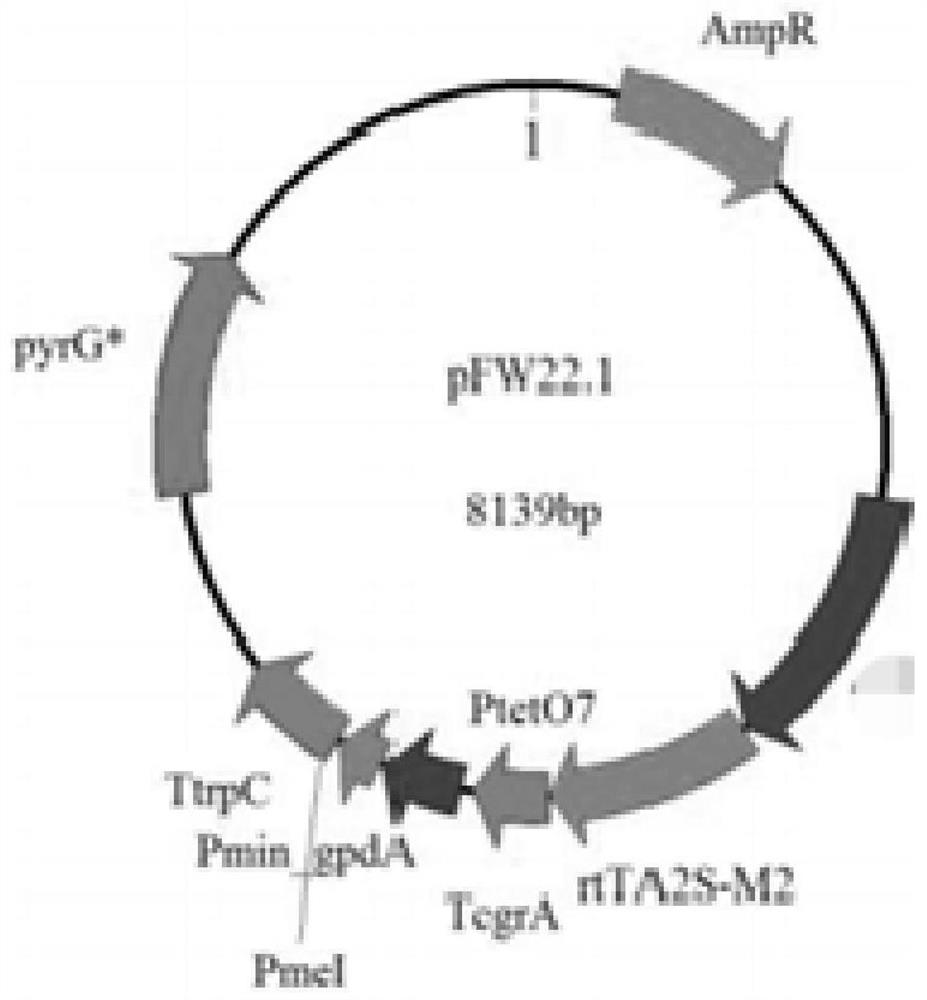
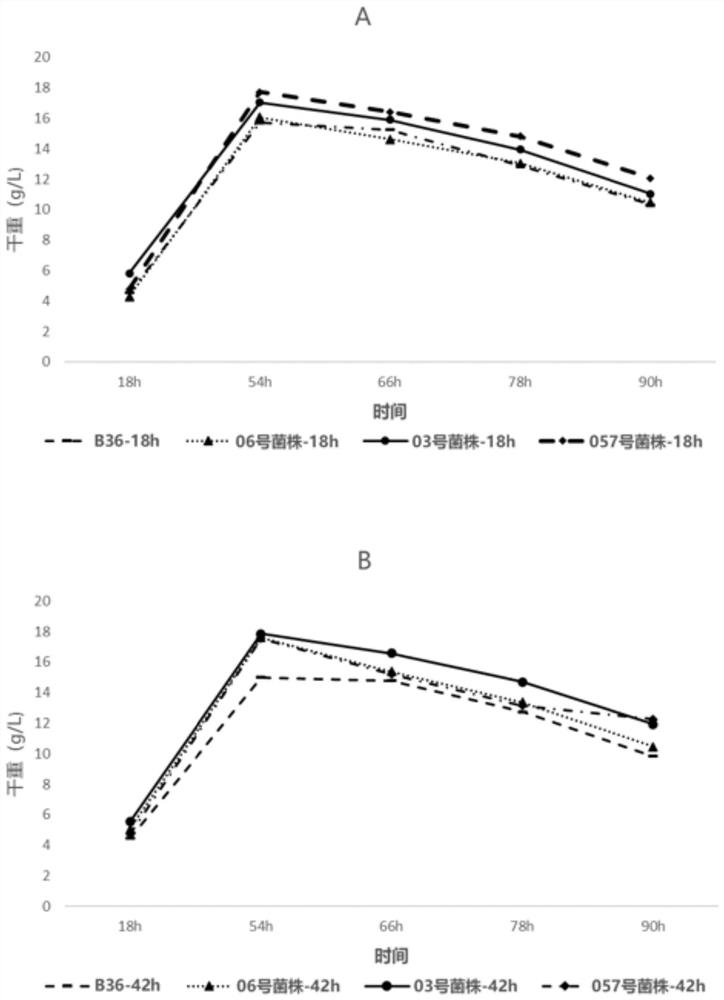
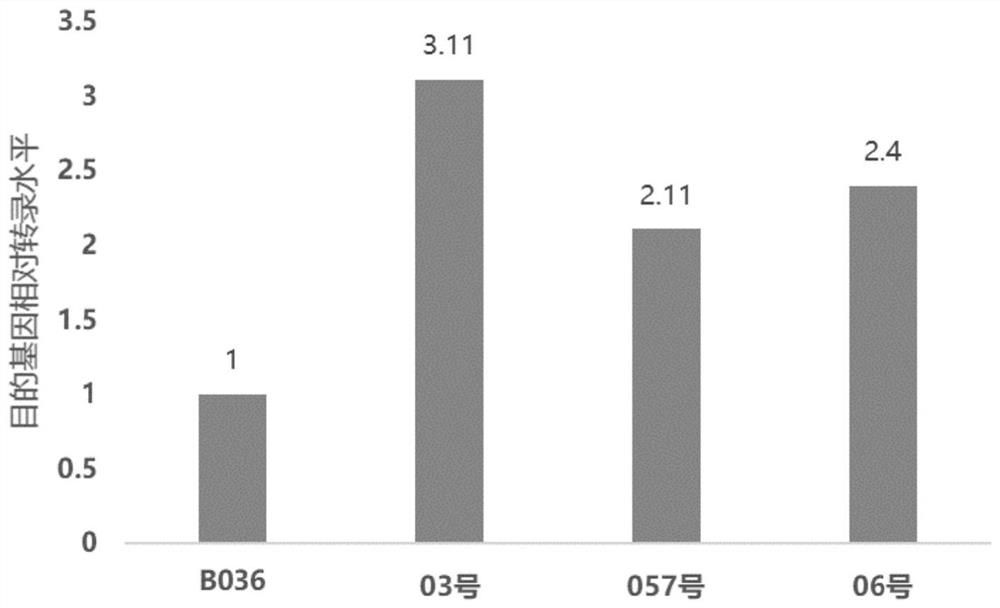
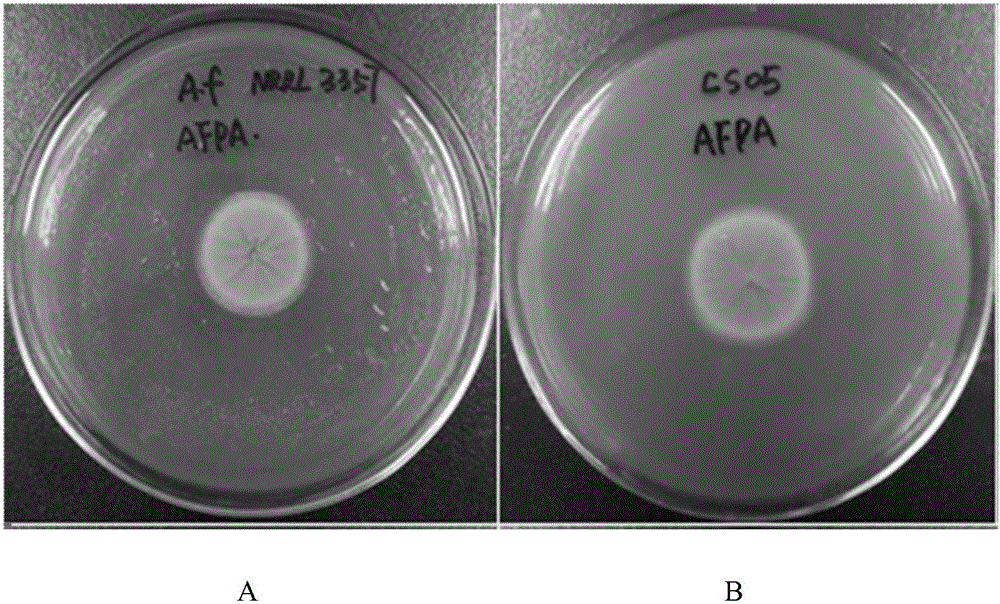
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
75 results about "Aspergillus variecolor" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
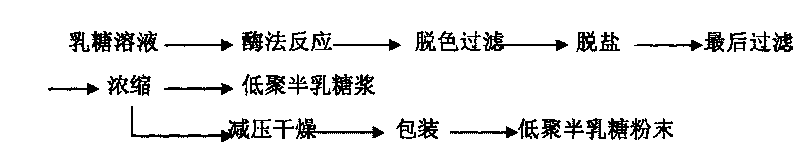
Aspergillus oryzae and method for preparing high purity galacto-oligosaccharides by using same
ActiveCN101691538ASimple processEase of industrial productionFungiMicroorganism based processesHigh concentrationUltrafiltration
The invention relates to a method for preparing high purity galacto-oligosaccharides, comprising the following product separation and purification steps: Aspergillus oryzae fermentation, ceramic membrane ultrafiltration, nanofiltration separation and the like. In the method, the Aspergillus oryzae separated from the soil is adopted as an original strain and the Aspergillus oryzae BLB-21 (with preservation number of CGMCC No.2951), a high efficiency transformed strain obtained through mutation screening in the laboratory, is directly used to ferment high concentration lactose solution, thus avoiding the steps of enzyme purification and the like in the process of preparing the galacto-oligosaccharides by an enzyme method and saving time and labor. The high purity galacto-oligosaccharides are obtained by ultrafiltration and nanofiltration separation, the process is ideal, the conditions are mild and the method has extensive industrial production prospect.
Owner:BAOLINGBAO BIOLOGY
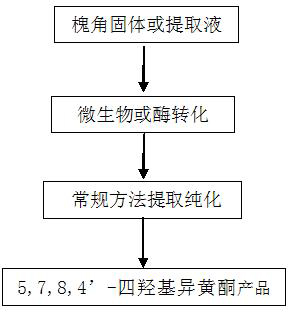
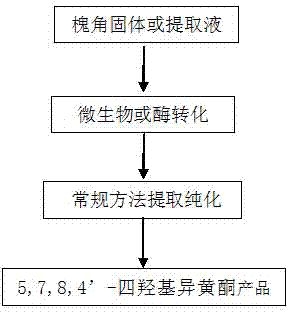
A strain of Aspergillus aculeatus and method for preparing 5,7,8,4'-tetrahydroxyisoflavones using the strain
ActiveCN102277304AStrong transformation specificityImprove conversion efficiencyFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyGlycoside
The invention relates to an Aspergillus aculeatus ZJ bacterial strain and an application thereof. The collection number of the Aspergillus aculeatus ZJ is CCTCC NO.M2011264. The bacterial strain is mainly used for converting effective components of the pod of Chinese scholartree to produce 5,7,8,4'-tetrahydroxyisoflavone. The specific method provided by the invention comprises the following steps of: acting the Aspergillus aculeatus ZJ with strong specificity or the produced enzyme on the pod of Chinese scholartree or extracting solution thereof; converting glucosides compounds including sophoricoside and the like, genistein and the like to produce the 5,7,8,4'-tetrahydroxyisoflavone. The invention provides the method for producing the 5,7,8,4'-tetrahydroxyisoflavone through utilizing the Aspergillus aculeatus with high specificity and high conversion efficiency to convert the sophoricoside; and the method provided by the invention has moderate conditions, green process and simple requirements on the process and the device, and has a very good application value.
