Method for improving production capacity of Aspergillus niger saccharifying enzyme and recombinant Aspergillus niger strain
A technology of Aspergillus niger strain and production capacity, applied in the field of bioengineering, can solve problems such as optimization of Aspergillus niger cell factory
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0063] The construction of embodiment 1 recombinant Aspergillus niger strain
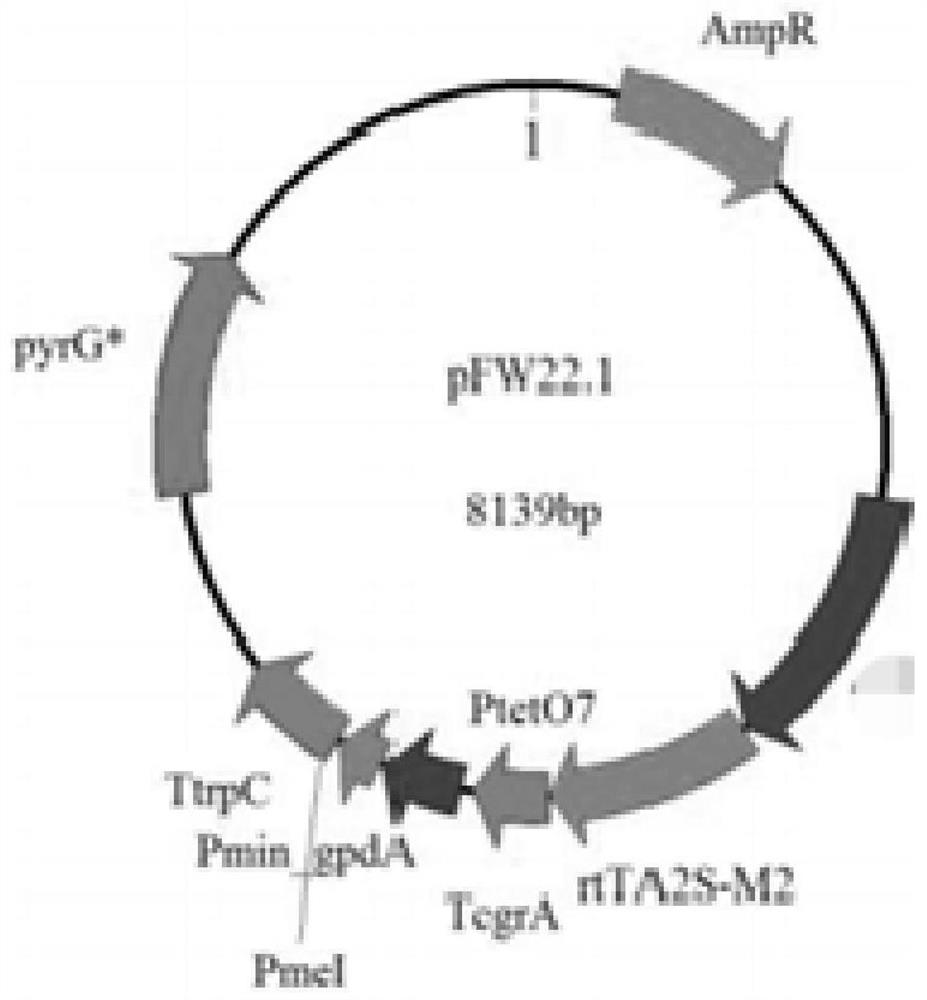
[0064]1) Through basic molecular cloning steps such as PCR, one-step cloning, gel recovery, and plasmid purification, a plasmid is constructed exogenously to integrate the target gene and the plasmid vector. In this example, the Phanta high-fidelity enzyme PCR system is used to amplify the target gene to integrate the target gene and the plasmid The vector, PCR system and reaction conditions are shown in Table 3 and Table 4; the plasmid used is the expression plasmid initiated by the Tet-on system, which is inserted into the PmeI restriction site on the plasmid pFW22.1 containing the inducible expression of the Tet-on system For the coding region of the above-mentioned genes that need to be overexpressed, the plasmid construction strategy is as follows: figure 1 .
[0065] 2) Transform the recombinant plasmid obtained in step 1) into Escherichia coli DH5α competent, use Tag Mix enzyme to colony PCR...
