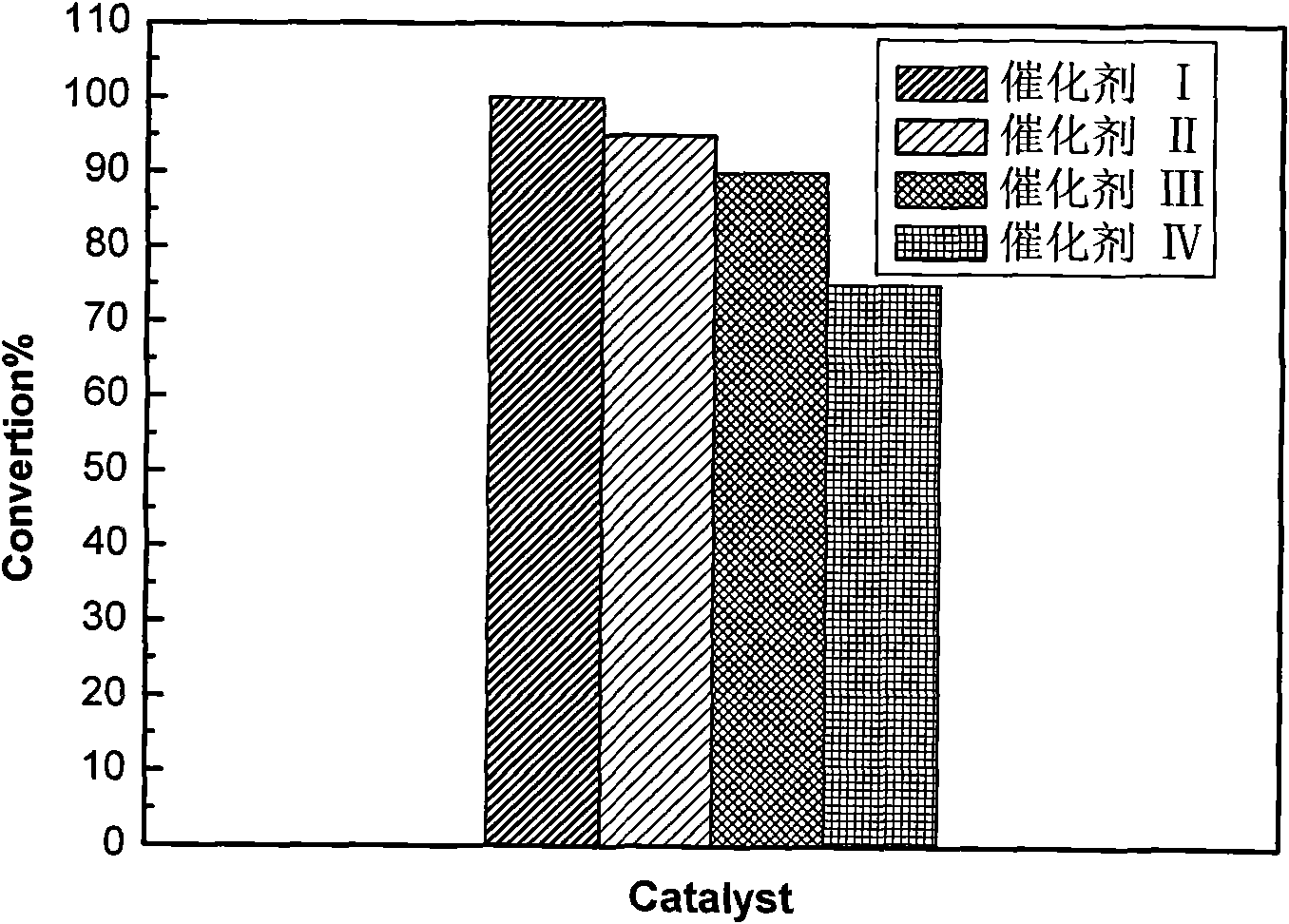
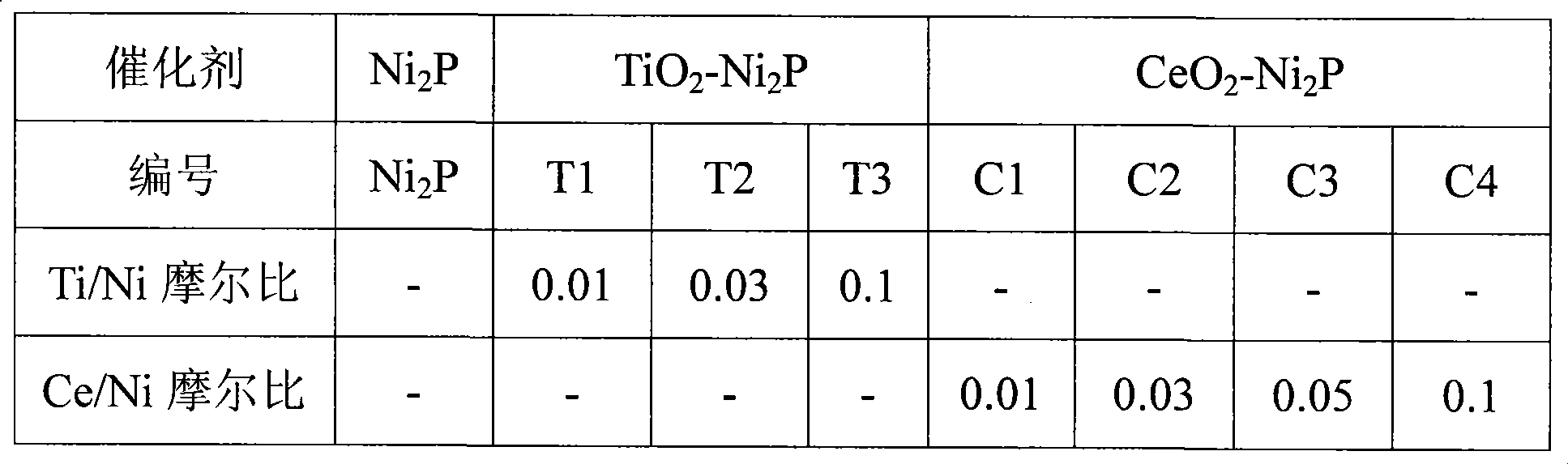
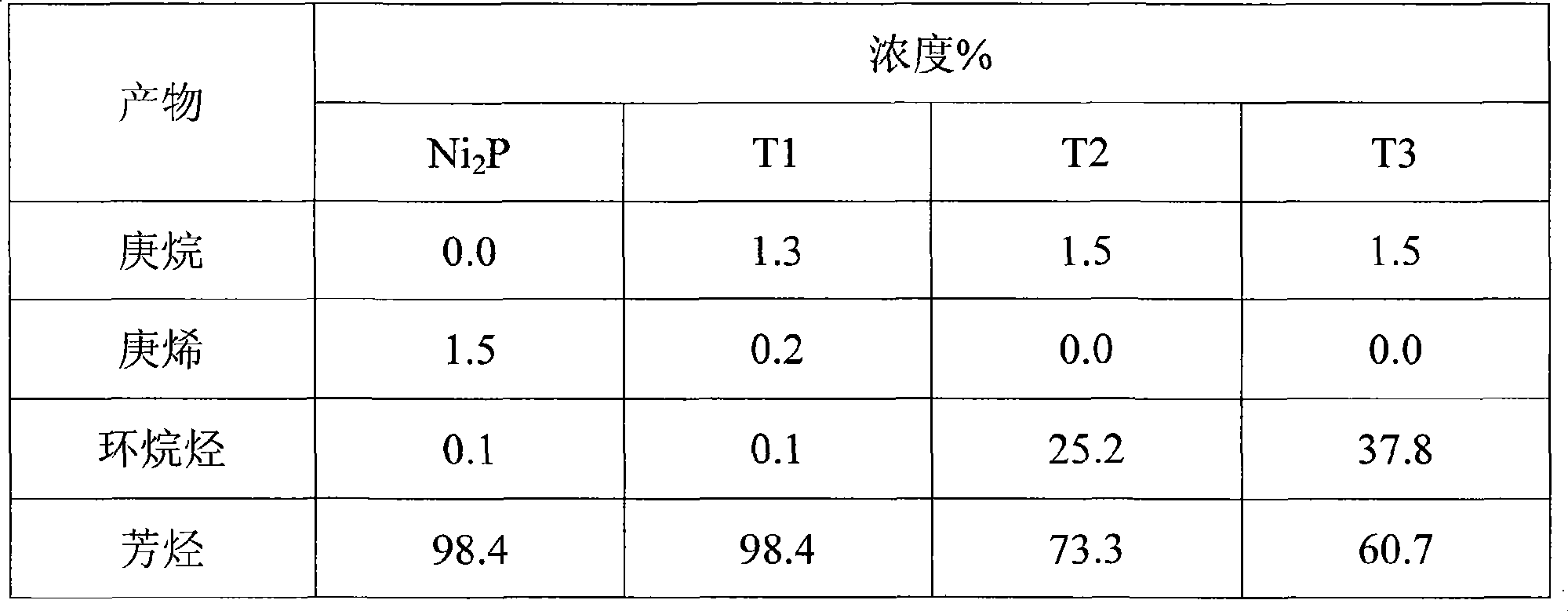
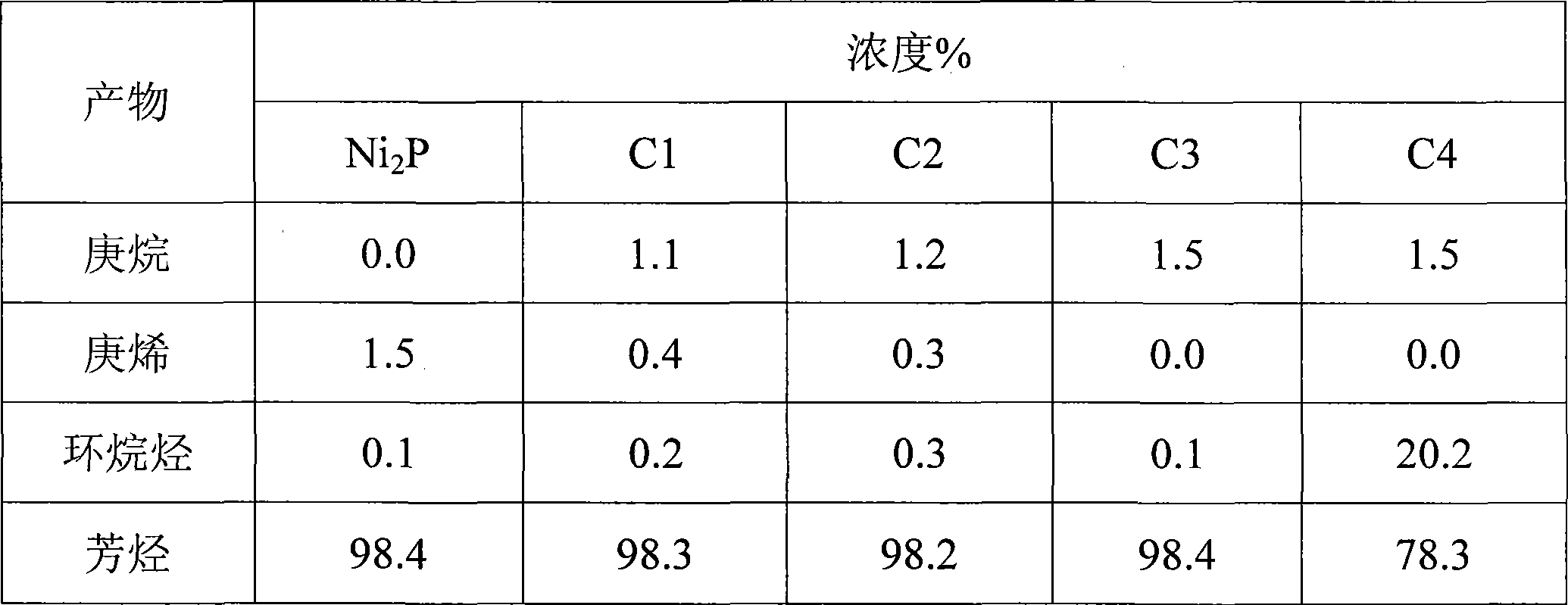
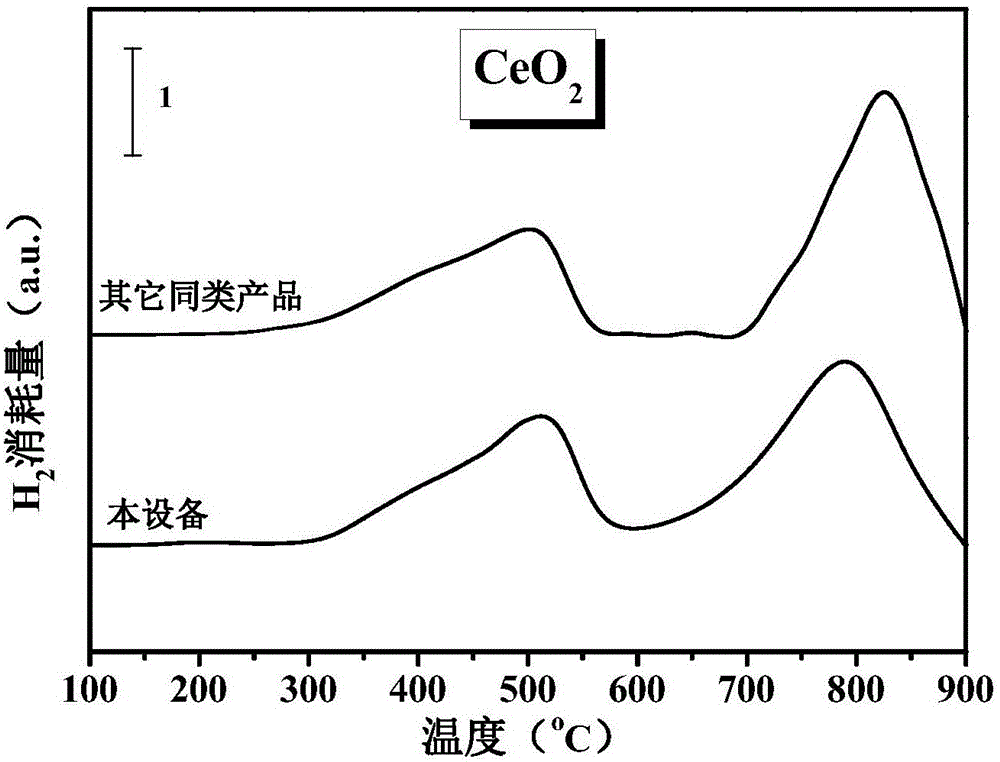
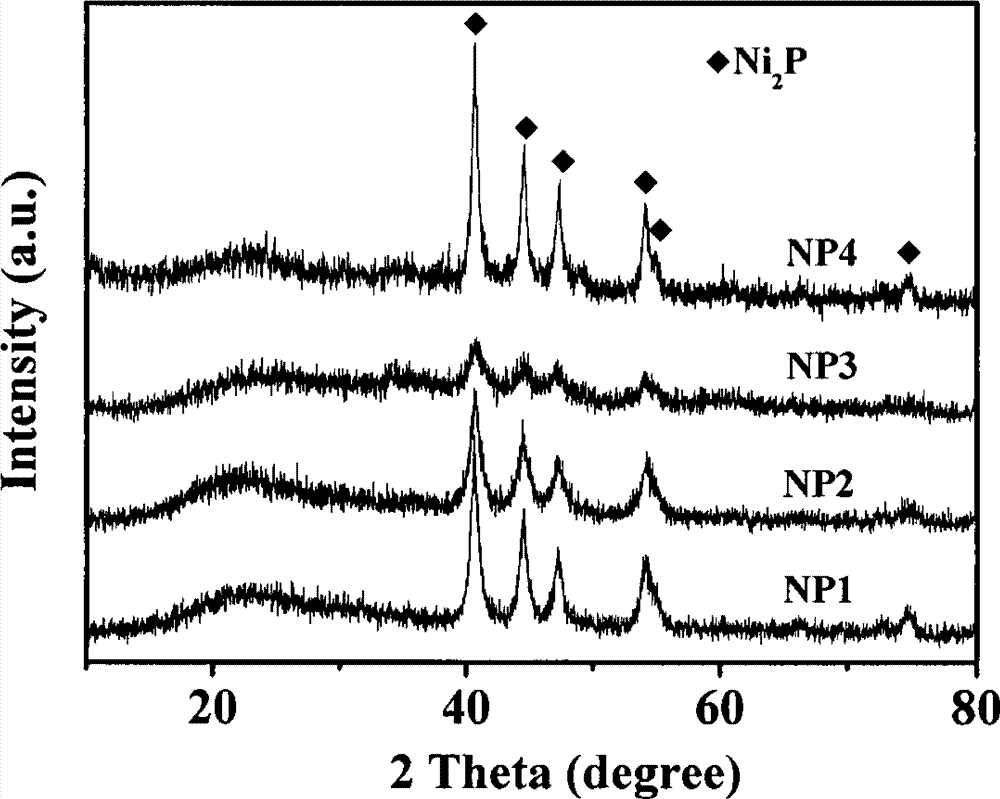
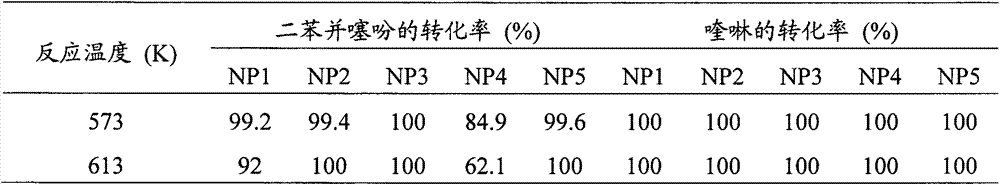
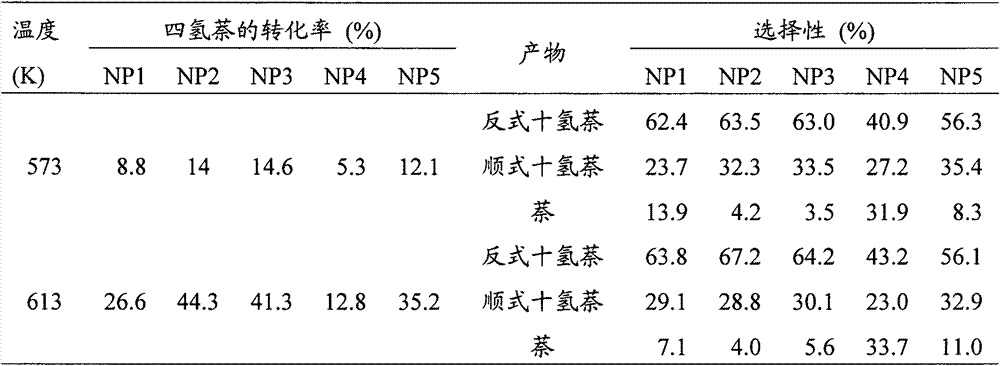
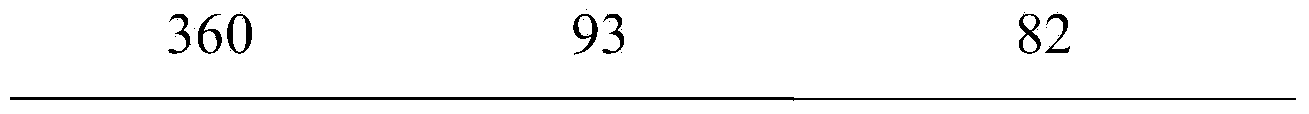Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
125 results about "Temperature-programmed reduction" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Temperature-programmed reduction (TPR) is a technique for the characterization of solid materials and is often used in the field of heterogeneous catalysis to find the most efficient reduction conditions, an oxidized catalyst precursor is submitted to a programmed temperature rise while a reducing gas mixture is flowed over it. It was developed by John Ward Jenkins whilst developing heterogeneous catalysts for Shell Oil company, but was never patented.
