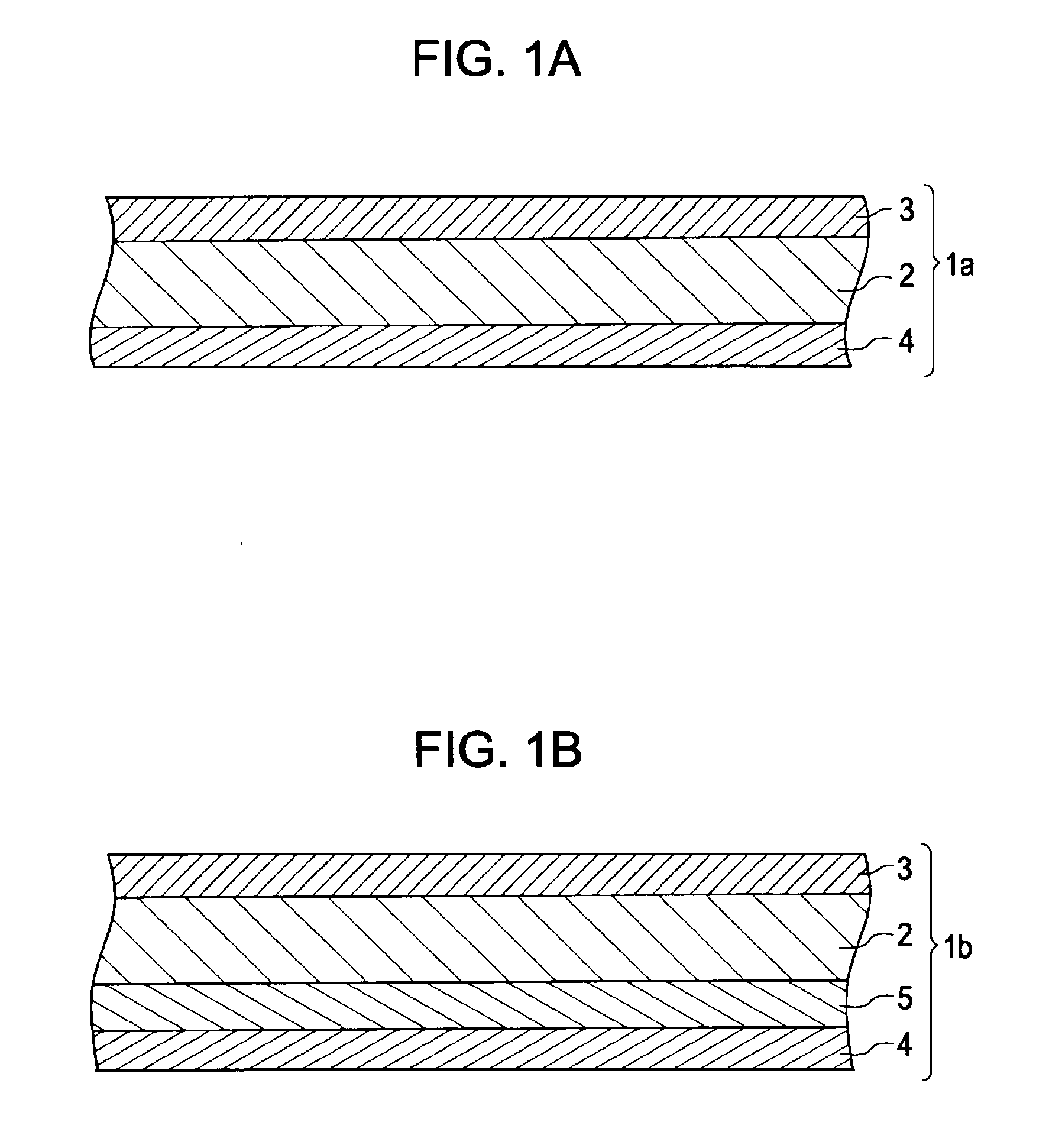
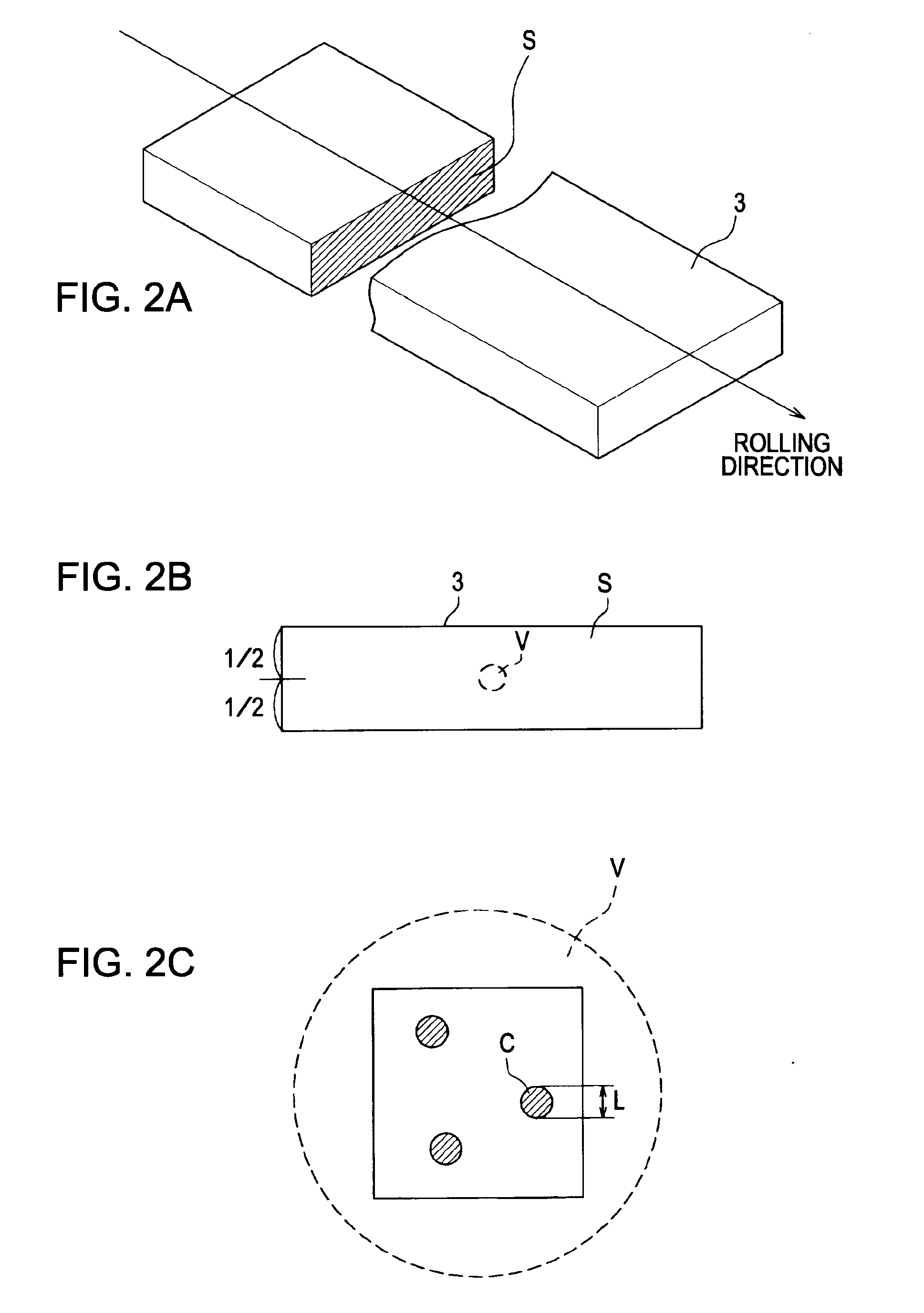
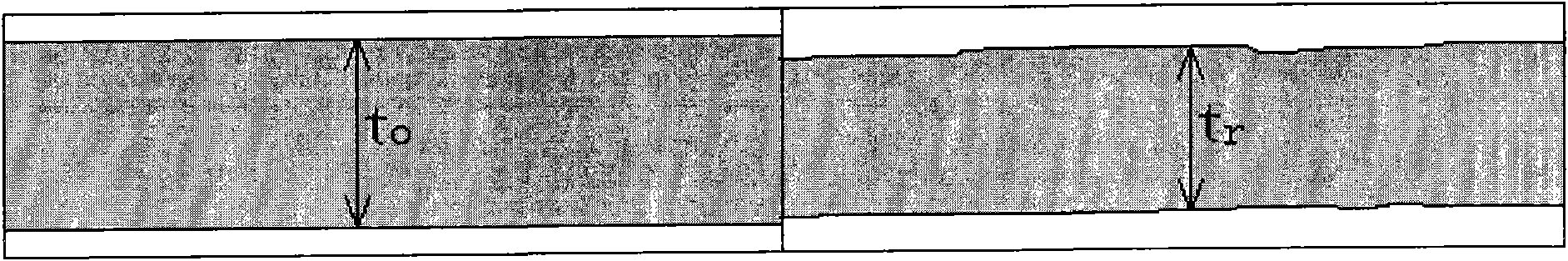
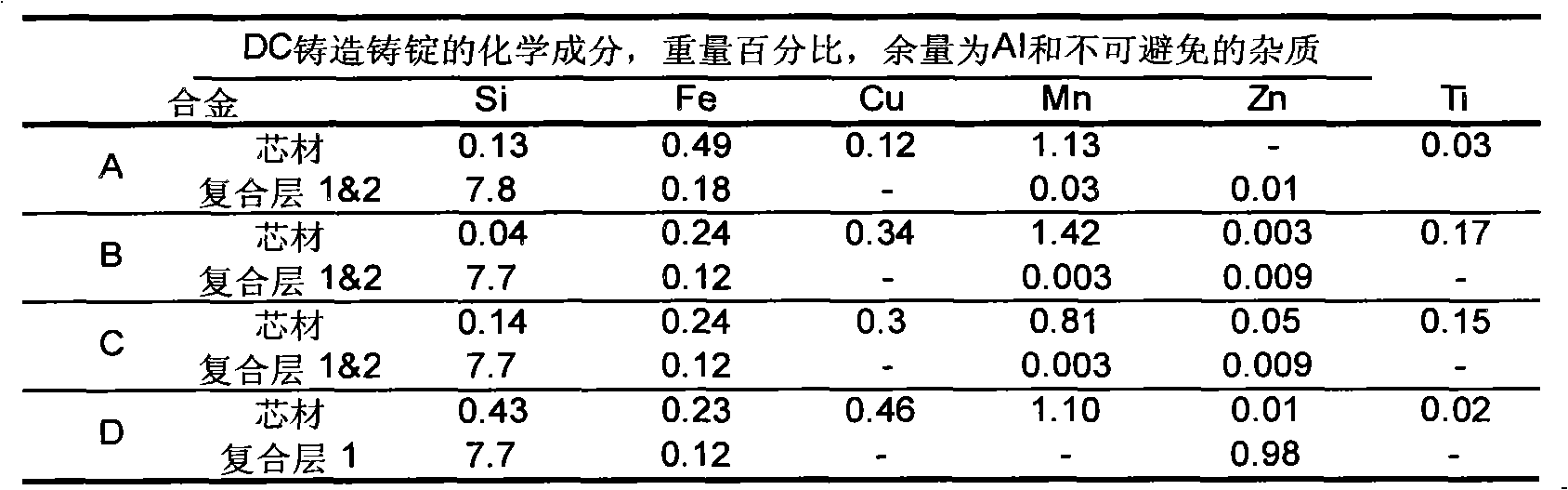
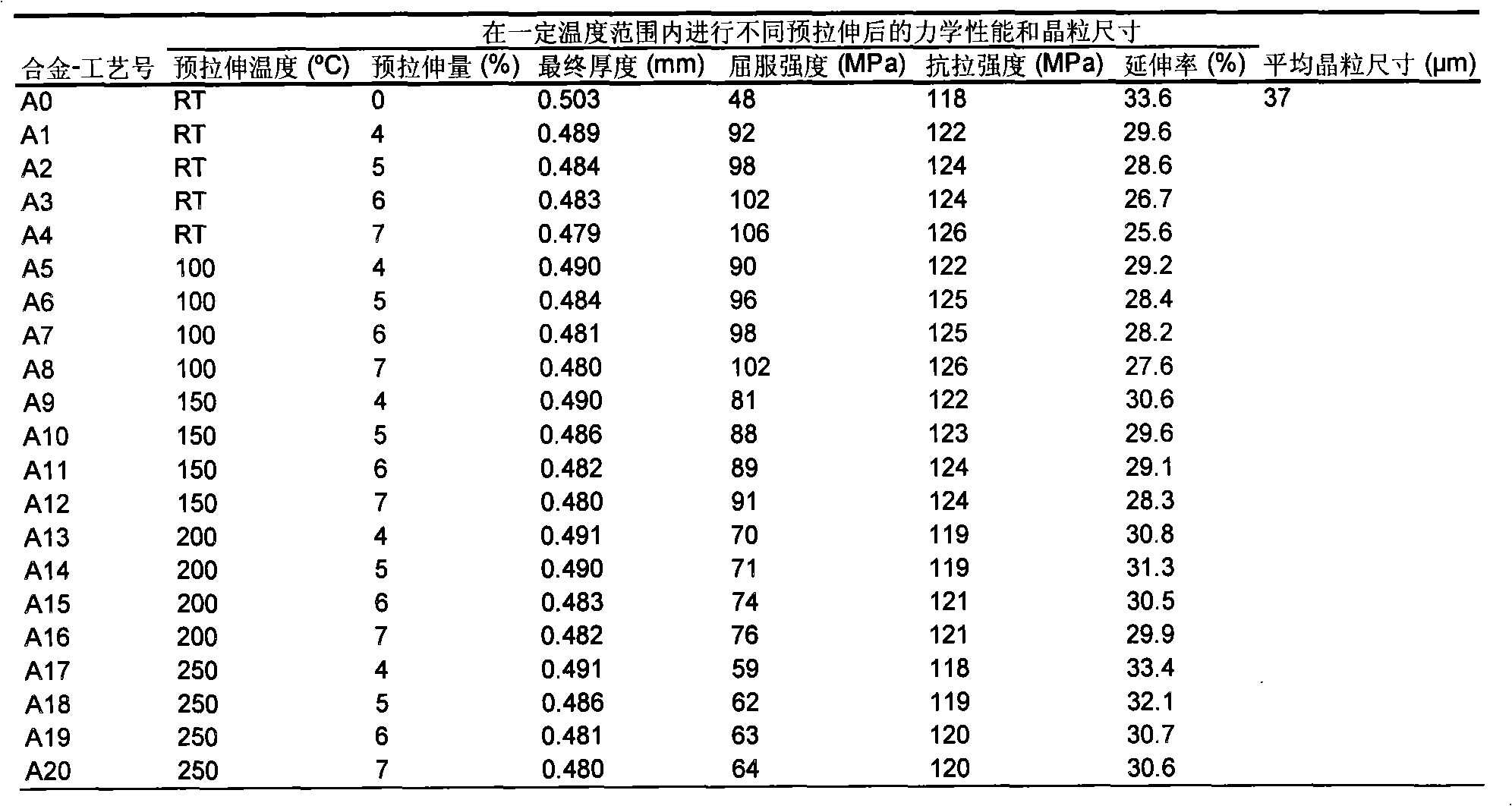
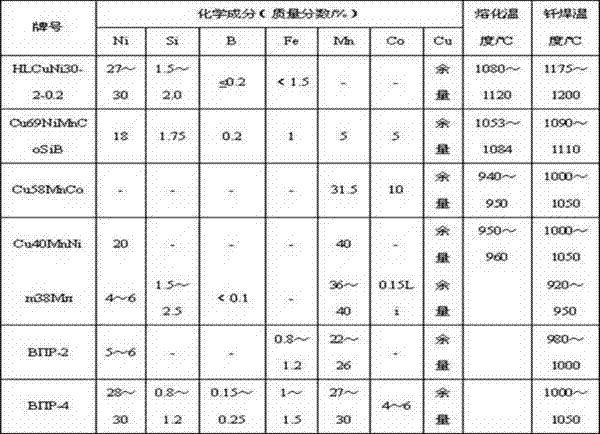
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
283results about How to "Excellent brazeability" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Compound Sealing Method for Vacuum Glass
ActiveUS20120321822A1Excellent brazeabilityPrevent annealingClimate change adaptationSoldering apparatusThermal shockBrazing
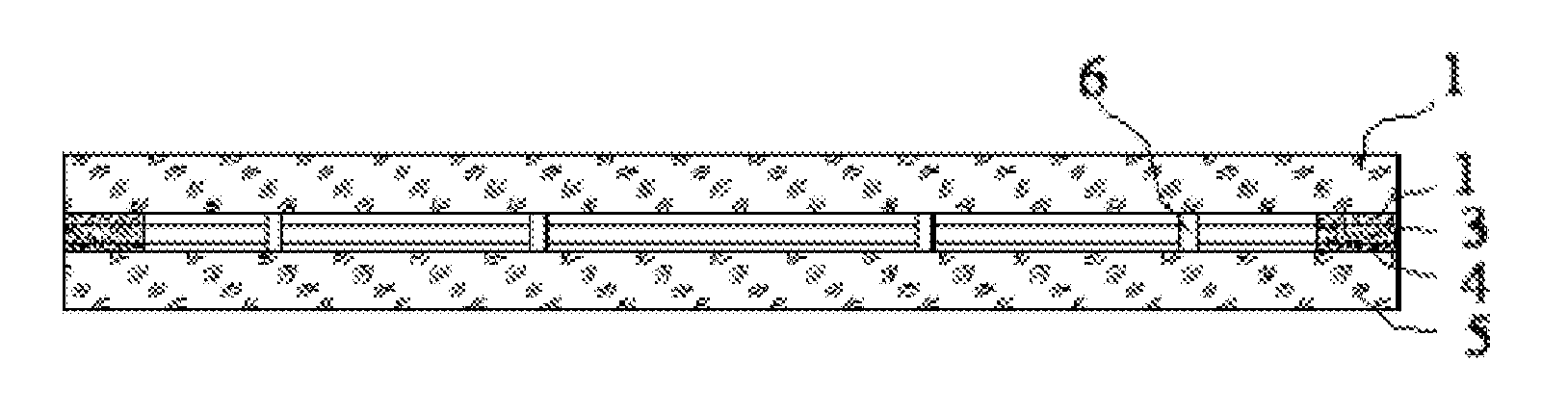
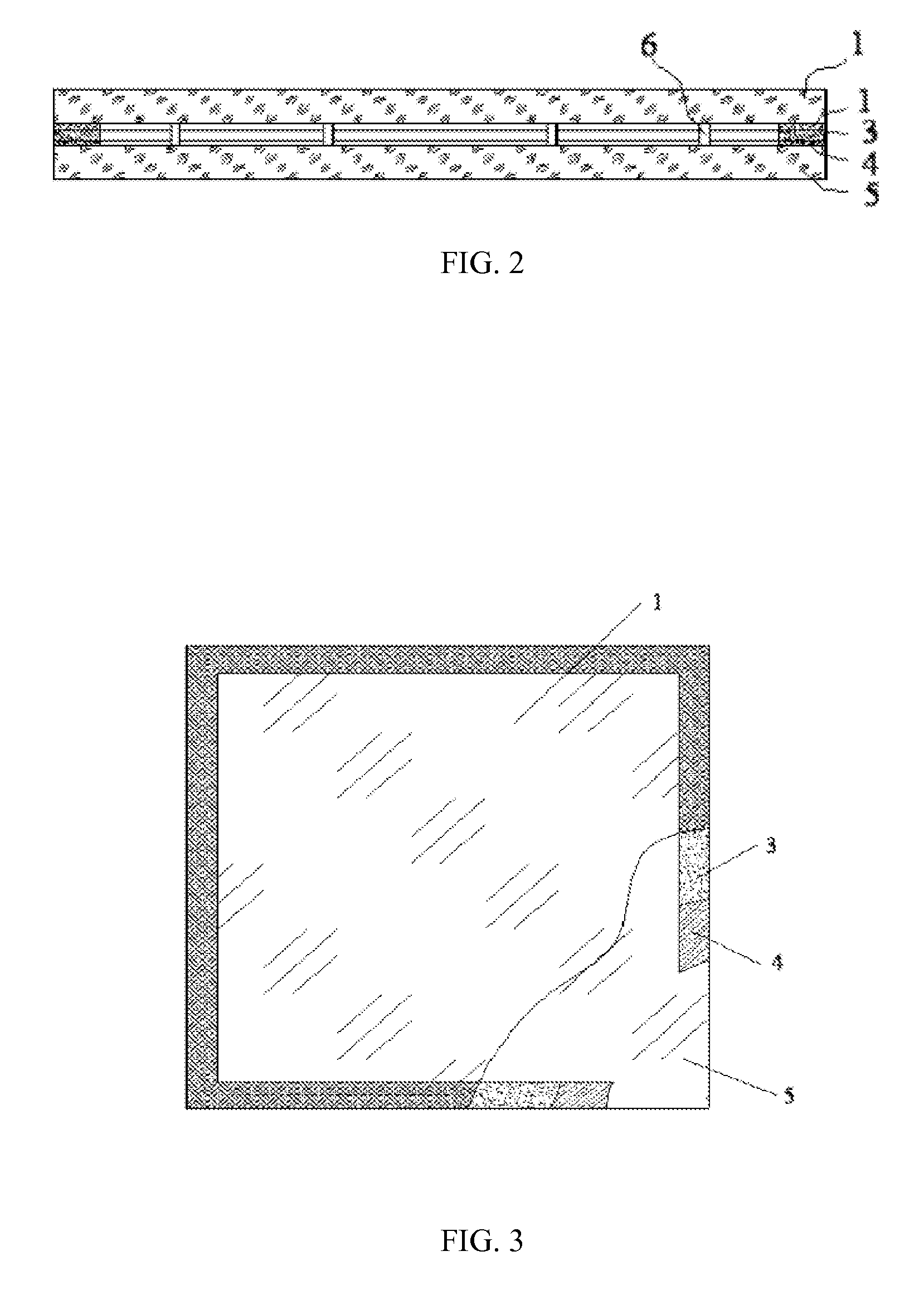
The invention relates to a compound sealing method for glass plates, which is characterized by realizing the air-tight joint between compounded glass plates in a preset position by using a metal brazing technology. The invention provides a brand new technological method for the compound sealing between glass plates. The method has the advantages of firm connection in sealing positions, high air tightness, favorable thermal shock resistance and the like, and the annealing of toughened glass are avoided because of a lower brazing temperature used, thereby providing convenience to the processing of toughened vacuum glass, toughened insulated glass and other toughened compound glass products
