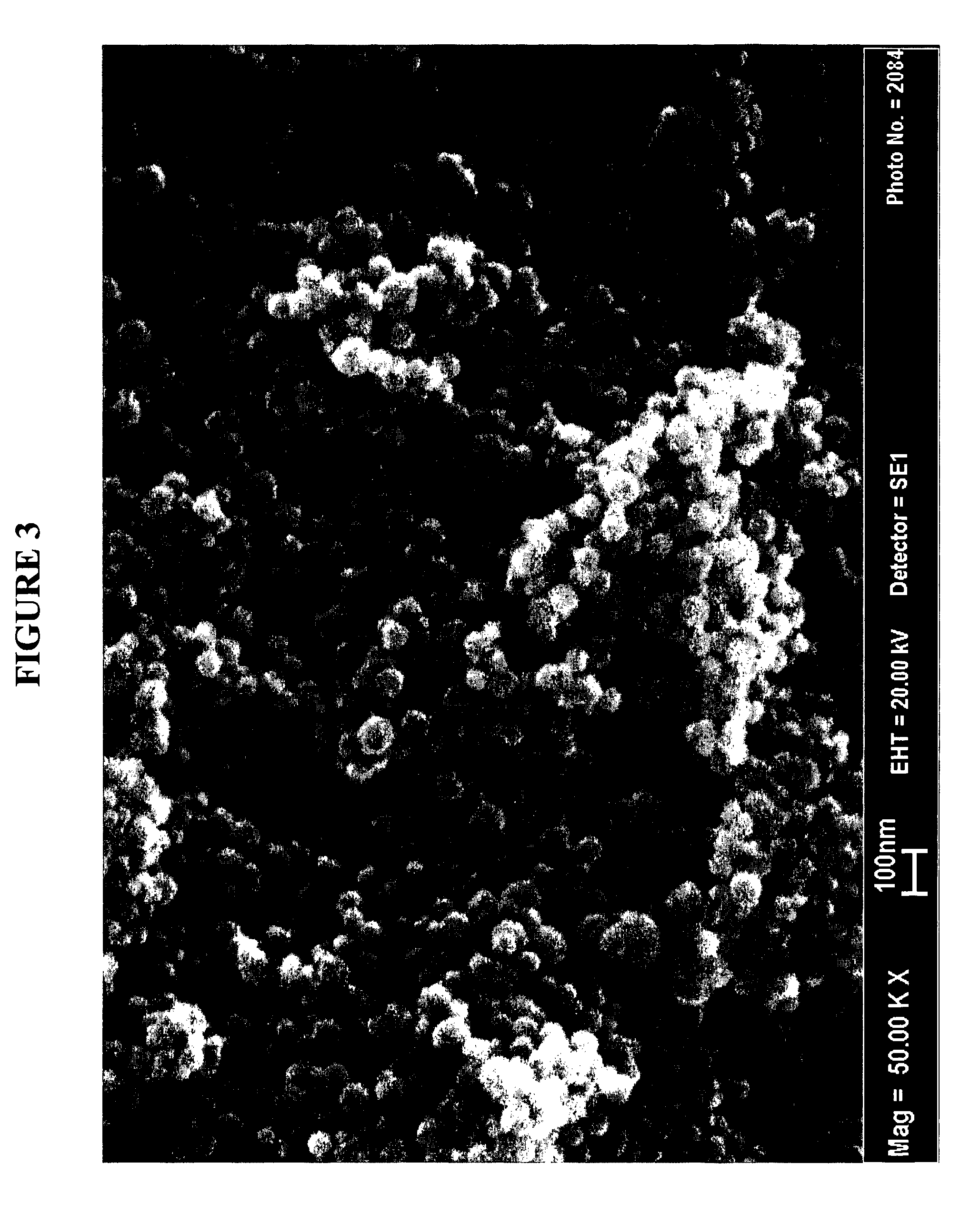
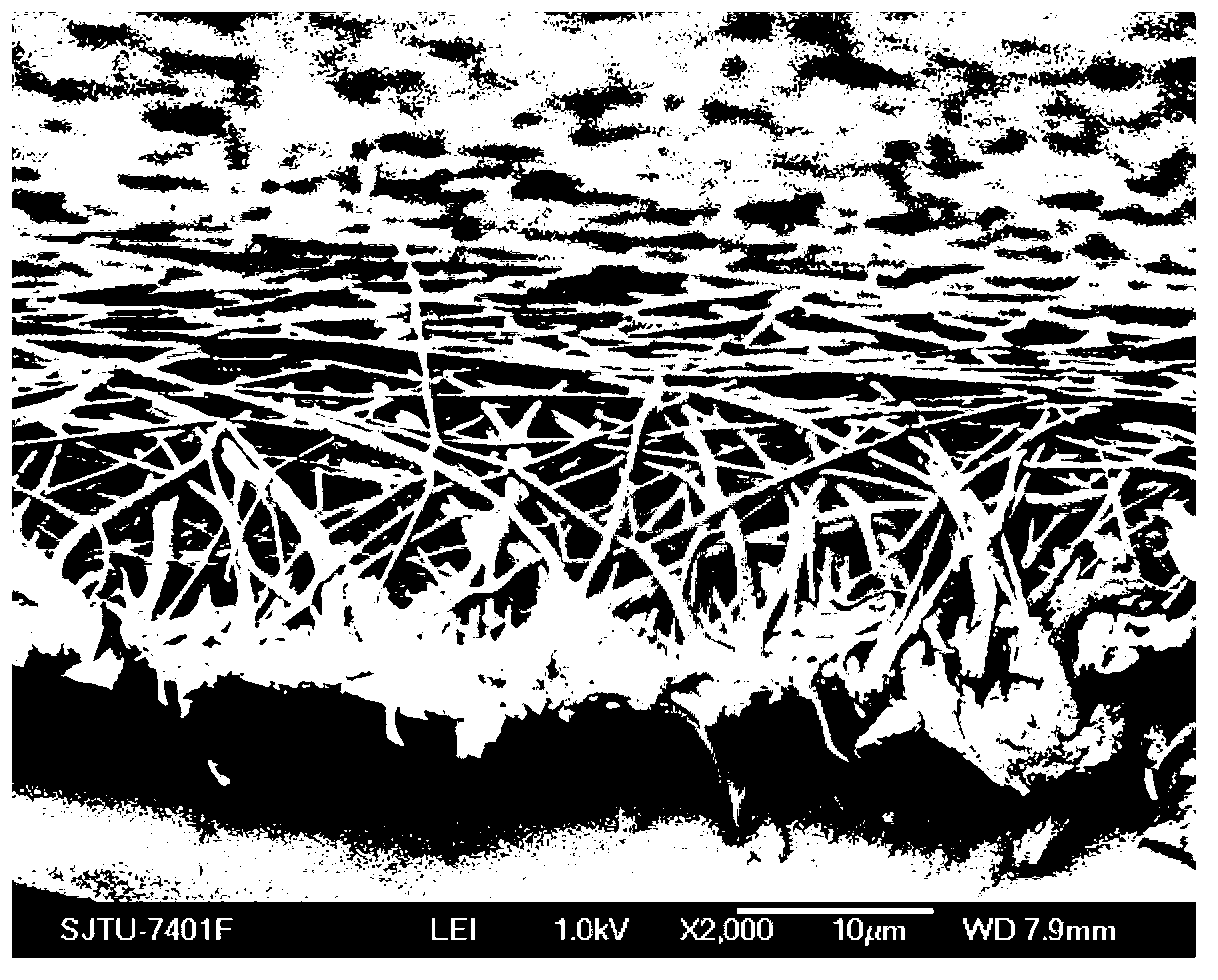
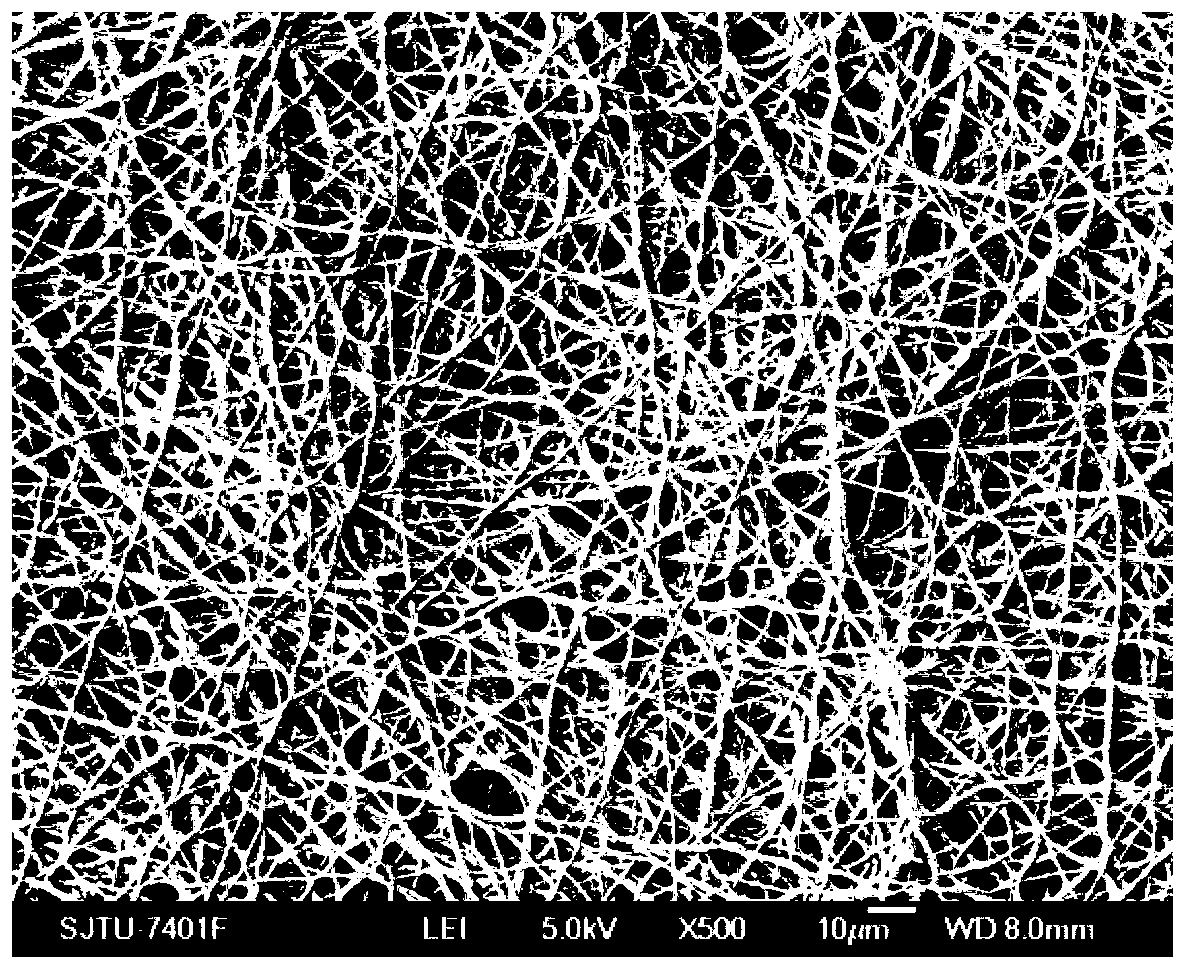
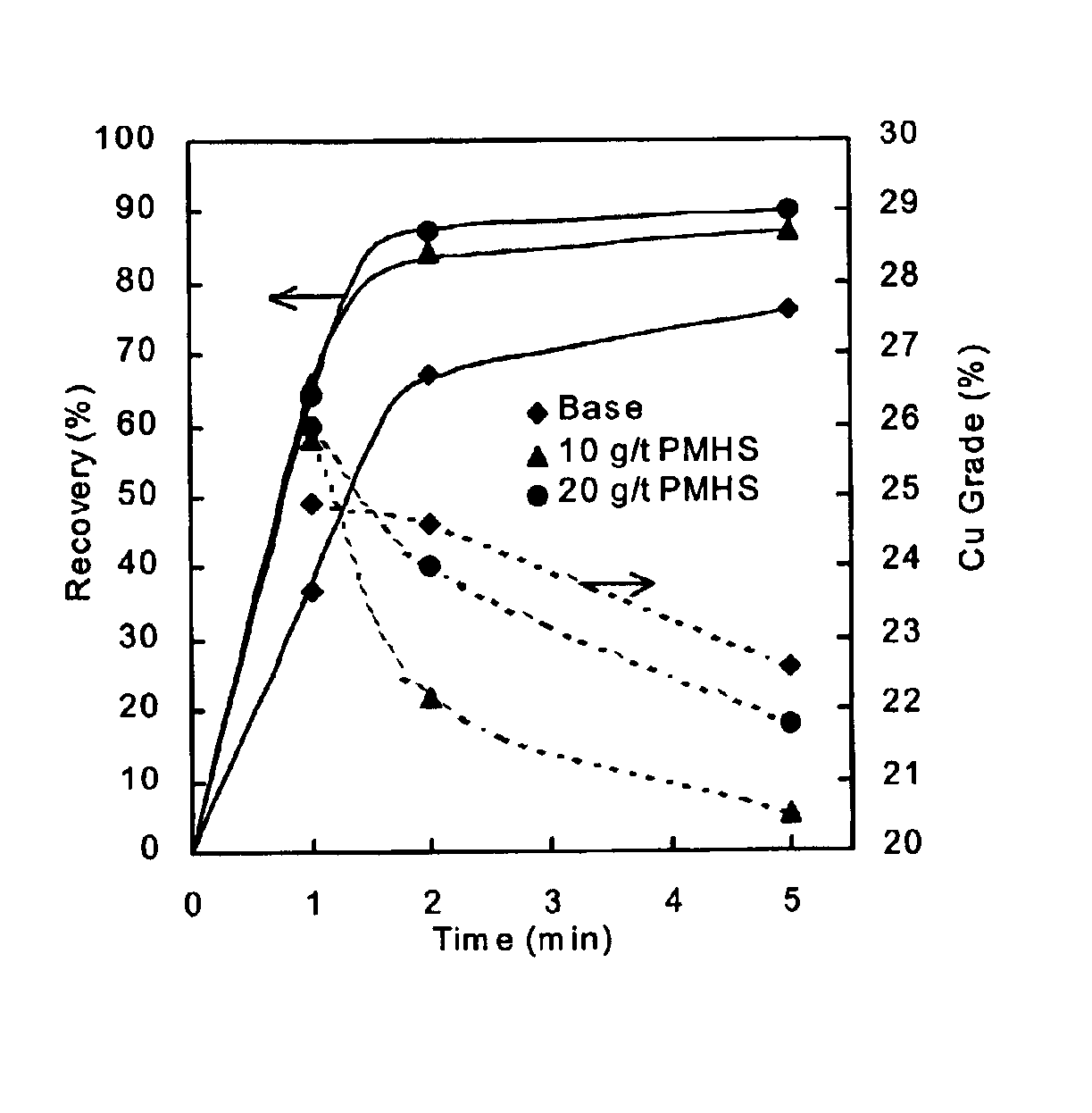
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
815 results about "Ultrafine particle" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Ultrafine particles (UFPs) are particulate matter of nanoscale size (less than 0.1 μm or 100 nm in diameter). Regulations do not exist for this size class of ambient air pollution particles, which are far smaller than the regulated PM₁₀ and PM2.5 particle classes and are believed to have several more aggressive health implications than those classes of larger particulates. In the EU UFP's in ambient air are empirical defined by a technical specification. Important detail is the size definition, which is stated as "The lower and upper sizes considered within this document are 7 nm and a few micrometres, respectively". Although the most common referral to UFP is "less than 0.1μm", this is incorrect for ambient air in the EU.
