Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
91 results about "Bias effect" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Belief-Bias Effect. The Belief-Bias Effect refers to the results that happen when an individual’s own values, beliefs, prior knowledge, etc. affects, or distorts, the reasoning process through the acceptance of invalid arguments or data.
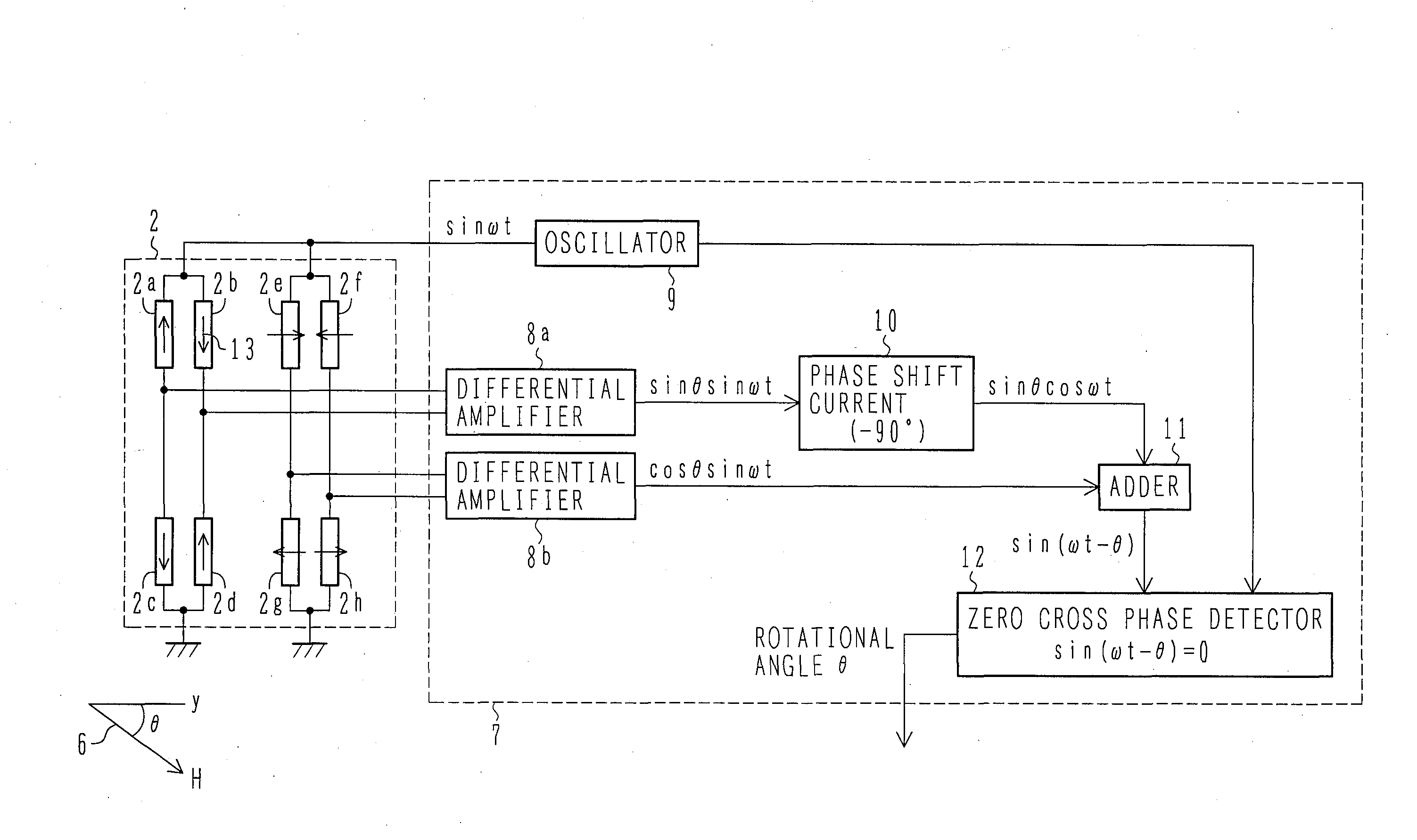
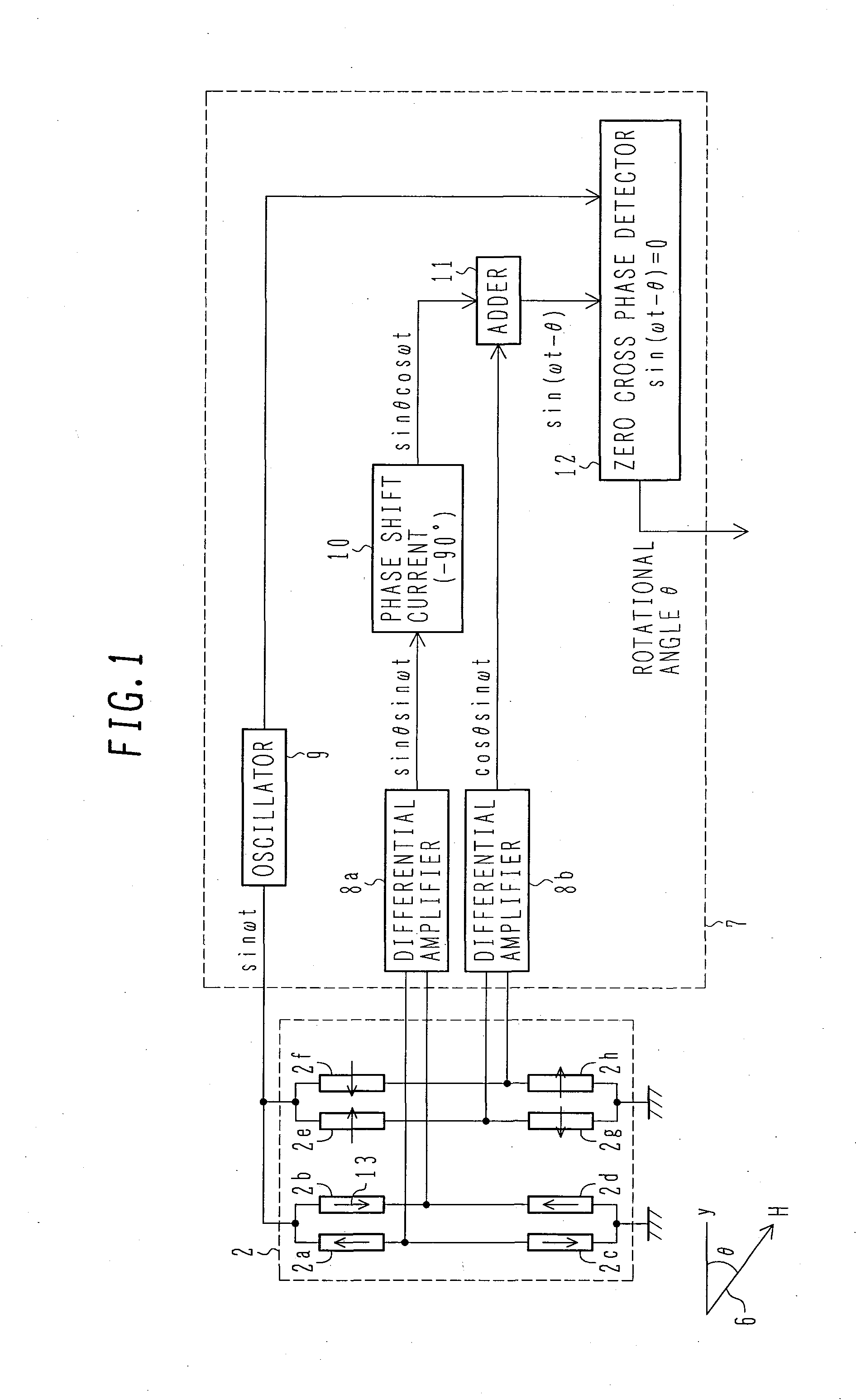
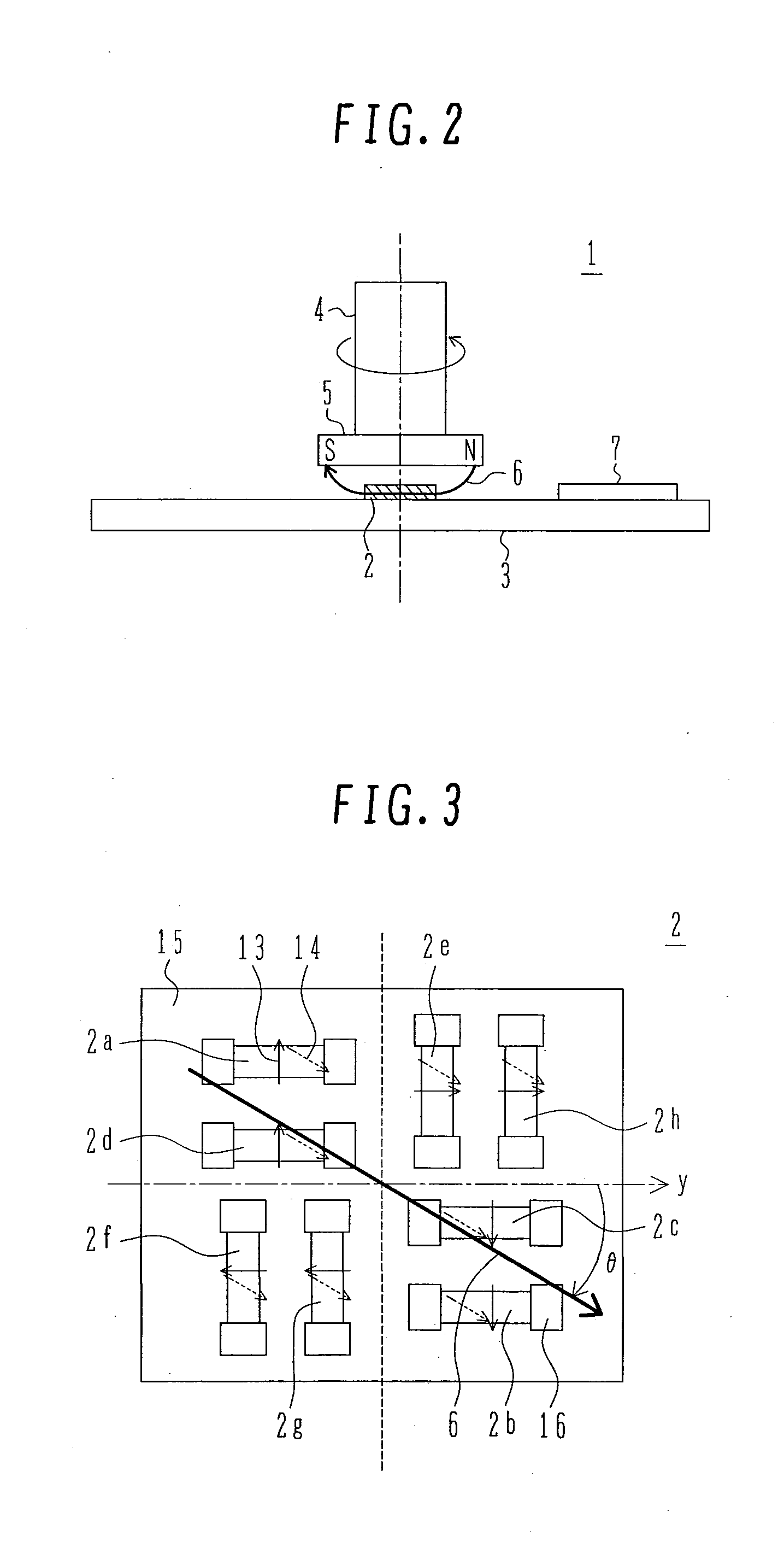
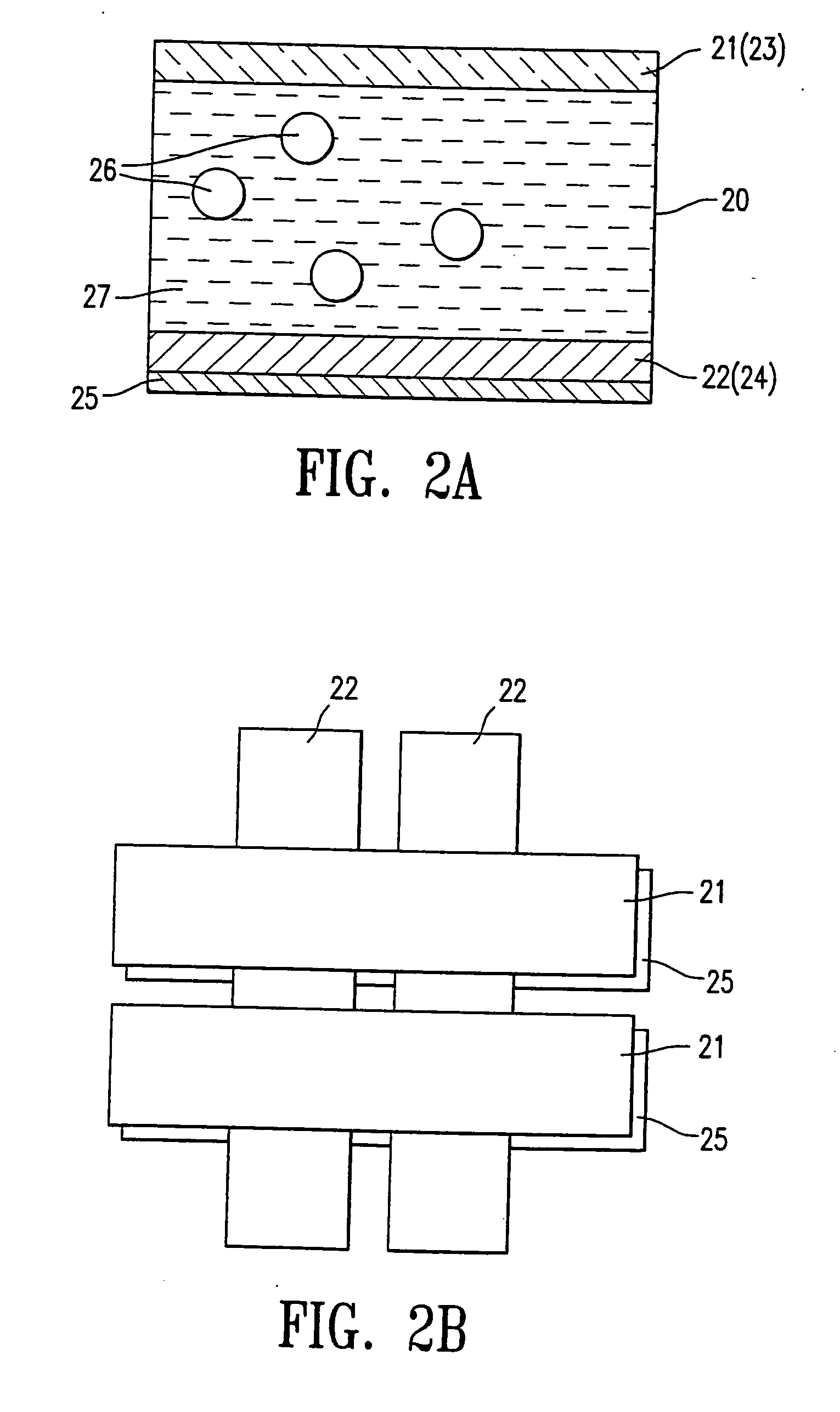
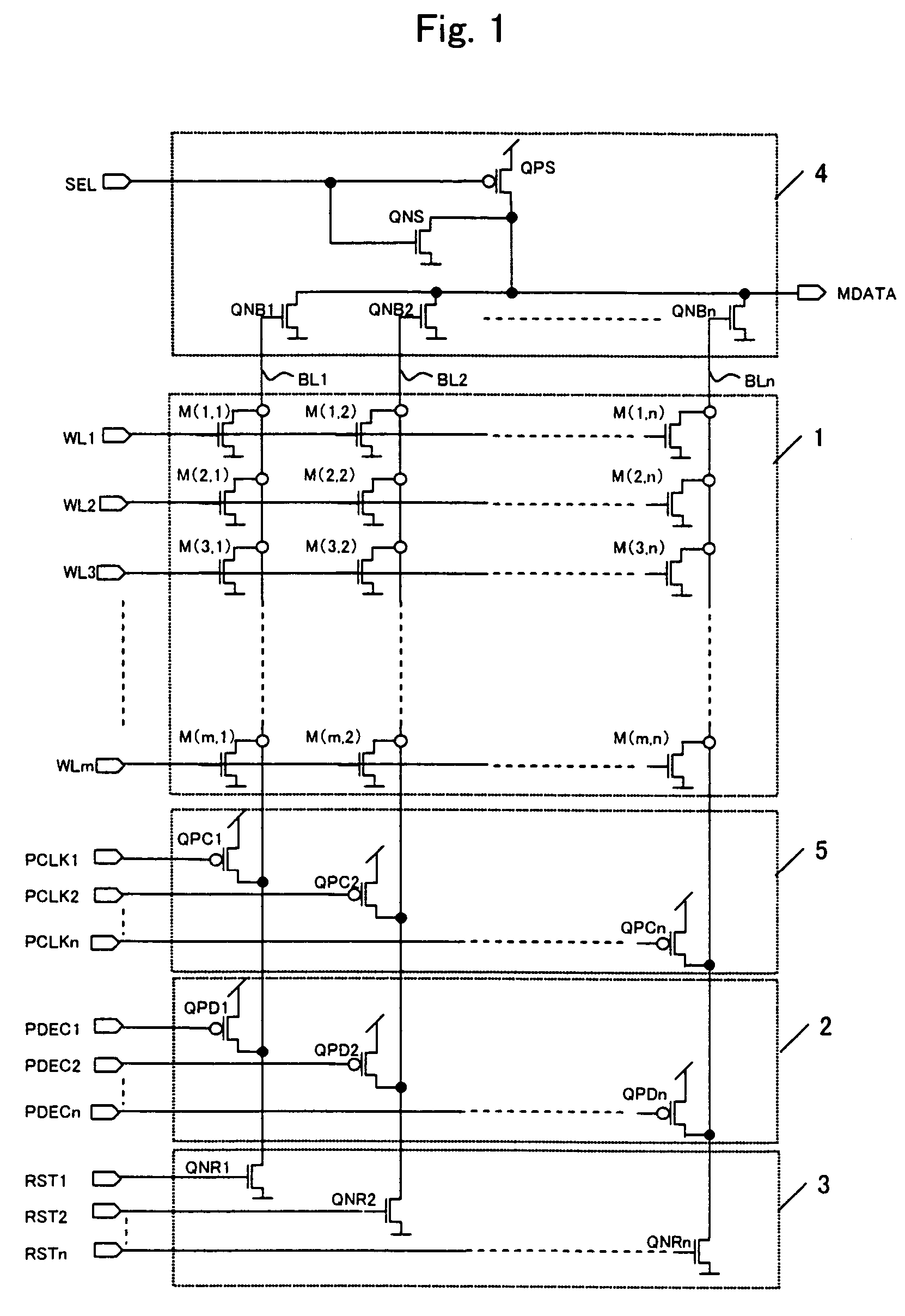
Displacement Sensor Using GMR Elements, Angle Sensor Using GMR Elements, And Semiconductor Device Used For Them
InactiveUS20080116886A1Avoid it happening againWithout impairing industrial productivityMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsSolid-state devicesMagnetizationEngineering
A highly accurate displacement sensor using GMR elements for detecting a displacement of a physical quantity such as angle is to be provided wherein a waveform distortion of output voltage is diminished.There are installed at least two Wheatstone bridge circuits having a predetermined angular offset and each comprising a plurality of GMR elements, the GMR elements each having a fixed magnetic layer