Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
65 results about "Memory window" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
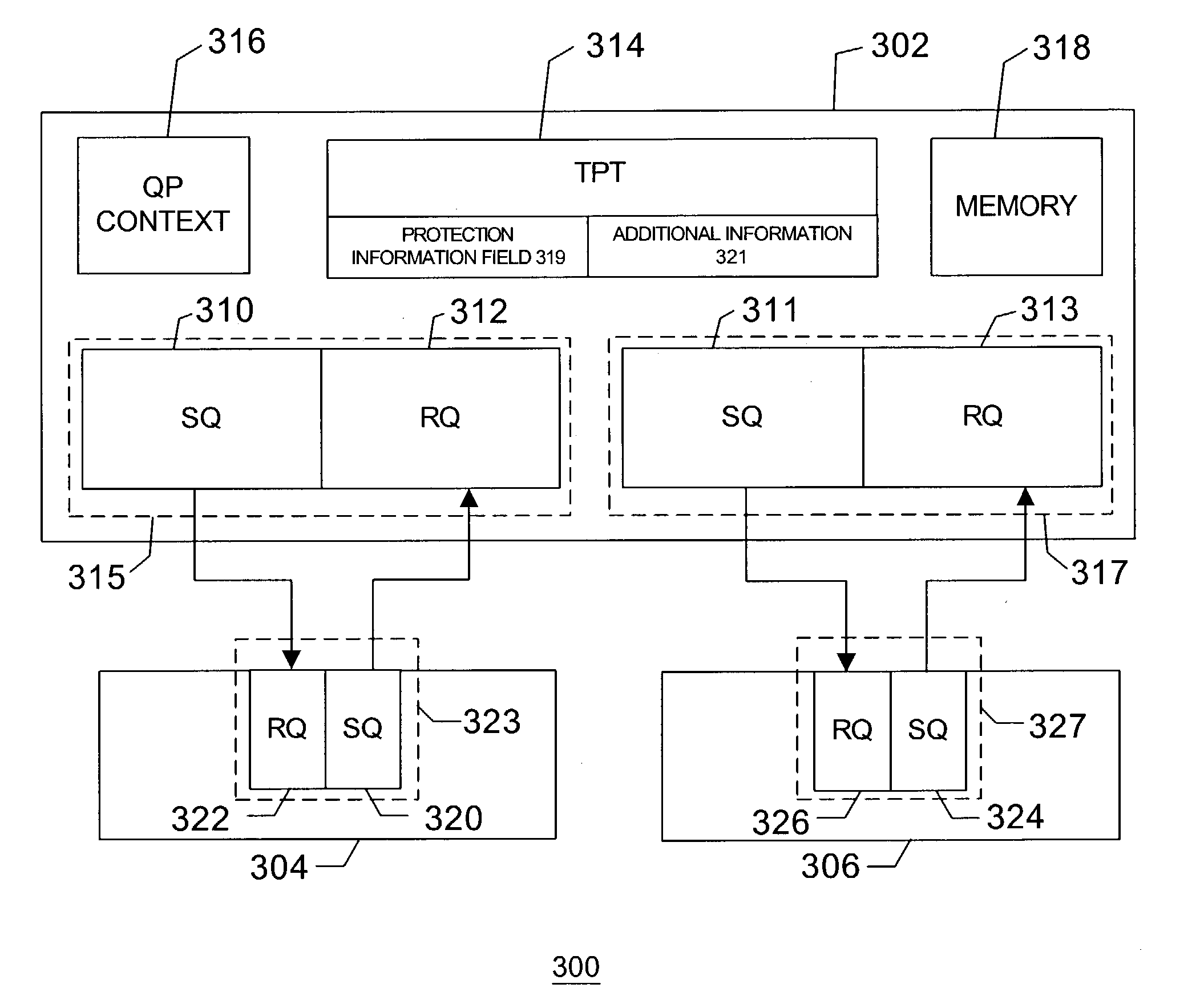
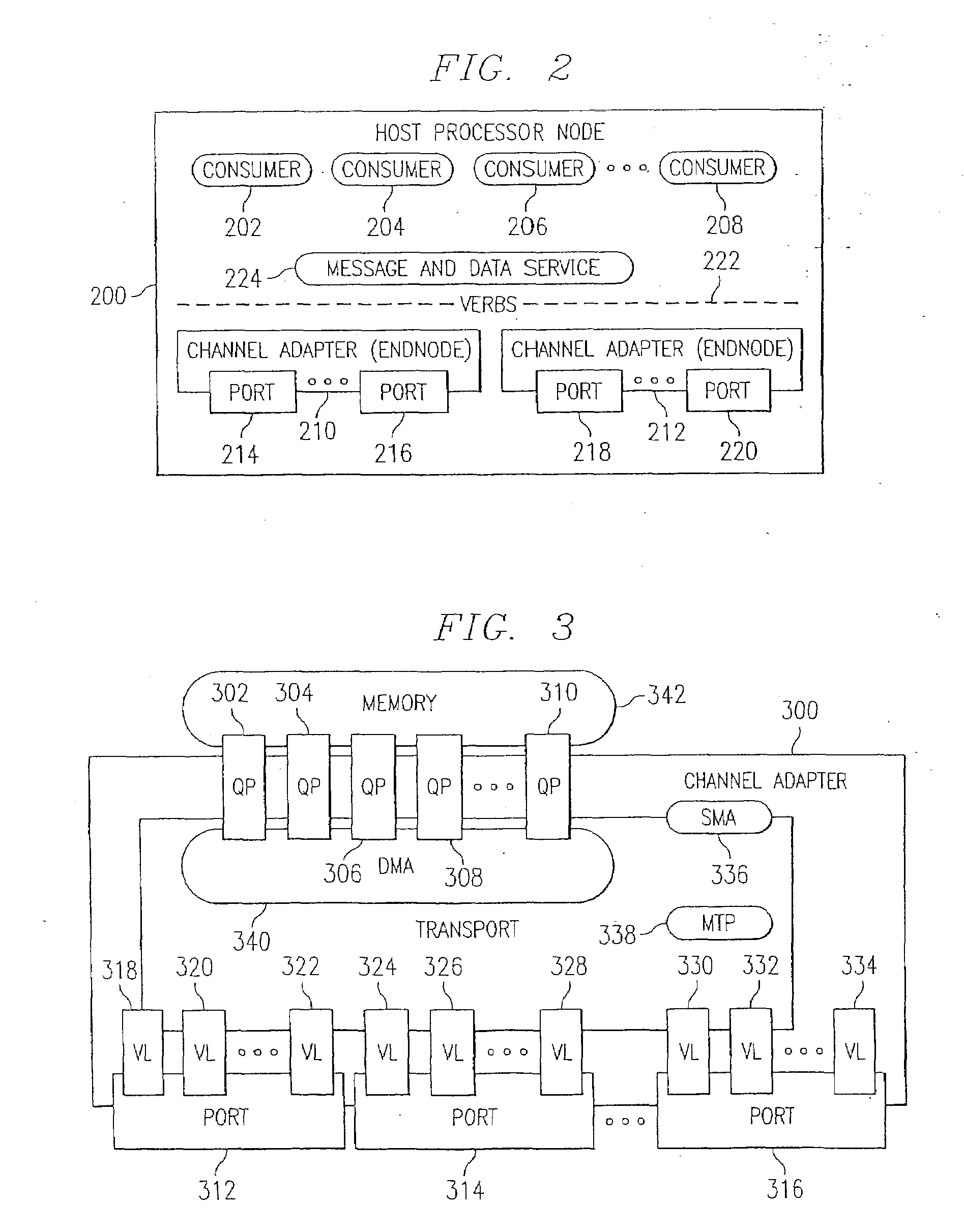
Binding a memory window to a queue pair
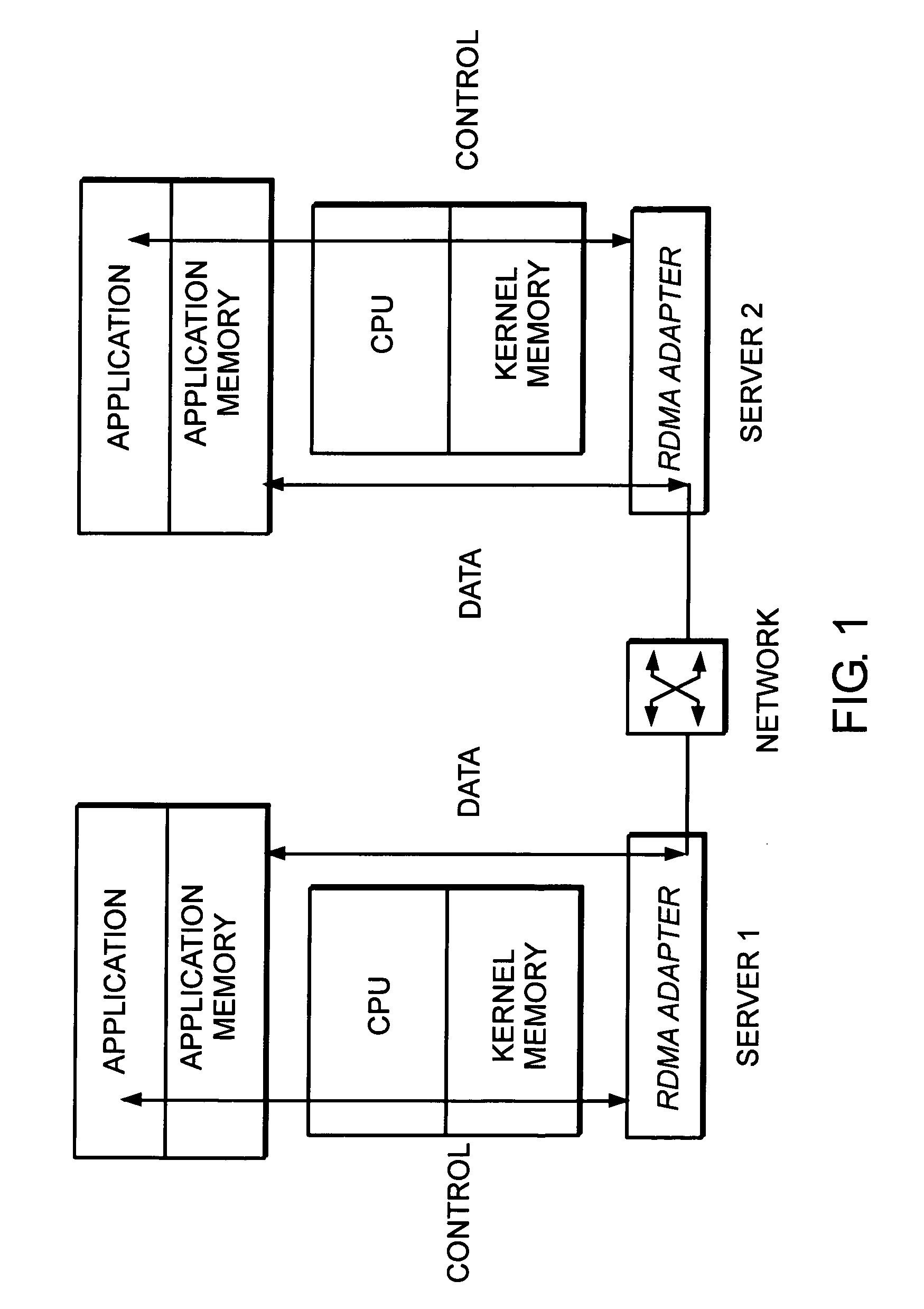
The disclosed embodiments may relate to memory window access and may include a memory window and plurality of queue pairs associated with a process. Each of the plurality of queue pairs may be associated with a memory window context that may have queue pair information. The memory window may be associated with a memory window context that includes a protection information field. Accordingly, access to memory window may be allowed if the queue pair information matches the protection information field.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
