Affinity foam fractionation for collection and purification of materials
A foam, substance technology for the purification and/or concentration of compounds that solves the problems of underdeveloped foam fractionation, lack of distribution activity, and lack of understanding of the method
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0075] Example 1 - Affinity foam fractionation with addition of cellulose hydrolyzate
[0076] [0051] The experimental results, summarized in Tables 1 and 2 appended hereto, show the typical influence of three factors on foaming behavior. The factors are: (1) the presence or absence of cells in the foaming medium; (2) the presence of different growth stages of the cells; and (3) the addition of hydrolyzate. Cells used in the cell-containing system were pre-grown in glucose-based medium (containing 10 g / L glucose). To study the effect of different growth phases, cells were harvested in late exponential growth (day 3 of batch culture) or stationary growth phase (day 15). The culture supernatant, which was used in all systems as the basal medium for the production of cellulase, was prepared by fermentation with the aid of a hydrolyzate-based medium. The broth was harvested on day fifteen and centrifuged to remove cells. Using the same basal culture supernatant helps ensure tha...
Embodiment 2
[0092] Example 2 - Affinity foam fractionation with addition of CMC:
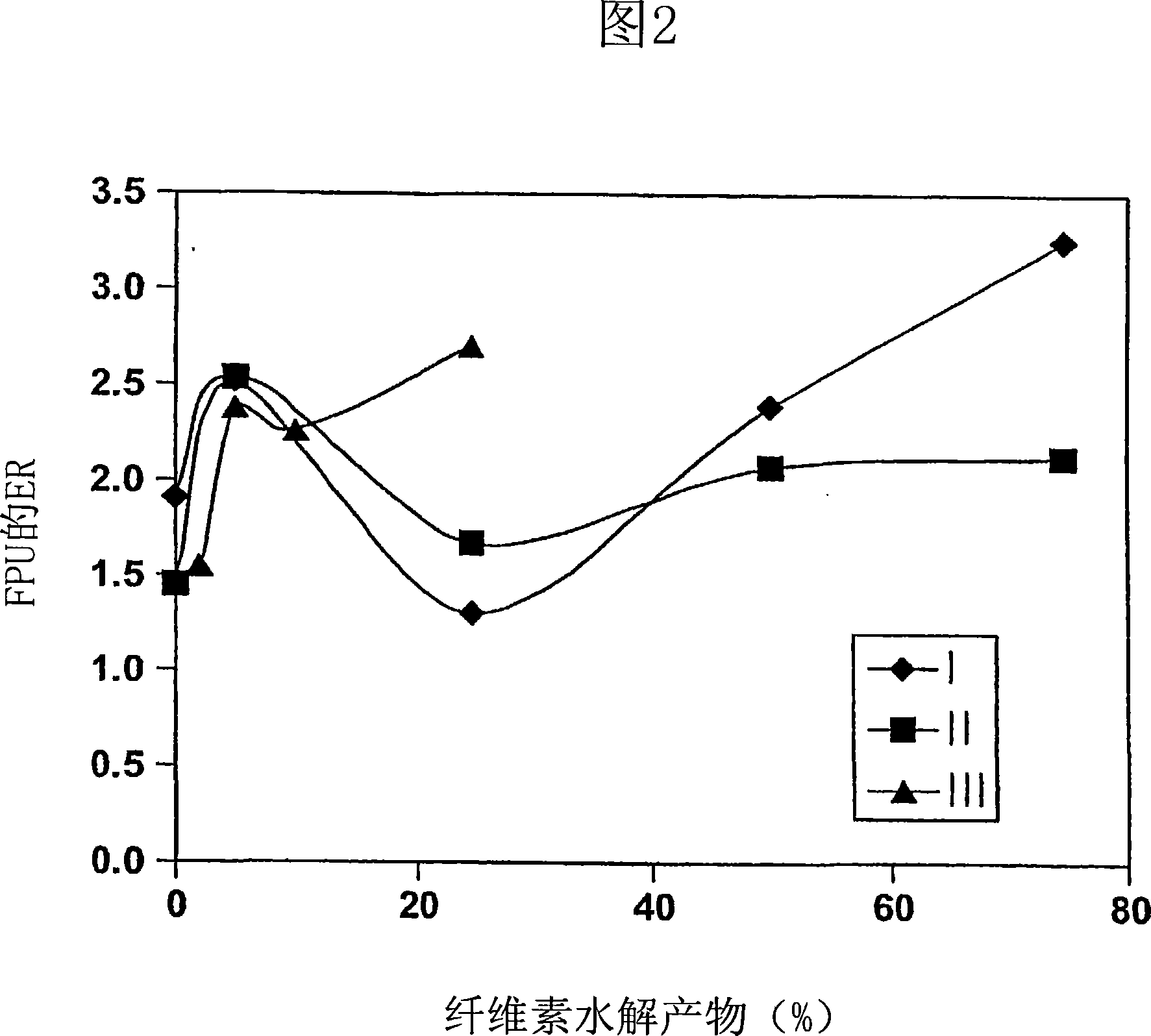
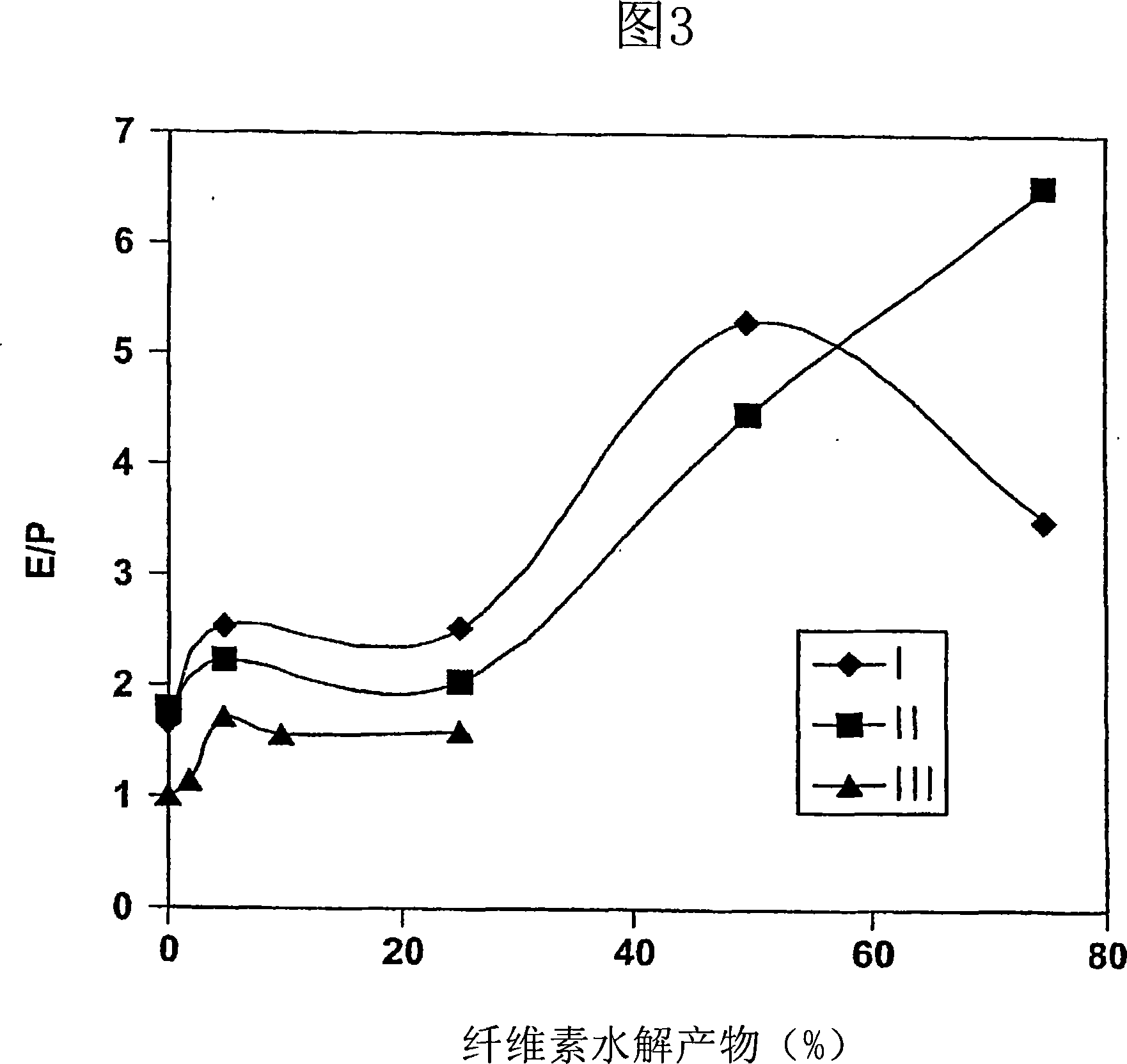
[0093] [0060] CMCs are modified, water-soluble, long-chain cellulose analogs. The potential application of CMCs for affinity foam fractionation of cellulases is discussed below. Experiments were performed on cell-free broth supernatant collected from hydrolyzate-based fermentations. To obtain a higher FPU (approximately 0.7) than the FPU of earlier batch cultures (approximately 0.3-0.4 FPU), the fermentation was supplemented with a continuous lactose-based feed after the steady state phase was reached. Three systems were compared: (a) culture supernatant (control); (b) supernatant added with 5% 5-g / L CMC solution; and (c) added 5% hardwood CH ( Containing the supernatant of reducing sugar of 16g / L). The ERs of FPU, extracellular proteins and reducing sugars are shown in FIG. 5 . CMC solutions were found to perform as well, if not better, than CH in terms of cellulase enrichment.
