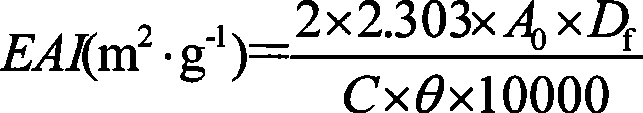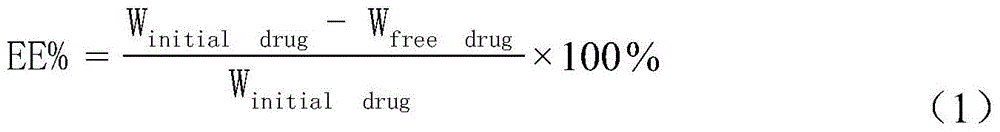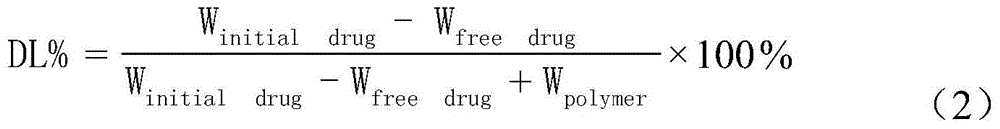Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
32 results about "Wheat germ agglutinin" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Wheat germ agglutinin (WGA) is a lectin that protects wheat (Triticum) from insects, yeast and bacteria. An agglutinin protein, it binds to N-acetyl-D-glucosamine and Sialic acid. N-acetyl-D-glucosamine in the natural environment of wheat is found in the chitin of insects, and the cell membrane of yeast & bacteria. WGA is found abundantly—but not exclusively—in the wheat kernel, where it got the 'germ' name from. In mammals the N-acetyl-D-glucosamine that WGA binds to is found in cartilage and cornea among other places. In those animals sialic acid is found in mucous membranes, e.g. the lining of the inner nose, and digestive tract.
Preparation method of wheat germ agglutinin and its application in inhibiting mammary gland cancer activity
InactiveCN1948337AImprove the utilization value of deep processingHigh yieldPeptide/protein ingredientsPeptide preparation methodsFreeze-dryingRed blood cell
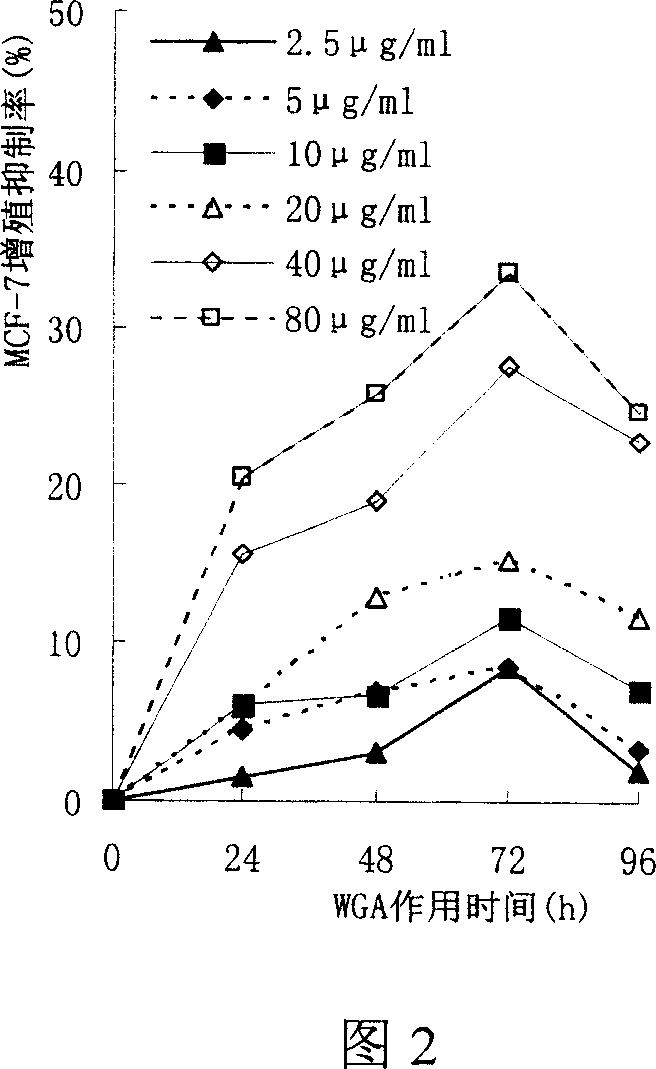
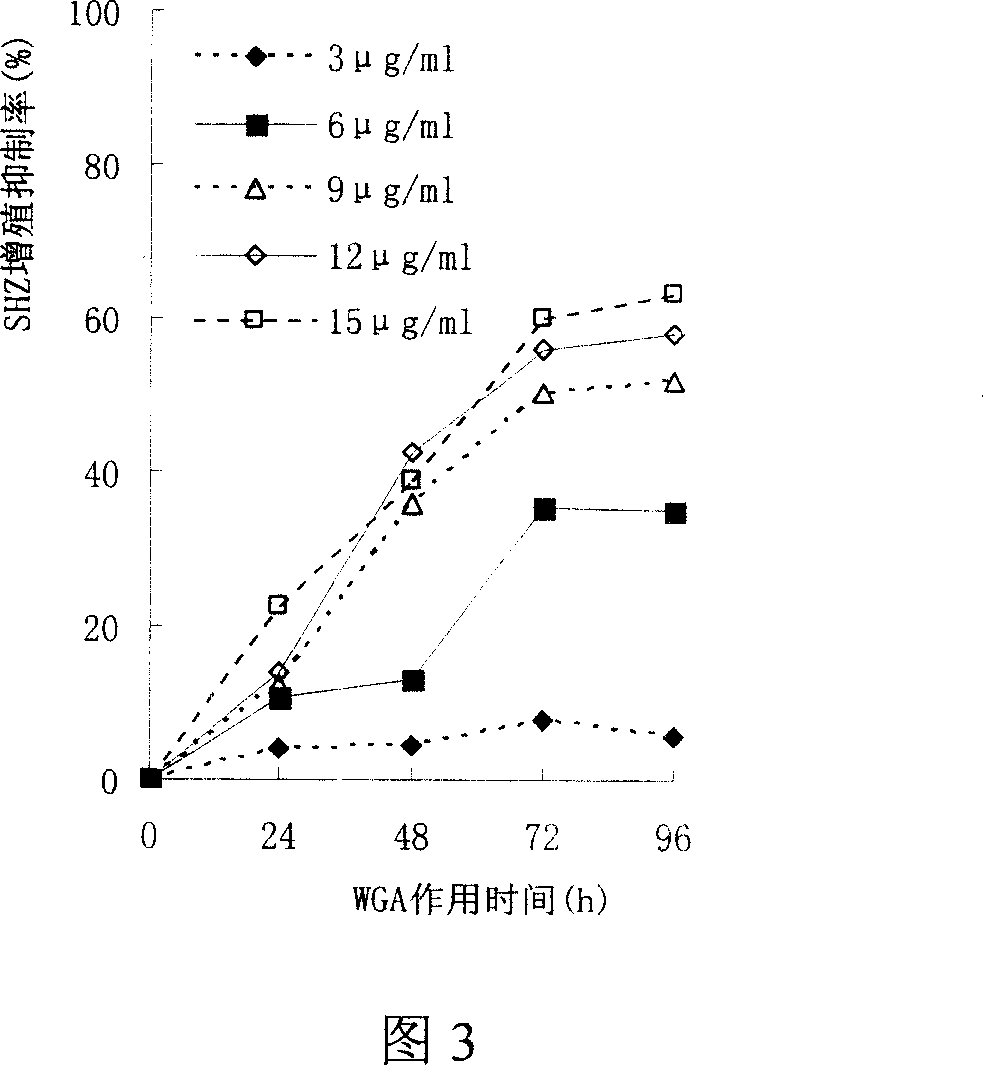
This invention relates to the preparation of wheat germ agglutinin (WGA) and its application in restraining breast cancer's activity. It belongs to a field of wheat by-product material's deep processing technology. The wheat germ was comminuted, degreased,deep comminuted, super sound intensified acid extracted, salting out, heat treated, ultrafiltrated and affinity chromatographed, then the composition which have red cell agglutinating activity was desalted and freeze dried, and at last WGA is gained. Cell culture determines that the WGA has depressant effect on rat breast cancer cell strain SHZ and trypsin dependent form human breast cancer cell strain MCF-7. This invention's technology design is scientific and reasonable, manipulate is convenient and procedure is not polluted. The invention provides groundwork for exploiting drug of restraining cancer, and can enhance the utilization value of wheat germ deep processing and related industry's economic returns.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Preparation method of SPIO.SiO2-WGA (Wheat Germ Agglutinin) intestinal wall targeting contrast agent
InactiveCN101843907AImprove detection signal contrastBreakthrough stabilityNMR/MRI constrast preparationsSolubilityIntestinal walls
The invention relates to a preparation method of a wheat germ agglutinin (WGA) packaging silica superparamagnetism (SPIO@SiO2-WGA) magnetic resonance nanometer contrast agent for biomedicine diagnosis. In the invention, water solubility conversion of oil soluble SPIO is realized by utilizing hexadecyl trimethyl ammonium bromide; silica packaging and surface amination of the SPIO are realized by adopting ethyl orthosilicate and aminopropyltriethoxysilane; and connection between the wheat germ agglutinin which has adsorption on the intestinal wall and a superparamagnetism silica sphere is realized by utilizing EDC / NHS in PBS solution. The obtained SPIO.SiO2-WGA magnetic resonance nanometer contrast agent has the advantages of uniform and stable particle diameters, low toxicity and obvious cell targeting effect.