Binding a memory window to a queue pair
ActiveUS7103744B2Minimized on demandUnauthorized memory use protectionParallel computingInformation field
The disclosed embodiments may relate to memory window access and may include a memory window and plurality of queue pairs associated with a process. Each of the plurality of queue pairs may be associated with a memory window context that may have queue pair information. The memory window may be associated with a memory window context that includes a protection information field. Accordingly, access to memory window may be allowed if the queue pair information matches the protection information field.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
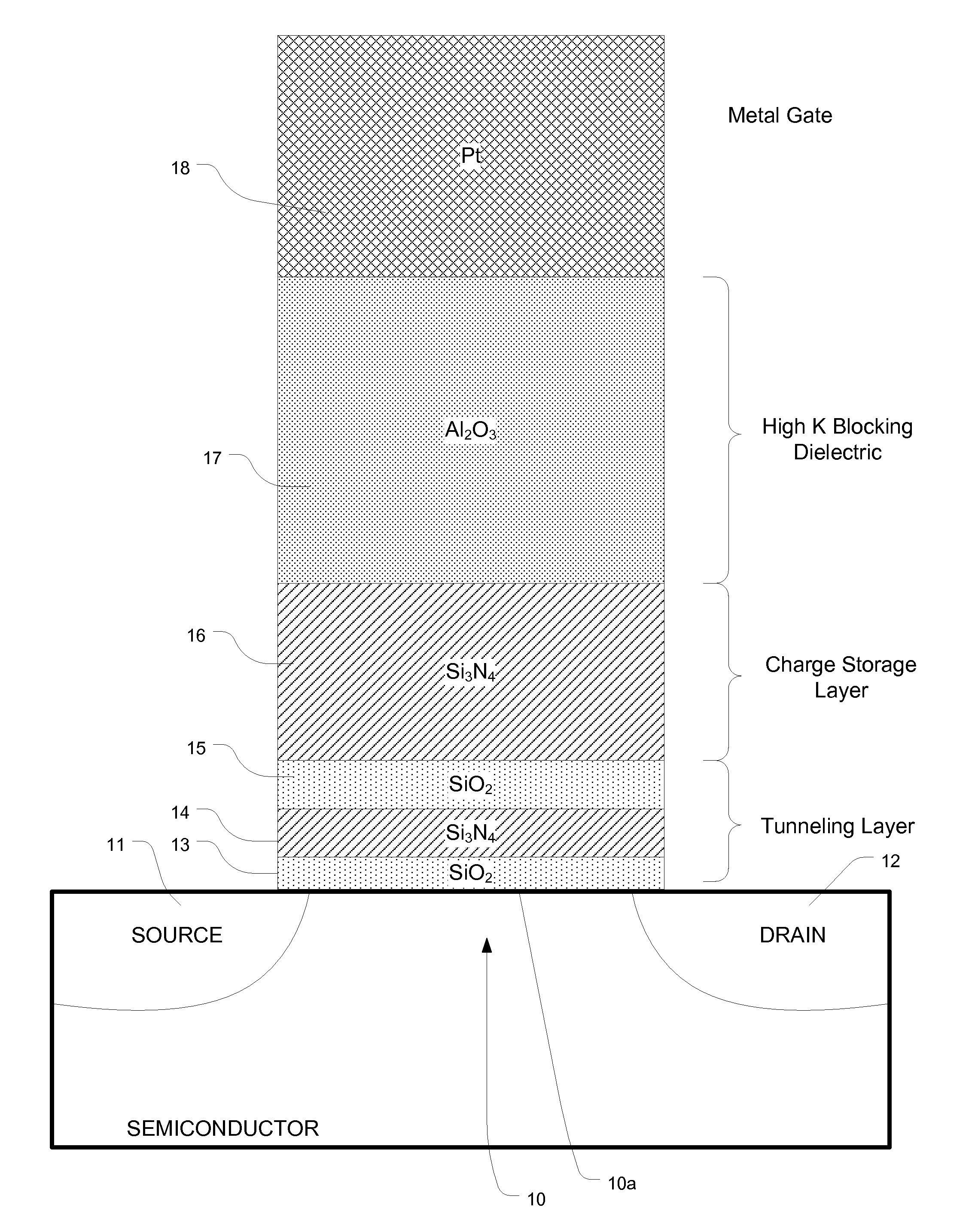
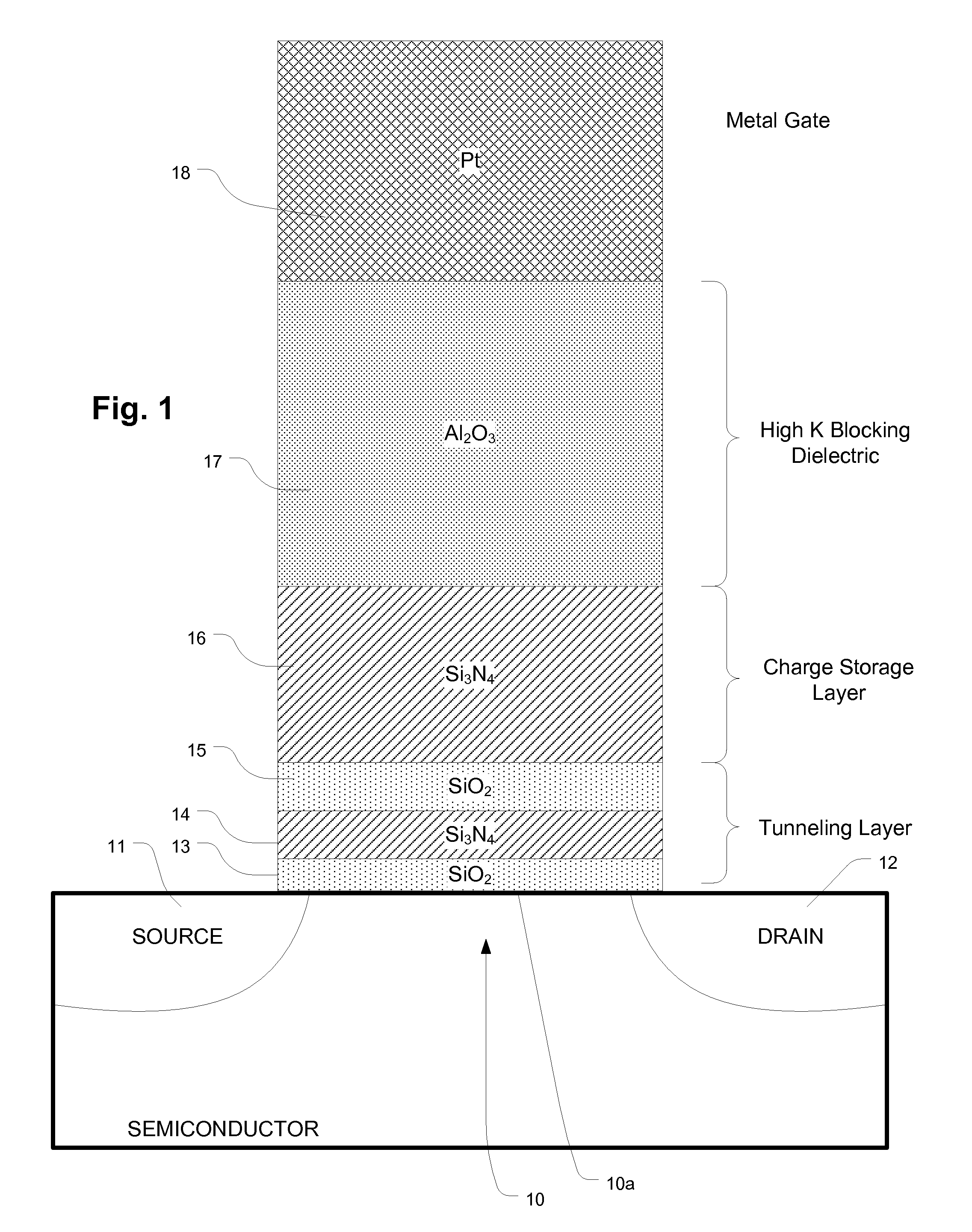