set to a predetermined magnetization direction. An AC power supply is use as a power supply of the Wheatstone bridge circuits and a displacement of a physical quantity such as a rotational angle is detected on the basis of AC-modulated outputs from the Wheatstone bridge circuits.An anisotropic self-bias effect of a free magnetic layer in each GMR element can be diminished and hence it is possible to remedy a waveform distortion of an output signal based on the anisotropic self-bias effect of the free magnetic layer.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
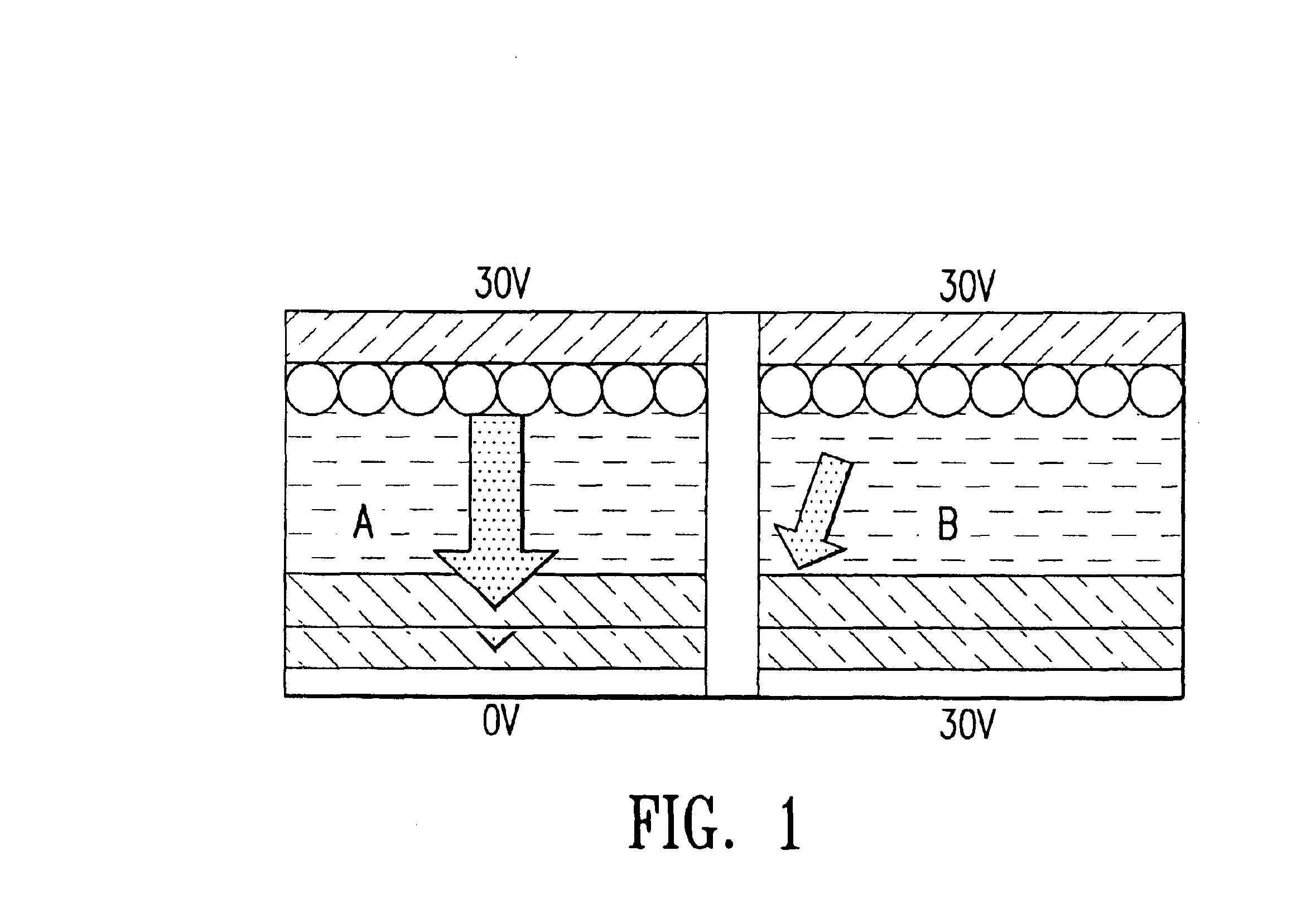
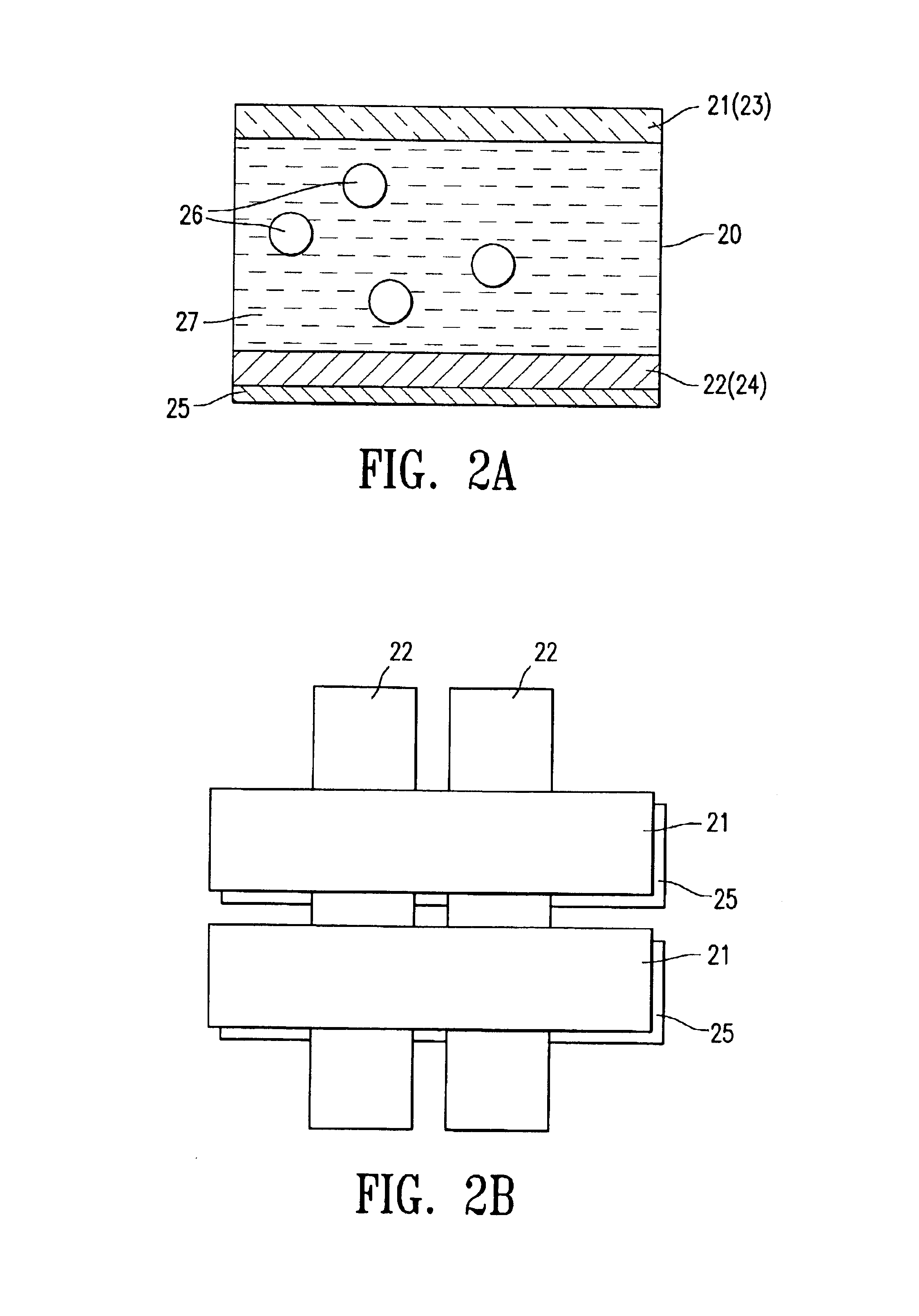
Electro-magnetophoresis display
ActiveUS6914713B2Avoid accidental movementInhibition effectStatic indicating devicesElectrographic processes using photoelectrophoresisMagnetic tension forceElectrical battery
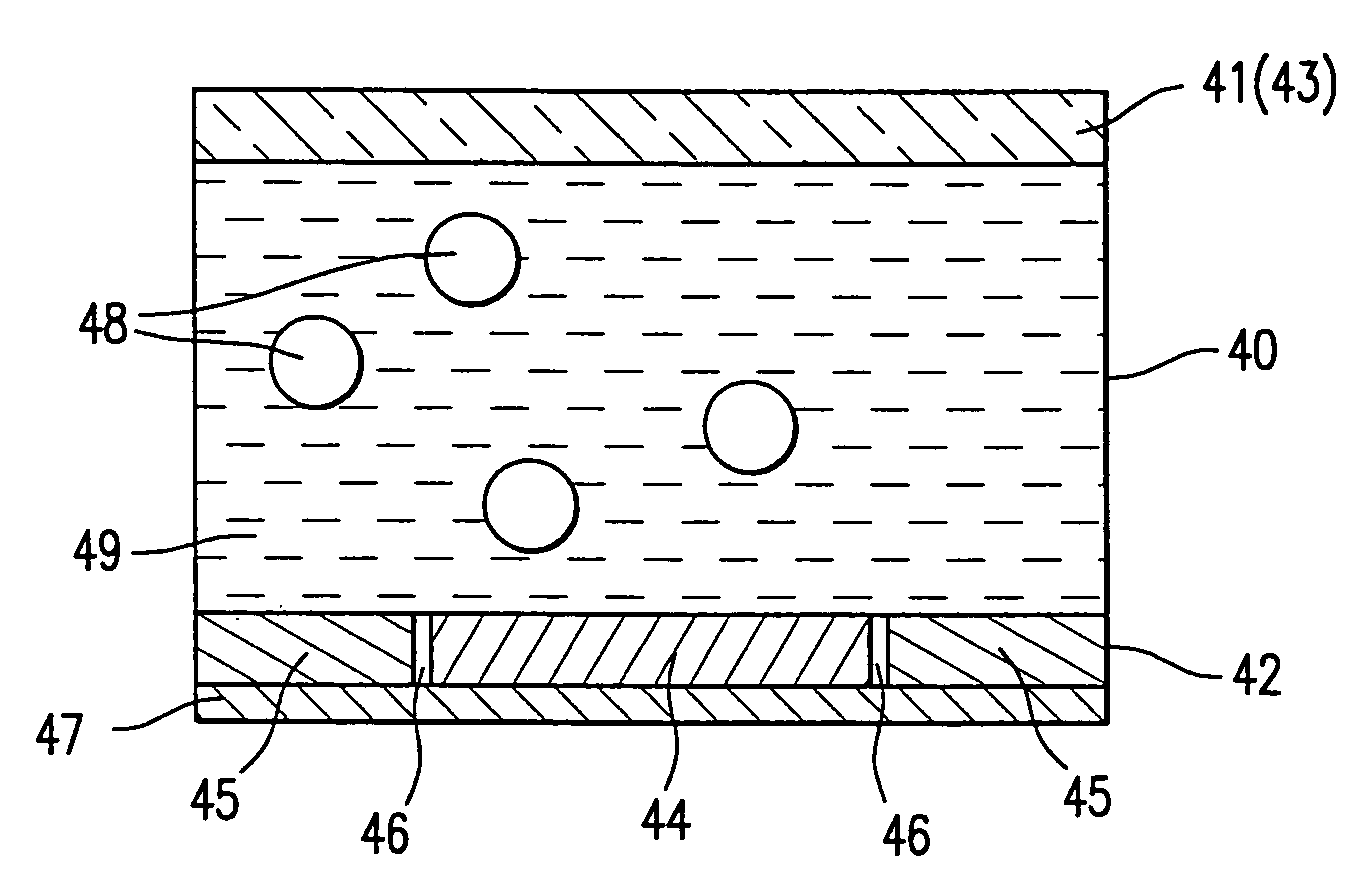
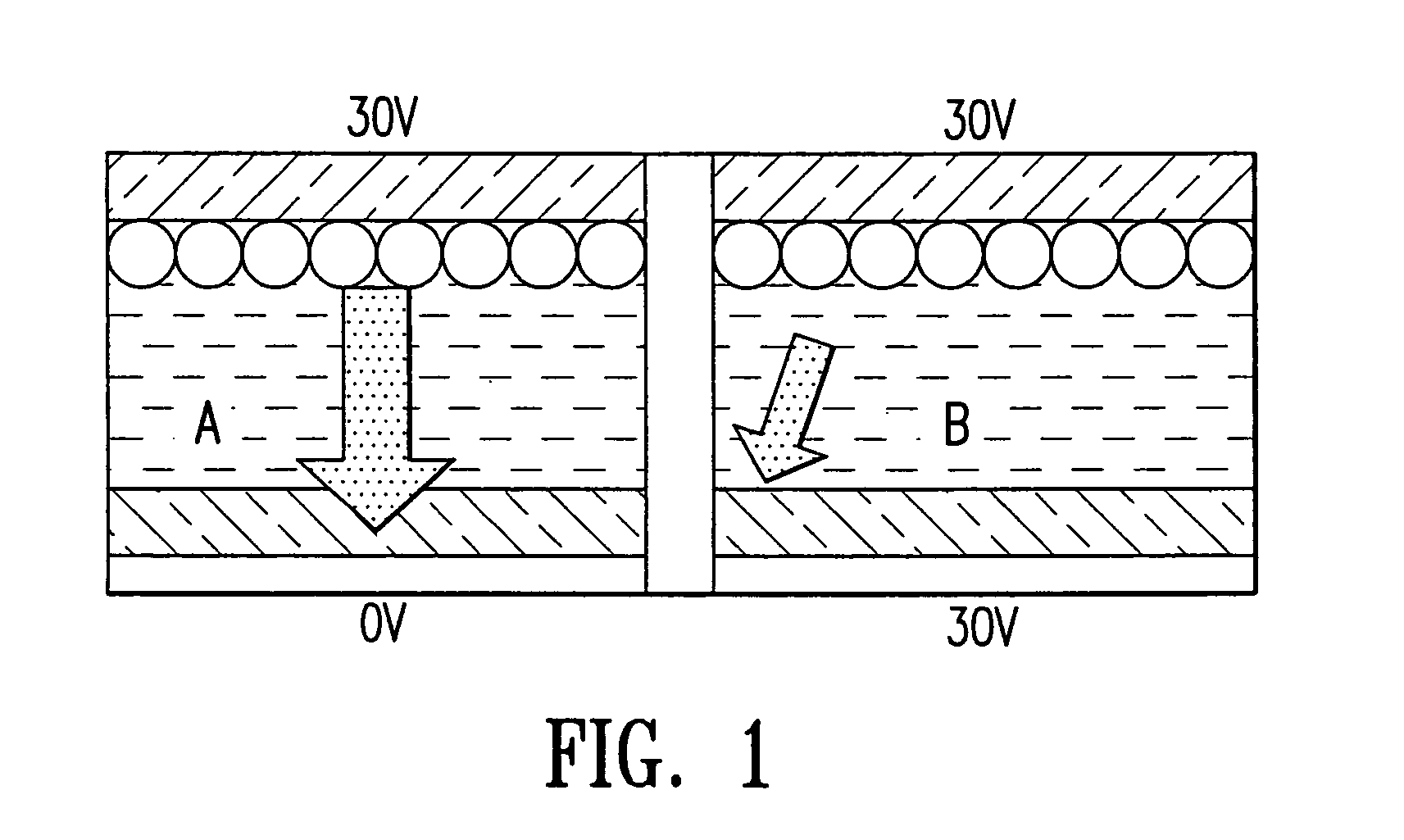
The present invention is directed to an electro-magnetophoresis display having either the traditional up / down or dual switching mode. The display cells are filled with an electro-magnetophoretic dispersion comprising particles suspended in a solvent and the particles are both charged and magnetized.The display of the invention