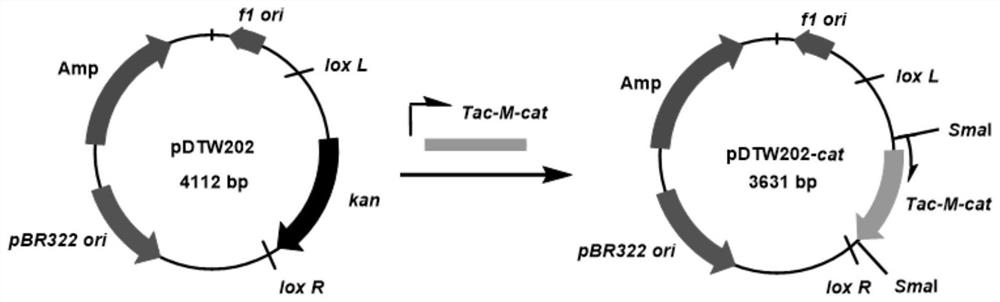
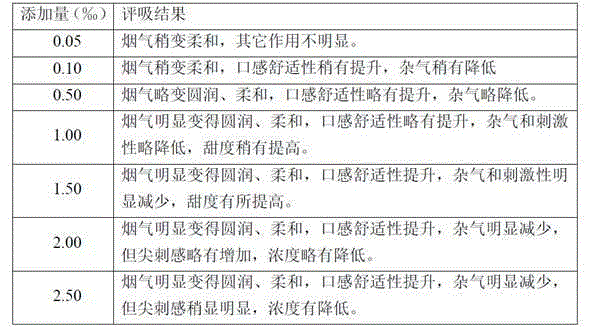
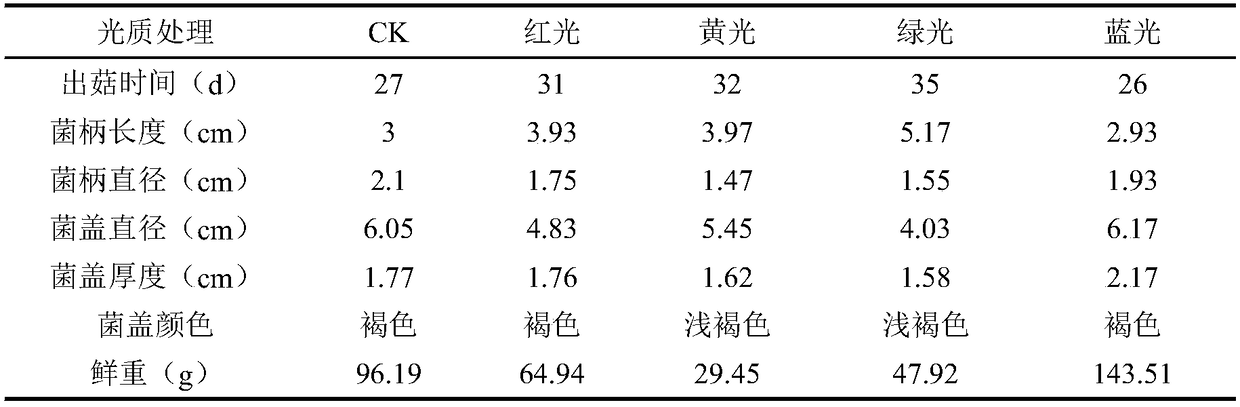
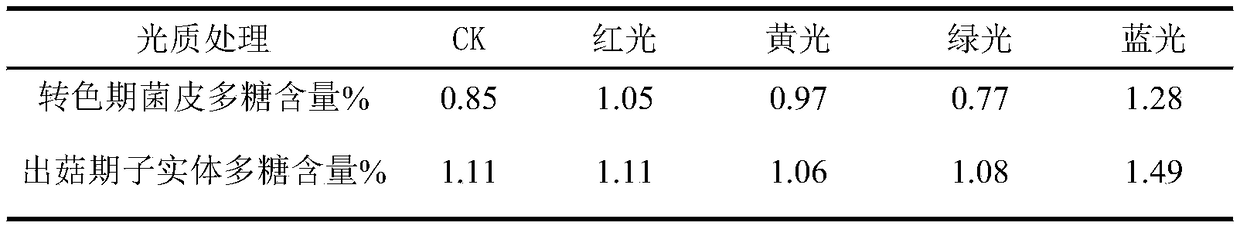
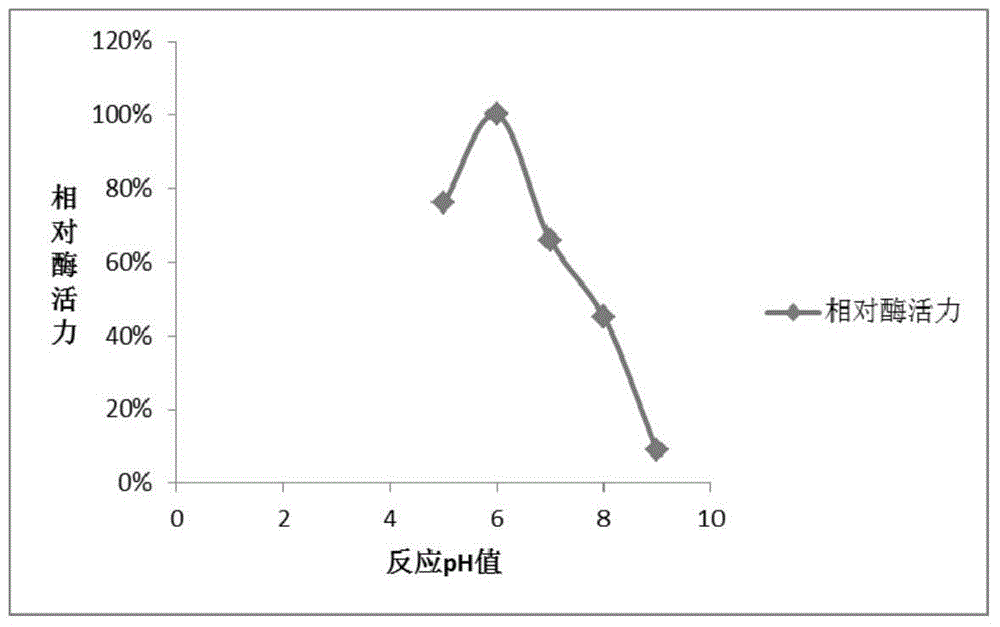
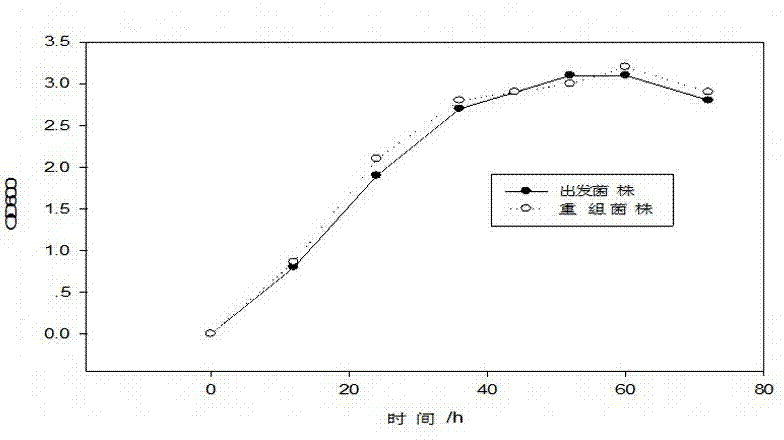
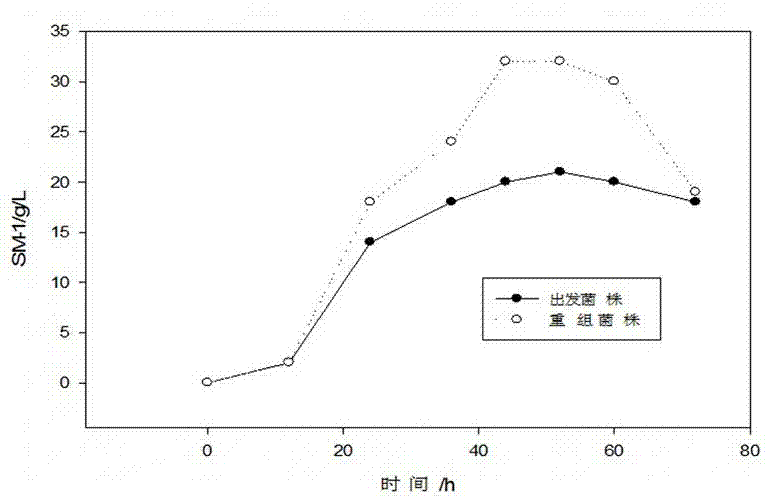
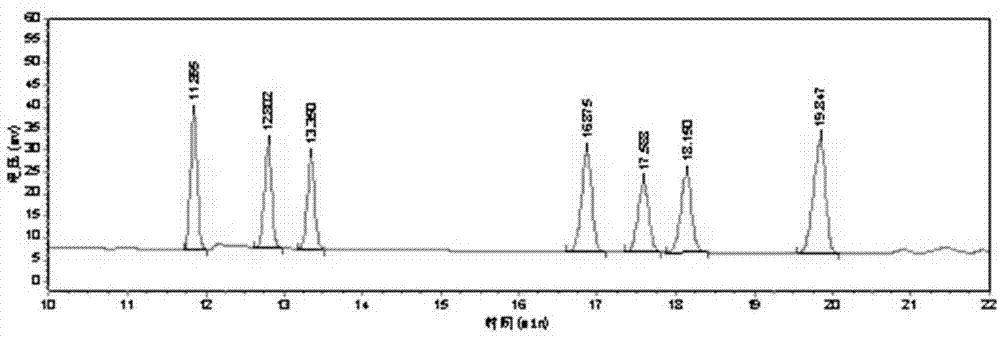
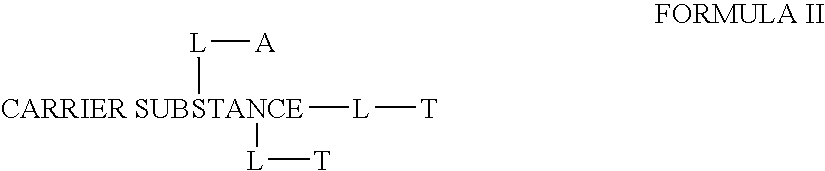Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
48 results about "Polysaccharide synthesis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Chloroquine coupled antibodies and other proteins with methods for their synthesis
InactiveUS20070166281A1Improve efficacyImprove transportBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsDrug conjugationTreatment effect
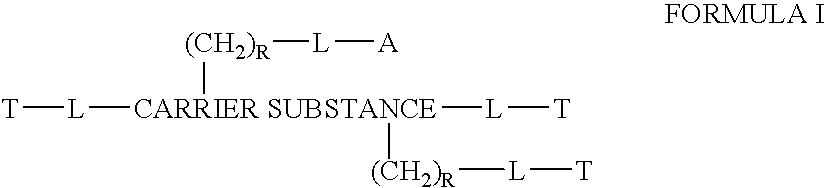
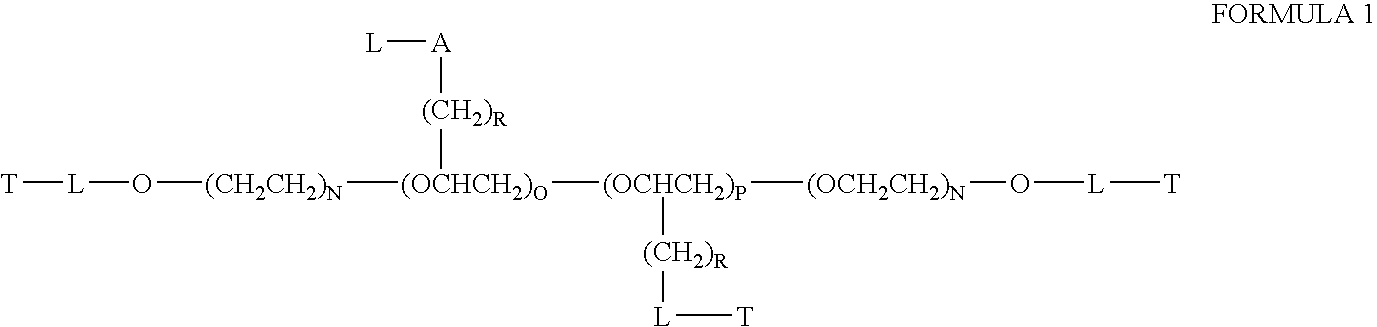
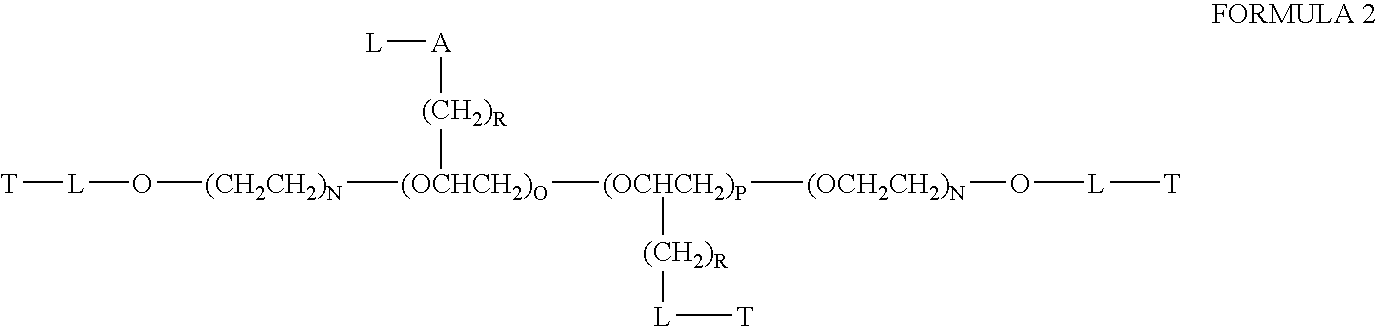
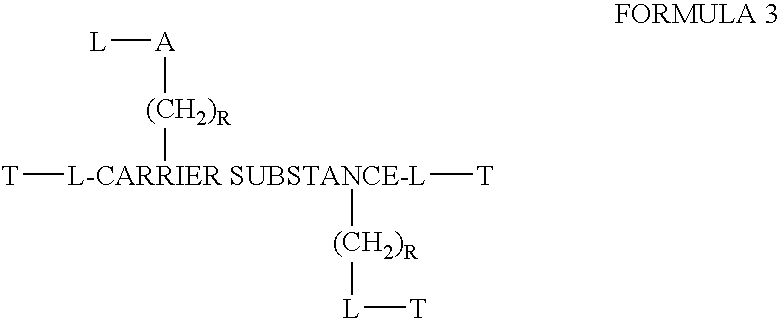
This invention discloses compositions of chloroquine-coupled active agents such as therapeutic antibodies or insulin, including methods for their preparation. The prior art has shown that chloroquines given as free drug in high enough concentration, enhances the release of various agents from cellular endosomes into the cytoplasm. The purpose of these compositions is to provide a controlled amount of chloroquine at the same site where the drug is delivered, thereby reducing the overall dosage needed. The compositions comprise a chloroquine substance coupled to a drug directly or through a variety of pharmaceutical carrier substances. The carrier substances include polysaccharides, synthetic polymers, proteins, micelles and other substances for carrying and releasing the chloroquine compositions in the body for therapeutic effect. The compositions can also include a biocleavable linkage for carrying and releasing the drug for therapeutic or other medical uses. The invention also discloses carrier compositions that are coupled to targeting molecules for targeting the delivery of chloroquine substances and antibody or insulin to their site of action.
