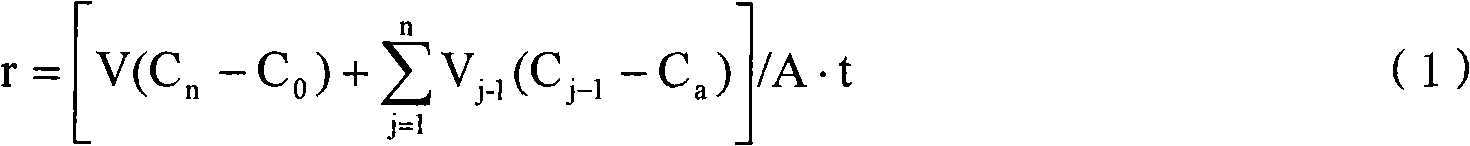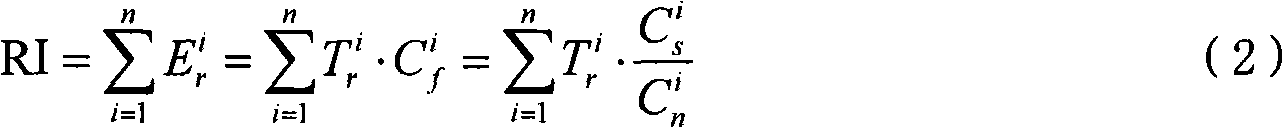Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
99results about How to "Reduce ecological risk" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Reductive degradable stabilizer of polluted soil, bottom mud and sludge as well as preparation method and using method of stabilizer
ActiveCN103436265AAchieve partial reductionReduce sizeContaminated soil reclamationOrganic fertilisersHealth riskSludge
The invention relates to a reductive degradable stabilizer for heavy metal and / or organic matter polluted soil as well as a preparation method and use of the stabilizer. The reductive degradable stabilizer can be used for quickly and efficiently stabilizing the heavy metals and the organic matters in the polluted soil by virtue of a synergistic effect of a plurality of active ingredients, and can also be used for further lowering the content of the organic matters, so that the purpose of lowering leaching toxicity of pollutants and health risk is realized; therefore, the reductive degradable stabilizer is a novel and efficient stabilizer which has the advantages of being wide in treatment substrate, capable of reducing the total amount of the organic matters, good in stabilizing effect, convenient to operate and the like, and has a wide range of application in the governance fields including polluted soil, bottom mud, sludge and the like.
Owner:付融冰
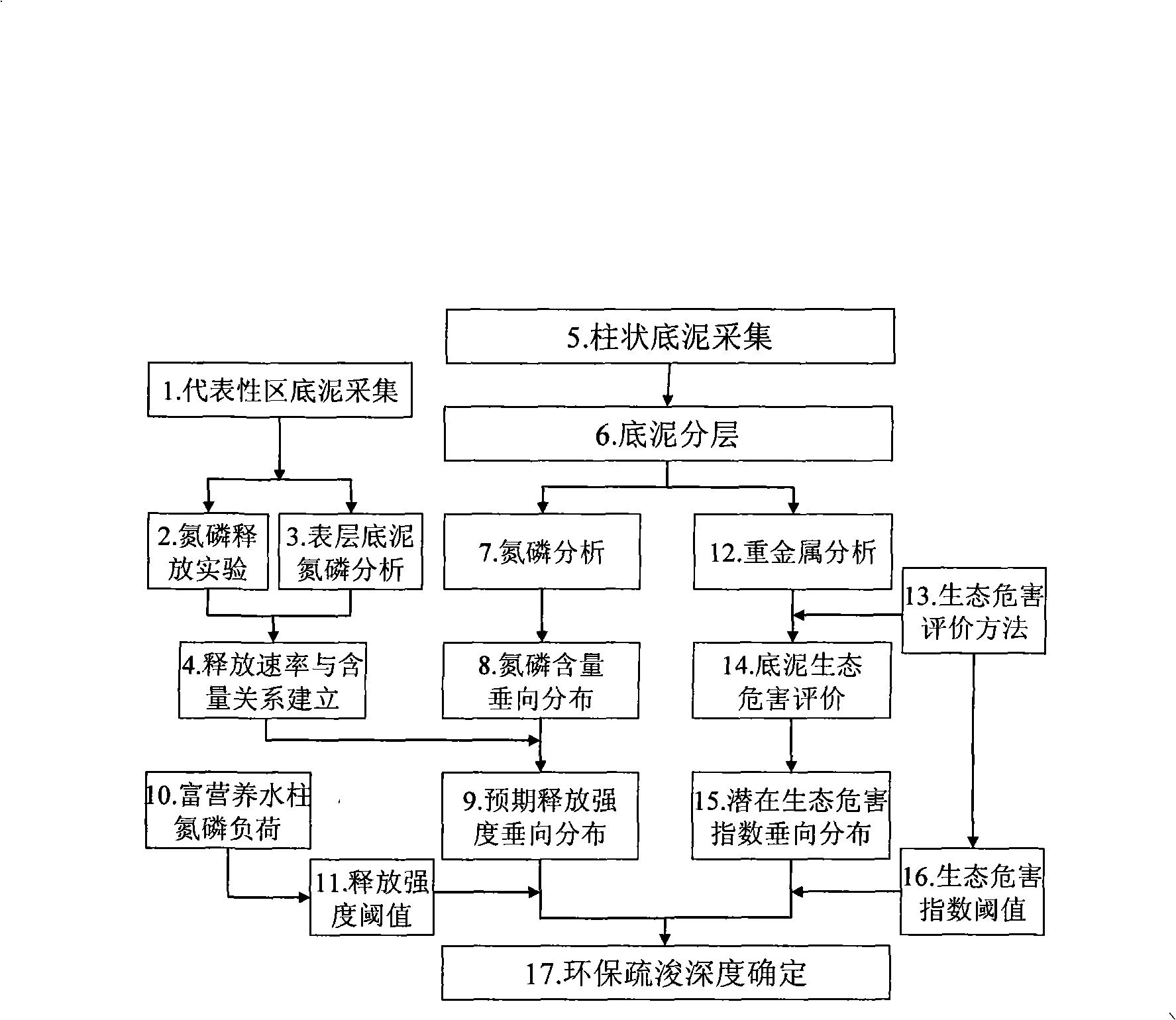
Polluted water body deposit environment-friendly dredging depth determination method
InactiveCN101266235APollution suppressionReduce ecological riskMaterial analysisSurface layerRed mud
The invention provides a determining method for polluted water bed mud environmental protection dredging depth, comprising analyzing and evaluating the releasing risk and ecological hazard risk of the pollutant at different layer side of the mud based on the vertical distribution of the pollutant in the bed mud by researching the relation of the releasing of bed mud pollutant nitrogen, phosphor or the like and the corresponding pollutant content and the ecological hazard evaluation corresponding with the content of the bed mud pollutant containing heavy metal; and determining the bed mud dredging depth based on the divided corresponding risk grade. After dredging, the anticipated release rate of the key pollutant such as nitrogen, phosphor at the new surface layer of bed mud-hydrosphere achieves or exceeds a release intensity threshold and the latent ecological hazard index of the heavy metal at the new surface layer of bed mud achieves or exceeds a hazard threshold, therefore the basis of the dredging depth is determined.
Owner:NANJING INST OF GEOGRAPHY & LIMNOLOGY
Nen River drainage basin typical region water ecology risk assessment method based on system dynamics decision model
InactiveCN105224772AAccelerate practical engineering applicationsMethod innovationSpecial data processing applicationsDecision modelEnvironmental resource management
The invention discloses a Nen River drainage basin typical region water ecology risk assessment method based on a system dynamics decision model, and relates to the Nen River drainage basin typical region water ecology risk assessment method. The method comprises the following steps: simulating different treatment schemes for tributary afflux, nonpoint source discharge, upland water and riverside pollution discharge factors which affect the amount of a pollution source input into the Nierji reservoir through the system dynamics decision model to achieve an affect that an ecological risk of a reservoir is lowered, and scheme decisions are realized ; evaluating the water ecology risk situations of different point locations in different time periods in a lake reservoir on the basis of a water ecology risk index system; constructing a sample space of a Bayesian network on the basis of Netica software; and calculating ecology risk happening probabilities of different degrees when each index is changed so as to realize Nen River drainage basin typical region water ecology risk assessment.The method is applied to river drainage basin typical region water ecology risk assessment.