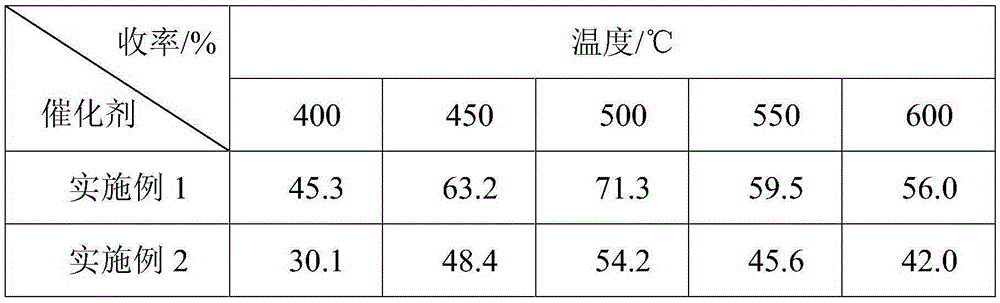
Process for preparing high dispersion supported type transition metal phosphide catalyst
InactiveCN101168132AIncreased dispersionReduce reunionPhysical/chemical process catalystsNitrogen preparationPhosphateActive component
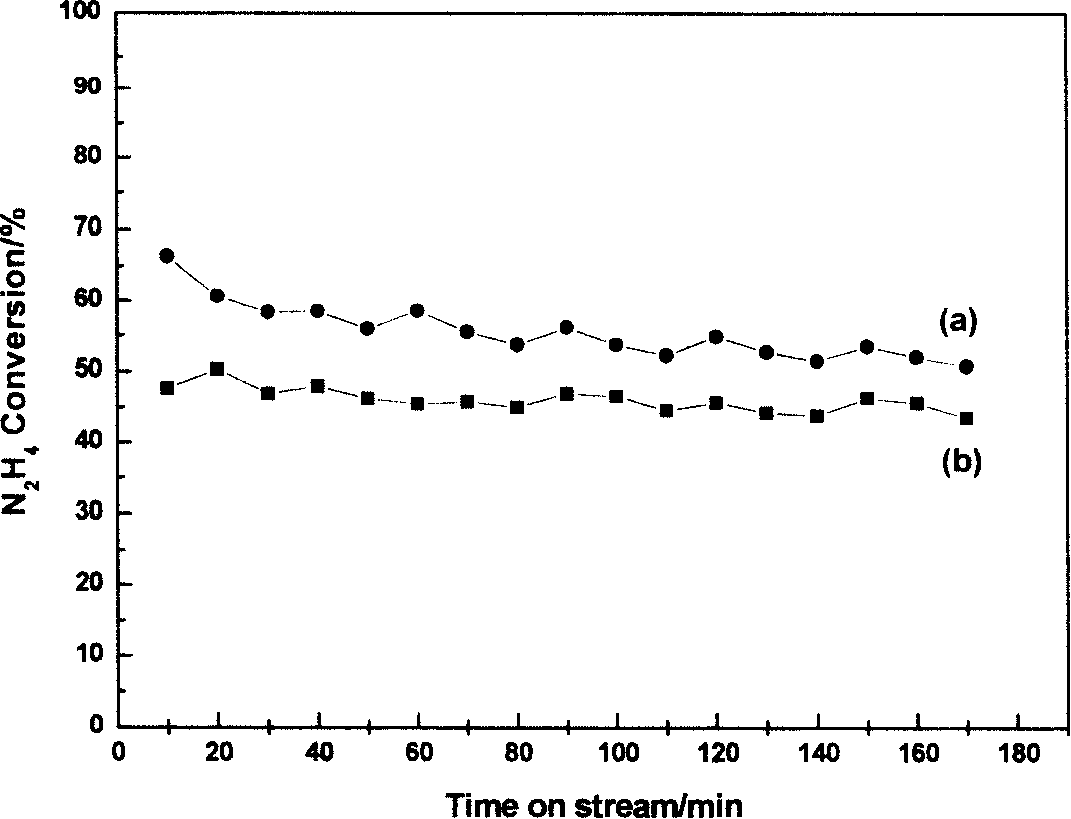
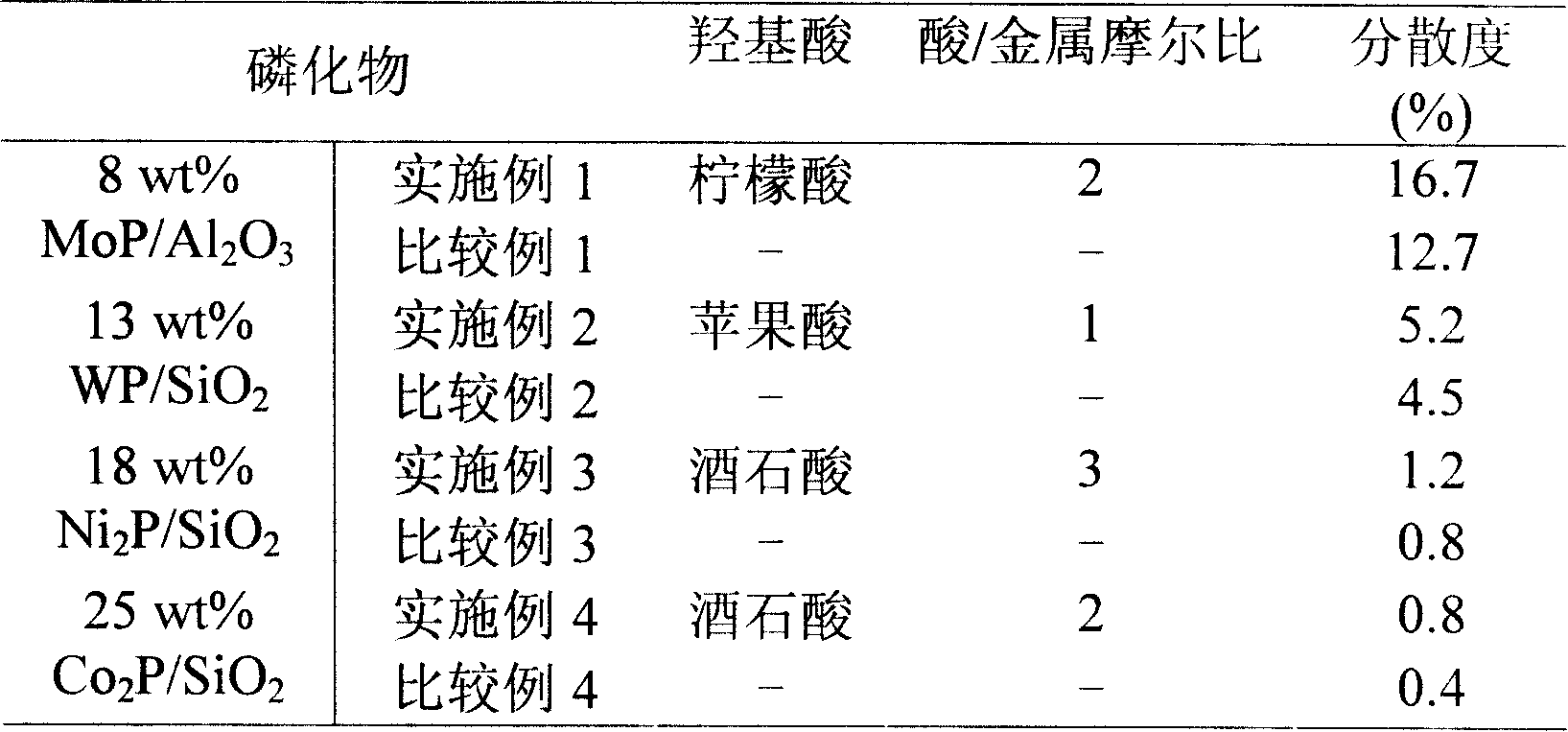
The invention relates to a catalyst of supported metal phosphide, in particular to a process for preparing the catalyst of high dispersive supported metal phosphide. The catalyst is composed of two parts of active components and a carrier which can be represented by AP / Z or B2P / Z, wherein the A of the active components is Mo or W, the B of the active components is Ni or Co, and the Z of the carrier is Al2O3 or SiO2. The operation steps of the catalyst are that transient metal salt and mammonium dihydrogen phosphate are dissolved in deionized water according to the stoichiometric ratio of targeted phosphide, and simultaneously moderate hydroxy acid as chelating agent is added to get the impregnating solution for preparing supported transition metal phosphide. The porous carrier is immersed in the impregnating solution, and is rested, the procedure gains temperature and returns after the impregnating solution is dried, roasted and under the atmosphere of hydrogen gas, and finally the supported transition metal phosphide is made. The supported transition metal phosphide prepared by the preparation method has the advantages of high dispersion, simple and convenient operation, low cost, no pollution, good repeatability and easiness of large scale preparation.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Preparation method of nickel phosphide
InactiveCN101734633ASolve the problem of sulfur poisoningIncrease investmentPhosphidesDispersityPhosphorous acid
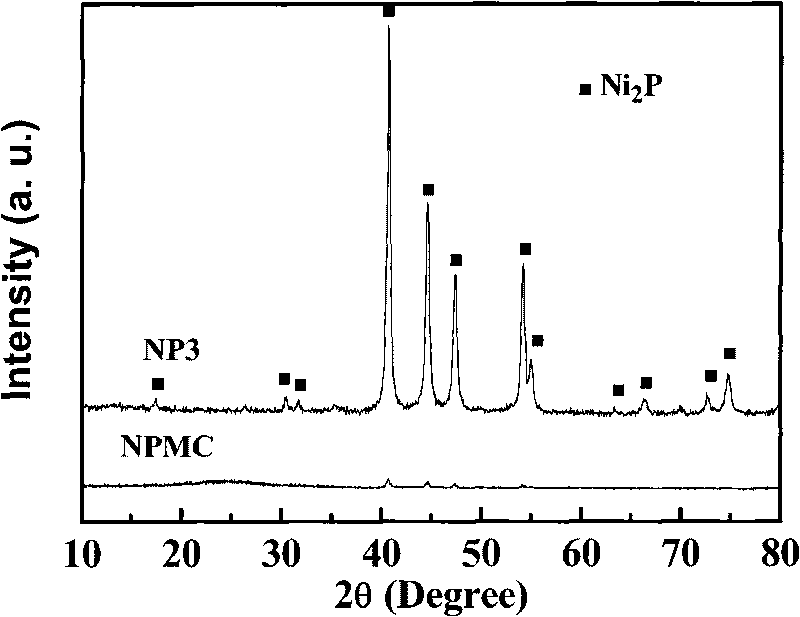
On the premise of deep hydrodesulfurization, the main problem in diesel fuel's hydrotreatment is to rid the refractory sulfide and hydrogenate polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon. Loaded nickel phosphide catalyst demonstrates higher hydrodesulfurization activity and better activity stability. However, the traditional nickel phosphide catalyst is prepared by temperature programming of nickel phosphide, so that dispersion degree of active components is low. In the invention, through solid-phase reaction between phosphorous acid ions and nickel ions, bulk phase and loaded nickel phosphide catalyst with higher active component dispersion degree and fine catalytic activity are obtained at low temperature. The invention is applicable to diesel oil hydroprocessing.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Preparation method of mesoporous confinement nickel-based methane dry reforming catalyst
ActiveCN103586030ALower requirementWill not cause secondary pollutionHydrogenMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsPtru catalystPhysical chemistry
The invention discloses a preparation method of a mesoporous confinement nickel-based methane dry reforming catalyst. The methane dry reforming catalyst takes high-temperature-resistant oxide with an orderly mesoporous duct as a carrier, so that nickel is uniformly dispersed in the duct. The preparation method of the methane dry reforming catalyst comprises the steps that mesoporous oxide with high-temperature stability serves as a carrier; a precursor, namely salt of nickel is transported into the mesoporous duct by alcohol under a stirring condition; the internal surface of the mesoporous duct is modified by an alocholic hydroxyl group, so that nickel can be dispersed better; vacuum drying, high-temperature calcination and H2-TPR (Temperature Programmed Reduction) are performed; and the methane dry reforming catalyst with good anti-carbon and anti-sintering property, high activity and high stability is prepared. The method has the advantages that the method is simple in preparation technology, lower in cost, pollution-free, and high in catalysis efficiency.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Preparation method of thermometal phosphide hydrofining catalyst
ActiveCN103157497AHigh activityAchieving synergyPhysical/chemical process catalystsSodium Hypophosphite MonohydrateNitrogen
The invention provides a preparation method of a thermometal phosphide hydrofining catalyst. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly, preparing a bulk phase WP or a WP loaded by a porous carrier material by adopting a traditional procedure warming reduction method, then soaking the bulk phase WP or the WP loaded by the carrier in a nickel chloride and sodium hypophosphite solution, drying, carrying out thermal treatment in nitrogen, passivating and washing to obtain the bulk phase thermometal phosphide WP-Ni2P catalyst or the catalyst loaded by the carrier, and bulk phase thermometal phosphide MoP-Ni2P catalyst or the catalyst loaded by the carrier can be obtained by adopting the same method. The method provided by the invention has characteristics that the method effectively utilizes temperature difference between the metal phosphide prepared by the procedure warming reduction method and the metal phosphide prepared by a hypophosphite resolving method, a novel preparation technology of the thermometal phosphide hydrofining catalyst is provided, the method realizes the synergy acceleration action of different metal phosphides, and the catalytic activity of the metal phosphide is effectively improved.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Boron nitride composite mesoporous oxide nickel-based catalyst and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN106975506AGood dispersionWill not cause secondary pollutionMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsHigh resistanceBoron nitride
The invention relates to a boron nitride composite mesoporous oxide nickel-based catalyst and a preparation method thereof. The nano-boron nitride as the carrier having high thermal stability and carbon deposition resistance is combined with active metal anchoring and dispersion based on mesoporous oxides so that the catalytic material having high resistance to sintering and carbon deposition is obtained. The preparation method comprises adding a surfactant and ammonia water into high thermal stability boron nitride and nickel precursors as reactants, carrying out ultrasonic agitation, loading active metal components to the boron nitride nanosheet layer, and carrying out in-situ coating on the surface with an oxide having a mesoporous channel structure. The coated mesoporous structure can realize high dispersion of the active nickel component. Through drying, high temperature calcination and programmed heating reduction, the nickel-based catalyst having high performances and a novel structure is prepared. The boron nitride composite mesoporous oxide nickel-based catalyst has the advantages of simple process, low production cost, no environment pollution and high catalytic efficiency.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Catalyst surface-characteristic comprehensive measuring device and application thereof
The instrument comprises carrier gas inlet, working gas inlet, other gas inlet, gas flow meter, mixer, the first and the second four-way valve, the first and the second six-way valve, saturator, heating furnace with programmed control temperature, sample tube with internal-inserted thermocouple, heat conductive pool, cold-trap, chromatographic column, hydrogen flame detector sampling and displaying of computer and spectrogram printing. The instrument with above devices can apply techniques of programmed temperature for reduction de-addendum, surface reaction, oxidation and decomposition as well as H2-O2 titration to carry on surface performance test for catalyst and to obtain spectrogram for each abovesaid performance of the catalyst.
