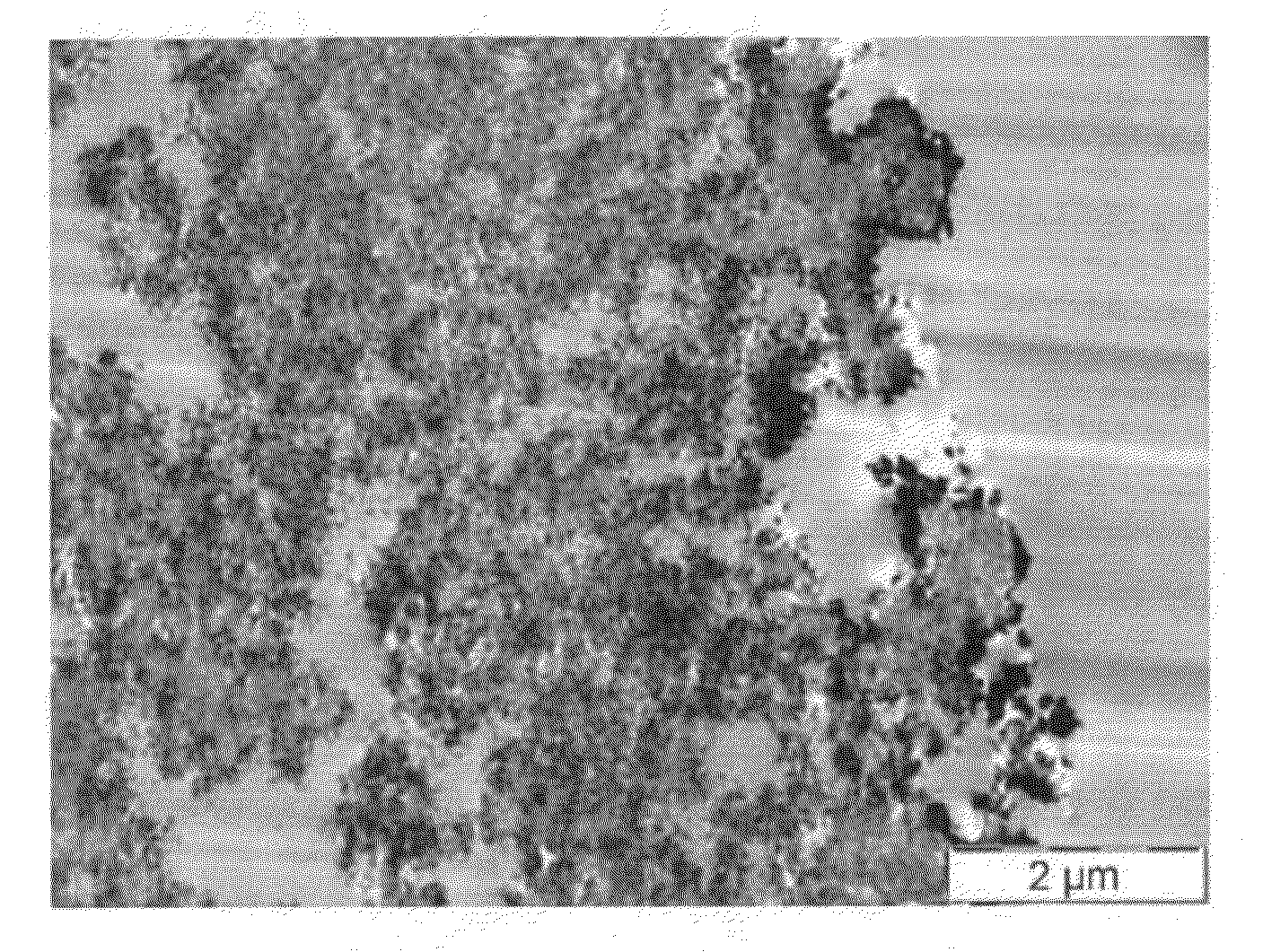
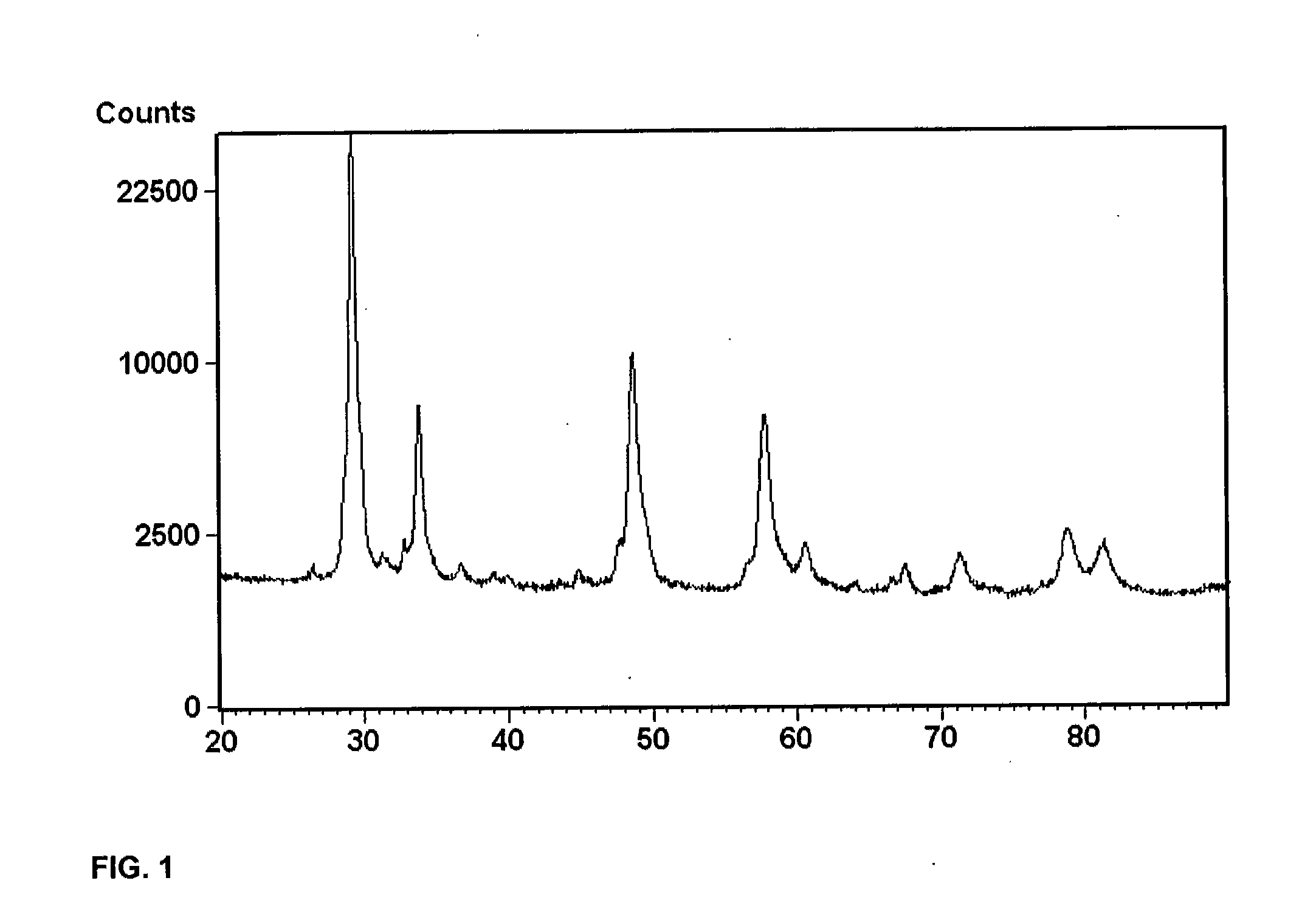
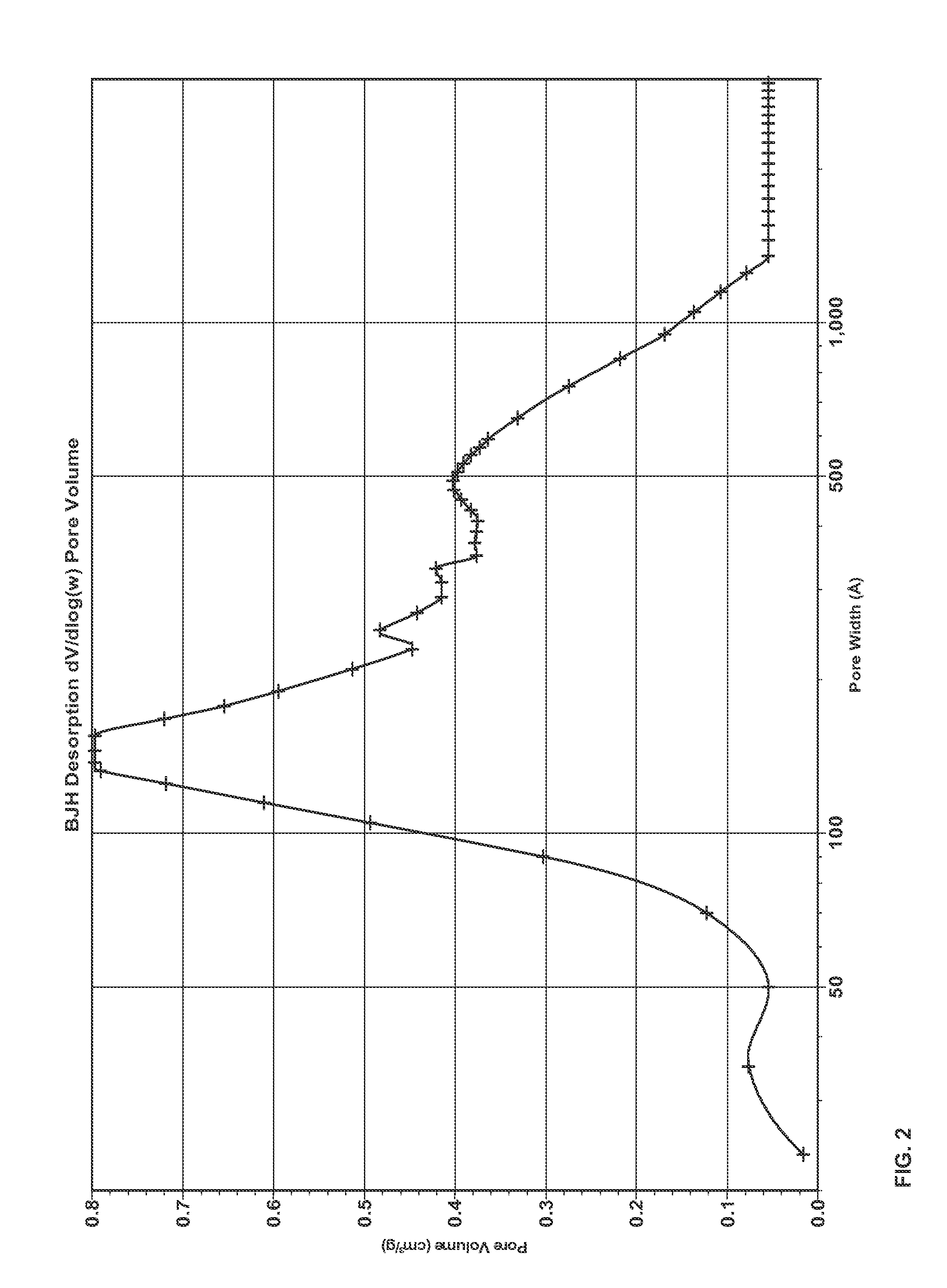
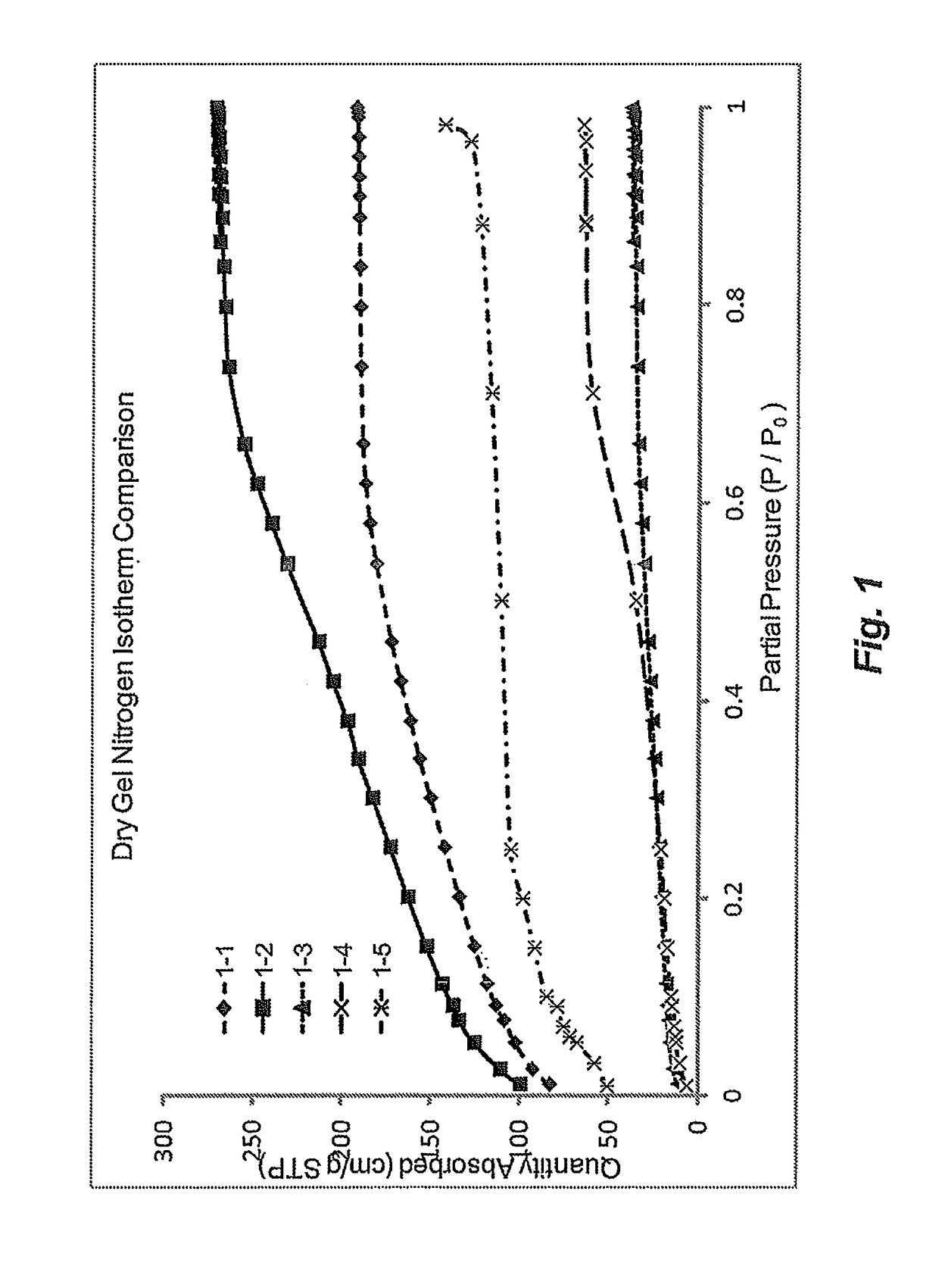
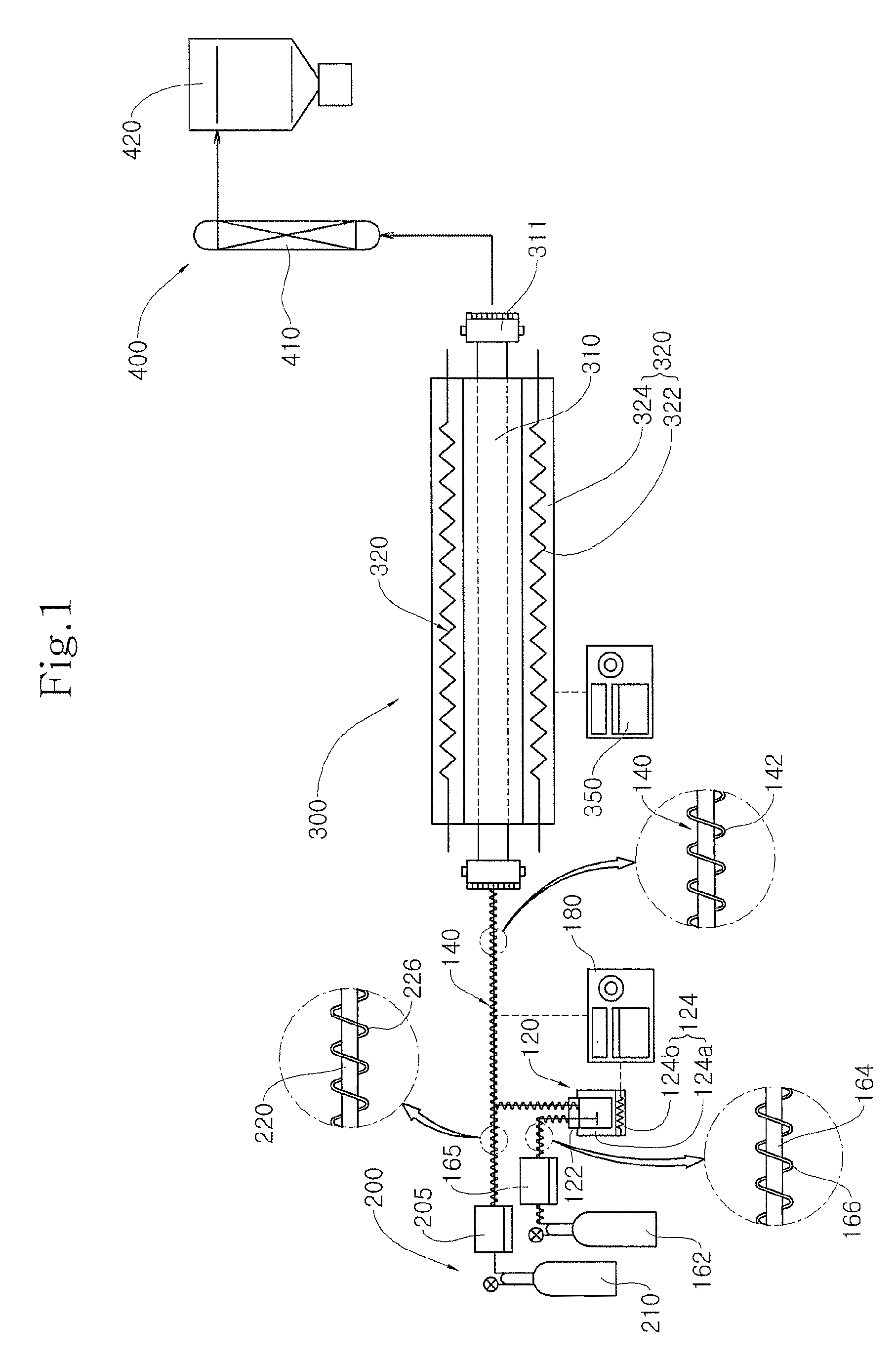
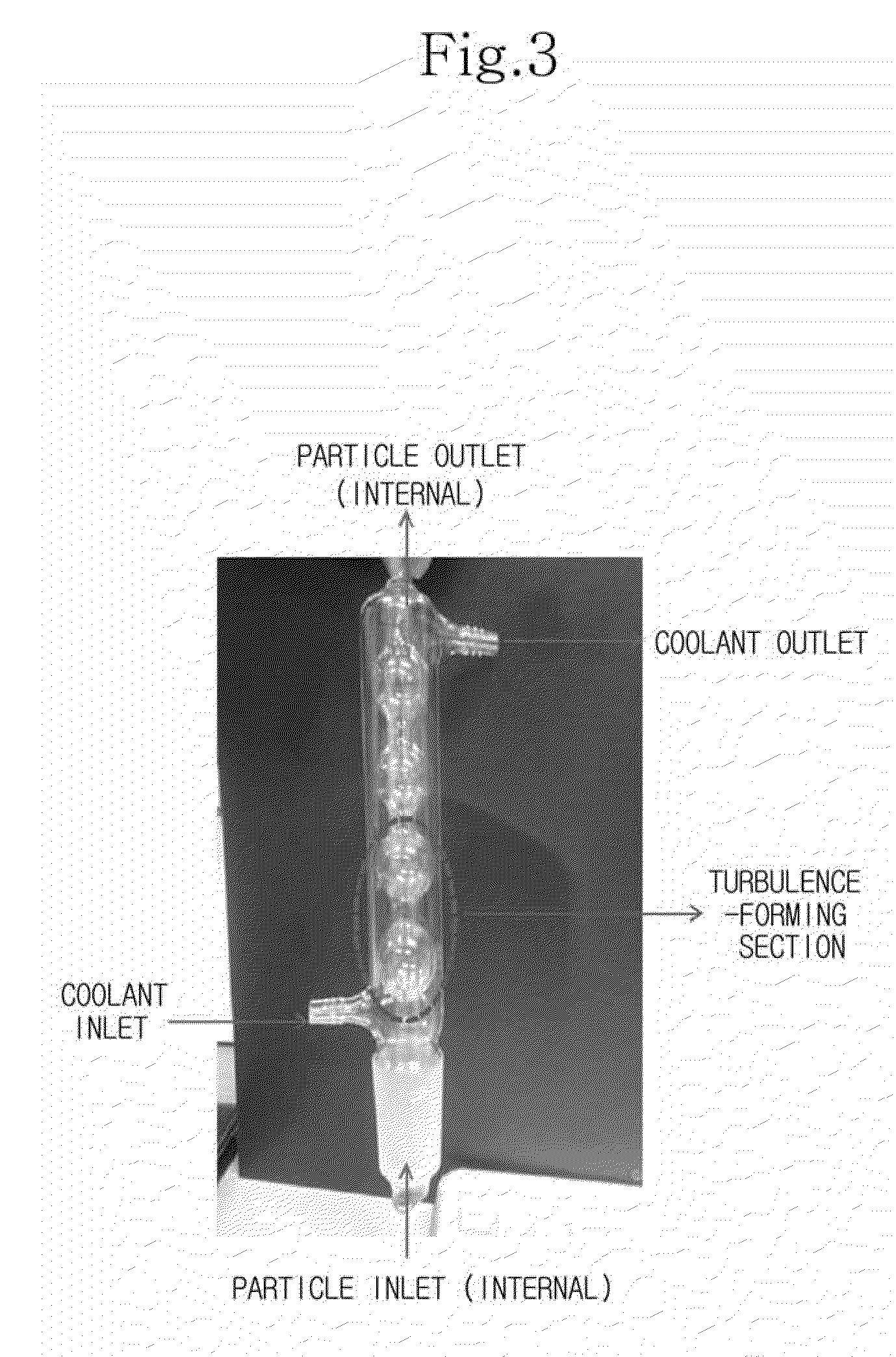
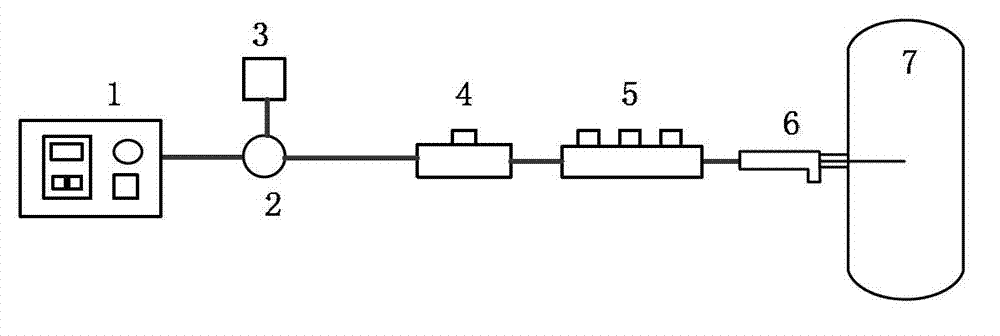
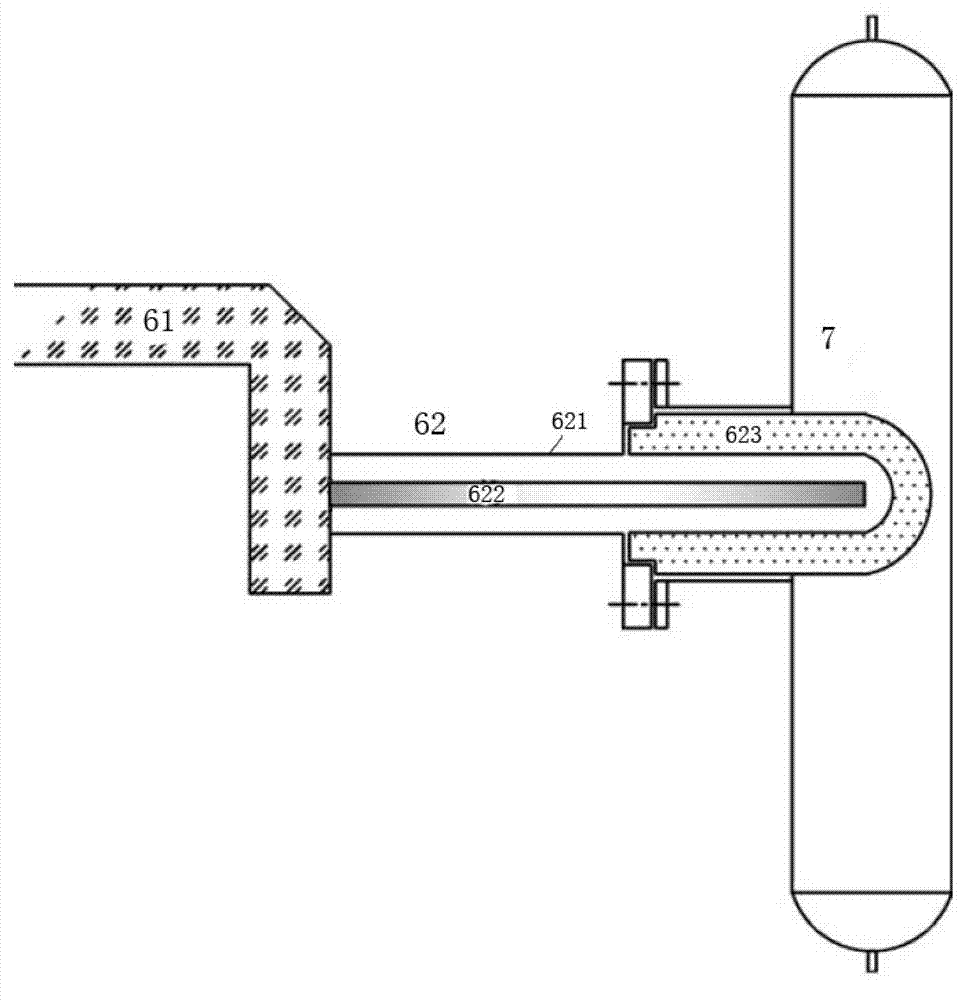
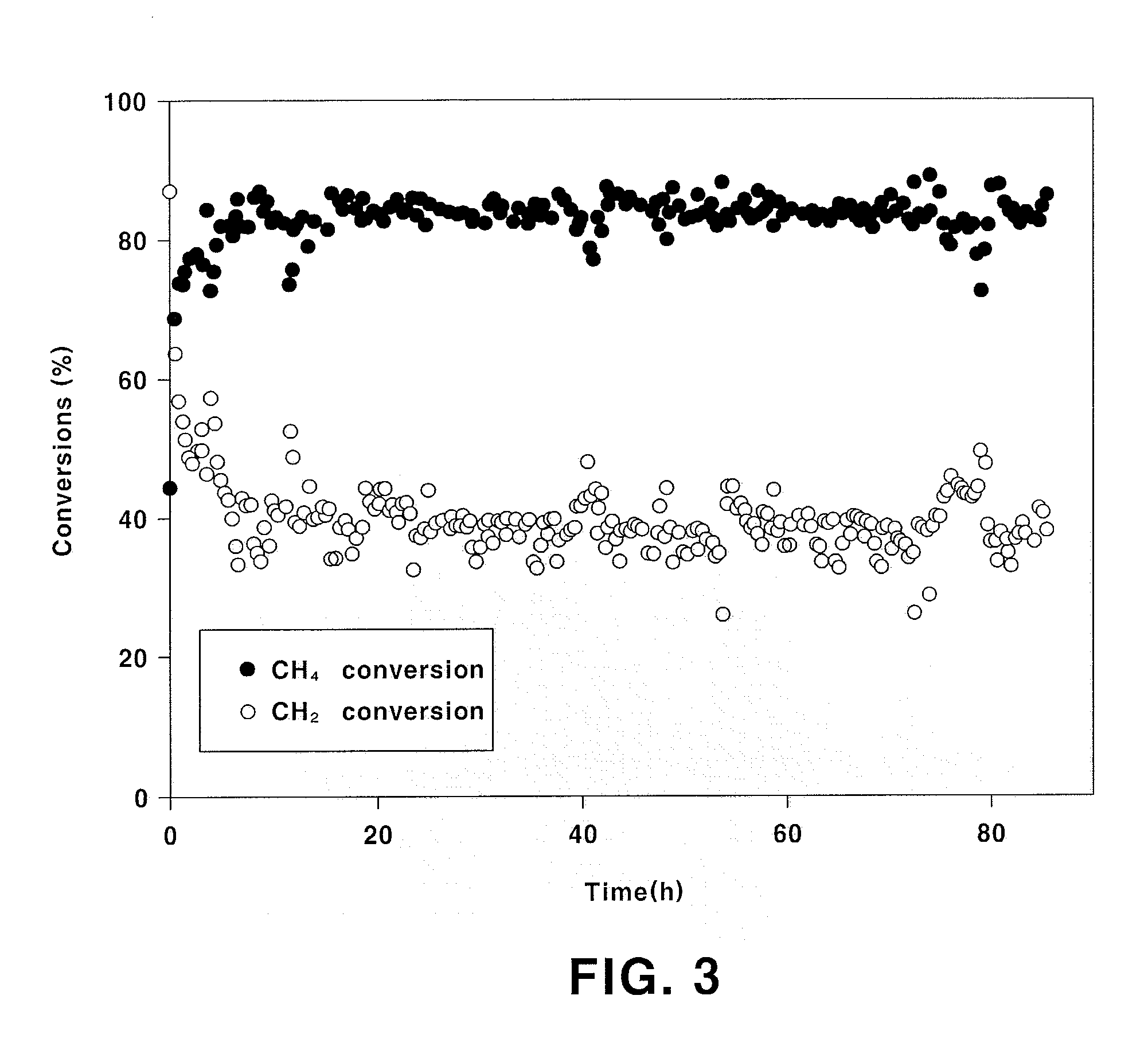
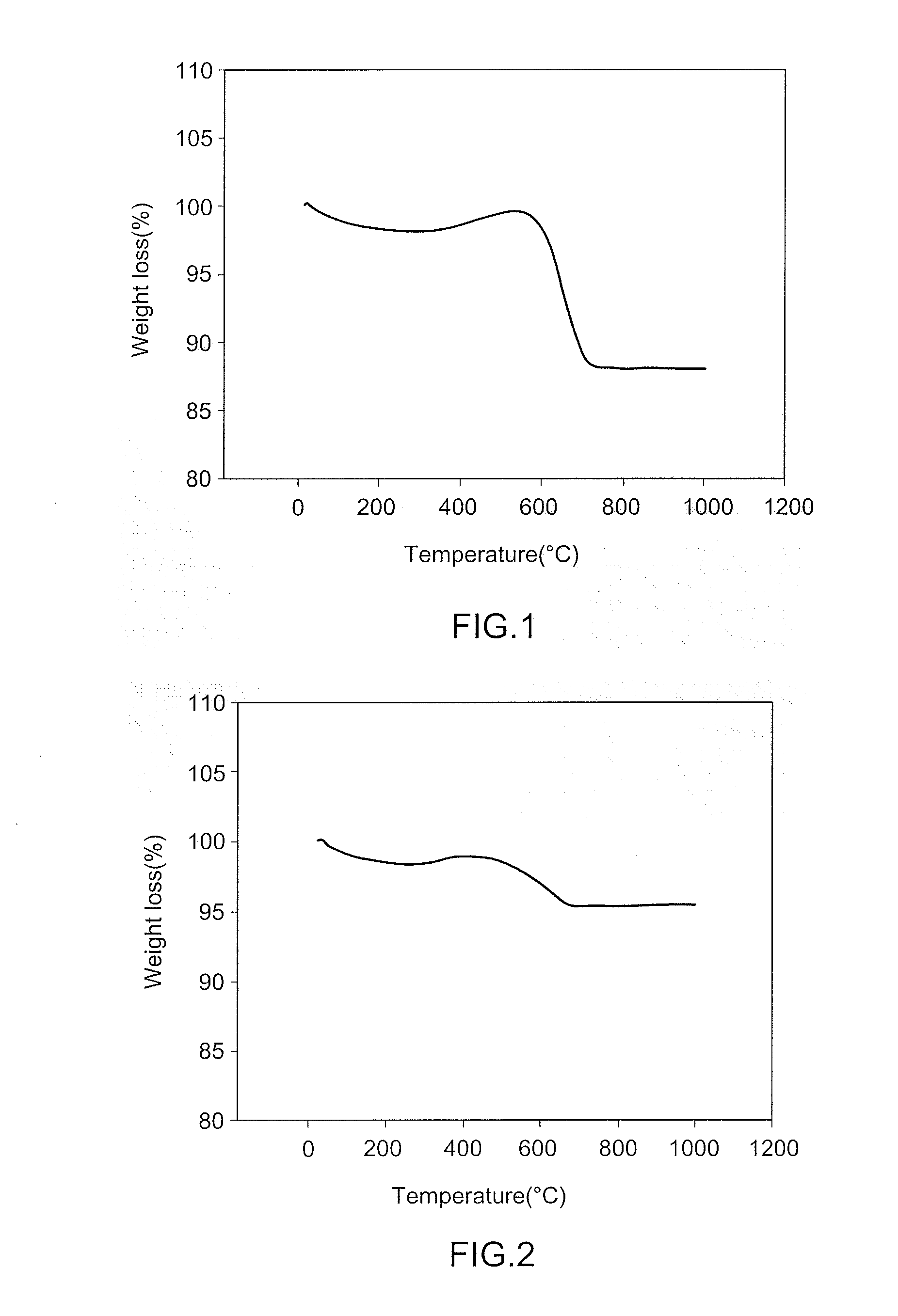
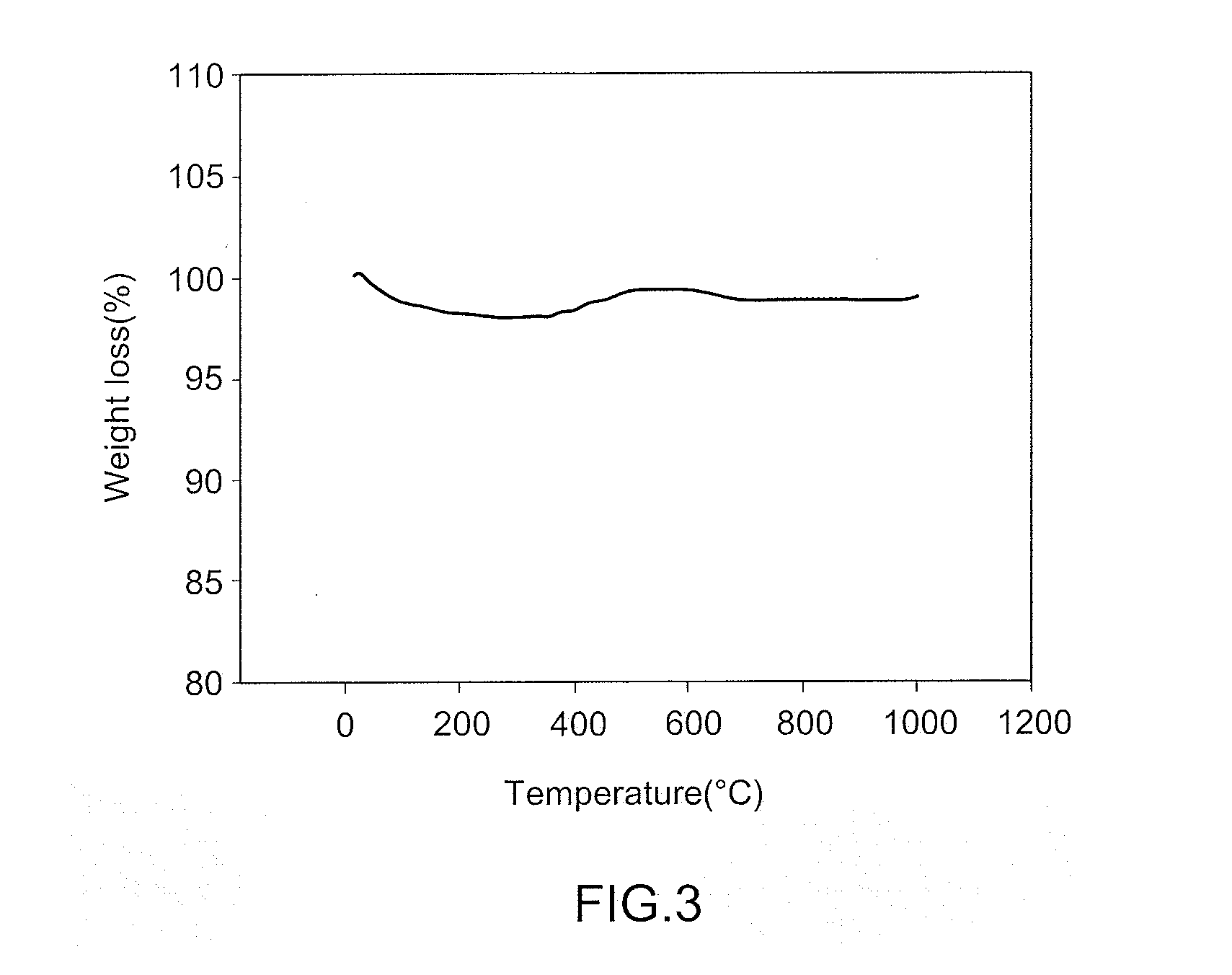
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
373results about "Heat treatments" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Porous inorganic composite oxide
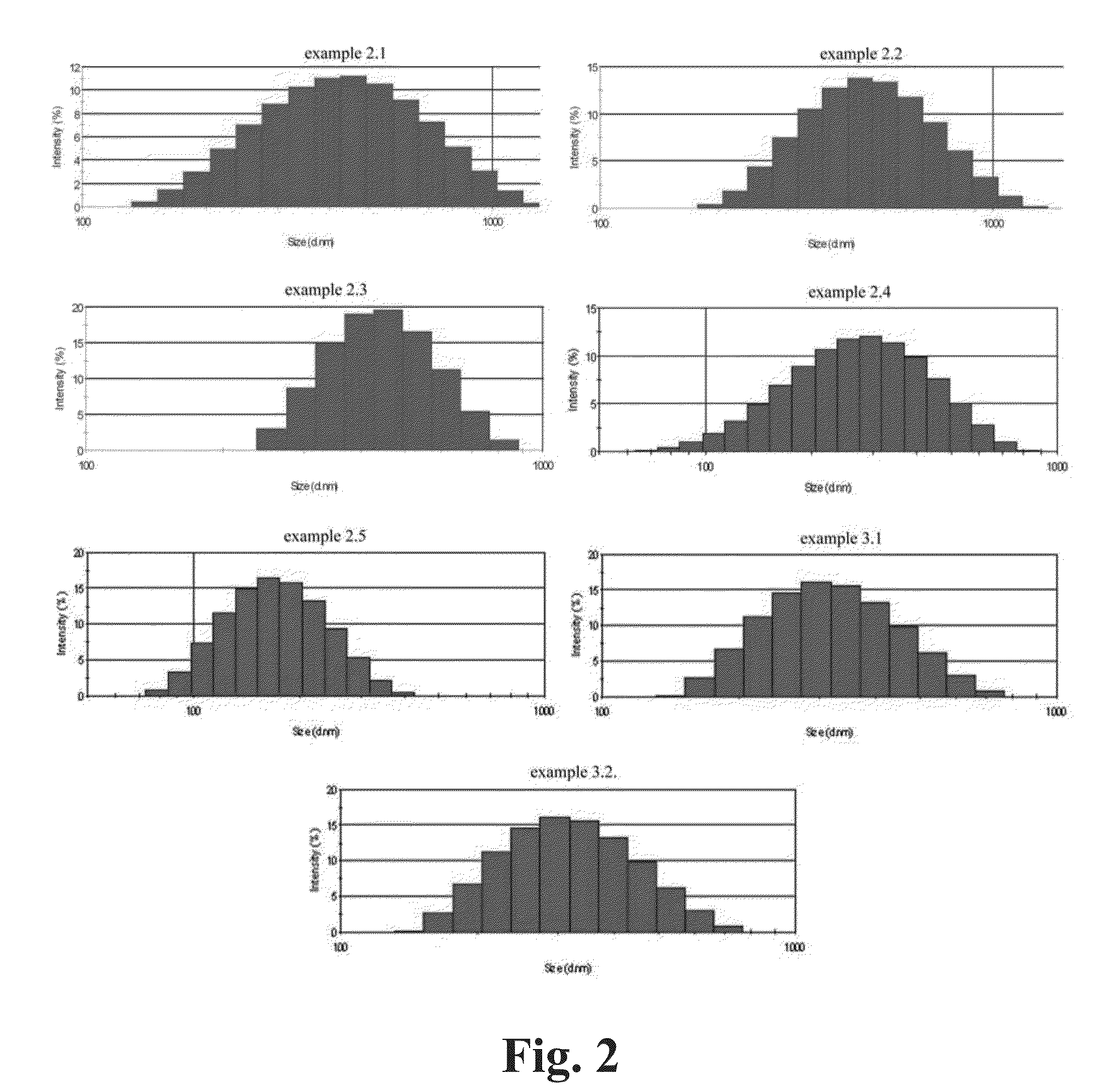
ActiveUS20120129690A1Improve thermal stabilityHigh pore volumeHeat treatmentsInternal combustion piston enginesPtru catalystCerium
A porous inorganic composite oxide containing oxides of aluminum and of cerium and / or zirconium, and, optionally, oxides of one or more dopants selected from transition metals, rare earths, and mixtures thereof, and having a specific surface area, in m2 / g, after calcining at 1100° C. for 5 hours, of ≧0.8235[Al]+11.157 and a total pore volume, in cm3 / g, after calcining at 900° C. for 2 hours, of ≧0.0097[Al]+0.0647, wherein [Al] is the amount of oxides of aluminum, expressed as pbw Al2O3 per 100 pbw of the composite oxide; a catalyst containing one or more noble metals dispersed on the porous inorganic composite oxide; and a method for making the porous inorganic composite oxide.
