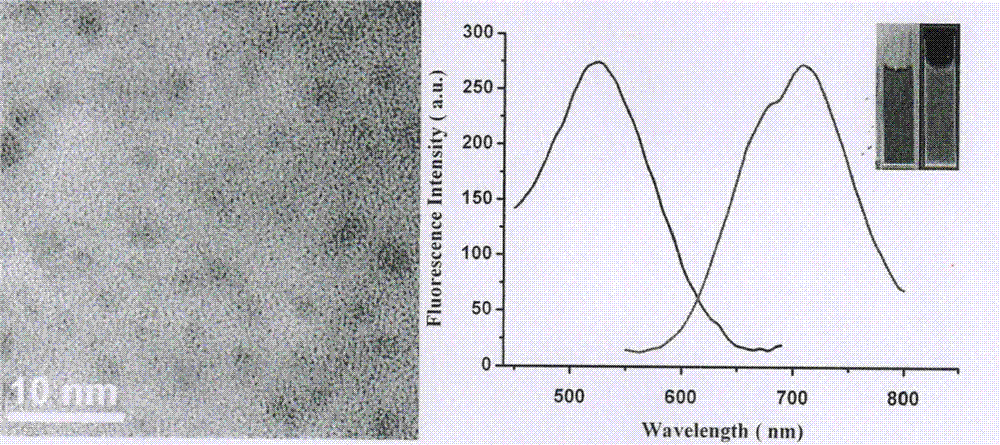
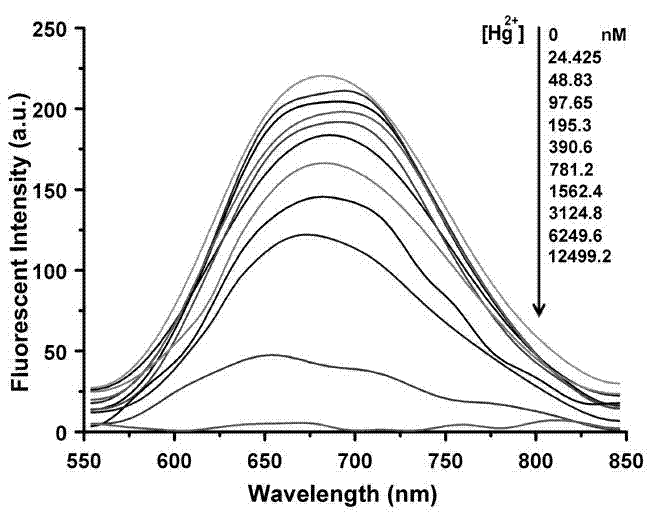
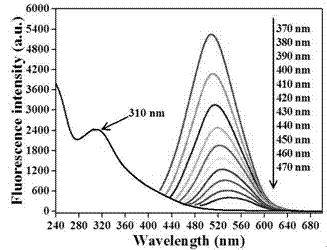
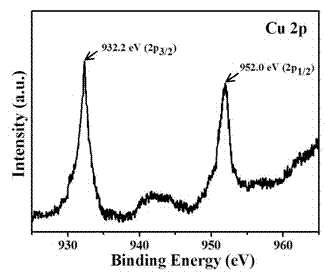
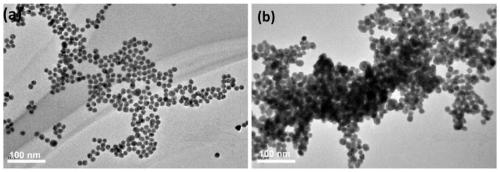
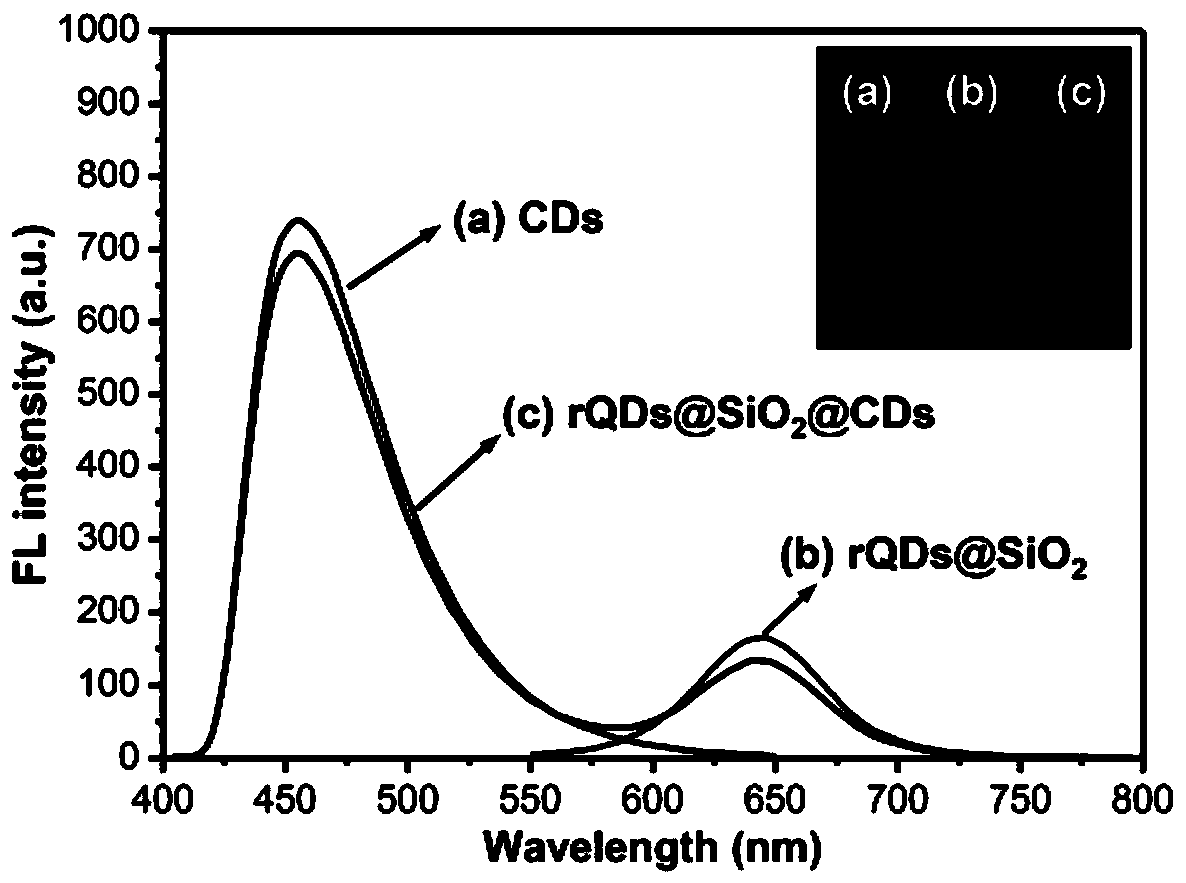
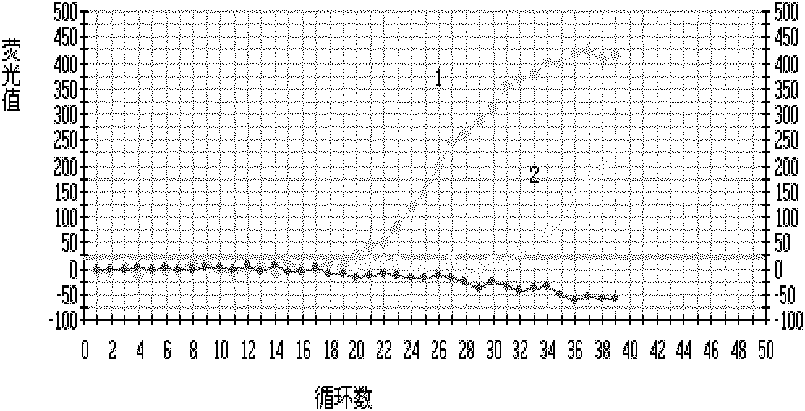
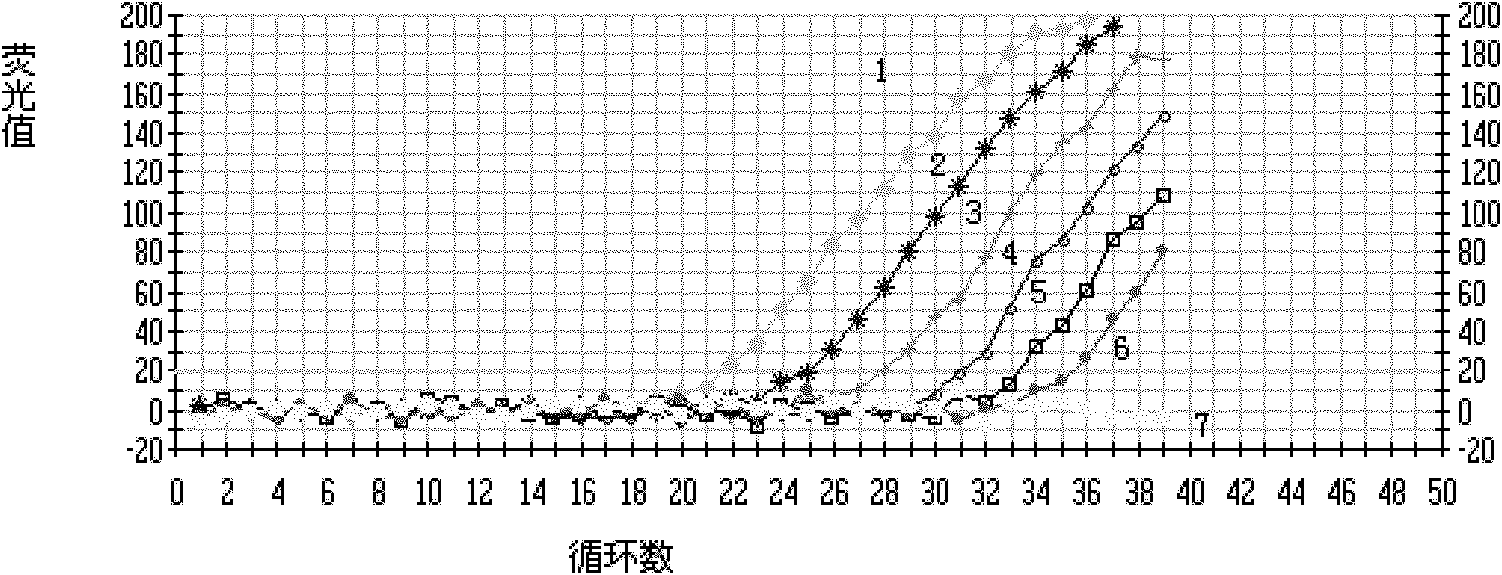
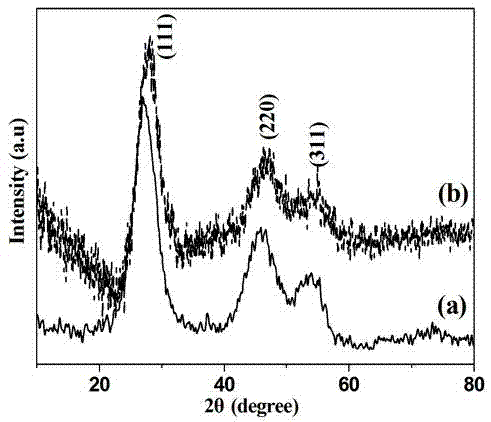
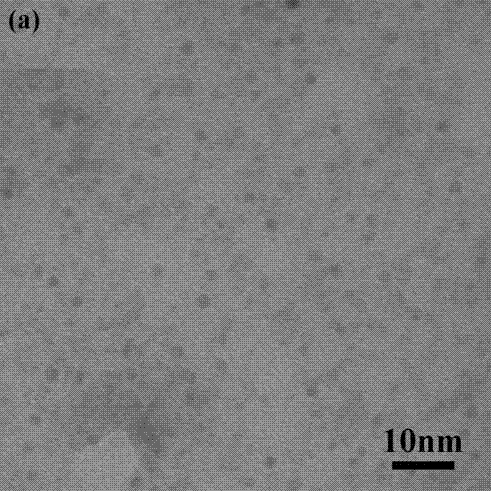
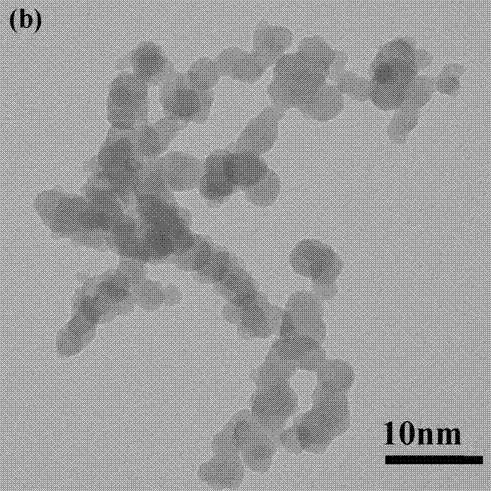
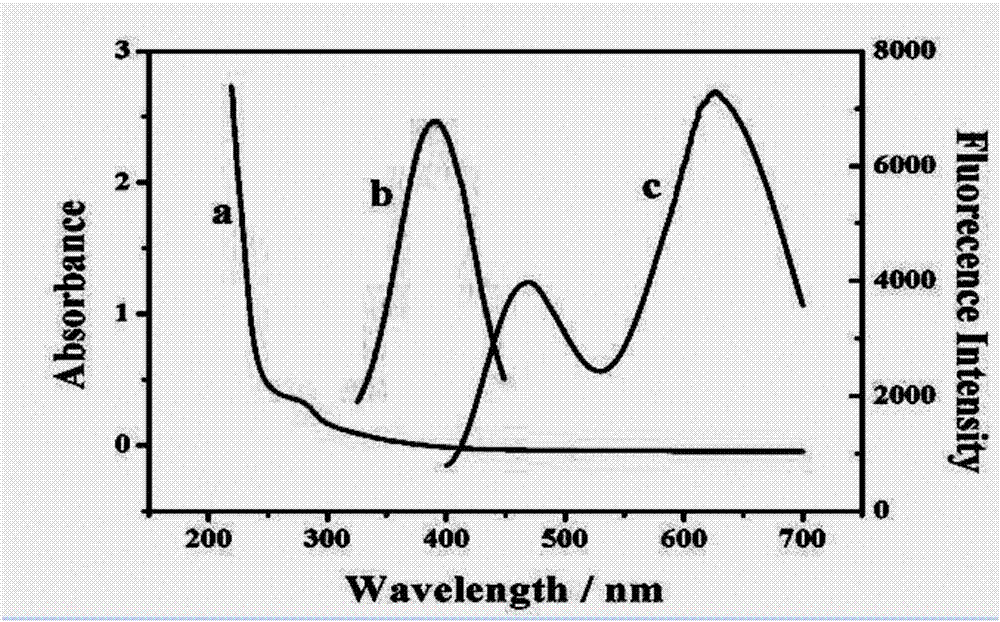
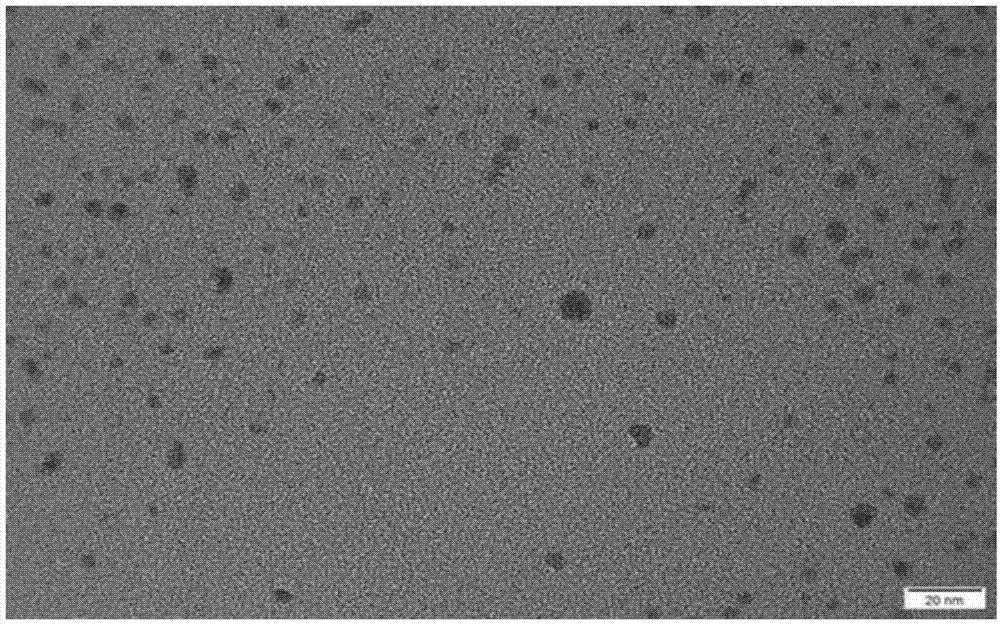
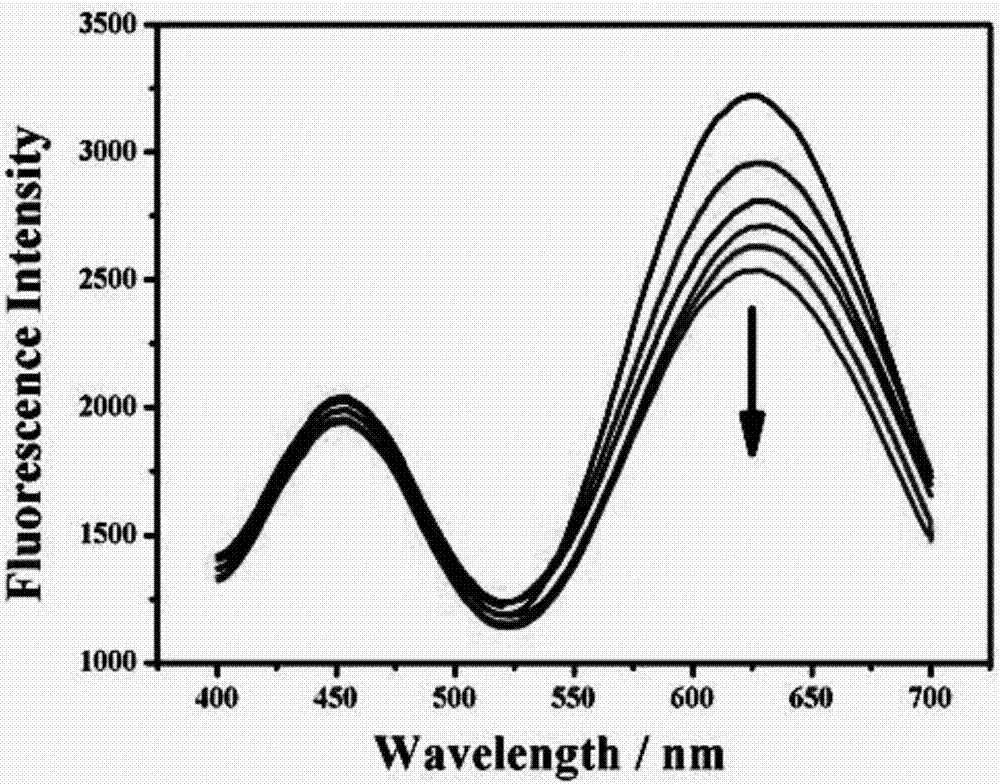
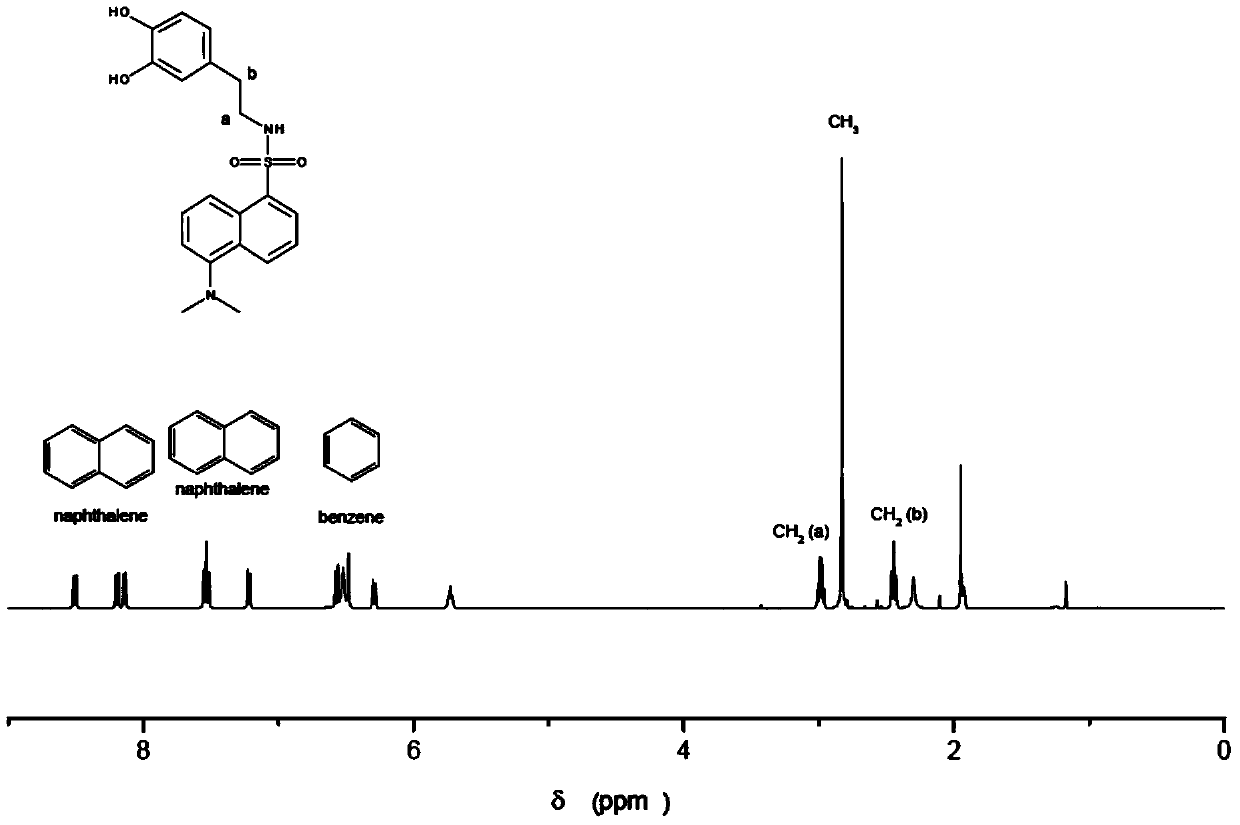
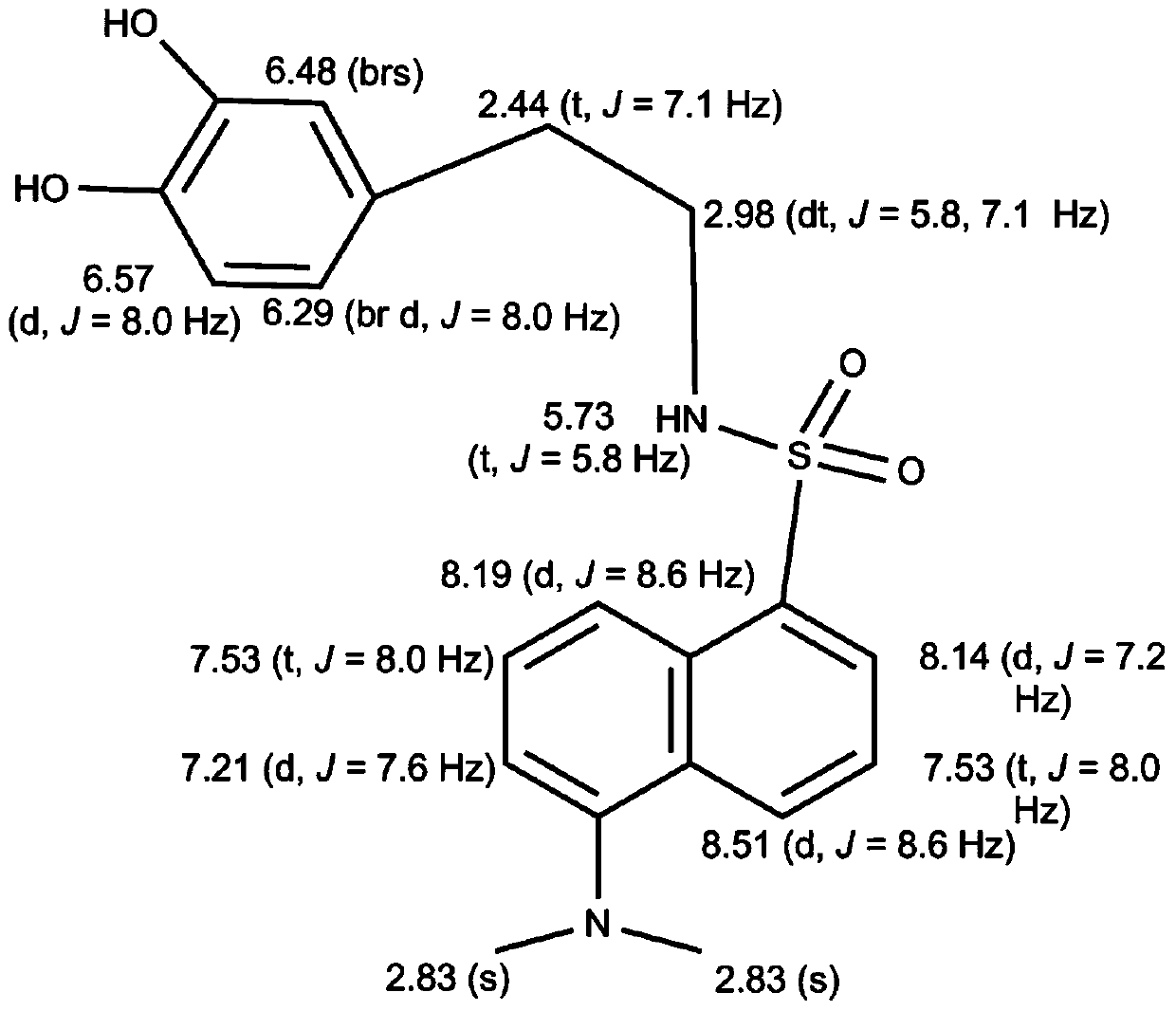
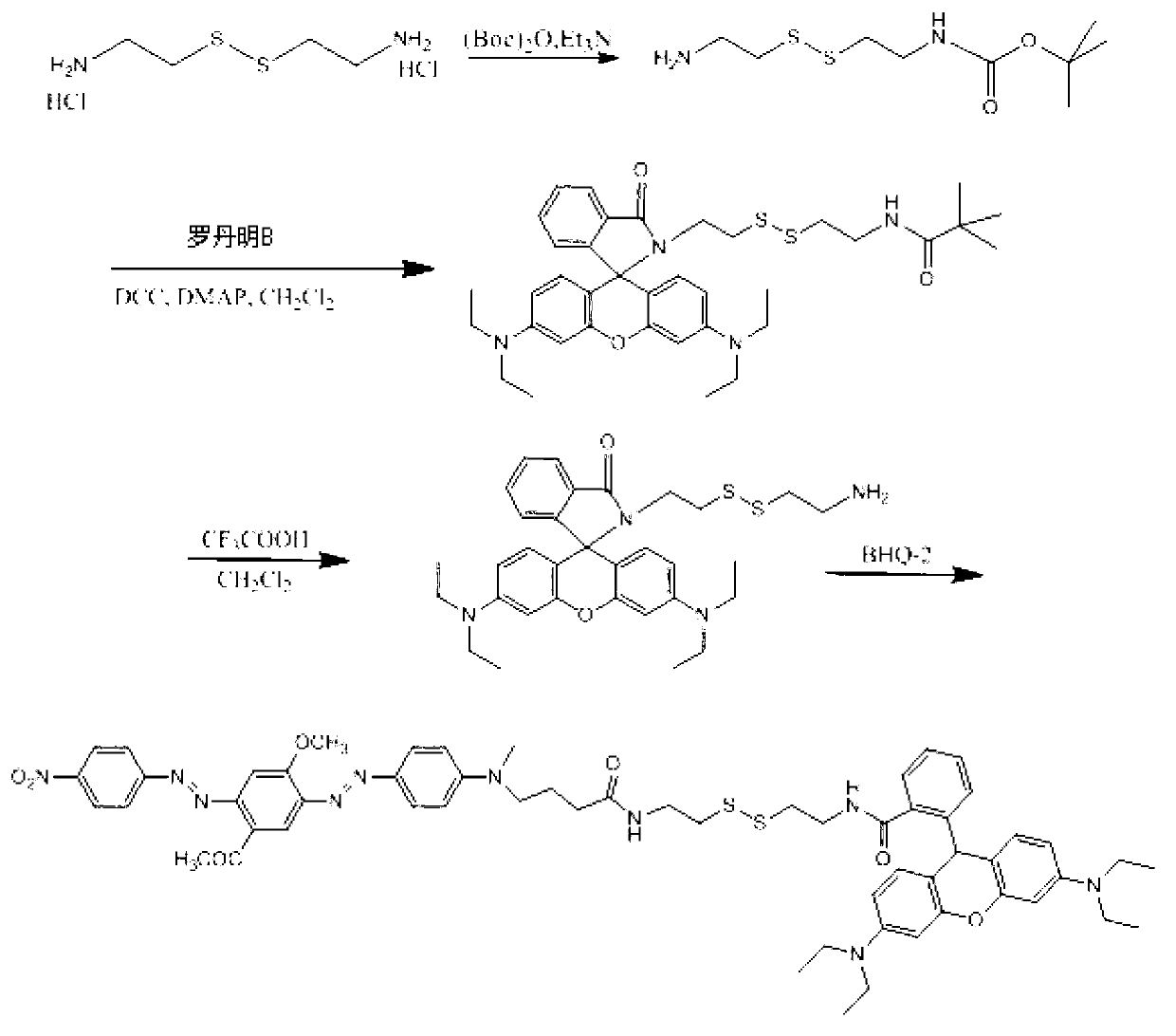
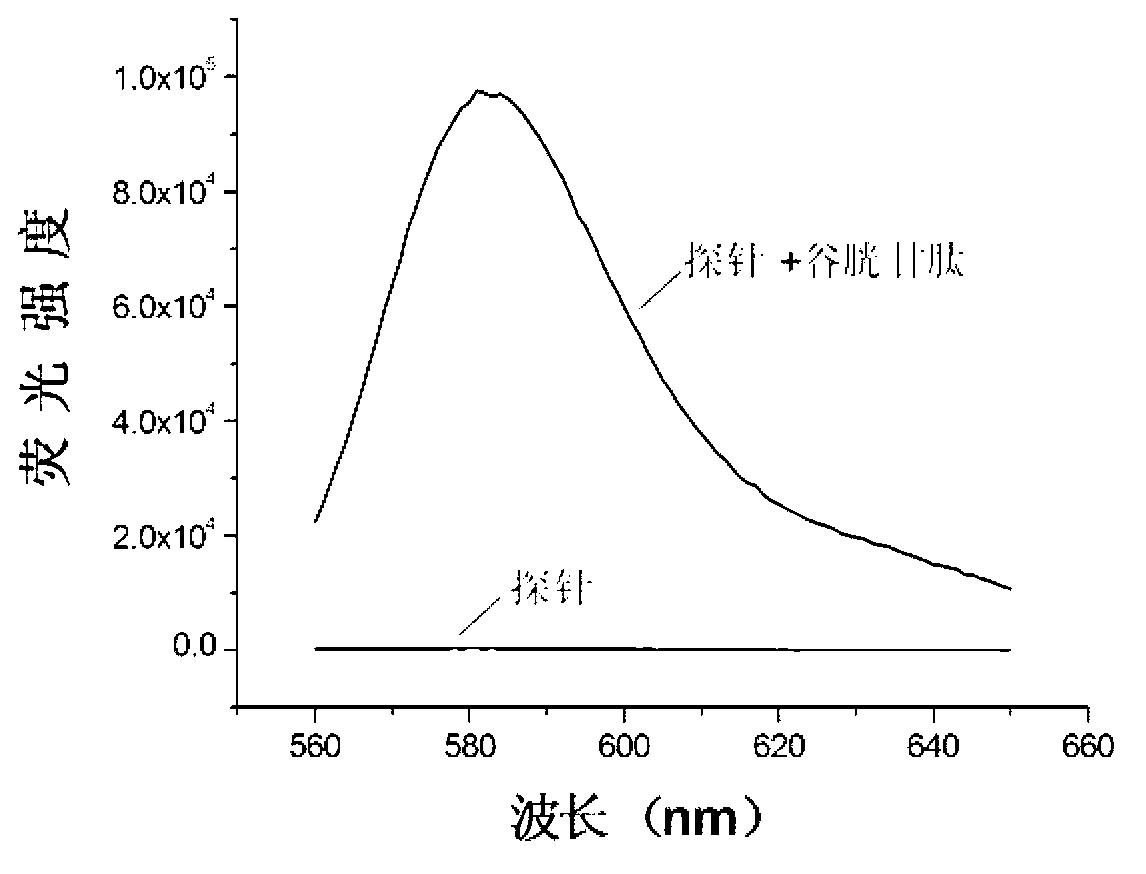
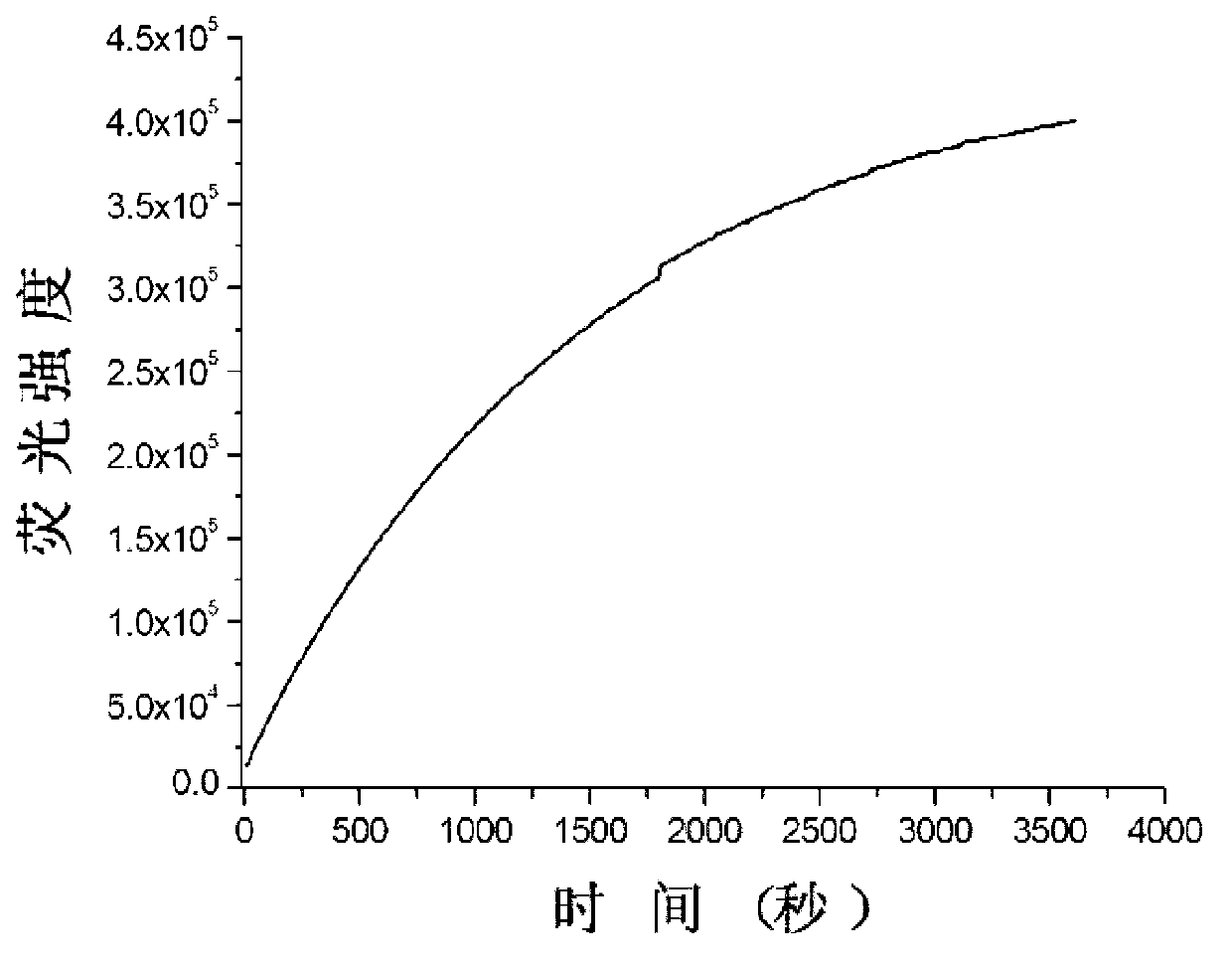
