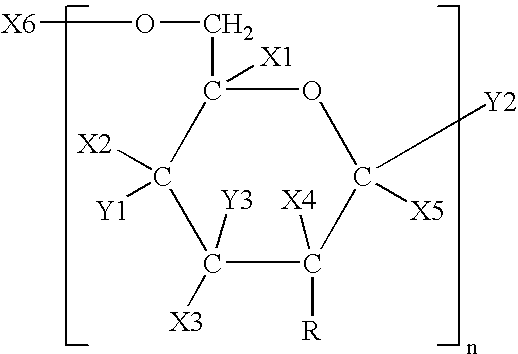
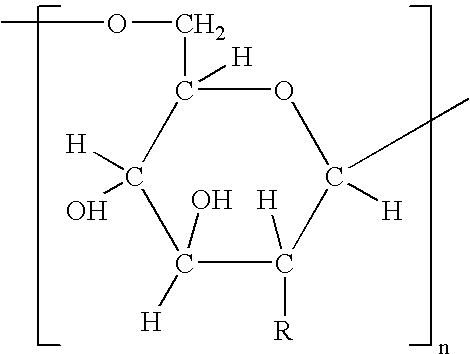
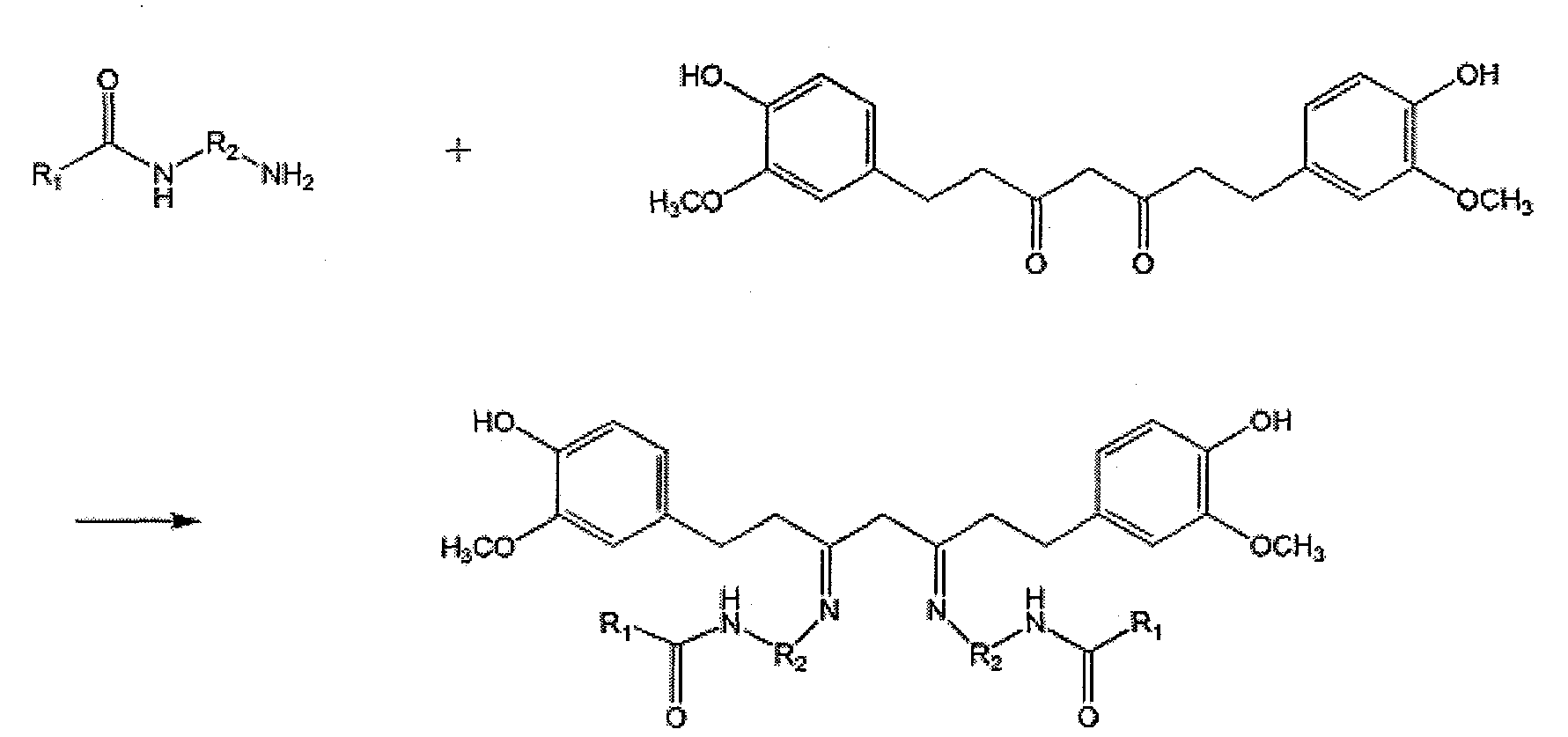
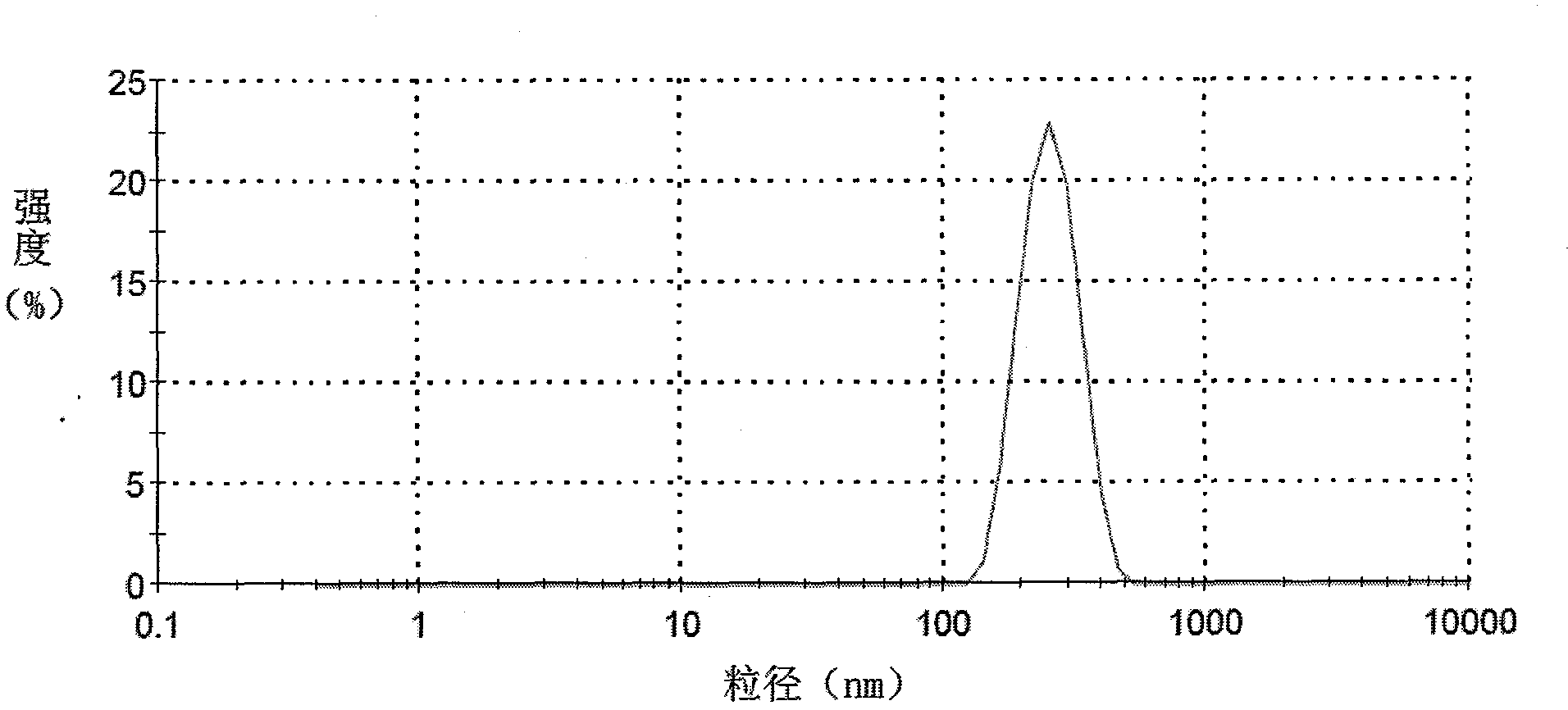
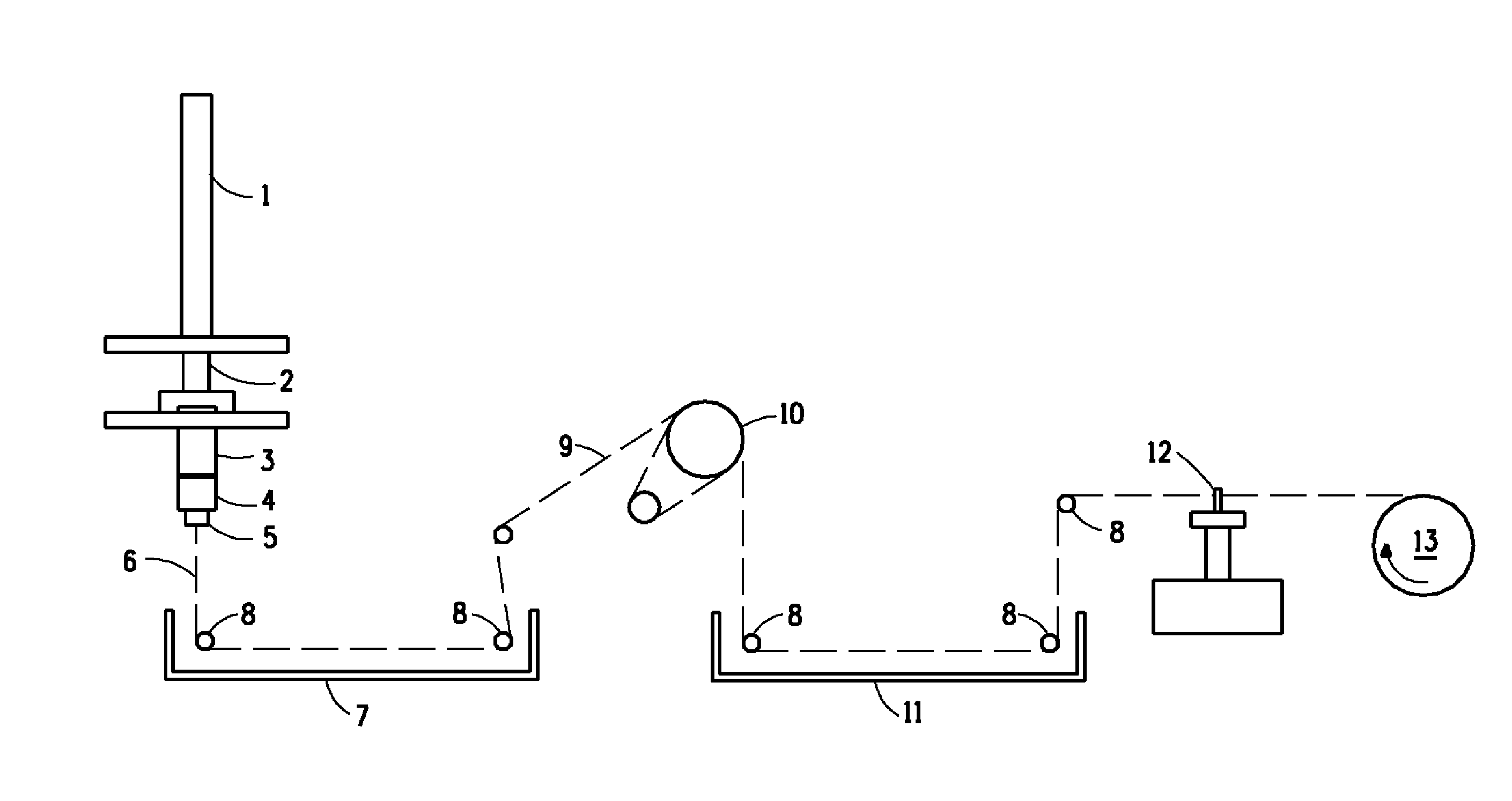
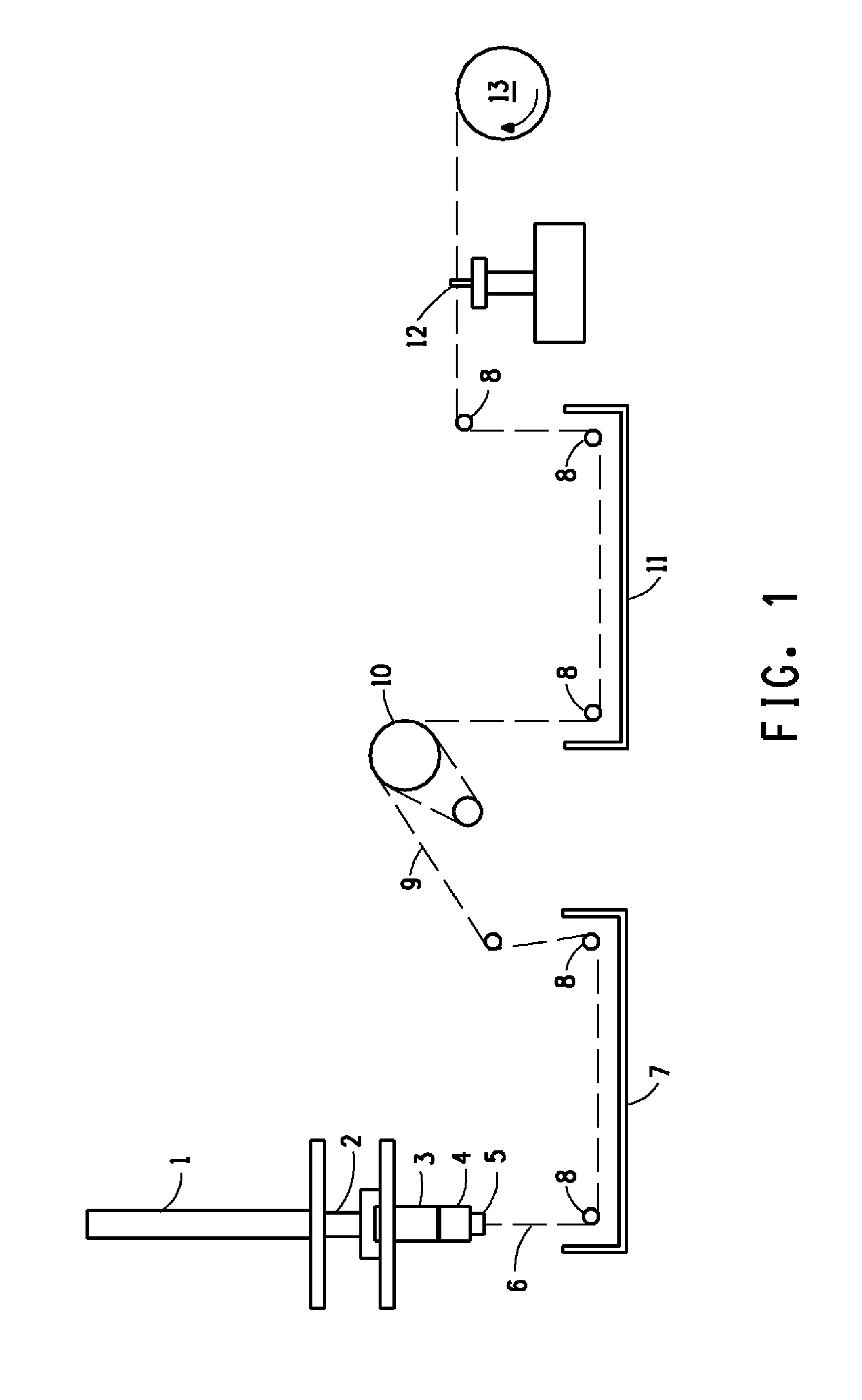
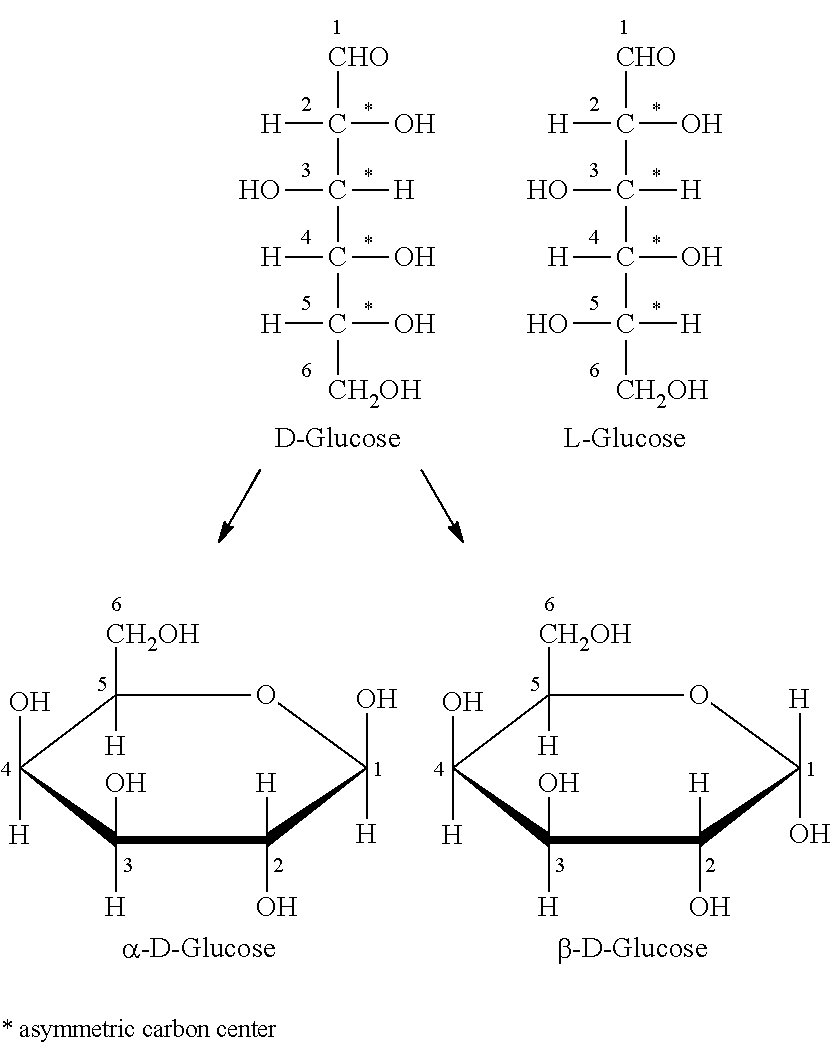
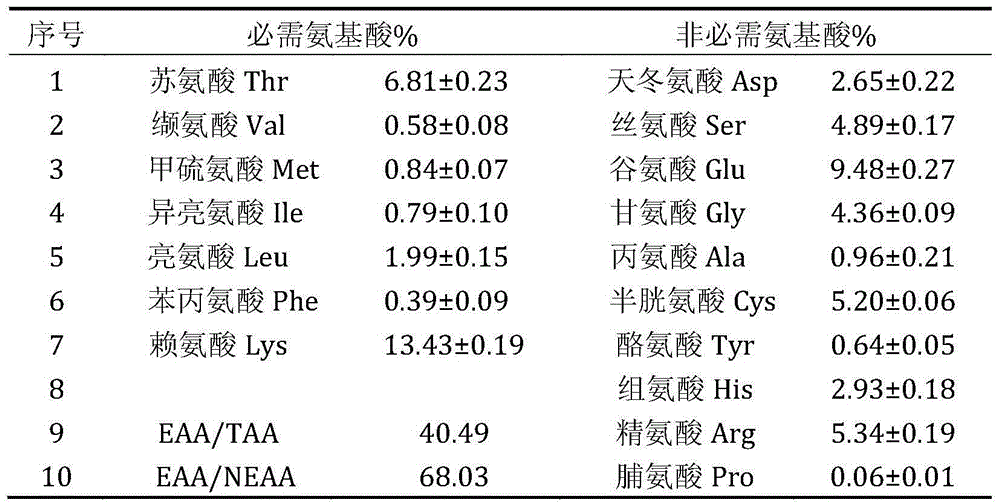
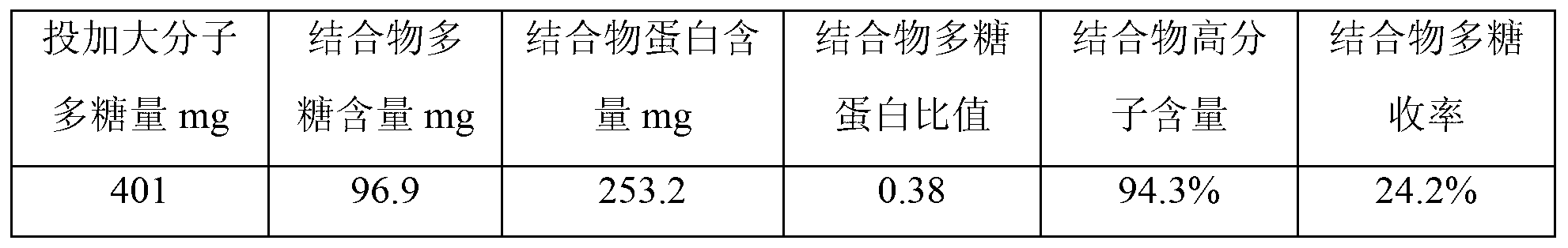
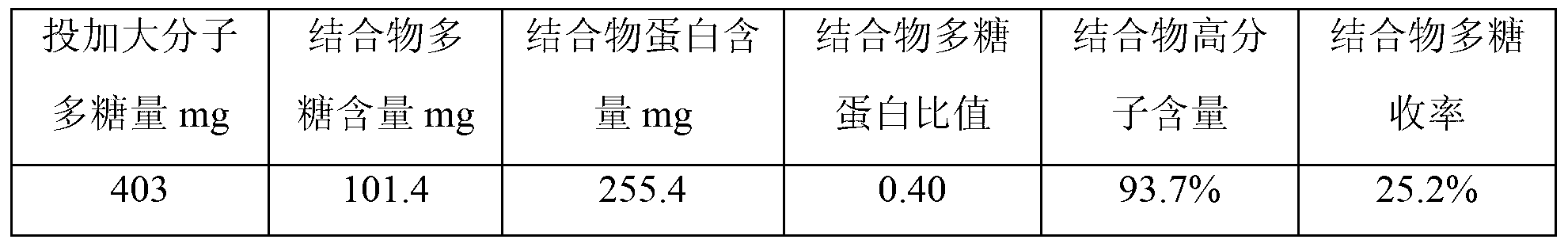
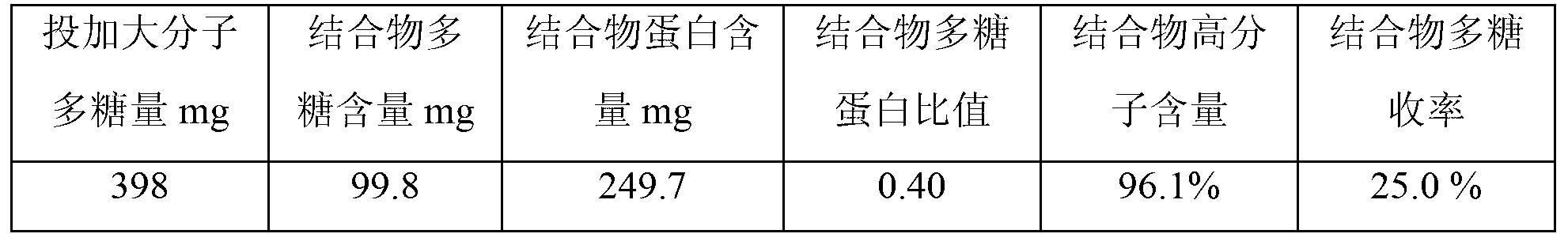
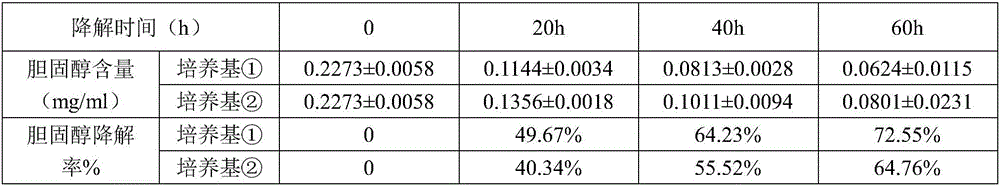
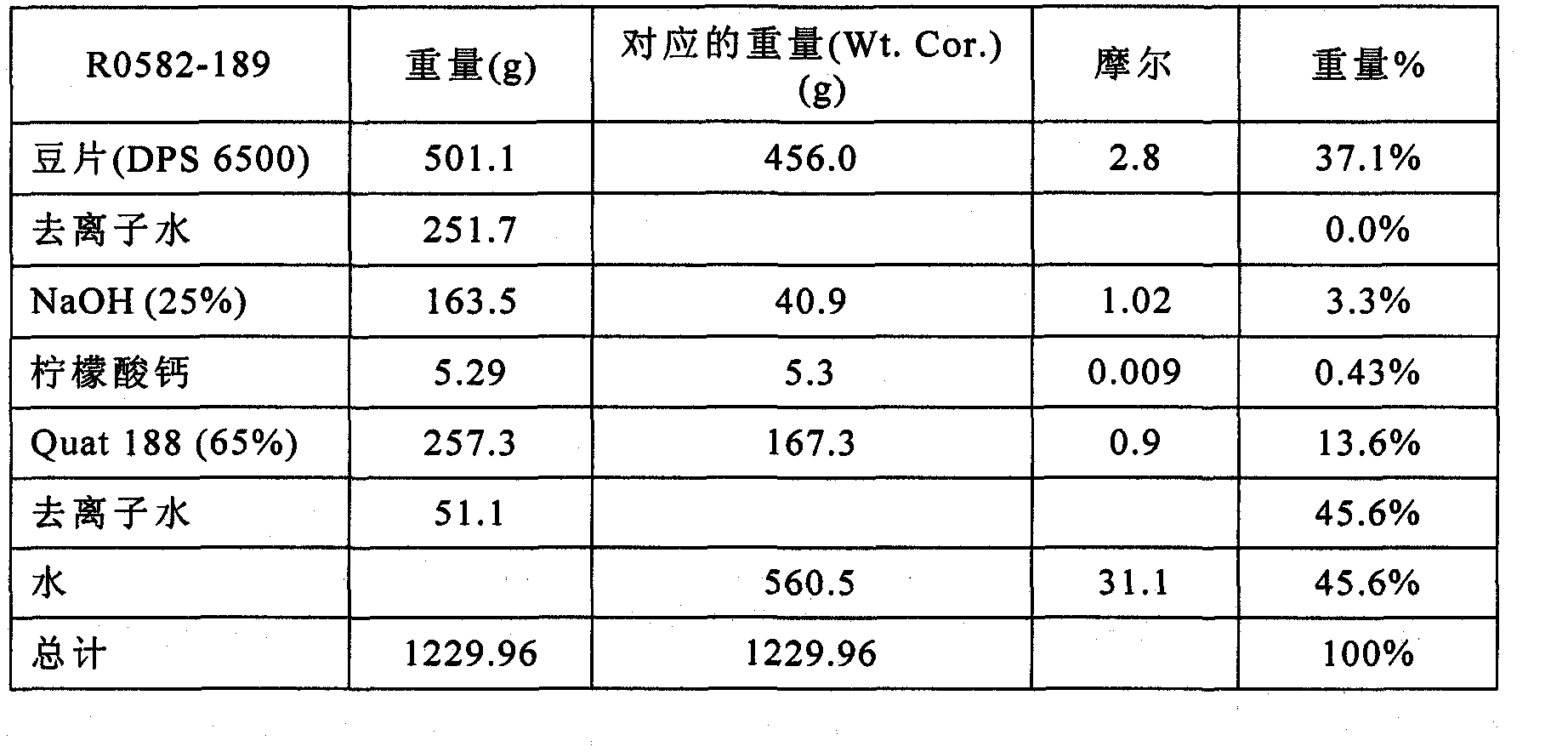
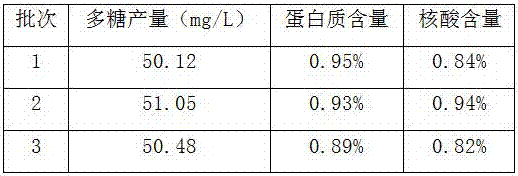
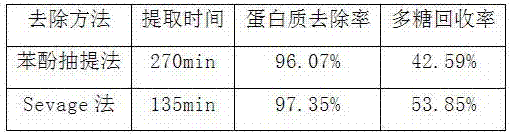