Owner:RHODIA OPERATIONS SAS
Preparation of polymeric resins and carbon materials
Methods for making carbon materials are provided. In at least one specific embodiment, the method can include combining one or more polymer precursors with one or more liquids to produce a mixture. The mixture can be an emulsion, dispersion, or a suspension. The liquid can include hexane, pentane, cyclopentane, benzene, toluene, o-xylene, m-xylene, p-xylene, diethyl ether, ethylmethylketone, dichloromethane, tetrahydrofuran, mineral oils, paraffin oils, vegetable derived oils, or any mixture thereof. The method can also include aging the mixture at a temperature and time sufficient for the polymer precursor to react and form polymer gel particles having a volume average particle size (Dv,50) of the polymer particles in gel form greater than or equal to 1 mm. The method can also include heating the polymer gel particles to produce a carbon material.
Owner:GEORGIA PACIFIC CHEM LLC
Reaction chamber for manufacturing a carbon nanotube, apparatus for manufacturing the carbon nanotube and system for manufacturing the carbon nanotube
ActiveUS7618599B2High purityHigh productHeat treatmentsMaterial nanotechnologyCarbon nanotubeProduct gas
Disclosed are a reaction chamber for manufacturing a carbon nanotube, an apparatus for manufacturing a carbon nanotube and a system for manufacturing a carbon nanotube. The reaction chamber includes a reaction furnace, a gas inlet, a gas outlet and a heat transfer member. The reaction furnace has a box structure for receiving a substrate wherein the reaction furnace provides a space for forming the carbon nanotube on the substrate. The gas inlet having a through-hole structure formed at a first portion of the reaction furnace and the gas outlet has a through-hole structure formed at a second portion of the reaction furnace. The heat transfer member has at least one rectangular through-hole structure formed at a third portion of the reaction furnace along a direction substantially in parallel to the substrate. The apparatus includes the reaction furnace, a gas supply member, a gas exhausting member and a heating member. The system includes the apparatus and a transfer apparatus.
Owner:SEMES CO LTD
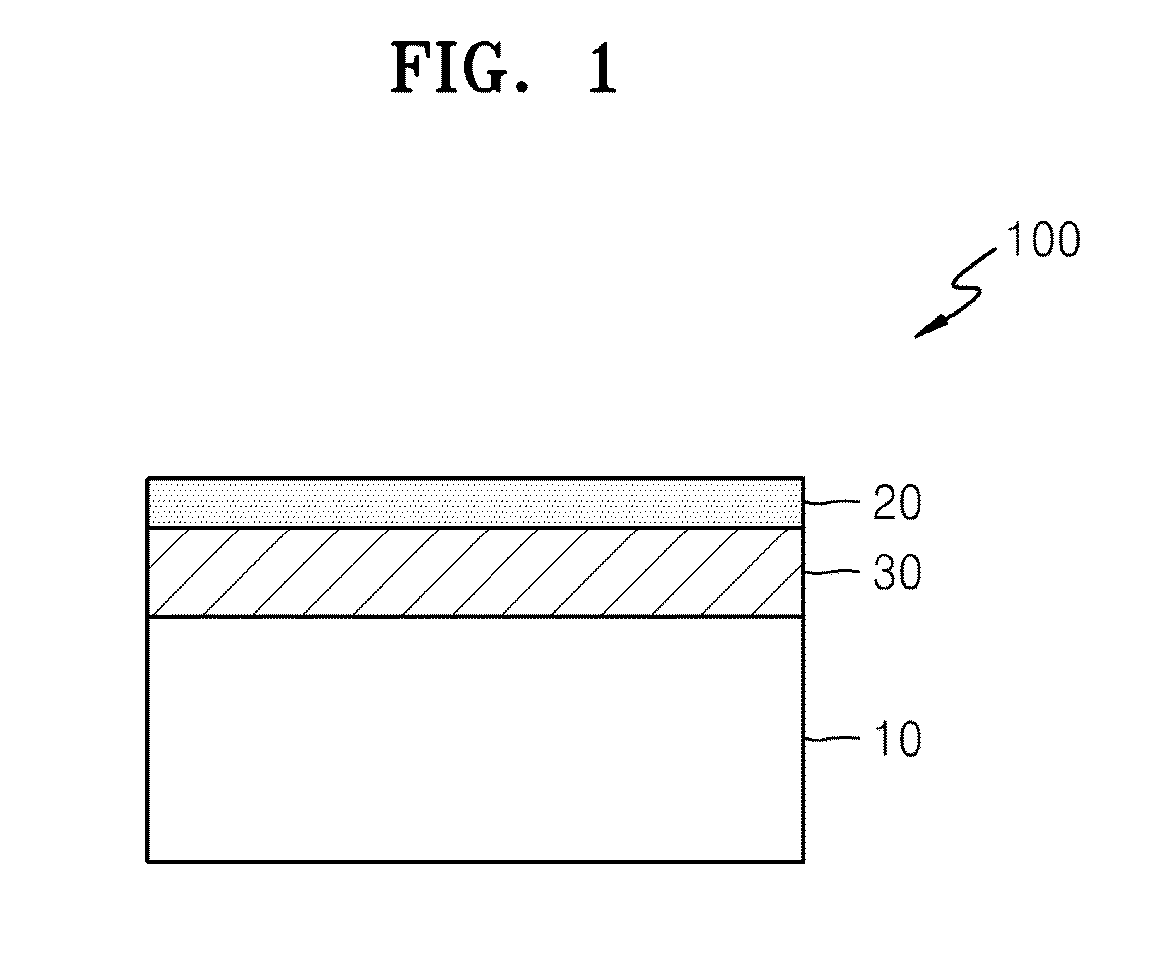
Graphene structure, graphene device including same, and method of manufacturing graphene structure
A method of manufacturing a graphene structure, the graphene structure, and a graphene device including the graphene structure, include depositing a metal layer over a silicon carbide substrate; and performing, at a first temperature, a heat treatment on the silicon carbide substrate over which the metal layer is deposited to form a composite layer and a graphene layer on the silicon carbide substrate. The composite layer includes a metal.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Manufacturing method for calcium fluoride crystal and processing method for calcium fluoride powder
InactiveUS6123764AImprove efficiencyHeat treatmentsPolycrystalline material growthCrucibleSingle crystal
A manufacturing method for a single crystal of calcium fluoride includes the steps of degassing calcium fluoride powder particles to desorb impurities from surfaces of the calcium fluoride powder particles, preprocessing the degassed calcium fluoride powder particles by fusing the degassed calcium fluoride powder particles in a crucible to obtain a preprocessed product, and re-fusing the preprocessed product in a crucible to grow a single crystal of calcium fluoride.
Owner:NIKON CORP
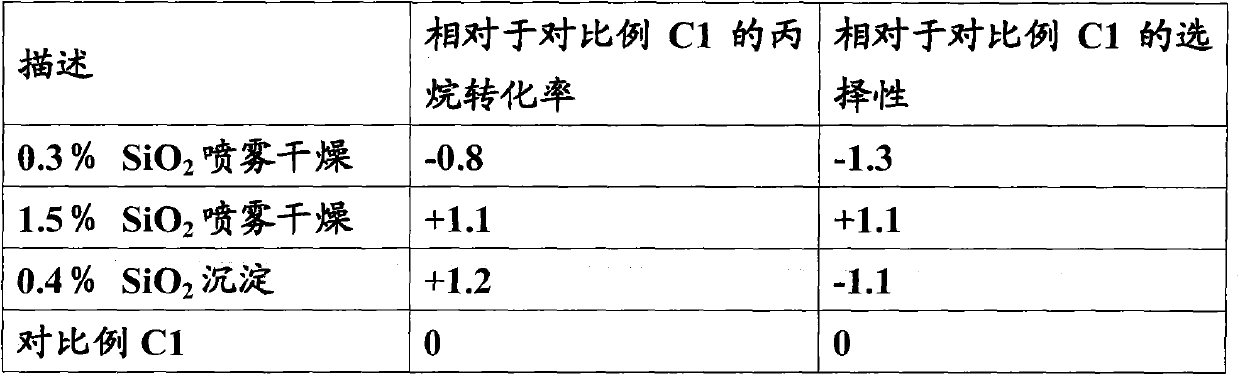
Catalyst for the synthesis of dimethyl carbonate from urea and methanol, preparation and use thereof
InactiveUS7271120B2Speed up the conversion processHigh selectivityHeat treatmentsOrganic compound preparationActive componentMethyl carbonate
A catalyst for the preparation of dimethyl carbonate from urea and methanol having a composition on weight base of: active component of from 20 to 50 wt %, and carrier of from 80 to 50 wt %, and prepared by equal-volume spraying and impregnating method is disclosed. The method for the synthesis of dimethyl carbonate can be carried out in a catalytic rectification reactor, said method comprising: (1) dissolving urea in methanol to form a methanol solution of urea; and (2) feeding the methanol solution of urea and methanol counter-currently into the reaction zone, wherein the reaction is carried out at conditions including reaction temperature of from 120° C. to 250° C., reaction pressure of from 0.1 MPa to 5 MPa, kettle bottom temperature of from 70° C. to 210° C., stripping section temperature of from 70° C. to 250° C., rectifying section temperature of from 70° C. to 280° C., and reflux ratio of from 1:1 to 20:1. The preparation of the catalyst according to the present invention is simple and has good repeatability, and the catalyst could further enhance the yield of DMC as well as conversion of urea in the catalytic rectification reactor.
Owner:INST OF COAL CHEM +1
Preparation of polymeric resins and carbon materials
Methods for making carbon materials are provided. In at least one specific embodiment, the method can include combining one or more polymer precursors with one or more liquids to produce a mixture. The mixture can be an emulsion, dispersion, or a suspension. The liquid can include hexane, pentane, cyclopentane, benzene, toluene, o-xylene, m-xylene, p-xylene, diethyl ether, ethylmethylketone, dichloromethane, tetrahydrofuran, mineral oils, paraffin oils, vegetable derived oils, or any mixture thereof. The method can also include aging the mixture at a temperature and time sufficient for the polymer precursor to react and form polymer gel particles having a volume average particle size (Dv,50) of the polymer particles in gel form greater than or equal to 1 mm. The method can also include heating the polymer gel particles to produce a carbon material.
Owner:GEORGIA PACIFIC CHEM LLC
Carbon composites and methods of manufacture
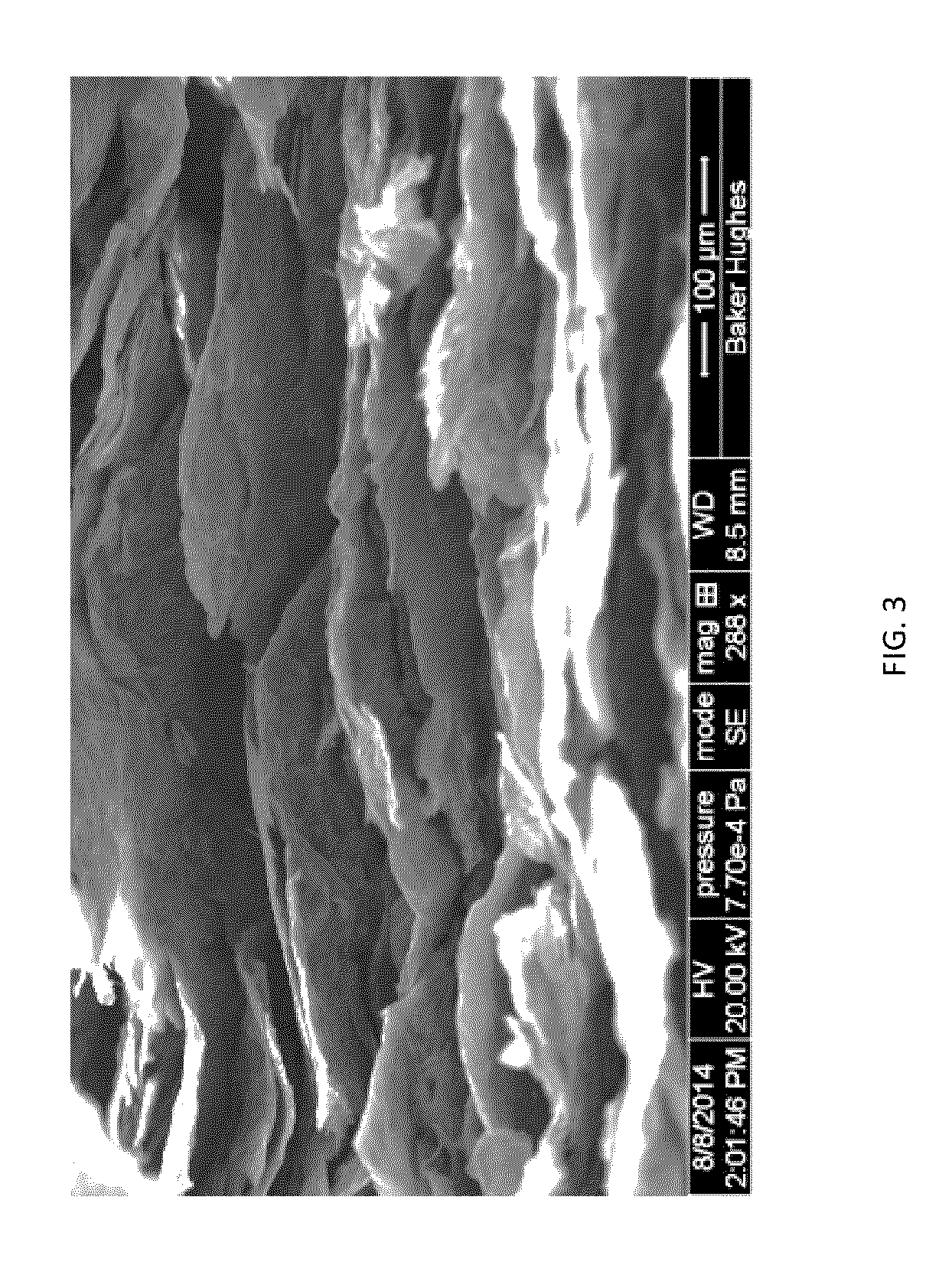
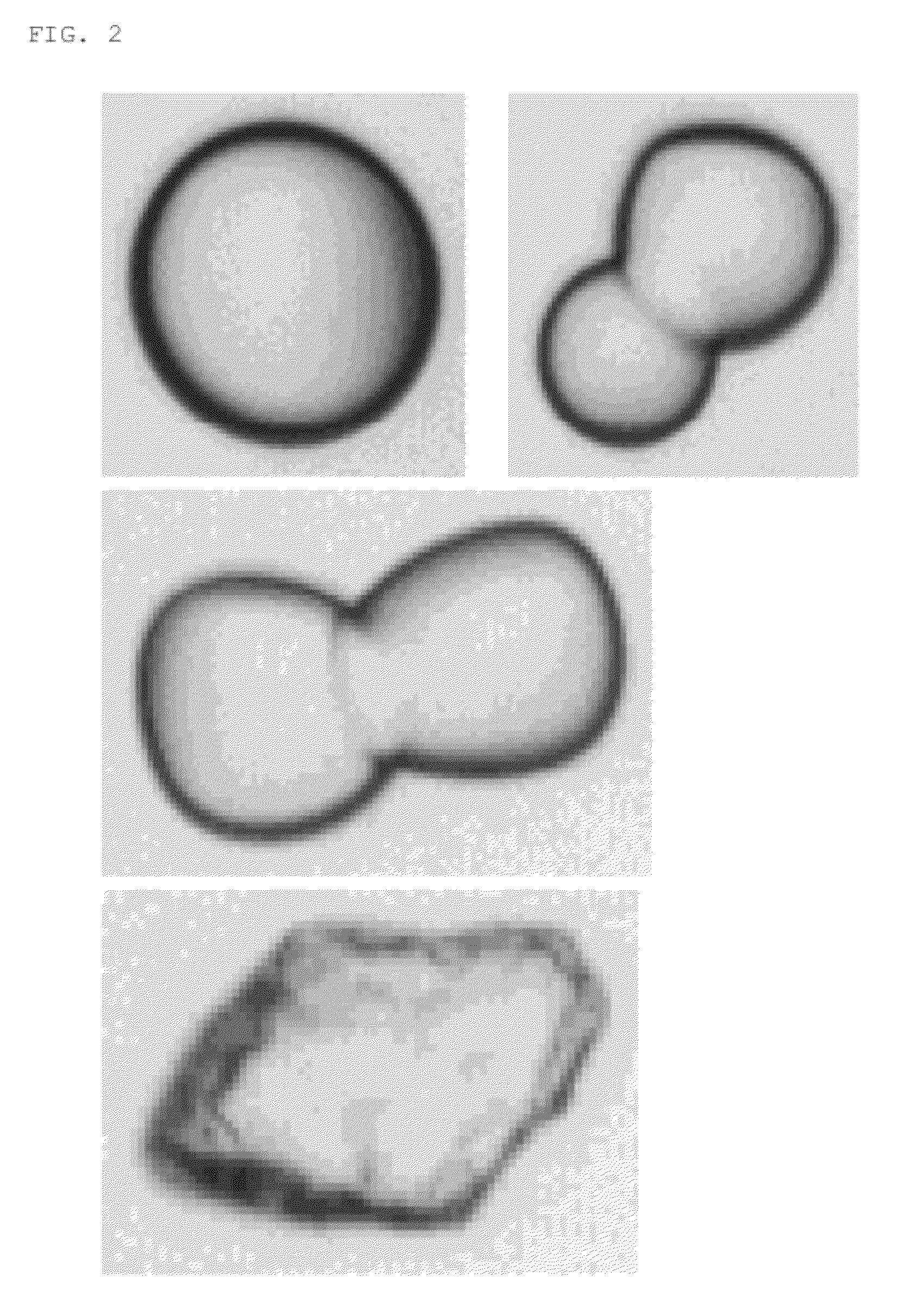
A method for the manufacture of a carbon composite comprises compressing a combination comprising carbon and a binder at a temperature of about 350° C. to about 1200° C. and a pressure of about 500 psi to about 30,000 psi to form the carbon composite; wherein the binder comprises a nonmetal, metal, alloy of the metal, or a combination thereof; wherein the nonmetal is selected from the group consisting of SiO2, Si, B, B2O3, and a combination thereof; and the metal is selected from the group consisting of aluminum, copper, titanium, nickel, tungsten, chromium, iron, manganese, zirconium, hafnium, vanadium, niobium, molybdenum, tin, bismuth, antimony, lead, cadmium, selenium, and a combination thereof.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Nickel on Strontium-Doped Calcium Aluminate Catalyst for Reforming
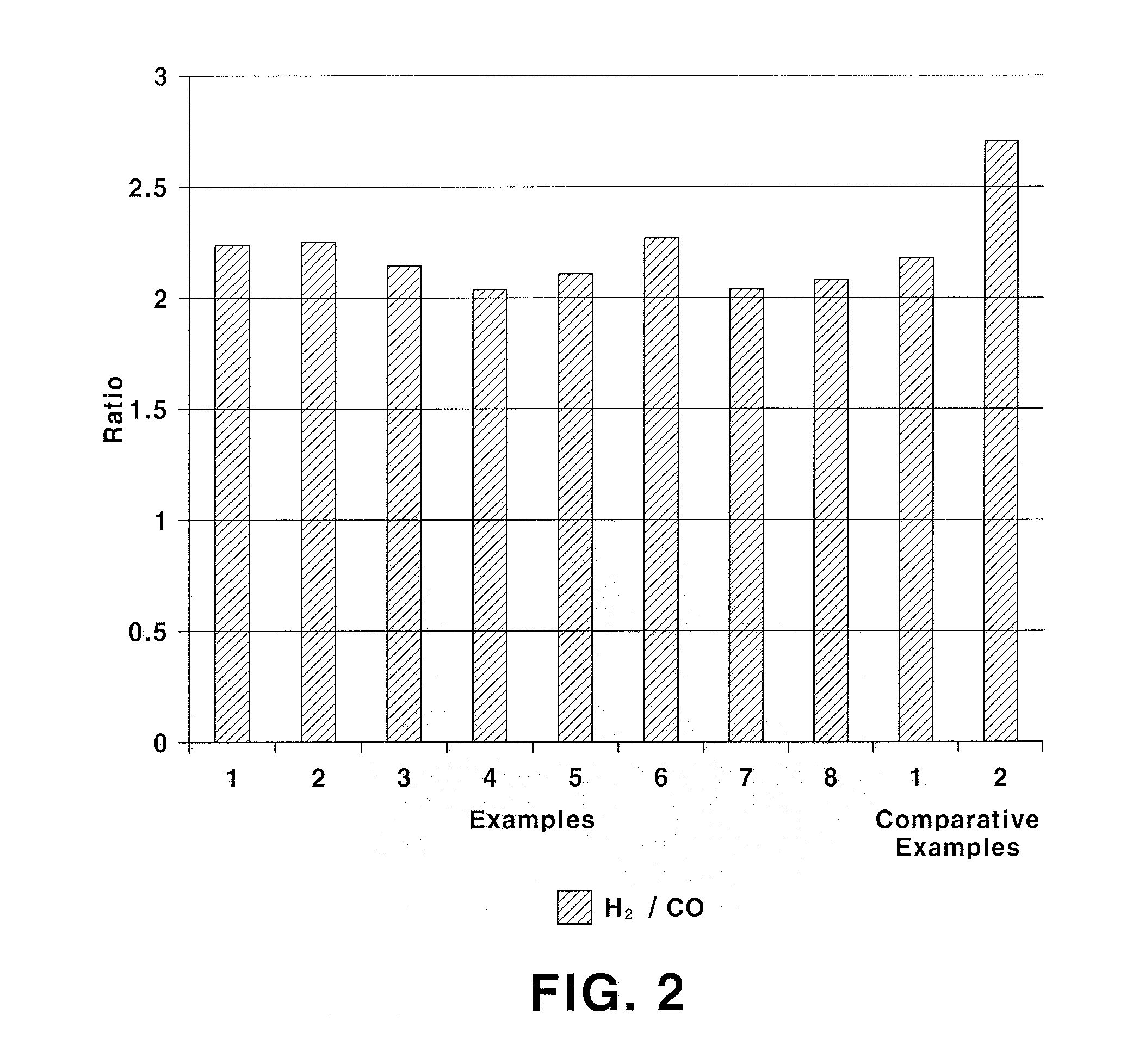
A promoted calcium-alumina supported reforming catalyst that is particularly useful for reforming reactions where low H2 / CO ratio synthesis gas, such as less than 2.3 is generated directly is disclosed. The catalyst comprises alumina, from about 0.3 wt % to about 35 wt % calcium oxide, from about 0.1 wt % to about 35 wt % of a strontium promoter, and from about 0.5 wt % to about 30 wt % nickel. The support is prepared by a method wherein the calcium oxide is combined with the alumina to form aluminum-rich calcium aluminates.