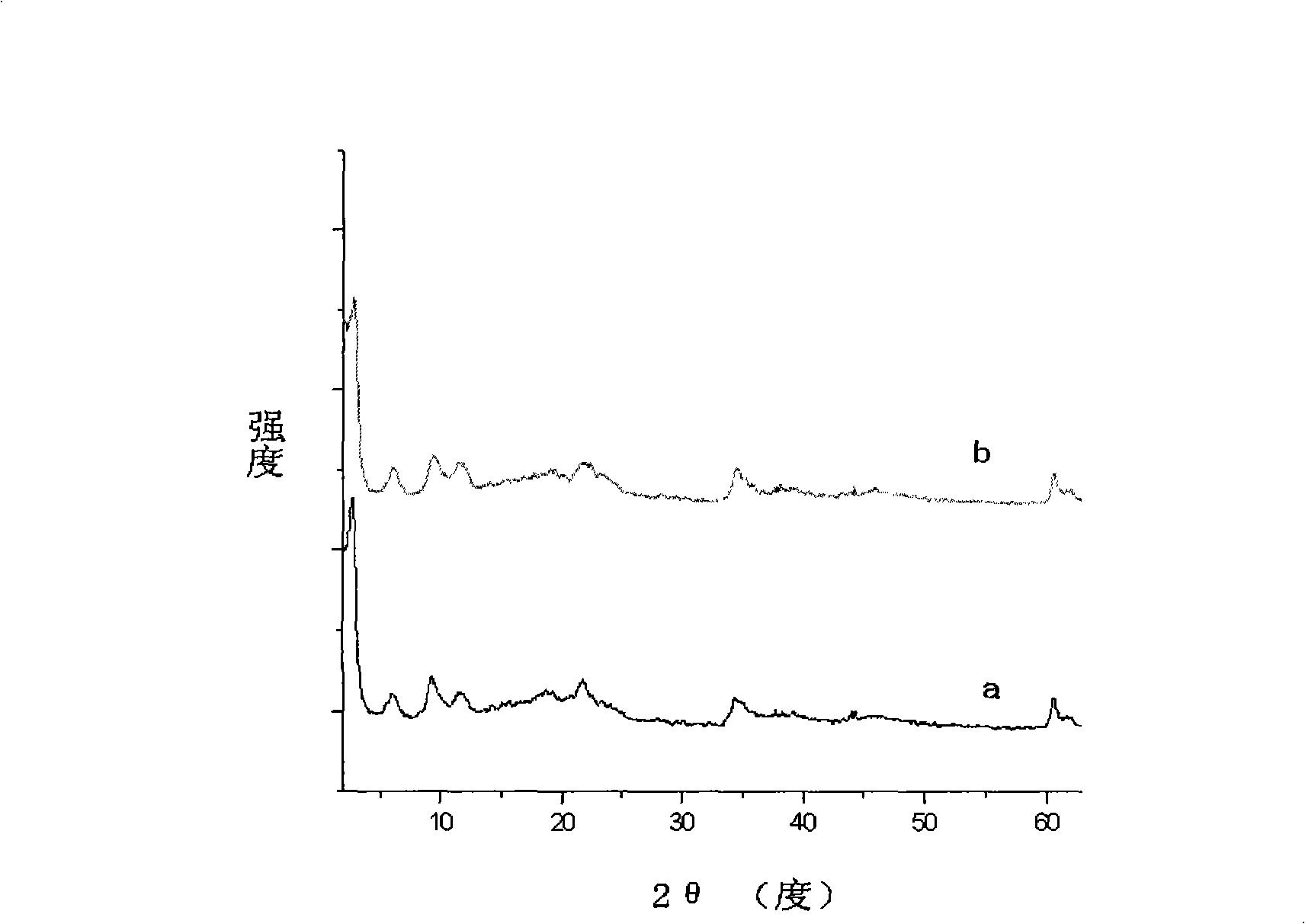
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
927 results about "Quenching (fluorescence)" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Quenching refers to any process which decreases the fluorescence intensity of a given substance. A variety of processes can result in quenching, such as excited state reactions, energy transfer, complex-formation and collisional quenching. As a consequence, quenching is often heavily dependent on pressure and temperature. Molecular oxygen, iodide ions and acrylamide are common chemical quenchers. The chloride ion is a well known quencher for quinine fluorescence. Quenching poses a problem for non-instant spectroscopic methods, such as laser-induced fluorescence.
