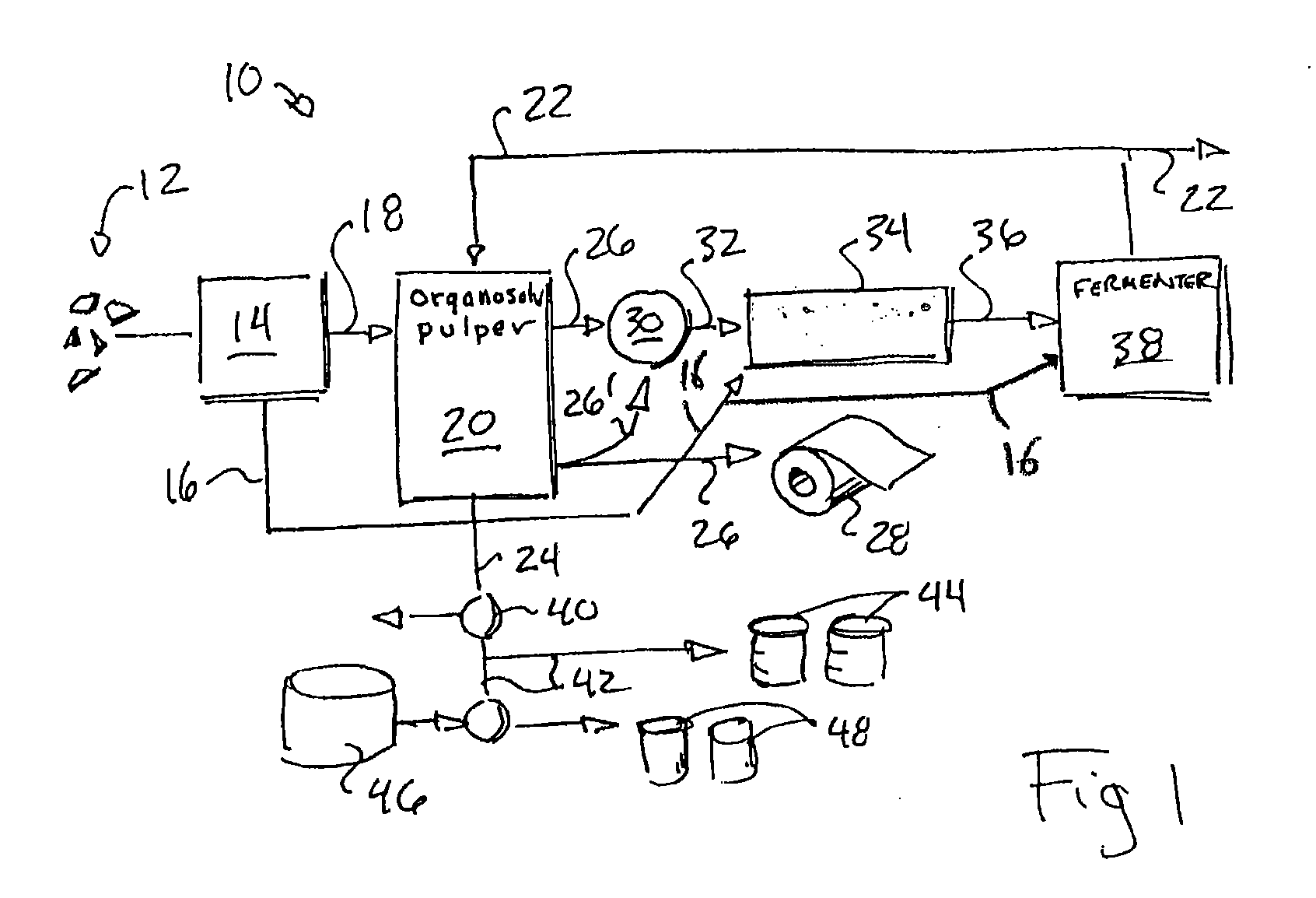
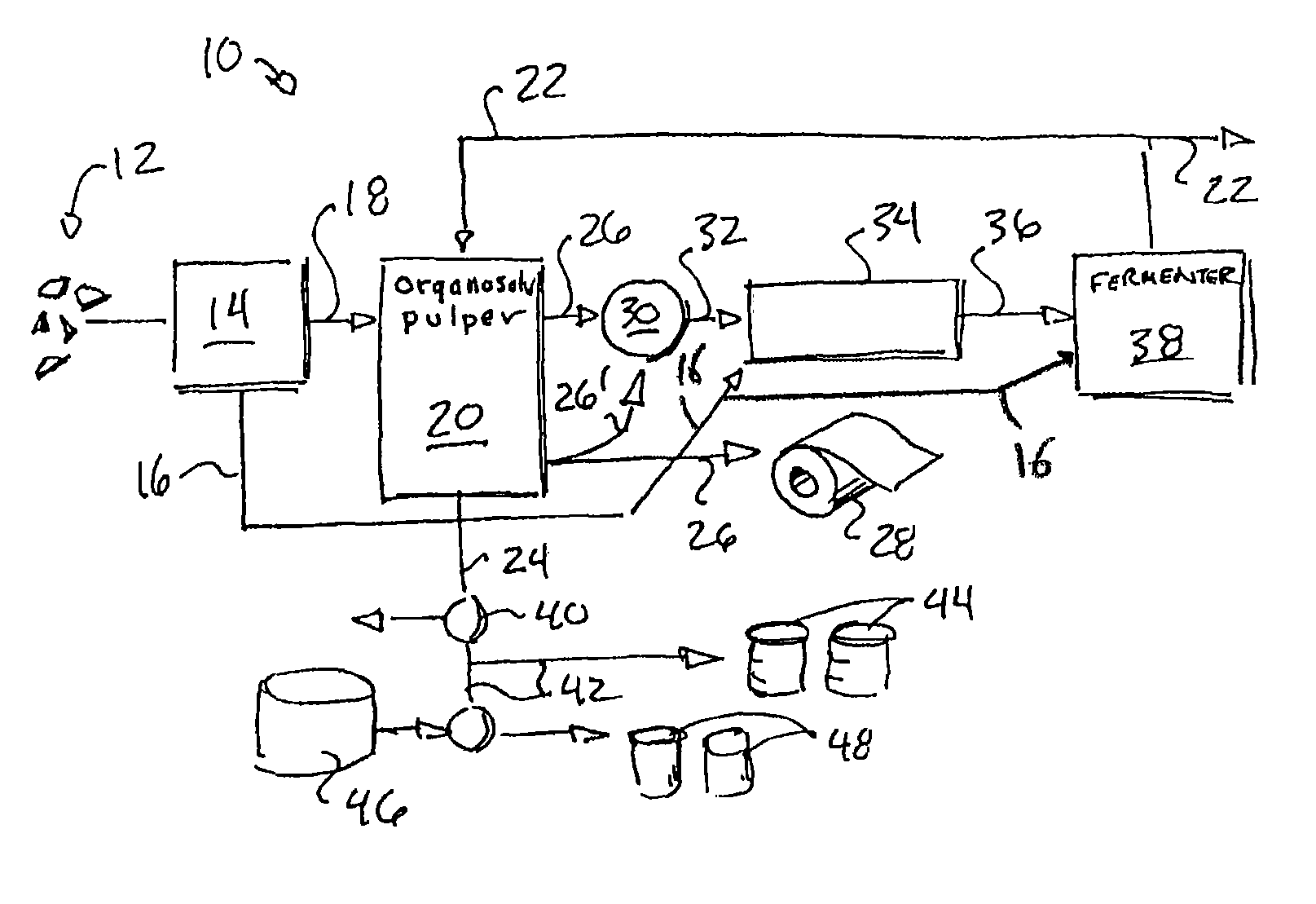
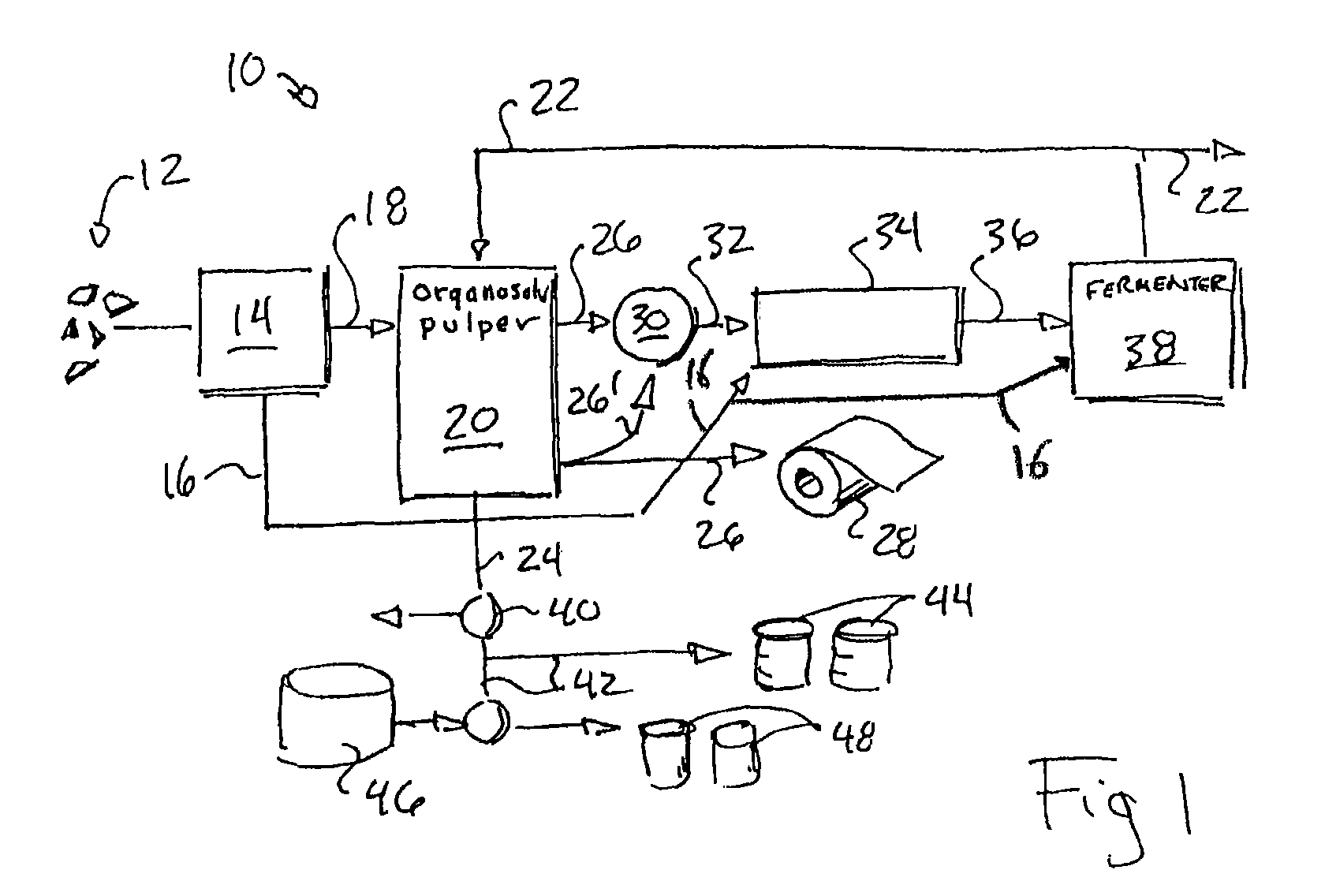
An organosolv process for producing bio-products by decomposing lignocellulosic materials comprises providing an initial lignin solvent with water, an acid, and a lignin dissolving chemical comprising at least one of an organic ester, butyl acetate, an organic furan, and furfural. The process also includes placing the lignin solvent in contact with a biomass to form a circulation solvent, and recycling at least a portion of the circulation solvent by circulating the circulation solvent back into contact with the biomass. The circulating of the circulation solvent occurs for a period of time, after which, the process then includes separating material such as chemicals and lignin from the circulation solvent. The chemicals can be recycled as new solvent or sold while lignin can be used as natural and renewable colorant for polymers such as poly lactic acid.
Owner:AMERICAN SCI & TECH
System for controlling sulfide generation
Systems and methods for reducing odors utilizes oxidation-reduction potential to characterize the quality of water or wastewater and control addition of a species thereto that reduces or inhibits biological sulfide generation. Oxidation-reduction potential is measured at a downstream station and, based on the measurement, a nitrate compound is added at an upstream station to promote inoffensive biological products instead of foul-smelling products.
Owner:EVOQUA WATER TECH LLC
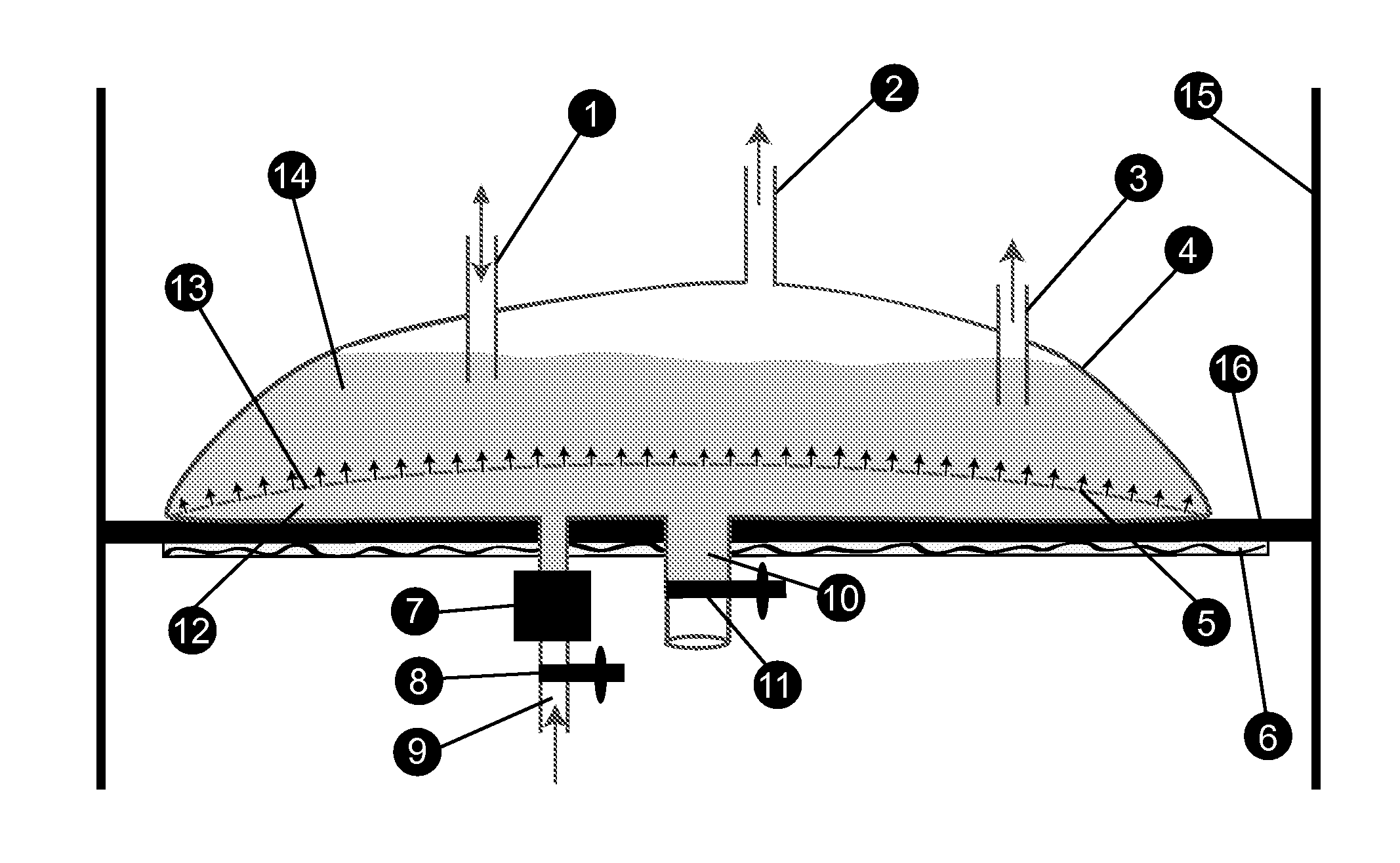
Lignin-Solvent Fuel and Method and Apparatus for Making Same
ActiveUS20090145021A1Reduce needSimple gravityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBiodieselHigh energy
The present invention is a process and apparatus for forming various bio-products from cellulosic plant material. The plant material is subjected to a pulping step in which lignin is extracted from the material by an aqueous lignin solvent to form a lignin-solvent mixture and purified cellulose. The lignin-solvent mixture can be separated from the water to form a high energy density fuel that can be used independently or combined with biodiesel. The purified cellulose can be used in conventional processes, e.g., paper making, or can be converted to fermentable sugars with a cellulase enzyme to produce other bio-products depending on the operating conditions of the fermenter. The bio-products produced by the fermenter can include the solvent that may be recycled for use in extracting the lignin.
