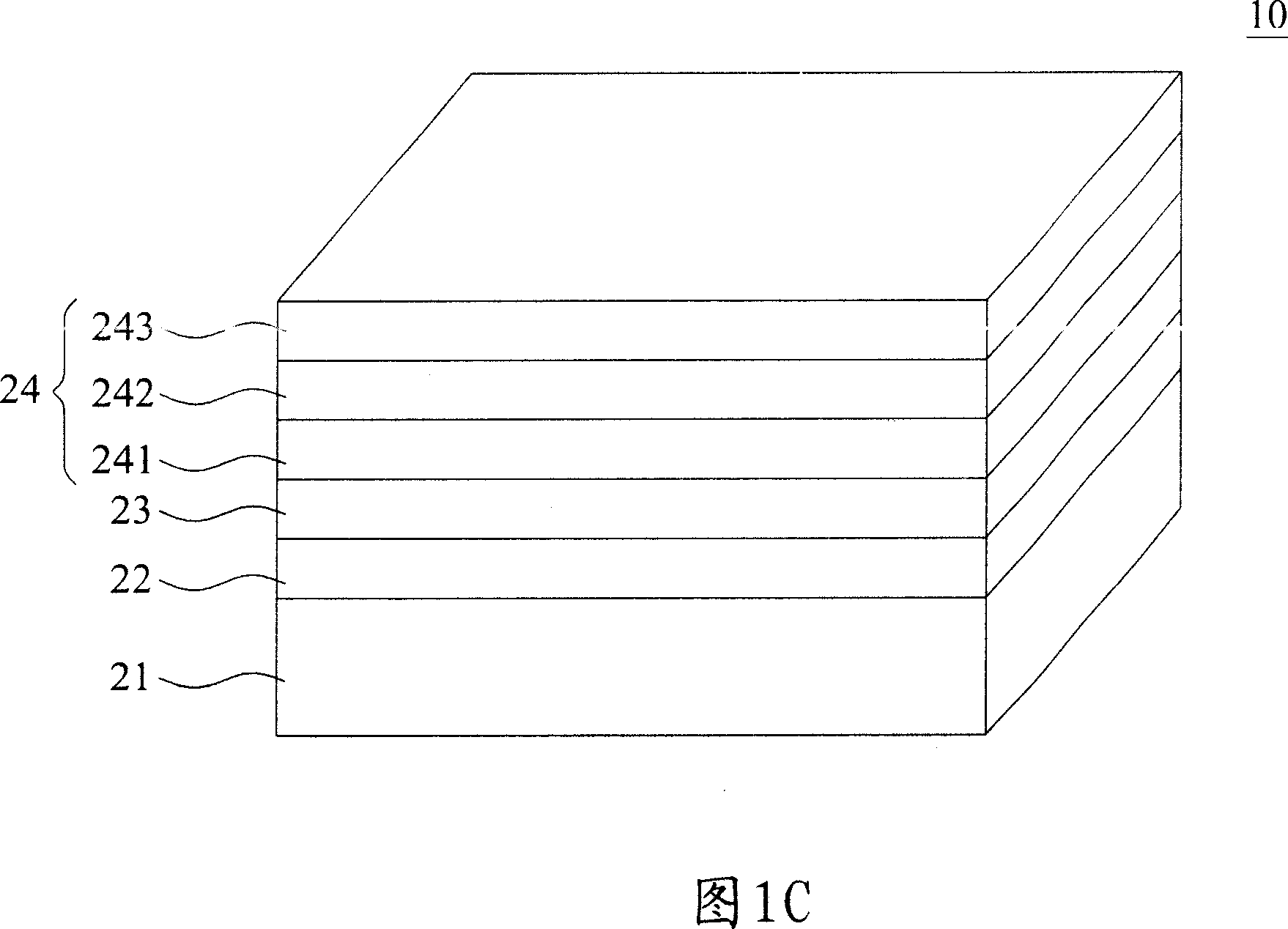
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1033results about How to "Enhance the outstanding effect" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
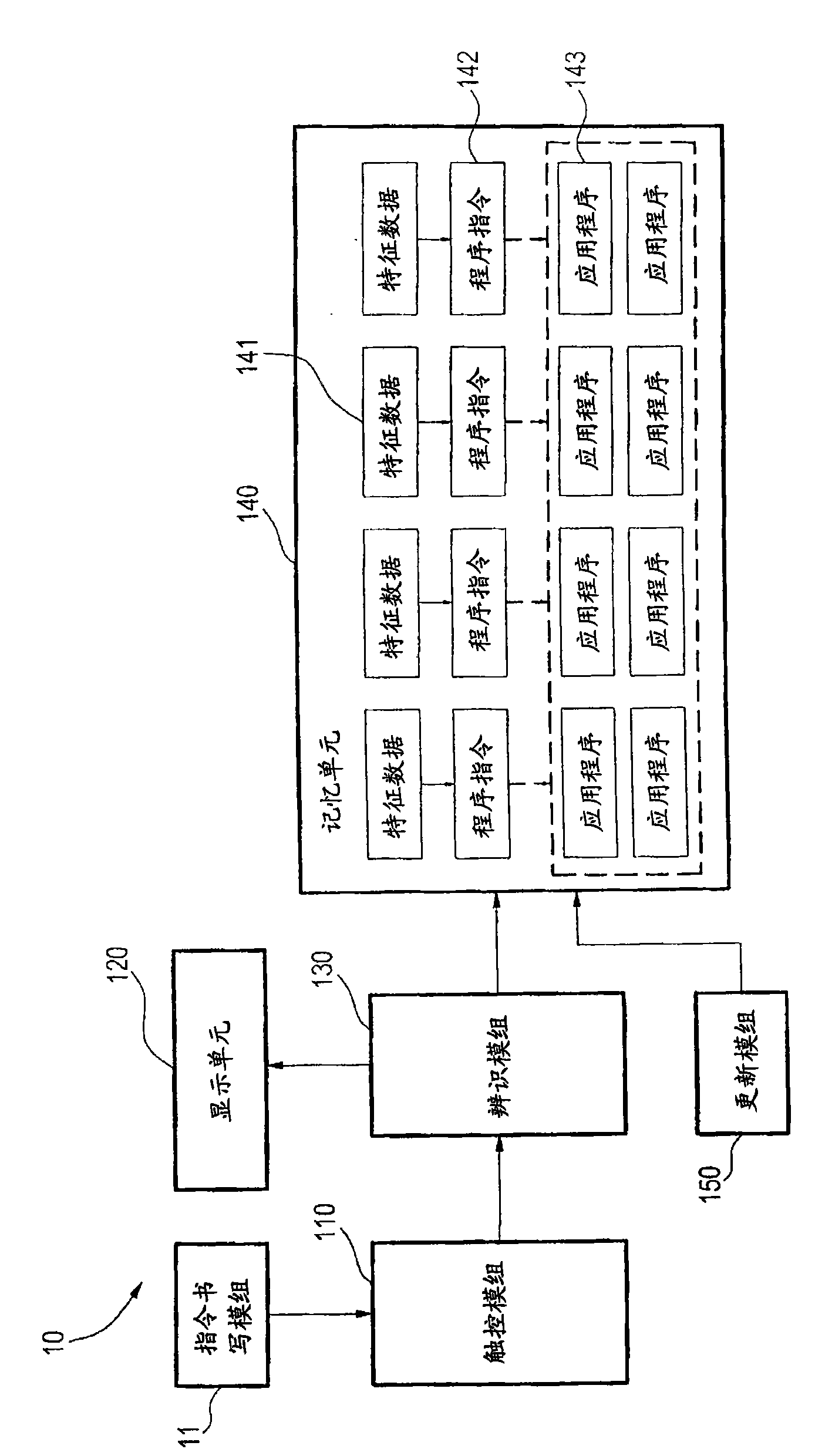
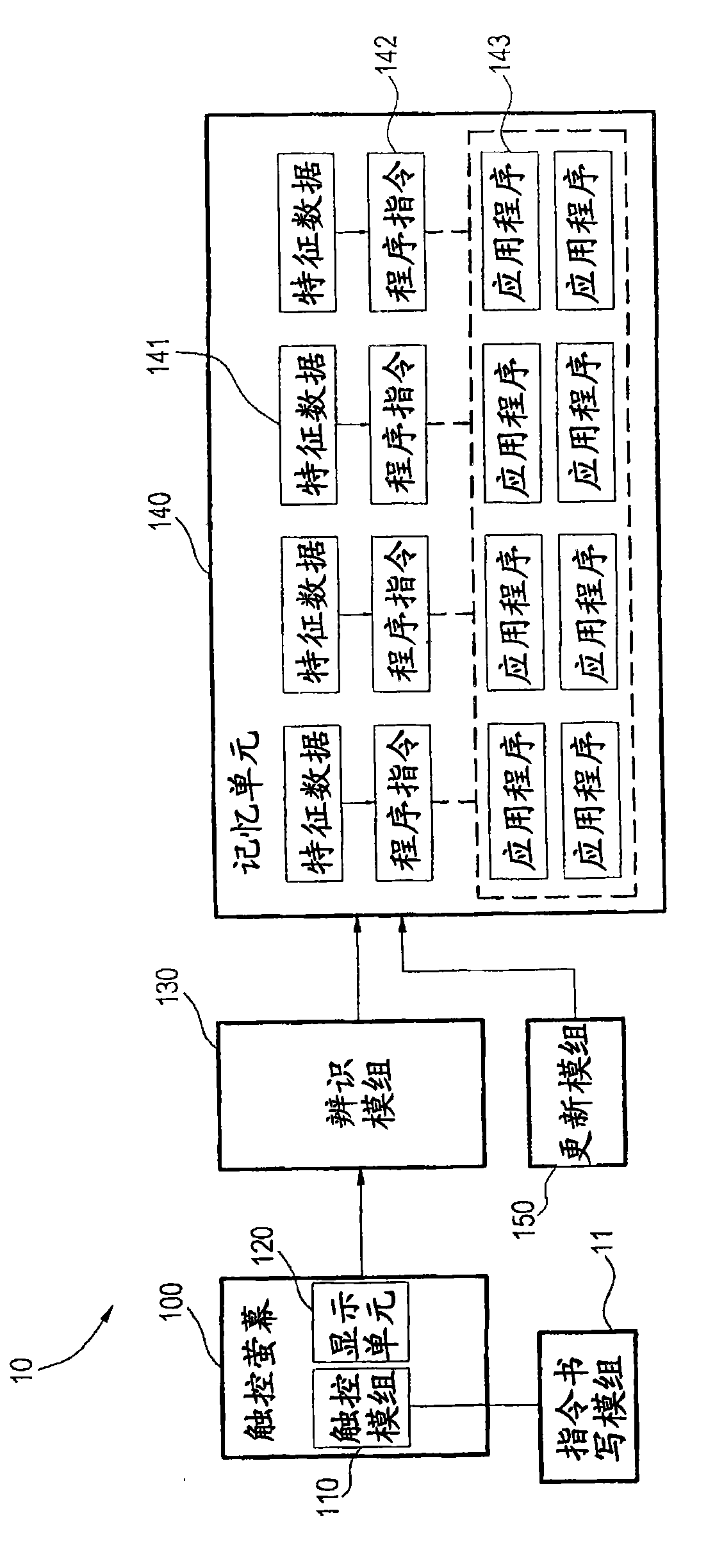
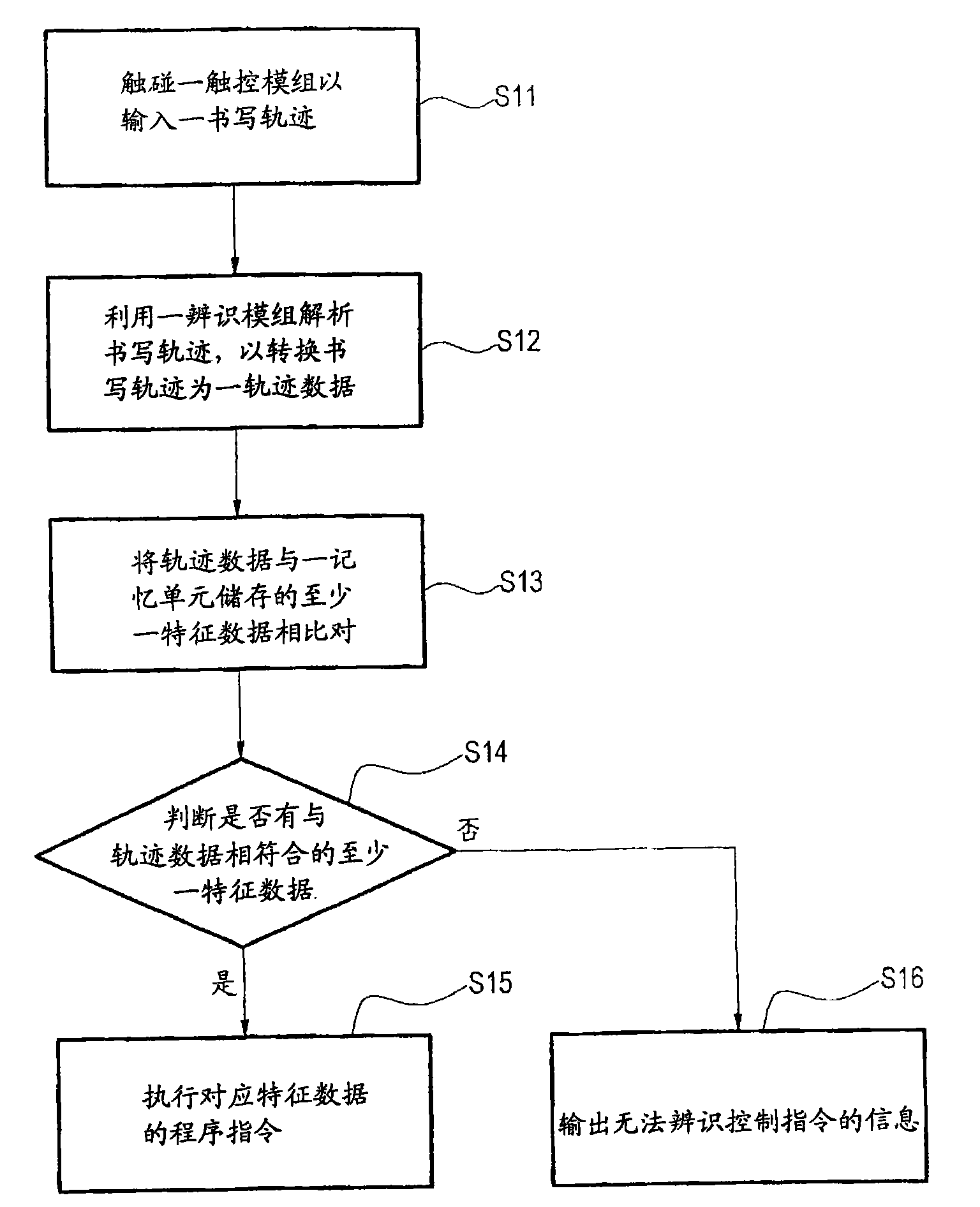
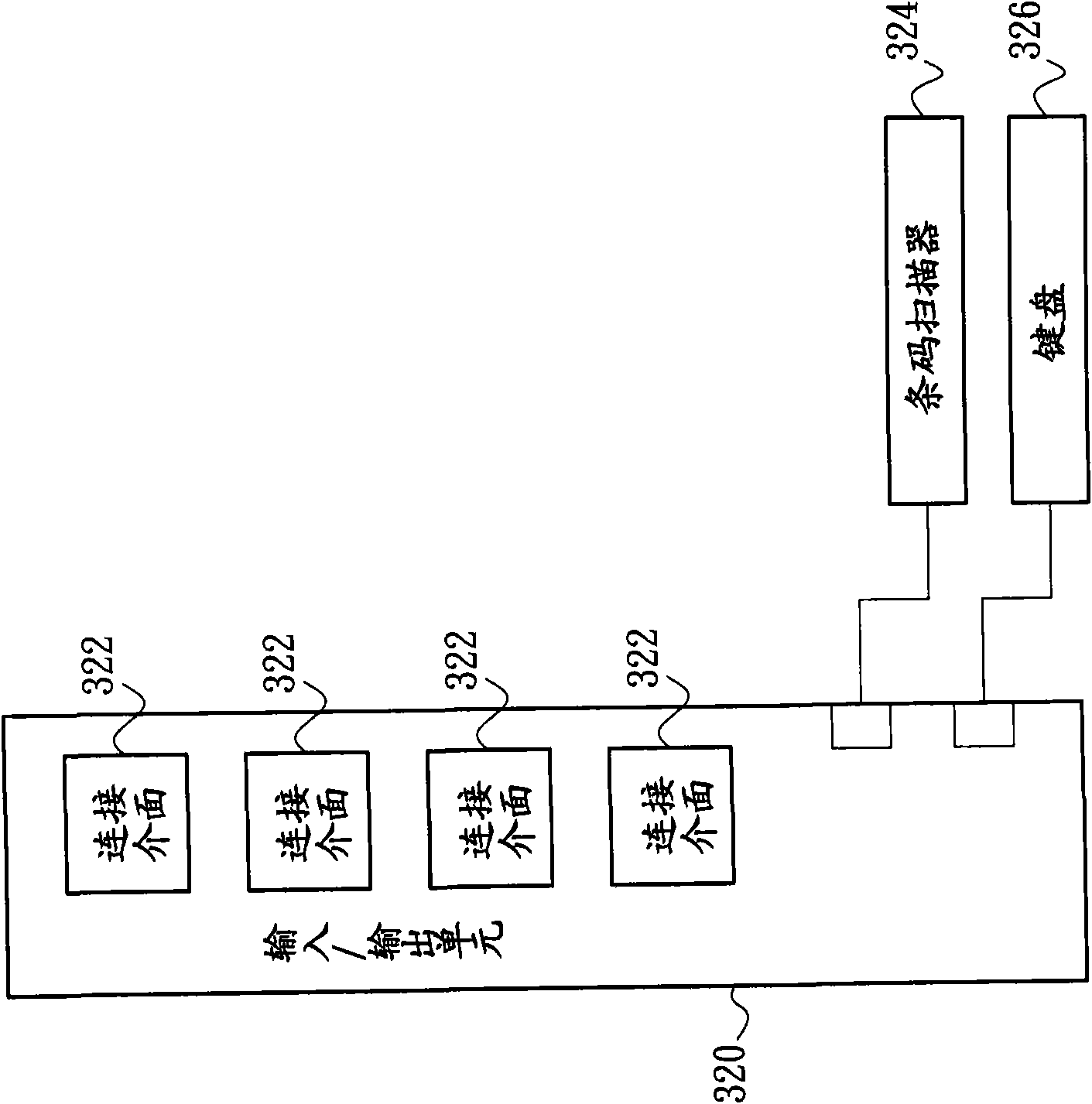
Method for inputting control command by handheld device and handheld device for inputting control command
InactiveCN101551720AShorten the timeImprove practicalityInput/output processes for data processingProgram instructionUser input
The invention relates to a method for inputting a control command by a handheld device and the handheld device for inputting the control command. The handheld device comprises a storage unit, a touch module and an identity module. The method comprises the steps: the touch module is touched to input a writing track; the writing track is resolved by using the identity module to convert the writing track into track data; the track data is compared with at least one feature data stored by the storage unit; whether at least one feature data conforms to the track data is judged to decide whether a program command corresponding to the feature data is executed, therefore, when a user inputs a writing track, the corresponding application program and the specific action thereof are started by the handheld device to reduce the time for searching the application program, and consequently, the practicability of the handheld device for the user can be improved.
Owner:INVENTEC APPLIANCES CORP
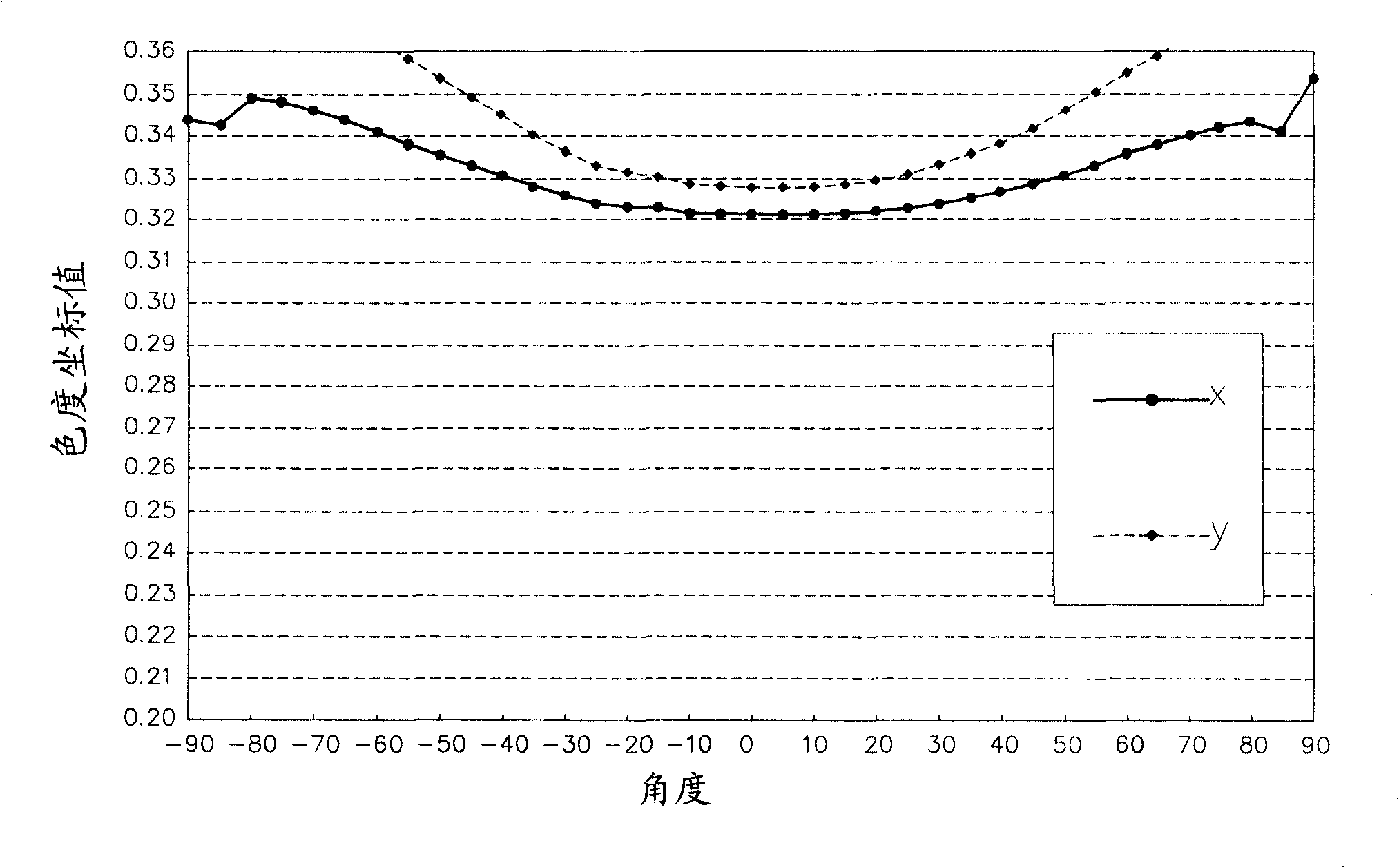
White light LED
InactiveCN101262032AImprove light color differenceIncrease path lengthSemiconductor devicesPath lengthFluorescence
The invention relates to a white light emitting diode which comprises a base, light emitting crystal grains arranged on the base, a first fluorescent layer which is arranged on the base and covers the light emitting crystal grains and a second fluorescent layer which is arranged on the first fluorescent layer and has a top area smaller than the top area of the first fluorescent layer; the light emitting crystal grains are positioned within orthographic projection range below the second fluorescent layer so as to increase the path length of the fluorescent layer that the forward light of the light emitting crystal grains passes through and improve the color evenness of the white light of the white light emitting diode.