Owner:SHANGHAI NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Preparation method of nickel phosphide catalyst carried by composite carrier
InactiveCN101612584ALittle loss of activityHigh activityCatalyst activation/preparationRefining to eliminate hetero atomsNickel saltPhosphate
The invention relates to a preparation method of a nickel phosphide catalyst carried by a composite carrier. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: firstly, using activated alumina and relative enzymes and alcohols as raw materials to prepare a composite carrier of TiO2-Al2O3 by adopting an improved sol-gel method; further, selecting suitable nickel salt and phosphate and carrying out ultrasound dipping and drying in microwaves to obtain a catalyst precursor; and finally, increasing a temperature by a program and reducing to obtain the composite support. The composite carrier of TiO2-Al2O3 prepared by the invention not only can effectively overcome the defect that nickel phosphide is apt to react with gamma-Al2O3 to generate AlP4 to lose the activity, but also overcomes the defect that a specific surface area of single TiO2 is relatively small, effectively exerts the strong metal-support interaction (SMSI) of the TiO2, thereby obtaining a hydrodesulfurization catalyst with remarkable activity efficacy.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Duplex metal phosphide catalyst for selective hydrogenation and olefin hydrocarbon removal as well as preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101474568ANo lossEnhanced selective hydrogenation activityCatalyst activation/preparationMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsMischmetalRare earth
The invention discloses a bi-metallic phosphide catalyst for selective hydrogenation for olefin removal and a preparation method thereof. The invention pertains to the hydrogenation refining technical field of the petroleum hydrocarbon products. The invention is characterized in that the cocatalyst of the catalyst is TiO2 or rare earth metal oxide and the main catalyst is the phosphide of one of the transition metal such as Mo, W, Fe, Co or Ni and the catalyst is prepared by conducting temperature programmed reduction on an oxidation state precursor thereof. When the molar ratio between the cocatalyst and the main catalyst is within 0.01-0.5, selective hydrogenation to the olefin of the aromatic hydrocarbon can be realized, with almost no loss of the aromatic hydrocarbon. The effect and benefit of the invention is to change the phosphide catalyst hydrogenation activity by simply changing the cocatalyst content, therefore, the bi-metallic phosphide catalyst is especially fit for the selective hydrogenation of olefin in reformate producing oil aiming at producing chemical grade BTX aromatic hydrocarbon in the refinery.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Preparation method and application of transition metal phosphide used for hydrogenating dechlorination
ActiveCN105344368AImprove hydrodechlorination activityImprove catalytic performancePhysical/chemical process catalystsPreparation from chloridesParticulatesDiammonium phosphate
The present invention discloses a preparation method and application of transition metal phosphide used for hydrogenating dechlorination. The preparation method comprises the following steps: 1. dissolving soluble metallic salt and diammonium phosphate in water, and dissolving polyethylene glycol in the solvent; 2. stirring an aqueous solution obtained in the step 1 at a temperature of 80 DEG C for 3 hours, then heating up the stirred aqueous solution to the temperature of 100 DEG C to dry the aqueous solution in a steaming manner, then drying at a temperature of 120 DEG C for 12 hours, and then calcining at a temperature of 500 DEG C for 5 hours to obtain an oxidizing precursor; and 3. grinding and tabletting the oxidizing precursor obtained in the step 2 into pieces, screening to obtain particulate matters with meshes of 20-40, and performing reduction on the particulate matters by a heating reduction method to obtain modified transition metal phosphide. When used as a catalyst, the phosphide performs hydrogenating dechlorination and has an significantly improved catalytic activity compared with an unmodified catalyst. The method is simple and easy to operate, and meanwhile can effectively improve hydrogenating dechlorination catalytic activity of the transition metal phosphide.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
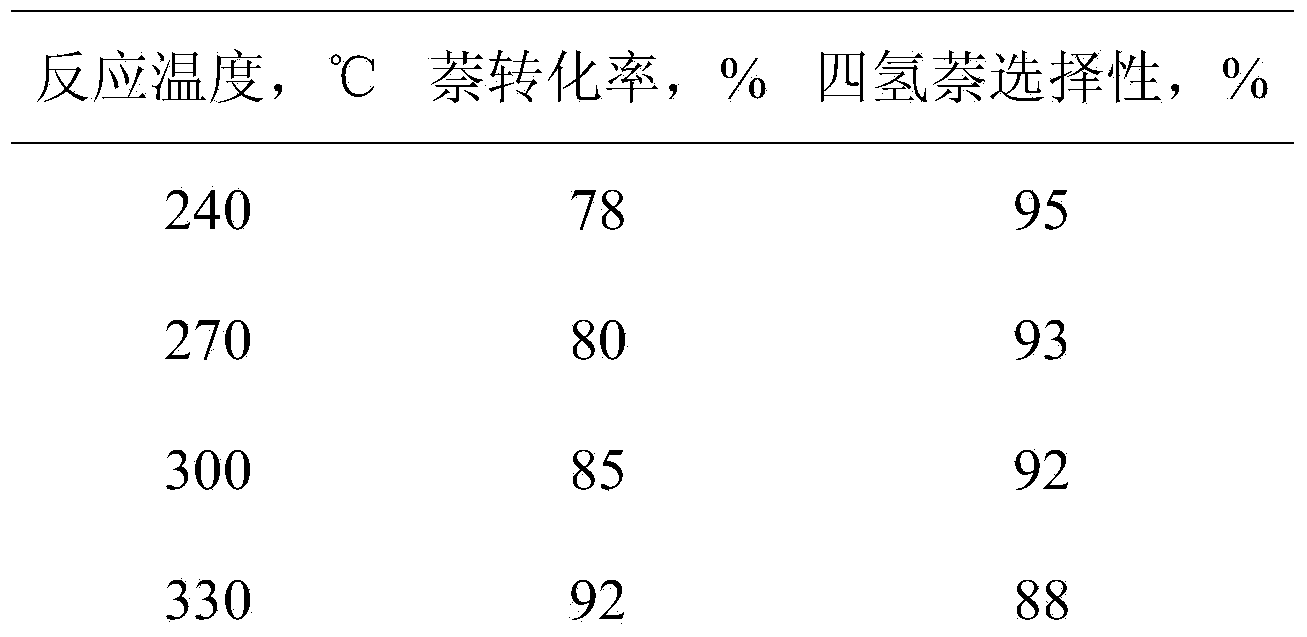
Catalyst for preparing tetrahydronaphthalene by naphthalene via selective hydrogenation as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN103657704AImprove efficiencyGood dispersionMolecular sieve catalystsHydrocarbon by hydrogenationActivated carbonHydrogenation reaction
The invention discloses a catalyst applicable to preparing tetrahydronaphthalene by naphthalene via selective hydrogenation as well as a preparation method and an application thereof. The catalyst has the main characteristics that one or more than one of active carbon or a molecular sieve Y, beta and ZSM-5 is used as a carrier and transition metal phosphide is loaded. The transition metal phosphide accounts for 5%-30% of the total mass of the catalyst; the catalyst is prepared by the steps of impregnating, roasting, raising the temperature and reducing by a procedure and the like. In the preparation process, a vacuum-ultrasonic impregnation technology can be introduced. A fixed bed reactor is adopted to continuously produce the tetrahydronaphthalene under a suitable hydrogenation reaction condition; the naphthalene conversion rate and the tetrahydronaphthalene selectivity are more than 90%.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
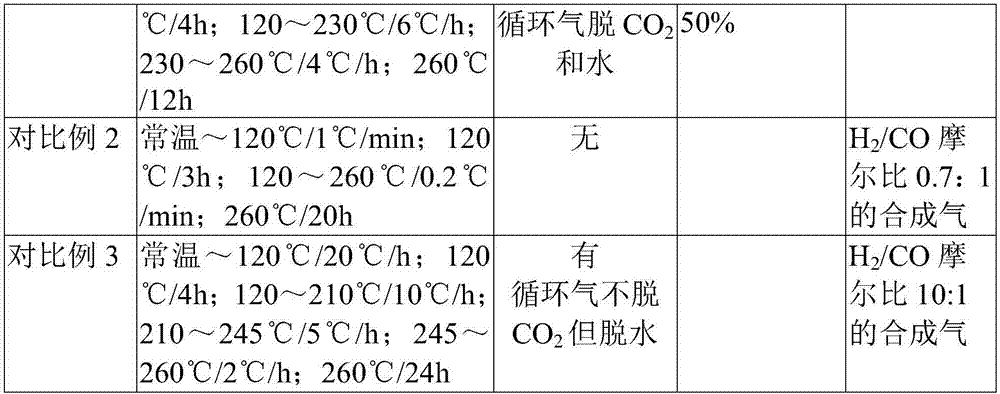
Reduction method for a Fischer-Tropsch synthesis iron-based catalyst
ActiveCN107149948AHigh activityLow selectivityCatalyst activation/preparationLiquid hydrocarbon mixture productionFluidized bedRoom temperature
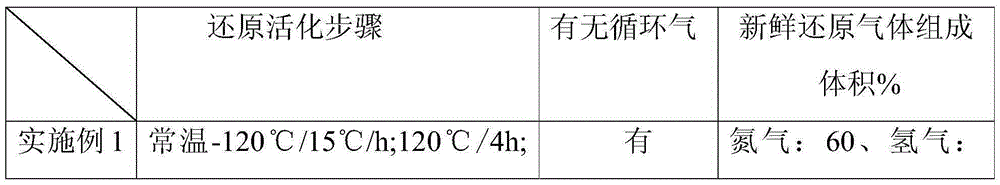
The present invention relates to the field of Fischer-Tropsch synthesis iron-based catalyst reduction, and discloses a reduction method for a Fischer-Tropsch synthesis iron-based catalyst. The reduction method comprises: in the presence of a reducing gas, carrying out programmed heating reduction on Fischer-Tropsch synthesis iron-based catalyst particles in a fixed fluidized bed reactor, wherein the programmed heating reduction comprises that the heating rate is 10-20 DEG C / h and constant temperature treatment is performed for 2-8 h at a temperature of 120 DEG C when the temperature is from room temperature to 120 DEG C, the heating rate is 5-10 DEG C / h and constant temperature treatment is performed for 3-10 h at a temperature of 220-230 DEG C when the temperature is from 120 DEG C to (220-230) DEG C, and the heating rate is 3-5 DEG C / h and constant temperature treatment is performed for 10-30 h at a temperature of 260-280 DEG C when the temperature is from (220-230) DEG C to (260-280) DEG C. With the reduction method of the present invention, the Fischer-Tropsch synthesis iron-based catalyst can be smoothly subjected to the reduction reaction so as to reduce the influence on the water and the catalyst strength, and with the application of the reduced catalyst in the Fischer-Tropsch synthesis, the advantages of no breaking, high catalyst activity, low CO2 selectivity and low low-carbon hydrocarbon selectivity can be provided.