Owner:松辽流域水资源保护局松辽流域水环境监测中心
Method and device for biochemically recharging and restoring polluted soils in chromium slag yard
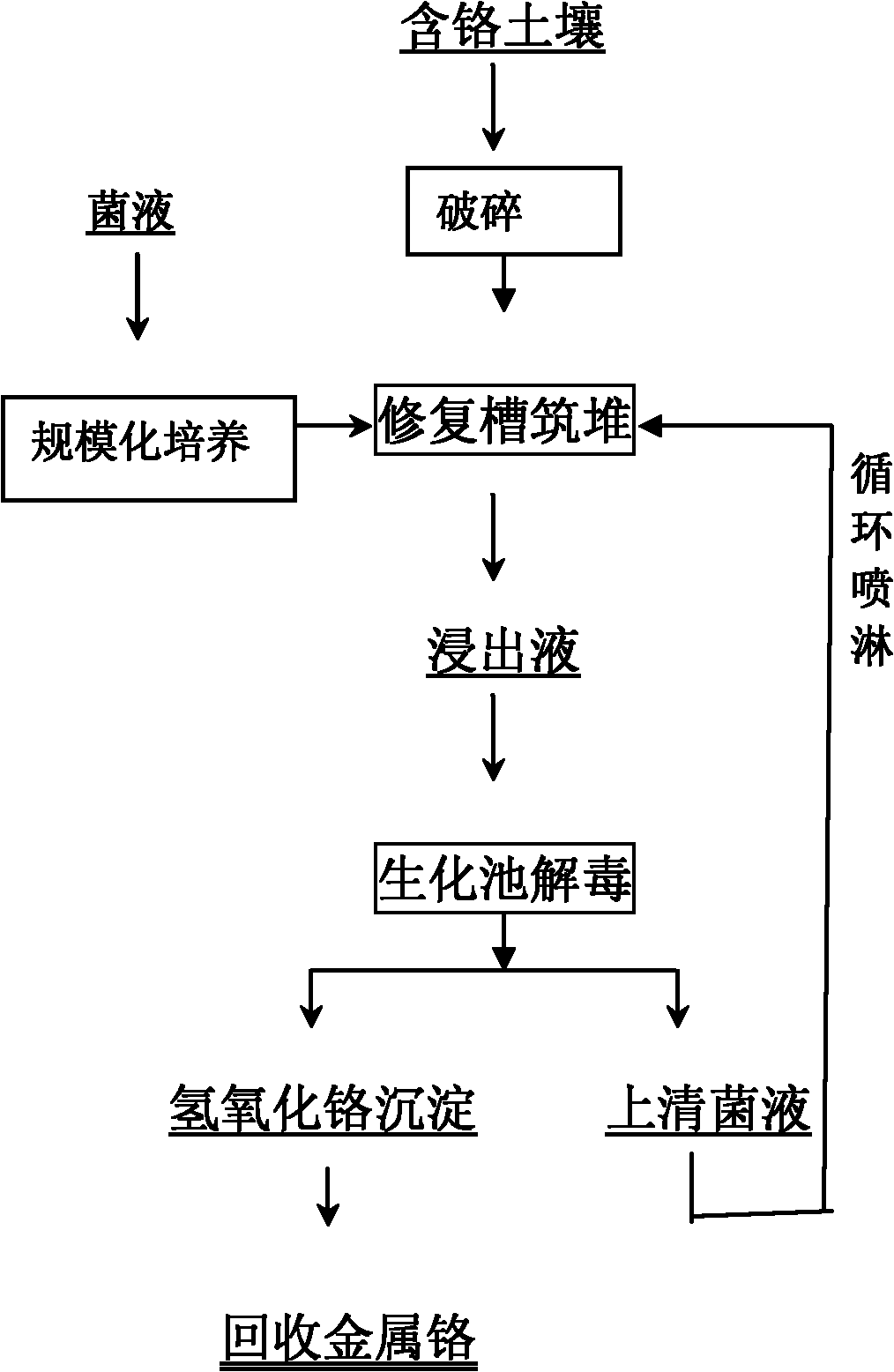
The invention discloses method and device for biochemically recharging and restoring polluted soils in a chromium slag yard. The device comprises a soil treatment groove containing soils to be treated, a middle pond, a biochemical pond and a bacteria culture pond. Every two parts are connected through a water pipe, chromium polluted soils are installed in the soil treatment groove to be heaped after being crushed by a 2cm sieve, the height of a mound is smaller than 0.8m, and the soils are sprayed by Cr (VI) reducing bacteria (Pannonibacter phragmitetus BB) culture medium with the spraying strength of 0.008-0.015m<3> / h.m<2>; and leachate is collected from the bottom of a soil groove to the middle pond, bacterial liquid in the middle pond is pumped into the biochemical pond by an alkali resistance pump, and bacterial liquid in the biochemical pond circulates again to be used for spraying the soils and is in circulating spraying for 5-7 days until the soil leachate does not contain Cr (VI). By adopting the invention to restore the polluted soils in the chromium slag yard, the removal rate of water-soluble Cr (VI) in the soils achieves 99 percent, and the concentration of Cr (VI) leaching toxicity in the soils after restoring is lower than 0.5mg / L and achieves a standard limited value of roadbed materials and concrete aggregates in Technical Specifications for Chromium Slag Pollution Control (HJ / T301-2007). Simultaneously, the invention has the advantages of having simple technology, low cost and no secondary pollution, improving the physicochemical property of the soils, and the like.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Stabilizing agent applicable to soil with combined pollution of heavy metals and semi-volatile organic compounds and use method thereof
InactiveCN103773379AReduce ecological riskReduced bioavailability and toxicityContaminated soil reclamationOrganic fertilisersWater contentHeavy metal chelation
The invention discloses a stabilizing agent applicable to soil with combined pollution of heavy metals and semi-volatile organic compounds and a use method thereof. The stabilizing agent comprises the following components in percentage by weight: 5-10% of heavy-metal chelating agent, 10-20% of cementing material, 55-65% of modified clay mineral and 10-15% of alkaline exciting agent, wherein the modified clay mineral is prepared by mixing hexadecyl trimethyl ammonium bromide and sodium lauryl sulfate according to the volume ratio of (1:0.8)-(1:1.2), and then adding the hexadecyl trimethyl ammonium bromide and the sodium lauryl sulfate into the clay mineral. The use method comprises the following steps of: mixing and grinding the cementing material, the modified clay mineral and the alkaline exciting agent till the obtained particles have the Brinell specific area of 5000-8000cm<2> / g, pass through 200 meshes and have the water content less than 3%, and directly adding the obtained mixture into the soil polluted by the heavy metals according to the mass ratio of 10-20%, mixing and stirring; preparing the heavy-metal chelating agent into 10-20% solution, spraying the solution into the soil polluted by the heavy metals, mixing and stirring. The stabilizing agent and the use method disclosed by the invention have the advantages that the traditional cement type components are not used, the leaching toxicity of the treated pollutants is obviously reduced, and the heavy metals and semi-volatile organic pollutants in the soil can be fast stabilized.
Owner:SHANGHAI ACADEMY OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCES
Method for treating heavy metal polluted soil
InactiveCN101085450AImprove processing efficiencyReduce ecological riskContaminated soil reclamationPollution soilEngineering
The invention relates to the treatment for contaminated soil. It comprises the isolation of surface contaminated soil, surface change over, contaminated soil filtering liquid collection and collection and discharge of water for cleaning the surface soil. It applies to the treatment for all kinds of complex precious metal contamination, preventing the secondary pollution, realizing safe use of the land.