Owner:LITE ON OPTO TECH (CHANGZHOU) CO LTD +1
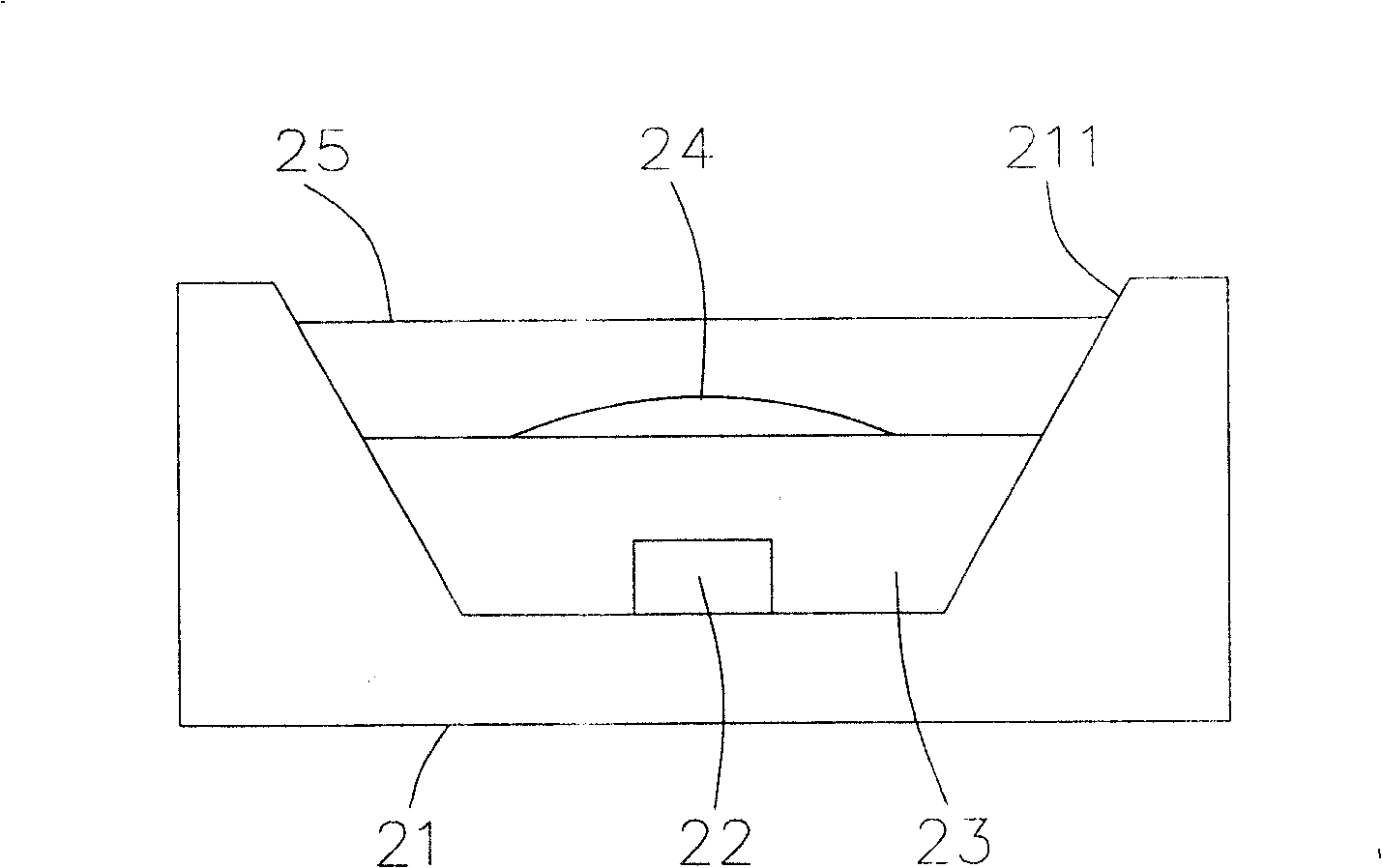
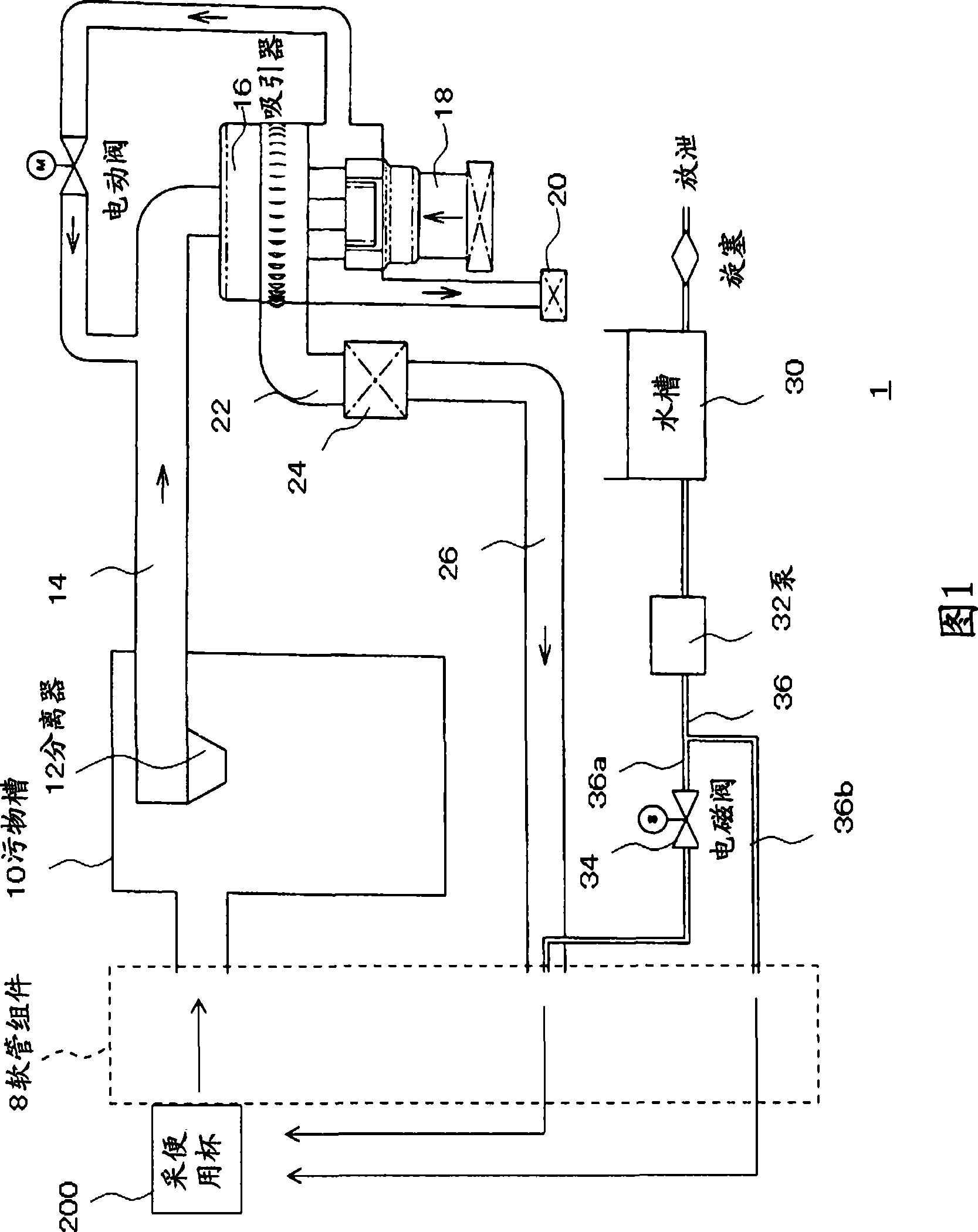
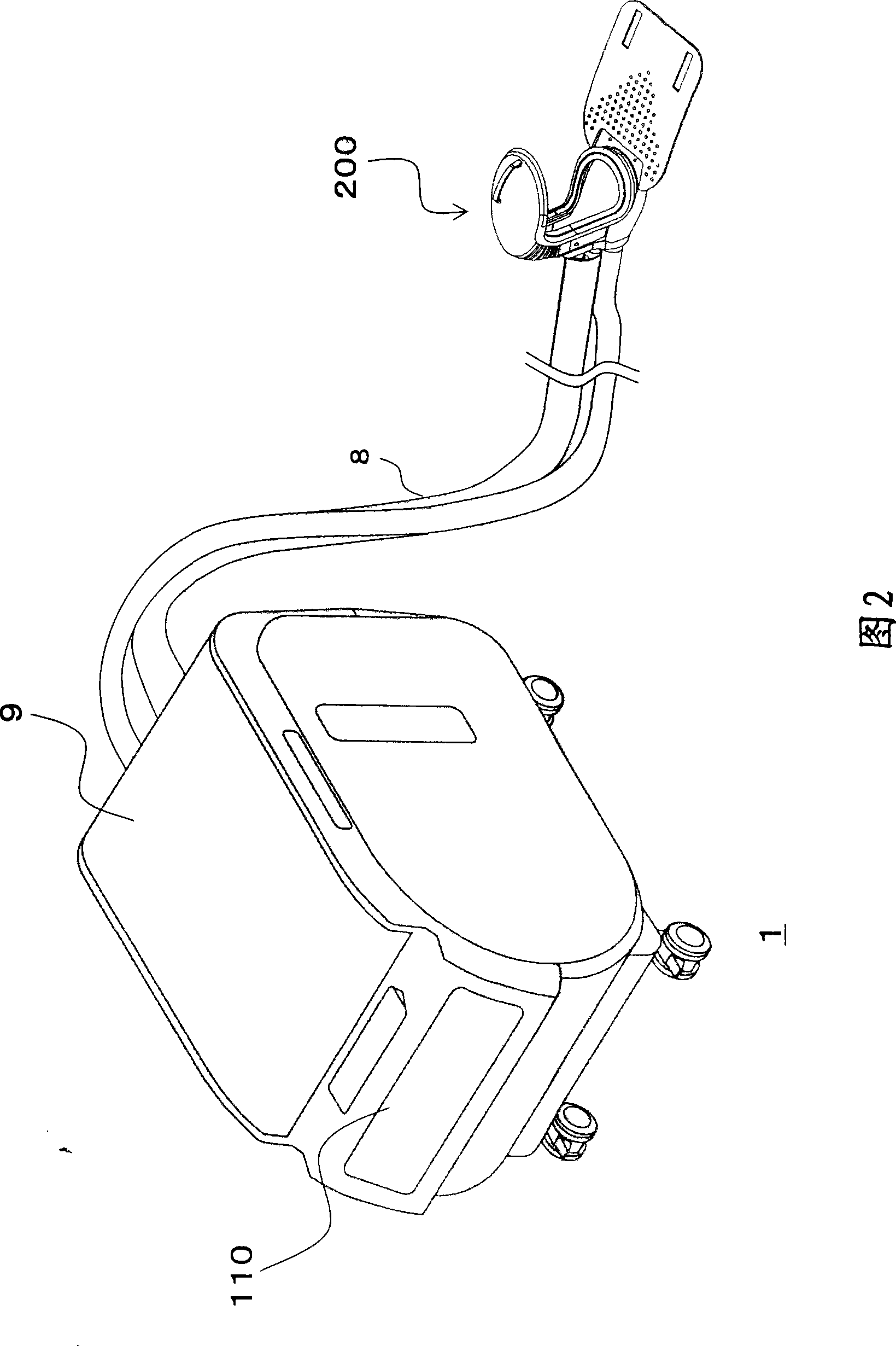
Waste treatment device
InactiveCN101396319APrevent leakageEnhance the outstanding effectMedical transportElastic componentWaste treatment
The invention is related to an excretion processing device for caring capable of performing washing of a caregiver respectively according to shapes of excrement and urine, and an excretion vessel capable of preventing excretion and the like leaking from an edge section of an opening section. The excretion processing device for caring includes a suction connector, an excretion reservoir, a water tank for accommodating the water, injection means and injection control means; the excretion vessel includes a cup section and an elastic component, wherein the cup section is provided with the opening section that surrounds anus and pubes and of which the edge part is a bending saddle shape; and the elastic component provided along the edge section of the opening section includes an flange projecting towards inner side of the opening section.
Owner:HEARTFUL CORP
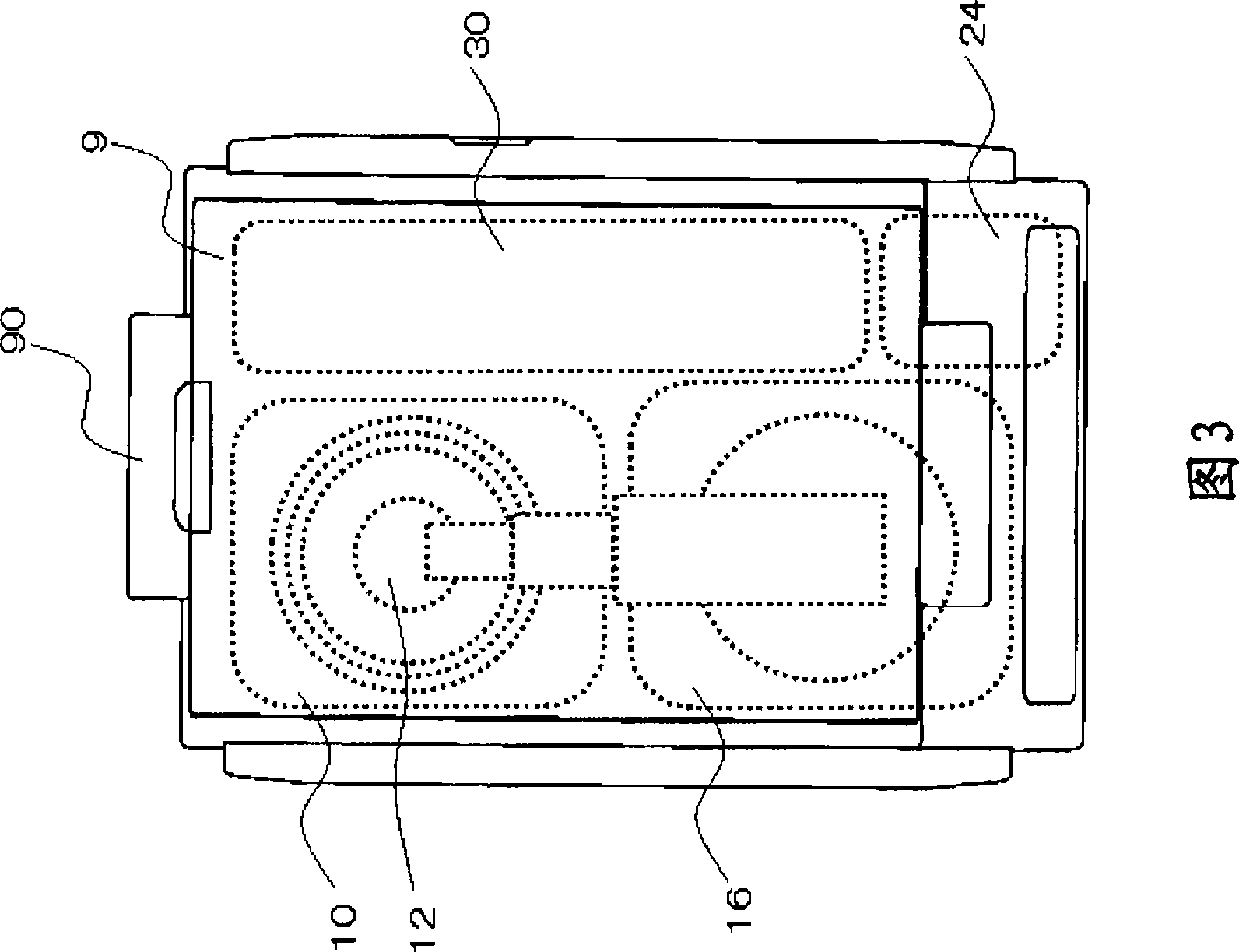
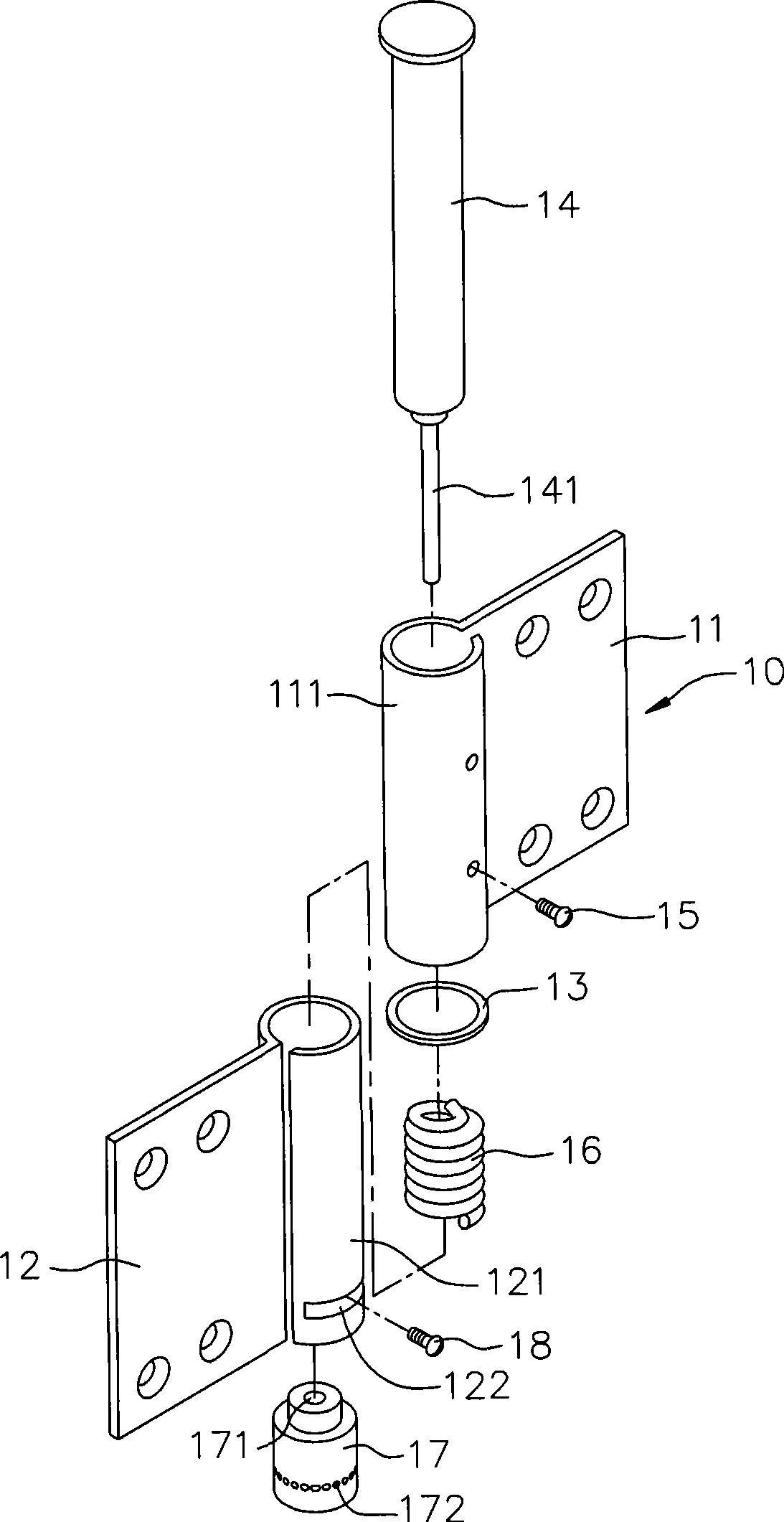
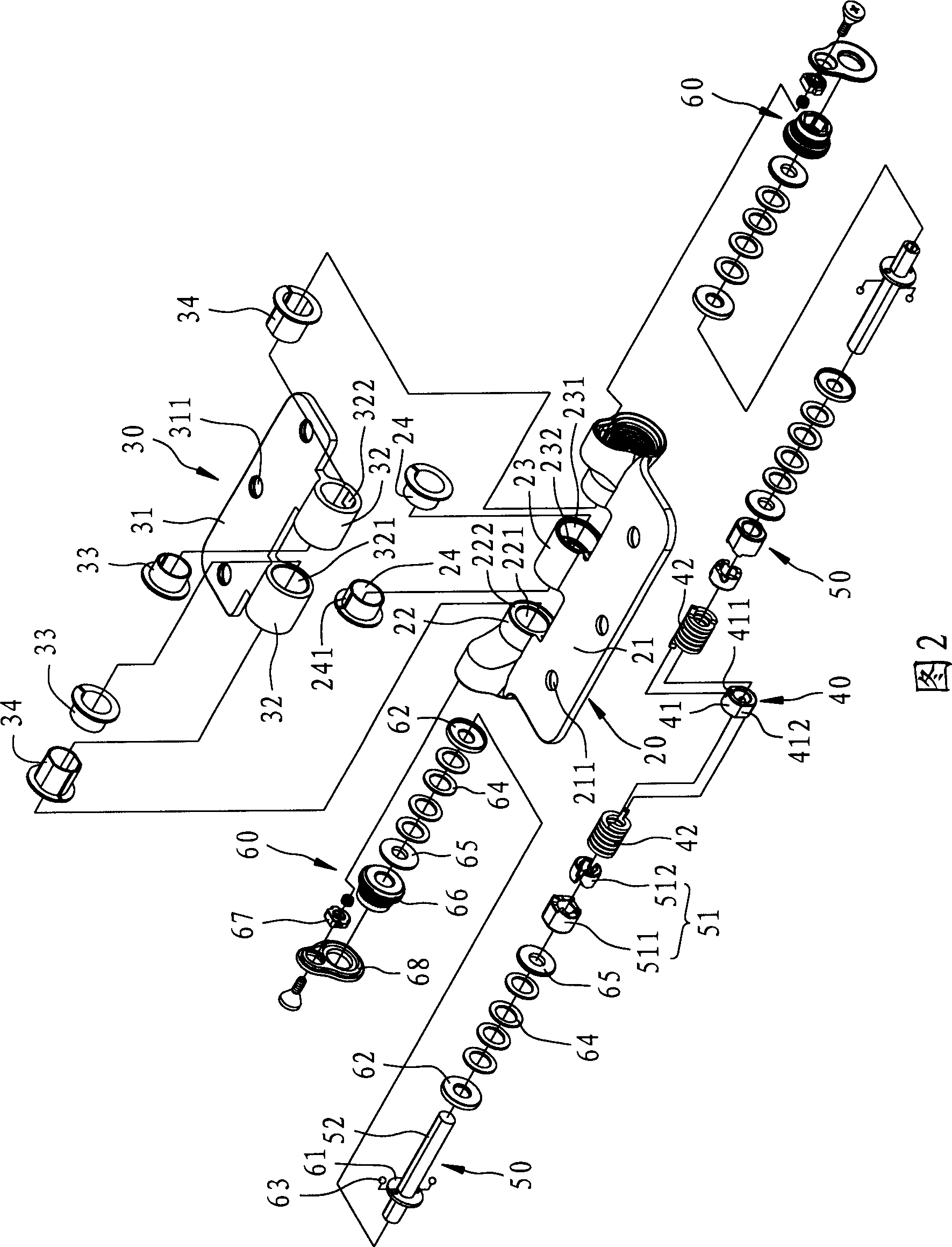
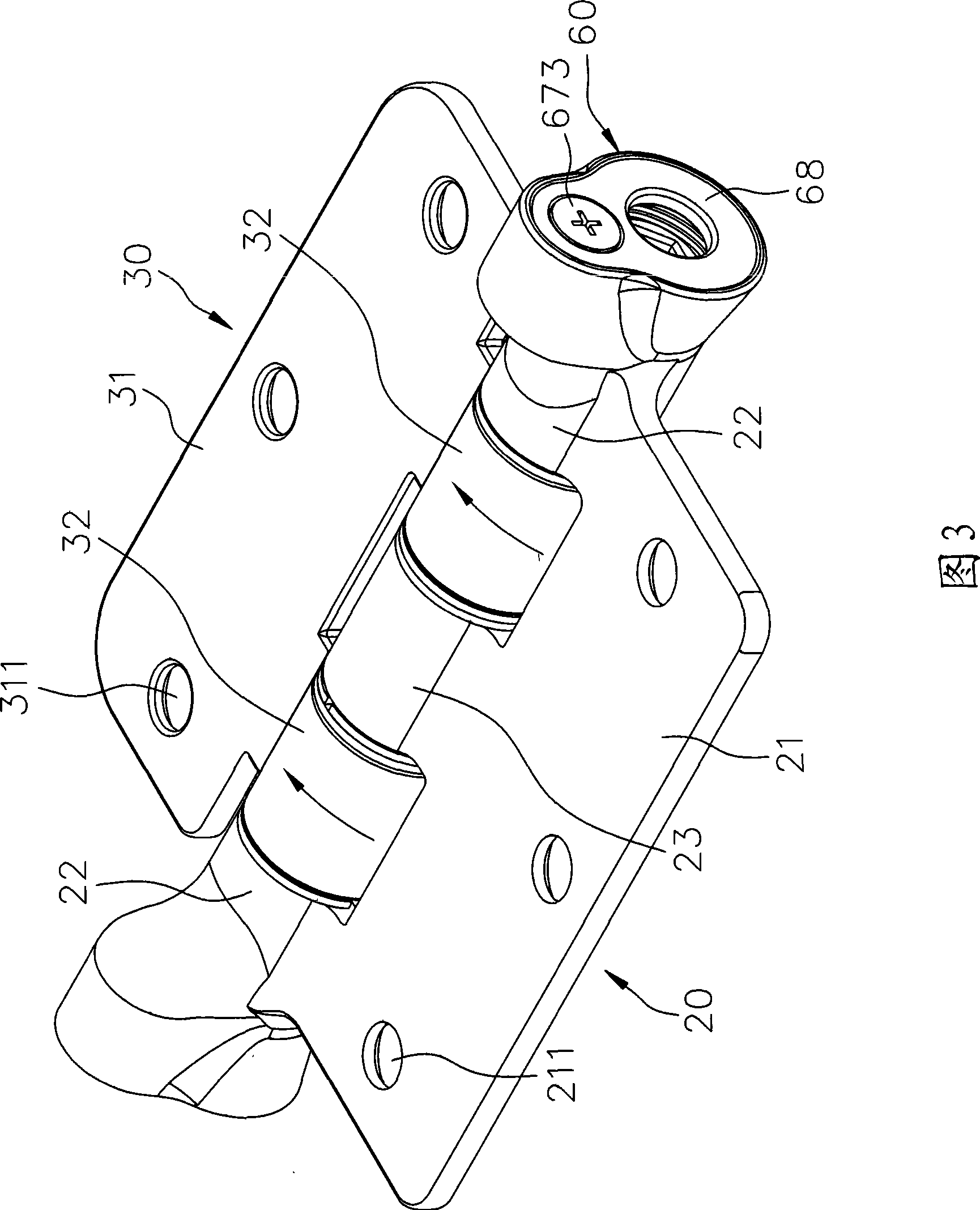
Pivot hinge device with torsion adjustable
The invention relates to a door pivot hinge device capable of adjusting a torque force. The door pivot hinge device comprises a first base plate unit, a second base plate unit, a torque force providing unit, a torque force adjusting unit and a speed adjusting unit. The first base plate unit and the second base plate unit are embedded into each other and can revolve. The torque force providing unit has a torsion spring capable of leading a door sheet to produce a torque force. The torque force adjusting unit has a mandrel and a single cam set, wherein the mandrel can drive the torsion spring through the single cam set so as to adjust the torque force. The speed adjusting unit has a brake disc, a plurality of elastic elements and an adjusting element, wherein the adjusting element can pressthe elastic element so as to adjust the rotation speed. Therefore, the door pivot hinge device has the adjustable torque force, and smooth operation for door opening and closing , and is suitable forhigh load.