Owner:SHANGHAI NAT ENG RES CENT FORNANOTECH
Preparing method of matrine nanoparticles modified by wheat germ agglutinin and application of matrine nanoparticles
InactiveCN104940142AAchieve specific targetingRich sourcesOrganic active ingredientsPowder deliveryWater bathsPolyvinyl alcohol
The invention relates to a preparing method of matrine nanoparticles modified by wheat germ agglutinin and application of the matrine nanoparticles. The method and application effectively solve the problems that preparing of the matrine nanoparticles modified by the wheat germ agglutinin and matrine are low in targeting and poor in using effect. According to the matrine nanoparticles modified by the wheat germ agglutinin, the matrine nanoparticles are connected with wheat germ agglutinin through chemical bonds, and matrine is dissolved into a water solution through water bath; polylactic acid-hydroxyacetic acid copolymer acetone is dissolved into an organic phase through water bath; the matrine water solution is dripped into the organic phase to form colostrums, the colostrums is injected into a polyving akohol water solution, acetone is volatilized, centrifugation is conducted, sediment and drying are conducted, and matrine nanoparticles are obtained; the matrine nanoparticles are dissolved through a PBS solution, carbodiimide and N-hydroxy succinimide is added, activation and centrifugation are conducted, supernate is added into a solution containing wheat germ agglutinin, incubation and centrifugation are conducted, sediment and drying are conducted, and the final matrine nanoparticles is prepared. According to the preparing method, the preparation condition is met easily, the raw material source is rich, the cost is low, and the preparing method is innovation of cancer therapeutic drug.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF CHINESE MEDICINE
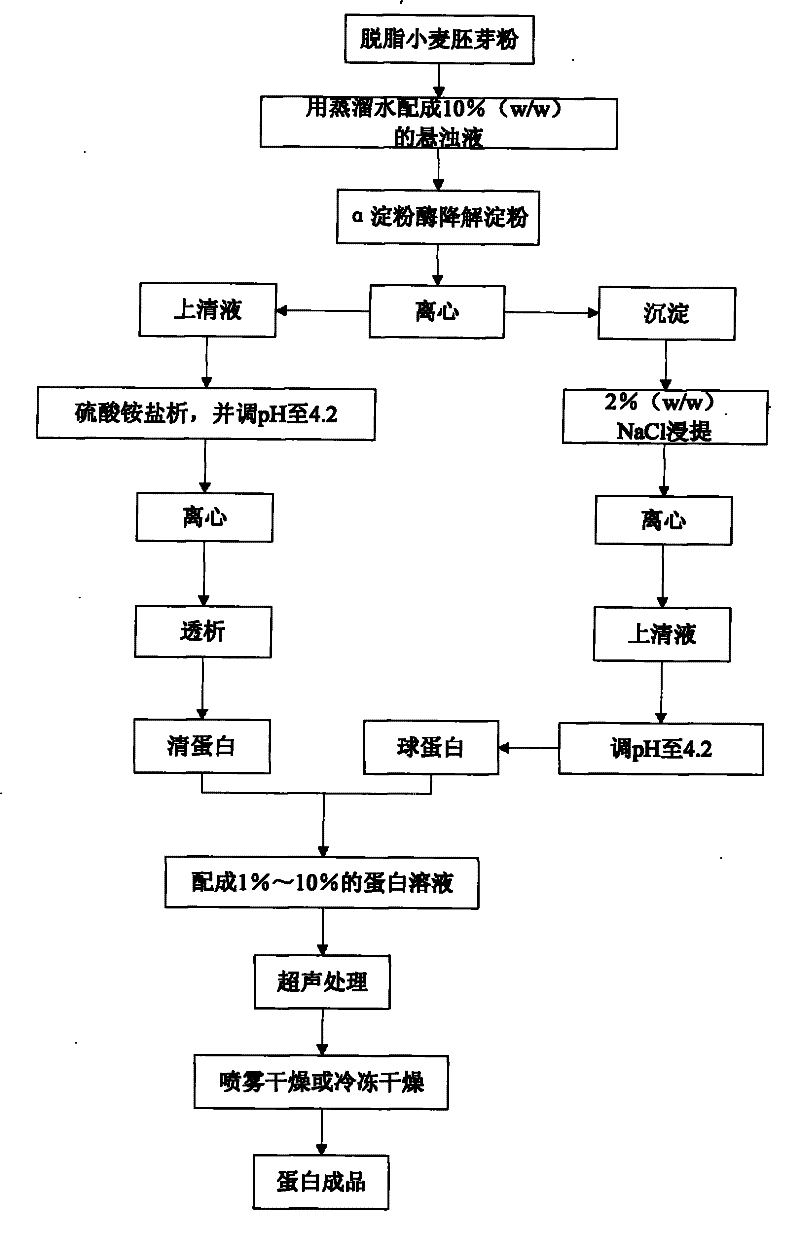
Method for improving wheat plantule protein capability with supersonic wave
ActiveCN101427728BImprove functional propertiesHigh yieldVegetable proteins working-upFood preparationSolubilityWheat germ
The invention relates to the field of bioengineering, particularly to a method for improving properties of wheat germ protein with ultrasonic wave. The method comprises extracting albumin and globulin from defatted wheat germ powder, respectively, and treating wheat germ albumin and globulin solution with ultrasonic wave. The inventive method can remarkably improve the solubility, effervescence, effervescent stability, emulsifying property and emulsifying stability of the wheat germ albumin and globulin.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