prevents undesired movement of the particles in the cells. The magnetic force generated by the magnetic layer(s) eliminates the need to provide cells with a threshold voltage high enough to avoid the cross talk and / or cross bias effects. In addition, the dual switching mode allows the particles to move in the up / down direction as well as the planar direction, thus providing a multicolor display of high color quality at very low cost.
Owner:E INK CALIFORNIA
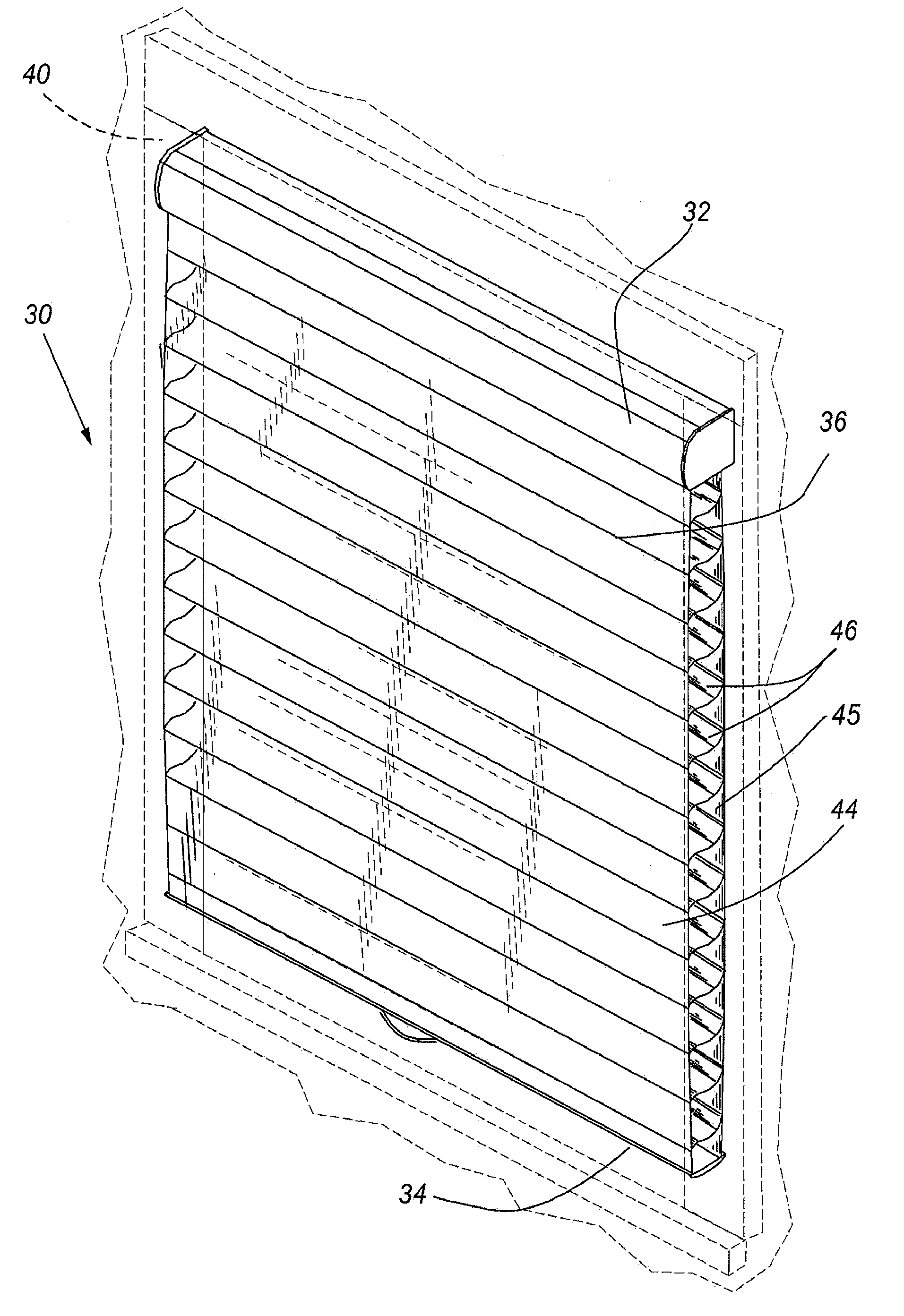
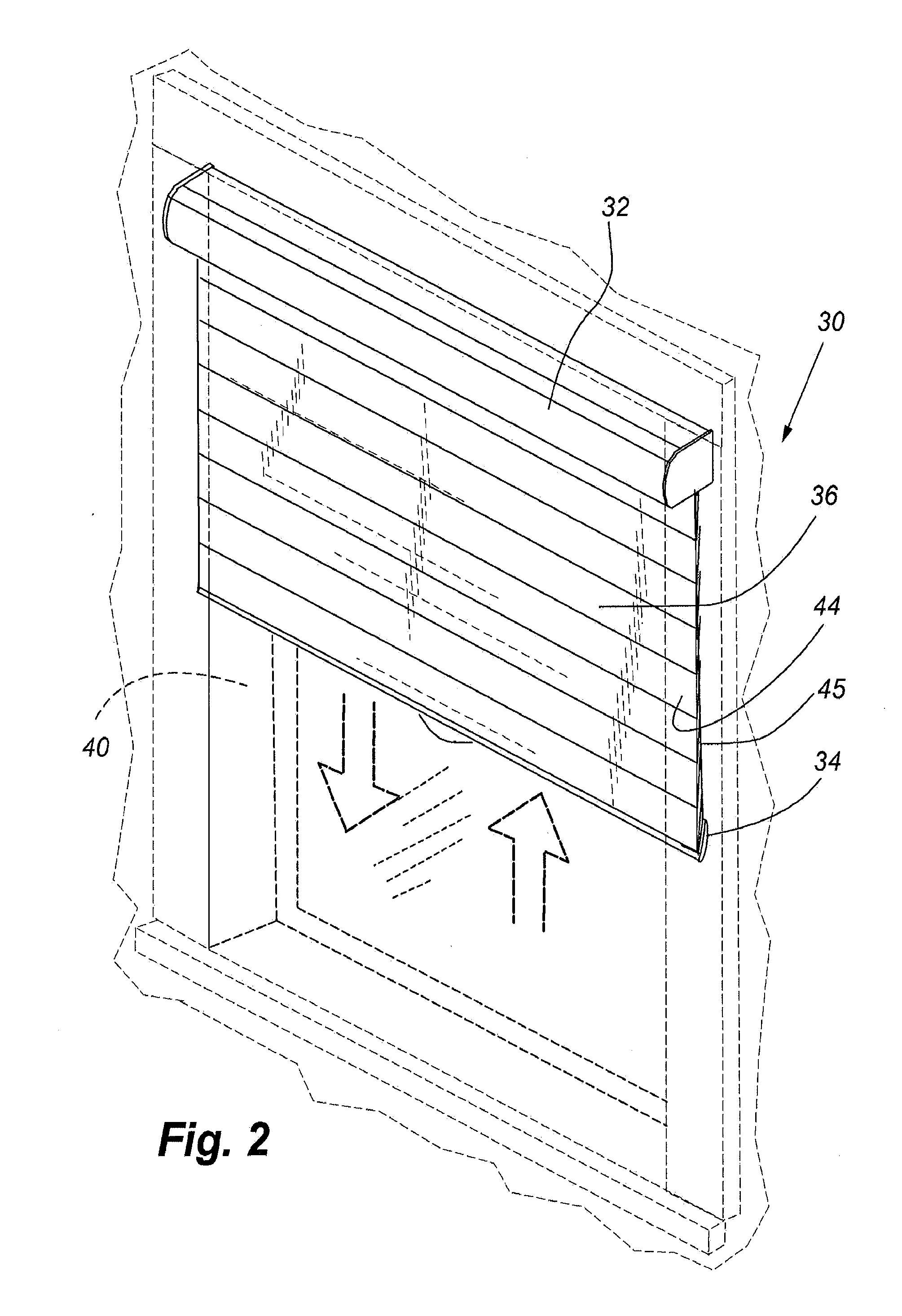
Cordless retractable roller shade for window coverings
ActiveUS20140216666A1Reduce biasRelieving biasExtensible doors/windowsCurtain accessoriesEngineeringMechanical engineering
A cordless retractable shade including an operating system for the shade that varies a biasing force of a spring to counterbalance the shade. The bottom rail of a retractable shade can be raised or lowered, and due to the operating system remains in any selected position of the covering between fully extended and fully retracted, without the use of operating cords. The system includes a method of negating and reversing the spring bias effect at a strategic position whereby the flexible vanes of the shade can be adjusted between open and closed.