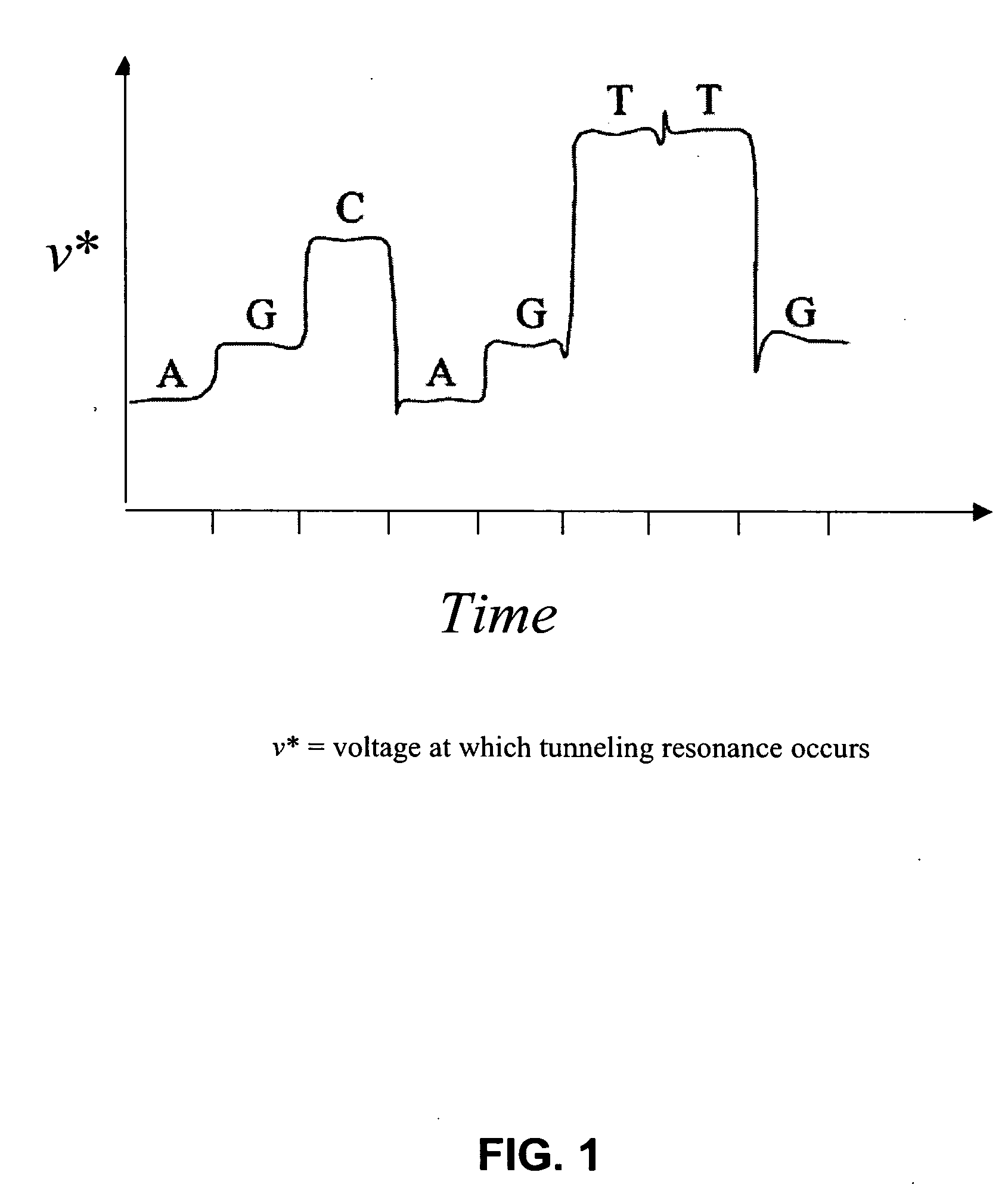
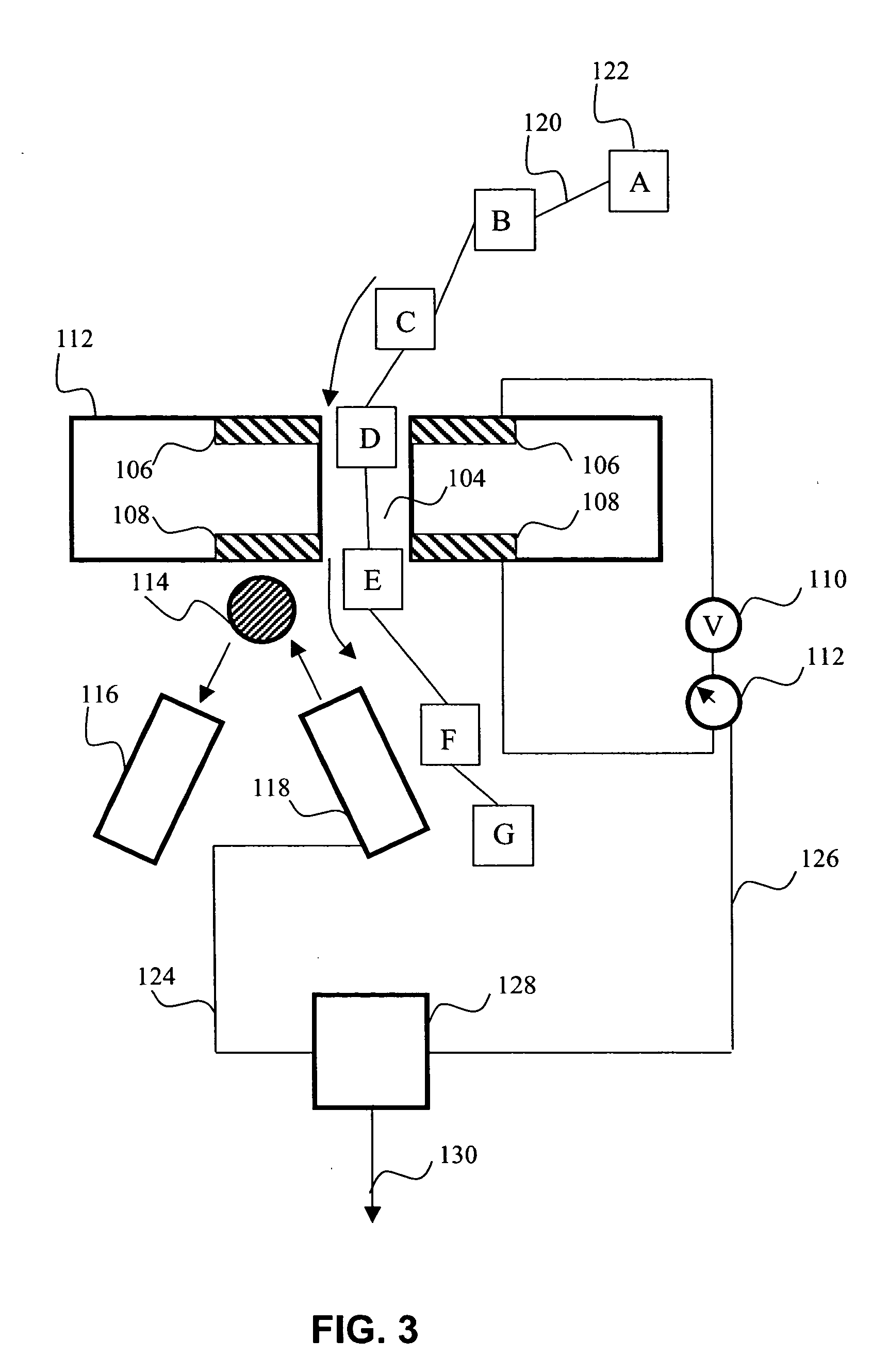
Characterization of biopolymers by resonance tunneling and fluorescence quenching
InactiveUS20060019259A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsFluorescenceBiopolymer
The present invention provides a method and apparatus for determining the identity of a monomeric residue of a biopolymer. The apparatus comprises a substrate having a nanopore, a potential-producing element for producing a ramped potential across electrodes adjacent to the nanopore, and a quenchable excitable moiety adjacent to the nanopore. As a biopolymer passes through the nanopore, the identity of monomeric residues of a biopolymer may be determined by detecting changes in (a) current across the electrodes and (b) a signal of the quenchable excitable molecule. The subject method and apparatus find use in determining the identity of a plurality of monomeric residues of a biopolymer, and, as such, may be employed in a variety of diagnostic and research applications.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
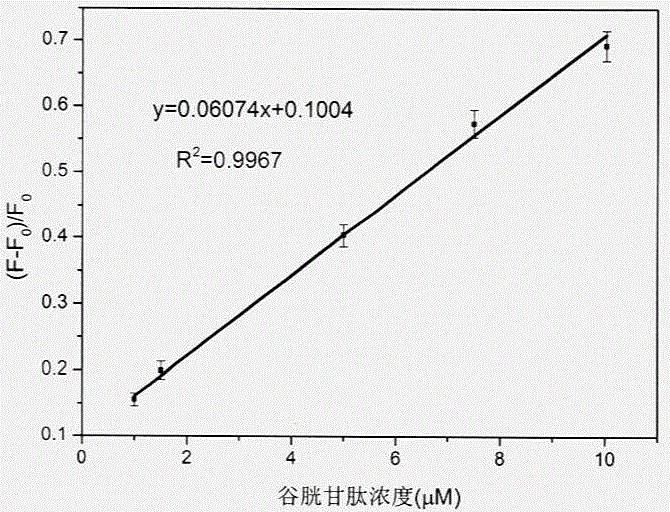
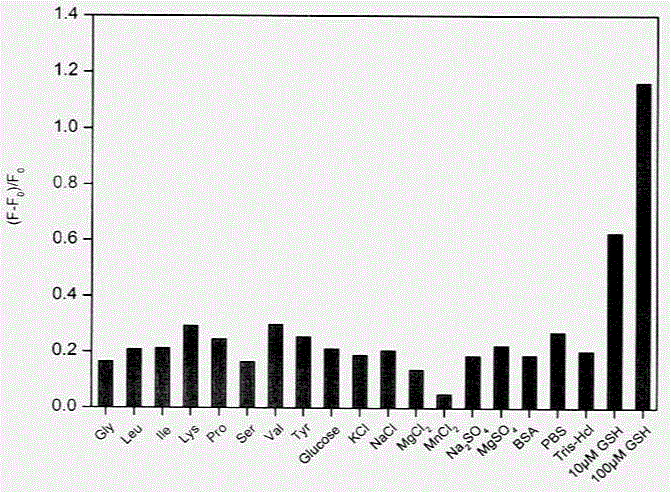
In-situ composite system based on carbon quantum dot/manganese dioxide nanometer sheet layer and using method for detecting content of glutathione
ActiveCN104597019ANo pollution in the processHigh precisionFluorescence/phosphorescenceTest sampleRedox
The invention discloses an in-situ composite system based on a carbon quantum dot / manganese dioxide nanometer sheet layer and a using method of the in-situ composite system. The using method comprises the following steps: firstly, completely quenching fluorescence by using a manner that carbon quantum dots are adsorbed on a manganese dioxide nanometer sheet layer prepared by reducing potassium permanganate in situ, and then quantitatively analyzing and determining the content of the GSH in a GSH to-be-tested sample based on a principle of causing digestion of the manganese dioxide nanometer sheet layer, releasing the carbon quantum dots and recovering the fluorescence thereof by virtue of a redox reaction between glutathione (GSH) and manganese dioxide. According to the in-situ composite system, the detection method is high in precision, the repeatability is good, a used carbon material is low in price, easily available, and free from polluting the environment, and has relatively good biological safety; meanwhile, the in-situ composite system is simple and convenient to operate, relatively strong in practicability, high in sensitivity, and excellent in selectivity of the GSH.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIV
800-nanometer continuous laser excited rare earth upconversion nanoparticles (UCNPs), and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN103450875AEffective absorptionAvoid quenchingLuminescent compositionsFluorescenceNanoparticle
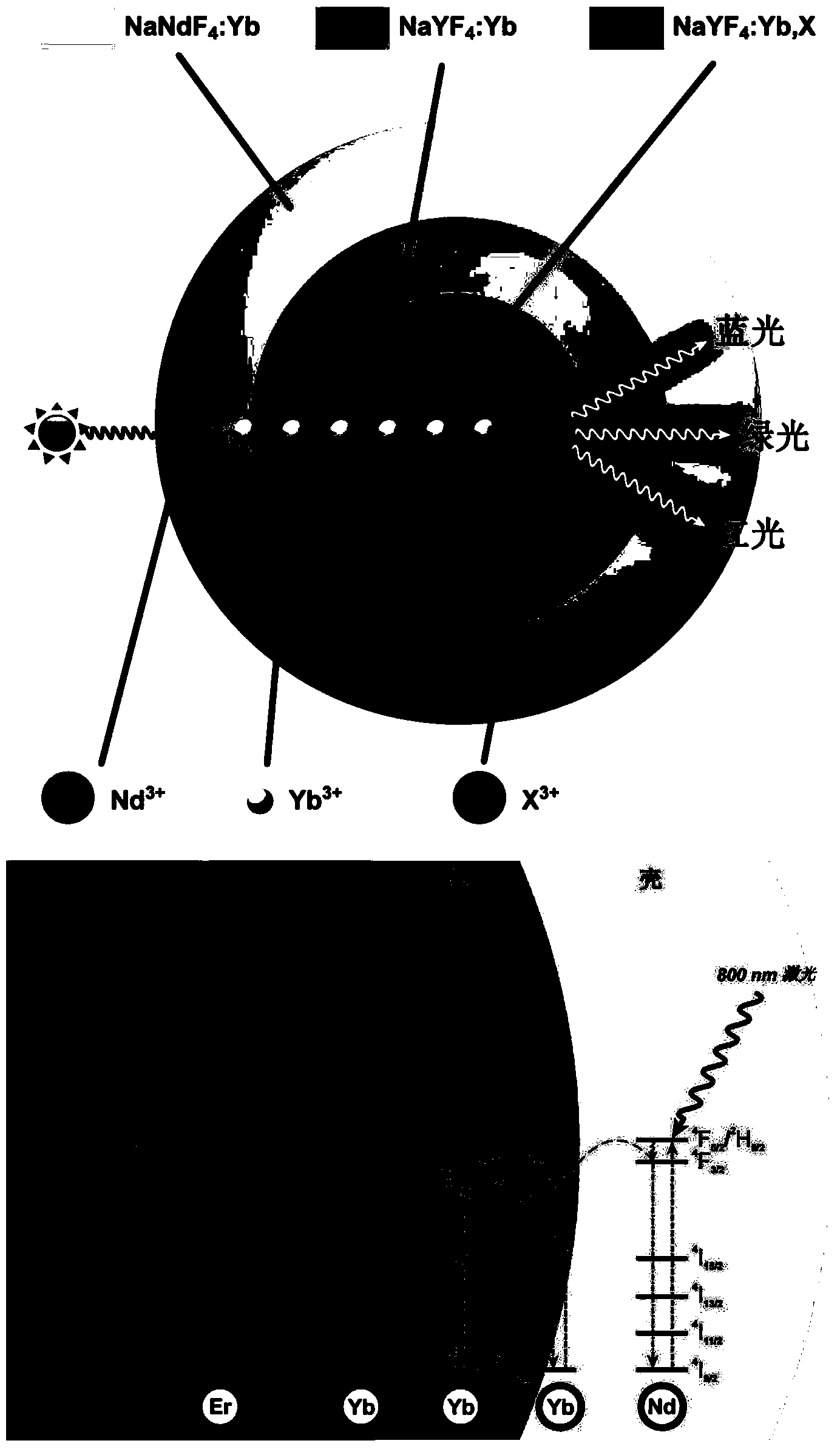
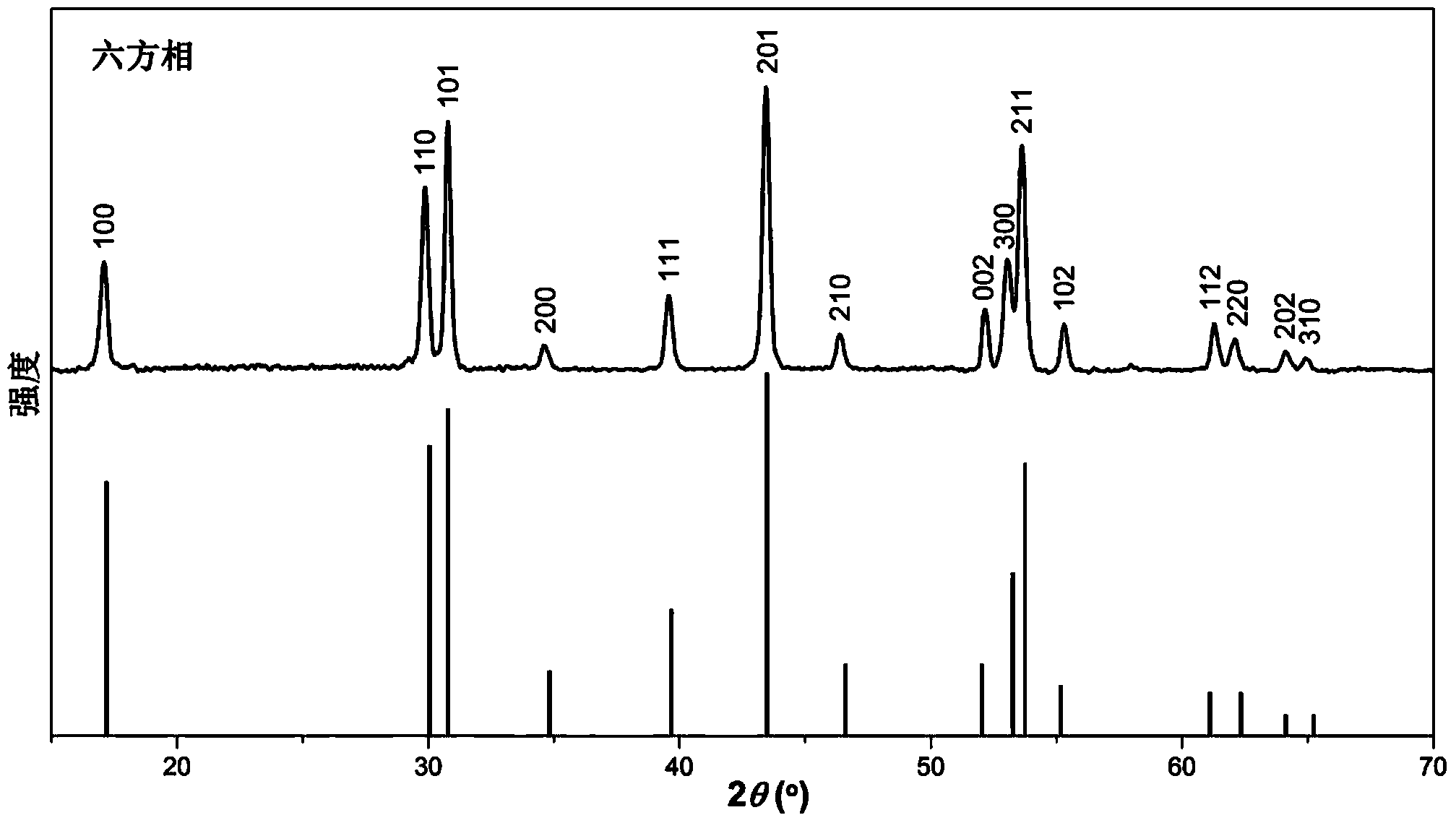
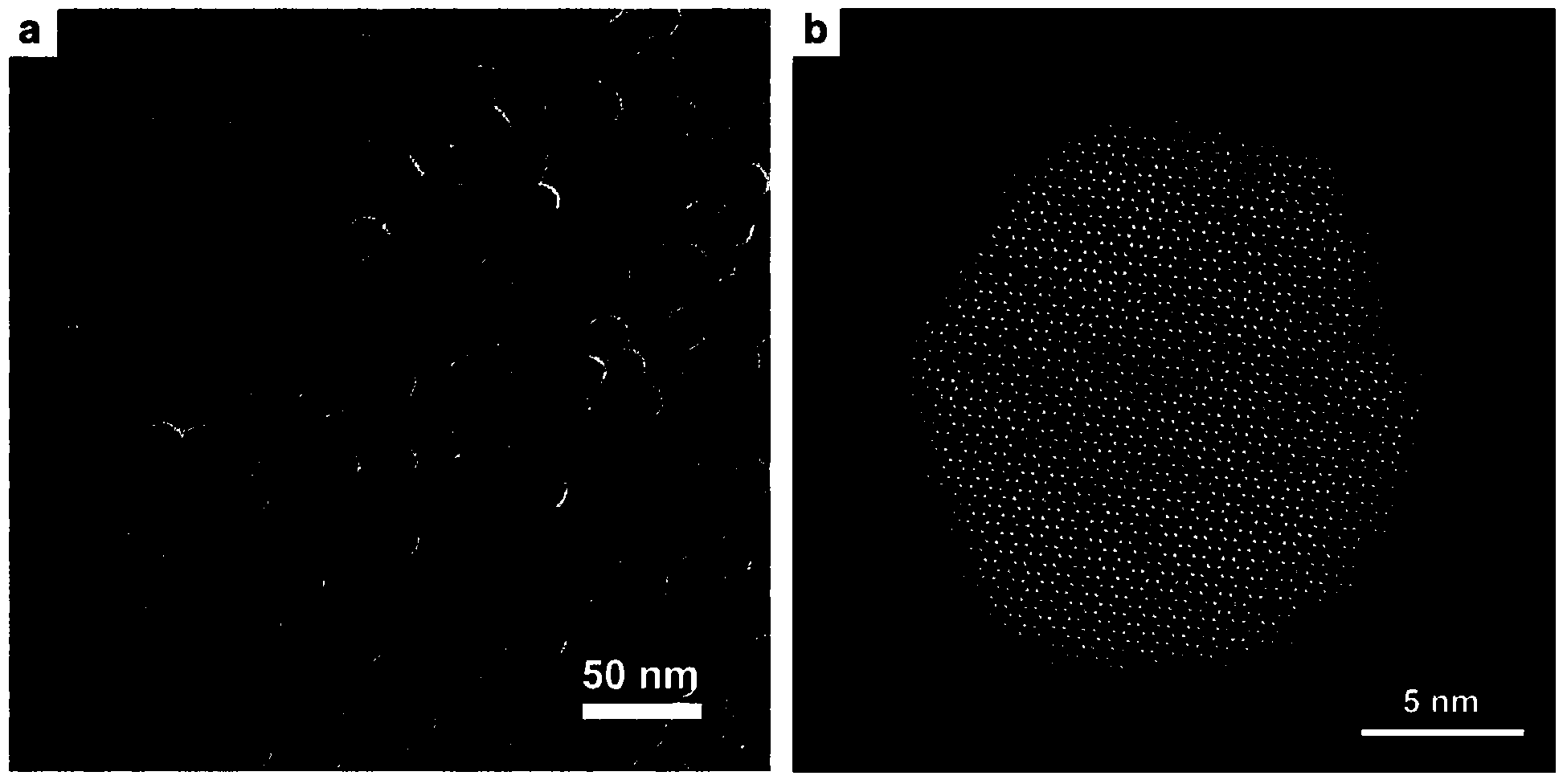
The invention provides 'core-shell-shell' rare earth upconversion nanoparticles (UCNPs) using Nd as a sensitizing agent. The rare earth UCNPs are characterized in that the shell layer of the rare earth UCNPs contains Nd<3+> and each layer contains Yb<3+>. The special microscopic nanostructure solves the problem about the quenching effect on upconversion fluorescence in an Nd doping process, so bright upconversion fluorescence can be obtained. Compared with the traditional Yb-sensitized UCNPs, the Nd-sensitized UCNPs have higher infrared absorption intensity so as to greatly improve upconversion efficiency and fluorescence. The Nd-sensitized UCNPs adopt 800-nanometer instead of 980-nanometer laser as an exciting light source, so the Nd-sensitized UCNPs have smaller overheating effect and stronger biological tissue penetrating power. Therefore, the novel rare earth upconversion material is expected to be widely applied in the field of biomedicines.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Nitrogen-doped carbon nanometer particle as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN103113886AOvercoming the technical problem of easy fluorescence quenchingEasy to prepareNon-macromolecular adhesive additivesInksMicrowave methodSolvent
The invention discloses a nitrogen-doped carbon nanometer particle as well as a preparation method and application thereof, belongs to the field of nanometer material science and is used for solving the technical problems that fluorescence quenching is easily caused to the aggregative state of the carbon nanometer particle due to surface passivation modifier which is added for the preparation of existing carbon nanometer particles. The nitrogen-doped carbon nanometer particle is prepared through a microwave method by using organic compounds containing polycarboxyl or polyhydroxy as materials and using ammonia water as a solvent and a nitrogen doping source. The invention further provides the application of the nitrogen-doped carbon nanometer particle as fluorescent ink and fluorescent glue. The preparation method disclosed by the invention is simple, low in cost, and convenient to realize large-scale production; the maximal fluorescent quantum efficiency of the solid film formed by the prepared fluorescent glue is as high as 84%; the prepared fluorescent ink is non-toxic, generates no precipitates after being placed for a long time, is strong in fluorescence characteristic and can be applied to various fields such as bio-imaging, biological product identification, information storage, information encryption, counterfeiting prevention, illumination and display, sensing and photovoltaic devices.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Fluorescent ion probe and its application in ion detecting
InactiveCN101153848AEasy to synthesizeSimple structureChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceLuminescent compositionsBenzoxazoleFluorophore