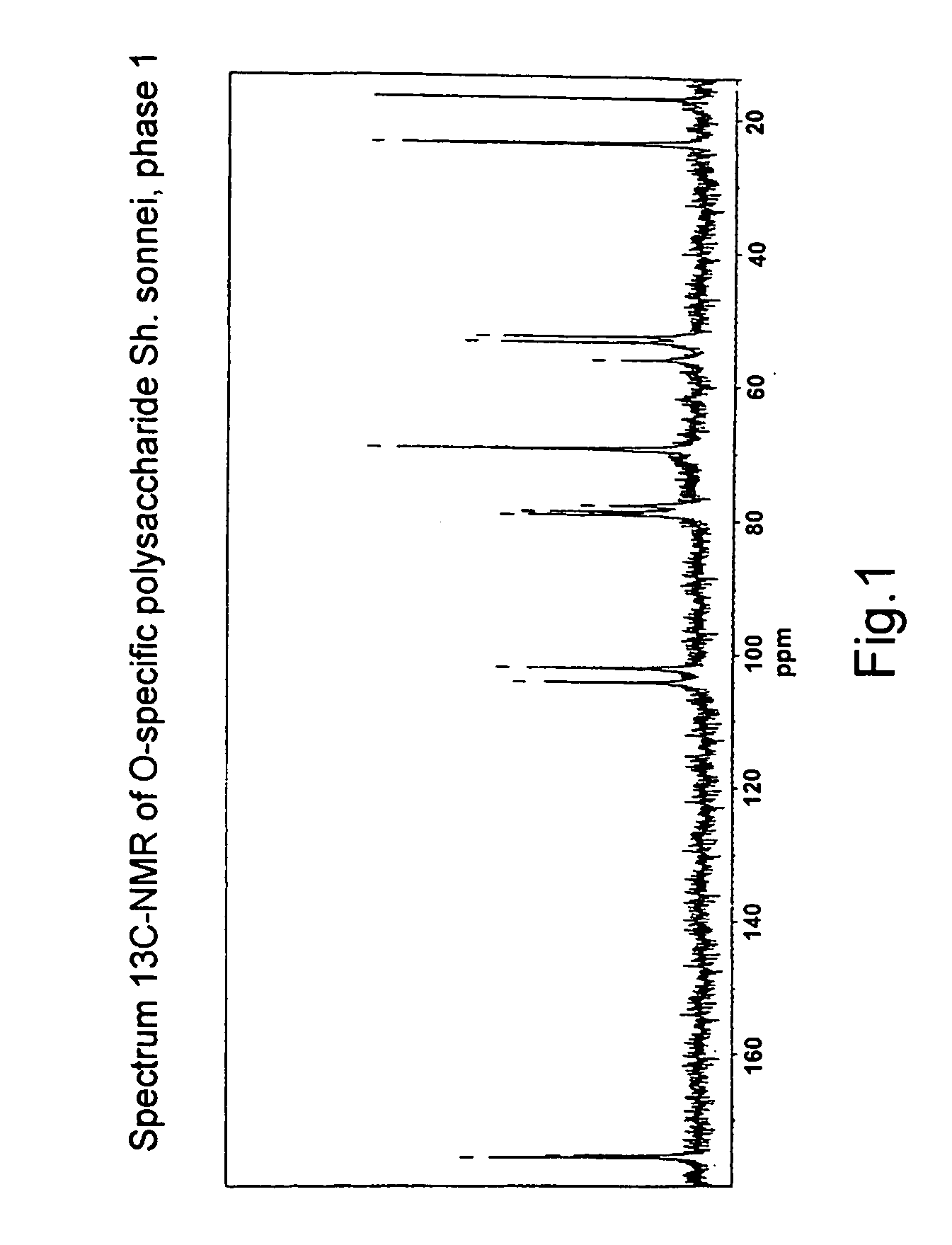
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
120 results about "Polysaccharide Vaccine" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A category of vaccines that use the extracted and purified outer polysaccharide coat of the particular bacteria.
Modified Polysaccharides
InactiveUS20070015678A1Little and no calcium bindingLittle and no and co-building propertyTransportation and packagingWater softeningPolysaccharide VaccinePolysaccharide
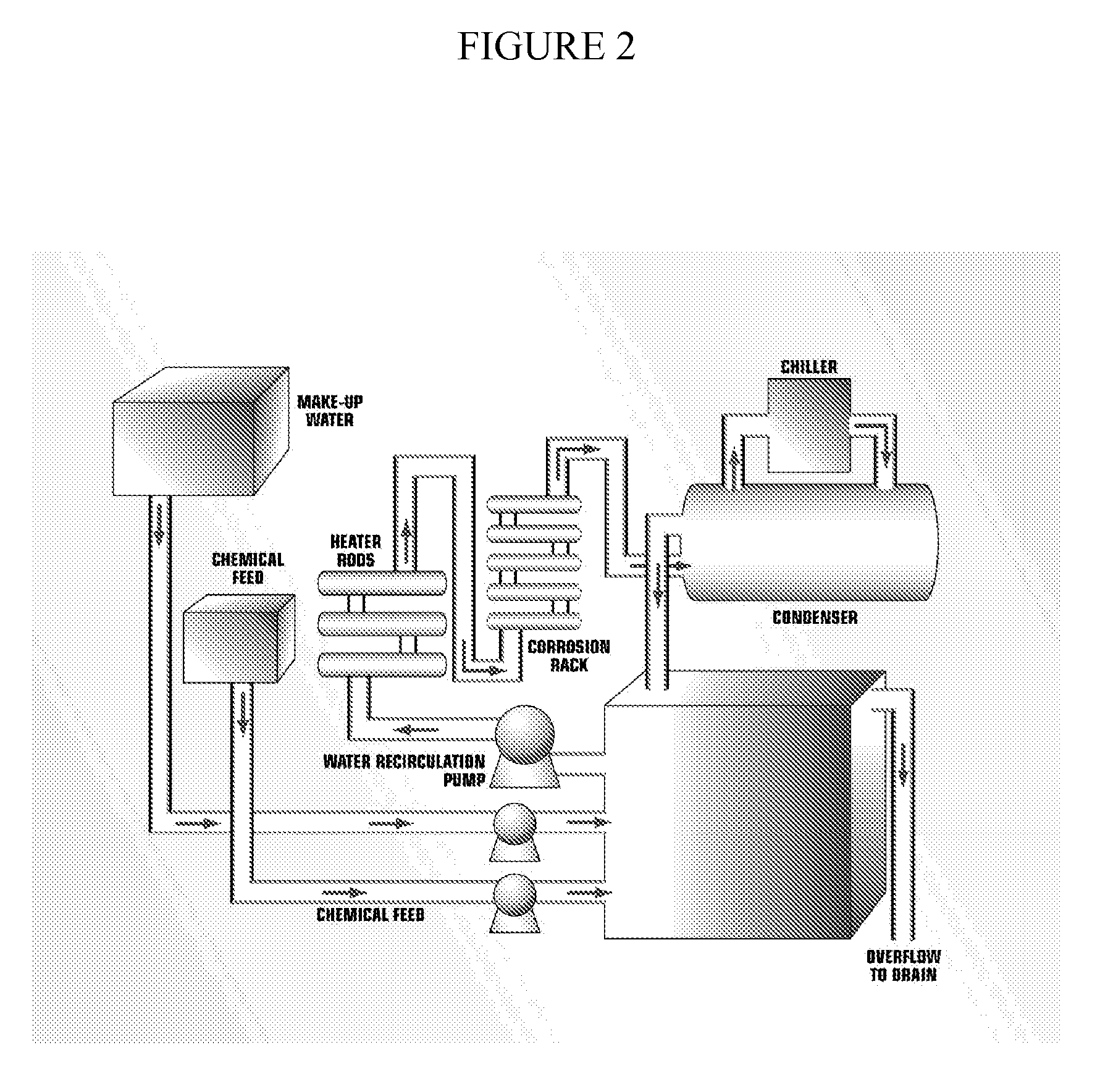
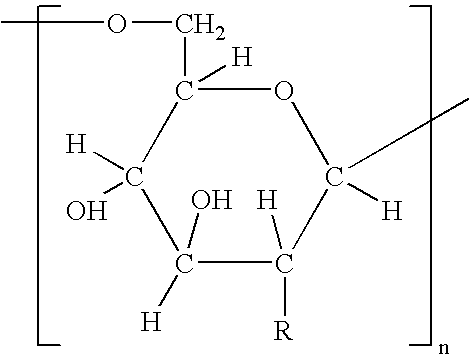
Modified polysaccharide polymers for use as anti-scalant and dispersant. The polymers are useful in compositions used in aqueous systems. The modified polysaccharides are also useful in detergent formulations, water treatment, dispersants and oilfield applications and as fiberglass binders. Such applications include a modified polysaccharide having up to about 70 mole % carboxyl groups per mole of polysaccharide ASU and up to about 20 mole % aldehyde groups per mole of polysaccharide ASU. The applications can also include a blend of modified polysaccharides and other synthetic polymers.