Owner:WISYS TECH FOUND
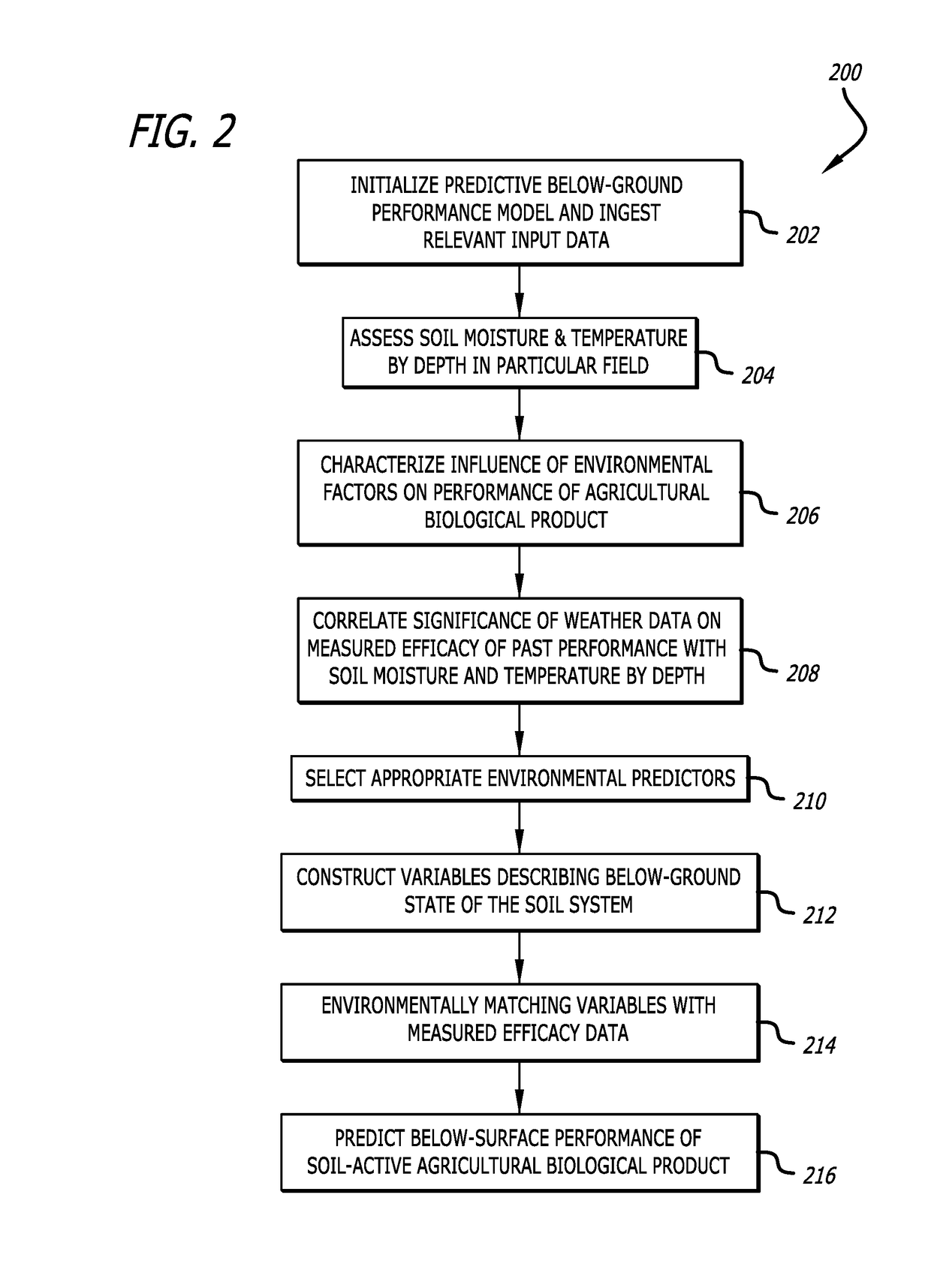
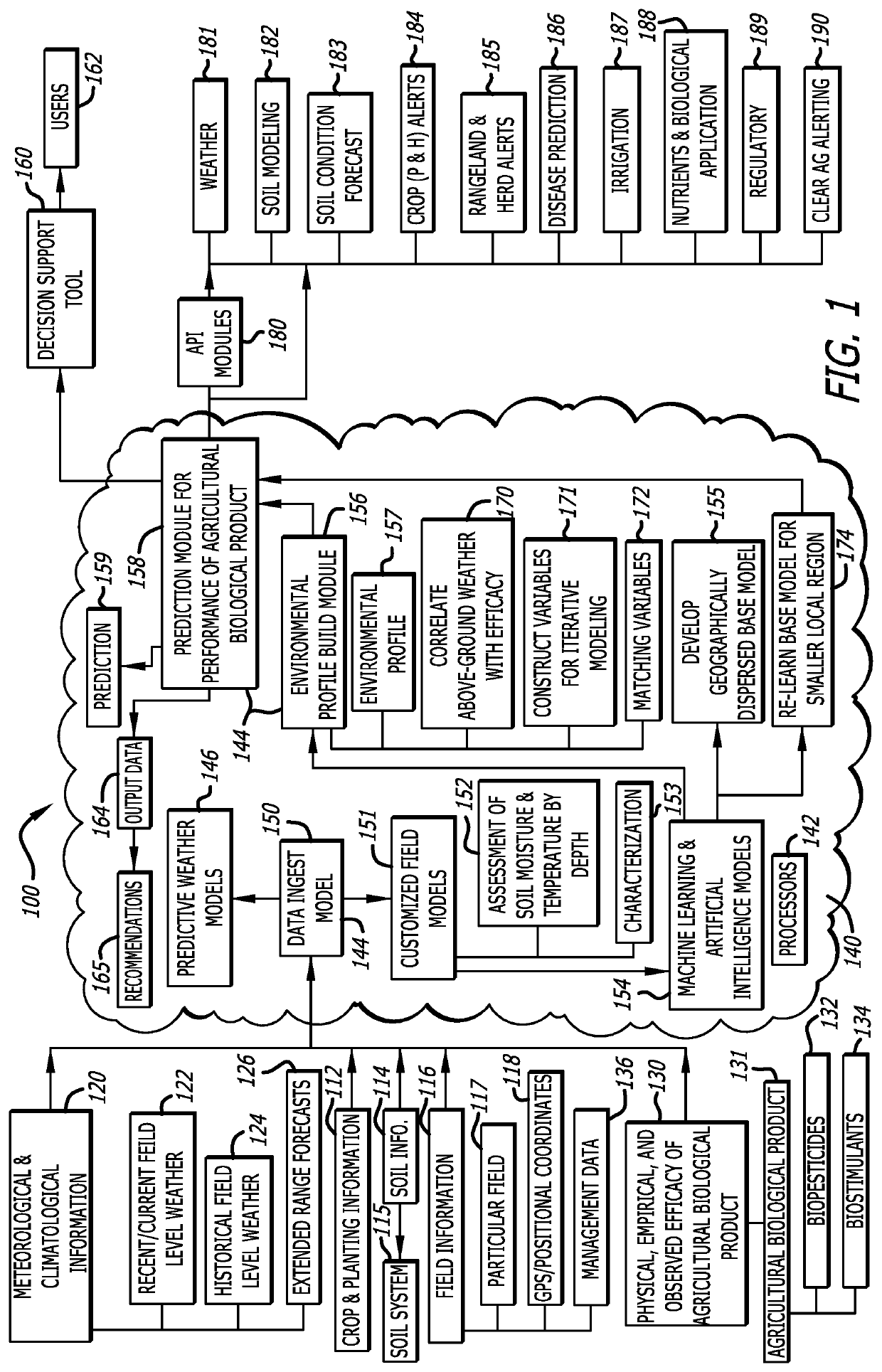
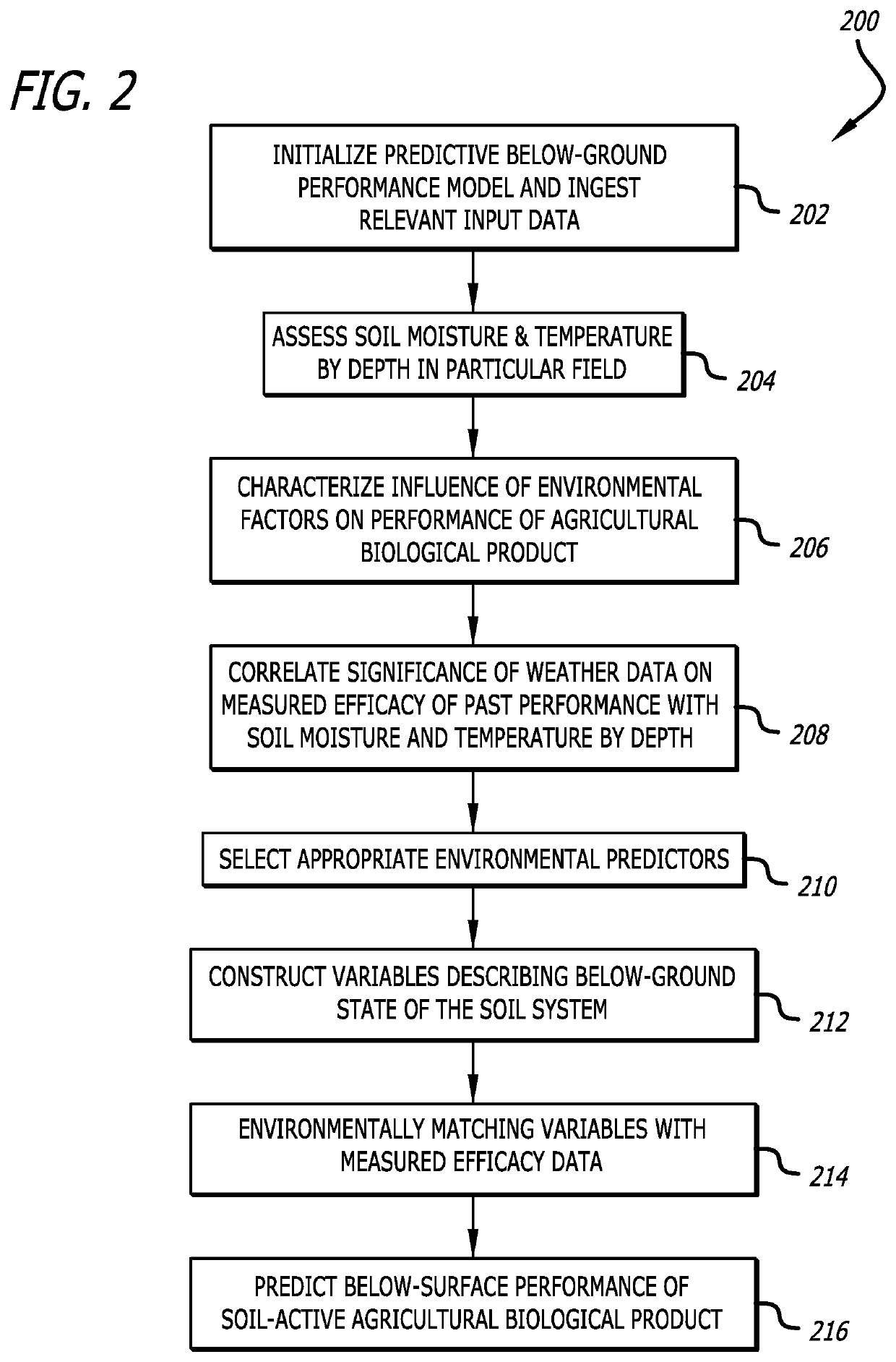
Modeling and prediction of below-ground performance of agricultural biological products in precision agriculture
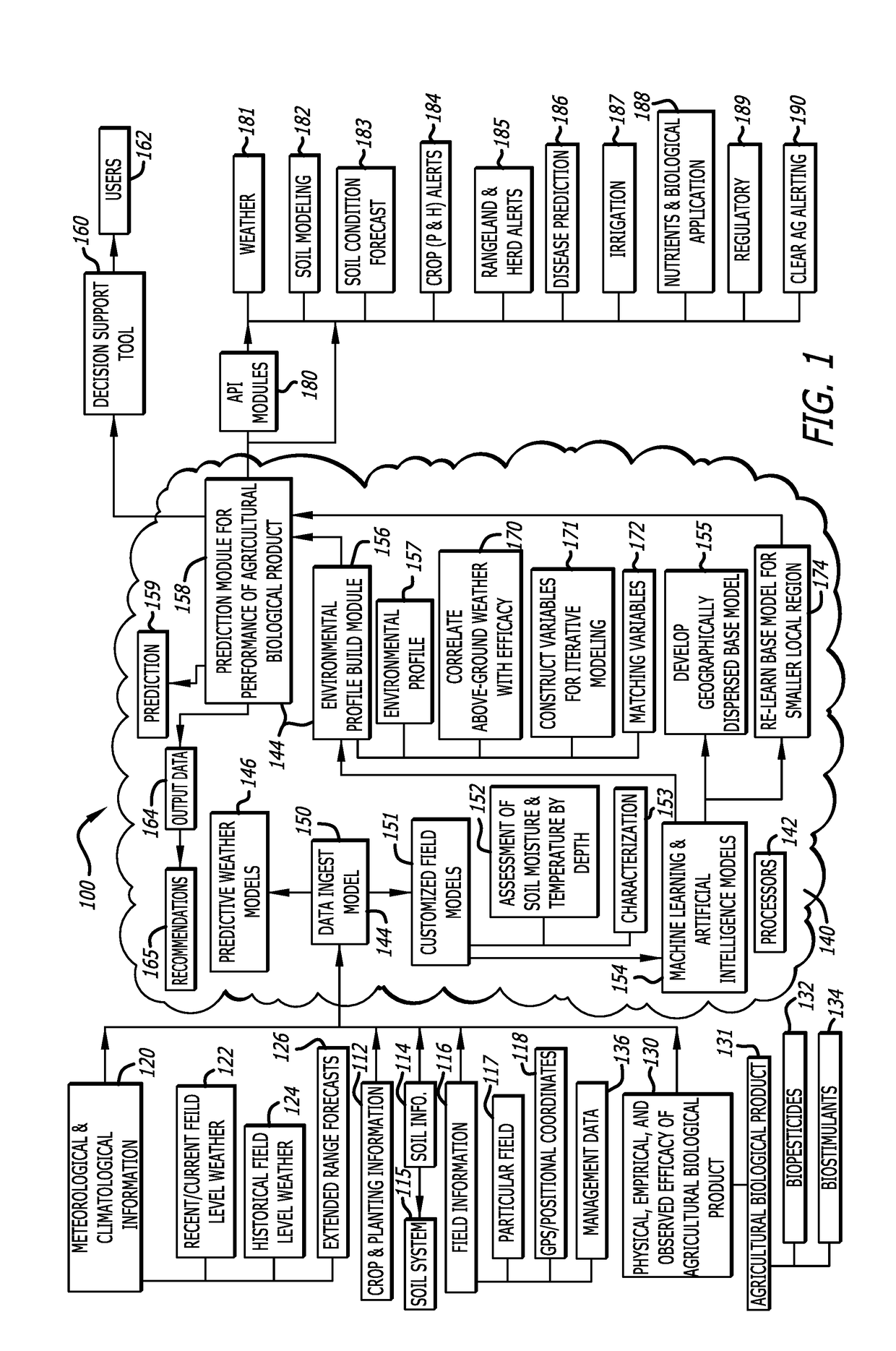
InactiveUS20190050741A1Identify wellEasy to identifyGeometric CADClimate change adaptationBiogenic StimulatorsPesticide
A below-ground agricultural biological performance modeling approach in precision agriculture combines customized field modeling with machine learning techniques for environmental matching of variables to describe a below-surface soil state, to understand and predict the performance of soil-active agricultural biological products such as bio-pesticides, bio-stimulants, plant growth regulators, and other biologically-derives soil adjuvants. The modeling approach characterizes the influence of environmental relationships on the performance of such soil-active agricultural biological products to develop a suite of predictive models to provide notifications, advisories, and recommendations for appropriate products for individual fields.