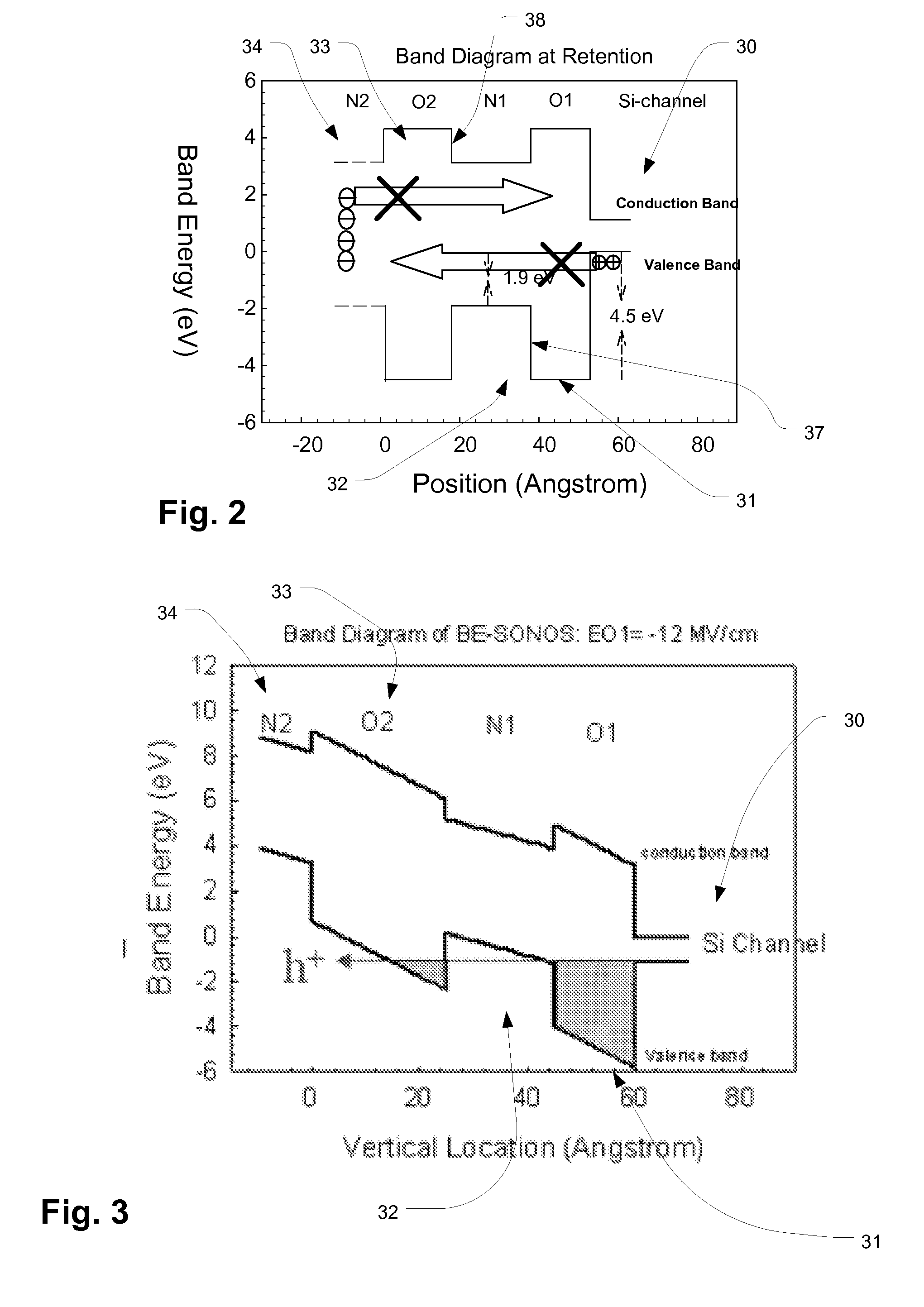
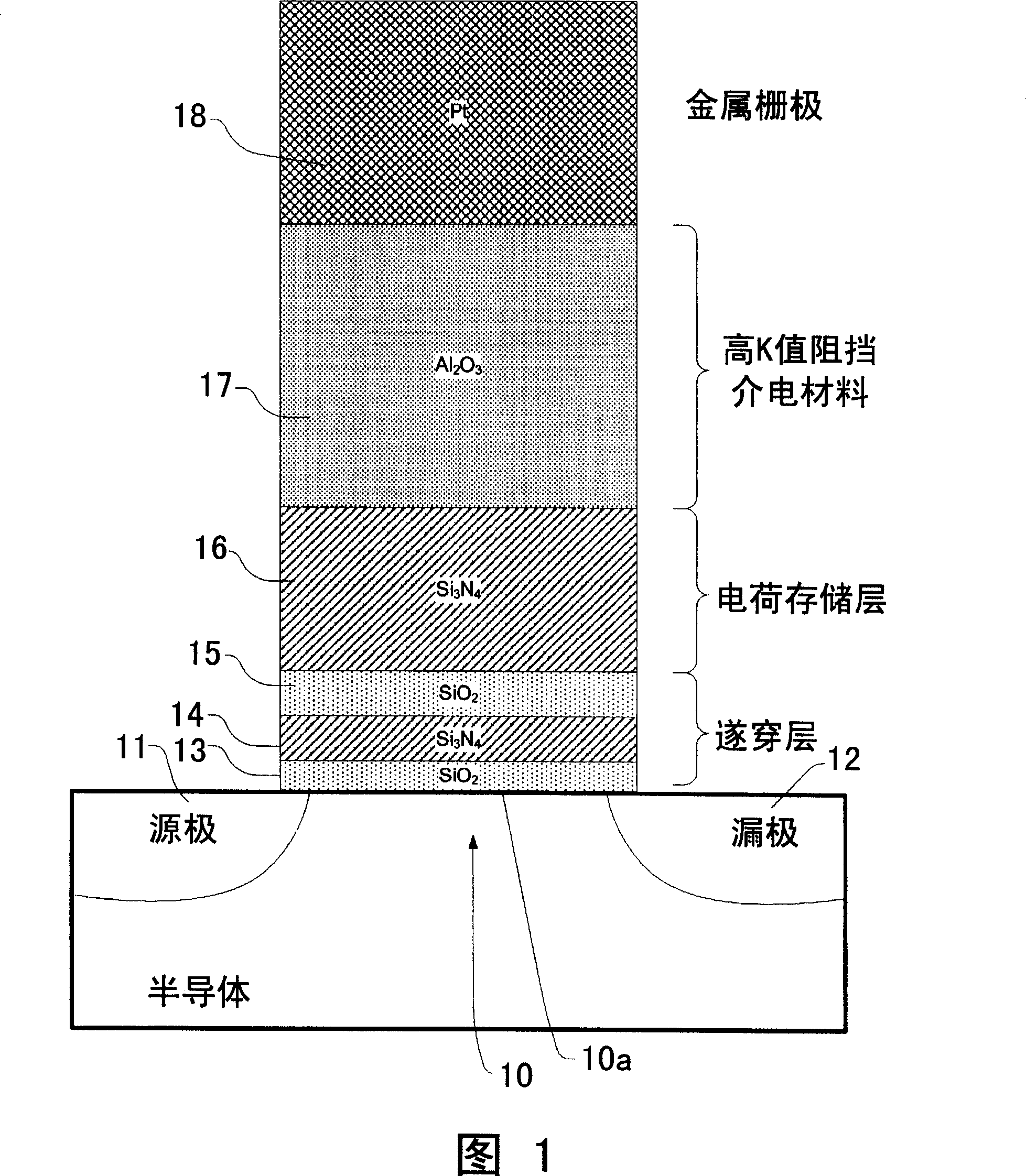
Charge trapping memory cell with high speed erase
InactiveUS20090039414A1Eliminates hole tunneling barrierEffectively preventing charge leakageSolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesDielectricTrapping
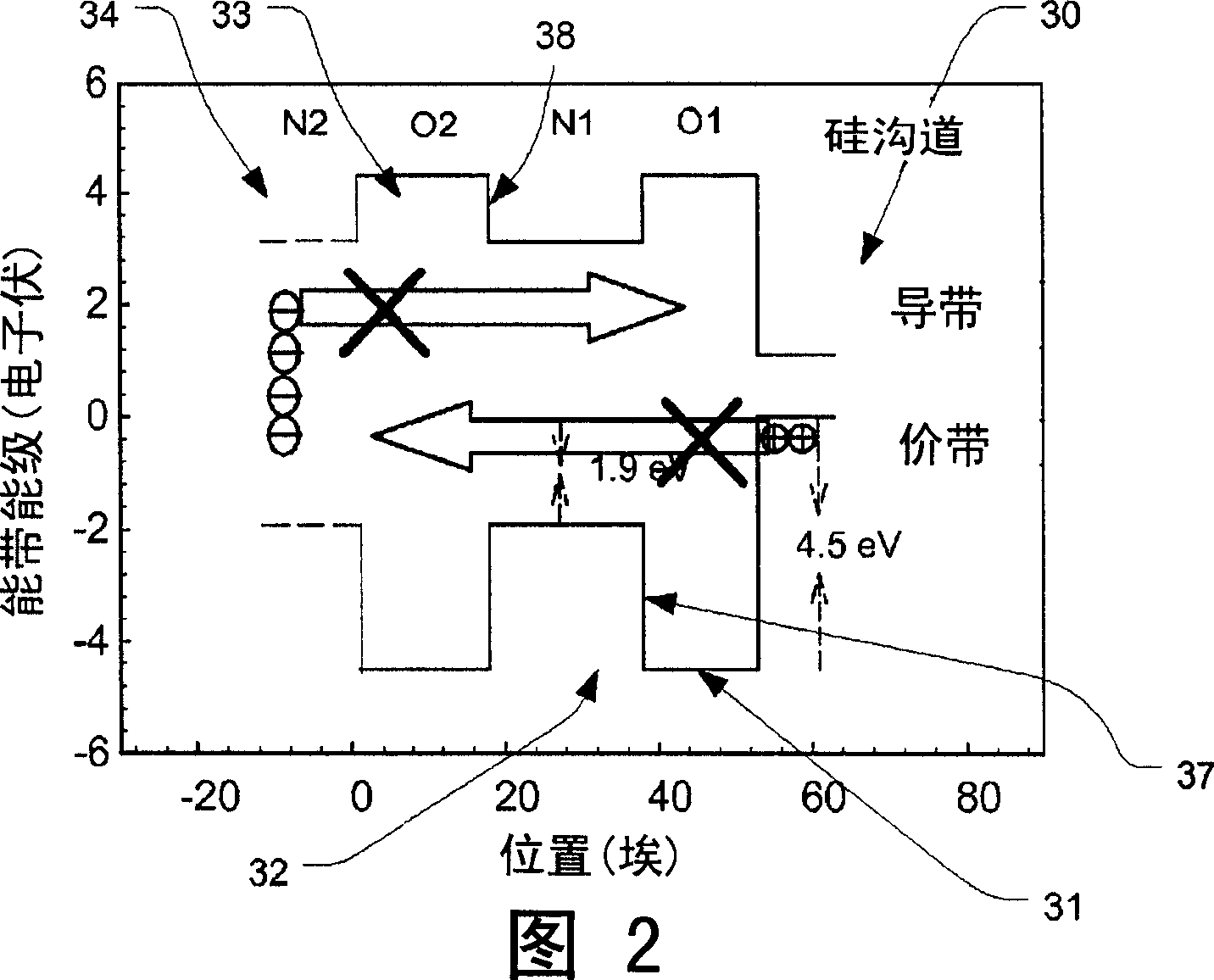
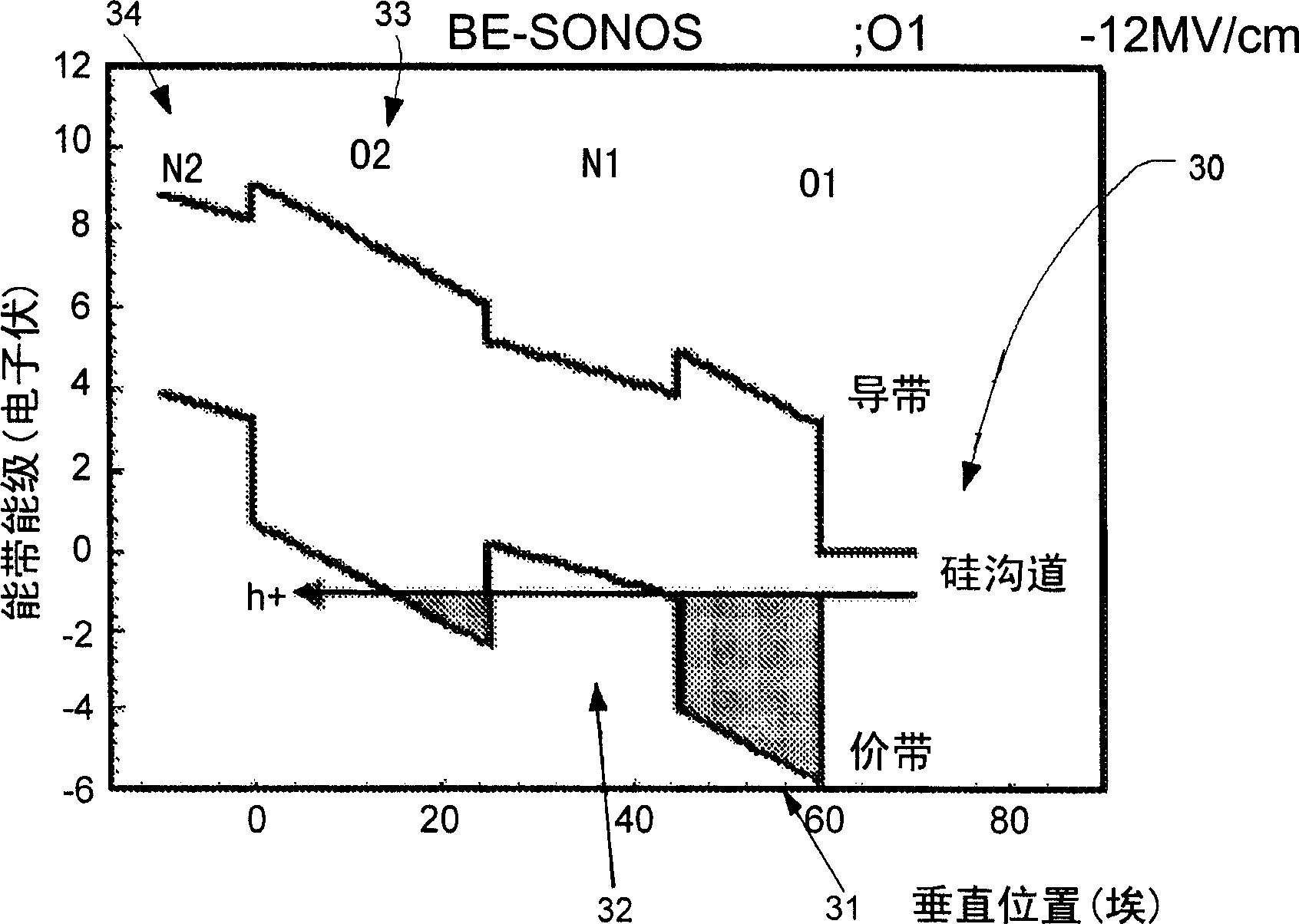
A band gap engineered, charge trapping memory cell includes a charge trapping element that is separated from a metal or metal compound gate, such as a platinum gate, by a blocking layer of material having a high dielectric constant, such as aluminum oxide, and separated from the semiconductor body including the channel by an engineered tunneling dielectric. Fast program and erase speeds with memory window as great as 7 V are achieved.