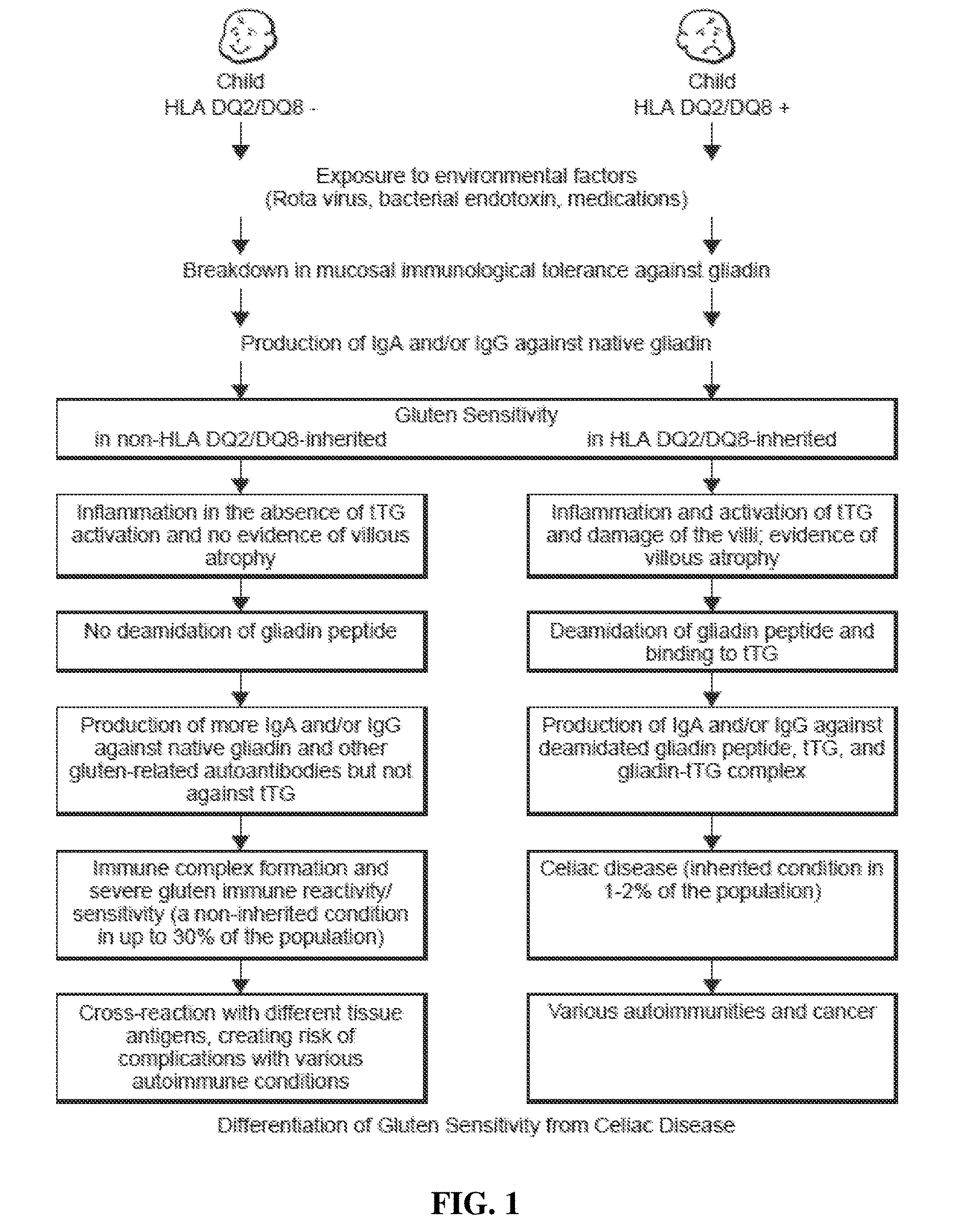
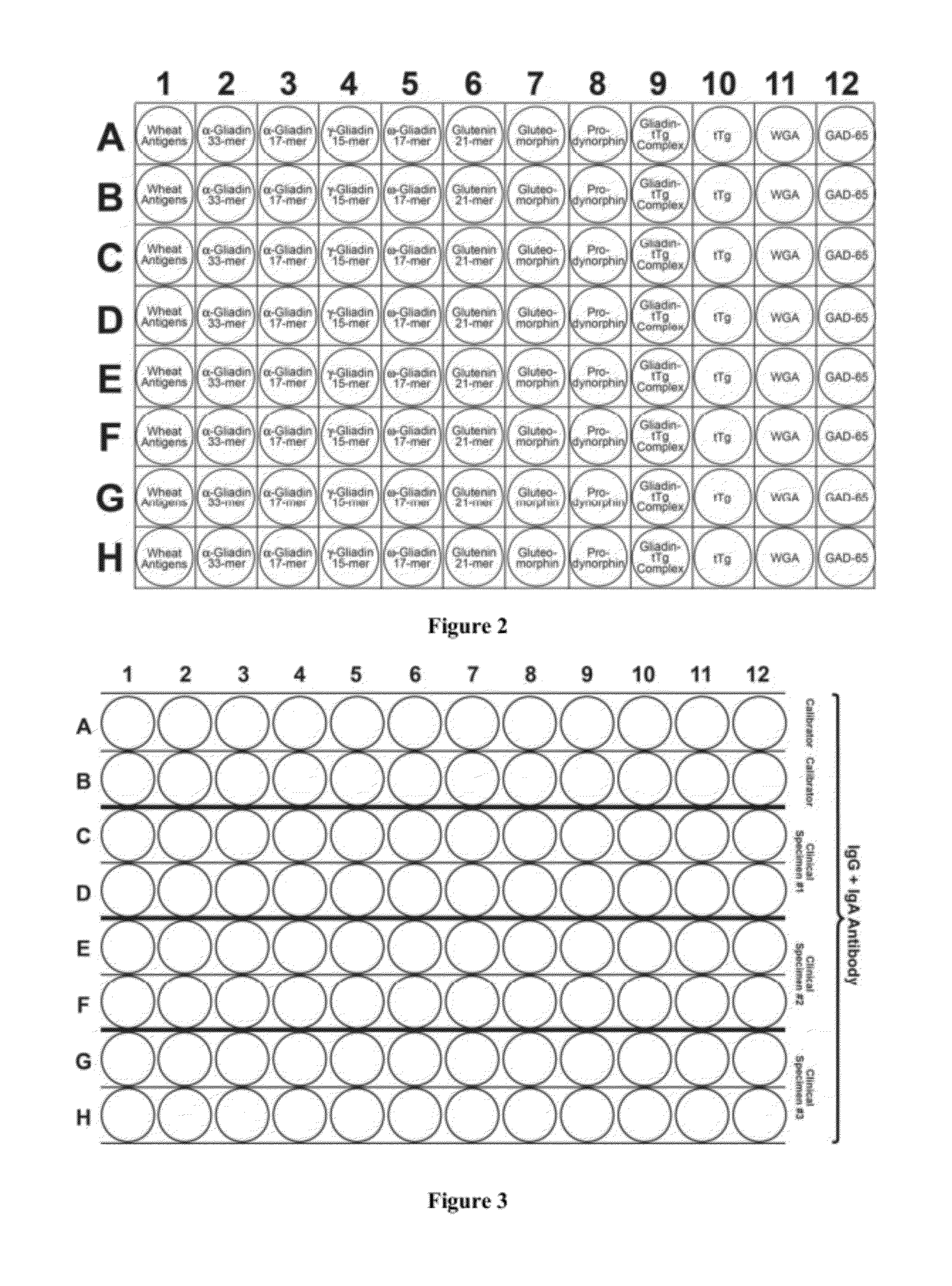
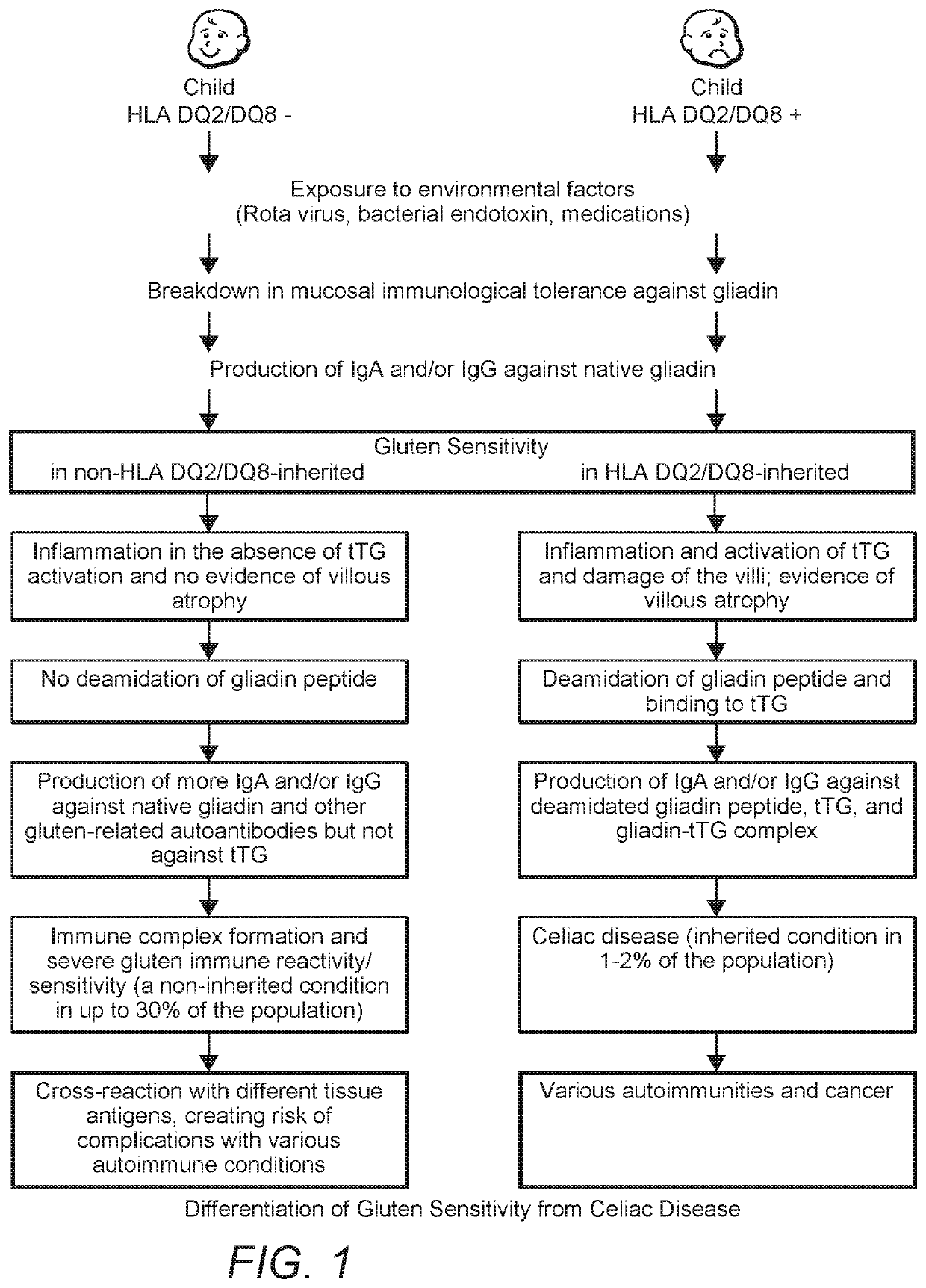
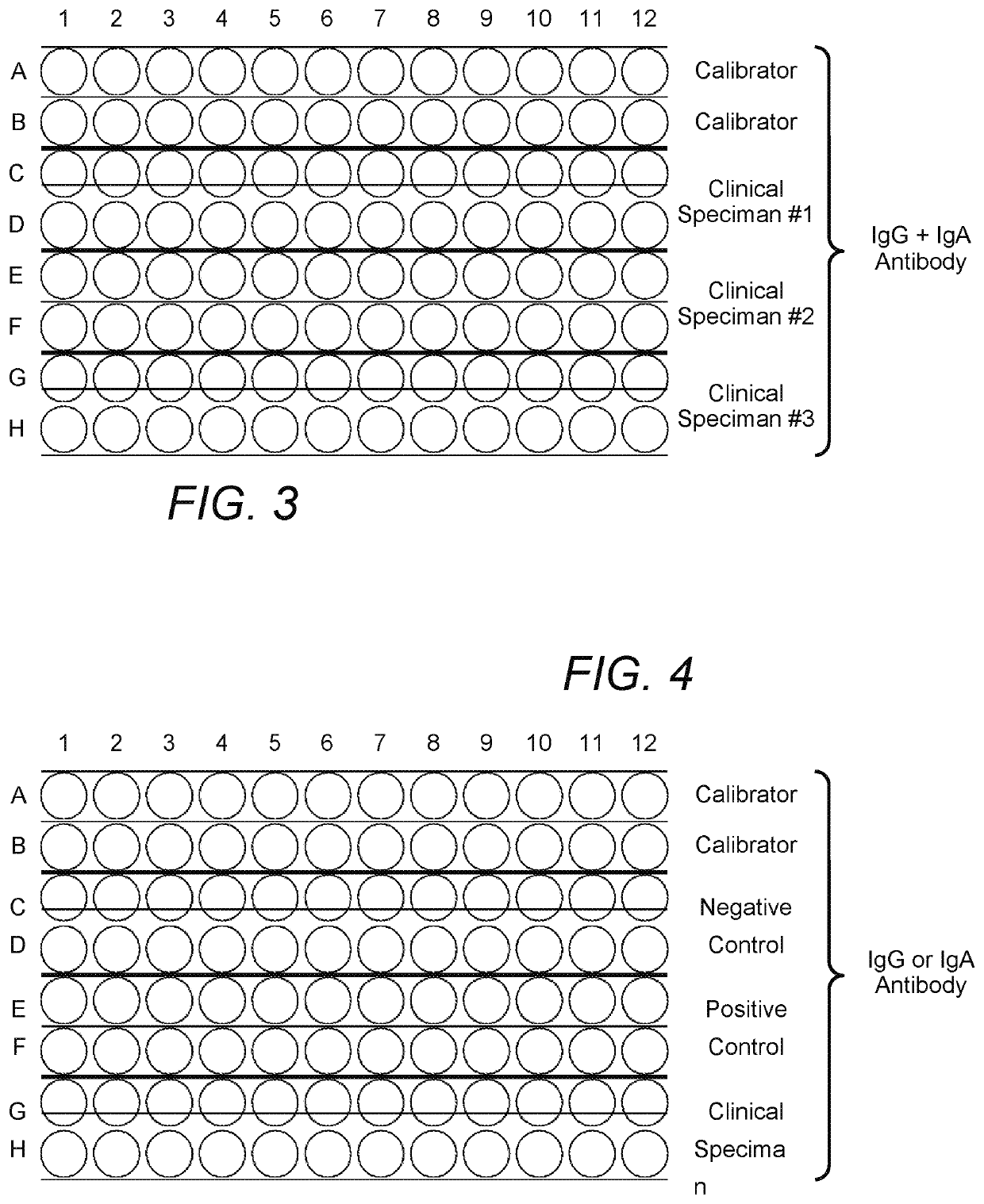
Methods and Apparatus for Detection of Gluten Sensitivity, and its Differentiation from Celiac Disease
Antibodies are used as biomarkers to assist in distinguishing gluten immune reactivity and sensitivity, silent celiac disease, Crohn's disease and other gut-related pathologies from classical celiac disease. In one class of embodiments, sera, saliva or other samples from a human or other animal are tested for antibodies to (a) a wheat antigen; (b) a gliadin antigen; and (c) one or more of a wheat germ agglutinin, a gluteomorphin, a glutenin, a deamidated glutenin, a prodynorphin, and a dynorphin. Test results are considered particularly interesting where the wheat antigen and the gliadin antigen are both selected from the group consisting of native and deamidated forms of α-gliadin 33-mer, α-gliadin-17-mer, γ-gliadin-15-mer, ω-gliadin-17-mer, and glutenin 21-mer. Test plates and kits can advantageously test for antibodies to at least three, five, seven or all of mixed wheat antigens, α-gliadin, γ-gliadin, ω-gliadin, glutenin, α-glutenin, wheat germ agglutinin, gluteomorphin, prodynorphins, transglutaminase-2, transglutaminase-3, transglutaminase-6, and gliadin-bound transglutaminase.
Owner:CYREX LAB LLC
Methods and apparatus for detection of gluten sensitivity, and its differentiation from celiac disease
Antibodies are used as biomarkers to assist in distinguishing gluten immune reactivity and sensitivity, silent celiac disease, Crohn's disease and other gut-related pathologies from classical celiac disease. In one class of embodiments, sera, saliva or other samples from a human or other animal are tested for antibodies to (a) a wheat antigen; (b) a gliadin antigen; and (c) one or more of a wheat germ agglutinin, a gluteomorphin, a glutenin, a deamidated glutenin, a prodynorphin, and a dynorphin. Test results are considered particularly interesting where the wheat antigen and the gliadin antigen are both selected from the group consisting of an α-gliadin-33-mer, an α-gliadin-17-mer, a γ-gliadin-15-mer, an ω-gliadin-17-mer, and a glutenin-21-mer. Test plates and kits can advantageously test for antigens to at least three, five, seven or all of α-gliadin, γ-gliadin, ω-gliadin, glutenin, wheat germ agglutinin, gluteomorphin, prodynorphins, transglutaminase-2, transglutaminase-3, transglutaminase-6, and gliadin-bound transglutaminase.