Owner:CLARIANT INT LTD
Carbon-silicon composite and manufacturing method thereof
Disclosed herein are a manufacturing method of a carbon-silicon composite, the manufacturing method including: (a) preparing a silicon-carbon-polymer matrix slurry including a silicon slurry, carbon particles, a monomer of polymer, and a cross-linking agent; (b) performing a heat treatment process on the silicon-carbon-polymer matrix slurry to manufacture a silicon-carbon-polymer carbonized matrix; (c) pulverizing the silicon-carbon-polymer carbonized matrix to manufacture a silicon-carbon-polymer carbonized matrix structure; and (d) mixing the silicon-carbon-polymer carbonized matrix structure with a first carbon raw material and performing a carbonization process to manufacture a carbon-silicon composite, the carbon-silicon composite, an anode for a secondary battery manufactured by applying the carbon-silicon composite, and a secondary battery including the anode for a secondary battery.
Owner:OCI
Alumina catalyst support
ActiveUS20120122671A1Increase the apertureImprove thermal stabilityHeat treatmentsInternal combustion piston enginesDopantGram
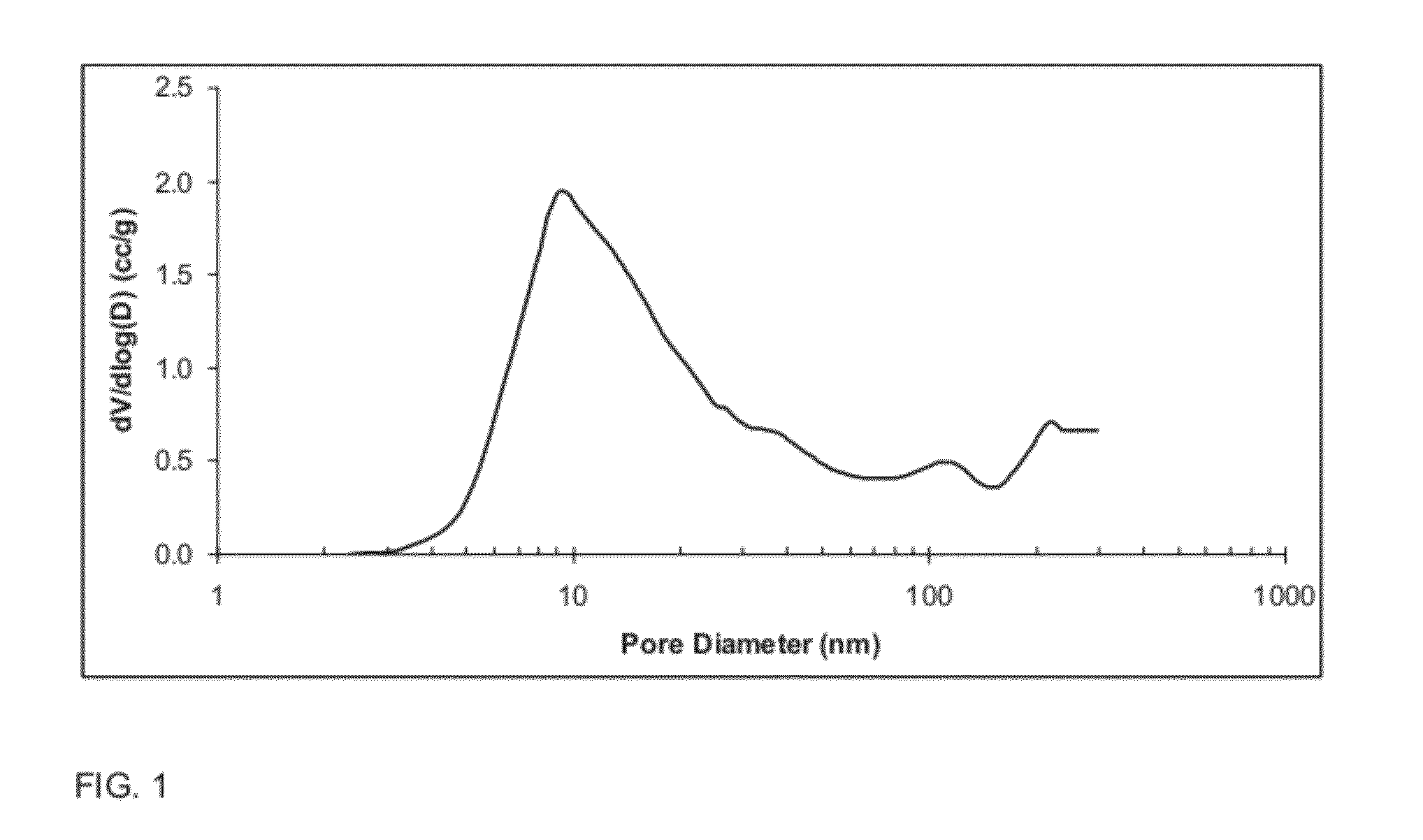
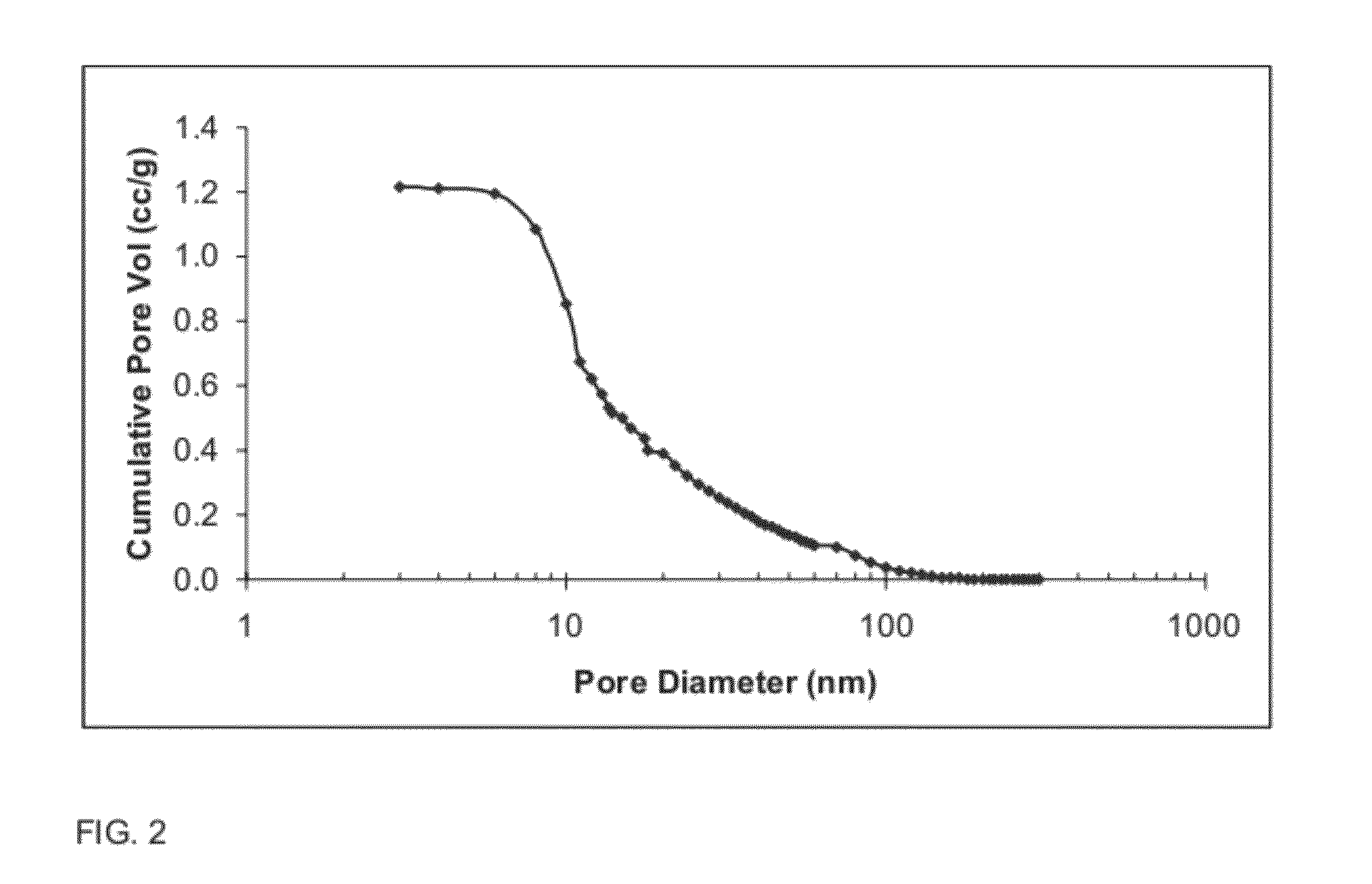
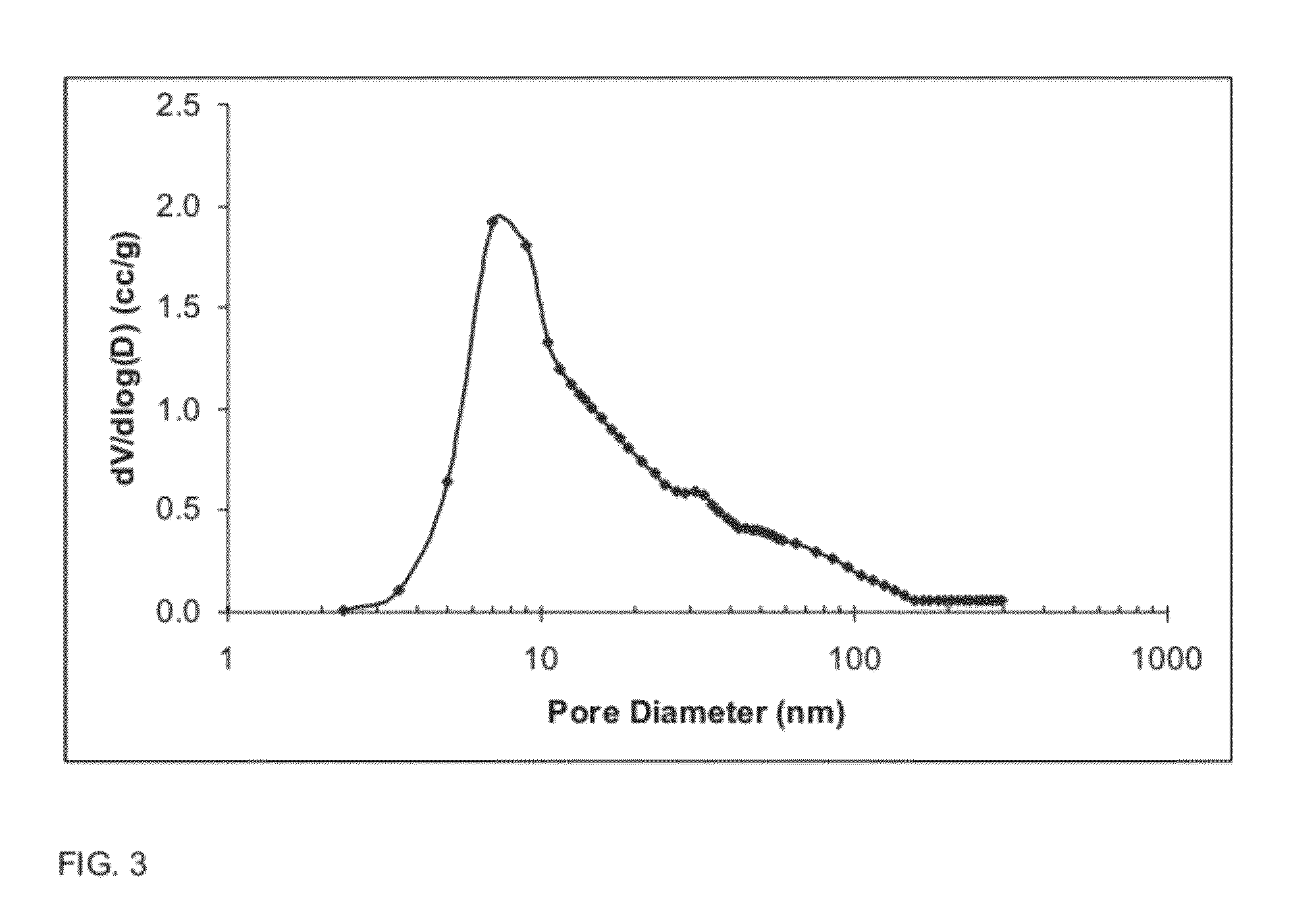
The present invention is directed to a high surface area, high pore volume porous alumina, comprising: aluminum oxide, optionally, silicon oxide and aluminosilicates, and optionally one or more dopants, said alumina having a specific surface area of from about 100 to about 500 square meters per gram and a total pore volume after calcination at 900° C. for 2 hours of greater than or equal to 1.2 cubic centimeters per gram, wherein less than or equal to 15% of the total pore volume is contributed by pores having a diameter of less than 10 nm.