The invention relates to a fluorescent ion probe (I) with high selectivity and high sensitivity in detection and the application of the fluorescent ion probe in identifying and detecting heavy metal ion and transition metal ion, wherein, the Y is an organic conjugate group with fluorescence transmitting function such as pyrene, naphthalene, 4-amidogen-1, 8-naphthyl imide, Dan sulfonamide, anthracene, carbazole, benzimidazoins, benzoxazoles, boron fluoride bipyrrole (BODIPY), fluorescein, 3, 4, 9, 10-perylenetetracarboxylic diimide or rhodamine B; the X is acylamino group, sulfoamino group or ester group. The fluorescent ion probe uses the fluorescence peak of fluorescence chromophore aggregate as the response signal to identify metal ion, thereby effectively avoiding the quenching effect of transition metal ion and heavy metal ion on fluorophore; moreover, the fluorescent ion probe realizes selective identification of heavy metal ion and transition metal ion in various solvents and aqueous solution in particular.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
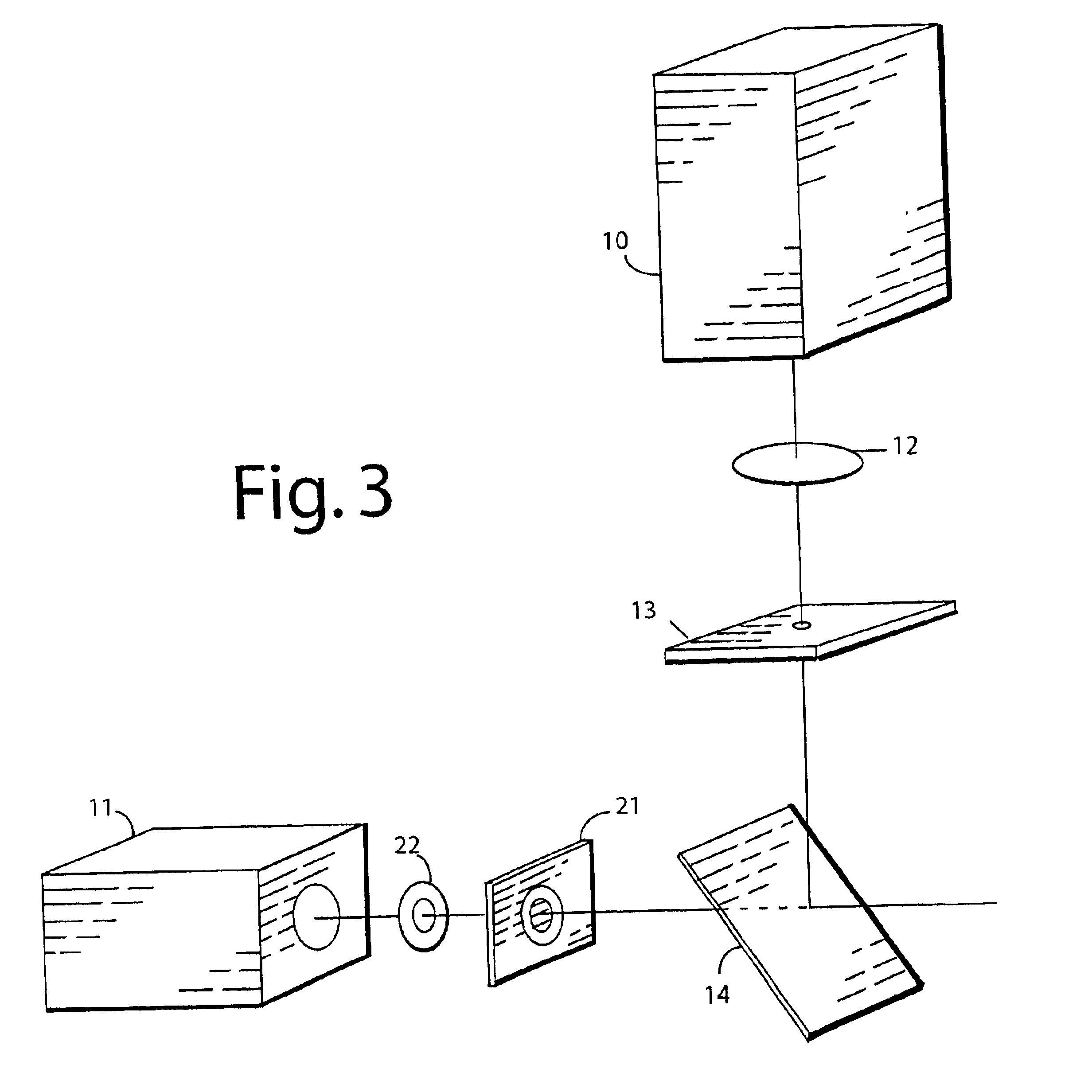
Superresolution in microlithography and fluorescence microscopy
InactiveUS6903347B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLuminescent dosimetersFluorescenceQuenching
In scanned optical systems such as confocal laser microscopes wherein a beam of light is focused to a spot in a specimen to excite a fluorescent species or other excitable species in the spot, the effective size of the excitation is made smaller than the size of the spot by providing a beam of light of wavelength adapted to quench the excitation of the excitable species, shaping this second beam into a pattern with a central intensity minimum, and overlapping this central minimum with the central intensity maximum of the focused spot, so that within the spot the intensity of quenching light increases with distance from the center of the spot, thereby preferentially quenching excitation in the peripheral parts of the spot, and thereby reducing the effective size of the excitation and thus improving the resolution of the system. In the preferred embodiment of the present invention, the central minimum of quenching light is narrowed further by creating the pattern of quenching radiation in the specimen by imaging onto the focal plane a plurality of pairs of sources of quenching light, arrayed at the vertices of a regular, even-sided polygon, the center of which is imaged in the specimen on the central maximum of exciting radiation, and such that the two members of each pair are on opposite vertices of the polygon and emit light mutually coherent and out-of-phase, and the light emitted by different pairs is incoherent with respect to each other.
Owner:BAER STEPHEN C
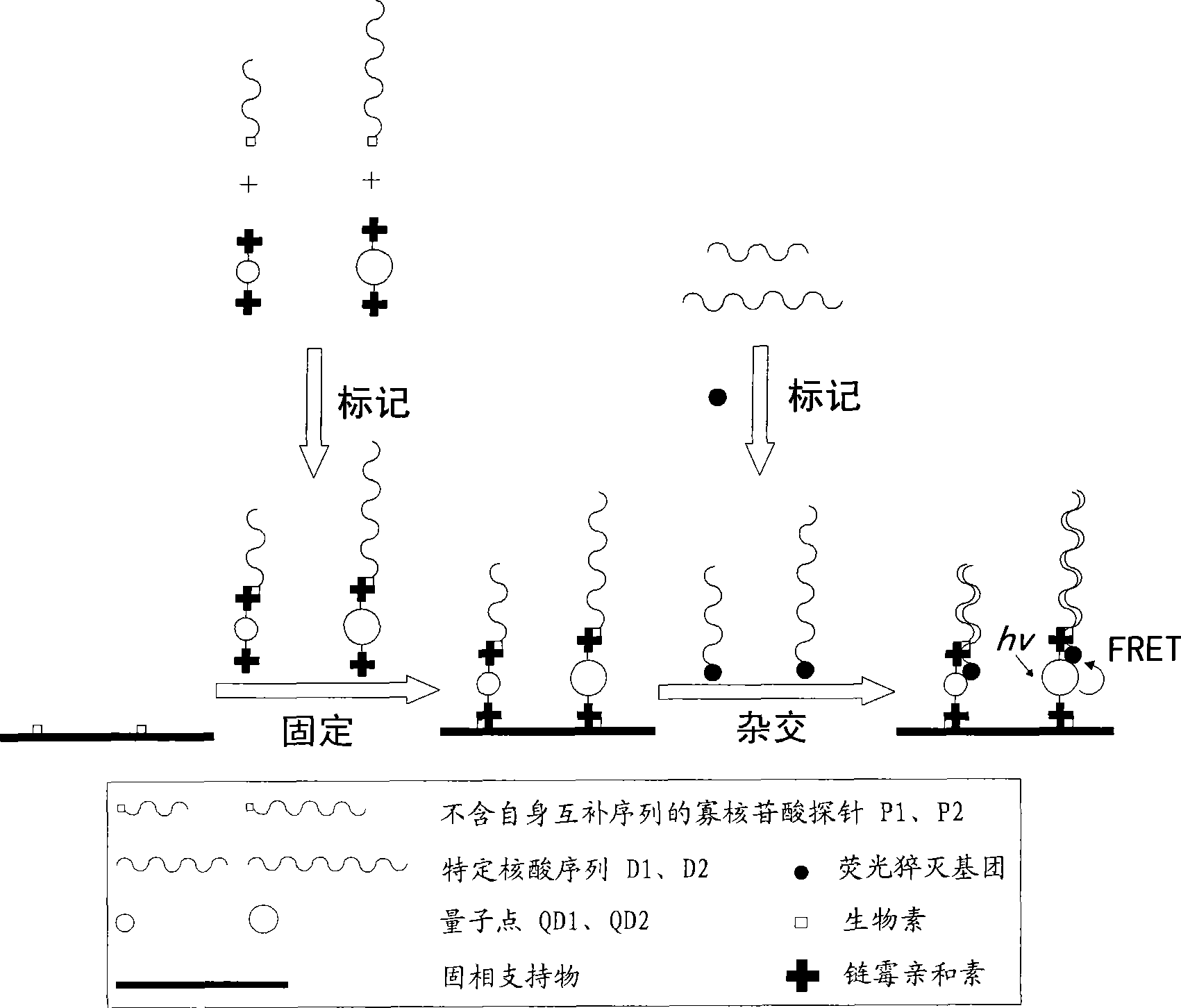
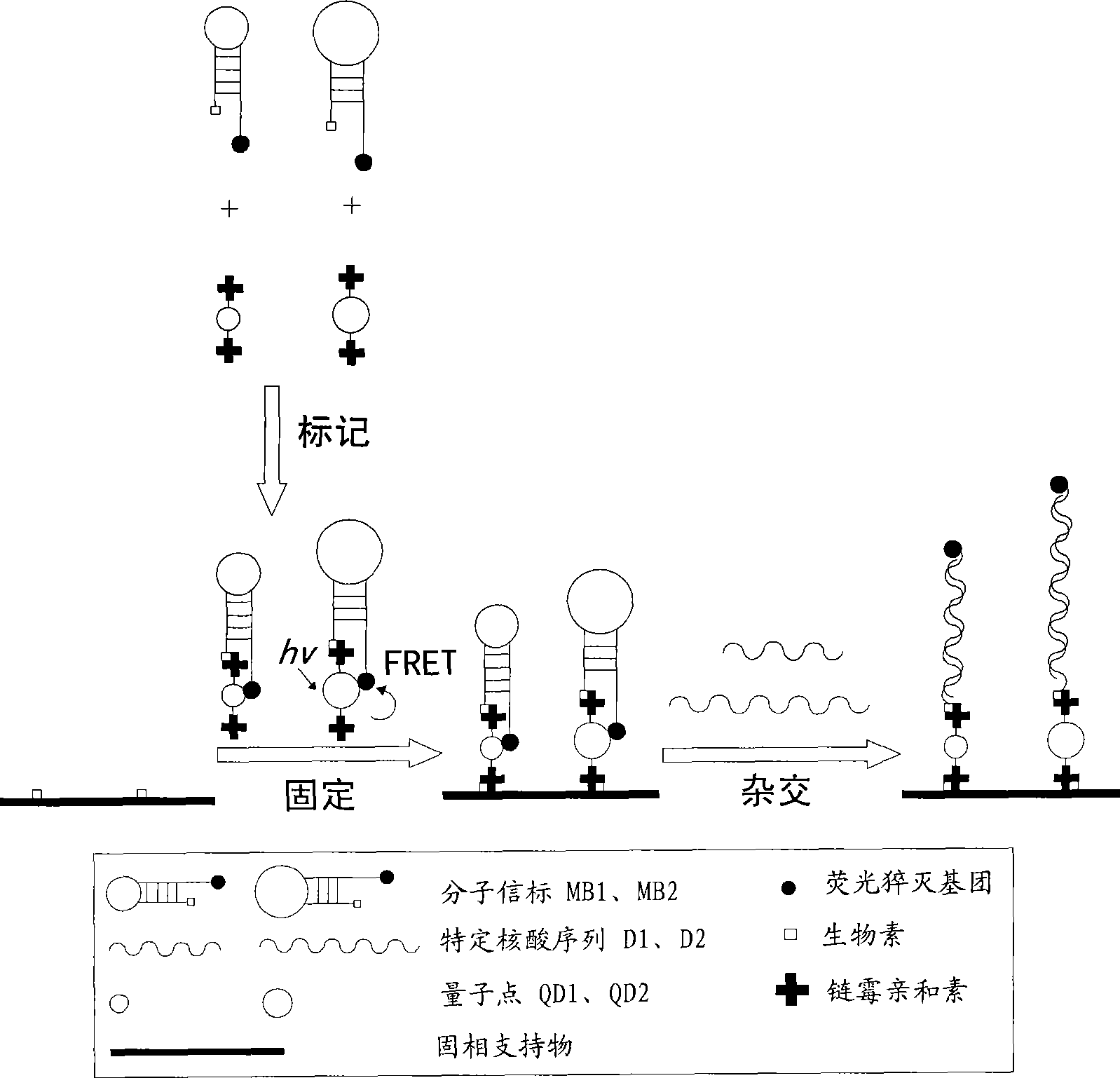
Multi-target quantum-dot mark nucleic acid chip and preparation method and detection method thereof
InactiveCN101519695AMultiple duplicate detection synchronizationEasy to makeMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescenceBiology
The invention discloses a multi-target quantum-dot mark nucleic acid chip and a preparation method and a detection method thereof, wherein the nucleic acid chip comprises a solid phase holder and an oligonucleotide probe array fixed on the surface of the solid phase holder, wherein the oligonucleotide probe array comprises at least two oligonucleotide probes which do not contain self-complementary sequences; one end of the oligonucleotide probe marks quantum dots and is fixed by the quantum dots, and the oligonucleotide probes with different sequences are marked by the quantum dots which emit fluorescence with different wavelengths; or the oligonucleotide probe array comprises at least two molecular beacons, wherein one end of the molecular beacon marks quantum dots and is fixed by the quantum dots, the molecular beacons with different sequences are marked by the quantum dots which emit fluorescent with different wavelengths, and the other end of the molecular beacon is marked by a fluorescence quenching group. By utilizing the basic-group complementation pairing principle and the FRET phenomenon, the detection of a plurality of special nucleic acid sequences in a nucleic acid sample to be detected can be simultaneously achieved; in addition, the invention has simple preparation and accurate, sensitive, simple, convenient and rapid detection and can detect a plurality of samples simultaneously.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF THIRD MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY OF PLA
Compounds for fluorescence imaging
InactiveUS20100278745A1Improved propertyReduce diffuseUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMicrobiological testing/measurementIonSolid phases
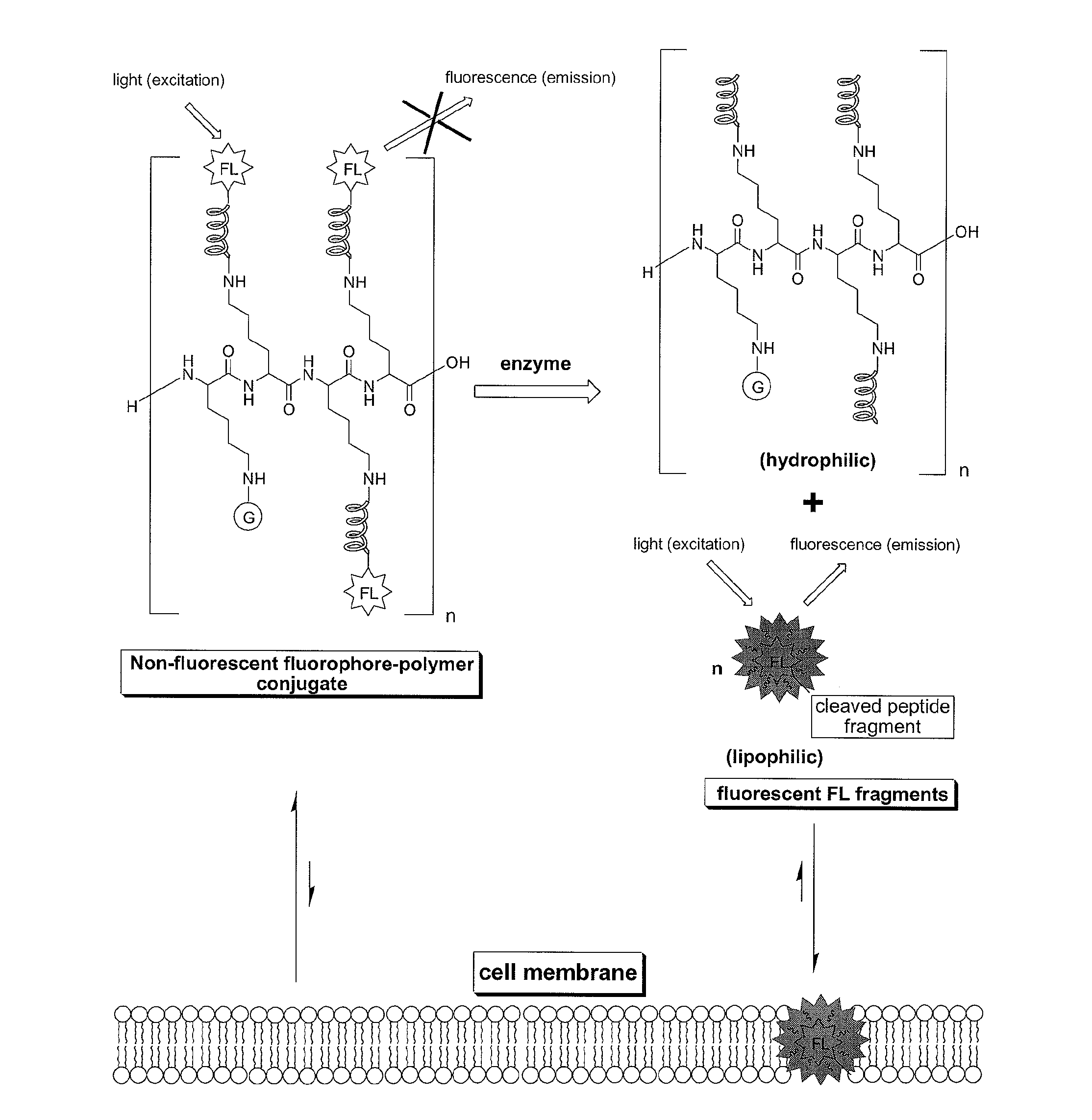
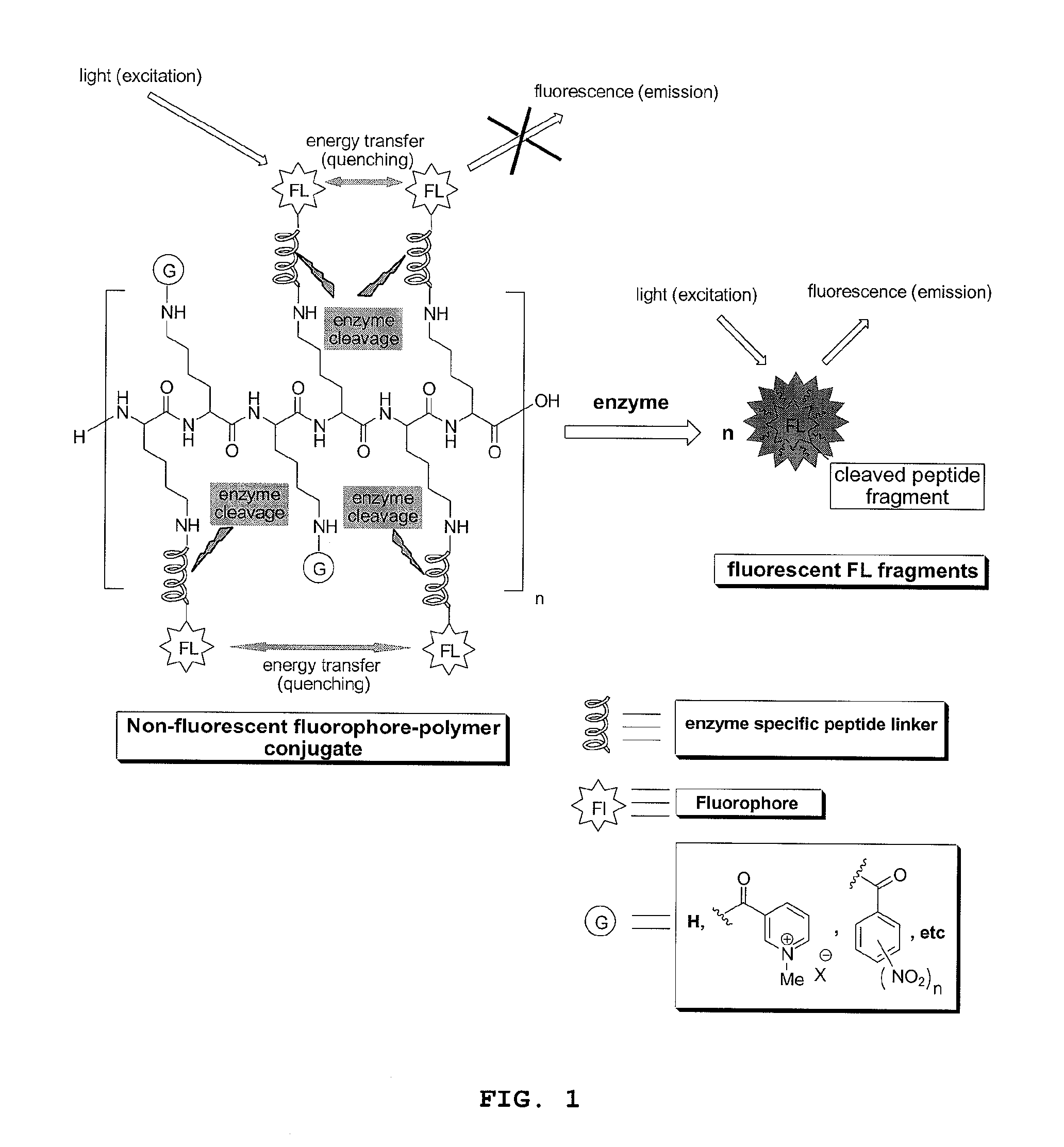
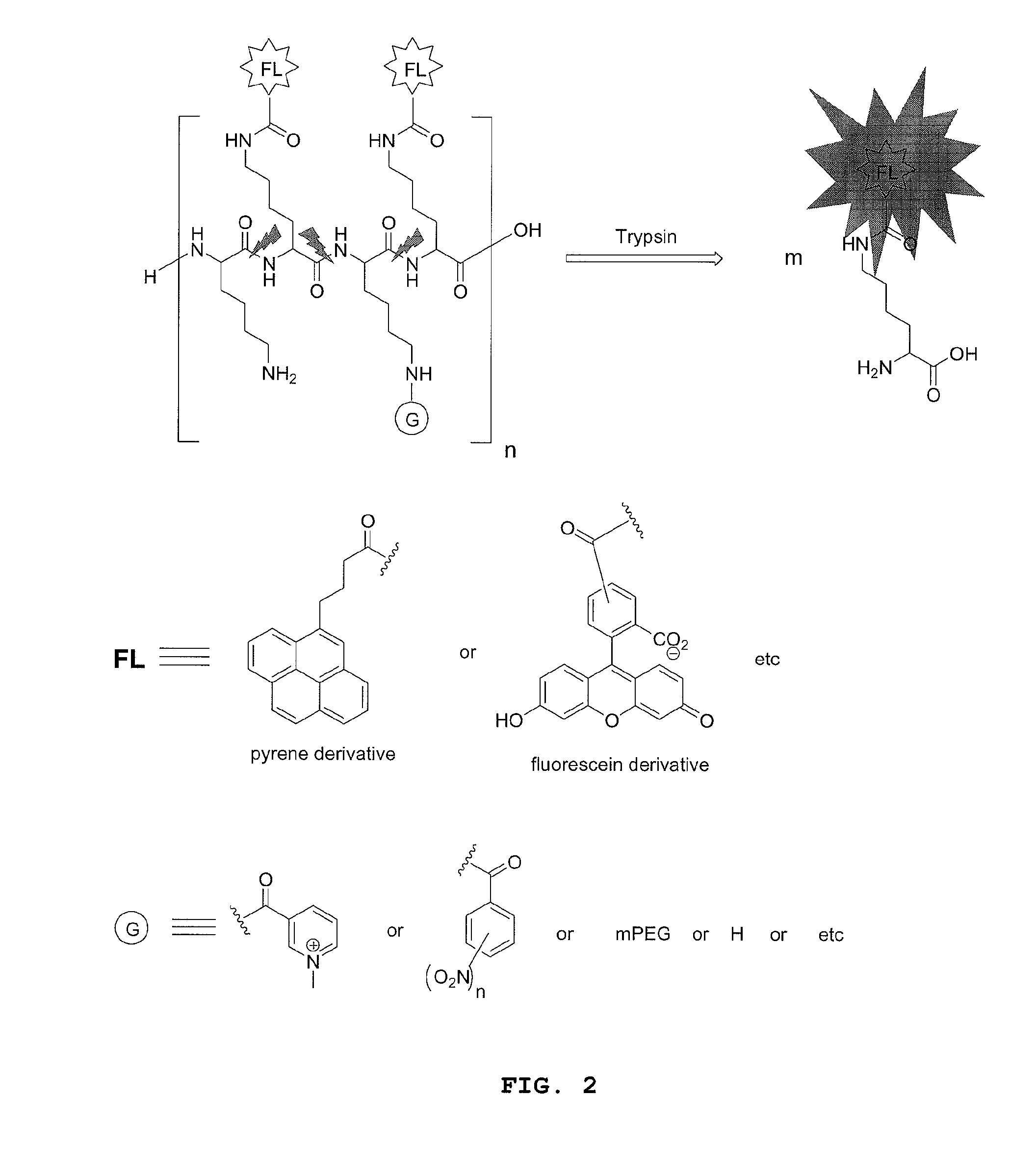
Methods and compositions involving enzyme-activatable fluorophore polymer imaging agents for photodetection of specific tissues and / or human diseases and disorders are provided. In certain embodiments, the imaging agent comprises a hydrophilic polymer backbone (e.g., poly(L)lysine), a hydrophobic fluorophore, and a hydrophilic solubilizing agent. The solubilizing agent may comprise a quarternary ammonium group (e.g., a 1-methylnicotinic group) to enhance self-quenching of the fluorophore. Various methods for the generation and purification of imaging agents are also provided, including methods involving solid phase probe extraction or ion exchange purification.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF GENEVA
S-triazine derivatives and application thereof to organic electroluminescence devices
InactiveCN103539751AHigh fluorescence quantum yieldOrganic chemistrySolid-state devicesOrganic electroluminescenceQuenching