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF APPL ECOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for building Nierji reservoir water ecological risk early warning model through fusion technology
InactiveCN105303007ARealization riskImplement decisionGeneral water supply conservationSpecial data processing applicationsEcological riskReservoir water
The invention discloses a method for building a Nierji reservoir water ecological risk early warning model through the fusion technology, and relates to a method for building a Nierji reservoir water ecological risk early warning model. A system dynamics decision-making module is adopted for risk early warning and decision making quantitative analysis, then a Bayesian network model is adopted for risk early warning and decision making quantitative analysis according to a quantitative analysis result, and therefore Nierji reservoir water ecological risk early warning and decision making are achieved. The Nierji reservoir water ecological risk early warning model is built, the system dynamics and the Bayesian network model technology are fused, quantitative advantages in early-warning and decision-making research are highlighted, and Nierji reservoir water ecological risk early warning and decision making are achieved. The accuracy of the model is verified based on comparison and analysis for current data, and the availability of the model is verified through early-warning research on relative risk source risks and decision-making research on control strategies.
Owner:松辽流域水资源保护局松辽流域水环境监测中心 +1
Biological leaching restoring method for heavy metal polluted soil
The invention discloses a biological leaching restoring method for heavy metal polluted soil. After Penicillium chrysogenum F1 spore liquid is cultured in an improved Czapek liquid medium, leaching fungus liquid is obtained, and then the heavy metal polluted soil is leached, dried and crushed. By restoring the heavy metal (Pb, Zn, Cd and Cu) compound polluted soil according to the biological leaching restoring method provided by the invention, the removing rate of Pb in the soil is 14%, the removing rate of Cd is 63%, the removing rate of Zn is 54% and the removing rate of Cu is 56%. The biological leaching restoring method for the heavy metal polluted soil provided by the invention has the advantages of high speed in taking effect, high efficiency in removing heavy metal, absence of secondary pollution, and the like.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
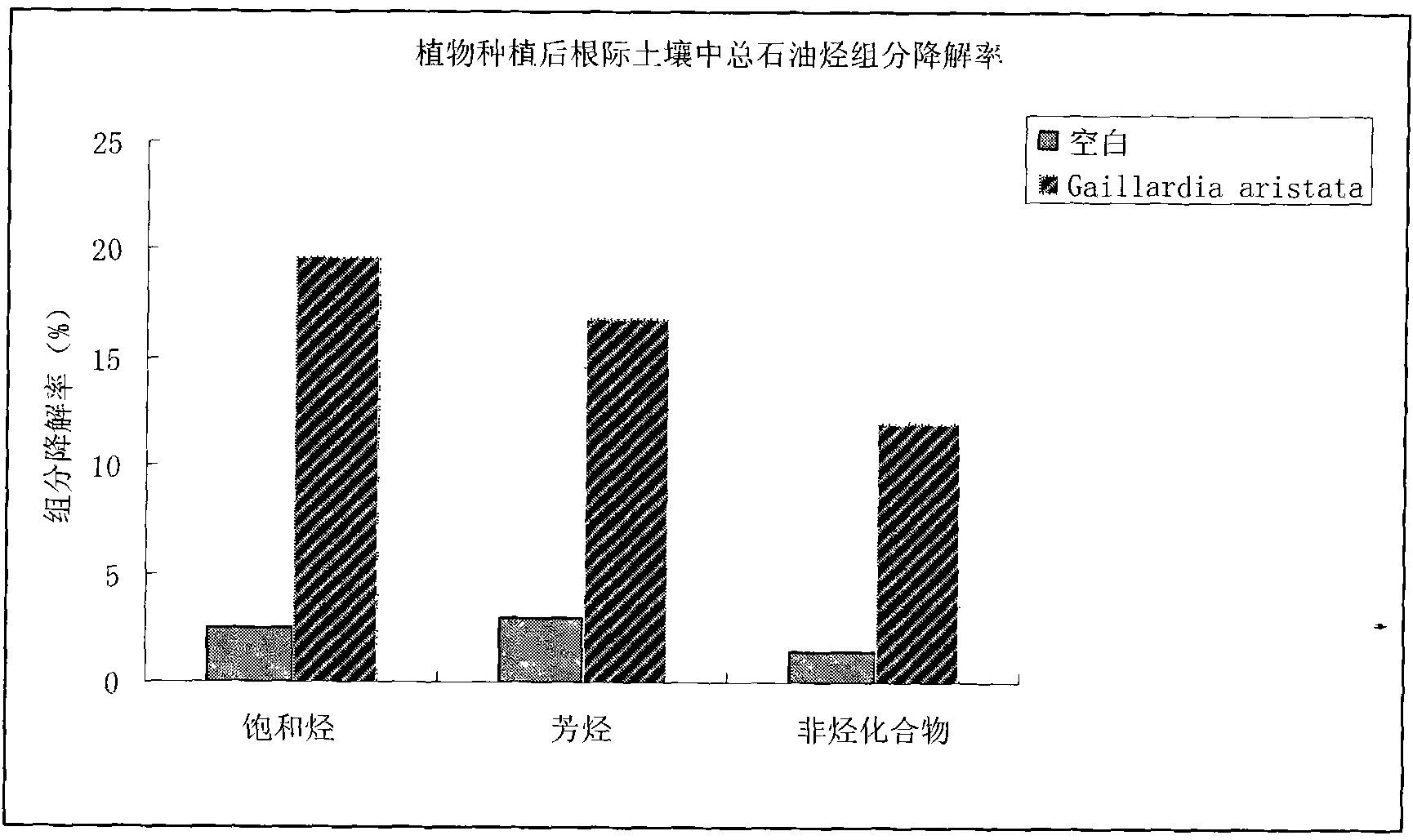
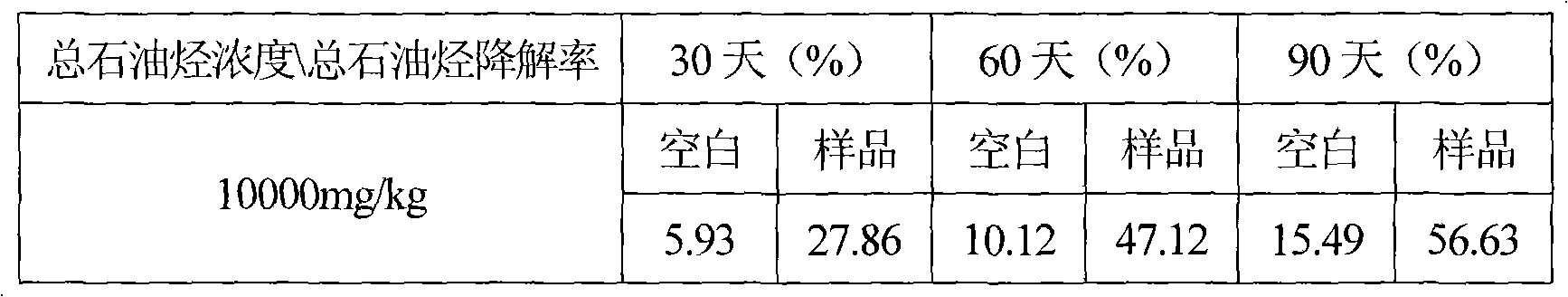
Method for remediating oil-contaminated soil by using gaillardia aristata pursh flower plants
InactiveCN102091715AImprove the degradation problemIncrease production capacityContaminated soil reclamationMicroorganismNatural degradation
The invention relates to the technical field of plant remediation of oil-contaminated soil, in particular to a method for treating and remediating oil-contaminated soil by using gaillardia aristata pursh flower plants. The method is to plant gaillardia aristata pursh in oil-contaminated soil. When the total petroleum hydrocarbon concentration of the soil is 10,000mg / kg, the growth amount of the plants is not inhibited basically, and the gaillardia aristata pursh can effectively degrade the total petroleum hydrocarbon in the oil-contaminated soil through the combined functions of the developed roots and root microbes to reduce the total petroleum hydrocarbon content in the contaminated soil. When the gaillardia aristata pursh is planted for 90 days, the degradation rate of the total petroleum hydrocarbon content in the contaminated soil can reach 56.63 percent which is nearly 4 times a blank natural degradation rate which is 15.49 percent. This proves that the gaillardia aristata pursh has high oil contamination resistance and high total petroleum hydrocarbon degradation capability. Thus, the total petroleum hydrocarbon in soil can be effectively removed by planting the gaillardia aristata pursh in the oil-contaminated soil, and removing all plants and well treating the plants in a centralized manner after the plants are mature.