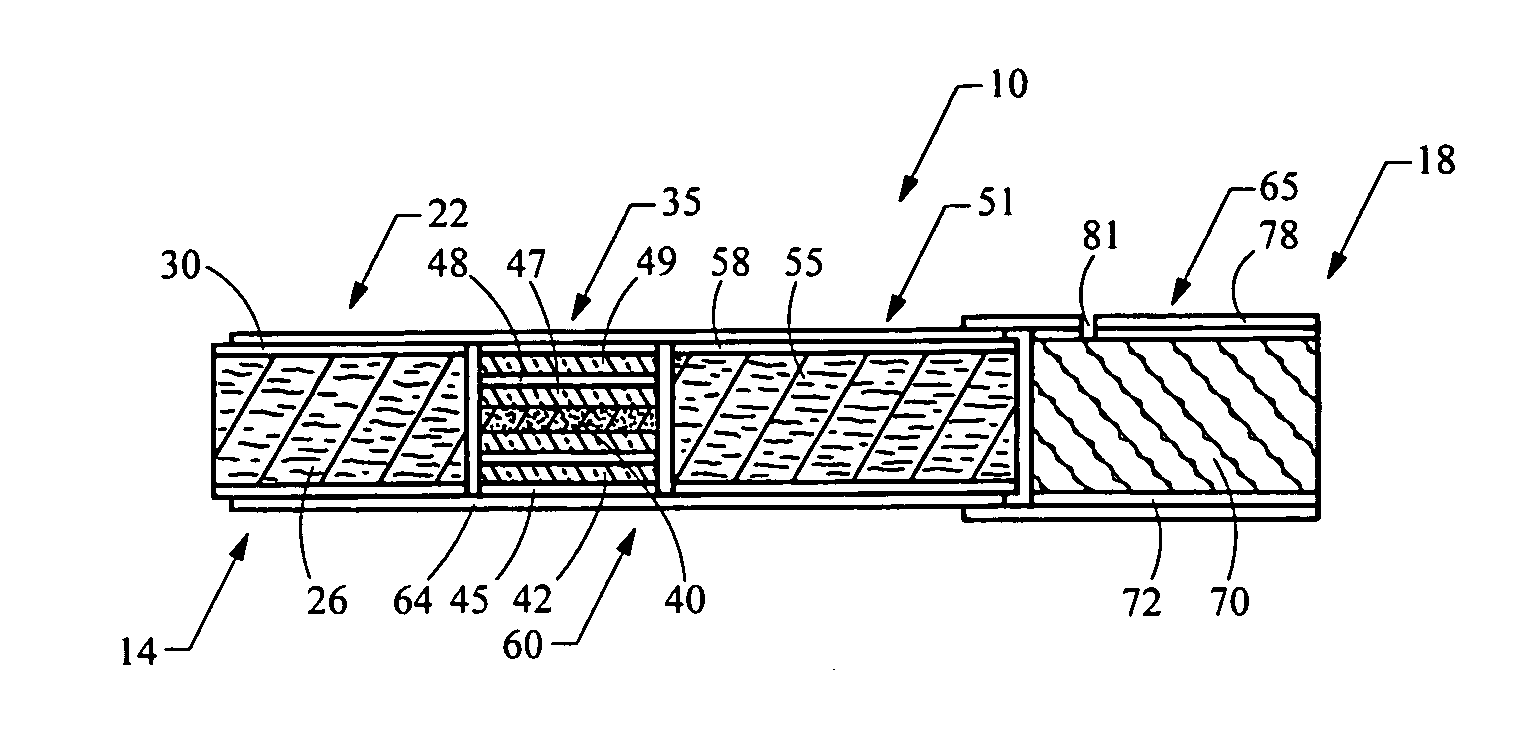
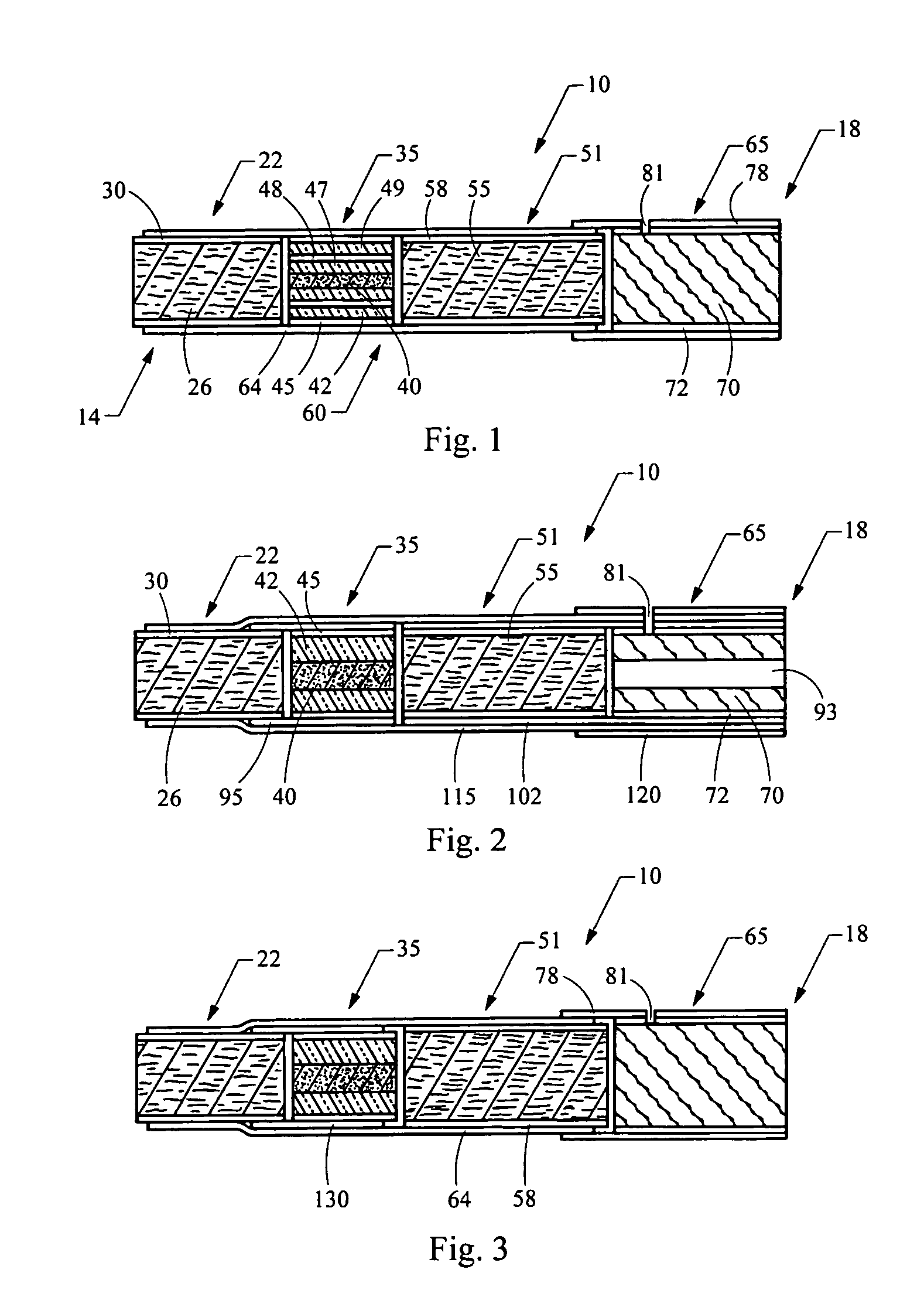
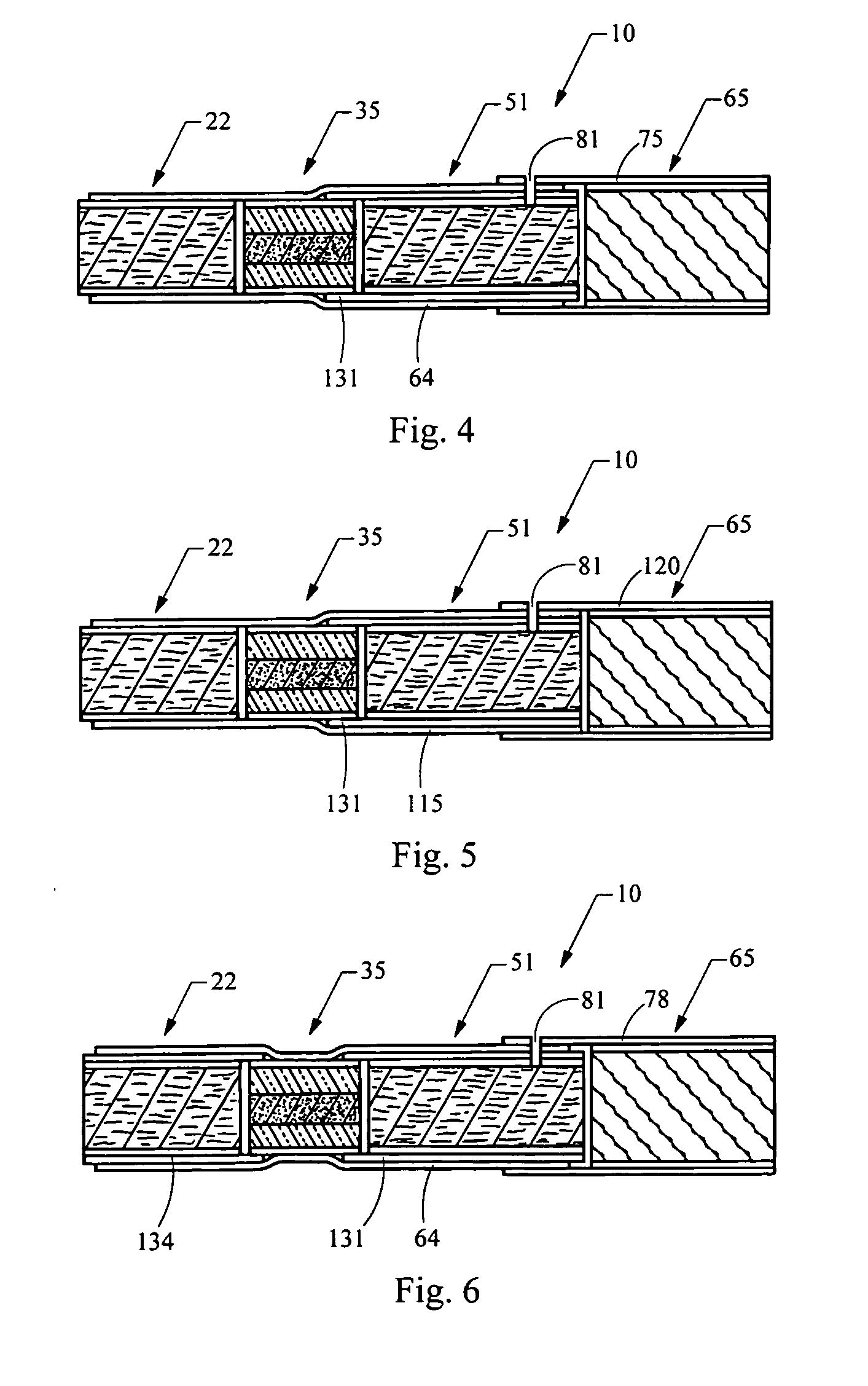
Smoking article
ActiveUS20070215168A1Reduce amountCarbon reductionTobacco preparationTobacco treatmentEngineeringFood flavor
A smoking article, such as a cigarette, includes a carbonaceous heat source. A mouth end piece segment is located at the mouth end of the smoking article, and the mouth end piece segment allows the smoking article to be placed in the mouth of the smoker to be drawn upon. The smoking article further incorporates an aerosol-generating segment located between the heat generation segment and the mouth end piece segment. The aerosol-generating segment incorporates an aerosol-forming material (e.g., glycerin and flavors). The heat generation segment is in a heat exchange relationship with the aerosol-generating region such that heat generated by the burning fuel element acts to volatilize aerosol-forming material for aerosol formation. The carbonaceous heat source is in intimate contact with coarse, fine or ultrafine particles of materials such as cerium oxide, or mixtures of cerium oxide and palladium chloride.
Owner:R J REYNOLDS TOBACCO COMPANY
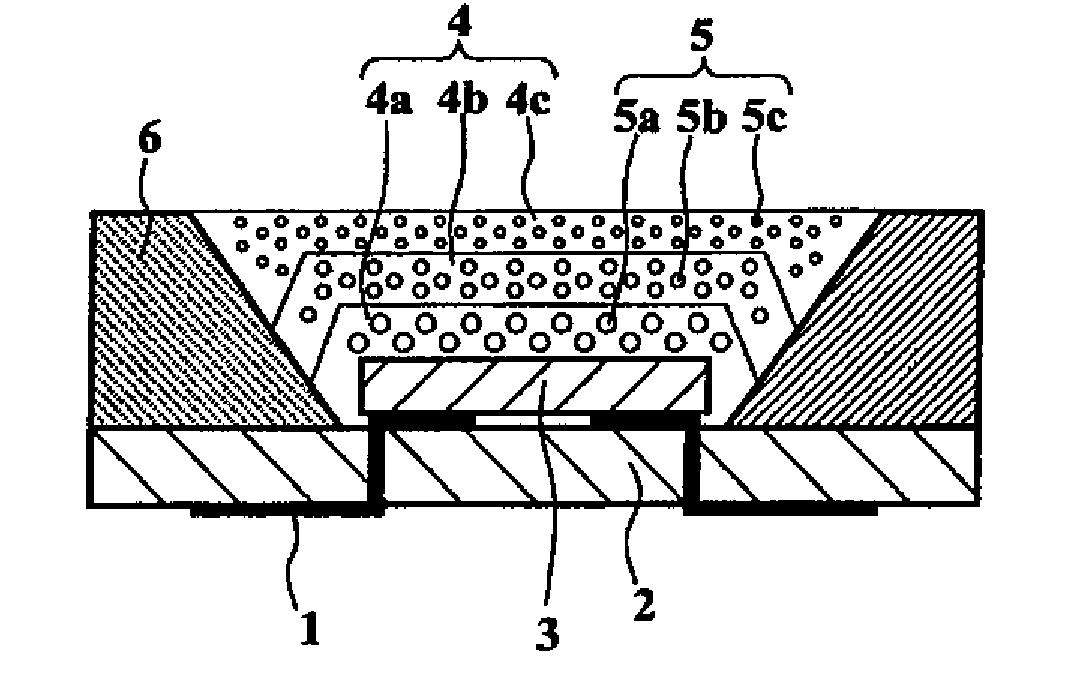
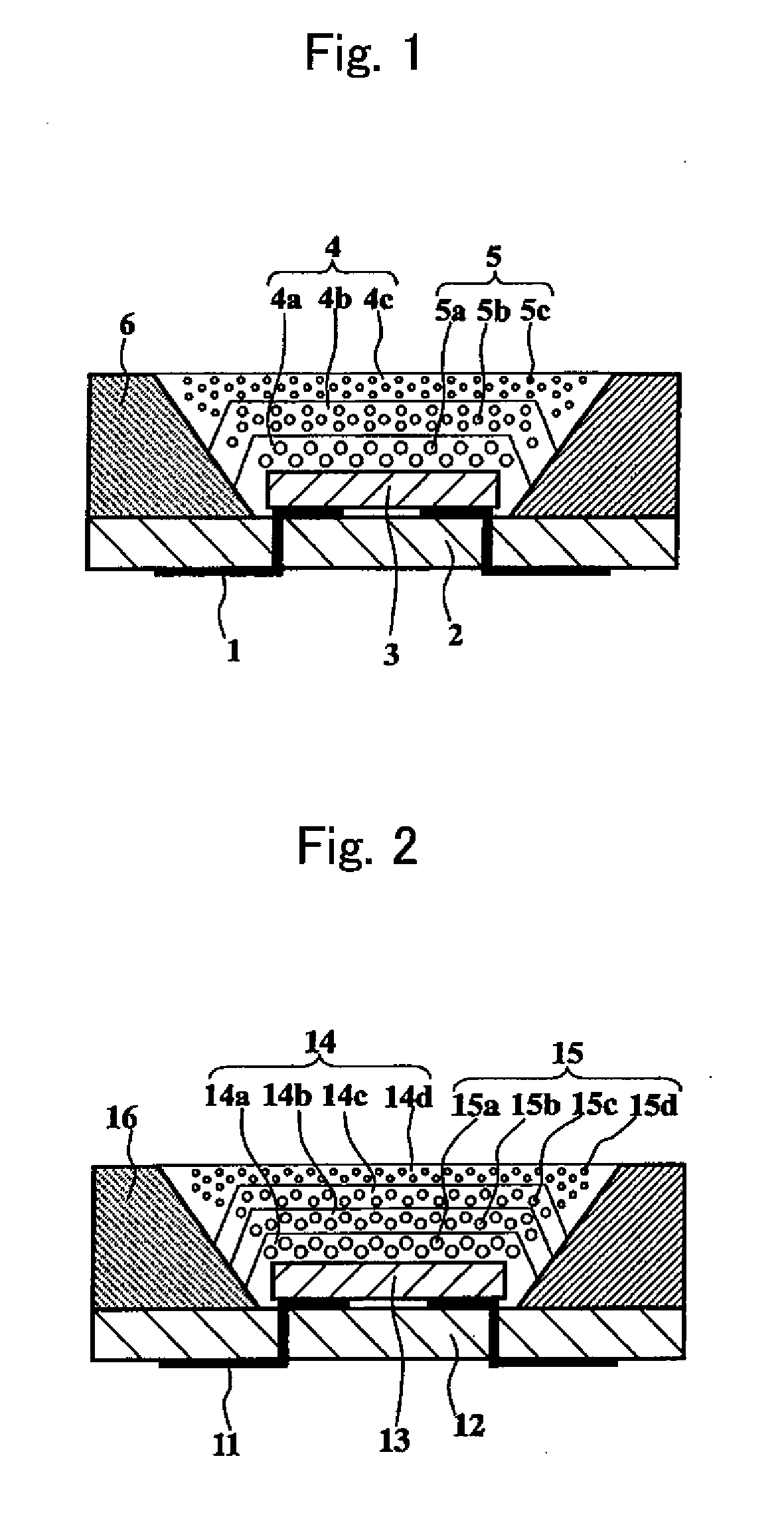
Wavelength Converter, Light-Emitting Device, Method of Producing Wavelength Converter and Method of Producing Light-Emitting Device
InactiveUS20080231170A1Reduce self-quenchingSolve low luminous efficiencyDischarge tube luminescnet screensLamp detailsPhosphorFluorescence
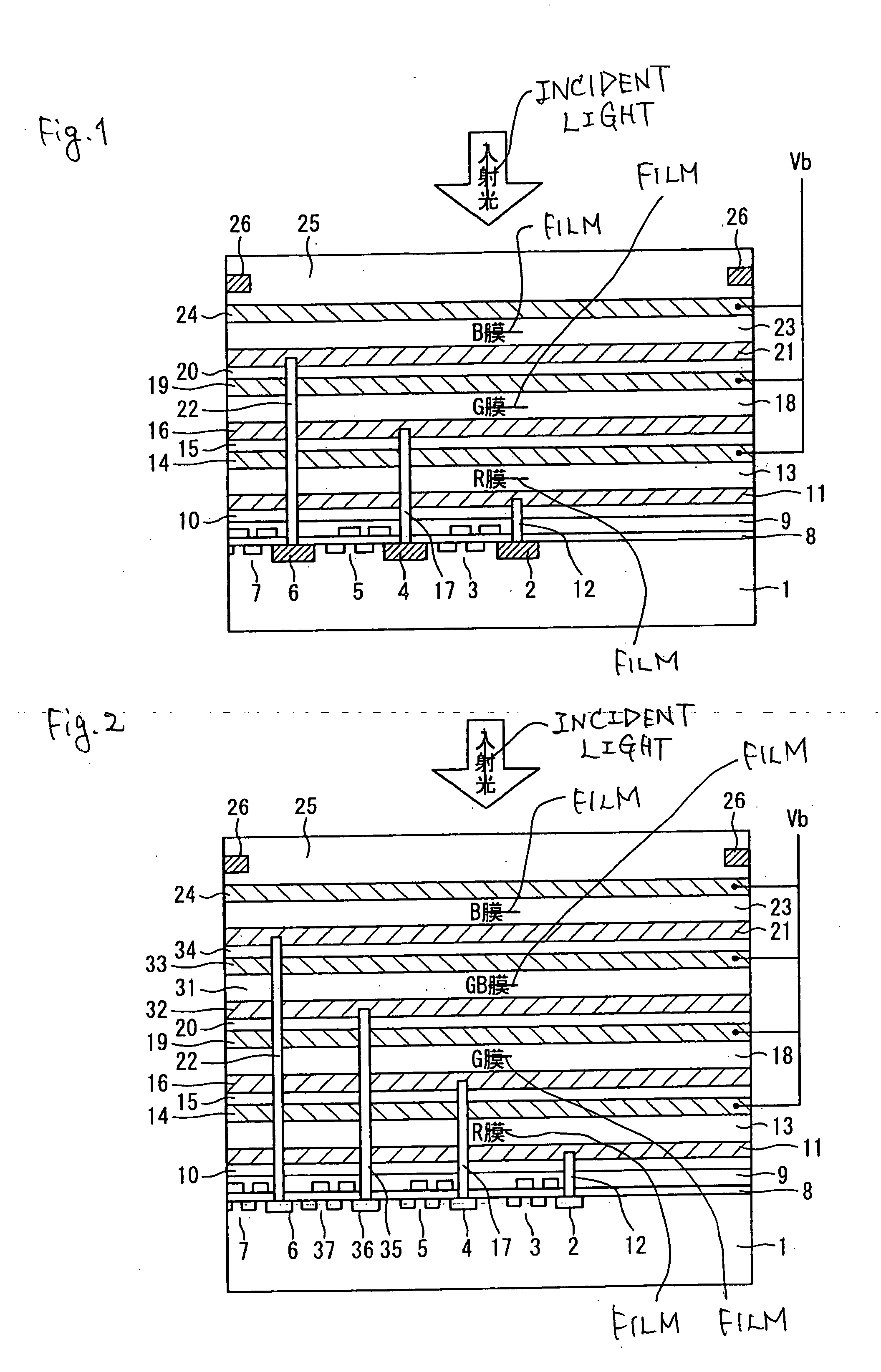
A light-emitting device comprises a light-emitting element 3 that is provided on a substrate 2 and emits excitation light, and a wavelength converter 4 that converts the excitation light into visible light. The visible light is output light. The wavelength converter 4 comprises a plurality of wavelength conversion layers 4a, 4b and 4c which respectively contain, as phosphors, at least one type of semiconductor ultrafine particles having a mean particle size of not more than 20 nm and at least one type of fluorescent substance having a mean particle size of not less than 0.1 μm in a resin matrix. Thereby, self-quenching of phosphors is reduced and high luminous efficiency is attained.