Owner:RHODIA OPERATIONS SAS
System and Method for Hydrothermal Reaction
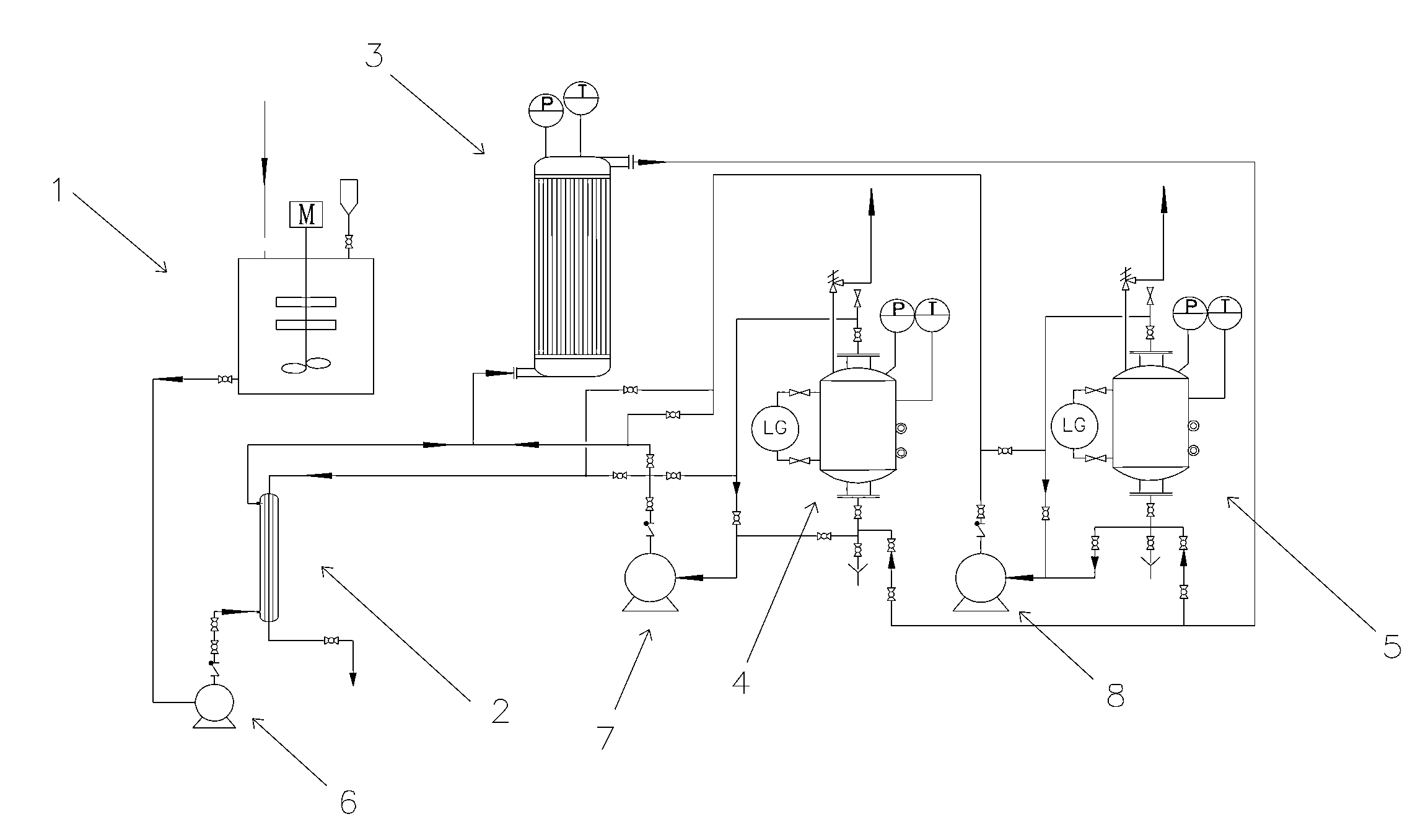
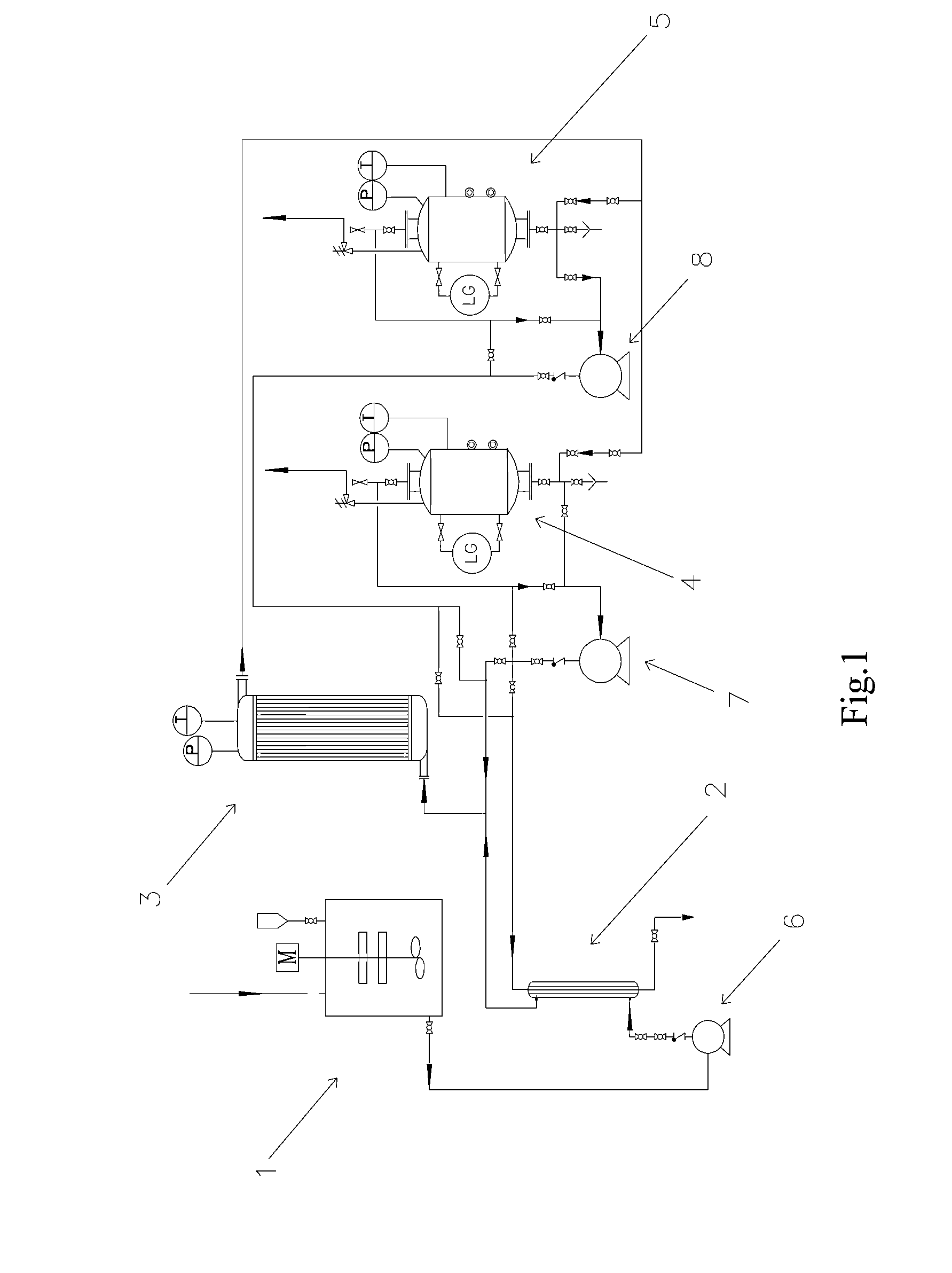
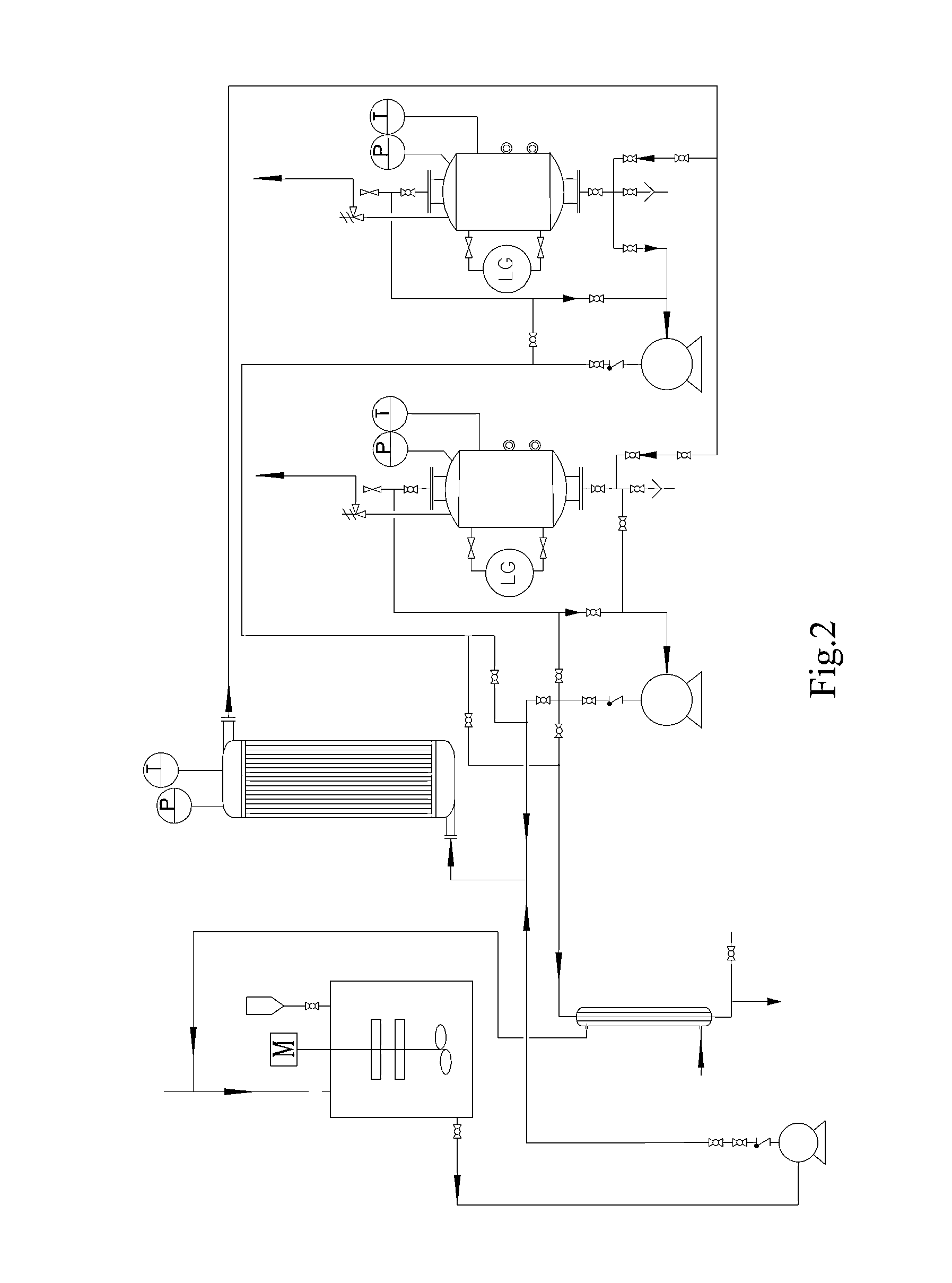
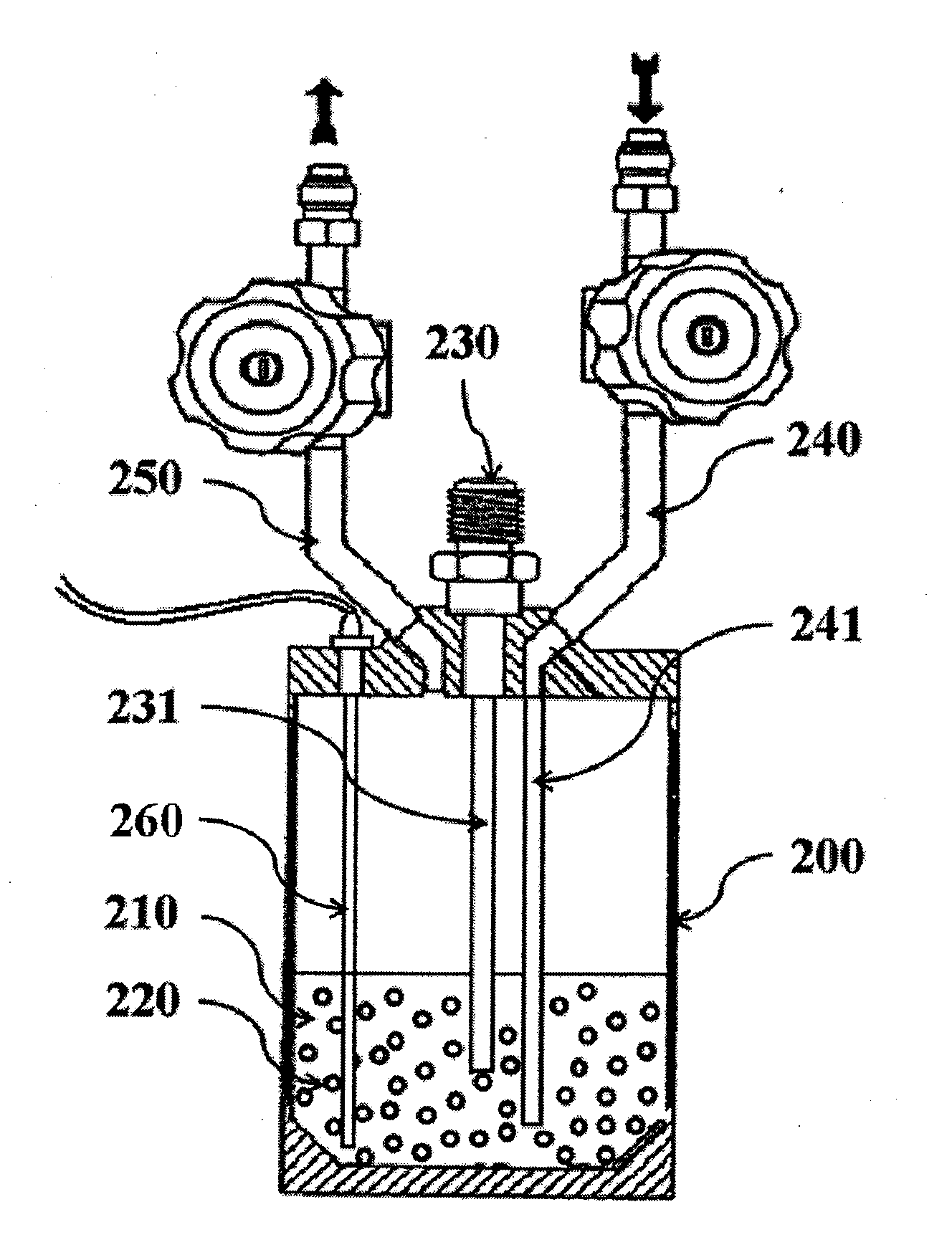
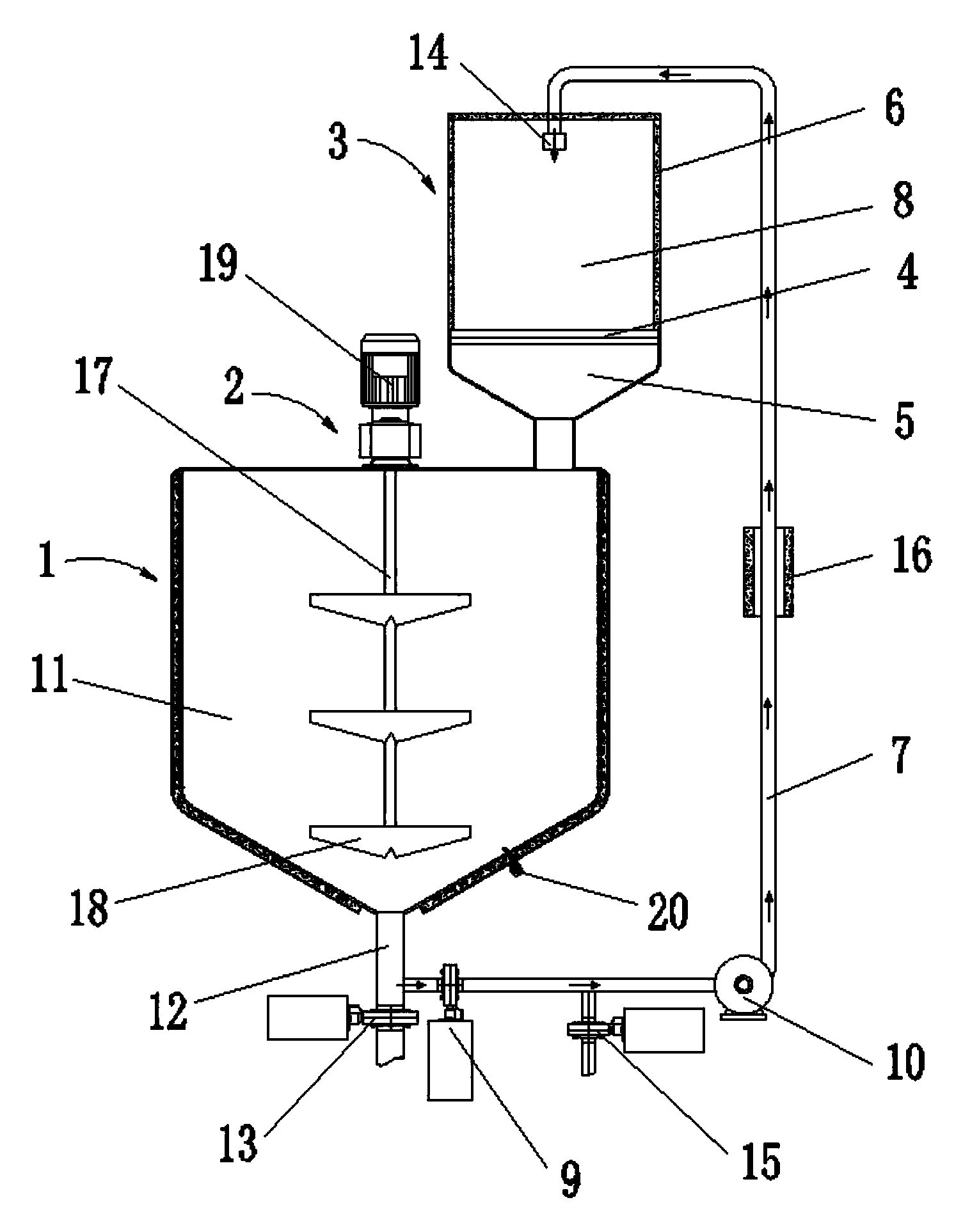
ActiveUS20140364676A1Avoid maintenance difficultiesImprove carrying capacityHeat treatmentsTransportation and packagingEngineeringHydrothermal reaction
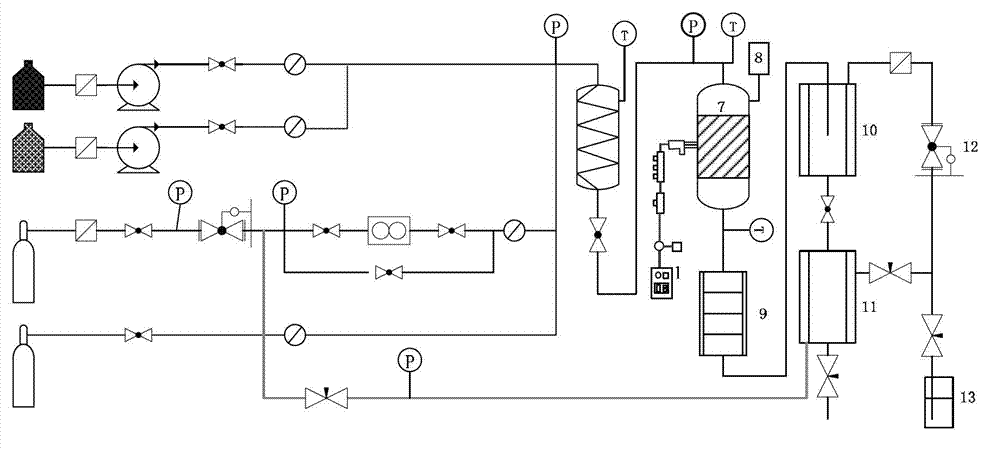
A system for hydrothermal reaction comprises a heater (3) including a circulating component for fluid flowing across and a heat source for heating fluid, and a reactor (4, 5) including a heat preserving container in communication with the circulating component via pipes. A method for hydrothermal reaction comprises heating the fluid including the reactant and water for hydrothermal reaction, and feeding the heated fluid to the heat preserving container to perform the hydrothermal reaction.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Method for preparing nanometer ultra-fine tourmaline powder
InactiveCN1557558AReduce reunionSmall particle sizeHeat treatmentsDrying solid materials with heatUltra fineGenerating capacity
The present invention relates to production of non-metal mineral powder, and is especially the preparation process of nano superfine tourmaline powder. The technological process includes the steps of: coarse crushing ore, airflow crushing, post-treatment, wet ball milling, spray drying, eliminating agglomeration of powder, and packing. The main technological prameters include calcining temperature of initially crushed powder in air of 300-800 deg.c, calcining time of 2-4 hr to obtain tourmaline powder in different colors, and ball milling period of 36-72 hr. Compared with available technology, the present invention has obviously reduced agglomeration of tourmaline powder, raised crushing efficiency, powder size reduced to 15-60 nm, obviously raised negative ion generating capacity, various color of the powder and wide application range.