Embodiment 2
[0084] Embodiment 2 Recombinant Aspergillus niger strain shaking flask fermentation experiment
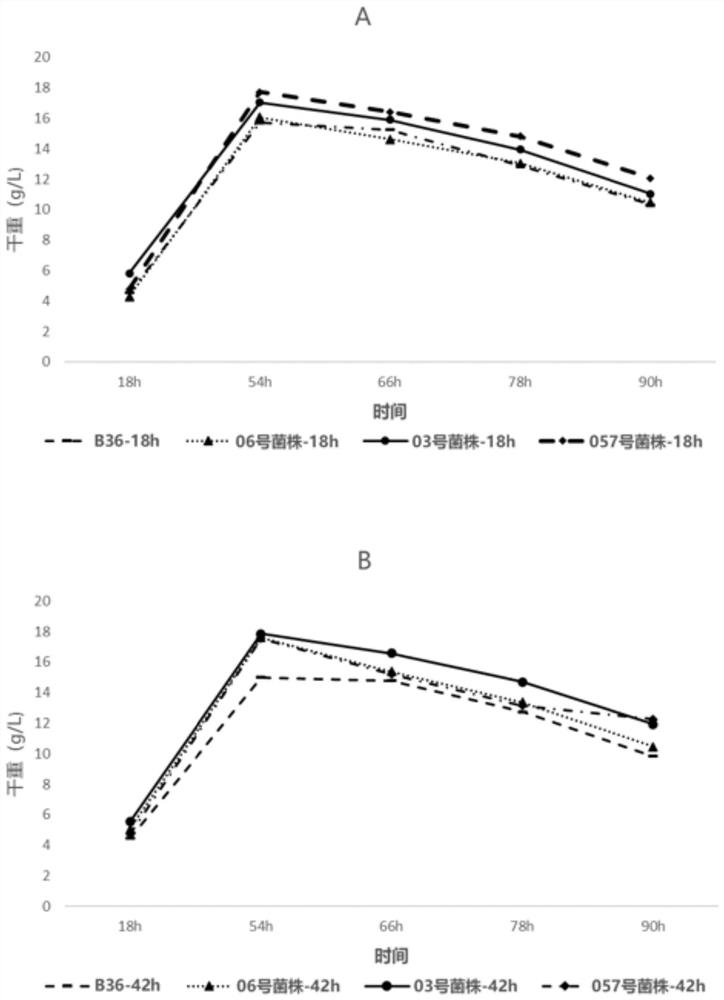
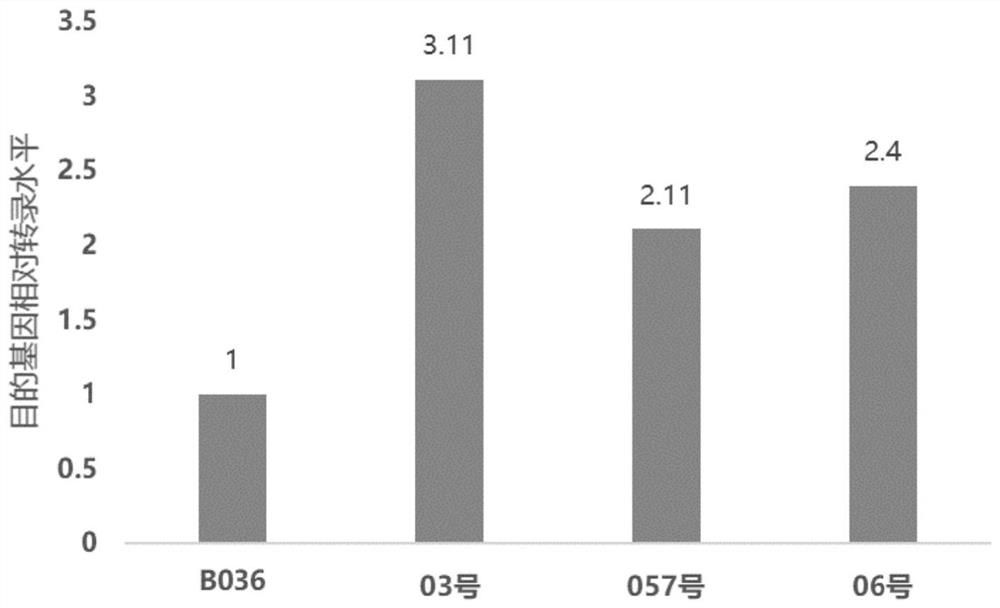
[0085] The shake flask experiment was carried out using the overexpression strain constructed in Example 1, and the culture medium was a shake flask culture medium. The inoculum size is 10 6 spores / ml, the culture condition is 30°C, 250rpm culture for 72h, add 5 glass beads to prevent balling, and shake flask fermentation, add 10μg / ml inducer Doxycycline (DOX ), since DOX needs to be kept away from light, it may be inactivated if exposed to light for a long time, so add DOX every 12 hours. Samples were taken every 24 hours after inoculation, and the dry weight of the bacteria, total secreted protein and glucoamylase activity were measured. And about 26 hours in the mid-logarithmic growth phase, that is, 8 hours after induction, the mycelia were preserved for mRNA extraction. In another parallel experiment group, DOX was added from 42h and added every 12h.
[0086] The dry weigh...
Embodiment 3
[0091] Embodiment 3 Recombinant Aspergillus niger strain reactor culture experiment
[0092] Batch culture fermentation: The culture was carried out on 5L tanks with weighing. The liquid volume of the 5L tank is 3L, and the inoculation volume is 10 6 spores / ml, and the culture medium is the initial fermentation medium of the reactor. The stirring speed and ventilation speed of the 5L tank were 750rpm and 2vvm respectively, the tank pressure was 0.05MPa, and the temperature was 30°C. During the batch culture, samples were taken every two hours after addition of the inducer DOX for monitoring the growth curve. When the online monitoring curve CER, OUR began to decrease, dissolved oxygen increased and then transferred to chemostat culture. When CER and OUR begin to decrease, it proves that the fermentation is over. At this time, feed feeding is started and the chemical constant fermentation stage is entered. The tail carbon and tail oxygen concentrations in the fermentor were...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com