Owner:LUOYANG LANDGLASS TECH CO LTD
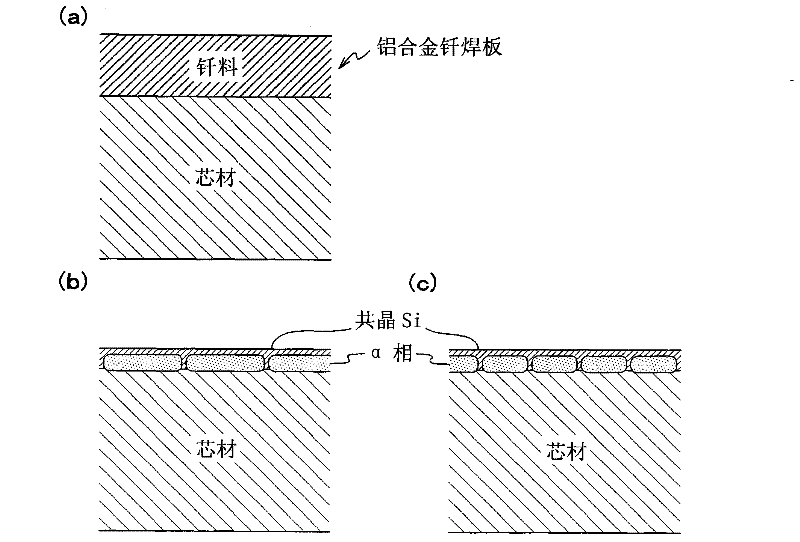
Aluminum alloy clad sheet for a heat exchanger and its production method
ActiveUS20090165901A1High elongationGood formabilityWelding/cutting media/materialsThin material handlingUltimate tensile strengthImpurity
Disclosed herein is an aluminum alloy clad sheet for a heat exchanger including a core layer, a sacrificial layer formed on one surface of the core layer, and a filler layer including an Al—Si based alloy formed on the other surface of the core layer. The core layer includes a predetermined amount of Si, Cu, Mn, Ti, and Mg, the remainder including Al and inevitable impurities, and the sacrificial layer includes a predetermined amount of Si, Mn, and Zn, the remainder including Al and inevitable impurities. The core layer has a crystal grain size after the brazing heat treatment at 595° C. for 3 minutes of at least 50 μm and less than 300 μm. The filler layer and the sacrificial layer are defined for their thickness, and the number of intermetallic compounds in the core layer is also defined to a predetermined range. By such constitution, the aluminum alloy clad sheet has improved fatigue life and post-braze strength, high corrosion resistance, and excellent erosion resistance and brazeability.