Owner:陈 建竹
Method for measuring high furnace burden face appearance and material flow track using laser ranging technique
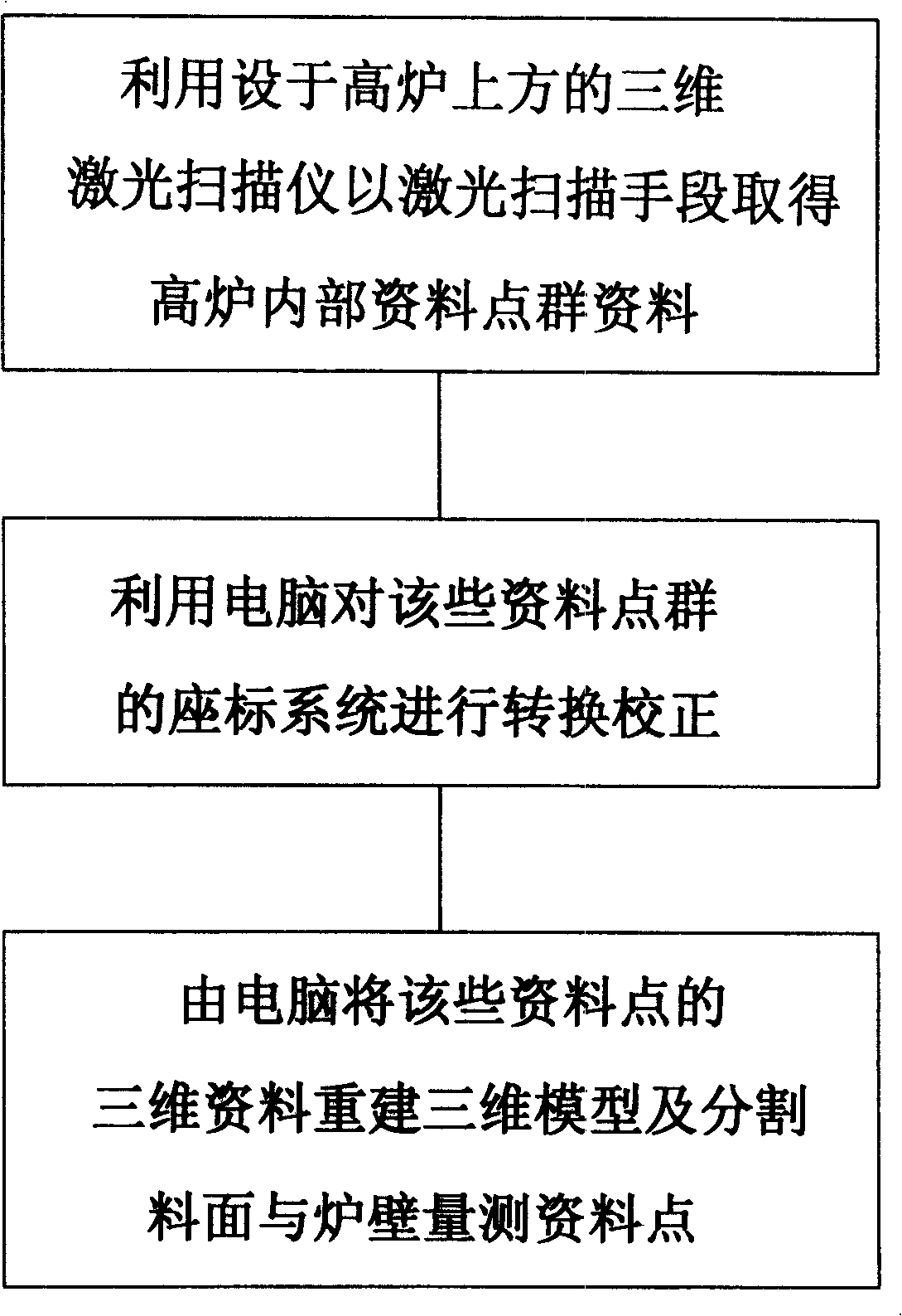
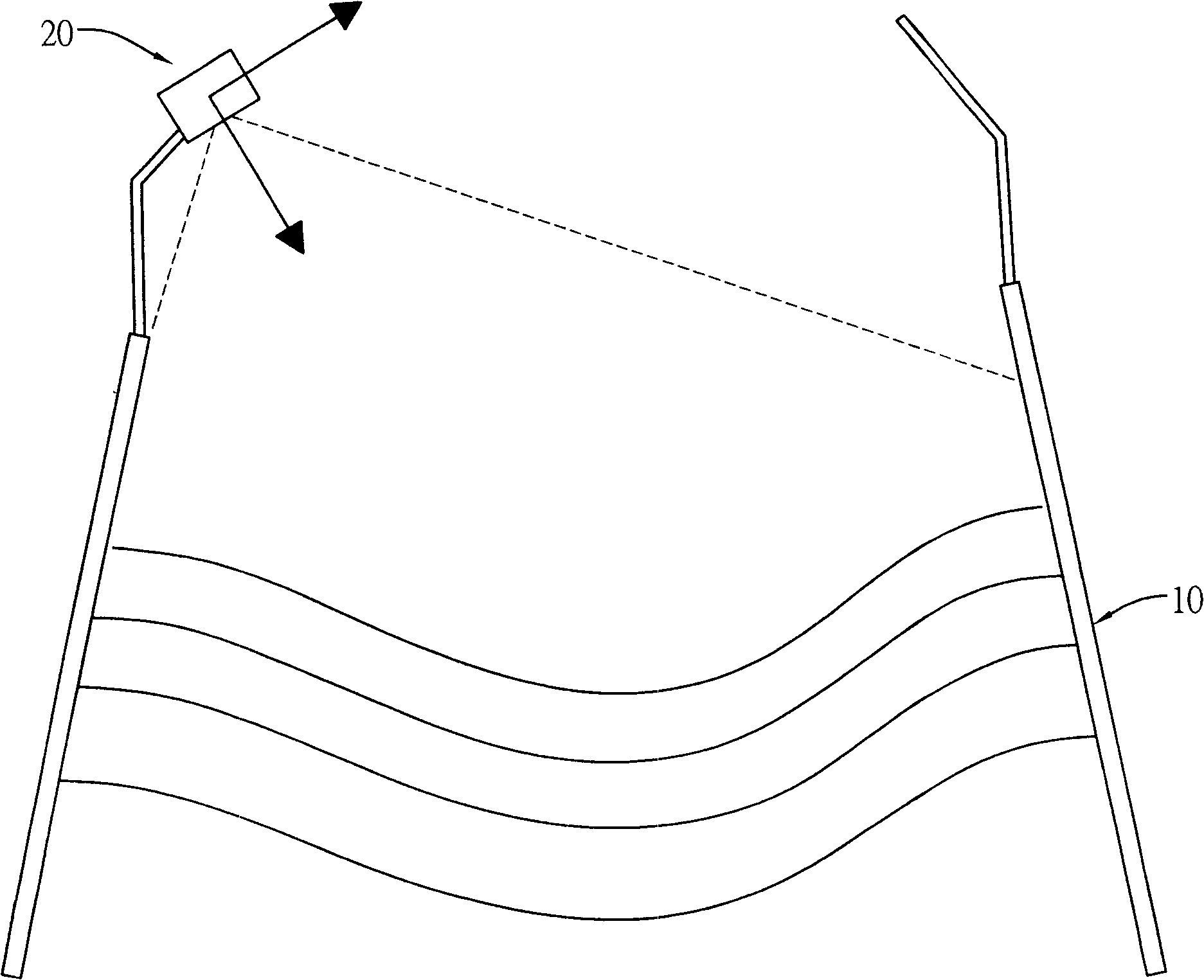
InactiveCN101256069AMeasurement has little effectAccurate and Practical Measurement MethodsUsing optical meansLaser rangingLaser scanning
The invention relates to a method for measuring blast burden shape and burden flow trajectory with the laser range-finding technique, which mainly includes the following steps: fetching the point group data in the blast furnace by the laser scanner equipped on the upper part of the blast burden with laser scanning method, rebuilding a three-dimensional model from the point group data by computer, achieving the measurement of blast burden shape, measuring the burden flow trajectory by the two-dimensional laser scanner equipped above the blast burden to form a blanking curve down from the hopper, and integrating the curve with the three-dimensional model by computer, for operators to confirm whether the blanking position is in accordance with the original set position, and according to the result verifying the burden distribution angle and burden turns number. The invention mainly uses the characters that the laser scanner is rapid, stable and accurate and the measurement is not affected by the blast furnace environment, coordinated with the computer process, which can be applied in blast burden investigation of the burden surface after burden distribution and the burden flow trajectory, in order to provide an accurate and practical measure method.
Owner:CHINA STEEL
Method for producing wood-plastic composite material
The invention relates to a method for preparing wood-plastic composite materials. The method comprises the following steps: 1) thoroughly mixing 50-100 weight parts of wood powder with 40-200 weight parts of fillers with a high-speed mixer, adding 1-20 weight parts of finishing agents into the high-speed mixer, and stirring at 80-120 DEG C for 10-20 min; 2) adding 10-20 weight parts of addition agents in the resulting powder mixture, stirring for 3-6 min to allow uniform dispersion; 3) delivering the resulting mixture produced in the step 2) to a fluidized bed dryer for drying until the water content is below 3%, granulating by using a ring mould pellet mill to obtain pressed pellets; and 4) mixing resin granules with pellets at a weight ratio of 1:(1-2) and extrusion-molding to obtain the final product. The preparation method is implemented by pressing and pelletizing wood powder, mixing wood pellets with plastic granules and conducting extrusion processing, overcomes material feeding difficulties, and can double the yield and increase production capacity.
Owner:中山市森朗环保装饰建材有限公司
Wafer packaging construction with array connecting pad and method of manufacturing the same
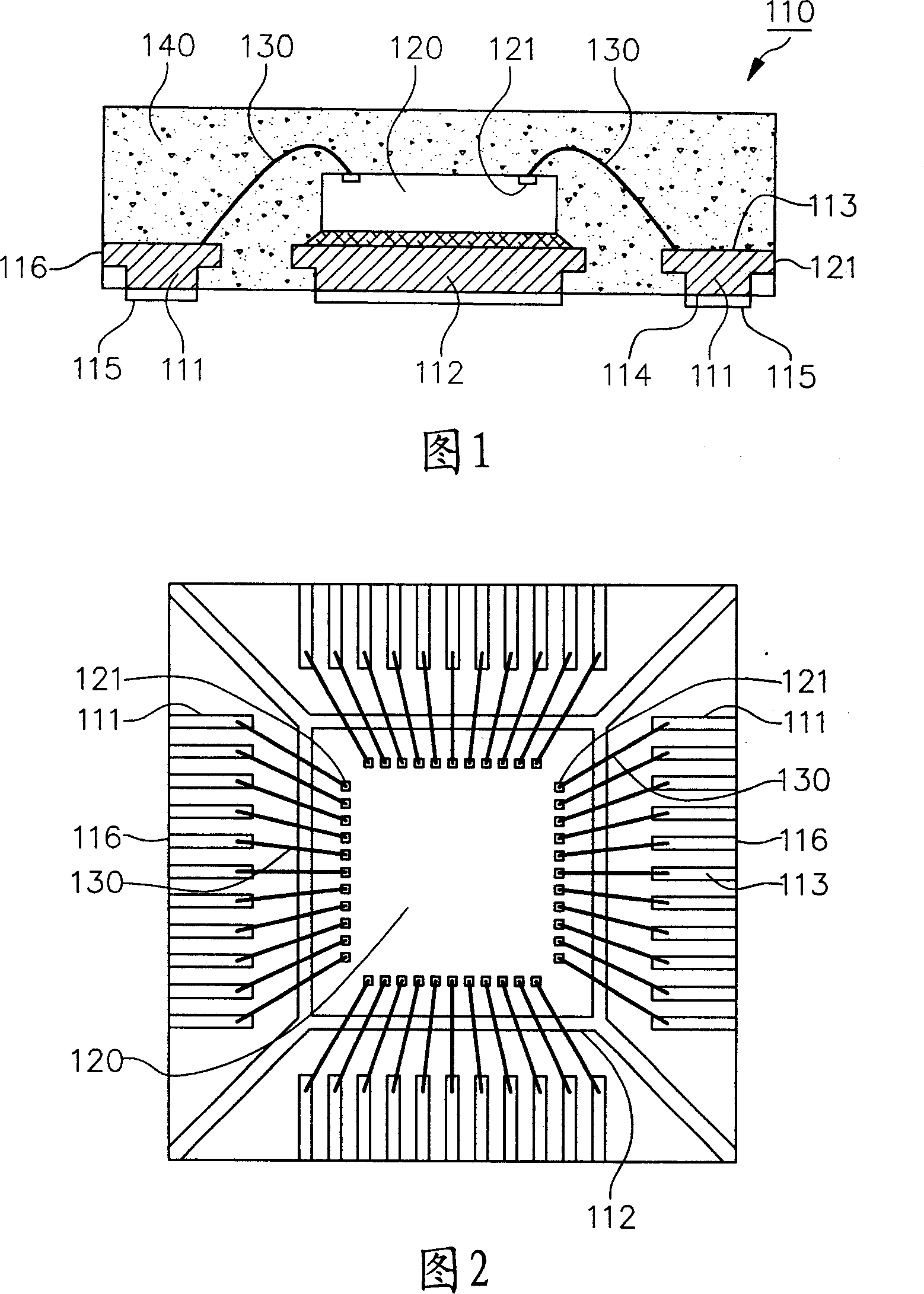
InactiveCN101131980AHigh densityPrevent rustSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesHigh densityEngineering
The present invention relates to a wafer packaging with array pads and its processing method. The wafer packaging mainly includes even numbers of wire-bonded pads, a wafer, even numbers of welding line and a sealing colloid. An upper and a lower combination layers are separately formed on cores of the wire-bonded pads, in which materials of the cores include copper. These welding lines electric connect the wafer with the upper combination layer of the wire-bonded pads. The sealing colloid seals these welding lines, cores and upper combination layers, in which only the lower combination layers are exposed out of the sealing colloid. The present invention can solve the former rusting problem of exposed cutting surface of pins in non-external-pin wafer packaging of conductor frame substrate, and has array pads which can achieve high density of wafer packaging. The processing method of the present invention keeps using a rigid conductive mold in packaging process to carry steps of electroforming, wafer attaching, wire bonding and packaging to achieve coherence of the packaging process.
Owner:CHIPMOS TECH INC
LED structure
InactiveCN101145570AConvenient series/parallel circuit connectionSimplify the linkSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesHigh pressureBare surface
The invention relates to a light-emitting diode structure which comprises a first substrate, an adhesive layer formed on the first substrate, a first ohmic connection layer formed on the adhesive layer, an epitaxial layer formed on the first ohmic connection layer, a first insulating layer covered on the exposed surfaces of the first ohmic connection layer and the epitaxial layer, a first current-conducting plate and a second current-conducting plate both formed inside the first insulating layer and electrically connected with the one end of the first ohmic connection layer and the epitaxial layer. With the arrangement of a first groove and a second groove, the complicated series / parallel circuit connection of the light-emitting diode structure can be performed conveniently, and thus the light-emitting diode structure, in a monomer form, is adapted to various operations in high pressure environment.
Owner:HELIO OPTOELECTRONICS
Radio frequency (rf) sensing system, RF display device, and puzzle system using the same
InactiveCN101383119AChange display informationSignificant progressIndoor gamesStatic indicating devicesGraphicsDisplay device
Owner:G TIME ELECTRONICS
Touch control panel device
InactiveCN101546242AImprove sensing sensitivitySensing sensitivity is uniformInput/output processes for data processingElectromagnetic interferenceEngineering
The invention relates to a touch control panel device, which comprises a substrate layer, an insulating layer and a plurality of first and second electrode groups. The insulating layer is formed on the surface of the substrate layer; each first electrode group comprises a plurality of first electrode plates and a plurality of first conducting wires which are electrically connected with the adjacent first electrode plates; and each second electrode group comprises a plurality of second electrode plates and a bridging conducting wire which is electrically connected with the adjacent second electrode plates. The first electrode groups and the second electrode plates in the second electrode groups are mutually and alternately formed on the surface of the insulating layer, and the bridging conducting wire is formed on the surface where the substrate layer and the insulating layer are connected. The device has the advantages that the device has simple structure and easy manufacture, and can reduce the electromagnetic interference from the outside.