The invention relates to s-triazine derivatives which not only can be used as organic light-emitting layers, but also can be used as main materials of phosphor materials to be applied to organic electroluminescence devices. The glass transition temperature of the s-triazine derivatives provided by the invention ranges from 70 DEG C to 180 DEG C, the triplet-state energy of the s-triazine derivatives is over 2.7eV, the molecular structure of the s-triazine derivatives contains an s-triazine group, and the s-triazine derivatives have the structural general formula I shown in the specification. The s-triazine derivatives provided by the invention have higher fluorescence quantum yield, high stability and higher steric hindrance so that the solid fluorescence quenching is avoided, and the brightness and efficiency of the devices can be well increased when the s-triazine derivatives are used as the light-emitting layers to be applied to the organic electroluminescence devices; in addition, the s-triazine derivatives have higher triplet-state energy and can be used as the main materials to effectively transfer the triplet-state energy to green and red phosphorescent materials, so that the brightness and efficiency of the organic electroluminescence devices made of the phosphor materials can be increased.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
N-CQDs (nitrogen-doped carbon quantum dots) with high fluorescence quantum yield as well as preparation method and application of N-CQDs
InactiveCN105802621AGood biocompatibilitySimple manufacturing methodFluorescence/phosphorescenceLuminescent compositionsEthylenediamineQuantum yield
The invention discloses N-CQDs (nitrogen-doped carbon quantum dots) with high fluorescence quantum yield and a preparation method of the N-CQDs. Alanine is taken as a carbon source, ethanediamine is taken as a surface passivator, and the N-doped carbon quantum dots with high fluorescence quantum yield is successfully prepared with a simple one-step hydrothermal method. Compared with carbon quantum dots synthesized with other protein or amino acid as a carbon source, the nitrogen content of the prepared N-CQDs can reach 61.1%, the average fluorescence lifetime is 4.43 ns, the highest fluorescence quantum yield can reach 46.2% and approaches the fluorescence quantum yield of the carbon quantum dots prepared with a laser ablation method and an electric arc method, and the N-doped carbon quantum dots have low cytotoxicity and excellent biocompatibility and has wide application value in biosensing and bioimaging. The invention further discloses a high quenching effect of NADH (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide) on fluorescence of the N-CQDs. On the basis that NADH has high quenching effect on fluorescence of the N-CQDs, high-sensitivity fluorescence biosensing for detecting NADH is established, the linear detection range is as low as 80 mu M, and the limit of detection is 25.1 nM.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Nano particles compounded of up-conversion nano particles and gold nanorods and preparation method and application of nano particles
InactiveCN103861103AGood treatment effectSignificant effectPowder deliveryEnergy modified materialsLight sourceNanotechnology
The invention provides nano particles compounded of up-conversion nano particles and gold nanorods and a preparation method and application of the nano particles, and belongs to the field of nano biomedicine. The method comprises the following steps: reacting up-conversion nuclear shell nano particles with a photosensitizer; and then, coupling with SiO2-coated gold nanorods to obtain the nano particles compounded of up-conversion nano particles and gold nanorods. The shell thickness of the SiO2-coated gold nanorods is 30-60nm. By means of the surface covalency or photosensitizer absorption of the up-conversion nano particles, the energy transfer efficiency is improved, so that the singlet oxygen yield is improved and the effect of photodynamics therapy is improved. Meanwhile, the acting distance betweeb the gold nanorods and the up-conversion nano particles is regulated to avoid the up-conversion fluorescence quenching phenomenon. According to the invention, upconversion and photodynamics therapy of the photosensitizer are combined with the photo-thermal effect of the SiO2-coated gold nanorods for preparing a synergic treatment nano platform. The purpose of two treatment ways are realized by one excitation light source is reached.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Carbon dots, preparation method therefor, carbon-dot composite material, preparation method therefor and luminescent LED (Light Emitting Diode)
ActiveCN106867528AImprove quantum efficiencyInhibition quenchingNanoopticsLuminescent compositionsSilicon dioxideLight-emitting diode
The invention provides a preparation method for carbon dots. The preparation method comprises the steps: mixing citric acid and urea in a solvent, and then, carrying out heating, so as to obtain a reaction solution; and carrying out centrifugal separation on the reaction solution, so as to obtain precipitates, i.e., the carbon dots, wherein the solvent is one or a mixture of two of water, glycerine and dimethylformamide. According to method, visible-light-all-waveband-luminescent carbon dots are prepared through adopting different solvents, and thus, the carbon-dot composite material provided by the invention can emit light in all wave band of visible light, particularly, white-light carbon-dot composite materials of different color coordinates and color temperatures can be obtained by adopting the carbon dots of different colors. Furthermore, the carbon-dot composite material provided by the invention employs silicon dioxide as a dispersion matrix, so that gathered induced fluorescence quenching can be inhibited, and the composite material has relatively high quantum efficiency. The invention further provides the preparation method for the carbon dots, the carbon-dot composite material, a preparation method therefor and a luminescent LED (Light Emitting Diode).