Owner:KOSAK KENNETH M
Production of defined monodisperse heparosan polymers and unnatural polymers with polysaccharide synthases
InactiveUS20080109236A1Surgical adhesivesPharmaceutical delivery mechanismPolysaccharide synthesisSugar
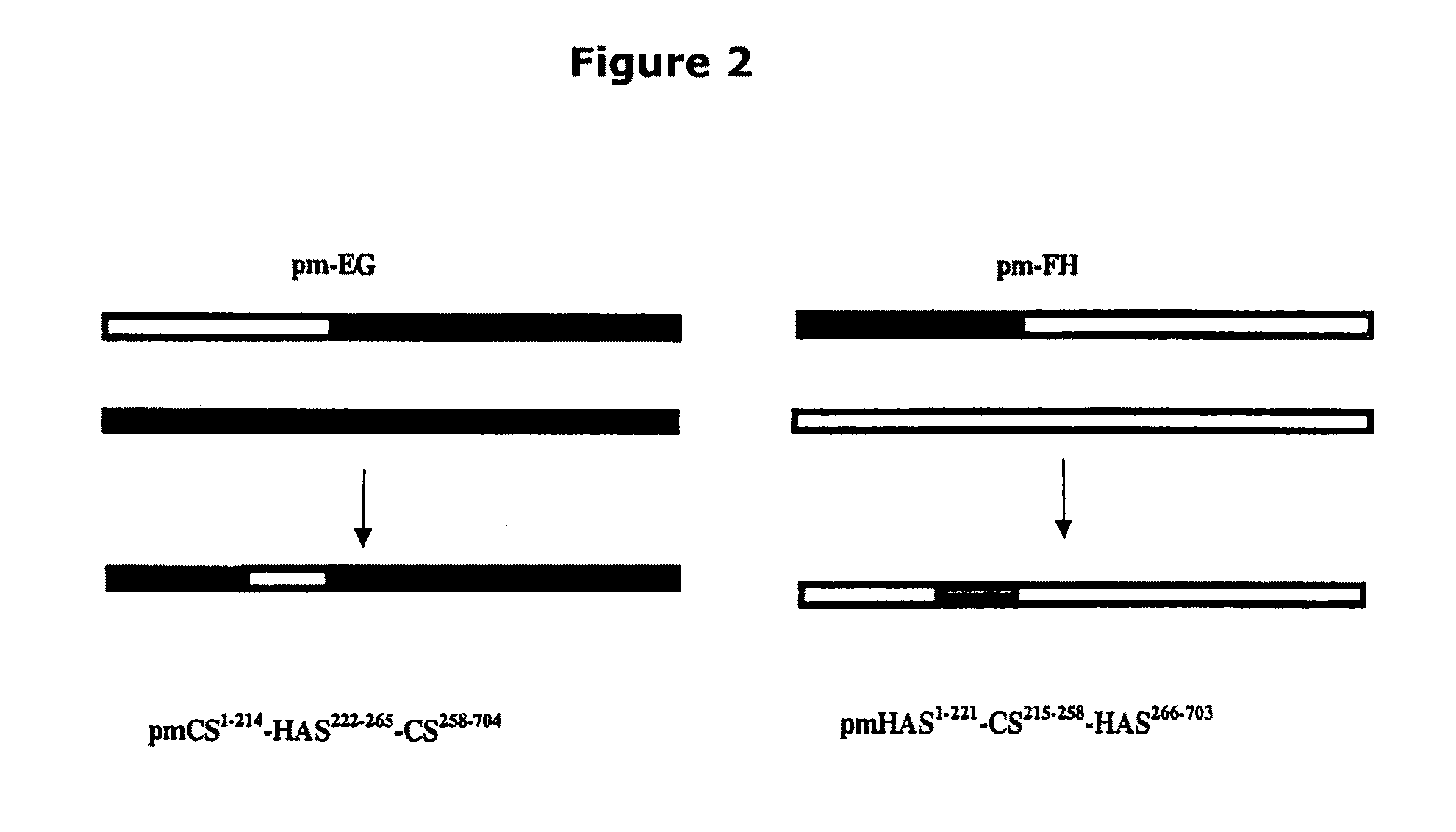
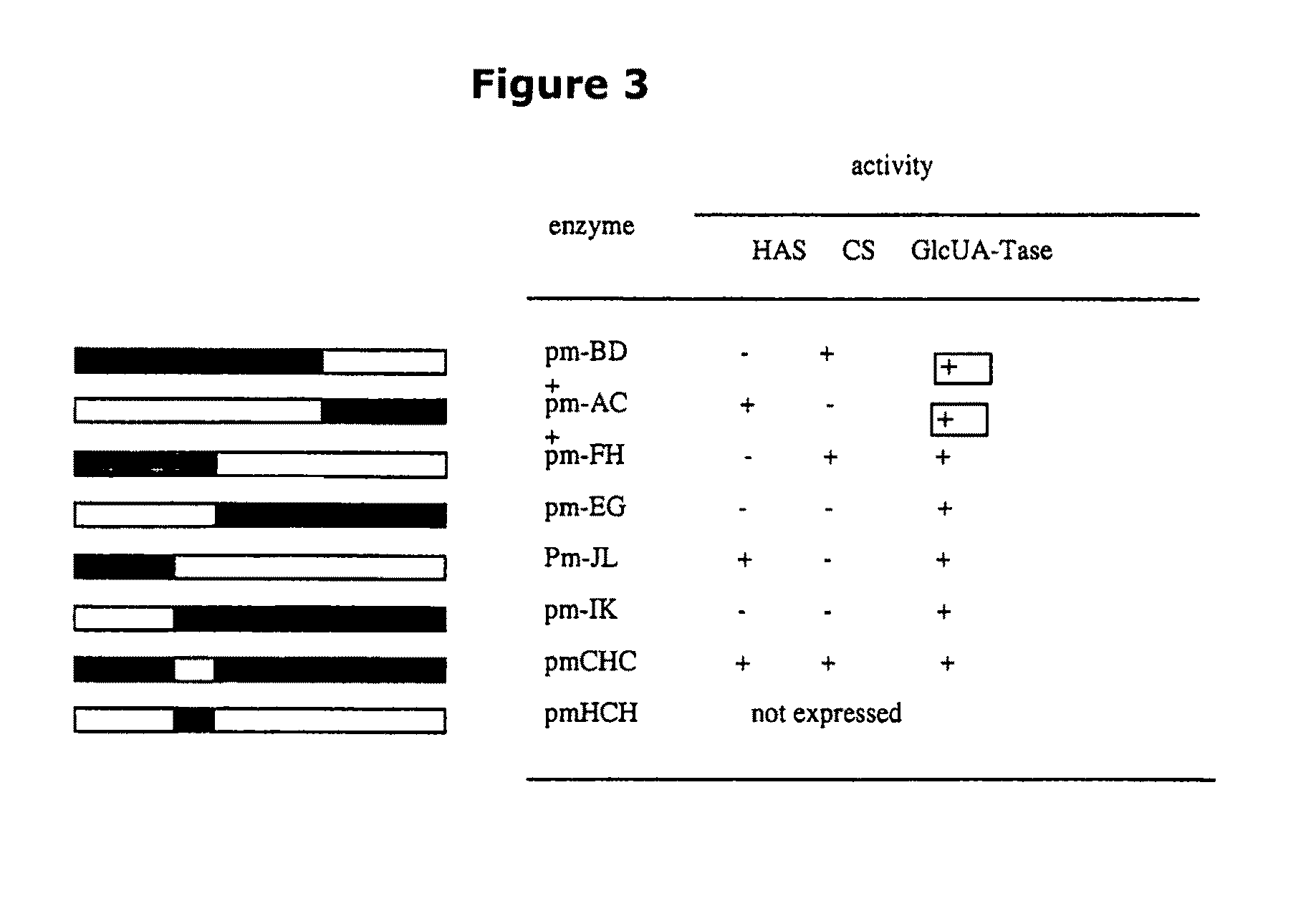
The present invention relates to methodology for polymer grafting by a polysaccharide synthase and, more particularly, polymer grafting using the hyaluronate or chondroitin or heparin / heparosan synthases from Pasteurella, in order to create a variety of glycosaminoglycan oligosaccharides having a natural or chimeric or hybrid sugar structure with a targeted size that are substantially monodisperse in size. The present invention also relates to methodology for polymer grafting by a polysaccharide synthase to form glycosaminoglycan polymers having an unnatural structure.
Owner:THE BOARD OF RGT UNIV OF OKLAHOMA
Chloroquine coupled nucleic acids and methods for their synthesis
InactiveUS20060040879A1Overcome limitationsFacilitated releaseSugar derivativesGenetic therapy composition manufactureTherapeutic effectPharmaceutical Substances
This invention discloses compositions and methods for preparing chloroquine-coupled nucleic acid compositions. The prior art has shown that chloroquines given as free drug in high enough concentration, enhances the release of various agents from cellular endosomes into the cytoplasm. The purpose of these compositions is to provide a controlled amount of chloroquine at the same site where the nucleic acid needs to be released, thereby reducing the overall dosage needed. The compositions comprise a chloroquine substance coupled to a nucleic acid directly or through a variety of pharmaceutical carrier substances. The carrier substances include polysaccharides, synthetic polymers, proteins, micelles and other substances for carrying and releasing the chloroquine compositions in the body for therapeutic effect. The compositions can also include a biocleavable linkage for carrying and releasing nucleic acids for therapeutic or other medical uses. The invention also discloses nucleic acid carrier compositions that are coupled to targeting molecules for targeting the delivery of nucleic acids to their site of action.