Owner:AKZO NOBEL NV
Polysaccharide vaccine for staphylococcal infections
ActiveUS20050118198A1Improving immunogenicityAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsNatural sourceIntracellular
The invention relates to compositions of a deacetylated poly N-acetylated glucosamine (dPNAG) of Staphylococci. The dPNAG may be isolated from natural sources or synthesized de novo. The invention also relates to the use of dPNAG as a vaccine for inducing active immunity to infections caused by Staphylococcus aureus, S. epidermidis, other related coagulase-negative or coagulase-positive Staphylococci, and other organisms carrying the ica (intracellular adhesion) locus. The invention further provides methods of use for antibodies directed to dPNAG, particularly for inducing passive immunity to the same class of infections.
Owner:THE BRIGHAM & WOMEN S HOSPITAL INC
Curcumin-polysaccharide conjugate as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102988999AHigh drug loadingHigh encapsulation efficiencyPowder deliveryAntipyreticSolubilitySide effect
The invention relates to a curcumin-polysaccharide conjugate as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: grafting amino acid at one terminal of a diamine compound to polysaccharide through amidation to obtain a polysaccharide macromolecule with a free terminal of amino acid; and introducing curcumin on the polysaccharide frame by a Schiff base reaction. The preparation method is characterized in that 1, the water solubility and in-vivo and in-vitro stability of the curcumin can be improved due to grafting modification on the curcumin, and the generated curcumin-polysaccharide conjugate can be used as a novel macromolecular medicament indepterminalently; 2, the curcumin-polysaccharide conjugate has a strong oral absorption promoting effect, is high in safety, and can achieve the effects of promoting medicament absorption, improving the curative effect, reducing the toxic and side effect of the conjugate and the like; and 3, the amphipathy of the polysaccharide molecule is improved by introducing the hydrophobic group curcumin, so that the curcumin-polysaccharide conjugate can be self-assembled into nano-micelle, and can be used as a vector of an insoluble medicament. The preparation method is simple, low in cost, and applicable to large-scale continuous production.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
Novel composition for preparing polysaccharide fibers
Solutions formed by combining poly(α(1→3) glucan) with CS2 in aqueous alkali metal hydroxide solution have been shown to produce the xanthated form of the poly(+(1→3) glucan). The solutions so formed have been shown to be useful for solution spinning into fiber of poly(α(1→3) glucan) when the spun fiber is coagulated in an acidic coagulation bath. The fibers so produced exhibit desirable physical properties. The poly(α(1→3) glucan) employed was synthesized by fermentation.
Owner:NUTRITION & BIOSCIENCES USA 4 INC
Tissue augmentation material and method
InactiveUS7968110B2Reduce deliveryAnti-incontinence devicesPharmaceutical delivery mechanismCelluloseCarrageenan
Owner:MERZ NORTH AMERICA
Multivalent pneumococcal capsular polysaccharide composition as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN103656632AStable physical and chemical propertiesPrevent diseaseAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsConjugate vaccineStreptococcus pneumoniae capsular polysaccharide
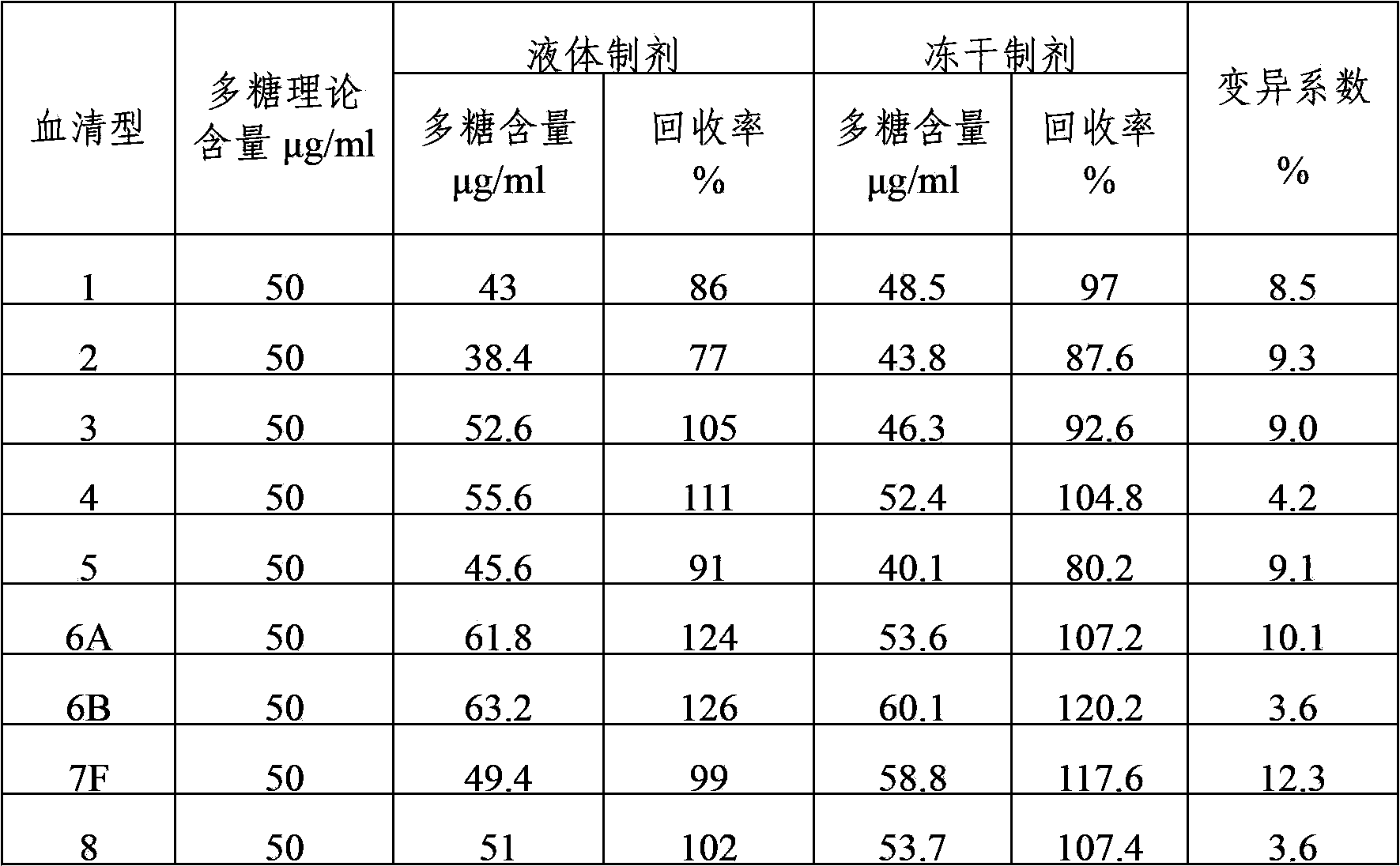
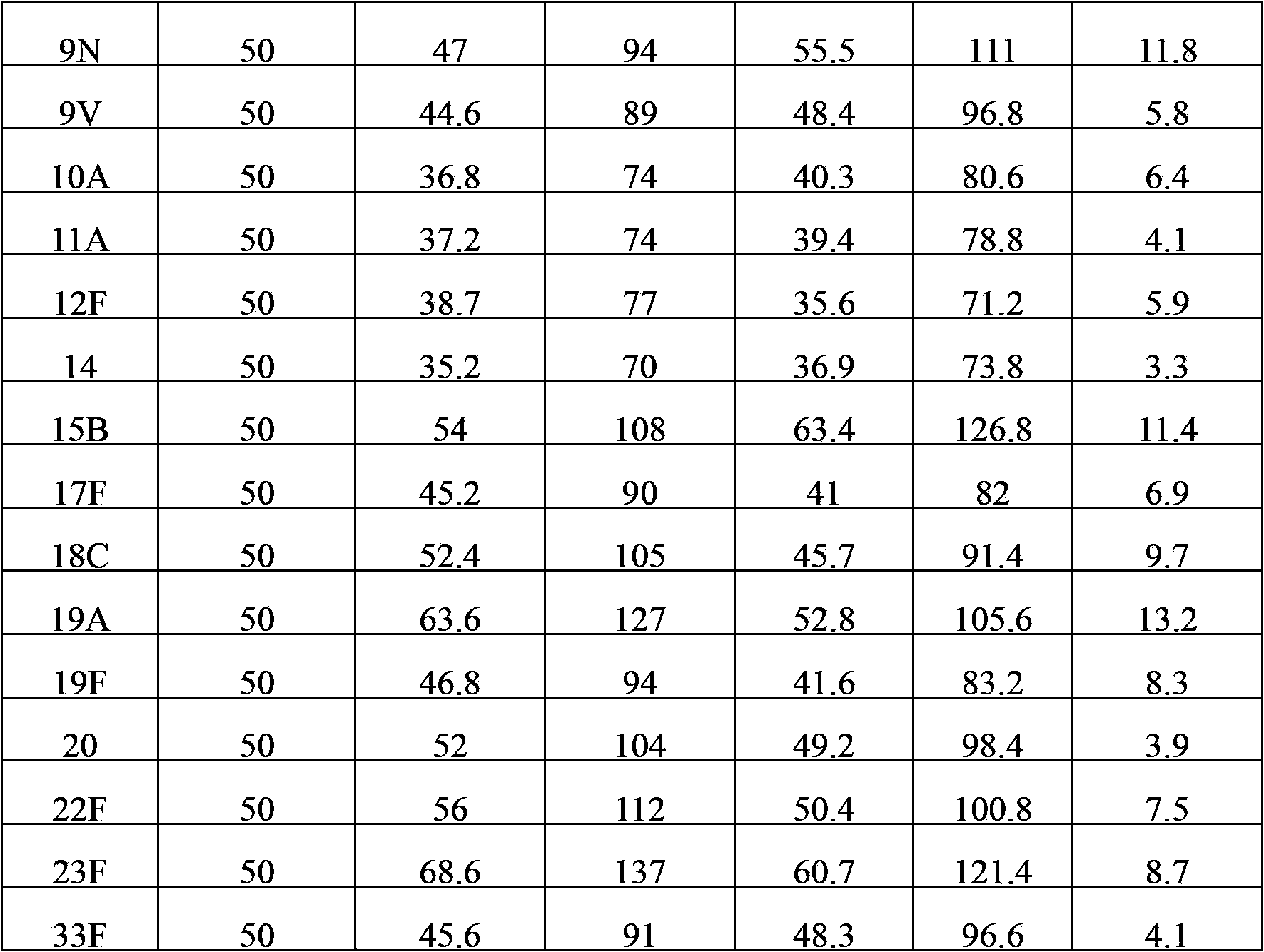
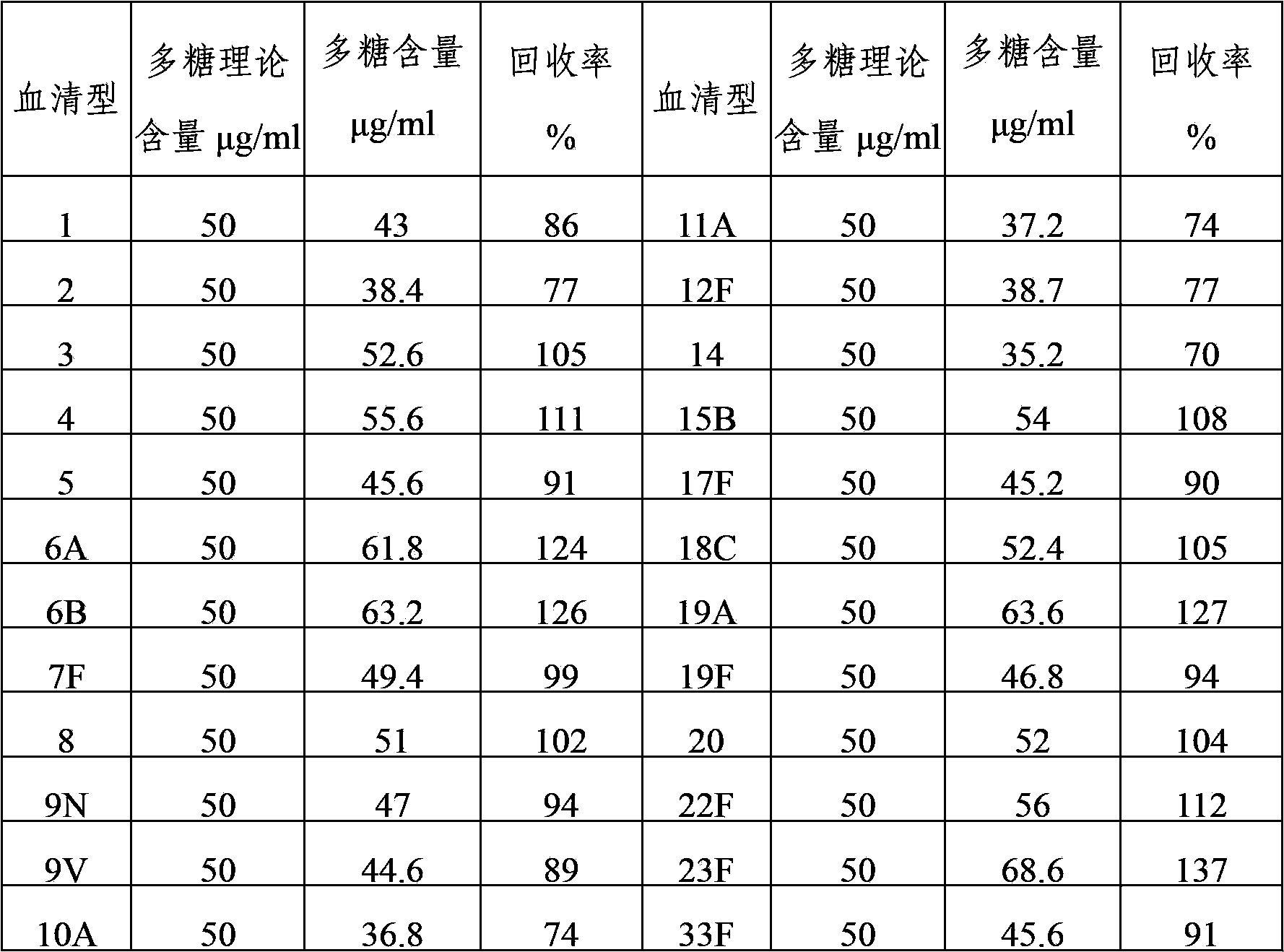
The invention provides a multivalent pneumococcal capsular polysaccharide composition as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The multivalent pneumococcal capsular polysaccharide composition contains a serotype 6A and at least one extra serotype selected from the group consisting of 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6B, 7F, 8, 9N, 10A, 11A, 12F, 14, 15B, 17F, 18C, 19A, 19F, 20, 22F, 23F and 33F. The multivalent pneumococcal capsular polysaccharide composition provided by the invention can be used for inducing an organism to generate humoral immunity, can generate a relatively good protecting effect for infectious diseases caused by the 24 common serotype pneumococcuses and is wide in immunity coverage rate and better in effect as comparison with various existing pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccines and conjugate vaccines sold on the market.