Owner:NANJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Xylanase/cellobiase composite enzyme and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101705215AAvoid pollutionAddress food shortagesBiofuelsMicroorganism based processesFiberAlcohol
The invention provides a xylanase / cellobiase composite enzyme prepared by using Aspergillus niger CGMCC 3.3147 and a preparation method thereof. The xylanase and the cellobiase can be efficiently co-produced through the Aspergillus niger, wherein the produced xylanase can reach 10,000 IU / g and the cellobiase can reach 900 IU / g through a preferable fermentation culture medium; and the prepared composite enzyme can be mixed-used directly with the cellobiase in the production of straw fermented alcohol, xylitol, citric acid and the like. The composite enzyme and the preparation method have great realistic significance for solving the problems of environment pollution, food shortage and energy crisis.
Owner:ANHUI BBCA FERMENTATION TECH ENG RES
Defensin and application thereof in preparation of medicines for resisting aspergillus
Owner:保罗生物园科技股份有限公司
Separation and optimization method and application of laccase-producing fungus strain
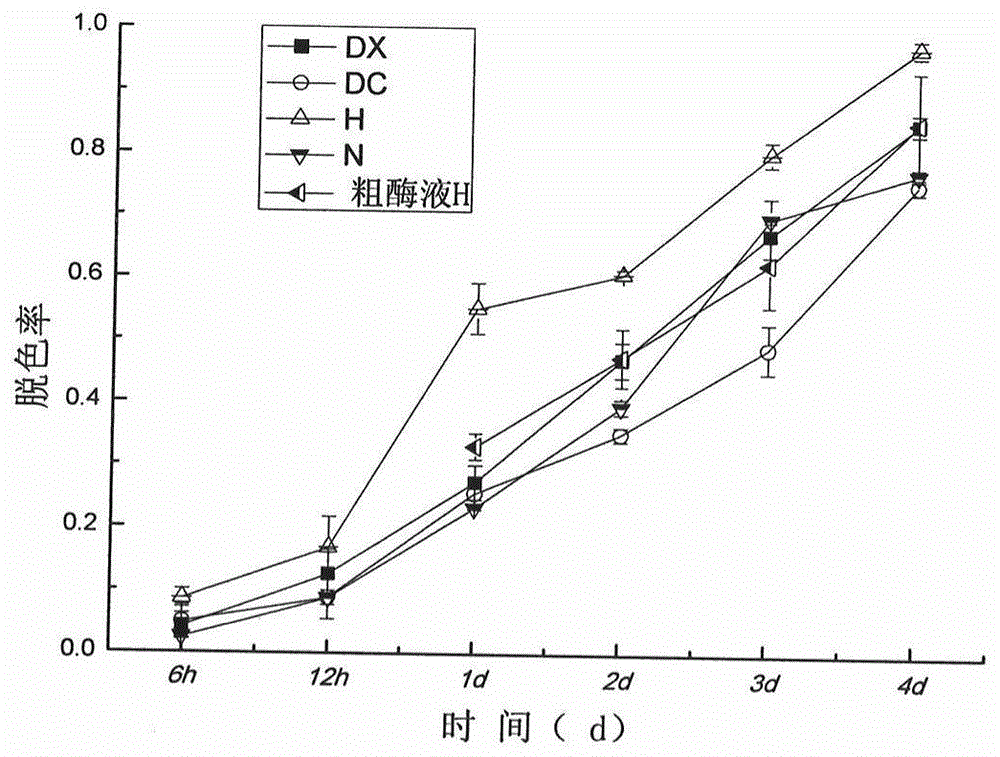
InactiveCN105733953AGood decolorization efficiencyFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologySequence analysis
The invention discloses a separation and optimization method and an application of a laccase-producing fungus strain. Through a color-changing reaction between guaiacol and laccase, a laccase-producing fungus is screened, and then according to morphologic observation and rDNA-ITS sequence analysis, myrothecium verrucaria is identified. The myrothecium verrucaria, as a patent preserved strain, is a strain highly producing laccase, and reaches 316 U / ml in enzyme activity of the produced laccase after optimization, which is higher than that of myrothecium verrucaria NF-05 by 45.08 U / ml. The enzyme activity and decolorizing rates on nine active dyes of the fungus strain are much higher than those of talaromyces, aspergillus and glomerella producing the laccase. Through a single factor experiment and uniform design, the optimum conditions of the myrothecium verrucaria producing the laccase are determined. Through HPLC, TLC and infrared spectrum, the myrothecium verrucaria is proved to have degradation on reactive green 19. The fungus separated from rhizosphere of taxus chinensis has excellent application prospect and potential in the fields of industrial wastewater treatment, green traffic, environment protection and sustainable development.