Owner:CHNA ENERGY INVESTMENT CORP LTD +1
Method for preparing supported nano copper nickel catalyst and application thereof in oxidative dehydrogenation reaction of alkylol amine
InactiveCN1827218AHigh yieldHigh reuse rateCatalyst carriersCatalyst activation/preparationNickel saltDehydrogenation
The invention discloses a method for preparing the carrier catalyst which can be used in aminoethyl alcohol dehydrogenation reaction to prepare the iminodiacetic acid, and relative usage. It comprises following steps: using the copper salt and nickel salt as main raw material, via dipping, drying, high-temperature baking and programmed increasing temperature, to from said catalyst nanometer copper nickel composite catalyst, then using said catalyst in aminoethyl alcohol dehydrogenation reaction to prepare the iminodiacetic acid. Said inventive catalyst has higher reaction activity. And the raw materials are easily to be attained, the producing cost is lower, and it has better application prospect.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV OF ENG SCI
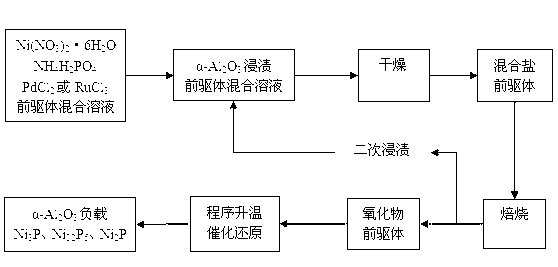
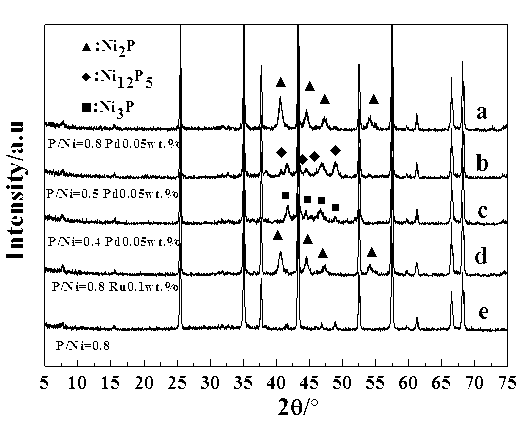
Preparation method for alpha-alumina supported nickel phosphide catalyst
InactiveCN103223348AAvoid the disadvantages of high temperature reductionSimple stepsPhysical/chemical process catalystsNickel catalystPtru catalyst
The invention provides a preparation method for an alpha-alumina supported nickel phosphide catalyst. The preparation method comprises the following steps of preparing an impregnation liquid, equivalent-volume impregnating, drying, calcining, carrying out the procedures again and reducing. The preparation method is improved based on a temperature-programmed reduction method. Nickel and phosphor precursors are transferred into nickel phosphide under the catalytic reduction action of a trace amount of Pd or Ru (less than or equal to 0.1 wt.%) by using the alpha-Al2O3 as a carrier. A core of the preparation method lies in that a reduction temperature is reduced to below a 500 DEG C by using catalytic action of Pd or Ru in the temperature-programmed reduction process, thereby effectively preventing the disadvantages brought by high temperature reduction. The preparation method has good practicability and usage effects without forming three wastes (waste gas, waste water and waste residues), and is safe and environment-friendly.
Owner:QINGDAO UNIV OF SCI & TECH
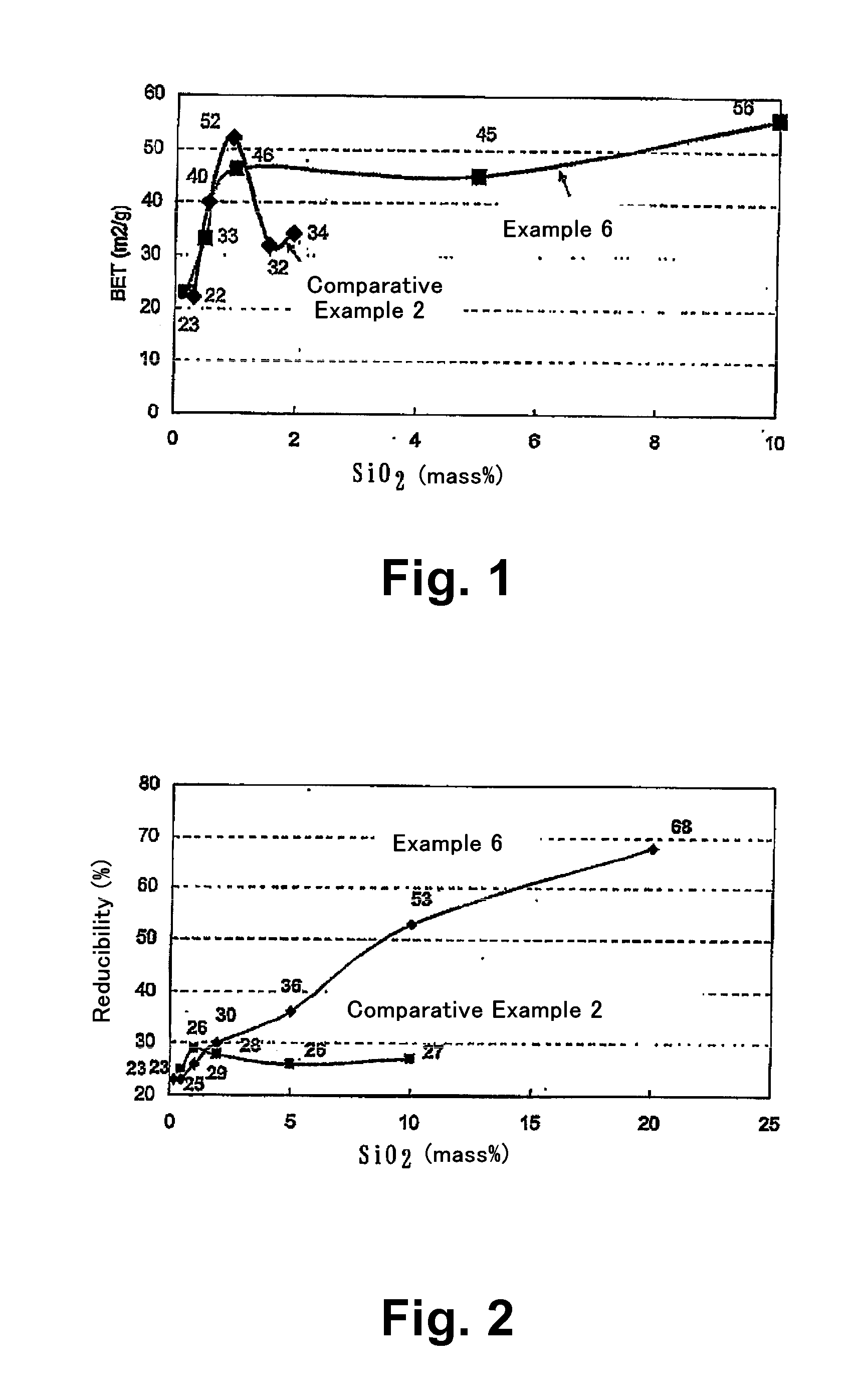
Complex oxide, method for producing same and exhaust gas purifying catalyst
ActiveUS20120316059A1Improve heat resistanceImprove reducibilitySilicaElectrical controlHeat resistanceCerium
Disclosed are a silicon-containing cerium composite oxide which is capable of maintaining a large specific surface area even used in a high temperature environment, and which has excellent heat resistance and reducibility, as well as a method for producing the composite oxide and a catalyst for exhaust gas purification employing the composite oxide. The composite oxide contains 2 to 20 mass-% silicon in terms of SiO2, has properties of exhibiting a specific surface area of not less than 40 m2 / g as measured by the BET method after calcination at 1000° C. for 5 hours, and a reducibility of not lower than 30% as calculated from measurement of temperature-programmed reduction from 50° C. to 900° C. after calcination at 1000° C. for 5 hours, and is suitable for a co-catalyst for a catalyst for exhaust gas purification.