Owner:SINOVAC RES & DEV
Pneumococcal dosing regimen
ActiveUS20140322263A1Bacterial antigen ingredientsCarrier-bound antigen/hapten ingredientsDosing regimenCoccidia
Owner:WYETH LLC
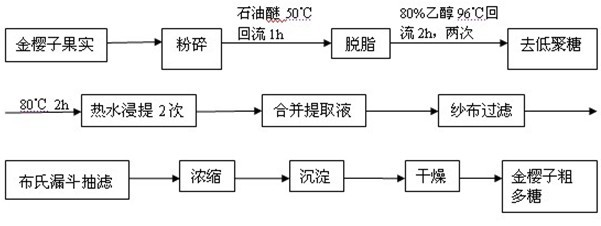
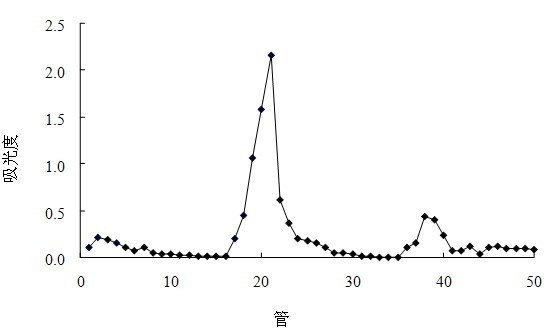
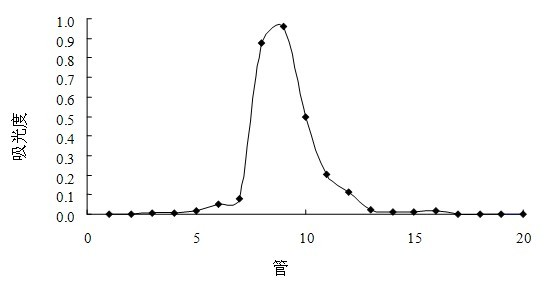
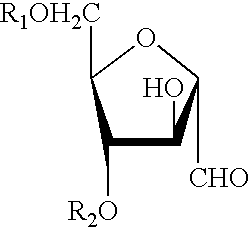
Preparation method of cherokee rose polysaccharide derivatives with antitumor activity
The invention discloses a preparation method of cherokee rose polysaccharide derivatives with an antitumor activity. The preparation method comprises the following steps: firstly smashing cherokee rose fruit, degreasing, removing oligosaccharide, lixiviating with hot water twice, then mixing extracts, filtrating, concentrating, precipitating and drying so as to obtain crude cherokee rose polysaccharide; adding diethylin ethyl amino ethyl (DEAE)-cellulose 52 to carry out static absorption for 30 minutes; washing with distilled water, filtering, and collecting filtrate so as to obtain the decolored crude cherokee rose polysaccharide; carrying out protein removal on a crude polysaccharide solution by using an enzyme method and a Sevag method; further separating the crude cherokee rose polysaccharide with the DEAE-cellulose 52, collecting, dialyzing, and freeze-drying so as to obtain cherokee rose polysaccharide; and finally, carrying out sulphating, carboxymethylation and hydrochloric acid degradation on the cherokee rose polysaccharide, and carrying out carboxymethylation on degradation products so as to obtain a plurality of cherokee rose polysaccharide derivatives. The plurality of cherokee rose polysaccharide derivatives have in vitro antitumor characteristics, and can be used for inhibiting the growth of three tumor cells, namely, ovarian cancer cells, liver cancer cells and rectal cancer cells.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Application for polysaccharide extraction of grateloupia filicina in preparing antitumor medicine and other medicines
InactiveCN101077356AGood anti-HIV-1 virus activityOrganic active ingredientsAlgae medical ingredientsThrombusTraditional medicine
The present invention relates to the application of one kind of Granteloupia cuminata polysaccharide extract in preparing medicine for treating blood coagulation, thrombus, AIDS and / or tumor, and provides its preparation process.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV OF T C M
Method of immunization using a Group B Streptococcus type II and type III polysaccharide conjugate vaccine
The process for depolymerizing Group B Types II and III streptococcal polysaccharide is disclosed which results in polysaccharide fragments having a reducing end suitable for conjugating to protein. Conjugate molecules, vaccines and their use to immunize mammals including humans are also disclosed.
Owner:BAXTER INT INC
Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharide of high molecular weight and detection method thereof
InactiveCN102718880AEasy to prepareImprove immune activityComponent separationImmunological disordersAlcoholFreeze-drying
The invention provides ganoderma lucidum polysaccharide of high molecular weight and a detection method thereof. The ganoderma lucidum polysaccharide of high molecular weight is obtained via water extraction, alcohol precipitation, purification, and freeze-drying. The preparation method of the ganoderma lucidum polysaccharide of high molecular weight is simple and is suitable for large-scale production. The polysaccharide content is more than 65 percent, and macrophages can be stimulated to produce nitric oxide (NO).
Owner:SHANGHAI ACAD OF AGRI SCI +1
Method for measuring polysaccharide content of medlar extracting solution
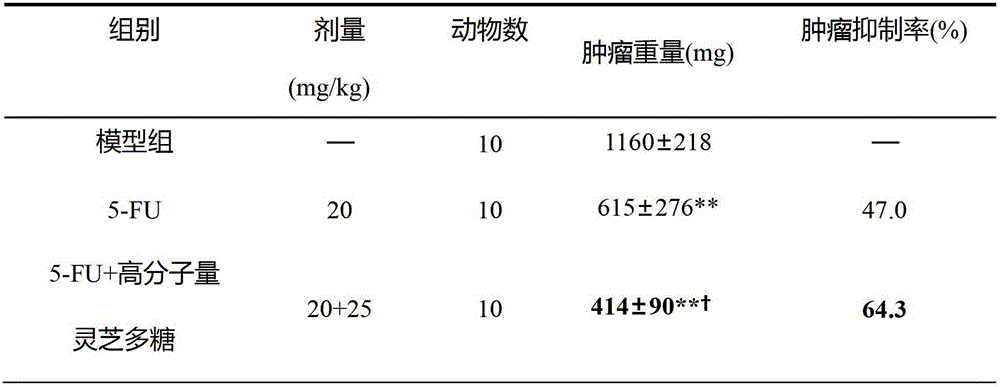
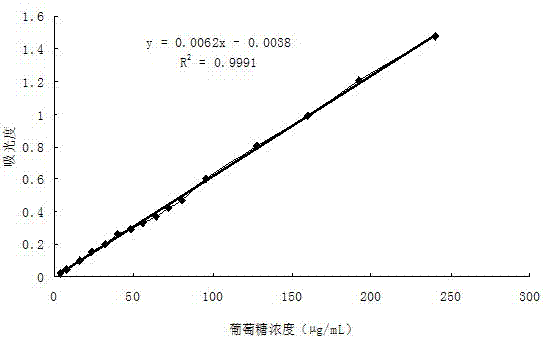
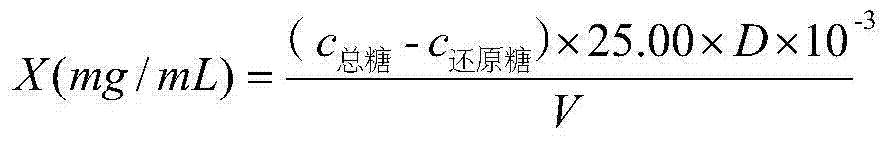
InactiveCN103884667AImprove accuracyGood reproducibilityColor/spectral properties measurementsPolysaccharide VaccineAbsorbance
The invention discloses a method for measuring polysaccharide content of a medlar extracting solution. The method comprises the following steps of (1) pretreating the medlar extracting solution; (2) preparing a reducing sugar and total sugar test solution; (3) preparing a standard curve; (4) preparing a reference solution for the reducing sugar and total sugar test solution; (5) measuring the absorbency of the reducing sugar and total sugar test solution, checking the standard curve, and calculating the polysaccharide content. According to the method, the medlar extracting solution is pretreated through lead acetate, and the deproteinized solution is transparent and clarified and is suitable for measurement of a spectrophotometric method; meanwhile, due to the method for preparing the reference solution, the absorption of a developing agent is avoided, and influence on the pigment of medlar is eliminated. By the measurement method disclosed by the invention, reducing sugar does not need to be removed, and the reducing sugar does not need to be prepared into solid crude polysaccharide for measurement, so that the problem a phenol-sulfuric acid method is easily affected by the reducing sugar is solved, and the safety of operation is improved. The method is quick, high in accuracy and high in repetitiveness, and is suitable for quality control during large-scale industrial production.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV OF TECH
Polysaccharide polymer having protein large molecule and its preparation method
The present invention relates to a protein macromolecule bearing polysaccharide-polymer in the field of biological technology and its preparation method. According to the concrete requirement the different polysaccharides, proteins, polymers and protective reagent can be selected, in which polysaccharide content is 0.01%-50%, protein content is 0.01%-50%, polymer content is 20%-80%, reagent content for protecting protein is 0%-10%. Its preparation method includes the following steps: (1), adding protein into polysaccharide solution; (2), mixing protein-polysaccharide and polyethylene glycol solution; (3), freeze-drying the formed mixed solution or water phase-water phase emulsion; (4), adding the obtained freeze-dried powder into organic solution of soluble polyethylene glycol to wash and remove polyethylene glycol so as to obtain particles; and (5), adding the obtained particles into the solution of liposoluble polymer and uniformly mixing them, making the emulsion be formed for standing-by. Said invention can be used for making protein medicine intervenient therapy.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
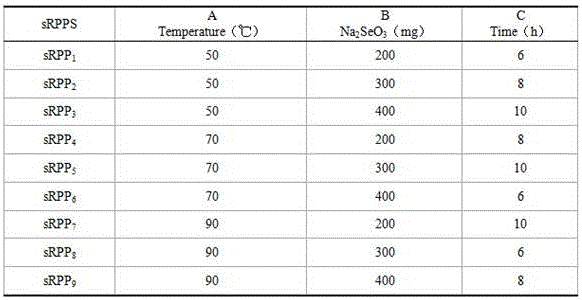
Selenium modification method for improving immunological competence of radix pseudostellariae polysaccharides
InactiveCN106589157AAvoid breakingFast manufacturingImmunological disordersDialysate samplePolysaccharide Vaccine
The invention provides a selenium modification method for improving the immunological competence of radix pseudostellariae polysaccharides. The selenium modification method comprises the following steps: taking the radix pseudostellariae polysaccharides, reacting with Na2SeO3 under certain conditions, cooling to a room temperature after the end of reaction, adjusting a pH value to 5-6 with anhydrous sodium carbonate, centrifuging, filtering and putting a solution into a 1000-D dialysis bag for flowing water dialysis; taking a dialysate sample once every 6 hours, detecting whether the dialysate sample contains sodium selenite or not by using an ascorbic acid method, and stopping dialysis when no sodium selenite residue exists or the red is not displayed; and performing Sephadex G-100 column chromatography on the solution to obtain the radix pseudostellariae polysaccharides. When nitric acid is used for reaction, the cleavage of a polysaccharide chain can be caused, so that oligosaccharides are formed, and the low yield of selenium-containing polysaccharides is caused. By using glacial acetic acid, the cleavage of the polysaccharide chain is difficultly caused, so that the yield of selenium-containing polysaccharides is improved.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
Preparation method of group C meningococcal capsular polysaccharide conjugate vaccine
InactiveCN105879020AHarm reductionReduce hydrolytic denaturationAntibacterial agentsCarrier-bound antigen/hapten ingredientsConjugate vaccineMeningococcal carriage
Owner:北京成大天和生物科技有限公司
Method of determining polysaccharide content in sea cucumbus
InactiveCN1624450AEasy to operateGood reproducibilityWeighing by removing componentPreparing sample for investigationAlcoholRoom temperature