Owner:DALIAN JIAOTONG UNIVERSITY
Aspergillus niger strain with high yield of beta-glucosidase and application
ActiveCN113403207AOvercome the disadvantages of pollutionEnhance β-glucosidase enzyme activityFungiMicroorganism based processesAlgluceraseEnzyme system
The invention belongs to the technical field of biomass material degradation and application of producing single-cell protein, and particularly discloses an aspergillus niger strain with high yield of beta-glucosidase and application. The preservation number of the aspergillus niger strain is CGMCC No. 22465, the activity of the beta-glucosidase produced by a fermentation method is up to 88IU / mL, a composite cellulase preparation is formed by simple compounding with a trichoderma reesei cellulase preparation, the enzyme system of the composite cellulase preparation is more balanced, the glucose release amount is increased by 35% or more under the condition of biomass high-solid enzymolysis, the cellulose conversion rate in the biomass material is greater than 90%, the application is completed in the straw single-cell protein, and the protein content in the straw single-cell protein product is greater than 25%.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Aspergillus fumigatus strain Bfum-5 and application thereof
ActiveCN105002098AThe effect of strong degradation of celluloseFungiMicroorganism based processesChemistryFilter paper
The invention relates to an aspergillus fumigatus strain Bfum-5 and its application and belongs to the field of microbial ecology. Preservation number of the aspergillus fumigatus strain Bfum-5 is CGMCC No.10929. The invention also provides a product and microbial inoculums used for degrading cellulose with the aspergillus fumigatus strain Bfum-5 as an active ingredient and a method for degrading cellulose based on the strain Bfum-5. Meanwhile, the invention provides an application of the strain Bfum-5 in the preparation of a product for degrading cellulose. Through CMC-Na hydrolyzation circle determination, filter paper degradation experiments and cellulase enzyme activity determination, it has been confirmed that the aspergillus fumigatus strain Bfum-5 has very strong capability of degrading cellulose.
Owner:北京大地聚龙生物科技有限公司
Microbial transformation preparation method for hydroxycamptothecin
InactiveCN101509023ADoes not affect growthThe operation process is simple and convenientMicroorganism based processesFermentationDry weightREFLEX DECREASE
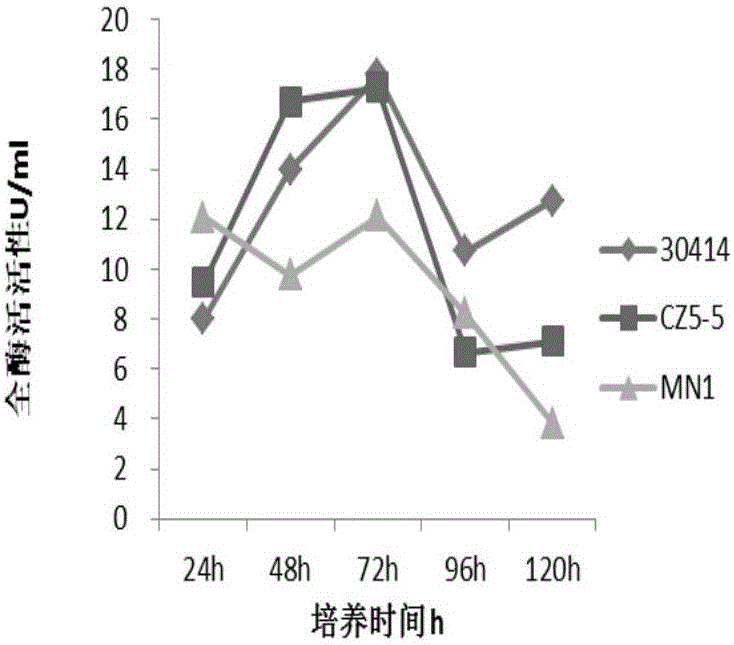
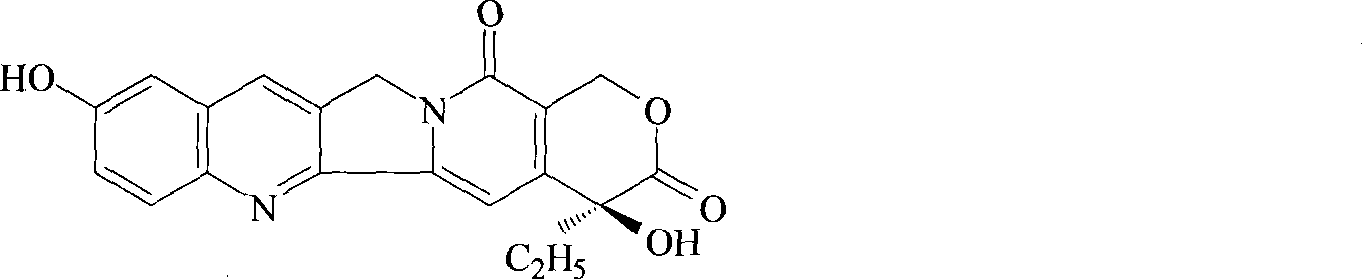