Owner:HUNTER DOUGLAS INC
Electro-magnetophoresis display
InactiveUS7142351B2Avoid accidental movementImprove color qualityThyristorSolid-state devicesDisplay deviceEngineering
The present invention is directed to an electro-magnetophoresis display having either the traditional up / down or dual switching mode. The display cells are filled with an electro-magnetophoretic dispersion comprising particles suspended in a solvent and the particles are both charged and magnetized. The display of the invention prevents undesired movement of the particles in the cells. The magnetic force generated by the magnetic layer(s) eliminates the need to provide cells with a threshold voltage high enough to avoid the cross talk and / or cross bias effects. In addition, the dual switching mode allows the particles to move in the up / down direction as well as the planar direction, thus providing a multicolor display of high color quality at very low cost.
Owner:E INK CALIFORNIA
Temperature measurement correction system and method for thermal infrared imager
InactiveCN109655162AAdaptableAvoid temperature measurement errorsRadiation pyrometryOptical ModuleEmissivity
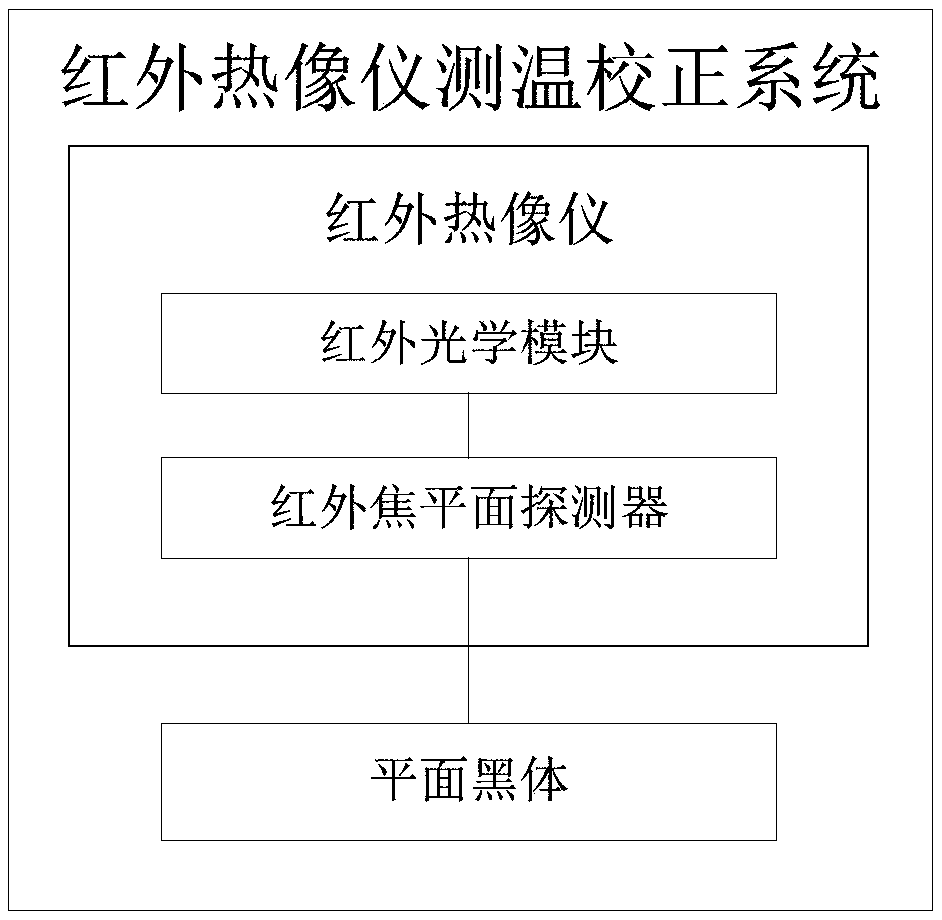
The invention provides a temperature measurement correction system and method for a thermal infrared imager. The system includes an infrared optical module, a plane black body and a high and low temperature box arranged in the thermal infrared imager, wherein a focal plane of the to-be-corrected thermal infrared imager is aligned with the plane black body through the infrared optical module, radiation of the plane black body is uniformly irradiated on the focal plane, a preset distance between the to-be-corrected thermal infrared imager and the plane black body is kept, the to-be-corrected thermal infrared imager is placed in the high and low temperature box for preheating, and subsequent calibration is performed after the temperature is stabilized. The system is advantaged in that the distance of a measured object is compensated by an optical system, influence of surface emissivity of the measured object and the environment temperature on temperature measurement is compensated by thecorrection method, the thermal infrared imager is made to be more adaptable to the measured object and the environment, gain and the bias effect of the thermal infrared imager on external radiation under different temperatures are accurately calibrated, a temperature measurement error caused by temperature change of an instrument in the temperature measurement process is avoided, an additional device such as a shutter is not needed for calibration, and the structure of the instrument is simplified.
Owner:INNO INSTR (CHINA) INC
Bicycle carrier
InactiveUS20070007316A1Minimal effortConsiderable versatilitySupplementary fittingsOther load carrying vehiclesDetentEngineering
A bicycle carrier provides a rotatable beam on which are mounted foldable support arms having first wheel support means for engaging and entrapping the upper peripheral regions of the wheels of a bicycle, the beam being rotatable into a bicycle carriage mode vertically above the vehicle when the arms are in an arm deployed position and lockable in that position. Resiliently-biased detent means are associated with the support arms mountings for positively locking the arms in the deployed position in relation to the beam, simple movement against the bias effecting disengagement.
Owner:WITCZAK JOHN
Cordless retractable roller shade for window coverings
A cordless retractable shade including an operating system for the shade that varies a biasing force of a spring to counterbalance the shade. The bottom rail of a retractable shade can be raised or lowered, and due to the operating system remains in any selected position of the covering between fully extended and fully retracted, without the use of operating cords. The system includes a method of negating and reversing the spring bias effect at a strategic position whereby the flexible vanes of the shade can be adjusted between open and closed.
Owner:HUNTER DOUGLAS INC
Electro-magnetophoresis display
InactiveUS20070268567A1Avoid accidental movementInhibition effectNon-linear opticsOptical elementsMagnetic tension forceDisplay device
The present invention is directed to an electro-magnetophoresis display having either the traditional up / down or dual switching mode. The display cells are filled with an electro-magnetophoretic dispersion comprising particles suspended in a solvent and the particles are both charged and magnetized. The display of the invention prevents undesired movement of the particles in the cells. The magnetic force generated by the magnetic layer(s) eliminates the need to provide cells with a threshold voltage high enough to avoid the cross talk and / or cross bias effects. In addition, the dual switching mode allows the particles to move in the up / down direction as well as the planar direction, thus providing a multicolor display of high color quality at very low cost.