A method for measuring content of polysaccharide in sea cucumber, has the characteristics that the shattered sample of sea cucumber is added into water solution containing 3%-5% base which is 35-45 times of the mess of sample, then the solution is put into the super sonic wave washing instrument waiting for 1.5-2.5 hours under 40-50deg.C; use acid to adjust PH value to be neutral; the solution is centrifuged for 15-25 min by 8000-12000rpm and then get some clear liquid in which ethanol is added when being stirred to make the density of ethanol reach 55-65%; then after standing for a night; it is centrifuged for 20-30min by 4000-4500rpm and the clear liquid is abandoned and the sediment is dissolute by water in which ethanol is added into, making the density of ethanol reach 80-90%, after standing for a night; use bushing to filter and use orderly absolute ethyl alcohol and acetone to wash and anhydrate for three times; it is dried to have no change of mass and cooled to reach the room temperature, then be weighed. The invention uses secondary ethanol sediment to purify the sample and super sonic wave washing instrument as reactor, chooses bushing as mess analysis container.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Method for extracting lipopolysaccharides from avian pasteurella multocida and preparing lipopolysaccharide vaccine
InactiveCN102120028AIncrease concentrationHigh purityAntibacterial agentsBacteriaAnimal virusMedicine
The invention provides a method for extracting lipopolysaccharides from avian pasteurella multocida and preparing a lipopolysaccharide vaccine. The method comprises the following eight steps of: 1, preparing culture solution of avian pasteurella multocida; 2, collecting the avian pasteurella multocida from the culture solution of avian pasteurella multocida; 3, crushing the avian pasteurella multocida by using ultrasonic wave; 4, crudely extracting solution of lipopolysaccharides from the avian pasteurella multocida crushed by the ultrasonic wave; 5, extracting concentrated solution of lipopolysaccharides from the crudely extracted solution of lipopolysaccharides; 6, performing enzymolysis on deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA) in the concentrated solution of lipopolysaccharides by using DNA and RNA enzymes; 7, preparing the purified lipopolysaccharides; and 8, preparing the lipopolysaccharide vaccine of avian pasteurella multocida from the purified lipopolysaccharides. According to animal immunization experiments and animal virus attacking experiments, after the lipopolysaccharide vaccine of avian pasteurella multocida, prepared by the method, is used for immunizing chickens for three times, the immunized chickens can be effectively prevented from suffering from avian pasteurella multocida disease.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
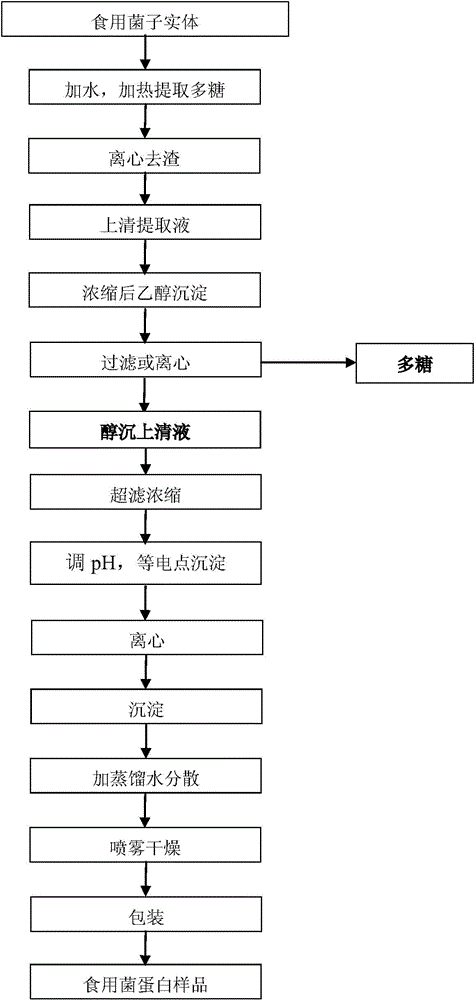
Method for recycling protein from supernatant obtained from edible fungus through polysaccharide extraction and alcohol precipitation
InactiveCN104402970AFull of nutritionReduce processing costsPeptide preparation methodsAlcoholUltrafiltration
The invention discloses a method for recycling protein from supernatant obtained from edible fungus through polysaccharide extraction and alcohol precipitation. The method comprises the following steps: taking the supernatant which is obtained from sporocarp of the edible fungus through the polysaccharide extraction and the alcohol precipitation; performing pressurization and ultrafiltration by adopting an ultrafiltration membrane with the cut-off molecular weight of 3-8 KD, wherein the pressure of the pressurization is 3-5 bar; performing the ultrafiltration to get a concentrated solution; adjusting the pH value to 4.0 to 5.0; mixing and performing the isoelectric precipitation; centrifuging; adding distilled water into the obtained protein precipitate, mixing, dispersing, spraying and drying, so as to obtain the recycled protein of the edible fungus. According to the method, the recycling rate of the protein is more than 70%, the content of the protein in samples is more than 70%, and the total sugar content is about 20%. Through the amino acid analysis, the nutrition of the recycled protein is rich. The treating cost of the waste alcohol precipitation liquid is effectively reduced when the edible fungus are processed through the polysaccharide extraction, and the benefit is increased through the integrated utilization.
Owner:庆元县金源真菌多糖制品有限责任公司
Dandelion polysaccharide extract and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102659958ASignificant anticomplement activityEasy to useOrganic active ingredientsImmunological disordersChromatographic separationSide effect
The invention discloses dandelion polysaccharide extract and a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation method of the dandelion polysaccharide extract includes subjecting a whole plant of dandelion to water extraction and ethanol precipitation, capturing components larger than 10000Da by dialysis, and subjecting the components to anion exchange column chromatographic separation to obtain the dandelion polysaccharide extract. The dandelion polysaccharide extract contains 7-8wt% of polysaccharide A, 22-23wt% of polysaccharide B, 17-18wt% of polysaccharide C, 6-7wt% of polysaccharide D, 1-2wt% of polysaccharide E, and 0.5-1.5wt% of polysaccharide F. The dandelion polysaccharide extract has evident anticomplementary activity, can be made into drugs and functional foods for preventing and / or treating systemic immunodeficiencies, and is safe to use and free of side effects. The preparation method of the dandelion polysaccharide extract is simple, the quality of the dandelion polysaccharide extract is stable, and the dandelion polysaccharide extract is applicable to large-scale production and has broad application prospect and market value.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV OF T C M
Hot water extraction method of dunaliella salina polysaccharide
The invention relates to a hot water extraction method of dunaliella salina polysaccharide. The hot water extraction method comprises the following steps: firstly, taking raw algae powder, performing ultrasonic blending, acetone washing and the like on the raw algae powder so as to remove impurities and beta-carotene; adding a PH regulator to regulate PH, adding a saline solution, leaving the solution to stand, performing centrifugation, adding ethyl acetate and distilled water, performing water bath soaking, performing alcohol precipitation, and performing suction filtration so as to obtain course polysaccharide; and finally, measuring polysaccharide content by adopting an anthrone-sulfuric acid method. Through the adoption of the hot water extraction method disclosed by the invention, the alcohol refluxing extraction can be avoided, the loss of polysaccharide in dunaliella salina can be obviously reduced, and the extraction amount of polysaccharide is increased; after the beta-carotene and protein are removed from the dunaliella salina, the ethyl acetate and the distilled water of 150-200ml are added in the dunaliella salina without the beta-carotene or the protein, water bath heating is performed, and the PH is regulated to 7-8, so that the ultrasonic extracting time can be shortened to 60-100min; therefore, when the extraction rate of the polysaccharide is not influenced, the extracting time is greatly shortened; the whole experimental temperature is controlled to be below 75 DEG C, so that the polysaccharide can be prevented from being damaged by excessively high temperature.
Owner:中山鼎晟生物科技有限公司
Method for preparing type b Haemophilus influenzae and polysaccharide conjugate vaccine
InactiveCN103251943AHigh yieldImprove stabilityAntibacterial agentsCarrier-bound antigen/hapten ingredientsConjugate vaccineFiltration
The invention discloses a method for preparing a type b Haemophilus influenzae and polysaccharide conjugate vaccine. The method comprises the following steps: S1, performing gel filtration chromatography purification of polysaccharide to obtain macromolecular Hib capsular polysaccharide; and S2, preparation of a polysaccharide-TT conjugate, which comprises the following sub-steps: S21, adding CNBr into a macromolecular Hib capsular polysaccharide liquor to activate for 15-25 minutes, then, adding adipic dihydrazide to derivate for 10-20 minutes to remove residual CNBr so as to obtain a polysaccharide-AH derivative, and S22, adding TT liquor to the polysaccharide-AH derivative, uniformly mixing and placing in an ice-bath, and adding EDAC powder, and separating, purifying, degerming and filtering the reactant to obtain the finished product. The method disclosed by the invention has the beneficial effects that the yield of qualified conjugates is improved, the raw material consumption in the conjugation process is reduced, and the stability of the production process and the consistency of quality of finished products are improved.
Owner:CHENGDU OLYMVAX BIOPHARM
Agaric polysaccharide functional food
InactiveCN105901698AEfficient degradationEfficient decompositionBacteriaFood hydrolysisCholesterolTremella
The invention belongs to the field of health food and specifically relates to agaric polysaccharide functional food. The functional food is composed of the following raw materials (by weight): 20-50 parts of auricularia auricula polysaccharide, 20-50 parts of tremella polysaccharide, 10-20 parts of ganoderma lucidum polysaccharide, 1-10 parts of taurine, 3-5 parts of L-arginine, 2-10 parts of fructo-oligosaccharide, 0.01-0.02 part of tea polyphenol, 10-80 parts of malt extract and 10-20 parts of lactobacillus plantarum powder. By the extraction method of polysaccharide, rate of polysaccharide extraction is boosted, the product has a good effect of enhancing immunity, and the product has good efficiency of degrading cholesterol.