Owner:CYREX LAB LLC
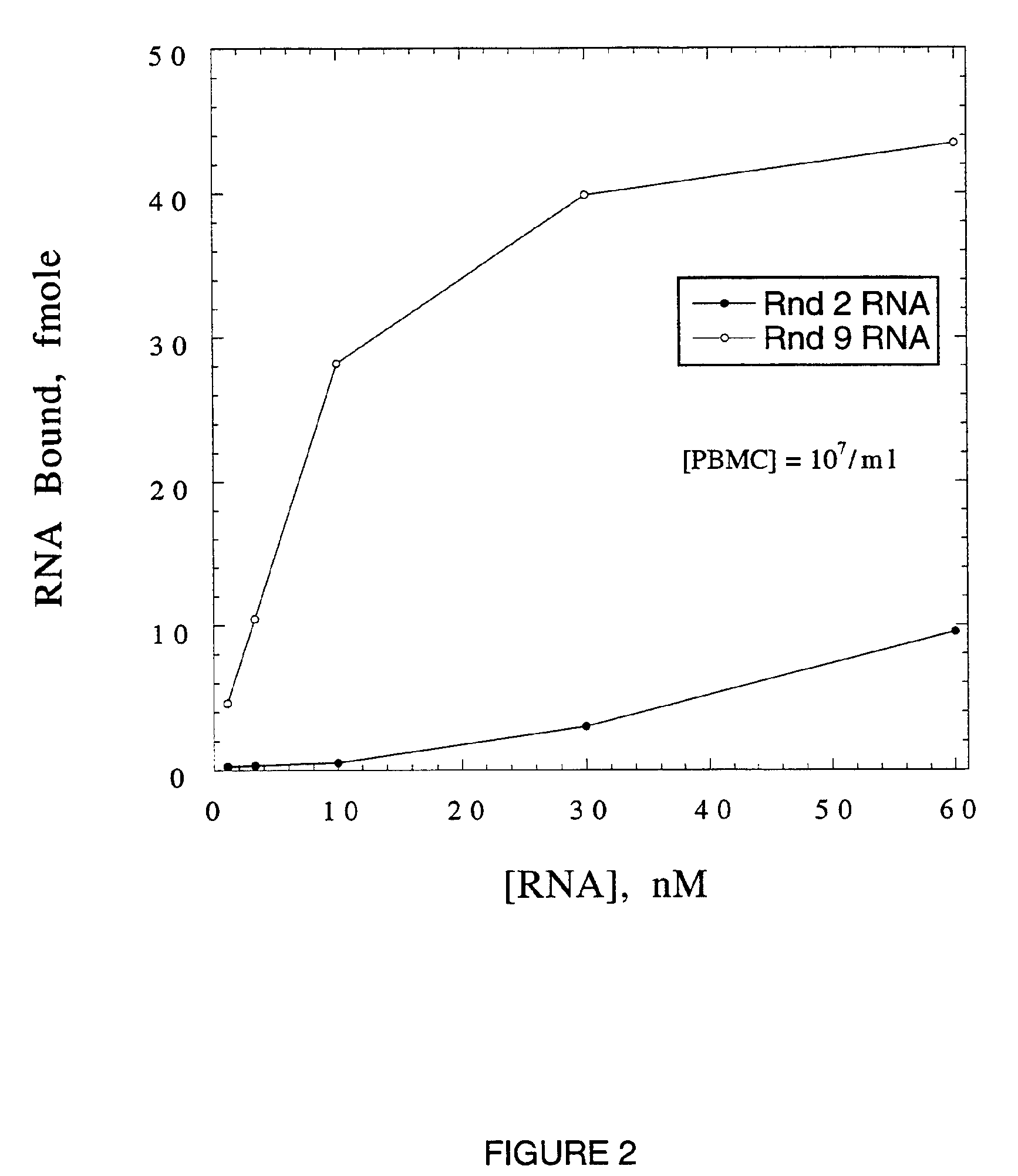
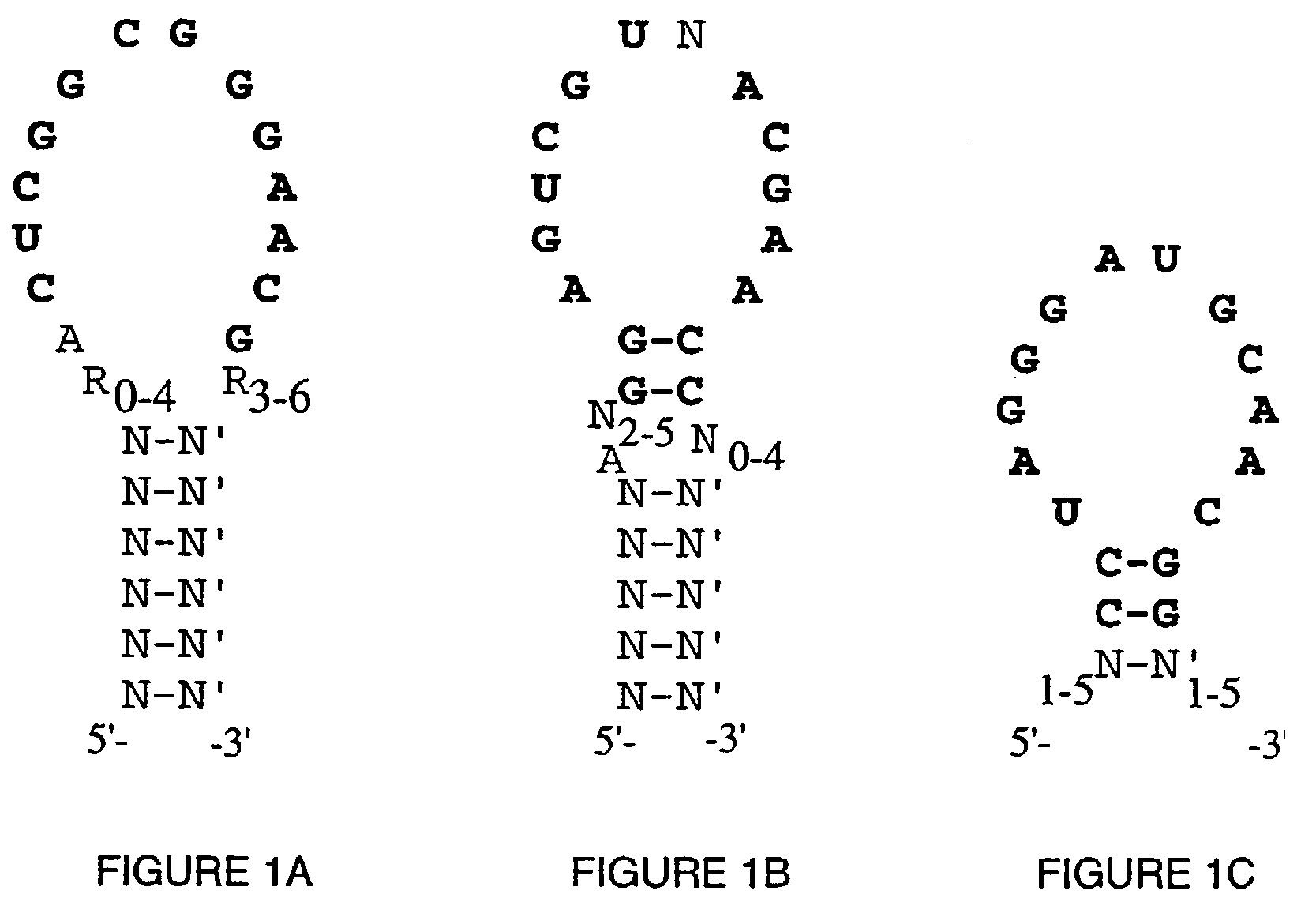
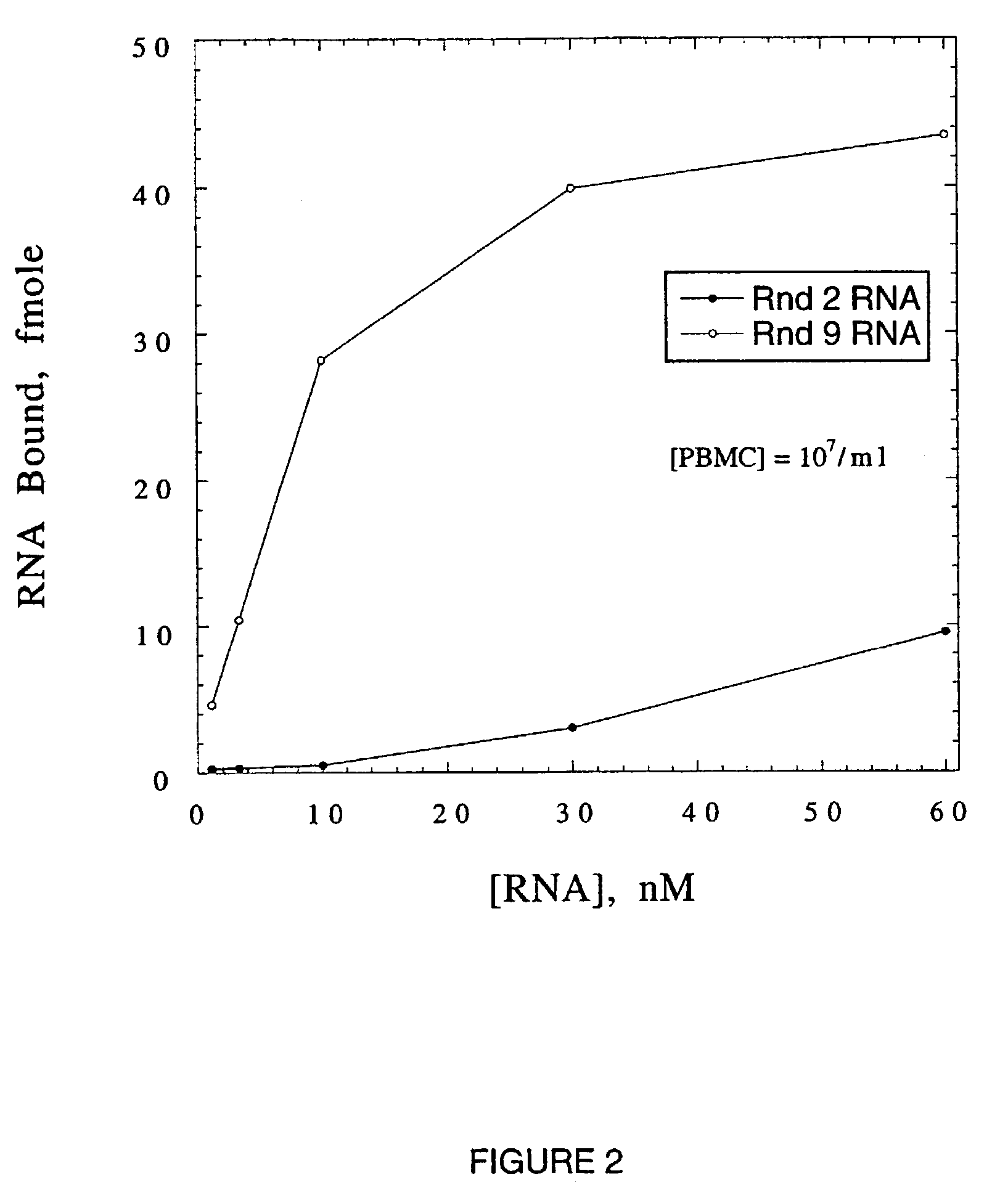
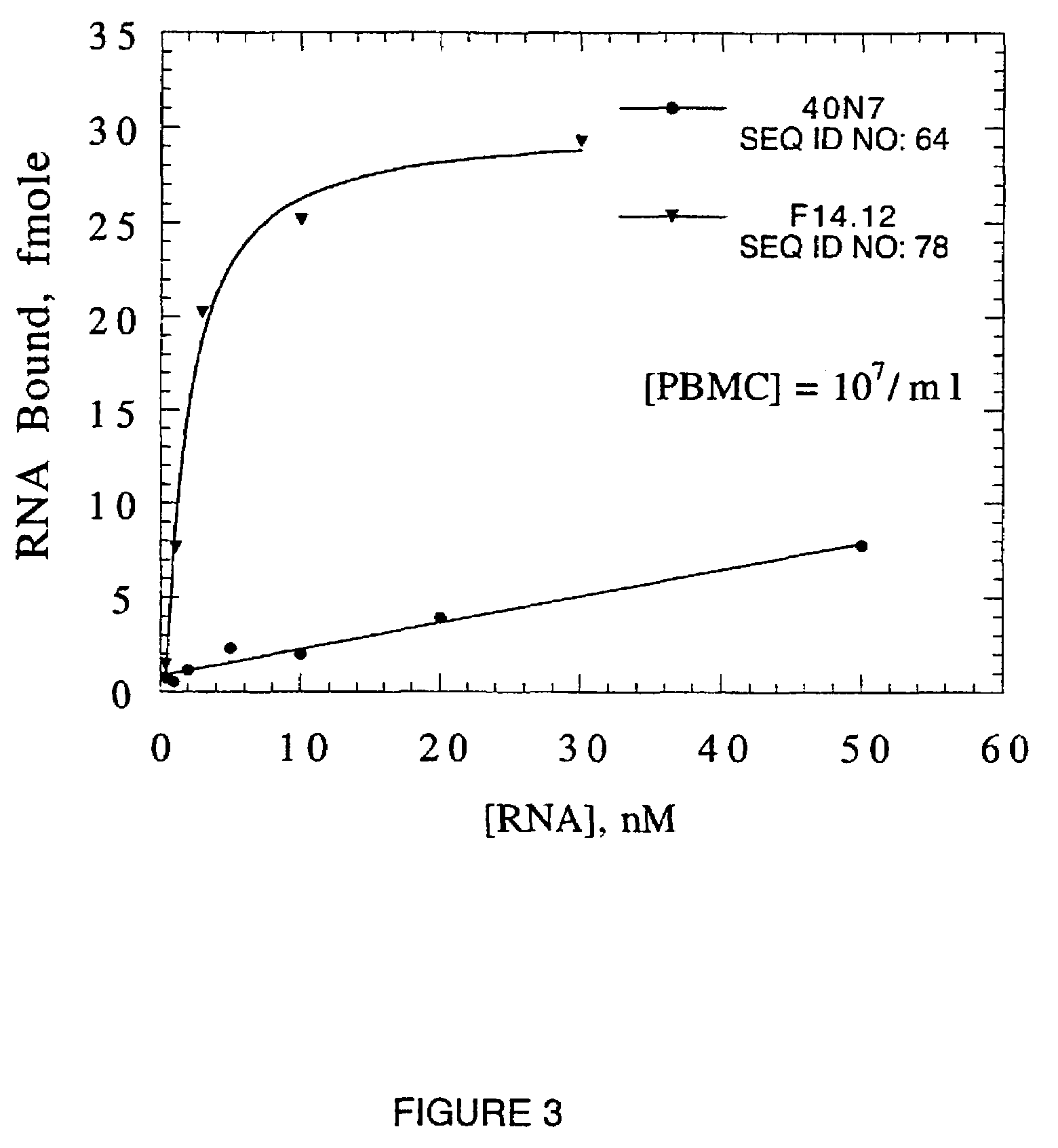
High Affinity Nucleic Acid Ligands To Lectins
InactiveUS20090118481A1High affinity bindingPeptide-nucleic acidsSugar derivativesP-selectinE-selectin
This invention discloses high-affinity oligonucleotide ligands to lectins, specifically nucleic acid ligands having the ability to bind to the lectins, wheat germ agglutinin, L-selectin, E-selectin and P-selectin. Also disclosed are the methods for obtaining such ligands. This invention discloses high-affinity oligonucleotide ligands to lectins, specifically nucleic acid ligands having the ability to bind to the lectins, wheat germ agglutinin, L-selectin, E-selectin and P-selectin. Also disclosed are the methods for obtaining such ligands.