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
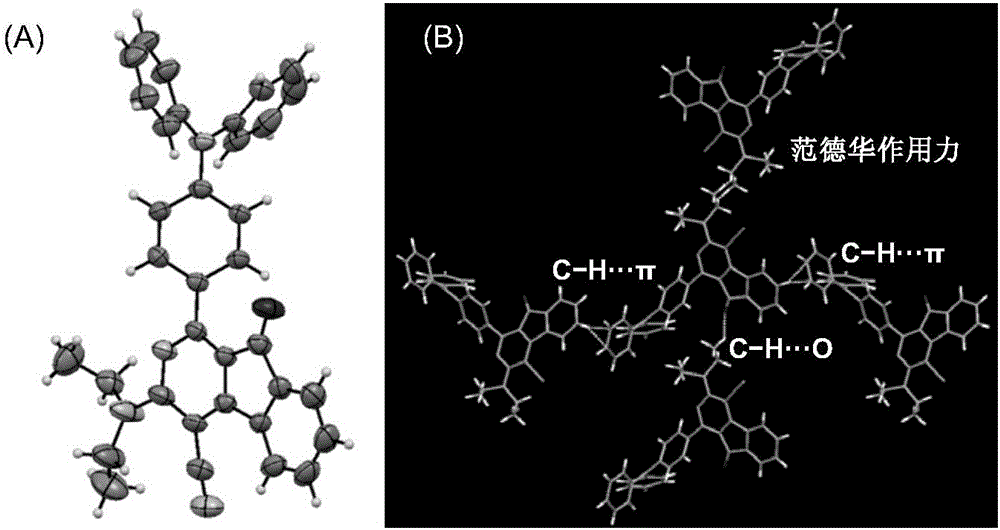
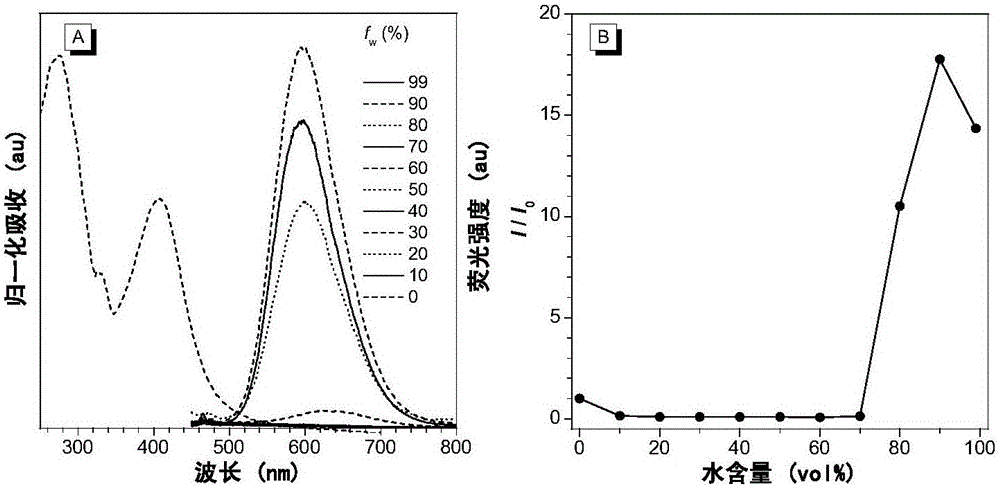
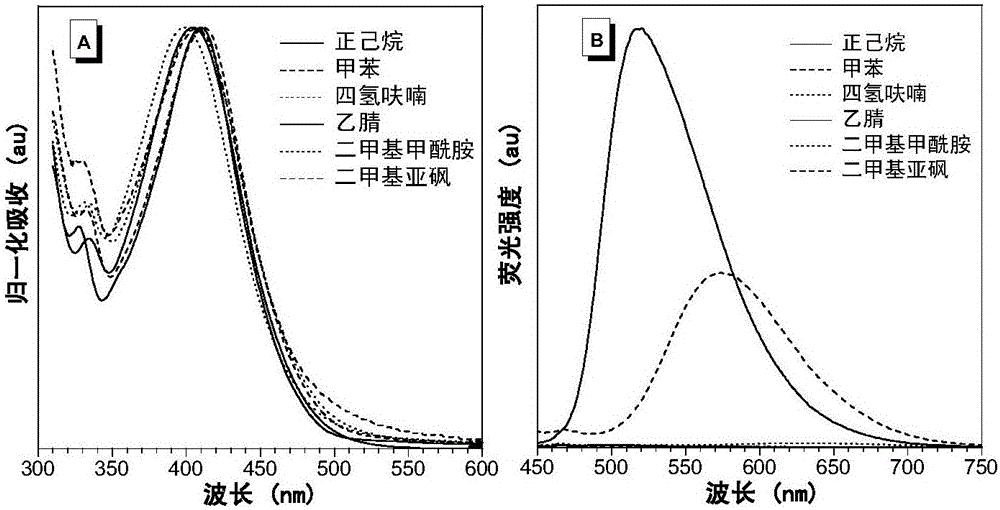
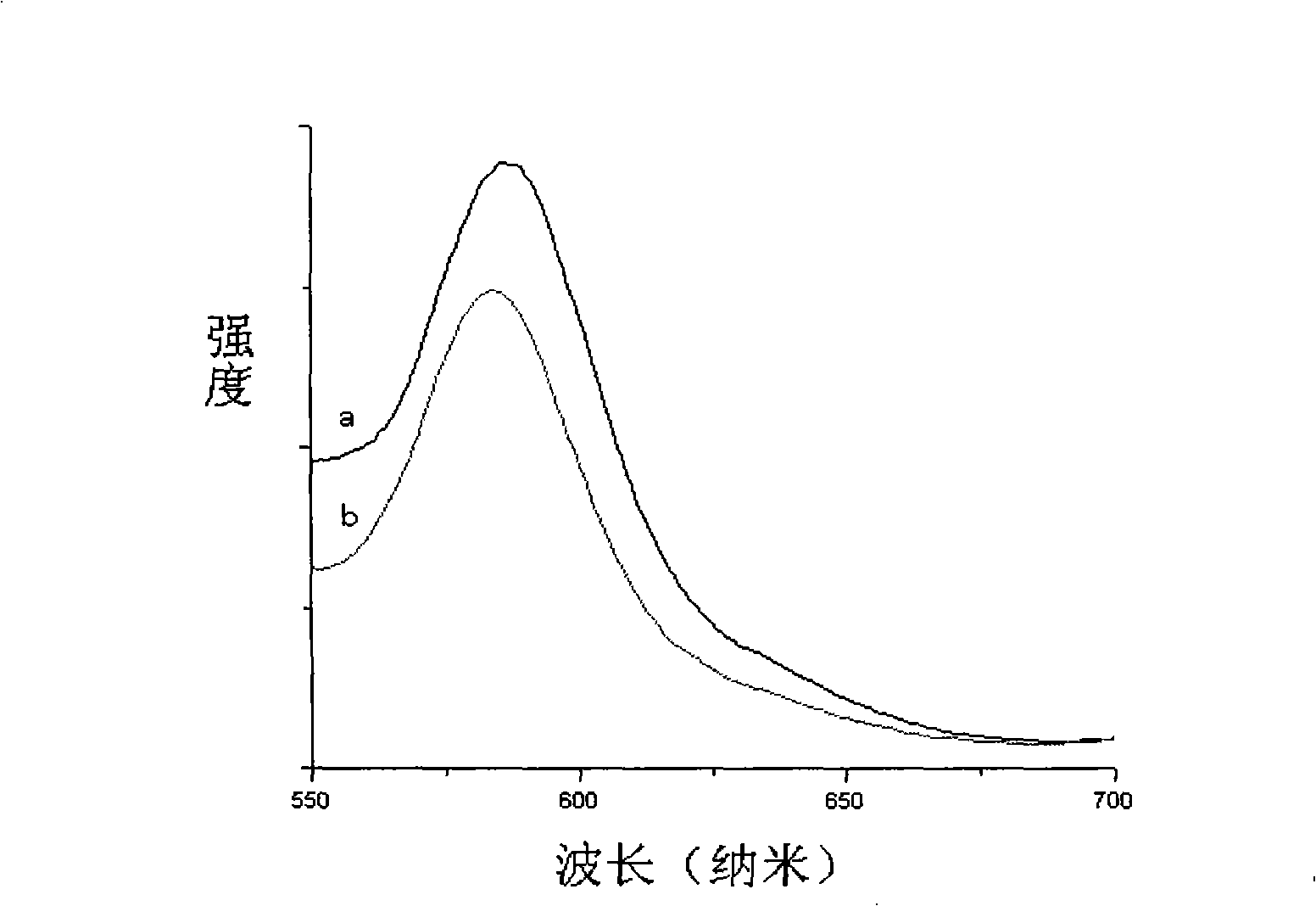
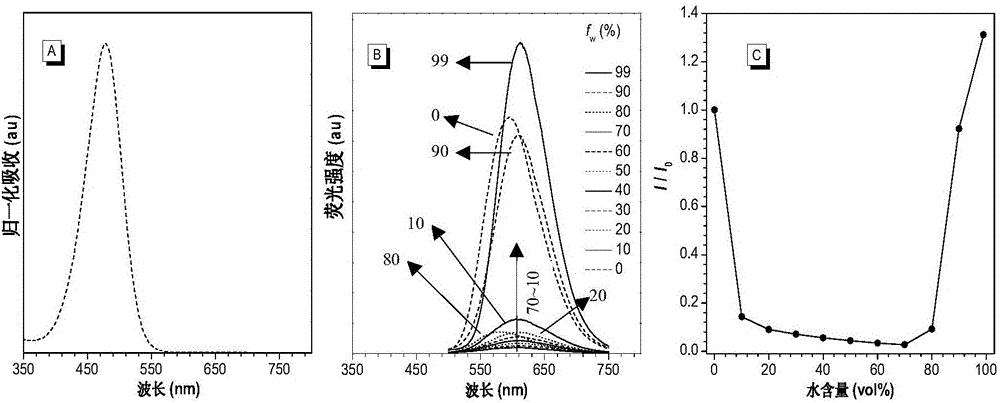
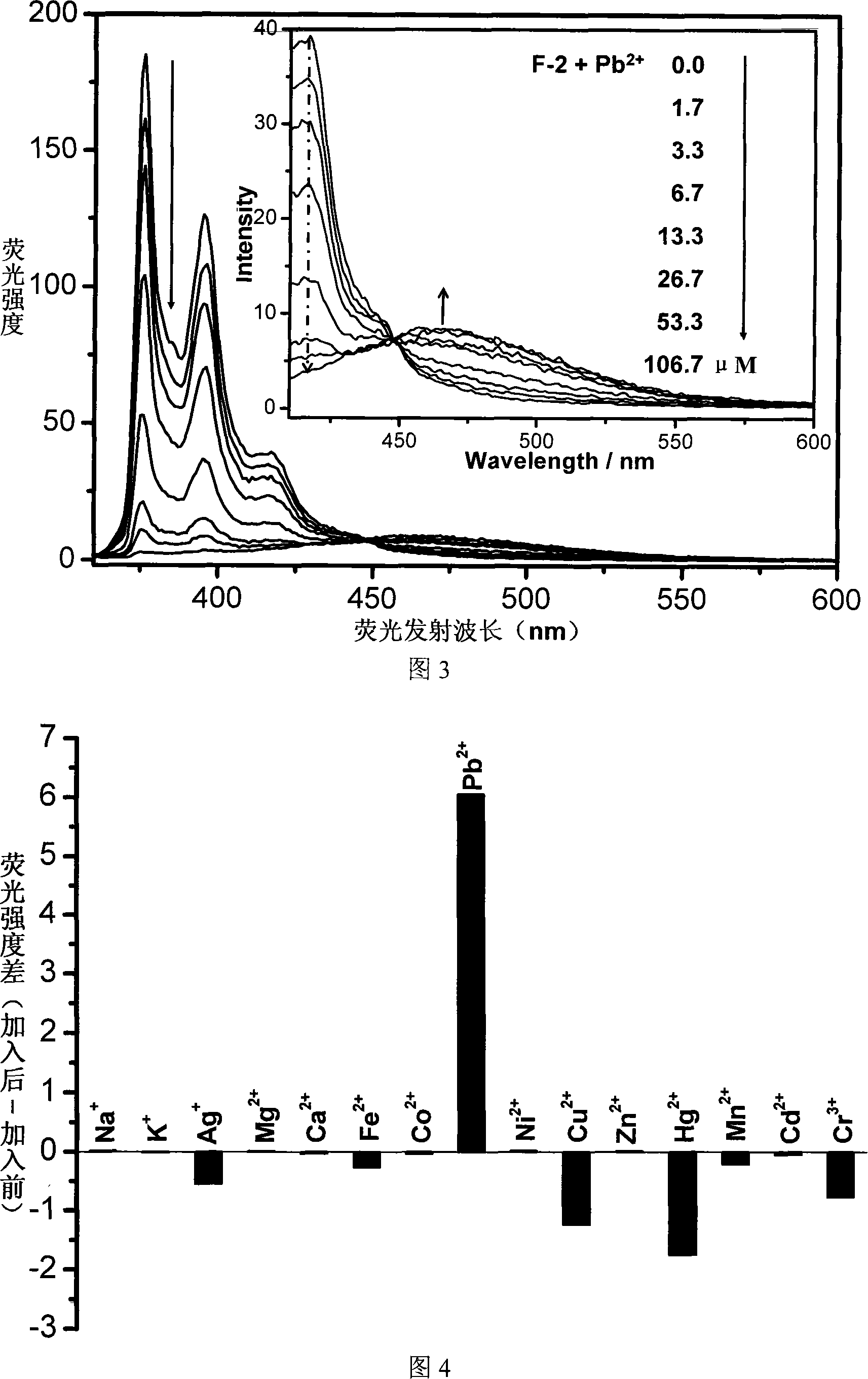
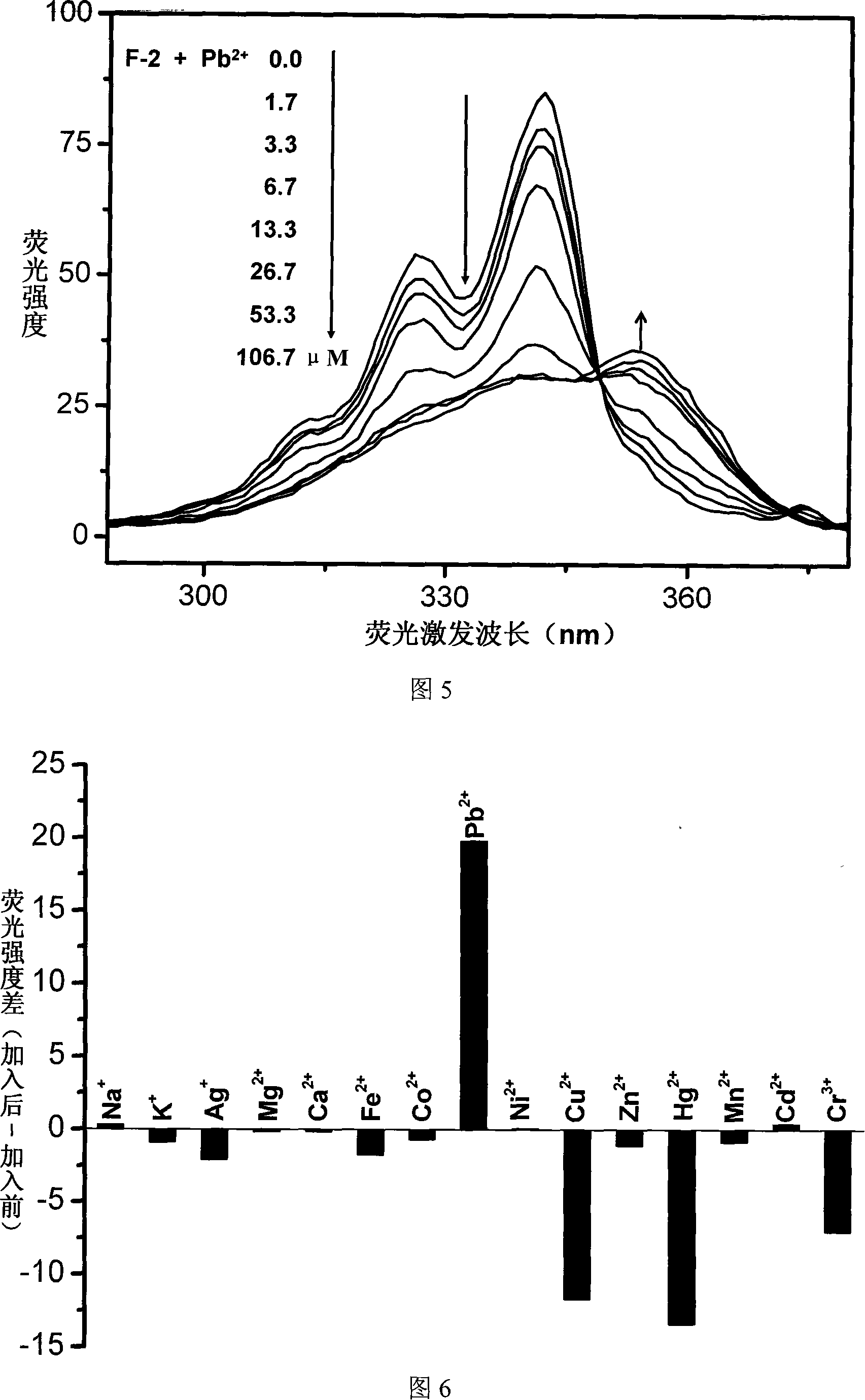
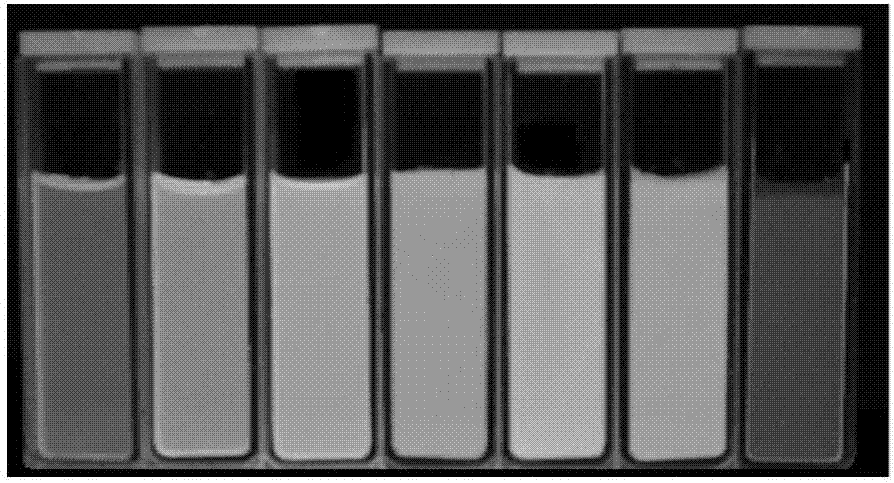
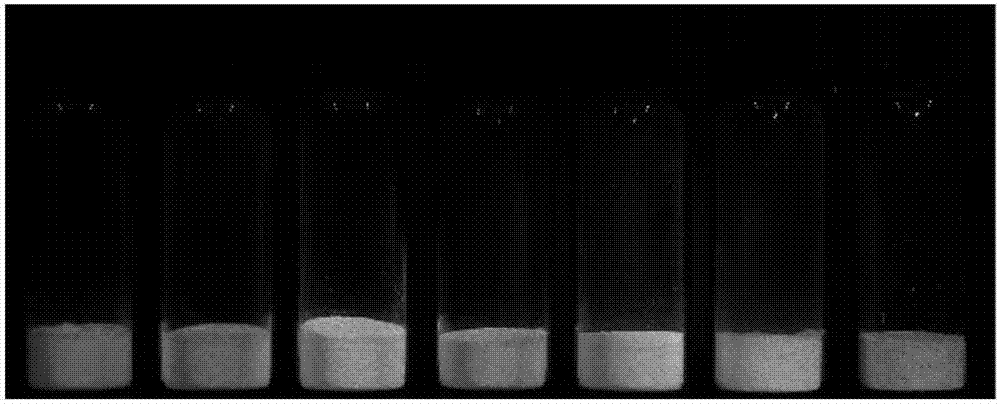
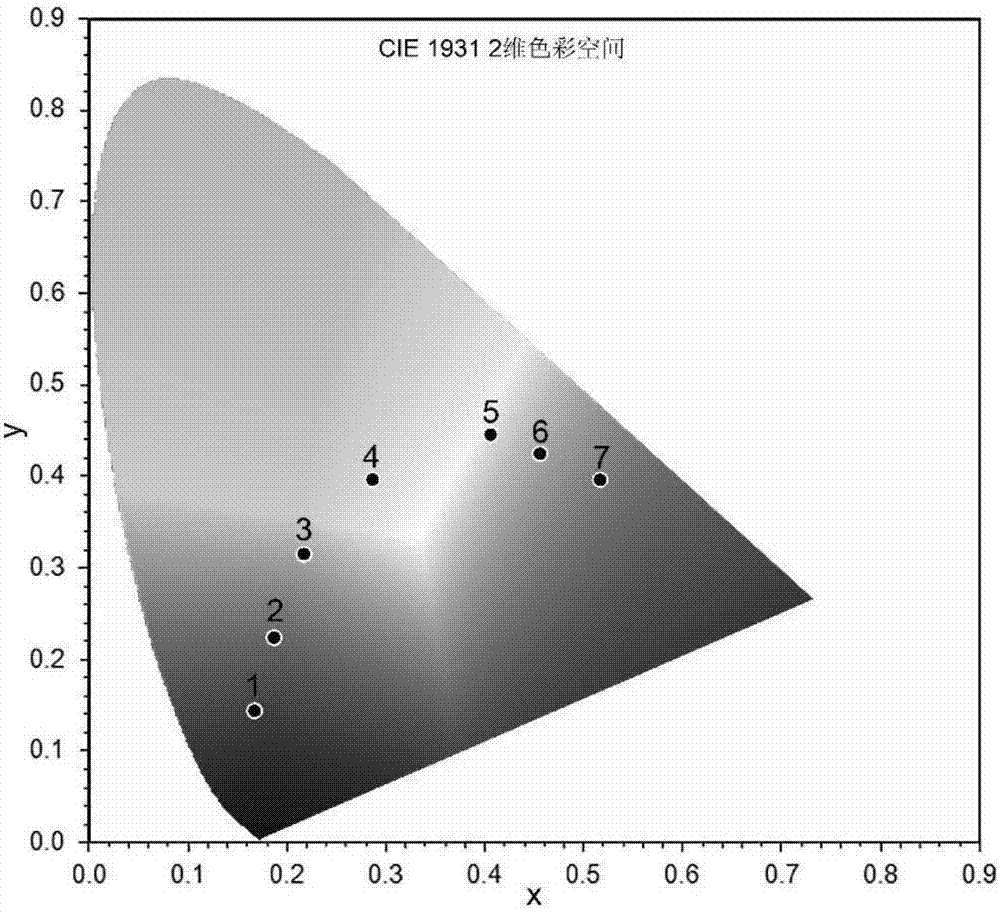
Pillar[5]arene and 2-hydroxy-3-naphthoic acid complex and preparation thereof and application in detecting iron ions and fluorine ions
InactiveCN105753662AOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic compound preparationMolecular fluorescenceFluorescent quenching
The invention provides a pillar[5]arene and 2-hydroxy-3-naphthoic acid complex.Copolymerized pillar[5]arene serves as a subject, 2-hydroxy-3-naphthoic acid serves as an object, C-H......pi and electrostatic attraction serve as driving force, partial 2-hydroxy-3-naphthoic acid provided with negative charges is included into a cavity of pillararene in an alkaline environment, the assembling process of the subject and the object is completed, and the stable pillar[5]arene and 2-hydroxy-3-naphthoic acid complex is formed.Iron ions are added to an alkaline aqueous solution of the complex, and the subject and the object are subjected to fluorescence quenching; fluorine ions are added, a complex is formed by the fluorine ions and the iron ions, so that the iron ions are separated from the cavity of copolymerized pillar[5]arene, and molecular fluorescence of the complex is reopened.Therefore, Fe<3+> can be determined through the pillar[5]arene and 2-hydroxy-3-naphthoic acid complex, and F<-> can be continuously identified through fluorescence quenching of the solution.