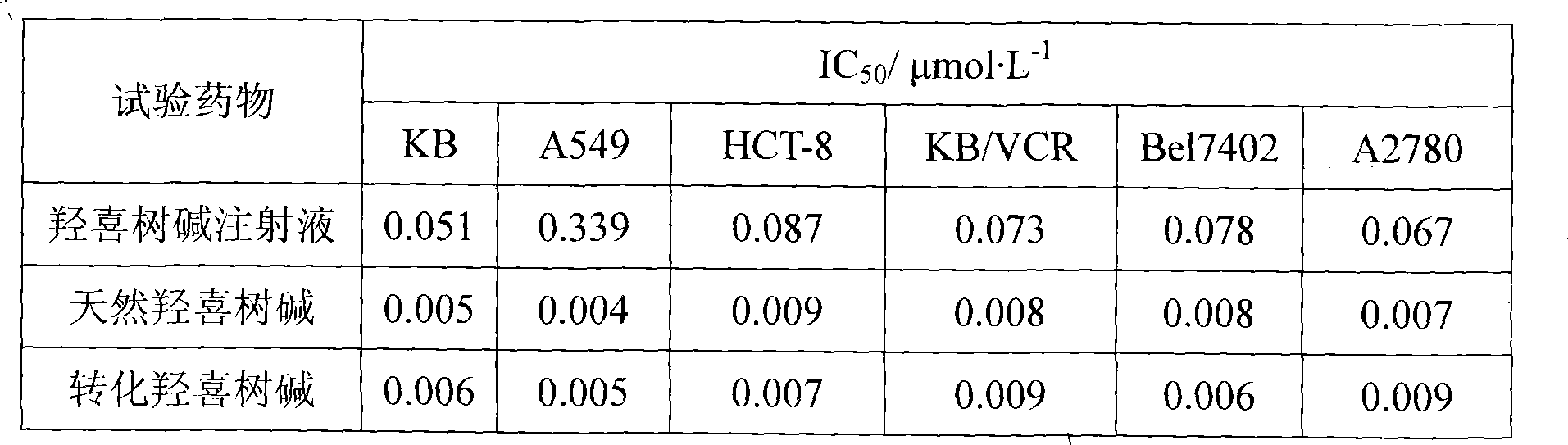
The invention belongs to the field of biotechnology, and particularly relates to a microbial transformation preparation method of hydroxycamptothecin. The invention conducts biotransformation to the camptotheca acuminata cells of a suspension culture by using non-toxic Aspergillus flavus Cr-1 strains (Aspergillus.flavus) and Rhizopus T-34 strains (Rhizopus sp.); the camptotheca acuminate cell cultures after the transformation experience separation and refining such as raw material crushing, reflex extraction, crystallization, silica gel column chromatography, crystallization, and the like, a pure hydroxycamptothecin product is obtained. The invention conducts biotransformation to the camptotheca acuminata cells of the suspension culture by using a microorganism so as to obtain a plant secondary metabolite hydroxycamptothecin which has an anti-tumor activity, wherein, the content of the plant secondary metabolite hydroxycamptothecin achieves 0.4% (g / g) of the dry weight of the cell; a new way of obtaining high-yield hydroxycamptothecin is established, thereby meeting the requirements of sustainable development; the method for separating the hydroxycamptothecin is simple, convenient and feasible; the purity of the product is high; therefore, the invention has good development prospect.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Method for synthesizing xylitol by aspergillus oryzae engineering bacteria with enhanced hemicellulose saccharification capacity
ActiveCN110982850AEnhanced hemicellulose saccharification abilityGood saccharification effectMicroorganism based processesFermentationEnzyme GeneGene Modification
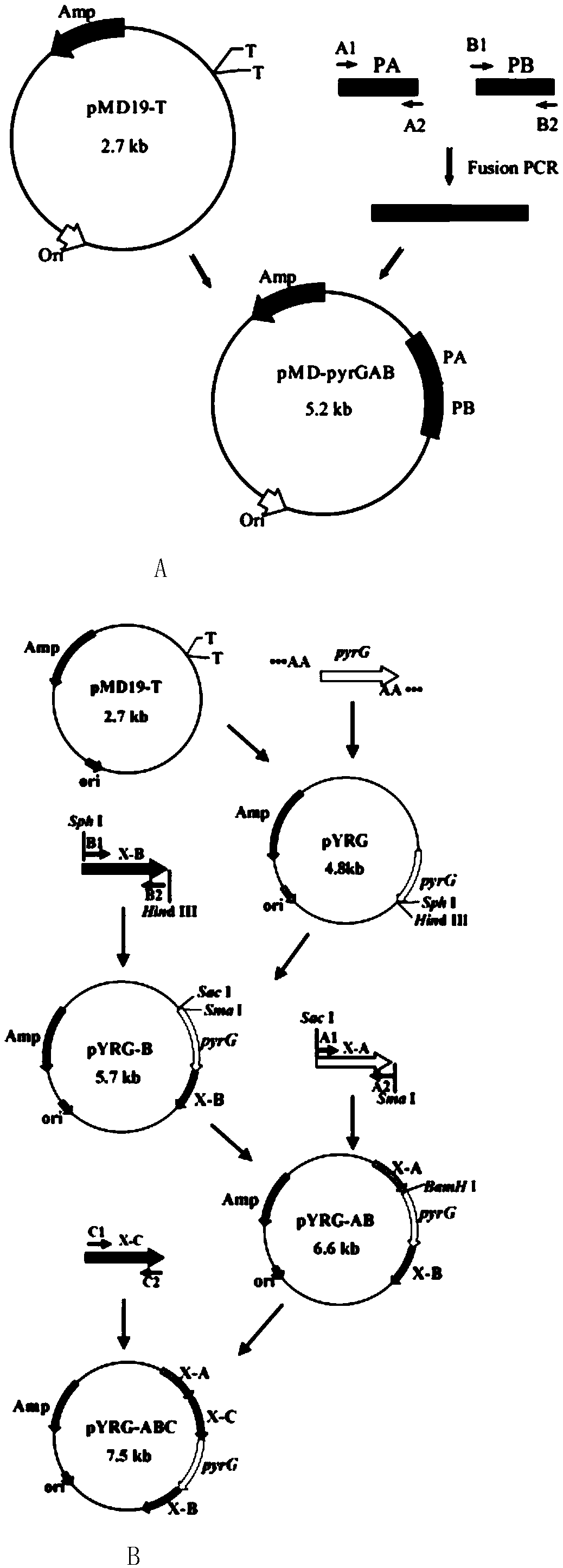
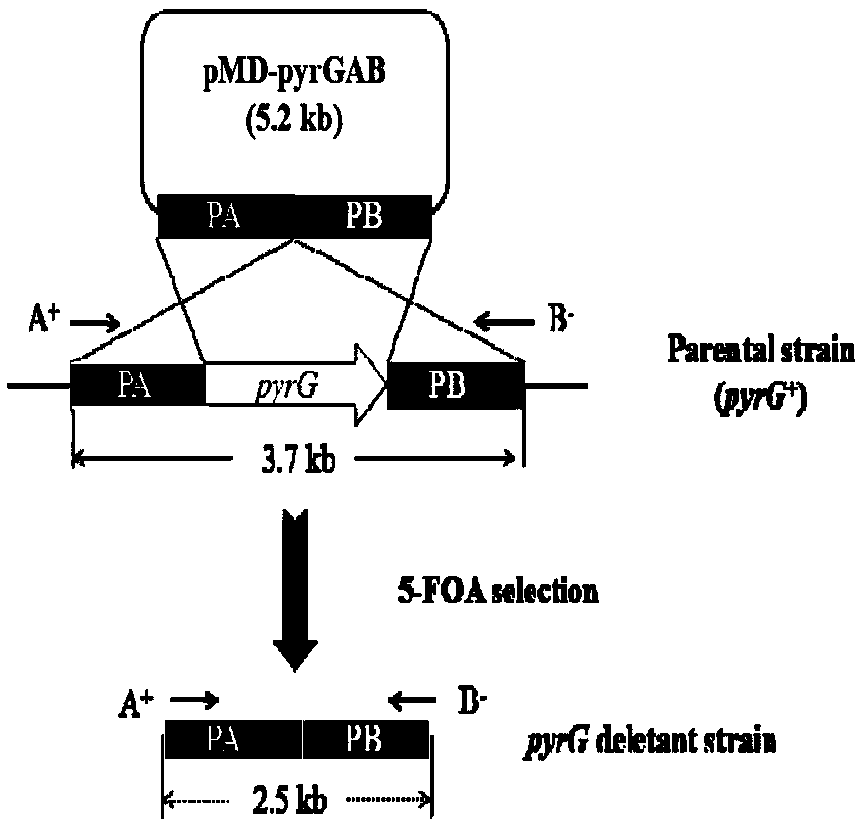
The invention discloses a method for synthesizing xylitol by aspergillus oryzae engineering bacteria with enhanced hemicellulose saccharification capacity. The method comprises the steps of 1) obtaining an aspergillus oryzae strain; 2) deleting an orotic acid nucleoside-5'-phosphate decarboxylase gene (pyrG) as a selection marker by utilizing a gene homologous recombination technology, constructing an uridine auxotroph homologous transformation system based on pyrG deletion, and providing uridine auxotroph host bacteria for subsequent gene modification; and 3) carrying out traceless deletion on the xdh gene by using a gene deletion technology of which the selection marker can be recycled to obtain the xylitol CBP engineering bacteria with enhanced hemicellulose saccharification capacity.