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF APPLIED ECOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for removing azo dye in water by using sodium alginate or gelatin coated nanoscale zero-valent iron
ActiveCN104888718AReduce oxidationAchieving co-immobilizationOther chemical processesMicroballoon preparationGelatinReactive brilliant red X-3B
The present invention relates to a method for removing azo dye in water by using sodium alginate or gelatin coated nanoscale zero-valent iron. According to the method, the sodium alginate or gelatin is a main raw material, CaCl2 is a crosslinking agent, and the nanoscale zero-valent iron is cooperatively immobilized. The study shows that, the nanoscale zero-valent iron is high in stability and is capable of staying stable for six months or more. The effect of removing azo dye active bright-red X-3B is studied, and the result shows that the removal effect is excellent with the removal rate of more than 99.6%. The immobilized nanoscale zero-valent iron prepared by this present invention is environmentally friendly and non-toxic, high in reaction activity and stability, and high in the effect of removing azo dye active bright-red X-3B.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF URBAN CONSTR
Porphyridium extracellular polysaccharide adsorbent and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105664862AGrow fastStrong stress resistanceOther chemical processesWater/sewage treatment by sorptionPorphyridiumElution
The invention relates to a porphyridium extracellular polysaccharide adsorbent and a preparation method thereof. The method comprises the steps of porphyridium extracellular polysaccharide separation purification treatment, porphyridium extracellular polysaccharide sulfonation treatment and porphyridium extracellular polysaccharide immobilization treatment. The adsorbent prepared with the method can selectively adsorb heavy metal ions and precious metal ions in water body. The porphyridium extracellular polysaccharide adsorbent has the advantages of fast reaction, high adsorbent capacity, high removal rate, and easy elution. The adsorbent can be repeatedly used, such that secondary pollution to the environment can be reduced. Therefore, the adsorbent is environment-friendly. With the adsorbent, ecological risks caused by pollution residue and species introduction are reduced. The adsorbent and the method are suitable for industrialized productions.
Owner:TIANJIN SANSHENG BIOTECH CO LTD
Heavy metal polluted soil composite repair agent and soil repair method thereof
InactiveCN109575929AImplement resourcesAchieve recyclingContaminated soil reclamationOrganic fertilisersSorbentSludge
The invention discloses a heavy metal polluted soil composite repair agent and a soil repair method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of soil repairing. The invention provides the heavy metal polluted soil composite repair agent. The heavy metal polluted soil composite repair agent is prepared by the following method: heating sludge in high-temperature vacuum, and washing and drying thesludge to obtain sludge biochar; heating forestry and agricultural residues in high-temperature vacuum, and washing and drying the forestry and agricultural residues to obtain forestry and agricultural residue biochar; mixing the sludge biochar with the forestry and agricultural residue biochar; and mixing the mixed biochar with a sodium citrate solution, performing oscillating reaction, and washing and drying the solution at the end of the reaction to obtain the heavy metal polluted soil composite repair agent. According to the heavy metal polluted soil composite repair agent and the soil repair method thereof, the sludge and the forestry and agricultural residues are used as the raw materials; the two biochars are mixed in different proportions, so that the ash content and the carbon content of the composite adsorbent are increased; and by use of the sodium citrate solution for modification, the activity of the biochar is improved, so that the content of heavy metal elements in a biological use state in the soil is effectively reduced.
Owner:PANZHIHUA IRON & STEEL RES INST OF PANGANG GROUP
Additive applied to polluted soil
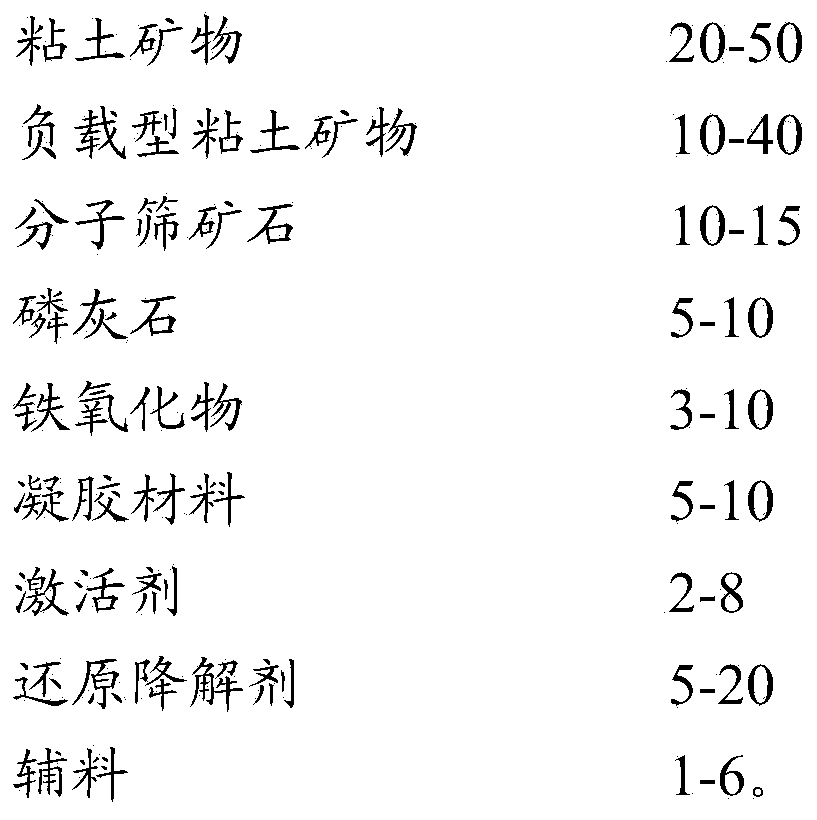
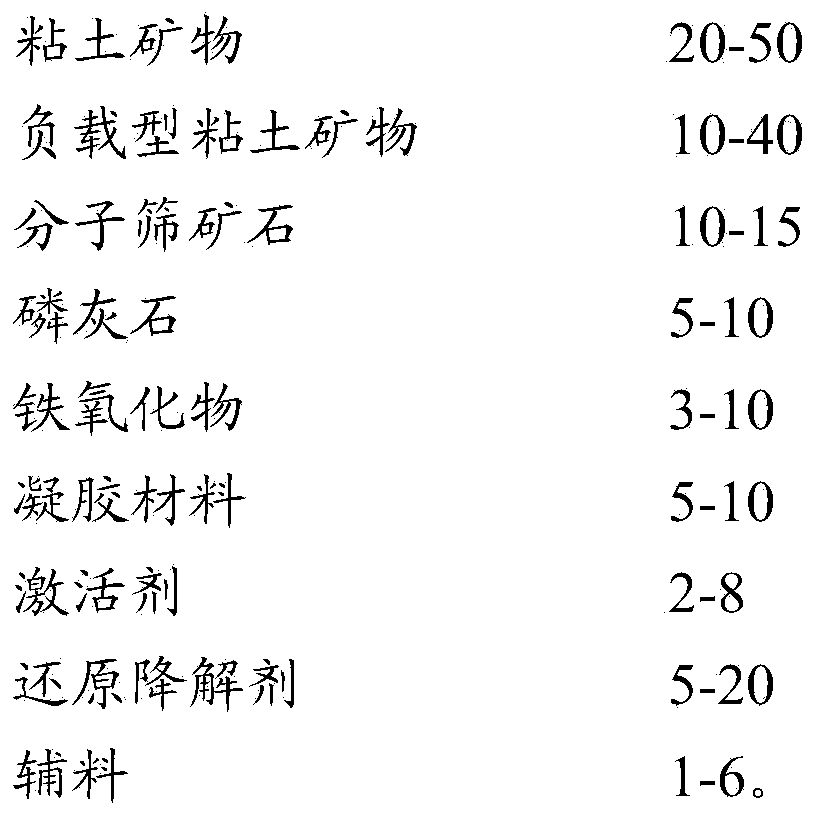
InactiveCN104449748AContent partially degradedReduce contentBuilding constructionsOrganic fertilisersClay mineralsApatite
The invention discloses an additive applied to polluted soil. The additive comprises, in parts by mass, 30-40 parts of a clay mineral, 20-30 parts of a supporting type clay mineral, 12-13 parts of a molecular sieve ore, 6-8 parts of apatite, 4-9 parts of an iron oxide, 6-9 parts of a gel material, 3-6 parts of an activator, 6-15 parts of a reducing degradation agent and 1-6 parts of an auxiliary material. The additive can stabilize heavy metals and organic matters in the soil quickly and efficiently under the synergistic action of various effective components and can further decrease the content of the organic matters, so that the leaching toxicity of pollutants is reduced, the risk is reduced, and the additive has the broad application prospect in the field of treatment of the polluted soil and the like.