Owner:E INK CALIFORNIA
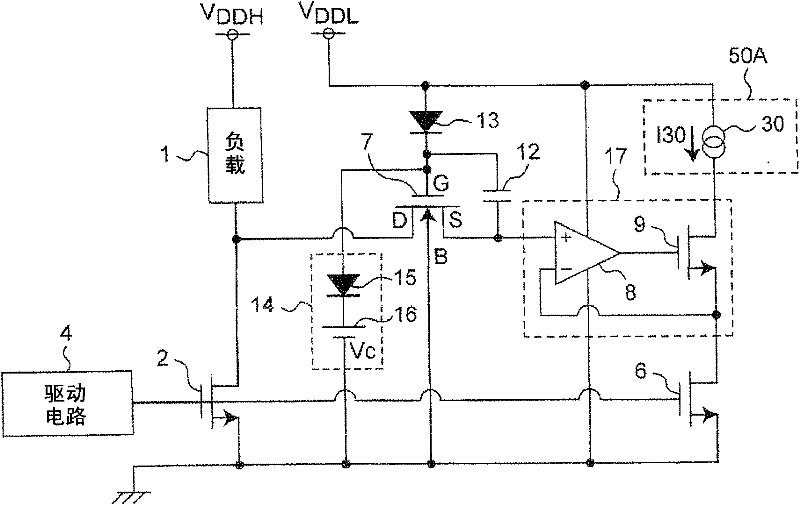
Current detection circuit
The present invention provides a current detection circuit. Using a electrostatic capacitor (12) and a diode (13), a gate voltage of a protecting MOSFET (7) is increased when a drain voltage of a power transistor (2) increases. A voltage clamp circuit (14) clamps the maximum voltage of the gate voltage of the protecting MOSFET (7)to a predetermined clamp voltage (Vc). A voltage control circuit (17) controls a drain voltage of a sense transistor (6) so as to substantially coincide with a source voltage of the protecting MOSFET (7). A detection circuit (40) detects the current of the drain of the sense transistor (6). Therefore, even if the substrate bias effect occurs in the protecting MOSFET of the current detection circuit of the power transistor, the current of a load is detected precisely by means of a high voltage negatively fed back by the operation amplifier on the basis of satisfying the resistant voltage between the source and gate of the protecting MOSFET.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Photocatalytic wastewater fuel cell capable of strengthening free radical reaction, and preparation method and application of photocatalytic wastewater fuel cell
ActiveCN106299418APromote degradationIncrease power generation capacityWater/sewage treatment by irradiationFuel cell controlEnergy recoveryElectrolyte
The invention relates to a photocatalytic wastewater fuel cell capable of strengthening a free radical reaction. The photocatalytic wastewater fuel cell comprises a photo-anode, a cathode, persistent organic pollutant wastewater, a light source, an electrolyte solution, a quartz reaction pool and an air vent, wherein the photo-anode and the cathode are respectively inserted into the electrolyte solution, which contains the persistent organic pollutant wastewater, in the quartz reaction pool, and are connected by an external circuit; 0.1-0.4mM ferrous ions are added into the electrolyte solution, and the pH value is adjusted to be 1.0-4.0; the cathode is close to the air vent which is continuously filled with air; the light source is turned on for irradiating the photo-anode and the cathode; the ferrous ions have a Fenton-like circular reaction with free radicals and related substances which are generated on the surfaces of the photo-anode and the cathode under the automatic bias effect of the photocatalytic fuel cell, so that the free radical reaction in a system is strengthened, and the performance of the photocatalytic fuel cell is greatly improved. The invention provides a more efficient and economical wastewater treatment and energy recovery method, and has a wide application prospect.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
MOS switching circuit with broadband and high linearity
InactiveCN102025358AEliminate non-ideal factorsImprove high frequency performanceElectronic switchingCapacitancePre-charge
The present invention belongs to the technical field of integrated circuit, specifically to a MOS switching circuit with broadband and high linearity. A MOS switch is the main body of the circuit; a grid voltage bootstrap circuit is used for stabilizing a switching tube grid source voltage; a substrate bias effect and a switch source drain parasitic junction capacitance are eliminated by isolating a substrate and enabling the substrate to follow an input signal when the switch is conducted; influences of the parasitic junction capacitance between the substrate and an isolated trap by a pre-charge-suspension structure. The main non-ideal factors of non-linearity generated by a common MOS switch are eliminated by the three aspects; and the linearity of the switch under high, middle and low frequency input signals is improved.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Method and apparatus to correct noise effects in quantitative techniques in magnetic resonance imaging
ActiveUS20160084929A1Accurate estimateCorrect noise effectDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsPattern recognitionElectronic form
In a method to correct noise effects in magnetic resonance (MR) images, which is executed in a processor (computer), the processor executes a fitting algorithm in order to calculate initial values for each of selected variables in signal model that models noise effects in a modeled, noise-containing MR image. The processor then iteratively executes the same or a different fitting algorithm, in order to generate final values for each of the selected variables. The processor is provided with an actual, acquired MR image that contains noise, and the processor uses the final values of the selected variables to calculate synthetic signal intensities in the MR image, thereby producing a synthetic MR image with no noise bias effects of errors. This synthetic image is made available in electronic form at an output of the processor, as a data file.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
CMOS gate voltage bootstrapping switch circuit
ActiveCN105187039AReduce input parasitic capacitanceThe potential of the output terminal dropsElectronic switchingAnalogue-digital convertersCMOSParasitic capacitance
The invention provides a CMOS gate voltage bootstrapping switch circuit which comprises a charge pump circuit, a gate electrode charge and discharge circuit, an input buffering circuit and a switch circuit. The charge pump circuit is electrically connected to the gate electrode charge and discharge circuit. The gate electrode charge and discharge circuit is electrically connected to the switch circuit. The input buffering circuit is arranged between the gate electrode charge and discharge circuit and the switch circuit. According to the invention, the input buffering circuit is adopted to drive a charge pump circuit. Such a design greatly reduces the input of parasitic capacitance because the input buffering circuit separates the inputted signal from an inputting end and the charge pump circuit. Beyond that, the CMOS gate voltage bootstrapping circuit provided by the invention overcomes the problems that a conventional CMOS gate voltage bootstrapping circuit only achieves constant gate-source voltage Vgs of a switching tube and omits a substrate bias effect to cause the non-linearity introduced by Vth change .
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
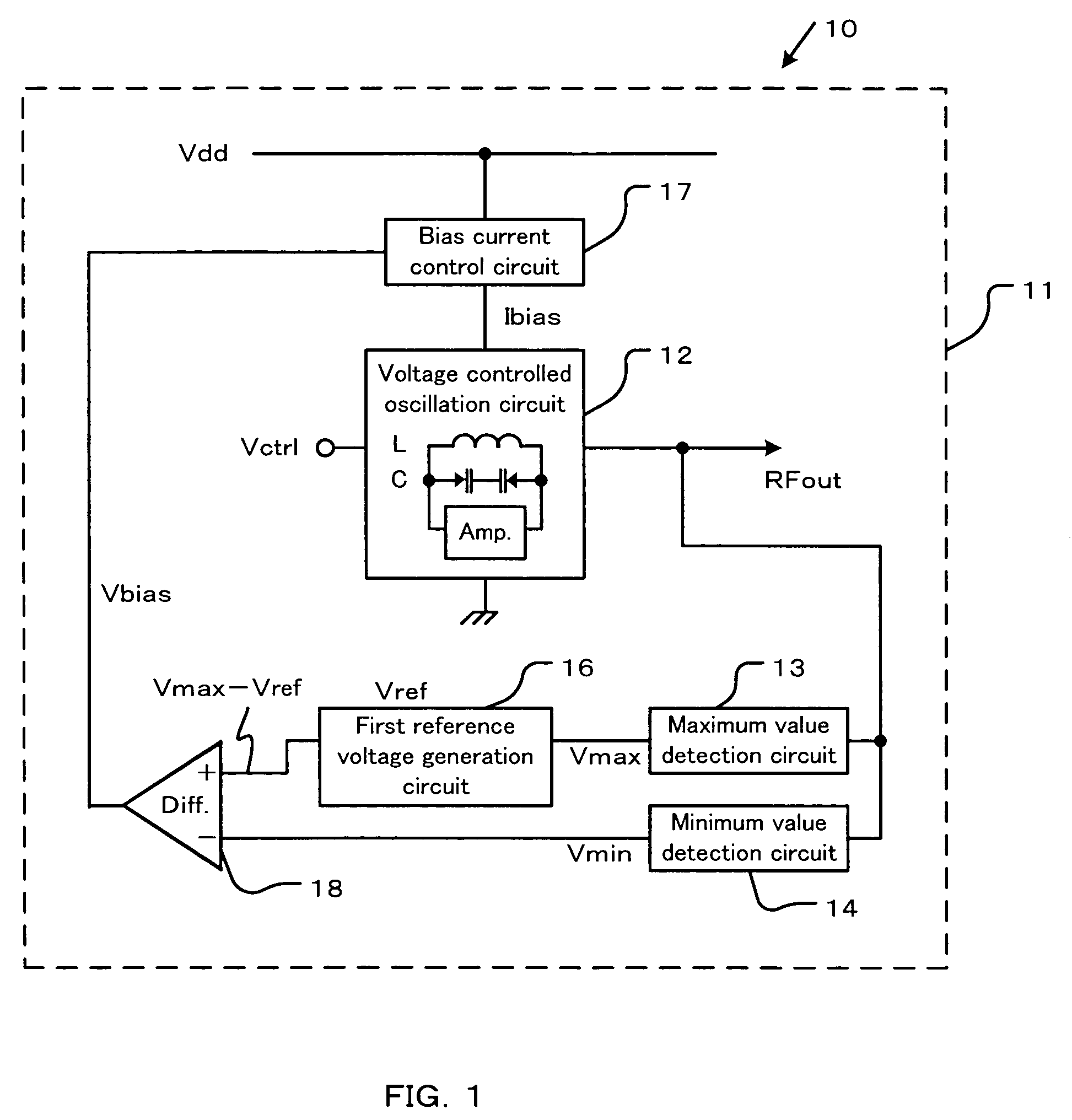
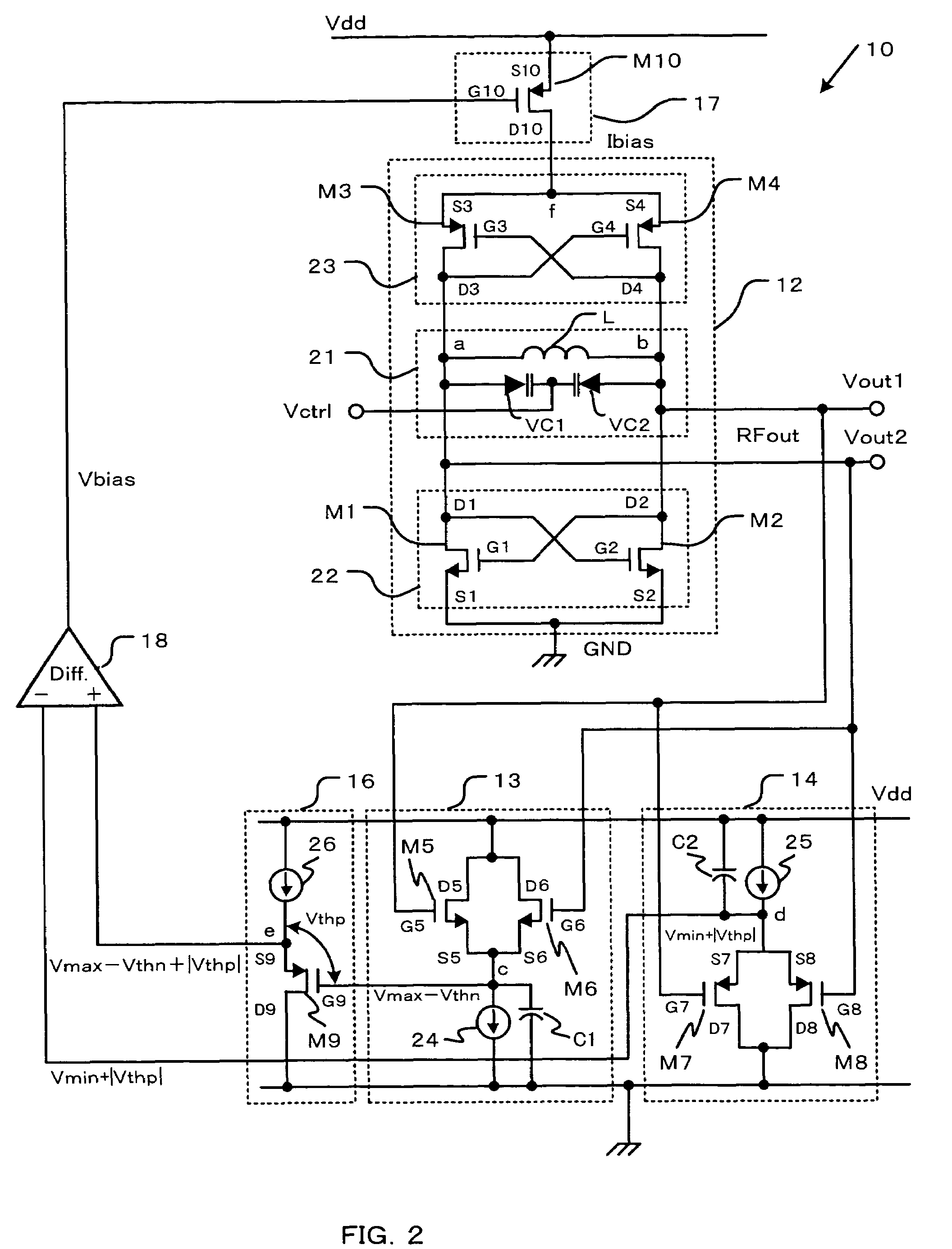
Semiconductor integrated circuit device and wireless communication device
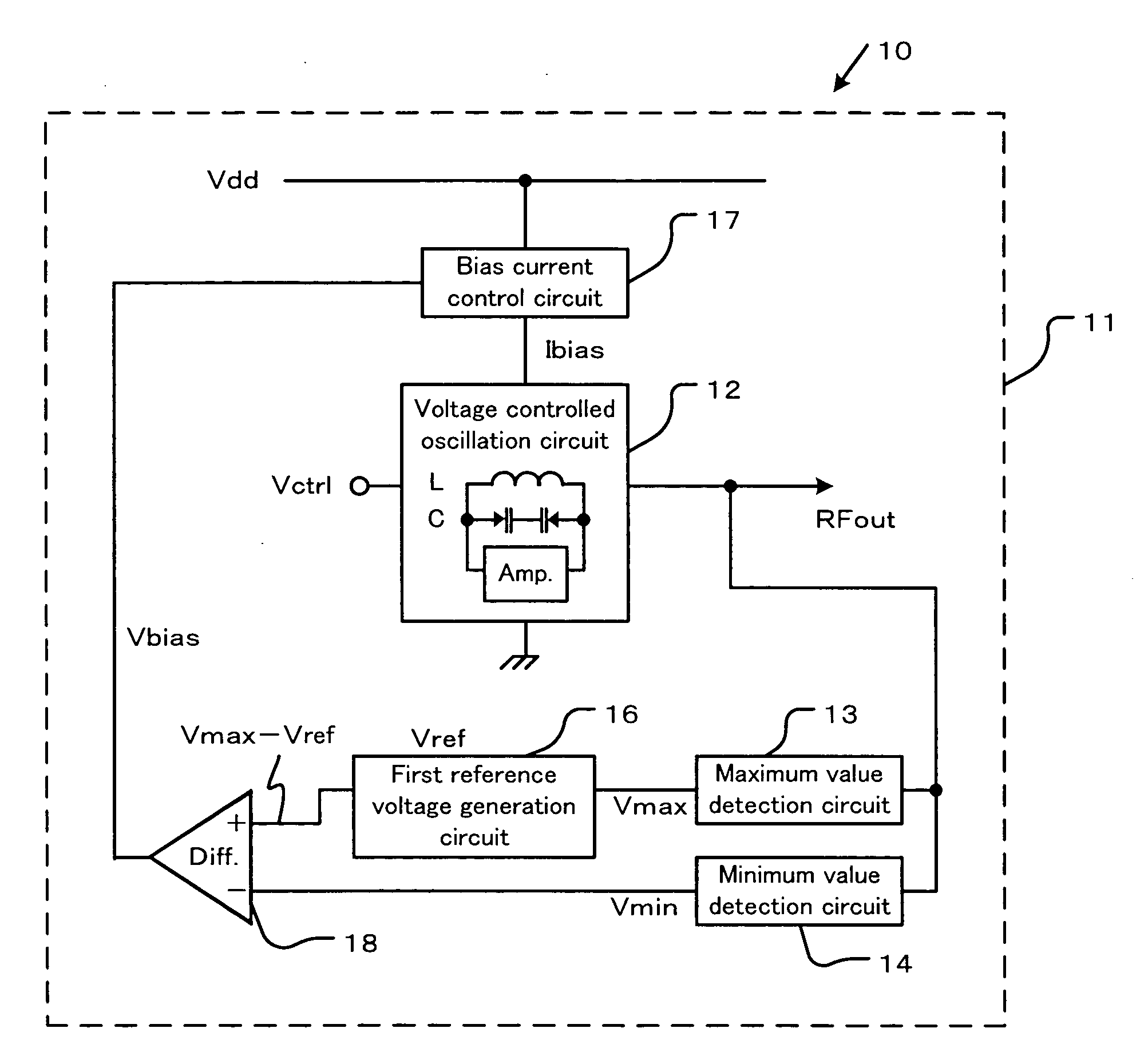
A semiconductor integrated circuit device having a voltage controlled oscillation circuit that is capable of sufficient oscillation performance and a wireless communication device having the semiconductor integrated circuit device are disclosed. A difference between the maximum value and the minimum value of the oscillation output signal is automatically controlled to be substantially equal to the first predetermined voltage which is the threshold voltage of the oscillation MOSFET for sufficient phase noise performance. It is further disclosed that the difference between the maximum value and the minimum value of the oscillation output signal may be varied by the change of the threshold voltage of the MOSFET caused by substrate bias effect, while maintaining the sufficient phase noise performance.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Semiconductor device, power supply device, and information processing device
InactiveCN101171678APreventive effectAvoid reverse currentTransistorDc-dc conversionInformation processingDrain current
Owner:ROHM CO LTD
High frequency switch circuit for inhibiting substrate bias effect in sampling hold circuit
InactiveCN101783580AGood linearity of equivalent resistanceImprove the signal-to-noise-distortion ratioPower conversion systemsEngineeringLinearity