Owner:DTN LLC
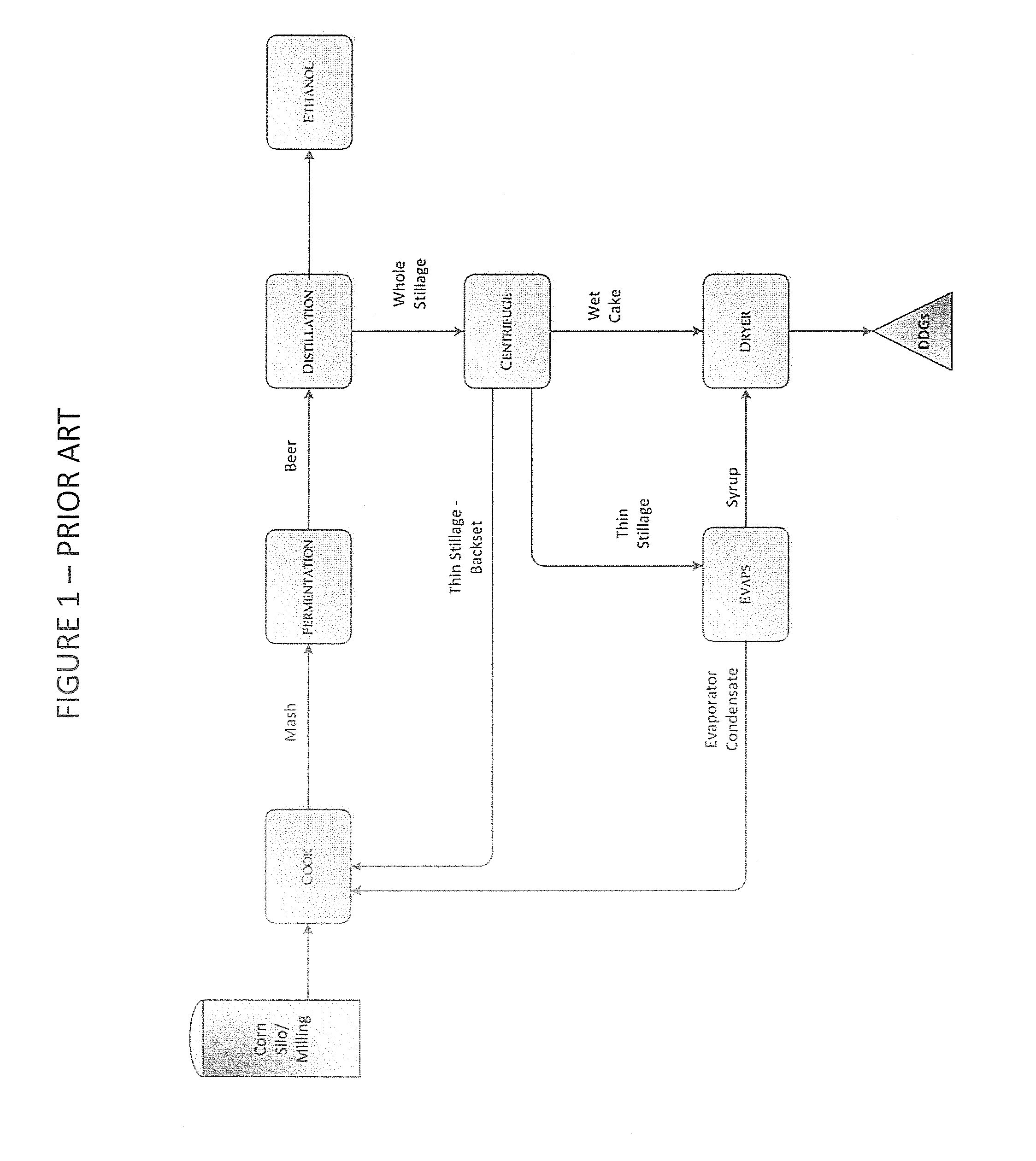
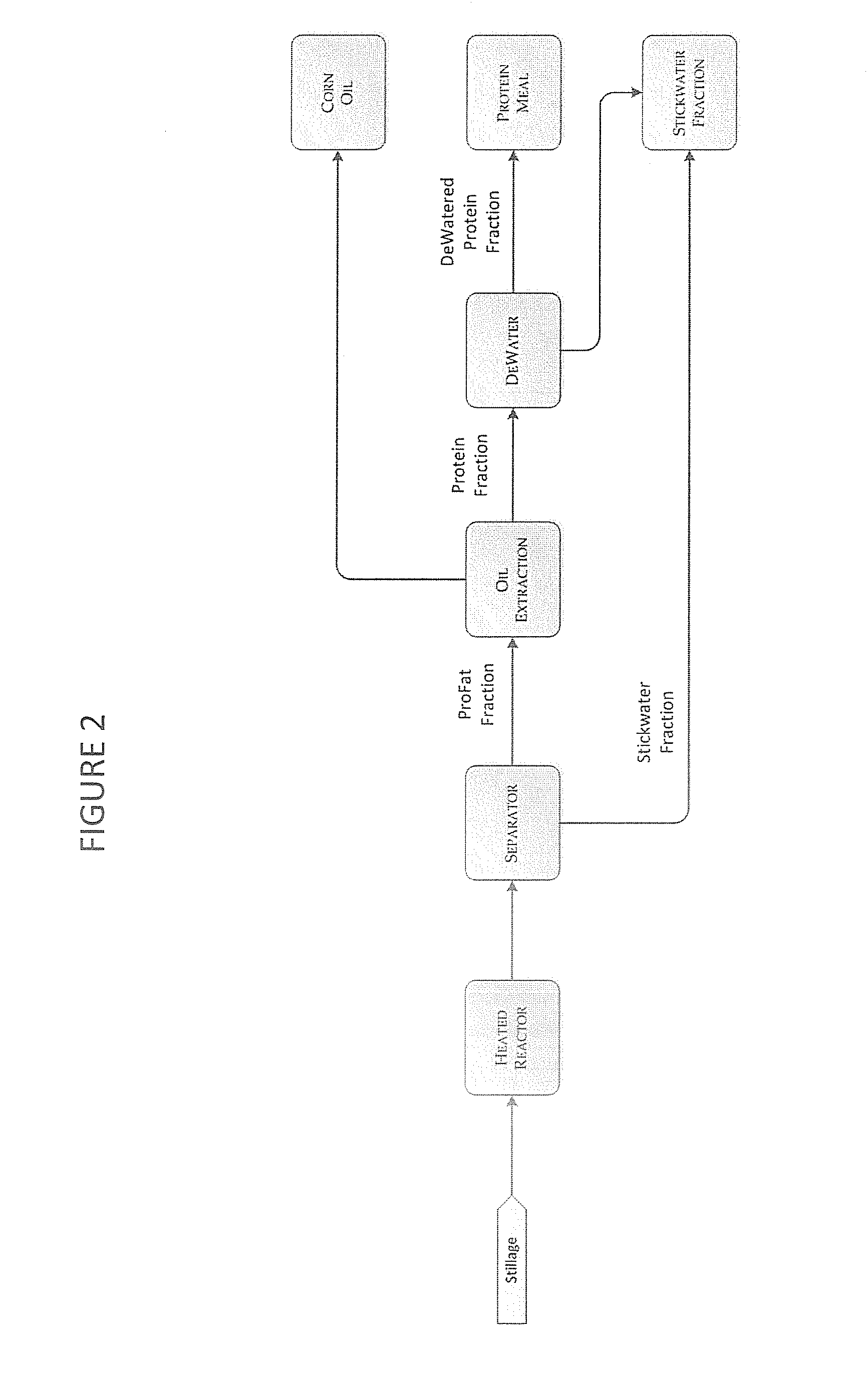
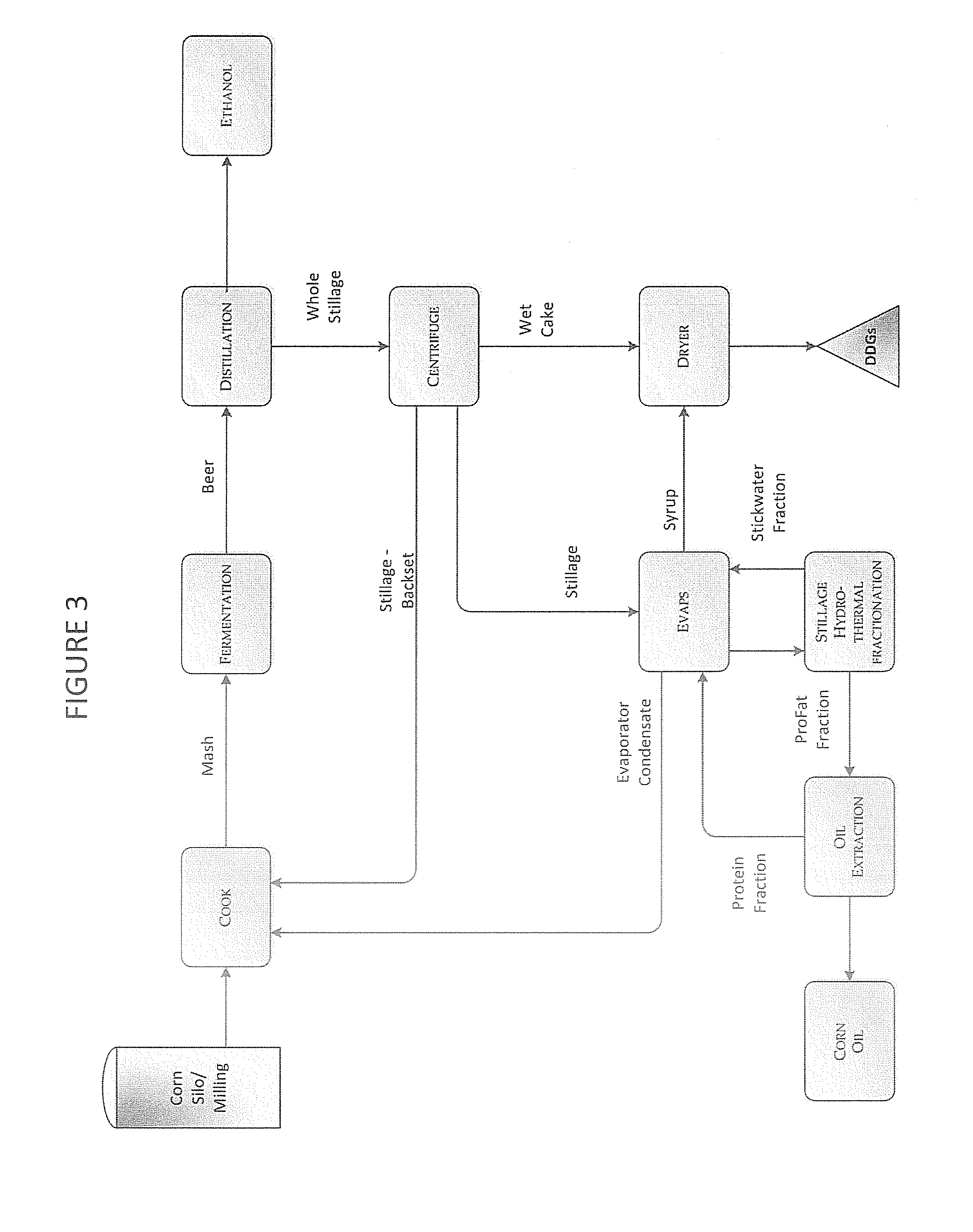
Process and method for improving the water reuse, energy efficiency, fermentation, and products of an ethanol fermentation plant
InactiveUS20130344554A1Increase heightGood coagulationFermented solutions distillation/rectificationOther chemical processesMetaboliteBio products
A method of processing stillage by hydrothermally fractionating stillage to create unique product fractions, by heating the stillage to a temperature of 250 degrees F. to 350 degrees F., and recovering a stickwater fraction from the stillage. Stickwater, oil, biomass, bio-products, extracts, metabolites, and treated water obtained from the method above. A method of performing ethanol fermentation by hydrothermally fractionating stillage to create unique product fractions by heating the stillage to a temperature of 250 degrees F. to 350 degrees F., separating the stillage into a ProFat fraction and a stickwater fraction, and recovering oil from the ProFat fraction.
Owner:TRUCENT INC
Affinity foam fractionation for collection and purification of materials
Owner:THE UNIVERSITY OF AKRON
Recombinant anaerobic acetogenic bacteria for production of isoprene and/or industrial bio-products using synthesis gas
This invention provides for recombinant anaerobic acetogenic bacterial cells having one or more nucleic acids whereby isoprene, mevalonate and / or other industrial bio-products are produced in a substantially oxygen-free culture condition using synthesis gas as energy and / or carbon source.
Owner:DANISCO US INC
Method for in-situ preparation of modified hydroxyapatite/polyvinyl alcohol nano-composite film
InactiveCN106178127AGood dispersionHigh adsorption selectivityMonocomponent synthetic polymer artificial filamentNon-woven fabricsComposite filmPolyvinyl alcohol
The invention relates to a method for in-situ preparation of a modified hydroxyapatite / polyvinyl alcohol nano-composite film. The method comprises the following steps: dropping a doped calcium nitrate solution to a polyvinyl alcohol water solution under a stirring condition, and then dropping a diammonium hydrogen phosphate solution and stirring at 40-70 DEG C for 12-24h, so that the in-situ generation of a doped modified hydroxyapatite / polyvinyl alcohol solution is achieved, wherein a calcium-phosphorus ratio is at 1.67; and then adding maleic anhydride and a catalyst, conducting stirring for 4-6h, so that a mixed solution is obtained, conducting electrostatic spinning, and drying an obtained film, so that the in-situ preparation of the modified hydroxyapatite / polyvinyl alcohol nano-composite film is achieved. The method disclosed by the invention is simple to operate; the interior of the film, which is prepared through in-situ cross-linking of the doped modified hydroxyapatite which is obtained from in-situ generation, has good dispersibility and stability, and meanwhile, the film has good biocompatibility; and the film, which can be used for separating and adsorbing a plurality of proteins, bio-enzymes as well as other bio-products, has a good adsorptive selectivity on the separation of the various proteins.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Oxygen assisted organosolv process, system and method for delignification of lignocellulosic materials and lignin recovery
An oxygen assisted Organosolv process for a more efficient delignification and producing bio-products by decomposing lignocellulosic materials comprises providing a lignin solvent with water, an acid, an oxidant and one or more lignin dissolving chemicals. The process also includes placing biomass in contact with oxidant, acid, water, the lignin solvent in any order or combined to form a recyclable solvent, and recycling at least a portion of the recyclable solvent by circulating the recyclable solvent back into contact with the biomass. The circulating of the recyclable solvent occurs for a period of time, during which, acid and oxidant may be added if necessary as they may be consumed by the process, after which, the process then includes separating material such as chemicals and lignin from the recyclable solvent. The chemicals can be recycled as new lignin dissolving solvent or sold, while lignin can be used as natural and renewable colorant for polymers such as poly lactic acid, or mixed with other polymers as an additive and extruded or injected to consumable polymeric parts, or can be used and the natural source of renewable aromatics. Application of an oxidant will help the overall fractionation process by changing the chemical characteristics of the lignin and therefore allows more lignin to be removed from biomass. At the end, the lignin is separated from the lignin dissolving solvent by a separation process to also reclaim the lignin dissolving solvent for the next fractionation process.
Owner:AMERICAN SCI & TECH CORP
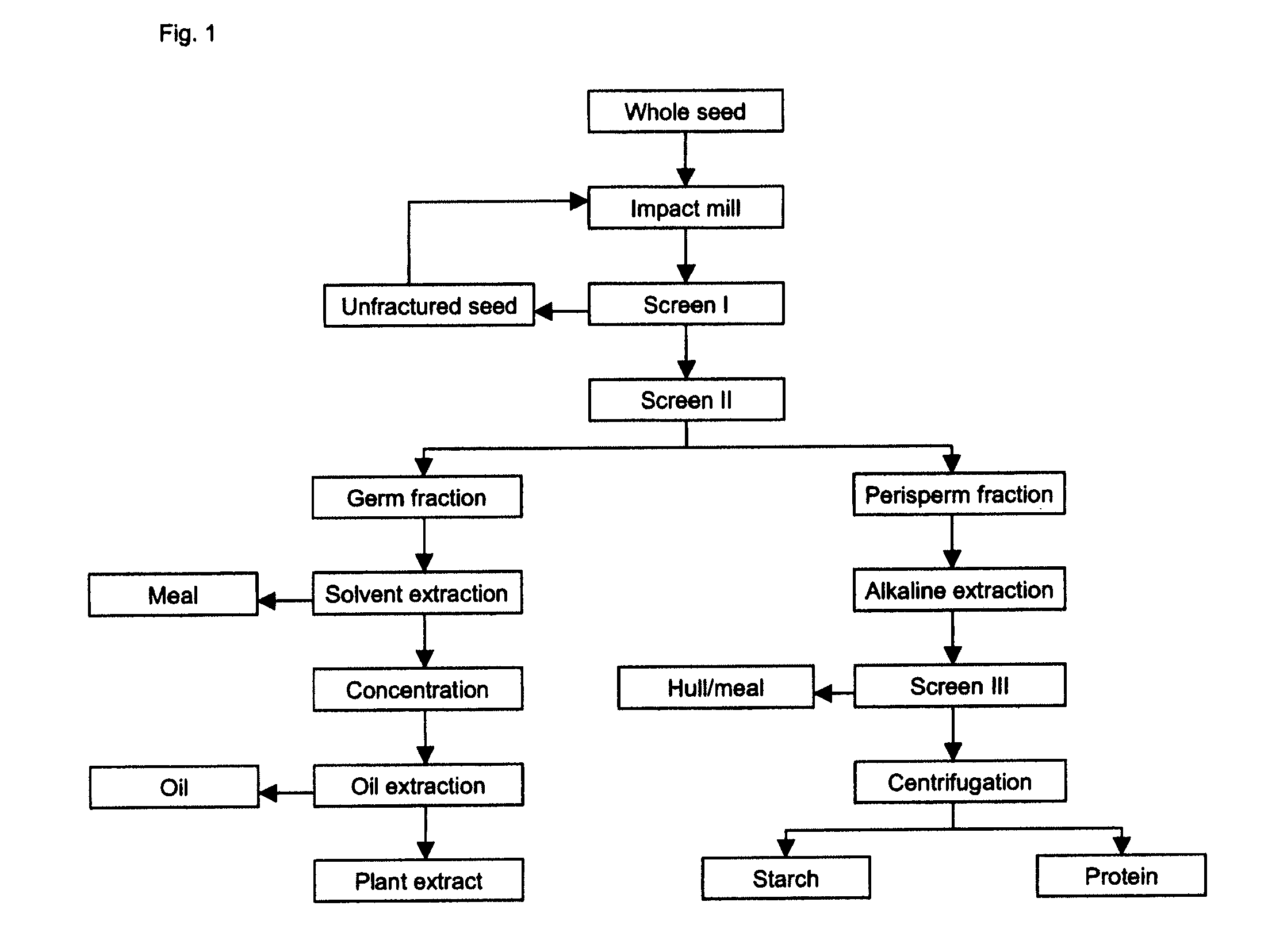
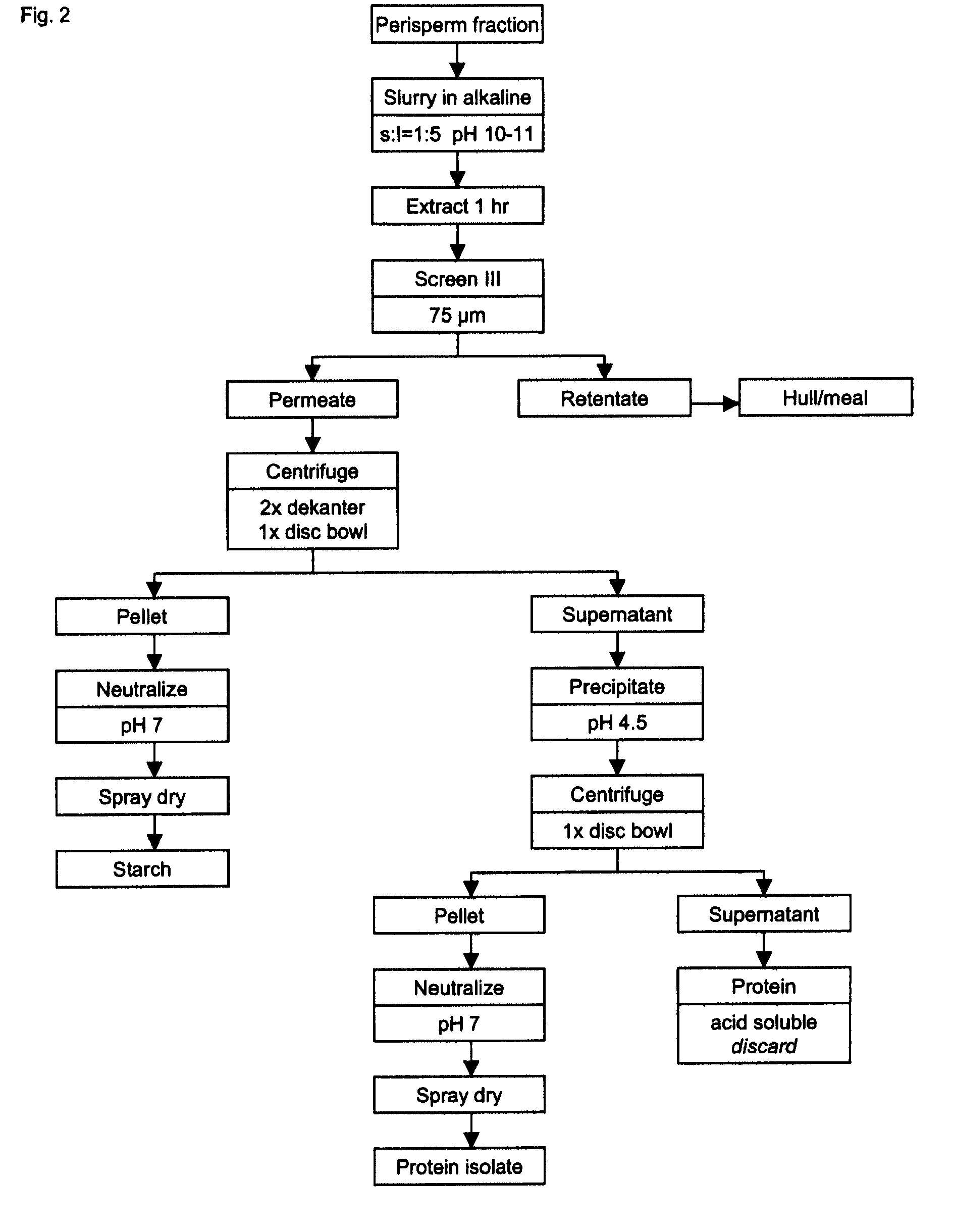
Process for seed and grain fractionation and recovery of bio-products
InactiveUS20090186136A1Reduce processing timeCommercial viability enhancedProtein composition from vegetable seedsFood preparationFractionationBio products
The present invention describes the fractionation and processing of seed of Saponaria vaccaria L, a species that can be grown on a large scale using conventional agricultural practices. The main products recovered are an extremely fine starch (0.5-1.5 μm) and a plant extract comprising saponins, cyclopeptides and phenolic compounds.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
Swine testicular cell strain ST-S suitable for suspension culture as well as acquisition method and application of swine testicular cell strain ST-S
Owner:JINYUBAOLING BIO PHARMA CO LTD +1
Method for preparing sapogenin through chenopodium quinoa willdL seed coat and separation and quantification method of sapogenin
InactiveCN109810163AIncrease profitImprove economyComponent separationSteroidsHydrolysateEvaporation
The invention provides a method for preparing sapogenin through chenopodium quinoa willdL seed coat and a separation and quantification method of the sapogenin, and belongs to the technical field of biological product processing. The method for preparing the sapogenin through the chenopodium quinoa willdL seed coat comprises the following steps that firstly, the chenopodium quinoa willdL seed coat, complex enzyme and deionized water are mixed and enzymolyzed to obtain enzymatic hydrolysate; then the enzymatic hydrolysate and ethyl alcohol are mixed, chenopodium quinoa willdL saponin in the enzymatic hydrolysate is extracted through ultrasonic waves, solid-liquid separation is conducted, and a chenopodium quinoa willdL saponin extracting solution is obtained; then the chenopodium quinoa willdL saponin extracting solution and hydrochloric acid are mixed and subjected to acidolysis to obtain acidolysis liquid; and finally, the acidolysis liquid is extracted through petroleum ether to obtain extract liquor, and a solvent in the extract liquor is removed through evaporation, and the sapogenin is obtained. According to the method, the chenopodium quinoa willdL seed coat serves as a raw material to prepare the sapogenin, the natural sapogenin raw material can be provided for a professional pharmaceutical factory, the comprehensive utilization rate and the economic added value of chenopodium quinoa willdL can further be increased, and reuse and sustainable development of resources are facilitated. The invention further provides a method for simultaneous separation and quantification of oleanolic acid and hederagenin in the chenopodium quinoa willdL seed coat through UPLC-MS.