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD
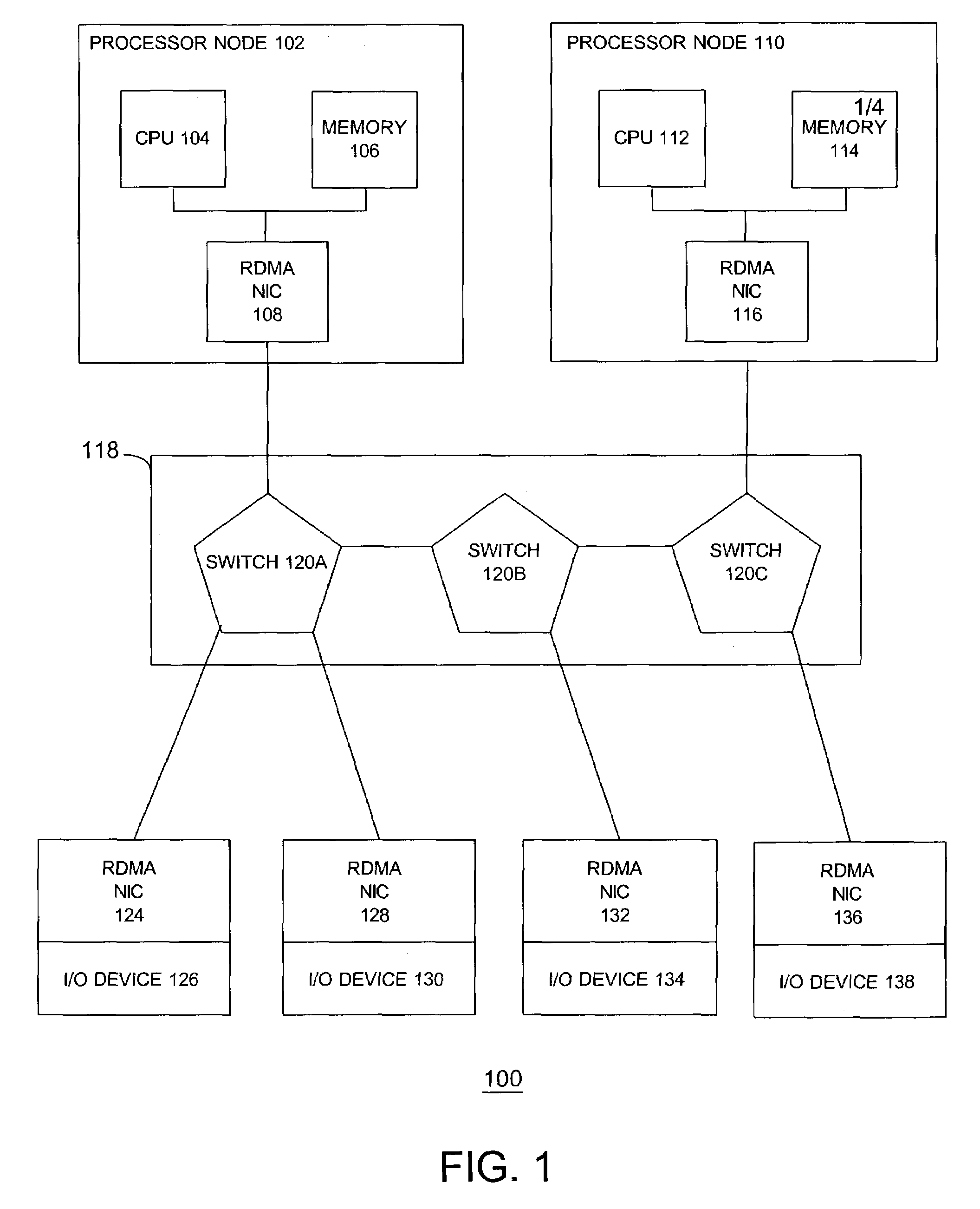
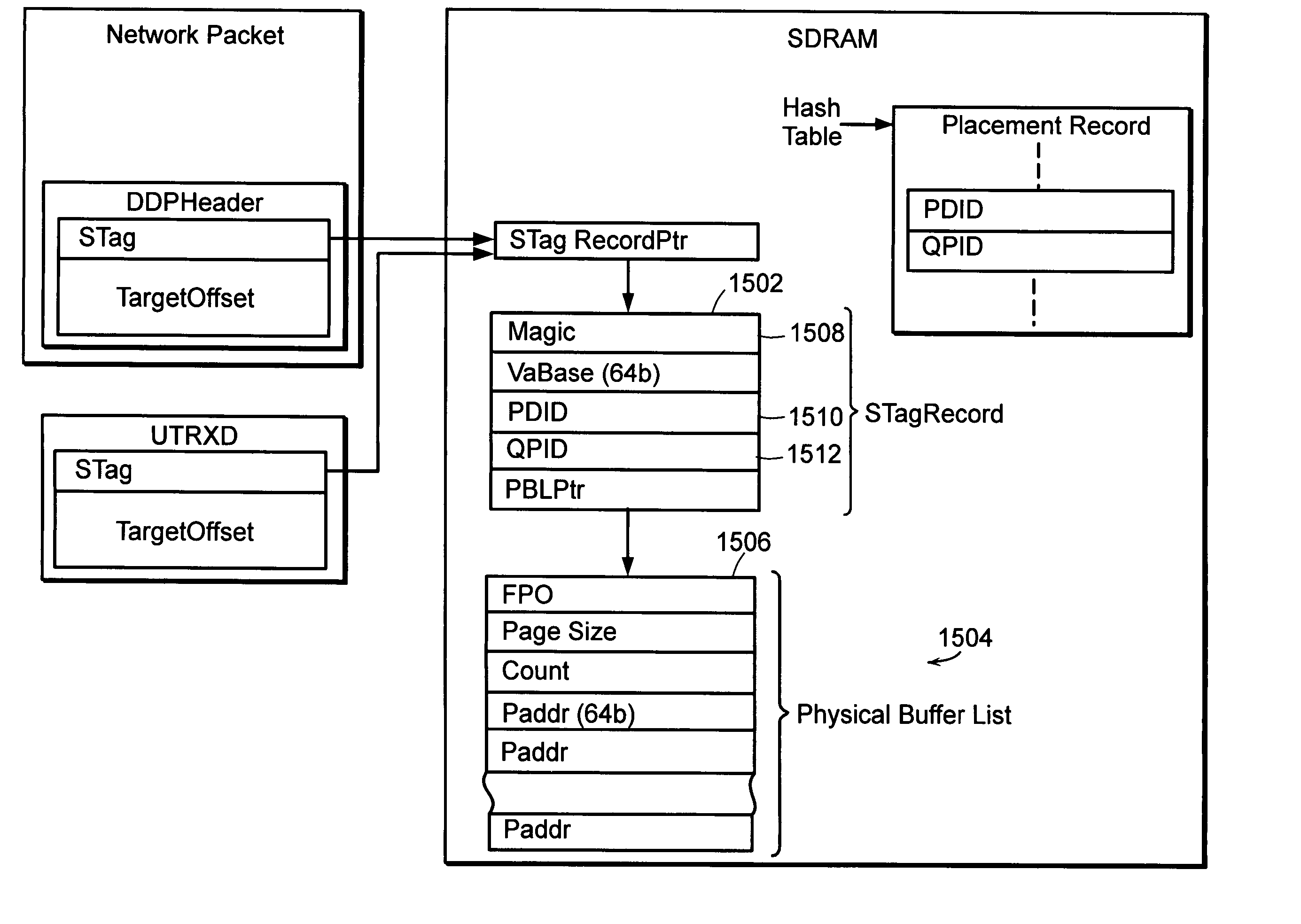
System and method for placement of sharing physical buffer lists in RDMA communication
InactiveUS20050223118A1Memory adressing/allocation/relocationMultiple digital computer combinationsVirtual memoryPhysical address
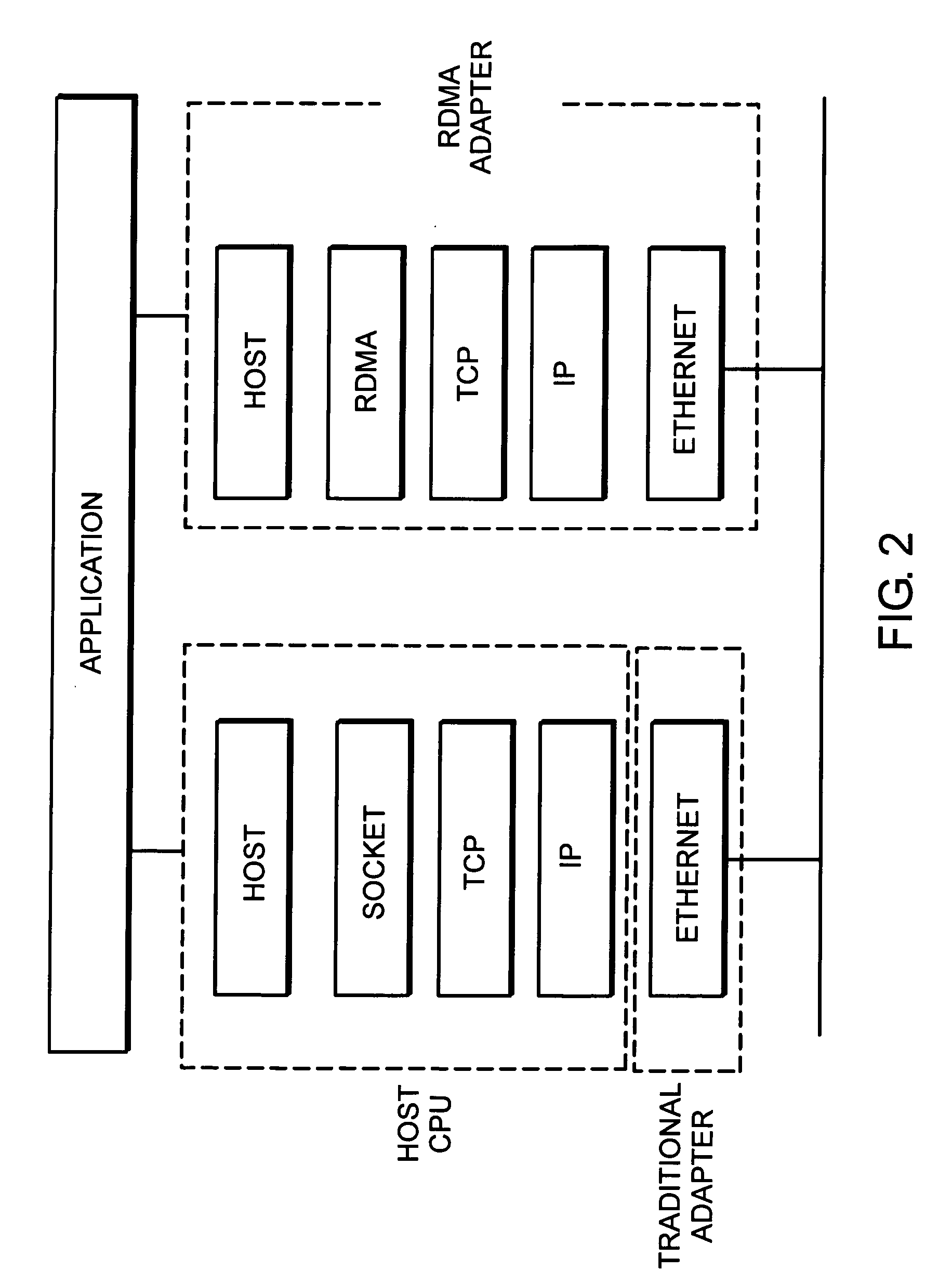
A system and method for placement of sharing physical buffer lists in RDMA communication. According to one embodiment, a network adapter system for use in a computer system includes a host processor and host memory and is capable for use in network communication in accordance with a direct data placement (DDP) protocol. The DDP protocol specifies tagged and untagged data movement into a connection-specific application buffer in a contiguous region of virtual memory space of a corresponding endpoint computer application executing on said host processor. The DDP protocol specifies the permissibility of memory regions in host memory and specifies the permissibility of at least one memory window within a memory region. The memory regions and memory windows have independently definable application access rights, the network adapter system includes adapter memory and a plurality of physical buffer lists in the adapter memory. Each physical buffer list specifies physical address locations of host memory corresponding to one of said memory regions. A plurality of steering tag records are in the adapter memory, each steering tag record corresponding to a steering tag. Each steering tag record specifies memory locations and access permissions for one of a memory region and a memory window. Each physical buffer list is capable of having a one to many correspondence with steering tag records such that many memory windows may share a single physical buffer list. According to another embodiment, each steering tag record includes a pointer to a corresponding physical buffer list.
Owner:AMMASSO
System, method, and storage medium for shared key index space for memory regions
InactiveUS20060095690A1Memory systemsMicro-instruction address formationOperational systemTerm memory
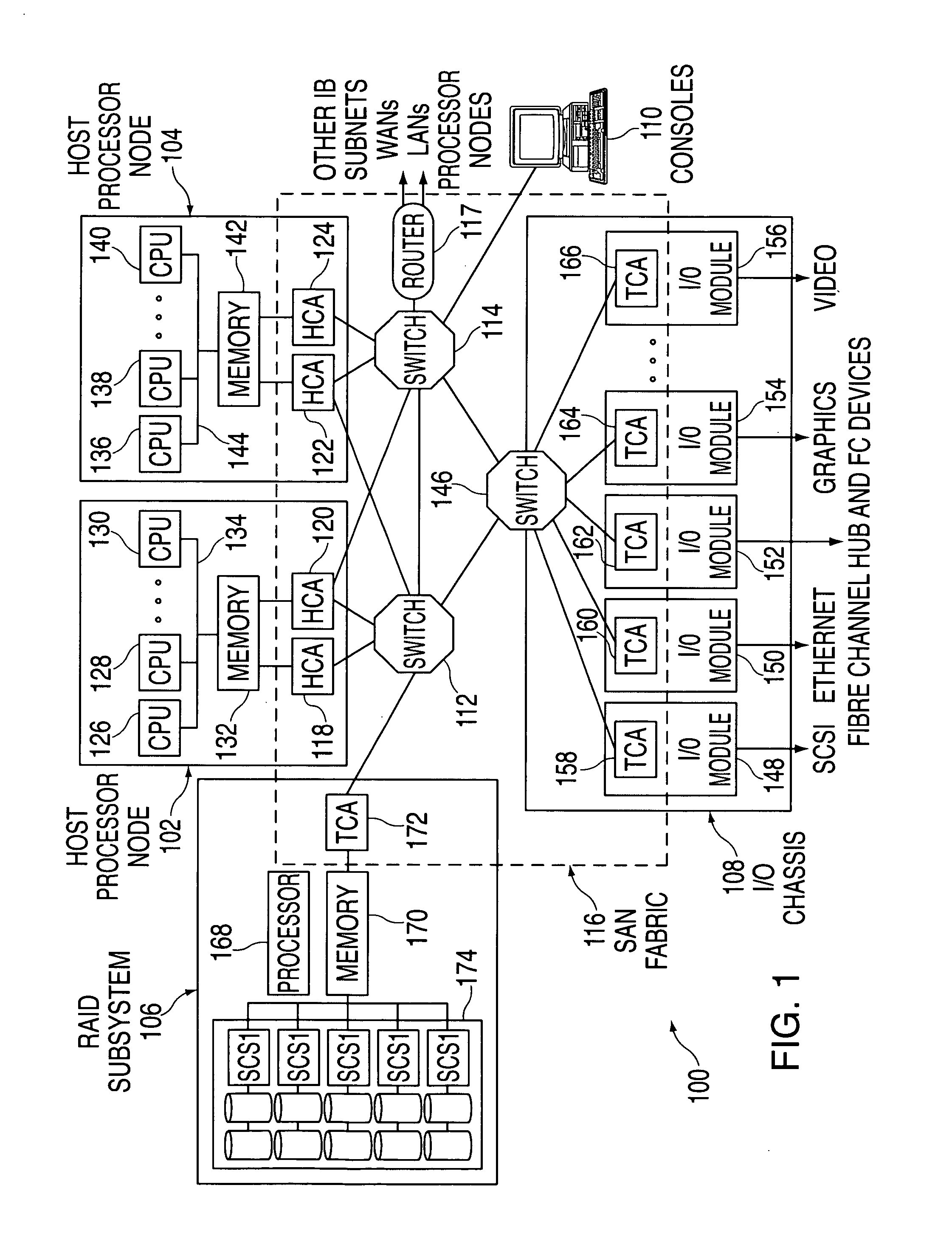
In a logical partitioning (LPAR) environment with InfiniBand™ host channel adapters (HCAs), multiple operating systems share the resources of a physical HCA. A mechanism for efficiently allocating memory regions (or memory windows) to different LPARs is provided, while ensuring that a memory region assigned to one LPAR is not accessible from another LPAR.