Owner:ELAN MICROELECTRONICS CORPORATION
LED, production method therefore and illuminator manufactured by the LED
InactiveCN101419962AEffective coolingEasy to change designPoint-like light sourceElectric circuit arrangementsElectricityTransmittance
The invention relates to an LED, a manufacturing method thereof and an illuminator made from the LED. The LED mainly comprises a base which is provided with a body; the body is made from a material with high thermal conductivity and high light transmittance, and forms an accommodating space which opens towards the top surface; the body is internally buried with at least two connecting pins which are electrically connected with the outside, the accommodating space is internally provided with at least one LED wafer, and heat radiation can be properly achieved by the body with the high thermal conductivity and the high light transmittance; and the LED can be combined with a firmly arranged plate to form an LED illuminator. The invention further relates to the manufacturing method of the LED. The method comprises the following steps: providing materials, molding, semi-sintering, electroplating and combination, gas protection and complete sintering, electroplating, wafer fixing, routing, packaging colloid and the like to manufacture the LED. The LED can effectively dissipate heat, has ambient light, and is easy to change the design for evaluating the cost so as to have high efficiency.
Owner:张守仁
Method for judging wafer thinning, device structure and device and its manufacture method
ActiveCN101339893ANot physically limitedEnhance the outstanding effectPolishing machinesSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementWafer thinningEngineering
The invention relates to a method for judging wafer thinning, device structure, mechanism and its manufacture method. Basis material is ground and removed from semiconductor device; current change in grinding device is detected and responds to multiple first group of device structure exposing with basis material; the grinding and removing step responds to detected current change and stops; polishing step is performed to repairing surface, and extra basis material is continuously removed; other one or multiple groups of device structures with exposing material is monitored to judge extra amount of basis material to be removed; the other one or multiple groups of device structures is positioned inside semiconductor device at known depth other than the position depth of the first group structure.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Touch control panel
InactiveCN101261559AEvenly distributedEnhance the outstanding effectInput/output processes for data processingCapacitanceElectrical resistance and conductance
The present invention relates to a touch control panel which comprises a control circuit and a touch screen connected with the control circuit. The control circuit is used for generating an X-Y coordinate signal. The touch screen comprises a transparent substrate and a transparent conductive film installed on the transparent substrate. The transparent conductive film comprises a plurality of capacitance inducers which are arranged along X-axis direction and Y-axis direction. These capacitance inducers are patterned to the pattern which has equalizing resistance capacitance distribution. The touch control panel according to the invention can accurately detect the position of the contact on the touch screen.
Owner:ELAN MICROELECTRONICS CORPORATION
Display device
InactiveCN101201485AAvoid damageImprove protectionStatic indicating devicesMagnetic/electric field screeningPhysicsLiquid-crystal display
The invention relates to a display device and comprises an image generating unit and a conductive film layer; the image generating unit can be a liquid crystal display panel and comprises a first substrate, a second substrate and a liquid crystal layer, wherein, the second substrate is arranged opposite to the first substrate; the liquid crystal layer is filled between the first substrate and the second substrate; the conductive film layer is arranged on one side of the second substrate. With the conductive film layer, the invention prevents the display device from damage of outer static passing through the gap between the panel and a frame as well as the edge of the surface of the panel, moreover, the invention can reinforce the shortcoming of the prior metal frame that the prior frame only can prevent the display device from damage of static passing through the gap between the panel and the frame, therefore, the invention can reduce the probability of damage of the display panel due to static and strengthen protection on the panel as well as prevent the panel from damage of outer static.
Owner:INVENTEC CORP
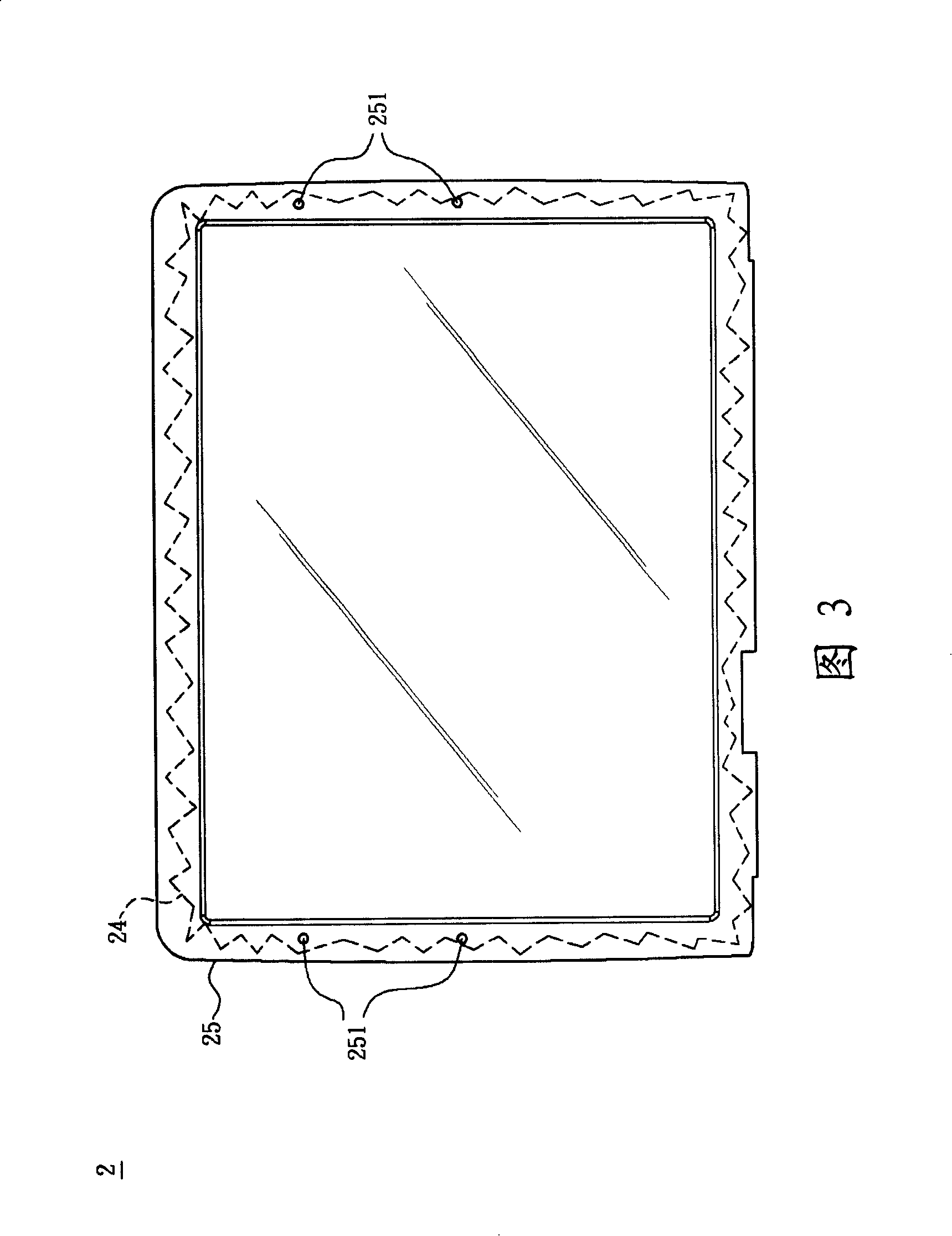
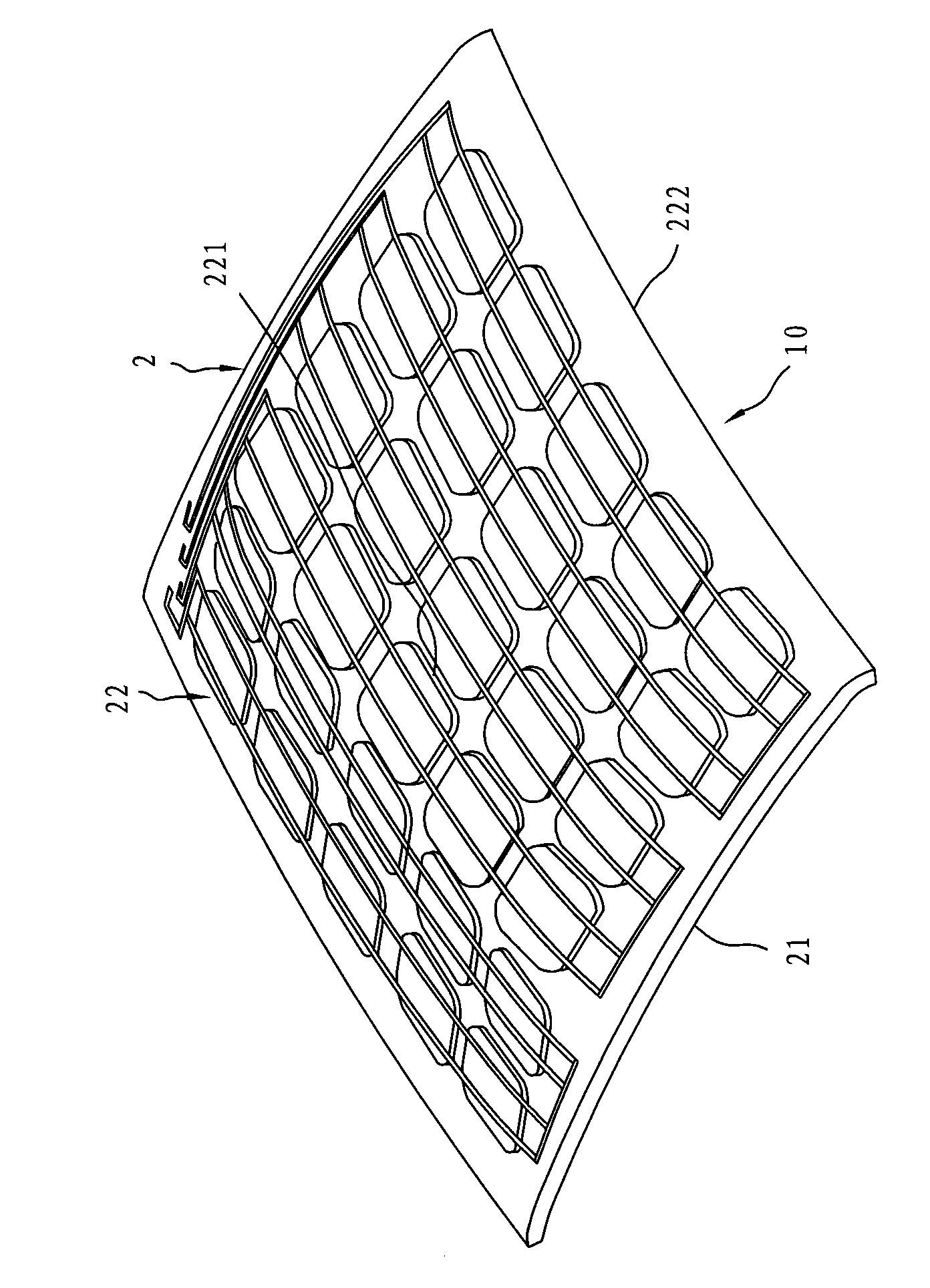
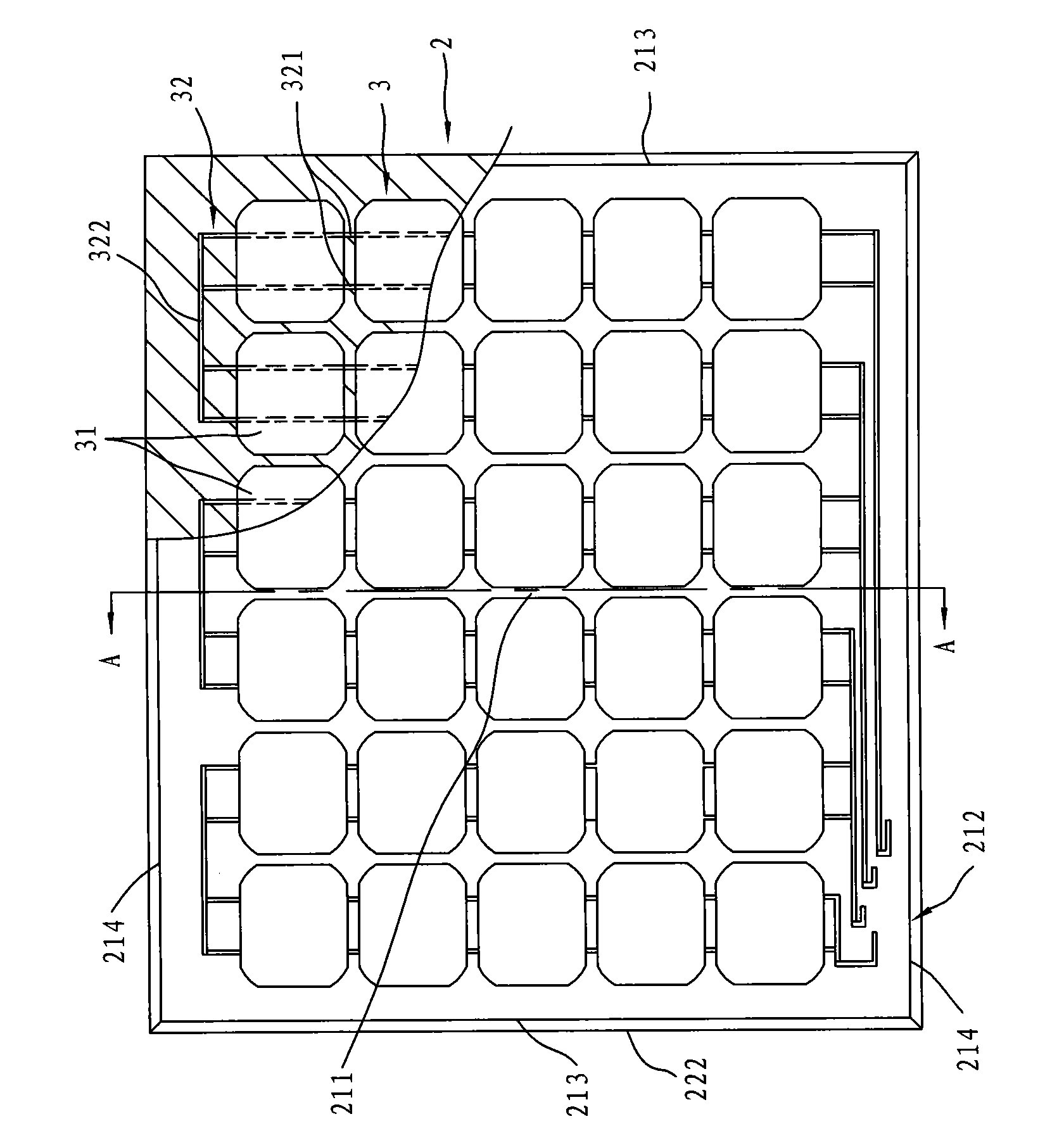
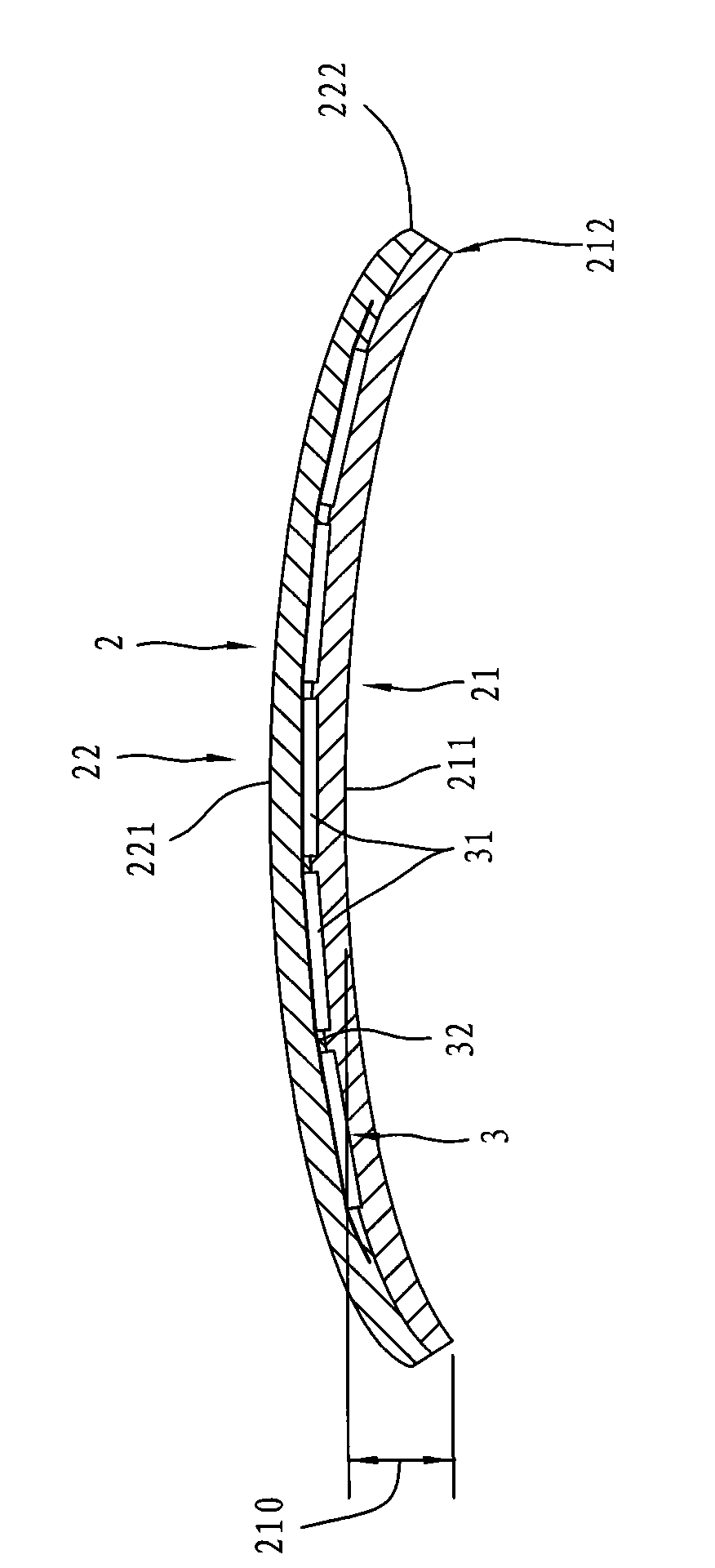
Arc-shaped solar panel and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN101673779AImprove aestheticsImprove integrityFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationAdhesiveHeight difference
The invention relates to an arc-shaped solar panel and a manufacturing method thereof. The arc-shaped solar panel comprises a transparent package base and a solar mode packaged inside the package base, wherein the package base comprises an arc-shaped face which has a high point close to a geometric center and a surrounding lower edge that surrounds the high point and has a height difference with the high point. During manufacturing, the solar module is first prepared and then clamped by an adhesive between two pieces of transparent substrates that can be molded and deformed when being heated and the combined body is heated to be softened and pressed by a die to form the arc-shaped solar panel with at least one arc-shape face. Through constant innovation in the manufacturing method and thefinished product, the solar panel is suitable to be arranged on a non-planar object.
Owner:GLORIA SOLAR
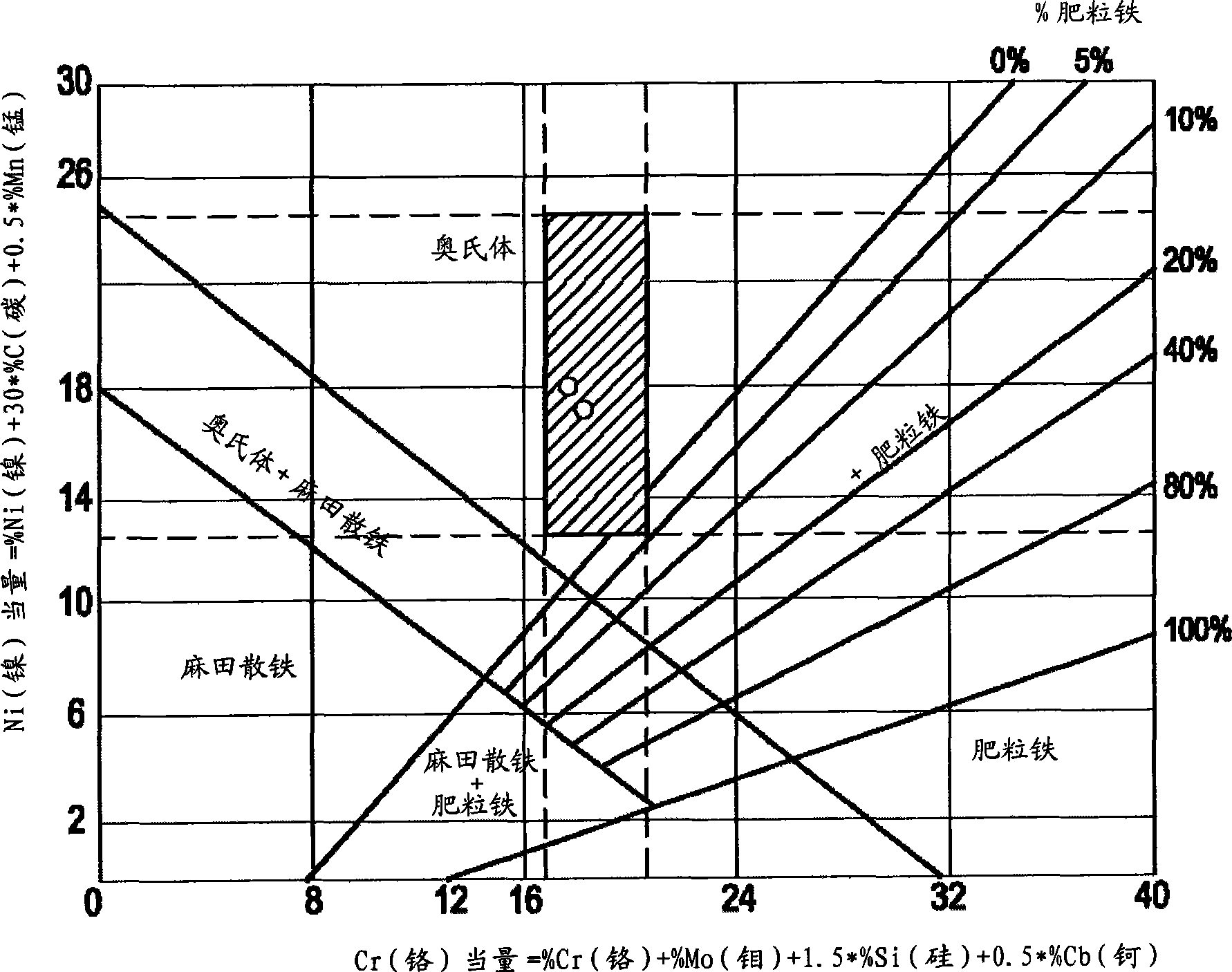
Chromium-manganese-nitrogen austenitic stainless steel
The invention relates to Cr-Mn-N austenite stainless steel. A proper amount of Mn and N are used to substitute expensive nickel to produce a novel Cr-Mn-N steel grade for reducing the cost for materials and maintaining the prior physical property and mechanical property. The Cr-Mn-N austenite stainless steel comprises the following composing elements in percentage by weight: 0.005 to 0.08 percent of carbon element, 0.3 to 0.9 percent of silicon element, 12.1 to 14.8 percent of manganese element, 0.001 to 0.04 percent of phosphorus element, 0.001 to 0.03 percent of sulfur element, 16 to 19 percent of chromium element, 0.5 to 1.8 percent of nickel element, 0.2 to 0.45 percent of nitrogen element, 0.001 to 0.3 percent of molybdenum element, 0.001 to 0.3 percent of copper element, and unavoidable trace elements during most manufacturing processes. The corrosion resistance, the strength and the elongation percentage of the Cr-Mn-N austenite stainless steel in marine atmosphere and acid atmosphere are the same as those of a 304 stainless steel material or are better than those of the 304 stainless steel material, and the Cr-Mn-N austenite stainless steel can reduce the cost for the materials. The Cr-Mn-N austenite stainless steel has the advantages of high elongation percentage, strong corrosion resistance, excellent casting formability and good high-temperature oxidation resistance.