Owner:ADVANCED TECHNOLOGY & MATERIALS CO LTD
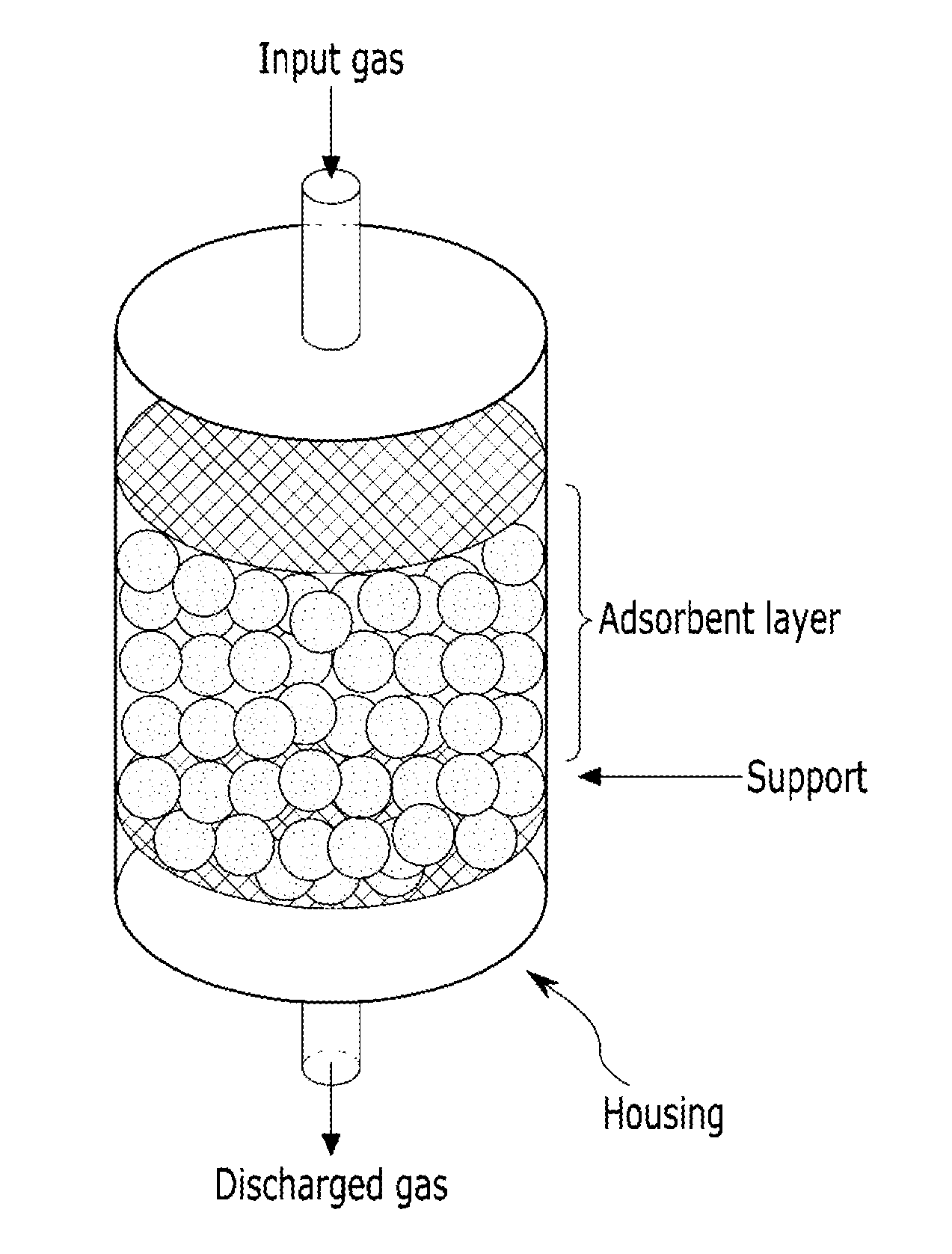
Carbon dioxide adsorbents and production methods thereof, carbon dioxide capture modules including the same, and methods for separating carbon dioxide using the same
ActiveUS20140305302A1Improve efficiencyImprove heat resistanceHeat treatmentsGas treatmentAlkaline earth metalChemical species
An adsorbent for carbon dioxide may include a mesoporous inorganic oxide having a crystalline halide of an alkali metal or alkaline earth metal supported thereto and a chemical species containing phosphorous (P), sulfur(S), or boron (B) supported thereto.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
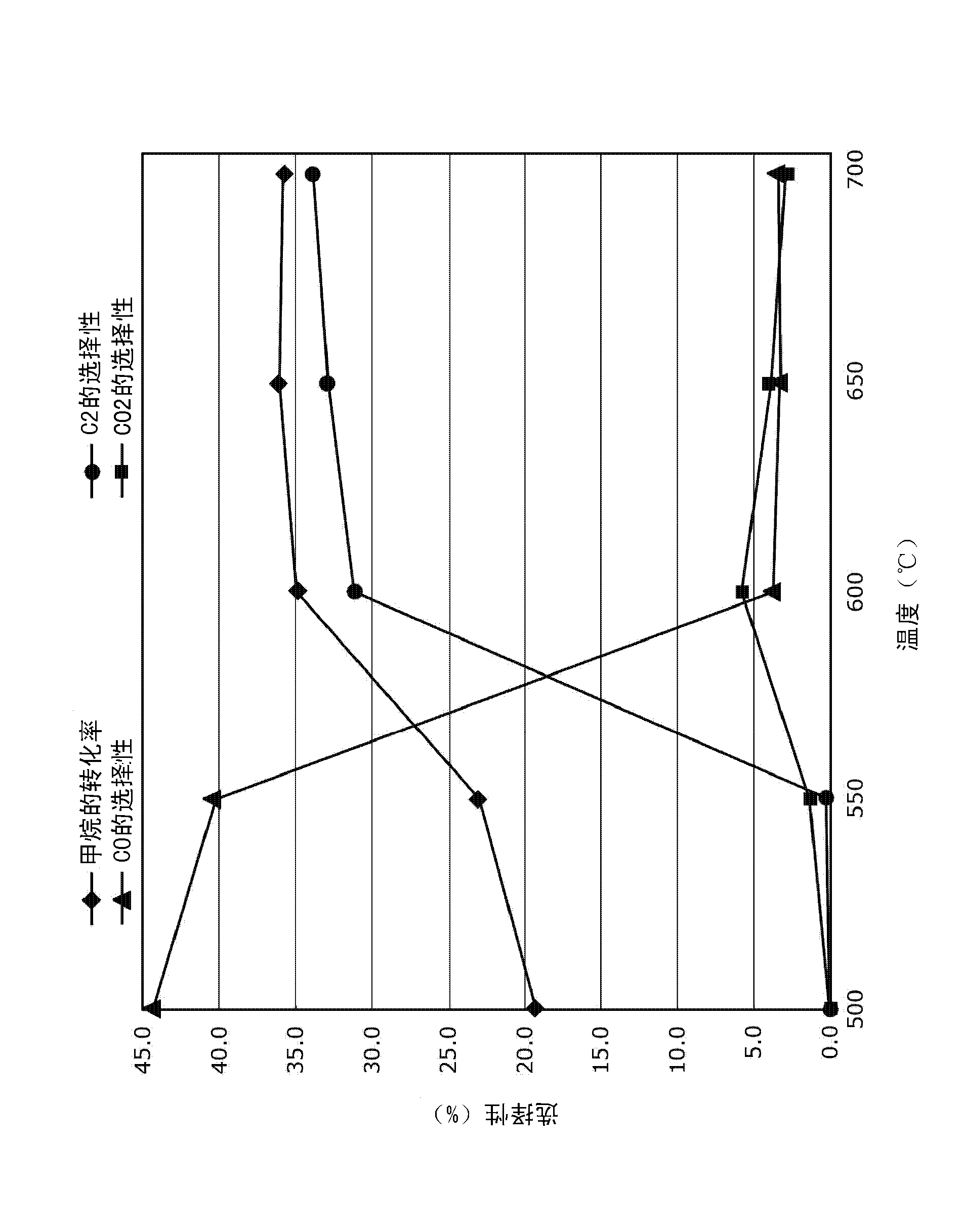
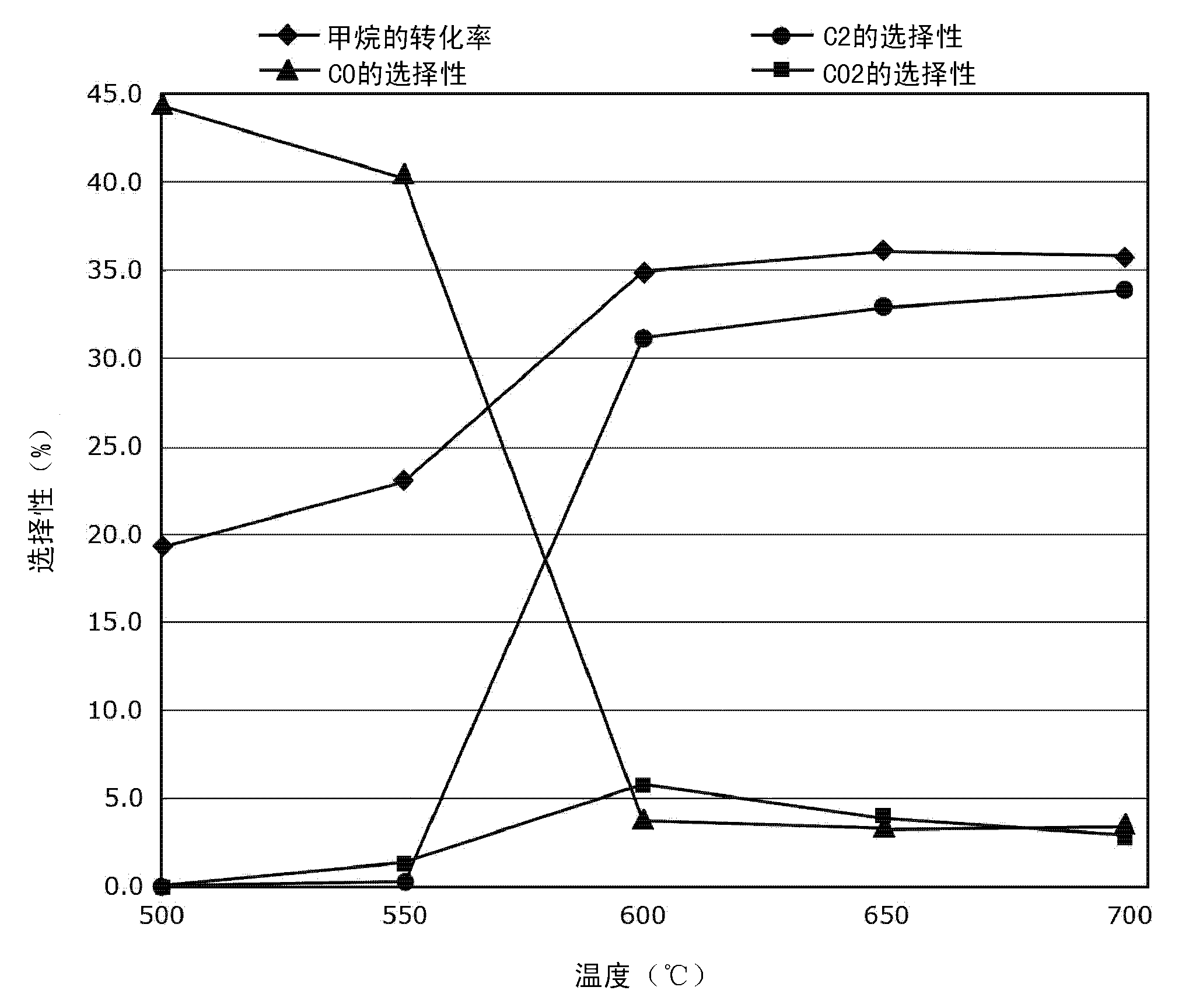
Process for the oxidative coupling of methane
A method for the oxidative coupling of hydrocarbons, such as the oxidative coupling of methane, includes providing an oxidative catalyst inside a reactor, and carrying out the oxidative coupling reaction under a set of reaction conditions. The oxidative catalyst includes (A) at least one element selected from the group consisting of the Lanthanoid group, Mg, Ca, and the elements of Group 4 of the periodic table (Ti, Zr, and Hf); (B) at least one element selected from the group consisting of the Group 1 elements of Li, Na, K, Rb, Cs, and the elements of Group 3 (including La and Ac) and Groups 5 - 15 of the periodic table; (C) at least one element selected from the group consisting of the Group 1 elements of Li, Na, K, Rb, Cs, and the elements Ca, Sr, and Ba; and (D) oxygen.
Owner:FINA TECH
Apparatus and methods for continuously growing carbon nanotubes and graphene sheets
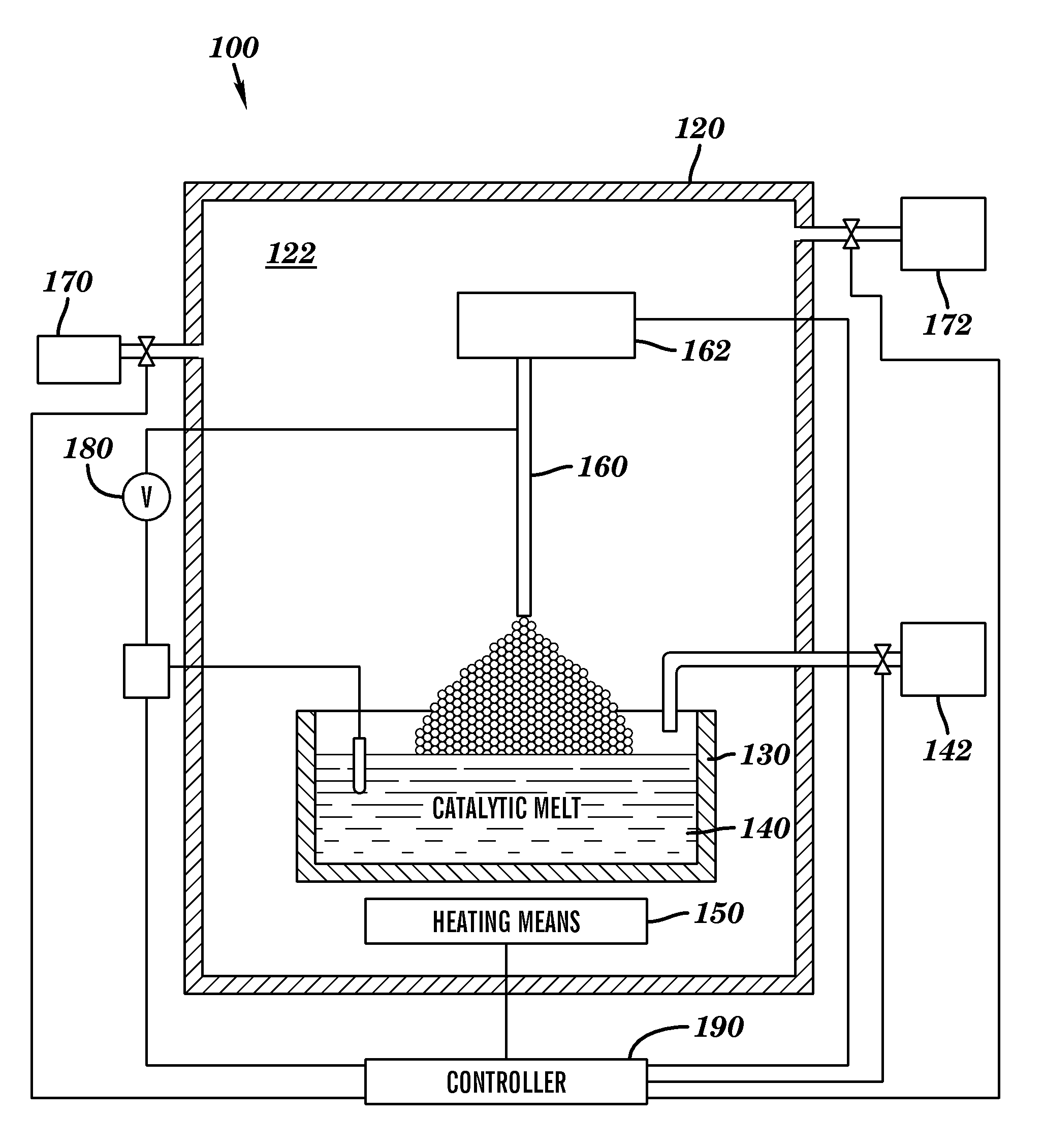
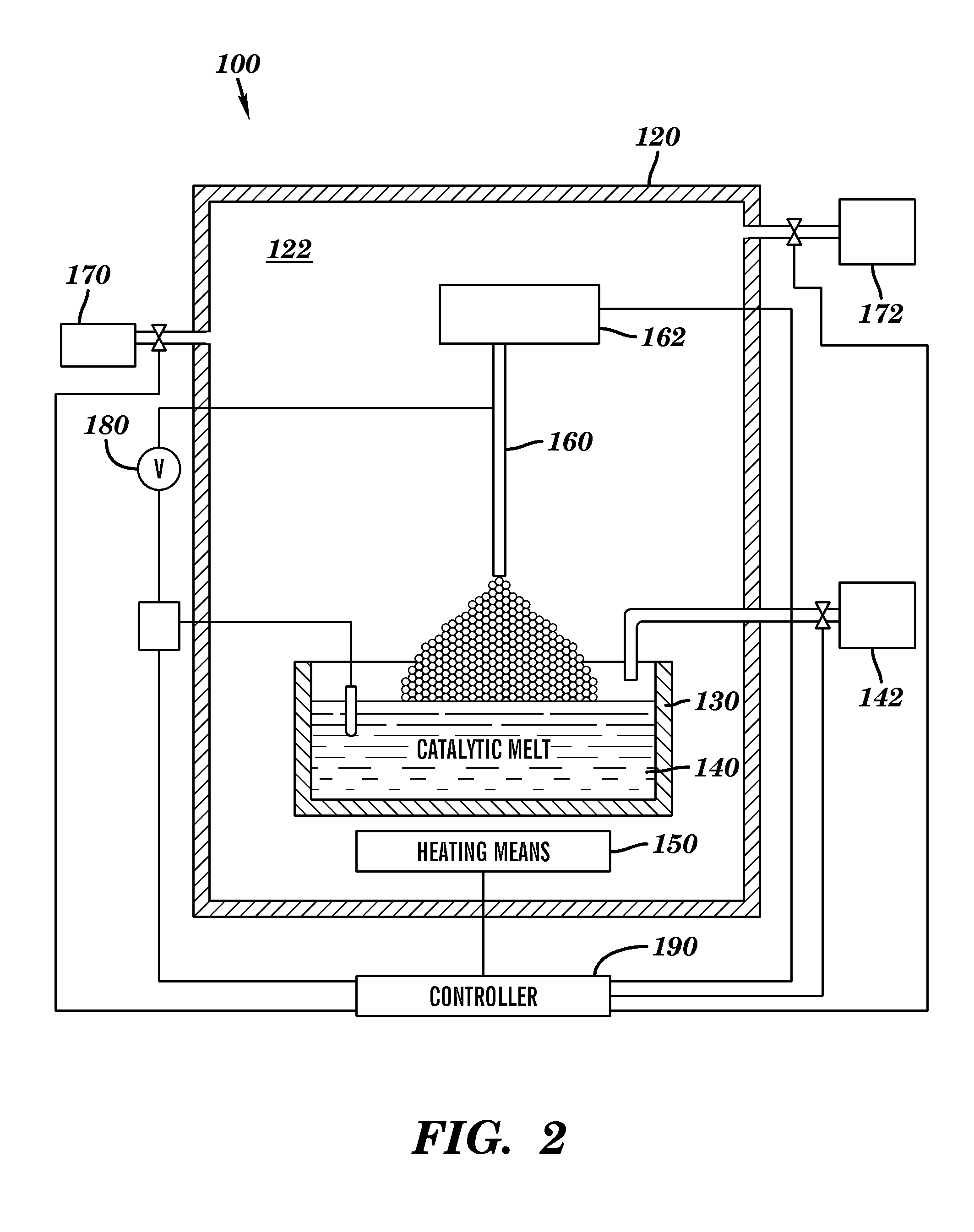
A method for continuously growing carbon nanotubes may include providing a melt comprising carbon and a catalyst at a temperature between about 1,200 degrees Celsius and about 2,500 degrees Celsius, selecting a carbon nanotube seed having at least one of a semiconductor electrical property and a metallic electrical property from a plurality of carbon nanotube seeds, contacting the selected carbon nanotube seed to a surface of the melt, and moving the selected carbon nanotube seed away from the surface of the melt at a rate operable to continuously grow a carbon nanotube, and continuously growing the carbon nanotube having the selected electrical property. Method for continuously growing a graphene sheet, and apparatus for continuously growing carbon nanotubes and graphene sheets are also disclosed.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Environment-friendly automatic-temperature-control quartz tube furnace device for pyrolysis of high polymer
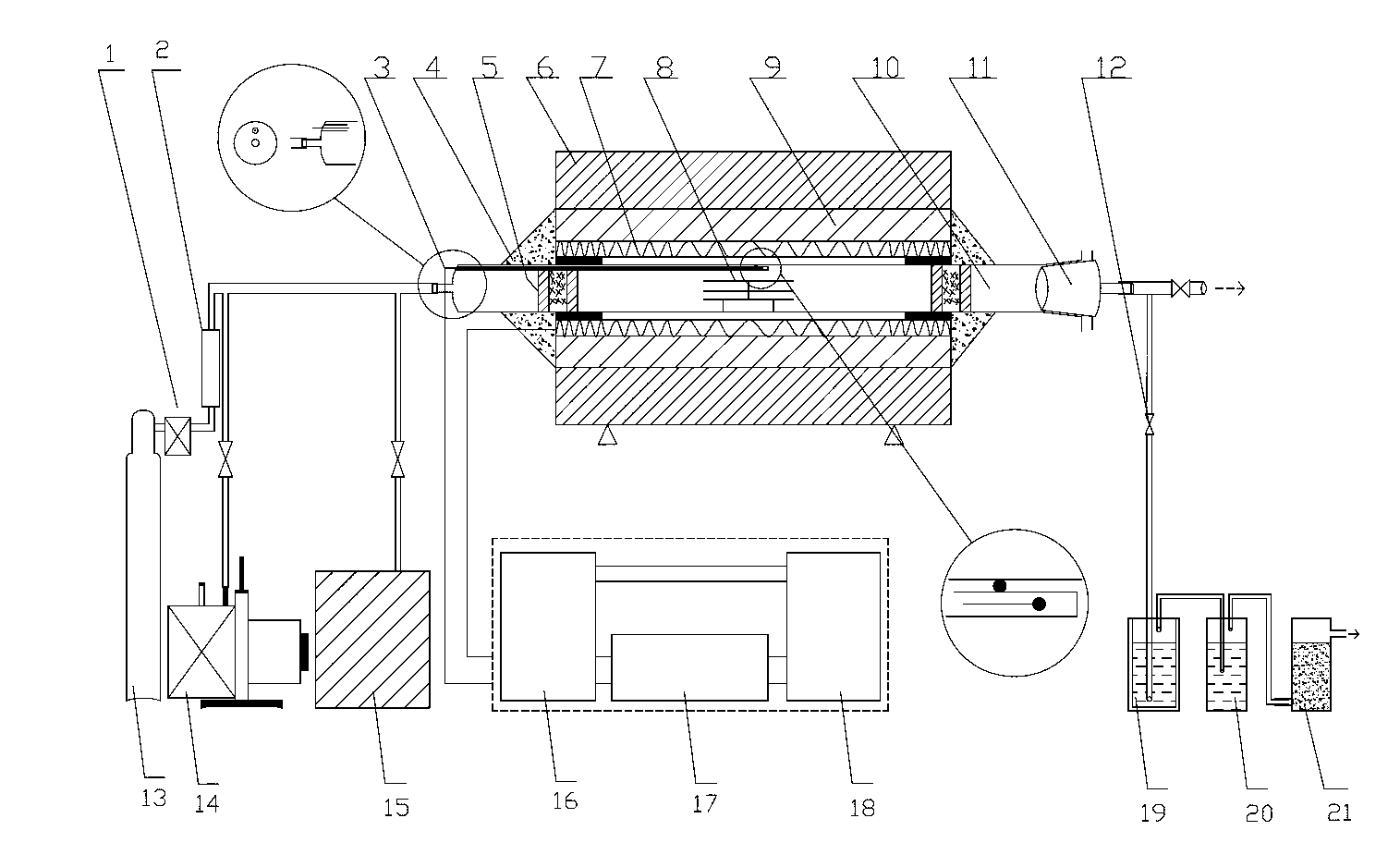
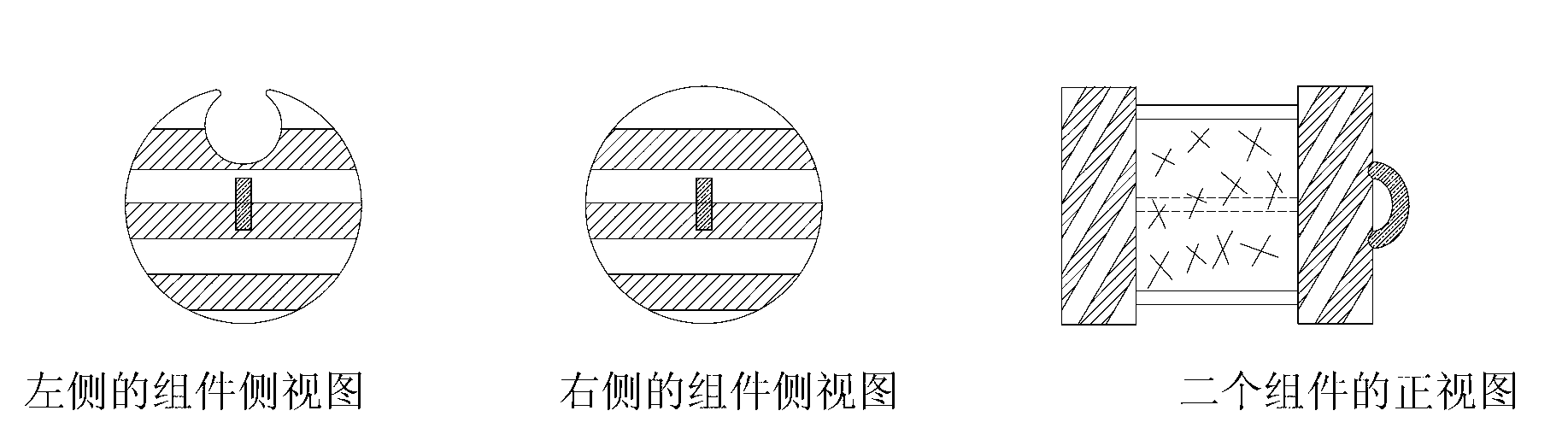
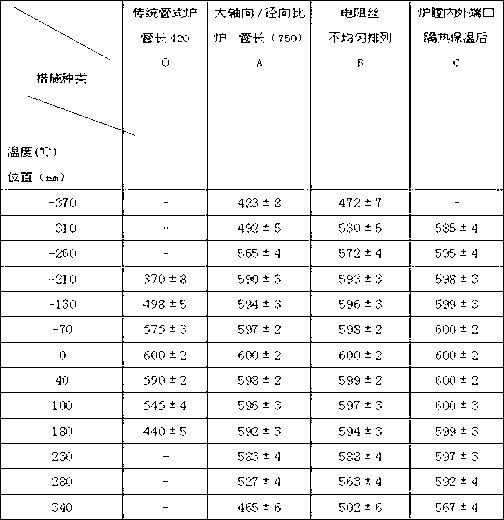
InactiveCN103017524AImprove insulation effectUniform temperature distributionHeat treatmentsFurnace typesTube furnaceEngineering
Tube furnaces for pyrolyzing or sintering are large in axial heat radiation, nonuniform in hearth temperature and low in machining amount. The invention discloses an environment-friendly automatic-temperature-control quartz tube furnace device for pyrolysis of high polymer, wherein the environment-friendly automatic-temperature-control quartz tube furnace device comprises a quartz glass tube furnace, a sample stand, a heat-isolation ventilation assembly, a fireproof heat-insulation furnace body, an automatic-heating temperature control device, a safety protection device and a tail gas treatment device. Different from other tube furnaces, the quartz tube furnace device is characterized in that a furnace body structure is improved by taking heat insulation measures additionally for inner and outer ports of a hearth, the axial-radial ratio of the tube furnace is high up to 12.5, resistance wires are arranged in a nonuniform winding manner and are arranged densely at the ports and sparsely in the middle, in addition, a safety protection bag and a tail gas purification column are arranged, and the furnace is internally vacuumized and is introduced with nitrogen. The environment-friendly automatic-temperature-control quartz tube furnace device disclosed by the invention is simple in equipment, low in investment, good in gas tightness, high in vacuum degree, convenient for heating as well as temperature measuring and controlling, and good in heat insulation effect, and is safe, energy-saving and environment-friendly, and an intra-furnace pyrolysis region is long and uniform in temperature, so that pyrolysis and doping reaction effects are good, and the processing amount is large. The environment-friendly automatic-temperature-control quartz tube furnace device can also be applied to other high-temperature reaction processes.