Owner:HUAQIAO UNIVERSITY
Genetically engineered bacterium with high yield of trans-aconitic acid as well as construction method and application of genetically engineered bacterium
ActiveCN112011470AWith a clear purposeEasy to filterFungiMicroorganism based processesChemical synthesisAconitic acid
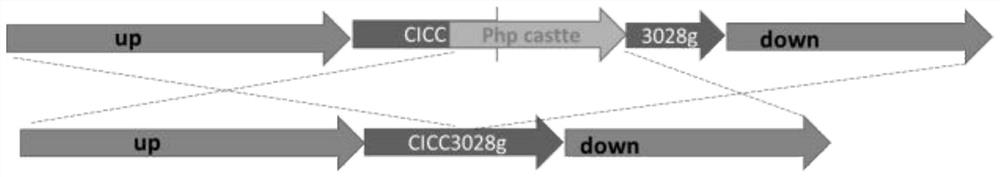
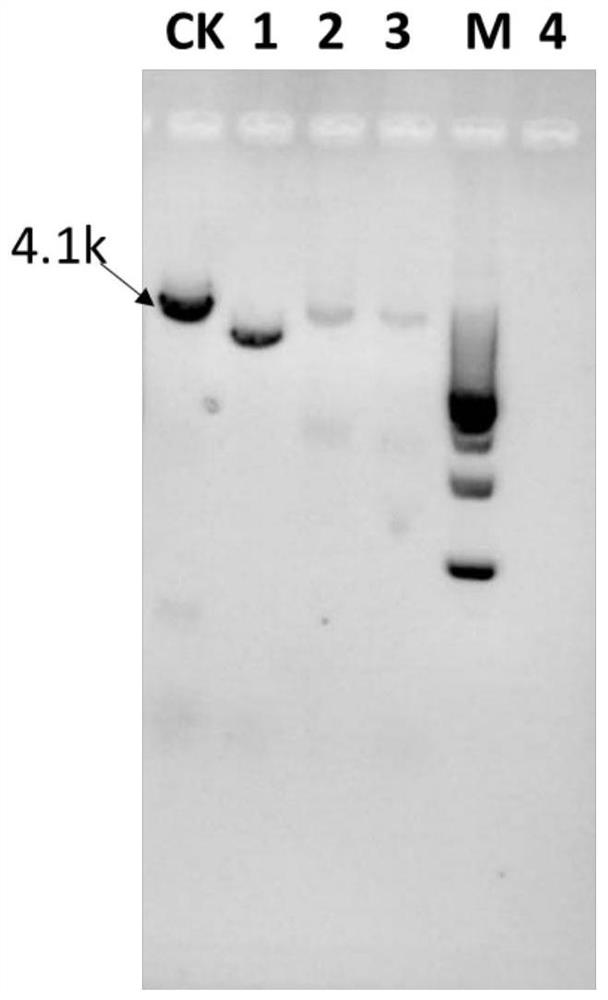
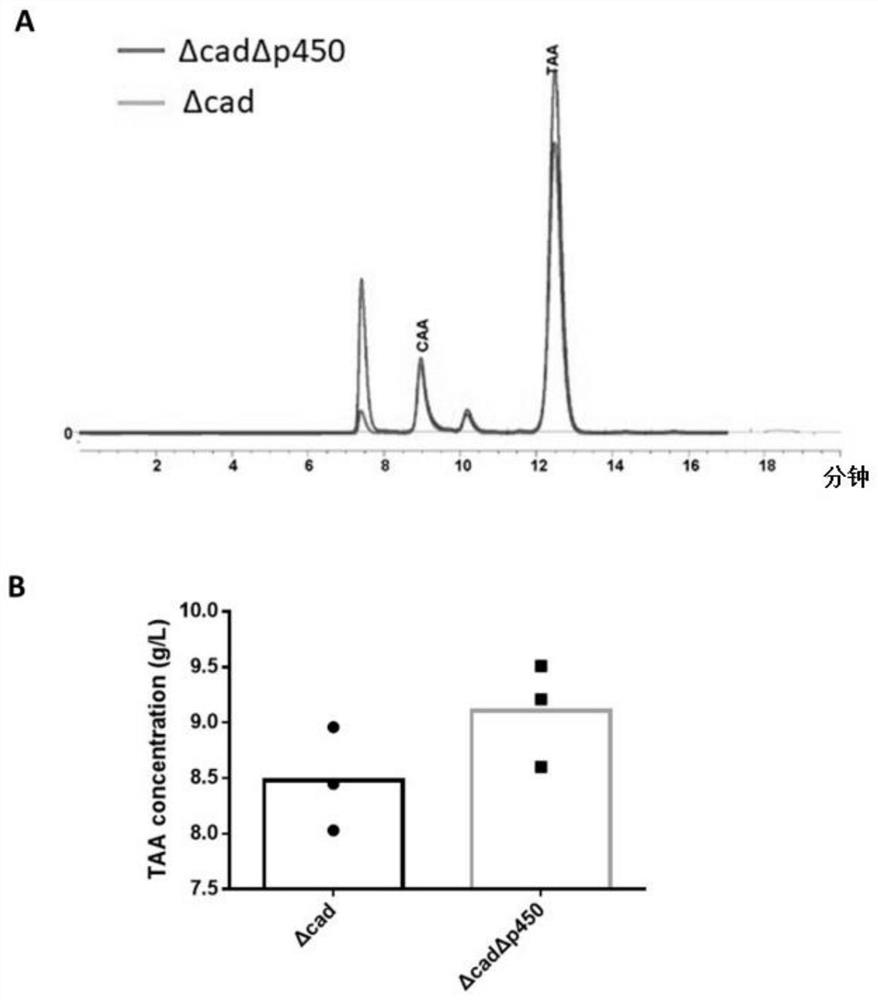
The invention discloses a genetically engineered bacterium with high yield of trans-aconitic acid as well as a construction method and application of the genetically engineered bacterium, and belongsto the field of genetic engineering. Chemical synthesis of trans-aconitic acid has the defects of more byproducts and complex process. Aiming to overcome the production defects of the trans-aconitic acid, the invention constructs the genetically engineered bacterium for producing the trans-aconitic acid. The method comprises the following steps: subjecting Cytochrome P450 monooxygenase gene CICC_3028g in At-delta cadA aspergillus terreus to gene mutation to obtain recombinant aspergillus terreus. The content of the trans-aconitic acid produced by fermentation of the recombinant aspergillus terreus is remarkably increased compared with that of trans-aconitic acid produced by the At-delta cadA aspergillus terreus.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI +1
Transaminase mutant derived from aspergillus terreus and application of transaminase mutant
ActiveCN111549011AHigh yieldAddressing deficiencies in synthesis techniquesBacteriaTransferasesAspergillus variecolorMutant
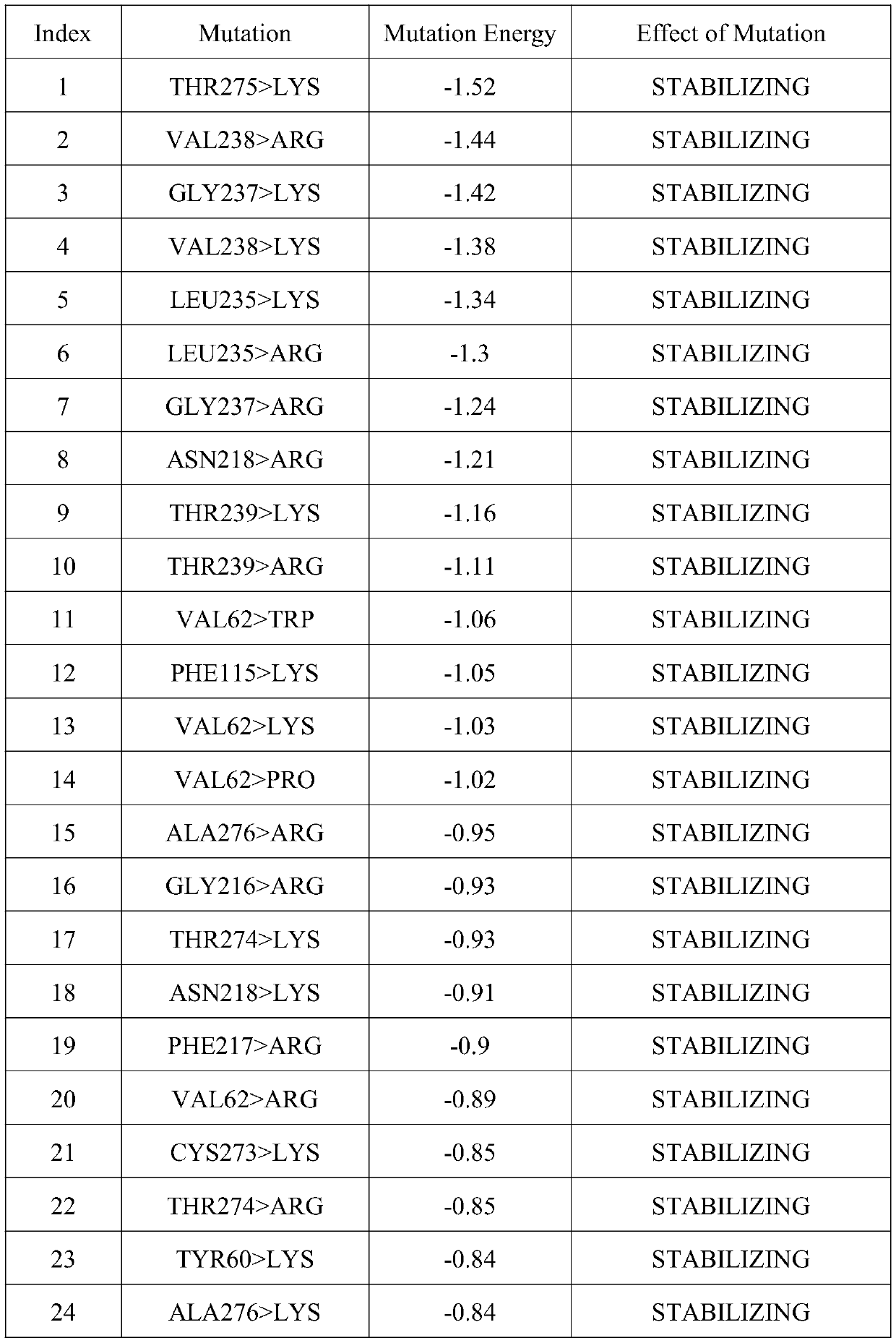
The present invention relates to a mutant polypeptide derived from aspergillus terreus NIH2624 transaminase (XP-001209325.1), a polynucleotide encoding the polypeptide, and an application of the polypeptide in the preparation of (R)-1-BOC-3-aminopiperidine. The transaminase is directionally modified through computer simulation, and modified amino acid sites are selected from one or more of Y60, V62, F115, W184, G216, F217, N218, L235, G237, V238, T239, C273, T274, T275 and A276. The mutant obtained by modification is applied to the production of (R)-1-BOC-3-aminopiperidine, has the advantagesof good stereoselectivity and catalytic activity, mild catalytic reaction, improvement of the activity by 61.9 times compared with wild transaminase under the same production conditions, obvious improvement of the chiral purity and yield of the product, and good application prospect.
Owner:卡柔恩赛生物技术湖北有限公司
Aspergillus oryzae functional enzyme preparation and application thereof
InactiveCN104404018ADelicate and soft tasteQuality improvementHydrolasesMicroorganism based processesAspergillus oryzaeEconomic benefits
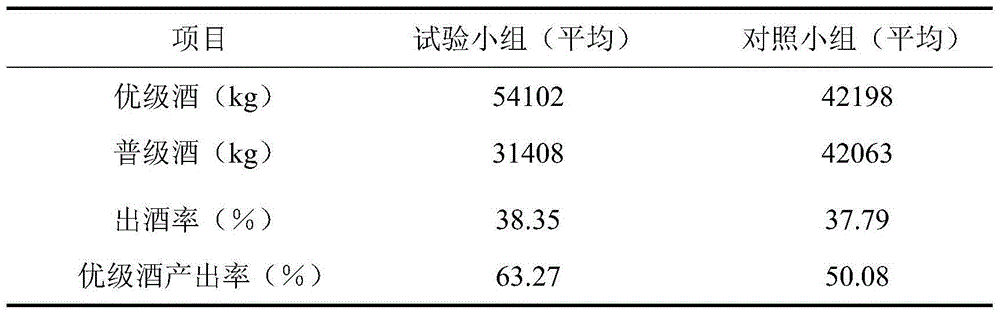
The invention discloses an aspergillus oryzae functional enzyme preparation and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of white wine brewing. The aspergillus oryzae functional enzyme preparation is prepared by performing solid state fermentation and drying on an aspergillus oryzae strain. In the white wine brewing process, the aspergillus oryzae functional enzyme preparation is additionally added into cooked and gelatinized main raw materials to be fermented. As the aspergillus oryzae functional enzyme preparation is added to ferment the raw materials, the process is simple and controllable, the wine yield and the high-quality rate of white wine can be effectively increased, the quality of the white wine is improved, and social and economic benefits are achieved.
Owner:JIANGSU YANGHE BREWERY JOINT STOCK
Bacterial strain for producing acid protease through liquid fermentation and application of bacterial strain