Owner:SOLVAY SPECIAL CHEM JAPAN LTD
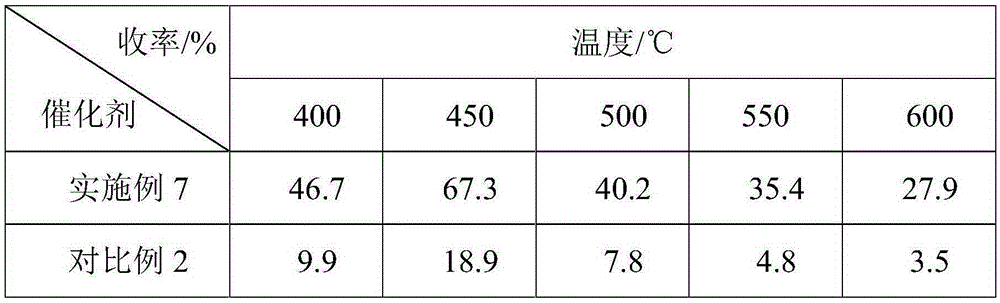
Loaded type transition metal phosphide catalyst as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN105251521AImprove hydrogenation activityImprove stabilityPhysical/chemical process catalystsOrganic compound preparationSilicon dioxideDimethyl oxalate
Owner:中科合成油内蒙古技术研究院有限公司
Nickel phosphide catalyst containing sulphur and application of nickel phosphide catalyst
InactiveCN104941673AHigh selectivityImprove hydrogenation activityOrganic reductionPhysical/chemical process catalystsToxicantSulfur
The invention relates to a nickel phosphide catalyst containing sulphur and application of the nickel phosphide catalyst. For the nickel phosphide catalyst, the molar ratio of nickel to phosphorus is 0.1-5, the content of phosphorus is 25% or below by atomic percentage. The nickel phosphide catalyst containing sulphur disclosed by the invention has high selectivity in selective hydrogenation reaction of unsatured unsaturated hydrocarbon compounds and nitrobenzene compounds, has selectivity equivalent to that of Ni2P prepared by adopting the traditional temperature programmed reduction method of phosphate, but has activity obviously improved. Compared with the viewpoint generally known in the prior art that sulphur has side effects for metal hydrogenation catalysts or metalloid hydrogenation catalysts, i.e., sulphur is a toxicant and can be used for greatly reducing the activity of the catalyst, the nickel phosphide catalyst containing sulphur provided by the invention has the advantage that by introducing an appropriate amount of sulphur into the Ni2P catalyst, the hydrogenation activity of the Ni2P catalyst can be significantly improved under the condition that the selectivity of the Ni2P catalyst is not affected.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
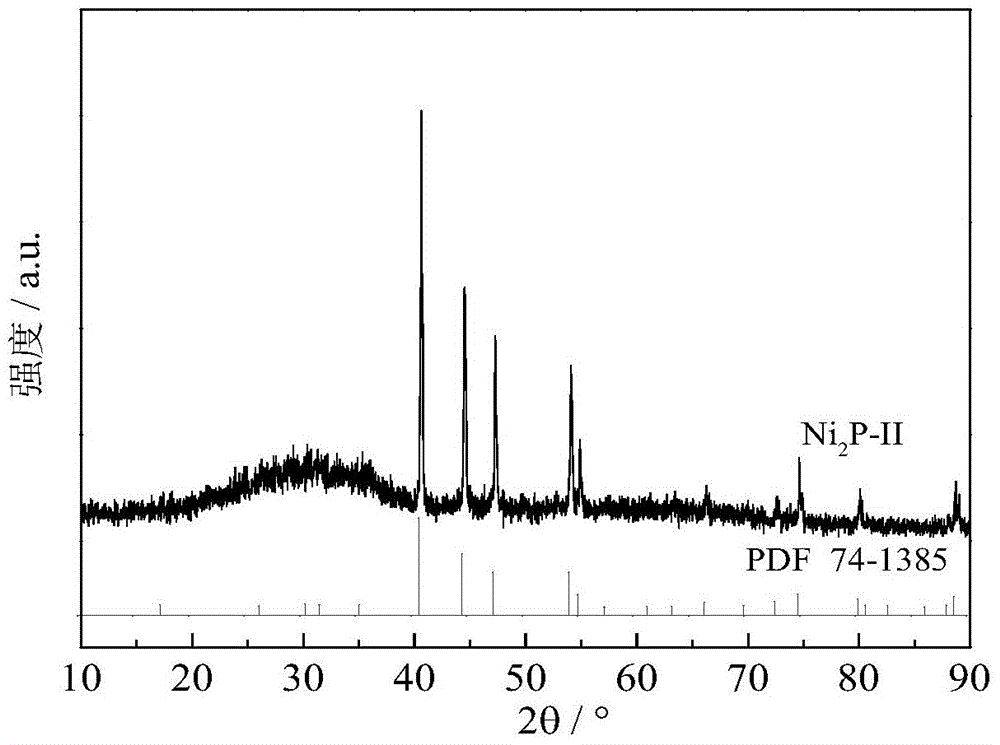
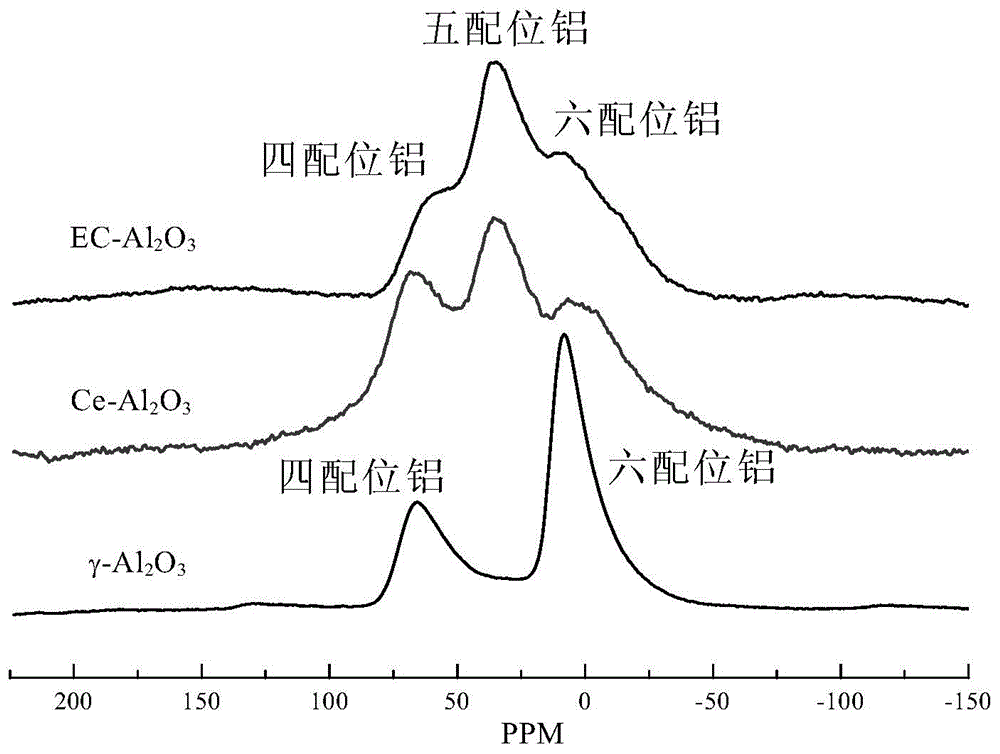
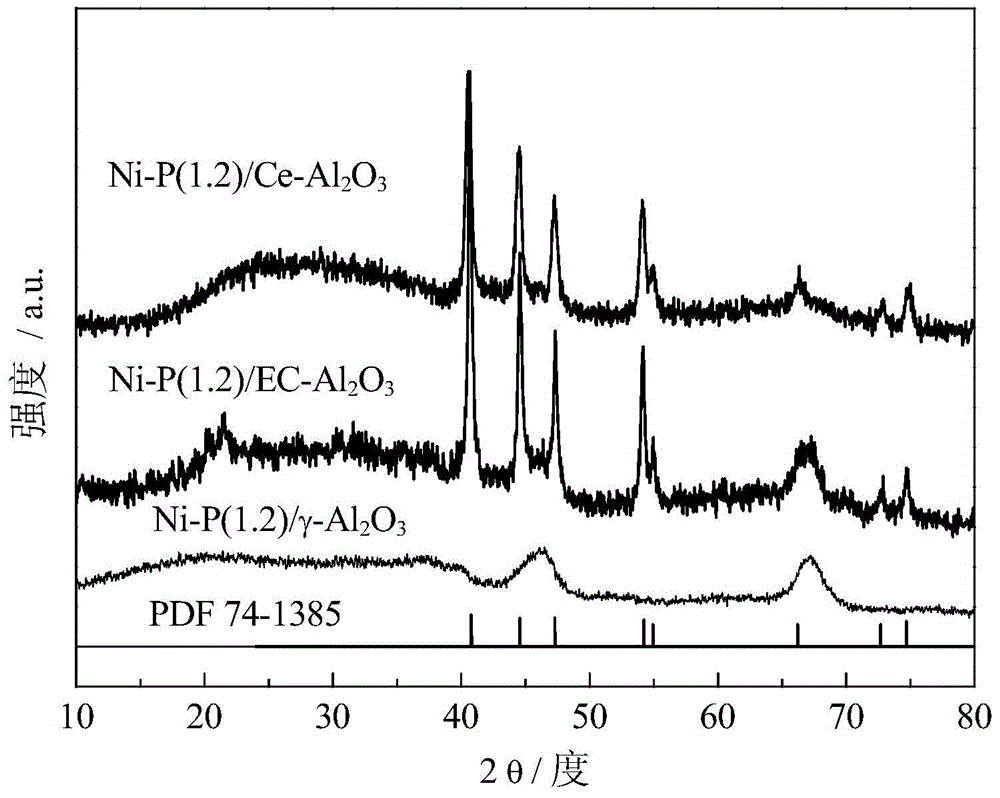
Ni2P/Al2O3 catalyst and preparation method therefor
InactiveCN104971749APhysical/chemical process catalystsHydrocarbon purification/separationHydrodesulfurizationPhosphate
The invention relates to a Ni2P / Al2O3 catalyst and a preparation method therefor. The preparation method comprises the step of performing temperature programmed reduction treatment on a precursor-carrier compound, wherein the precursor is falcial phosphate, and the carrier is an Al2O3 carrier which is rich in 5-coordination aluminum. According to the preparation method disclosed by the invention, the Al2O3 which is rich in the 5-coordination aluminum is used as the carrier, the phosphate with a low P / Ni ratio is used as the precursor, and a temperature programmed reduction method is used for preparing the high-activity Ni2P catalyst. The hydrodesulfurization (HDS) activity of the supported Ni2P / Al2O3 catalyst obtained by the preparation method to dibenzothiophene (DBT) is equivalent to that of the catalyst using SiO2 as the carrier.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Dehydrogenation catalyst reduction method
ActiveCN102380425AEasy to useEvenly dispersedCatalyst activation/preparationHydrocarbonsDehydrogenationMetal particle
The invention discloses a dehydrogenation catalyst reduction method. Dehydrogenation catalyst is platinum family loading catalyst and is in programmed temperature rising reduction before being used, the programmed temperature rising reduction is performed within a temperature range between 350 DEG C and 600 DEG C, and temperature rising speed ranges from 0.5 DEG C / min to 10 DEG C / min. In an activating process of the dehydrogenation catalyst, after platinum-base catalyst is prepared by a conventional method, conventional constant-temperature reduction operation is omitted, a programmed temperature-rising reduction method is utilized to realizing activation reduction for the catalyst, so that metal particles of the catalyst after being in reduction are dispersed more uniformly, sizes of theparticles are proper, and surface area of exposed elementary substance Pt is enlarged. Accumulation of activated metal of the catalyst due to deep reduction of dehydrogenation activated metal is avoided, deep reduction of addition agent components which do not need reduction can also be avoided, accordingly, service performances of the catalyst are improved, and particularly, selectivity of objective products and stability of long-term reaction are improved.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Preparation method of supported Ni2P catalyst
InactiveCN103861625AAvoid generatingEfficient use ofMolecular sieve catalystsNickel phosphateFixed bed
The invention discloses a preparation method of supported Ni2P catalyst. The preparation method of the supported Ni2P catalyst comprises the following steps: preparing a silicon dioxide, MCM-41, SBA-15, aluminium oxide, titanium oxide, HY molecular sieve or HZSM-5 molecular sieve supported nickel oxide precursor by adopting an impregnation way; reducing the supported nickel oxide precursor into a supported Ni precursor in a fixed bed reactor, then introducing hydrogen, introducing a triphenylphosphine or tri-n-octylphosphine solution into the fixed bed reactor at a certain temperature, and phosphating for a period of time at constant temperature, thus obtaining the supported Ni2P catalyst in situ. Compared with a general method for preparing the supported Ni2P catalyst by adopting a supported nickel phosphate temperature programmed reduction method, the preparation method of the supported Ni2P catalyst is simple and practicable, generation of aluminium phosphate owning to reaction between phosphorus species and aluminium oxide in a carrier can be avoided, and the phosphorus species can be effectively utilized.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Method for reducing Fischer-Tropsch synthesis iron-based catalyst
ActiveCN106552632AHigh activityReduce the impactHeterogenous catalyst chemical elementsCatalyst activation/preparationParaffin waxParaffin oils