Owner:IBM CORP
Semiconductor Device
InactiveUS20110175083A1Sufficient reduction in power consumptionFrequency of refresh can be lowTransistorSolid-state devicesSemiconductor materialsDevice material
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Method and System For Address Translation With Memory Windows
InactiveUS20080098197A1Avoid levelingMemory systemsMicro-instruction address formationParallel computingTranslation table
Disclosed are a method and system for address translation with memory windows. The method comprises the steps of designating a memory region having a set of virtual addresses, each virtual address having an associated real address; and providing one or more translation tables for translating the virtual addresses to the real addresses; A memory region protection table entry (MRPTE) defines access rights for the memory region, and includes one or more pointers to the one or more translation tables. A memory window is bound to the memory region to provide access to a subset of the virtual addresses. A memory window protection table entry (MWPTE) defines access rights for the memory window, and includes one or more pointers to the one or more translation tables to translate the subset of virtual addresses to real addresses.
Owner:IBM CORP
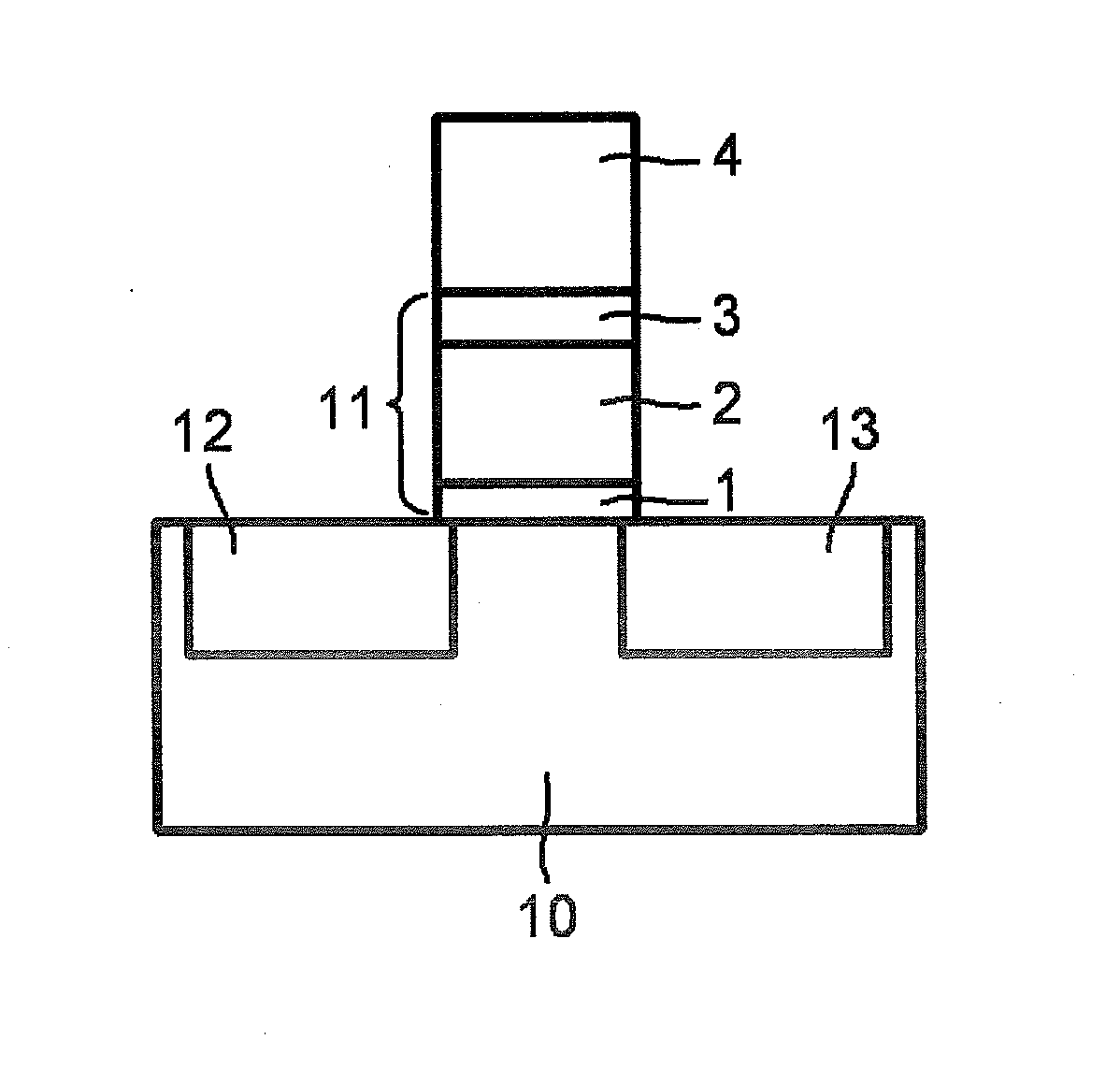
Semiconductor ferroelectric storage transistor and method for manufacturing same
ActiveUS20150171183A1Improve data retentionReduce power consumptionSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectrical conductorEngineering
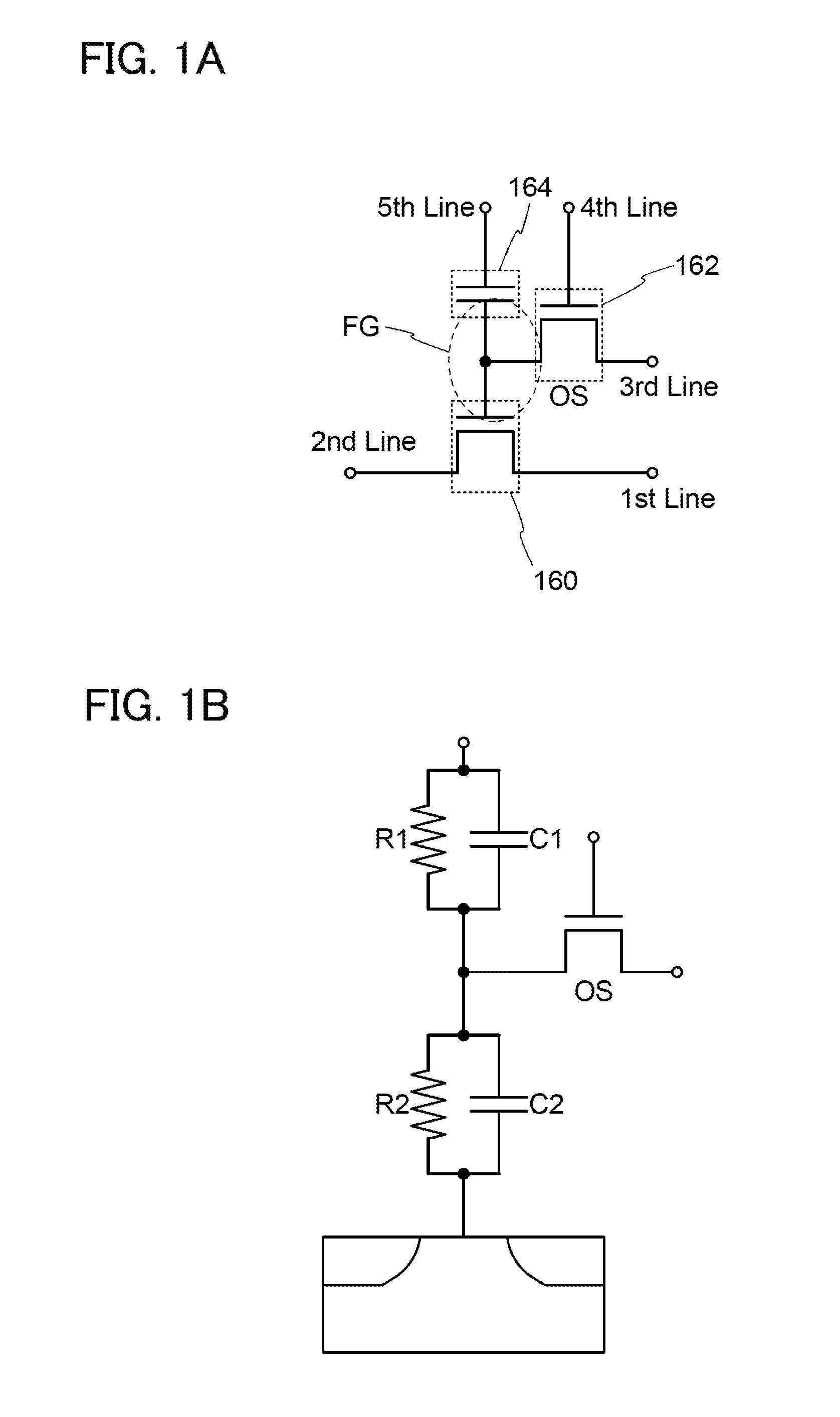
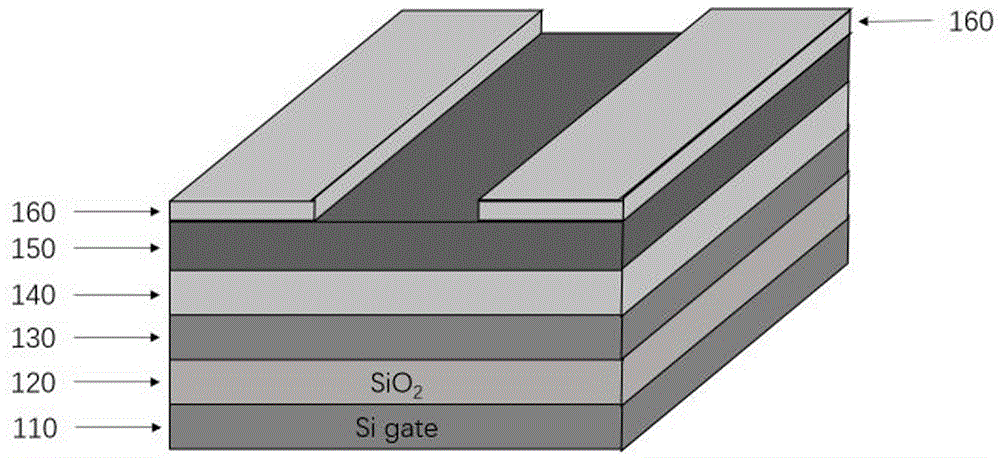
Provided is a ferroelectric field effect transistor (FeFET) which has a wide memory window even if the ferroelectric film thickness is 200 nm or less, and which has excellent data retention characteristics, pulse rewriting endurance and the like. An FeFET which has a structure wherein an insulating body (11) and a gate electrode conductor (4) are sequentially laminated in this order on a semiconductor base (10) that has a source region (12) and a drain region (13). The insulating body (11) is configured by laminating a first insulating body (1) and a second insulating body (2) in this order on the base (10), and the second insulating body (2) is mainly composed of an oxide of strontium, calcium, bismuth and tantalum.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH
Resistive random access memory based on organic/inorganic hybrid perovskite material and fabrication method of resistive random access memory
ActiveCN105789434ASimple structureImprove thermal stabilityElectrical apparatusStatic random-access memoryGas phase
The invention discloses a resistive random access memory based on an organic / inorganic hybrid perovskite material and a fabrication method of the resistive random access memory. The resistive random access memory comprises a bottom electrode, a top electrode and a resistance changing functional layer material, wherein the resistance changing functional layer material is arranged between the bottom electrode and the top electrode and comprises one layer or multiple layers of organic / inorganic hybrid perovskite thin film materials. The fabrication method comprises the following steps of (1) cleaning a substrate; (2) depositing the bottom electrode on the substrate by employing a physical vapor deposition technique; (3) forming the organic / inorganic hybrid perovskite thin film material on the bottom electrode as a resistance changing functional layer by techniques such as spin coating, dip coating and vacuum evaporation; and (4) depositing the top electrode on the resistance changing functional layer by employing the physical vapor deposition technique. According to the resistive random access memory, the structure is simple, and low-temperature and low-cost fabrication can be carried out; and the fabricated device has the technical advantages of large memory window, low conversion voltage, high conversion speed, multi-value storage capability, favorable thermal stability and device durability and the like.