The invention provides an aspergillus niger strain and an application thereof in fermentation production of acid protease. The invention provides an Aspergillus niger ESP1023 strain (Aspergillus niger ESP1023), which is characterized in that the Aspergillus niger ESP1023 strain (Aspergillus niger ESP1023) is preserved in the China Center for Type Culture Collection (CCTCC), and the preservation number is CCTCC NO: M 2018829. By utilizing the Aspergillus niger ESP1023 strain and the method for producing the acid protease through liquid fermentation, the zymoprotein purity in the obtained fermentation liquor is high, and the enzyme activity is high.
Owner:安琪酶制剂(宜昌)有限公司
Mutated Aspergillus oryzae strain
The present invention relates to a mutated Aspergillus oryzae strain. Specifically, the invention relates to a mutated Aspergillus oryzae strain of which the productivity is improved by being compared with a non-mutated strain, endogenous enzymes, such as amylase and / or foreign protein, and food-purpose lipase, preferably the food-purpose lipase selected from rhizomucor miehei lipase, thermomyces lanuginosus lipase and fusarium oxysporum lipase. The invention also relates to various applications of the strain.
Owner:WILMAR SHANGHAI BIOTECH RES & DEV CENT
Xylanase/cellobiase composite enzyme and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101705215BAvoid pollutionSolve the energy crisisBiofuelsMicroorganism based processesMicrobiologyAspergillus variecolor
The invention provides a xylanase / cellobiase composite enzyme prepared by using Aspergillus niger CGMCC 3.3147 and a preparation method thereof. The xylanase and the cellobiase can be efficiently co-produced through the Aspergillus niger, wherein the produced xylanase can reach 10,000 IU / g and the cellobiase can reach 900 IU / g through a preferable fermentation culture medium; and the prepared composite enzyme can be mixed-used directly with the cellobiase in the production of straw fermented alcohol, xylitol, citric acid and the like. The composite enzyme and the preparation method have great realistic significance for solving the problems of environment pollution, food shortage and energy crisis.
Owner:ANHUI BBCA FERMENTATION TECH ENG RES
Plant ferment and preparation method and application thereof in skin care products
The invention discloses plant ferment, and a preparation method and application thereof in skin care products. According to the invention, a papaya and a mango are used as raw materials, a microbial inoculum composed of saccharomycetes, aspergillus niger and lactic streptococci is used for fermentation, and an enzyme activity keeping agent is added in the fermentation process to prepare the plantferment. The plant ferment provided by the invention contains tartaric acid and protease with an exfoliating effect and also comprises polyphenol, flavone, SOD enzyme and other components with antioxidant functions; the tartaric acid can soften skin cutin, the protease has a stripping effect on cuticle, and the antioxidant phenol, flavone and SOD enzymes can remove free radicals, so skin injuriesare reduced; and through the synergistic effect of the above components, the texture degree of skin can be effectively reduced, and skin elasticity is improved.
Owner:佛山市博仁生物科技有限公司
Preparation of amylase-rich compound enzyme as well as strain and application of compound enzyme
ActiveCN111549006AIncrease enzyme activityEfficient amylase production capacityFungiFood processingBiotechnologyPectinase
The invention provides preparation of an amylase-rich compound enzyme as well as a strain and application of the compound enzyme. A cultured fermentation product contains amylase, neutral proteases, xylanases, cellulases, glucanases and pectinases. Aspergillus oryzae is named as aspergillus oryzae BAK200312, and the preservation number of the Aspergillus oryzae is CGMCC No.19617. The invention provides a rich complex enzyme system. The used aspergillus oryzae strain is obtained by strict domestication, has strong enzyme production capability, high amylase yield and high enzyme activity, and isan aspergillus oryzae strain with efficient amylase production capability.