Owner:QINGHAI NORMAL UNIV
Modeling and prediction of below-ground performance of agricultural biological products in precision agriculture
A below-ground agricultural biological performance modeling approach in precision agriculture combines customized field modeling with machine learning techniques for environmental matching of variables to describe a below-surface soil state, to understand and predict the performance of soil-active agricultural biological products such as bio-pesticides, bio-stimulants, plant growth regulators, and other biologically-derives soil adjuvants. The modeling approach characterizes the influence of environmental relationships on the performance of such soil-active agricultural biological products to develop a suite of predictive models to provide notifications, advisories, and recommendations for appropriate products for individual fields.
Owner:DTN LLC
Method for the manufacture of bio-products with a modified sugar profile
ActiveUS9689011B2Low costHydrolasesProtein composition from vegetable seedsContinuous mixingBio products
The invention relates to a method for the production of a solid bio-product wherein at least 80% of the original indigestible oligosaccharide (raffinose, stachyose and verbascose) content has been degraded into digestible mono- and disaccharides, comprising the following steps: 1) providing a mixture of milled or flaked or otherwise disintegrated biomass, comprising oligosaccharides and optionally polysaccharides and further comprising proteinaceous plant parts, water and one or more enzyme preparations containing α-galactosidase(s); 2) reacting the mixture resulting from step (1) under continuous mixing and under conditions where the water content in the initial mixture does not exceed 65% by weight, for 0.15-36 hours at a temperature of about 20-65° C.; 3) incubating the reacted mixture from step (2) at a temperature and in a time period which inactivate said α-galactosidase(s), as well as solid bio-products obtainable by such method. The invention further relates to uses of the bio-product and a food, a feed, a cosmetic or pharmaceutical product or a nutritional supplement containing the solid bio-product.
Owner:HAMLET PROTEIN AS
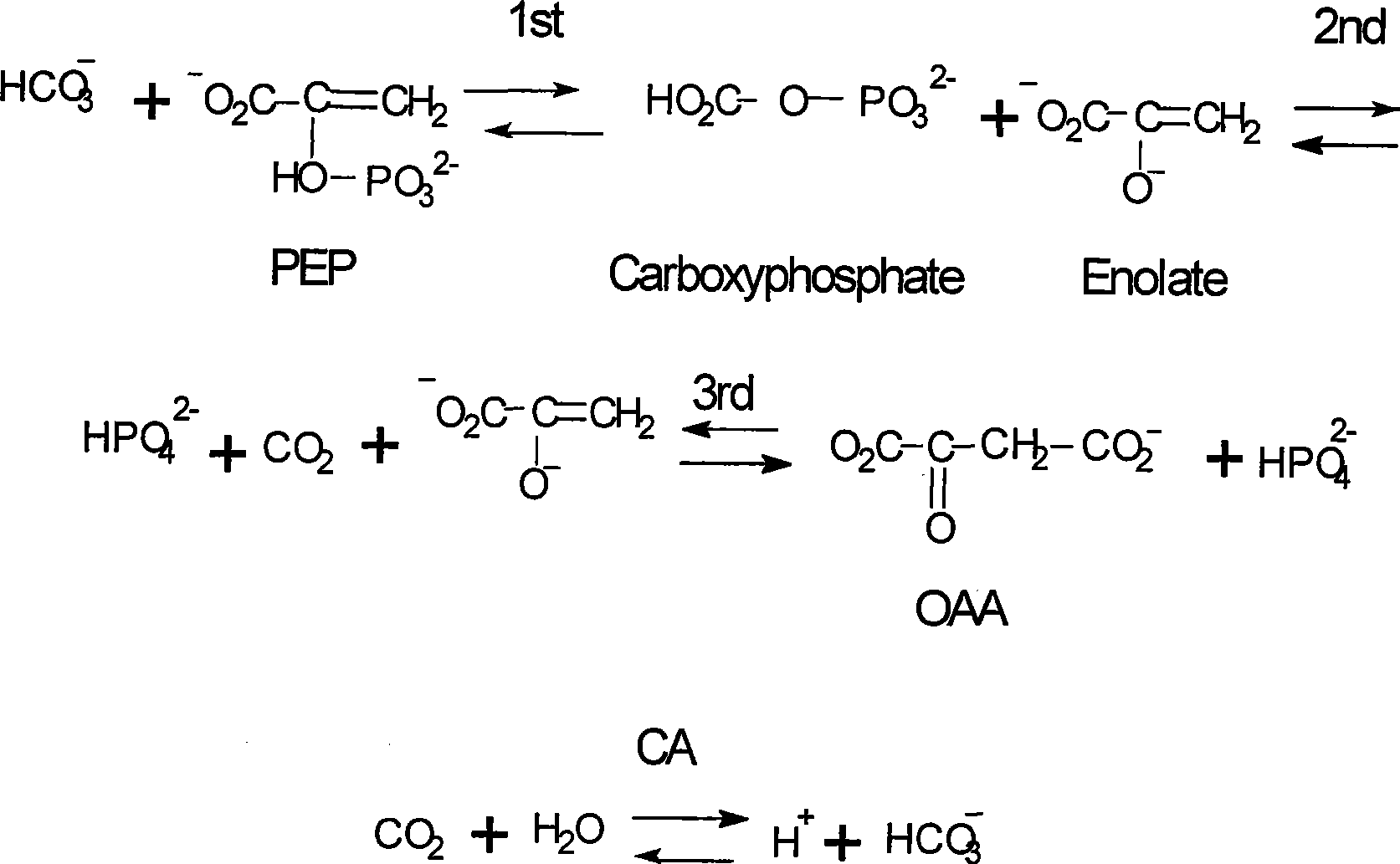
Integrated process for dual biocatalytic conversion of co2 gas into bio-products by enzyme enhanced hydration and biological culture
InactiveUS20150024453A1Improve scalabilityImprove processing efficiencyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsHydration reactionPower station
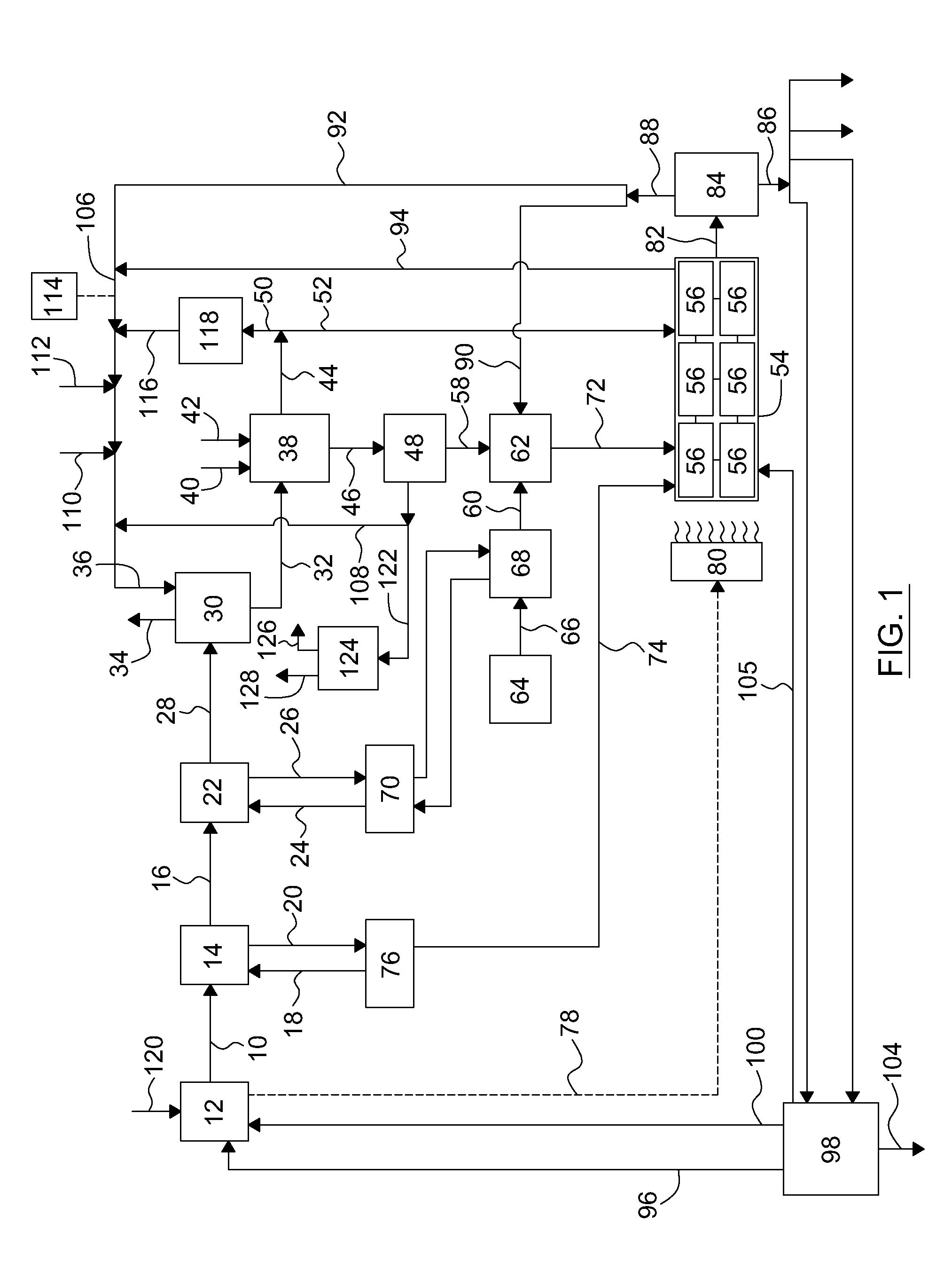
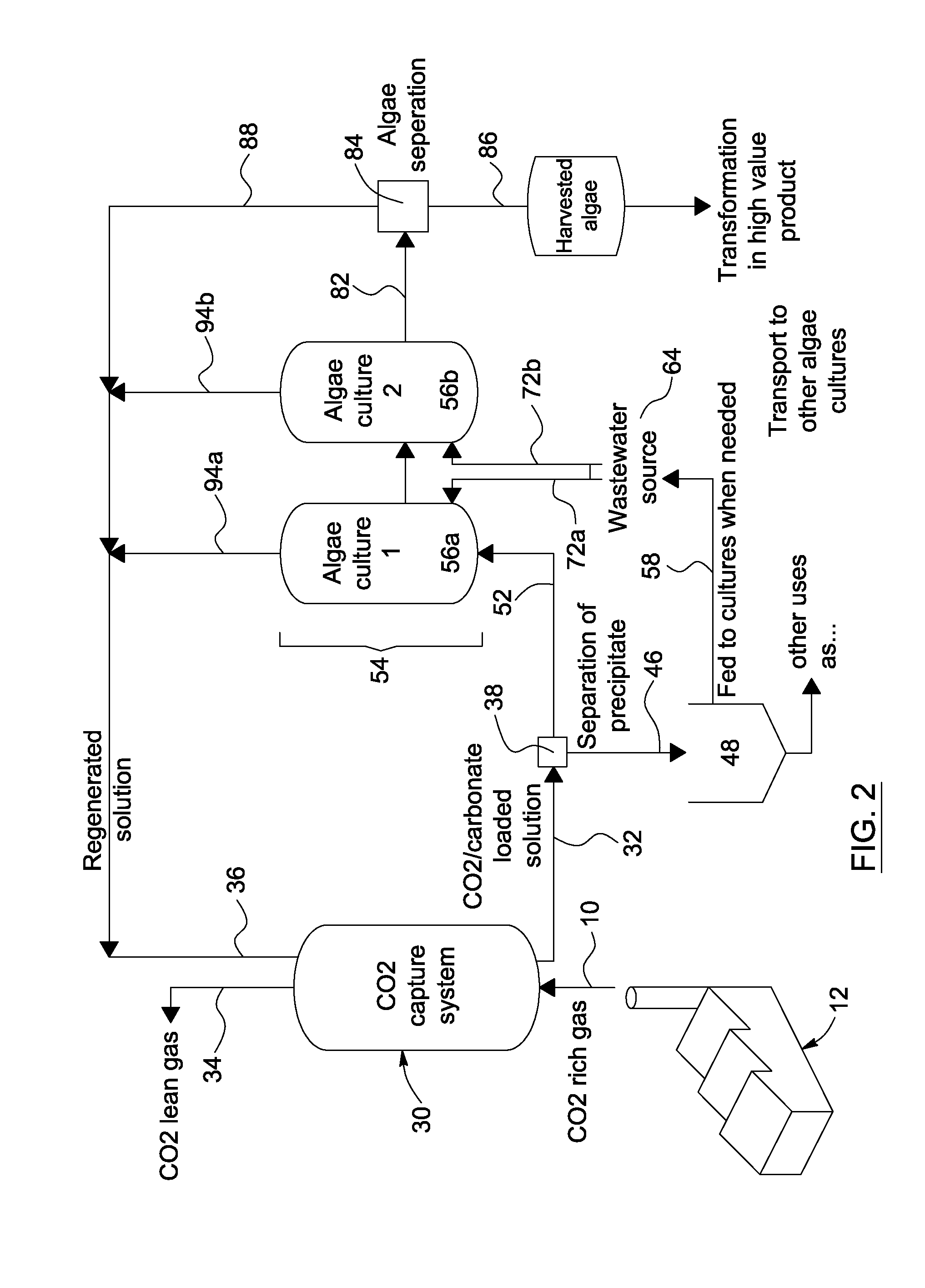
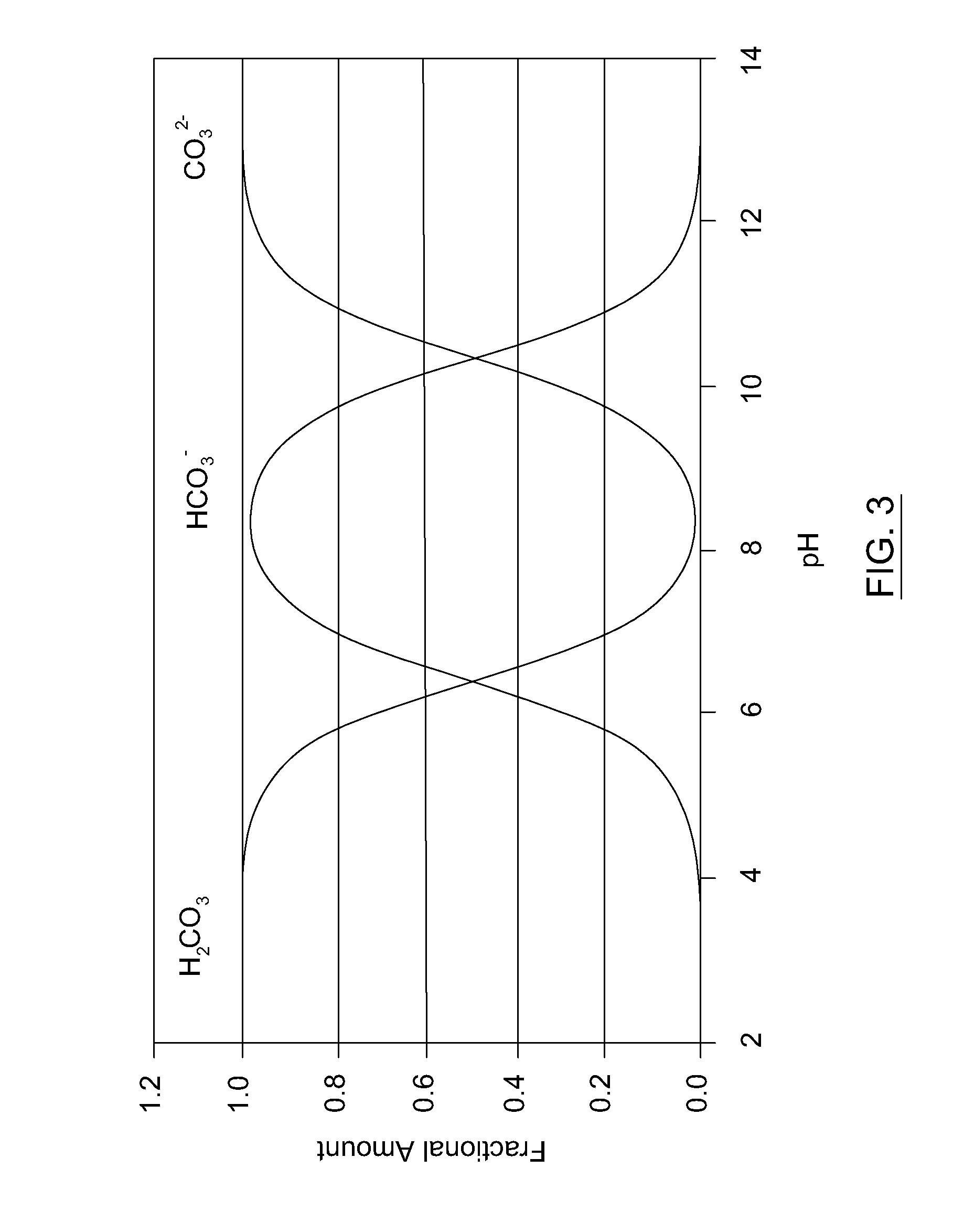
A method, process, apparatus, use and formulation for dual biocatalytic conversion of CO2 containing gas into carbon containing bio-products by enzymatic hydration of CO2 into bicarbonate ions in the presence of carbonic anhydrase and metabolic conversion of the bicarbonate ions into carbon containing bio-products in a biological culture. The dual biocatalytic conversion may be relatively constant with controlling a feeding of the bicarbonate ions to the biological culture in accordance with demands of the biological culture by retaining over-production of bicarbonate ions and feeding part of the over-production to the biological culture in accordance with nutrient demands of the biological culture. Bicarbonate ions may also be reconverted to generate a pure CO2 gas stream. The CO2 containing gas may be derived from operations of a power plant which receives a carbon-containing fuel for combustion, and the biological culture may be an algae culture.