Owner:SOOCHOW KH BIO SCI & TECH CO LTD KHB
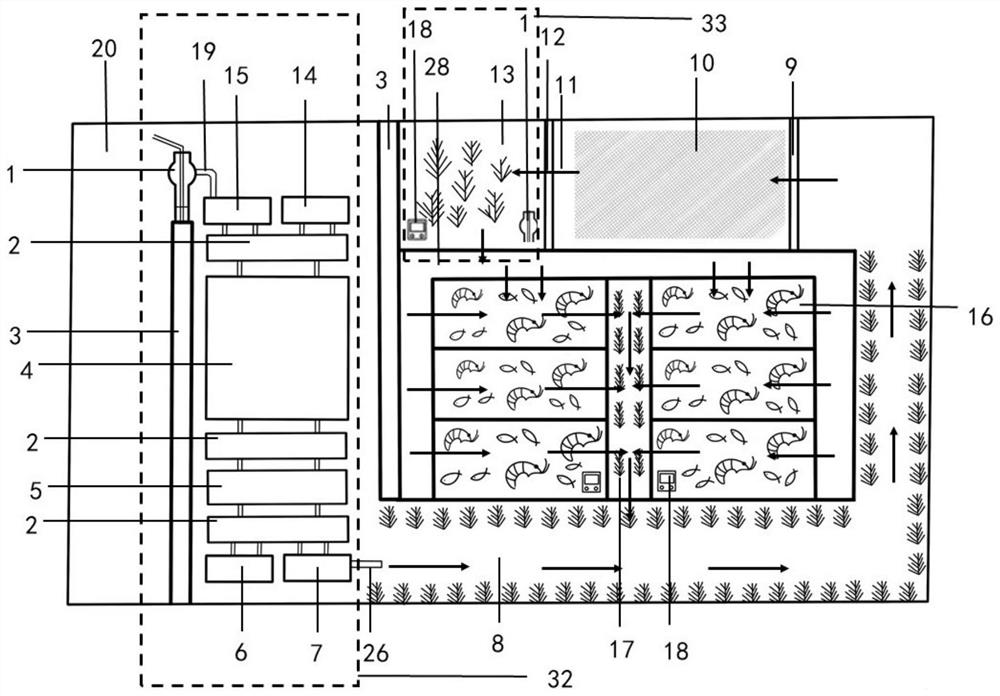
Purification system for integrated culture of fishes and shrimps
InactiveCN111919808AAvoid pollutionQuality improvementPisciculture and aquariaAgriculture gas emission reductionWater sourceWater quality
The invention provides a purification system for integrated culture of fishes and shrimps. The purification system comprises an integrated vertical subsurface flow wetland, a river channel, a water purification pond, a water storage pond and a culture pond, wherein the integrated vertical subsurface flow wetland is used for preliminary purification of a water source; the river channel is connectedwith the integrated vertical subsurface flow wetland through a water pipe for further water quality purification; the water purification pond and an outlet end of the river channel are isolated by anoverflow dam, thus promoting water quality; an inlet end of the water storage pond and an outlet end of the water purification pond are isolated by a subsurface flow dam; an outlet end of the water storage pond is isolated from the integrated vertical subsurface flow wetland by an isolating device; after the water quality is finally purified and monitored, water flows into the culture pond through a water pump; and freshwater shrimps and Ietalurus punetaus are mixed-cultured in the culture pond, and culture wastewater in the culture pond flows into the river channel through a drainage channelfor purification, and the water in the river channel then flows into the water purification pond and the water storage pond for circular purification. According to the purification system, by employing a four-stage water purification treatment system, the aquaculture wastewater can be used after being circularly purified, and zero wastewater discharge is almost realized, thereby avoiding pollution to the surrounding water environment.
Owner:SHANGHAI OCEAN UNIV
Preparation method of porous nano antibacterial particles and composite nanofiltration membrane, and composite nanofiltration membrane
PendingCN110694493AImprove hydrophilicitySmall apertureSemi-permeable membranesMembranesUltrafiltrationPolyamine
The invention discloses a preparation method of porous nano antibacterial particles and a composite nanofiltration membrane and the composite nanofiltration membrane. The preparation method of the porous nano-antibacterial particle composite nanofiltration membrane comprises the following steps: 1, adding porous copper-coated TiO2 nano-antibacterial particles into a basic solution, and uniformly embedding the porous nano-antibacterial particles into the basic solution through ultrasonic dispersion or strong stirring to prepare a monomer solution; wherein the basic solution is a polybasic acylchloride solution and a piperazine aqueous solution, or a polybasic acyl chloride solution and an aqueous solution of a mixture of piperazine and polyamine; and 2, carrying out interfacial polymerization reaction on the monomer solution on the surface of an ultrafiltration support membrane layer to obtain the porous copper-coated TiO2 nano antibacterial particle composite nanofiltration membrane.The prepared porous copper-coated titanium dioxide nano antibacterial particle composite nanofiltration membrane is large in water flux, high in desalination rate, resistant to bacterial pollution, easy to clean and capable of being widely applied to the application fields of sewage treatment, material concentration, decoloration, desalination of alkaline water or seawater and the like.