Owner:HANGZHOU BIOCOM BIOLOGICAL TECH
Method for producing chitosanase by using Aspergillus usamii
The invention discloses a method for producing chitosanase by using Aspergillus usamii, which belongs to the technical field of biological engineering. In the method, agricultural and sideline products such as bran, soybean cake powder and rapeseed cake powder are used as fermentation substrates, a proper amount of inorganic nitrogen source, chitosan, inorganic salt, surfactant and the like are added, and the chitosanase is produced by the solid fermentation of an Aspergillus usamii E001 strain. The invention provides the formula and culture conditions of a solid fermentation culture medium for test production of chitosanase by the Aspergillus usamii E001 in a laboratory, and the chitosanase activity of a mature fermented grain material of the medium reaches 1,942 to 2,461U / g. The method has the advantages of simple equipment, small investment, quick effectiveness, low production cost, environmentally-friendly, high activity of chitosanase fermentation enzyme, and the like, contributes to the development and utilization of chitosanase and has high economic and practical value.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Compound microorganism formula
InactiveCN110655292AAvoid cakingPromote reproductionBiological sludge treatmentBiological water/sewage treatmentBiotechnologyActinomyces
The invention relates to a composite microorganism formulation. The compound microorganism formula is prepared from the following raw materials in percentage by weight: 36 to 44% of bacillus subtilis,8 to 12% of moss bacteria, 9 to 11% of polymyxa, 7 to 9% of aspergillus, 3 to 6% of nocardia, 1 to 5% of protease, 3 to 5% of digestive enzyme, 3 to 7% of saccharomycetes, 4 to 7% of cellulase, 6 to8% of actinomycetes and 3 to 5% of amylase. The compound microorganism formula provided by the invention contains a plurality of aerobic and anaerobic microorganisms, the microorganisms generate a plurality of enzymes, unpleasant odor is eliminated, harmful microorganisms are inhibited, the content of BOD and COD in leachate in excrement is reduced, the subsequent treatment load is reduced, and the compound microorganism formula is suitable for sewage treatment of industry, agriculture, life and the like and has a wide application range.
Owner:才莉
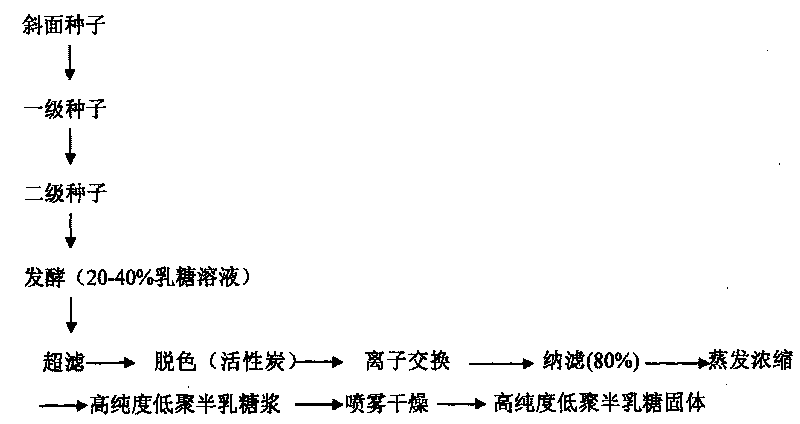
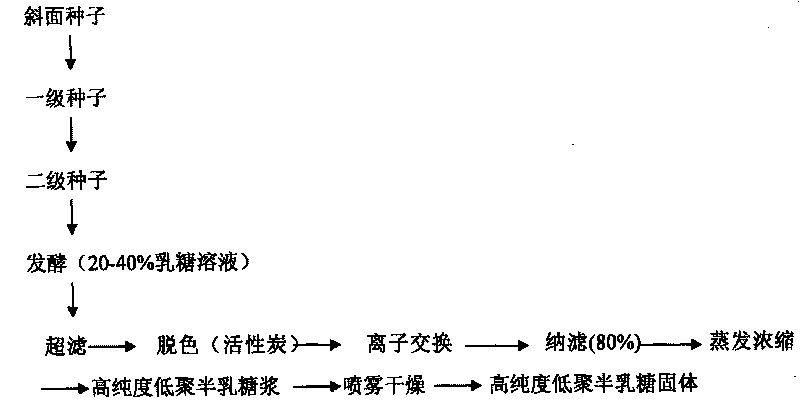
Aspergillus oryzae blcy-006 strain and application thereof in preparation of galactooligosaccharide
ActiveUS20210139938A1Improve abilitiesLow production costFungiFungi based processesBiotechnologyAspergillus oryzae
Provided are an aspergillus oryzae BLCY-006 strain and an application thereof in the preparation of a galactooligosaccharide. The strain produces β-galactosidase, and the enzyme activity can reach 300 U / ml after culturing and fermentation, which is more than 50% higher than traditional β-galactosidase activity. The enzyme also has lactose and glucose resistance properties.
Owner:SHANDONG BAILONG CHUANGYUAN BIO TECH
Method for improving production capacity of Aspergillus niger saccharifying enzyme and recombinant Aspergillus niger strain
ActiveCN113061539AIncrease production capacityFungiMicroorganism based processesCoenzyme A biosynthesisAspergillus niger
The invention discloses a method for improving production capacity of Aspergillus niger saccharifying enzyme and a recombinant Aspergillus niger strain. The method comprises the following steps: integrating uracil defective (pyrG-) strains with high yield of aspergillus niger saccharifying enzyme by using a Tet-on system through a promoter of an exogenous plasmid and utilizing homologous recombination, so that at least one of acyl-coenzyme A dehydrogenase coding genes, acetyl-coenzyme A acyltransferase coding genes or cytochrome P450 monooxygenase coding genes is over-expressed; and the saccharifying enzyme production capacity of the aspergillus niger is greatly improved by regulating and controlling a fatty acid metabolic pathway.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
A kind of composite microbial bacterial agent suitable for the treatment of black and odorous water
ActiveCN108441444BImprove the problem of smelly and blackHigh transparencyFungiBacteriaCandida tropicalisAspergillus niger
The invention provides a compound microorganism agent for treating a black and odorous water body. The compound microorganism agent comprises compound bacteria and a compound enzyme preparation, wherein the compound enzyme preparation comprises candida tropicalis, candida utilis, bacillus natto, bacillus subtilis, bacillus licheniformis, nitrobacter, achromobacter denitrificans, nitrosomonus, acinetobacter, lactobacillus, aspergillus niger, aspergillus oryzae and photosynthetic bacteria; the compound enzyme preparation comprises protease, amylase, lipase, sucrase, and cellulase.