Owner:ADVANCED INT MULTITECH CO LTD
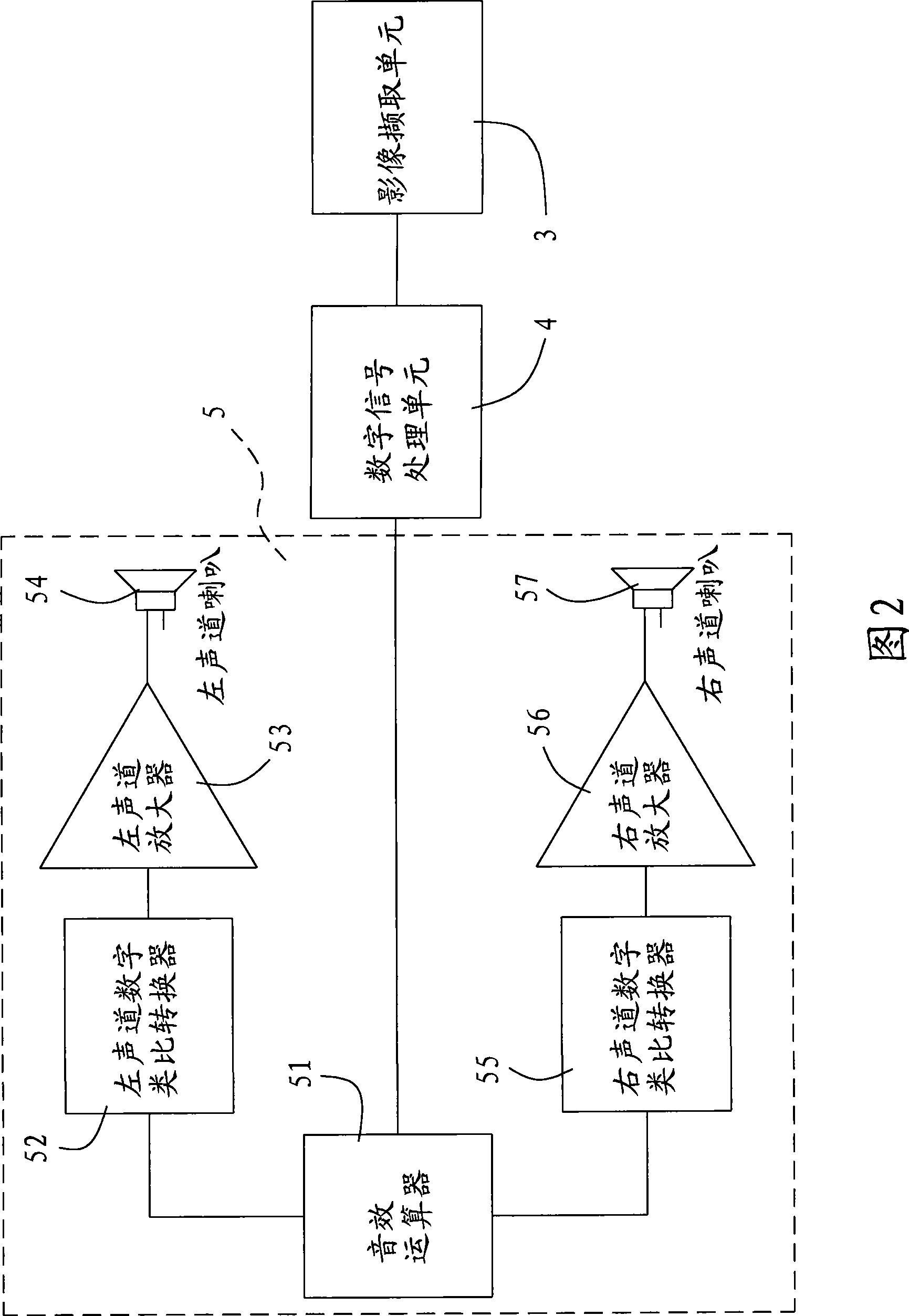
Electronic device and method capable of sound effect regulation according to customer location
InactiveCN101453598AAppropriate sound effectsSimple structureTelevision system detailsColor television detailsControl parametersEnvironmental sounds
The invention relates to an electronic device and a method capable of adjusting sound effect according to position of a user. The electronic device capable of adjusting the sound effect according to the position of the user comprises an image acquisition unit, a digital signal processing unit and a sound effect generating unit. The image acquisition unit is used for acquiring an image of the user and a surrounding environment thereof; the digital signal processing unit analyzes the image, identifies the position of the user, and generates a corresponding sound effect control parameter according to a relative position between the user and the electronic device; and the sound effect generating unit generates environmental sound effect suitable for the position of the user according to the sound effect control parameter. The device and the method use the image acquisition unit to acquire the image, and use the digital signal processing unit to analyze the image in order to acquire the position of the user, so the device and the method can provide the sound effect suitable for users at different positions.
Owner:ACER INC
Assemble and disassemble portable type marine vehicle
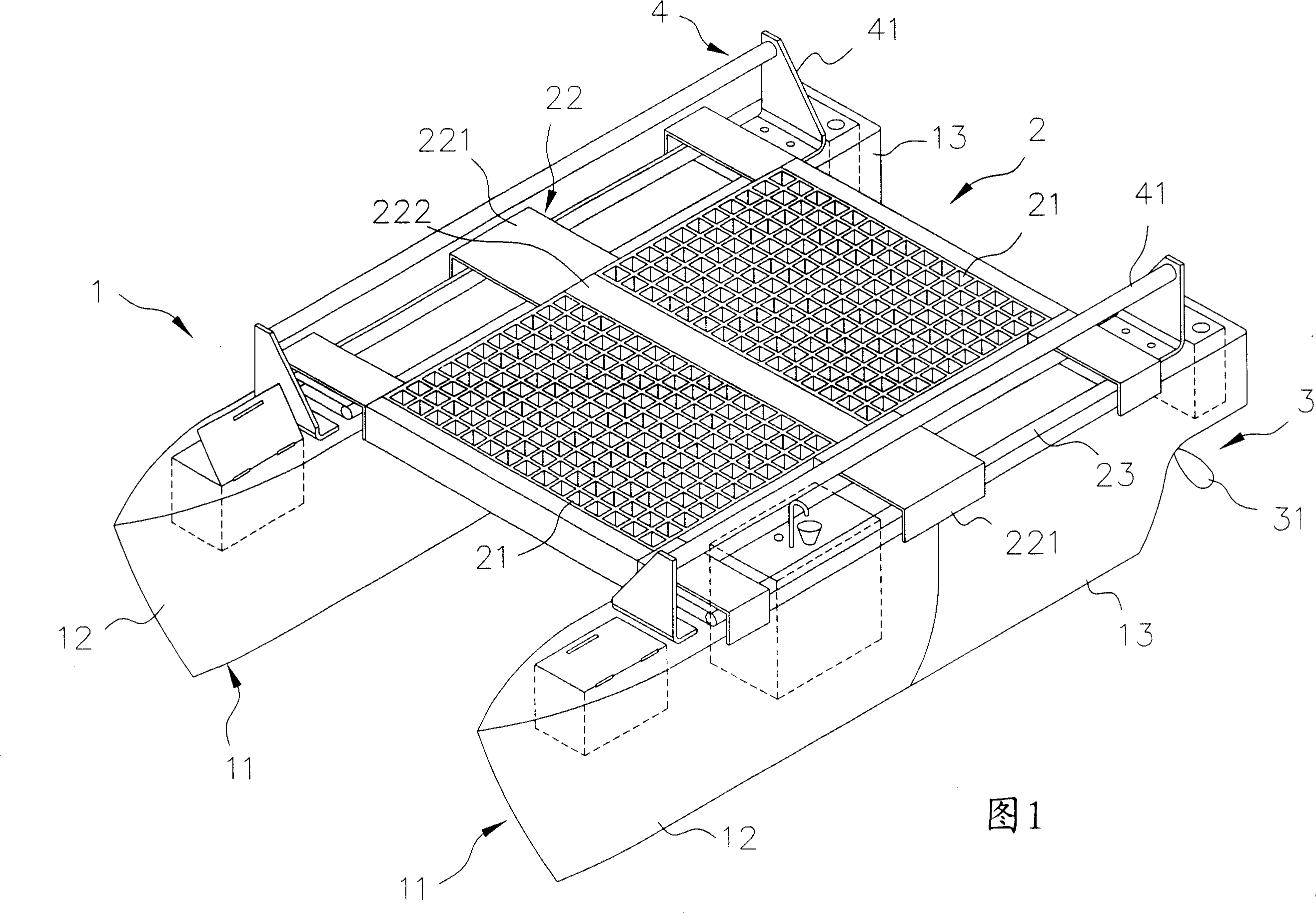
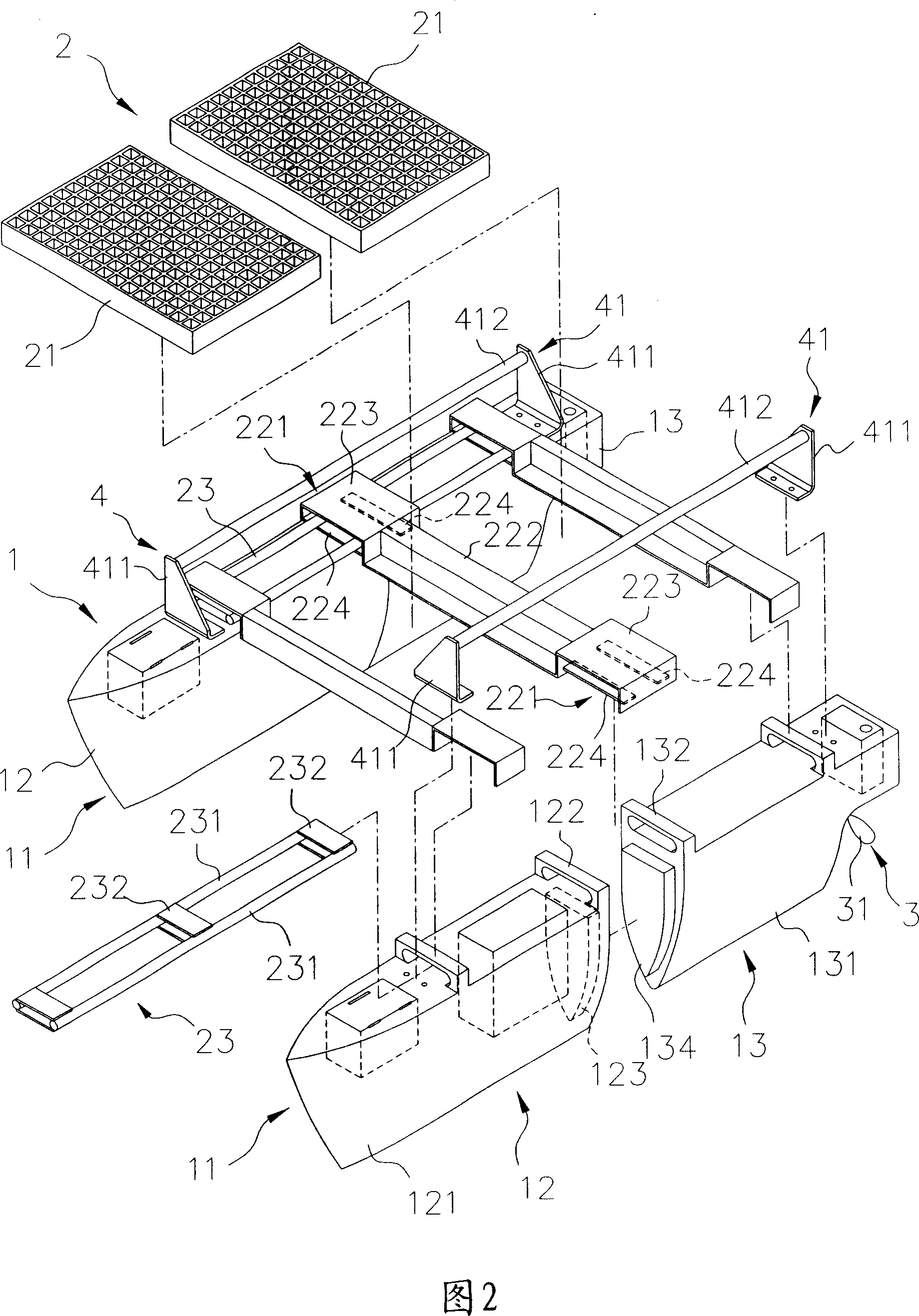
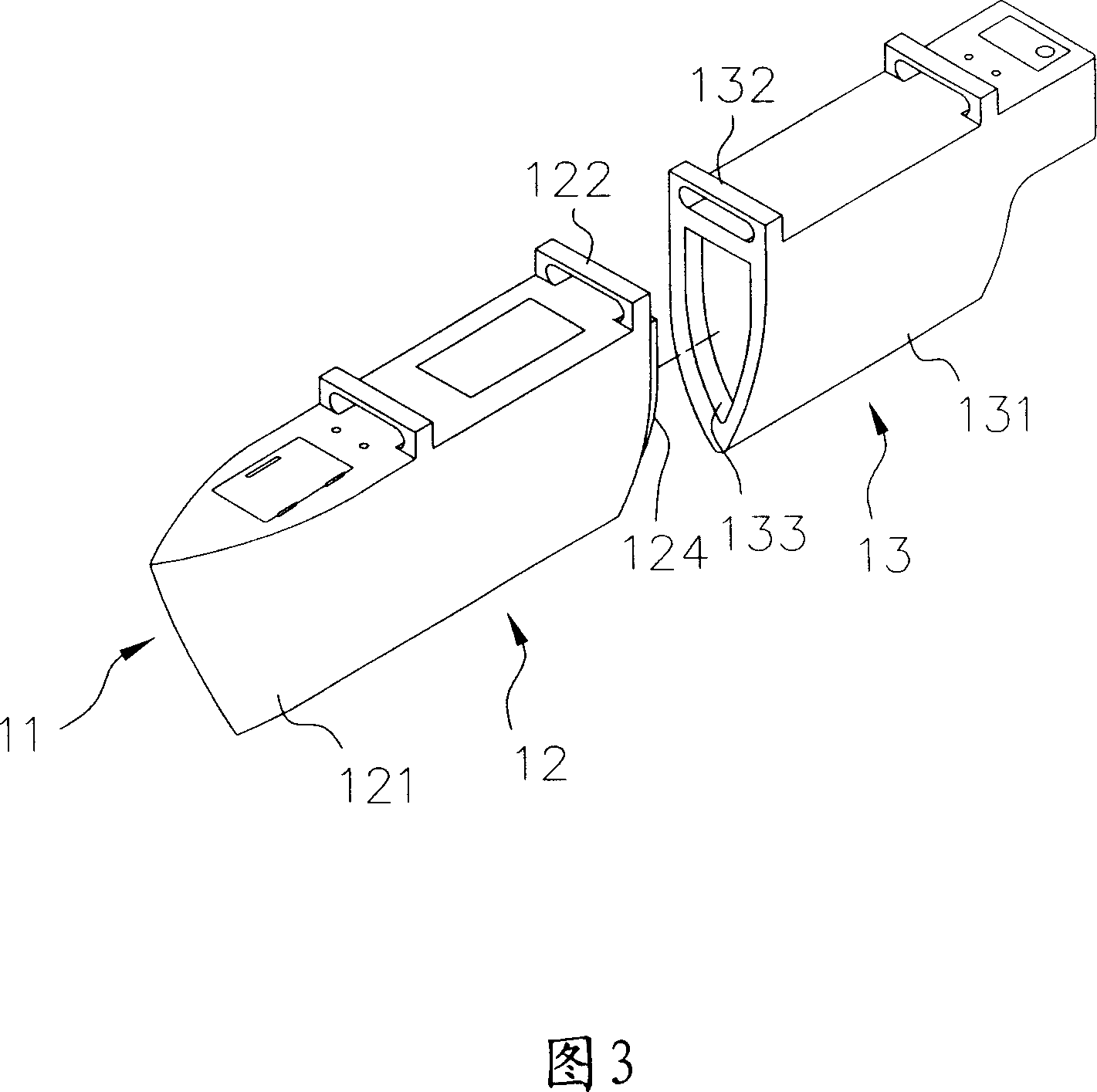
InactiveCN101092159ANot prone to overturningEasy to carryVessel salvagingFoldable/inflatable hullsSternPower unit
The invention relates to portable marine vehicle. It includes hull unit, interlock unit, and power unit. The hull unit has many distant hulls each of which has hollow bow and stern. The interlock unit has at least one foot stool and fished beam set. The power unit is respectively set in the stern to drive the hull and control the direction. The invention uses many hulls design to supply prefer incline righting capacity, more activity space through the interlock and hull units.