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD
Recovered high strength multi-layer aluminum brazing sheet products
InactiveUS20080274367A1Excellent brazeabilityHigh post-braze tensile strengthWelding/cutting media/materialsThin material handlingIngot castingHigh intensity
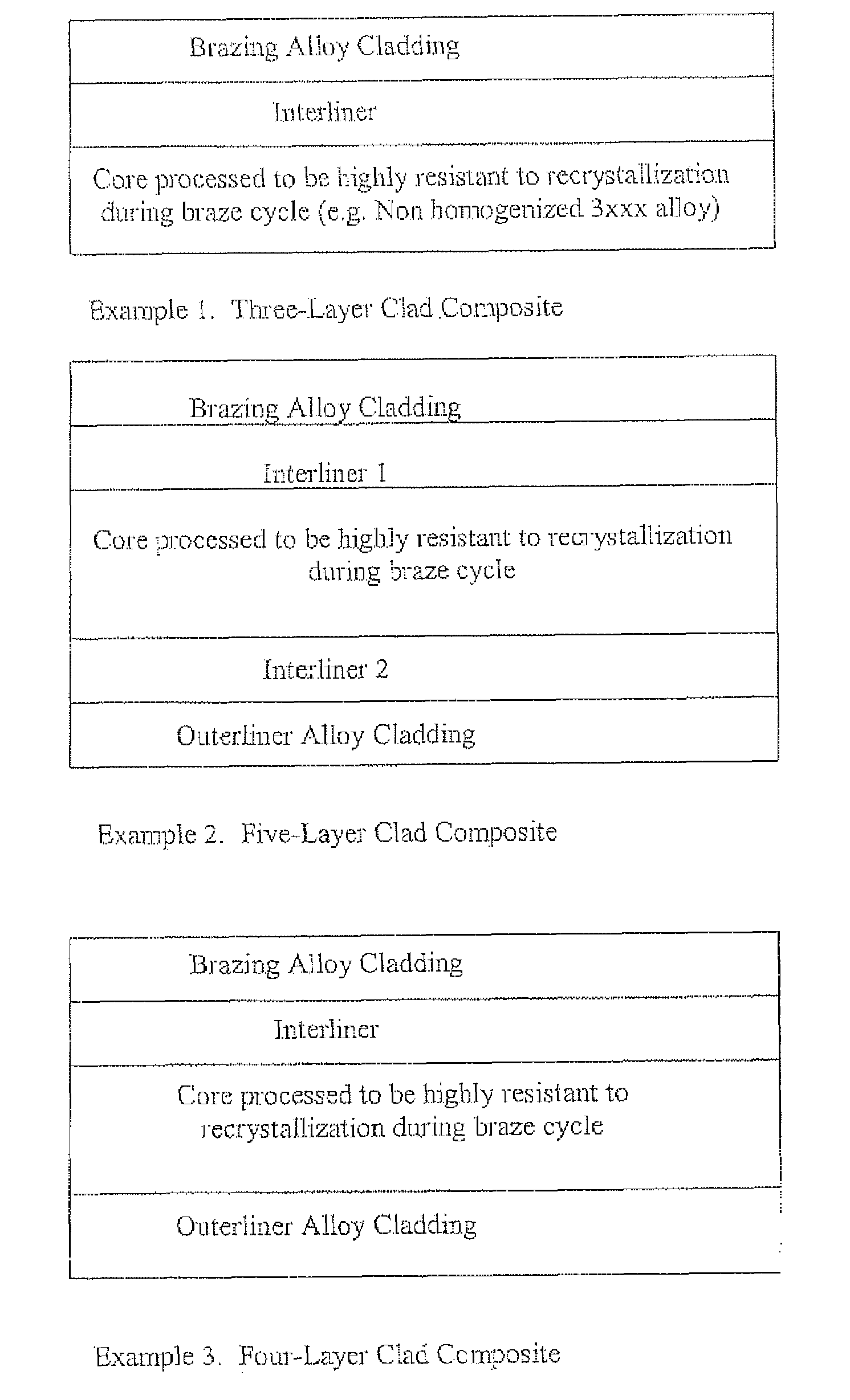
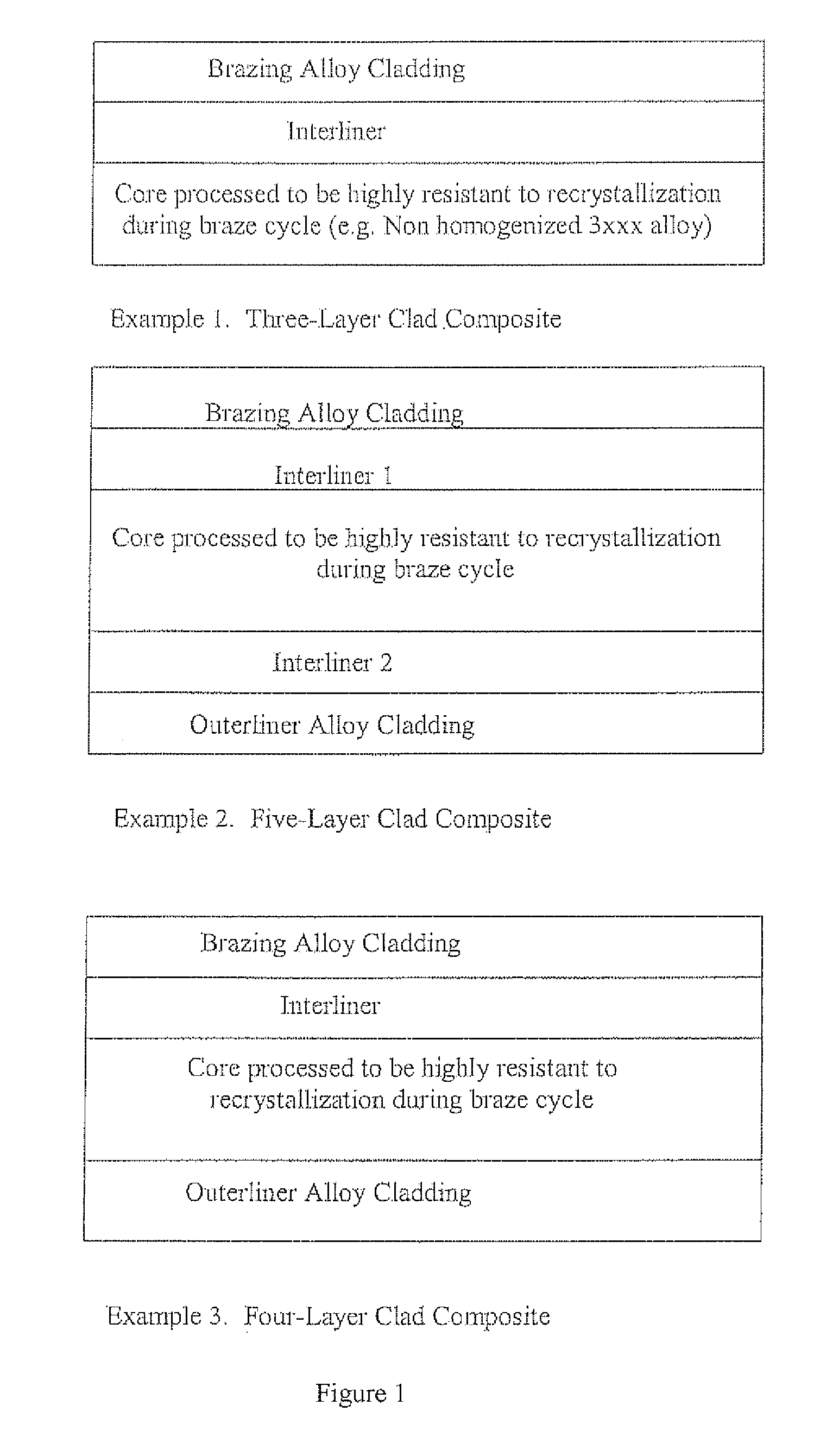
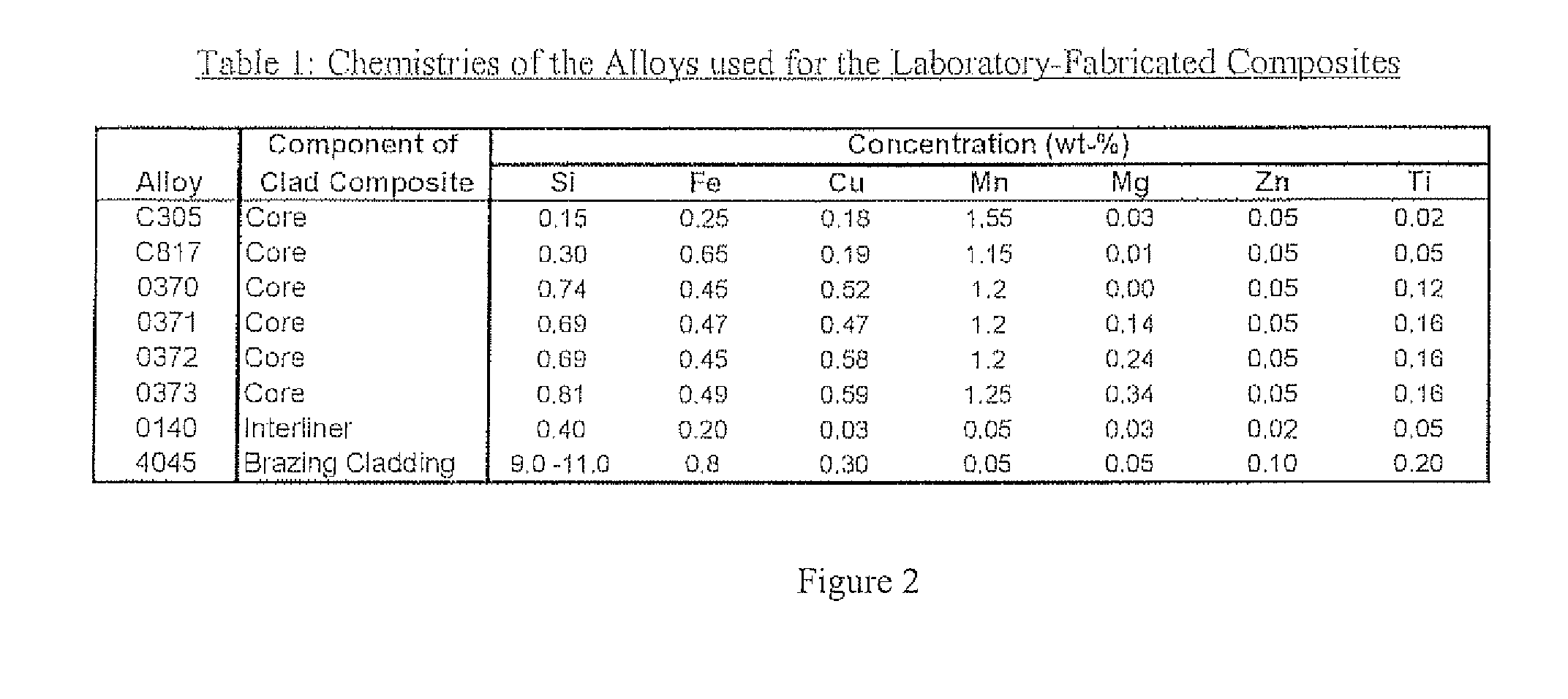
A multi-layer metallurgical product comprising a core aluminum alloy, purposefully tailored through chemistry and processing route to resist recrystallization during the brazing cycle to intentionally exploit the higher strengths immediately after brazing of a deformed and recovered microstructure, the core aluminum alloy being positioned on one side to an aluminum alloy interliner designed to be resistant to localized erosion, which, in turn, is adjacent to a 4xxx cladding alloy. The multi-layer product can be fabricated at least in part via any multi-alloy ingot casting processes such as the Simultaneous Multi-Alloy Casting process or the Unidirectional Solidification of Castings process.
Owner:ARCONIC INC
Aluminum alloy clad sheet for heat exchanger
InactiveUS20100183897A1Prevent deterioration in brazeabilityInhibit deteriorationWelding/cutting media/materialsCoatingsImpurityMaterials science
An aluminum alloy clad sheet for heat exchangers includes a core layer, a sacrificial layer disposed on one side of the core layer, and a brazing layer of an Al—Si alloy disposed on the other side of the core layer, wherein the core layer contains Si: 0.15% to 1.6% by mass, Mn: 0.3% to 2.0% by mass, Cu: 0.1% to 1.0% by mass, Ti: 0.02% to 0.30% by mass, and the remainder of Al and incidental impurities, and the sacrificial layer contains Zn: 4.0% to 10.0% by mass, Cr: 0.01% to 0.5% by mass, and the remainder of Al and incidental impurities.