Owner:深圳市君脉膜科技有限公司
Plant glyphosate-resistant gene and applications thereof
InactiveCN102816777AIncrease diversityReduce ecological riskSsRNA viruses positive-senseMicrobiological testing/measurementResistant genesNucleotide
The invention discloses a plant glyphosate-resistant gene and applications thereof. The nucleotide sequence of the glyphosate-resistant gene is SEQIDNO:1, SEQIDNO:3 or SEQIDNO:5 and encoded amino acid sequences are SEQIDNO:2, SEQIDNO:4 or SEQIDNO:6 respectively. A glyphosate-resistant plant prepared throuhg the plant glyphosate-resistant gene can apparently display glyphosate-resistant herbicides, novel choices are provided for cultivating glyphosate-resistant herbicides, and the diversity of the transgenic technology of the glyphosate-resistant herbicides is added, accordingly, ecological risks of the transgenic technology of the glyphosate-resistant herbicides are reduced.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Preparation method and application of sediment-water interface phosphorus release control material
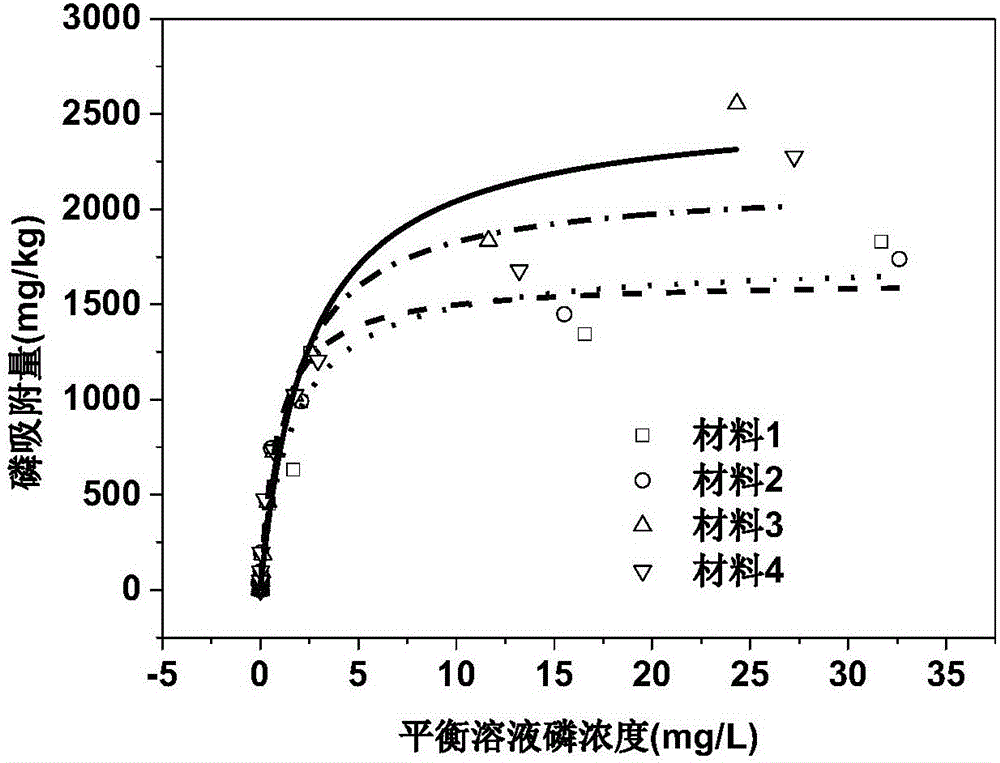
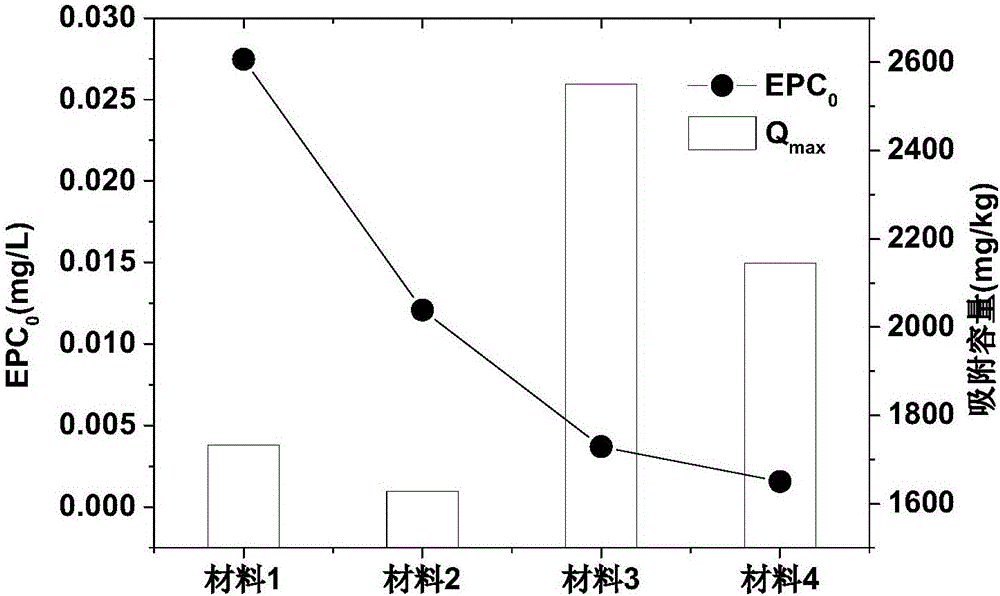
ActiveCN106277672ADecrease the adsorption-desorption equilibrium concentrationLess materialFixation/solidifcation sludge treatmentContaminated waterways/lakes/ponds/rivers treatmentIron saltsPhosphate
The invention provides a preparation method and application of a sediment-water interface phosphorus release control material. For the first time, a lake sediment and kaolin mixture is used as a basic raw material, and processes like oxidation, iron salt modification, granulation and calcination are adopted, so that adsorption-desorption balance concentration EPC0 value of the material to phosphate is remarkably lowered, linear distribution coefficient Kd value of the material is increased, and the material can effectively reduce sediment interstitial water phosphate concentration and can inhibit sediment-water interface phosphate release. The material itself has weak phosphate desorption capability and high adsorption and buffering capability, so that the material can truly realize effective obstruction and control on sediment-water interface phosphorus release. The material is low in material cost, high in social and economic benefit and safety, free of ecological risk to lake water, energy-saving and environment-friendly and has remarkable effect on controlling sediment-water interface phosphorus release in different lake areas of the Dian Lake in the process of application.
Owner:CHINESE RES ACAD OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCI
Method for remedying heavy metal-contaminated soil by combining chemical reduction and chemical leaching
ActiveCN103611725AImprove rinsing efficiencyGood removal effectContaminated soil reclamationEthylene diamineCentrifugation
The invention relates to a method for remedying heavy metal-contaminated soil by combining chemical reduction and chemical leaching, and aims to provide a method for remediation by virtue of combination of chemical reduction and chemical leaching. The method is used for eluting iron and manganese oxides to improve an effect of removing heavy metals from soil by using a leaching agent. The method comprises the following steps of performing leaching by using a reducing agent aqueous solution, namely performing vibratory washing on the contaminated soil by using the reducing agent aqueous solution, and filtering washing liquid after centrifugation; and performing leaching by using a Na2EDTA (Ethylene Diamine Tetraacetic Acid) aqueous solution, namely adding the Na2EDTA aqueous solution into the contaminated soil leached by the reducing agent aqueous solution for vibratory washing, and filtering washing liquid after centrifugation.
Owner:ZHONGKE DINGSHI ENVIRONMENTAL ENG CO LTD
Ultraviolet-biological coordinate process for controlling hard-to-degrade organic gas
InactiveCN101327401AImprove removal efficiencyImprove stabilityDispersed particle separationAir quality improvementHigh concentrationBio filtration
The present invention discloses an ultraviolet-organism combinational process that belongs to the environmental governing technical field and controls the organic gas that is difficult to be degraded. The ultraviolet oxidation technology is adopted as the pre-treatment unit; the organism filtering technology is adopted as the main process to form an ultraviolet-organism combinational process. Compared with the single organism filtering technology and the single ultraviolet oxidation technology, the ultraviolet-organism combinational process overcomes the weaknesses that the traditional organism filtering technology has low treatment efficiency, and takes large land areas, etc. during processing the organic gas that is difficult to be degraded and has high concentration. At the same time, the combinational process can effectively overcome the weakness that the ultraviolet oxidation technology has incomplete decomposition and produces the toxic product, and reduces the hidden danger for the surrounding environment and the health of the human body.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Preparation method of potassium hydroxide modified magnetic corncob biochar composite material applied to removal of imidacloprid in water
PendingCN111871369ARealize resource utilizationStrong magnetic separation abilityOther chemical processesWater contaminantsPotassium hydroxidePhysical chemistry
The invention discloses a preparation method of a potassium hydroxide modified magnetic corncob biochar composite material for removing imidacloprid in water, which comprises the following steps: carrying out mixing pyrolysis (KOH-CBC) on corncob biochar (CBC) and potassium hydroxide (KOH), loading ferric chloride (FeCl3.6H2O) and zinc chloride (ZnCl2) to the KOHCBC, and carrying out secondary pyrolysis to obtain potassium hydroxide modified magnetic corncob biochar KOH + Fe / ZnCBC. The material prepared by the invention has good physicochemical properties, has a high removal rate on imidacloprid in water, and has a maximum adsorption capacity of 433.1 mg / g at 35 DEG C. In addition, the material shows high magnetic separation capacity, and efficient separation and regeneration with a waterbody can be achieved after adsorption.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
Preparation method and application of efficient removing materials for interstitial water phosphate of sediments
ActiveCN106311129ALess materialHigh porositySludge treatmentOther chemical processesPhosphateDesorption
The invention provides preparation method and application of efficient removing materials for interstitial water phosphate of sediments. Lake sediments are initiatively taken as basic materials of the materials and are subjected to calcination and alkaline washing, then the obtained material is mixed with kaolin, and mixed powder obtained is modified via ferric salt and then pore-forming agents are added for granulation and calcination shaping is peformed, and the low EPCo value and high Qmax value efficient removing materials for the interstitial water phosphate of the sediments are obtained. Concentration of the interstitial water phosphate of the sediments can be effectively cut down through the materials, and release of the phosphate of the sediments-water interfaces is restrained; desorption capacity of phosphate of the materials is weak and adsorption capacity is large, so that effective resistance and control of the materials on the sediments-water interfaces can be truly realized; the materials are low in cost, good in social and economic benefits, high in security, free of ecological risk on lake water, energy saving and environment friendly and remarkable in control effect on the sediments-water interfaces of different lakes of the Dian Lake during application.
