Genetic Engineering Bacteria Deleting 21 Coding Exopolysaccharide Synthesis Genes and Its Application
An extracellular polysaccharide, encoding gene technology, applied in the fields of genetic engineering and fermentation engineering, can solve the problems of low PHB yield and the like
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0045] Construction of embodiment 1 knockout plasmid
[0046] Using the CRISPR / Cas9 knockout system to knock out exopolysaccharide synthesis and transport gene clusters requires the construction of a knockout plasmid pTargetF-galF-wza. The construction process of the plasmid is as follows:
[0047] (1) Through the analysis of the website http: / / crispr.mit.edu / , select a 20nt N that is complementary to the target sequence of the target gene 20 Sequence (see the underlined sequence in the primer pTargetF-galF-wza-F in Table 1).
[0048] (2) Using the plasmid pTargetF as a template, use the forward primer pTargetF-galF-wza-F (the 5' end is the N in step (1) 20 sequence) and reverse primer pTargetF-R, amplified to obtain the introduction of N 20 Sequence of the open-circle plasmid. The PCR amplification product was verified by electrophoresis and purified and recovered.
[0049] (3) Since the recovered product may contain the template plasmid pTargetF, which will affect subseq...
Embodiment 2
[0053] The construction of embodiment 2 genetically engineered bacteria WJW09
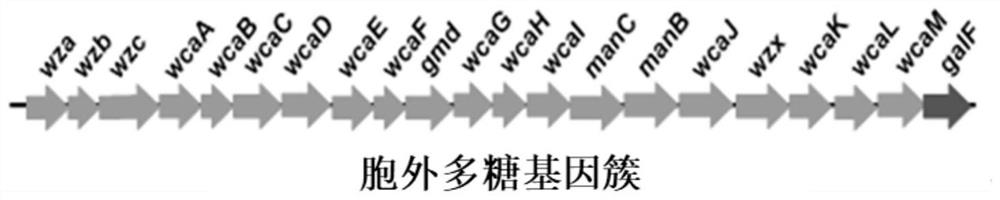
[0054] Using the CRISPR / Cas9 knockout system to knock out the exopolysaccharide synthesis and transport gene cluster to obtain WJW09, the gene cluster includes wza, wzb, wzc, wcaA, wcaB, wcaC, wcaD, wcaE, wcaF, gmd, wcaG, wcaH, wcaI, There are 21 genes including manC, manB, wcaJ, wzx, wcaK, wcaL, wcaM, and galF. The NCBI accession numbers of these gene sequences are "BAE76576.1", "BAE76575.1", "BAA15913.1", "BAA15912. 1", "BAA15911.1", "BAE76574.1", "BAE76573.1", "BAE76572.1", "BAA15910.1", "BAA15909.1", "BAA15908.1", "BAA15907.1" , "BAA15906.1", "BAA15905.1", "BAA15901.1", "BAA15900.1", "BAA15899.1", "BAE76571.1", "BAA15898.1", "BAA15897.1", " BAA15896.1". Specific steps are as follows:
[0055] (1) Construction of homology arm knockout fragments
[0056] Extract the genome of Escherichia coli W3110, use the genome as a template, and use the homology arm primers galF-wza-U-F / galF-wza-U-R, galF...
Embodiment 3
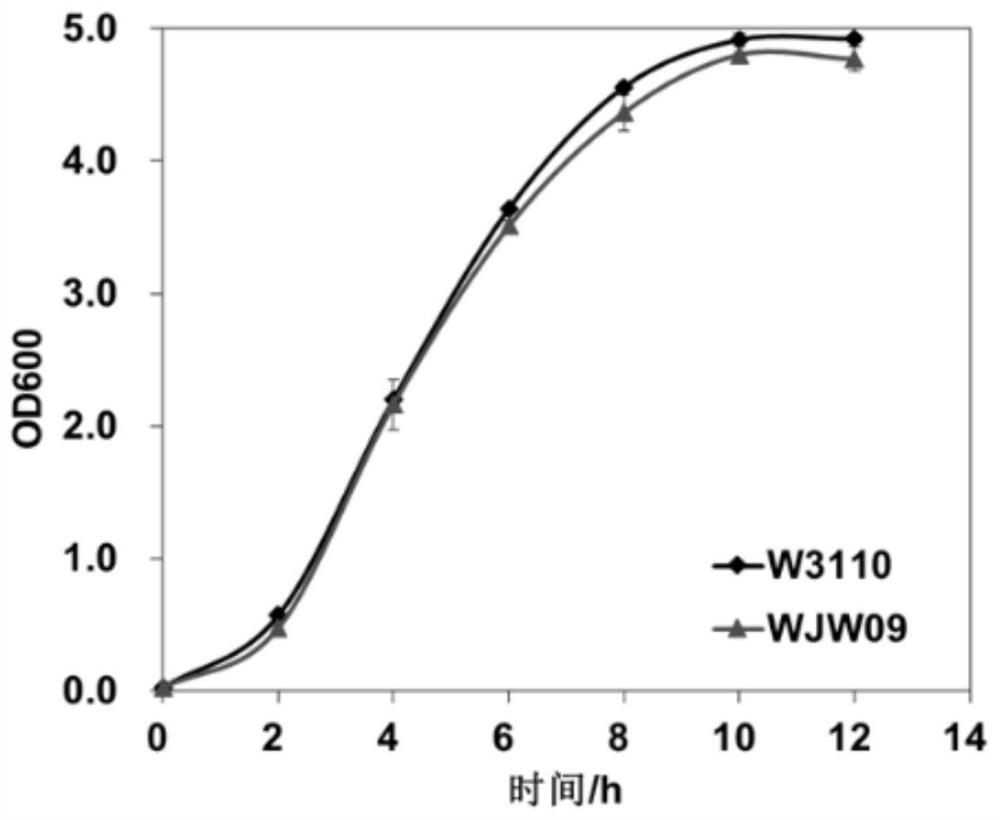
[0065] The growth status of embodiment 3 bacterial strain WJW09
[0066] LB medium: yeast powder 5g / L, tryptone 10g / L and NaCl 10g / L.
[0067] WJW09 and W3110 were inoculated into LB medium respectively, cultured at 37°C, and their growth curves were measured.
[0068] The results show that: if image 3 As shown, the growth of strains WJW09 and W3110 is basically the same, indicating that knockout of 21 exopolysaccharide synthesis and transport-related genes does not affect cell growth and can be used in industrial production.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com