Owner:GILEAD SCI INC
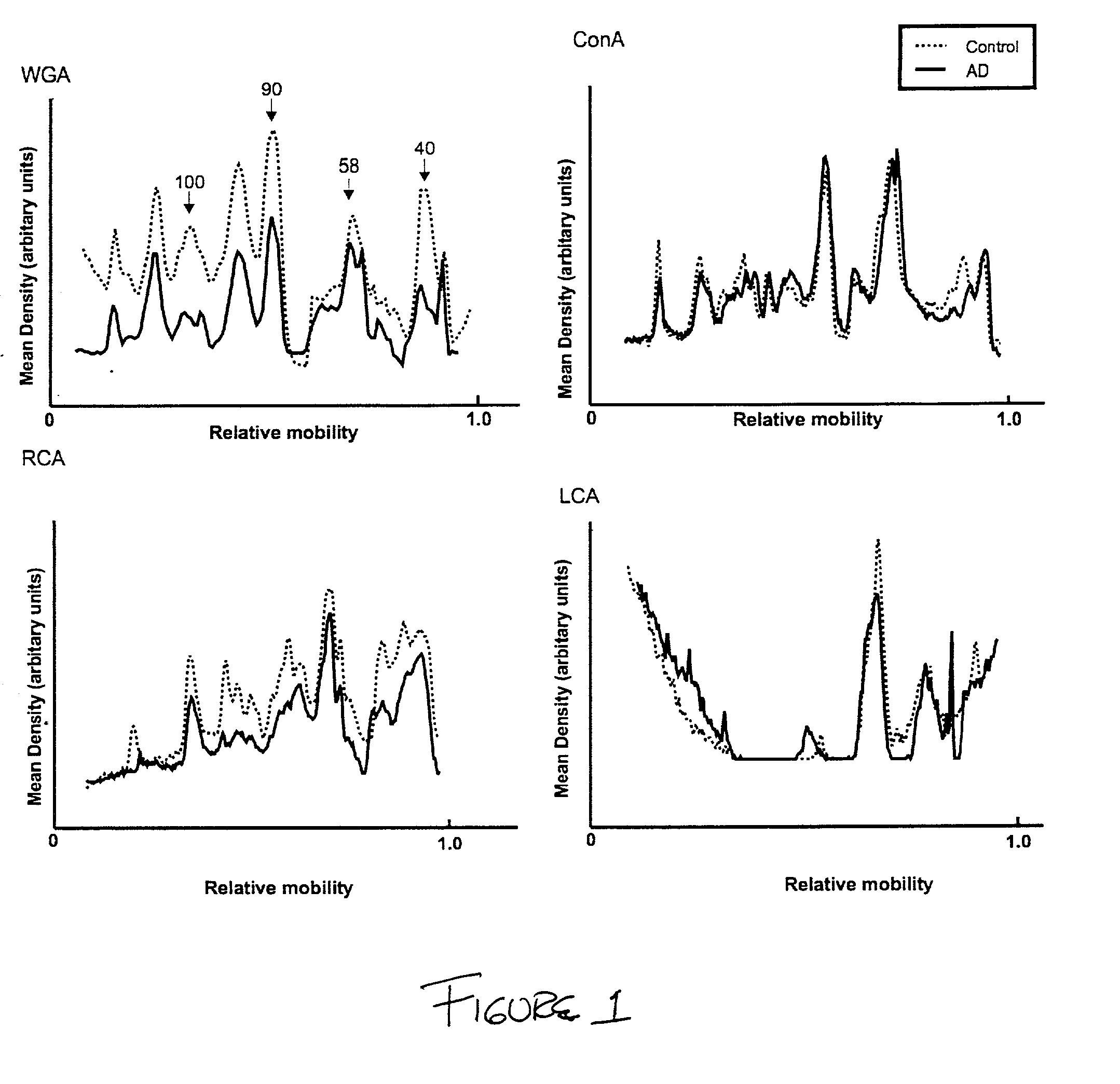
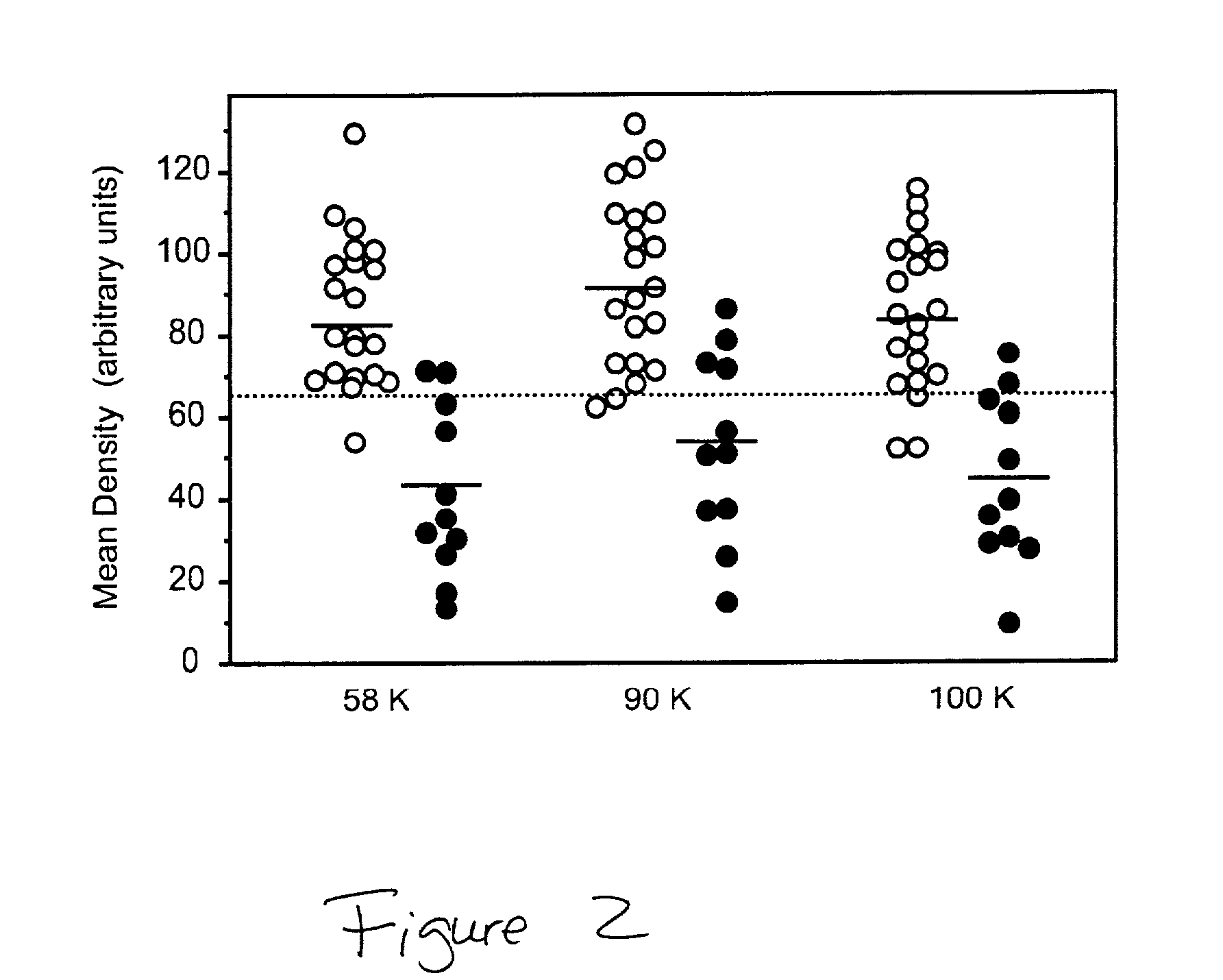
Method for the diagnosis of Alzheimer's Disease and other prion related disorders
InactiveUS20020150878A1High sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisButyrylcholinesteraseAcetylhomocholine
The invention provides a method for the diagnosis of dementia and transmissible spongiform encephalopathies in a subject by detecting the levels of glycoproteins that bind wheat germ agglutinin. The invention also provides a method for diagnosis of dementia and transmissible spongiform encephalopathies in a subject by comparing the levels of glycoproteins that bind wheat germ agglutinin with the glycosylation patterns of biomarkers, acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase.
Owner:AXONYX INC +1
Lectin conjugates for mucin hydration
The invention provides, inter alia, conjugates of a hydratable polymer (such as PEG, polyethylene glycol) and a lectin (such as wheat germ agglutinin, WGA), compositions comprising these conjugates, as well as methods and targeted uses of these conjugates and compositions for, e.g., lubricating, maintaining hydration of, rehydrating, and / or inhibiting microorganism colonization of a biological surface in need thereof.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
High affinity nucleic acid ligands to lectins
InactiveUS7399752B2High affinity bindingPeptide/protein ingredientsOrganic chemistry methodsE-selectinP-selectin
This invention discloses high-affinity oligonucleotide ligands to lectins, specifically nucleic acid ligands having the ability to bind to the lectins, wheat germ agglutinin, L-selectin, E-selectin and P-selectin. Also disclosed are the methods for obtaining such ligands.