The invention discloses a high frequency switch circuit for inhibiting substrate bias effect in a sampling hold circuit, comprising a first substrate bias-inhibiting high frequency switch unit, a second substrate bias-inhibiting high frequency switch unit and a transmission gate switch, wherein the first substrate bias-inhibiting high frequency switch unit consists of two NMOS (N-channel Metal Oxide Semiconductor) transistors and two PMOS (P-channel Metal Oxide Semiconductor) transistors, the second substrate bias-inhibiting high frequency switch unit consists of two NMOS transistors and two PMOS transistors and the transmission gate switch consists of one NMOS transistor and one PMOS transistor. In the high frequency switch circuit, because a feed through signal introduced by a switch parasitic capacitor can be grounded through a by-pass, the variation of the input end does not affect the output end after the switch is turned off, thereby the hold function of high precision is realized. The switch design of inhibiting the substrate bias effect is utilized. Because the variation of a threshold voltage caused by the inequality of a substrate and a source electric potential is inhibited, the linearity of the equivalent resistance of the switch circuit is better and the signal-to-noise distortion ratio of the circuit is improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Novel Si-APD (Silicon-Avalanche Photo Diode) device
ActiveCN104180790ASolve complexityReduce complexityOptical rangefindersSemiconductor devicesNegative feedbackSilicon
The invention discloses a novel Si-APD (Silicon-Avalanche Photo Diode) device. The novel Si-APD device comprises a first single Si-APD and a second single Si-APD which are arranged adjacently in parallel, wherein the first single Si-APD corresponds to a light window and serves as a light detection unit; the second single Si-APD is set in backlight and serves as a breakdown voltage detection unit; the first single Si-APD and the second single Si-APD share the same negative pole. Based on the principle that the properties of adjacent devices in the integrated circuit technology are consistent with each other, and paired Si-APDs are adopted; the first single Si-APD is used for detecting light and the second single Si-APD serves as the breakdown voltage detection unit; an optimal bias effect can be achieved, just by means of detecting the dark current of the second single Si-APD, stabilizing the value of the dark current via a negative feedback control loop, and utilizing the voltage when the value of the dark current is maintained at a set value to serve as the work bias voltage of the first single Si-APD, so that the complicacy problem of the traditional dynamic bias is solved, the complicacy degree and cost of a distance measuring system are lowered, and the novel Si-APD device is simple and practical.
Owner:ASSOC OPTO ELECTRONICS CHONGQING
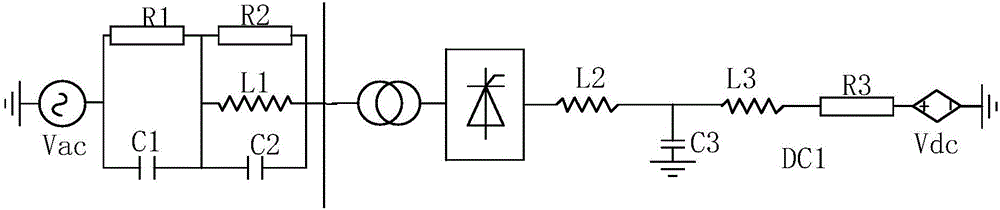
Method for determining harmonic instability of single-circuit high-voltage direct-current power transmission system
InactiveCN104113072ANegative sequence impedance parameter omittedElectric power transfer ac networkFault locationTransformerHarmonic
The invention discloses a method for determining harmonic instability of a single-circuit high-voltage direct-current power transmission system. The method is characterized in that the direct-current magnetic bias effect of transformers is taken into account, a direct-current magnetic bias coefficient is introduced to the process of derivation, a negative sequence impedance parameter of the alternating-current side is omitted, and only positive sequence secondary impedance of the alternating-current side and fundamental frequency impedance of the direct-current side are adopted to determine whether the system suffers from harmonic instability. A novel method for determining whether a single-circuit high-voltage direct-current system suffers from harmonic instability is put forward.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Harmonic instability determination method for light-weight high-voltage direct-current power transmission 12-pulse wave converter
ActiveCN106208033ANegative sequence impedance parameter omittedReliable resultsDc circuit to reduce harmonics/ripplesModulation theoryTransformer
The invention discloses a harmonic instability determination method for a light-weight high-voltage direct-current power transmission 12-pulse wave converter. The harmonic instability determination method comprises the following steps of obtaining a relation of modulation from a direct current side current to an alternating current side, and a relation of modulation from an alternating current side voltage to the direct current side according to a 12-pulse wave converter switching function modulation theory; for low-order harmonics, setting a direct current side fundamental frequency harmonic current to be Idcl(t) at a t moment; modulating the direct current side harmonic current to the alternating current side through the converter as follows: a formula which is as shown in the specification; in a (t+<delta>t) moment, obtaining harmonic voltage change as follows: a formula which is as shown in the specification; obtaining harmonic instability engineering criterion of a single-circuit direct current line according to current ratio at the (t+<delta>t) moment and the t moment as follows: a formula which is as shown in the specification; and when a formula which is as shown in the specification is workable, showing that the current in the direct current side system is increased constantly, the system is instable, and the harmonic instability is excited. According to the harmonic instability determination method, by combination with a direct current magnetic bias effect of a transformer, a direct current magnetic bias coefficient is introduced; negative sequence impedance parameters at the alternating current side are omitted; the alternating current side positive sequence secondary impedance and the direct current side fundamental frequency impedance are adopted to determine whether the harmonic instability occurs or not, so that the determination method is more accurate and reliable.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
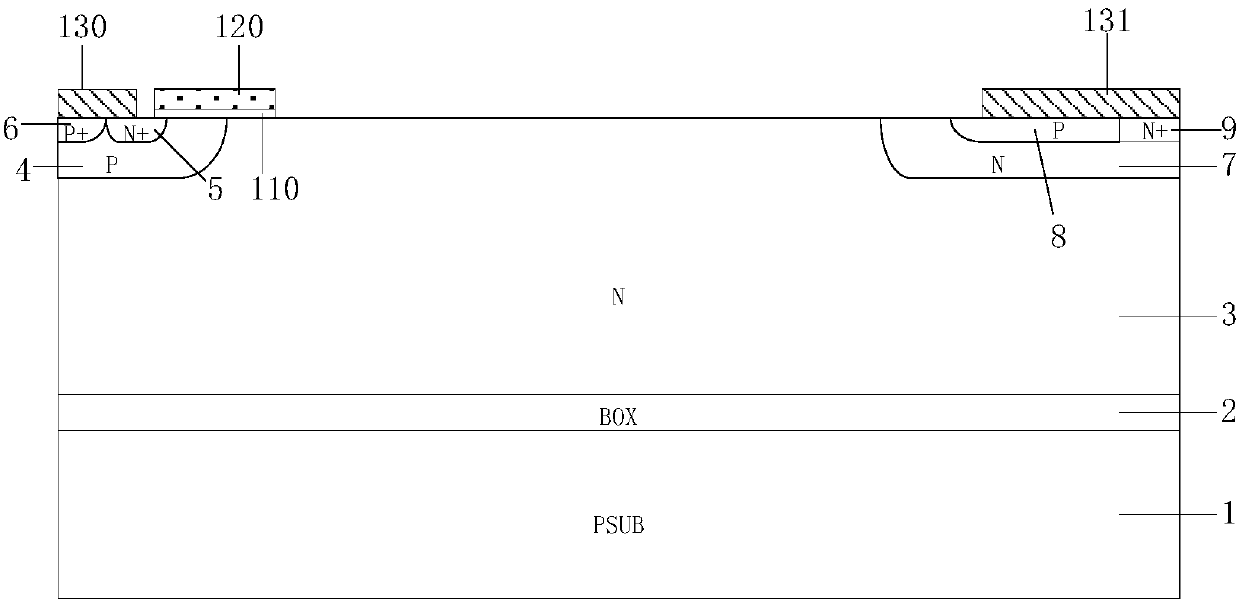
Transverse insulated gate bipolar transistor
InactiveCN107068744AThere is no negative resistance phenomenonImprove breakdown voltageTransistorSolid-state devicesPower flowCharge carrier
The invention belongs to the semiconductor power device technology field, and particularly relates to a transverse insulated gate bipolar transistor. In the invention, a poly-diode is formed on a surface of a drift region of a member and a PMOS and a Zener diode are formed in proximity to a collector; in a blocking state, under an action of charges and a field plate which are supplied through depleting the drift area in a reverse bias state of a polycrystalline diode on the surface of the member, voltage resistance higher than that that of a traditional structure is obtained while a doping concentration of the drift region of the member; in a process of switching off the member, a voltage change of a collector and a self-bias effect formed by a surface polycrystalline diode and a zener diode make PMOS near the collector automatically start and conduct and accelerate carrier extraction in an LIGBT so as to improve switching off speed of the member; in a conductive state, the PMOS around the collector is in a switching off state and an access of electronic current is cut off. As a result, the transverse insulated gate bipolar transistor has higher breakthrough voltage, and, in the process of switching off, has faster switching off speed and switching off loss.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
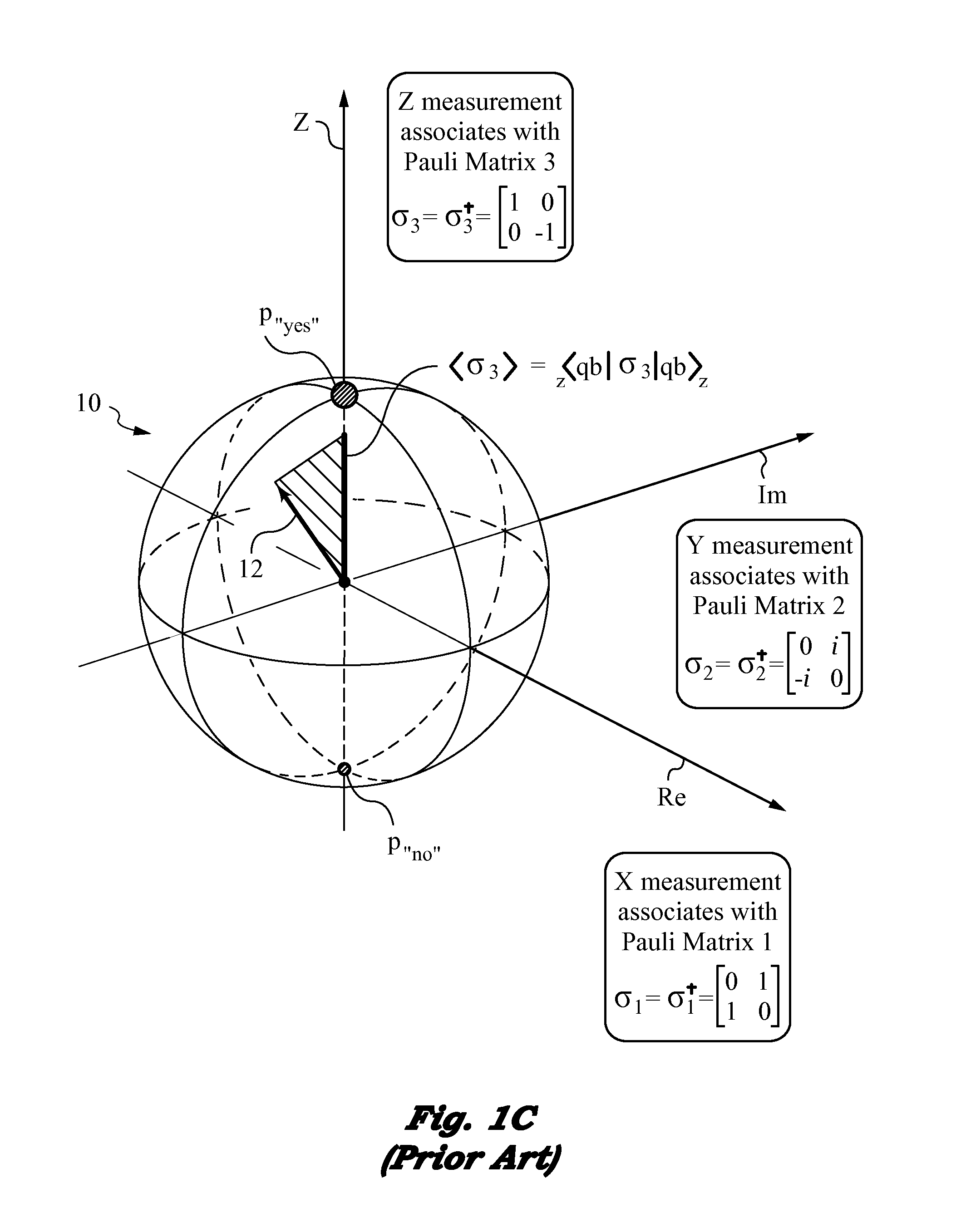
Biasing effects on the contextualization of a proposition by like-minded subjects considered in a quantum representation
InactiveUS20160180238A1Address biasing effectQuantum computersArtificial lifeComputer scienceQuantum
The present invention concerns methods and apparatus for detecting biasing effects induced by one or more biasing entities when using a quantum representation of like-minded subjects and their shared contextualizations of propositions. Like-minded subjects are understood to be any sentient beings, e.g., human beings, that use shared contextualizations modulo certain propositions and exhibit analogous measurable indications in response to these propositions. Measureable indications can take on the form of responses, actions, behaviors or any measurable aspects that can be collected from the subjects in response to the propositions. Contextualizations that are mutually incompatible are represented by non-commuting quantum mechanical operators while compatible contextualizations are represented by commuting quantum mechanical operators.