Owner:简圣恒
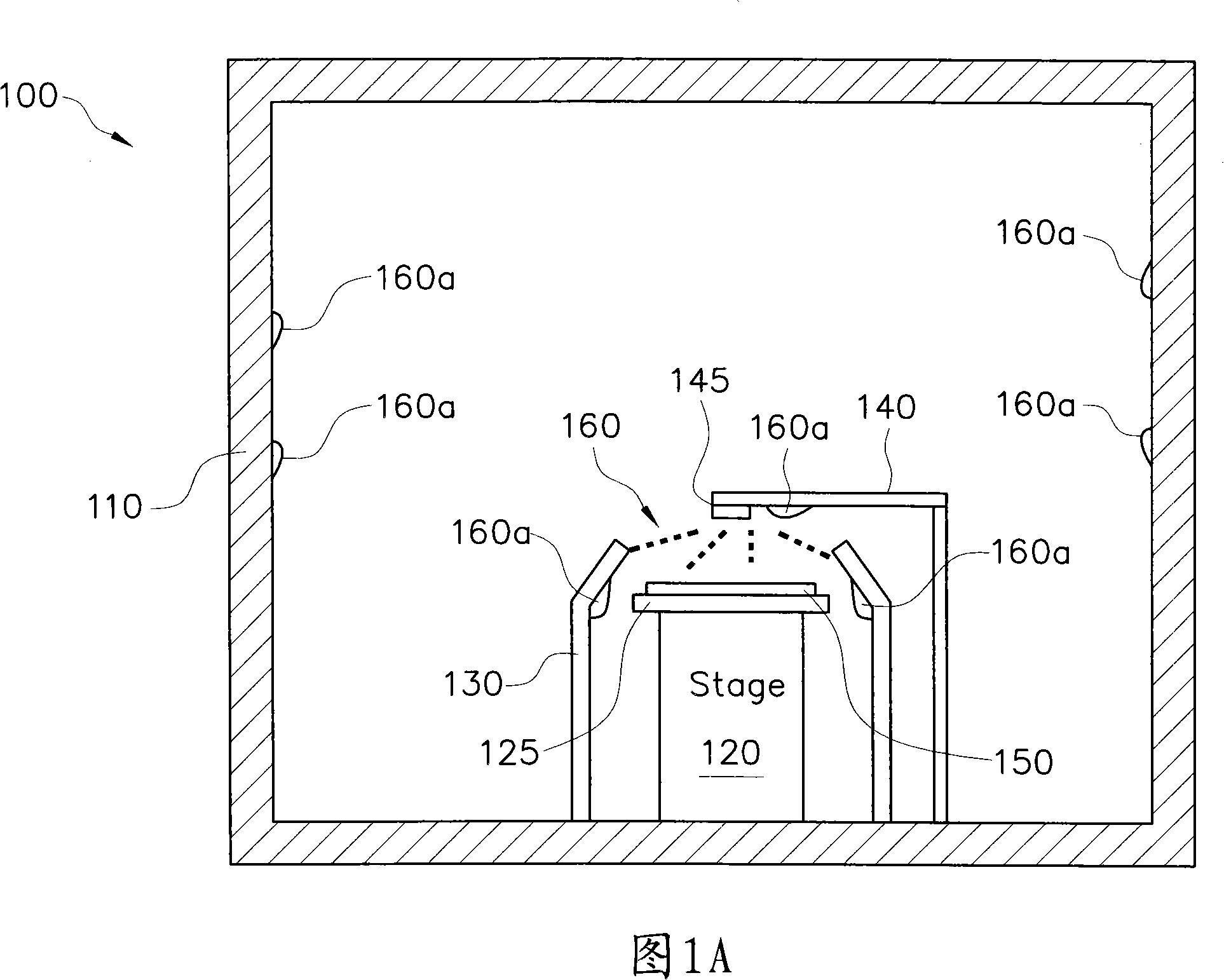
Apparatus and methods of cleaning substrates
ActiveCN101131925APrevent residual crystallizationEasy to cleanSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCleaning using liquidsChemical reactionEngineering
The invention relates to a wafer cleaning method and an apparatus used in said method. The apparatus comprises an enclosure; a stage within the enclosure; at least one first wall around the stage within the enclosure; a plate within the enclosure and above the stage, operable to enclose a first region between the stage and the first wall; and an exhauster part coupled to the first region between the stage and the first wall. The method for cleaning a wafer includes: putting the stage with a wafer into a closed vessel which is arranged in the enclosure; spraying a first chemical onto the surface of a substrate with a first nozzle; spraying a second chemical onto the surface of the substrate with a second nozzle to avoid the products generated by chemical reaction between the first and the second chemical in the first and the second nozzle. The invention is suitable for practicality since an airtight space therein is arranged between a cleaning enclosure and a cleaning stage to avoid short circuit or opening of the integrated circuit on the wafer by means of preventing liquid ammonium sulfate residue from crystallizing when cleaning the wafer.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
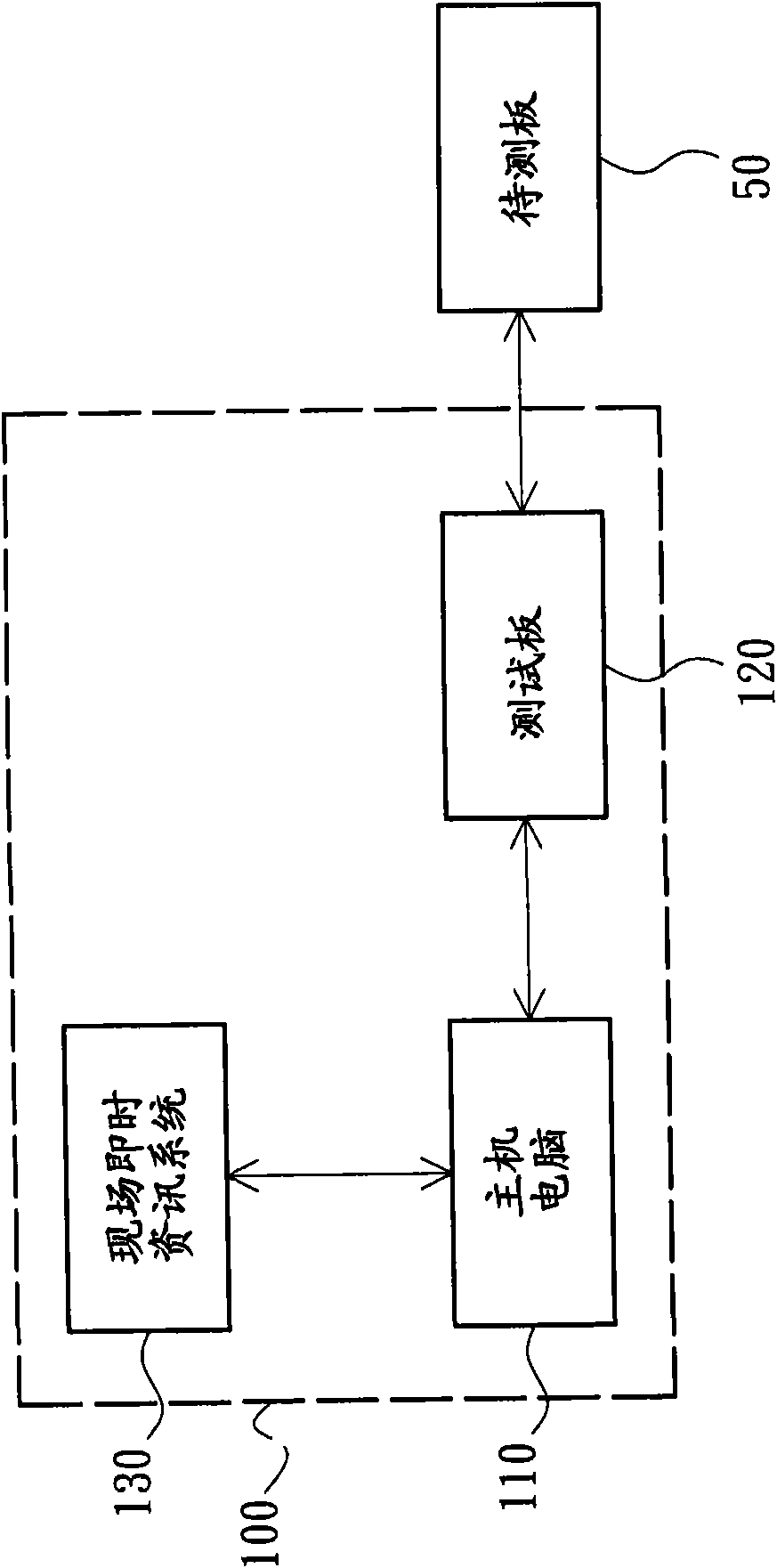
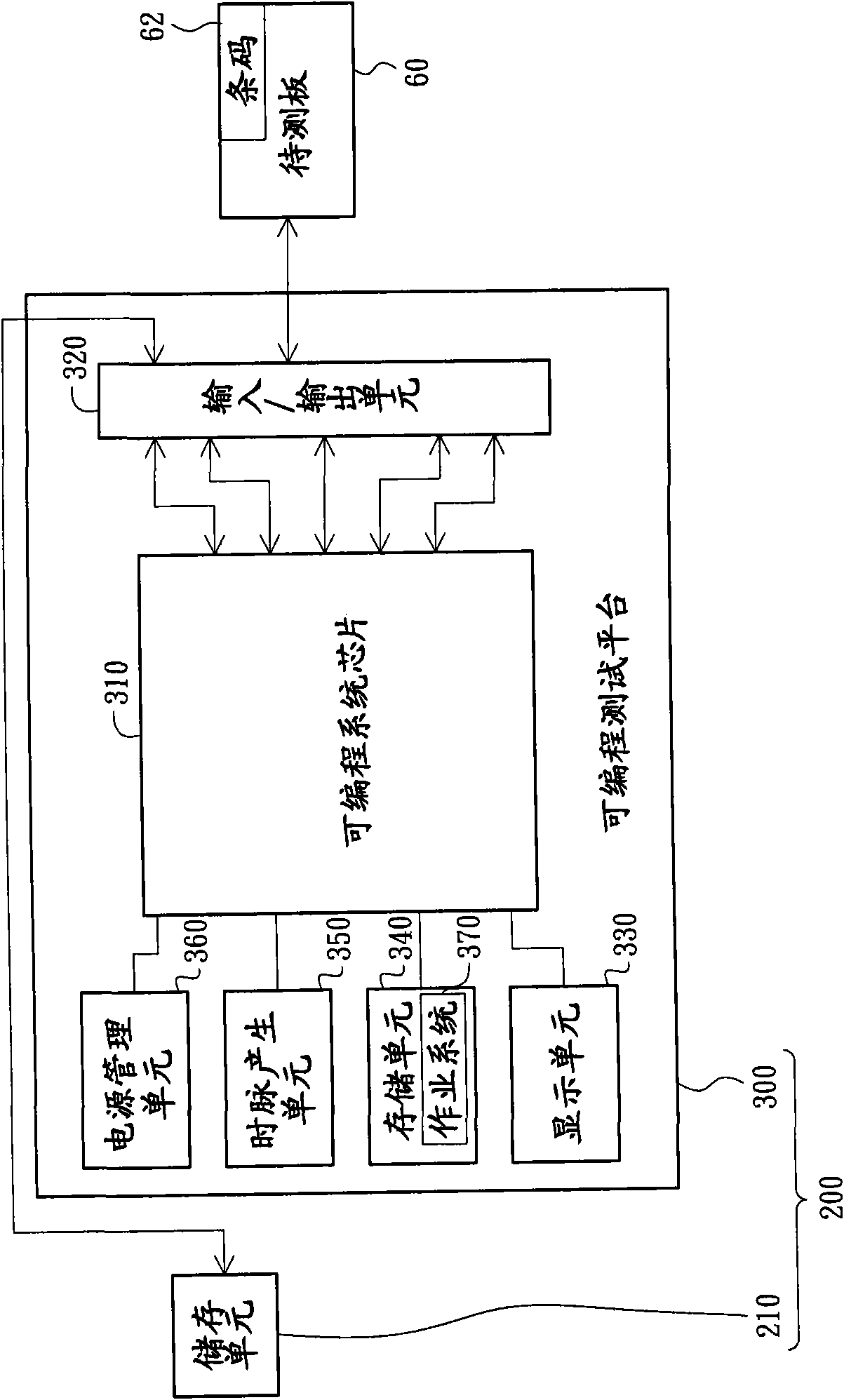
Testing device
InactiveCN101576603AReduce testing costsShorten test timeElectronic circuit testingTest fixtureComputer science
The invention relates to a testing device which is suitable to test a plurality of different types of boards to be tested. The testing device comprises a programmable testing platform and a storage cell. The programmable testing platform comprises a programmable system chip, a storage cell and an input / output cell, wherein the storage cell is electrically connected to the programmable system chip, and an operating system is stored in the storage cell. The input / output cell is electrically connected to the programmable system chip, one of the boards to be tested, and the storage cell. The input / output cell is suitable to produce a starting signal according to an input operation, and the programmable system chip is suitable to select a preset testing process according to the starting signal and to test the board to be tested and electrically connected to the input / output cell according to the preset testing process. The storage cell is used for storing a testing result output by the programmable system chip. The testing device can lower the testing cost and shorten the testing time.
Owner:UNIVERSAL SCIENTIFIC INDUSTRIAL (SHANGHAI) CO LTD +1
Foam concrete composite heat preservation wall body with concrete blocks and construction method thereof
InactiveCN102691363AWidely used valueCause secondary pollutionWallsHeat proofingFoam concreteBuilding energy
The invention provides a foam concrete composite heat preservation wall body with concrete blocks, belonging to the field of building energy conservation. The foam concrete composite heat preservation wall body is used for buildings, such as dwellings, workshops, hotels and the like, and is particularly suitable for new rural reconstruction. The wall body provided by the invention is prepared by constructing different combinations of five concrete precast blocks with different shapes with cement mortar. According to a quantity of floors, the wall body is reinforced, and a wall post and a ring beam can be borne by using wall body reinforcing ribs with different quantities, different manners and different specifications. Ordinary concrete is cast at positions of posts and beams in the hollow wall body, and foam concrete with a concentration of 200-400 kg / m<3> is cast at the other positions, so as to form the heat preservation and sound insulation wall body, and carry out mortar plastering and decoration. When the wall body provided by the invention is more than or equal to 250 mm thick, an average volume weight of the wall body is less than or equal to 600 kg / m<3>, a heat conduction coefficient is less than or equal to 0.4 W / (m2.K), and a pressure-resistant strength of a wall surface is more than or equal to 20 MPa. The wall body provided by the invention has the advantages of convenience and rapidness of construction. Furthermore, the wall body is firm, durable, mild, environment-friendly and safe.
Owner:洛阳原生建筑工程技术有限公司
Method and system for wafer inspection
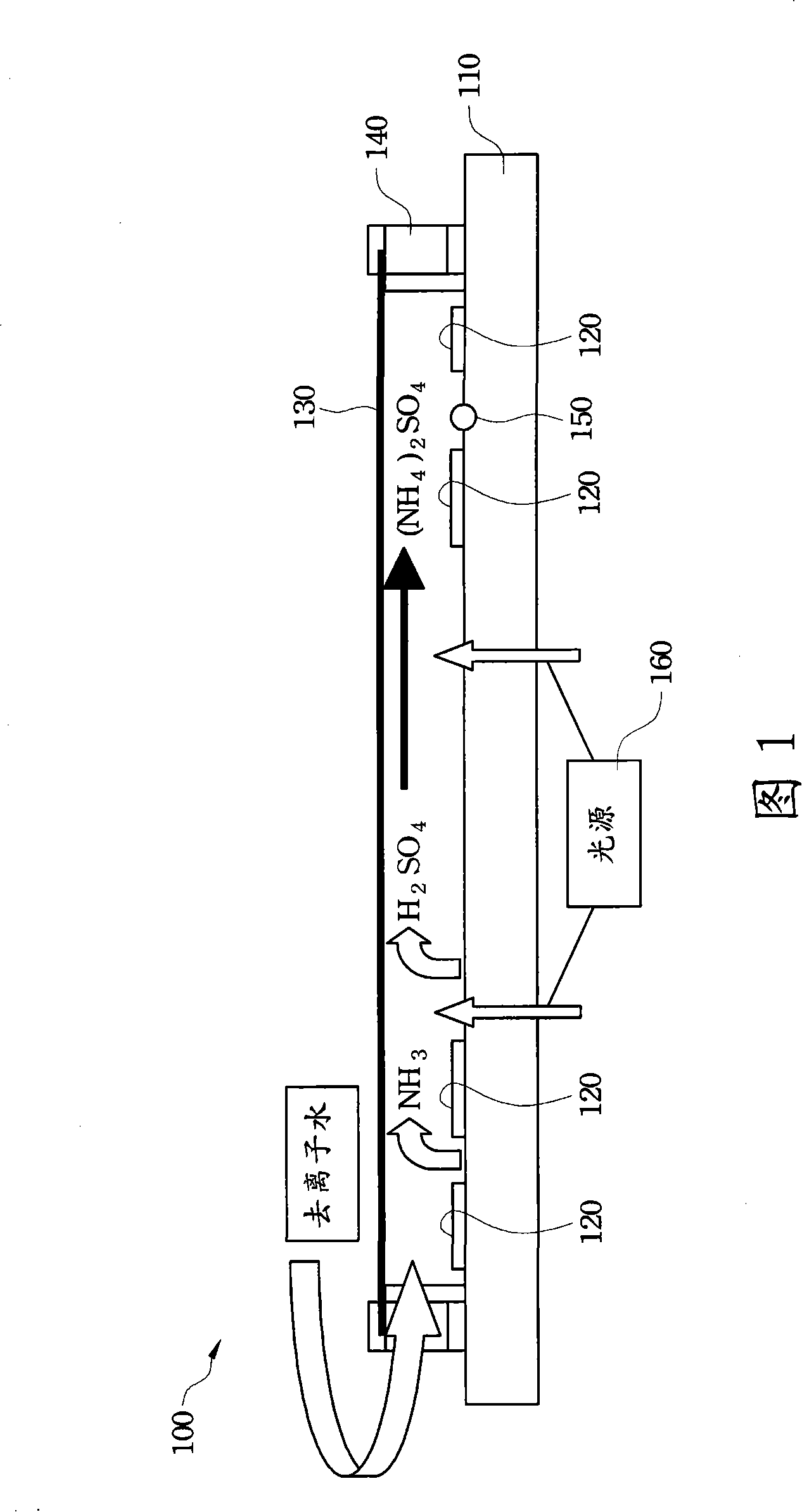
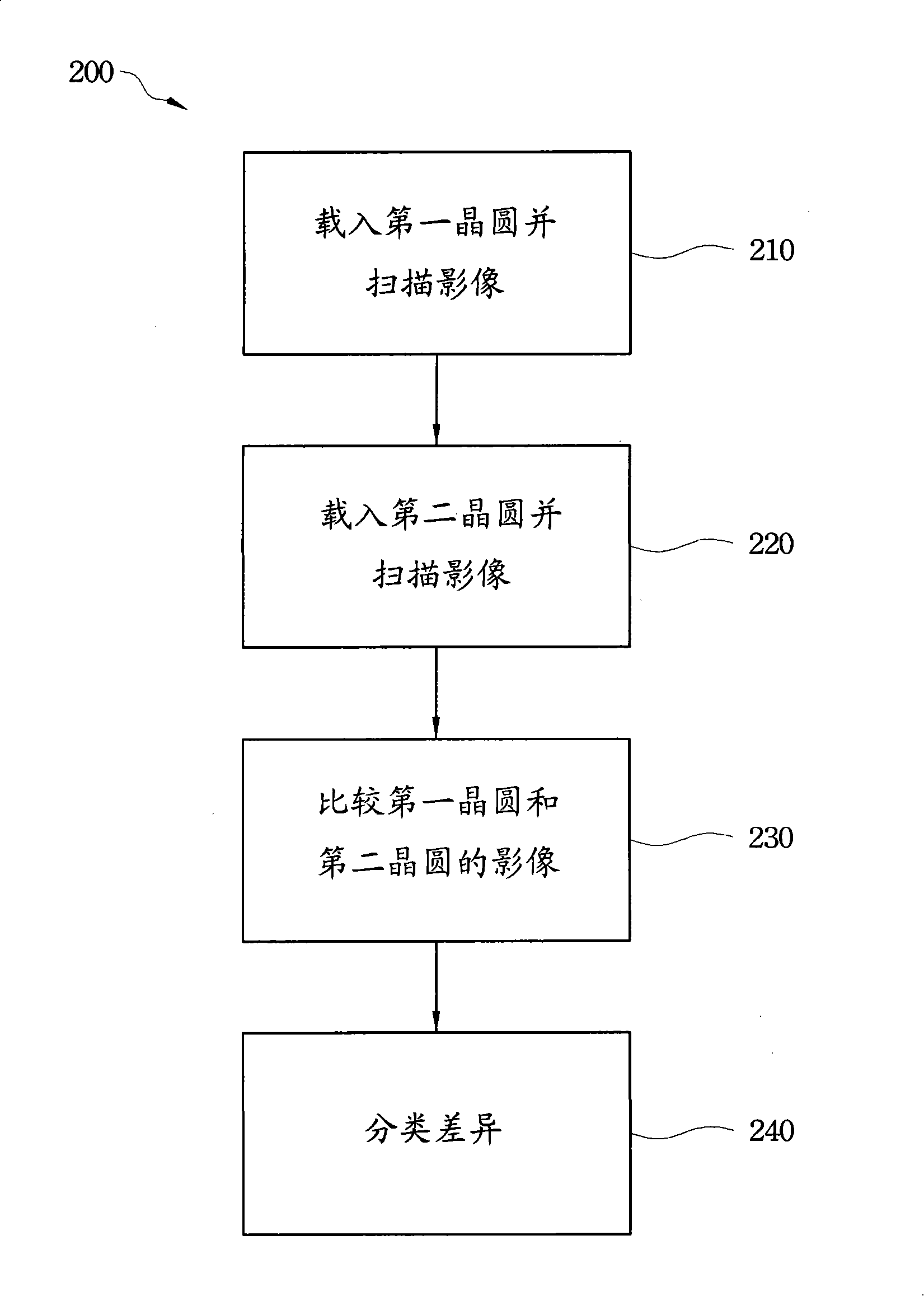
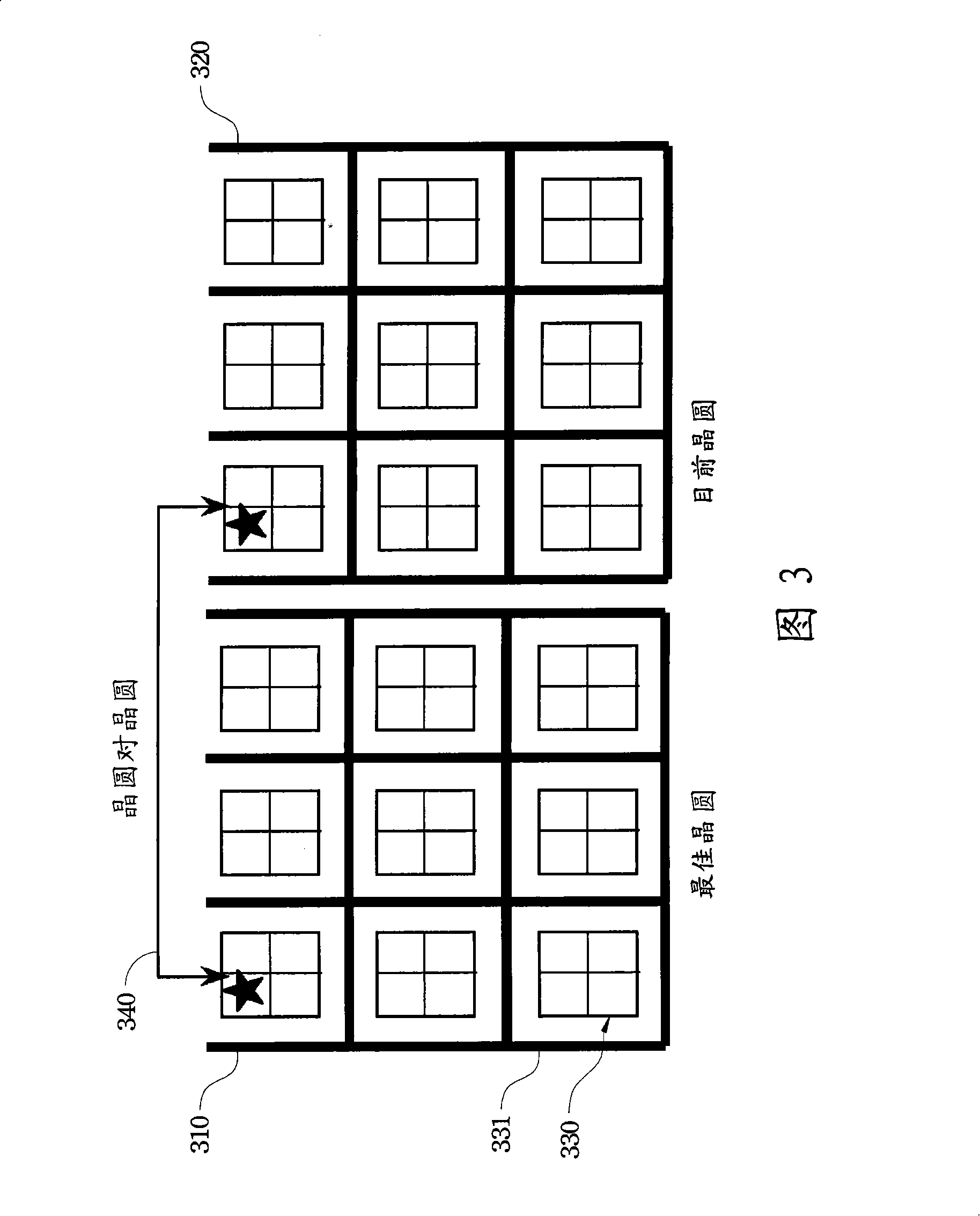
ActiveCN101241084AExpensive to improveImprove time-consuming shortcomingsImage enhancementImage analysisEngineeringSemiconductor
The invention relates to a method and a system for inspecting wafers, wherein the method for inspecting semiconductor wafers which are patterned by a photomask comprises loading a first wafer and scanning a first image of the first wafer, loading a second wafer and scanning a second image of the second wafer, comparing the first and the second image, and classifying a difference detected between the first and second images as a potential defect on the photomask. The potential defect includes a haze defect on the photomask. The invention improves the defaults of the prior art, such as costliness and time-consumption, by tightly monitoring the defaults on the semiconductor wafers.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Stacked integrated circuit and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN101527300AImprove qualityPrevent oxidationSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEngineeringWafer bonding
The present invention relates to a stacked integrated circuit and manufacturing method thereof. The formation of bonding pad protective layer over exposed bonding pad materials between stacked integrated circuit (IC) dies or wafers is described in preferred embodiments in which the bonding pad protective layer is formed in the integrated process of forming wafer bonding pads. The bonding pad protective layer prevents the exposed bonding pad materials from oxidation and corrosion in open-air or other harsh environments. By providing a bonding pad protective layer on exposed bonding pad materials, significant product reliability improvement is expected on ICs having a three-dimensional ''stacked-die'' configuration.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Diffusion brightening film sheet
InactiveCN101354455ASimple structureReduce bright linesPrismsNon-linear opticsDiffusionOptoelectronics
The invention relates to a diffusion brightening film, comprising a substrate and a prism structure. The substrate is provided with a first surface and a second surface; the first surface and the second surface are opposite to each other; the substrate is provided with diffusion material and the prism structure is arranged on the second surface.