Owner:HARBIN UNIV OF COMMERCE
Nanoparticles and systems and methods for synthesizing nanoparticles through thermal shock
ActiveUS20180369771A1Increase temperatureHeat treatmentsMaterial nanotechnologyThermal energyThermal shock
Systems and methods of synthesizing nanoparticles on substrates using rapid, high temperature thermal shock. A method involves depositing micro-sized particles or salt precursors on a substrate, and applying a rapid, high temperature thermal pulse or shock to the micro-sized particles or the salt precursors and the substrate to cause the micro-sized particles or the salt precursors to become nanoparticles on the substrate. A system may include a rotatable member that receives a roll of a substrate sheet having micro-sized particles or salt precursors; a motor that rotates the rotatable member so as to unroll consecutive portions of the substrate sheet from the roll; and a thermal energy source that applies a short, high temperature thermal shock to consecutive portions of the substrate sheet that are unrolled from the roll by rotating the first rotatable member. Some systems and methods produce nanoparticles on existing substrate. The nanoparticles may be metallic, ceramic, inorganic, semiconductor, or compound nanoparticles. The substrate may be a carbon-based substrate, a conducting substrate, or a non-conducting substrate. The high temperature thermal shock process may be enabled by electrical Joule heating, microwave heating, thermal radiative heating, plasma heating, or laser heating.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
Delivery Equipment for the Solid Precursor Particles
InactiveUS20140072479A1Effectively minimize heating temperatureImprove thermal stabilityHeat treatmentsGaseous chemical processesThermal stabilityHeating temperature
The present invention discloses a delivery equipment for the solid precursor particles, which is applied to the deposition of thin film. The delivery equipment for the solid precursor particles mainly comprises a container, a feeding material inlet, a feeding material tube, a feeding gas inlet, a feeding gas tube, and an output. A plurality of solid precursor particles are stored in the carrier liquid of the container, and then heated to be vapor, removed through the output of the container. The solid precursor particles are prepared by sublimation or grounding and uniformly dispersed in the carrier liquid. The disclosed delivery equipment for the solid precursor particles can reduce the required heating temperature, increase the thermal stability, prolong the used life time, and then increase the using efficiency of the precursors.
Owner:NANMAT TECH
Vanadia—titania catalyst for removing nitrogen oxides and method for manufacturing the same
ActiveUS9101908B2Large specific surface areaGood dispersionHeat treatmentsDispersed particle separationVanadium dioxideTitanium
Provided is a method for preparing a vanadia-titania catalyst, comprising: vaporizing a titanium precursor; conveying the vaporized titanium precursor to a reaction unit together with an oxygen supplying source; reacting the vaporized titanium precursor conveyed to the reaction unit with the oxygen supplying source to produce titania particles; condensing the titania particles, collecting and recovering them; mixing the recovered titania particles with a vanadium precursor solution; drying the mixture of the titania particles with the vanadium precursor solution; and calcining the dried mixture under oxygen atmosphere or air. Provided also is a vanadia-titania catalyst obtained by the method. The vanadia-titania catalyst has a large specific surface area, uniform and fine nano-scaled size, and high dispersibility, thereby providing excellent nitrogen oxide removal efficiency, particularly in a low temperature range of 200° C.-250° C.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
Microwave heating device and application thereof
InactiveCN102773055AImprove sealingUniform microwave distributionHeat treatmentsEnergy based chemical/physical/physico-chemical processesHydrodesulfurizationProcess engineering
The invention provides a microwave heating device and an application thereof, wherein the device comprises a microwave reactor and a microwave generation and transmission device, the microwave generation and transmission device comprises a microwave source, a circulator, a water load, a directional coupler, an automatic tri-dowel regulator and a waveguide according to a microwave transmission sequence, in the waveguide section, a mode of converting a rectangular wave guide into coaxial transmission is adopted, and a probe enters the center of the reactor from the side wall of the microwave reactor for guiding the microwave into the reactor. According to the device, microwaves in the reactor are uniformly distributed; and moreover, the device has good sealing performance, can be practically applied for any reaction which utilizes microwave to heat, such as an application of continuous oil product hydrodesulfurization, technological conditions can be alleviated, the oil product desulfurization degree is effectively improved, and the oil refining economical efficiency is improved.
Owner:北京众诚汇微能源科技有限公司 +1
Preparation method of lithium titanium composite oxide doped with dissimilar metal, and lithium titanium composite oxide doped with dissimilar metal prepared thereby
InactiveUS20140322609A1High crystallinityIncrease battery capacityHeat treatmentsAlkali titanatesDischarge efficiencyPhysical chemistry
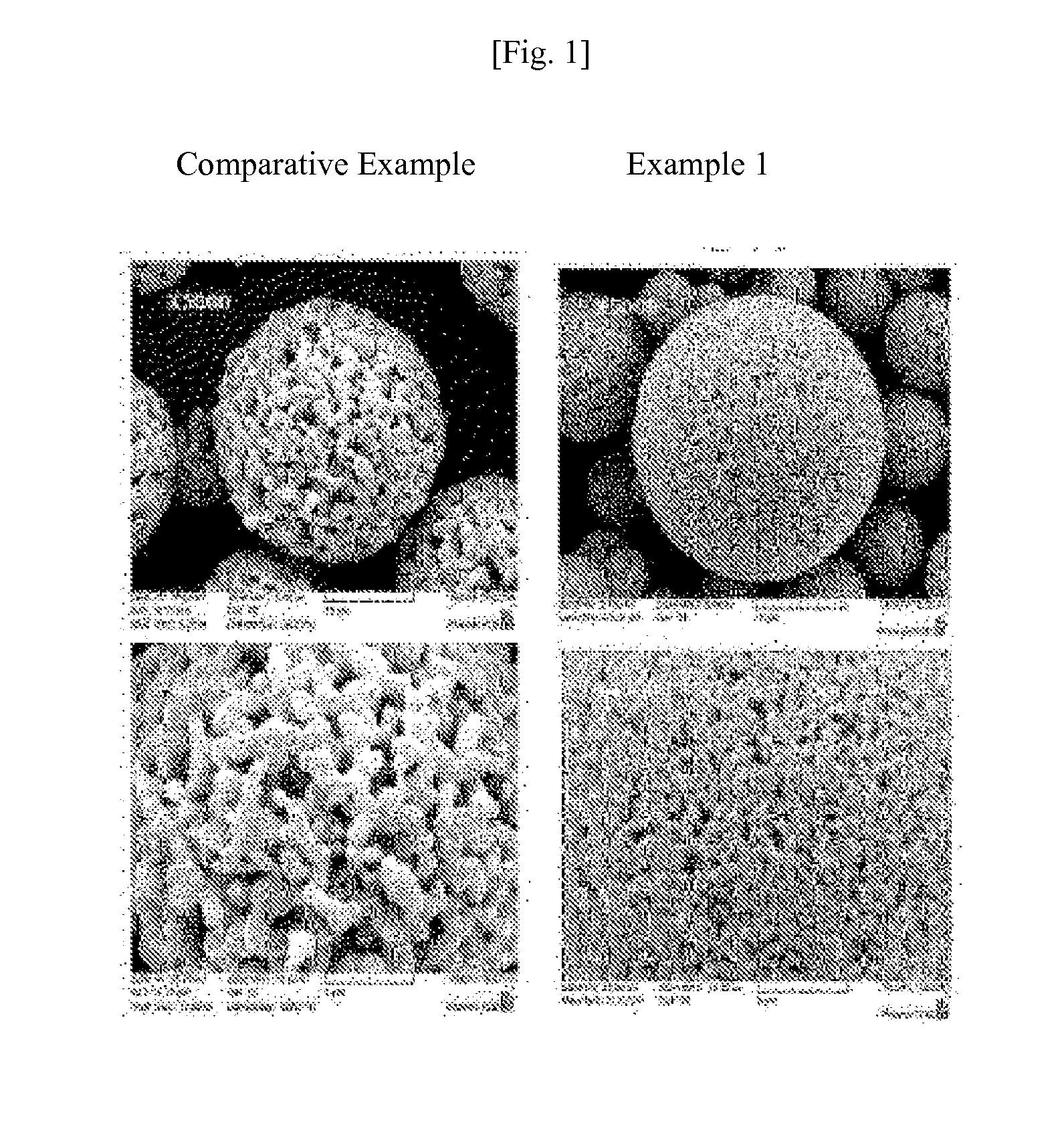
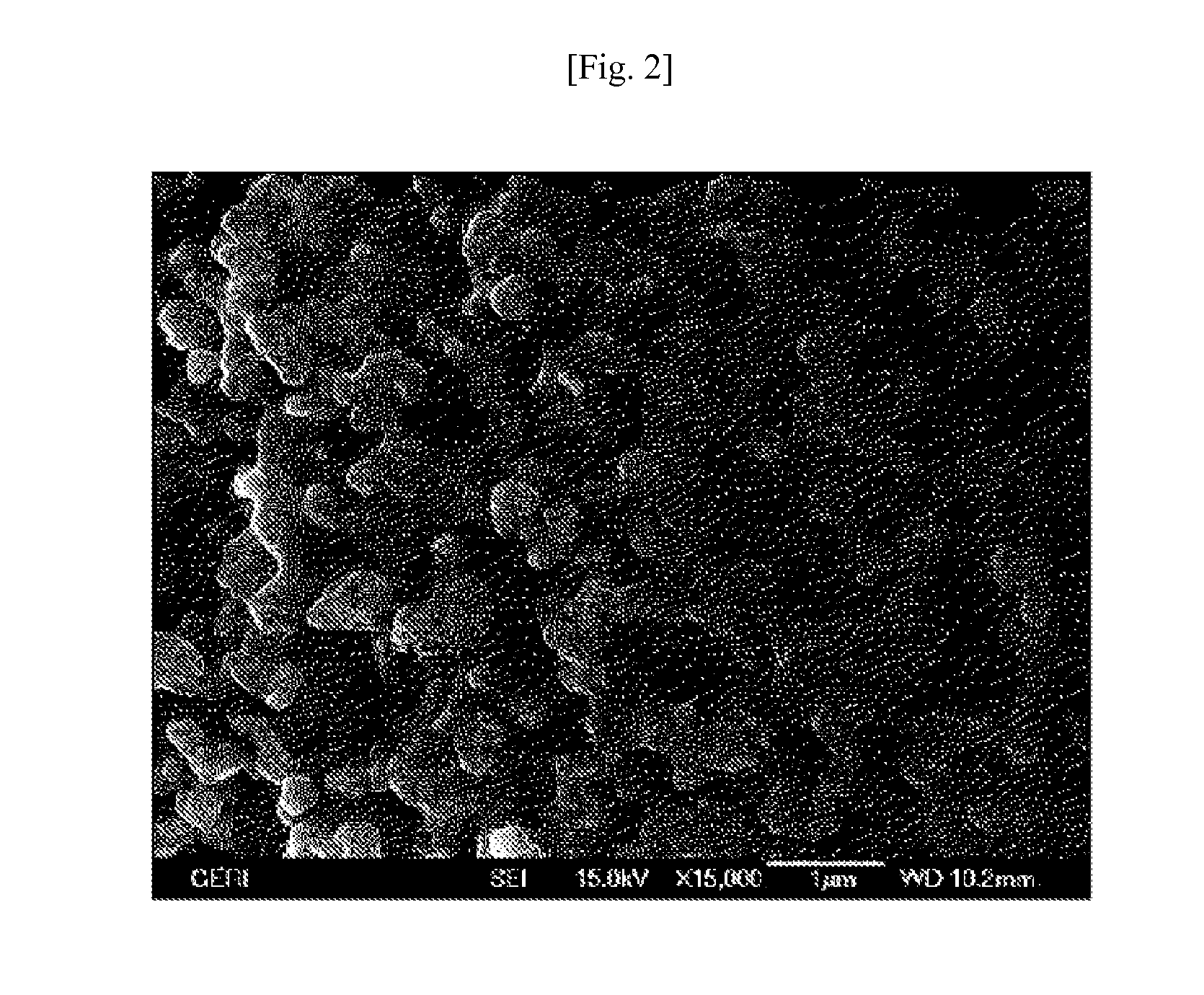
The present invention relates to a preparation method of a lithium titanium composite oxide doped with a dissimilar metal, and a lithium titanium composite oxide doped with a dissimilar metal prepared thereby, and more particularly, to a preparation method of a lithium titanium composite oxide doped with a dissimilar metal in which sizes of primary particles are finely controlled by doping a dissimilar metal and using a spray-drying method, and a lithium titanium composite oxide doped with a dissimilar metal prepared thereby.According to the present invention, the preparation method of a lithium titanium composite oxide doped with a dissimilar metal, and the lithium titanium composite oxide doped with a dissimilar metal prepared thereby allow sizes of primary particles to be finely controlled as compared with conventional lithium titanium composite oxide, and inhibit rutile titanium dioxide generation, thereby providing a battery with a high initial charge-discharge efficiency and a high rate capability.