Owner:GRIMAT ENG INST CO LTD
System for accessing a region of memory using remote address translation and using a memory window table and a memory region table
InactiveUS6854032B2Memory adressing/allocation/relocationUnauthorized memory use protectionMemory windowPhysical address
A system for permitting remote user access to regions of memory that have been exported for remote direct memory access purposes. The system supports dynamically changing access privileges to remote users without requiring intervention from an operating system. The system may include a memory region table and a memory window table for supporting address translations. Entries in the memory window table may include a region remote access key and a window remote access key. The memory region table may include fields for a physical address, an access value, a protection domain value, and a length of memory region.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
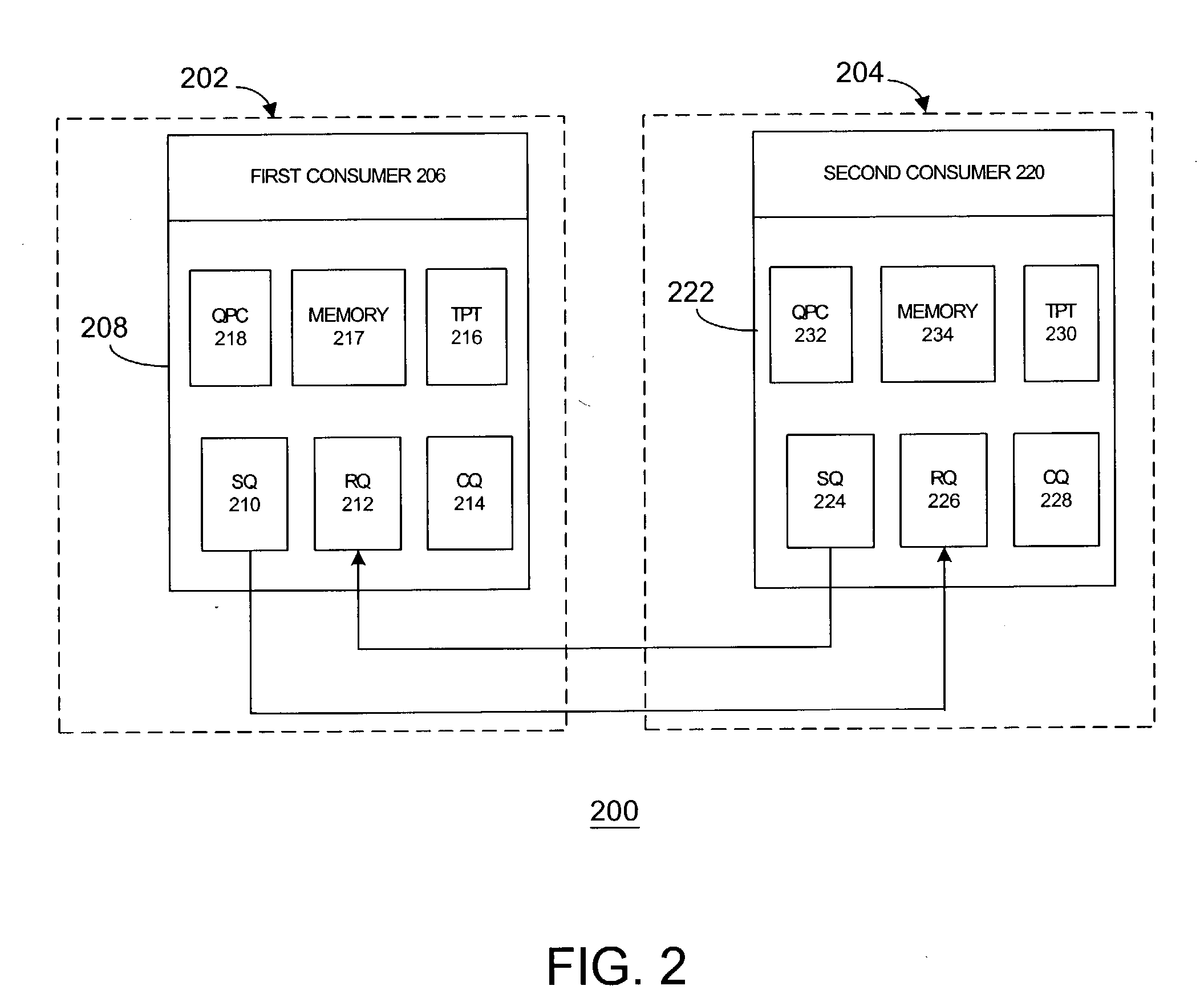
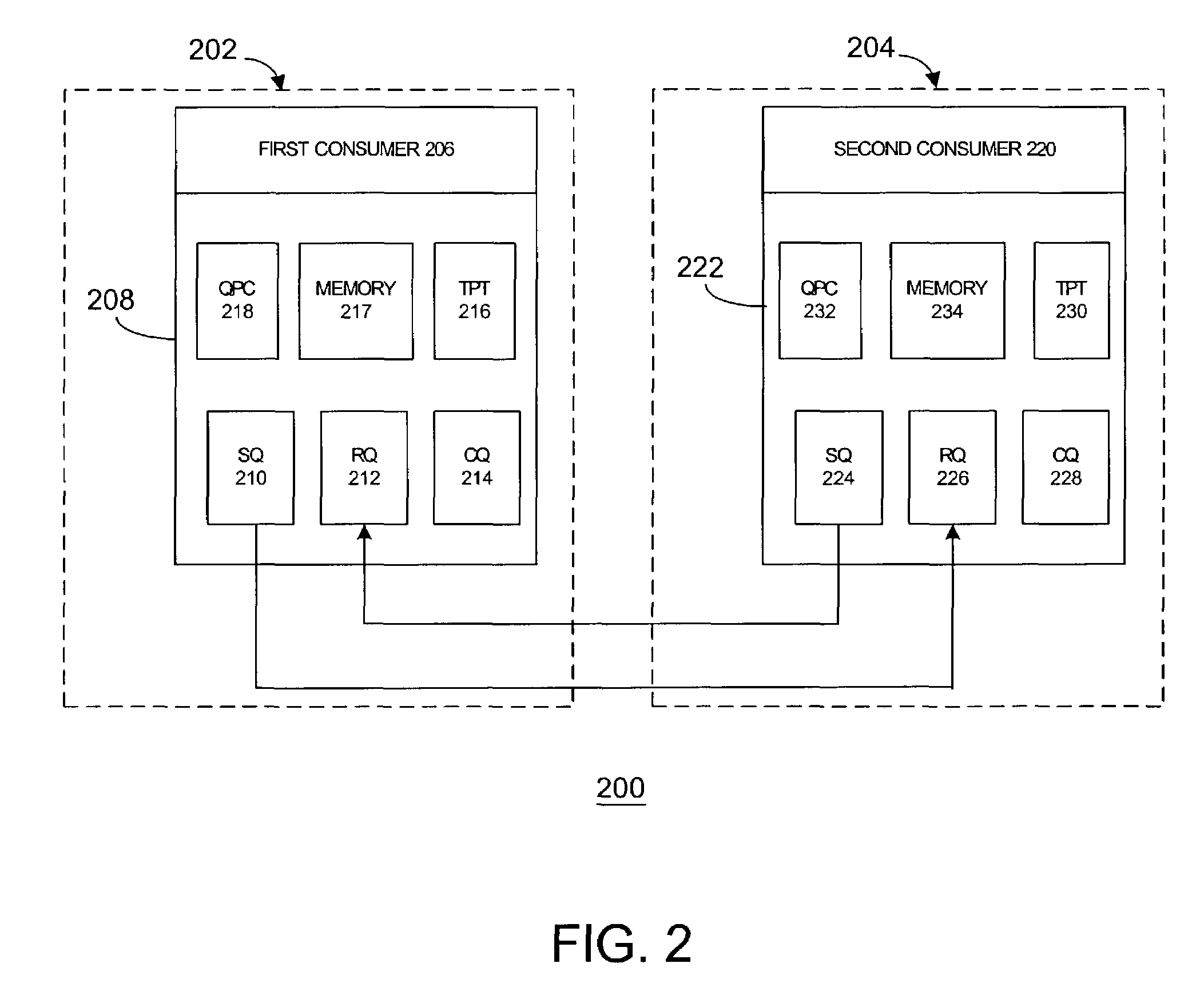
Queue pair/window association
ActiveUS20040193908A1Digital data processing detailsDigital computer detailsProtection domainOperating system
The disclosed embodiments may relate to memory window access, which may include a memory window and protection domain associated with a process. The memory window access setting or bit may also allow a plurality of memory windows to be associated with a protection domain for a process. The memory window access setting or bit may allow access to the memory window to be for the queue pairs in a certain protection domain or a designated queue pair.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
Method and device for off-loading message digest calculations
ActiveUS7120858B2Integrity can be determineCode conversionError detection onlyDirect memory accessData integrity
A method and device for off-loading from an application program the calculation of a data-integrity-checking value for specified data in a computer system. The data may be included in a message together with the integrity-checking value or may be in a portion of a memory window for direct memory access. The method includes communicating a selected data-integrity-checking scheme from a specified set of schemes to another processor to off-load calculation of the data-integrity-checking value. A related method associates a message to be received with a data-integrity-checking scheme, so that a receiving processor can calculate the data-integrity-checking value and transmit both the value and the message to another processor.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Method for controlling a central processing unit for addressing in relation to a memory and controller
InactiveUS20040177230A1Down compatibility to machine codesReduce susceptibilityMemory adressing/allocation/relocationNext instruction address formationAction CodeTraffic capacity
The present invention is based on the finding that free CPU operation code identifiers of a CPU or CPU operation code identifiers useable for any reason can be used to control supporting means upstream of the CPU, which is able to form, responsive to these operation code identifiers, a new, for example, physical address in relation to a second memory area having a second memory which is larger than the, for example, logic memory size addressable by the CPU. By means of the special operation code identifiers, it is thus possible in the course of an executable machine code to address the supporting means which monitors the data traffic via which the operation codes to be processed or the operation code identifiers are provided to the CPU, from the memory to the CPU, and which can take measures in relation to the new formed address when certain special operation code identifiers occur. In this way, on the one hand, a complicated redesign of the CPU and, on the other hand, the necessity of a software-resetting of the current memory window complicated as regards both the executable machine code and the processing speed are avoided.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
Dual-layer floating gate flexible organic memory device and preparation method therefor
InactiveCN105576124AAvoid breakingReduce pollutionSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOrganic memoryFlexible circuits
The invention relates to a dual-layer floating gate flexible organic memory device and a preparation method therefor. The dual-layer floating gate flexible organic memory device mainly comprises a substrate, a dielectric layer, a control gate, a barrier layer, a first floating gate layer, an isolating layer, a second floating gate layer, a tunneling layer, an organic semiconductor layer, a source electrode and a drain electrode, wherein the source electrode and the drain electrode are positioned above the tunneling layer. A dual-layer gold nanocrystalline is taken as the floating gate layers, so that the memory window of the memory device can be improved, and the working voltage range can be expanded; a femtosecond laser reduction technology is adopted, so that a link of intermediate repeated electrode deposition is reduced, the production process is simplified, the pollution doping in the production is lowered, and the product yield can be improved; the barrier layer, the isolating layer and the tunneling layer adopted by the dual-layer floating gate flexible organic memory device all adopt high-dielectric-constant graphene oxide, so that leakage current can be effectively lowered, the stability of the memory can be improved, and the working voltage can be lowered; all the materials adopted by the memory device are flexible and can be bent, so that the memory device can be applied to flexible circuits; and in addition, the femtosecond laser reduction technology and a vacuum thermal evaporation and spin coating technology adopted in the preparation method of the invention are mature in technology and low in product, so that the large-scale production of the dual-layer floating gate flexible organic memory device can be realized.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
Semiconductor element and device using the same
InactiveUS20090073158A1Low costSuppressing rewrite degradationCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingLow voltageDiffusion layer
A memory element having a large memory window and a high reliability is provided at low cost by performing high speed write and erase operations at a relatively low voltage and suppressing rewrite degradation. A memory element includes a semiconductor layer arranged on an insulating substrate, a first diffusion layer region and a second diffusion layer region having a conductivity type of P-type, a charge accumulating film for covering a channel region between the first diffusion layer region and the second diffusion layer region and being injected with charges from the channel region, and a gate electrode positioned on a side opposite to the channel region with the charge accumulating film in between.