Owner:GILEAD SCI INC
Wheat germ agglutinin modified salmeterol xinafoate chitosan nanoparticle preparation
ActiveCN102406615AEffective concentration time is longReduce dosePowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsChitosan nanoparticlesSide effect
The invention provides a wheat germ agglutinin modified salmeterol xinafoate chitosan nanoparticle preparation and a preparation method thereof, relating to the technical field of medicines. In the invention, an ion cross-linking method is used for preparing salmeterol xinafoate chitosan nanoparticles; and by utilizing the characteristic that the alveolar epithelium has specific sugar receptor N-acetyl glucosamine, wheat germ agglutinin modified salmeterol xinafoate chitosan nanoparticles are prepared, so that the specific sugar receptor N-acetyl glucosamine of the alveolar epithelium can be combined through the wheat germ agglutinin to enable the salmeterol xinafoate chitosan nanoparticles to have the targeting property of guiding the alveolar membrane. In-vitro sugar-binding test results show that the wheat germ agglutinin modified salmeterol xinafoate chitosan nanoparticles have the advantage of guiding the alveolar membrane, thus the administration dosage can be lowered, and the toxic side effect can be reduced; and by the slow release of the medicament, the effective concentration maintaining time of the medicament in the lung is long, thereby enhancing the treatment effect. The preparation provided by the invention can be used for preparing medicaments for treating asthma, chronic bronchitis or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
Owner:上海市第八人民医院
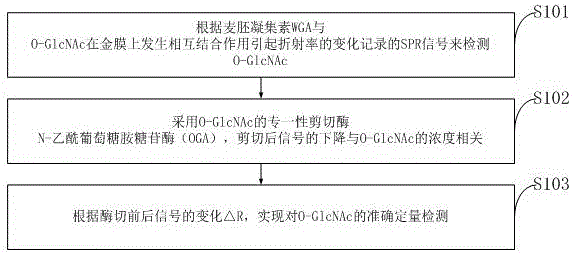
Quantitative detection method of O-GlcNAc
InactiveCN106645038AEasy to operateAvoid interferencePhase-affecting property measurementsDisease diagnosisEnzyme digestionCancer cell
The invention discloses a quantitative detection method of O-GlcNAc, comprising the following steps: detecting O-GlcNAc according to SPR signals recorded according to change of the refractive index caused by the inter combination effect of wheat germ agglutinin WGA and O-GlcNAc on a gold film; cutting O-GlcNAcase (OGA) by using the specificity of O-GlcNAc, wherein signal decrease after cutting is related to the concentration of O-GlcNAc; and according to change of signal delta R before and after enzyme digestion, realizing accurate and quantitative detection of O-GlcNAc. The quantitative detection method of O-GlcNAc has low requirements on samples which can be detected after simple treatment, is simple in operation, has a wide linear range relative to the previously reported work, and can be applied to detection of O-GlcNAc in cancer cells.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCIENCES
Medical dressing containing wheat germ globulin
InactiveCN107137751AImprove antibacterial propertiesEnhance anti-inflammatoryAbsorbent padsBandagesMedical productGlycerol
The invention relates to a medical dressing containing wheat germ globulin, and belongs to the technical field of medical products. The medical dressing comprises, by weight, 1-10 parts of calcium alginate, 20-30 parts of sodium alginate, 1-10 parts of chitosan, 3-8 parts of glycerol, 1-6 parts of wheat germ globulin, 0.0001-0.0005 part of nano-silver and 180-220 parts of deionized water. The medical dressing uses the wheat germ globulin with the immune effect, so that the medical dressing has good anti-inflammation and antibacterial effects, promotes growth of new granulation tissue and epithelial cells and can greatly improve the wound healing effect, and the medical dressing is particularly suitable for the situation that wounds are deep.
Owner:河南福切尔生物科技有限公司
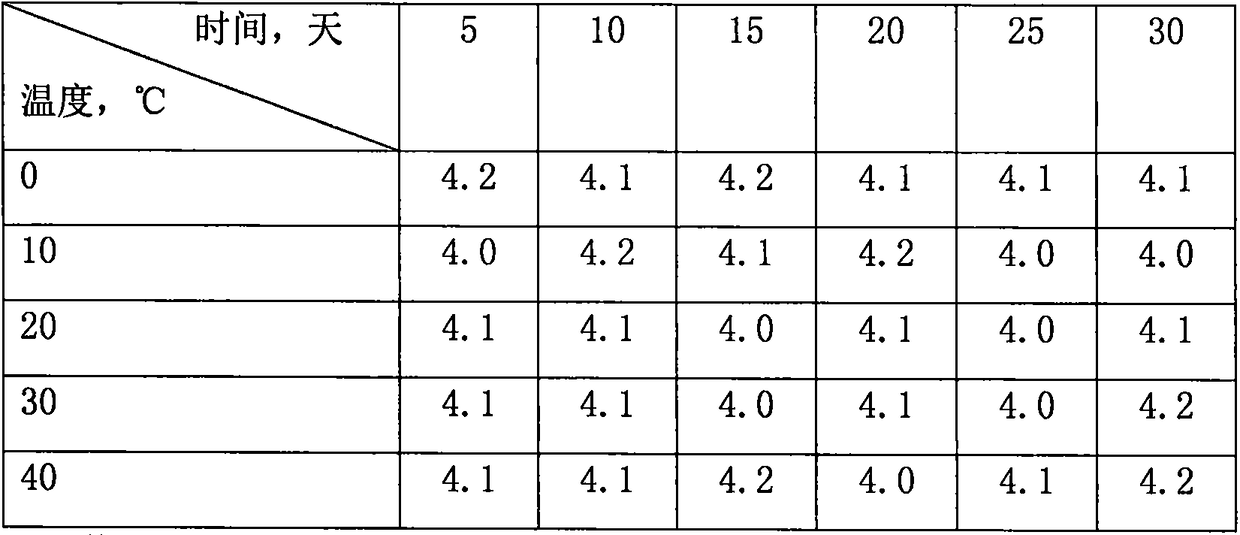
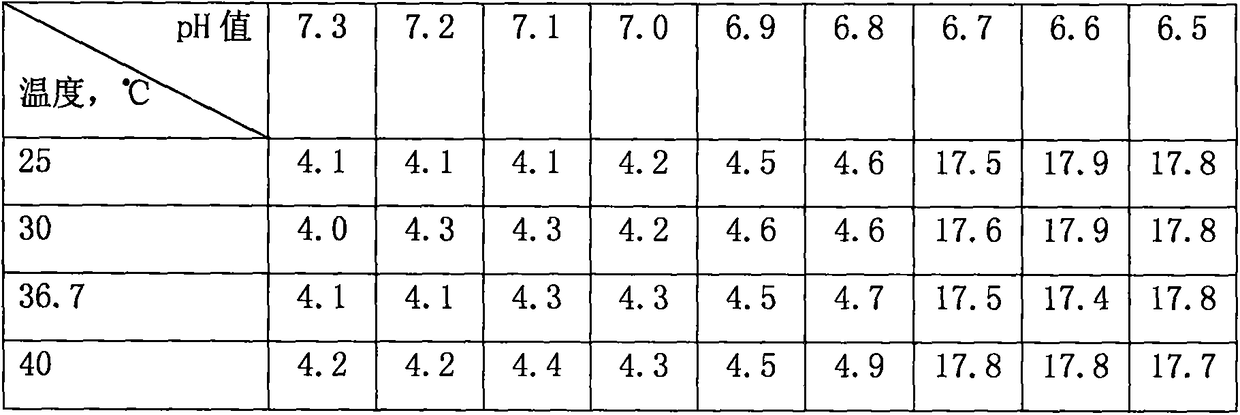
Composition capable of improving stress resistance of hybrid liriodendron body embryo seedlings and realizing promoting effect and application of composition
InactiveCN107927007AImprove stress resistanceHas a growth-promoting effectPlant growth regulatorsBiocideSilicic acidEmbryo
The invention discloses a composition capable of improving stress resistance of hybrid liriodendron body embryo seedlings and realizing a promoting effect. The composition is prepared from 5 to 10 parts of wheat germ agglutinin, 5 to 10 parts of peanut agglutinin, 5 to 10 parts of sodium lignosulphonate, 5 to 10 parts of high-dispersion silicic acid, 10 to 20 parts of sodium dodecyl sulfonate and70 to 140 parts of kaolin. According to the composition disclosed by the invention, massive experiments are conducted for screening; the wheat germ agglutinin and the peanut agglutinin of which the weight ratio is 1 to 1 are creatively adopted as main active ingredients and matched with the sodium lignosulphonate, the high-dispersion silicic acid, the sodium dodecyl sulfonate and the kaolin with optimal use amounts. Experimental results show that the composition provided by the invention has the beneficial effects that the resistance of the hybrid liriodendron body embryo seedlings to adversetemperature environments of 4 DEG C low temperature and 40 DEG C high temperature is remarkably enhanced, and the drought resistance of the hybrid liriodendron body embryo seedlings can be obviously improved. The composition disclosed by the invention has the advantages of scientificity and reasonability in component matching, greenness, environmental protection, low toxicity and important practical application value.
Owner:HUAIYIN TEACHERS COLLEGE
Preparation method of in-vivo self-assembled targeting drug carrier
InactiveCN108379590AMacromolecular non-active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsO carboxymethyl chitosanIn vivo
The invention relates to a precursor solution of active targeting nano-drug particles and a preparation method of the precursor solution. The precursor solution of active targeting nano-drug particlesis prepared from 6-O-carboxymethyl chitosan, 6-amino-alpha-cyclodextrin, 6-amino-belta-cyclodextrin, 6-amino-gamma-cyclodextrin, L-histidine and wheat germ agglutinin, has multiple drug-carrying factors, and can be assembled in organisms automatically. The preparation method includes, firstly, preparing three types of cyclodextrin grafted 6-O-carboxymethyl chitosan from raw materials of 6-amino-alpha-cyclodextrin, 6-amino-belta-cyclodextrin, 6-amino-gamma-cyclodextrin and 6-O-carboxymethyl chitosan; secondly, preparing poly L-histidine from the raw material of histidine and condensating agents, namely 1-ethyl-(3-dimethylaminopropyl) carbodiimide (EDC) and N-hydroxysuccinimide (NHS); thirdly, dissolving the three types of cyclodextrin grafted 6-O-carboxymethyl chitosan and the poly L-histidine in alkalescent water for injection, and then adding wheat germ agglutinin (WGA) to obtain the precursor solution which can be assembled into the nano particles carrying drug-carrying factors andtargeting factors in faintly acid normal saline.
Owner:QINGDAO UNIV
Defatted wheat germ powder extract and new use thereof
InactiveCN109953351ALow costWide variety of sourcesPeptide/protein ingredientsAntinoxious agentsSocial benefitsSide effect
The invention discloses a defatted wheat germ powder extract and a new use thereof. The extract comprises a main component of wheat germ globulin, defatted wheat germ powder is extracted by a sodium chloride solution with the mass concentration of 2%-4%, and a wheat germ globulin oral liquid is prepared. The invention also provides the use of the defatted wheat germ powder extract (namely the wheat germ globulin oral liquid) in drugs for preventing or treating acute nitrite poisoning. The wheat germ globulin oral liquid has remarkable detoxification effect, can significantly shorten the phenomenon of mice after nitrite poisoning, and can prevent and treat nitrite poisoning. The wheat germ globulin oral liquid is verified to have no toxic or side effects by toxicological experiments, is verified to have good preventive and therapeutic effects on mice with acute nitrite poisoning by pharmacological experiments, and has broad market prospects and important economic and social benefits.
Owner:HENAN COOP MEDICAL SCI & TECH INST CO LTD
Wheat germ globulin for blood substitute
InactiveCN106749579AImprove immunityPerformance is not affectedPlant peptidesFermentationWheat germBlood substitute
The invention relates to a wheat germ globulin for a blood substitute and belongs to the technical field of medicinal and pharmaceutical substances. The scope of extracting molecular weight of the wheat germ globulin is 55+ / -3 KDa, 23+ / -3 KDa and 16.5KDa. The wheat germ globulin is acquired after the modified protease is purified. According to invention, the immune performance of the wheat germ globulin is utilized; the wheat germ globulin is added into the blood substitute, so that the use safety of the blood substitute is greatly promoted; the irritability phenomenon is greatly reduced.