Owner:PRODISC TECH INC
Double patterning strategy for contact hole and trench
ActiveCN101446760ASmall minimum feature sizeSimple methodSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotomechanical coating apparatusResistEngineering
A method of lithography double patterning includes forming a first resist pattern on a substrate, the first resist pattern including at least one opening therein on the substrate; curing the first resist pattern; forming a second resist pattern on the substrate; forming a material layer on the substrate; and removing the first and second resist patterns to expose the substrate. Thereby, double resist pattern, that is the first resist pattern and the second resist pattern, is formed by using lithography double patterning, a separated spcacing between the first resist pattern and the second resist pattern results in a reduced minimum features size.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
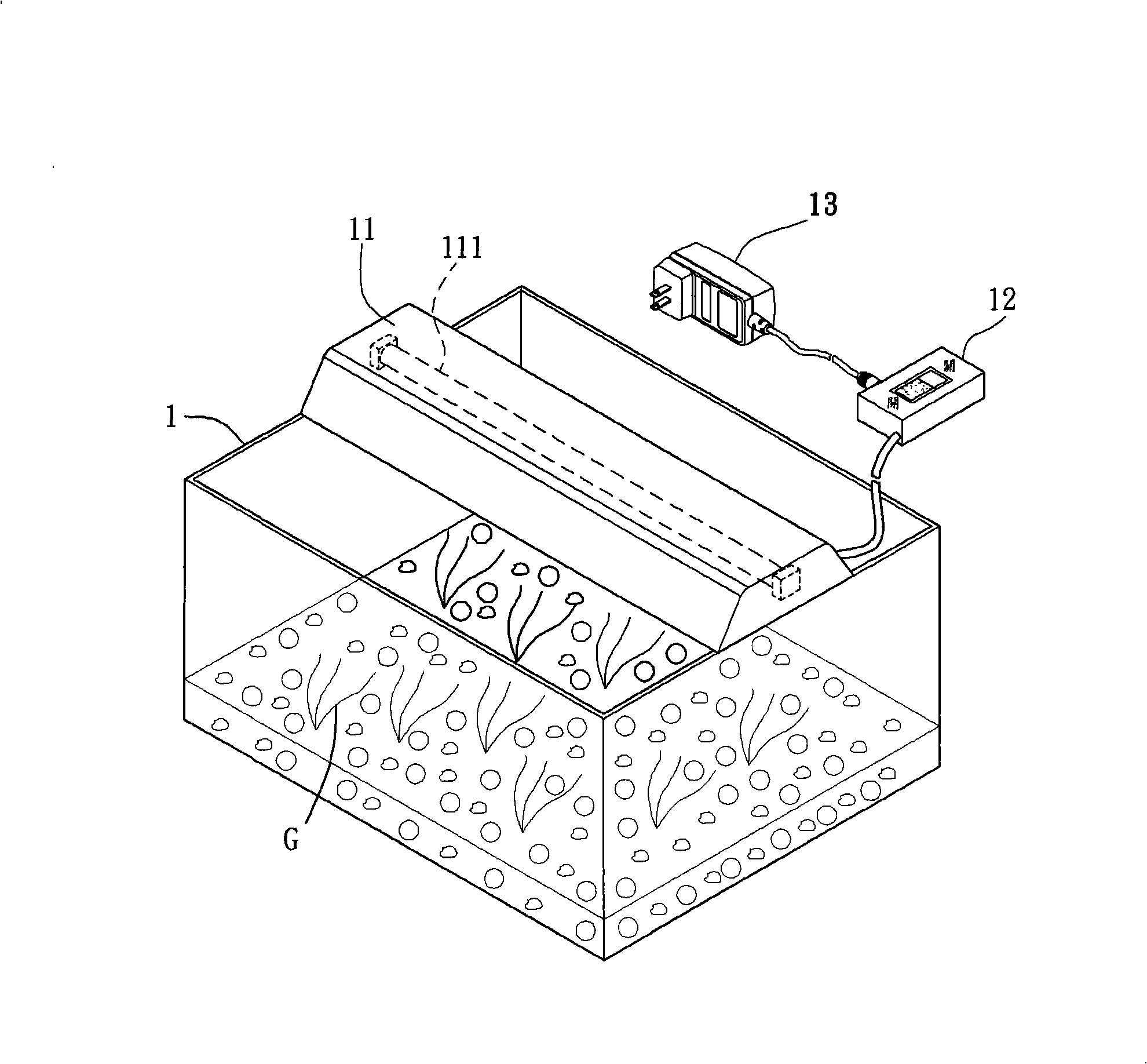
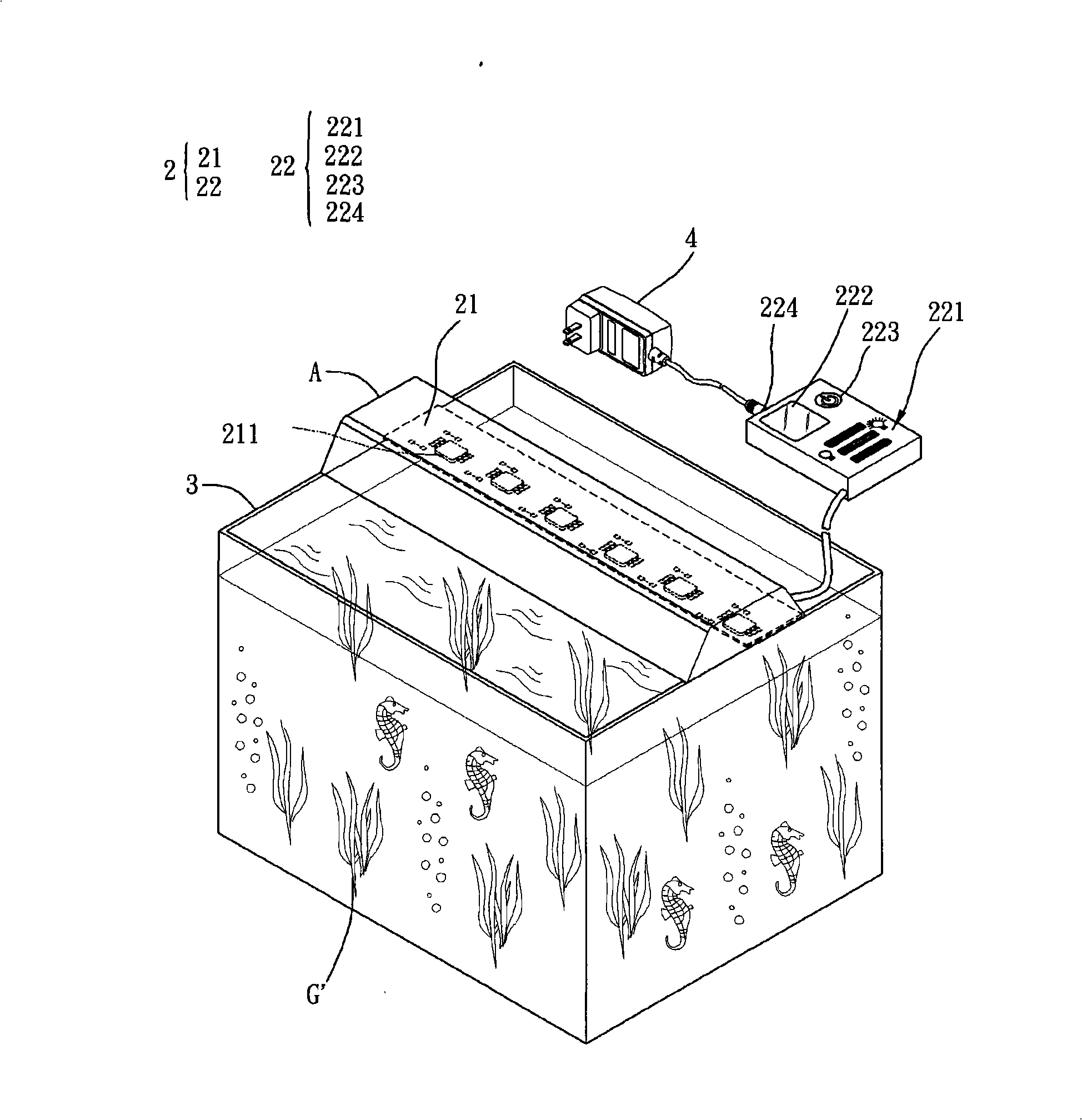
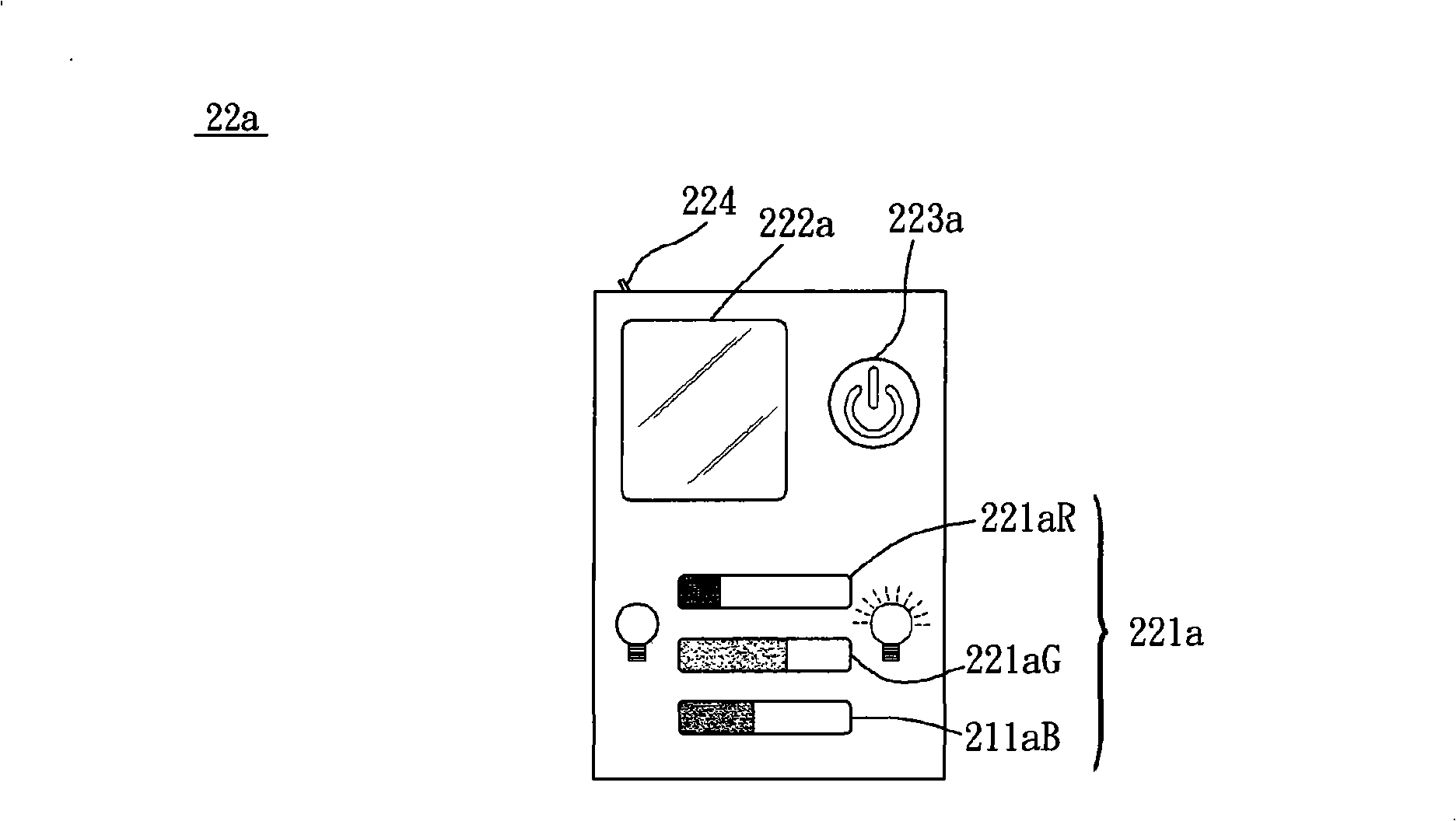
Aquatic animals lamp
InactiveCN101324313ALess power consumptionSolution to short lifeLight source combinationsPoint-like light sourceAquatic animalLight beam
The invention relates to an aquarium lamp, which comprises an illumination unit and a control unit. The illumination unit includes a plurality of LEDs, which are arranged adjacent to each other and can emit light beams of different color systems. The control unit is electrically connected with the LEDs for controlling the LEDs of different color systems respectively. Compared with the prior well-known art, the LEDs can obviate frequent replacement of light sources of the aquarium lamp and can further provide stable light beam, improve the utilization rate, reduce the power consumption and lower the use cost due to the advantages of the LEDs such as low power consumption, long service life, good color saturation, high light emission efficiency and controllable color temperature. Additionally, the control unit can control the LEDs of different color systems respectively to provide light beams of different color systems for a user, thus controlling the growth speed of aquatic weeds, improving the changing of light in aquarium and enhancing the purchasing desire of consumers.
Owner:PRODISC TECH INC
Shopping guide service method and system for sales field
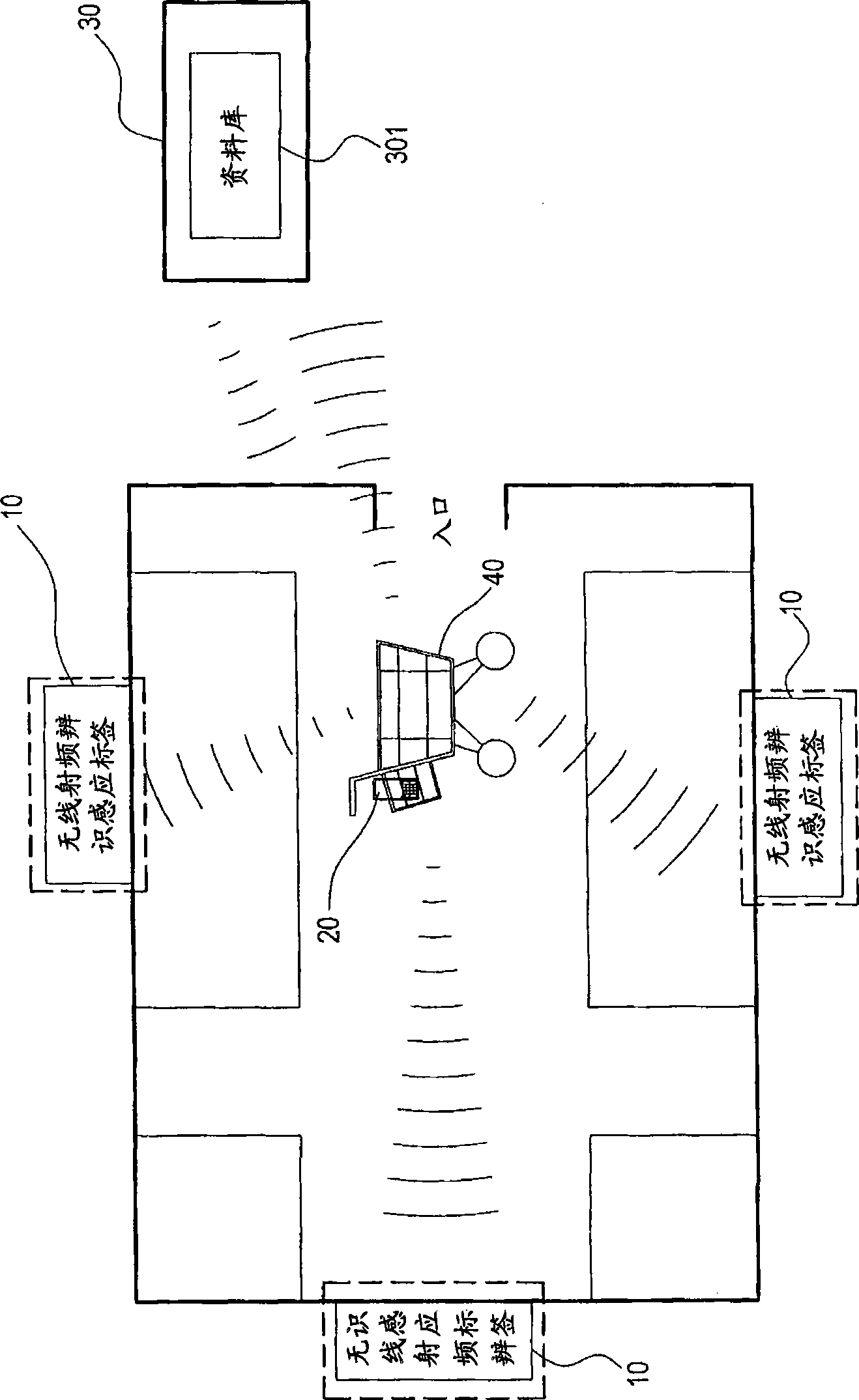
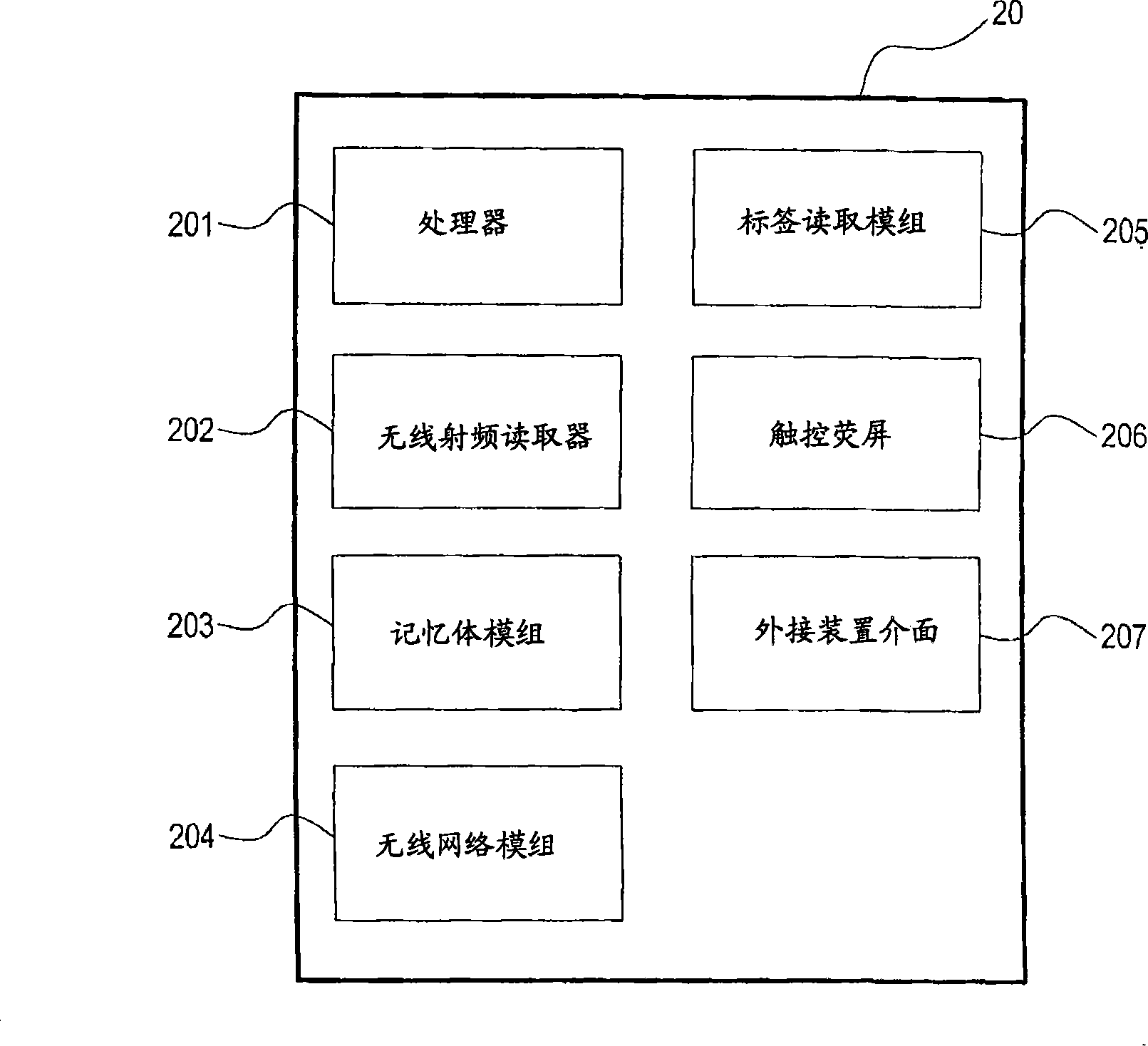
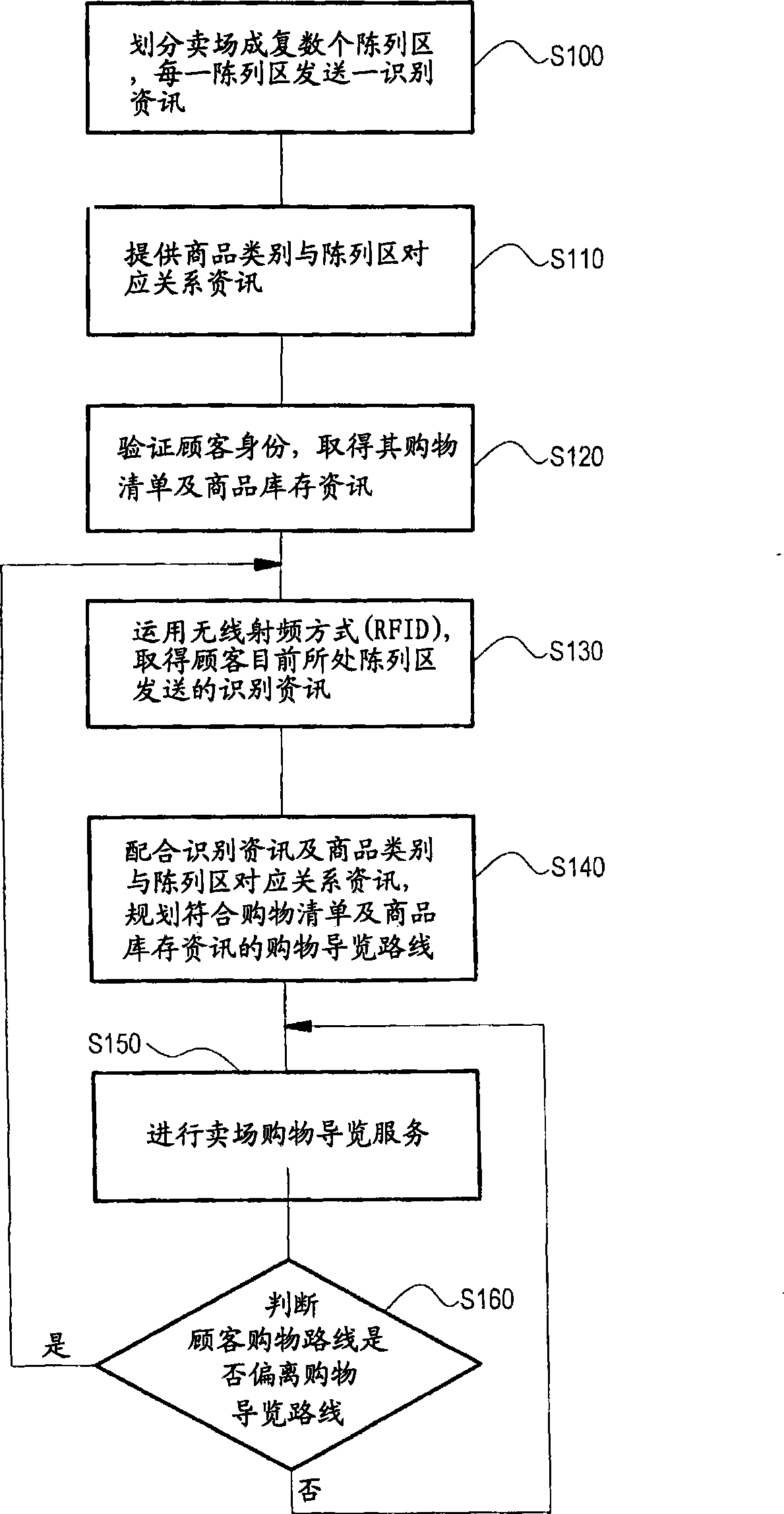
InactiveCN101499154AOptimize system structureSkill improvedCo-operative working arrangementsCommerceService systemPersonal identification number
The invention provides a method for providing market shopping guide service and a system thereof. The method includes steps as follows: firstly, reading a client personal identification number in a membership card by a guide device and transmitting to a market servo for identifying by wireless method; secondly, obtaining commodity information and client information relative to the client identification number; finally, layouting the market shopping route for providing shopping guide service. The guide device can layout a new shopping route according with present client position when client deviates away the shopping route. The shopping guide service provides a sales promotion information, commodity price, inventory status and rapid payment on the shopping guide route. The market shopping guide service system includes: a plurality of wireless RF identifying induction labels, at least one guide device containing a wireless RF reader and a processor, and a servo. The method and the system can help customer finding commodity needed to buy rapidly or obtaining the commodity sales promotion information in shopping, and can help market increasing profit which cause win-win situation between the customer and the market.