Owner:CHINESE RES ACAD OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCI
Wastewater treatment agent and application method thereof
InactiveCN109133323AAdequate responseReduce energy consumptionWater contaminantsWater/sewage treatment by sorptionCross-linkHigh energy
The invention discloses preparation of a wastewater treatment agent and an application method thereof. At present, extensive attention of researchers is paid to a heterogeneous Fenton technology in the field of organic wastewater treatment. Due to low cost and high catalytic activity, nanometer pyrite has excellent application potential in the heterogeneous Fenton field. However, separation and recovery of the nanometer pyrite from a liquid phase need to use ultrafiltration, nanofiltration and other high-energy-consumption means, and the cost is high; the nanometer pyrite Fenton system is lowin effluent pH value and high in iron content, and has relatively high environmental risk. By virtue of the fixation effect of sodium alginate gel on nanometer pyrite grains and the cross-linking effect of sodium alginate molecules and iron ions, the wastewater treatment agent with advantages of being easy to separate and low in cost is prepared in the invention. The agent prepared in the invention has the advantages that the defect that the nanometer pyrite is difficult to separate is effectively overcome, and the environmental risk of the nanometer pyrite is weakened. By adopting the wastewater treatment agent prepared in the invention and the application method thereof, organic wastewater can be effectively treated, and the agent has wide application prospects.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF GEOSCIENCES (BEIJING)
Composting contaminated soil restoration method through straw
InactiveCN106903151AEasy to removeReduce ecological riskBio-organic fraction processingClimate change adaptationContaminated soilsAgriculture
The invention discloses a composting contaminated soil restoration method through straw. The method comprises the following steps that the straw is mixed with contaminated soil, initial compost raw materials are obtained and mixed with active biological carbon for composting treatment, and restoration of the contaminated soil is completed. The restoration method is capable of simultaneously reducing the effectiveness of various pollutants and has the advantages of low cost, simple process, convenient operation, high restoration efficiency, free of toxic and side effect and the like. Through the method, stacking of agricultural straw can be reduced, reduction treatment and resource utilization of agricultural straw solid waste are achieved, the pollutants in the soil can be effectively removed, and efficient restoration of the contaminated soil is achieved. The in-site restoration method is adopted, cost and pollution caused by transportation of raw materials or the contaminated soil can be reduced, meanwhile, the physicochemical property of the contaminated soil can be improved, the restored soil can be used for subsequent resource recycling, and the method has wide application prospects.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Soil smoldering remediation method for heavy metal co-contaminated soil
ActiveCN103817146ASignificance of real environmental protectionImprove water retentionContaminated soil reclamationSoil scienceIn situ remediation
The invention belongs to the technical field of remediation of heavy metal contaminated soil, and particularly relates to a soil smoldering technology for treatment and remediation of heavy metal co-contaminated soil. The soil smoldering remediation method mainly comprises the following steps: plant straws are covered with soil to form a covered body; the outer layer is a soil layer, and the straws or a mixture of straws and soil are arranged inside; the inside is kept in an anaerobic condition, and the soil smoldering treatment is then carried out. Through solidification, absorption, chelation, complexation and other various reactions, the heavy metal co-contaminated soil treated by applying the technology provided by the invention achieves a reduced proportion of chemical forms which can easily migrate and diffuse to the environment, and an increased proportion of chemical forms which are difficult to release to the environment. Therefore, environmental and ecological risks from heave metals are reduced. The technology provided by the invention can simultaneously fix multiple heave metals, reduce the heave metal absorption and accumulation by plants, effectively kill various pathogenic bacteria in soil and increase the biomass of crops, and is a simple, high-efficient, easy-to-operate and low-cost in-situ remediation technology for heavy metal co-contaminated soil.
Owner:SHAOGUAN TAOLIN GREEN TECH
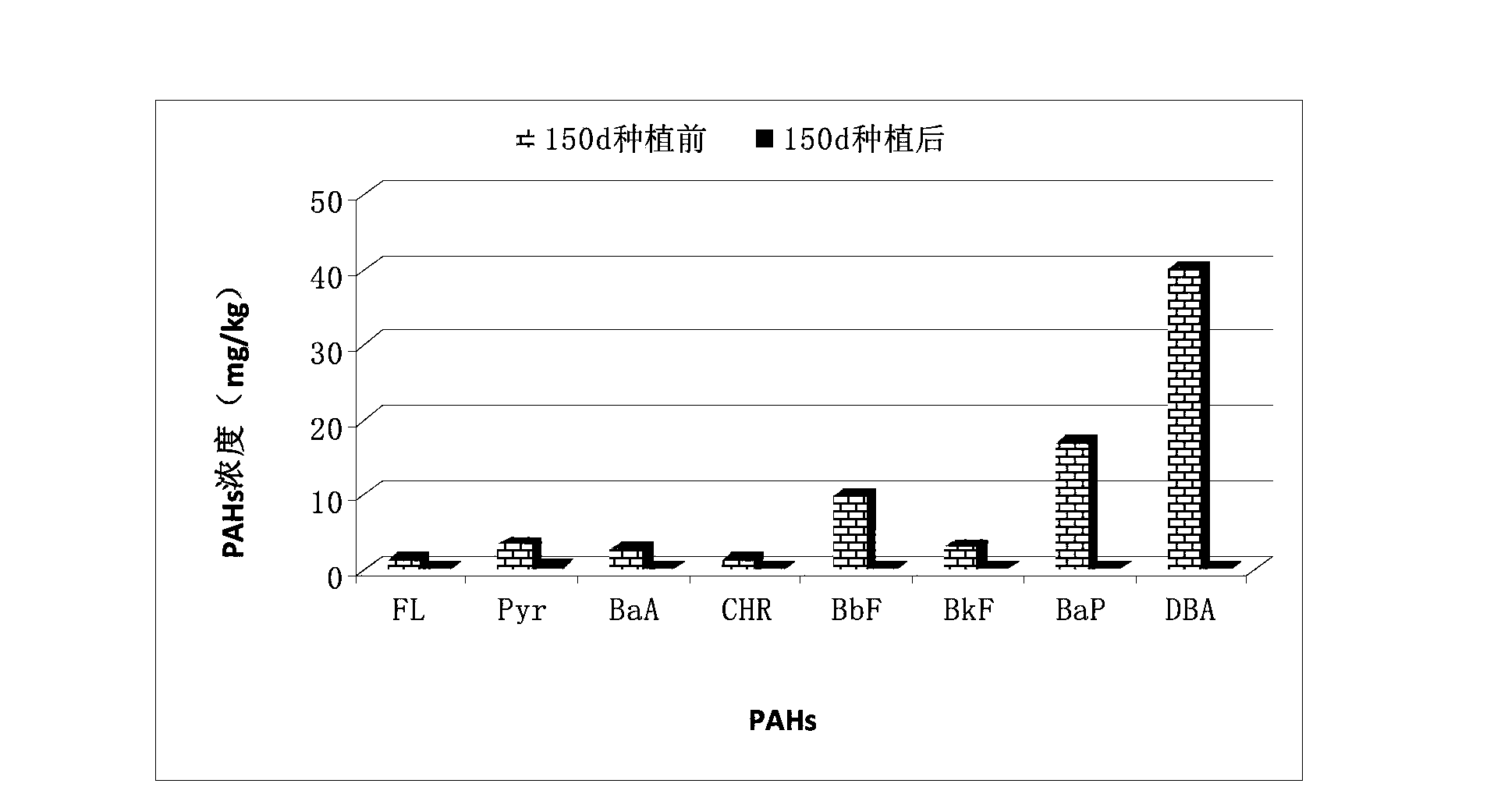
Remediation method for soil contaminated by polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) by using gramineous plant Festuca arundinacea
ActiveCN103769411AReduce degradationReduce production capacityContaminated soil reclamationPolycyclic aromatic hydrocarbonFestuca arundinacea
The invention relates to the field of plant remediation technology for soil contaminated by PAHs, specifically to a remediation method for soil contaminated by PAHs by using the gramineous plant Festuca arundinacea. The gramineous plant Festuca arundinacea is planted in soil contaminated by PAHs; in the process of germination, growth and maturation of the plant, PAHs in the soil are degraded, removed or substantially reduced through combined action of the growth process and root exudates of the plant. According to the method, the ornamental plant Festuca arundinacea is planted in the soil contaminated by PAHs for remediation of the soil contaminated by PAHs; compared with a traditional contaminated soil treatment method, the method provided by the invention has the advantages of small investment, small work amount, low technical requirements, etc. Moreover, as Festuca arundinacea is an ornamental and economic plant, planting of Festuca arundinacea enables PAHs contamination in environmental soil to be effectively degraded and contaminated plants not to enter into a food chain, thereby utmostly reducing ecological risks caused by treatment of the contaminated soil.