Owner:NORTHWEST NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Mercury ion detection method
InactiveCN103884701ADetection interference is smallImplement selective detectionFluorescence/phosphorescenceMercuric ionIon pairs
The invention discloses a mercury ion detection method which is characterized by comprising the following steps: (1) mixing a standard mercury ion solution and a gold nanocluster solution, and establishing a standard curve for detecting the fluorescence signal quenching of nanocluster and the mercury ion quantity; and (2) mixing a sample solution with the gold nanocluster solution, substituting the quenching intensity of the fluorescence signal of the nanocluster into the standard curve, thereby obtaining the content of the mercury ion in the sample. The method has the advantages that the sensitivity is high, the interference of other ions on detection of the mercury ion is slight, and selective detection of the mercury ion can be realized, so that the aim of rapidly detecting the mercury ion concentration is achieved. The method has wide application prospects in mercury ion detection.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU TOBACCO RES INST OF CNTC
Preparation method of quantum dot@Cu nano-cluster ratiometric fluorescent sensor and application thereof in Cu<2+> detection
InactiveCN104745194AFix interferenceHigh precisionFluorescence/phosphorescenceLuminescent compositionsFluoProbesFluorescent quenching
The invention discloses a preparation method of a quantum dot@Cu nano-cluster ratiometric fluorescent sensor and application thereof in Cu<2+> detection, belonging to the technical field of fluorescence sensing. According to the preparation method, CuNCs prepared by taking polyethyleneiminen as a template is coupled to the surface of silicon dioxide coated CdSe QDs to prepare CdSe QDs@CuNCs ratiometric fluorescent sensor having CdSe QDs and CuNCs double-fluorescence emission signals. When Cu<2+> exists in a solution, amino of polyethyleneimine and Cu<2+> are subjected to complexing to form a copper-amine complex, thereby avoiding the problem that CuNCs fluorescence quenching is caused but the fluorescence intensity of CdSe QDs is unchanged because electrons are transferred from amino to CuNCs. With the increase of Cu<2+> concentration, the intensity ratio of two fluorescence emission peaks of CdSe QDs and CuNCs is reduced gradually, thereby realizing sensitive fluorescent and visual detection on Cu<2+>.
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV
Fluorescent wide chroma test paper for visually detecting copper ions as well as preparation method and application of test paper
ActiveCN107345910AAvoid interferenceWide range of discolorationFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluorescenceColor changes
The invention discloses fluorescent wide chroma test paper for visually detecting copper ions as well as a preparation method and application of the test paper. The preparation method comprises the following steps: by taking a three-color ratio fluorescence probe as ink and taking filter paper as a solid-phase carrier through an inkjet printer, uniformly printing, thereby obtaining the test paper capable of visually detecting the copper ions, wherein the three-color ratio fluorescence probe refers to blue carbon dots, green quantum dots and red quantum dots, and the quantum dots are all modified by 3-mercaptopropionic acid. The three-color ratio fluorescence test paper is constructed to be used for visually detecting the copper ions by utilizing double-quenching principle first, the prepared detection test paper has the advantage that the color change range is wide compared with the conventional double-ratio fluorescence test paper, and along with addition of the detection object, test paper colors can be obviously identified by naked eyes from light scarlet, light flesh color, deep orange, grass green, dark olive green, slate blue, royalblue to cyanic color (Figure 4).
Owner:NANJING MEDICAL UNIV
Compound with aggregation induced luminescence property and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN106565606AHigh photoactivation efficiencyImprove signal-to-noise ratioOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceCancer cellCytotoxicity
The invention discloses a compound with an aggregation induced luminescence property and a preparation method and application thereof in lipid droplet targeting light activating fluorescence imaging. The structure of the compound and the structure of an intermediate product of the compound are represented as the formula I and the formula II, and the formula I can be converted to generate the formula II under the light condition. The compound in the formula I is prepared through the following steps that a compound in the formula III and a compound in the formula IV are dissolved in acetonitrile under the protection of nitrogen, light avoiding reaction is conducted, and the 1,2-dihydro-2-diphenyleneimine ketone compound in the formula I is generated. The novel compound with the aggregation induced luminescence property has the aggregation induced luminescence advantage and can effectively overcome the aggregation induced quenching defect of traditional fluorescent dye, and thus lipid droplet targeting specificity light activating fluorescence imaging in a living cell can be achieved; in addition, the compound has the advantages that the light activating efficiency and the signal-to-noise ratio are high, the cytotoxicity is small, the Stokes shift is large, and the capability of the compound to enter cells is high; and cancer cells and normal cells can be effectively distinguished.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Preparation method and application of single-particle double-emission ratiometric fluorescent probe
ActiveCN110194950AImprove stabilityRealize visual detectionMaterial nanotechnologyNanoopticsSilicon oxideQuenching
The invention discloses a preparation method and application of a single-particle double-emission ratiometric fluorescent probe. Specifically, the preparation method of the single-particle double-emission ratiometric fluorescent probe includes: firstly preparing carboxylated silicon oxide with embedded red CdTe quantum dots, and then conducting surface covalent coupling of aminated blue carbon dots to construct the double-emission ratiometric fluorescent probe. The ratiometric fluorescent probe provided by the invention combines a fluorescence quenching system constructed by gold nanoparticlesand can be used for fluorescence enhanced detection of pesticide thiram, on the basis of fluorescence resonance energy transfer between gold nanoparticles and carbon dots, blue fluorescence can quench, red fluorescence silicon oxide is used as the internal standard, after adding of thiram, as the strong bonding effect of gold nanoparticles and sulfur atoms results brings about agglomeration, blue fluorescence recovers, and the process of closing and reopening of blue fluorescence can be realized, thus realizing the detection of thiram. The method has the advantages of high sensitivity, goodselectivity, strong anti-interference ability and low detection limit, and also can be used for detection of practical samples.
Owner:中科合肥智慧农业谷有限责任公司
Reagent for detecting brucella and complex probe fluorescence quantitative PCR (polymerase chain reaction) brucella detection method
InactiveCN102146466ASimple and efficient operationGuaranteed specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceQuenchingFluorescence
The invention provides a reagent for detecting brucella. The reagent comprises an upstream primer, a downstream primer, a fluorescence probe and a quenching probe; the gene sequence of the upstream primer is 5'-caagggcaaggtggaagatt-3'; the gene sequence of the downstream primer is 5'-ctgcgaccgatttgatgttt-3'; the gene sequence of the fluorescence probe is 5'-fam-atcgtttccgggtaaagcgtcgcca-P-3'; and the gene sequence of the quenching probe is 5'-cgctttacccggaaacga-Dabcyl-3'. The invention also provides a complex probe fluorescence quantitative polymerase chain reaction (PCR) brucella detection method using the reagent. The method is simple and convenient in operation, efficient, quick and specific; the detection time of the brucella is greatly shortened; the quantitative detection of a sample can be completed in about 2 hours; and the reagent and the method have significance for early diagnosis of brucella disease.
Owner:浙江国际旅行卫生保健中心
Core-shell structured quantum dot composite nanocrystalline fluorescence probe and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104726085AImprove performanceImprove luminous efficiencyMaterial nanotechnologyNanoopticsIonQuantum yield
The invention belongs to the technical field of preparation of nanometer materials and bioanalysis detection, and particularly relates to a core-shell structured quantum dot composite nanocrystalline fluorescence probe and a preparation method thereof. The invention provides the preparation method for a ZnSe quantum dot core-shell structured composite nanocrystalline. The shell of the composite nanocrystalline is a composite silicon dioxide shell containing ZnS semiconductor clusters, and by the coating of the composite silicon dioxide shell, the photochemical stability and quantum yield of quantum dots are obviously improved; meanwhile, based on the fluorescence quenching effect of the quantum dots, the fluorescence probe used for detecting trance heavy metal ions is prepared. According to the preparation method disclosed by the invention, the reaction condition is mild, the operation method is simple, the prepared core-shell structured composite nanocrystalline has good physicochemistry stability and biocompatibility, and the prepared probe has very high sensibility and good stability, and has wide application prospect in the fields of biosensors, fluorescence probes, biomarkers and the like.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
Rate type fluorescent probe used for mercuric ion detection and preparing method thereof
InactiveCN107884376AHigh sensitivityHigh selectivityFluorescence/phosphorescenceMercuric ionFluorescence
The invention provides a rate type fluorescent probe used for mercuric ion detection. The probe is formed by dual-emitter nanometer material gold / silver nanoclusters wrapped by bovine serum albumin, and the fluorescence-emission wavelength is 400-550 nm and 580-680 nm. The dual-emitter nanometer material gold / silver nanoclusters are synthesized through a one-pot method by using the bovine serum albumin (BSA) as a reducing agent and a stabilizer. The synthesized gold / silver nanoclusters (Au / Ag NCs) have two emission peaks, wherein Ag NCs serves as a reference signal Au NCs serves as a responsesignal and is used for selective recognition of Hg2+. When the dual-emitter gold / silver nanoclusters serve as the rate type fluorescent probe, the Ag NCs fluorescent signal intensity is kept unchangedbasically, and Au NCs is selectively combined with Hg2+ to cause fluorescence quenching. The method is quick, simple, low in detection limit, wide in linear range and high in selectivity.
Owner:SICHUAN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Dopamine derivative, molecular imprinted polymer and preparation methods and application of dopamine derivative and molecular imprinted polymer
InactiveCN103992252AEfficient separationLow detection limitSulfonic acid amide preparationFluorescence/phosphorescenceMolecularly imprinted polymerSorbent
The invention discloses a dopamine derivative, a molecular imprinted polymer and preparation methods and application thereof. The dopamine derivative comprises dansyl dopamine, carbazole sulfonyl dopamine and the like. The dopamine derivative is synthesized from a fluorescent color former precursor and dopamine through sulfonation reaction. The fluorescent molecular imprinted polymer is prepared by using the fluorescent dopamine derivative, integrates specific sample pretreatment and fluorescence detection and is linked with an ELISA (Enzyme-Linked Immuno Sorbent Assay) plate, so as to form a fluorescent sensor, and series acidic organic pollutants, including bisphenol A and 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid, in an environmental water sample are directly assayed according to the change of fluorescence quenching values before / after sample application.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
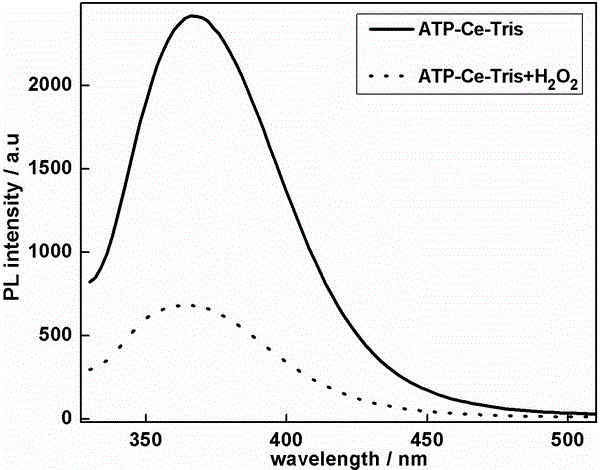
Preparation method of rare-earth coordination polymer fluorescence probe and application of rare-earth coordination polymer fluorescence probe in H2O2 and glucose detection
InactiveCN105949473AReduce fluorescenceFluorescence/phosphorescenceLuminescent compositionsCatalytic oxidationOxidative enzyme
The invention discloses a preparation method of a rare-earth coordination polymer fluorescence probe and an application of the rare-earth coordination polymer fluorescence probe in H2O2 and glucose detection and belongs to the technical field of optical sensing. The preparation method comprises steps as follows: triphosadenine is mixed with a Tris-HCl buffer solution containing Ce<3+>, and the rare-earth coordination polymer fluorescence probe ATP-Ce-Tris is prepared; when H2O2 is present in the solution, Ce<3+> in the ATP-Ce-Tris is oxidized into Ce<4+> by H2O2 to result in fluorescence quenching of the ATP-Ce-Tris, and accordingly, detection of H2O2 is realized; simple and sensitive detection of glucose is further realized through fluorescence quenching of the ATP-Ce-Tris due to H2O2 which is produced through catalytic oxidation of glucose by glucose oxidases.
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV
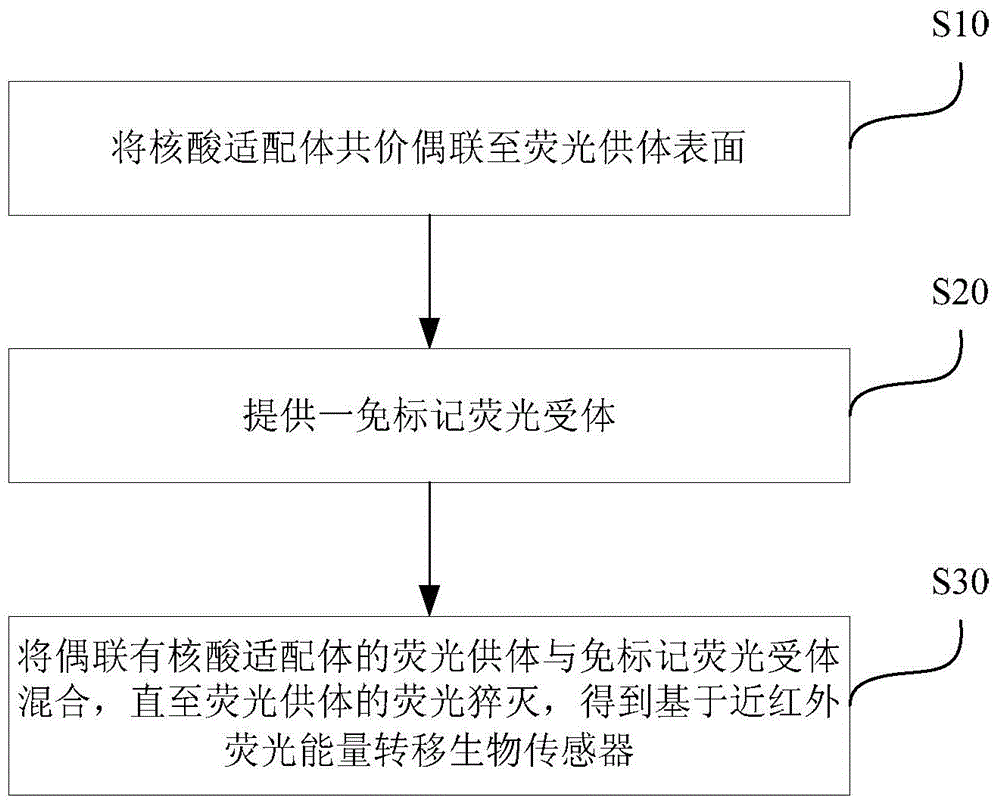
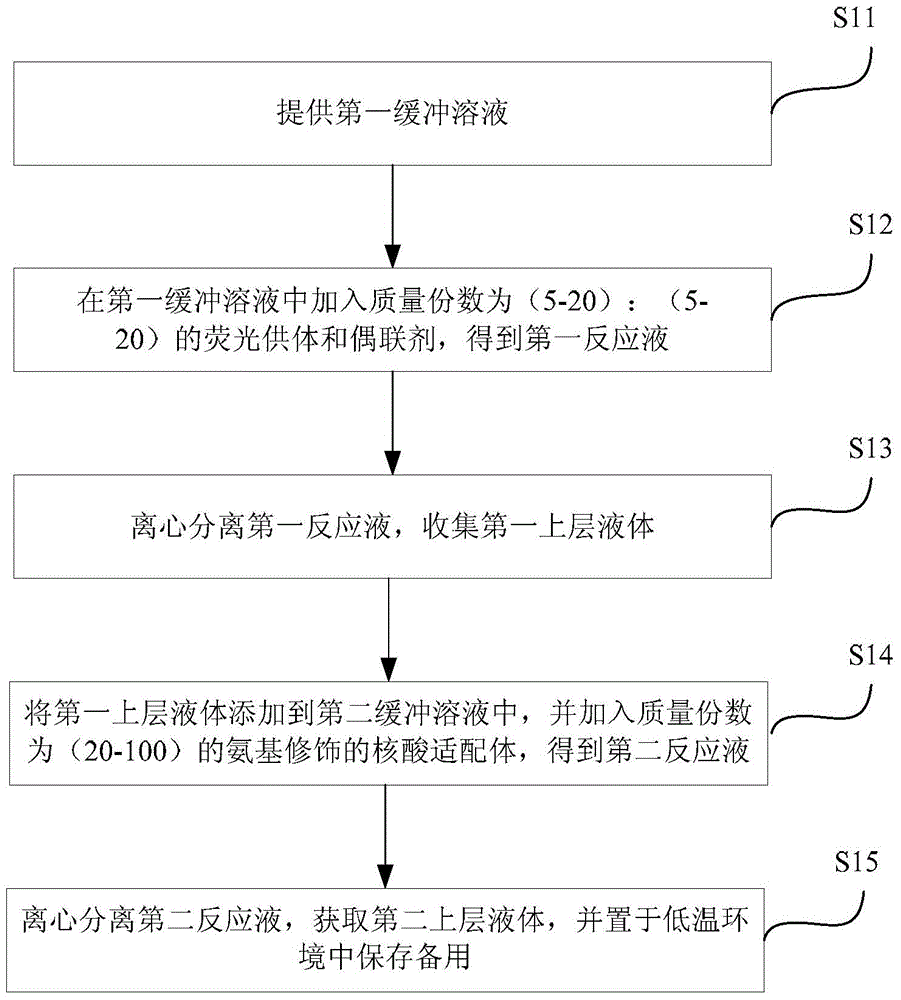
Construction method for near infrared fluorescence energy transfer based biosensor
ActiveCN104697968AAvoid optical interferenceHigh detection sensitivityFluorescence/phosphorescenceQuenchingLabel free
The invention provides a construction method for a near infrared fluorescence energy transfer based biosensor. The method includes: subjecting a nucleic acid aptamer to covalent coupling to a fluorescent donor surface, mixing the nucleic acid aptamer coupled fluorescence donor with a label-free fluorescent receptor till fluorescence quenching of the fluorescence donor, thus obtaining the near infrared fluorescence energy transfer based biosensor. As the sensor detection window is located in a near infrared region, the background fluorescence, the background fluorescence, scattered light, light absorption and other optical interference can be well overcome, and the detection sensitivity is improved. The biosensor can be directly applied to complex biological matrix analysis.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Homogenous assay for enzymatic activity
InactiveUS20050106655A1Reduce the amount of solutionLess quenchingMicrobiological testing/measurementNickel organic compoundsProteinase activityFluorescence
Owner:PIERCE BIOTECHNOLOGY
Biological thiol fluorescent probe as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN103102338AImproving the imaging signal-to-noise ratioHigh fluorescence stabilityOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceQuenchingImaging Signal
The invention discloses a biological thiol fluorescent probe. According to the biological thiol fluorescent probe, a first fluorophore is used as an energy donor for emitting fluorescence, and a second fluorophore or quenching group is used as an energy acceptor for absorbing fluorescence. The biological thiol fluorescent probe has the structure of R-S-S-R', wherein R comprises the first fluorophore, and the R' comprises the second fluorophore or quenching group. The invention further provides a preparation method and an application of the biological thiol fluorescent probe. The biological thiol fluorescent probe uses the fluorescence intensity per se to attenuate or quench, thus the imaging signal to noise ratio is increased. In addition, the biological thiol fluorescent probe has high fluorescence stability after the thiol is subjected to reaction. The biological thiol fluorescent probe is easy to prepare and can be prepared at normal temperature and pressure and neutral pH value.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH
Method for preparing rhodamine intercalation hydrotalcite luminescent material
InactiveCN101255334AImmobilizationEvenly dispersedHydrotalciteSilicon compoundsSlurryMembrane reactor
A hydrotalcite composite luminescent material with rhodamine intercalation, which pertains to abio-organic composite luminescent material. The process is preparing solution A with mole ratio of bivalence and tervalence cation M2+ / M3+=2.0-4.0; adding laser dye sulphonated rhodamine and sodium salt of dodecylbenzene sulfonic acid into mixed solution of ethanol and water and fully dissolving to obtain solution of sulphonated rhodamine and dodecyl benzene sulfone acid group containing anion with negative charge B; mixing solution A, B into solution C, preparing NaOH solution; communicating solution C and NaOH solution into full-back-liquid mixing membrane reactor to react, mixing to obtain red slurry, introducing the red slurry into hydrothermal kettle, reacting, absterging by CO2, de-ionized water and absolute ethyl alcohol and centrifugally separating, vacuum drying. Then hydrotalcite system with co-intercalation of suphonated rhodamine and dodecyl sulfone acid group is obtained. Advantages of the invention are that dye molecular is immobilized, and fluorescence quenching caused by dye aggregation is reduced.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Benzylidene indandione compound and preparation thereof and application in specific imaging of lipid droplet
ActiveCN106674028AEasy accessEasy to manufactureOrganic chemistryOrganic compound preparationFluorochrome DyePhotochemistry
The invention belongs to the field of medical materials, and discloses a benzylidene indandione compound and a preparation thereof and an application in specific imaging of a lipid droplet. The structure of the benzylidene indandione compound is as shown in a formula I. The benzylidene indandione compound has the advantage of aggregation-induced emission, and the defects of aggregation-induced quenching of a traditional fluorescent dye can be effectively overcome, so that the specific fluorescence imaging of the lipid droplet in a living cell can be achieved; furthermore, the benzylidene indandione compound has a two-photon absorption cross-section which is high in living cell penetration rate, high in signal to noise ratio, small in cytotoxicity, large in stokes shift and large in near infrared region. The formula I is as shown in the specification.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Organic electroluminescent device, method of preparing same, display substrate, and display apparatus
ActiveUS20160301024A1Inhibition of agglomerationHigh quantum yieldSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingQuantum yieldFiber
This invention provides an organic electroluminescent device, a method of preparing the same, a display substrate comprising the same, and a display apparatus. According to the invention, the agglomeration and self quenching of quantum dots can be effectively prevented as the quantum dots are uniformly dispersed in electroluminescent polymer fibers. Due to the fluorescence resonance energy transfer effect between the electroluminescent polymer and the quantum dots, a higher quantum yield is achieved, and the luminescence efficiency of the quantum dots can be improved accordingly. Furthermore, since the light emission from the quantum dots is achieved by the fluorescence resonance energy transfer effect, which is an energy transfer process without damage to the quantum dots, the damage to quantum dots is less and thus the lifetime thereof can be beneficially increased, as compared to the direct charge injection mode of the prior art.