Owner:KOSAK KENNETH
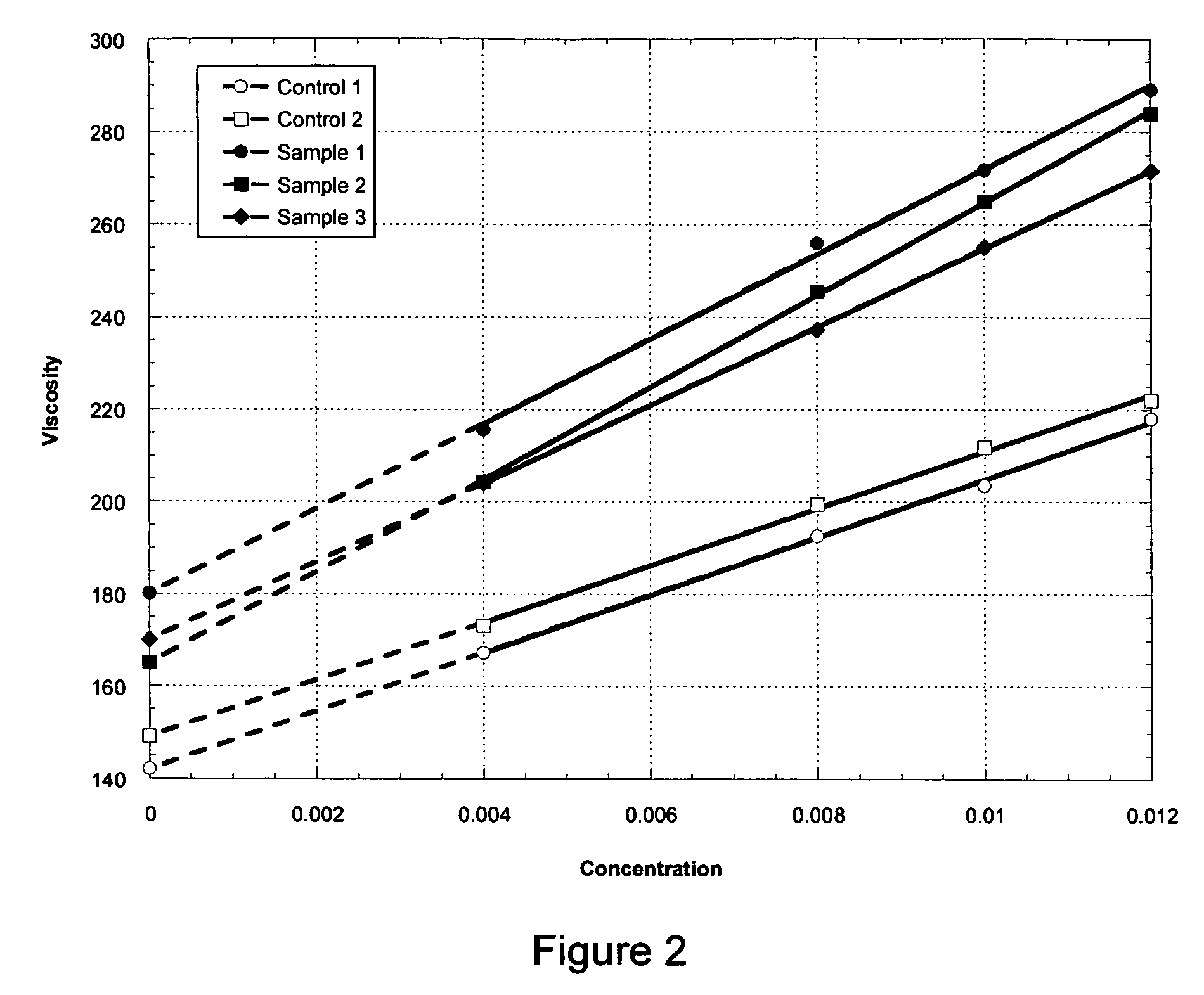
High viscosity diutan gums
ActiveUS7868167B2Increase productionImproved viscosity propertiesBiocideBacteriaBiotechnologyPhysical property
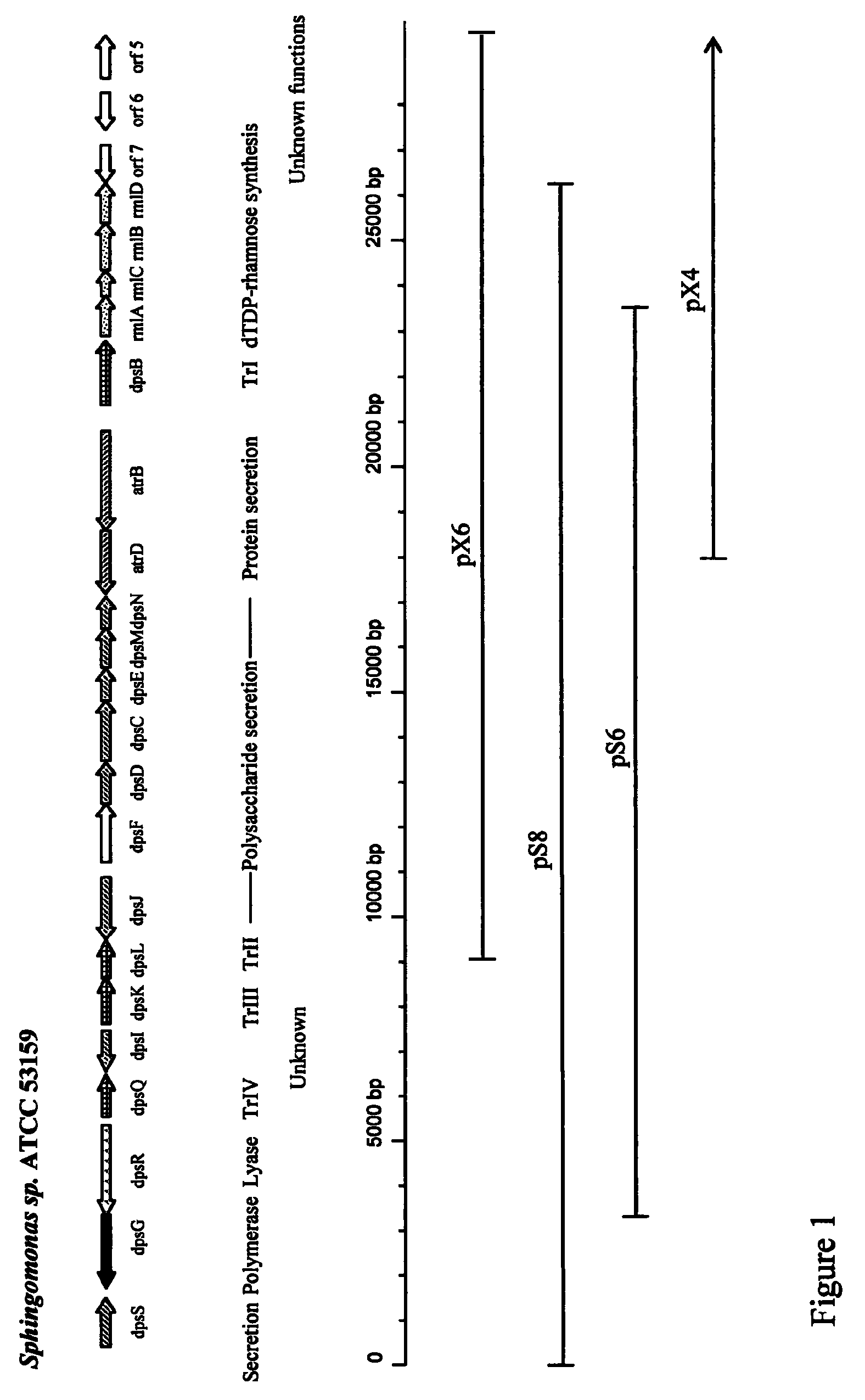
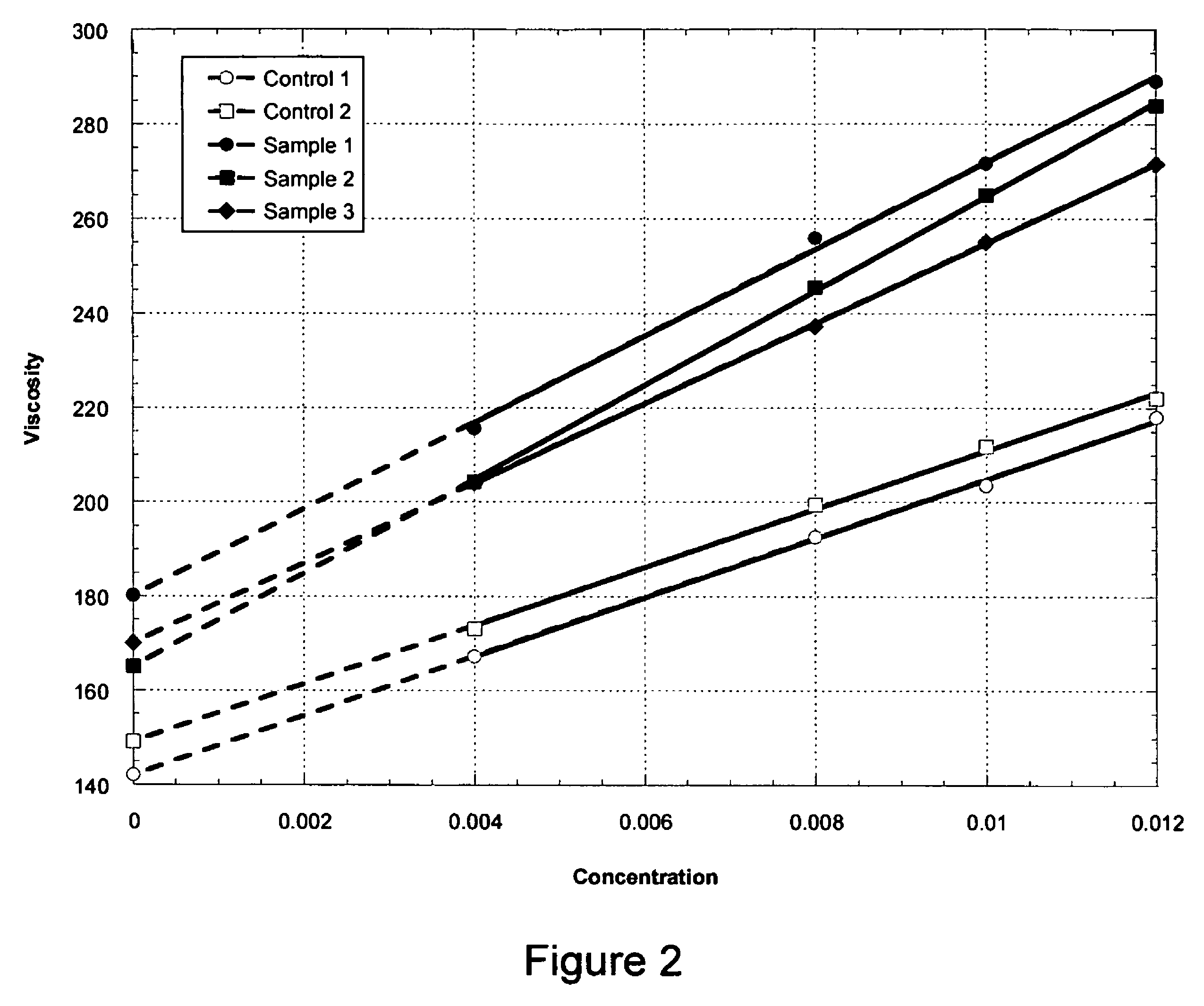
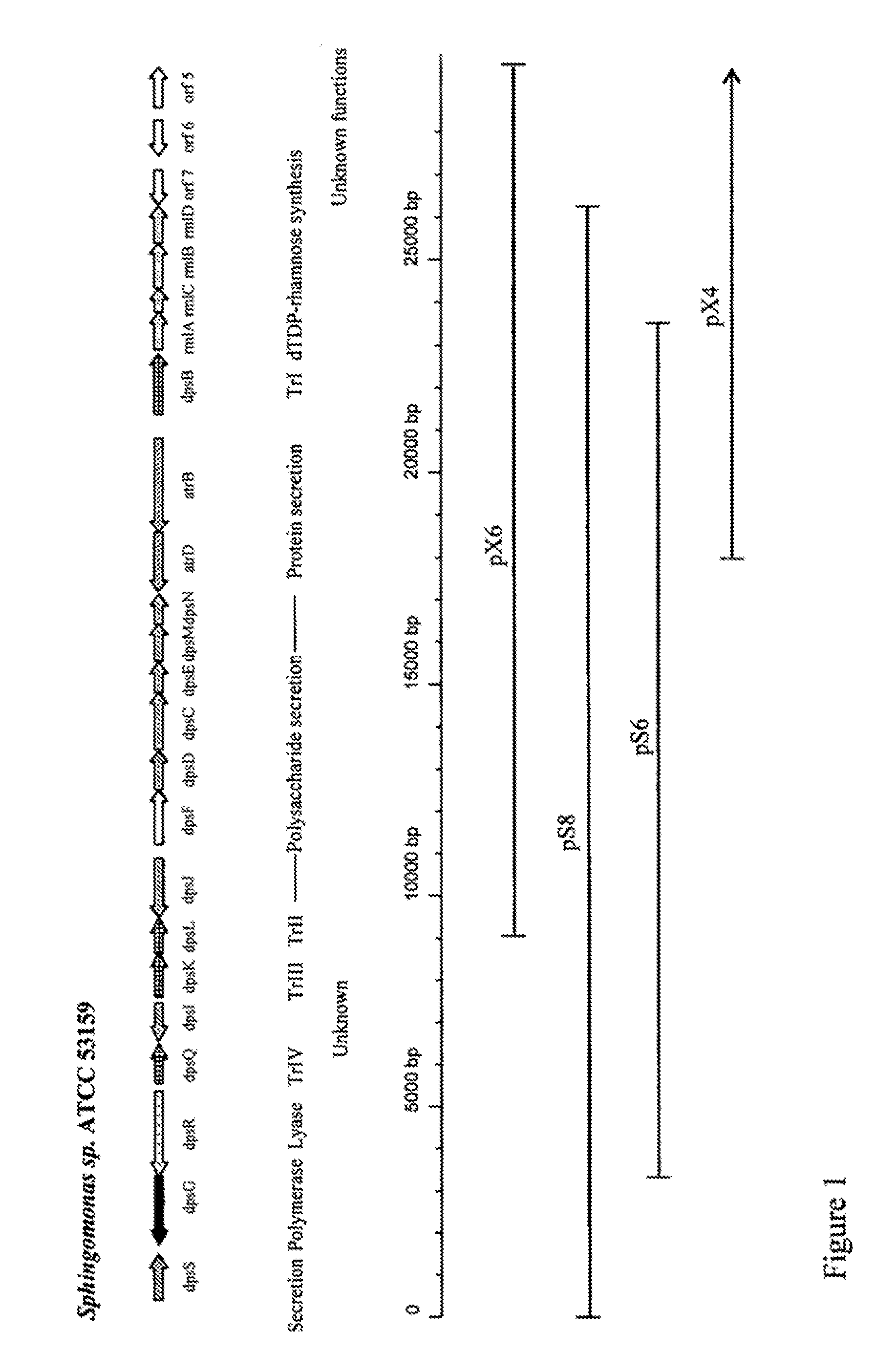
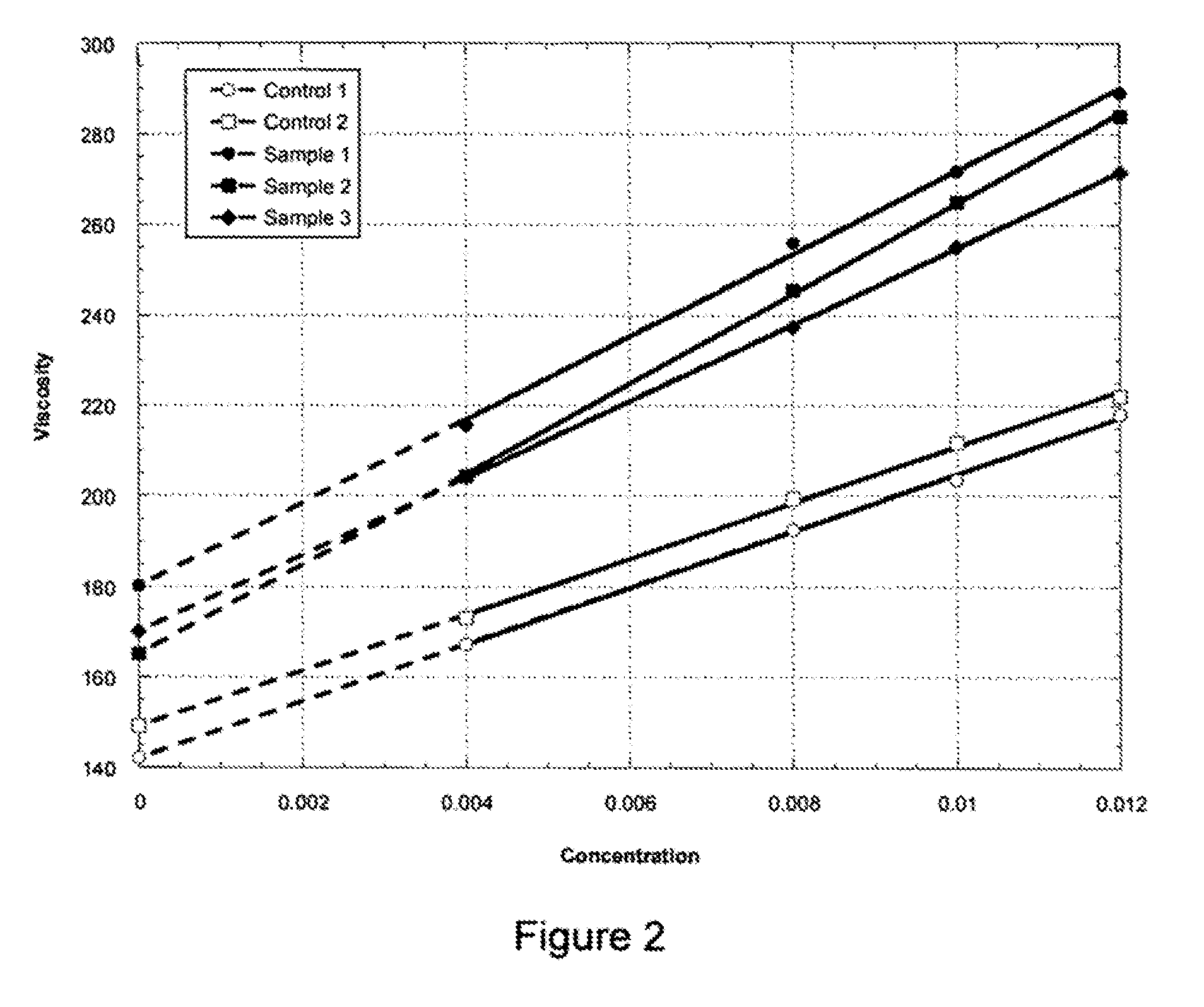
The production of a diutan polysaccharide exhibiting increased viscosity properties as compared with previously produced polysaccharide of the same type of repeating units. Such an improved diutan polysaccharide is produced through the generation of a derivative of Sphingomonas sp. ATCC 53159 that harbors a multicopy broad-host-range plasmid into which genes for biosynthesis of diutan polysaccharide have been cloned. The plasmid provides the capability within the host Sphingomonas strain to produce multiple copies of genes for such polysaccharide synthesis. In such a manner, a method of not just increased production of the target diutan polysaccharide, but also production of a diutan polysaccharide of improved physical properties (of the aforementioned higher viscosity) thereof is provided. Such a diutan polysaccharide has proven particularly useful as a possible viscosifier in oilfield applications and within cement materials. The inventive methods of production of such an improved diutan polysaccharide, as well as the novel cloned genes required to