Owner:CO2 SOLUTION
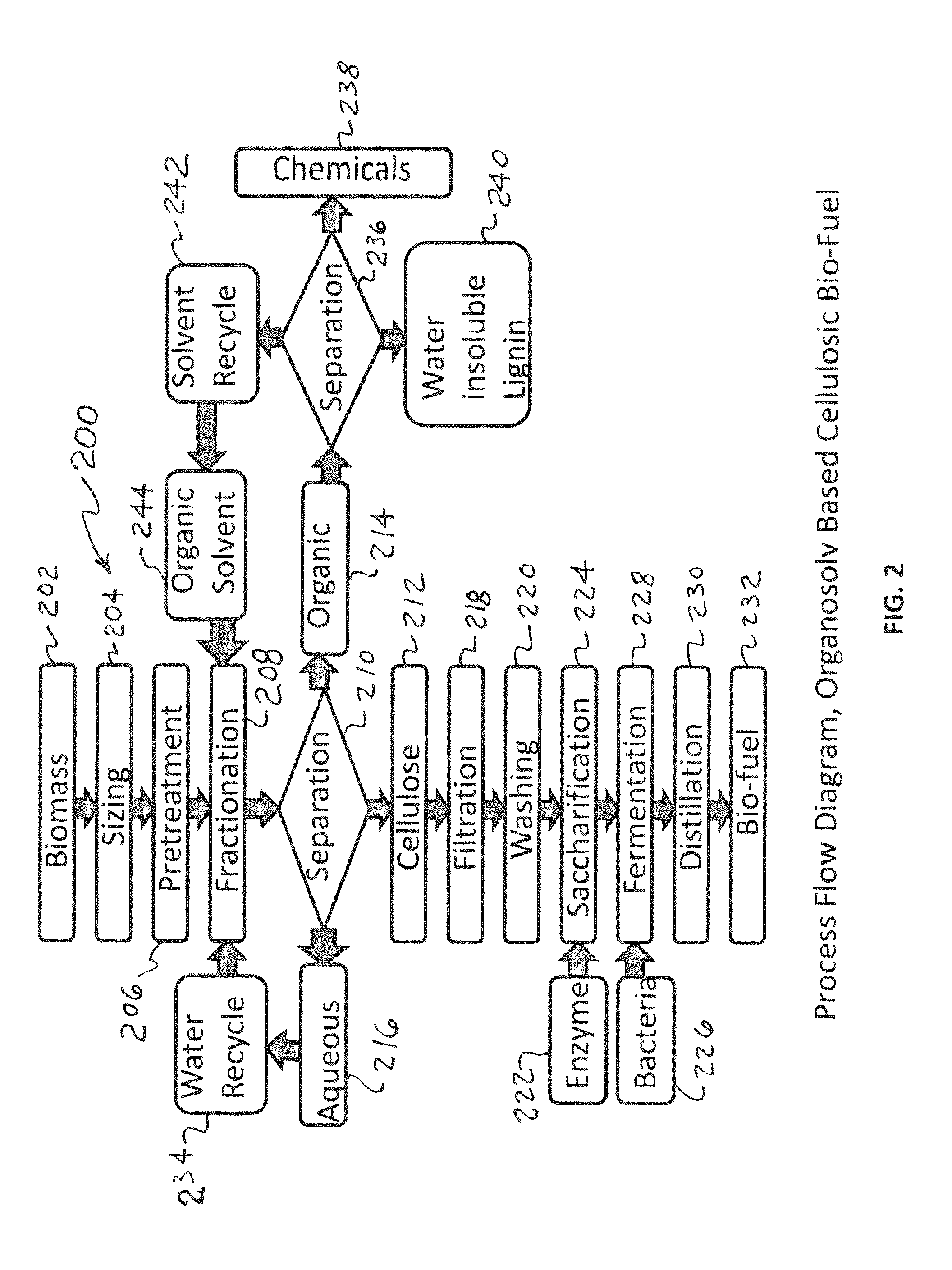
Biorefining Method
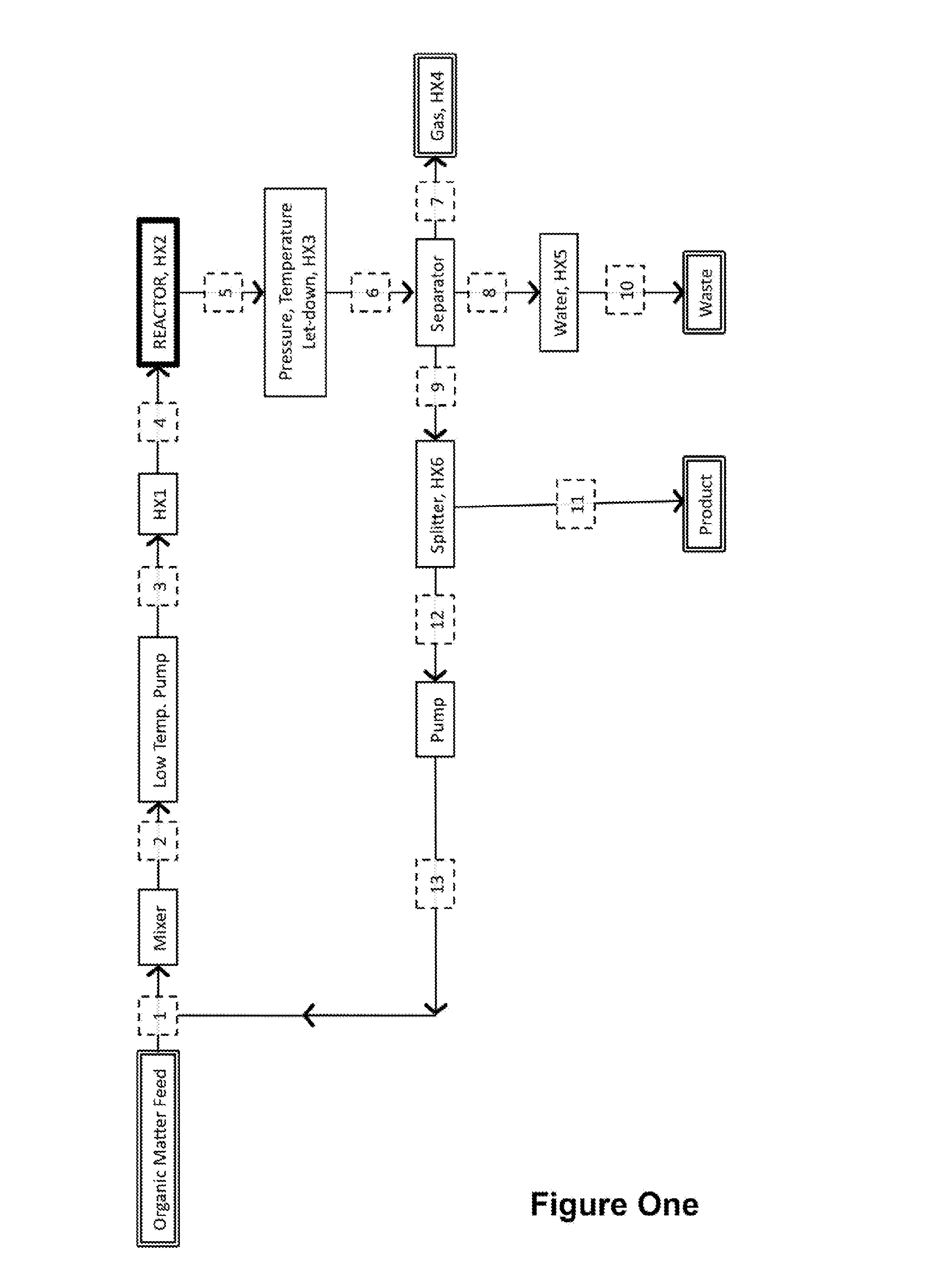
ActiveUS20160114307A1Reduce problem sizeReduces development of pressureProcess control/regulationOther chemical processesBio productsBiorefining
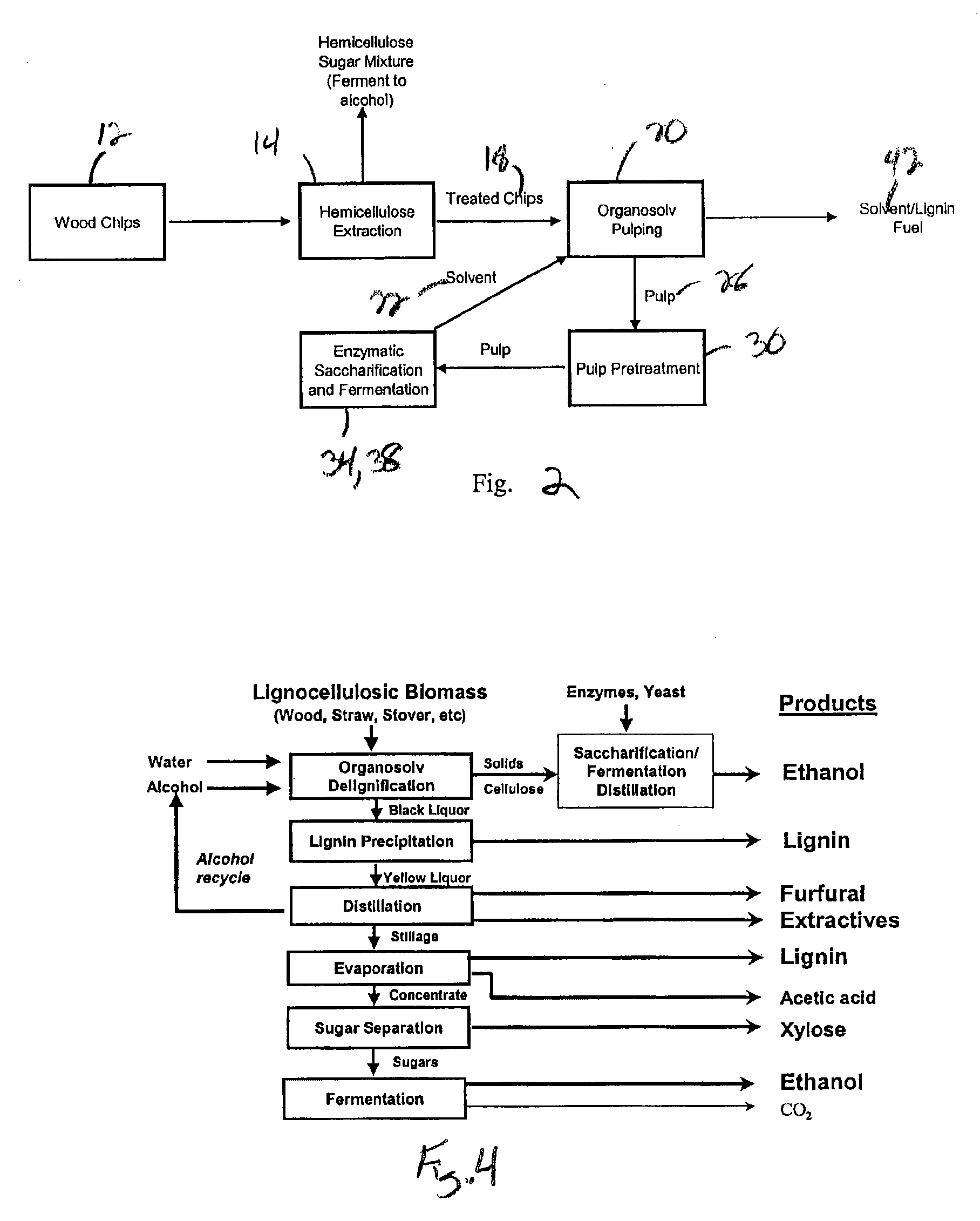
The present invention relates generally to the generation of bio-products from organic matter feedstocks. More specifically, the present invention relates to improved methods for the hydrothermal / thermochemical conversion of lignocellulosic and / or fossilised organic feedstocks into biofuels (e.g. bio-oils) and / or chemical products (e.g. platform chemicals).
Owner:LICELLA PTY LTD +2
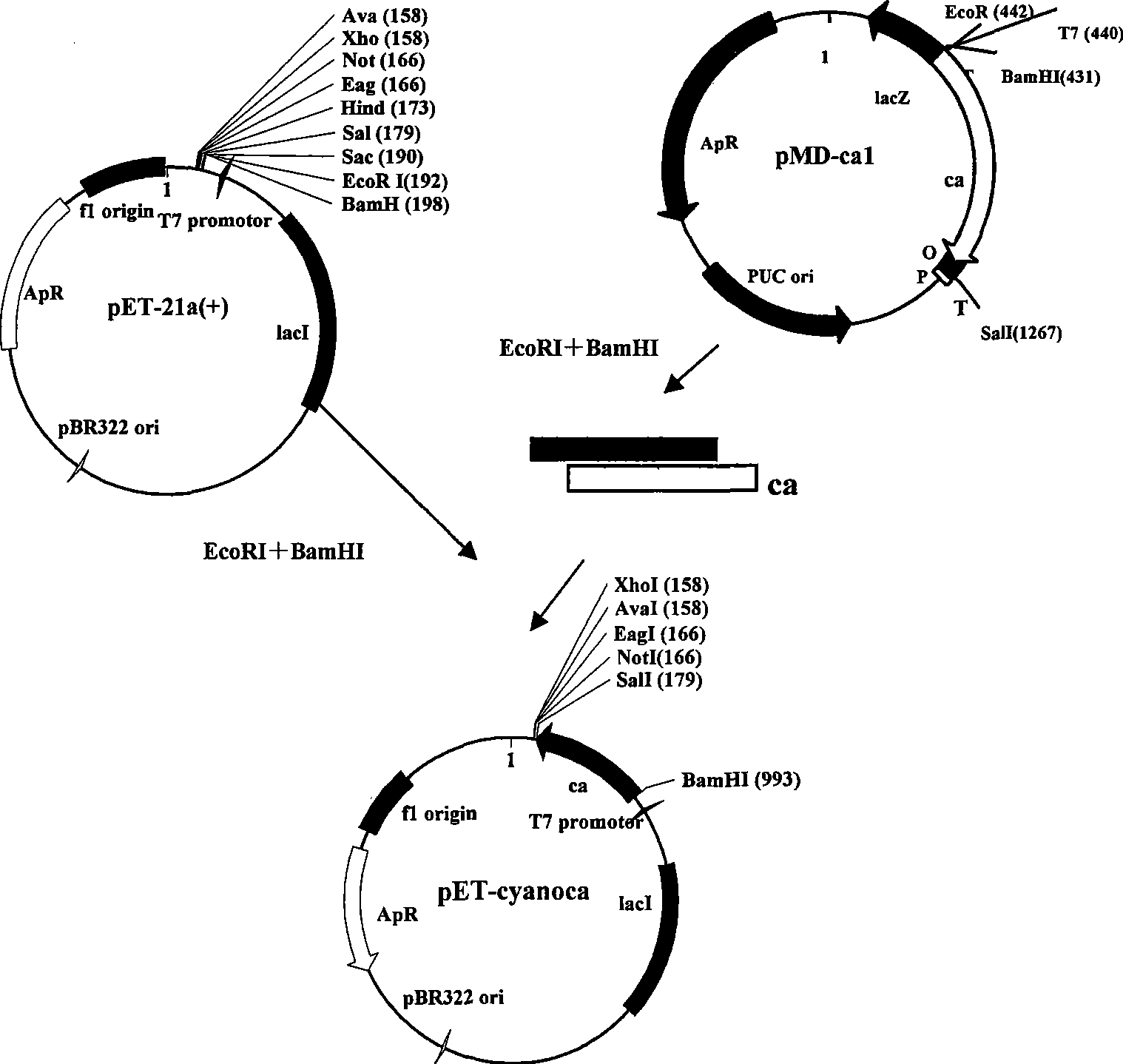
Recombinant plasmid and genetic engineering bacteria for producing succinic acid, production method and use thereof
The invention discloses a recombinant plasmid for producing succinic acid and a succinic acid high-yield genetic engineering bacterium. The invention also discloses a method for preparing the recombinant plasmid and the genetic engineering bacterium. The invention simultaneously discloses application of the recombinant plasmid and the genetic engineering bacterium to the preparation of biological products for fermentation production of the succinic acid in the genetic engineering. The genetic engineering bacterium which is established by the recombinant plasmid has high stability, and improves the growth rate compared with the original strain BL21 (DE3); and the yield of the succinic acid is greatly improved under the condition of addition of revulsant with different concentrations, namely lactose or IPTG and two-stage fermentation of completely anaerobic or aerobic accumulation of biomasses and oxygen-free acid fermentation.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Harvesting and purification or perfusion yielder (HAPPY) device
InactiveUS20160083685A1Easy to useHigh cell density cultureBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsPorous substrateBiochemistry
A modular device comprising one or more porous substrate subunits comprising a binding substrate that is capable of interacting with a target biological product, either during, or at the end of a manufacturing cycle; and methods of using the device to harvest or purify a biological product.