Owner:KYOCERA CORP
Conductive adhesive agent with ultrafine particles
ActiveUS7262511B2Improve working efficiencyUniform and good thermal conductivity propertySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsConductive materialMicrometerFluid viscosity
The present invention provides a conductive adhesive agent capable of being diluted with a solvent to give good coating workability and allowing formation of a conductive joint excellent in both thermal conductivity and electrical conductivity by inhibiting a gas generated when a binder resin is heat-cured after attachment of a part. The conductive adhesive agent according to the present invention is a conductive adhesive agent wherein, based on 100 parts by weight of silver powder having an average particle diameter of micrometers, which is used for a conductive medium, e.g. as a main component, 1 to 10 parts by weight of silver fine particles having an average particle diameter of nanometers is used in combination therewith and 5 to 15 parts by weight of thermosetting resin as a binder resin component and 10 parts or less by weight of solvent for adjustment of a fluid viscosity are blended therein as essential components, and by selection of such a blending ratio, generation of a gas component during heating and curing of the thermosetting resin to prevent formation of voids, and at the same time, fabrication of a conductive joint excellent in thermal conductivity and electrical conductivity is achieved.
Owner:HARIMA CHEM INC +1
Antireflection material and polarizing film using the same
InactiveUS6777070B1Improve anti-reflection effectReduce image contrastSynthetic resin layered productsCoatingsRefractive indexDisplay device
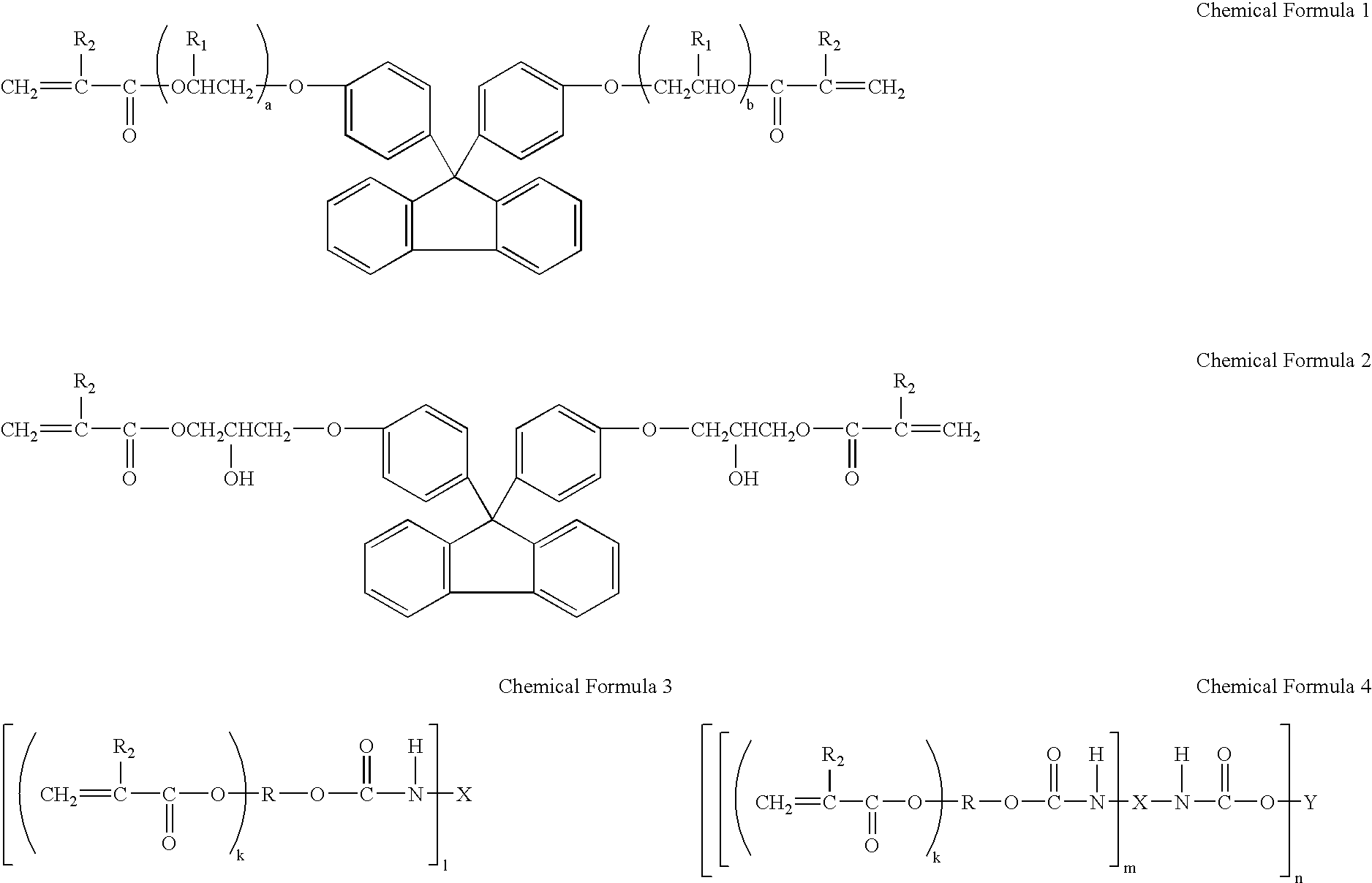
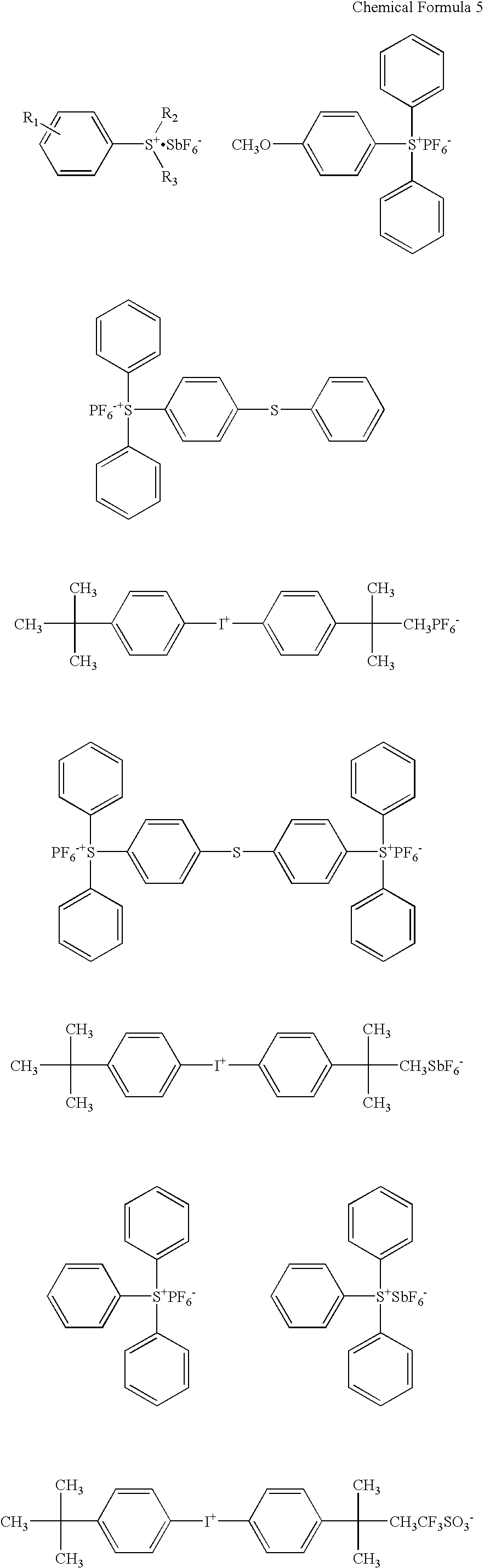
An anti-reflection material and a polarization film which exhibit superior anti-reflection properties by preventing external light such as sunlight, fluorescent light, etc., from being reflected on a display, which yield a clear image without sparkling and reduces image contrast, and which exhibit superior wear resistance, chemical resistance, and contamination resistance, as well as exhibit optical stability. A hard coat layer is provided on one surface or two surfaces of a transparent substrate directly or via another layer, and an anti-reflection film having a lower refraction index than the hard coat layer is further provide on the hard coat layer. The hard coat layer consists of at least {circle around (1 a polymer polymerizing (metha)acrylate compound having a fluorene structure; {circle around (2 a polymer polymerizing urethane (metha)acrylate compound and ultrafine particles having a high refraction index; and {circle around (3 radiation and / or thermosetting resin and surface-treated titanium oxide ultrafine particles.
Owner:TOMOEGAWA PAPER CO LTD
Process for producing ultrafine particles
ActiveUS20070084308A1Improve surface activityNovel functionNanotechTransportation and packagingGas phaseReactive gas
The ultrafine particle producing process introduces materials for producing ultrafine particles into a thermal plasma flame under reduced pressure to form a vapor-phase mixture, introduces a reactive gas and a cooling gas toward an end portion of the thermal plasma flame in supply amounts sufficient for quenching the vapor-phase mixture to generate the ultrafine particles and allows the resultant ultrafine particles to come into contact with the reactive gas so as to produce the ultrafine particles whose surfaces are coated with a thin film including one or more components compound derived from decomposition and / or reaction of the reactive gas, for example, an elementary carbon substance and / or a carbon. According to the process, thin film-coated ultrafine particles having high level uniformity in particle size and shape can be produced.
Owner:NISSHIN SEIFUN GRP INC
Process for the production of ultrafine particles
A new, cost effective process for the production of ultrafine particles which is based on mechanically activated chemical reaction of a metal compound with a suitable reagent. The process involves subjecting a mixture of a metal compound and a suitable reagent to mechanical activation to increase the chemical reactivity of the reactants and / or reaction kinetics such that a chemical reaction can occur which produces a solid nano-phase substance. Concomitantly, a by-product phase is also formed. This by-product phase is removed so that the solid nano-phase substance is left behind in the form of ultrafine particles. During mechanical activation a composite structure is formed which consists of an intimate mixture of nano-sized grains of the nano-phase substance and the reaction by-product phase. The step of removing the by-product phase, following mechanical activation, may involve subjecting the composite structure to a suitable solvent which dissolves the by-product phase, while not reacting with the solid nano-phase substance. The process according to the invention may be used to form ultrafine metal powders as well as ultrafine ceramic powders. Advantages of the process include a significant degree of control over the size and size distribution of the ultrafine particles, and over the nature of interfaces created between the solid nano-phase substance and the reaction by-product phase.
Owner:WESTERN AUSTRALIA UNIV OF THE
Apparatus for and method of sampling and collecting powders flowing in a gas stream
InactiveUS20060096393A1High purity samplingEnough timeCombination devicesSequential/parallel process reactionsEngineeringAirflow
A device for sampling of a mixture of ultrafine particles within a moving gas stream includes a suction generator, at least one sample collection element, and a conduit structure coupling the sample collection element with the suction generator. In some embodiments, the suction generator is configurable to separate by suction a portion of a gas stream containing a plurality of ultrafine particles, and to entrain with a motive fluid forming an output mixture. In some embodiments, a conduit is configured to accept a gas stream containing ultrafine particles and to channel it to the collection element.