Owner:INVENT LY LLC
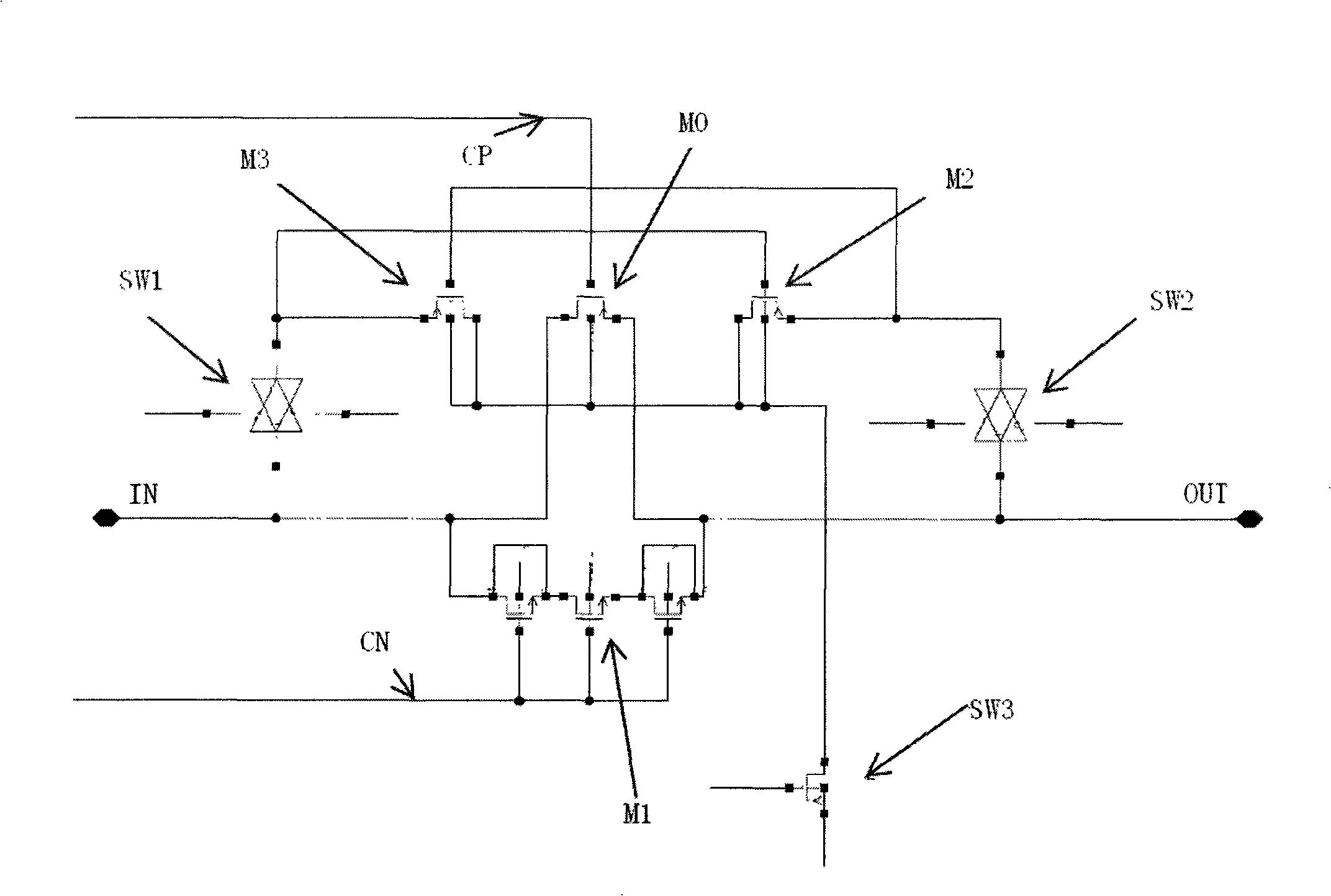
Analog switch chip design method and chip device
InactiveCN101272138ADoes not affect bandwidthDoes not affect off-isolation performanceElectronic switchingCharge injectionCMOS
The invention provides a design method of an analog switch chip which controls the time sequence by a clock circuit and controls the work of the substrate bias canceling circuit of a main switch MOS in a standard CMOS technique analog switch circuit by an additional switch module. The invention also provides a chip device which comprises a standard CMOS technique analog switch circuit, a substrate bias canceling circuit, an additional switch module and a clock circuit. The substrate bias canceling circuit is connected with the substrate of the main switch MOS; a secondary switch provided by the additional switch module is respectively connected with the substrate bias canceling circuit and a power supply voltage; the clock circuit provides a chip device control time sequence. The analog switch chip of the invention improves the bandwidth of the analog switch as well as the turn-off isolation and charge injection properties of the analog switch, which simultaneously ensures the substrate bias effect to be cancelled and improves the conducting impendence property.
Owner:方泰开曼公司
Semiconductor memory device having bit line precharge circuit controlled by address decoded signals
A semiconductor memory device includes a memory cell array, a charge circuit which compensates for OFF leakage current developed at selected bit lines, a reset circuit having a ground potential corresponding to a potential at non-selected bit lines, a read circuit constituted by a plurality of transistors whose gates are connected to the bit lines, and a bit line precharge circuit which charges the selected bit lines for a fixed time period. As a result of adopting such a configuration, there is no need to provide a transmission gate, such as a column decoder, to a charging path between the read circuit and the bit lines, so that a low-power supply voltage operation can be effected without the influence of a substrate bias effect.
Owner:SOCIONEXT INC
Voltage generator
InactiveUS6927621B2Data holding time is cut downSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingVoltage generatorSubstrate bias voltage
When the substrate bias voltage Vbb lowers by the pumping operation of the charge pump circuit, a drain-to-source resistance of the N-transistor becomes high. When a first power supply voltage Vcc is set at high value, a drain-to-source current of the N-transistor increases (I+ΔI1), however the drain-to-source current decreases (I+ΔI1−ΔI2) by the increase of the drain-to-source current owing to the substrate bias effect so that the increase of the potential of the node N34 caused by the increase of the first power supply voltage VCC is restrained. As a result, a reference level of the substrate bias voltage Vbb does not largely lower than the reference level of the substrate bias voltage Vbb when the first power supply voltage VCC is in a standard level.
Owner:LAPIS SEMICON CO LTD
Electro-magnetophoresis display
InactiveUS20050243406A1Avoid accidental movementImprove color qualityThyristorSolid-state devicesDisplay deviceEngineering
The present invention is directed to an electro-magnetophoresis display having either the traditional up / down or dual switching mode. The display cells are filled with an electro-magnetophoretic dispersion comprising particles suspended in a solvent and the particles are both charged and magnetized. The display of the invention prevents undesired movement of the particles in the cells. The magnetic force generated by the magnetic layer(s) eliminates the need to provide cells with a threshold voltage high enough to avoid the cross talk and / or cross bias effects. In addition, the dual switching mode allows the particles to move in the up / down direction as well as the planar direction, thus providing a multicolor display of high color quality at very low cost.
Owner:E INK CALIFORNIA
Level shift circuit
InactiveCN1433076ALower threshold voltageHigh speed entryLogic circuits coupling/interface using field-effect transistorsSolid-state devicesLow voltageEngineering
In a level shift circuit according to the invention, either an input signal IN or an inverted input signal XIN, which are input into the gate electrodes of n-type transistors 1, 2 for signal input, is also given to the substrate of that n-type transistor via p-type transistors 5, 6 for substrate bias. When the signal IN or XIN rises and changes, the threshold voltages of the n-type transistors 1, 2 for signal input is lowered due to the substrate bias effect. Consequently, even if the signal IN or XIN has a low voltage level, operation is carried out at high speeds. Also, when either an output signal OUT or an inverted output signal XOUT is changed to a high voltage level, the transistors 5, 6 for substrate bias become non-conducting, and thus the input signal IN or the inverted input signal XIN is not supplied to the substrate of the n-type transistors 1, 2 for signal input other than when the signal is changing. Consequently, a constant passing-through current does not flow to the substrate of these transistors.
Owner:SOCIONEXT INC
FINFET dynamic random access memory unit and processing method thereof
ActiveCN102683418AImprove reading efficiencyImprove writing efficiencySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesCMOSStatic random-access memory
The invention provides a FINFET dynamic random access memory unit and a processing method thereof. The FINFET dynamic random access memory unit comprises a substrate, a body region, a source electrode, a drain electrode, a fin, a source electrode metal layer, a grid dielectric layer, a grid electrode and a passivation layer. The FINFET dynamic random access memory unit provided by the invention stores the produced carriers in the body region at the lower part a transistor, and based on the substrate bias effect of the transistor, by regulating the charges in the body region of the devices, the FINFET dynamic random access memory unit makes the threshold voltage of the devices vary so as to realize the aim of information storage. The FINFET dynamic random access memory unit is simple in principle, can obtain higher speed, cannot damage the charges stored in the body region during the data reading process, and improves the maximum refresh time; and the FINFET dynamic random access memory unit uses the FinFET structure, so that the reading and writing efficiency is improved. The processing method provided by the invention is simple in technology and compatible to the conventional CMOS (Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor) technology, and the dynamic random access memory unit formed by the method cannot damage the charges stored in the body region during the reading process and improves the maximum refresh time.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Device and method for correcting pixel output nonlinear response of image sensor
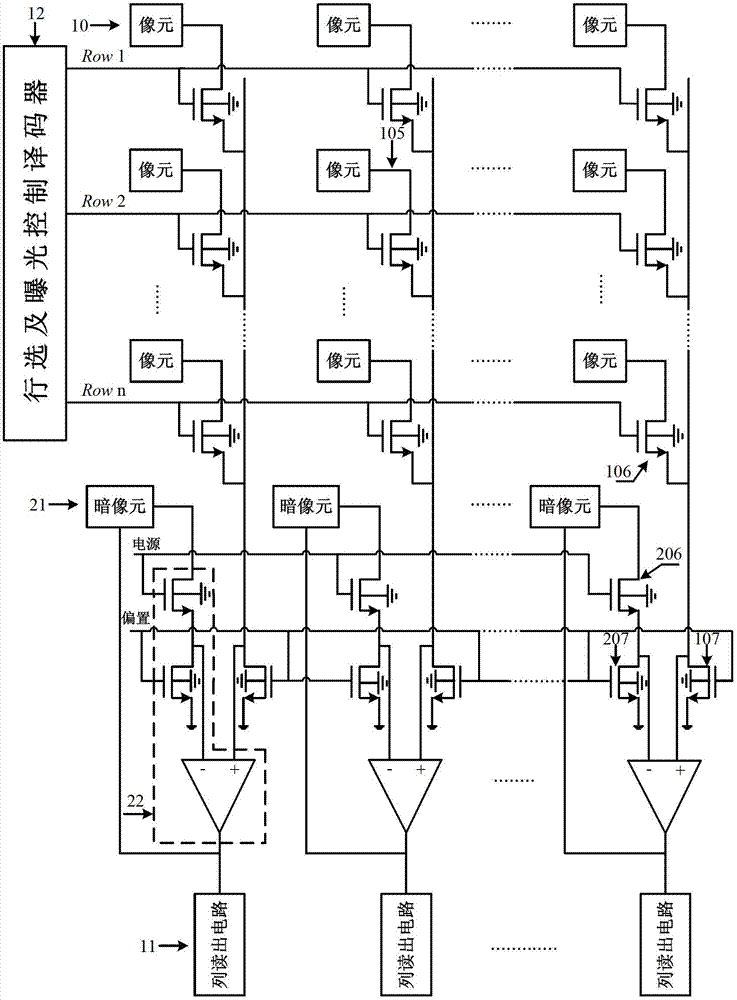
ActiveCN103118235AImprove image qualityImprove linearityTelevision system detailsColor television detailsImaging qualityExposure control
The invention discloses a device and a method for correcting pixel output nonlinear response of an image sensor. The device comprises a photosensitive pixel array, a dark pixel, a photosensitive pixel row selection switch, a dark pixel switch, a photosensitive pixel bias current source, a dark pixel bias current source, a linear circuit, a simulating line reading circuit and a row selection and exposure control decoder. Compared with traditional image sensors, a nonlinear correcting circuit formed by the dark pixel and the linear circuit is added, the correcting circuit occupies smaller chip area, effectively restrains nonlinear problems caused by substrate bias effects, linearity of pixel output signals and imaging quality of image sensors are improved greatly.