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF APPL ECOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
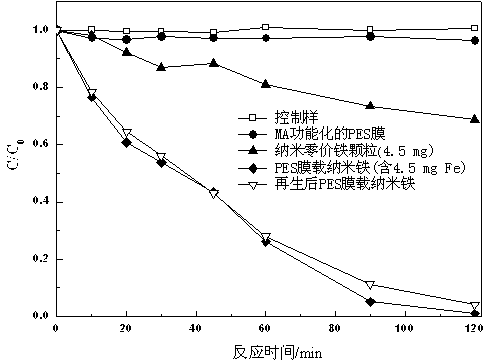
Preparation method and application of nano iron-based polyether sulfone (PES) organic-inorganic composite material
InactiveCN103318997AEasy to operateLow costWater/sewage treatment by reductionGreen teasMicrofiltration membrane
The invention discloses a method for preparing a nano iron-based polyether sulfone (PES) organic-inorganic composite material. The method comprises the following steps: (1) pretreating a PES microfiltration membrane; (2) functionalizing the PES microfiltration membrane through methacrylic acid (MA); (3) respectively performing sodium ion exchange and iron ion exchange on the functionalized PES microfiltration membrane; (4) completely soaking the PES microfiltration membrane containing iron ions in an aqueous solution of green tea, so as to form the nano iron-based PES organic-inorganic composite material through the reducing action of the aqueous solution of the green tea. By utilizing the reducing action of the materials, wastewater containing antibiotics, bromate ions, bromo-organic matters and chloro-organic matters is respectively repaired under room temperature conditions. The method is low in process cost, and easy to operate and has the environment-friendly effects, the prepared organic-inorganic composite material is high in degradation capacity, high in stability and long in service cycle, and the composite material can effectively fix iron nanoparticles, is easy to recover and regenerate, belongs to an environment-friendly functional material and is suitable for industrial production.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Control method for sporadic plaques of spartina alterniflora in coastal wetland
InactiveCN108401754ASimple and fast operationLow costInvasive species monitoringPlant protectionChemical controlCvd risk
The invention discloses a control method for sporadic plaques of spartina alterniflora in a coastal wetland, and is control for the sporadic plaques of the spartina alterniflora which is newly formedor formed in the early secondary invasion stage after restoration in the coastal wetland. Hydrological change characteristics of the coastal wetland are combined, and an environmentally friendly chemical agent is timely sprayed, so that accurate, effective and rapid elimination of the sporadic plaques of invasive species of the spartina alterniflora is achieved to prevent and control further spreading, the environmental and biological risk which may be generated in a chemical process is reduced, and a necessary and clear technical support and theoretical basis are provided for remedial management of residual small plaques after early-stage intercepting and large-scale treatment of the plaques of the newly formed spartina alterniflora and rapid prevention and control of the sporadic plaquesof the spartina alterniflora in the secondary invasion. The control method only needs to be implemented once, and the weed killing rate can reach 95%; no large-scale machinery is needed to facilitateoperation, the precise prevention and control can be implemented point-to-point, and the cost is low; the environmental and biological risk which may be generated in a traditional chemical control process is avoided.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
Method for separating and removing tetracycline antibiotics from livestock/poultry culture wastewater
InactiveCN105600998AIncrease ion concentrationSeparation and removal to achieveWater/sewage treatment by centrifugal separationWaste water treatment from animal husbandryEcological environmentEnvironmental engineering
The invention relates to a method for separating and removing tetracycline antibiotics from livestock / poultry culture wastewater, particularly a method for lowering tetracycline antibiotic ecological environment risks in the livestock / poultry culture wastewater recycling process, belonging to the field of water pollution control and resource regeneration. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: adding about 10-100mM of strong electrolytes (NaCl, MgCl2, MgSO4 and salt brine) into the wastewater to increase the ion concentration in the solution; adding acids (hydrochloric acid, nitric acid and sulfuric acid) to regulate the pH value of the wastewater to 1-5, sufficiently stirring to promote destabilization, aggregation and settling of suspended particulate matters and soluble organic matters in the wastewater, and carrying out solid-liquid separation, thereby separating the tetracycline antibiotics from the wastewater. The suspended particulate matters and soluble organic matters in the wastewater are removed, thereby achieving the goal of separating the tetracycline antibiotics, and lowering the antibiotic pollution risks in the livestock / poultry culture wastewater recycling process.
Owner:INST OF URBAN ENVIRONMENT CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Stabilizer suitable for heavy metal contaminated soil and application method thereof
ActiveCN102343357BFast and effective stabilizationReduce ecological riskContaminated soil reclamationClay mineralsHeavy metal chelation
A stabilizer suitable for heavy metal contaminated soil and an application method thereof belong to the technical field of contaminated soil remediation treatment. The invention is characterized in that: the soil stabilizer comprises the following components by mass: 5%-8% of heavy metal chelants, 10%-20% of gelled materials, 50%-65% of clay mineral, 10%-15% of alkaline excitants; the gelled material, clay mineral and alkaline excitant are mixed and grinded to obtain a Blaine specific surface area of 5000-8000 cm2 / g; the mixture is sieved by a 200-mesh sieve, and the water content is less than 3%; the heavy metal chelant is prepared into a solution by water with a mass percent of the chelant being 20%-40%. The stabilizer and soil are uniformly mixed, and conserved for above 5 days. The main components of the stabilizer are mostly natural materials; after the stabilizer is used, heavy metal contaminants in soil can be rapidly and effectively stabilized, and the toxicity of the contaminants is reduced. The materials used are economical and easily available, and do not cause secondary contamination, and the stabilizer is a rapid and high-efficient stabilizer for heavy metal contaminated soil.
Owner:SHANGHAI BAOFA ENVIRONMENTAL TECH CO LTD
Separation and recovery method for ferrum and manganese in electrolytic manganese residues
The invention discloses a method for efficiently decomposing complex ferrum and manganese phases in high-ferrum electrolytic manganese residues and synchronously recycling ferrum and manganese. The electrolytic manganese smelting waste residues containing the complex ferrum and manganese phases are subjected to neutral roasting under the protective atmosphere (N2), and by controlling the roasting conditions, the complex ferrum and manganese phases in the manganese residues are decomposed into ferric oxide and trimanganese dioxide. Meanwhile, volatile matters, crystal water and the like in the electrolytic manganese residues are removed in the neutral roasting process, and ferrum and manganese in the manganese residues achieve upgrade. The products of the neutral roasting can be directly subjected to dissociation through ball milling, efficient separation and recovery of ferrum and manganese are achieved through stepped magnetic separation, or by means of reduction roasting treatment, the ferric oxide is further reduced into ferroferric oxide, the reduction roasting products are subjected to the ball-milling-magnetic separation process, and then ferrum and manganese separation and recovery are achieved. The method is suitable for various kinds of Fe-Mn ore or manganese residues which are difficult to treat, and has the beneficial effects that the application range is wide, the process equipment is simple, and operation is easy. Efficient decomposition of the complex ferrum and manganese phases and separation and recovery of the ferrum and manganese phases in the high-ferrum electrolytic manganese residues can be achieved, and reduction and recycling of ferrum-manganese-contained solid waste can be achieved.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com