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD
Preparation method of high-thermal conductivity graphene-Sn-Ag composite brazing filler metal
ActiveCN104400247AImprove performanceSolve reunionWelding/cutting media/materialsSoldering mediaDensity differenceCvd graphene
The invention discloses a preparation method of a high-thermal conductivity graphene-Sn-Ag composite brazing filler metal, ad relates to a preparation method of a high-thermal conductivity composite brazing filler metal. The preparation method has the following purposes: the problem of graphene floating and agglomeration in the preparation and application process of the composite brazing filler metal is solved by reducing a greater density difference between graphene and an Sn-Ag brazing filler metal matrix through plating a metal on the graphene; meanwhile, the graphene is dispersed more uniformly in the brazing filler metal matrix; and the reliability of sealing and brazing is improved by improving the heat conductivity of the composite brazing filler metal through adding the graphene. The method comprises the following steps: (1) the metal is plated on the graphene; and (2) the ball milling, the mixing and the medium-temperature smelting are performed for the metal-plated graphene and the Sn-Ag brazing filler metal to obtain the high-thermal conductivity composite brazing filler metal. The prepared composite brazing filler metal is high in thermal conductivity, has a higher wettability compared with a traditional Sn-Ag brazing filler metal, and is a composite brazing filler metal accordant with the present development tendency of an electronic industry as a connecting material of traditional large-scale integrated circuits.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Paste composition for aluminum brazing
ActiveCN101462208ALong-term storage stabilityLong-term stabilityWelding/cutting media/materialsSoldering mediaMethacrylateOrganic solvent
A paste composition for aluminum brazing of the invention contains 40 to 65% by weight of a metal powder for brazing (a), 5 to 35% by weight of a fluoride type flux (b), 1 to 10% by weight of a methacrylic acid ester type polymer (c), and 10 to 40% by weight of an organic solvent (d); and the component (d) is a hydrocarbon type organic solvent having no aromatic ring and no hydroxyl group and the composition is in a paste-like state having a viscosity of 6,000 to 200,000 mPa.s at 23 DEG C. and accordingly, the storage stability and applicability (practically, discharge property and pressure stability by using a dispenser) and brazing property can be improved in good balance. Additionally, the invention provides an aluminum brazing method used for brazing aluminum members, wherein the above paste composition for aluminum brazing is coated on aluminum members so as to heat the aluminum members in a predetermined structure.
Owner:HARIMA CHEM INC +1
Aluminum alloy brazing sheet having high-strength and production method therefor
ActiveUS20090020585A1Small thicknessImprove conductivityPretreated surfacesWelding/cutting media/materialsHigh intensityVolumetric Mass Density
An aluminum alloy brazing sheet having high strength comprising:a core alloy; an Al—Si-based filler alloy cladded on one side or both sides of the core alloy, wherein the core alloy is composed of an aluminum alloy containing 0.3-1.2% (mass %, the same applies the below) Si, 0.05-0.4% Fe, 0.3-1.2% Cu, 0.3-1.8% Mn, 0.05-0.6% Mg, and containing one or more elements selected from the group consisting of 0.02-0.3% Ti, 0.02-0.3% Zr, 0.02-0.3% Cr and 0.02-0.3% V, the balance of Al and unavoidable impurities; and wherein, after the aluminum alloy brazing sheet is subjected to brazing, the core alloy features a metallic structure in which a density of intermetallic compounds having a grain diameter of at least 0.1 μm is at most ten grains per μm2.
Owner:FURUKAWA SKY ALUMINUM CORP +1
Brazing sheet of aluminum alloy
ActiveUS20090162686A1Improve corrosion resistanceAvoid problemsWelding/cutting media/materialsHeat exchange apparatusFiller metalImpurity
A brazing sheet of aluminum alloy composed of a core material and a first brazing filler metal covering one surface of the core material. The core material contains as an essential component 0.2-1.0 mass % of Cu and as optional components at least one species of no more than 1.5 mass % of Si, no more than 1.8 mass % of Mn, no more than 0.35 mass % of Ti, and no more than 0.5 mass % of Mg, with the remainder being Al and inevitable impurities. The first brazing filler metal has a liquid phase ratio (X %) at 600° C. and a thickness (Y μm) such that X and Y satisfy the following relationship: (1) 30≦X≦80, (2) Y≧25, and (3) 1000≦X×Y≦24000. The brazing sheet provides good brazeability and maintains high corrosion resistance after brazing on the surface cladded with the brazing filler metal.
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD
Low-melting-point lead-free solder alloy
ActiveCN102936669ALow melting pointUniform tissueWelding/cutting media/materialsSoldering mediaShock resistanceUltimate tensile strength
The invention relates to a low-melting-point lead-free solder alloy which belongs to the technical field of welding materials and is used for solving the problem that the conventional solder alloys are high in melting point and low in shearing strength. The low-melting-point lead-free solder alloy comprises the following components in percentage by weight: 10-30% of Bi, 2.2-3.0% of Ag, 0.5-1.0% of In, 0.004-0.008% of P and the balance being tin. The low-melting-point lead-free solder alloy also can comprise 0.002-0.005% of RE and 0.002-0.005% of Co. According to the low-melting-point lead-free solder alloy, the melting point is low, the alloy eutectic temperature is about 170-200 DEG C, the shearing strength is good and between 21-28N / mm<2>, the RE is capable of improving the glossliness of the solder alloy and refining the grains, the Co is capable of improving the soldering performance and the shock resistance, and Zr has the function of homogenizing and refining the alloy tissues.
Owner:上海一远电子科技有限公司
Aluminum alloy brazing sheet and manufacturing method thereof as well radiator part
ActiveCN102554585AHigh elongationHigh erosion residual thickness ratioHeat exchange apparatusIngotFiller metal
The invention discloses an aluminum alloy brazing sheet and a manufacturing method thereof as well as a radiator part manufactured by using the aluminum alloy brazing sheet. The method comprises the following steps: casting an aluminum alloy ingot; homogenizing the ingot, cooling the ingot, and then carrying out conventional face-milling on the ingot; coating single-sided or double-sided aluminum-silicon brazing filler metal layer on the ingot so as to form a composite material; heating the composite material; carrying out hot rolling and cold rolling on the heated composite material so as to form a cold rolled material with a first thickness; carrying out complete softening and annealing on the cold rolled material; and carrying out prestretching on obtained sheet after softening and annealing so as to obtain a final aluminum alloy brazing sheet with a second thickness less than the first thickness. A sheet manufactured by using the method disclosed by the invention has more processing combinations, can be processed by using more flexible processes, and can satisfy good formability and brazability.
Owner:GRANGES ALUMINUM SHANGHAI CO LTD
Low-temperature copper-based brazing filler metal for high-temperature resistance clean steel and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102773632AEasy to useImprove cleanlinessWelding/cutting media/materialsSoldering mediaCopperTemperature resistance
The invention provides a low-temperature copper-based brazing filler metal for high-temperature resistance clean steel and a preparation method thereof. The low-temperature copper-based brazing filler metal is prepared by raw materials in percentage by weight as follows: 4-10% of Ni, 10-30% of Mn, 0.2-1.8% of Zr, 0.2-3.5% of Hf, 0-1% of W, 0-1% of Co, 0.1-0.25% of Ti, 0.02-0.2% of B, 0.8-2.0% of Ge, 0-0.5% of Li and a residual amount of Cu. According to the low-temperature copper-based brazing filler metal provided by the invention, various trace elements are added in copper, so that the using property of the brazing filler metal is improved; a melting process is protected by using gas, a high-temperature resistant quartz glass tube is inserted into molten brazing filler metal alloy after being vacuumized to be in a negative pressure state, so that filament welding strips with different diameters can be directly obtained; techniques of later-stage squeezing, drawing in a reducing manner and the like can be cancelled; the introduction amount of impurities in a production process of the brazing filler metal can be reduced; the cleanliness of the brazing filler metal is improved; the brazing filler metal does not contain an easily-volatile element Zn and can be applicable to vacuum brazing; the brazing filler metal does not contain silver and does not contain any toxic elements; and the brazing filler metal has the advantages of low cost, no pollution, good brazing property and the like.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU RES INST OF MECHANICAL ENG CO LTD
High-strenght aluminum alloy brazing sheet and method of manufacture
InactiveUS20120129003A1High strengthExcellent brazeabilityExhaust apparatusMachines/enginesFilling materialsImpurity
An aluminum alloy brazing sheet having a core material of an aluminum alloy, and a filler material cladded on the core is disclosed. The core material is an aluminum alloy having about 0.05 to about 1.2 mass Si, about 0.05-about 1.0 mass % Fe, about 0.05-about 1.2 mass % Cu, and about 0.6-about 1.8 mass % Mn, balance Al and the inevitable impurities. The filler material includes an aluminum alloy having about 2.5-about 13.0 mass % Si. Also, there is provided a method of manufacturing such an aluminum alloy brazing sheet.
Owner:FURUKAWA SKYALUMINUM
Lead-free solder for micro alloyed eutectic alloy of stannum and zinc
InactiveCN101092006AImprove antioxidant capacityExcellent brazing performanceWelding/cutting media/materialsSoldering mediaAlloy elementZinc
The invention discloses a micro-alloying tin-zinc eutectic alloy tinless solder that the main constituent is Sn-Zn eutectic alloy, Zn is 8-10wt% and the rest is Sn, adding one or the complex from Ga, P, Al, Ge, and Mg, the content of single alloy element is below 0.1%. The invention extremely maintains the feature of Sn-Zn eutectic alloy, and has the advantages of strong oxidation resistance, simple constituents, easy to recycle, etc.
Owner:有研科技集团有限公司
Fluxing agent
InactiveUS20060231162A1Additional componentReduce developmentWelding/cutting media/materialsWelding/soldering/cutting articlesPolyvinyl alcoholWater soluble
A flux or a flux preparation, which contains complex alkali metal fluorides and additionally includes a water-soluble polymer, preferably polyvinyl alcohol or a polyvinyl alcohol derivative. The water-soluble polymer may be contained in the flux preparation as a granulate or powder or used as a water—soluble package for the flux or flux preparation.