Owner:NO 771 INST OF NO 9 RES INST CHINA AEROSPACE SCI & TECH
Semiconductor device, power supply device, and information processing device
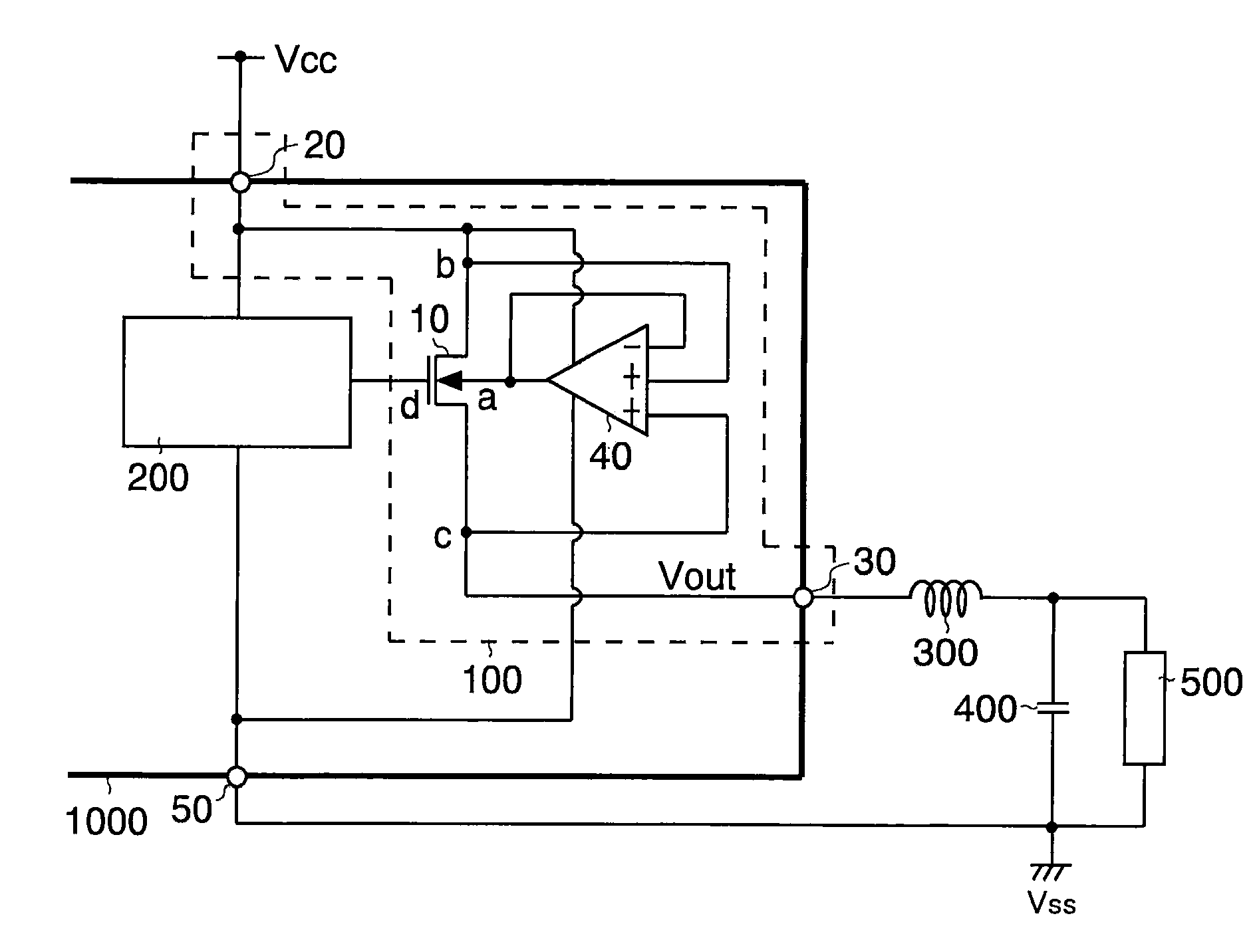
InactiveUS20090128219A1Increase potential differenceReduce potential differenceTransistorDc-dc conversionDrain currentInformation processor
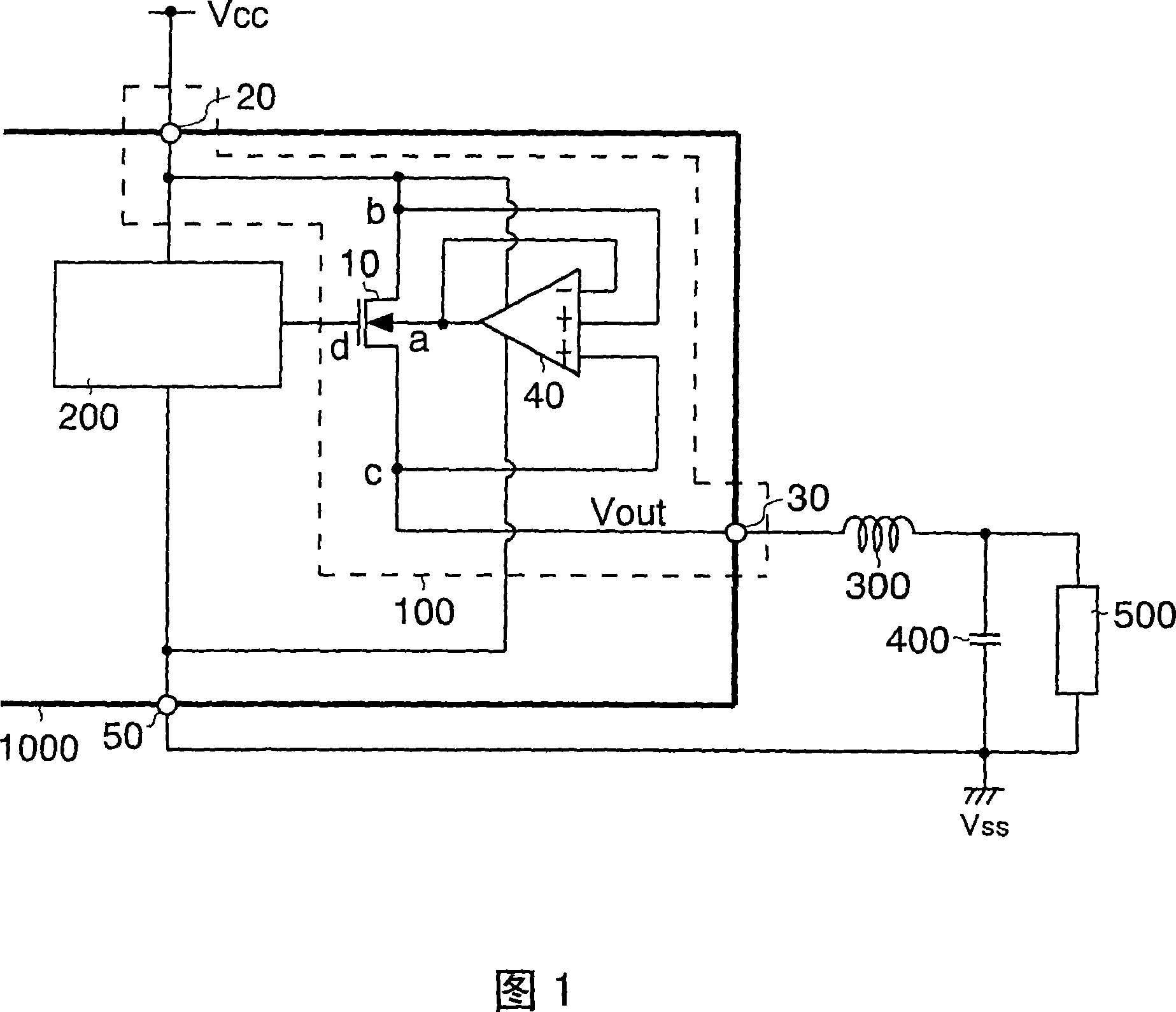
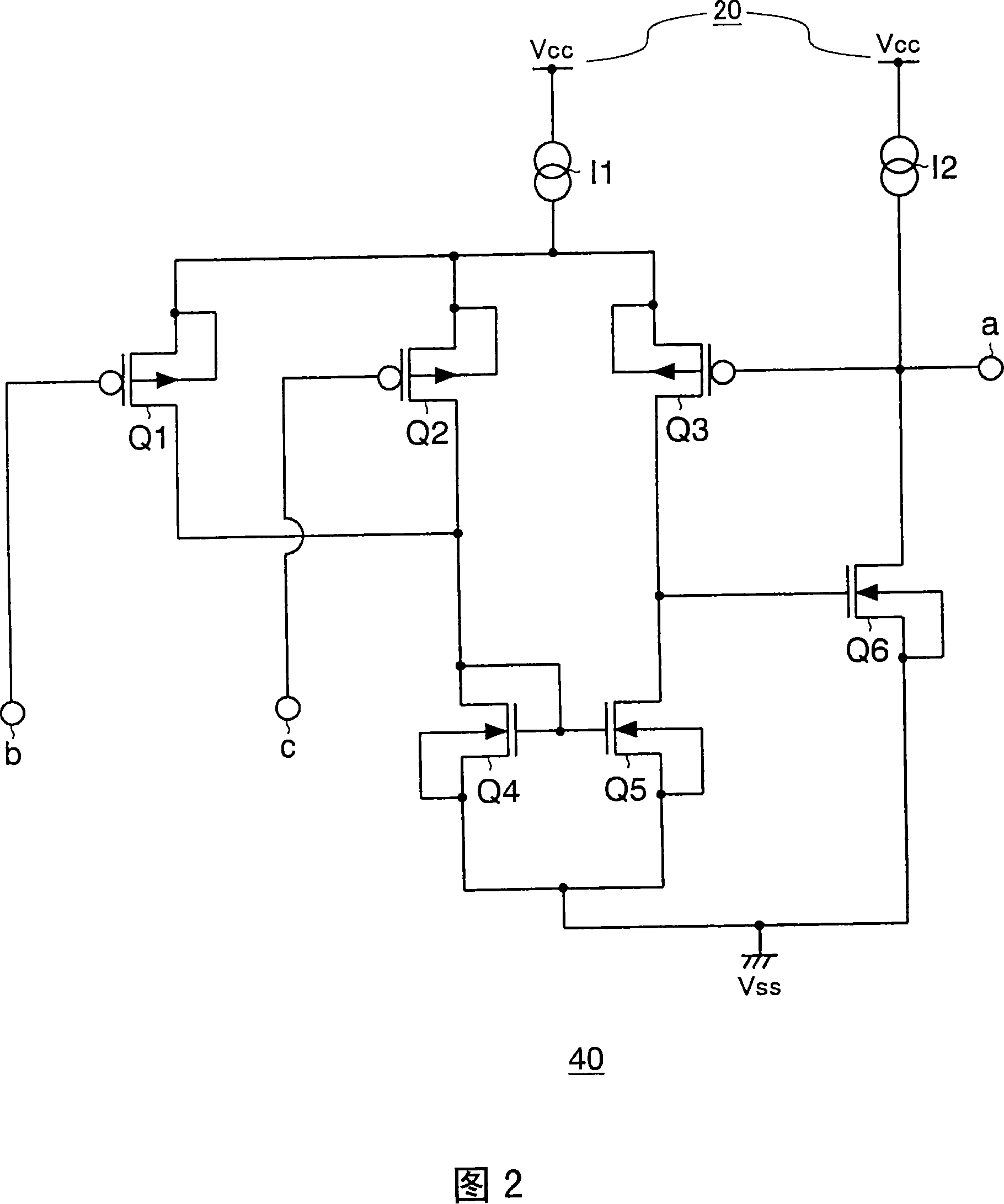
A semiconductor device (100) includes a MOS transistor (10) having a back gate region “a”, a first region “b” serving as one of a source region and a drain region, and a second region “c” serving as the other of the source region and the drain region. The semiconductor device further includes an input terminal (20) connected to the first region “b” and to which an input voltage is applied from outside the semiconductor device (100), an output terminal (30) connected to the second region “c” and outputting an output voltage outside the semiconductor device (100), and a back gate control circuit (40) for applying the input voltage or the output voltage to the back gate region “a”. With this configuration of the semiconductor device having the output MOS transistor, even when a reverse bias is applied between the input and the output terminal, the terminals are insulated from each other and lowering of the drain current by the substrate bias effect can be suppressed.
Owner:ROHM CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com