The invention relates to the field of reduction of a Fischer-Tropsch synthesis catalyst, and concretely relates to a method for reducing a Fischer-Tropsch synthesis iron-based catalyst. The method comprises the following steps: under existence of reduction gas, a slurry containing the Fischer-Tropsch synthesis iron-based catalyst is subjected to temperature programmed reduction, the temperature programmed reduction comprises the following steps: under normal temperature to 120 DEG C, the heating rate is 10-20 DEG C / h, then the catalyst is kept at the constant temperature of 120 DEG C for 2-8 h; under 120 DEG C to (220-230) DEG C, the heating rate is 5-10 DEG C / h, then the catalyst is kept at the constant temperature of 220 DEG C-230 DEG C for 3-10 h; under (220-230)DEG C to (260-280)DEG C, the heating rate is 3-5 DEG C / h, and then the catalyst is kept at the constant temperature of 260 DEG C-280 DEG C for 10-30 h. The method solves the problem that a liquid solvent is greatly taken out such as paraffin during the catalyst reduction process, influence of the iron-based catalyst in the reduction process is reduced, catalyst is not broken, the activity of the reduced catalyst is high, CO2 selectivity is low, and the light hydrocarbon selectivity is low.
Owner:CHNA ENERGY INVESTMENT CORP LTD +1
Program heating analysis equipment and method for testing property of its catalyst
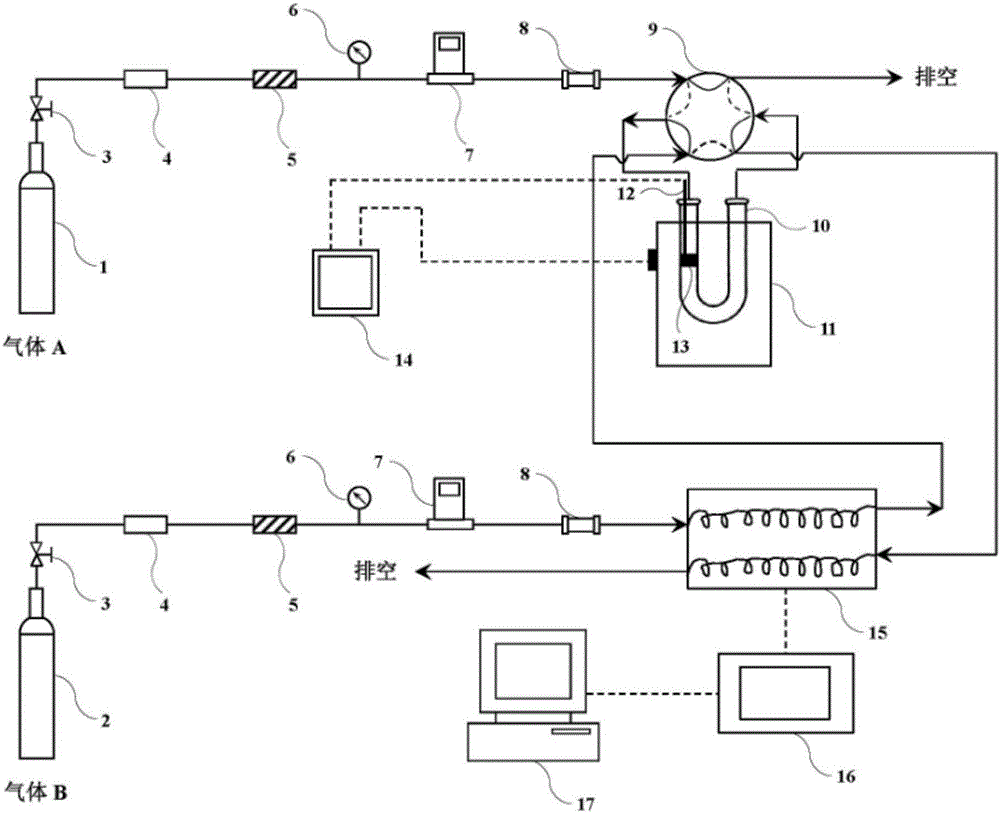
ActiveCN105067752ARealize switchingShorten the timeChemical analysis using catalysisTemperatue controlDesorptionReaction tube
The invention provides a program heating analysis equipment and a method for testing property of its catalyst, which can be used for testing program heating reduction, program heating oxidation and temperature programmed desorption. The program heating analysis equipment comprises a first air supply pipeline, a second air supply pipeline, a pressure-reducing valve, a pressure-stabilizing valve, a constant flow valve, a compression gauge, a mass flowmenter, a non return valve, a six-way valve, a U-shaped reaction tube, heating furnaces, a thermocouple, a temperature controller, a thermal conductance pool detector, a data processing work station and a computer. The design of the six-way valve can conveniently realize the switching of two ways of gas, a purpose of simultaneous operation of a pretreatment process of a catalyst sample and a base line recording process of the equipment can be reached, time is greatly saved, and testing efficiency is increased; design of three heating furnaces is convenient for replacing the high temperature heating furnace, waiting time for cooling the heating furnace is saved, and testing efficiency is increased.
Owner:CHONGQING INST OF GREEN & INTELLIGENT TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Method for preparing transition metal phosphide
InactiveCN1666817AHigh surface areaSimple and fast operationCatalyst activation/preparationPhosphorChemical measurement
The invention relates to the preparation method of a transition metal phosphide. The main operation processes are: dissolve the target phosphor-origin matters and the dissolvable metal salt in water, add hydroxyl acid, the mole ratio of the hydroxyl acid to metal is 0.2-4.5, get the gel in 70-90 Deg. C, froth and solidify in 100-160 Deg. C, burn it in 500 Deg. C for more than four hours to get the front body of target phosphide, revert the front body using program calefactive reverting technology, passivate it in house temperature to get big-area phosphide. The surface area of the invention is as 10 times as the original one.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Preparation method of highly dispersed nanocatalyst
ActiveCN108295848AGood dispersionNo aggregationCatalyst activation/preparationMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsOxygen vacancyHydrogen atmosphere
The invention discloses a preparation method of a highly dispersed nanocatalyst. The method comprises the following steps: (1) respectively preparing a metal salt solution and a precipitant solution,continuously dropwise adding the metal salt solution into the precipitant solution under continuous stirring, continuing the stirring, performing a primary low-temperature hydrothermal reaction, filtering, washing and drying the obtained product, performing a secondary low-temperature hydrothermal reaction, and performing filtration and vacuum drying on the obtained reaction product to obtain a metal oxide carrier rich in oxygen vacancies; and (2) loading a noble metal on the metal oxide carrier by adopting an impregnation technology, and performing temperature-programmed reduction in a hydrogen atmosphere to obtain the highly dispersed nanocatalyst. The method has the advantages of low cost, rich and easily available raw materials, mild preparation conditions and strong universality; andthe highly dispersed nanocatalyst prepared by using the oxygen vacancy supported noble metal has the advantages of good catalytic activity, good product selectivity and great potential industrial catalytic application potential.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Preparation method of silica supported nickel phosphide catalyst
InactiveCN104772154APhysical/chemical process catalystsRefining to eliminate hetero atomsNickel phosphateDispersity
A supported nickel phosphide catalyst has quite high hydrogenation desulfurization activity and relatively good activity stability. A traditional nickel phosphide catalyst is prepared by a way of temperature programming reduction of nickel phosphate, and the dispersion degree of active components is relatively low. Firstly, a silica supported nickel precursor is reduced or roasted under a hydrogen atmosphere, then a phosphating solution is introduced and phosphorization is carried out at lower temperature, and thus the Ni2P / SiO2 catalyst having quite high dispersion degree of the active components and having quite high hydrogenation desulfurization and denitrification activity is obtained. The catalyst can also be used for hydrogenation treatment on diesel oil and for production of clean diesel oil, and also can be used in sulfur-resisting hydrogenation reactions of other occasions.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Catalytic agent capable of utilizing furfuryl alcohol liquid-phase catalytic hydrogenation to prepare 1,5- pentanedio as well asl preparation method and application of same
ActiveCN102872897ARegulatory activityHigh activityMolecular sieve catalystsOrganic compound preparationMolecular sieveHydrogen atmosphere
The invention relates to a catalytic agent capable of utilizing furfuryl alcohol liquid-phase catalytic hydrogenation to prepare pentanediol, which is characterized in that an H-USY molecular sieve serves as a carrier, an isovolumetric impregnation method is adopted to introduce an active metal component, drying and roasting are carried out, and in-situ temperature-programmed reduction is carried out under a hydrogen atmosphere so as to prepare the catalytic agent. The catalytic agent has high-activity and selectivity for utilizing the furfuryl alcohol hydrogenation to prepare the pentanediol.