Owner:SOLVAY FLUOR GMBH DE
Process of producing aluminum fin alloy
InactiveUS6165291ALower (more negative) corrosion potentialImprove thermal conductivityWelding/cutting media/materialsHeat exchange apparatusMetallurgyHeat sink
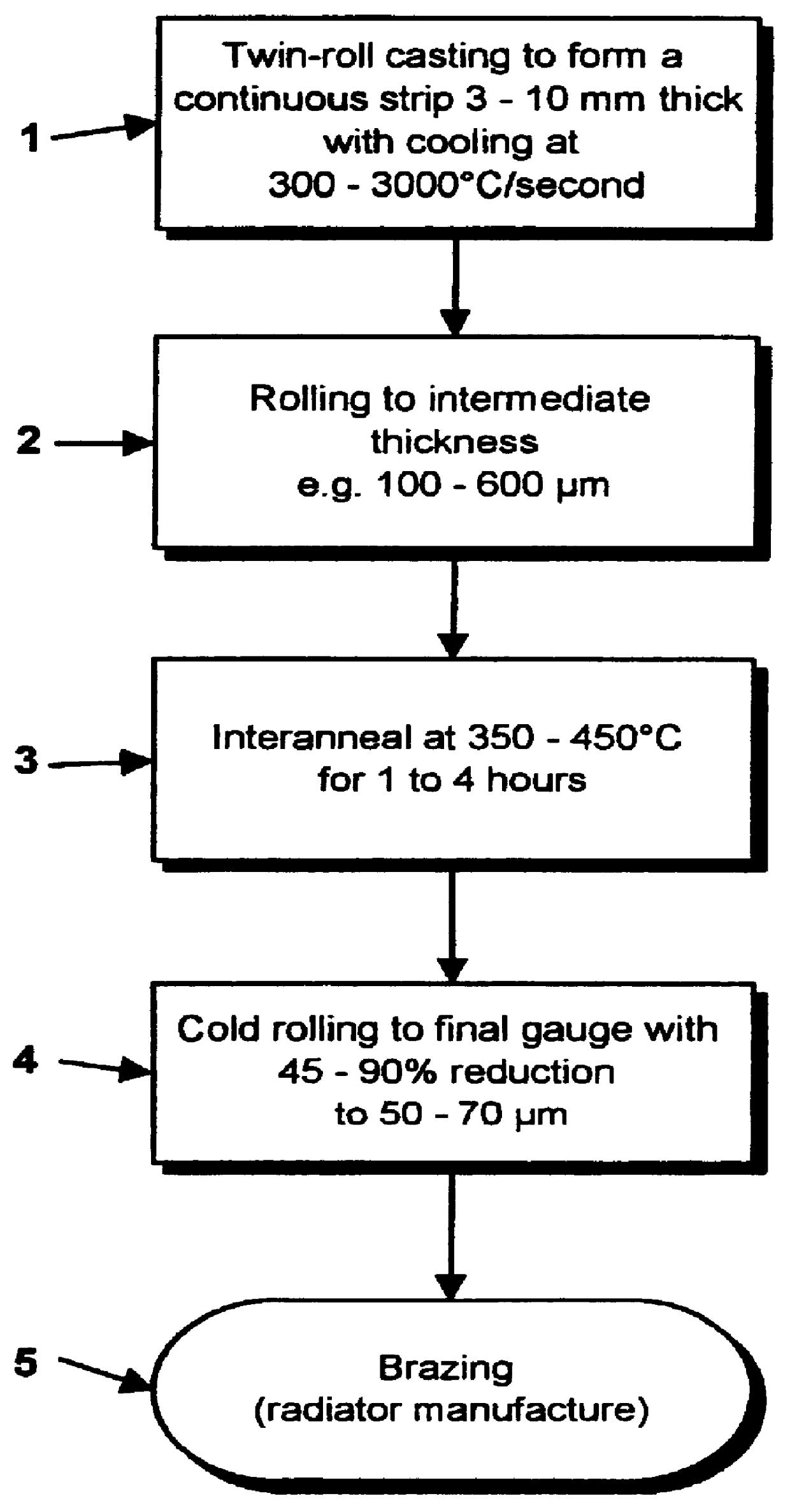
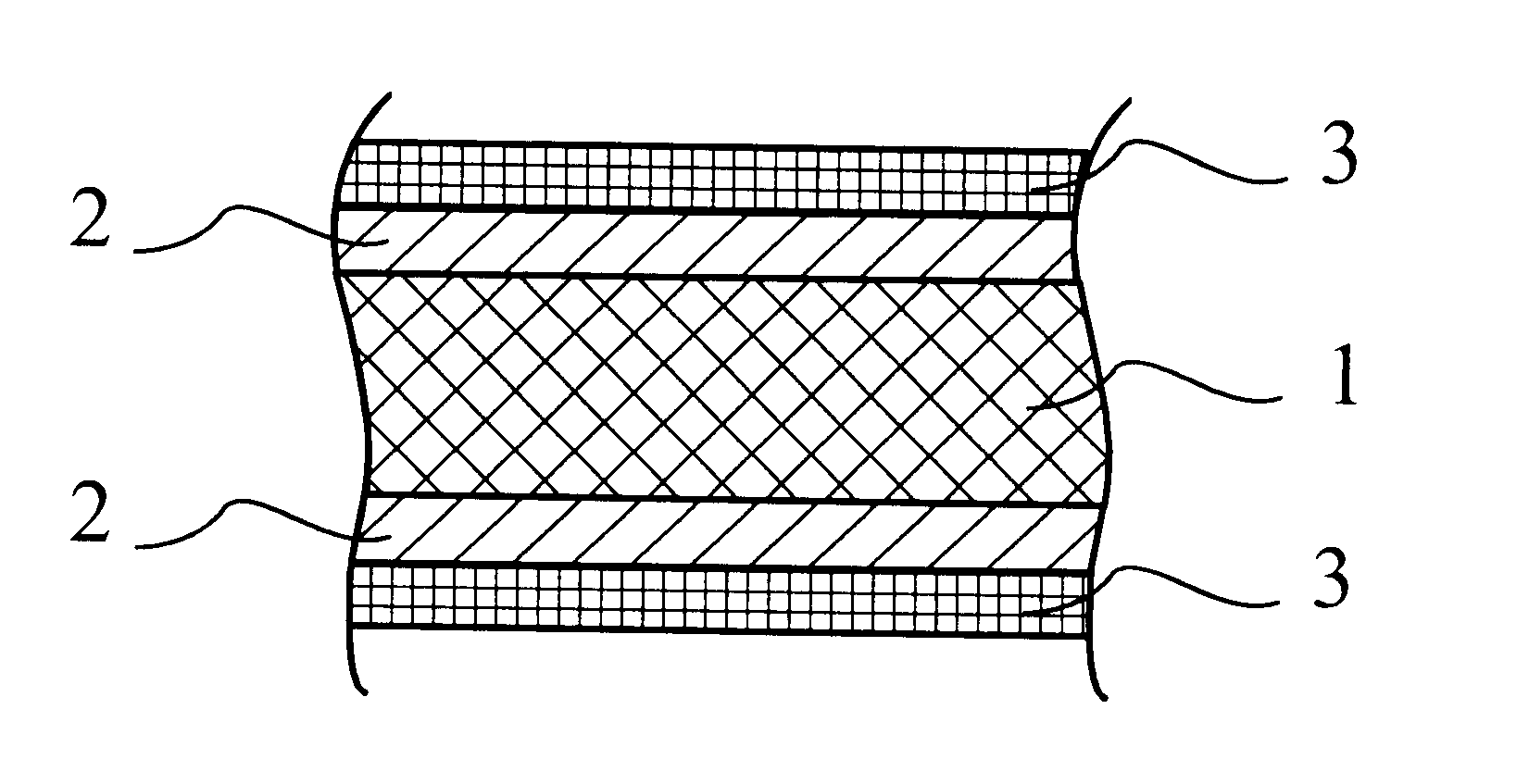
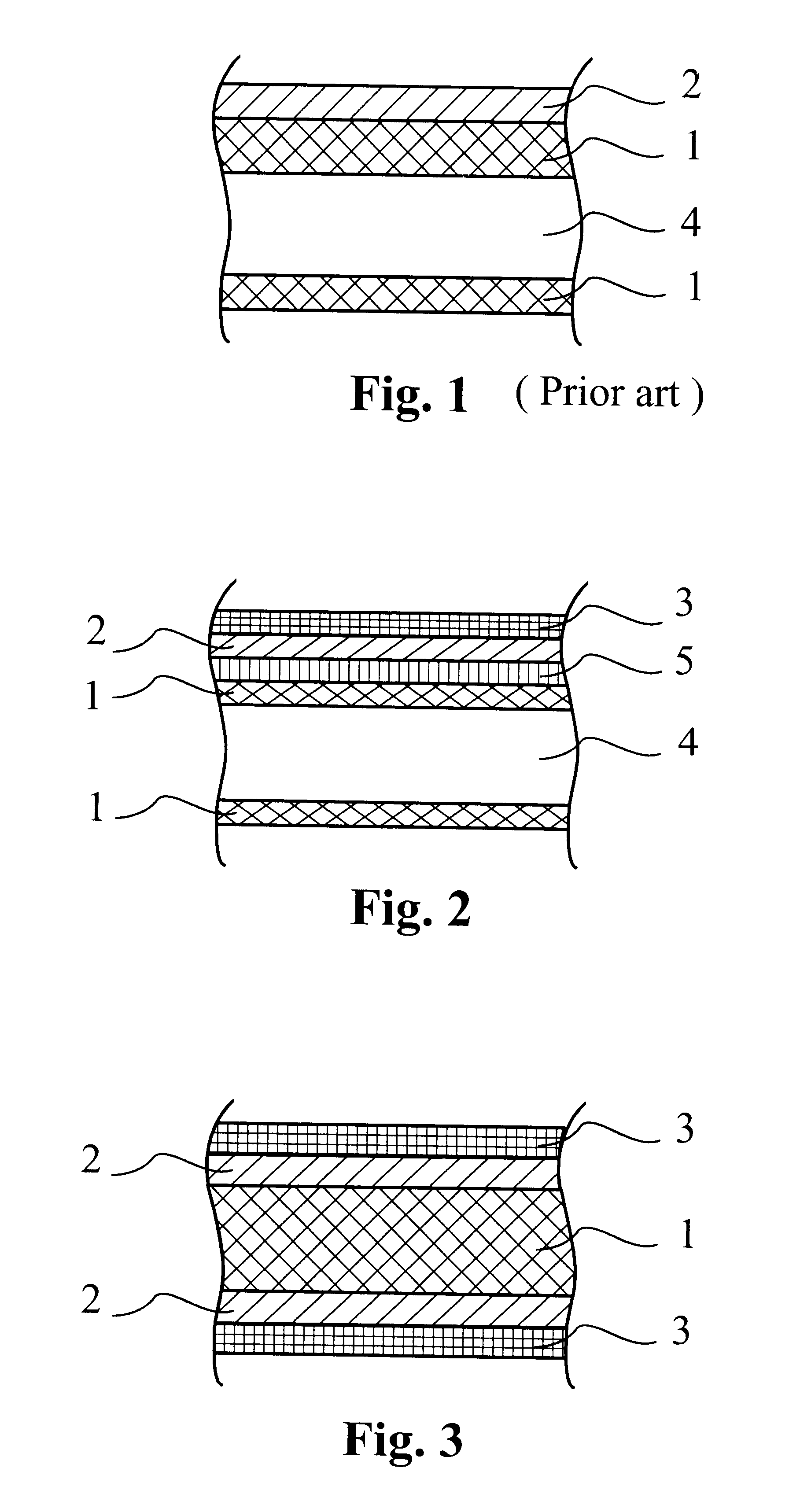
An aluminum alloy fin stock of lower (more negative) corrosion potential and higher thermal conductivity is produced by a process, which comprises continuously strip casting the alloy to form a strip, cold rolling the strip to an intermediate gauge sheet, annealing the sheet and cold rolling the sheet to final gauge. Lower corrosion potential and higher thermal conductivity are imparted by carrying out the continuous strip casting while cooling the alloy at a rate of at least 300 DEG C. / second, e.g. by conducting the casting step in a twin-roll caster.
Owner:NOVELIS INC
Brazing product having a low melting point
InactiveUS6596413B2Excellent brazeabilityReduce the temperatureSurface reaction electrolytic coatingVacuum evaporation coatingTO-18Silicon
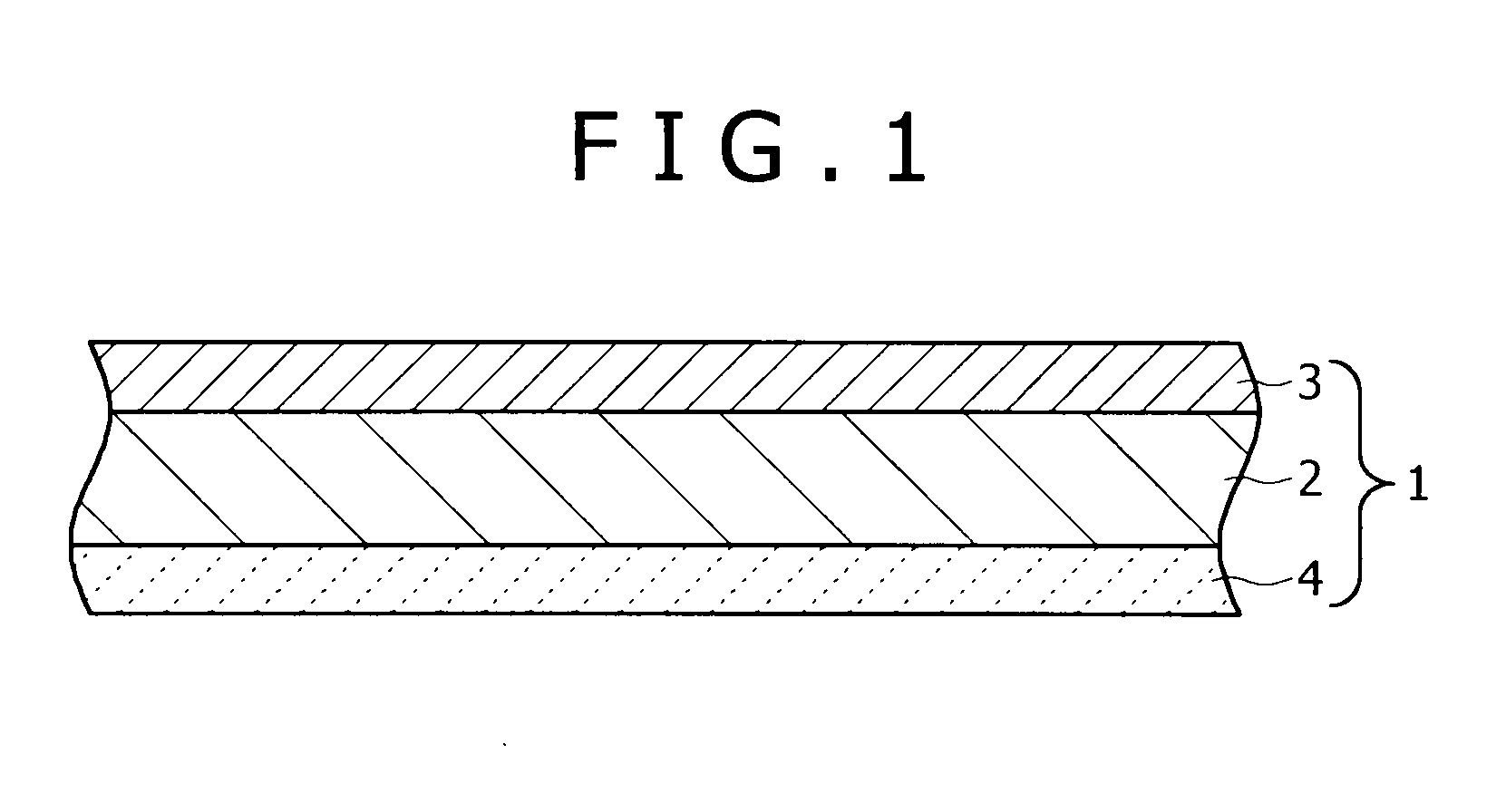
Disclosed is an aluminium brazing product, such as a brazing sheet product, having a substrate (1) of an aluminium alloy comprising silicon in an amount in the of 2 to 18% by weight, and on at least one outer surface a layer (2) comprising nickel, wherein a separately deposited layer (3) is applied on one side of the layer (2) comprising nickel and the layer (3) comprising a metal such that taken together the aluminium base substrate (1) and all layers exterior thereto form a metal filler having a liquidus temperature in the range of 490 to 570° C., and preferably in the range of 510 to 550° C. The invention also relates to a method of manufacturing such a brazing product and to a brazed assembly comprising at least one component made of the brazing sheet product.