Owner:BOE TECH GRP CO LTD
Nitrogen doped graphene quantum dots as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN110499155AHigh yieldUniform structureMaterial nanotechnologyNanoopticsFluorescenceNitrogen doped graphene
The invention discloses nitrogen doped graphene quantum dots as well as a preparation method and application thereof in detecting mercury ions and cysteine and belongs to the technical field of fluorescence sensation. The preparation method comprises the following steps: dissolving a carbon source compound and a nitrogen source compound into water so as to obtain a mixed water solution, and performing a hydrothermal reaction under an alkali condition, so as to obtain the nitrogen doped graphene quantum dots, wherein the carbon source compound is 1,3,6-trinitropyrene; the nitrogen source compound is tryptophan; and the alkali condition is adjusted by using sodium hydroxide. The preparation method is high in yield, and gram-grade synthesis can be achieved at one time. Due to doping of high-content nitrogen atoms, the prepared nitrogen doped graphene quantum dots have glue fluorescence and have unique mercury ion selectivity. On the basis of quenching of mercury ions upon fluorescence ofthe nitrogen doped graphene quantum dots, sensitive fluorescence detection on the mercury ions can be achieved, and the detection limit is low. As the fluorescence quenched by the mercury ions can berecovered by using the cysteine, fluorescence detection on the cysteine can be achieved with the combination of the nitrogen doped graphene quantum dots and the cysteine.
Owner:广西医科大学附属肿瘤医院
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com

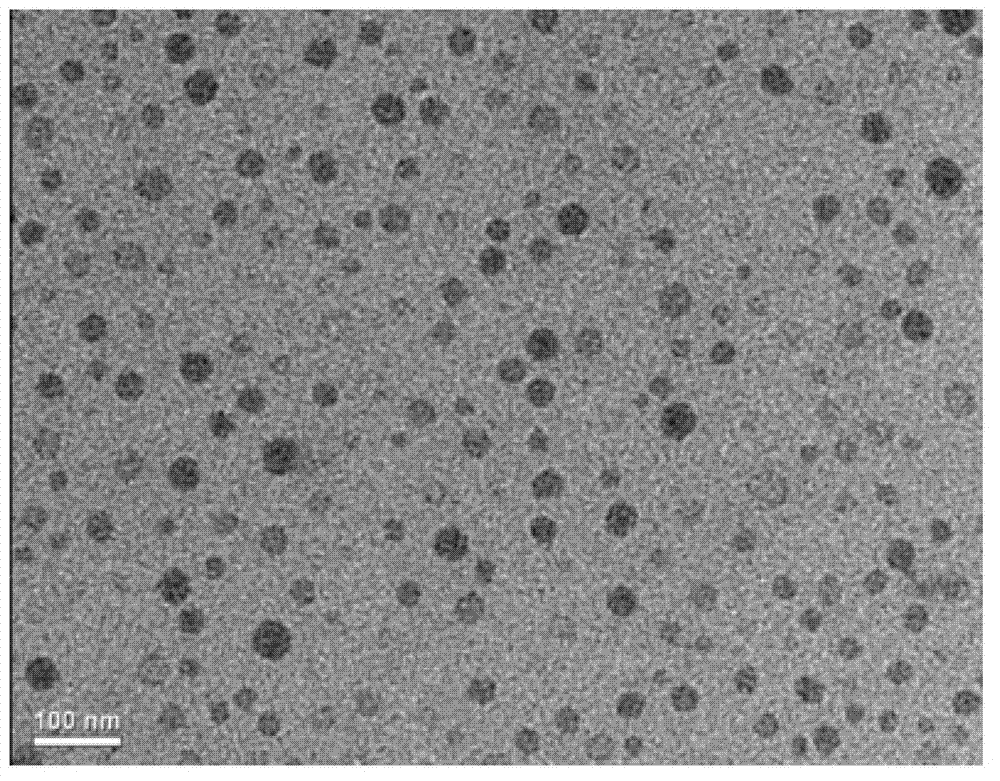
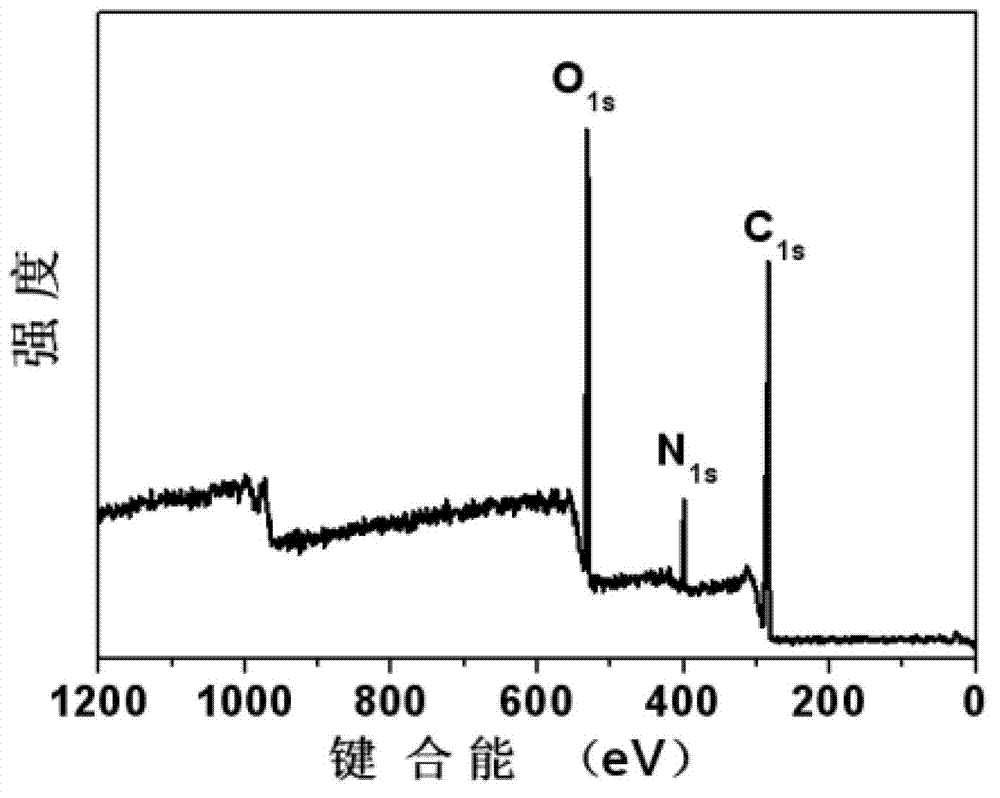
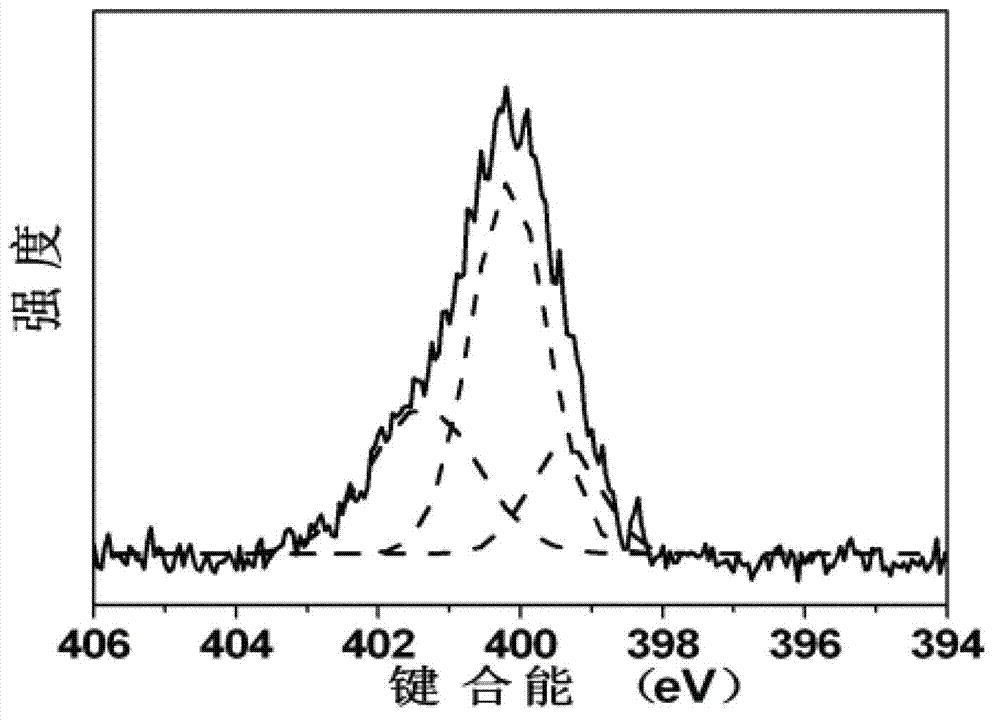
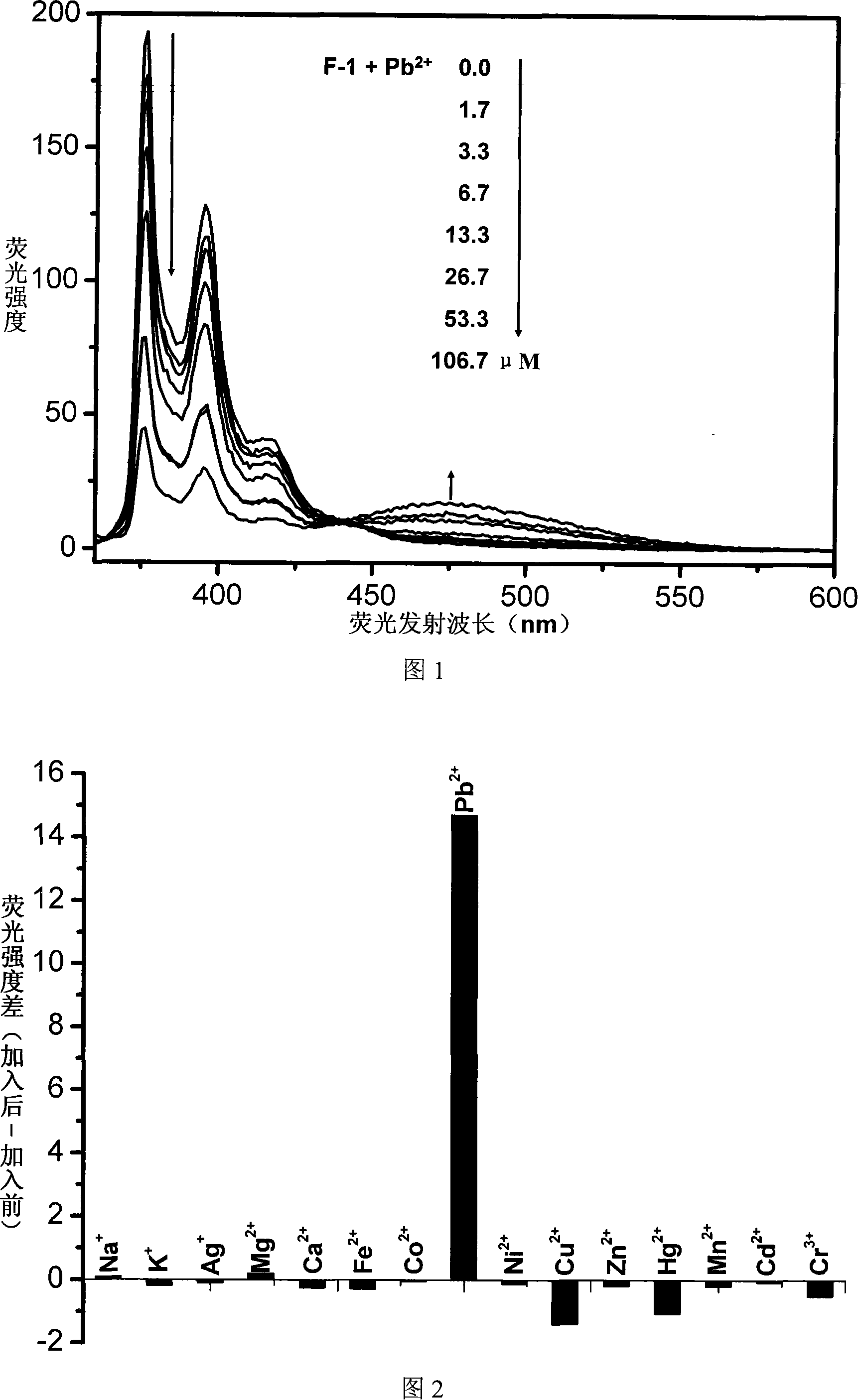

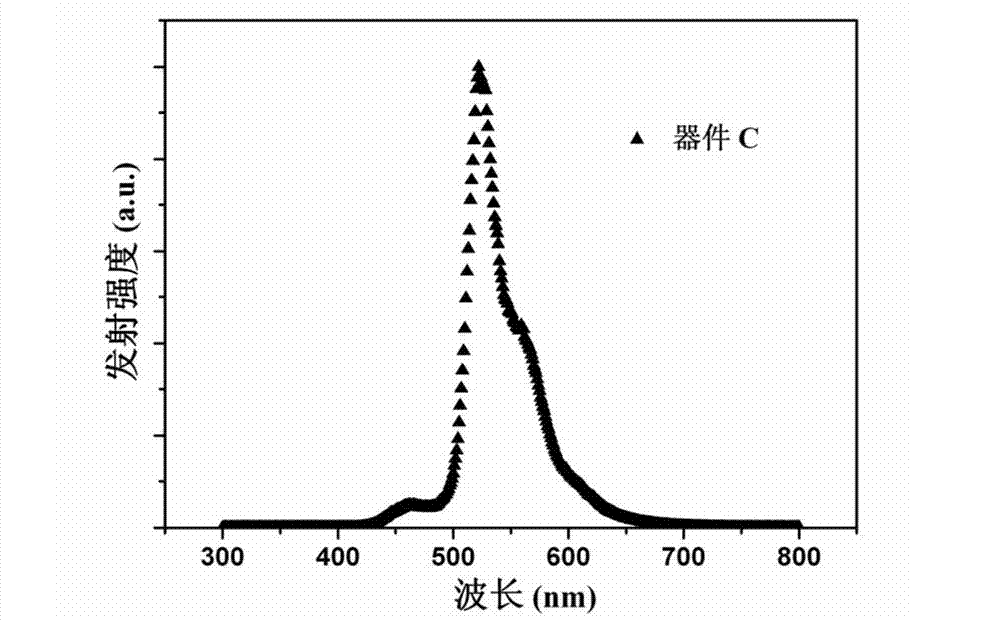


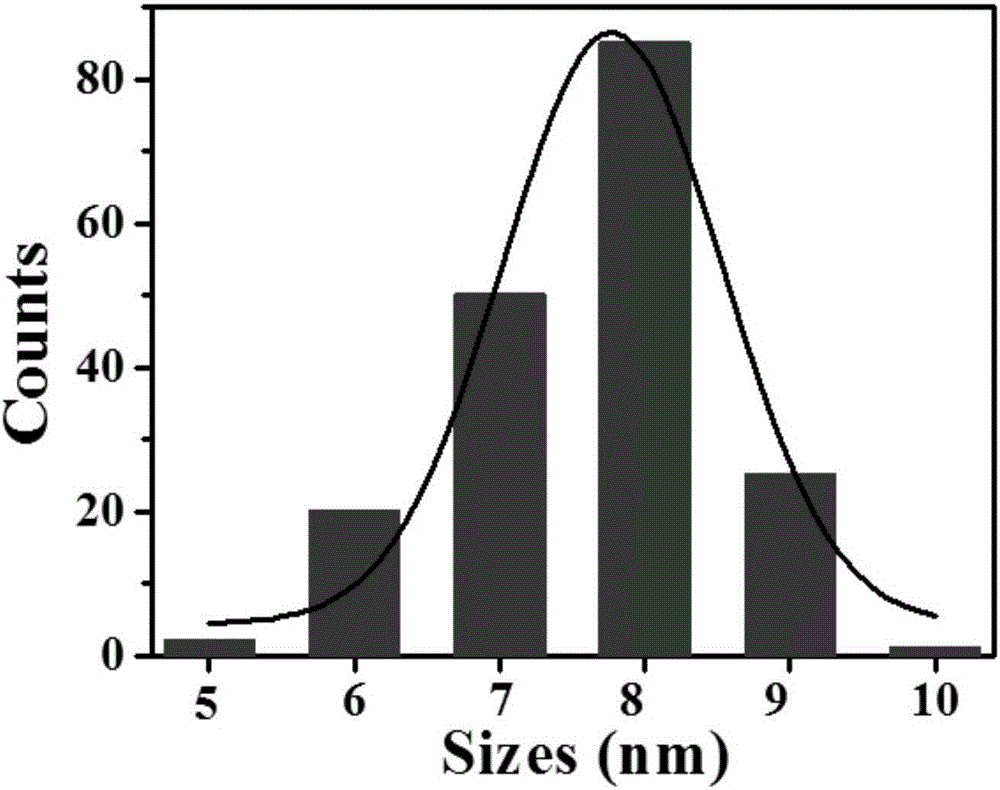
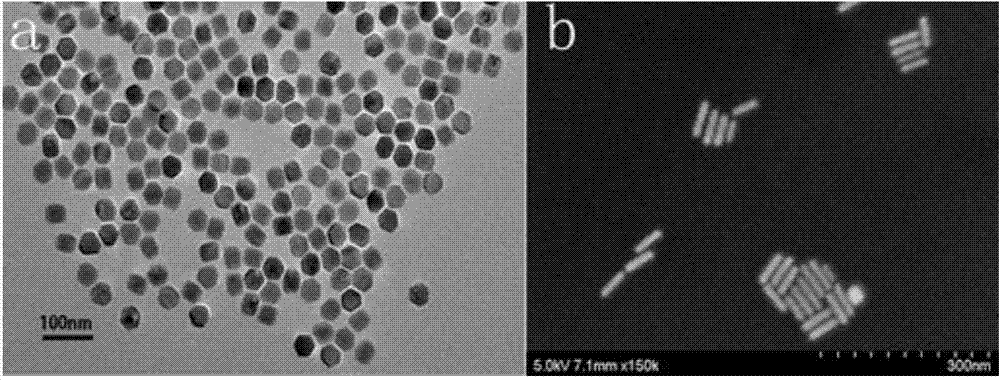
![Pillar[5]arene and 2-hydroxy-3-naphthoic acid complex and preparation thereof and application in detecting iron ions and fluorine ions Pillar[5]arene and 2-hydroxy-3-naphthoic acid complex and preparation thereof and application in detecting iron ions and fluorine ions](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/9701a422-70b5-4870-9f49-92bcf764c7de/160401111727.PNG)
![Pillar[5]arene and 2-hydroxy-3-naphthoic acid complex and preparation thereof and application in detecting iron ions and fluorine ions Pillar[5]arene and 2-hydroxy-3-naphthoic acid complex and preparation thereof and application in detecting iron ions and fluorine ions](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/9701a422-70b5-4870-9f49-92bcf764c7de/160401111731.PNG)
![Pillar[5]arene and 2-hydroxy-3-naphthoic acid complex and preparation thereof and application in detecting iron ions and fluorine ions Pillar[5]arene and 2-hydroxy-3-naphthoic acid complex and preparation thereof and application in detecting iron ions and fluorine ions](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/9701a422-70b5-4870-9f49-92bcf764c7de/160401111735.PNG)