Owner:恒光新材料(江苏)股份有限公司
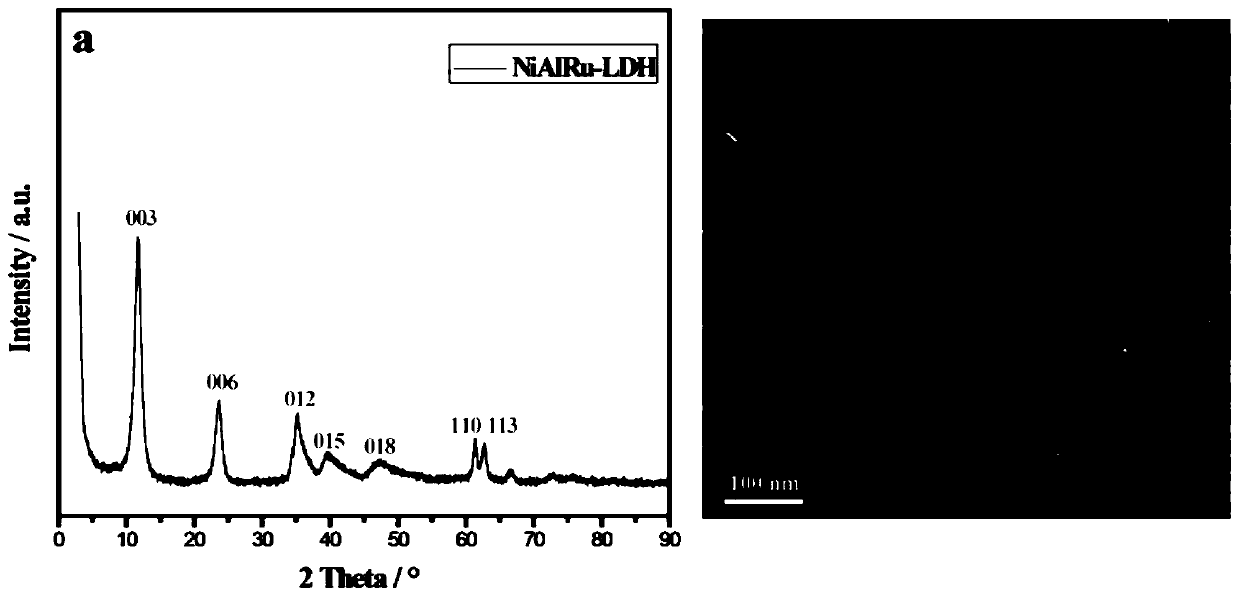
Preparation of confinement structure ruthenium-nickel core-shell bimetallic nano-catalyst and application thereof in catalyzing dimethyl terephthalate selective hydrogenation
ActiveCN110102313AEvenly dispersedStrong interactionMaterial nanotechnologyOrganic compound preparationNano catalystHydrogen atmosphere
The invention discloses preparation of a confinement structure ruthenium-nickel core-shell bimetallic nano-catalyst and application thereof in catalyzing dimethyl terephthalate selective hydrogenation. The structure of the catalyst is that Ru@Ni core-shell metal nanoparticles are uniformly embedded in a weakly crystallized aluminium-doped nickel metallic oxide shell, and peripheral aluminium-dopednickel metallic oxide has a confinement effect on the Ru@Ni core-shell metal nanoparticles. The preparation method comprises the steps that a NiAlRu ternary hydrotalcite precursor is synthesized through a double drop method, then temperature-programmed reduction is applied in a hydrogen atmosphere, and the confinement structure ruthenium-nickel core-shell bimetallic nano-catalyst is obtained. Ina dimethyl terephthalate selective hydrogenation reaction, by means of the catalyst, not only is the conversion rate of dimethyl terephthalate is improved, but also the selectivity of dimethyl 1,4-cyclohexanedicarboxylate is greatly improved, the outstanding reaction stability is achieved, and thus the reaction performance of hydrogenation is improved.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Application of transition metal phosphide in catalytic conversion of lignin
InactiveCN104177223AReduce tensionLow costOxygen-containing compound preparationOrganic compound preparationAdditional valuesCatalyst support
The invention discloses an application of a transition metal phosphide in catalytic conversion of lignin; the transition metal phosphide is a Z-AB / C loaded type catalyst or an assistant-free tungsten phosphide catalyst (loaded type and non-loaded type), wherein Z is an assistant, A is a transition metal W or Mo, B is phosphorus, and C is a catalyst carrier; the catalyst is prepared by adopting an impregnation method for preparation and then carrying out hydrogen gas temperature programmed reduction. The invention provides a method for preparing organic chemical phenolic substances through catalytic conversion of the lignin with the phosphide catalyst, and the lignin is converted into small molecular compounds with high additional values through a one-step reaction, so as to realize high-efficiency utilization of the lignin.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Method for synthesizing VIII first-row transition metal and molybdenum/tungsten double-metal carbide catalyst at low temperature
InactiveCN107185570AReduce pollutionEasy to operatePhysical/chemical process catalystsHydrocarbon by hydrogenationIsomerizationDecomposition
The invention provides a method for synthesizing VIII first-row transition metal and molybdenum / tungsten double-metal carbide catalyst at low temperature and belongs to the technical field of material preparation and application. The method is characterized in that double-metal oxide is obtained through hydrothermal treatment, and carbon-thermal hydrogen reduction is performed to prepare pure-phase double-metal carbide. Compared with a traditional arc-melting method and a programmed-temperature reduction method, the method has the advantages that the method is low in temperature, simple to operate, energy-saving, small in product particle, little in surface carbon pollution, and the like; the method is promising in application prospect; the prepared double-metal carbide catalyst is applicable to hydrogenation, dehydrogenation, hydrogenolysis, deoxidization, methane syngas, isomerization, ammonia decomposition, hydrogen evolution reaction, hydrogen oxidation reaction, oxygen reduction reaction, water gas transformation, catalyst carriers and the like.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
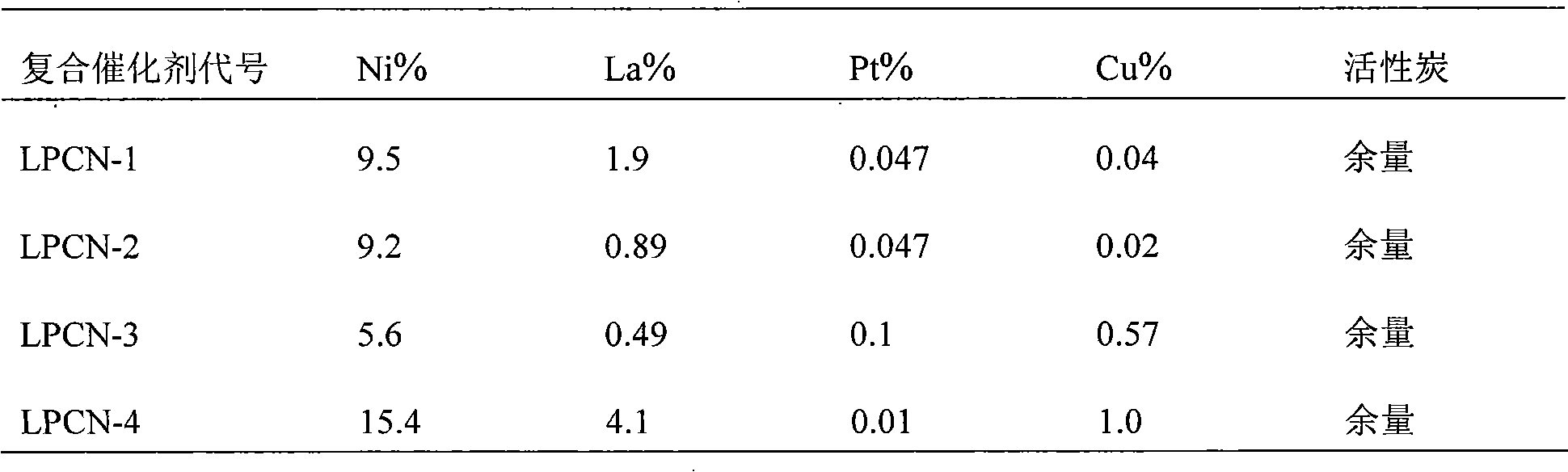
Catalyst containing trace noble metals for dehydrogenating organic hydrogen storage medium and preparation method
InactiveCN101786004AReduce dosageLow costHydrogenMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsActivated carbonDehydrogenation
The invention relates to a catalyst containing trace noble metals for dehydrogenating an organic hydrogen storage medium and a preparation method. The catalyst comprises 5-15% of Ni, 0.5-4% of La, 0.01-0.1% of Pt, 0.02-1% of Cu and the balance of carrier active carbon of which the specific surface area is between 100m<2> / g and 1800m<2> / g. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: firstly using processed active carbon as a carrier, using a relevant soluble salt to carry metals, such as the Ni, the La, the Pt, the Cu and the like, then drying and calcining for 3-5h at 300-500 DEGC under the protection of nitrogen gas to prepare the precursor of the catalyst, and finally performing temperature programmed reduction. In the preparation process, by properly proportioning all components and by adopting a combined strategy of alternately using chemical mixing and physical mixing, a multi-component composite catalyst is finally obtained. Therefore, the excellent synergistic catalysis is generated among all components to improve dehydrogenation catalytic activity under the condition that the noble metals are used as few as possible.
Owner:淮安市淮安区综合检验检测中心
Fischer synthesis method for highly selectively producing liquid hydrocarbon
ActiveCN101186835AImprove conversion rateLow selectivityLiquid hydrocarbon mixture recoveryCobalt metalSynthesis methods
Provided is a highly selective fischer-tropsch process for producing liquid hydrocarbon, which comprises that a mixing air of hydrogen and carbonic oxide is contacted with an catalyst under fischer-tropsch synthesis condition. The process is characterized in that the catalyst contains efficient quantity of cobalt metal component and oxide of alumina, wherein the RT value of the cobalt metal component is 400 DEG C to 1000 DEG C, the RT value is the summit temperature corresponding to the first reduction peak of the first reduction peak in a reduction spectrogram of cobalt which exists in an oxidation state form when representing the catalyst with the employment of temperature programmed reduction. Compared with the existing technology, the C5+ selectivity of the process provided by the invention is remarkably increased.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com