produce the improved diutan within such a method, are also encompassed within this invention. Additionally, the novel engineered Sphingomonas strain including the needed DNA sequence is encompassed within this invention.
Owner:CP KELCO U S INC
Production of defined monodisperse heparosan polymers and unnatural polymers with polysaccharide synthases
The present invention relates to methodology for polymer grafting by a polysaccharide synthase and, more particularly, polymer grafting using the hyaluronate or chondroitin or heparin / heparosan synthases from Pasteurella, in order to create a variety of glycosaminoglycan oligosaccharides having a natural or chimeric or hybrid sugar structure with a targeted size that are substantially monodisperse in size. The present invention also relates to methodology for polymer grafting by a polysaccharide synthase to form glycosaminoglycan polymers having an unnatural structure.
Owner:THE BOARD OF RGT UNIV OF OKLAHOMA
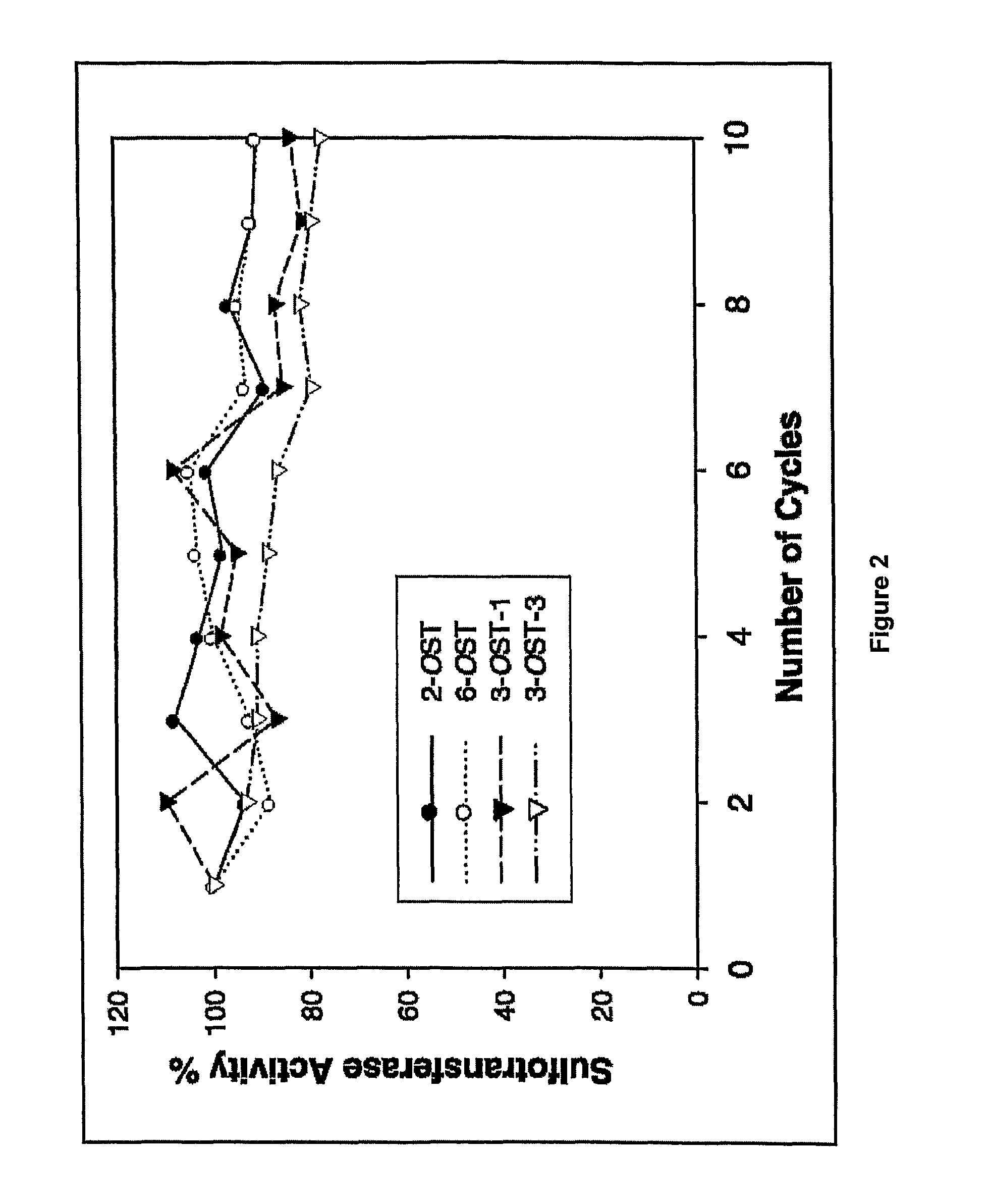
Enzymatic synthesis of sulfated polysaccharides
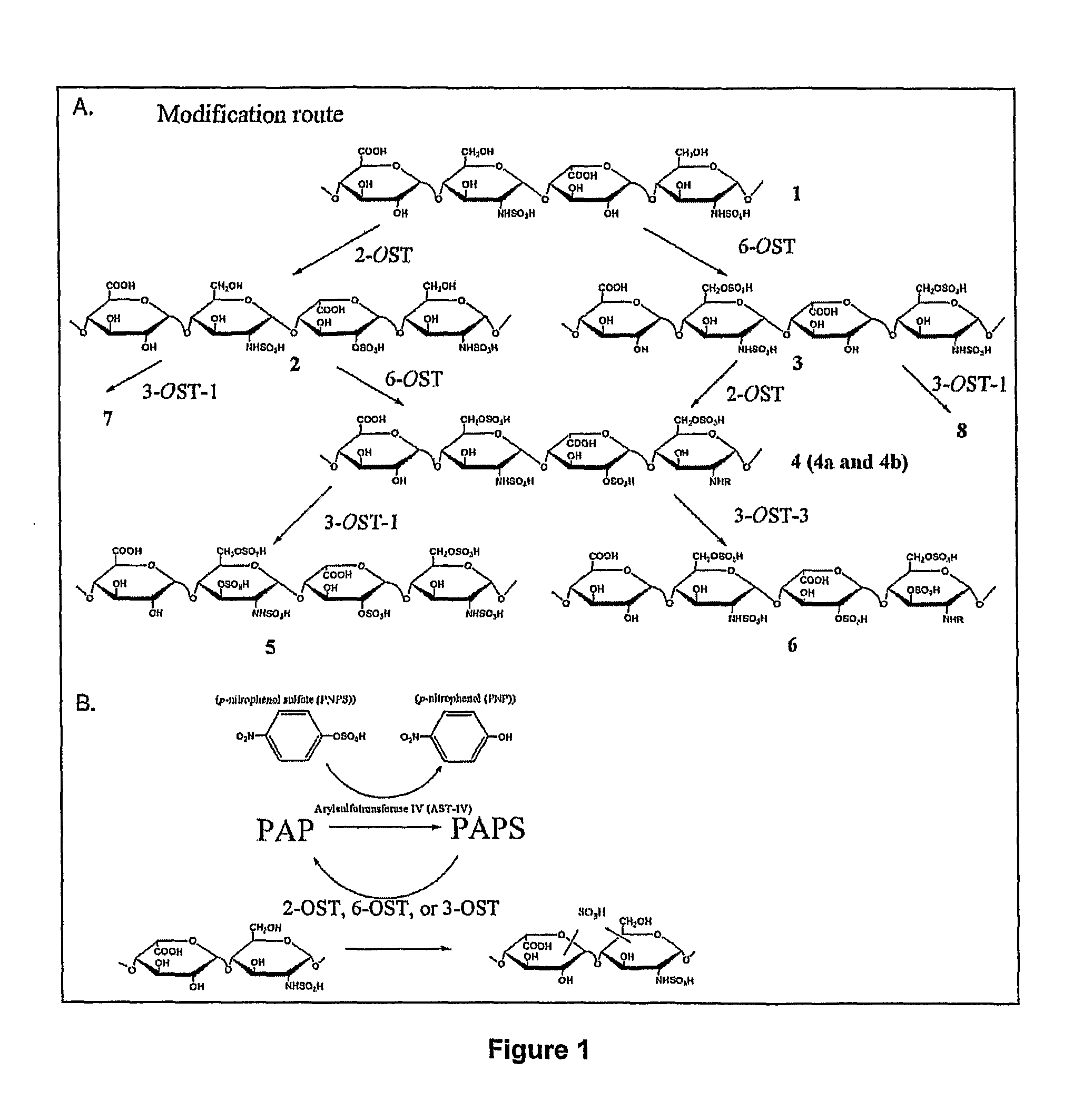
Heparin is synthesized from a polysaccharide comprised of a 1-4 glycosidically linked alternating polymer of uronic acid and glucosamine residues, wherein the uronic acid is selected from iduronic and glucuronic acid, wherein the glucosamine is partially N-sulfated; by a series of selective reactions catalyzed by recombinant enzymes.