Owner:POSCO 38 5 +2
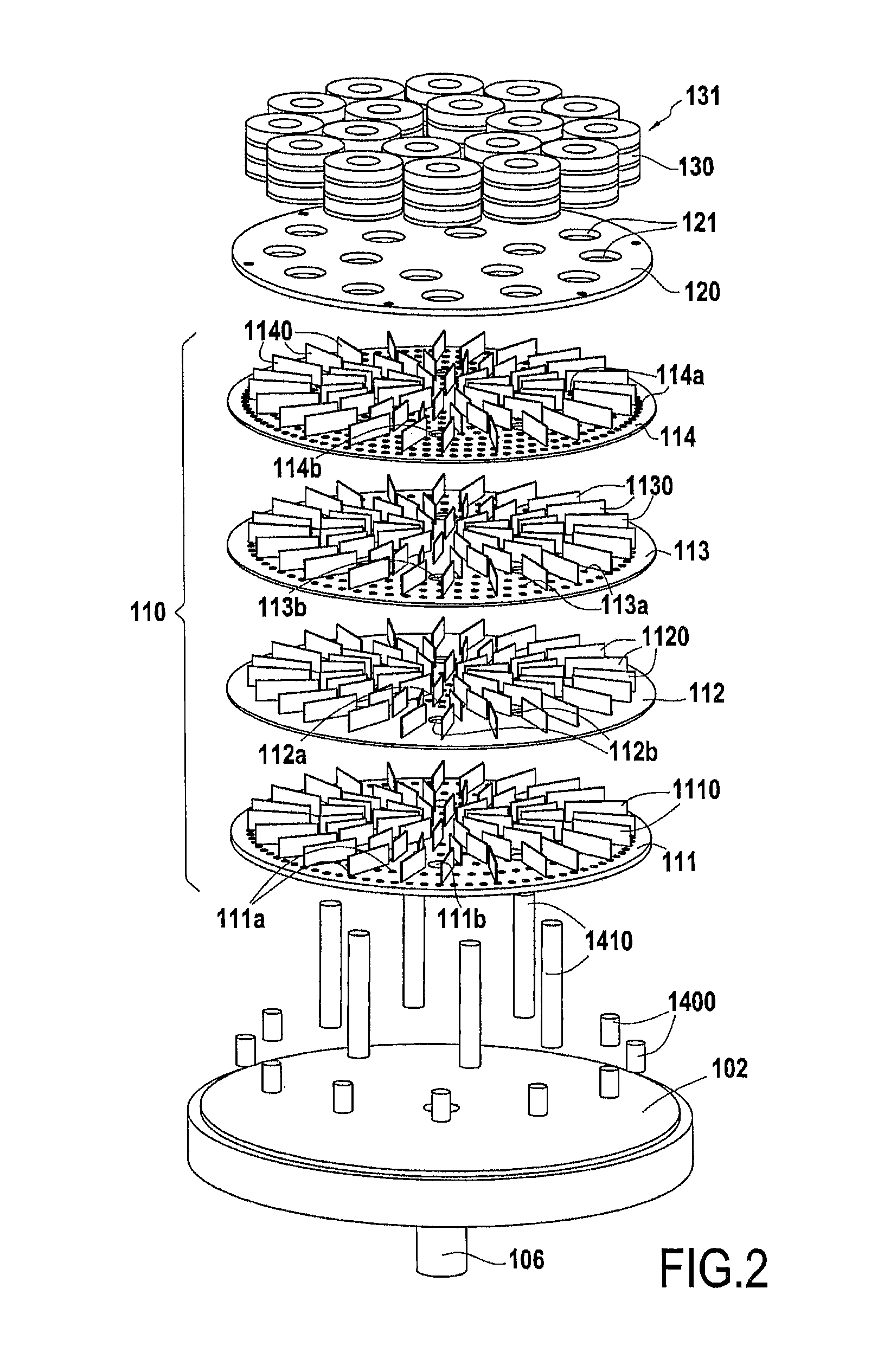
A cvi densification installation including a high capacity preheating zone
ActiveUS20170002466A1Improve productivityIncrease volumeHeat treatmentsMuffle furnacesProcess engineeringReaction chamber
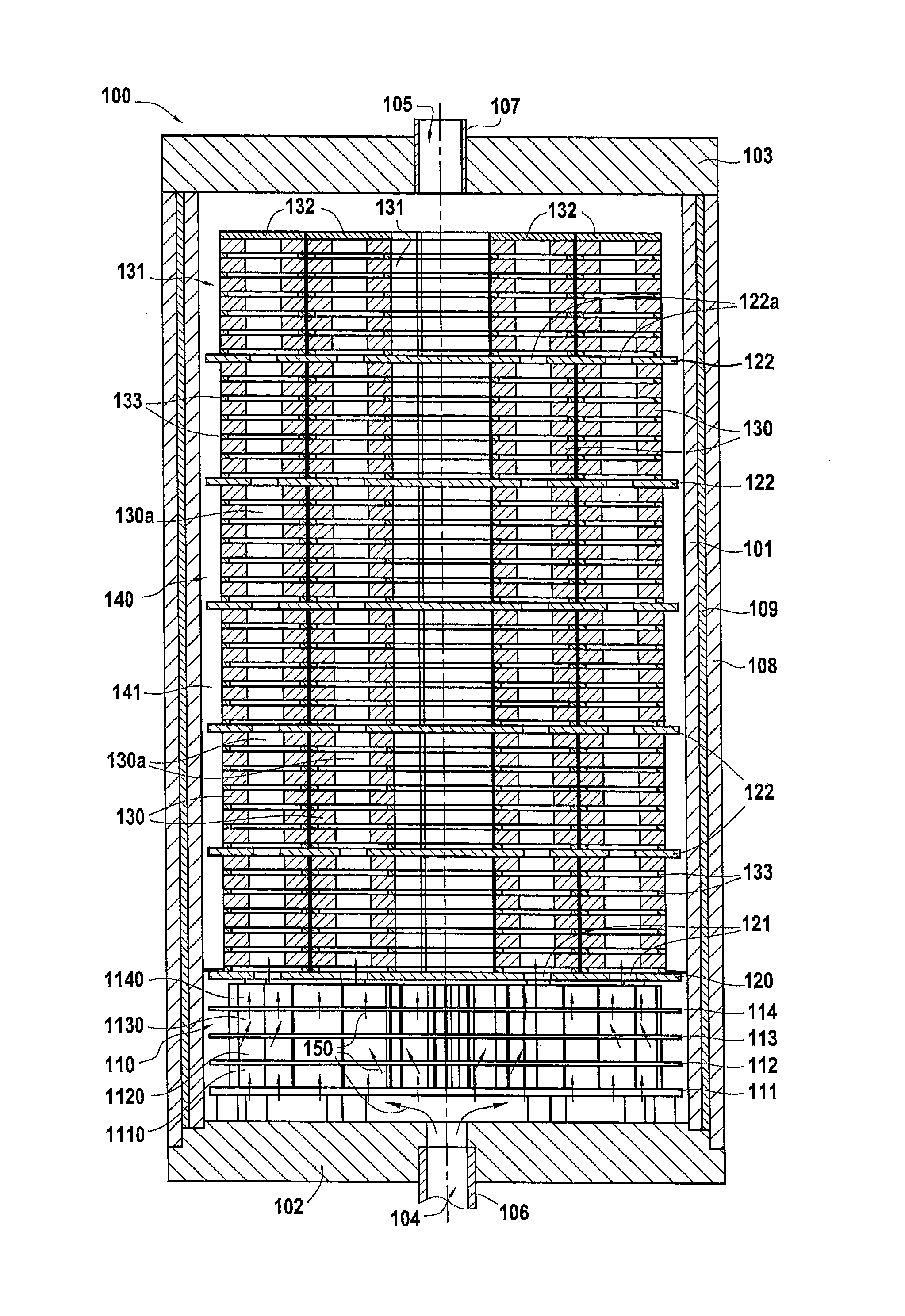
A thermochemical treatment installation includes a reaction chamber, at least one gas inlet, and a gas preheater chamber situated between the gas inlet and the reaction chamber. The preheater chamber has a plurality of perforated distribution trays held spaced apart one above another. The preheater chamber also includes, between at least the facing distribution trays, a plurality of walls defining flow paths for a gas stream between said trays.
Owner:SAFRAN CERAMICS SA
Chroma alumina catalysts for alkane dehydrogenation
InactiveCN104010725AHeat treatmentsHeterogenous catalyst chemical elementsAlkali metal oxideDehydrogenation
Provided are methods of making dehydrogenation catalyst supports containing bayerite and silica. Silica-stabilized alumina powder, prepared by spray drying of bayerite powder, precipitating silica in a bayerite slurry with an acid, or impregnation or co-extrusion of bayerite with sodium silicate solution was found to be a superior catalyst support precursor. Catalysts prepared with these silica containing support materials have higher hydrothermal stability than current CATOFIN TM catalysts. Also provided is a dehydrogenation catalyst comprising Cr2O3, an alkali metal oxide, SiO2 and Al2O3, and methods of using said catalyst to make an olefin and / or dehydrogenate a dehydrogenatable hydrocarbon.
Owner:BASF AG
Synthetic amorphous silica powder and method for producing same
The synthetic amorphous silica powder of the present invention is characterized in that it comprises a synthetic amorphous silica powder obtained by applying a spheroidizing treatment to a silica powder, and by subsequently cleaning and drying it so that the synthetic amorphous silica powder has an average particle diameter D50 of 10 to 2,000 μm; wherein the synthetic amorphous silica powder has: a quotient of 1.00 to 1.35 obtained by dividing a BET specific surface area of the powder by a theoretical specific surface area calculated from the average particle diameter D50; a real density of 2.10 to 2.20 g / cm3; an intra-particulate porosity of 0 to 0.05; a circularity of 0.75 to 1.00; and an unmolten ratio of 0.00 to 0.25.
Owner:MITSUBISHI MATERIALS CORP
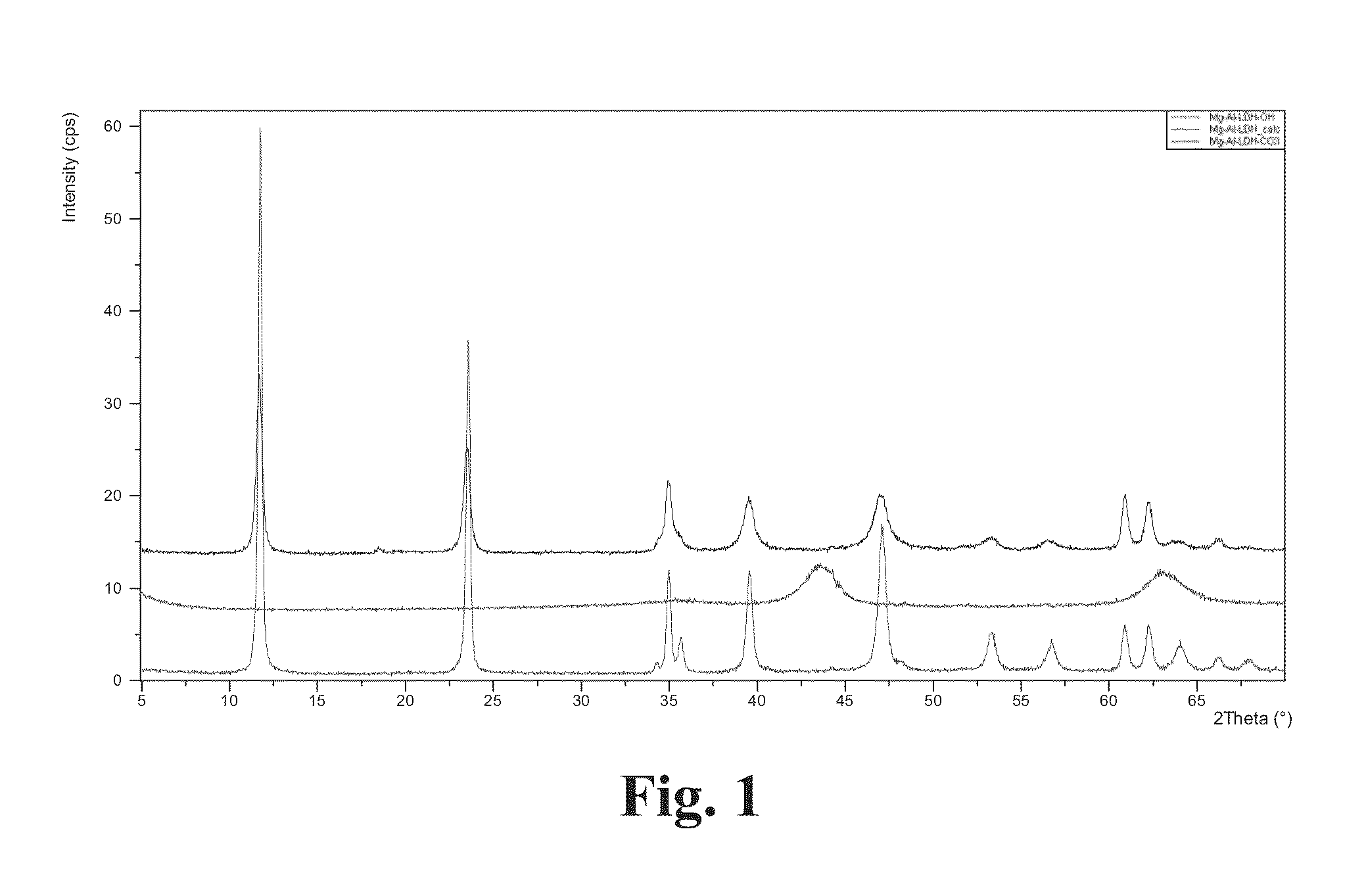
Method of producing inorganic layered double hydroxides, novel inorganic layered double hydroxides and uses of the same
InactiveUS20130095323A1Eliminate the problemStable gelMaterial nanotechnologyHeat treatmentsDietary supplementPetrochemistry
Novel nanosized layered double hydroxide materials and a method of producing the same as well as uses of said material. The novel materials are uniform and have the general formula I[M2+1-xM3+x(OH)2][An-x / n.zH2O] IwhereinM2+ is selected from Mg2+, Ca2+, Mn2+, Fe2+, Co2+, Ni2+, and Zn2+M3+ is selected from Al3+, V3+, Cr3+, Fe3+, Co3+, Sc3+, Ga3+, and Y3+,An- stands for an anion,x stands for a value in the range from 0.2 to 0.33,n is an integer from 1 to 4 andz is an integer from 1 to 10.The particle size is less than 1 μm. The material can be used in heterogeneous catalysis in organic chemistry and petrochemistry, magnetic materials, pharmaceutical applications, electrode materials, tissue engineering, cosmetics, and dietary supplements.
Owner:LICENTIA OY
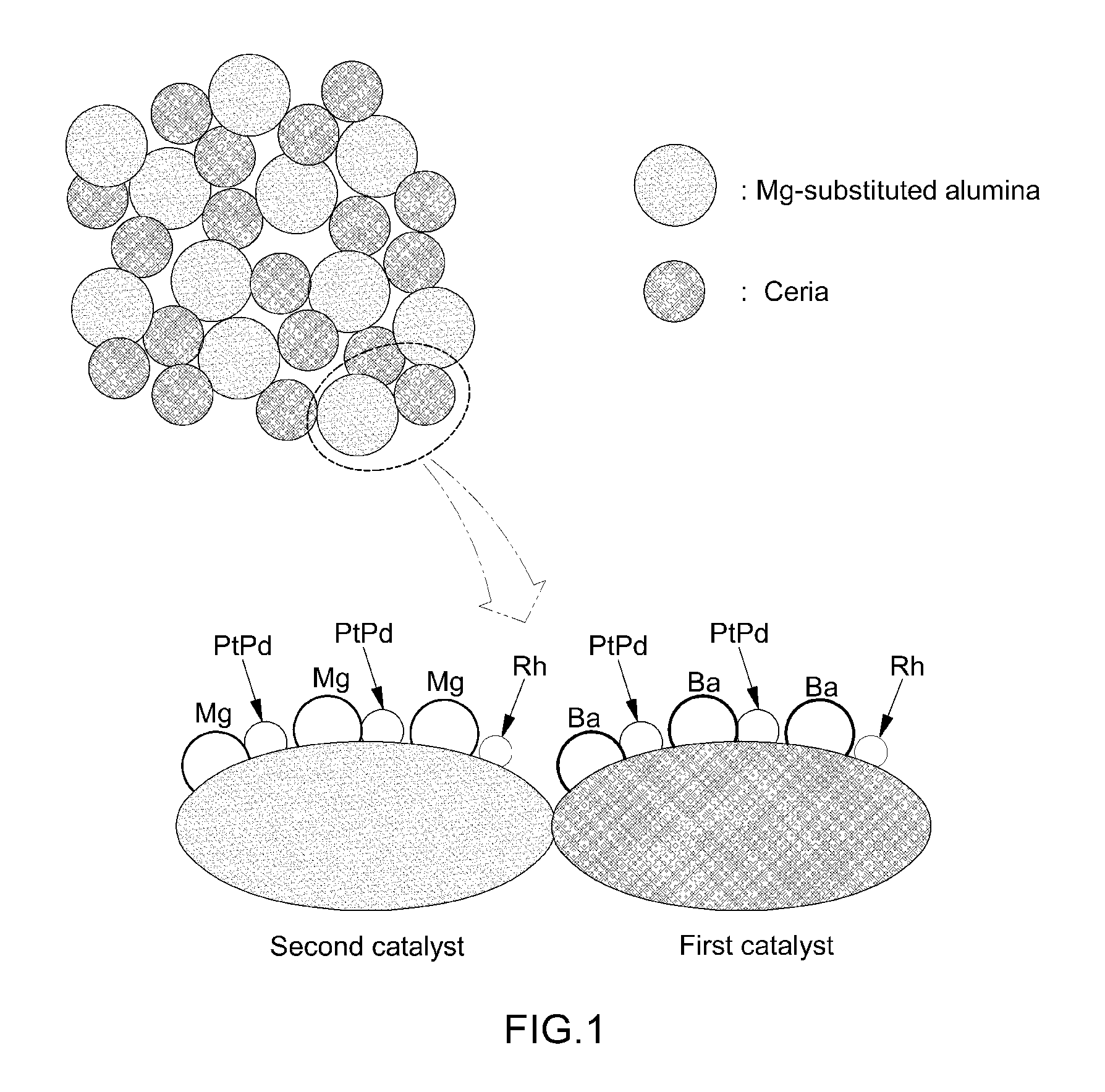
Lnt catalyst with enhanced nitrogen oxide storage capacity at low temperature
InactiveUS20140171302A1Improved NOx storage capacityInhibits thermal desorptionHeat treatmentsInorganic chemistryHoneycombNitrogen oxide
Disclosed is a lean NOx trap (LNT) catalyst with enhanced NOx storage capacity at low temperature. More particularly, an LNT catalyst with enhanced NOx storage capacity at low temperature and significantly inhibited thermal desorption is prepared by coating a washcoat on a honeycomb-type carrier and drying and baking the same. The washcoat contains a first catalyst powder in which barium (Ba) and a precious metal are supported on a ceria support, and a second catalyst powder in which a precious metal is supported on a magnesium (Mg)-substituted alumina support The LNT catalyst of the present invention is useful as a NOx reducing catalyst for a passenger diesel vehicle.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD
Grease melting stirring system and oil grease melting processing method
ActiveCN104107669AReduce heat lossFast meltingHeat treatmentsRotary stirring mixersOil and greaseControl valves
The invention relates to the technical field of grease processing, particularly to an grease melting stirring system which comprises a liquid grease storage tank, a stirring device, a melting device and a liquid circulation pipe, wherein the melting device comprises a heating layer and a stock bin communicated with the storage tank; the heating layer is arranged on the stock bin; a gap from which melted grease can flow into the stock bin is formed in the heating layer; the melting device further comprises a heat preservation cover; the heat preservation cover is arranged on the stock bin and a heating cavity is formed between the heating layer and the heat preservation cover; one end of the liquid circulation pipe is connected with the storage tank; the other end of the liquid circulation pipe passes through the top of the heat preservation cover to enter the heating cavity; a control valve for controlling liquid to flow and a circulation pump for supplying power for liquid circulation are arranged on the liquid circulation pipe. The invention further provides a grease melting processing method. Compared with the prior art, the grease melting stirring system has the advantages of being simple in structure, convenient to use, high in melting efficiency and convenient to clean.
Owner:SUZHOU DAODAXIN ENG TECH
Iron-modified ni-based perovskite-type catalyst, preparing method thereof, and producing method of synthesis gas from combined steam co2 reforming of methane using the same
InactiveUS20140145116A1Improve conversion rateResistant to deactivationHeat treatmentsHydrogen/synthetic gas productionHigh carbon dioxideCarbon deposition
The present invention relates to an Fe-modified perovskite-type catalyst, a method for preparing same and a method for preparing a synthesis gas by a combined reforming reaction using same. More particularly, it relates to a catalyst for a combined natural gas / steam / carbon dioxide reforming reaction having a perovskite structure with La and Sr introduced at the A site and Ni and Fe introduced at the B site with specific molar ratios and a method for producing a synthesis gas for Fischer-Tropsch synthesis or methanol synthesis using the catalyst by the combined reforming reaction. The catalyst of the present invention exhibits higher carbon dioxide conversion rate, significantly reduced catalyst deactivation caused by carbon deposition and improved long-term catalyst stability and activity, as compared to the existing catalyst for reforming reaction prepared by the impregnation method.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
Catalyst for reforming hydrocarbons
ActiveUS20140148332A1Maximize resistanceMaximized resistance to carbon depositionHeat treatmentsHeterogenous catalyst chemical elementsSyngasAluminium oxides
Provided is a catalyst for preparing a syngas by reforming methane wherein a nickel-based catalyst is mixed with a metal oxide catalyst. More particularly, alumina is used as a support and a metal oxide catalyst including magnesia, nickel, vanadium, tungsten, iron, molybdenum or chromium is used to inhibit carbon deposition and maintain or improve catalytic activity.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
Popular searches
Catalyst activation/preparation Metal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalysts Cell electrodes Double layer capacitors Carbon preparation/purification Hybrid/EDL manufacture Physical/chemical process catalysts Fibre chemical features Chemical/physical/physico-chemical stationary reactors Liquid-gas reaction processes
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com