Owner:邵素英
Preparation method of metal organic framework nano vaccine without refrigerated storage
InactiveCN112022836AImprove stabilityOvercome the problem of cold chain transportationAntiinfectivesPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsCold chainAdjuvant
The invention relates to a preparation method of a metal organic framework nano vaccine without refrigerated storage. The nano vaccine still keeps good biological activity when exposed to high-temperature, enzyme and long-term room temperature environments, the stability of the vaccine is remarkably improved, and the cold chain transportation problem of the vaccine is solved. The nano vaccine canenhance immune response, has a good adjuvant effect and can be used for preparing attenuated vaccines, protein vaccines, polysaccharide vaccines, nucleic acid vaccines or polypeptide vaccines. The nano vaccine takes polyethylene glycol as a mineralizer, the particle size is controllable, no organic reagent, microwave, high temperature or other severe conditions are involved in the process, the structures and activities of antigens and adjuvants cannot be damaged, the preparation process is simple, mature and stable, and large-scale production can be achieved.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
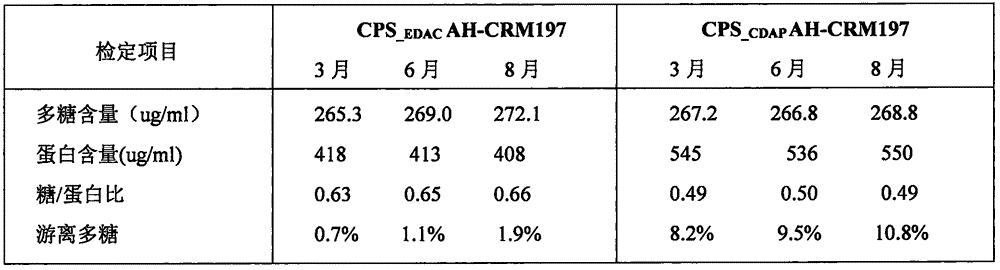
Process for activating Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib) polysaccharide conjugate vaccine
ActiveCN102626515AAvoid harmImprove securityAntibacterial agentsCarrier-bound antigen/hapten ingredientsTetrafluoroborateFreeze-drying
The invention discloses a process for activating a Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib) polysaccharide conjugate vaccine, which comprises the following steps of: A, preparing Hib polysaccharide; B, dissolving 1-Cyano-4-dimethylaminopyridinium tetrafluoroborate (CDAP) by using acetonitrile into a solution; C, preparing the Hib polysaccharide into a solution; D, adding the CDAP solution to the Hib polysaccharide solution, and stirring for 2-5 minutes at the room temperature; E, dissolving adipic dihydrazide (ADH) by using NaHCO3 into a solution, adding the ADH solution to a mixed solution, and stirring for 0.5-2 hours at the room temperature; and F, collecting eluent of the void volume from a loading solution after the reaction is ended at a SephadexG-25 gel chromatography column balanced in advance by water for injection, and performing freeze drying to obtain a Hib polysaccharide-ADH derivative. The process for activating the Hib polysaccharide conjugate vaccine has the beneficial effects that the quality index of the prepared Hib polysaccharide-ADH can reach the industrial standard, and moreover, the safe and nontoxic CDAP is adopted to serve as an activating agent instead of cyanogen bromide which is greatly harmful to human and environment, and therefore, the safety is enhanced, and the harm to the human and the environment are avoided.
Owner:CHENGDU OLYMVAX BIOPHARM
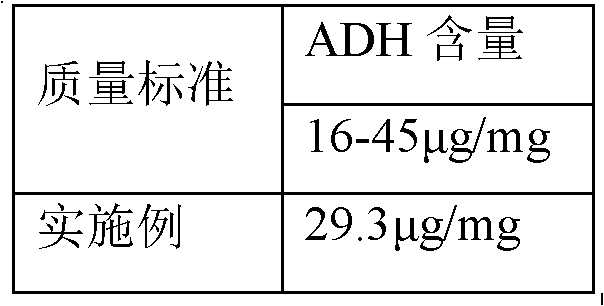
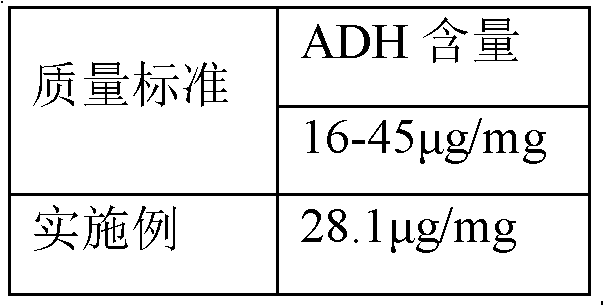
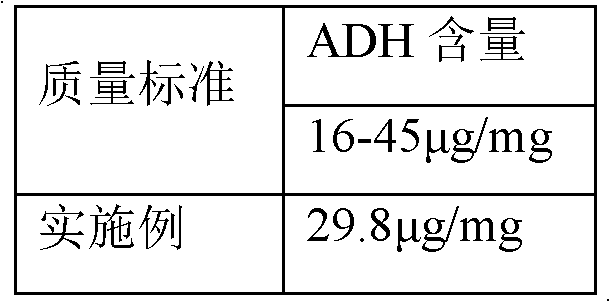
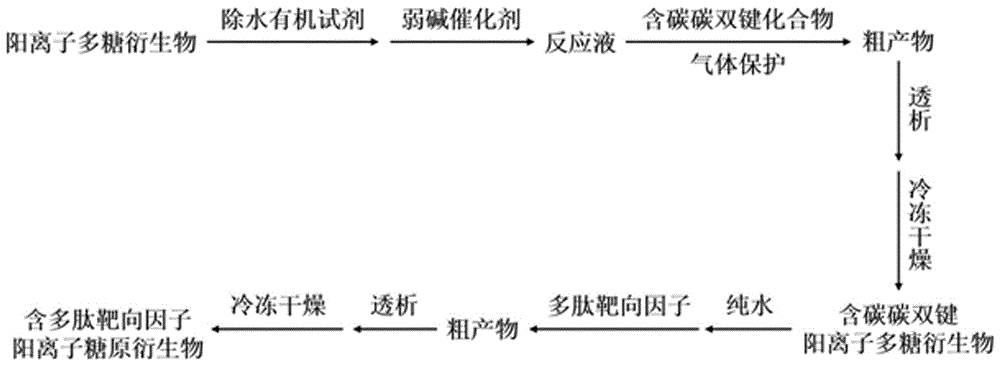
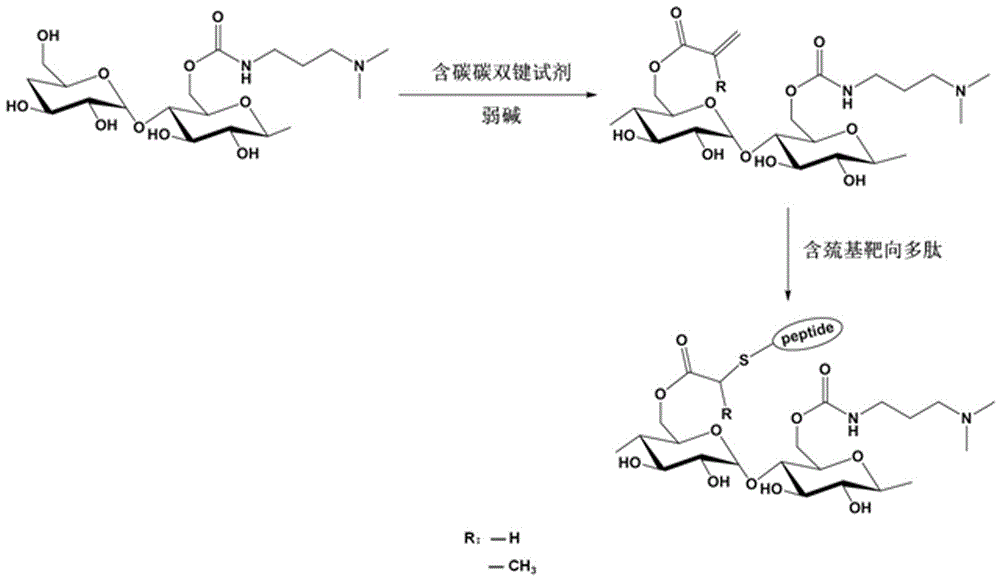
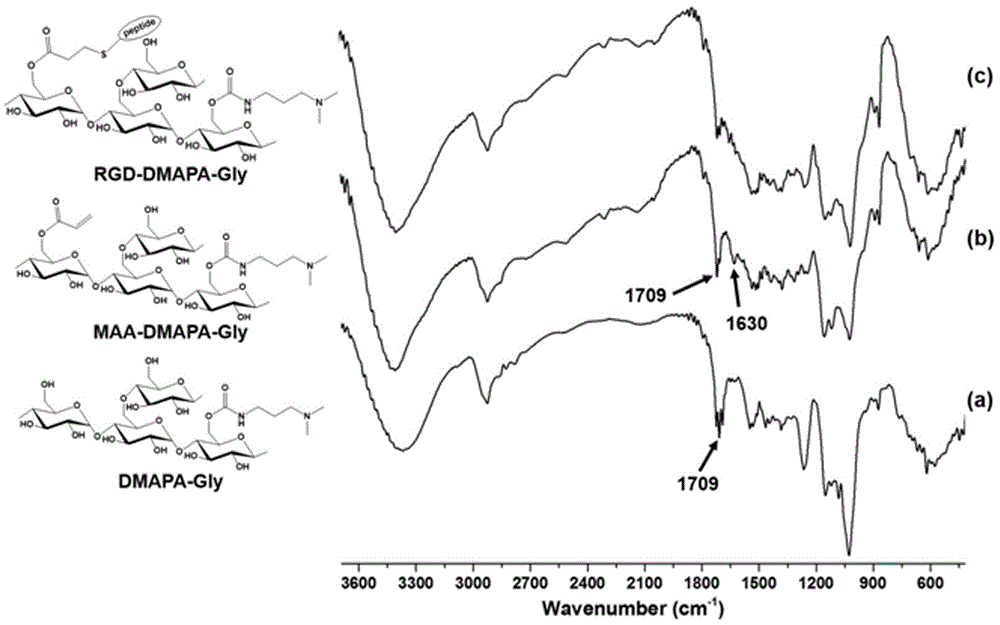
Polysaccharide derivative containing polypeptide targeting factor and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN106749517ASimple processEasy to operateSomatostatinsDepsipeptidesChemical reactionStrong acids
The invention discloses a polysaccharide derivative containing a polypeptide targeting factor and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises that a polypeptide targeting factor and a polysaccharide derivative containing a 3-dimethylaminopropylamine group as a raw material undergo a mercapto-alkene click chemical reaction at the room temperature. The preparation method has mild reaction conditions, is free of strong acid and strong alkali reagents and maximally keeps the biological activity of the polypeptide and the polysaccharide. The preparation method has simple processes, is easy to operate and needs cheap equipment and raw materials. The polysaccharide derivative containing a polypeptide targeting factor can be used as a drug or a gene carrier having performances of targeted transport to a lesion location and thus the polysaccharide derivative has a certain application prospect in the field of biomedicine.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Methods of producing cross-linked polysaccharide particles
A substantially boron-free method for making a cationic guar comprising: reacting particles of polysaccharide with a derivatizing agent to produce derivatized polysaccharide particles, washing the particles, and contacting, prior to or after the step of washing, the particles with a crosslinking agent compound. Also disclosed are methods for making crosslinked derivatized polysaccharides that include contacting particles of a polysaccharide with a first crosslinking agent and / or second cross-linking agent in an aqueous medium under conditions appropriate to intra-particulately crosslink the particles. The first and / or second crosslinking agent can include a copper compound, a magnesium compound, a calcium compound, an aluminum compound, p-benzoquinone, glyoxal, a titanium compound, a dicarboxylic acid, a dicarboxylic acid salt, a phosphite compound or a phosphate compound. The crosslinked polysaccharide of the present invention is especially useful in personal care formulations, especially formulations comprising silicone since it improves silicone deposition.