Owner:河南康一元生物科技股份有限公司
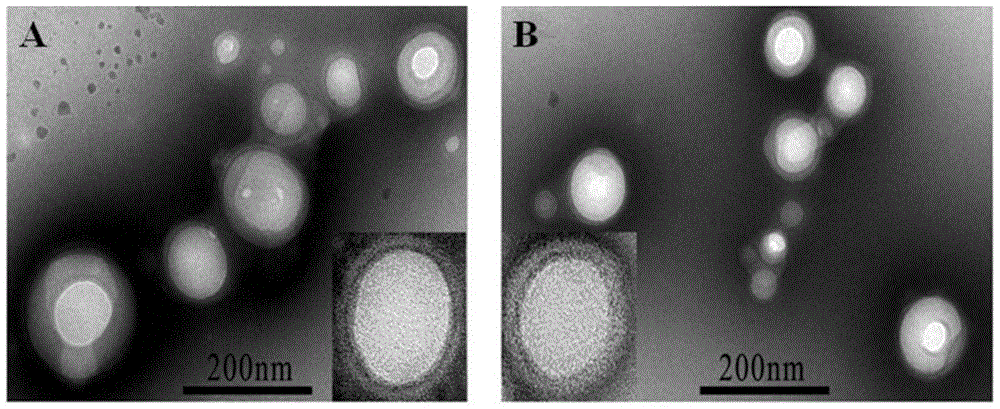
Polymer nanoparticles carrying water-soluble small peptide and modified by wheat germ agglutinin and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105688183AIncrease uptakeSmall particle sizePeptide/protein ingredientsMacromolecular non-active ingredientsLow speedOrganic solvent
The invention relates to polymer nanoparticles carrying water-soluble small peptide and modified by wheat germ agglutinin and a preparation method thereof. The average particle size of the nanoparticles is 140nm, the encapsulation efficiency reaches 50%, and the drug loading capacity is 11%. The preparation method comprises the following steps: (1) dissolving NR2B9c in water to obtain an internal water phase; (2) dissolving a polymeric material in dichloromethane to obtain an oil phase; (3) adding the internal water phase into the oil phase and performing ultrasonic treatment to obtain W / O primary emulsion; (4) adding the W / O primary emulsion into an emulsifier-containing external water phase and performing ultrasonic treatment to obtain W / O / W compound emulsion; and (5) diffusing the W / O / W compound emulsion in a diffusive-phase solution, adding sulfhydrylated WGA, stirring at a low speed for incubation, removing the organic solvent, freezing and centrifuging to obtain NR2B9c-entraped WGA modified polymer nanoparticles, wherein perfect brain targeting is realized through intranasal administration.
Owner:NANJING MEDICAL UNIV
Protein separating and enriching method
InactiveCN103614439AQuantitative and comparativePeptide preparation methodsFermentationAgglutinin-BMass spectrometry
The invention discloses a protein separating and enriching method. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: subjecting a sample to a primary lectin affinity chromatography, then carrying out an enzymatic hydrolysis on the sample, then subjecting the sample to a secondary lectin affinity chromatography, finally separating the sample by utilizing HPLC, and sequencing with a mass spectrum instrument. The agglutinin used in the method comprises concanavalin A, wheat germ agglutinin, PHA phaseolus vulgaris agglutinin, etc. The glycopeptides in the processed sample is analyzed and retrieved in a database by a capillary liquid chromatography-ESI-MASS or a capillary liquid chromatography-MADLI-TOF-MASS. The method has the advantages that various saccharide species can be collected in one time, the labeled polypeptide can be enriched through an affinity method, and a quantitative and comparative analysis is advantageously to be achieved through adopting an isotope labeled reagent.
Owner:刘军
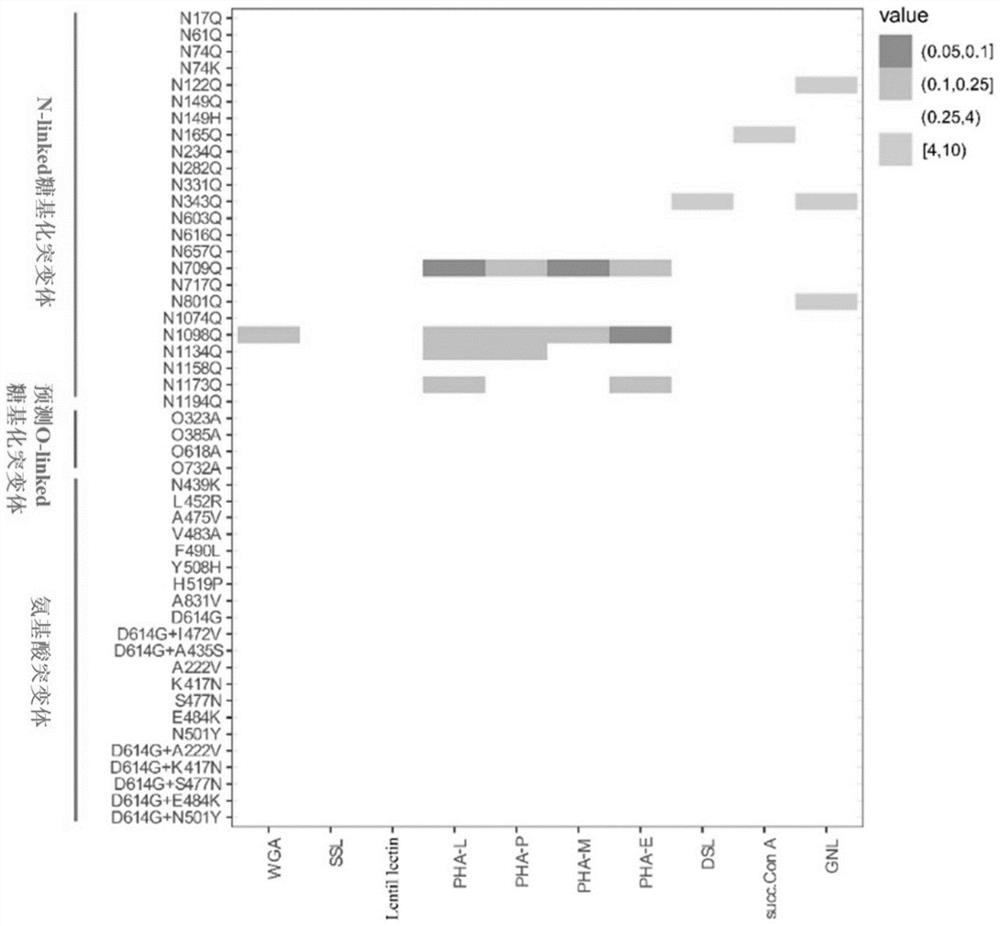
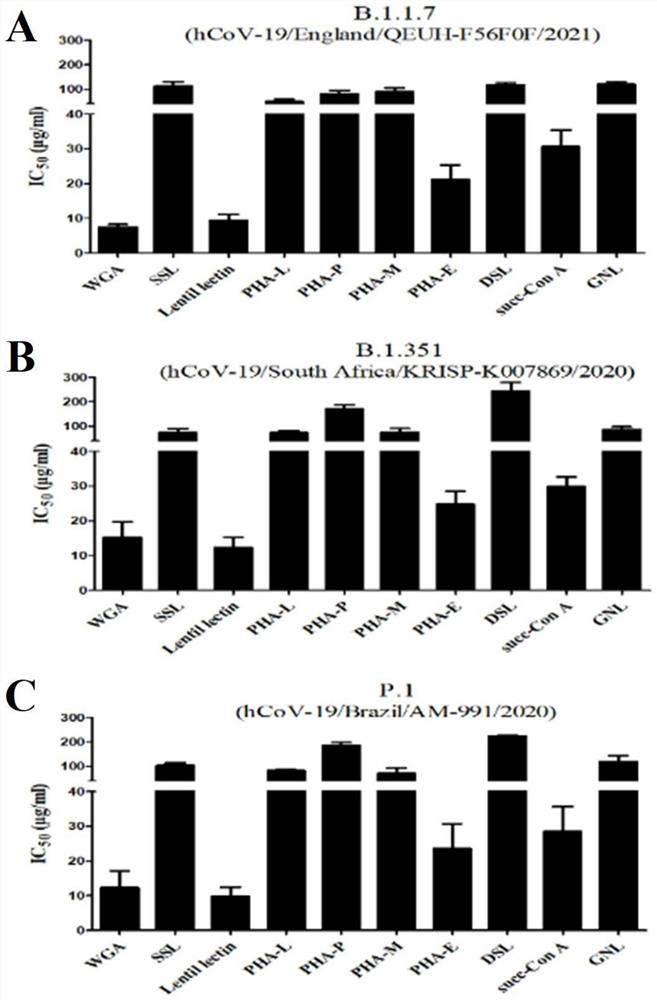
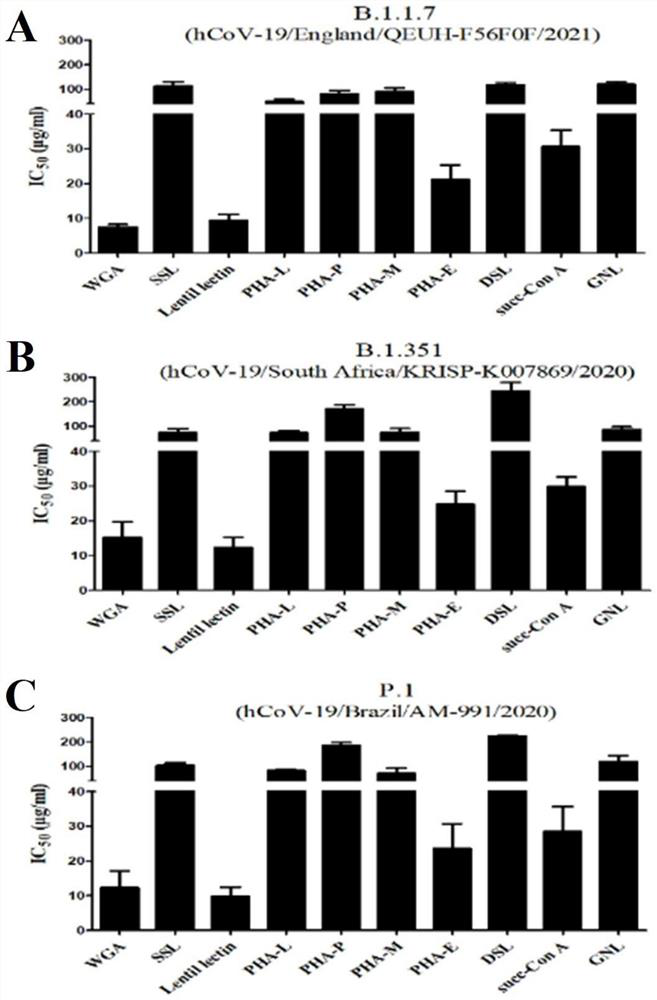
Application of wheat germ agglutinin in the preparation of products for inhibiting coronavirus
ActiveCN113244373BGood antiviral activityAvoid infectionPeptide/protein ingredientsAntiviralsAgglutininPharmaceutical drug
The invention discloses the application of wheat germ agglutinin in the preparation of products for inhibiting coronaviruses. The invention finds for the first time that the wheat germ agglutinin is effective against SARS‑CoV, MERS‑CoV, SARS‑CoV‑2 and SARS‑CoV‑2 mutant strains. It has good antiviral activity, and also shows certain antiviral activity to vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV), which can be used to treat and prevent infection caused by coronavirus, and can be used as a candidate drug for the prevention and treatment of coronavirus infection. Good application value.