Owner:UMICORE AG & CO KG +1
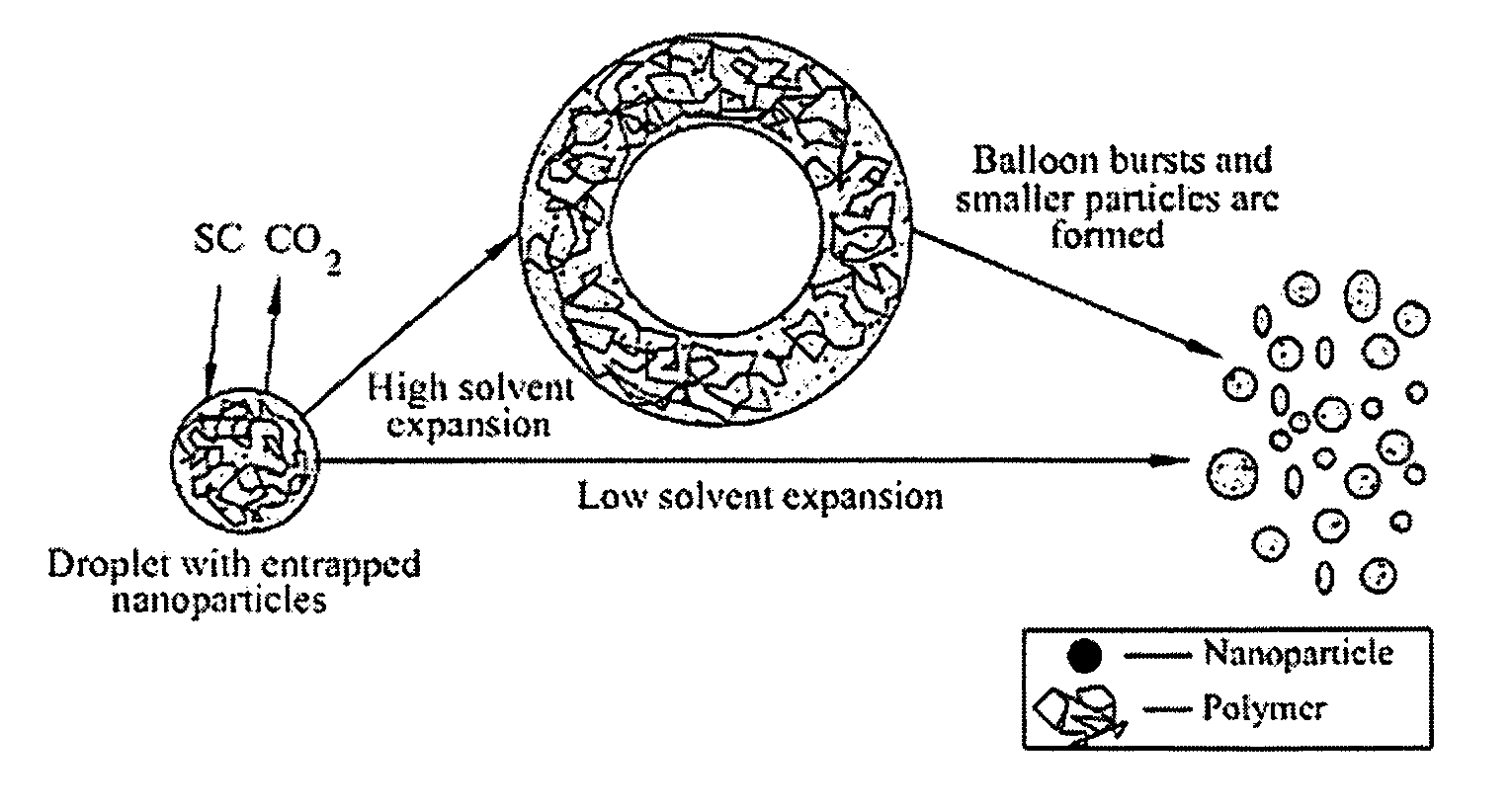
Polymer coating/encapsulation of nanoparticles using a supercritical antisolvent process
InactiveUS20050191491A1Speed up the processGranule coatingPretreated surfacesSolventSupercritical carbon dioxide
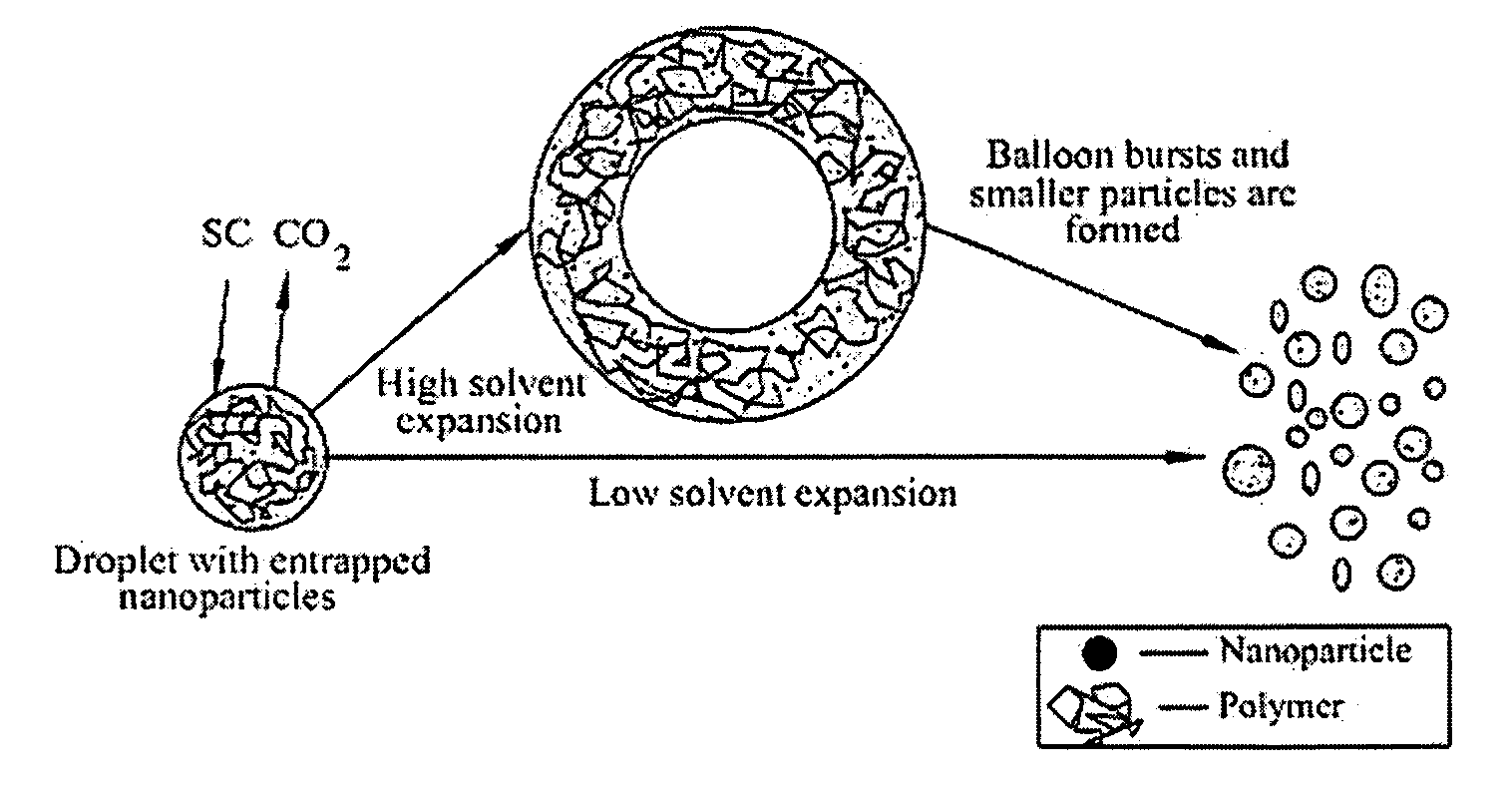
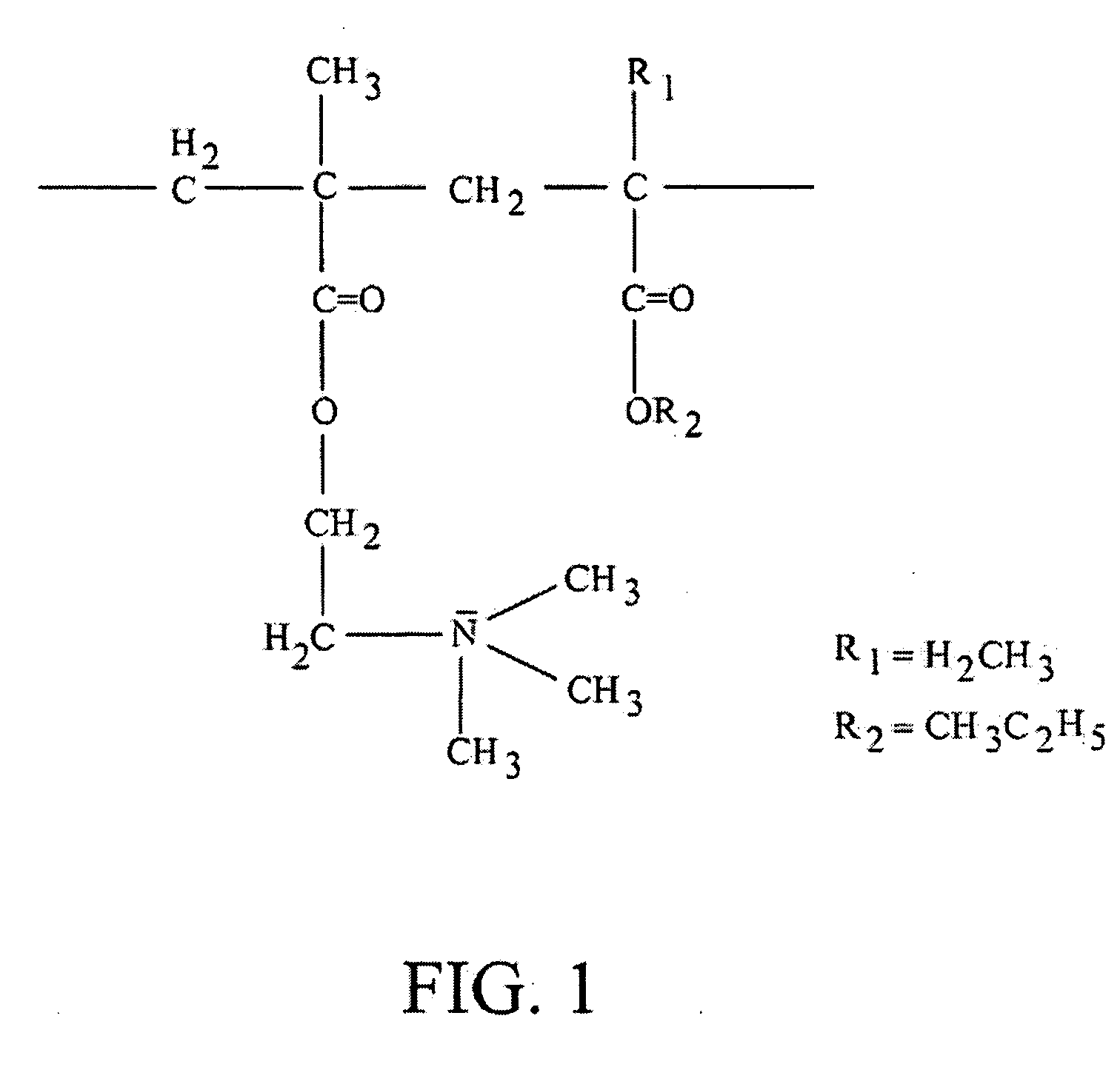
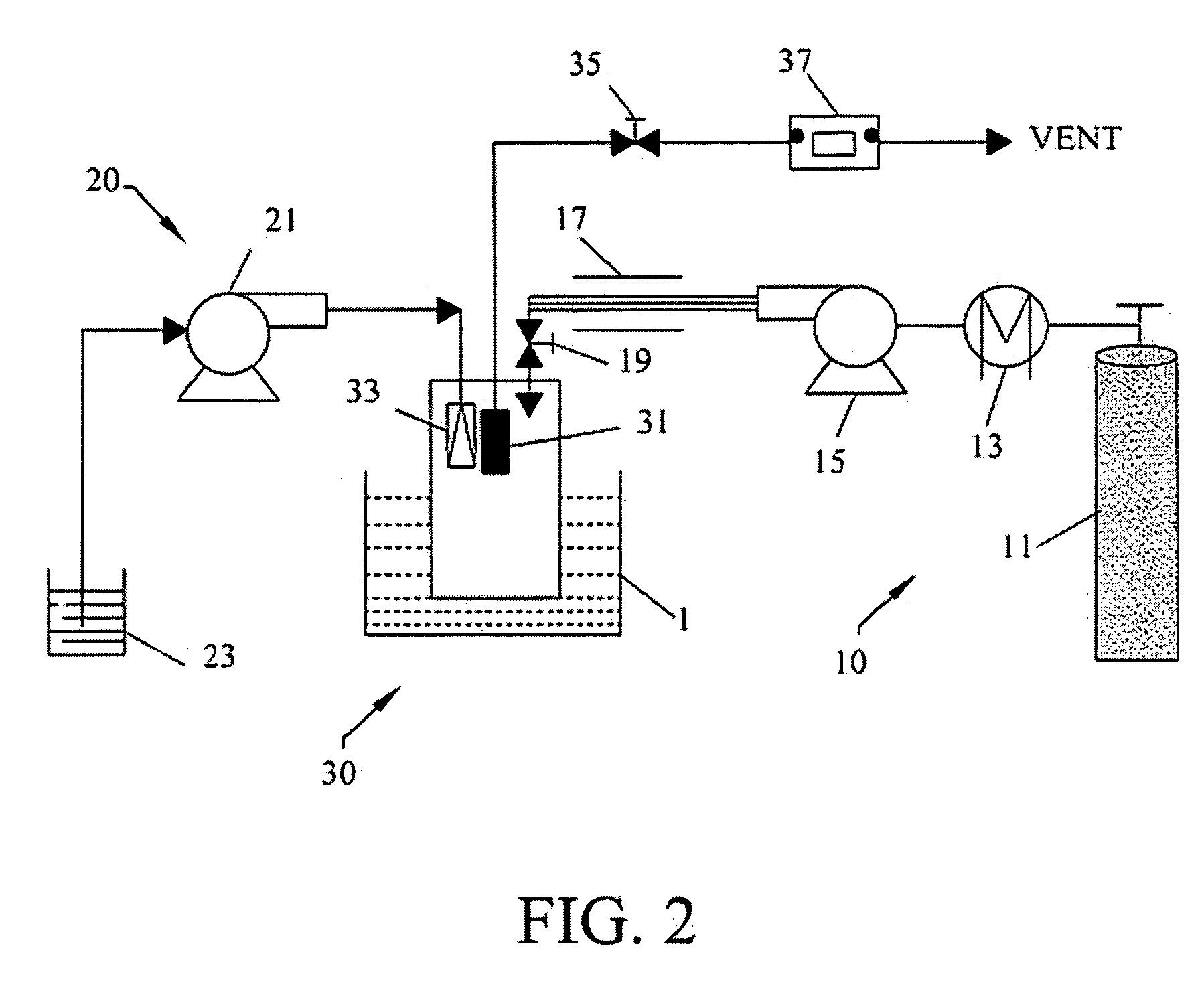
A process, method and / or system for preparing polymer-coated nanoparticles and / or other ultrafine particles utilizing a supercritical fluid, e.g., supercritical carbon dioxide (SC CO2), as an antisolvent that may be added to a solution of a polymer and an organic solvent in which insoluble nanoparticles or the like are suspended. The coating process occurs when the supercritical fluid (e.g., SC CO2) and the nanoparticle-containing suspension are combined to cause the suspended nanoparticles to precipitate as coated nanoparticles. Processing parameters for optimizing and / or enhancing the efficacy and / or efficiency of the coating process, method and / or system and for controlling the coating and / or agglomeration of coated particles are also described. The process, method and / or system has wide ranging applicability, e.g., for coating and / or encapsulation of pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, food products, chemicals, agrochemicals, pesticides, polymers, coatings, catalysts and the like.
Owner:NEW JERSEY INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
Photoelectric converting film stack type solid-state image pickup device
InactiveUS20050205879A1Efficiently taken outPhotoelectric chargeNanoinformaticsSolid-state devicesQuantum dotPhotoelectric conversion
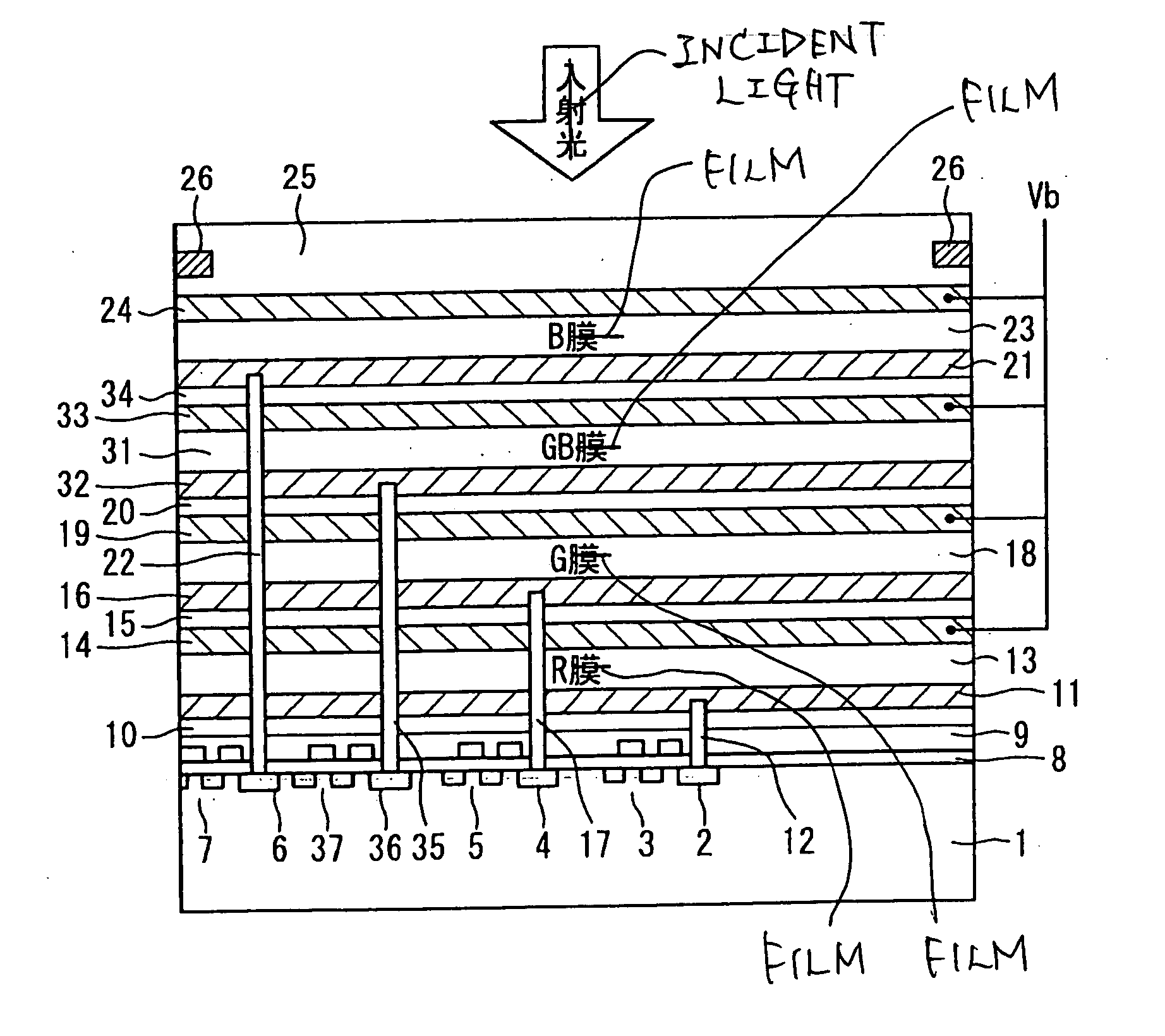
A photoelectric converting film stack type solid-state image pickup device comprising: a semiconductor substrate in which a signal read circuit is formed; and at least one photoelectric converting film interposed between two electrode films, said at least one photoelectric converting film being stacked above the semiconductor substrate, wherein a signal corresponding to an intensity of incident light is read outside by the signal read circuit, the signal being generated by photoelectric conversion with the photoelectric converting film, wherein the photoelectric converting film comprises: a first layer comprising: an ultrafine particle including (i) a quantum dot contributing to the photoelectric conversion and (ii) a material having a band gap larger than that of the quantum dot, the quantum dot being coated with the material; and a hole transport layer stacked on the first layer.