Owner:RHODIA OPERATIONS SAS
Extraction and purification method of capsular polysaccharide in 336-type staphylococcus aureus
ActiveCN107058421AIncrease productionEase of clinical productionMicroorganism based processesFermentationStaphylococcus cohniiPurification methods
Owner:LANZHOU INST OF ANIMAL SCI & VETERINARY PHARMA OF CAAS
Method of isolating biologically active fraction containing clinically acceptable native S-lipopolysaccharides obtained from bacteria producing endotoxic lipopolysaccharides
InactiveUS20070031447A1High yieldImprove the immunityOrganic active ingredientsBacterial antigen ingredientsAklanonic acidPolysaccharide Vaccine
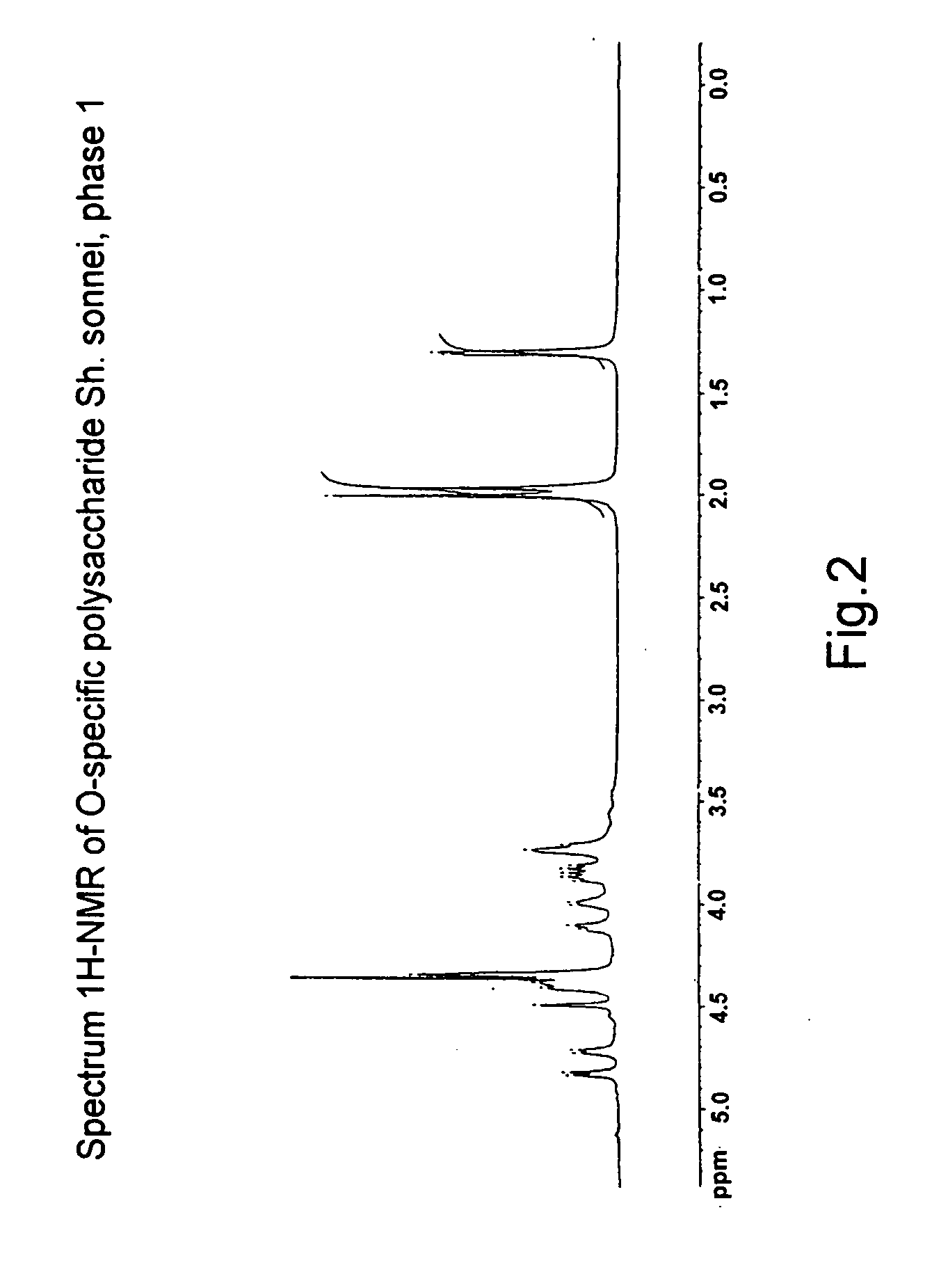
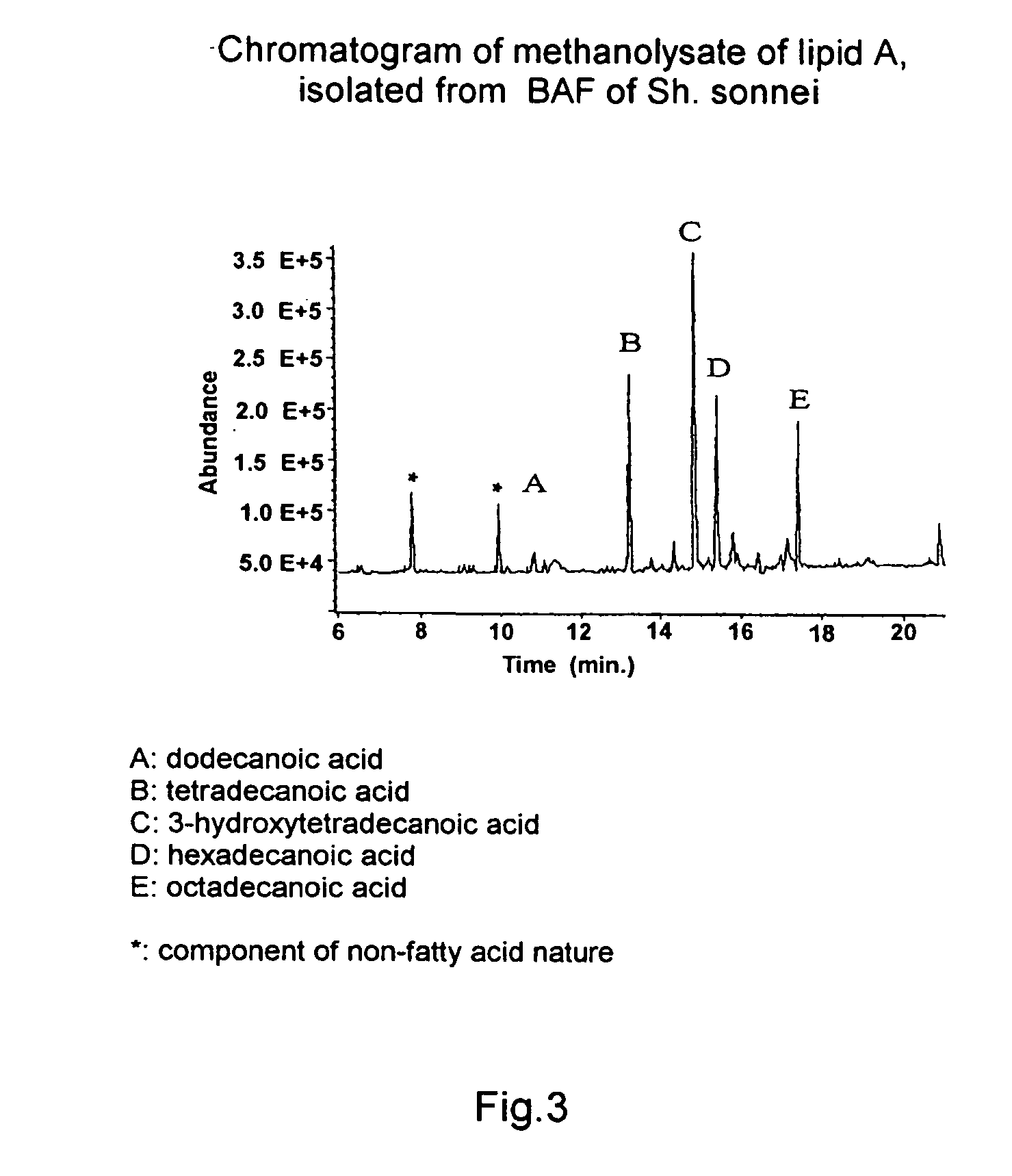
A biologically active fraction (BAF) is presented containing mainly S-lipopolysaccharide (LPS) from gram-negative bacteria producing endotoxic LPSs. These fractions are characterized in that in the lipid A of S-LPS the mole ratio of D-glucosamine and β-hydroxy acids selected from the group comprising β-hydroxydecanoic, β-hydroxydodecanoic, β-hydroxytetradecanoic, β-hydroxyhexadecanoic, is approximately 2:1-4, and the mole ratio of D-glucosamine and higher fatty acids, connected both by amide and ester links, in the lipid A of S-LPS is approximately 2:3-7. A method of isolating BAF, containing mainly S-LPS from gram-negative bacteria producing endotoxic S-LPSs, is also presented. The obtained BAFs have pyrogenicity at the level of commercial polysaccharide vaccines and low endotoxicity, have high immunogenicity, which makes it possible to use them as vaccines for mammals, including humans. They are an inducer of cytokines and also may be considered to be a prophylactic tolerogenic anti-shock preparation.
Owner:APARIN PETR +1
Chlorella polysaccharide
InactiveCN107573430AHigh yieldSimple extraction processImmunological disordersAntineoplastic agentsAlcoholFreeze-drying
The invention provides a chlorella polysaccharide and belongs to the technical field of polysaccharide extraction. The extraction of the chlorella polysaccharide comprises the following steps: (1) preparing an alga solution by chlorella powder, adding an active polypeptide, selecting a sodium phosphate buffer solution as an extracting agent, repeatedly performing freezing and thawing, ultrasonic treatment and centrifuging, and taking supernate to obtain a crude protein extracting solution; (2) performing vacuum concentration on the supernate until the volume of the supernate is 1 / 10-3 / 10 of the volume of the supernate before the vacuum concentration, and performing alcohol precipitation and centrifuging to obtain a crude polysaccharide; (3) performing redissolving and removing proteins byusing a trichloroacetic acid method; and (4) performing vacuum concentration and freeze drying to obtain the chlorella polysaccharide. The extracted chlorella polysaccharide provided by the inventionhas excellent effects of promoting organism immunity and the resisting tumors and can be used in health care products. The extraction process of the chlorella polysaccharide is simple, the operabilityis high, and the production cost is low.
Owner:兰溪市哥特生物技术有限公司
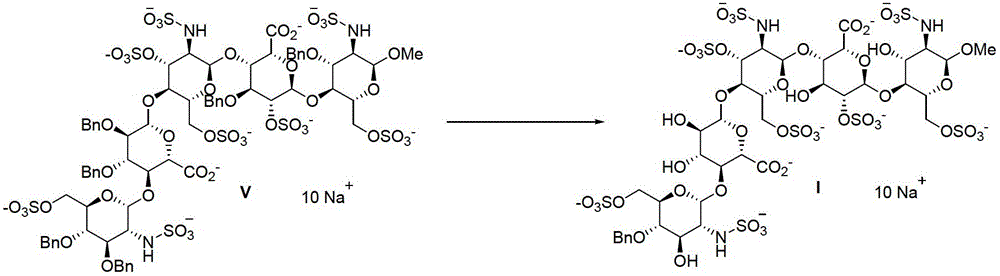
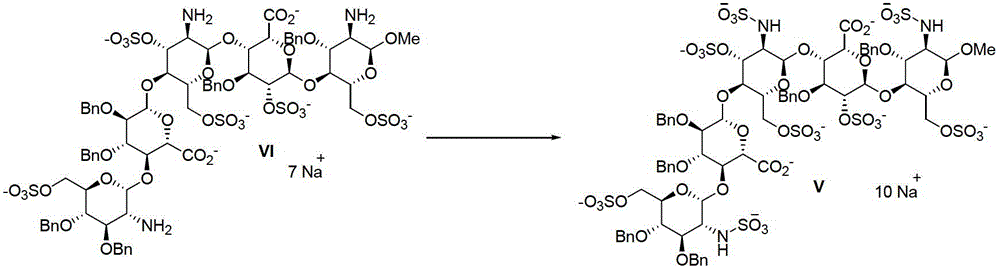
Methods for preparing class-one polysaccharide derivative and intermediate of class-one polysaccharide derivative
InactiveCN102718808AReduce pollutionMild reaction conditionsSugar derivativesHydrogen atmosphereReaction temperature
The invention discloses a method for preparing a class-one polysaccharide derivative. The method includes the steps: adding palladium-carbon catalysts into organic solvents of a compound V or mixed solvents of organic solvents and water; and mixing the catalysts and the solvents to completely react in hydrogen atmosphere to obtain the class-one polysaccharide derivative. The organic solvents can be conventional solvents for the reaction in the field and include one or more of methanol, ethanol, isopropyl alcohol, n-butyl alcohol, N, N-dimethyl formamide, acetic ether and dimethyl sulfoxide, the volume-mass ratio of the organic solvents or the mixed solvents of the organic solvents and the water to the compound V is 1-10000ml / g, the content of palladium-carbon is 1%-20%, the weight ratio of the palladium-carbon to the compound V is preferably 0.00001-1:1, and the reaction temperature ranges from -20 DEG C to 80 DEG C. The method has the advantages that reaction conditions are moderate, side reaction is less, yield is high, environmental pollution is low, and the method is suitable for industrial production.
Owner:HSING PHARMACEUTICALS CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com