Owner:NIAZI SARFARAZ K
Sugar cane stem specific expression promoter and plant expression vector thereof
InactiveCN101280312AHigh priming activityFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionBioproductsBiological product
The invention relates to a special and high-effective expression promoter of a sugar cane stem and an expression vector of a plant, a PCR method is enlarged after the total DNA is extracted from sugar cane, and then the expression vector is connected with a pMD-18T vector, the cell of bacillus coli DH5Alpha is transformed, through selecting the masculine, the promoter of the sugar cane hexose transportation protein gene PST2(Alpha) is cloned and obtained, the length of the promoter is 1968bp, through replacing the composition CaMV35S promoter on the expression vector pCAMBIA1301 of the plant, a new expression vector of the plant is constructed, and the name is pCAMBIA1900. By obtaining the promoter, an effective tool is provided for the research of the sugar cane trans-gene and the sugar cane molecular in the biology, and the essential condition of the research and the development of the biological product with high additional archery is particularly created for adopting the sugar cane as the bioreactor production. Therefore, the obtaining of the promoter has an important theoretical and practice significance.
Owner:INST OF TROPICAL BIOSCI & BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF TROPICAL AGRI SCI
Plant waste bio-product pomace extract concentrates and processes of producing same
A processes is provide herein for converting waste bio-product pomace to useful bio-product extracts. The process includes the steps of forming a mixture of water as a solvent and a specified quantity of the waste bio-product pomace. Then optionally adding a suitable quantity of citric acid to the water / waste bio-product mixture. Then heating waste bio-product pomace / water mixture to an elevated temperature below the boiling point of water. Then optionally adding a suitable quantity of sodium metabisulfite to the heated waste bio-product pomace / water mixture Then stirring heated waste bio-product pomace / water mixture for a suitable time to disperse the waste bio-product uniformly in the water solvent. Then cooling the stirred, heated waste bio-product pomace / water mixture to a suitable lower temperature at a rate of about 60° C. per hour. Then removing solids from the stirred waste bio-product pomace / water mixture. Then clarifying the cooled stirred water / waste bio-product mixture. Then concentrating the clarifying cooled stirred waste bio-product pomace / water mixture under the influence of a suitable vacuum and at a suitable increased temperature until the concentrate has a BRIX of about 20 to about 22. This provides a concentrated useful bio-product comprising antioxidant-enriched liquids comprised of the natural elements extracted from said waste bio-products.
Owner:DALHOUSIE UNIV
Lignin-solvent fuel and method and apparatus for making same
ActiveUS8211189B2Reduce needSimple gravityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBiodieselHigh energy
The present invention is a process and apparatus for forming various bio-products from cellulosic plant material. The plant material is subjected to a pulping step in which lignin is extracted from the material by an aqueous lignin solvent to form a lignin-solvent mixture and purified cellulose. The lignin-solvent mixture can be separated from the water to form a high energy density fuel that can be used independently or combined with biodiesel. The purified cellulose can be used in conventional processes, e.g., paper making, or can be converted to fermentable sugars with a cellulase enzyme to produce other bio-products depending on the operating conditions of the fermenter. The bio-products produced by the fermenter can include the solvent that may be recycled for use in extracting the lignin.
Owner:WISYS TECH FOUND
Centrifugal separating assembly for positioning a layer of a fluid biological product at a selected location
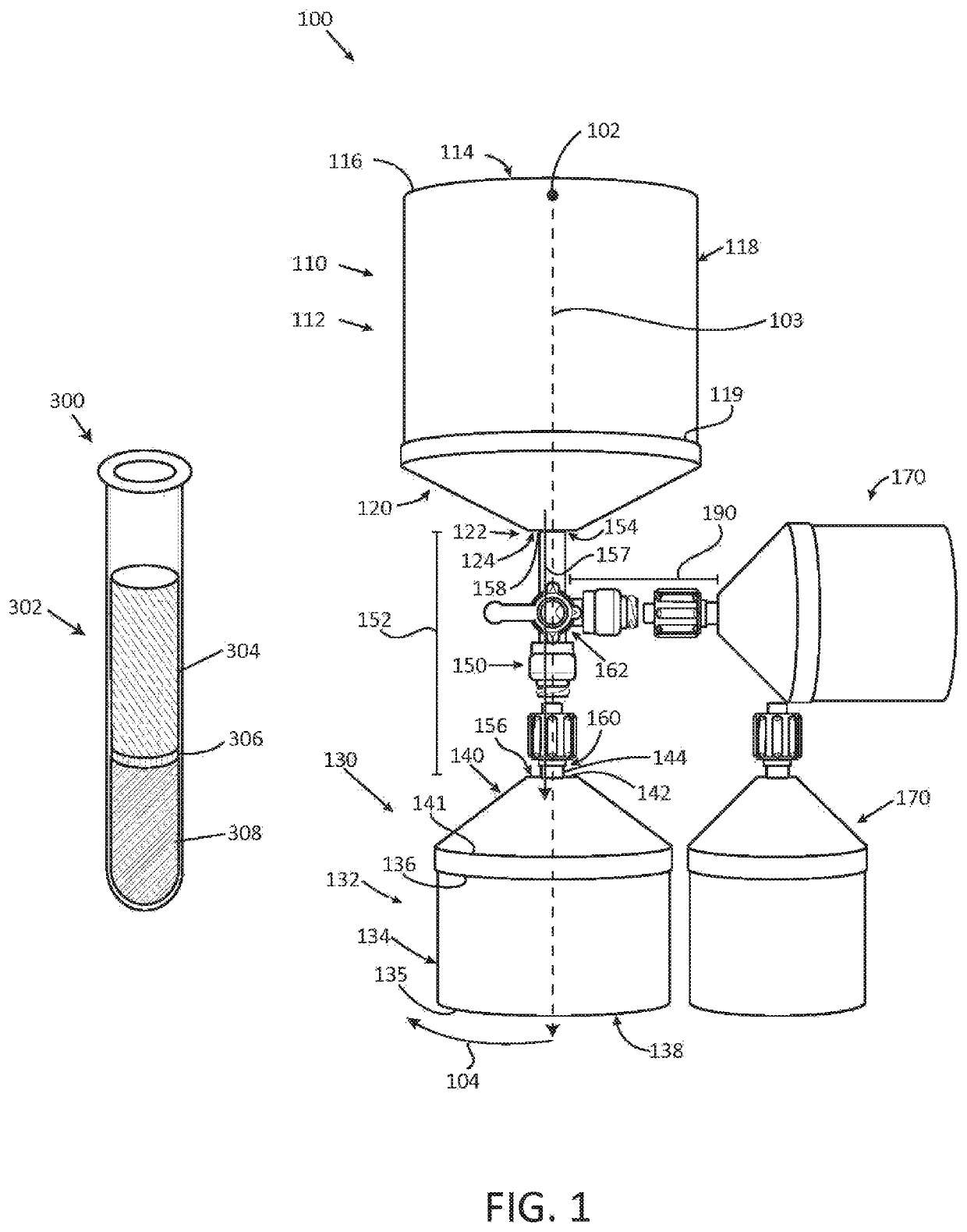
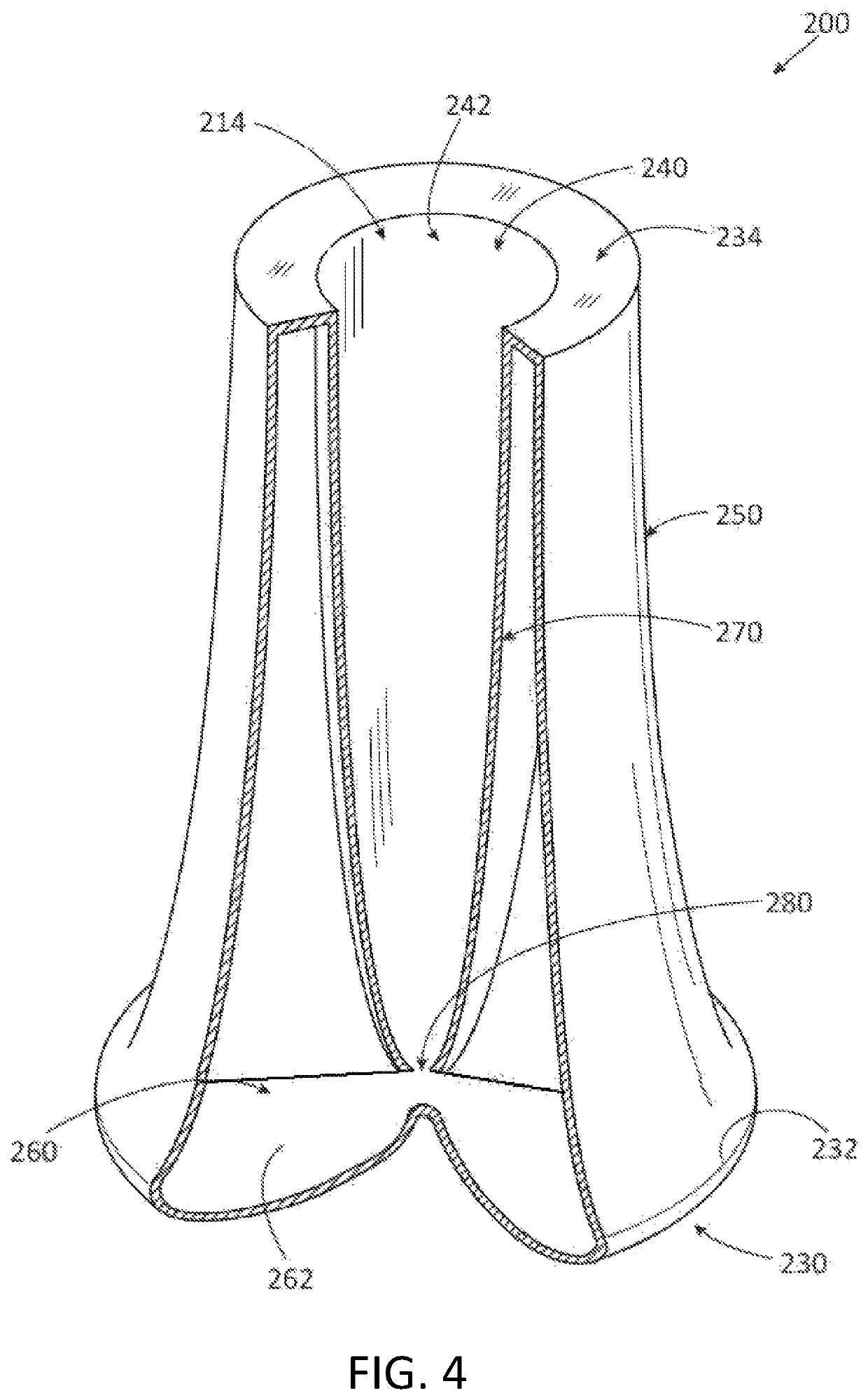
ActiveUS10561783B2Other blood circulation devicesLaboratory glasswaresCentrifugationStructural engineering
A centrifugal separating assembly for separating a fluid biological product into discrete components by centrifugation is disclosed. The assembly includes a first container defining a first cavity adapted to receive a human biological product, the first container having a circular upper wall, a cylindrical sidewall, and a concave shaped bottom wall. The assembly further includes a second container defining a second cavity adapted to receive discrete components. The first container is positioned within the second container, and moveable to a selected position within the second container so that a layer of a fluid biological product will be at a desired location after centrifugation.
Owner:HAMANDI ZIAD +1
Compositions and Methods for Reducing Pesticide-Induced Plant Damage and Improving Plant Yield
PendingUS20220015371A1Reduce the amount requiredGood for healthBiocideBacteriaBiotechnologyMicroorganism
Agricultural management products and method, particularly plant, seed, and soil treatment products and methods of manufacturing and using the same. Compositions and methods for reducing chemical pesticide-induced plant damage and / or improving plant yield, including combinatorial compositions and methods for treating plants, seed, and soil. Plant treatment products include a plant treatment component and, preferably mixed with, a microbial fermentation product. The microbial fermentation product includes cellular material of cultured microorganisms and one or more anaerobic metabolite products of the cultured microorganisms Preferably, the microbial fermentation product comprises a whole culture lysate of a microbial fermentation suspension culture, including liquid fermentation culture medium components and lysed microorganisms. The plant treatment component of the product includes one or more pesticides or plant growth regulators. Plant treatment products can be applied to or around plants or seeds to enhance growth, health, or productivity of the plants.
Owner:CYTOZYME LABORATORIES INC
Method for preparing carbon nano-tubes by using biological product as catalyst precursor
InactiveCN101891183AHigh yieldHigh purityNanostructure manufactureChemical industryGas phaseHydrogen-Ion Concentrations
The invention relates to a method for preparing carbon nano-tubes by using a biological product as a catalyst precursor. The method comprises the following steps of: dewatering and drying the biological product, grinding the dried biological product for 10 to 40 minutes, putting the ground biological product into a chemical vapor deposition furnace, raising the temperature to 800 to 1,100 DEG C within 4 to 6 hours under the protection of argon, introducing the argon and natural gas into the chemical vapor deposition furnace in a volume ratio of 6-10:1, controlling the flow rates of the gases to be between 70 and 160 milliliters / minute, performing reaction for 30 to 60 minutes at the temperature of between 800 and 1,100 DEG C and cooling the reaction product to room temperature under the protection of the argon so as to obtain black powder; and reacting the black powder with acid solution of which the hydrogen ion concentration is between 2 and 6 mol / liter for 20 to 40 minutes and cleaning the reaction product with distilled water until the reaction product is neutral so as to obtain the carbon nano-tubes. The method can greatly reduce preparation cost, has high process safety and is an environmental-friendly, low-carbon and energy-saving production process; and the yield of and the purity of the prepared carbon nano-tubes are high.