Owner:FUJIFILM HLDG CORP +1
Production Of Barium Titanate Compounds
InactiveUS20070202036A1High purityLow costMaterial nanotechnologyAlkaline earth titanatesBarium titanateSpherical shaped
An ultrafine powder of barium titanate including solid solutions and doped compounds that meets up to specific characteristics is produced by method comprising two main steps. The first step is a reaction, typically in a Segmented Flow Tubular Reactor, between reactants to produce cubic-structure barium titanate composed of non-agglomerated ultrafine particles having a shape of given aspect ratio, usually a generally spherical shape, of low density corresponding at most to 90% of the intrinsic density, all particles being smaller than 1 micron and having a narrow particle size distribution and wherein the ratio of Ba:Ti including substitutents and dopants is very close to the ideal stoichiometry. This is followed by subjecting the powder produced in the first step to a second stage solvothermal post treatment typically in an autoclave at temperature less than 400° C. to convert the cubic-structure particles of low density to ultrafine tetragonal particles of increased density corresponding to at least 90% of the intrinsic density while maintaining the same aspect ratio, and maintaining the size of all particles below 1 micron, the narrow particle size distribution span, and the given ideal stoichiometry. The produced particles can have a non-spherical facetted shape such as cube-like.
Owner:JONGEN NATHALIE +1
Antibacterial filtering material for mask and method for manufacturing antibacterial filtering material
InactiveCN102872653AHigh retention rateEasy to prepareFiltration separationNon-woven fabricsFiberMicrometer
The invention discloses an antibacterial filtering material for a mask and a method for manufacturing the antibacterial filtering material. The filtering material for the mask comprises antibacterial agents, polymeric nano-fibers and a supporting non-woven fabric. The method for manufacturing the antibacterial filtering material includes spinning the polymeric nano-fibers on the supporting non-woven fabric via solution or fusant of the polymeric nano-fibers added with the antibacterial agents by means of electrostatic spinning. The filtering material for the mask is high in rejection to ultrafine particles, bacteria and viruses, the method for manufacturing the filtering material is simple, cost is low, and the antibacterial filtering material and the method are suitable for industrial production. In addition, the mask made of the antibacterial filtering material is good in breathability, and rejection to sodium chloride aerosol particles with the sizes of 0.3 micrometer can be higher than 90%.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Methods of increasing flotation rate
Methods of increasing the rate of separating hydrophobic and hydrophilic particles by flotation have been developed. They are based on using appropriate reagents to enhance the hydrophobicity of the particles to be floated, so that they can be more readily collected by the air bubbles used in flotation. The hydrophobicity-enhancing reagents include low HLB surfactants, naturally occurring lipids, modified lipids, and hydrophobic polymers. These methods can greatly increase the rate of flotation for the particles that are usually difficult to float, such as ultrafine particles, coarse particles, middlings, and the particles that do not readily float in the water containing large amounts of ions derived from the particles. In addition, new collectors for the flotation of phosphate minerals are disclosed.
Owner:MINERAL & COAL TECH
Chemical Analytic Apparatus and Chemical Analytic Method
InactiveUS20080226500A1Improve magnetic efficiencyImprove accuracyLaboratory glasswaresBiological testingCompound (substance)Miniaturization
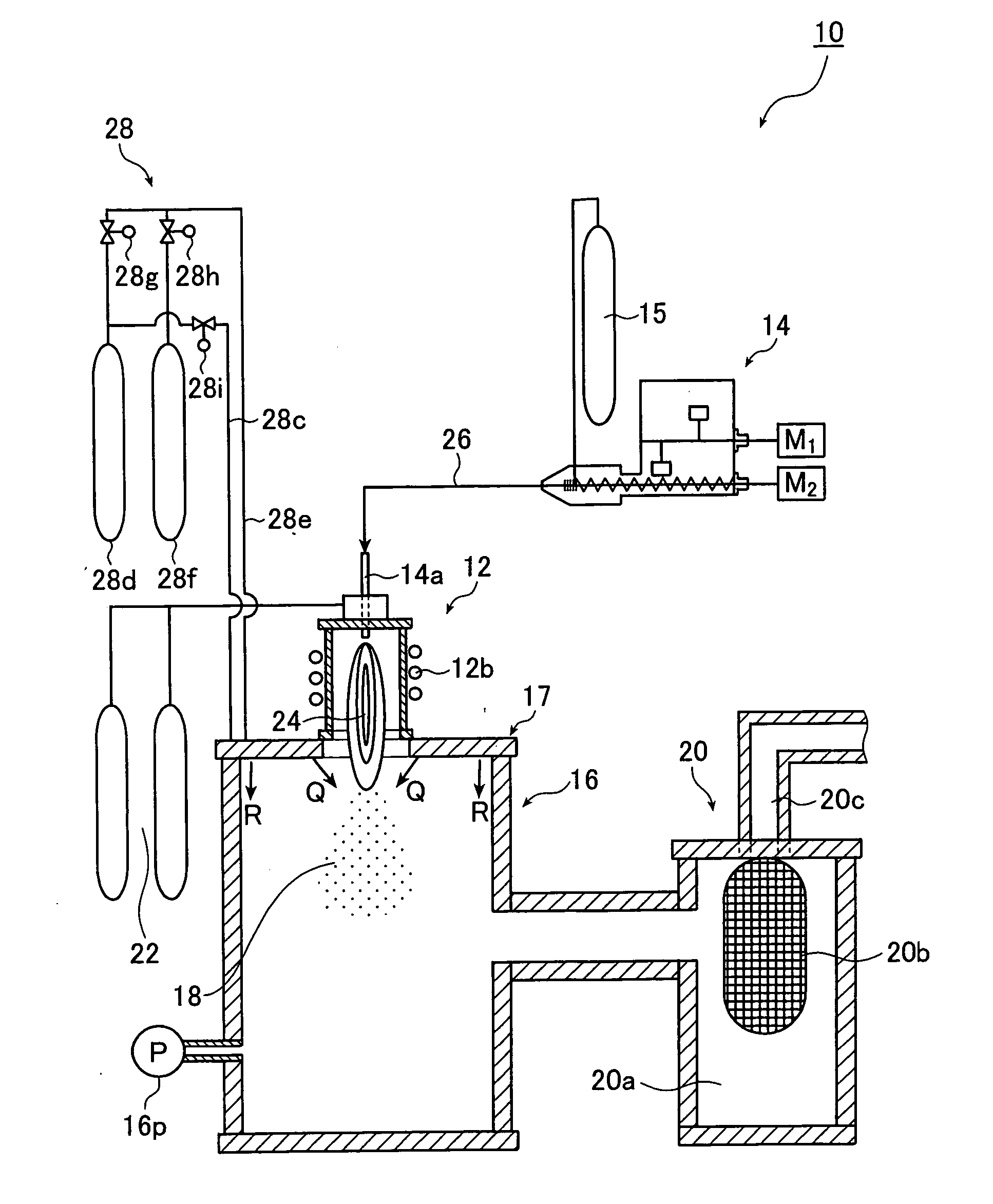
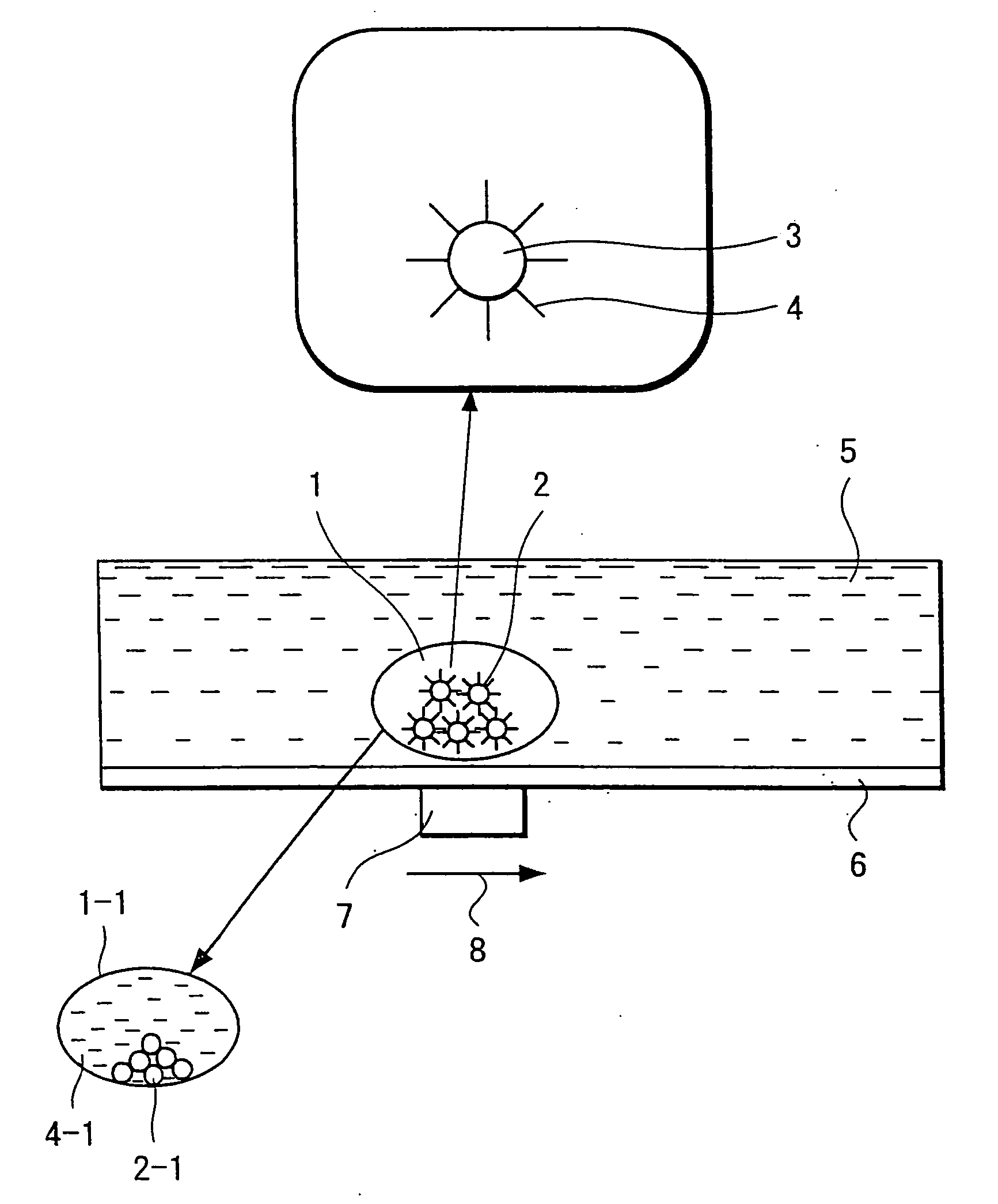
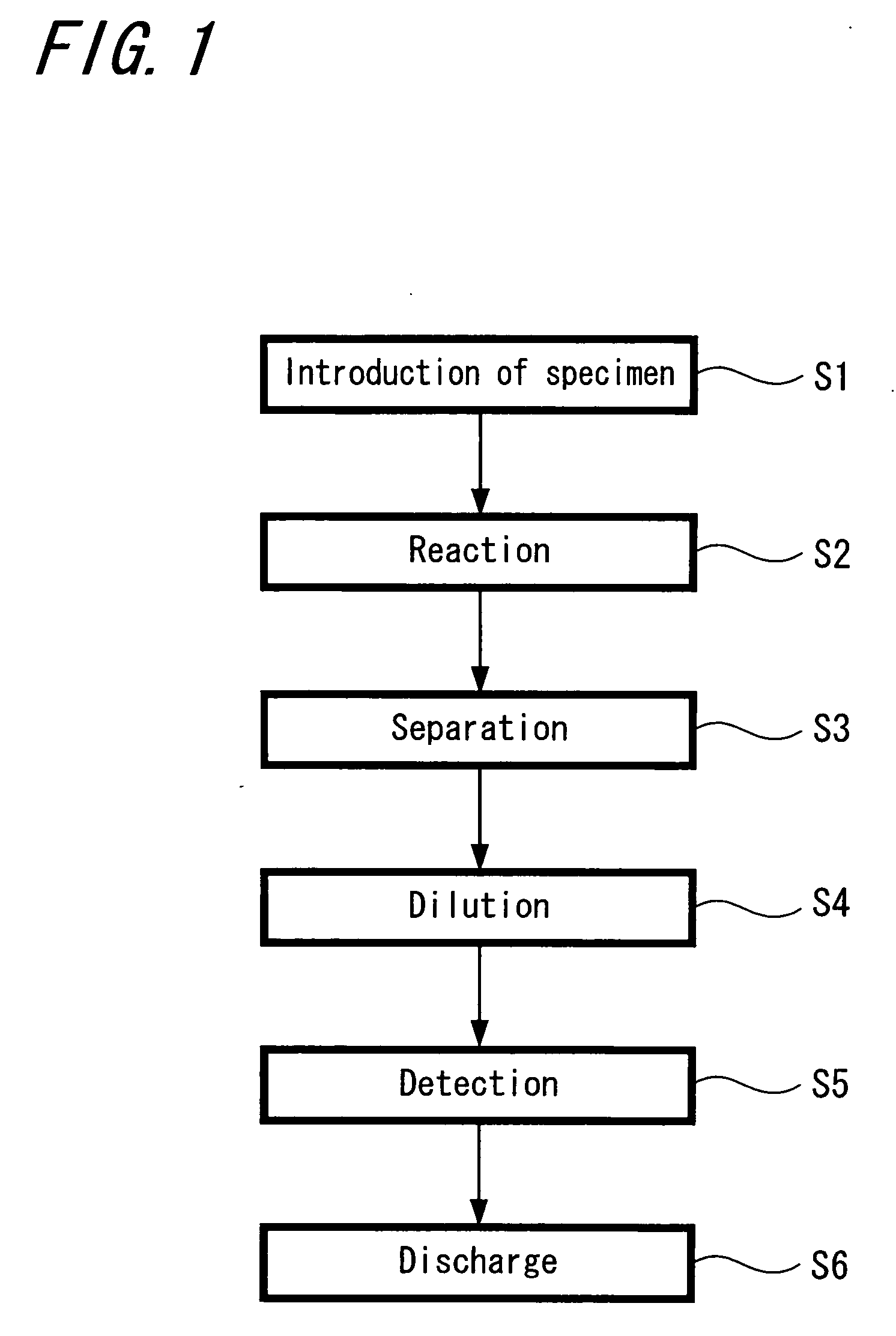
A chemical analytic apparatus of the present invention is the one which proposes that a miniaturization, a making low-cost and portability are possible and also the operation of each process of separation, concentration and dilution of specimen is possible, and which includes: an introduction means (S1) that introduces a droplet to which magnetic ultrafine particles are mixed into another liquid that differs from the droplet while maintaining a single droplet; a conveyance means by which the droplet that includes the magnetic particles is conveyed in another liquid of the introduction means by applying magnetic field externally to the magnetic ultrafine particles; and processing means (S2 to S6) by which operations for processing of chemical analysis are performed one by one in the process in which the droplet to which the magnetic ultrafine particles are mixed is conveyed by the conveyance means
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
Composite particle for dielectrics, ultramicroparticulate composite resin particle, composition for forming dielectrics and use thereof
InactiveUS20030151032A1High dielectric constantSmall dielectric loss tangentSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesInorganic particleResin-Based Composite
The dielectric-forming composition according to the invention is characterized by consisting of: composite particles for dielectrics in which part or all of the surfaces of inorganic particles with permittivity of 30 or greater are coated with a conductive metal or a compound thereof, or a conductive organic compound or a conductive inorganic material; and (B) a resin component constituted of at least one of a polymerizable compound and a polymer. In addition, another dielectric-forming composition according to the invention is characterized by containing: ultrafine particle-resin composite particles composed of (J) inorganic ultra fine particles with the average particle size of 0.1 mum or smaller, and (B) a resin component constituted of at least one of a polymerizable compound and a polymer, wherein part or all of the surfaces of the inorganic ultrafine particles (J) are coated with the resin component (B), and the ultrafine particle-resin composite particles contain 20% by weight or more of the inorganic ultrafine particles (J); and inorganic particles with the average particle size of 0.1 to 2 mum and permittivity of 30 or greater, or inorganic composite particles in which a conductive metal or a compound thereof, or a conductive organic compound or a conductive inorganic material is deposited on the part or all of the surfaces of the inorganic particles.