Owner:POWERCHINA WATER ENVIRONMENT GOVERANCE
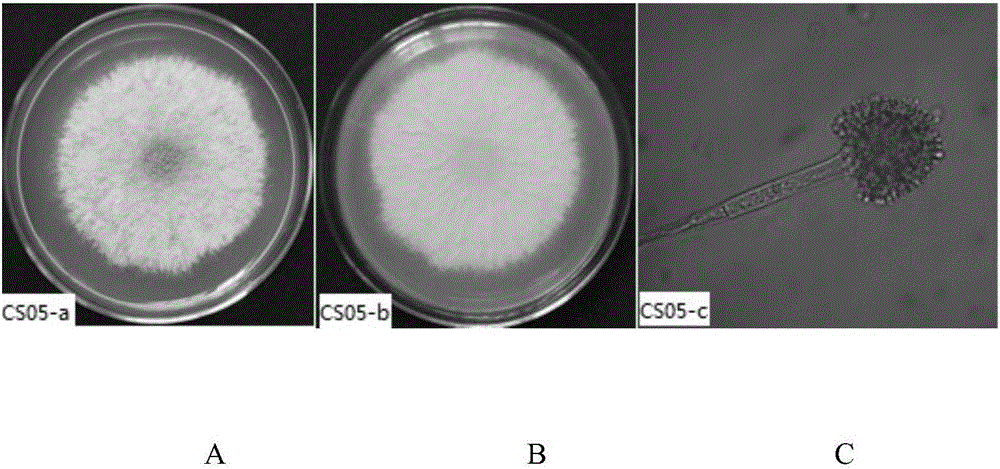
Aspergillus flavus CS05 with high yield of aflatoxin B1 and application thereof
InactiveCN106167766AIncrease productionFungiMicroorganism based processesAflatoxin BAspergillus flavus
The invention discloses an Aspergillus flavus CS05, which is preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection with a preservation number of CCTCC NO:M2016271. The Aspergillus flavus provided by the invention has strong aflatoxin B1 (AFB1) production ability. The Aspergillus flavus has high toxin yield in PDA medium, corn, wheat, soybean, soybean meal, cottonseed, cottonseed meal and other feed raw materials and by-products, and can be used as an AFB1 toxin production strain in AFB1 production, also can be used for the technical research of AFB1 prevention and control, and provides an experimental material for AFB1 biosynthesis mechanism, synthesis condition and removal method sturdy.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
High-production β-glucosidase Aspergillus niger strain and its application
ActiveCN113403207BOvercome the disadvantages of pollutionEnhance β-glucosidase enzyme activityFungiMicroorganism based processesCelluloseEnzyme system
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Solid-state fermentation wheat bran feed, and preparation method and application thereof
The invention provides a solid-state fermentation wheat bran feed, and a preparation method and an application thereof. The feed comprises the following raw materials in parts by weight: 1-3 parts ofwheat bran, 1.2-3.2 parts of a nutrient solution, 0.15-0.45 part of an aspergillus niger-trichoderma viride-streptomyces rouxii composite bacterial suspension and 0.05-0.15 part of a candida tropicalis suspension. The preparation method comprises the following steps: respectively activating and culturing aspergillus niger, trichoderma viride, streptomyces rouxii and candida tropicalis, then compounding the aspergillus niger, the trichoderma viride and the streptomyces rouxii, mixing an obtained mixture with wheat bran for primary fermentation, and adding candida tropicalis for secondary fermentation after completion of primary fermentation. According to the invention, by selection of the streptomyces rouxii, the aspergillus niger and the trichoderma viride, abundant enzymes like cellulase,pectinase and amylase can be generated in the growth process, so components like cellulose uneasily utilized by animals in wheat bran can be easily degraded; meanwhile, the candida tropicalis can berapidly propagated by utilizing a fermentation product, namely reducing sugar in the later period of fermentation, and a large amount of mycoprotein is generated at the same time; and through synergistic effect of the streptomyces rouxii, the aspergillus niger and the trichoderma viride, the content of cellulose in the feed can be effectively reduced.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
Transeliminase encoding gene and enzyme and preparation and application
InactiveCN111254154AEfficient degradationHigh activityFermentationGenetic engineeringHeterologousPentagalacturonic acid
The invention discloses a preparation and application of a transeliminase encoding gene derived from Aspergillus parasiticus, and an enzyme of the transeliminase encoding gene, that is, a gene of transeliminase is cloned to a pichia pastoris expression vector by using a technical method of gene engineering, then a pichia pastoris recombinant strain for heterologous expression of the enzyme can beobtained, the strain is capable of heterologously expressing the prepared transeliminase and efficiently degrading pectin polysaccharides and polygalacturonic acid (PGA). The transeliminase disclosedby the invention can be widely applied to fields such as agriculture, industry, foods, feed additives, medicines and pectin oligosaccharide preparation.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Aspergillus aculeatus bacterial strain and method for preparing 5,7,8,4'-tetrahydroxyisoflavone by using same
ActiveCN102277304BAbundant resourcesStrong transformation specificityFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyGlycoside
The invention relates to an Aspergillus aculeatus ZJ bacterial strain and an application thereof. The collection number of the Aspergillus aculeatus ZJ is CCTCC NO.M2011264. The bacterial strain is mainly used for converting effective components of the pod of Chinese scholartree to produce 5,7,8,4'-tetrahydroxyisoflavone. The specific method provided by the invention comprises the following steps of: acting the Aspergillus aculeatus ZJ with strong specificity or the produced enzyme on the pod of Chinese scholartree or extracting solution thereof; converting glucosides compounds including sophoricoside and the like, genistein and the like to produce the 5,7,8,4'-tetrahydroxyisoflavone. The invention provides the method for producing the 5,7,8,4'-tetrahydroxyisoflavone through utilizing the Aspergillus aculeatus with high specificity and high conversion efficiency to convert the sophoricoside; and the method provided by the invention has moderate conditions, green process and simple requirements on the process and the device, and has a very good application value.
Owner:NANJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
A high temperature resistant Aspergillus fumigatus strain 23# and its application
ActiveCN110129211BImprove growth abilityPromote growthFungiBio-organic fraction processingBiotechnologyCellulose
The invention discloses a high temperature-resistant Aspergillus fumigatus strain Aspergillus fumigatus 23#, and the preservation number is CGMCC No.17190. The growth temperature of the strain is 28-50°C. A method for preparing cellulose crude enzyme liquid, characterized in that it comprises the following steps: Step 1, inserting Aspergillus fumigatus 23# into a slant medium for multiplication culture to obtain seeds; the temperature for the multiplication culture is 28-37°C , the cultivation time is 48~96h; and the rotating speed of shaker cultivation is 180~200r / min; step 2, insert the described seed obtained in step 2 into the enzyme-producing medium for fermentation and cultivation, and separate the fermented liquid to obtain crude cellulose Enzyme liquid; the temperature of the fermentation culture is 28-37° C., and the culture time is 48-96 hours. The Aspergillus fumigatus 23# of the present invention has strong growth ability, strong sporulation ability, and high temperature resistance of 50°C.
Owner:TIANJIN AGRICULTURE COLLEGE
A method for rapidly preparing high-activity cellulase with low-cost carbon source
ActiveCN107988187BIncrease vitalityReduce pollutionMicroorganism based processesGlycosylasesBiotechnologyAspergillus fumigatus
The invention provides a method for rapidly preparing high activity cellulase by using a cheap carbon source, relating to the technical field of biology. In the method for rapidly preparing high activity cellulase by using the cheap carbon source, liquorice residue is used as the carbon source, Trichoderma reesei, fusarium oxysporum and aspergillus fumigatus are mixed and fermented so as to prepare the high activity cellulase. Trichoderma reesei ATCC 56764, Fusarium oxysporum BN and Aspergillus fumigatus HY are mixed and fermented, thereby remarkably shortening fermentation time and remarkablyimproving the activity of cellulase. The activity of the cellulase generated through mixed fermentation of the three strains is greater than the sum of activities of the cellulase generated by the three strains separately, that is, the three strains play a synergistic role through mixed fermentation.
Owner:HUAIYIN TEACHERS COLLEGE
A kind of method for preparing high f value oligopeptide using chlorella powder as raw material
ActiveCN110951808BIncrease productionImprove securityPeptide preparation methodsFermentationActivated carbonEngineering
The invention provides a method for preparing high-F-value oligopeptide by taking chlorella powder as a raw material. The method comprises the following steps: adding trypsin into chlorella protein according to 70000-90000 U / mg protein under the conditions that the pH is 8 and the temperature is 27-52 DEG C to carry out first enzymolysis; then carrying out second enzymolysis by using recombinant carboxypeptidase derived from aspergillus niger, wherein the enzymolysis conditions are as follows: the pH is 6.5-7.5, the enzyme addition amount is 3-7% of the protein amount and the enzymolysis temperature is 27-40 DEG C; and then adjusting the pH to 4.5, adding activated carbon according to a solid-to-liquid ratio of 1 to 10 to remove impurities, and conducting filtering to obtain a high-F-valueoligopeptide solution. According to the method for preparing the high-F-value oligopeptide, chlorella is taken as the raw material, the protein content is high, the cost is low and the yield is high.The F value of the product is easy to elevate, the production cost of an enzyme method is reduced, the energy consumption in a later purification process is reduced, environmental pollution is reduced, the high-F-value oligopeptide is effectively prepared, and industrial production and application of the high-F-value oligopeptide are promoted.
Owner:BEIJING TECHNOLOGY AND BUSINESS UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com