Owner:THE UNIV OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHAPEL HILL +1
High viscosity diutan gums
ActiveUS20080319186A1Increased biosynthetic productionHigh viscosity propertySugar derivativesBacteriaBiotechnologyPhysical property
The production of a diutan polysaccharide exhibiting increased viscosity properties as compared with previously produced polysaccharide of the same type of repeating units. Such an improved diutan polysaccharide is produced through the generation of a derivative of Sphingomonas sp. ATCC 53159 that harbors a multicopy broad-host-range plasmid into which genes for biosynthesis of diutan polysaccharide have been cloned. The plasmid provides the capability within the host Sphingomonas strain to produce multiple copies of genes for such polysaccharide synthesis. In such a manner, a method of not just increased production of the target diutan polysaccharide, but also production of a diutan polysaccharide of improved physical properties (of the aforementioned higher viscosity) thereof is provided. Such a diutan polysaccharide has proven particularly useful as a possible viscosifier in oilfield applications and within cement materials. The inventive methods of production of such an improved diutan polysaccharide, as well as the novel cloned genes required to produce the improved diutan within such a method, are also encompassed within this invention. Additionally, the novel engineered Sphingomonas strain including the needed DNA sequence is encompassed within this invention.
Owner:CP KELCO U S INC
Artificial nutrient medium for Phellinus linteus fluid culture and method for fermentation of Phellinus linteus polysaccharide
InactiveCN101348803APromote growthIncrease productionMicroorganism based processesFermentationPhellinus igniariusTryptophan
The invention provides a synthetic medium for culturing a phellinus igniarius liquid. The synthetic medium takes glucose as a carbon source and 20 kinds of amino acid as a nitrogen source, and consists of inorganic salt and vitamin. The ratio of carbon to nitrogen is designed as 50 to 1; and the specific concentration g / l is as follows: the glucose: 30 to 80 grams; glutamic acid: 0.1 to 1.5 grams; glutamine: 0.1 to 1.5 grams; aspartic acid: 0.1 to 1.5 grams; asparagines: 0.1 to 1.5 grams; glutamic acid: 0.01 to 0.1 gram; tryptophan: 0.01 to 0.1 gram; valine: 0.01 to 0.1 gram; alanine: 0.01 to 0.1 gram; etc. During the whole culture process of the synthetic medium, phellinus igniarius mycelium is quick in growth; the yield of the phellinus igniarius mycelium can reach 20 grams per liter to the highest degree; simultaneously no agricultural and sideline product is introduced as the carbon source and the nitrogen source; substances such as proteins in the medium, medium compositions and so on are not carried; phellinus igniarius exopolysaccharide produced through fermentation has high purity and stable quality; and the yield of phellinus igniarius polysaccharide can reach 0.198 gram per liter to the highest degree. The synthetic medium has the advantages of clear compositions, stable quality and so on, and can be used for mass culture of the phellinus igniarius liquid and research of the regulation and control rule of polysaccharide anabolism.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
Extreme halophilic archaea engineering bacteria for producing bioplastics PHBV by effectively utilizing carbon source
ActiveCN103451201AIncrease concentrationSolve stickyBacteriaMicroorganism based processesHaloferax mediterraneiProtein C
The invention discloses extreme halophilic archaea engineering bacteria for producing bioplastics PHBV (Poly-(HydroxyButyrate-co-Hydroxy Valerate)) by effectively utilizing a carbon source. The recombined extreme halophilic archaea is extracellular polysaccharide synthesis function-deficient engineering bacteria obtained by deleting at least one protein function expressed by an extracellular polysaccharide synthesis cluster in the genome of the extreme halophilic archaea Haloferax mediterranei. The extreme halophilic archaea has the advantages that infectious microbe is not easy to pollute, PHA (Poly Hydroxy Alkanoate) is convenient to extract, the PHBV from a non-correlated carbon source can be synthesized, and the like, and is considered as a highly preponderant PHBV producing strain. The extracellular polysaccharide synthesis function-deficient strain engineering bacteria are characterized in that the polyhydroxyalkanoate can be produced from various carbon sources such as glucose, starch and whey more efficiently in contrast with a wild type strain, the concentration of the PHBV is 20% higher than that of the wild type strain under the same fermentation conditions, and the problems such as sticking, lots of bubbles and dissolved oxygen reduction of a culture solution caused by extracellular polysaccharide accumulation are also solved.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Application of glycosyltransferase gene
InactiveCN112280795ASafeImprove screening efficiencyBacteriaMicroorganism based processesNucleotideBacilli
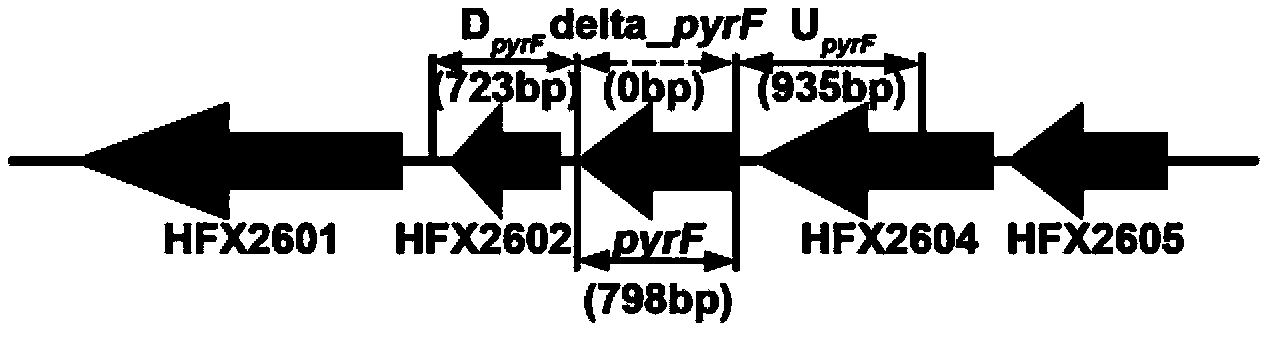
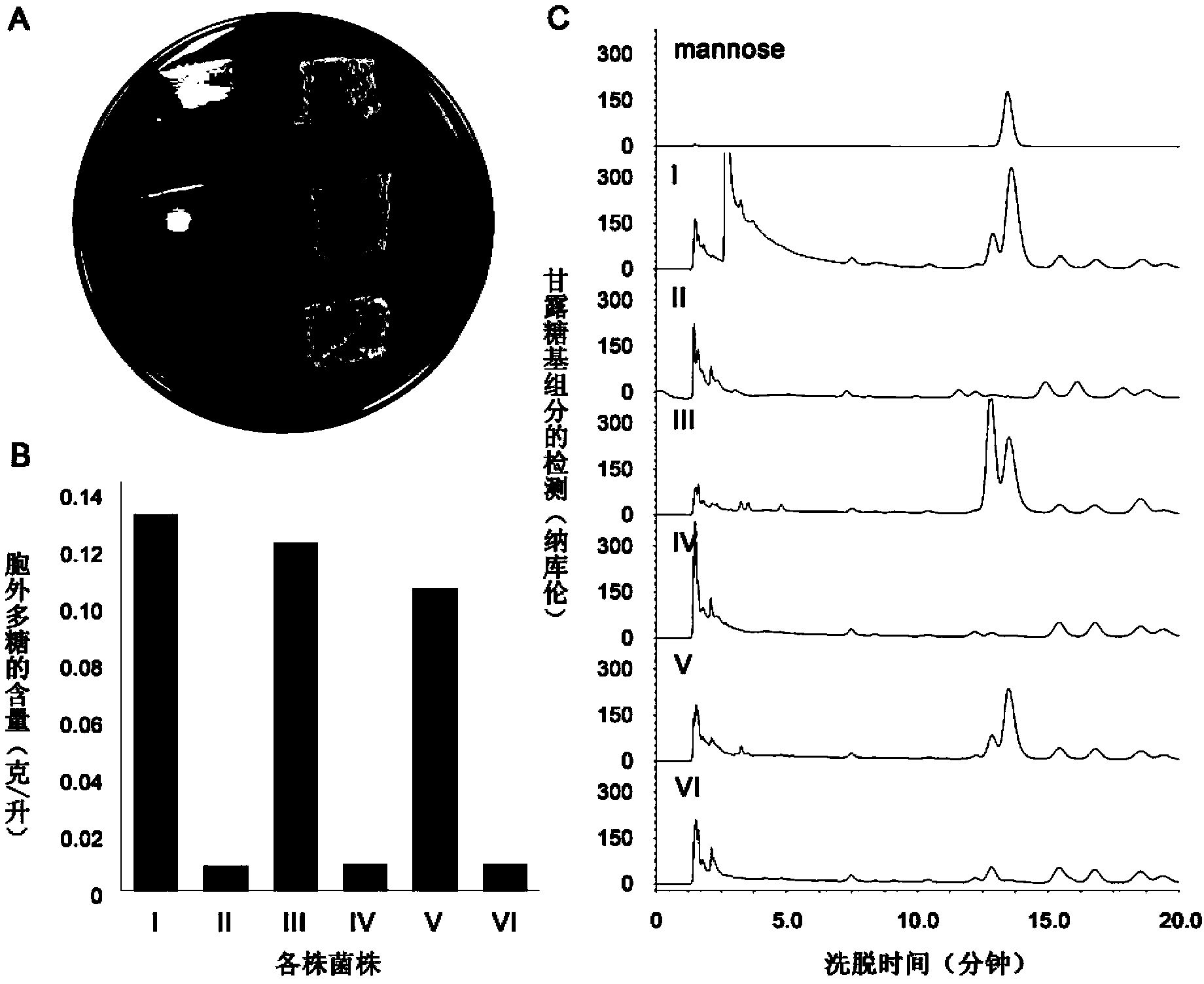
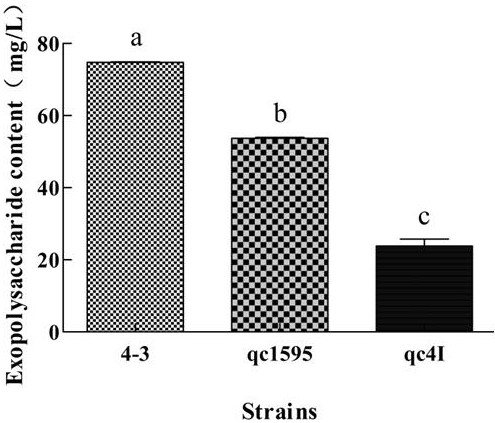
The invention discloses an application of a glycosyltransferase gene, namely an application of the glycosyltransferase gene in improving the synthesis of lactobacillus plantarum exopolysaccharides; wherein the glycosyltransferase gene is a gene orf1595 or a gene cps4I, the nucleotide sequence of the gene orf1595 is as shown in SEQ ID NO: 1, and the nucleotide sequence of the gene cps4I is as shownin SEQ ID NO: 2; an orf1595 or cps4I gene and a temperature-sensitive plasmid are recombined to construct a knockout vector, the knockout vector is introduced into a food-borne lactobacillus plantarum competent cell, and then a gene knockout strain is constructed through homologous recombination; a phenol sulfuric acid method is adopted to determine the exopolysaccharide production capacity of the strain, it is found that the exopolysaccharide production capacity of the knocked-out strain is lower than that of a wild strain, orf1595 or cps4I genes play a key role in exopolysaccharide synthesis, and the method has huge potential in the fields of exopolysaccharide biosynthesis research and application.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for increasing yield of pullulan
InactiveCN105624233AIncrease productionIncrease production capacityFermentationBiotechnologyPullulan
The invention discloses a method for increasing the yield of pullulan. The method comprises the following steps: after activating aureobasidium pullulans, inoculating a seed medium; after OD600 is greater than 0.3, inoculating seeds into a fermentation medium; monitoring OD600 of a fermentation liquid in real time; when OD600 is greater than 0.2 and less than 0.3, adding a compounding agent I which accounts for 0.02-0.03% of the volume of the fermentation liquid, so as to greatly increase the bacterium growth velocity and remarkably shorten the logarithmic growth phase; when OD600 is greater than or equal to 0.6, adding a compounding agent II which accounts for 0.03-0.05% of the volume of the fermentation liquid. The substrate conversion speed can be accelerated, the polysaccharide synthesis performance can be improved, and the yield can be greatly increased.