Owner:JSR CORPORATIOON
Hard coat film, antireflection hard coat film, optical element and image display
InactiveUS20070178297A1Suppress cracksCurl suppressionSynthetic resin layered productsCellulosic plastic layered productsOptoelectronicsHardness
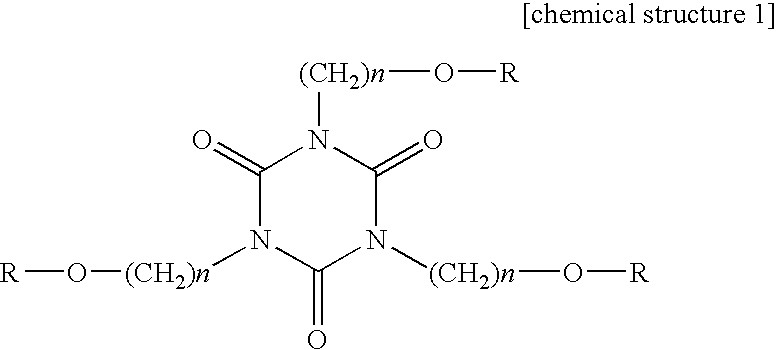
A hard coat film of the present invention comprises a hard coat layer, which is a cured coat layer, provided on at least one side of a transparent plastic film substrate, wherein a hard coat layer forming material comprises urethane acrylate (A); isocyanuric acid acrylate (B) and inorganic ultrafine particles (C), and has a high hardness and suppresses curling due to cracking and cure shrinkage.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
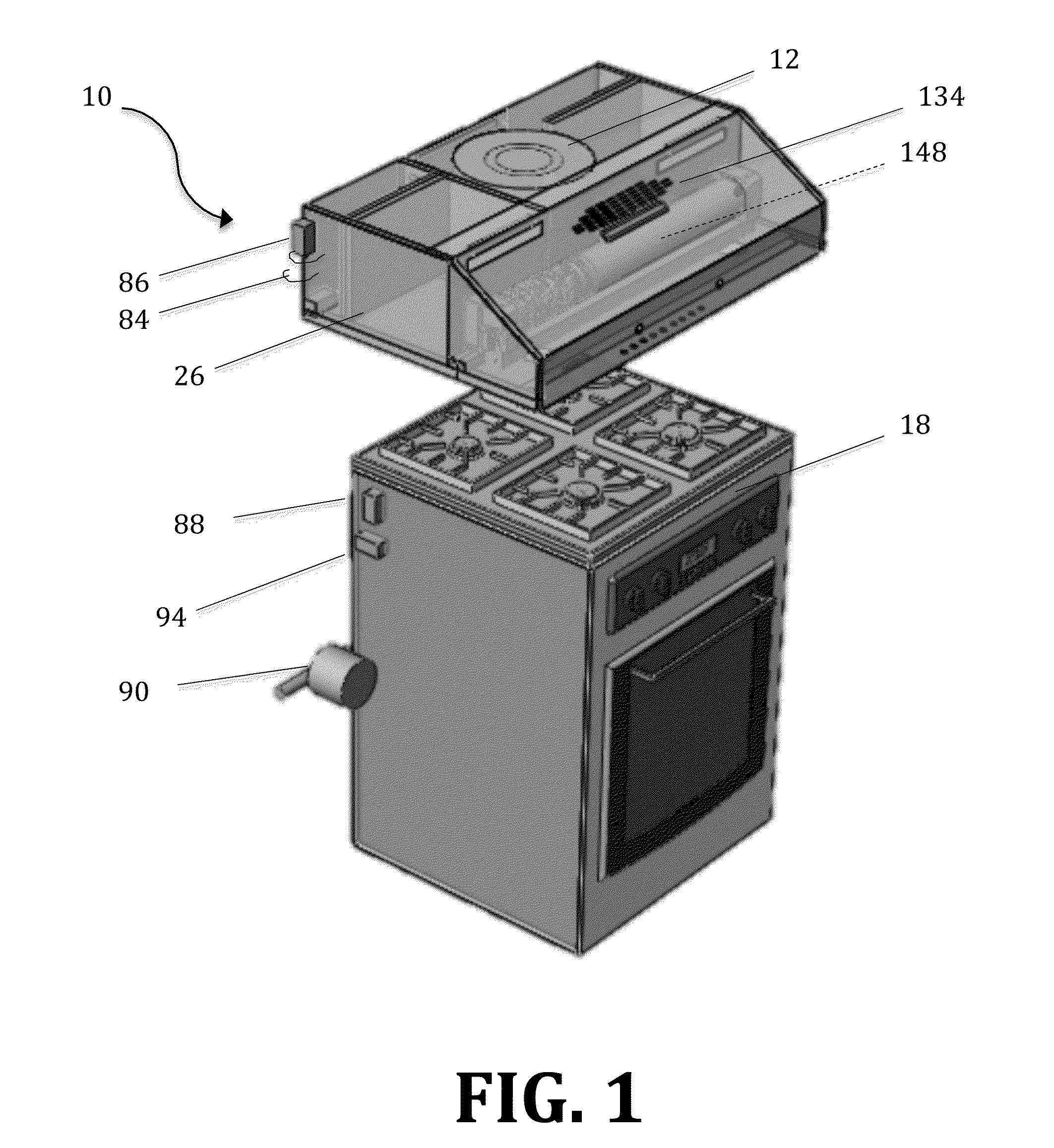
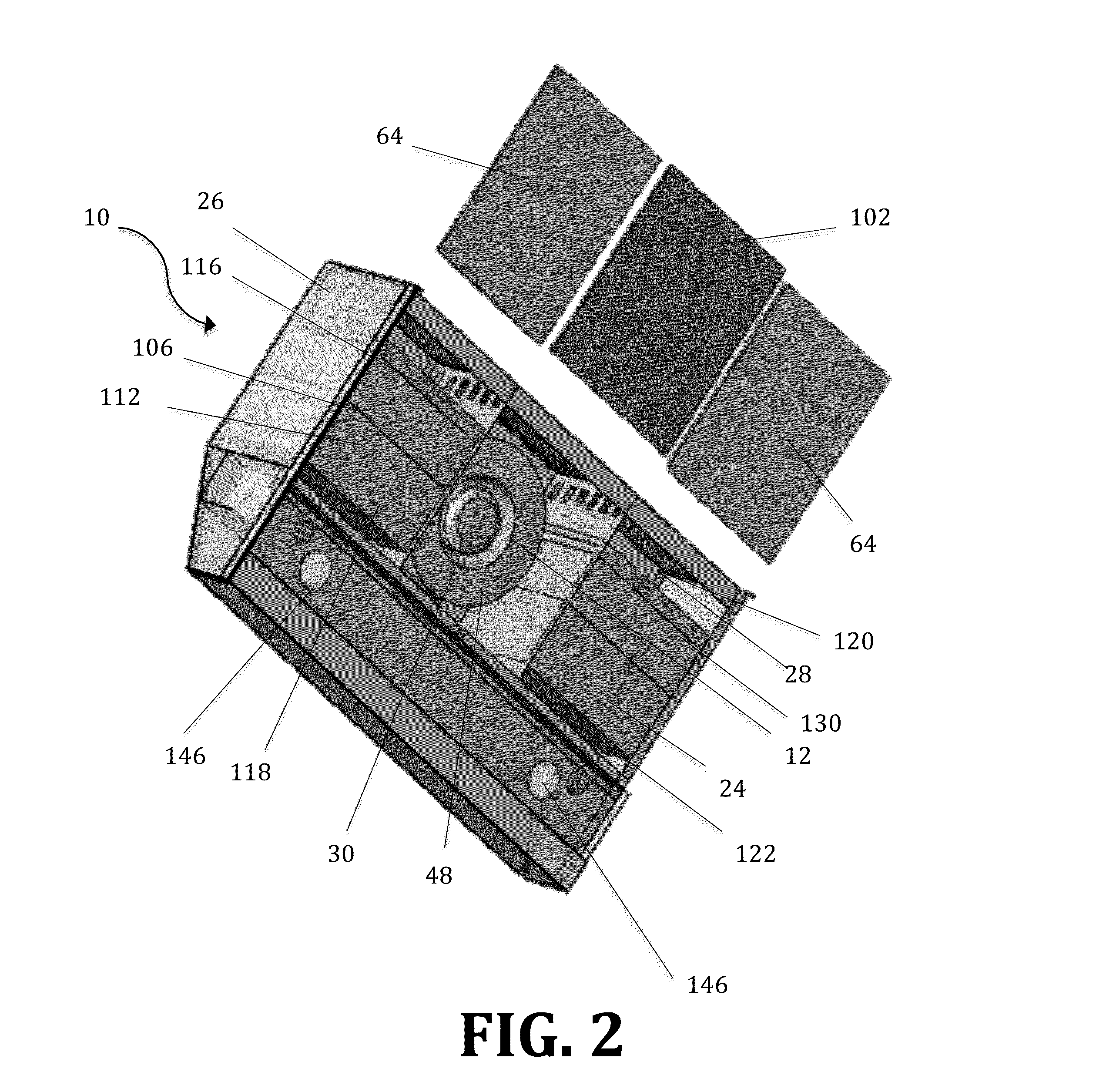
Cookery Air Purification and Exhaust System
InactiveUS20150226439A1Safely and efficiently removeAvoid operationLiquid surface applicatorsDomestic stoves or rangesPollutantUltra fine
An air filtration and exhaust system is described. The system comprises a microcontroller, a power supply, and a series of sensors that detect the presence of airborne contaminants such as ultra fine particles, smoke, natural gas and radon gas. In the presence of these airborne contaminants, the system is designed to inactivate and prevent operation of nearby food preparation appliances. Once these contaminants have been safely removed, the operation of these appliances is restored. In addition, the ventilation system may be equipped with a purification subassembly, which safely and efficiently removes such containments from the area. The system may also comprise an alarm that is activatable in the presence of these contaminants.
Owner:MIKULEC CONRAD S
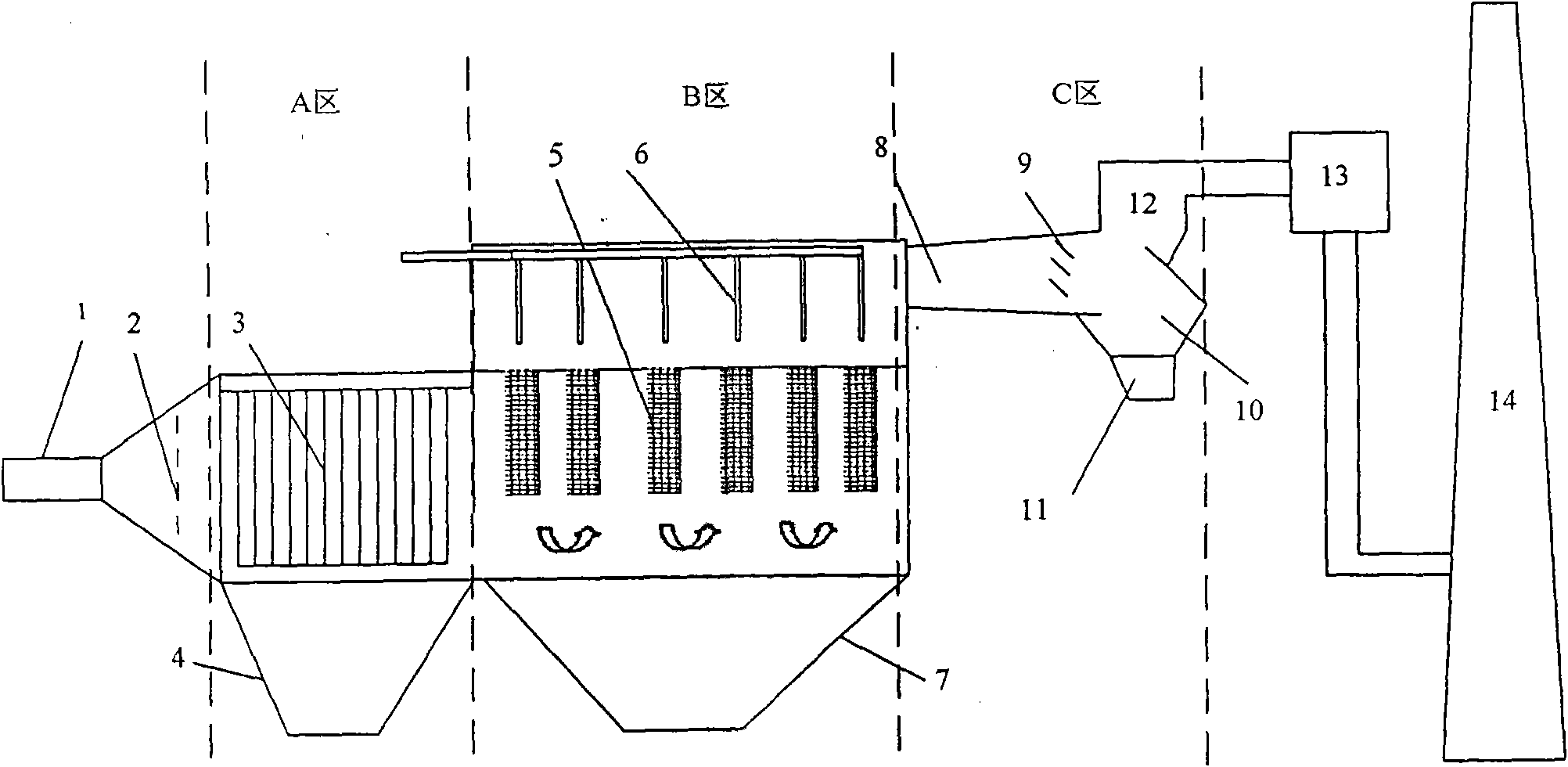
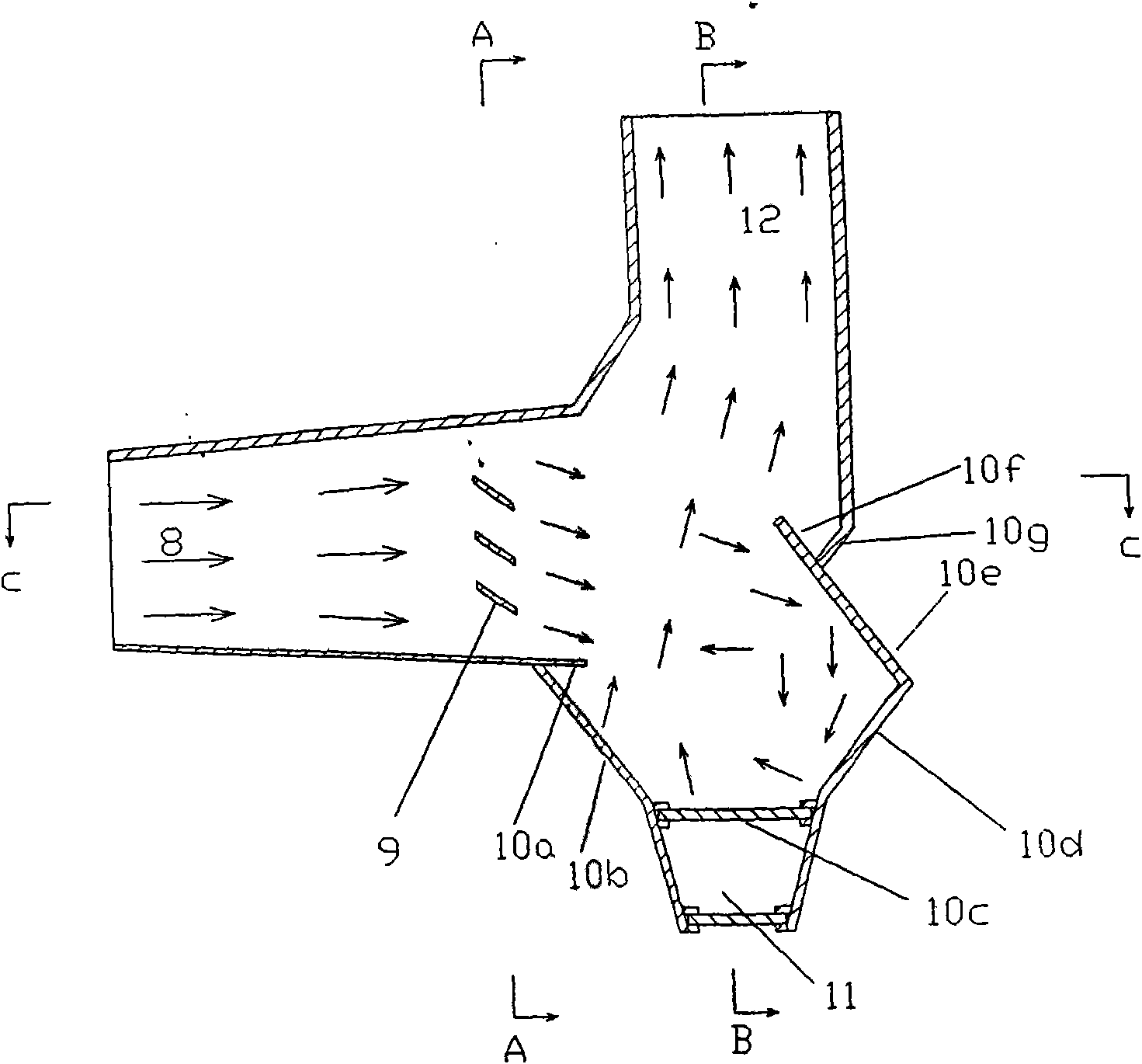
Ultrafine particle deduster
InactiveCN101664623AImprove adsorption capacityIncrease capture rateCombination devicesFiberIsosceles trapezoid
The invention relates to an ultrafine particle deduster used for treating industrial fumes. Specifically, an electro-bag compound deduster of the second-grade filtration mode is improved, an onflow vortex mechanism is arranged between the outlet of a filter bag dedusting mechanism and the inlet of an induced draft fan, and the onflow vortex mechanism comprises an onflow vortex chamber, a fume inlet tube and a fume outlet tube; the onflow vortex chamber is in bucket shape of which the cross section is an inversed isosceles trapezoid, and the bottom of the onflow vortex chamber is connected withan ash bucket chamber. Secondary treatment fume which contains finer particulate matters enters the fume inlet tube; airflow downwards deflects after passing through an air deflector and enters the onflow vortex chamber, and finer particulate matters and the inner wall of the onflow vortex chamber diffuse and collide to accelerate ultrafine particles to precipitate, thus separating ultrafine particulate matters from fume. The filter efficiency of the ultrafine particle of the invention can reach above 99.99%; under the condition that the resistance of the deduster body is smaller than 1000Pa(other conditions are same), an anode or cathode fiber filter bag of which the mesh aperture is 5 mu m is used, and the outlet concentration of the deduster is smaller than 15mg / Nm<3>.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH +1
Smoking article
A smoking article, such as a cigarette, includes a carbonaceous heat source. A mouth end piece segment is located at the mouth end of the smoking article, and the mouth end piece segment allows the smoking article to be placed in the mouth of the smoker to be drawn upon. The smoking article further incorporates an aerosol-generating segment located between the heat generation segment and the mouth end piece segment. The aerosol-generating segment incorporates an aerosol-forming material (e.g., glycerin and flavors). The heat generation segment is in a heat exchange relationship with the aerosol-generating region such that heat generated by the burning fuel element acts to volatilize aerosol-forming material for aerosol formation. The carbonaceous heat source is in intimate contact with coarse, fine or ultrafine particles of materials such as cerium oxide, or mixtures of cerium oxide and palladium chloride.