Owner:SHARP KK
Protection domain groups
ActiveUS20040205379A1Error detection/correctionEmergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnectionProtection domainParallel computing
The disclosed embodiments may relate to protection domain group, which may include a memory region associated with a process. The protection domain group may also include a plurality of memory windows associated with the memory region. Also included may be a plurality of protection domains, each of which may correspond to a memory window. The protection domains may allow access to the memory region via a corresponding memory window.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
Memory window access mechanism
ActiveUS7565504B2Minimized on demandDigital data processing detailsDigital computer detailsProtection domainOperating system
The disclosed embodiments may relate to memory window access, which may include a memory window and protection domain associated with a process. The memory window access setting or bit may also allow a plurality of memory windows to be associated with a protection domain for a process. The memory window access setting or bit may allow access to the memory window to be for the queue pairs in a certain protection domain or a designated queue pair.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
Three-dimensional NAND type ferroelectric memory, manufacturing method and operation method thereof
ActiveCN110071116AImprove reliabilityIncreased durabilitySolid-state devicesDigital storageGate stackDielectric layer
The invention provides a three-dimensional NAND type ferroelectric memory, and a manufacturing method and an operation method thereof. The three-dimensional NAND type ferroelectric memory inserts an auxiliary gate material layer between a ferroelectric layer and a dielectric layer based on the existing ferroelectric memory structure to constitute a three-dimensional NAND type ferroelectric memory,and the gate stack layer of the unit comprises a main gate material layer, the ferroelectric layer, the auxiliary gate material layer and the dielectric layer and separately performs programming anderasing operation on the ferroelectric layer by cooperation with the auxiliary gate material layer, thereby effectively improving the reliability of the ferroelectric memory, that is, increasing the memory window, improving the durability of the device and improving the holding characteristics of the device.
Owner:INST OF MICROELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for improving properties of non-volatile floating-gate organic thin film transistor type memorizer
InactiveCN106299122AImprove performanceImprove retention characteristicsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingQuantum wellBottom gate
The invention relates to a method for improving properties of a non-volatile floating-gate organic thin film transistor type memorizer, and provides a non-volatile floating-gate organic thin film transistor type memorizer with a bottom-gate top contact structure. According to the non-volatile floating-gate organic thin film transistor type memorizer with the bottom-gate top contact structure, a charge storage layer adopts an organic insulation polymer film doped with quantum dot material; the quantum dot material is of a core-shell structure, and the highest occupied molecular orbital of the nuclear material is higher than that of a shell material, the lowest unoccupied molecular orbital of the nuclear material is lower than that of the shell material, a quantum well is formed between the nuclear material and the shell material, so that the captured electric charges are limited in the nuclear material, the electric charge capture ability of the charge storage layer is improved, and then the memory window of the non-volatile floating-gate organic thin film transistor type memorizer is increased, retention characteristics thereof are significantly improved. The provided method is simple, easy to operate, low in invested cost and enhances the memory property of the memorizer.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Improved NiO-based resistive random access memory (RRAM) and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN102005536AAvoid Erase and Write FailuresImprove stabilityElectrical apparatusDigital storageMetal-insulator-metalContinuous scanning
The invention belongs to the technical field of integrated circuits and particularly relates to an improved NiO-based resistive random access memory (RRAM) and a manufacturing method thereof. A memory unit comprises a substrate and a metal-insulator-metal (MIM) structure; a top electrode is a metal membrane which is made of copper, aluminum and the like and can be used in an interconnecting process; and a variable-resistance insulator is an Al2O3 / NiO / Al2O3 medium membrane with a nano laminated structure. The MIM structure in the invention presents stable double-resistance state transition and memory characteristic under the condition of direct current voltage continuous scanning excitation; and compared with the memory unit of an RRAM which adopts a medium membrane only with a NiO single-medium layer structure, the memory unit has a larger memory window and higher resistance value stability. The memory unit has good prospect in practical application to a NiO material RRAM. The invention further provides a manufacturing method of the memory unit.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
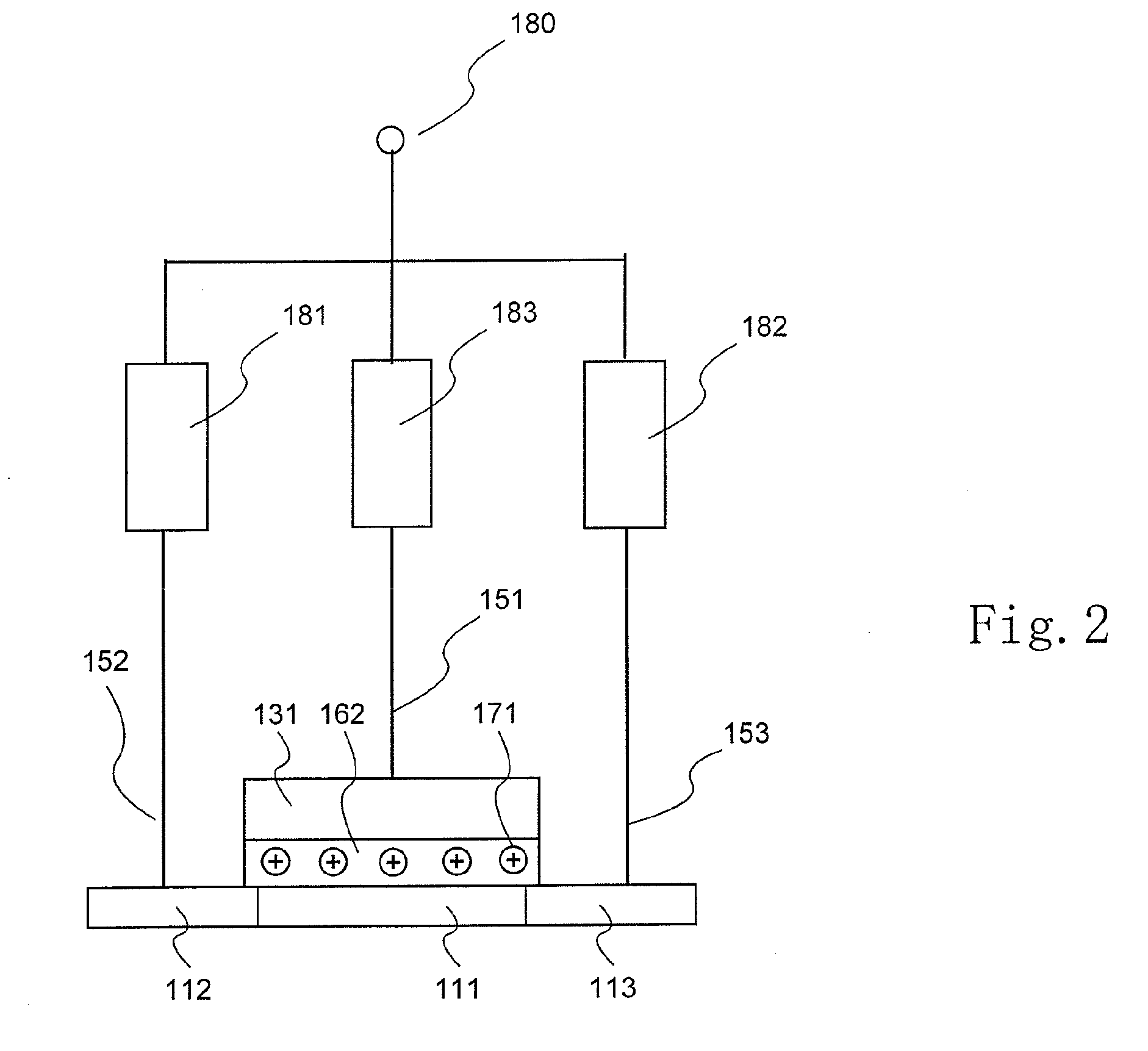
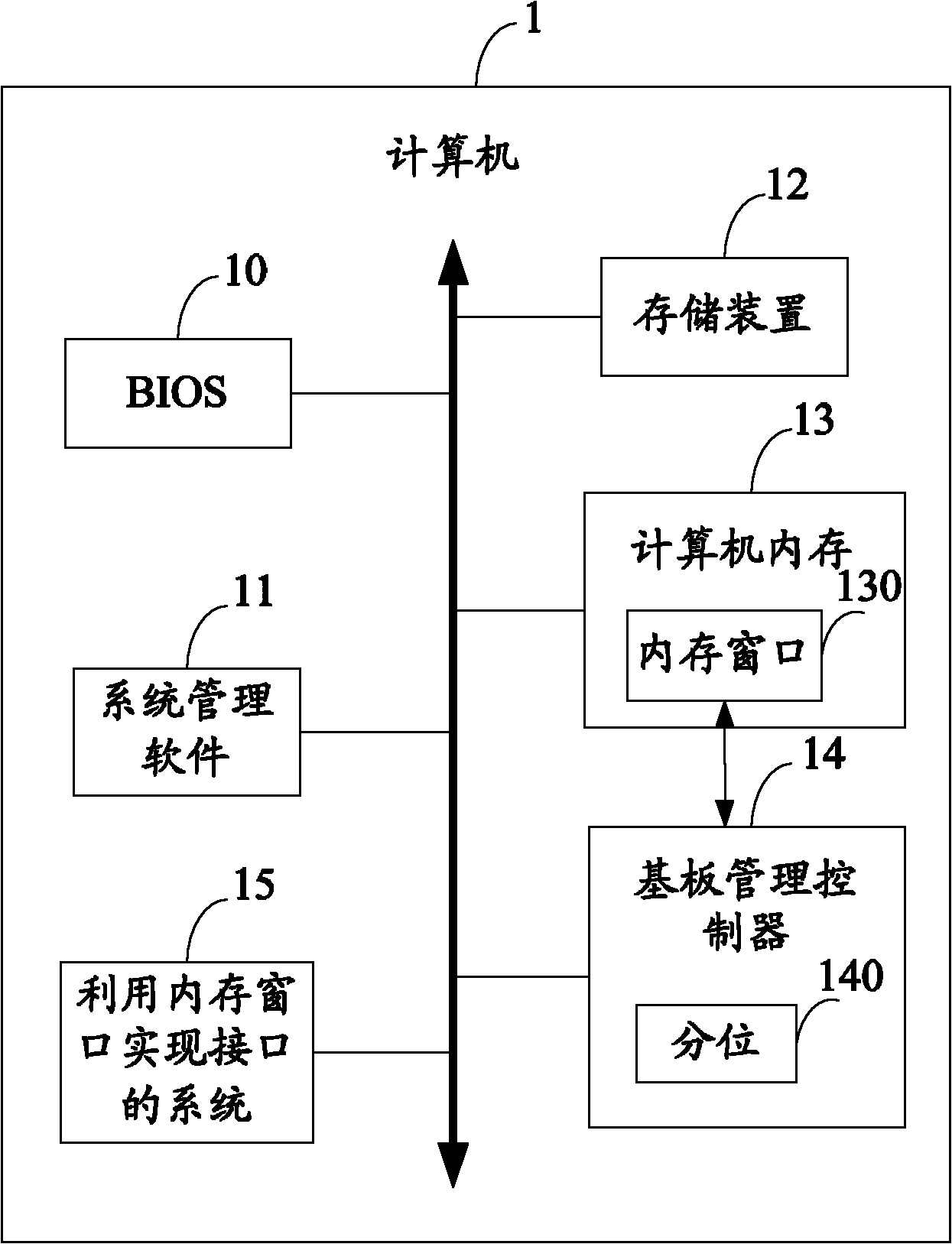
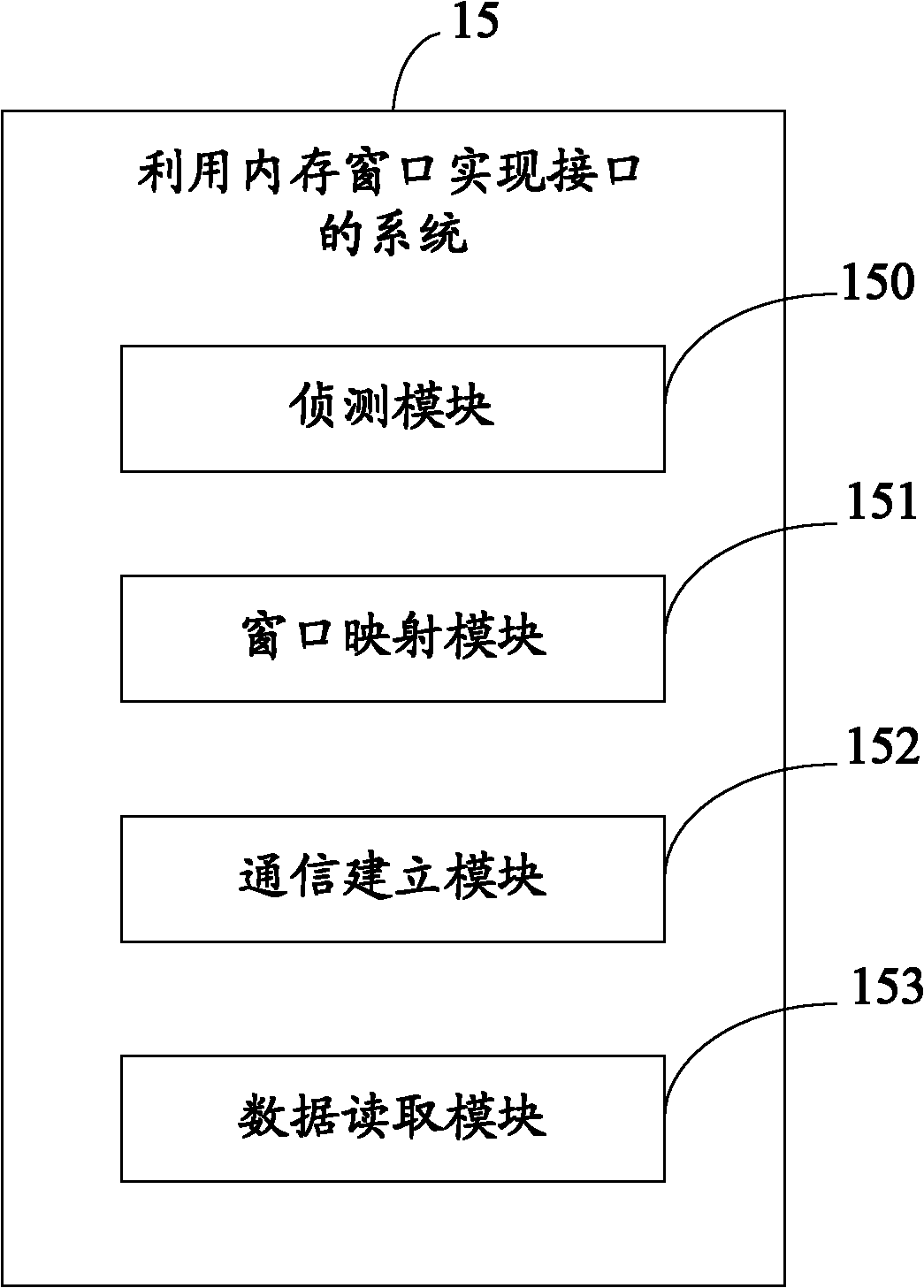
System and method for realizing interface by using memory window
Owner:HONG FU JIN PRECISION IND (SHENZHEN) CO LTD +1
Flash memory device and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN101132007ASolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingData memoryGroup element
The invention relates to a flash memory device and a manufacturing method thereof, comprising a source diffusion zone and a drain diffusion zone in an active region of a silicon semiconductor substrate for fixing the distance, a multilayer charge storage layer on the substrate, and a control gate formed on the charge storage layer, wherein, the charge storage layer comprises a tunnel oxide film formed on the silicon semiconductor substrate, a silicon nitride film formed on the tunnel oxide film including a plurality of small crystal by injecting the 14 group elements into the silicon nitride film. The flash memory device maintains a good programme and erasure operation of the SONOS device and improves the trap density and memory window. Owing to the energy barrier difference between the small crystal and the silicon nitride, the electron or cavity captured by the small crystal of the deep trap are not easy to escape so as to improve the data memory performance of the device.