[0094] [0061] Sever...
Embodiment 3
[0095] Example 3 - Affinity foam fractionation with addition of xylan hydrolyzate:
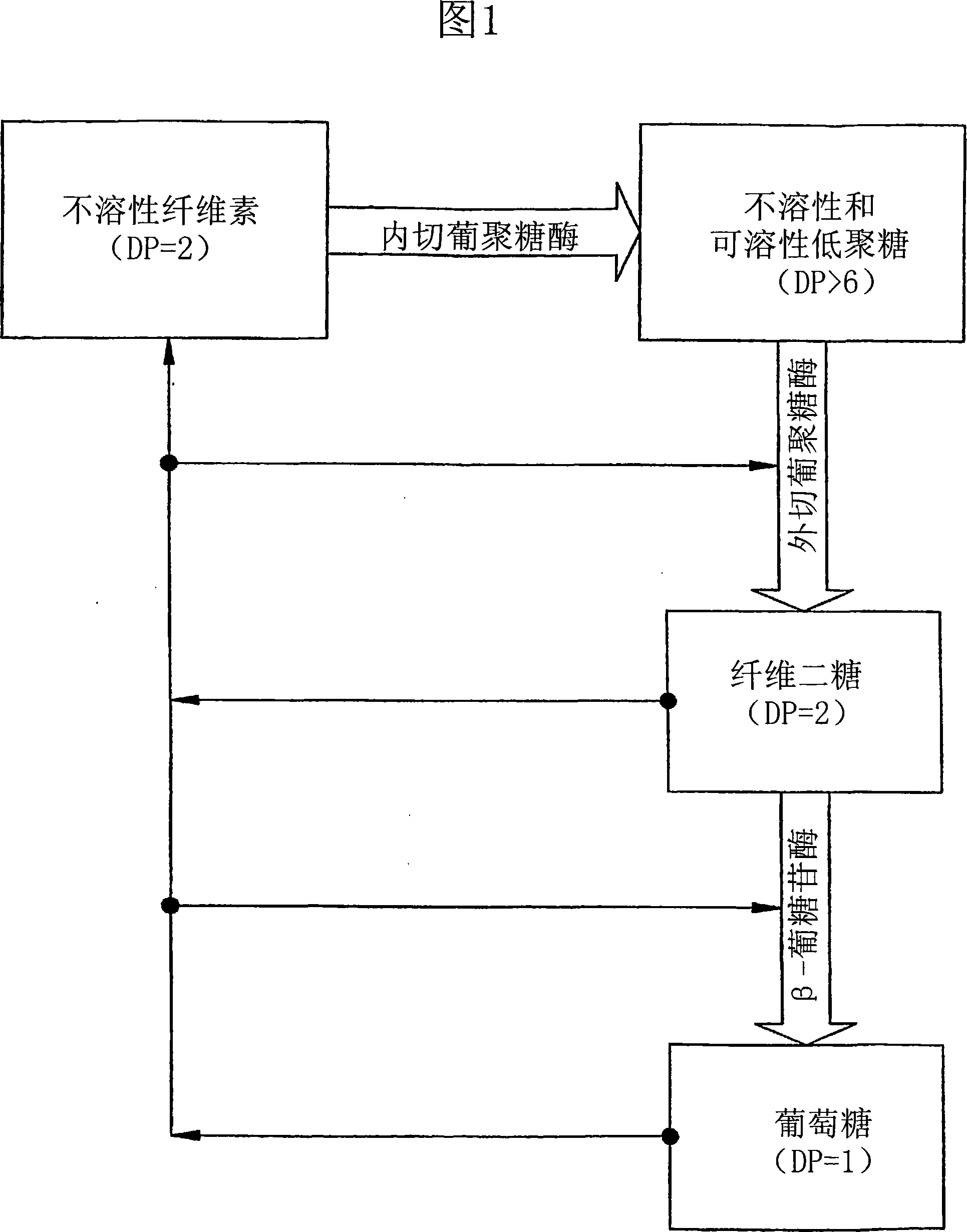
[0096] [0062] Table 3 presents the results of experiments comparing the effect of xylan hydrolyzate (XH) and cellulose (hardwood) hydrolyzate (CH) in cellulase affinity foam fractionation. Cell-free broth supernatants were collected from lactose-based fermentations as described in the Materials and Methods section. Lactose based broths, although having a much higher FPU (approximately 0.9), did not prove to have very good foaming properties. Poor bubbling was associated with much lower concentrations of extracellular proteins, confirming earlier observations that cellulases do not elicit efficient bubbling compared to certain other proteins present in the culture broth, and proceed through foam fractionation. The selective separation of cellulose requires the affinity bubbling developed in this work.
[0097] [0063] XH has a stronger foaming ability than CH, as shown in Table 3 that XH obt...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com