Owner:R J REYNOLDS TOBACCO COMPANY
High pressure media milling system and process of forming particles
InactiveUS20050258288A1Small particle sizeIncrease surface areaPowder deliveryCapsule deliveryDiagnostic agentEngineering
The present invention relates to a media mill system and a method using the same to produce fine and ultra-fine particles useful in diagnostic agents, pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, nutraceuticals and the like.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
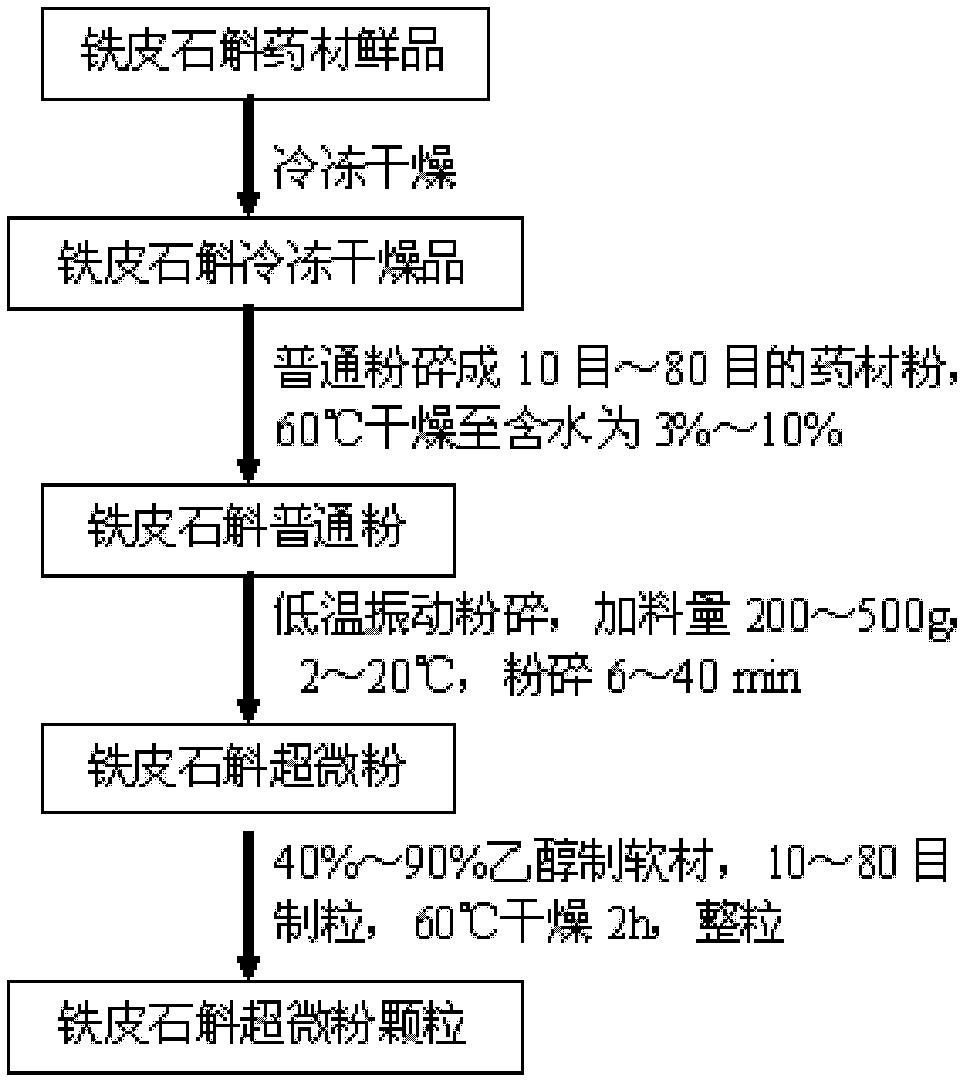
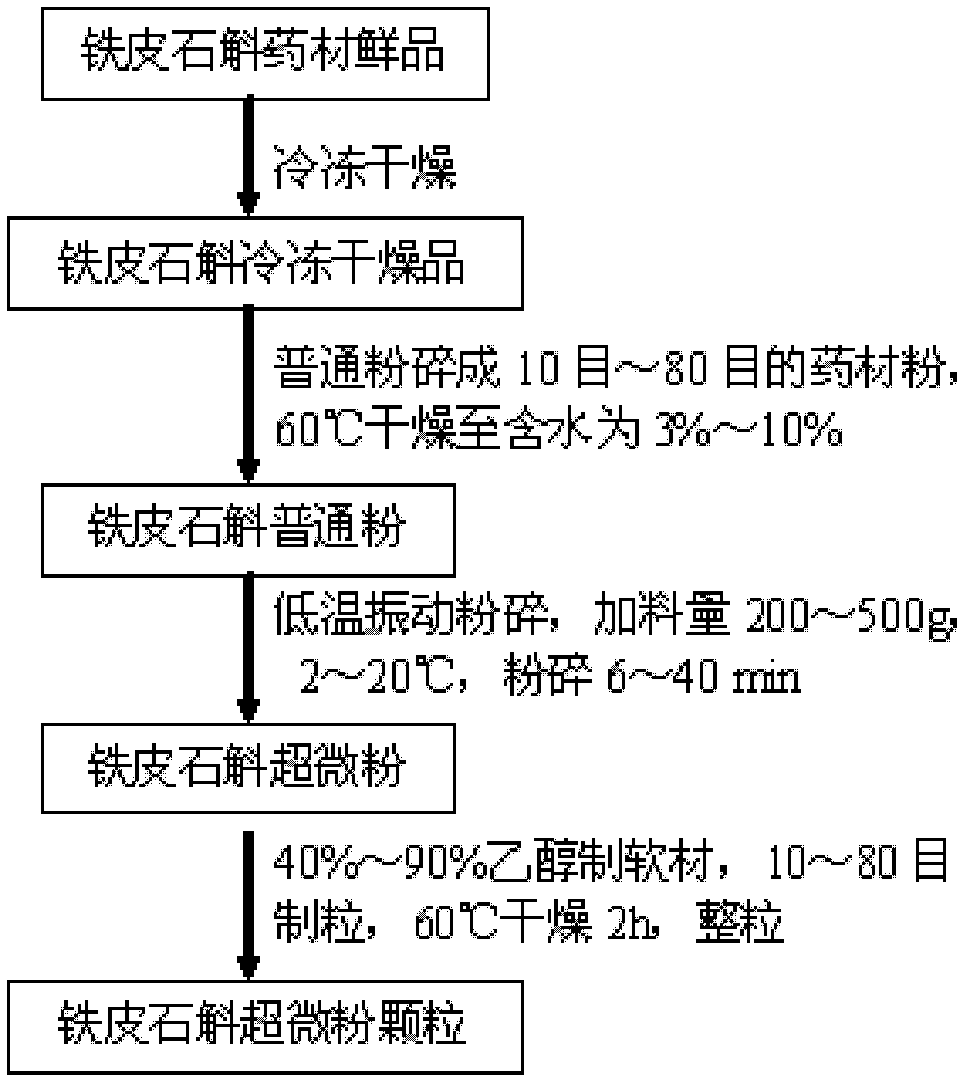
Processing method capable of reserving all components of dendrobium officinale
The invention provides a processing method capable of reserving all components of dendrobium candidum. The processing method comprises the following steps: (1) preliminarily processing the medicinal material; (2) freeze-drying in vacuum; (3) preparing common powder; (4) preparing ultrafine powder; and (5) preparing ultrafine particles, wherein the step of freeze-drying in vacuum comprises the following three processes: pre-freezing; sublimation drying; and desorption drying. The product produced by the method has the advantages of fresh color, aromatic flavor and fully reserved nutrient components without loss, and is convenient to serve; meanwhile, the product is thoroughly dewatered, thus being convenient for long-term preservation, reprocessing and transportation at normal temperature.
Owner:蔡光先 +3
Filter Medium, Process for Producing the Same, Method of Use Thereof, and Filter Unit
InactiveUS20080307971A1Increase pressure dropIncrease pressureCombination devicesDispersed particle filtrationFiberElectrospinning
The present invention provides a filter medium reducing an increase in pressure drop while in use even in an environment where ultrafine particles form a large proportion of the particles to be collected. The filter medium includes a porous polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) membrane, an air-permeable supporting member and a web layer made of polymeric fibers formed by electrospinning (charge induction spinning, electrostatic spinning). The filter medium of the present invention may include an air-permeable adhesive layer adjacent to the web layer.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
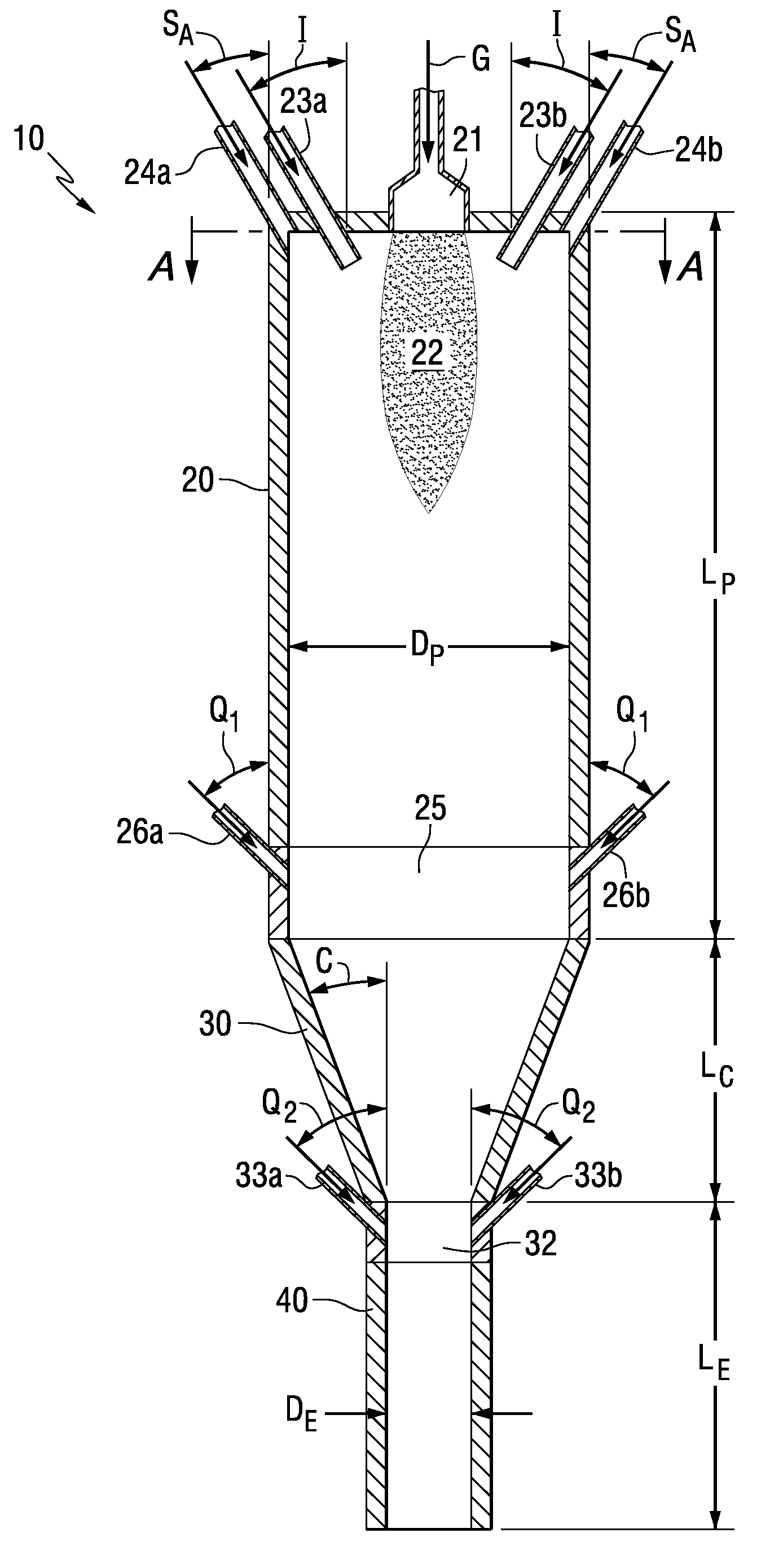
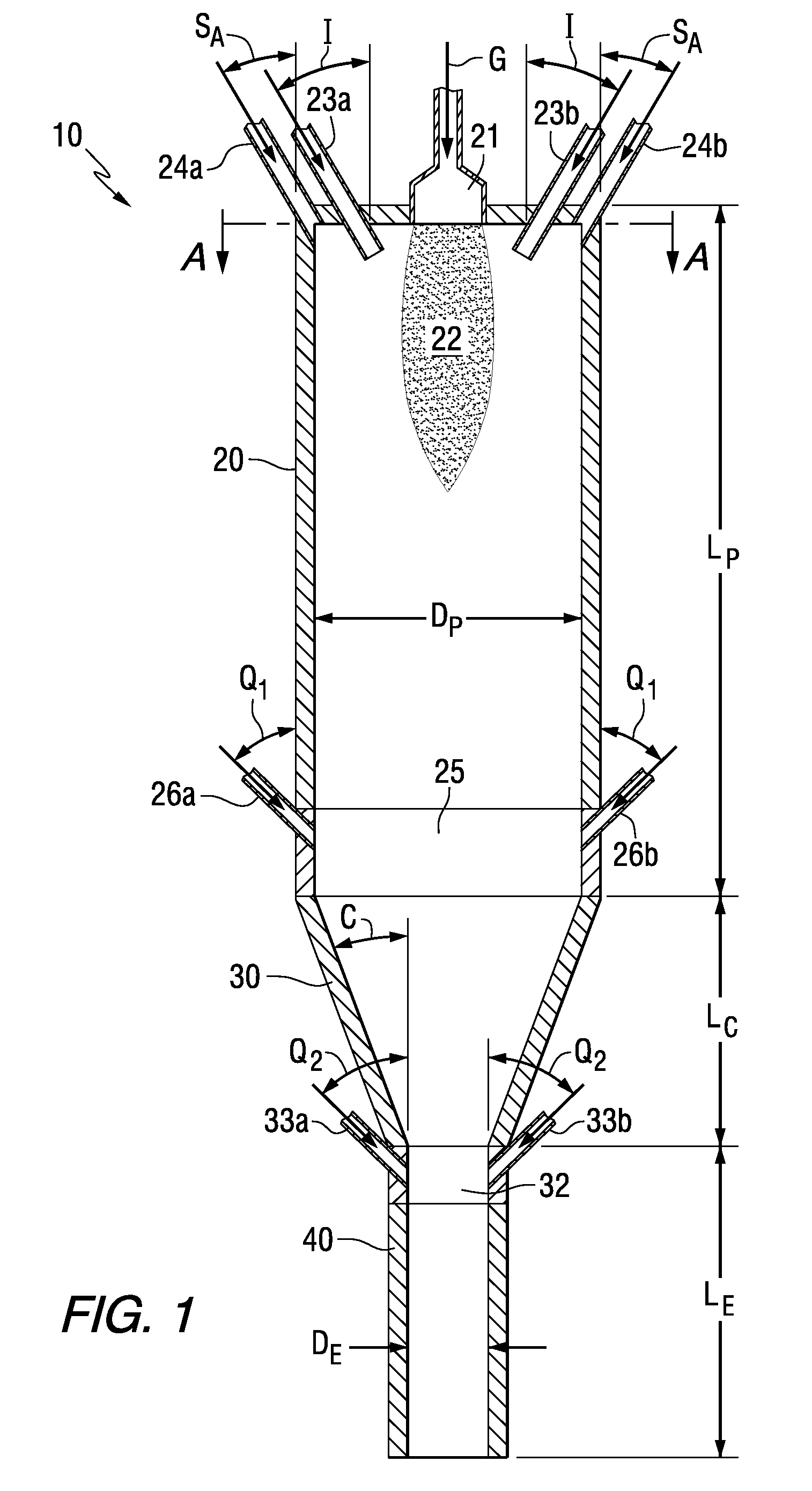
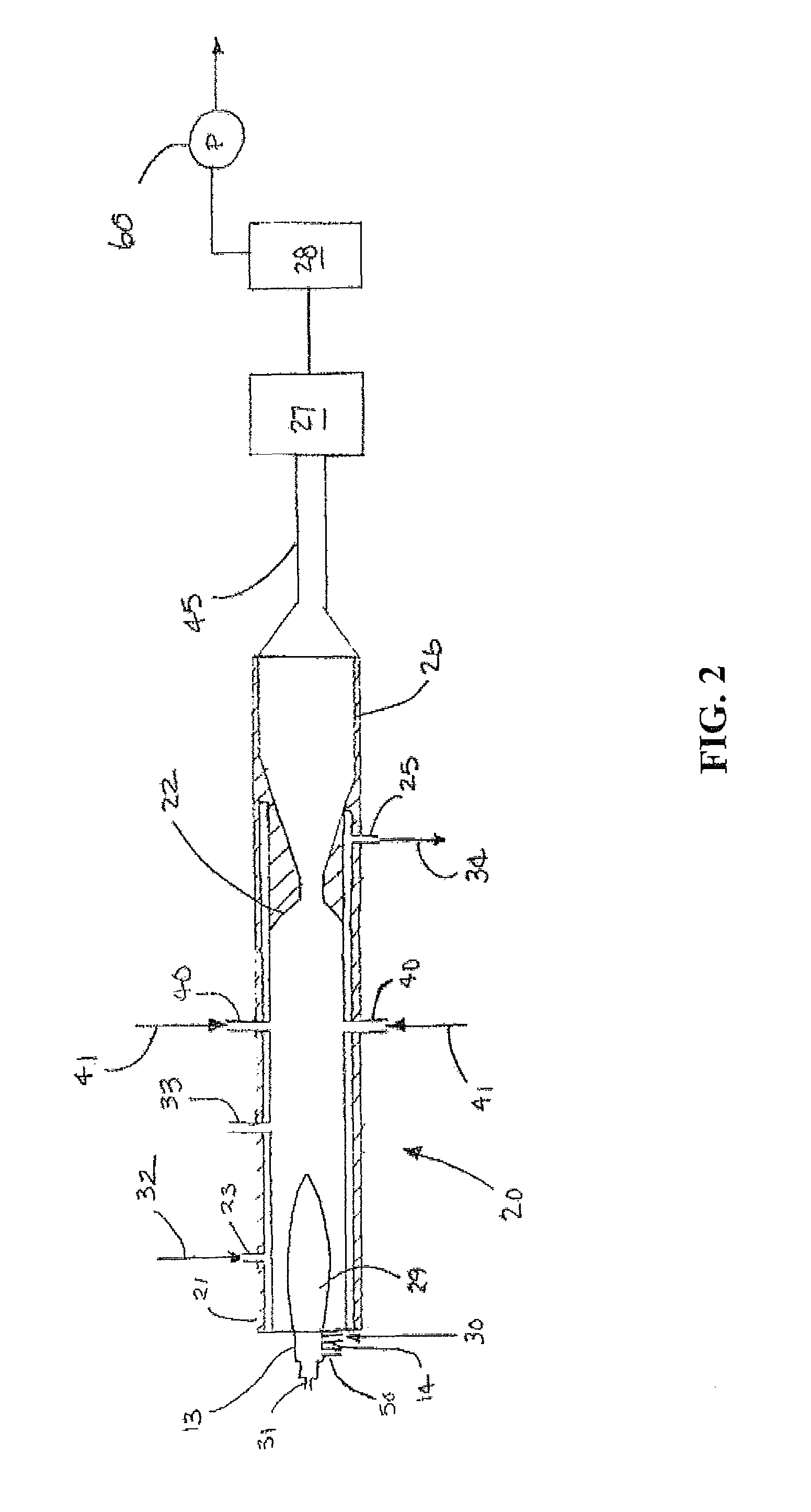
Production of Ultrafine Particles in a Plasma System Having Controlled Pressure Zones
InactiveUS20100314788A1Constant pressureMaterial granulation and coatingMaterial nanotechnologyEngineeringPlasma chamber
A system and method for making ultrafine particles are disclosed. A high temperature plasma is generated at an inlet end of a plasma chamber into which precursor materials are introduced. A converging member is located adjacent an outlet end of the plasma chamber. During operation, a substantially constant pressure and / or material flow pattern is maintained to reduce or eliminate fouling of the system.