Owner:DANA CANADA CORP
High-strength aluminum alloy composite and resultant product
InactiveUS20050095447A1High post-braze strengthCorrosion resistanceRigid pipesHeat exchange apparatusSiluminAlloy composite
A high-strength aluminum alloy tubestock is for heat exchangers. The tubestock includes a core with low to moderate Si content to promote strengthening without excessively compromising corrosion resistance. A braze liner on the core exterior employs a Zn+Mg+Si water-side liner that will not experience undesirable melting during brazing. The water-side liner preferably comprises between about 0.2-0.5% Si, between about 2.5-5.0% Zn, between about 1.3-2.5% Mg, less than about 0.1% Cu, less than about 0.35% Fe and less than about 0.25% Mn, with the remainder comprising Al and tolerable impurities. The core preferably comprises between about 0.5-1.3% Mn, between about 0.1-0.3 Mg, between about 0.4-0.7% Cu, between about 0.15-0.5% Si, between about 0.01-0.25% Ti and less than about 0.5% Fe, with the remainder comprising Al and tolerable impurities. The braze liner preferably comprises an Al—Si-base alloy. A tubular member made from the foregoing tubestock is also disclosed.
Owner:ARCONIC INC
Ferritic stainless steel sheet for egr coolers
InactiveCN102131946AExcellent brazeabilityImprove corrosion resistanceNon-fuel substance addition to fuelInternal combustion piston enginesMetallurgyMaterials science
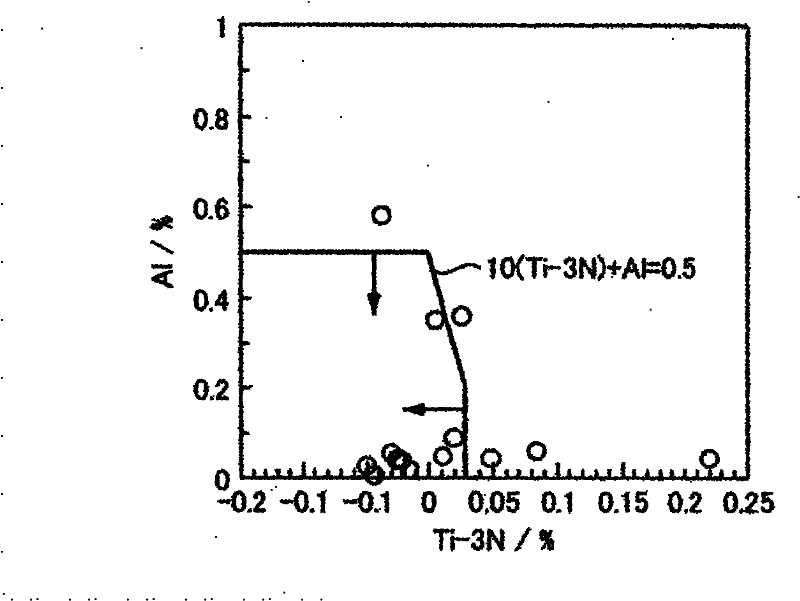
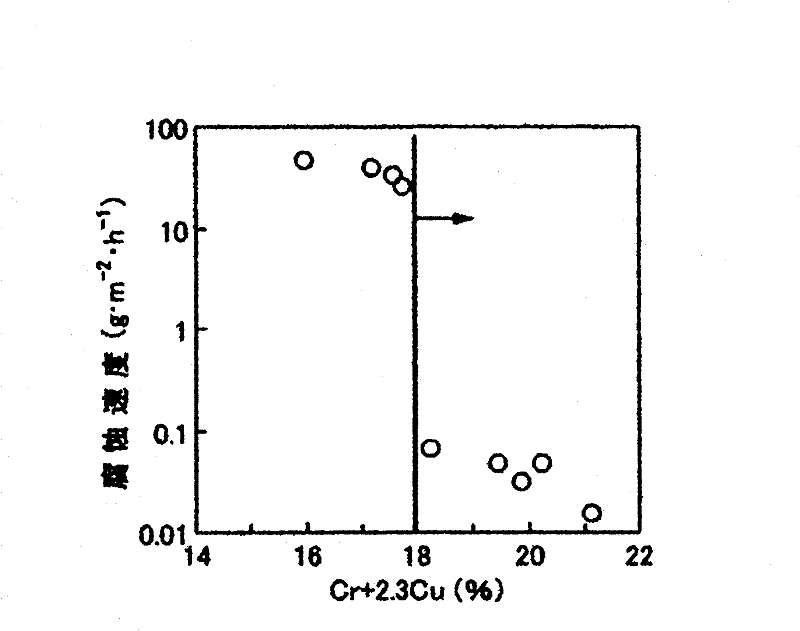
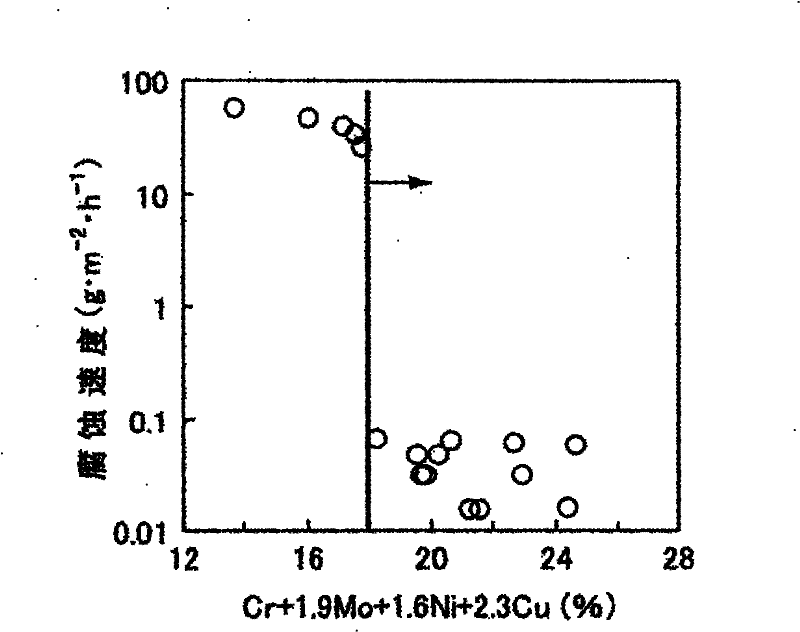
Disclosed is a ferritic stainless steel sheet for EGR coolers, which is characterized by containing at least, in mass%, not more than 0.03% of C, not more than 0.05% of N, not less than 0.1% but not more than 1% of Si, not less than 0.02% but not more than 2% of Mn, not less than 0.2% but not more than 1.5% of Cu, not less than 15% but not more than 25% of Cr, not less than 8(C + N)% but not more than 1% of Nb, and not more than 0.5% of Al, with the balance made up of Fe and unavoidable impurities. The ferritic stainless steel sheet is also characterized in that Ti is further contained therein in an amount satisfying formulae (1) and (2) in mass%, and that the amounts of Cr and Cu are within the ranges satisfying formula (3), wherein (1) Ti - 3N is not more than 0.03; (2) 10(Ti - 3N) + Al is not more than 0.5; (3) Cr + 2.3Cu is not less than 18.
Owner:NIPPON STEEL & SUMIKIN STAINLESS STEEL CORP
Water-base aluminum-brazing composition and process of brazing
InactiveUS20060102691A1Improve corrosion resistanceExcellent brazeabilityCooking-vessel materialsVehicle componentsWater basedMeth-
An aqueous aluminum brazing composition containing an organic binder and zinc-based flux which prevents precipitation of the zinc-based flux having a large specific gravity while securing excellent brazeability. The thixotropic index of the brazing composition is adjusted to 1.01-1.20 by adding (meth)acrylic acid / (meth)acrylate copolymer emulsion to the brazing composition as a precipitation inhibitor in an amount of 0.03-1.50 wt % of 100 wt % of the brazing composition. Since the (meth)acrylic acid / (meth)acrylate copolymer emulsion is used as the precipitation inhibitor in a specific amount instead of other types of compounds used for powder-containing paint such as ultrafine particle silica, poly(meth)acrylate, or polyvinyl alcohol, precipitation of the zinc-based flux can be prevented without impairing brazeability.
Owner:SUMITOMO LIGHT METAL INDS LTD +1
Method of producing an aluminum alloy brazing sheet
InactiveCN1982047AExcellent brazeabilityHigh strengthWelding/cutting media/materialsHeat exchange apparatusNumber densityMetal
A method of producing an aluminum alloy brazing sheet which has a clad of a sacrificial anode material / a core alloy / an intermediate material / a filler alloy, each of which has a specific composition, wherein number density ratios N 1 / N 2 and N 1 / N 3 each are 1.5 or more, in which a number density ((the number of grains) / [mu]m 3 ) of an intermetallic compound having a sphere-equivalent grain diameter of 0.1 [mu]m or less present in the core alloy, the intermediate material, and the sacrificial anode material, is represented by N 1 , N 2 , and N 3 , respectively.
Owner:FURUKAWA SKY ALUMINUM CORP
Lead-free solder alloy
ActiveCN101208174AAvoid yellowingInhibited porosityPrinted circuit assemblingWelding/cutting media/materialsDrop impactImpurity
Disclosed is a lead-free solder alloy exhibiting improved drop impact resistance even after thermal aging while being good in soldering properties, void formation and discoloration. Specifically disclosed is a solder alloy consisting essentially of, in mass %, (1) 0.8-2.0% of Ag, (2) 0.05-0.3% of Cu, (3) one or more elements selected from not less than 0.01% and less than 0.1% of In, 0.01-0.04% of Ni, 0.01-0.05% of Co and 0.01-0.1% of Pt, and if necessary (4) one or more elements selected from Sb, Bi, Fe, Al, Zn and P in an amount of not more than 0.1% in total, and the balance of Sn and unavoidable impurities.
Owner:SENJU METAL IND CO LTD
Process for producing an aluminium alloy brazing sheet, aluminium alloy brazing sheet
ActiveUS20060014043A1Improved liquid film migration resistanceLow susceptibility to LFMFurnace typesWelding/cutting media/materialsIngotMn alloy
Disclosed is a process for producing an Al—Mn alloy sheet with improved liquid film migration resistance when used as core alloy in brazing sheet, including the steps of: casting an ingot having a composition comprising (in weight percent): 0.5<Mn≦1.7, 0.06<Cu≦1.5, Si≦1.3, Mg≦0.25, Ti<0.2, Zn≦2.0, Fe≦0.5, at least one element of the group of elements of 0.05<Zr≦0.25 and 0.05<Cr≦0.25; other elements<0.05 each and total<0.20, balance Al; homogenisation and preheat; hot rolling; cold rolling (including intermediate anneals whenever required), and wherein the homogenisation temperature is at least 450° C. for a duration of at least 1 hour followed by an air cooling at a rate of at least 20° C. / h and wherein the pre-heat temperature is at least 400° C. for at least 0.5 hour.