Owner:SHANXI DATONG UNIV
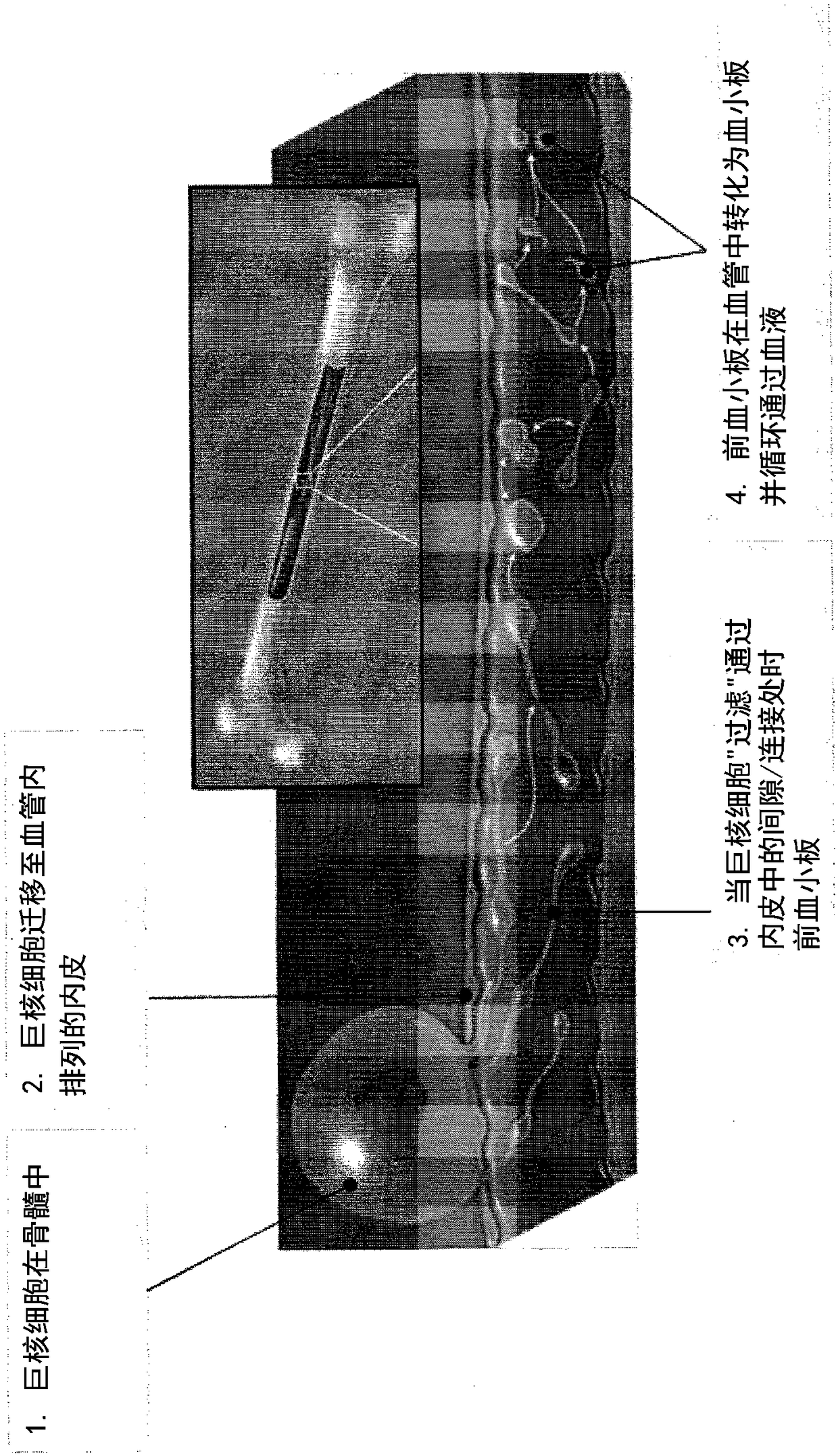
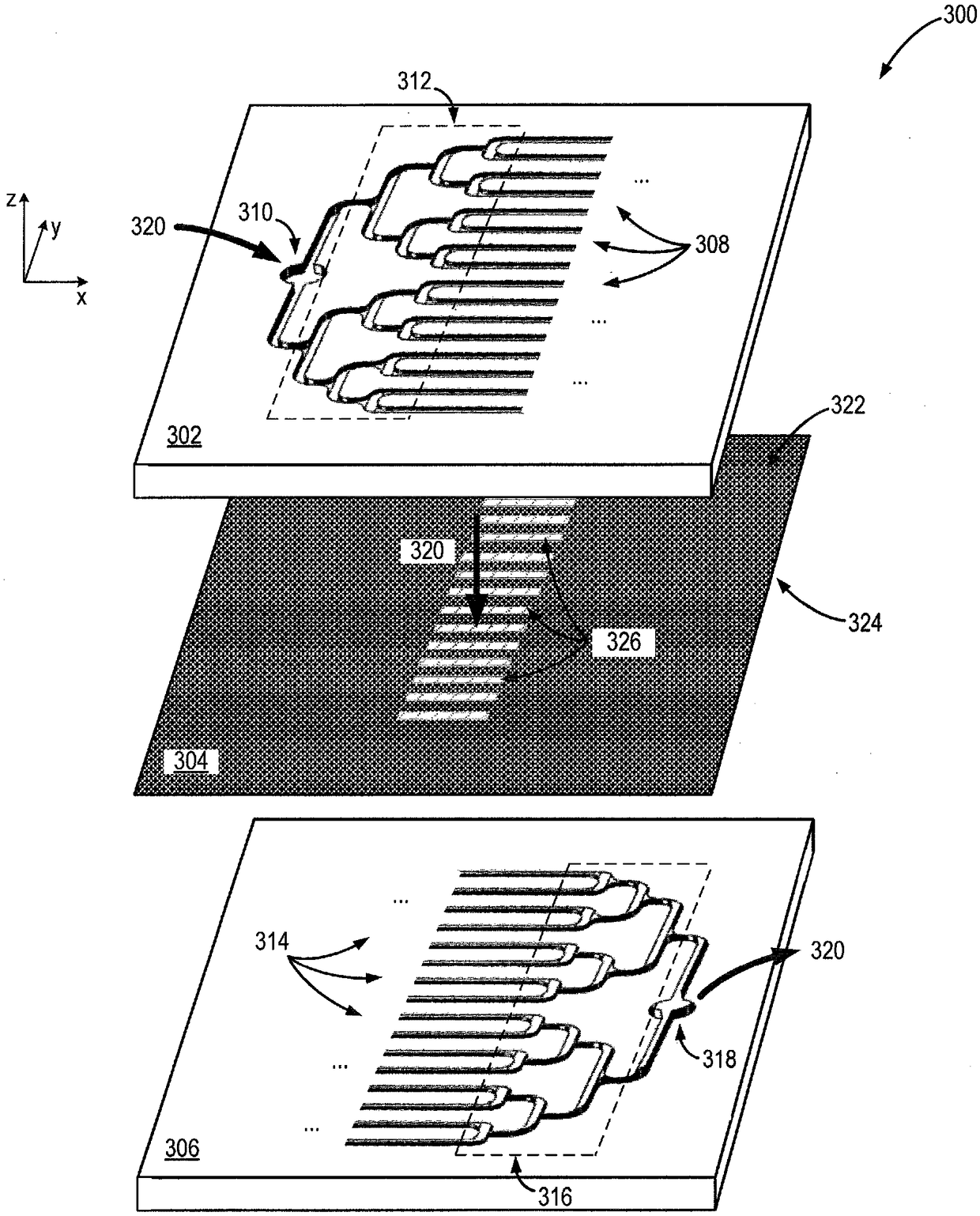
System and method for producing blood platelets
A system and method for generating biological products is provided. In some aspects, the system includes a first substrate having formed therein a plurality of inlet channel extending substantially along a longitudinal direction, and a second substrate having formed therein a plurality of outlet channel corresponding to the plurality of inlet channel and extending substantially along the longitudinal direction, the second substrate configured to releasably engage the first substrate. The system also includes a permeable membrane, arranged between the substrates, forming microfluidic pathways between respective inlet and outlet channels and configured to selectively capture biological source material capable of generating biological products, wherein at least one channel is tapered transversally to control a pressure differential profile regulating perfusion through the permeable membrane.
Owner:THE BRIGHAM & WOMEN S HOSPITAL INC
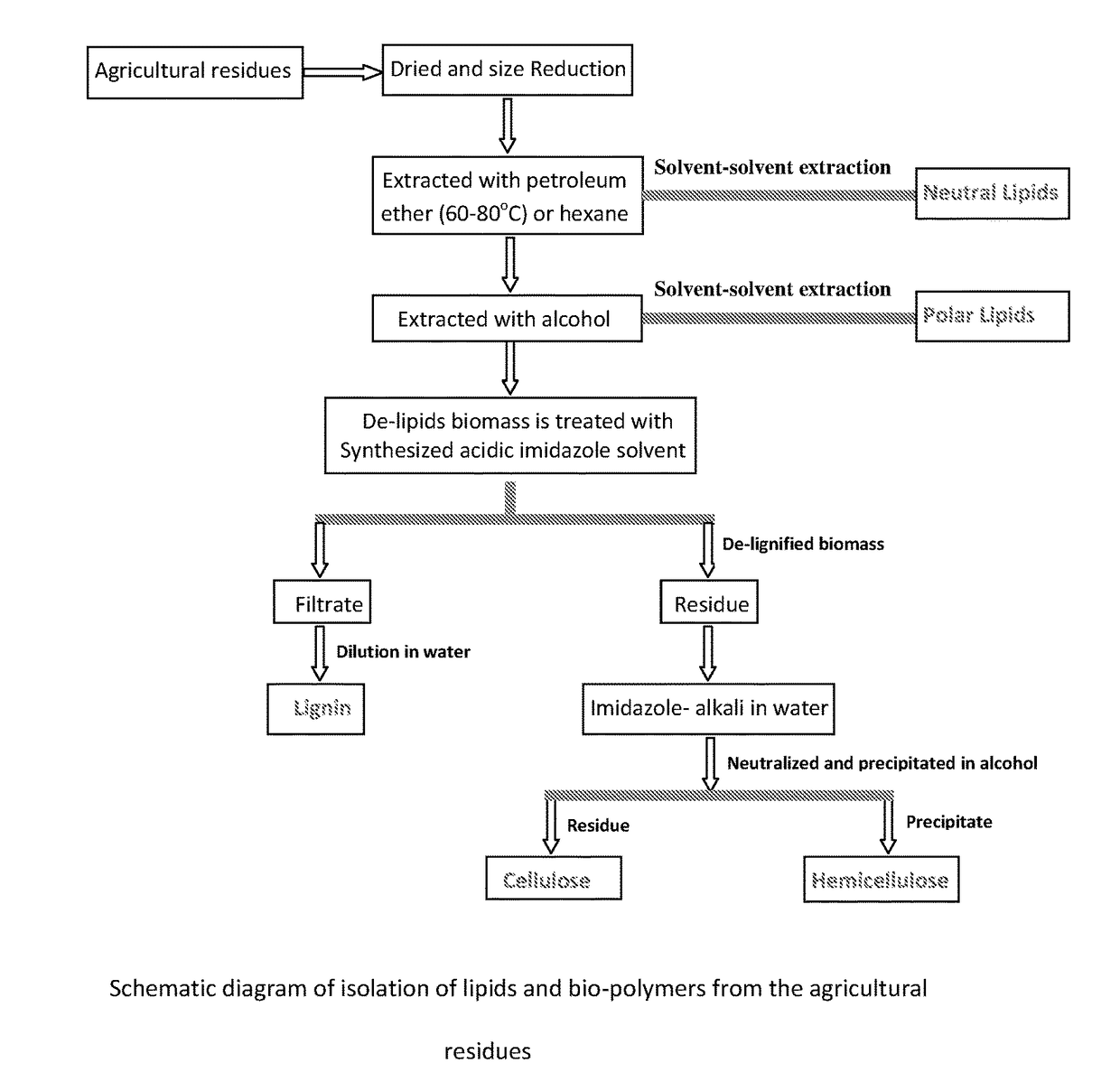
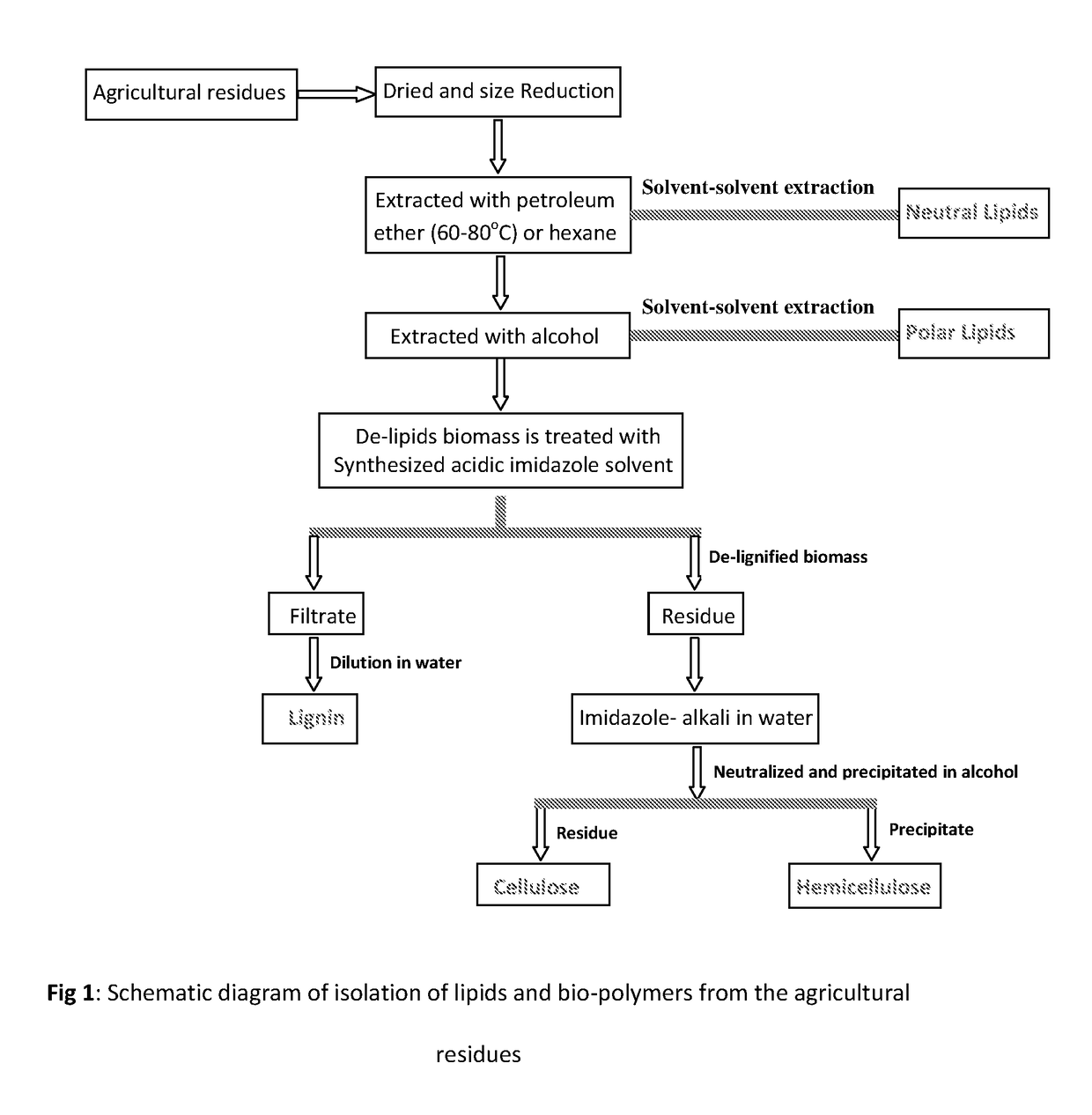
An eco-friendly process for the isolation of biopolymers from agricultural residues
ActiveUS20180201870A1Less crystallineEasy to optimizeFatty-oils/fats separationFatty-oils/fats productionMicrobial agentBiopolymer
Agricultural residues (biomasses) have come-up as potential valuable renewable resources for transformation into many bio-products. To achieve this goal, the isolation of major biopolymers in their purest form through an economical process is demanded for synthesis of the target fine chemicals without impurities. However, the difficulty of fractionating the biomass into cellulose, hemicellulose and lignin by a simple method has greatly limited their isolation from agricultural residues. Also, the lipids and waxes present on the surface of the agricultural residues protect it from external chemical and microbial agents. To overcome this issue, the lipids and waxes have been isolated from the biomass through two step organic solvents extraction. Thereafter lignin, hemicellulose and cellulose are isolated successively from the de-waxed biomass.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
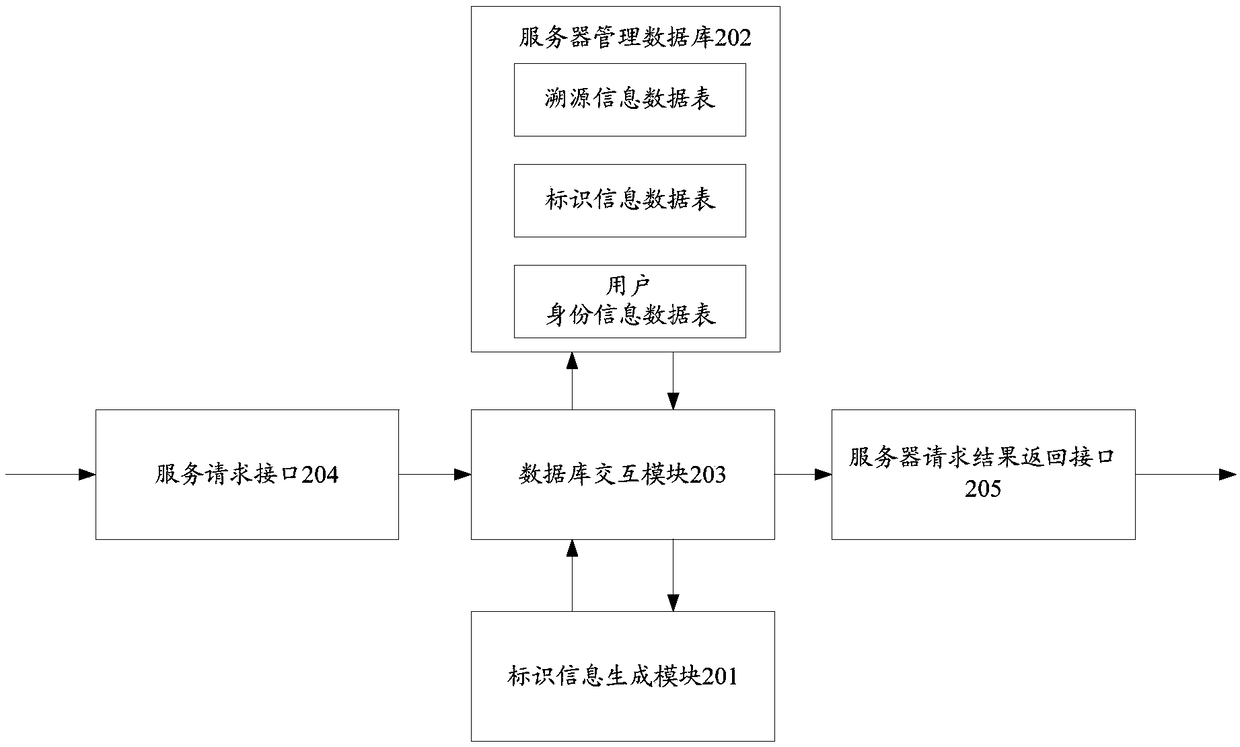
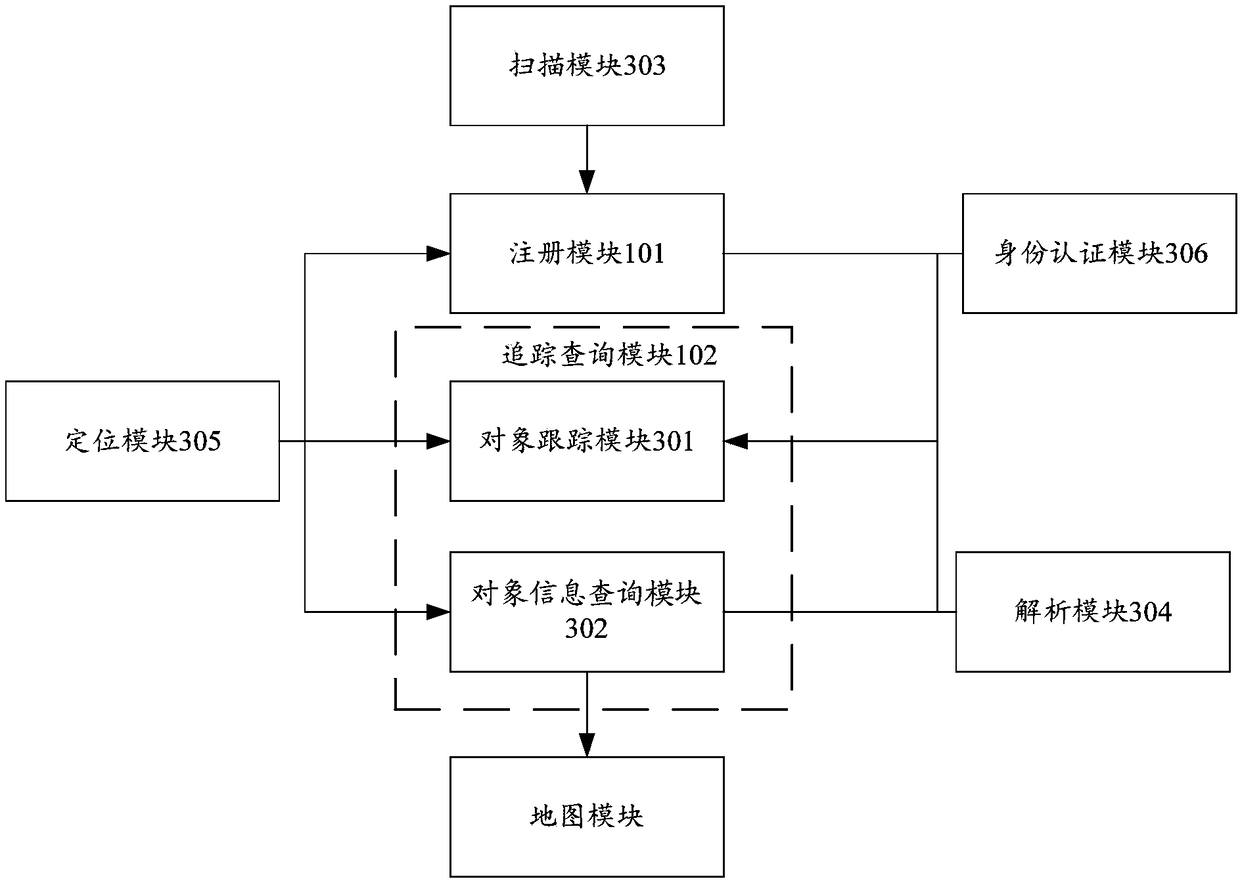
Object identity tracing method, terminal device and server
ActiveCN108564379ACommerceSpecial data processing applicationsTemporal informationObjective information
The invention provides an object identity tracing method, a terminal device and a server, and relates to the technical field of bio-product identity tracing. The method involves an identifier information generation module used for generating target identifier information for a target object based on a registration request sent by the terminal device, and a management database used for executing target operation based on an operation request sent by scanning the target identifier information through the terminal device, wherein the target identifier information includes at least one of DNA sequence information of the target object, registration time and registration position GPS coordinates; and the operation request includes a tracing information recording request or a tracing informationquery request. Three types of objective information including the DNA sequence information of a bio-component, geographic information of a circulation node and time information are combined to serve as a tracing information identifier, so that the objectivity and universality of tracing information are ensured and the problem that a bio-component identity of the target object cannot be determinedin a tracing process in an existing tracing technology is effectively solved.