Owner:天津北洋百川生物技术有限公司
Preparation method of injectable self-adaptive natural hydrogel adhesive
ActiveCN113248732AImprove adhesionGood antibacterial effectSurgical adhesivesPharmaceutical delivery mechanismPolymer scienceCarboxyl radical
The invention provides a preparation method of an injectable self-adaptive natural hydrogel adhesive. The preparation method comprises the following steps: firstly, synthesizing gelatin-phenylboronic acid from carboxyl phenylboronic acid and gelatin through an amidation reaction, or synthesizing polysaccharide-phenylboronic acid from amino phenylboronic acid and natural polysaccharide; synthesizing gelatin-dopamine or polysaccharide-dopamine from dopamine and gelatin or natural polysaccharide through an amidation reaction; and dissolving the gelatin-phenylboronic acid / polysaccharide-phenylboronic acid in a phosphate buffer solution, dissolving the gelatin-dopamine / polysaccharide-dopamine in a phosphate buffer solution containing natural polyphenol substances, and uniformly mixing two obtained solutions to realize a spontaneous esterification reaction of phenylboronic acid and polyphenol so as to generate reversible boric acid ester bonds, thereby finally preparing the injectable self-adaptive natural hydrogel adhesive. The hydrogel adhesive disclosed by the invention has good biological adhesion and antibacterial and anti-inflammatory effects, and is attached to the surface of a tissue to play a repairing role; and the hydrogel adhesive has good mechanical self-adaptive performance and can be matched with deformation and frequency of different dynamic tissues.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Abortus Brucella vaccine recombinant strain and application thereof in preparing vaccine
InactiveCN101575587APromote eradicationImprove purification effectAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsVirulent characteristicsBiology
The invention discloses an abortus Brucella vaccine recombinant strain and an application thereof in preparing vaccine. The recombinant strain is a strain obtained by deactivating capsular polysaccharide synthesis protein gene and carboxyl uridine phosphate decarboxylase gene in the abortus Brucella strain S19. The obtained recombinant strain has small virulence and can be used as vaccines to immunize animals without needs of deactivation. The inoculated animal generates no lipopolysaccharide antibody and the virulent virus strain-infected animal can be distinguished from novel vaccine strain immunized animal by serological reaction. The recombinant strain is beneficial to improving the Brucella vaccine, researching diagnosis and identification reagents and developing the Brucella vaccine and matched diagnosis and identification reagents, and has extremely important significance in deracinating and purifying the global animal Brucella.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
A strain of Escherichia coli with reduced membrane wall and its high-production phb application
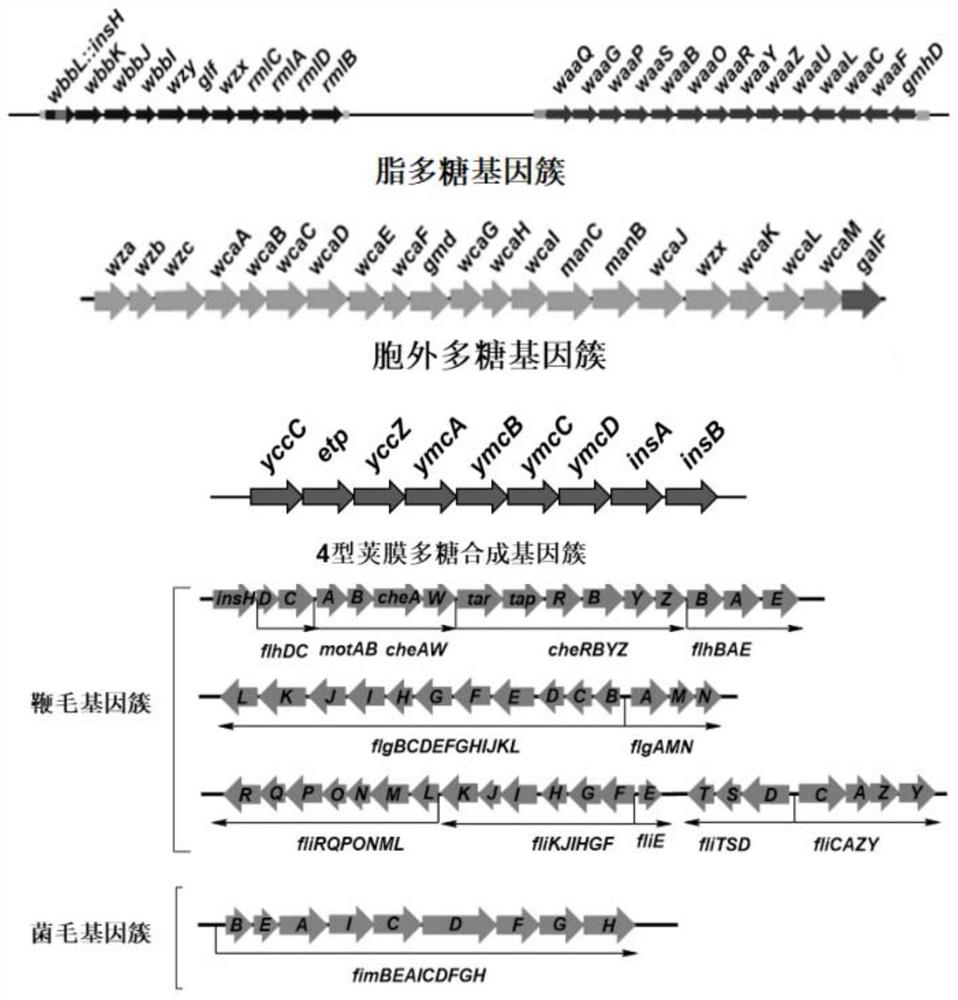
The invention discloses an Escherichia coli membrane wall-reduced chassis strain and the application of the high-yielding PHB strain, belonging to the fields of genetic engineering and fermentation engineering. The present invention knocks out the core sugar gene cluster gmhD-waaQ and the O-antigen gene cluster wbbL-rmlB of the lipopolysaccharide on the wild-type Escherichia coli W3110 genome, the extracellular polysaccharide gene cluster galF-wza, and the type 4 capsular polysaccharide synthesis gene cluster yccC- ymcD, three flagellar gene clusters flhE-motA, fliY-fliR, flgN-flgL, and a pilus gene cluster fimB-fimH to obtain strain WJW08, and then transform the genes related to PHB synthesis into the strain to obtain recombinant strain WJW08 / pBHR68, Under normal fermentation conditions, the recombinant bacterium can synthesize 81.9% PHB of dry cell weight, which is 54.6 times that of the wild control bacterium W3110 / pBHR68 (1.5%).
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Carboxymethylated ganoderma lucidum polysaccharide, synthesis and purification method and application thereof as tobacco humectant
The invention relates to a synthesis and purification method of carboxymethylated ganoderma lucidum polysaccharide. The method includes the steps of: adding ganoderma lucidum polysaccharide and sodium hydroxide into a solvent to conduct stirring dissolving, then adding chloroacetic acid, carrying out stirring reaction at 65-85DEG C for 2-4h, performing cooling, adjusting the pH value to neutral, conducting alcohol precipitation and filtering, collecting the precipitate, then dissolving the precipitate in water, and carrying out alcohol precipitation, dialysis, and freeze drying to obtain light brown cotton-like carboxymethylated ganoderma lucidum crude polysaccharide. Test proves that: the carboxymethylated ganoderma lucidum polysaccharide provided by the invention has very good physical and sensory moisturizing effects, also can reduce cigarette stimulation and miscellaneous gas, improves the mellow and full sense and comfort of cigarette smoke, and can applied as an excellent performance tobacco humectants in cigarettes.
Owner:CHINA TOBACCO HENAN IND
Use of sodium nitroprusside in ganoderma lucidum submerged fermentation for producing ganoderma lucidum polysaccharide
InactiveCN102796782APromote productionEasy to synthesizeFermentationExperimental researchSubmerged fermentation
The invention discloses a use of sodium nitroprusside in ganoderma lucidum submerged fermentation for producing ganoderma lucidum polysaccharide. After ganoderma lucidum submerged fermentation solution culture lasting for 3-5 days, sodium nitroprusside as an inducer is added into a ganoderma lucidum submerged fermentation solution to induce ganoderma lucidum polysaccharide production in ganoderma lucidum submerged fermentation. Sodium nitroprusside crystals as nitric oxide donors are dissolved in water so that a sodium nitroprusside aqueous solution is formed and is used as an inducer for ganoderma lucidum submerged fermentation used for producing ganoderma lucidum polysaccharide. Through slowly releasing nitric oxide in cells, sodium nitroprusside can promote secondary metabolite ganoderma lucidum polysaccharide synthesis. A result of an experimental research shows that through utilization of an appropriate amount of sodium nitroprusside in a ganoderma lucidum fermentation solution, a ganoderma lucidum polysaccharide yield can be effectively increased by 25 to 160%.
Owner:ANHUI SCI & TECH UNIV
Method for improving polysaccharide content of mushroom variety 808
InactiveCN109348990AHigh in polysaccharidesImprove agronomic traitsCultivating equipmentsMushroom cultivationBiotechnologyPolysaccharide synthesis
The invention discloses a method for improving polysaccharide content of mushroom variety 808. The method includes the following specific steps: preparing raw materials, preparing mother seeds, preparing original seeds, preparing cultivation bags, culturing the cultivation bags at 25 DEG C with light intensity of 0 Lx, and placing the cultivation bags under blue light conditions for color conversion and fruiting management until hyphae are full of the bags. According to the method, the polysaccharide content can be obviously improved, the agronomic characteristics of the mushrooms are optimized, the yield of the mushrooms is improved, the activity of lignin degrading enzyme laccase and polysaccharide synthesis key enzyme UG Pase enzyme and the expression amount of correlative coding genesare improved, and the support for optimizing the existing mushroom cultivation mode, improving the planting benefits of the mushrooms and boosting the development of the mushroom processing industry is provided.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
Compositions and methods for regulating polysaccharides of a plant cell
Novel plant polysaccharide synthesis genes and polypeptides encoded by such genes are provided. These genes and polynucleotide sequences are useful regulating polysaccharide synthesis and plant phenotype. Moreover, these genes are useful for expression profiling of plant polysaccharide synthesis genes.
Owner:ARBORGEN
Method for eliminating side product polysaccharide in fermentation production of pyrroloquinoline quinone, and application of method
ActiveCN103361390ALower synthetic levelsAchieve removalMicroorganism based processesFermentationBiotechnologyMicroorganism
The invention provides a method for eliminating a side product polysaccharide in fermentation production of pyrroloquinoline quinone. According to the method, in microorganism fermentation production of pyrroloquinoline quinone, a gene knockout method is used for knockout of an important gene in a polysaccharide synthetic gene cluster of a pyrroloquinoline quinone production strain so that the production strain loses the capability of exopolysaccharide synthesis without reducing the capability of producing pyrroloquinoline quinone. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the important gene mpq_1844 in the polysaccharide synthetic gene cluster of the PQQ (pyrroloquinoline quinone) production strain Methylovorussp.MP688 is successfully knocked out by a double-exchange homologous recombination method, the gene knockout strain of the original production strain no longer synthesizes exopolysaccharide, thus the metabolism side product polysaccharide generated in microorganism fermentation production of the pyrroloquinoline quinone is eliminated, the aim of simplifying the purification technique is achieved and the foundation is laid for industrial and efficient preparation of pyrroloquinoline quinone.