Owner:NOVELIS KOBLENZ GMBH
Clad material, method for manufacturing said clad material, and apparatus for manufacturing said clad material
InactiveCN1933928AControl tensionIncrease cooling rateHeat exchange apparatusMetal rolling arrangementsMeeting placeMolten metal
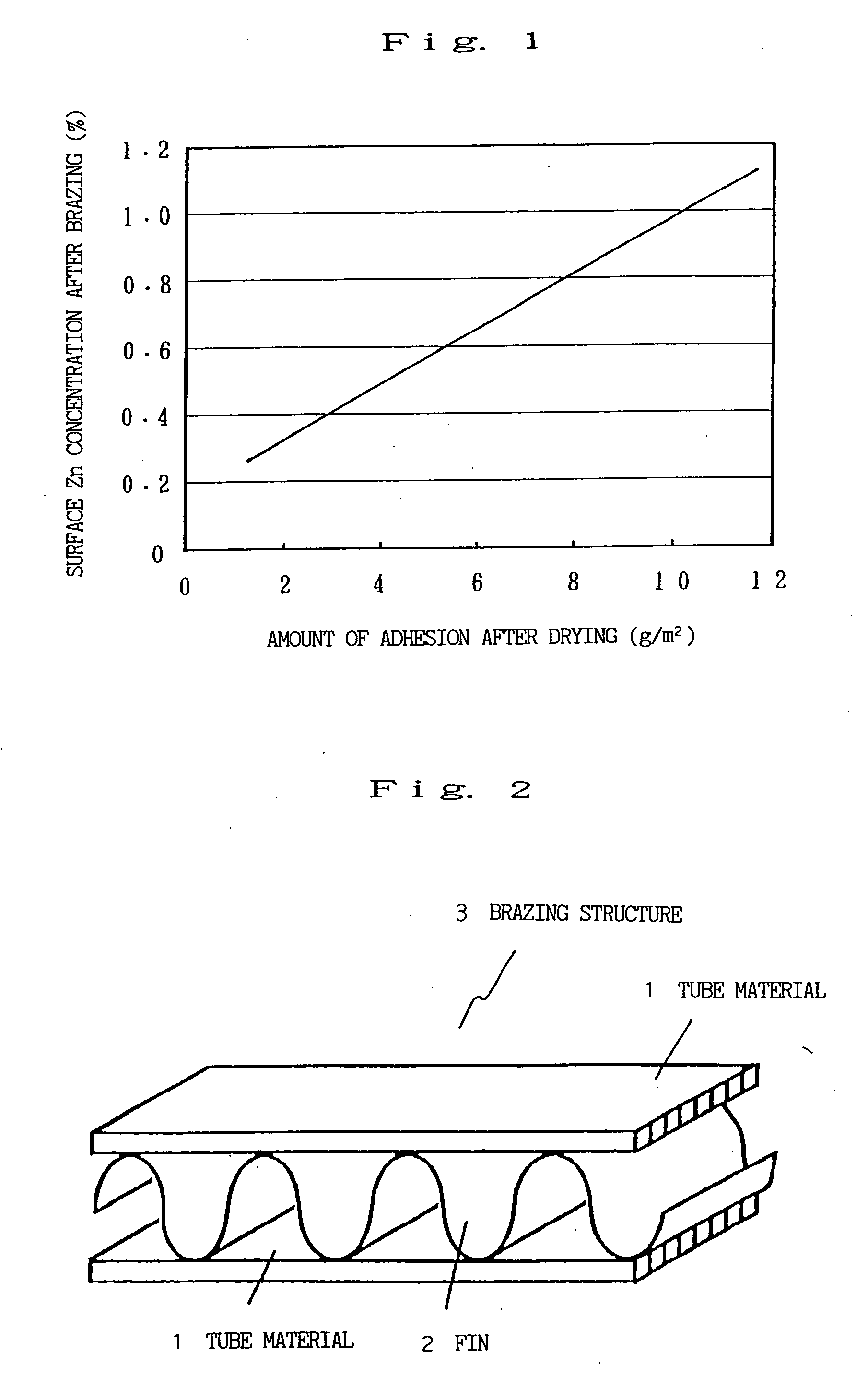
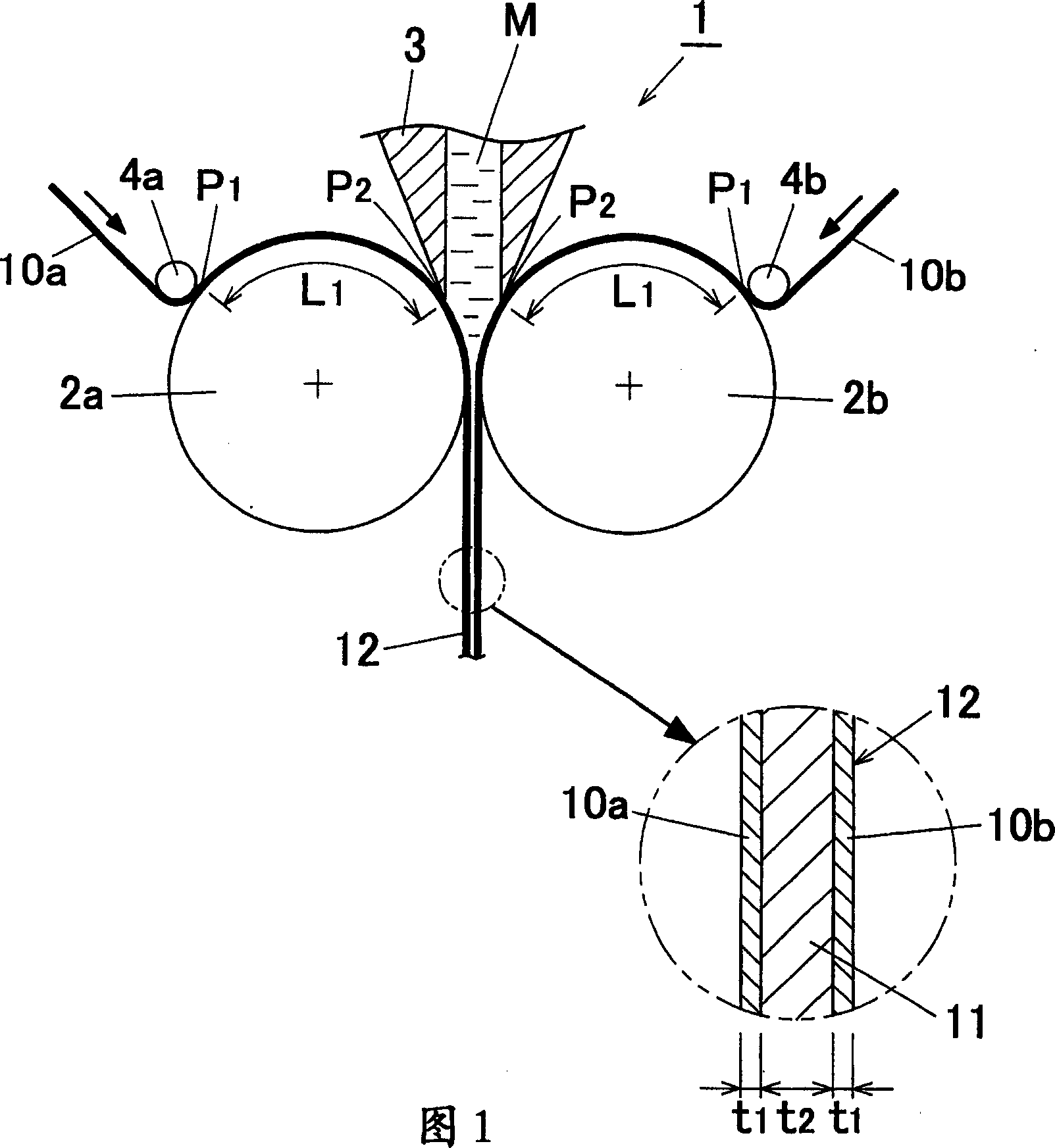
A method for manufacturing a clad material in which a core material is cast and skin materials are pressure-bonded thereon aims to prevent deterioration of adhesiveness of the core material and the skin materials while keeping sufficient cooling rate of the core material, prevent thickness variation and / or breakage of the skin materials during the manufacturing process, and keep the surface property of the cooling rolls constant. The method for manufacturing a clad material (11) includes the steps of continuously supplying molten metal (M) into a gap between a pair of cooling rollers (2a) (2b) to cast a core material, and cladding skin materials (10a) (10b) on both surfaces of the core material with hot rolling by continuously supplying the skin materials on peripheral surfaces of the cooling rollers so that the skin materials prevent direct contact between the cooling rollers and the molten metal, wherein the skin materials are supplied so as to come into contact with the peripheral surfaces of the cooling rollers, and wherein a contact distance (L1) from a contact starting point (P1) where the skin material begins to come into contact with the cooling roller to a meeting point (P2) where the skin material begins to come into contact with the molten metal is set to 100 times or more of a thickness (t1) of the skin material.
Owner:SHOWA DENKO KK
Brazing and casting process of metal ceramic composite lining board
InactiveCN102554385AGuarantee job securityImprove wear resistanceWelding/cutting media/materialsSoldering mediaCleansing AgentsFiller metal
The invention relates to a brazing and casting process of a metal ceramic composite lining board. The brazing filler metal adopted by the process comprises the following ingredients by weight percent: 10-70% of Cu powder, 20-70% of Ti powder and 5-20% of surface active elements. The process comprises the following steps of: adding 10-20% of ceramic particles serving as a wetting enhanced phase into the brazing filler metal to prepare a composite brazing filler metal, cleaning a metal layer and a ceramic layer by using an organic solvent cleaning agent, fixedly assembling the metal layer and the ceramic layer in a sequence of the ceramic layer, the composite brazing filler metal, the metal layer, the composite brazing filler metal, the ceramic layer, the composite brazing filler metal and the metal layer, placing the fixedly-assembled metal layer and ceramic layer in a vacuum brazing furnace for brazing, after brazing, placing a metal ceramic layer and a metal matrix into a casting die, pouring liquid steel and casting. The prepared metal ceramic composite lining board has the advantages of good toughness, high wear-resisting property and high corrosion-resisting property, and meanwhile, the metal ceramic layer occupies a small part of the lining board and is low in cost, thus improving the production efficiency, saving the production halt and change time and comprehensively increasing the economic benefit for the industries of cement, metallurgy, mine, electricity and the like.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Aluminum alloy brazing material, brazing member, brazed article and brazinh method therefor using said material, brazing heat exchanging tube, heat exchanger and manufacturing method thereof using sai
InactiveCN1726114AAvoid excessive corrosionReduce the predetermined thicknessWelding/cutting media/materialsHeat exchange apparatusPlate heat exchangerImpurity
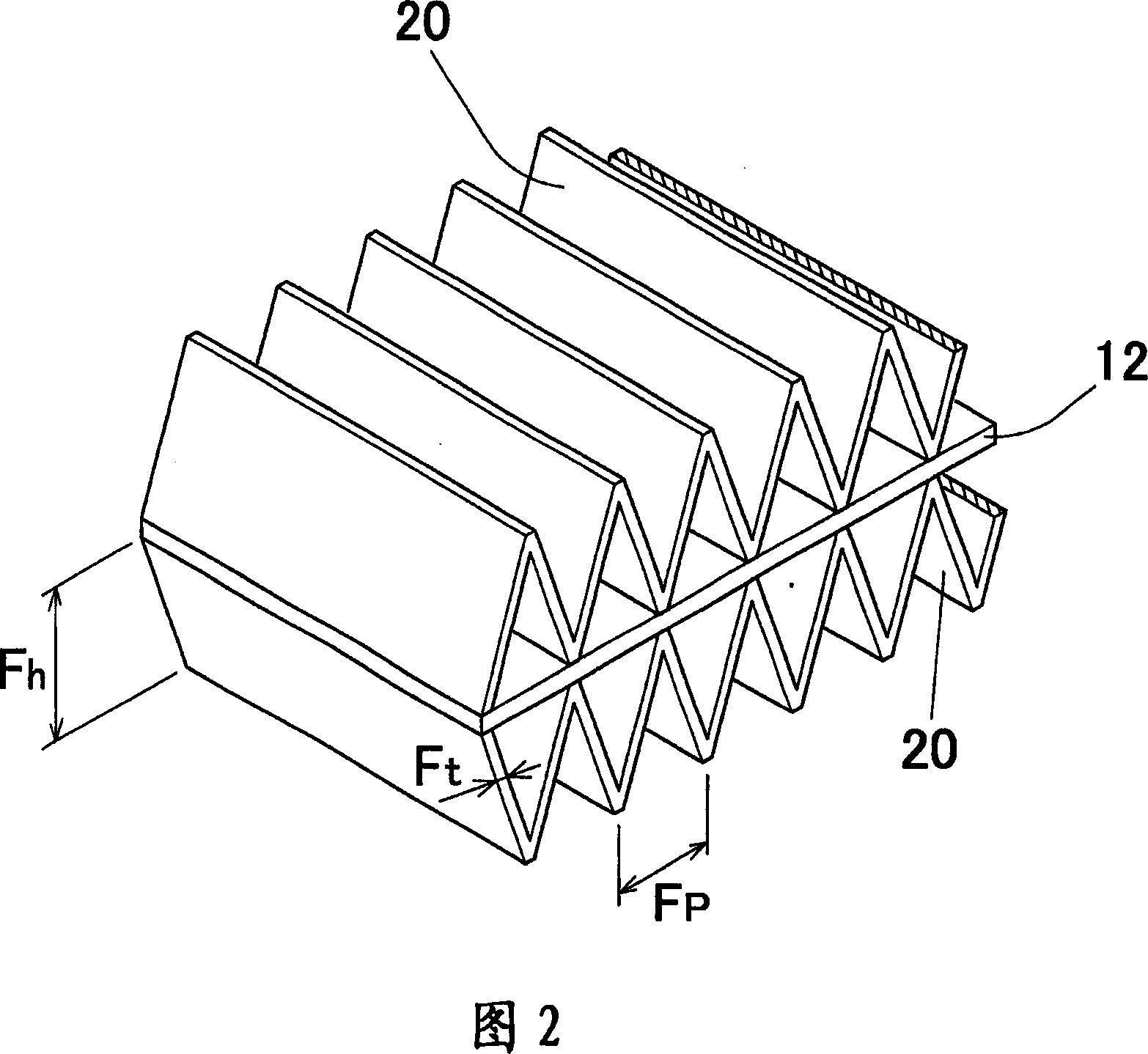
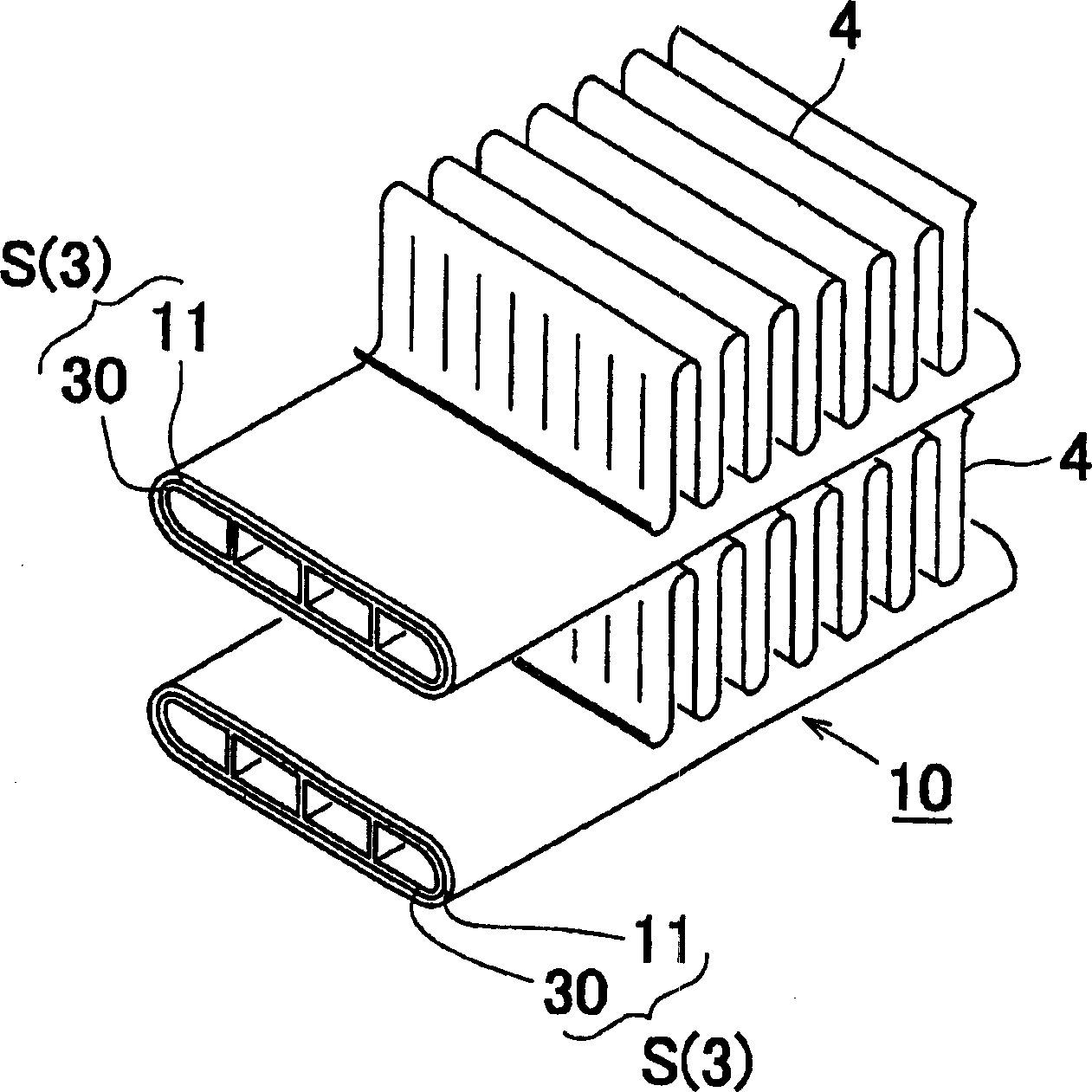
A heat exchanger 10 includes a brazing heat exchanging tube S and a fin 4. The heat exchanging tube S and the fin 4 are brazed with each other via the brazing layer 11 of the heat exchanging tube S. The brazing layer 11 is formed by spraying of a brazing material consisting of Si: 6 to 15 mass%, Zn :1 to 20 mass%, at least one of Cu: 0.3 to 0.6 mass% and Mn: 0.3 to 1. 5 mass, and the balance being aluminum and inevitable impurities.
Owner:SHOWA DENKO KK
Preparation method of gold-tin alloy solder foil
InactiveCN102912175AEasy to prepareSmall Brazing Temperature ResponseWelding/cutting media/materialsSoldering mediaTemperature responseHeating time