Owner:INVENTEC APPLIANCES CORP
High-speed UV light curing control device for printing press
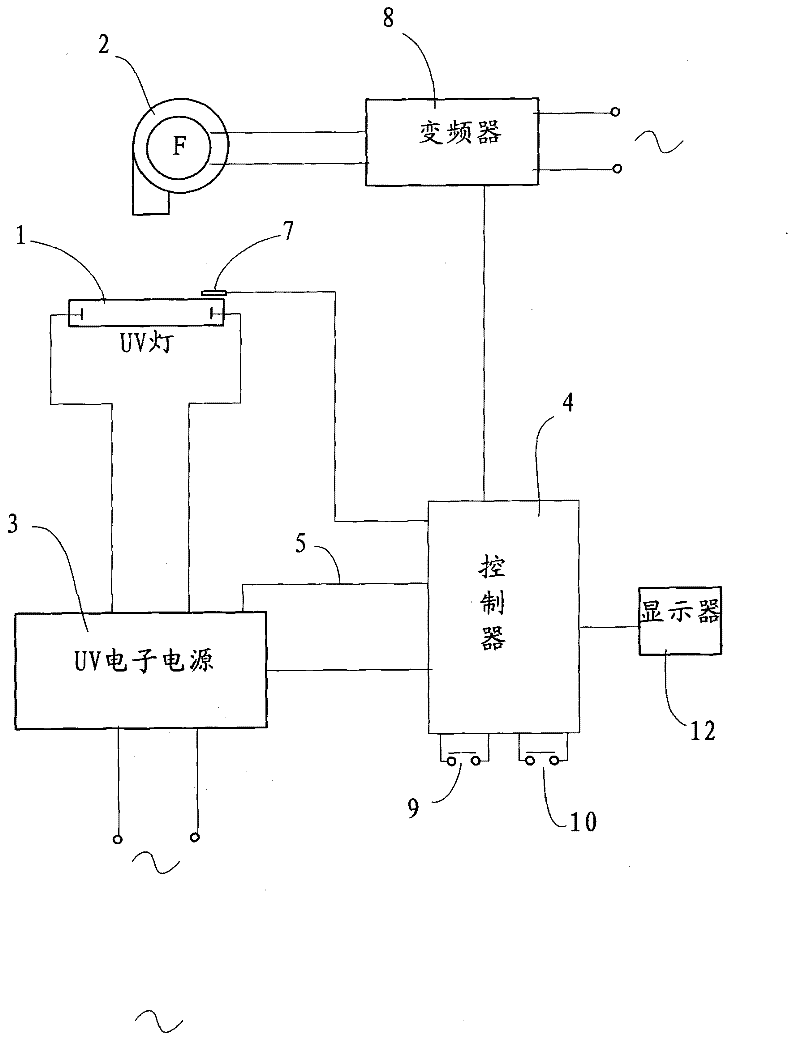
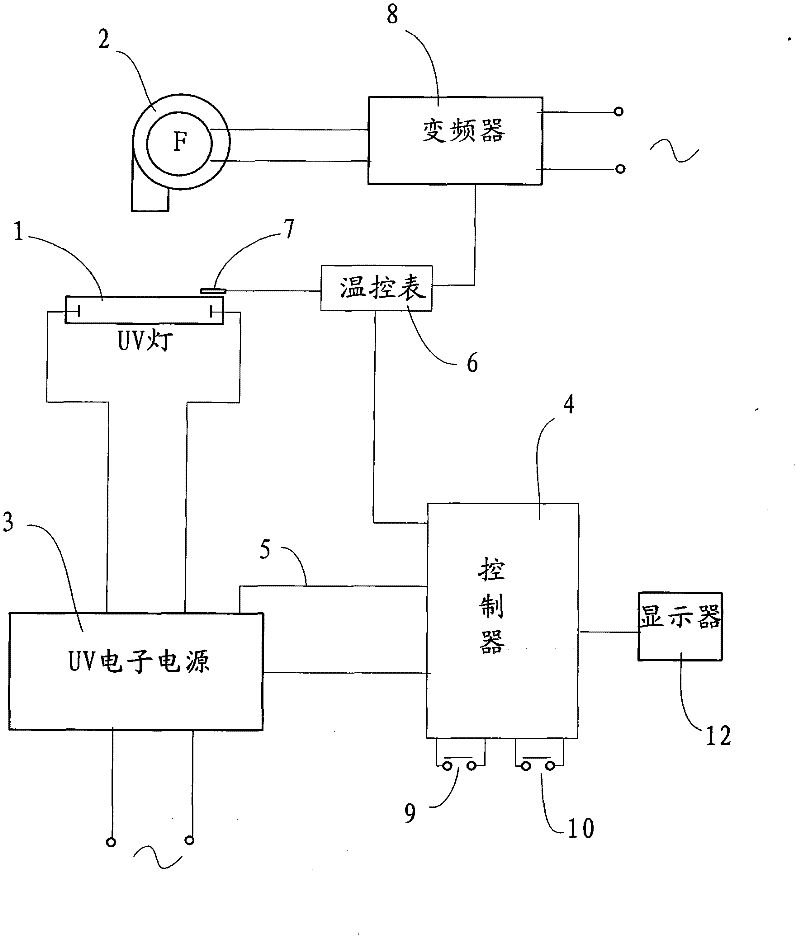
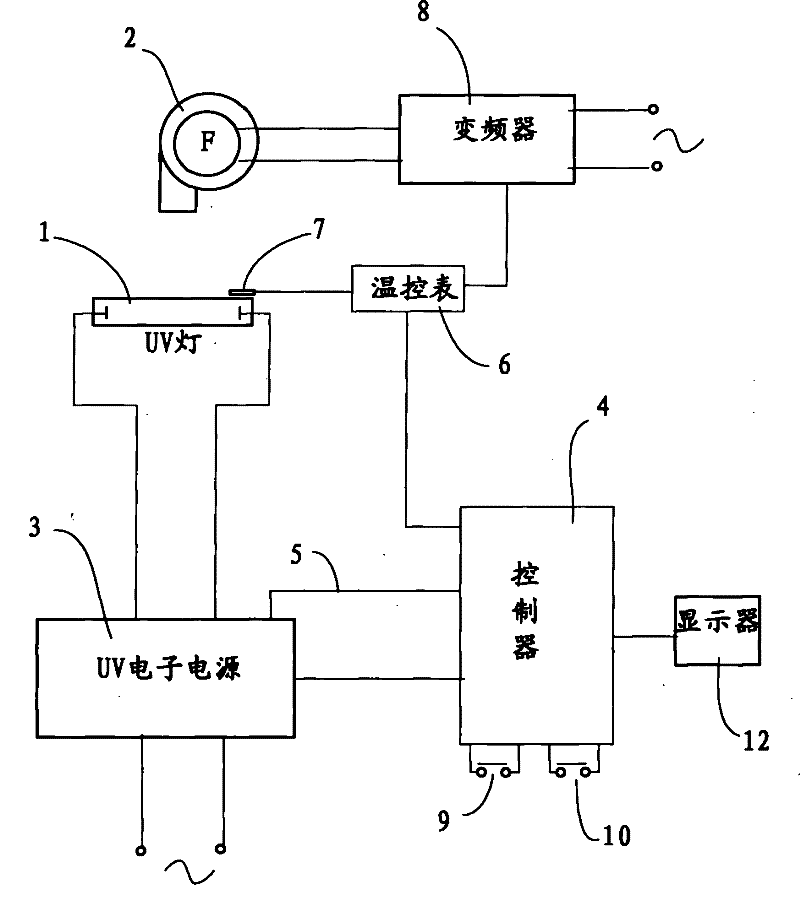
ActiveCN102259477AEasy curingGuaranteed to workPrinting press partsTemperature controlFrequency changer
The invention relates to light curing equipment and particularly relates to a high-speed UV (ultraviolet) light curing control device which comprises a UV lamp provided with a spotlight cover, a fan, a UV electronic power supply provided with a fault detection signal wire, a controller and a frequency converter, wherein the output end of the UV electronic power supply is connected with a UV lamp, and the fault detection signal wire of the UV electronic power supply is connected with the controller; the illumination region of the UV lamp is provided with a temperature sensor which is electrically connected with the controller; the output end of the frequency converter is connected with the fan; and the input end of the controller is at least provided with a start button and a power-reducing button, and the output end of the controller is respectively connected with the UV electronic power supply and the control end of the frequency converter. The novel device provided by the invention can be used for realizing the automation of the temperature control and on-off control on a light curing device, thus the printing quality and the printing efficiency are further ensured.
Owner:GUANGDONG LONGXING PACKAGING IND
Lamp tube status judgement circuit and its controller
InactiveCN101193486ASimple structureFunction increaseElectrical apparatusElectric lighting sourcesEngineeringOperating frequency
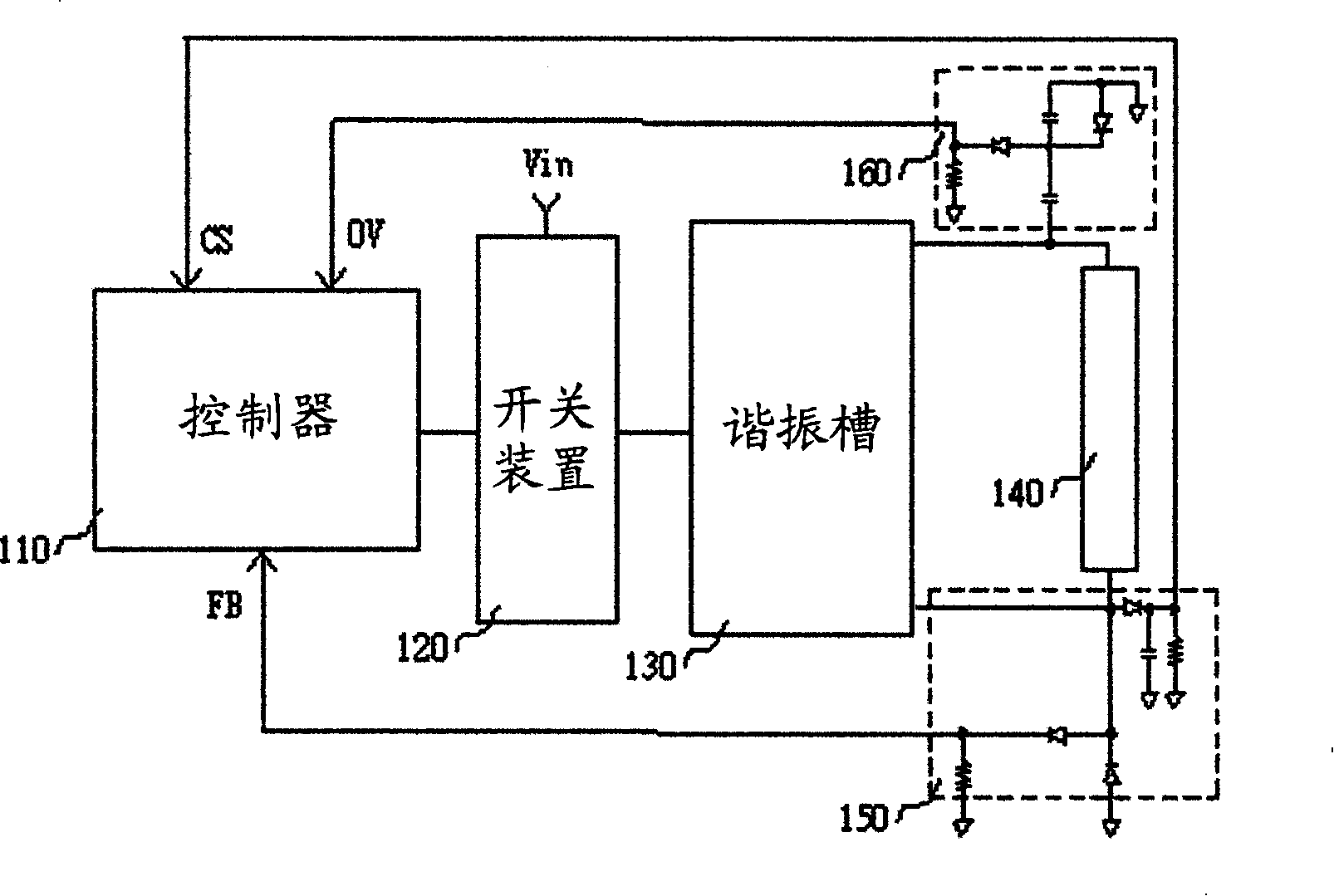
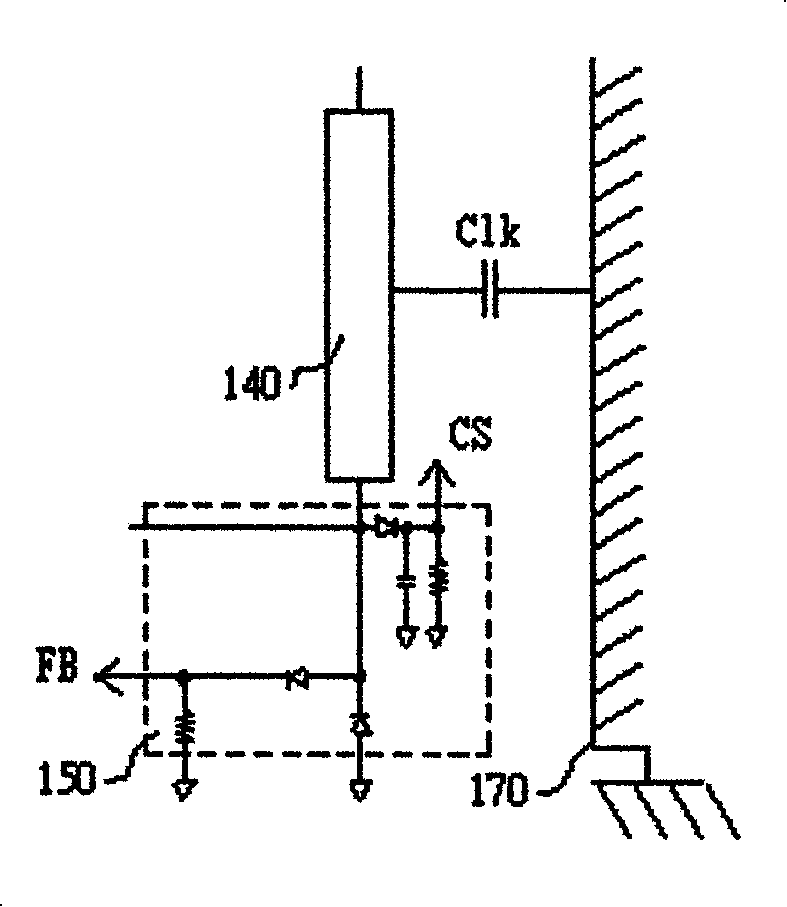
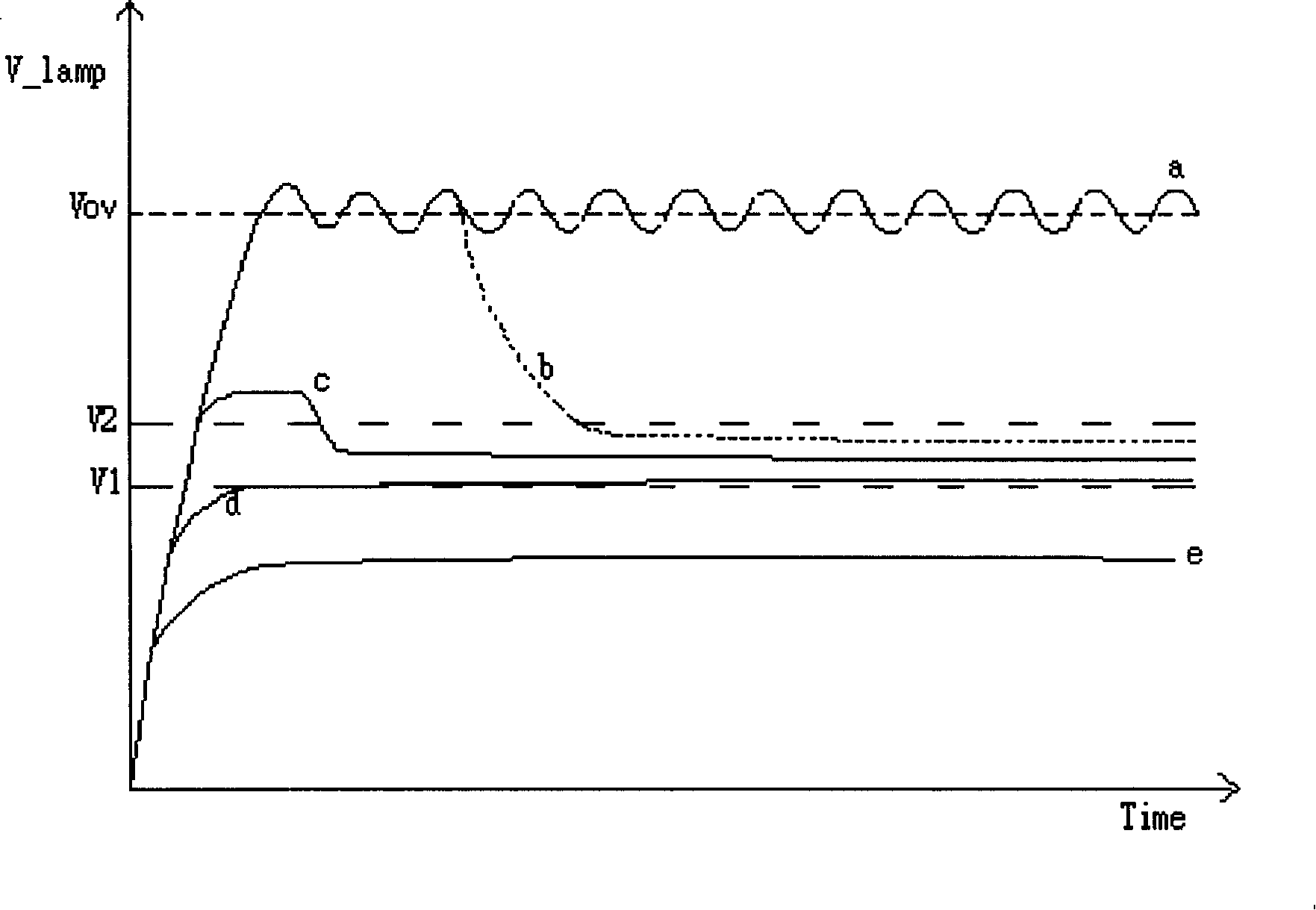
The invention relates to a DC / AC conversion circuit for driving a load. The DC / AC conversion drive circuit comprises a switch device, a resonant groove, a voltage detection circuit and a controller. The switch device is coupled with a DC power. The resonant groove is coupled with the switch device and the load which converts the electric power of the DC power from the switch device into an AC signal in order to drive the load. The voltage detection circuit is coupled with the load and generates a voltage detection signal according the load voltage. The controller is coupled with the voltage detection circuit and the switch device and controls the electric power of the DC power that is transmitted to the resonant groove through the switch device. The controller decides the change of the operating frequency on the basis of the voltage detection signals.
Owner:BEYOND INNOVATION TECH
Wave generator
InactiveCN101105167AExtended service lifeLow costMachines/enginesEngine componentsElectric power systemGravitational force
The invention relates to a wave electric power system, which comprises a floating element, a rope unit, a kinetic energy unit, and a power generation unit. The floating element has gravitational force lower than the buoyant force of seawater and can float up and down with wave. The rope unit has a rope connecting the floating element, and the rope crosses over seacoast with height of drop and in penetrated into inland far away form sea surface. The kinetic energy unit allows the rope to be coiled, and has a traction force not larger than the gravitational force of the floating element, so that the rope can carry out reciprocating movement under the action of gravitational force and traction force to generate kinetic energy. The power generation unit receives the kinetic energy from the kinetic energy unit, converts the kinetic energy to electric energy and then output. Thereby, the kinetic energy and power generation unit are far away seacoast, so as to prolong the service life thereof.
Owner:李贻萍
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com