Owner:NAT INST FOR FOOD & DRUG CONTROL
Application of wheat germ agglutinin to preparation of product for inhibiting coronavirus
ActiveCN113244373AGood antiviral activityAvoid infectionPeptide/protein ingredientsAntiviralsAgglutininVesicular stomatitis virus VSV
The invention discloses application of wheat germ agglutinin to preparation of a product for inhibiting a coronavirus, and it is first time for the invention to finds that the wheat germ agglutinin has relatively high antiviral activity on SARS-CoV, MERS-CoV, SARS-CoV-2 and SARS-CoV-2 mutant strains, and also shows certain antiviral activity on vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV), can be used for treating and preventing infection caused by the coronavirus, can be used as a candidate medicine for preventing and treating a coronavirus infection, and has relatively high application value.
Owner:NAT INST FOR FOOD & DRUG CONTROL
Removal of serum albumin from human serum or plasma
InactiveUS20050272643A1Easy to separateEfficient methodCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsPeptide/protein ingredientsBlood plasmaPorous beads
A method of removing serum albumin from blood serum or plasma includes contacting the blood serum or plasma with a sugar-binding protein such as a lectin (e.g., Concanavalin A or wheat germ agglutinin) immobilized on an insoluble support such as a porous bead (e.g., agarose). The method may be practiced by immobilizing a sugar-binding protein on an insoluble support, preparing blood serum or plasma for contacting with the insoluble support having the sugar-binding protein immobilized thereon, contacting the prepared blood serum or plasma with the insoluble support having the sugar-binding protein immobilized thereon to absorb glycosylated proteins from the blood serum or plasma leaving an unbound fraction containing serum albumin, and differentially eluting glycosylated proteins with different sugars from the insoluble support contacted with the blood serum or plasma.
Owner:WINDBER RESEARCH INSTITUTE
A composition capable of improving the stress resistance and growth-promoting effect of somatic embryo seedlings of Liriodendron chinensis and its application
InactiveCN107927007BImprove drought resistancePromote growthBiocidePlant growth regulatorsBiotechnologyLiriodendron
The invention discloses a composition capable of improving stress resistance of hybrid liriodendron body embryo seedlings and realizing a promoting effect. The composition is prepared from 5 to 10 parts of wheat germ agglutinin, 5 to 10 parts of peanut agglutinin, 5 to 10 parts of sodium lignosulphonate, 5 to 10 parts of high-dispersion silicic acid, 10 to 20 parts of sodium dodecyl sulfonate and70 to 140 parts of kaolin. According to the composition disclosed by the invention, massive experiments are conducted for screening; the wheat germ agglutinin and the peanut agglutinin of which the weight ratio is 1 to 1 are creatively adopted as main active ingredients and matched with the sodium lignosulphonate, the high-dispersion silicic acid, the sodium dodecyl sulfonate and the kaolin with optimal use amounts. Experimental results show that the composition provided by the invention has the beneficial effects that the resistance of the hybrid liriodendron body embryo seedlings to adversetemperature environments of 4 DEG C low temperature and 40 DEG C high temperature is remarkably enhanced, and the drought resistance of the hybrid liriodendron body embryo seedlings can be obviously improved. The composition disclosed by the invention has the advantages of scientificity and reasonability in component matching, greenness, environmental protection, low toxicity and important practical application value.
Owner:HUAIYIN TEACHERS COLLEGE
A kind of dual targeting liposome with man and wga modification and its preparation method and application
ActiveCN105055318BIncrease concentrationImprove the effect of chemotherapyHydroxy compound active ingredientsMacromolecular non-active ingredientsEntrapmentWilms' tumor
The invention discloses a double targeting liposome with 4-amino-benzene-alpha-D-mannopyranoside (MAN) and wheat germ agglutinin (WGA) modifiers and a preparation method thereof and application. The double targeting liposome is composed of a liposome and modifiers on the surface of the liposome. The modifiers on the surface of the liposome are 4-amino-benzene-alpha-D-mannopyranoside and wheat germ agglutinin. The invention further provides a medicine carrying liposome which is obtained by using a targeting liposome to perform entrapment of medicines. The medicines can concretely be epirubicin hydrochloride and / or resveratrol. According to the double targeting liposome, double ligands are adopted to perform modification and entrapment of the two medicines, the double targeting effect is achieved, so that the medicines are targeted to the glioma part when striding the blood-brain barrier and are enriched at the tumor position; meanwhile, the two medicines in entrapment can have synergistic or additive curative effect on the focus position, and the curative effect of chemotherapy is improved. A novel idea is provided for preparing medicines for treating glioma, and the double targeting liposome is of great theoretical significance and clinical significance.
Owner:SHIHEZI UNIVERSITY
Salmeterol xinafoate chitosan nanoparticle preparation modified by wheat germ agglutinin
ActiveCN102406615BEffective concentration time is longReduce doseOrganic active ingredientsPowder deliverySide effectChitosan nanoparticles
The invention provides a wheat germ agglutinin modified salmeterol xinafoate chitosan nanoparticle preparation and a preparation method thereof, relating to the technical field of medicines. In the invention, an ion cross-linking method is used for preparing salmeterol xinafoate chitosan nanoparticles; and by utilizing the characteristic that the alveolar epithelium has specific sugar receptor N-acetyl glucosamine, wheat germ agglutinin modified salmeterol xinafoate chitosan nanoparticles are prepared, so that the specific sugar receptor N-acetyl glucosamine of the alveolar epithelium can be combined through the wheat germ agglutinin to enable the salmeterol xinafoate chitosan nanoparticles to have the targeting property of guiding the alveolar membrane. In-vitro sugar-binding test results show that the wheat germ agglutinin modified salmeterol xinafoate chitosan nanoparticles have the advantage of guiding the alveolar membrane, thus the administration dosage can be lowered, and the toxic side effect can be reduced; and by the slow release of the medicament, the effective concentration maintaining time of the medicament in the lung is long, thereby enhancing the treatment effect. The preparation provided by the invention can be used for preparing medicaments for treating asthma, chronic bronchitis or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
Owner:上海市第八人民医院
Hormone detection reagent and kit
InactiveCN109813881ALow costIncrease productionBiological testingHormones regulationAnti-Müllerian hormone
The invention relates to an anti-mullerian hormone (AMH) detection reagent. The detection reagent comprises an anti-mullerian hormone antibody, wheat germ agglutinin and a solid-phase carrier, the solid-phase carrier is coated with one of the anti-mullerian hormone antibody and the wheat germ agglutinin, and the other one of the anti-mullerian hormone antibody and the wheat germ agglutinin is marked with a marker. The detection reagent is mainly characterized by being formed from the anti-AMH antibody and the wheat germ agglutinin (WGA) through a sandwich method. The detection reagent is highin detection sensitivity, high in specificity and suitable for large-scale popularization.
Owner:WUXI MATERNAL & CHILD HEALTH HOSPITAL +2
Methods and apparatus for detection of gluten sensitivity, and its differentiation from celiac disease
Antibodies are used as biomarkers to assist in distinguishing gluten immune reactivity and sensitivity, silent celiac disease, Crohn's disease and other gut-related pathologies from classical celiac disease. In one class of embodiments, sera, saliva or other samples from a human or other animal are tested for antibodies to (a) a wheat antigen; (b) a gliadin antigen; and (c) one or more of a wheat germ agglutinin, a gluteomorphin, a glutenin, a deamidated glutenin, a prodynorphin, and a dynorphin. Test results are considered particularly interesting where the wheat antigen and the gliadin antigen are both selected from the group consisting of native and deamidated forms of α-gliadin 33-mer, α-gliadin-17-mer, γ-gliadin-15-mer, ω-gliadin-17-mer, and glutenin 21-mer. Test plates and kits can advantageously test for antibodies to at least three, five, seven or all of mixed wheat antigens, α-gliadin, γ-gliadin, ω-gliadin, glutenin, α-glutenin, wheat germ agglutinin, gluteomorphin, prodynorphins, transglutaminase-2, transglutaminase-3, transglutaminase-6, and gliadin-bound transglutaminase.
Owner:CYREX LAB LLC
Preparation method of graphene drug carrier with folic acid and WGA (Wheat Germ Agglutinin) as targeting factors
ActiveCN108392636AInorganic non-active ingredientsMacromolecular non-active ingredientsCarboxymethyl-gamma-cyclodextrinCyclodextrin
The invention relates to a graphene nano drug carrier with folic acid and wheat germ agglutinin as double targeting factors and prepared by adopting oxidized graphene, 6-carboxymethyl-gamma-cyclodextrin, the folic acid and wheat germ agglutinin (WGA) as main raw materials and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: firstly adopting the oxidized graphene and paratoluensulfonyl chloride as raw materials, activating hydroxide radicals of the oxidized graphene, grafting L-lysine, and adopting hydrazine hydrate for reduction of the oxidized graphene grafted with the lysine; then reacting with the 6-carboxymethyl-gamma-cyclodextrin and the folic acid under the common catalysis of 1-ethyl-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)carbodiimide (EDC) and N-hydroxysuccinimide (NHS) to generate nano graphene grafted with gamma-CD (Cyclodextrin) and the folic acid at the same time, then assembling the wheat germ agglutinin and the gamma-CD to prepare the graphene nano drug carrier with the folic acid and the wheat germ agglutinin as double targeting factors.
Owner:QINGDAO UNIV
Preparation method of SPIO.SiO2-WGA (Wheat Germ Agglutinin) intestinal wall targeting contrast agent
InactiveCN101843907BImprove detection signal contrastEvenly distributedNMR/MRI constrast preparationsSolubilityIntestinal walls
The invention relates to a preparation method of a wheat germ agglutinin (WGA) packaging silica superparamagnetism (SPIO@SiO2-WGA) magnetic resonance nanometer contrast agent for biomedicine diagnosis. In the invention, water solubility conversion of oil soluble SPIO is realized by utilizing hexadecyl trimethyl ammonium bromide; silica packaging and surface amination of the SPIO are realized by adopting ethyl orthosilicate and aminopropyltriethoxysilane; and connection between the wheat germ agglutinin which has adsorption on the intestinal wall and a superparamagnetism silica sphere is realized by utilizing EDC / NHS in PBS solution. The obtained SPIO.SiO2-WGA magnetic resonance nanometer contrast agent has the advantages of uniform and stable particle diameters, low toxicity and obvious cell targeting effect.
Owner:SHANGHAI NAT ENG RES CENT FORNANOTECH
Abnormal sugar chain glycoprotein detection reagent and preparation method thereof
PendingCN112129948AImprove stabilityExtended shelf lifeBiological testingColor markerLentil agglutinin
The invention relates to an abnormal sugar chain glycoprotein detection reagent and a preparation method thereof. The detection reagent takes purified water as a solvent, and comprises the following components: 10-50mg / L of mixed lectin, 1-3g / L of disperse blue and 4-20mg / L of a divalent metal ion stabilizer, wherein the pH of the detection reagent is adjusted to be greater than or equal to 9.0 through a pH regulator; the mixed lectin is a mixture of concanavalin, datura agglutinin, lentil agglutinin, wheat germ agglutinin, E-type red kidney bean agglutinin, L-type red kidney bean agglutinin,citrus fruit powder spore agglutinin, peanut agglutinin, castor agglutinin I and Korean locust agglutinin; and the mixed lectin is subjected to PEG pre-modification treatment. The design principle ofthe abnormal sugar chain glycoprotein detection reagent is that abnormal sugar chain glycoprotein in blood is condensed into particles through the mixed lectin, wherein the disperse blue participatesin condensation reaction and serves as a color marker, and observation and identification of the condensate particles are facilitated.
Owner:浙江瑞生医疗科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com