Owner:INST OF BIOENG ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI OF THE CHINESE
Preparation method of injectable adaptive natural hydrogel adhesive
ActiveCN113248732BImprove adhesionGood antibacterial effectSurgical adhesivesPharmaceutical delivery mechanismPolymer scienceCarboxyl radical
The preparation method of injectable self-adaptive natural hydrogel adhesive, first synthesizes gelatin-phenylboronic acid with carboxyphenylboronic acid and gelatin through amidation reaction, or synthesizes polysaccharide-phenylboronic acid with aminophenylboronic acid and natural polysaccharide; And through amidation React dopamine and gelatin or natural polysaccharides to synthesize gelatin-dopamine or polysaccharide-dopamine; then dissolve gelatin-phenylboronic acid / polysaccharide-phenylboronic acid in phosphate buffer solution, gelatin-dopamine / polysaccharide-dopamine in polyphenol-containing substances In the phosphate buffer solution, the two are mixed well, and the spontaneous esterification reaction between phenylboronic acid and polyphenols can occur, forming a reversible borate bond, and finally an injectable self-adaptive natural hydrogel adhesive is prepared. ; The hydrogel adhesive of the present invention has good bioadhesion and antibacterial and anti-inflammatory effects, and can be attached to the tissue surface and play a repairing role; it has good mechanical self-adaptive properties and can match different dynamic tissues deformation and frequency.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
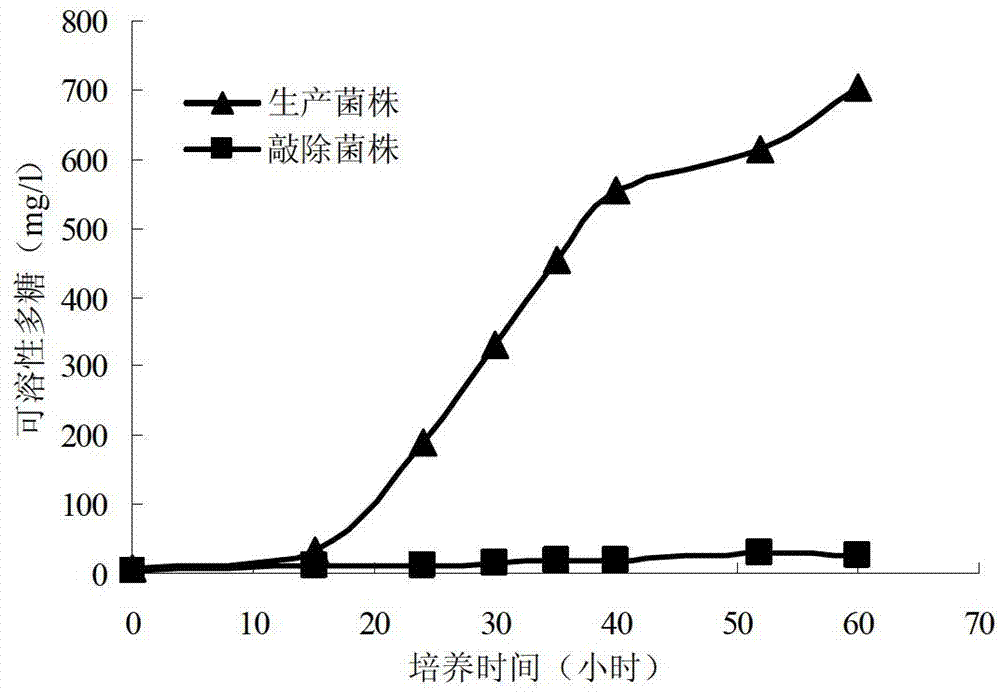
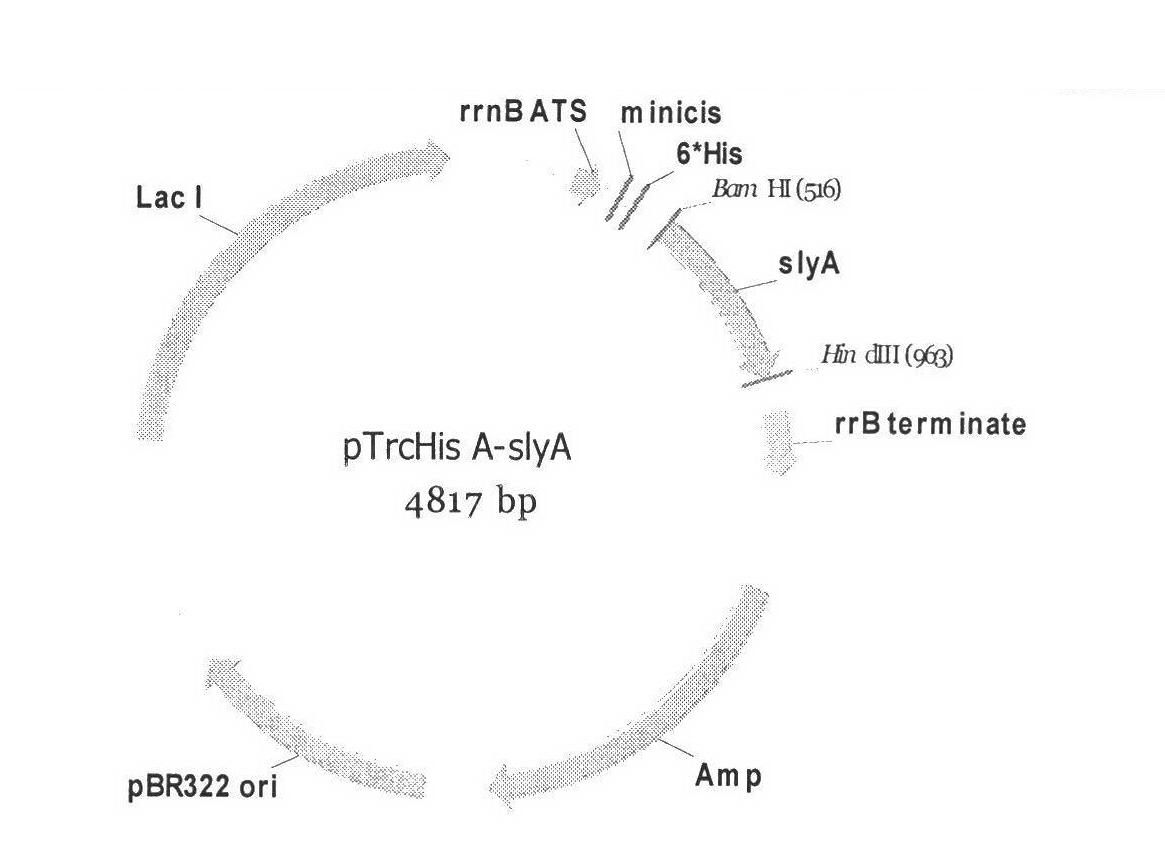
Engineered Escherichia coli and method for producing chondroitin
The invention discloses engineered Escherichia coli for high yielding capsular polysaccharide and a method for producing chondroitin by the aid of the capsular polysaccharide. Synthetic gene cluster transcriptional regulation factor slyA protein of the capsular polysaccharide is over expressed in the Escherichia coli, and expression of a synthetic gene cluster of the capsular polysaccharide in the Escherichia coli is promoted, so that the capsular polysaccharide produced by the Escherichia coli K4 is increased. The yield of the capsular polysaccharide after fermenting and culturing the engineered Escherichia coli is 112% higher than that of capsular polysaccharide produced by original bacteria, and the chondroitin with purity higher than 93% is obtained by means of collection and preparation. The engineered Escherichia coli and the method lay a certain foundation for developing fermentation production of chondroitin sulfate.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
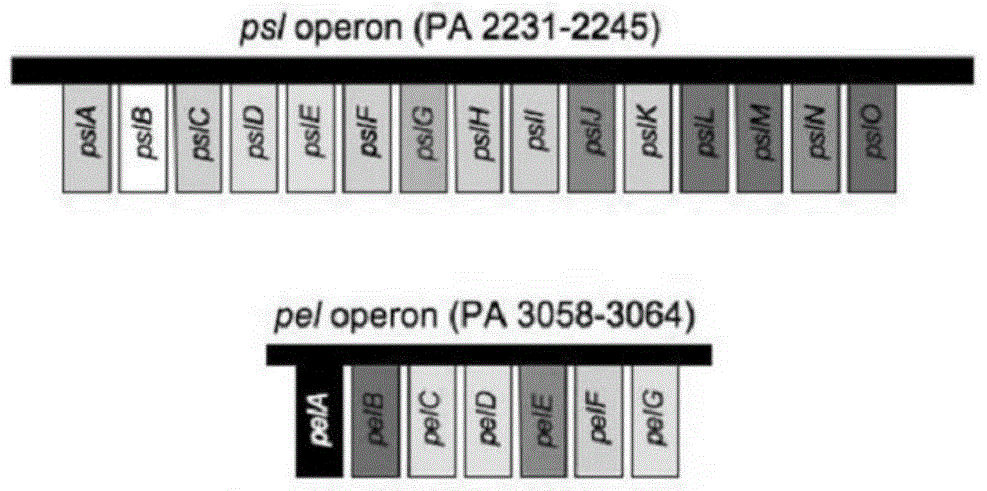
The method for increasing the production of rhamnolipid and its specific Pseudomonas aeruginosa
ActiveCN104099388BIncrease productionReduced synthesis abilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesRhamnolipidMicrobiology
The invention discloses a method for preparing rhamnolipid and its special Pseudomonas aeruginosa. The method for preparing rhamnolipids includes 1) and 2): 1) constructing a recombinant Pseudomonas aeruginosa with reduced Psl polysaccharide synthesis ability and / or reduced Pel polysaccharide synthesis ability compared with Pseudomonas aeruginosa as the starting bacterium 2) fermenting the recombinant Pseudomonas aeruginosa to obtain rhamnolipids. The experiment of the present application proves that compared with Pseudomonas aeruginosa as the starting bacterium, the rhamnolipid synthesis ability of recombinant Pseudomonas aeruginosa with reduced Psl polysaccharide synthesis ability and / or reduced Pel polysaccharide synthesis ability is improved.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
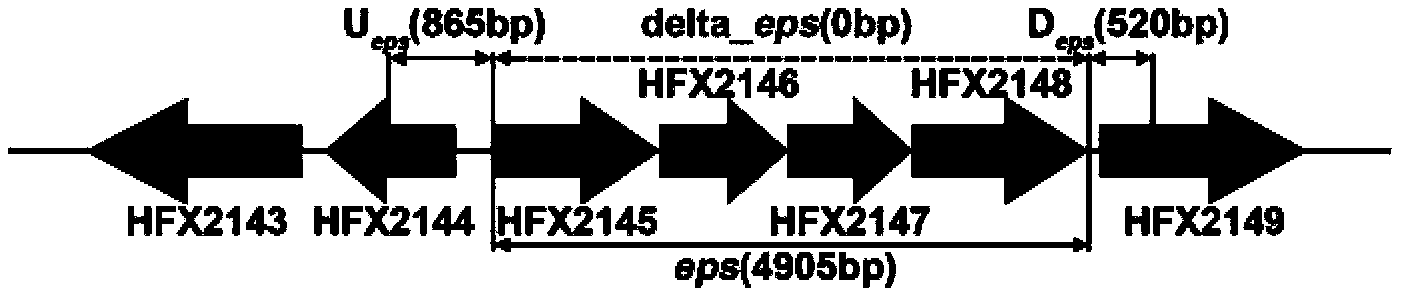
Genetic Engineering Bacteria Deleting 21 Coding Exopolysaccharide Synthesis Genes and Its Application
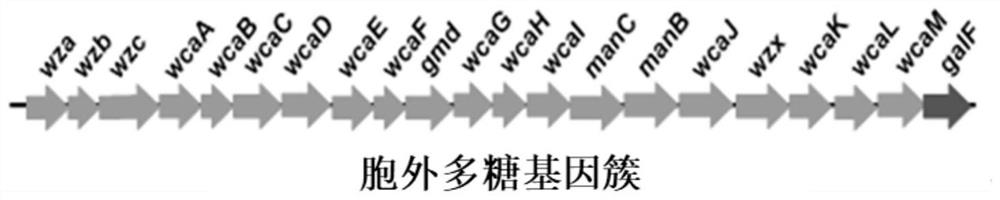
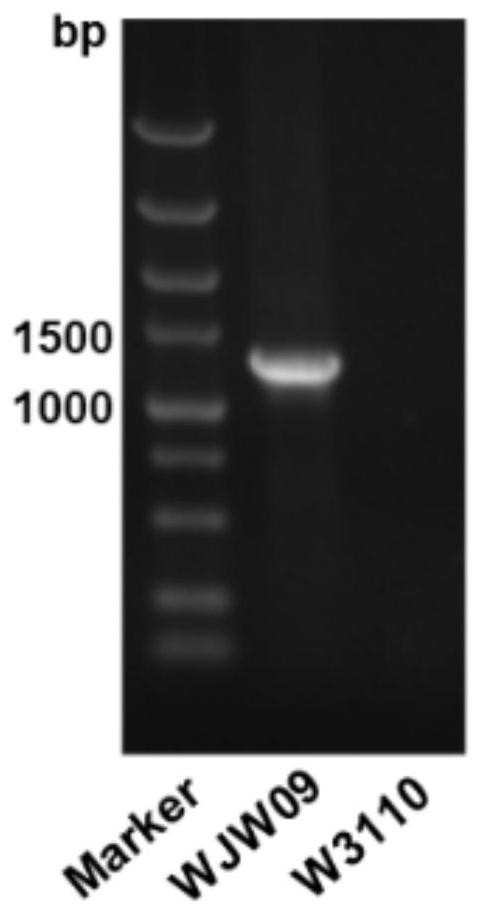
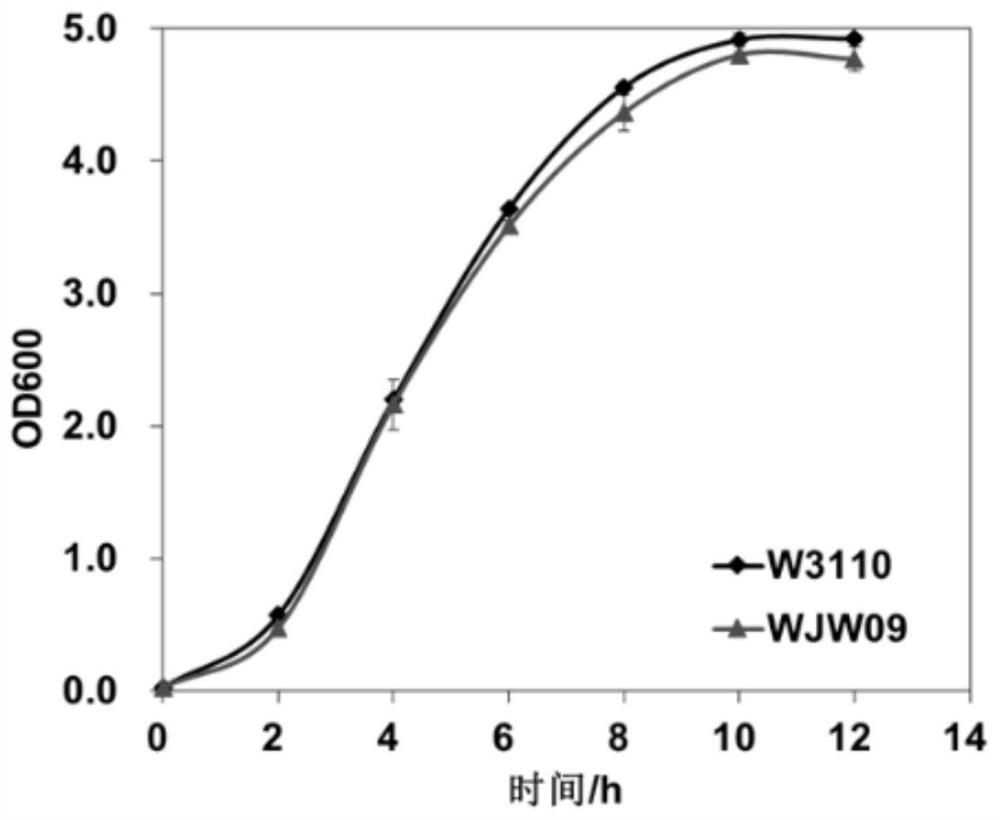
The invention discloses a genetically engineered bacterium with deficiency of 21 encoded exopolysaccharide synthetic genes and application thereof, and belongs to the field of gene engineering and fermentation engineering. A mutant bacterium WJW09 is obtained by knocking out 21 genes in charge of exopolysaccharide synthesis and transfer on an escherichia coli W3110 genome through a CRISPR / Cas9 knockout system, with the WJW09 strain as a host bacterium, a PHB synthesis gene cluster phaCAB is heterologously expressed through pBHR68, PHB synthesized through WJW09 / pBHR68 can reach 57.2% of the drycell weight, while PHB synthesized through W3110 / pBHR68 only accounts for 1.5% of the dry cell weight. The PHB volumetric production of the recombinant bacterium WJW09 / pBHR68 is 38 times that of thecontrast bacterium W3110 / pBHR68 (1.5%).