The invention provides a preparation method of a gold-tin alloy solder foil, which relates to a manufacturing process of a refractory gold-base alloy material, particularly a preparation method of a gold-tin eutectic alloy solder foil. In the method, the composition is finely adjusted to prepare the gold-tin alloy, wherein the tin content in the alloy is 20.0-21.0%; graphite crucible smelting and graphite mold casting are adopted to obtain a fine ingot structure; and uniform heat treatment and 220-265 DEG C hot rolling are adopted, wherein the deformation amount of the gate is less than 30%, the heating time is longer than 5 minutes, and final rolling thickness is 0.02-0.1mm. The gold-tin alloy solder foil prepared by the method provided by the invention has the advantages of quick temperature response and favorable solderability. The method is simple and easy to implement, has the advantage of high production efficiency, and is suitable for industrial mass production.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
Aluminum alloy brazing sheet and heat exchanger
InactiveCN102205676AExcellent brazeabilityNo leaksStationary conduit assembliesHeat exchanger casingsPlate heat exchangerMicrometer
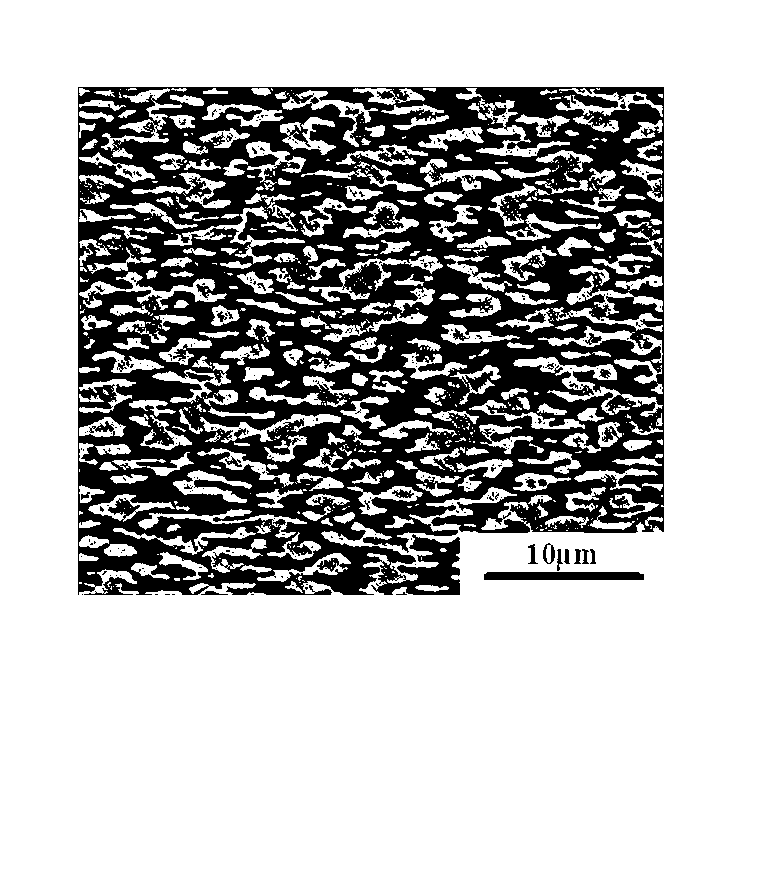
The present invention provides an aluminum alloy brazing sheet that is applied particularly to a tube material of a heat exchanger and is excellent in brazability and erosion resistance. The aluminum alloy brazing sheet has a core material comprising an Al-Mn system alloy and a brazing filler metal comprising an Al-Si system alloy containing Fe by 0.45 mass % or less on one surface or both the surfaces of the core material and is characterized in that, after subjected to a brazing treatment for 3 minutes at 600 DEG C, the area ratio of eutectic Si that is the flow passage of the brazing filler metal in a cross section of a solidified brazing filler metal is 35% or less; and the grain size in the rolling direction at the center section in the sheet thickness direction of the core material is 80 micrometers m or more.
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD
Plate-type heat exchanger, hot water apparatus, and method for manufacturing plate-type heat exchanger
InactiveUS20170176047A1Excellent brazeabilityCurb wasteSpacing meansReinforcing meansPlate heat exchangerEngineering
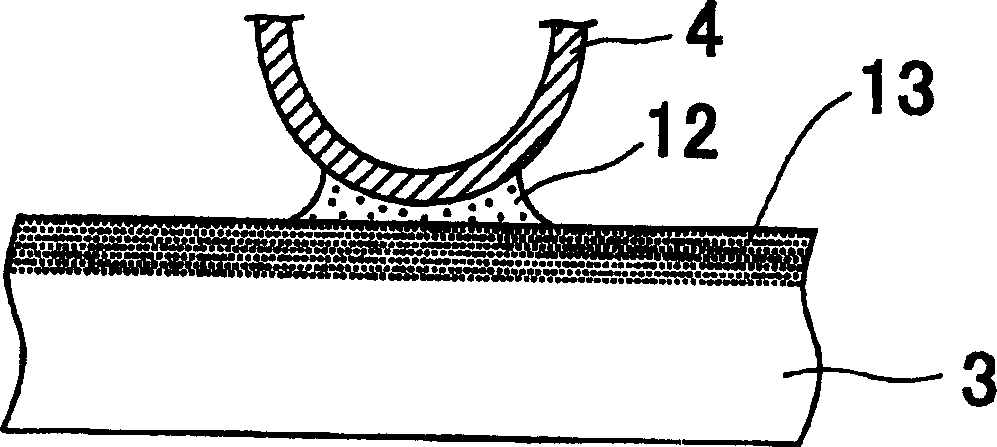
A plate-type heat exchanger includes a first heat transfer plate and a second heat transfer plate. The first heat transfer plate has a joint projection portion. The second heat transfer plate has a joint recess portion in which the joint projection portion is fitted. The joint projection portion and the joint recess portion are brazed to each other.
Owner:NORITZ CORP
Composite zinc-aluminum flux cored wire containing beryllium and magnesium and rubidium salt and preparation method of flux cored wire
ActiveCN102935559AImprove cleanlinessImprove intergranular corrosion resistanceWelding/cutting media/materialsSoldering mediaRare-earth elementAluminum fluoride
The invention discloses a composite zinc-aluminum flux cored wire containing beryllium and magnesium and rubidium salt. The composite zinc-aluminum flux cored wire comprises a wire body consisting of an outer metal skin and core brazing flux powder, wherein the outer metal skin is prepared by the following raw materials by weight percent: 80.5 to 98.5% of zinc, 0.01 to 6.5% of silver, 0.01 to 3% of copper, 0.001 to 2% of nickel, 0.001 to 0.5% of beryllium, 0.001 to 1.2% of magnesium, 0.001 to 0.5% of rare earth element and the balance of aluminum; and the brazing flux powder is prepared by the following raw materials by weight percent: 15 to 35% of aluminum fluoride, 30 to 75% of cesium fluoride, 2.5 to 10% of rubidium fluoride, and the balance of potassium fluoride. The invention also provides a preparation method of the composite zinc-aluminum flux cored wire. The preparation method has the advantages that trace Be and Mg are introduced based on the conventional Zn-Al-Ag-Cu alloy system in the brazing filed, so that the cleanness of the wire can be improved, the quality and the reliability of a brazing joint are ensured, and the intercrystalline corrosion resistance of the wire can be greatly improved, and as a result, the phenomenon of 'embrittlement' can be delayed or inhibited.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU RES INST OF MECHANICAL ENG CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com