Owner:PPG IND OHIO INC
Photocatalyst containing metallic ultrafine particles and process for producing said photocatalyst
InactiveUS7759281B2Improve dispersion stabilityCatalyst activation/preparationMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsHigh concentrationDispersion stability
There is disclosed a photocatalyst which comprises a substrate having a photocatalytic function and metallic nanocolloid particles that are supported on the substrate by the use of a metallic nanocolloid liquid substantially free from a protective colloid formation agent. A highly active photocatalyst containing metallic ultrafine particles is provided by bringing a substrate such as fine particles having a photocatalytic function into contact with a metallic nanocolloid liquid which is substantially free from a protective colloid formation agent, and which has favorable dispersion stability even if containing metallic nanocolloid particles in a relatively high concentration. Accordingly the photocatalyst containing metallic ultrafine particles can be produced at a low cost without being restricted on the place of production.
Owner:NIPPON SHEET GLASS CO LTD
Method for preparing charcoal nanometer zero-valent iron compound with one-step method
InactiveCN108854950AGood value for moneySmall environmental footprintOther chemical processesWater contaminantsIron saltsAntibiotic Y
The invention discloses a method for preparing a charcoal nanometer zero-valent iron compound with a one-step method. The method comprises the following steps of after adsorbing water-soluble iron salt with biomass, performing heating pyrolysis by virtue of microwaves under the anaerobic condition; and reducing iron ions into zero-valent iron by taking pyrolysis gas in the pyrolysis process as a reducing agent, adsorbing zero-valent iron ultrafine particles in situ by taking charcoal produced in the pyrolysis process as a porous adsorption carrier, and synthesizing the charcoal nanometer zero-valent iron compound with the one-step method and low cost. Charcoal zero-valent iron provided by the invention has very strong adsorption performance and the ability of reducing and degrading organicchloride, bisphenol A and antibiotics, has obvious adsorption and passivation effects to heavy metals and can provide an effective repair material to removal or passivation of organic chloride residues, bisphenol A, the antibiotics and heavy metal residues which are difficultly degraded in water body and soil.
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV
Hard coat film, antireflection hard coat film, optical element and image display
InactiveUS7569269B2High hardnessCurl suppressionSynthetic resin layered productsCellulosic plastic layered productsPolymer scienceCarbamate
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
Ink-jet recording medium and method for production thereof
InactiveUS20040096598A1Less in surface wavinessAttractive appearanceDuplicating/marking methodsCoatingsAlkaline earth metalAdhesive
The object of the present invention is to provide an ink jet recording medium which is high in gloss and ink absorption and excellent in image colorfulness and adhesion of the coats and a method for producing the same. According to the present invention, there is provided an ink jet recording medium which comprises a support, an undercoat layer containing a salt of an alkaline earth metal and an adhesive provided on the support and an ink-receiving layer provided by coating a coating solution containing inorganic ultrafine particles on the undercoat layer. The undercoat layer preferably contains the adhesive in an amount of 0.05-0.8 time the amount of the salt of alkaline earth metal in weight ratio. Furthermore, the undercoat layer preferably contains an organic pigment. The alkaline earth metal is preferably calcium or magnesium, and more preferably the salt of the alkaline earth metal is a carbonate. The inorganic ultrafine particles are of an amorphous synthetic silica produced by a gas phase method or an alumina compound. There is further provided a method for producing the ink jet recording medium according to which the ink-receiving layer is provided after the undercoat layer is coated and subjected to a hot calendering treatment.
Owner:MITSUBISHI PAPER MILLS LTD
Thermal transfer sheet and protective layer transfer sheet
ActiveCN101048290AGood transferabilityImprove antistatic performanceInk ribbonsThermographyHigh densityPlasticizer
The invention provides a thermal transfer sheet and a protective layer transfer sheet. It is intended to provide a sheet of excellent transfer performance, in particular, a thermal transfer sheet that excels in transfer sensitivity and adhesion between base material and dye layer and that can be used in high-speed photographic printing with high transfer sensitivity, being capable of providing a photographic print of high density and high clearness, and a protective layer transfer sheet that excels in transfer performance, being markedly low in the generation of static electricity at the time of transfer. Further, it is intended to provide a photographic print that excels in antistatic performance, plasticizer resistance and transparency. There is provided a sheet with a base material, in particular, a thermal transfer sheet (I) comprising a laminate of, sequentially arranged, a base material, an underlayer and a dye layer, or a protective layer transfer sheet (II) comprising a base material and, detachably superimposed on at least part of the surface thereof, a protection transfer laminate including a conductive layer, characterized in that the underlayer and conductive layer are each one produced using colloidal inorganic pigment ultrafine particles.
Owner:DAI NIPPON PRINTING CO LTD
Antireflection film containing ultrafine particles, polarizing plate and liquid crystal display device
InactiveUS6033743AGood dispersionAvoid whiteningLiquid crystal compositionsTelevision system detailsMeth-Liquid-crystal display
An antireflection film, containing ultrafine particles, formed of a resin composition having excellent dispersibility of ultrafine particles in a binder resin and capable of preventing whitening, a polarizing plate, and a liquid crystal display device are provided. At least one resin layer is provided on a transparent substrate film directly or through other layer(s), and at least one of the resin layer has a controlled refractive index and is formed of a resin composition containing ultrafine particles. The outermost layer has a lower refractive index than an underlying layer in direct contact therewith. The resin composition contains a carboxyl-containing (meth)acrylate as part or the whole of a binder resin component. A polyfunctional acrylate having in its molecule three or more acryloyl groups may be added to the binder resin component in order to further enhance the properties of the hard coating.
Owner:DAI NIPPON PRINTING CO LTD
Polymer coating/encapsulation of nanoparticles using a supercritical antisolvent process
Owner:NEW JERSEY INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
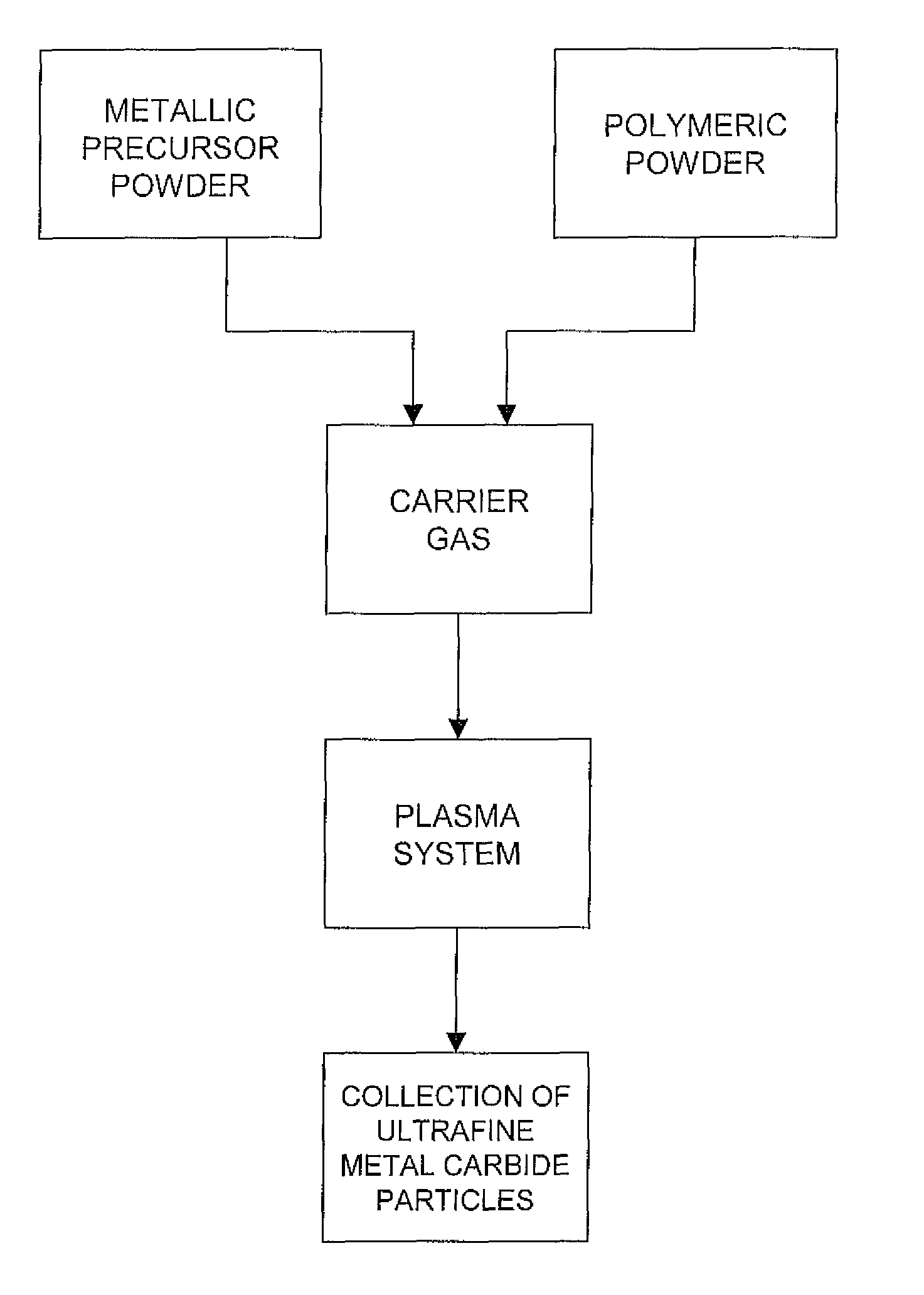
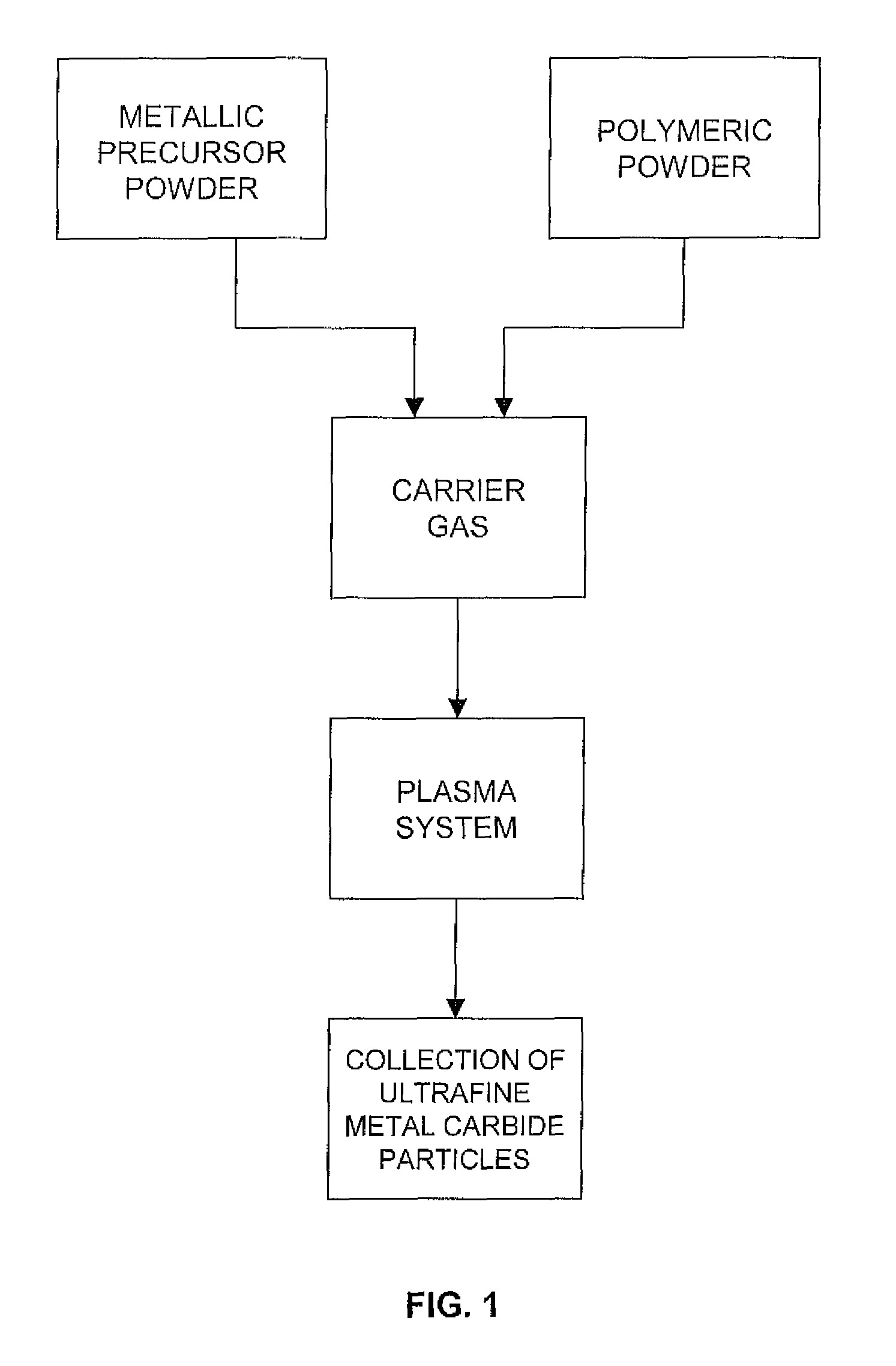
Production of ultrafine metal carbide particles utilizing polymeric feed materials
The production of ultrafine metal carbide powders from polymeric powder and metallic precursor powder starting materials is disclosed. In certain embodiments, the polymeric powder may comprise polypropylene, polyethylene, polystyrene, polyester, polybutylene, nylon, polymethylpentene and the like. The metal precursor powder may comprise pure metals, metal alloys, intermetallics and / or metal-containing compounds such as metal oxides and nitrides. In one embodiment, the metal precursor powder comprises a silicon-containing material, and the ultrafine powders comprise SiC. The polymeric and metal precursor powders are fed together or separately to a plasma system where the feed materials react to form metal carbides in the form of ultrafine particles.
Owner:PPG IND OHIO INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com