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
UDPG pyrophosphatase produced from aureobasidium pullulans, coding gene, carrier and application
The invention discloses UDPG pyrophosphatase produced from aureobasidium pullulans, a coding gene, a carrier and application to improvement of the yield of exopolysaccharides of the aureobasidium pullulans. An amino acid sequence of the UDPG pyrophosphatase is as shown in SEQ ID NO.1. The gene engineering technology is utilized for over-expression of the UDPG pyrophosphatase in an original fungus of the aureobasidium pullulans, the yield of pulullan in recombined aureobasidium pullulans can be improved by 32%, the yield of beta-1,3 glucan in the recombined aureobasidium pullulans can be improved by 55%. The UDPG pyrophosphatase is proofed to participate in the synthesis of two exopolysaccharides from the molecular aspect, so as to provide a technological base and methodological guidance to modify a synthetic pathway of the exopolysaccharides of the aureobasidium pullulans according to the metabolic engineering technology.
Owner:HANGZHOU NORMAL UNIVERSITY
S. pneumonia and capsular polysaccharide synthesis method, SPD-0064 gene coding product and purpose of coding product
InactiveCN105950511AIncrease productionInterfere with or inhibit bindingBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementSequence pointGene cluster
The invention discloses S. pneumonia in the technical field of bio-pharmacy. The S. pneumonia comprises an S. pneumonia serum type strain, wherein the S. pneumonia serum type strain includes one or a plurality of kinds of capsular polysaccharide generating inhabiting genes with integral lack, partial lack, sequence point mutation or sequence point lack. When the capsular polysaccharide generating inhabiting genes have one or a plurality of kinds of changes of partial lack, sequence point mutation or lack, the function and the activity of the SPD-0064 genes or coded products of the SPD-0064 genes can be influenced; the goal of interfering or inhibiting the combination of SPD-0064 gene coding products and capsular polysaccharide gene clusters is achieved, so that the transcription function of the capsular polysaccharide gene clusters is interfered or damaged; the capsular polysaccharide yield is finally increased.
Owner:遵义医学院第三附属医院
High-specific heat capacity microbe biological polysaccharide SM-1 and its preparation method and use
InactiveCN104498561AReduce elevationReduce churnCosmetic preparationsOrganic active ingredientsSide chainFermentation
The invention belongs to the technical field of microbe polysaccharide and relates to high-specific heat capacity microbe biological polysaccharide and its preparation method and use. The preparation method comprises that a bacillus subtilis strain capable of effectively accumulating extracellular capsular polysaccharide is selected from nature and then is subjected to 16rs DNA identification, a polysaccharide synthesis approach-related gene is adjusted and modified so that a yield is improved, and through microbial fermentation, alcohol precipitation, and drying and refining, the high-specific heat capacity microbe biological polysaccharide is prepared. The high-specific heat capacity microbe biological polysaccharide has a structure skeleton mainly comprising glucose, galactose, mannose and glucuronic acid, has a side chain tail end obtained by connection polymerization of pyruvic acid and acetyl groups, is a polymer, has molecular weight of 5000-30000Da, is named as SM-1, has a good water retention capacity and a high-specific heat capacity, has moisture retention and infrared radiation resistance, and has a good application value in the cosmetic industry.
Owner:杨红兵
Method of identifiying a serotype of klebsiella pneumoniae and application thereof
ActiveUS20100136534A1Reduce mortalityRapid diagnosisSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementPolysaccharide synthesisClinical diagnosis
The present invention relates to a method of identifying a serotype of Klebsiella pneumoniae, in particular to a method using specific polymerase chain reaction (PCR) primer sets designed according to a fragment of a capsular polysaccharide synthesis (cps) region to identify a K57 or a NTUH-N1 serotype and its application. NTUH-N1 is a novel serotype which differs from the previously reported 77 serotypes. This PCR-based cps genotyping method not only solves the problems of insufficient specificity and sensitivity caused by conventional immune method, but can be applied in clinical diagnosis with the advantages of rapidity and low cost. In addition, the rate of unidentifiable strains can also be reduced by this method.
Owner:NAT TAIWAN UNIV
Carboxymethylation astragalus polysaccharide, synthesis and purification method and application of carboxymethylation astragalus polysaccharide as tobacco humectant
InactiveCN104892788AImprove solubilityIncrease concentrationTobacco treatmentBulk chemical productionAstragalus polysaccharideEthanol precipitation
The invention relates to a synthesis and purification method for a carboxymethylation astragalus polysaccharide. The synthesis and purification method includes steps of stirring and dissolving an astragalus polysaccharide and sodium hydroxide in solvents; adding chloroacetate into the solvents; stirring the chloroacetate and the solvents to allow the chloroacetate and the solvents to react with one another for 3-4h at the temperatures of 50-70 DEG C to obtain products; cooling the products; regulating a pH (potential of hydrogen) value of the products until the products are neutralized; carrying out ethanol precipitation on the products; filtering the products; collecting precipitates; dissolving the precipitates in water; carrying out ethanol precipitation on the precipitates; dialyzing the precipitates; freezing and drying the precipitates to obtain a white flocculent carboxymethylation astragalus crude polysaccharide. The synthesis and purification method has the advantages that as proved by tests, excellent physical and sensual moisture retention effects can be realized for cigarettes by the carboxymethylation astragalus polysaccharide, irritation and offensive odor of the cigarettes can be reduced, the mellow and full sensation and the comfort of smoke of the cigarettes can be improved, and the carboxymethylation astragalus polysaccharide can be applied to the cigarettes as a tobacco humectant with excellent performance.
Owner:CHINA TOBACCO HENAN IND
Method for increasing polysaccharide content of shiitake mushroom variety 808
ActiveCN113717863AHigh in polysaccharidesOptimizing Fermentation ConditionsFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyMycelium
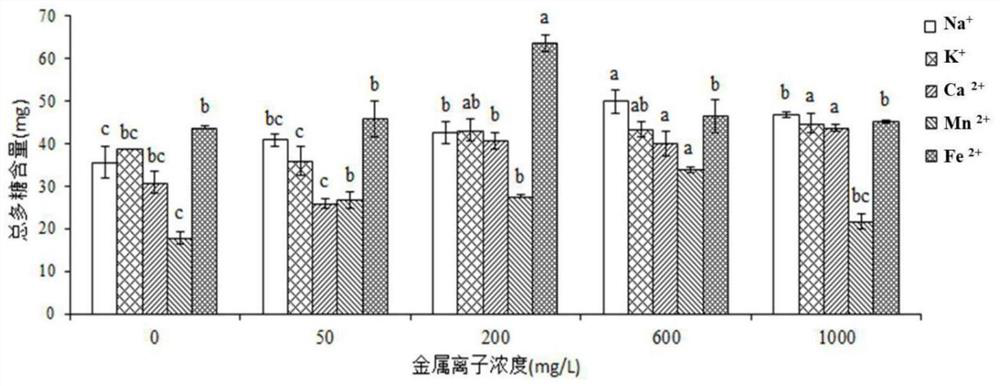
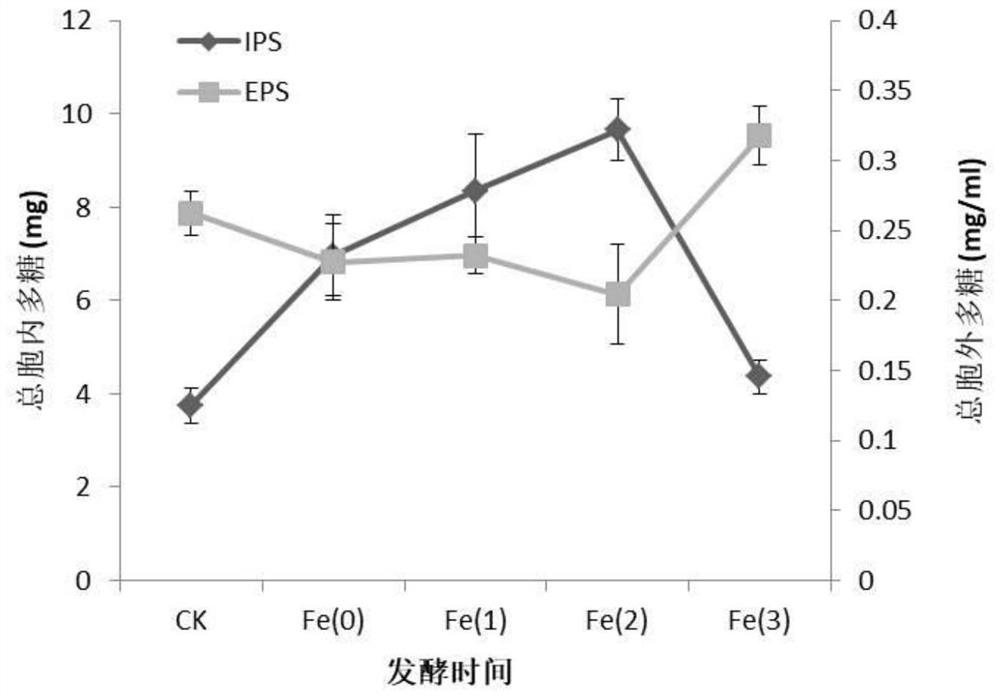
The invention discloses a method of a culture medium formula for increasing content of lentinan. The method comprises the following specific steps: preparing a culture medium, preparing a mother strain, preparing fermentation liquor, adding Fe<2+> with a proper concentration, inoculating, standing and culturing at 25 DEG C for 60 d, and collecting mycelia to extract polysaccharide; and preparing a cultivation bag, adding Fe<2+> with a proper concentration, inoculating, mycelium growing, fruiting, collecting sporocarps, and extracting sporocarp polysaccharide. Exogenous metal ions with a proper concentration are added within optimal induction time, growth of mycelia is promoted, expression quantity and enzyme activity of a key enzyme gene for polysaccharide synthesis are improved, the polysaccharide content of the shiitake mushroom mycelia is obviously improved, meanwhile, Fe <2+> with a proper concentration improves activity of a key enzyme for sporocarp polysaccharide synthesis, and the sporocarp polysaccharide content is increased. The method provides support for optimizing a shiitake mushroom fermentation mode, improving the content of shiitake mushroom mycelia and sporocarp polysaccharide and boosting development of shiitake mushroom processing industry.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
High Viscosity Diutan Gums
ActiveUS20110282051A1Increase productionImproved viscosity propertiesSugar derivativesBacteriaBiotechnologyPhysical property
The production of a diutan polysaccharide exhibiting increased viscosity properties as compared with previously produced polysaccharide of the same type of repeating units. Such an improved diutan polysaccharide is produced through the generation of a derivative of Sphingomonas sp. ATCC 53159 that harbors a multicopy broad-host-range plasmid into which genes for biosynthesis of diutan polysaccharide have been cloned. The plasmid provides the capability within the host Sphingomonas strain to produce multiple copies of genes for such polysaccharide synthesis. In such a manner, a method of not just increased production of the target diutan polysaccharide, but also production of a diutan polysaccharide of improved physical properties (of the aforementioned higher viscosity) thereof is provided. Such a diutan polysaccharide has proven particularly useful as a possible viscosifier in oilfield applications and within cement materials. The inventive methods of production of such an improved diutan polysaccharide, as well as the novel cloned genes required to produce the improved diutan within such a method, are also encompassed within this invention. Additionally, the novel engineered Sphingomonas strain including the needed DNA sequence is encompassed within this invention.
Owner:CP KELCO U S INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com