Owner:DONGBU HITEK CO LTD
Single-layer barium strontium titanate (BST) film based charge trapping memory and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN106783863AStable hold characteristicGood retention propertiesSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesBarium strontium titanateTrapping
The invention discloses a single-layer barium strontium titanate (BST) based charge trapping memory. The charge trapping memory is structurally formed by a P-type Si substrate, an SiO2 tunneling layer, a barium strontium titanate trapping barrier layer and a Pd electrode layer from bottom to top. Meanwhile, the invention further discloses a preparation method of the memory. The method includes: cleaning and blow-drying the P-type Si substrate; forming the barium strontium titanate trapping barrier layer on the Si substrate through a magnetron sputtering method; forming the SiO2 tunneling layer between the P-type Si substrate and the barium strontium titanate trapping barrier layer through a specific annealing process; forming the Pd electrode layer on the barium strontium titanate trapping barrier layer through the magnetron sputtering method. The charge trapping memory composed of the P-Si substrate / SiO2 tunneling layer / barium strontium titanate trapping barrier layer / Pd electrode layer structures is prepared with the specific materials; as is shown on the test that compared with an existing memory of the same type, the memory has the advantages that a memory window is larger, data retention is better, and the memory is resistant to fatigue, high in writing in / erasure speed and broad in application prospect.
Owner:HEBEI UNIVERSITY
Protection domain groups to isolate access to memory windows
ActiveUS8291176B2Minimized on demandError detection/correctionEmergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnectionProtection domainParallel computing
The disclosed embodiments may relate to protection domain group, which may include a memory region associated with a process. The protection domain group may also include a plurality of memory windows associated with the memory region. Also included may be a plurality of protection domains, each of which may correspond to a memory window. The protection domains may allow access to the memory region via a corresponding memory window.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
Charge trapping memory cell with high speed erase
InactiveCN101369583AImprove data retentionHigh-speed programming operationSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesTrappingBlocking layer
The invention discloses a charge trapping memory cell with high speed erase including a charge trapping element that is separated from a metal or metal compound gate through a blocking layer and separated from a semiconductor substrate comprising a channel through a processing tunneling dielectric material. The blocking layer is a material having a high dielectric constant, such as aluminum oxide. The metal or metal compound gate is such as platinum metal gate. Fast program and erase speeds with memory window as great as 7 V are achieved by the charge trapping memory cell.
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD
Application for taking thin film transistor with adjustable threshold voltage as nonvolatile memory
ActiveCN107301879AIncrease storage capacitySolve power consumptionTransistorDigital storageBottom gateEngineering
The invention discloses an application for taking a thin film transistor with adjustable threshold voltage as a nonvolatile memory. A top-gate memory is formed by the top gate, the barrier layer, the storage layer, the tunneling layer and the channel layer of the thin film transistor; and a bottom-gate TFT (Thin Film Transistor) is formed by the channel layer, the bottom gate oxidization layer and the bottom gate of the thin film transistor. The top-gate memory is operated to realize the ''Program / Erase'' operation of the nonvolatile memory, and the bottom-gate TFT is operated to realize the ''read'' operation of the nonvolatile memory. Through the separation of the ''Program / Erase, P / E'' operation and the ''read'' operation, a large memory window of the memory is realized, and the performance, including the reliability, the working speed and the like, of the memory can be improved.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Method for forming shallow trench isolation (STI) structure used for flash memory
ActiveCN102184887AFast depositionReduce oxidation reactionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGas phaseChemical vapor deposition
The invention provides a method for forming a shallow trench isolation (STI) structure used for improving the 'smiling face' effect of a flash memory. The method comprises the following steps: providing a semiconductor substrate, wherein a tunneling oxidization layer and a floating gate polycrystalline silicon layer are sequentially formed on the surface of the semiconductor substrate; forming a hard mask layer on the surface of the floating gate polycrystalline silicon layer, sequentially etching the hard mask layer, the floating gate polycrystalline silicon layer, the tunneling oxidization layer and the semiconductor substrate, and forming a shallow trench in the semiconductor substrate; adopting in-situ steam generation process to form a liner oxidization layer covering the surface of the shallow trench; and adopting chemical vapor deposition to form an isolation medium layer filling the shallow trench. Through the STI structure forming method for the flash memory, the smiling face problem of the floating gate tunneling oxide caused by the traditional process can be effectively solved, the programming and erasure efficiency of the flash memory can be improved, and the read current of the flash memory in an erasure state can be increased, thus achieving the purpose of increasing a memory window.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUAHONG GRACE SEMICON MFG CORP
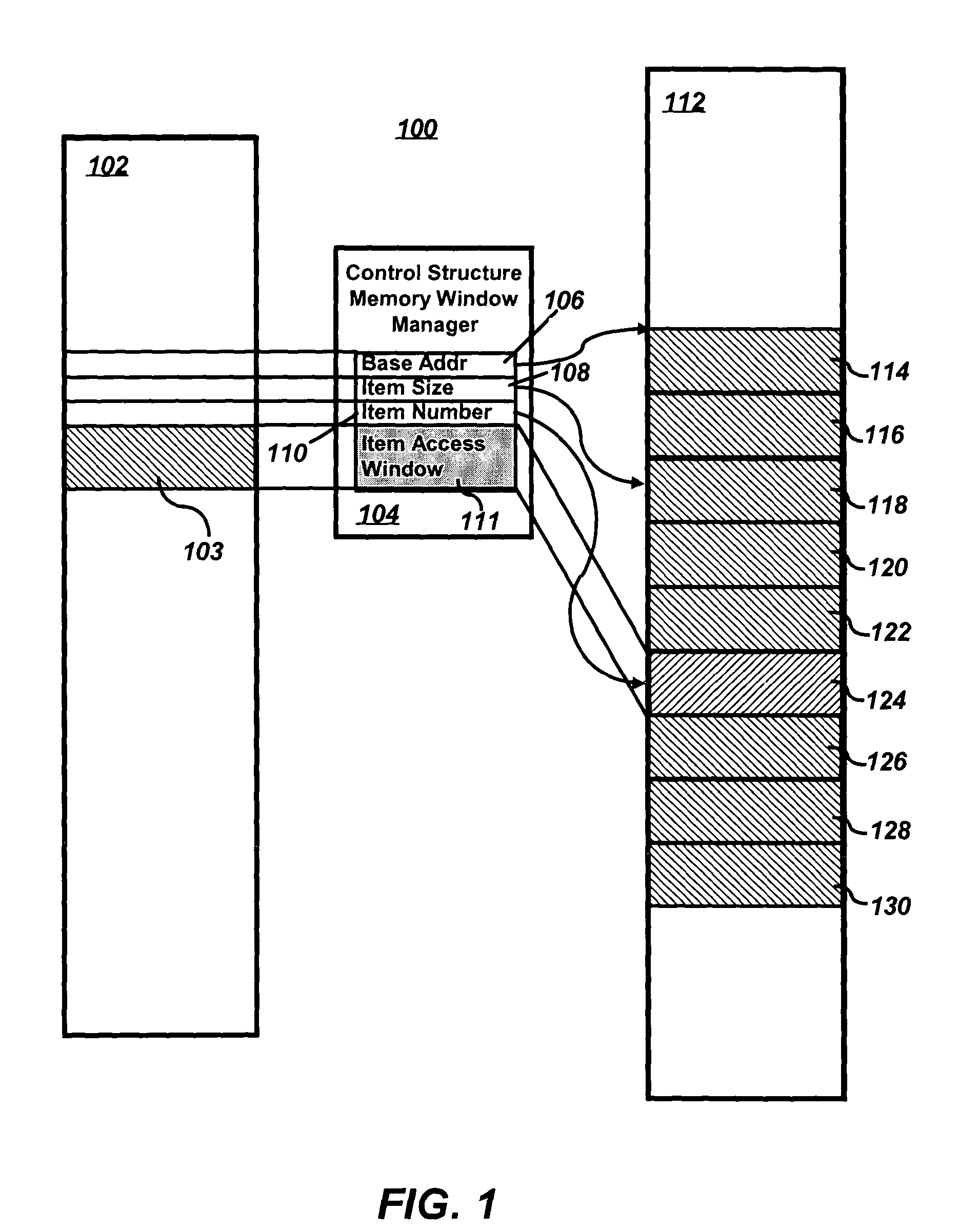
Memory window manager for control structure access
ActiveUS7085910B2Simple structureMemory adressing/allocation/relocationMicro-instruction address formationWindow managerComputer architecture
Methods and systems for managing control structure access by a processor are disclosed. In general, a processor can communicate with a plurality of control structures. A memory window manager can then be implemented, which communicates with said processor and said plurality of control structures. The memory window manager specifies which control structure among said plurality of control structures is accessible by said processor. The memory window manager also specifies which control structure can be mapped into an address space of said processor.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
ADAPTIVE REFRESHING AND READ VOLTAGE CONTROL SCHEME FOR A MEMORY DEVICE SUCH AS AN FeDRAM
A memory device, such as an FeDRAM device, includes a memory array including a plurality of rows, each row having a plurality of storage elements (e.g., FeFETs). The memory device further includes a plurality of refresh trigger circuits, each refresh trigger circuit being associated with a respective one of the rows. Each refresh trigger circuit is structured to produce an output signal indicative of an estimated degradation of a memory window of one or more of the storage elements of the associated one of the rows. The memory device also further includes control circuitry coupled to each of the refresh trigger circuits, wherein the control circuitry is structured and configured to determine whether to initiate a refresh of the storage elements of a particular one of the rows based on the output signal produced by the refresh trigger circuit associated with the particular one of the rows.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH
Storage unit of resistive random access memory (RRAM), manufacturing method of storage unit and electronic device
InactiveCN108305936AImprove storage densityImprove durabilitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesStatic random-access memoryRandom access memory
The invention provides a storage unit of an RRAM, a manufacturing method of the storage unit and an electronic device. The manufacturing method of the storage unit comprises that a semiconductor substrate is provided, and a stacked structure which comprises first electrode layers and isolation layers stacked alternatively is formed on the semiconductor layer; a resistive random layer is formed inthe sidewall of the stacked structure; and a second electrode layer is formed in the sidewall of the resistive random layer at least to form storage units. The method can improve the storage density,endurance and a memory window. The storage unit of the RRAM and the electronic device have similar advantages.
Owner:SEMICON MFG INT (SHANGHAI) CORP +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com