Owner:INST OF MEDICINAL PLANT DEV CHINESE ACADEMY OF MEDICAL SCI
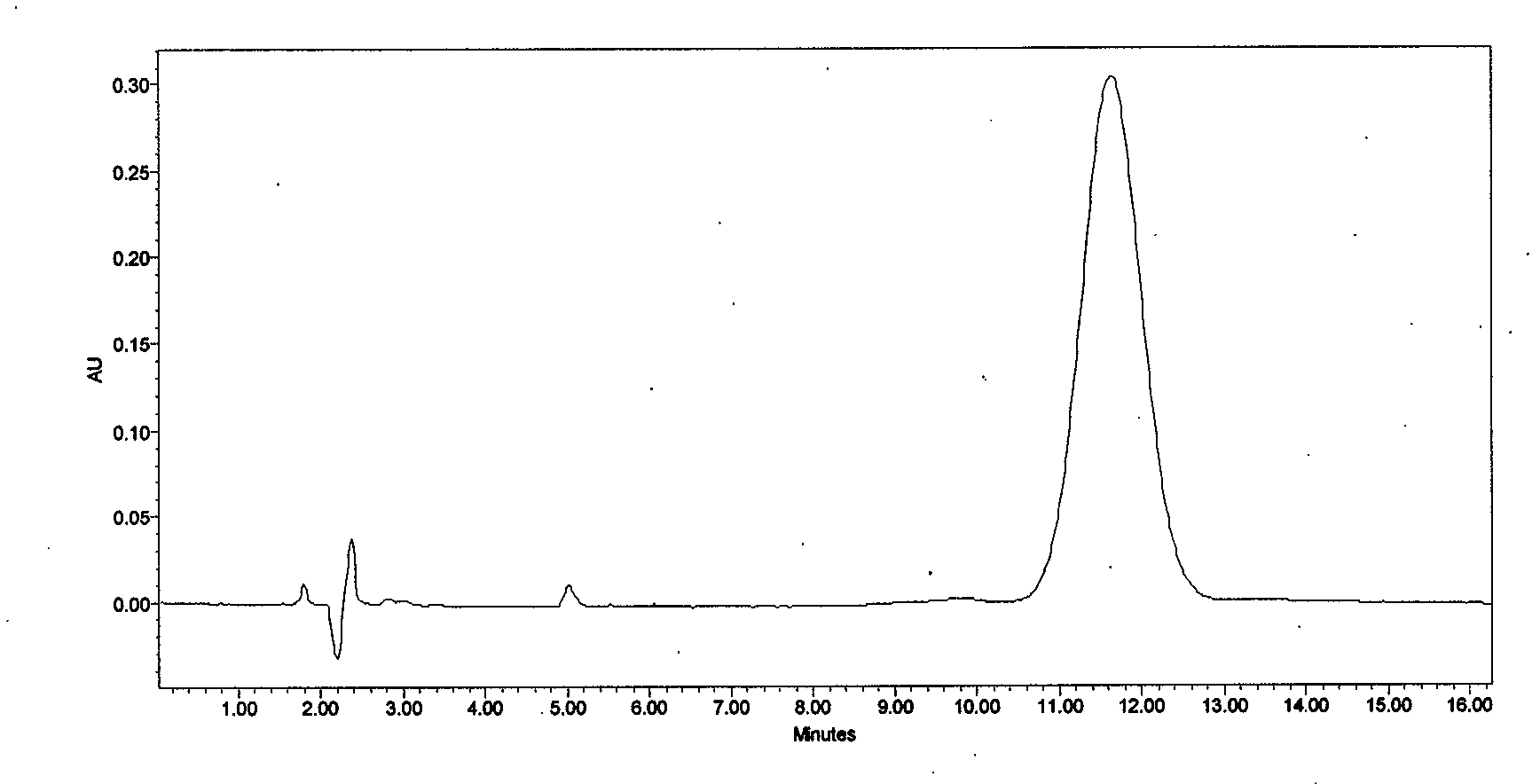
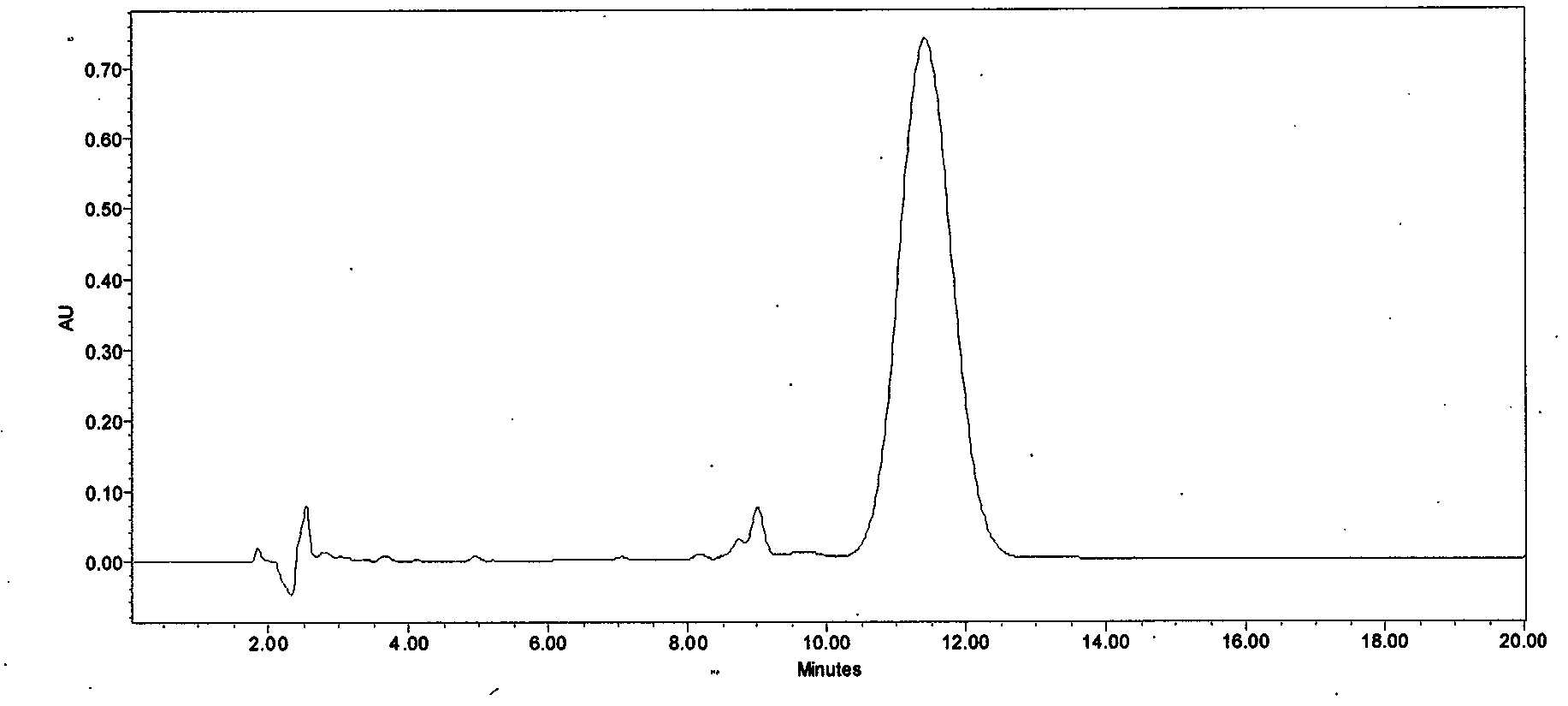
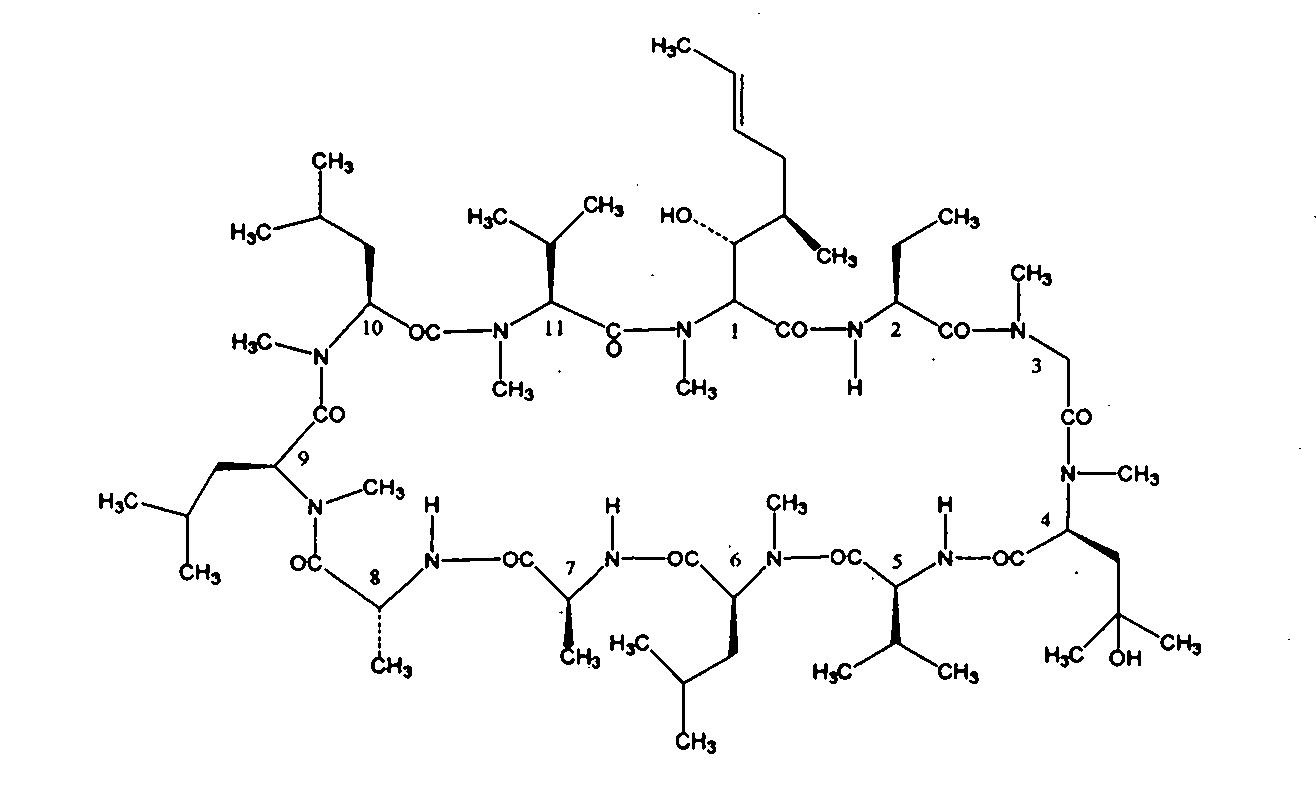
Preparation method of high-purity cyclosporin A derivative
ActiveCN103073624AEfficient removalHigh clarityPeptide preparation methodsChromatographic separationMicrosphere
The invention discloses a method for preparing a cyclosporin A derivative by using a fermentation culture product of filamentous fungi tolypocladium inflatum. According to the method, a filter aid is adopted; with steps such as leaching, discoloring, adsorption, crystallization, and the like, a cyclosporin A derivative crude extract is obtained; and the crude extract is subjected to chromatographic separation by using polymer microspheres, such that the high-purity cyclosporin A derivative product is obtained. The method provided by the invention has the advantages that: cyclosporin A derivative is extracted and separated by using macroporous resin; the process is simple and feasible, and is suitable for industrialized productions; the polymer microspheres are used in chromatographic separation of the product for a first time, and high-purity cyclosporin A derivative product can be prepared.
Owner:NCPC NEW DRUG RES & DEV
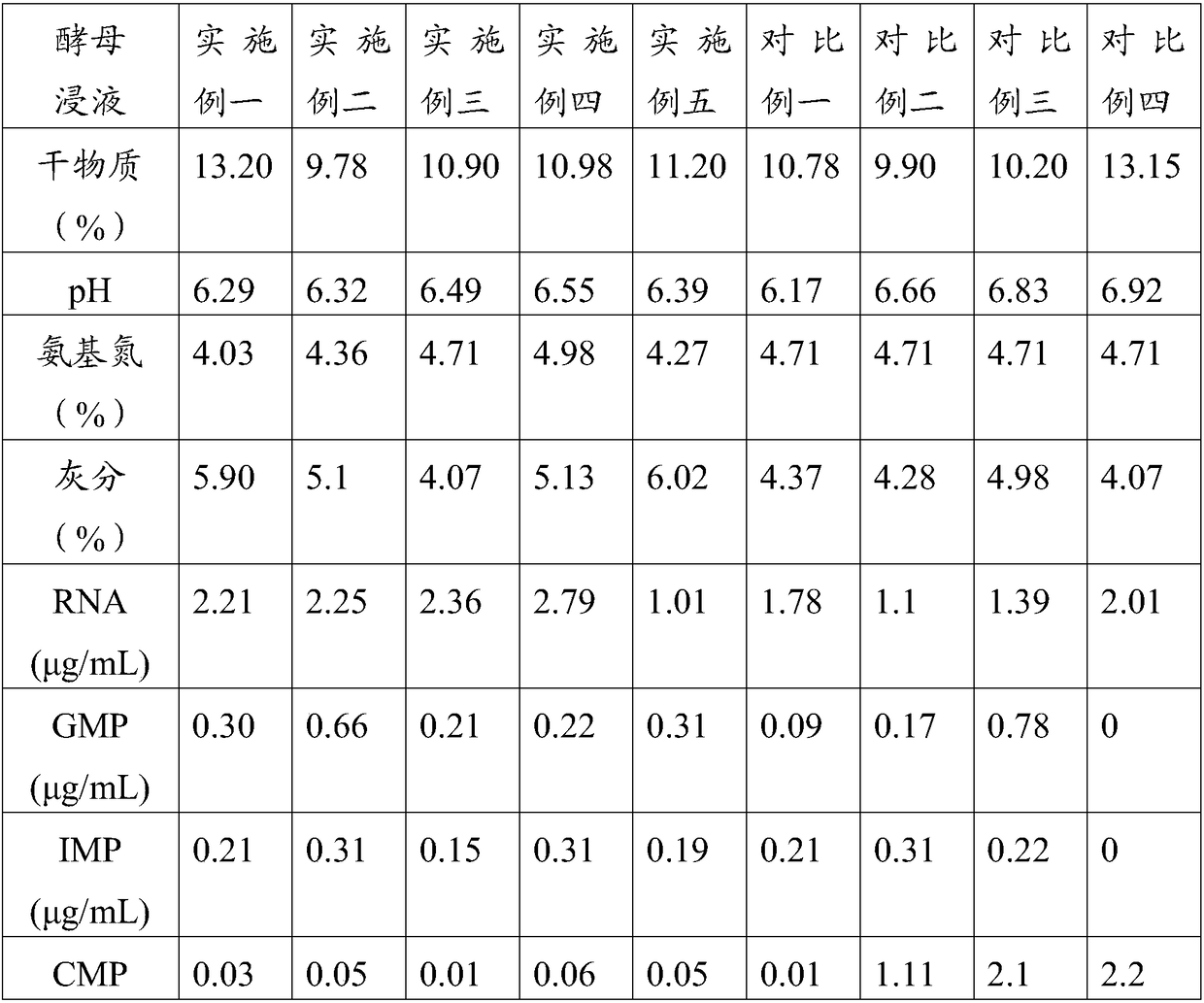
Yeast extract liquid, preparation method, and application of same
ActiveCN108330069AShort heating timeReduce heat damageFungiMicroorganism lysisVacuum extractionHeating time
The invention relates to the technical field of bio-products, and especially relates to a yeast extract liquid, a preparation method, and an application of same. The invention provides the method of high-effectively preparing the yeast extract liquid in vacuum, which includes steps of: 1) preparing yeast milk by culturing saccharomyces cerevisiae; 2) autolysis: regulating the yeast milk to weak-acidity to perform autolysis; 3) vacuum extraction: performing vacuum treatment to the autolyzed material and heating the material until boiling; 4) separating the liquid to obtain the yeast extract liquid. The invention also discloses the yeast extract liquid prepared through the method. The method is low in reaction temperature, is high in vacuum degree, is short in material heating time and is high in extraction degree, is very suitable for extracting substances having high boiling point and thermosensitivity and being easy to oxidize. The method also can reduce thermal damage on thermosensitive substance effectively and can greatly increase yield and improve quality of the product.
Owner:ANGELYEAST CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com